-
湖泊是淡水资源的重要载体,对区域生态环境的维护发挥着重要的作用[1]。随着中国经济的快速发展以及城镇面积的大幅扩张,国内生产与生活用水需求日益增长,由此造成的湖泊环境与生态破坏现象不胜枚举,湖泊水华暴发、水体缺氧等问题频频发生,并由此引发了一系列经济与社会问题[2]。洱海亦出现了水体富营养化的现象[1],水生生态系统逐步退化、湖泊水体富营养化进程加快等问题日益突出[3],同时针对洱海的相关研究[4]发现,其水质呈现变坏的趋势,暗藏蓝藻水华暴发的隐患。
蓝藻水华通常是指在富营养化水体中出现蓝藻大量繁殖的现象,主要表现为水体表面覆盖着一层蓝绿色并伴有恶臭气味的浮沫,水体藻细胞浓度一般都达到并超过1.5×107个·L−1,叶绿素a质量浓度大于10 mg·m−3[5]。叶绿素a(chlorophyll a, Chl-a)是浮游植物(藻类)中最常见的色素,其质量浓度是评价水体富营养化程度的核心参数[6]。传统的湖泊营养状态评价方法主要依赖于对水体的实地取样分析,然而该方法易受局部天气与环境影响,取样与测试过程也比较耗时耗力、成本较高,较难实现对湖泊富营养状态在精细时空尺度上的监测[7]。与之相比,遥感(remote sensing, RS)技术具有覆盖范围广、获取资料快、周期短等优点,可弥补传统水质采样的诸多不足,因此,已被广泛应用于湖泊水环境和水生态等方面的监测。目前,在利用遥感技术的水质参数反演方面,反演方法经历了分析法、经验法、半经验法、机器学习和综合法[8],已建立起具有较高精度和一定普适性的水质参数反演模型,可以用于宏观的水质评价[9-10]。并且形成了遥感反演叶绿素a质量浓度的多种算法,但不同的算法也存在一定的局限性[11],且不同的算法在不同的传感器之间的适应性也存在差异[12]。
已有许多针对不同地区、不同季节、不同水质参数、不同的反演方法和算法、不同的卫星遥感数据源的水质反演方面的研究。潘鑫等[13]利用高分六号卫星影像,采用3种模型对太湖进行叶绿素a质量浓度反演,得出了适合高分六号卫星影像太湖叶绿素a质量浓度反演的模型。郑震[14]基于OLI影像,建立了叶绿素a质量浓度反演的数学回归模型,分析了东张水库叶绿素a质量浓度的时空分布特点。陈命男[15]利用Landsat 8数据,建立了淀山湖的叶绿素a反演的回归模型。但雨生等[16]基于Sentinel-2数据建立了可靠的BP神经网络模型,用以监测平寨水库水质。马丰魁等[17]以密云水库为研究对象,采用BP神经网络算法反演4个水质参数,并且得到了较为可信的研究结果。徐鹏飞等[18]建立了神经网络模型,对千岛湖清洁水体的叶绿素a质量浓度进行反演,并利用该模型对千岛湖的叶绿素a质量浓度进行时空特征分析。
由此可见,已有许多利用遥感数据反演水质参数的研究,分析方法亦较为成熟,这些研究为不同地区湖泊的水质监测提供了可靠的参考依据。但内陆水体光学特征具有较强的区域性和季节性[8],而且针对叶绿素a反演的各种算法仍受到季节和地理位置等的限制[11],致使各地区建立的水质参数反演模型不具有普适性。为此,针对不同地区、不同季节及不同的传感器[11],仍需要根据实际情况有针对性地建立适合当地的相关模型,为水污染防治提供合理的数据支撑[19]。近年来,利用遥感技术监测洱海水质情况的研究主要包括蓝藻水华的空间分布特征[20]、土地利用变化与水质的关系[21]、干季水质的时空变化[22]等。毕顺等[23]利用OLCI数据,采用了三波段模型对洱海2017年4月19日叶绿素a质量浓度的分布进行了估算。但该研究的三波段模型中第三波段的选取需要满足一系列的假设条件,且三波段模型主要适用于中高浓度叶绿素水体,不适用于高度浑浊水体[11];还有研究[24]表明,OLCI数据虽具有较高辐射分辨率,但其空间分辨率(为300 m)较低,在中小型内陆水体的监测上能力有限。由于洱海属中型湖泊,因此,选用空间分辨率较高的多光谱遥感影像能较为准确地获取水质采样点的反射率数据,这也是提高模型水质反演精度较为主要的因素之一[25]。
鉴于以上所述,本研究选取空间分辨率较高、也是近些年最流行的多光谱遥感数据之一的Sentinel-2数据,以较少利用Sentinel-2数据反演叶绿素a质量浓度的洱海作为研究区域,建立2种叶绿素a质量浓度反演模型,反演洱海叶绿素a质量浓度的空间分布,旨在利用不同数据源和方法探索适用于洱海流域的叶绿素a质量浓度反演模型,为相关部门的水质监测和水污染防治提供参考。
-
洱海位于大理市,湖泊面积约256 km2,是云南省第二大高原淡水湖泊,也是大理市和周边乡村居民的生产生活用水供给源地。其水量补给主要为大气降水和入湖径流,周边主要入湖河流有29条。洱海区域属高原季风气候类型,四季温和、平均温度较小,日照差大,光照充足,干湿季节分明,雨季季节分配不均[1]。作为受人类活动干扰严重的中型湖泊,2010—2019年期间洱海综合营养状态指数为38.8 ~ 43.1,属中营养水平;2014—2019年,整体水质类别为Ⅱ ~ Ⅲ类,水质呈现变坏趋势,污染物主要来源于降水产生的地表径流所携带的禽畜养殖、农村生活和农田污染[3-4]。
-
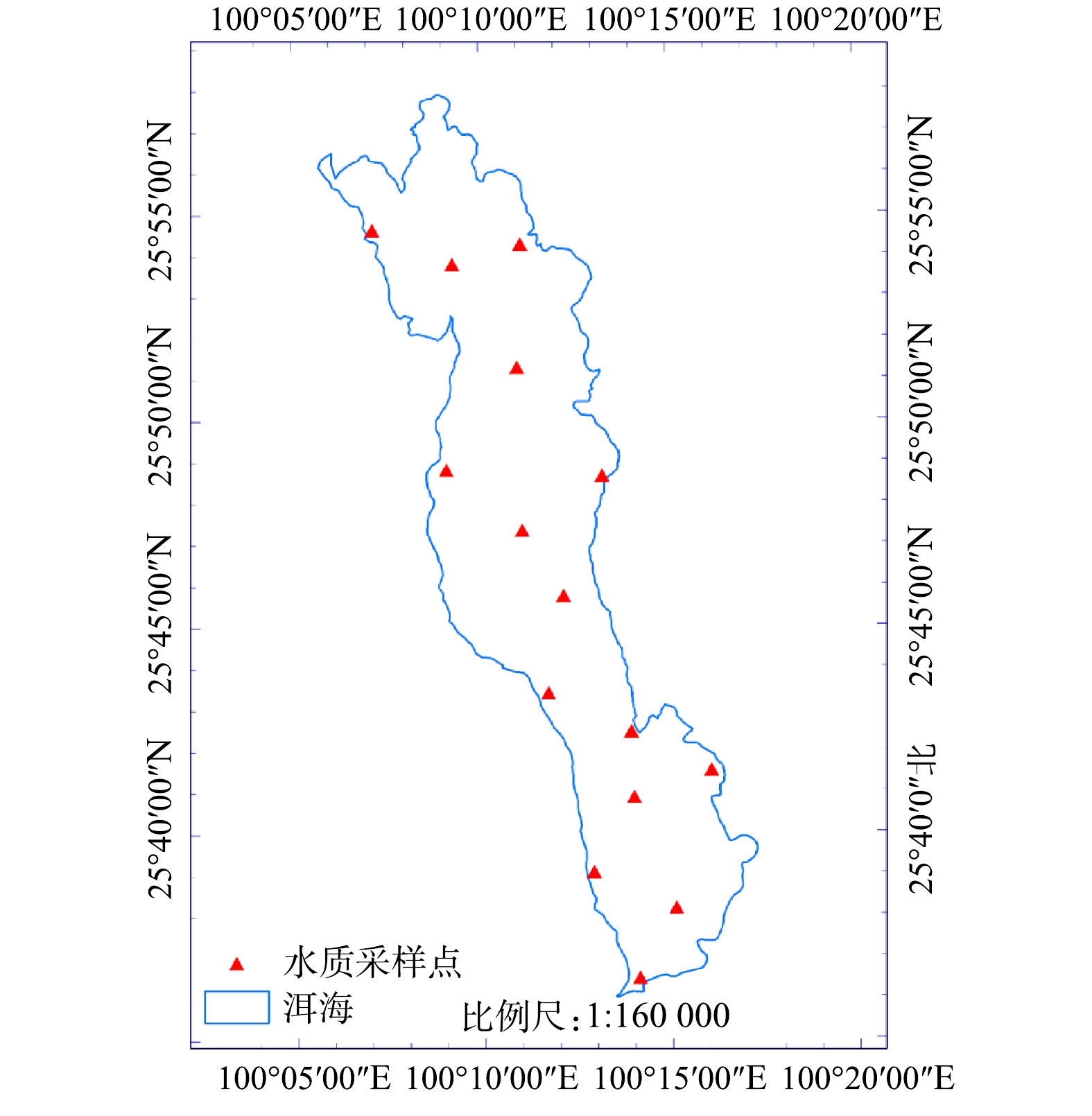
1)叶绿素a质量浓度数据。叶绿素a质量浓度实测数据来源于云南省水环境监测中心大理州分中心,水质监测点共计15个(图1),采用2019年10月9日、2019年11月8日2期监测数据,共计30条,即每月监测1次,每次采集15个水质样品,水质采样在当天完成。
2) Sentinel-2卫星数据及预处理。此次研究采用的是Sentinel-2数据,卫星数据从欧洲空间局(European Space Agency, ESA)网站下载,数据信息见表1。Sentinel-2是欧洲空间局哥白尼计划下的一个地球观测任务,该计划是由2颗相同的卫星Sentinel-2A与Sentinel-2B组成的卫星群,单颗卫星重返周期为10 d,Sentinel-2的卫星2颗互补,重返周期为5 d。Sentinel-2的每颗卫星都搭载相同的多光谱影像仪(multispectral instrument, MSI)。该影像仪可拍摄涵盖可见光、近红外与短波红外的13个波段影像。MSI的拍摄方式是推扫式,影像幅宽达到290 km。通过Sentinel-2获取的各波段信息如表2所示。
在光学数据中,Sentinel-2卫星在红边范围含有3个波段的数据,为快捷反演大区域叶面积指数、叶绿素质量浓度等生物物理量指标提供了可能[26]。本次研究直接获取Sentinel-2卫星的L2A级数据。L2A级数据在L1C级数据的基础上,利用ESA提供的Sen2cor模型进行处理生成。从2018年3月开始,ESA逐渐向全球用户提供L2A级产品,并于2018年12月覆盖到全球。L2A级数据在生成过程中,会对L1C级数据进行大气校正、云雪检测、地形校正、场景分类等一系列处理[27],可直接用于下游产品。
为便于使用ENVI 5.3提取各采样点反射率,利用SNAP软件将2期影像都按照同样的方法进行重采样,将其重采样为10 m,之后,波段由13减至12个(减少了短波红外-卷云B10波段)。分别提取水质采样点2期影像的水体反射率。
-
在水质参数的反演工作中,获取与水质参数关系密切的敏感波段,将其作为模型的输入因子,这样建立的模型具有更高的预测精度[28]。本研究通过Pearson相关分析来获取与叶绿素a质量浓度关系密切的敏感波段,Pearson相关系数是一种线性相关系数,通过Pearson相关分析可以得出不同波段或者波段组合与叶绿素a质量浓度的相关性强弱,可进一步剔除弱相关的、可能干扰反演模型建立的波段信息。由于水体的反射特性主要位于可见光和近红外波段,且有研究[29]表明,可见光和近红外的反射率可以成功地用以反演水体的叶绿素a质量浓度,因此,首先选择4个可见光波段和4个红边波段进行相关性分析,然后利用置信度为99.9%(P < 0.001)的波段进行波段组合,进一步分析各波段组合的反射率与叶绿素a质量浓度的相关性。
目前,常用的波段组合方式有单波段比值、双波段比值、波段差值、三波段和四波段模型。对于Sentinel-2数据来说,双波段比值对叶绿素质量浓度更加敏感[30],因此,双波段比值是本研究首选的波段组合方式之一,另外还选择了单波段比值。根据但雨生等[16]基于Sentinel-2卫星数据与平寨水库叶绿素a质量浓度的相关分析研究结果,叶绿素a质量浓度与组合波段B5/B4、(1/B4-1/B5)×B6、(1/B4-1/B5)×B7和(1/B4-1/B5)×B8的Pearson相关系数最大。另外,叶绿素质量浓度与归一化植被指数(normalized difference vegetation index, NDVI)呈线性关系[31],所以本研究选择具有代表性的波段比值、三波段模型以及NDVI筛选与叶绿素a质量浓度显著相关的敏感波段。利用15个采样点提取的2期共30条水体反射率数据,与实测叶绿素a质量浓度数据进行Pearson相关分析,分别在单波段、单波段比值和双波段比值中选取相关系数最大的叶绿素a反演波段。如表3所示,B6、B7/B6和(B6+B8)/(B7+B8a)反射率与叶绿素a质量浓度呈现0.001水平的显著性,且相关系数最大。因此,最终选择B6、B7/B6和(B6+B8)/(B7+B8a)作为叶绿素a质量浓度的反演波段。
需要说明的是,在进行Pearson相关分析之前,需要对各波段、波段组合提取的采样点反射率数据以及实测叶绿素a质量浓度数据进行Shapiro-Wilk检验。在25组数据中(波段或波段组合的采样点反射率数据24组(表3);实测叶绿素a质量浓度数据1组),6组数据符合正态分布,其余数据基本符合正态分布。
-
BP (back propagation)神经网络是一种按误差逆向传播算法训练的多层前馈网络,能学习和存储大量的“输入-输出”模式的映射关系,而无需事前揭示描述这种映射关系的数学方程[32]。BUCKTON等[33]和SCHILLER等[34]利用MERIS数据和2层BP神经网络模型反演了叶绿素、悬浮物、黄色物质3个水质参数,得出神经网络模型完全可以用来反演Ⅰ类水质和Ⅱ类水质参数,且反演精度远高于经验模型的结论。BP神经网络具有自适应、自学习、自组织和非线性映射的功能,非常适用于模拟各种错综复杂的非线性关系。已有研究[16]证明,具有1个隐含层的3层网络可以逼近任意非线性函数。本研究所采用的即是具有1个输入层、1个隐含层和1个输出层的3层BP神经网络结构。其中,隐含层的神经元节点数可根据3种经验公式[32]选择,本研究由经验公式(式(1))进行确定。
式中:M为隐含层神经元个数;m和n分别为输入层和输出层神经元个数;a为1 ~ 10的整数。
根据输入输出层神经元个数3和1,由式(1)计算得到M的取值为3 ~ 12的整数。分别从单波段、单波段比值、双波段比值中选取与叶绿素a质量浓度显著相关且相关系数最大的波段和波段组合B6、B7/B6和(B6+B8)/(B7+B8a)作为神经网络的输入数据(波段组合使用软件PIE-Basic 6.3完成),与之相对应的实测叶绿素a质量浓度作为输出数据。30组数据随机分为训练数据23组和检验数据7组,采用feedforwardnet函数建立神经网络。trainglm作为训练函数,双曲正切函数sigmoid为传递函数,线性函数purelin作为输出层函数。训练次数设置为1 000次,学习速率为0.01,训练目标为1×10−6。设置参数后,分别选择不同的神经元节点数对神经网络进行反复训练,最终获得决定系数R2最大、均方根误差(root mean square error, RMSE)最小的神经网络结构,此时隐层神经元节点数为4 (表4)。
-
根据构建BP神经网络时随机产生的训练样本23组,也就是利用与BP神经网络相同的特征波段B6、B7/B6和(B6+B8)/(B7+B8a)及其数据,建立多元线性回归模型(式(2))。
式中:C为Chl-a质量浓度,mg·L−1;x1代表B6波段;x2代表单波段比值B7/B6;x3代表双波段比值(B6+B8)/(B7+B8a)。
采用决定系数R2、均方根误差(RMSE)、平均绝对误差百分比(mean absolute percentage error, MAPE)3个指标评价模型效果。MAPE的计算方法见式(3),7条检验数据对2种模型的检验结果如表5所示。
式中:δ为所有检验样本的相对误差绝对值的平均值;m为检验样本总数;yi为第i个检验样本的叶绿素a质量浓度的实测值;
ˆyi -
从本研究的叶绿素a质量浓度数据的采集时间和Sentinel-2卫星影像的时间来看,2种数据没有在时间上做到非常好的匹配。10月9日,叶绿素a质量浓度实测数据与10月12日Sentinel-2卫星数据间隔3 d;11月8日,叶绿素a质量浓度实测数据与11月9日Sentinel-2卫星数据间隔1 d。根据来源于美国国家海洋和大气管理局国家环境信息中心(NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information)的气象站点(该气象站点位于洱海湖体西南部,大理市气象局东南部)数据,研究区10月9日—10月10日无降水,10月11日降水量为0.508 mm,10月12日降水量为0.254 mm,10月9日—10月12日4 d内最大平均风速为2.16 m·s−1,日平均温度变化最大为1.2 ℃;11月8日—11月9日无降水量,最大平均风速为1.59 m·s−1,日平均温度升高2.3 ℃。此外,来源于美国国家航空航天局(National Aeronautics and Space Administration, NASA)提供的大气再分析资料MERRA-2数据显示,10月9日—10月12日,大理市地区日照时数的最大值和最小值分别为5.92 h和4.85 h,变化值最大为1.07 h;11月8日—11月9日,日照时数减少0.10 h。因此,时间上的差异对数据产生的影响很小。此外,鉴于本研究存在的数据在时间匹配上的误差,且叶绿素a质量浓度变化受风速、降水、流速、营养元素等因子影响[35],可建立包含风速、降水、流速、营养元素等因子的模型,以减少因为数据不能在时间上完全匹配所产生的叶绿素a质量浓度的估算误差,这可以在一定程度上避免因卫星数据时间分辨率以及卫星数据云量过多造成的与实测数据的时间匹配问题。
-
数据的Shapiro-Wilk检验结果显示,B9、B5/B4、B7/B6、B8a/B8、(1/B4-1/B5)×B6、(1/B4-1/B5)×B7没有呈现显著性(p > 0.05),说明以上6组数据符合正态分布。其余19组数据的峰度绝对值小于10并且偏度绝对值小于3,这些数据的正态检验直方图也都显示为钟形(中间高两端低),说明这些数据基本符合正态分布。根据本研究的实测叶绿素a质量浓度数据与对应水质样品采样点的Sentinel-2影像反射率的相关分析结果,建立模型所采用的对叶绿素a质量浓度敏感的波段都处于0.001的显著水平,分别是在单波段、单波段比值、双波段比值中相关系数最大的波段和波段组合B6、B7/B6和(B6+B8)/(B7+B8a)。根据表3,B5/B4、(1/B4-1/B5)×B6、(1/B4-1/B5)×B7和(1/B4-1/B5)×B8与叶绿素a质量浓度的相关系数很小,分别为−0.009、−0.128、−0.086、−0.098。这说明以上波段组合与叶绿素a质量浓度存在弱相关关系或几乎没有相关关系,与但雨生等[16]的研究存在差异。在但雨生等[16]的研究中,采用与叶绿素a实测数据准同步的Sentinel-2影像,在秋季,采用了同样的相关分析方法,因此,出现这种差异可能由不同研究区的水体光学特征的差别所引起,也就是说可能由于不同研究区水体的固有光学特征和表观光学特征的差异,导致同一卫星传感器的所接收的水体反射信息存在差别。此外,NDVI与叶绿素a质量浓度的相关系数为0.489,P值为0.006,说明NDVI与叶绿素a质量浓度存在0.01水平的显著性。
-
本研究选用多元线性回归模型以及可以模拟各种非线性关系的BP神经网络模型来进行湖泊水叶绿素a质量浓度的反演。从对2种模型的检验结果来看,BP神经网络模型的MAPE为21.36%,小于线性回归模型27.90%;RMSE为0.002 8,小于线性回归模型的0.004 5。从2种模型的决定系数R2来看,本研究的多元线性回归模型的3个自变量(B6、B7/B6和(B6+B8)/(B7+B8a))只能用来解释因变量(叶绿素a质量浓度)方差的78.8%,远低于BP神经网络模型(R2 = 0.925)。这说明BP神经网络模型的预测精度要高于线性回归模型。这与赵玉芹等[36]基于SPOT 5遥感影像建立了多元线性回归模型、BP神经网络模型和径向基神经网络模型,对渭河陕西段水域的4种水质参数进行反演所得出的结论几乎一致,均认为BP神经网络模型的预测精度最高。同样,岳佳佳等[37]以黄石磁湖为研究区,利用IKONOS遥感影像和水质采样数据构建了多元线性回归模型、BP神经网络模型和径向基神经网络模型,对比后,亦得出神经网络模型反演结果优于多元线性回归模型。此外,杨柳等[38]也使用ETM+数据和准同步实测的2种水质数据,建立多个隐含层为1的BP神经网络模型,得出了BP神经网络方法反演水质参数结果好于线性回归方法的结论。
在水质参数反演中,BP神经网络虽然较多元线性回归模型有较高的精度,但是也存在一些缺点。BP神经网络的设计通常需要确定网络的层数、输入层的节点数、隐含层的节点数、输出层神经元个数、网络的初始权值,需要选择不同的传递函数和训练方法。本研究使用feedforwardnet函数建立神经网络,该函数自动对数据进行归一化处理,可以根据train函数自动确定网络的输入层和输出层数。如图2所示,本研究的BP神经网络输入层数为3,分别为Sentinel-2卫星数据的B6、B7/B6和(B6+B8)/(B7+B8a)3个特征数据。将这3个特征数据按照不同的权值wij分别输入到隐含层各个神经元,再和各神经元阈值bj求和,之后激活传递函数(双曲正切函数sigmoid),接着通过一定的权值wjk由隐层进入输出层,与输出层阈值bk求和后激活输出函数(线性函数purelin),随后按减少误差的原则,从输出层经过隐含层,回到输入层,不断调整各连接权值,进行反复训练。虽然这样可以不断地提高正确率,但BP神经网络的一些参数的选择依然没有依据,隐含层的神经元个数也只能依据经验公式进行试凑,网络的权值是通过训练样本和学习率参数得到的,这也导致了BP神经网络的不稳定。除此之外,BP神经网络每次训练的初始权值是随机给定的,导致了其不可重现性;网络还存在样本依赖性,主要依赖于选择的训练样本是否典型,所以,应避免样本集合代表性差、矛盾样本多、存在冗余样本等问题;再者,网络容易陷入局部最优,需要实时检测误差率的变化以确定最佳训练次数。相比之下,径向基网络模型具有结构可靠、不依赖初始权值等优点。吴倩等[39]认为径向基网络模型是值得推广的光谱反演叶绿素模型。同时需要注意的是,吴倩等[39]的研究采用地物光谱仪测定采样点水体反射光谱,波谱区间为325 ~ 1 075 nm,光谱采样间隔为1.6 nm,光谱分辨率为3.5 nm,光谱分辨率较高,且径向基网络模型同时也存在丢失信息、数据不充分时无法工作等缺点。本研究旨在探索适用于秋季洱海流域的叶绿素a质量浓度的遥感反演模型,采用的是Sentinel-2多光谱数据,波段配置不同也会影响叶绿素a的反演[11],因此,依然使用了在各个地区利用遥感反演水质参数比较成熟的BP神经网络模型。
-
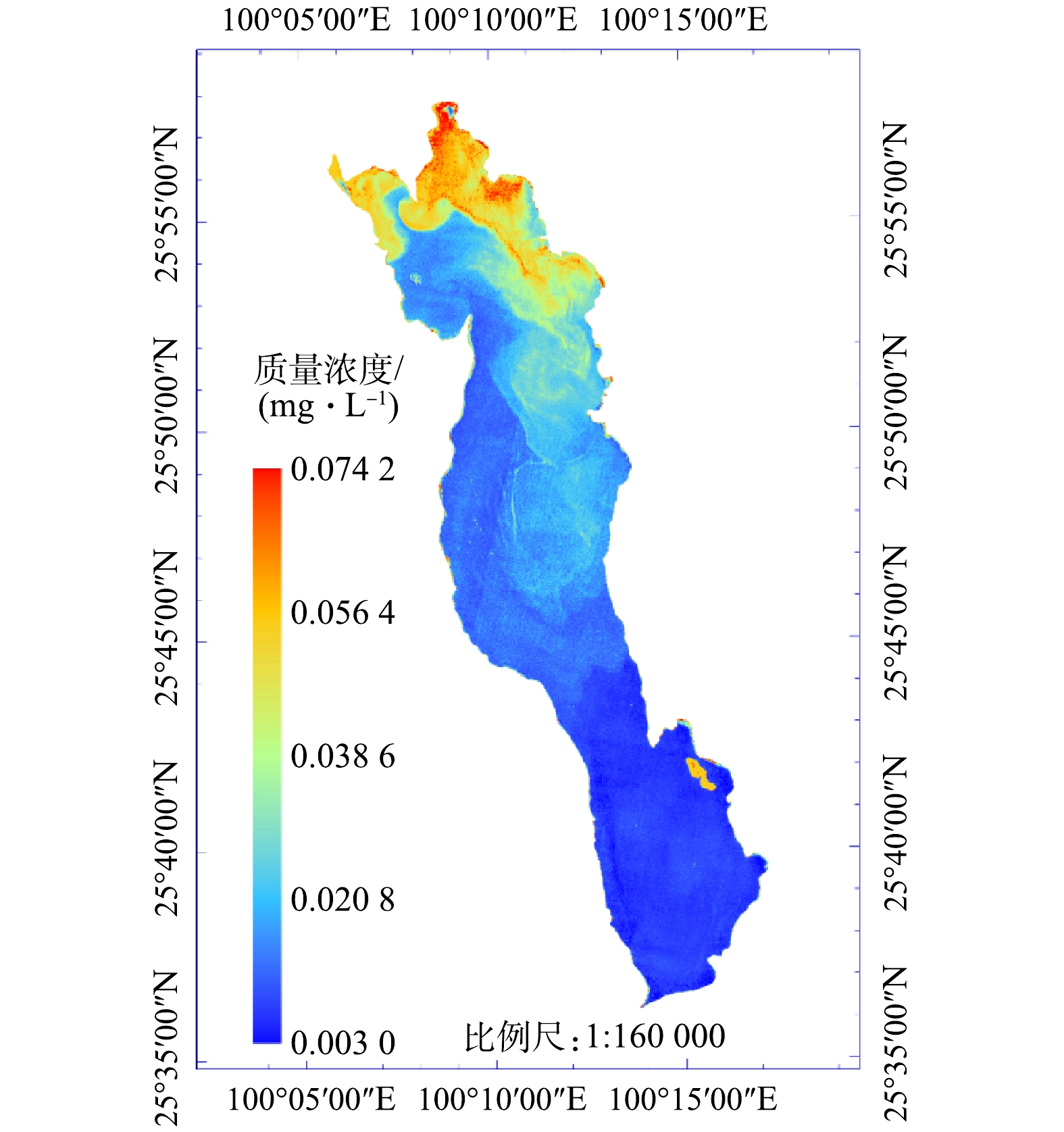
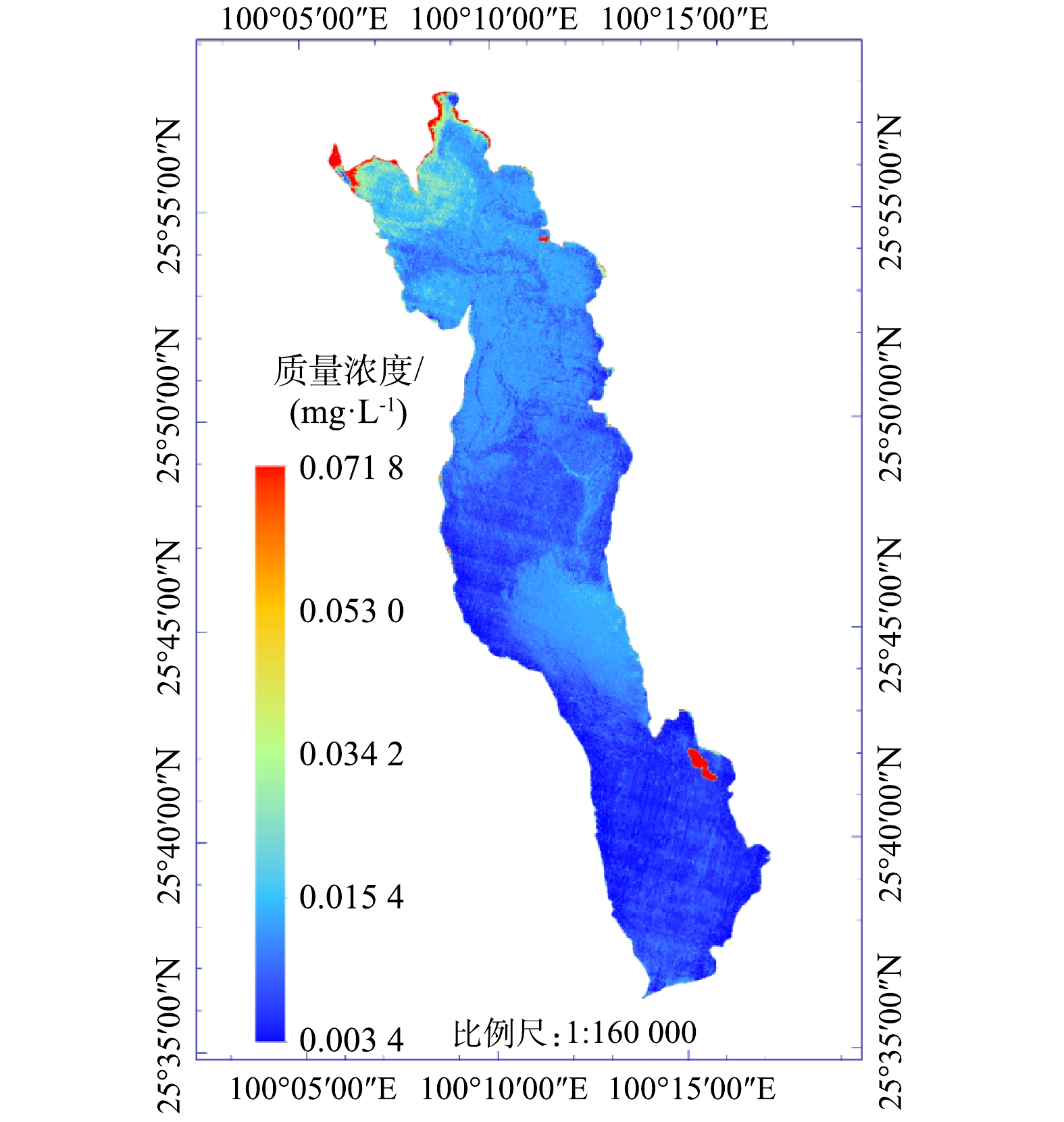
如表5所示,BP神经网络的模型预测误差要比多元线性回归模型小,采用构建好的BP神经网络模型对洱海秋季2019年10月12日、11月9日2 d的叶绿素a质量浓度进行反演,结果见图3和图4。由反演结果可以看出,利用Sentinel-2影像可从宏观上反演叶绿素a质量浓度,并且可以非常直观地展现叶绿素a质量浓度的空间分布,这也是遥感监测的优势体现。利用这一优势,结合地理信息系统(geographic information system, GIS)以及人工智能(artificial intelligence, AI)技术,构建蓝藻水华及富营养化监测预警系统是未来的研究方向之一[40]。如以10 mg·m−3叶绿素a质量浓度作为藻华发生的临界值[41],利用以上技术结合适用于当地的BP神经网络模型,可以构建藻华发生的预警系统,这也是本研究的实际意义之一。
由洱海2 d的反演结果可以看出,叶绿素a质量浓度均呈现洱海北部高于南部的分布状态,且洱海北部沿岸地区叶绿素a质量浓度值最大。10—11月,叶绿素a质量浓度出现扩散,北部较高质量浓度逐渐向洱海中部扩散,叶绿素a质量浓度最大值降低,分布面积扩大。从叶绿素a质量浓度来看,10月最大值为0.074 2 mg·L−1,最小值为0.003 0 mg·L−1;11月最大值为0.071 8 mg·L−1,最小值为0.003 4 mg·L−1。10月与11月相比较而言,洱海叶绿素a质量浓度区间基本没有发生变化。根据11月的反演结果,洱海叶绿素a质量浓度仍然呈北部大于南部的趋势。这与祁兰兰等[22]利用GF-1卫星数据的研究结果(2014—2019年11月,洱海叶绿素a质量浓度在空间上均呈现南部>中部>北部)相反。
为了进一步探寻造成此结果的原因,首先想到的是将叶绿素a质量浓度与水体富营养化联系起来。这是因为叶绿素a质量浓度是藻类生物量的指标,可以很容易的与水体富营养化联系,而营养化水平与叶绿素a质量浓度又是成正相关的[42],因此,将2019年11月9日Sentinel-2A的真彩色合成影像通过3%的线性拉伸显示(图5),通过目视解译,可以看出洱海北部的水华现象。其次,由于本研究使用的是Sentinel-2数据,而通过查询,没有与祁兰兰等[22]研究中相同日期(2019年11月22日)的Sentinel-2数据,未能与其做对比实验。相应地,在11月9日,也没有查询到高分一号WFV洱海区域的数据,也不能利用祁兰兰等[22]采用的反演模型对本研究结果做对比验证。但是,WANG等[41]的研究显示,洱海叶绿素a质量浓度在2016年11月、2017年11月均为北部高于南部;TAN等[42]的研究同样表明2016年11月洱海北部叶绿素a质量浓度高于南部。这种结果的差异可能是祁兰兰等[22]研究所采用模型的区域性限制,该模型最早是利用环境一号卫星CCD数据以太湖为研究区建立的[43],后来被朱利等[44]证明高分一号WFV数据与环境一号CCD数据在波段设置上具有很强的一致性,并将该模型用于高分一号WFV数据的太湖叶绿素a质量浓度反演。
-
1)在秋季的洱海流域,对于Sentinel-2卫星数据,与叶绿素a质量浓度具有显著的相关关系(P < 0.001),且在单波段、单波段比值和双波段比值中相关系数最大的分别为B6、B7/B6和(B6+B8)/(B7+B8a)。
2)使用BP神经网络,建立了适用于秋季洱海流域的叶绿素a质量浓度反演模型。对比使用同样数据建立的多元线性回归模型,BP神经网络模型的平均绝对误差百分比(MAPE)和均方根误差(RMSE)均小于多元线性回归模型,决定系数R2大于多元线性回归模型。总体来说,BP神经网络模型的精度高于线性回归模型,可使用Sentinel-2数据,利用本研究构建的BP神经网络模型反演叶绿素a质量浓度,能得到较可靠的反演结果。
3)通过构建的具有4个隐含层神经元节点的3层BP神经网络模型,反演洱海2019年10月12日、11月9日叶绿素a质量浓度,结果均显示洱海北部叶绿素a质量浓度明显高于南部。因此,基于Sentinel-2影像和BP神经网络模型可以宏观监测叶绿素a质量浓度的空间分布。




 下载:
下载: