-
市政污水排放是城市水环境污染的重要来源。RAHMAN等[1]采用PMF受体模型解析了达卡市高尔山湖污染来源,发现在旱季42.94%的点源营养物质来自于市政污水。引起城市水资源紧张的主要因素是城市人口密度和用水强度等。ZHAO等[2]对京津冀城市群的水资源承载力的研究发现,有近50%的城市水资源承载力处于超负荷状态,其人口密度、城市公共用水强度和节水投资强度是影响城市水资源承载力的主要因素。造成城市水生态破坏的重要原因是城市对土地的开发利用。LUO等[3]对河南沙颖河流域内郑州、平顶山、许昌、周口等9个地市的研究发现,与河流水质相比,土地利用变化和城市化对水生态状况的影响更大。由此可见,城市建设会给水生态环境系统带来巨大威胁,而我国当前城市化水平处于历史高点,故城市在水环境、水资源和水生态方面面临着巨大压力,亟需采取有效的改善方案。
我国华北区域的水污染严重、水资源严重匮乏和水生态问题突出。相关各城市均采取了一系列措施来改善水生态环境质量,并取得了一定成效。潘留明等[4]介绍了天津市在外环河水环境改善中采用投菌、浮床、沉床和人工湿地工艺实现了水环境质量提升。侯晓帮等[5]介绍了在洛阳市瀍河水环境整治中采用控源截污、清淤疏浚、河道复氧、生态补水等水质保障措施。王勇等[6]介绍了青岛市在墨水河治理过程中通过采用截污、清淤、绿化和中水回用等工程措施,实现了水体COD和氨氮浓度的大幅削减。尽管上述案例对制定城市水生态环境质量提升有一定借鉴作用,但不难看出当前城市水生态环境治理对策在系统性方面仍存在欠缺,多数城市在水生态环境整治中仅着眼于城市单个河流或湖泊的水环境质量提升,对水资源和水生态方面的考虑不足。因此,在城市水生态环境治理中,应建立起从城市整个水体角度考虑的“水环境、水资源、水生态”三水统筹推进的系统治理思路。
针对上述问题,本研究将从“水环境、水资源、水生态”三方面对华北片区内79个城市建成区面临的水生态环境问题进行解析,并给出城市水生态环境质量提升分阶段目标、综合整治对策建议,为实现区域内城市水生态环境质量提升提供参考。
-
研究区域共包含79座城市 (图1) ,包括北京市、天津市,以及河北、山西、山东、河南、陕西、江苏 (北) 和安徽 (北) 等省的77座城市,主要涉及黄河、淮河和海河三大流域。其中,区域内黄河干流长2 078 km,主要支流包括无定河、汾河和渭河等,涉及24个城市;区域内淮河流域北部包含洪汝河、沙颍河、西淝河等水系,涉及29个城市;海河流域内包含北运河、永定河、大清河、子牙河和南运河五大水系,涉及22个城市;此外,汉中、安康、南阳和滁州4市位于长江流域。研究区流域总面积约1.01×106 km²,区域地表水资源量1.304×1011 m³,约占我国水资源总量的6%。
-
本研究中水环境质量相关数据来源于研究区域内各省市《2016—2020年生态环境状况公报》,水资源相关数据来源于区域内各省市《2020年水资源公报》,有关城市涉给排水基础设施建设情况的相关数据来源于《2020年中国城市建设统计年鉴》,工业废水排放量及工业源COD排放量分别来源于《2018年中国城市统计年鉴》和《2018年各省市统计年鉴》。
-
城市水生态环境系统是一个由“水环境、水资源和水生态”构成的相互联系和作用的复杂动态系统,任何“一水”出现问题,其他“两水”都会受到影响。从水环境角度来看,污染物排放量激增使得水质下降,进而造成水资源使用价值下降、水生态系统破坏;从水资源角度来看,取水量增大使得水资源短缺,进而造成污染物降解困难,水生生境恶化;从水生态角度来看,水生态空间被侵占进而使得水体自净和水源涵养功能消失。城市水生态环境系统涵盖了城市所有涉水方面,包括城市污水收集处理、再生水回用、雨水收集利用、河湖岸带和水生生物等关键节点 (图2) ,对保持城市水生态环境健康具有不可或缺的作用。城市的高速发展极易使上述某关键节点出现问题进而波及整个水生态环境系统。为此,从“三水”角度总结了华北片区水生态环境特征,并从污水收集处理、再生水利用、河岸带和水生生物等关键节点对相关问题进行了深入解析。
-
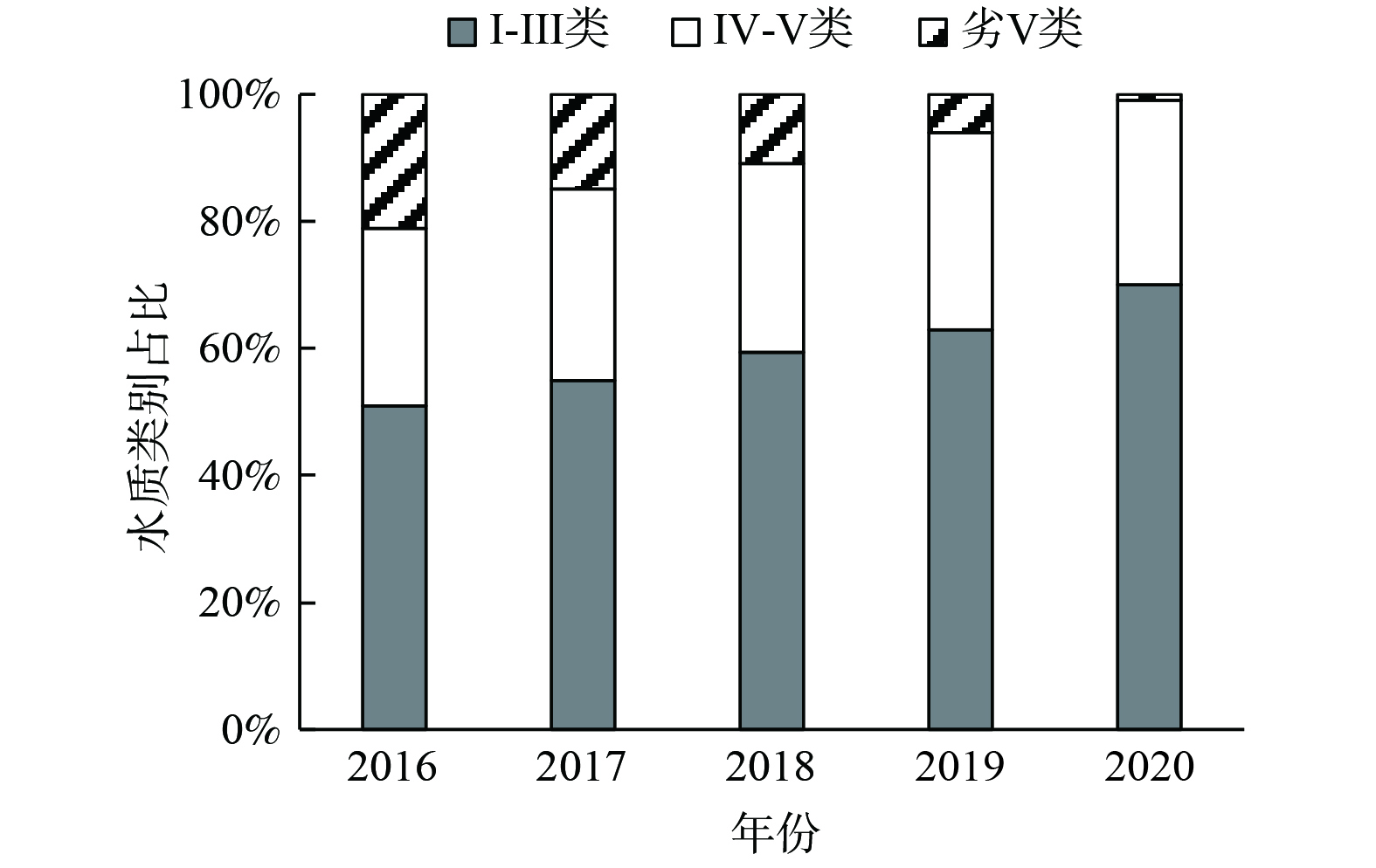
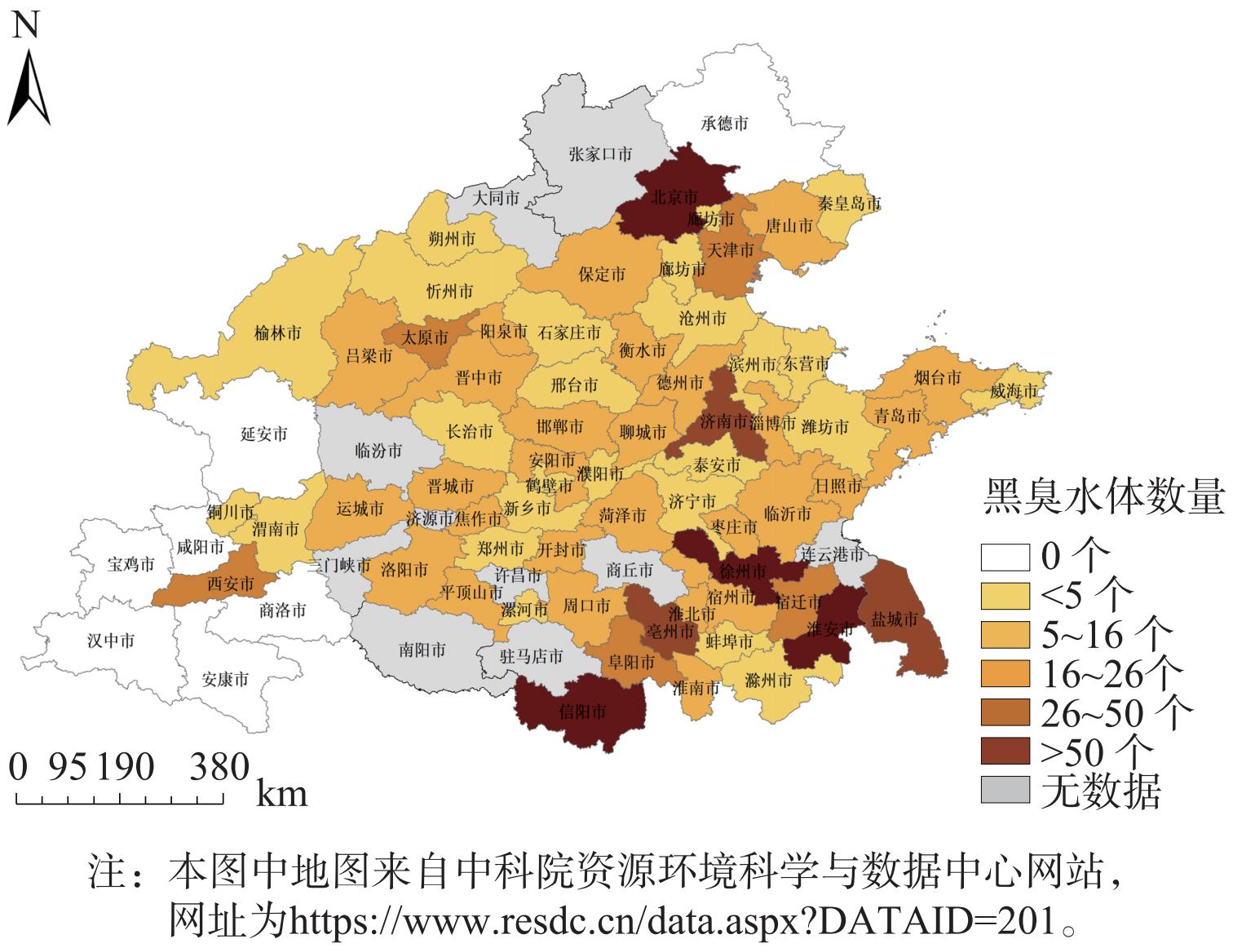
1) 水环境状况。研究区域内共有省控及以上断面1 000余个。2016—2020年,这些断面水环境质量大幅改善 (图3) ,水质优III比例由2016年的51.31%升至2020年的71%,劣V类比例由2016年的20.93%降至1.6%,水质为IV类及以下主要污染因子为COD、氨氮。但这些断面水质还不能代表城市内水体水质状况,城市内河湖由于受各类污染物大量排放的影响,水质明显更差。2019年,该地区城市内水体劣V类水质占比高达36%,以COD和氨氮污染为主。其中,北京市北小河、通惠河、护城河、凉水河、昆明湖等11个水体共计21个点位中有13个点位水质类别在IV类及以下,占比达61.9%;北小河上游,通惠河上游和昆明湖3处监测结果为劣V类水质;天津市海河、北运河、子牙河、新开河4条城区内水体共计8个点位中仅子牙河 (下游) 和新开河 (上游) 2个点位达到了IV类水质,其余6个点位均为劣V类水质。2020年区域内城市黑臭水体共计835条 (图4) ,占全国黑臭水体数量的28.65%,主要集中在河南、山东和江苏 (北) 3省城市内。其中,北京市、信阳市、徐州市和淮安市的黑臭水体数量在50条以上。
2) 水生态状况。区域内城市水生态系统健康状况整体较差,城市河湖水系连通性被破坏,部分城市水生态系统接近崩溃。同时表现出明显的地区集聚效应,在人口密集的工业城市河湖水生态系统健康程度均极差,如京津冀工业区、山西大同周边以矿业为主的工业区,以及山东、河南的国家粮食生产地区[7]。
北京市的北运河水生态健康状态处于一般健康状态。与上世纪80年代相比,天津市浮游动物、底栖动物、大型鱼类和水生植物种类锐减,分布水平明显降低。除北运河外,天津全市水体水生态健康状态普遍处于“一般”状态,水生态健康状况脆弱;廊坊市10个河流监测断面中7个断面水生态健康状态处于“轻度污染”水平;淮河流域河南段11个地市河流生态系统健康状况处于“脆弱”水平的断面近75%[8];渭河宝鸡至渭南段水生态系统处于亚健康状态,生物完整性状况呈病态,物种损失严重[9]。
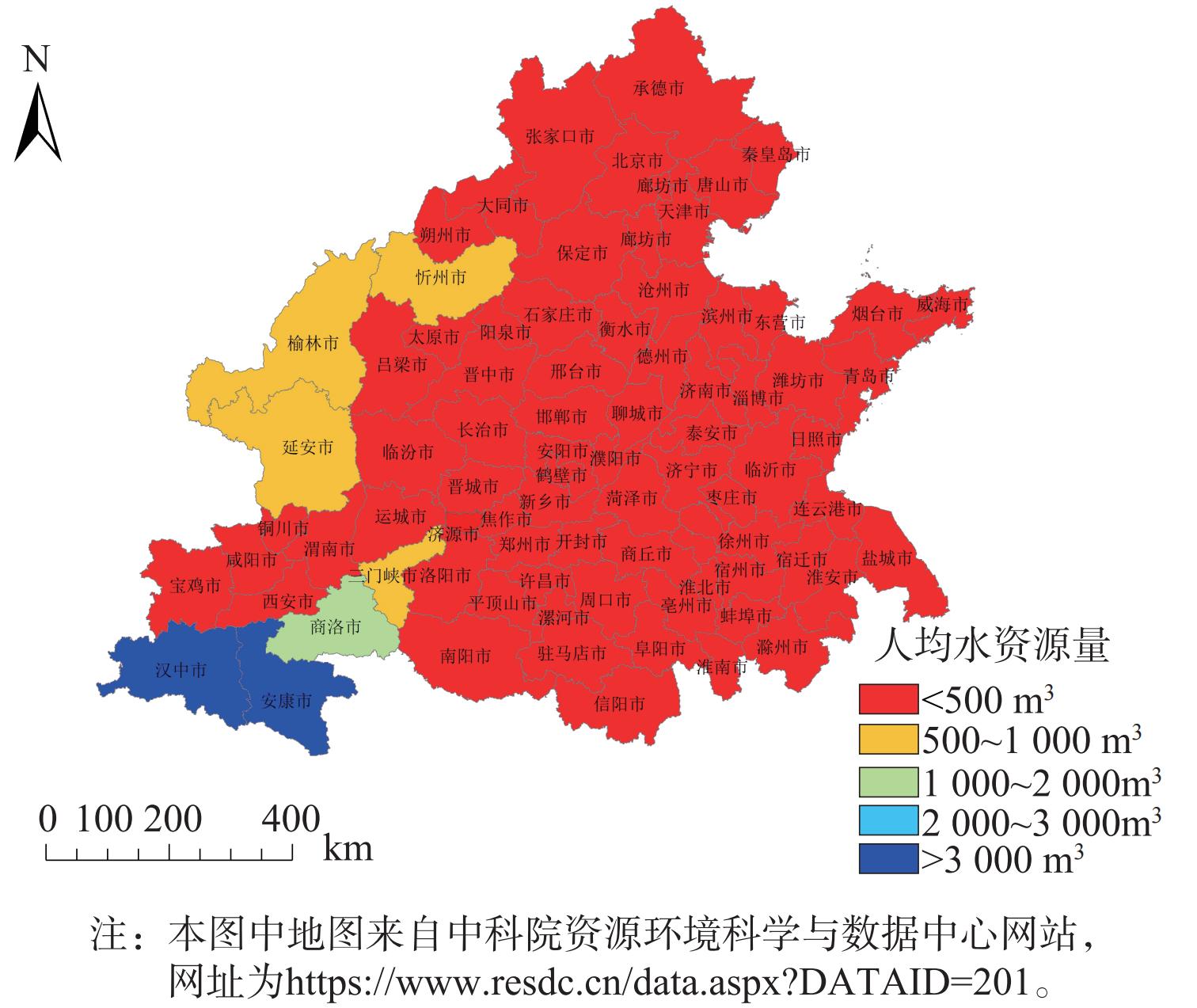
3) 水资源状况。研究区域城市水资源极度匮乏,“有河皆干”现象突出。区域内人均水资源量仅为357 m³,约为全国的1/6,属于极度缺水的地区,各城市人均水资源总量见图5。区域内79个城市中除汉中市和安康市外,其余均存在不同程度的水量型缺水问题,其中58个城市人均水资源量不足500 m³,处于极度缺水状态,加之区域内城市水环境质量普遍较差,区域内多数城市存在不同程度的水质型缺水问题,如郑州、盐城、连云港、宿迁、宝鸡、西安、临汾和运城等城市。区域内城市水量型和水质型缺水问题严重,其中京津冀城市群水量型和水质型缺水问题更加突出,已严重制约了城市的可持续发展。
-
1) 生活污水排放量大,污水收集和处理设施存在短板。区域内主要城市生活污水排放量与城镇人口数量见图6。城镇人口基数越大城市生活污水排放量越高,由此带来的生活污染问题则更加严重。研究区域内城市人口密集,2019年区域内城镇人口约2.6×108,占全国城镇人口的32%。城市居民的日常生活会产生大量生活污水需收集处理,故在生活污水收集处理方面存在极大的挑战。基于区域城镇人口分布情况,北京、天津、青岛,以及各省会城市等城镇化水平较高的城市常常面临更严峻的生活污水收集处理问题。对于区域内其他城市而言,尽管人口数量的差异会使其城镇生活污水排放量比发达地区的更少,但其污水收集处理设施的建设也相对落后,导致其同样面临着生活污水直排入河的问题。基于此,对研究区域内城市污水收集处理系统开展分析。
研究区域内2020年城市建成区排水管网密度仅9.77 km·km−2,低于11.11 km·km−2的全国均值,整体排水管道建设较为滞后。研究区域内2020年各城市建成区管网密度见图7。79个城市中有57个城市建成区管网密度低于全国均值。管网建设滞后的问题主要集中在山西省、陕西省和河南省的省辖城市,其管道密度分别为7.68、7.34和8.86 km·km−2。区域内多数城市基础设施建设欠账多,尤其是城中村、城乡结合部等存在管网建设空白区,建成区管网建设滞后,导致污水收集率低,存在生活污水直排入河湖现象。区域内多数城市雨污分流的排水体制推行较快,但老城区的排水体制仍多以合流制为主,夏季降雨集中期间易发生溢流污染、内涝和水体反黑臭等问题。
排水管网建设的滞后造成研究区域污水收集率普遍偏低,大量生活污水排入河道。按污染物去除效果核算,区域内多个城市污水收集处理率仅约50%,如新乡、邢台等。2016年西安市长安区因污水管网建设不到位,使每天近8×104 t生活污水进入皂河河道。2020年山东省菏泽市因排水管网不完善,致其生活污水收集率仅为51.9%,赵王河、外护堤河、青年湖等水体都存在生活污水直排的现象,小黑河等水体部分河段呈现重度黑臭。
2020年研究区域城市污水处理厂平均运行负荷率为72%,低于77.86%的全国均值 (图8) 。统计数据显示,79个城市中有49个城市污水处理厂运行负荷率低于全国均值,多数城市污水处理能力已满足城市需求,甚至出现“大马拉小车”的现象。污水处理厂的低运行负荷率暴露了城市在污水处理方面存在“重建厂、轻管网”的问题,致使大量生活污水未经处理直接排放,污水处理设施的效能无法完全发挥。此外,部分城市污水处理设施超负荷运行,如三门峡市和延安市等。城市污水处理厂超负荷运行会使用大量污水溢流进河道,污水处理效果下降,出水水质变差。
尽管统计数据表明,区域内绝大多数城市污水处理能力已满足城市需求,但各地城市的快速扩张、人口聚集,使得多数城市在污水处理上存在着不均衡、不协调的问题。如北京市67座污水处理厂,有10座运行负荷率低于30%,但同时又有多座超负荷运行。部分城市污水处理实际效能低,污水处理厂排放标准执行不到位。唐山、秦皇岛、滨州等城市仍有14座污水厂未按“水十条”要求执行一级A排放标准。
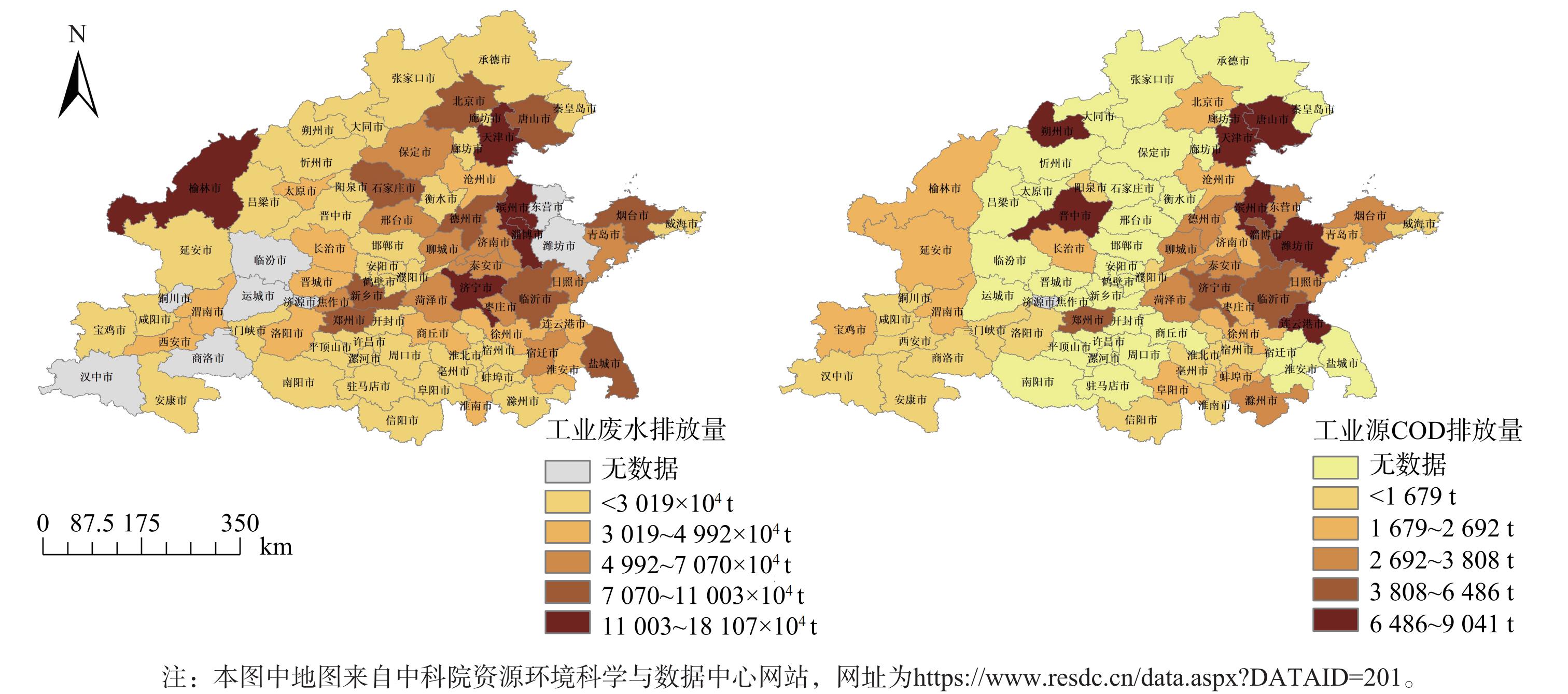
2) 工业废水排放量大,钢铁、制药、石化行业污染严重。研究区域2017年部分城市工业废水和COD排放量见图9。2017区域工业废水排放量为3.376×109 t,占全国废水排放量的30.91%。其中,京津冀城市群和山东省是工业污染最为严重的地区,工业废水排放量1.857×109 t,占区域排放总量的55.02%。本研究收集的48个城市工业源COD共排放1.5×105 t,其中天津、唐山、潍坊和滨州等城市工业源污染物 (以COD计) 排放较为突出。
区域内各城市的工业基础扎实,目前依靠资源消耗而增加产值的企业是区域的经济主导,由此也带来了更加严重的污染问题。2019年区域内钢材产量占全国的52.7%,石油、煤炭等加工业营收占全国41.86%,医药制造业营收占全国38%。这些行业是区域经济增长的主要力量,但同时也严重威胁着区域内城市水生态环境质量,特别是京津冀地区钢铁、石化、制药、造纸、农副食品加工等行业的工业污染排放贡献较大。尽管各城市希望通过建设工业园区来解决工业污染排放问题,但由于入园要求低、工业废水处理难度大和园区管理经验不足等问题导致园区废水处理效果差,污染物集中排放,使园区逐渐成为城市内水环境污染最为严重的地区之一。例如,石家庄经开区内有30多家药企,园区污水处理厂受来水可生化性差、水质波动较大,导致运行不稳定[10];2019年天津工业源COD、氨氮、总氮和总磷排放量分别为5 583、449、1 366和60 t,天津滨海工业区内有近1 000家石化和化工企业,污染排放负荷大、污水水质差异大,且含有大量难生物降解有机污染物和重金属,严重影响周边水体水质[11]。区域部分城市主要工业类型见表1。
3) 季节性径流污染严重。研究区域2019年逐月降水量及京津冀区域I-III类水质占比变化见图10。区域内降水季节分配很不均匀,主要集中在夏季。从京津冀区域地表水监测数据来看,城市水体水质与降雨量存在明显相关性。随着雨季来临,I-III类水质断面占比呈下降趋势,受初期雨水径流影响,6月份水体水质最差。而随着秋冬季降水量的减少,地表水水质逐渐变好。由此说明,造成雨季城市水体水质下降的重要原因是降雨径流引起的面源污染。
地表径流污染是城市面源污染的直接来源。近年来,研究区域城市面积不断扩大,不透水下垫面面积占比增大,下垫面容易累积大量污染物,造成径流水质普遍较差,特别是6月份径流水质最差。如太原市6月份工业区道路降雨径流中COD、氨氮分别为219 mg·L−1、2.05 mg·L−1 [12];天津市6月份老城区道路降雨径流中COD、氨氮分别为276.65 mg·L−1、5.02 mg·L−1[13]。各主要污染物平均浓度均高于我国地表水环境质量V类标准。
合流制溢流及管道沉积物是面源污染重要来源,也是导致城市水体黑臭的重要因素。我国多数城市合流制排水体系截流倍数取1~2,造成排水系统对CSO的截流效率偏低,大量污水溢流进入河道,特别是雨天极易发生水体返黑臭现象。付朝臣等[14]对北京中心城区合流制溢流污染监测发现,溢流污水水质极差,COD为267 mg·L−1、氨氮为10.6 mg·L−1。管道沉积物的“零存整取”是溢流污水水质极差的重要原因之一,李海燕等[15]分析北京城区溢流污水的不同来源污染负荷后发现,沉积物污染负荷贡献率高达80%。
-
1) 城市建设用地的扩张。城市建设用地的不断扩张是造成研究区域城市水域面积减少的重要原因之一。近年来,区域内城市建成区面积不断增加,其中有相当一部分增加的面积是通过缩窄河床、围湖造地等侵占城市水域空间的方式进行扩张的,这些活动造成了城市河湖水面面积大幅萎缩、斑块化数量增加等现象。河南省沿黄河流域8个地市1987—2002年湿地面积减少了19.18%,斑块化数量增加了21.27%[16];海河流域自1950年以来,受城市开发建设影响湿地水面面积减少了72%[17];贾梦圆等[18]对天津市不同发展条件下的土地利用变化情况的模拟结果表明,截至2025年,天津市主要水域均为易受城市扩张威胁的水生态敏感区域,大量二级河道、排水干渠、坑塘水面等毛细水网将在城市建设过程中被填埋和侵占。
2) 河湖岸带的开发利用。河湖岸带的开发利用是引起研究区域水体富营养化加剧的重要因素之一。研究区域内城市为防洪、稳固河岸和追求景观娱乐效果,对城市内河湖岸带进行了一系列的开发利用,如河道渠道化、裁弯取直、河湖岸带硬化和岸边植被带园林化等。淮河流域河南段11个地市自1950年以来建设的硬质化边坡长度达1.1×104 km,其城市河流边坡硬质化现象普遍[19];京津冀非生态用途占有缓冲带比例高达48%,北京温榆河流域大约6 km的河岸带生态系统被开发占用[20]。城市对河湖岸带的开发利用隔断了水陆生态系统之间的联系,使河岸区域复杂多样的生境变得均一化,生物多样性减弱,水体自净化能力下降,也降低了河湖岸带控制径流污染的能力,造成富营养化问题加重,对水生态系统健康造成严重威胁。如北京潮白河下游水体流动性差,夏季富营养化严重,团城湖、玉渊潭湖和奥运湖等湖泊均处于轻度-中度富营养状态;自2012年起天津海河干流连续多年5—6月暴发蓝藻水华[21];2018—2019年衡水市衡水湖处于轻度富营养水平。
3) 城市取排水量的增加。城市取排水量的增加引起的水质下降是造成城市水体生境退化及生物多样性减弱的主要原因。区域内2004—2019年工业和生活取水量增加了约16%,冶金、石化、造纸、等高耗水企业众多,人口密集,导致生活和工业取用水量增多,大量工业废水及生活污水排入城市水体。区域内城市河湖污废水等非常规水源补给十分明显,占比已超过60%,其京津冀河湖2001—2012年污径比范围为18.2%~71.6%,平均污径比为35.7%[22]。城市水体接纳大量污水导致水质明显下降,黑臭现象频发,水生态系统遭到严重破坏,生物种类和生物量也呈锐减状况,有的城市水生态系统甚至难以恢复。夏会娟等[23]发现,北京市清河和通惠河由于接纳了大量生活污水和工业废水,水生植物生境被破坏,造成其水生植物多样性处于较低水平,清河植被生物完整性值在0.23~0.38,处于一般水平,通惠河植被生物完整性值低于0.23,处于较差水平。
-
1) 水资源开发利用强度大。研究区域内各城市2020年水资源总量及开发利用强度见图11。区域内京津冀、河南北部及山东北部水资源匮乏的城市水资源开发利用强度普遍较高。区域内降水量少且分布不均,造成江河径流量小,地表水资源条件先天不足,但人口产业发达造成生产、生活和生态环境用水刚需大,导致水资源开发利用强度极大,造成河流断流问题突出,加剧了区域内水资源短缺的现象。2020年区域水资源开发利用强度达到了56.13%,超过了世界公认的40%的安全警戒线。其中,海河流域水资源开发利用强度最大,已达到106%,以至于大部分支流长期处于断流状态。王晨等[24]发现,2018年春季京津冀地区13个城市均有干涸河道分布,其中保定、张家口、北京、石家庄4个城市的干涸河道长度均超过500 km,石家庄河道干涸比达到了44%。此外,城市对水资源的高强度开发利用使城市生产生活产生大量污染物排入水体,造成城市水环境质量不断下降,区域内城区劣V类水质的水体占比高达36%,进一步使城市陷入了水质型缺水的困境。
2) 水资源浪费严重。截至2021年底,研究区域内已建成节水型城市58个 (含县级市) ,占全国已建成节水型城市数量的43%。尽管如此,区域内仍有部分城市在生活、市政、工业用水方面均存在不同程度的水资源浪费现象。区域内2020年各城市生活、市政和工业用水指标统计情况见表2。
在生活用水方面,2020年区域内有18个城市居民生活用水量高于《城市居民生活用水量标准 (征求意见稿) 》中给出的第二阶梯用水量,住建部“关于印发《国家节水型城市考核标准》的通知” (建城[2018]25号) 中规定的节水器具普及率达到100%,但该区域多数城市未达到该要求,城市生活用水存在浪费现象。在市政公共供水方面,该区域城市公共供水管道漏损率约12.88%,超过节水城市考核标准中规定的10%的要求,有63个城市未达到该要求。其中,张家口、承德、枣庄、淮北和蚌埠等市的供水管道漏损率在17%左右。区域内2020年城市公共供水漏损水量共13.36亿m³,占全国地级及以上城市漏损水量的19.37%。在工业用水方面,近年来该区域工业节水力度不断加大,但在有数据统计的63个地级城市中仍有18个城市工业用水重复利用率低于节水城市考核标准中规定的83%的目标要求。
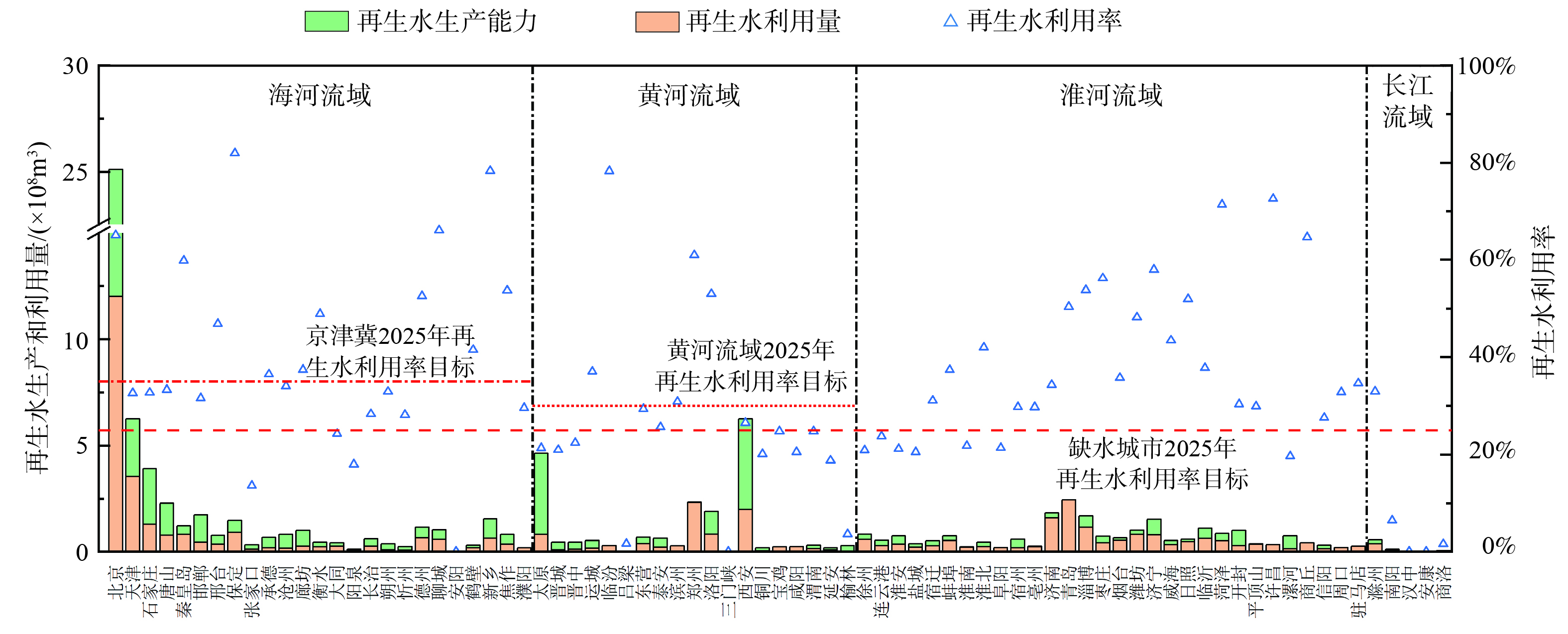
3) 再生水利用水平仍有提升空间。华北片区城市2020年再生水利用情况见图12。华北片区城市再生水利用水平仍由较大提升空间。从生产设施利用效率来看,仅郑州和青岛等14个城市再生水生产设施利用率达到90%以上,生产设施得到充分利用,需扩大生产能力。而多数城市生产设施面临闲置困境,太原和沧州等32个城市再生水生产能力仅发挥不到50%,需大力开发再生水利用途径。整体来看,淮河流域城市再生水生产设施利用水平较其他区域城市更高。从再生水利用率角度来看,海河流域和淮河流域城市再生水利用率水平整体较淮河流域更高。根据住建部《“十四五”城镇污水处理及资源化利用发展规划》 (发改环资〔2021〕827号;2021年6月) ,到2025年,全国地级及以上缺水城市再生水利用率目标达到25%以上,京津冀地区达到35%以上,黄河流域中下游地级及以上缺水城市力争达到30%。目前,石家庄、太原和大同等30个城市尚未达到其所对应规划目标,需进一步提高再生水利用率。
-
基于对华北片区城市水生态环境问题的解析发现,制约城市水生态环境改善的根本原因在于城市面临的水生态环境问题是复杂多变。因此,在城市水生态环境治理中,建立起从整个城市水体角度考虑的“三水”统筹推进的系统治理思路是实现城市水生态环境质量全面提升的根本方法。为此,研究以“三水”统筹兼顾、多措并举和协调推进为理念,提出了近期 (2021—2025年) 、中期 (2026—2030年) 和远期 (2031—2035年) 3个阶段的水生态环境综合整治对策。
1) 近期阶段对策。近期阶段区域城市重点任务是推进城市点、面源污染深度减排,节水型城市构建,实现水环境质量提升及水资源状况改善,并辅以水体生态修复措施。
全面开展城市污染负荷削减工作。在生活源方面,需补齐污水收集与处理设施短板,对于排水管网密度低的城市,如阳泉、信阳、三门峡等市,加大排水管网建设力度,消除管网空白区;治理污水直排问题,设置截污管,完善北京、天津等管网建设较快城市人口聚集区生活污水毛细管网建设,提高污水收集率;对混错接和破损问题,开展混错接改造和老化破损管网修复工作,提升污水管网排放质量与水平;对污水处理效能低和执行排放标准落后的问题,加快推进唐山、秦皇岛和滨州等城市污水处理厂一级A提标改造。
在工业源削减方面,重点解决唐山、邯郸等城市钢铁行业,石家庄、东营等城市制药行业,天津、青岛、淄博等城市石化行业,榆林等城市煤化工行业等重点行业工业废水污染问题;推动全部工业企业入园,实施工业集聚区生态化改造,促进工业企业的良性集聚;完成钢铁、制药、石化等污染行业清洁生产改造;淘汰或改进现有落后的钢铁、石化、制药等工业废水处理技术;加强工业园区管理,完善园区污水收集处理设施,实现工业废水分类收集、分质处理。
在面源污染削减方面,各城市需全面开展汛期管网清淤工作防止初期降雨污染河湖;总结迁安、北京和天津海绵城市建设的经验与教训,形成适用于新老城区分区实施海绵城市建设的技术模式;构建“池-网-厂-河”联动机制,强化各污水处理厂处理水量的科学调配;坚持“点、线、面”结合,通过源头治理、末端拦截、分散调蓄、就地处理等方式,削减合流制溢流污染和面源污染;针对水资源短缺问题,需加强雨水的收集利用,构建“渗滞为主、蓄排结合、净用相辅”的综合雨水利用系统。采取上述污染负荷削减措施,使2025年受城市影响控制断面优III比例达60%以上,劣V比例降至15%以下,城市水体水功能区基本达标,建成区海绵城市建设占比达40%。
在节水城市构建方面,各城市要依据用水类型的不同遵循不同的量水发展原则,优化水资源配置,北京和天津等人水矛盾突出的城市,遵循“以水定人”的原则;唐山和烟台等水供需矛盾突出的城市,遵循“以水定产”的原则;运城和南阳等城水矛盾突出的城市,遵循“以水定城”原则。系统推进城市工业、生活和市政节水措施,初步完成节水型城市构建。提高城市工业用水重复利用率,特别是西安、邯郸和郑州等;控制缺水城市人均日生活用水量低于第二阶梯用水量,特别是北京、太原和西安等;控制城市供水管网漏损率在9%以下,特别是张家口、枣庄和淮北等。加大缺水城市再生水回用力度,特别是京津冀城市群;针对区域内河流干涸断流问题,各城市可参考北京市永定河干涸断流恢复的案例,制定相应的河流水量恢复方案,通过对再生水、雨洪水和工程引水等水资源的合理配置维持城市河流生态需水量,提高城市水体生态基流保障率。使2025年城区再生水利用率达35%以上,其中京津冀地区城市达40%以上,万元工业产值用水量降至16 m³以下,其中京津冀地区城市降至11 m³以下,城区部分河流恢复有水。
在水体生态修复方面,需强化河湖水生态空间管控,划分三带 (水域带、岸线带、缓冲带) 四区 (保护区、保留区、控制利用区、开发利用区) 的河流廊道水域岸线,严禁侵占水域及生态缓冲带,已被侵占的水域空间逐步恢复。针对水体富营养化、自净能力差等问题,各城市应通过河湖缓冲带修复、水系连通、水体水质净化和截污等工程措施,初步恢复城市水体自然特性和水生生境,改善水体水质,提高水体自净能力,抑制富营养化进程,以使2025年水生生物完整性指数达到“一般”水平。
2) 中期阶段对策。中期阶段在实现城市水环境质量提升的基础上,形成“水环境、水资源、水生态”统筹推进的系统治理格局,同时进一步提升水环境质量,推进水资源合理利用,初步恢复城市水生态系统。
全面完成节水型城市构建,持续推进城市全系统节水。在工业节水方面,严控钢铁、石化等高耗水行业新增产能,降低高耗水行业比重;推广一批适用于钢铁、石化等高耗水行业先进成熟的节水工艺、技术和装备;进一步提高城市工业用水效率,京津冀地区城市钢铁、制药和石化等行业用水效率需达国际先进水平;强化企业用水管理,加强节水技术改造,培育一批节水标杆园区和企业。在生活节水方面,推广节水器具,加强生活小区的节水型载体的建设力度,利用价格杠杆调整水价,促进节水。在市政节水方面,需加强城市节水基础的建设和管理,优化供用水结构,提升管网运行的管理水平,加快老旧供水管网的改造,进一步降低城市供水管网漏损率。在再生水回用方面,各城市应依托城镇污水厂提供再生水生产能力,同步加强再生水管道建设,加大工业和市政对再生水的利用力度;进一步加大城区河流生态补水力度,提高生态基流保障率。实现到2030年城区再生水利用率达到45%以上,其中京津冀地区城市达50%以上,万元工业产值用水量降至13 m3以下。其中,京津冀地区城市降至9 m³以下,城区主要河流恢复有水。
此外,该阶段仍需持续推进城市点、面源污染深度减排,加大前期污染减排措施的实施力度,进一步削减城市点、面源污染负荷,并同步推进构建污染物减排措施长效监管机制构建。实现到2030年受城市影响控制断面优III比例达70%以上,劣V比例降至5%以下,城市水体水功能区基本达标,建成区海绵城市建设占比达到50%。
在水生态修复方面,需加快推进城市河湖缓冲带建设,实现城区河湖缓冲带全面修复,强化河湖缓冲带管控,恢复水陆生态系统之间的联系,全面恢复河流水生生境,人工引导恢复河道生物种群和水生动植物群落,提高生物多样性,初步恢复城市水生态系统。采用上述措施使2030年区域内城市水生生物完整性指数达到“好”的水平。
3) 远期阶段对策。远期阶段重点实现城市水生态系统全面恢复,构建以城市水生态系统健康为导向的“三水”统筹机制,城市水生态系统得到全面恢复。
在水生态恢复方面,实现河湖缓冲带全面恢复,全面恢复水生动植物群落结构和食物链,构成良性稳定的水生态系统,促进河道生态系统的动态平衡和自我修复。还需加强城市水生态环境的科学管理,实现城市水生态系统功能的长效保持,使2035年城市水生生物完整性维持“好”的水平。
此外,还需全面完成城市污染减排措施、节水措施及河流水量保障措施的长效监管、运营及维护机制的构建,实现水生态环境质量持续向好。使2030年受城市影响控制断面优III比例达80%以上,消除劣V类断面,城市水体水功能区全面达标,建成区海绵城市占比达60%以上,城区再生水利用率达50%以上,其中京津冀地区城市达55%以上,万元工业产值用水量降至11 m3以下,其中京津冀地区城市降至8 m³以下,城区全部河流恢复有水。
-
1) 区域内城市水生态环境质量普遍较差,水体黑臭现象突出;城市水生态系统健康状况整体较差,部分城市接近崩溃;多数城市水资源极度短缺,水量型和水质型缺水问题突出。
2) 区域内城市水生态环境问题的内在因素包括:区域内城市生活污水排放量大,污水收集和处理设施仍存在短板;区域内城市钢铁、制药、石化行业污染严重,特别是山东省和京津冀城市群;季节性径流污染严重;城市建设用地的扩张、河湖岸带的开发利用和城市取排水量的增加等人类活动造成城市河湖面积萎缩、生境被破坏和生物多样性下降等水生态问题;受工业、生活和市政用水浪费,水资源匮乏导致开发利用强度大的影响造成城市河流干涸断流问题突出。
3) 从“水环境、水资源、水生态”三方面提出了9项指标,给出了近期 (2021—2025年) 、中期 (2026—2030年) 和远期阶段 (2031—2035年) 分阶段目标,并提出了“三水”统筹推进的分阶段综合整治对策,近期阶段以污染减排和节水城市构建为重点,辅以水生态修复措施,实现水环境质量提升;中期需全面推进“三水”统筹治理,实现水资源合理利用,水环境质量进一步提升,水生态系统初步恢复;远期阶段在实现水环境质量提升和水资源合理利用的基础上,实现城市水生态系统全面恢复,构建以城市水生态系统健康为导向的“三水”统筹考核机制,城市水生态环境保护修复取得实质性进展。
Analysis of the current situation of urban water ecological environment and comprehensive improvement measures in North China
- Received Date: 29/12/2021
- Available Online: 31/12/2022
-
Key words:
- north china region /
- urban water ecological environment /
- water resource /
- policies for comprehensive regulation and remediation
Abstract: In this paper, the problems and the intrinsic factors residing in urban aquatic ecological environment in North China were analyzed from three aspects, i.e. the water quality, the water resources and the urban aquatic ecology. Results showed that the quantity of the domestic sewage discharged in urban area was huge, but there were still shortcomings in sewer networks and sewage treatment facilities. Pollution resulted by the discharges from the iron and steel, pharmaceutical and petrochemical industries were prominent, especially in the cities of Shandong Province and the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban cluster. Urban non-source pollution caused by seasonal rainfall could not be ignored. Urban water ecosystems were severely damaged, the water area shrank significantly, the shoreland zones of urban rivers and lakes were severely damaged, the eutrophication of urban waters was enhanced, and the biodiversity declined. Problems with the urban water resources include the shortage of per capita water resources, over-exploited water resources, the waste of water resources in urban area, the insufficient flow rate in rivers, and the bad connectivity between waterbodies. In response to the above problems, termed objectives, solutions for the improvement and comprehensive remediation of urban aquatic ecological environment for cities North China was proposed in this paper. For the three terms, namely, the short-term (2021-2025), the medium-term (2026-2030) and the long-term (2031-2035), a roadmap for the improvement of urban aquatic ecological environment in the region was also formed.












 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
