-
厌氧氨氧化(anaerobic ammonium oxidization, anammox)是一种自养脱氮过程,相比于传统的硝化反硝化工艺,可大幅度减少曝气成本和碳源投加成本,是一种理想的新型脱氮工艺。然而,厌氧氨氧化菌易受环境因素影响,在外界刺激下容易产生胞外聚合物使污泥聚团上浮,进而流出反应器导致反应器内生物量减少,影响该工艺的氮去除效率[1-2]。
由于厌氧氨氧化微生物的生长进行得相对缓慢,提高anammox颗粒的机械强度和沉降速度对于更好地保持反应器中的污泥浓度至关重要。有研究表明,颗粒内部的传质限制和微生物的包裹作用使颗粒污泥的核心具有了产生无机沉淀的有利条件,而增大无机物含量可明显提高颗粒的沉降速度[3]。另外,对于anammox颗粒污泥,由anammox反应导致的pH梯度可为颗粒内部无机沉淀的聚集创造更有利的条件[4]。厌氧氨氧化颗粒的机械强度会因磷灰石的积累而增加,故发生颗粒破碎的机率更低,被从反应器中冲出的生物质也更少[5]。若能将无机沉淀与anammox颗粒污泥有机结合,则可同时提高anammox颗粒污泥的机械强度和沉淀性能,进而提高反应器运行的稳定性。
磷肥是现代农业维持粮食产量的重要支撑。随着人口的增加,农业生产对磷肥的需求也急剧增加。然而,据预测来自磷酸盐岩的磷可能会在50~100 a内枯竭。因此,开发磷肥新来源,实现磷的可持续利用十分必要[6]。其中,废水被认为是实现磷可持续利用的重要资源之一。全球生产的磷中大约有10%被排入废水[6]。通过聚磷菌(polyphosphate accumulating organisms,PAO)将废水中的磷以多聚磷酸盐的形式聚集在活性污泥中,或在流化床反应器中沉淀为磷酸钙(Cax(PO4)y)和磷酸铵镁(MgNH4PO4)颗粒,一系列的磷回收工艺已被研究者开发出来[7-9]。其中,流化床结晶作为一种有效的磷回收技术,具有较高的反应速率且能够产生较高品质的磷产品,已被用于处理不同种类的废水[10]。
结晶流化床反应器与颗粒污泥膨胀床有相似的构造及流态,为anammox工艺与磷结晶在同一反应器内的进行提供了可能。本研究借鉴了用于磷回收的结晶反应器的概念,并将其与anammox工艺集成,利用厌氧氨氧化和羟磷灰石(hydroxyapatite,HAP)结晶的共反应机制开发了一种可同时实现脱氮和回收磷的高效工艺,并且探究了其在不同温度条件下运行的稳定性,以期为利用anammox工艺实现磷回收提供参考。
-
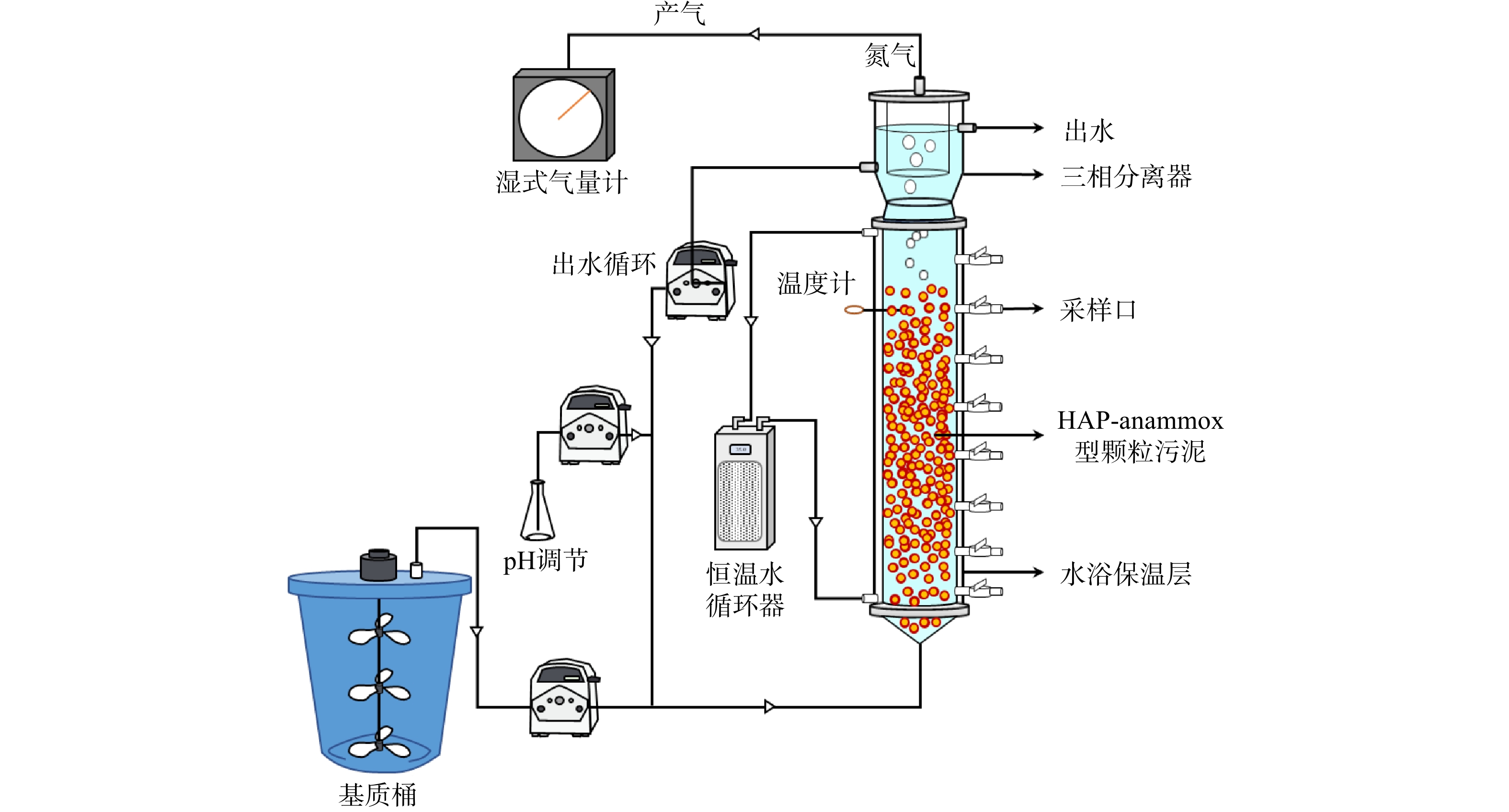
本研究中的生物反应装置如图1所示。该装置包含3个膨胀颗粒污泥床反应器。反应器的有效容积均为5 L。在连续实验中,合成废水被蠕动泵连续泵入反应器底部,从三相分离器流出的出水被蠕动泵再次循环至进水口。3个反应器(R1、R2、R3)的反应区均被水浴层覆盖,由恒温水循环器分别控制在35、25和15 °C。水浴层的外部覆盖遮光保温层,用以保持温度恒定,并避免光能自养生物的增殖。每天通过插入反应区内部的针式温度计对反应器的温度进行记录,以确保反应区的温度保持在设定温度范围(±1°C)内。反应器内产生的氮气由反应器顶部的三相分离器收集,并通过湿式气量表进行记录。在反应器运行的过程中,根据反应器的实际运行状况,通过向循环管中添加H2SO4溶液的方式调节反应系统的pH。反应器的侧面开有一系列等距(10 cm)的取样口,用以采取水样或者污泥样品。
-
表1为本研究中各反应器在不同阶段的运行参数。在开始本实验之前,R1运行温度为35 °C,氮负荷为5 g·(L·d)−1,R2与R3均使用R1的颗粒污泥作为种泥,且均在35 °C、氮负荷10 g·(L·d)−1条件下稳定运行。进水设置的总氮与总磷均参照厌氧消化液的总氮与总磷。进水中亚硝态氮与氨氮的质量之比RIS设为1.0~1.32。R1的进水总磷维持在11.40 mg·L−1,R2与R3的进水总磷均维持在22.80 mg·L−1。3个反应器的进水Ca2+质量浓度均设为81.60 mg·L−1。参考文献[11]的研究结果,在进水中添加了其他矿物质成分和微量元素。
-
每2 d从反应器中收集进水和出水样品,通过0.45 μm孔径的膜过滤器过滤,并在分析前储存在4°C的冰箱中。
NH+4 NO−2 NO−3 -
为测试不同温度条件下的厌氧氨氧化比活性(specific anammox activity, SAA),分别选取了3个反应器中的颗粒污泥作为种污泥,使用有效容积为120 mL的血清瓶,添加培养液至100 mL后置于恒温水浴震荡培养槽以110 r·min−1的震荡速度进行培养。为避免基质浓度不足及其浓度过高带来的抑制作用,活性实验中采用的总氮浓度为220 mg·L−1,其中氨氮的质量浓度为100 mg·L−1 、亚硝态氮的质量浓度为120 mg·L−1。在培养过程中,通过注射器定期计量并排出在血清瓶顶空部分积累的氮气,用于SAA计算。详细的活性实验流程参考文献[13]。所有的活性实验均进行3次重复。本研究使用Gompertz方程(式(1))对实验数据进行分析,拟合得出SAA。
式中:N代表产生的氮气体积,mL;P0代表氮气产生的潜力;Rmax代表最大氮气产生速度,mL·h−1;t为培养时间,h;λ代表迟滞期时间,h。
对SAA和温度之间的关系,分别使用Arrhenius方程(式(2))和CTMI模型(Cardinal temperature model with inflection)(式(3))进行拟合。
式中:k是速率常数,A是指前因子;Ea是反应的活化能,kJ·mol−1;R是通用气体常数;T是热力学温度,K。
式中:不同温度下的SAA在拟合中被用作μmax, g·(g·d)−1;Tmin和Tmax分别为可能的anammox反应的最低和最高温度,℃;Topt是SAA等于其最佳值μopt时的温度,℃。
颗粒污泥的沉降速度通过一系列的沉降实验进行测试。每组沉降实验均将颗粒污泥按照粒径分为不同组别,每个组别随机选取测试10~15个污泥颗粒。在1 m的沉降管中测试污泥颗粒的沉降速度,并根据粒径分布计算得到颗粒平均沉降速度。
各阶段稳定期的挥发性悬浮固体(volatile suspended solids,VSS)和总悬浮固体(total suspended solids,TSS)浓度根据APHA方法[12]进行分析。从TSS浓度中减去VSS以计算污泥中灰分的含量。污泥中的主要矿物种类使用OLYMPUS BTX Bench X射线衍射系统进行分析。
荧光原位杂交(fluorescence in situ hybridization,FISH)的固定和杂交程序参考文献[14-15]进行。从反应器中取出anammox-HAP颗粒,用多聚甲醛固定,并嵌入O.C.T.化合物(Sakura Finetek,Torrance,CA)中过夜,然后用低温切片机(OSK 97LF509,Ogawa Seiki Co.,LTD,日本)制备厚度为 30 μm 的冷冻切片。之后将切片与16S rRNA靶向寡核苷酸探针Amx820进行杂交(该探针与Candidatus Kuenenia stuttgartiensis和Candidatus Brocadia anammoxidans特异性结合),然后通过Carl Zeiss LSM 710 ZEN共聚焦激光扫描显微镜(CLSM,confocal laser scanning microscope)对切片进行观察。
-
分别探究了anammox-HAP颗粒污泥型膨胀床在35、25、15 °C温度条件下的氮去除效果,结果如图2所示。在每个运行温度条件下,均通过提高进水总氮和缩短HRT的方式,逐步提高进水氮负荷。在35 °C和25 °C条件下,实验初始总氮负荷均设定为5 g·(L·d)−1;在15 °C的条件下,初始总氮负荷设为2.5 g·(L·d)−1。
在不同的氮负荷条件下,anammox-HAP型反应器均能表现出良好的总氮去除效率。根据文献[16]报道的厌氧氨氧化反应式(见式(4)),约有占总氮11%的氮会在anammox反应中被转化为硝态氮,故理论上anammox反应的最高总氮去除率约为89%。在3个不同温度条件下,本系统可分别实现(44.90±0.32)、(17.12±0.97)、(8.79±0.14) g·(L·d)−1的氮去除速率;同时,反应器的平均总氮去除率均达到85%以上;而在最高负荷下,反应器的平均总氮去除率分别为(89.79±0.66)%、(85.61±4.85)%、(87.92±1.38)%。
随着anammox进行,反应器中的氢离子被消耗。因此,在anammox工艺中,随着进水浓度和氮负荷的提高,反应器中的pH会逐渐升高[17]。在本研究的各反应器中,均出现了出水pH随进水氮负荷升高而逐渐升高的现象。pH对于anammox反应和HAP结晶反应均为重要影响因素。过高或过低的pH会导致游离氨或游离亚硝酸的积累,进而影响anammox工艺的脱氮性能。另外,较低的pH也不利于HAP结晶反应的进行。有研究表明,在pH为7的条件下,仅有25%的磷可通过Ca-P沉淀去除,但在pH为9的条件下,大约有80%的磷可被去除[18]。在本研究中,通过在回流管中添加H2SO4的方式,将反应器的pH控制在8.0~9.0,以同时满足anammox细菌及HAP结晶形成对pH的要求。
在35°C条件下,随着进水磷负荷的升高,反应器的磷去除速率也逐渐提高。在整个过程中,磷的去除效率保持在(71.61±6.82)%。与R1相比,在R2与R3中,随着磷负荷逐渐升高,磷的去除速率维持在相对稳定的水平。这导致在反应器运行后期,磷去除率逐渐降至40%以下。HAP结晶的形成受到多种因素的影响,如溶液中晶核的数量、溶液过饱和指数、Ca/P、温度等[19]。在本研究中,将R1的进水Ca/P设定为R2与R3的2倍,且R1的运行温度高于R2及R3。这些因素均可能导致在R2和R3中HAP结晶形成的驱动力弱于R1,进而造成磷去除率较低。
-
现有报道的anammox菌种分属6个属,这些菌种的最适温度均为25~40 °C的中温范围[20-21]。随着运行温度从最适温度区间降低,反应器中的细菌活性也逐渐下降。据报道,anammox细菌的表观活化能约为55~80 kJ·mol−1,亦即若将35°C时细菌的活性作为参照,当反应器中的温度降为15 °C时,anammox的活性水平将低于35°C时活性的25%[13]。
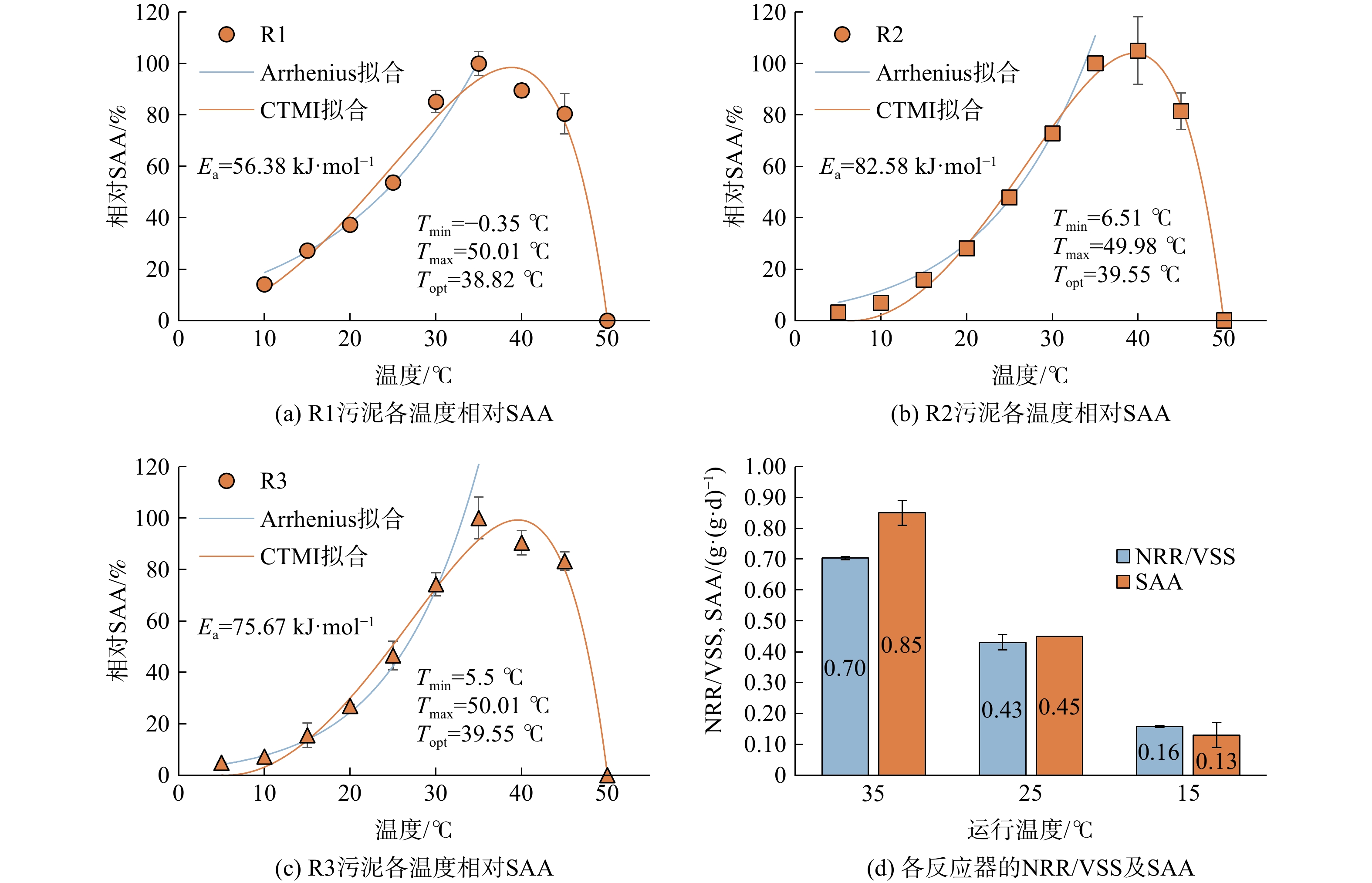
为评估厌氧氨氧化工艺在不同温度下的最大脱氮能力,以及SAA对温度的响应,分别取在不同运行温度下(35、25、15 °C)驯化后得到的anammox污泥,并在摇床中测试了污泥在5~50 °C条件下的SAA,结果如图3所示。进行SAA测试时,R1已经在35 °C下运行了数年。R2和R3从R1接种,并已分别在25 °C和15 °C下运行了约半年。通过CTMI方程拟合,可发现在不同温度下培养的anammox污泥最高活性所在温度均为35~40 °C。本研究中厌氧氨氧化污泥的优势菌种为“Candidatus Kuenenia stuttgartiensis”,其最适温度与其他富含“Candidatus Kuenenia stuttgartiensis”的报告基本一致[20]。在所有3个实验中,温度对低于35 °C的SAA影响可用Arrhenius方程进行拟合,其决定系数(R2)超过0.98。这表示可使用最佳温度下的SAA准确预测较低温度下的SAA,从而评估厌氧氨氧化工艺在不同温度下的脱氮能力,以避免在温度降低或接种来自在不同温度下运行的其他反应器厌氧氨氧化污泥时负荷过载。
计算得到R1中anammox污泥的Ea为56.38 kJ·mol−1,在较低温度下培养的R2和R3中anammox污泥,其Ea分别增加到82.58 kJ·mol−1和75.67 kJ·mol−1。以35 °C作为参考温度,来自R1、R2和R3的污泥在20 °C下的SAA分别为35 °C条件下的37%、28%和27%。当温度为10 °C时,该值下降到14%、7%和7%。
在本研究的整个运行阶段,R1、R2、R3的最高单位生物量氮负荷分别达到(0.70±0.01)、(0.43±0.02)、(0.16±0.00) g·(g·d)−1。同时,在反应器外进行的SAA比活性测试中,3个反应器中的污泥活性分别达到了(0.85±0.04)、(0.45±0.00)、(0.13±0.04) g·(g·d)−1 。在anammox工艺中,SAA常被用来评价工艺的脱氮能力。在SAA实验中,通常会选取对anammox细菌最适宜的基质浓度及其他环境条件,故实际工况下反应器的脱氮能力往往会低于SAA实验中得到的最大活性[22]。本研究结果表明,在不同温度条件下,反应器的实际脱氮能力与SAA实验中得到的数值高度一致,在35°C与25°C条件下仅略低于SAA,在15°C条件下甚至略高于在反应器外测得的SAA。这表明在anammox-HAP颗粒污泥型膨胀床反应器中,anammox能够充分利用基质,脱氮能力较好。
-
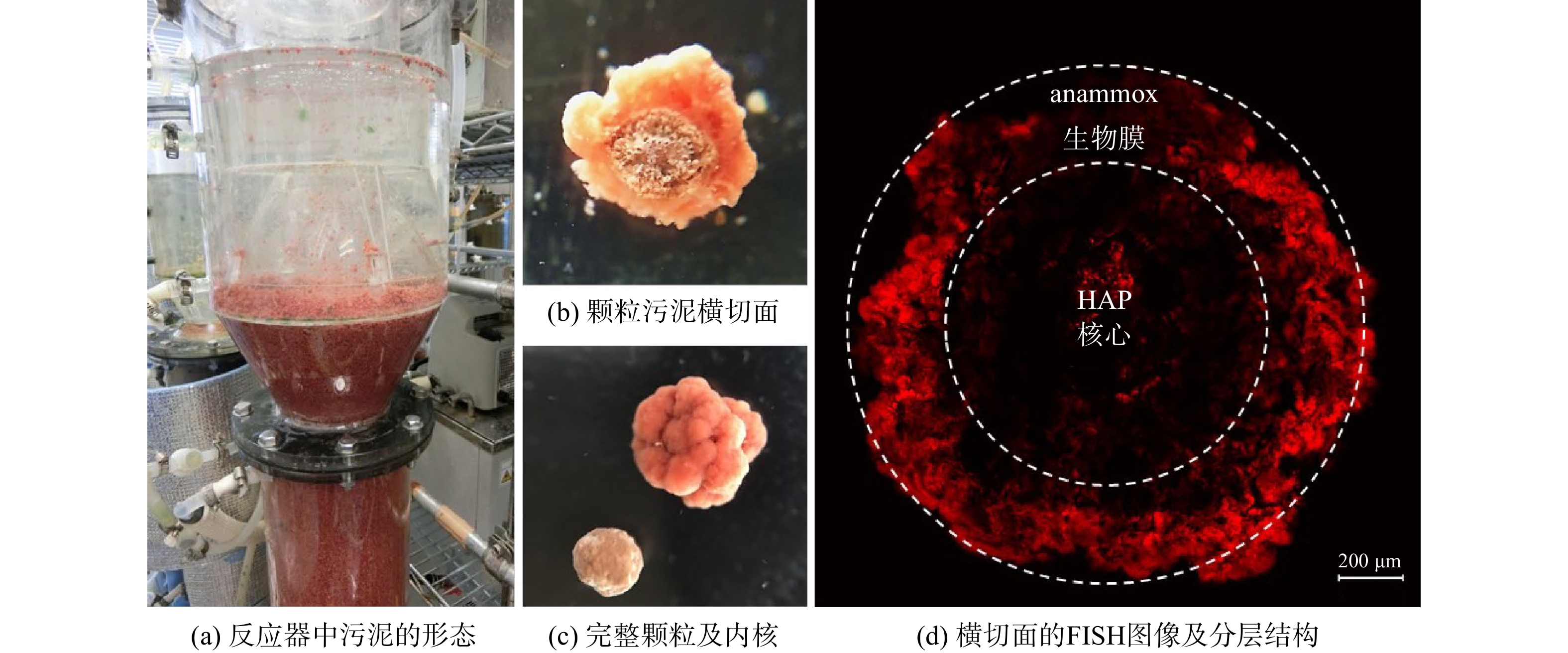
脱氮和磷回收的同步过程依赖于anammox-HAP复合颗粒污泥的形成。在反应器的稳定运行阶段,对反应器中颗粒的结构进行分析,结果如图4所示。通过横切面的观察,可很清楚地看到颗粒内形成了双层结构。颗粒中心是较为坚硬的无机核心,外部包裹的是较为柔软的鲜红色生物膜。在不同运行温度下,反应器中的颗粒污泥均保持了良好的结构稳定性。通过对颗粒污泥切片的FISH染色观察,结合Amx820探针(红色)的荧光强度可发现,细菌主要分布在颗粒外层200~500 μm。而在颗粒核心中,几乎没有观察到Amx820强度,即不含anammox细菌。此外,即使在颗粒的外层也可观察到明显的荧光强度差异。荧光仅在最外层厚度约为100 μm的生物膜中展现出较高强度,且随着厚度加深而明显降低。这表明尽管厌氧氨氧化颗粒可比絮状污泥聚集更多细菌,但过大的粒径不适合传质并限制了厌氧氨氧化细菌在颗粒更深部分的生长,故在长期运行过程中,需采取有效策略来控制颗粒污泥的粒度。
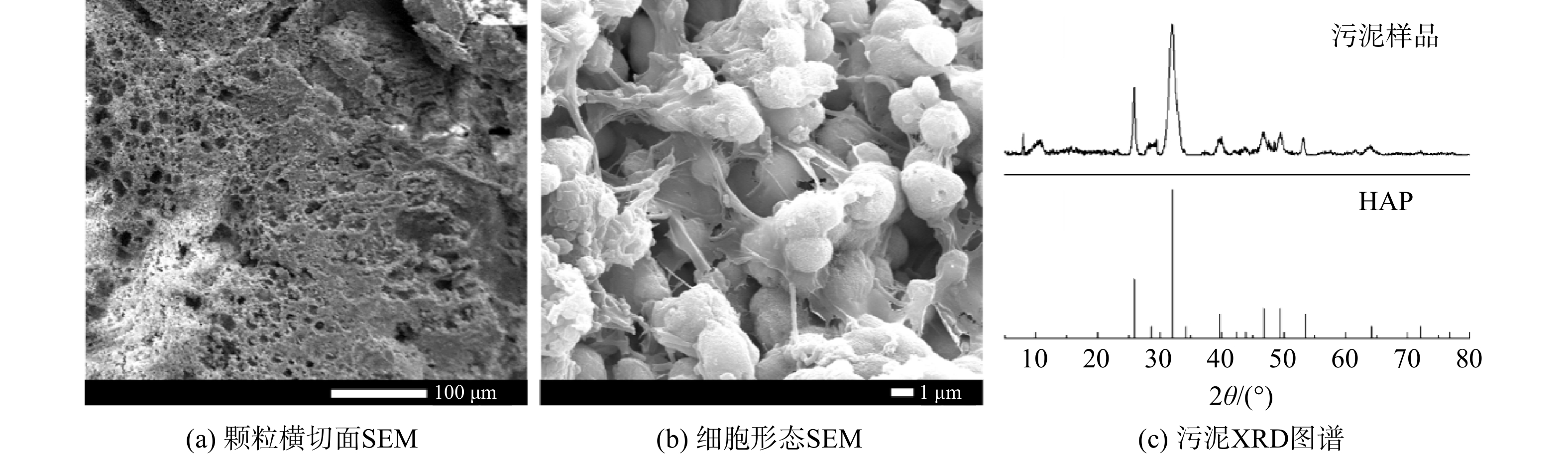
由于磷含量高,anammox-HAP颗粒污泥型膨胀床反应器中形成的污泥与普通污泥有很大不同,其微观形态和晶体特征如图5所示。根据前期研究[16],磷在接近纯培养的anammox菌中的含量仅占1.40%。然而,在anammox-HAP型反应器中,磷含量可高达污泥干重的10%~15%[23]。通过对污泥样品的XRD进行分析,可发现污泥中的主要结晶成分为羟基磷灰石(hydroxyapatite, HAP)。在本研究中,不同温度条件下的反应器内均可稳定形成类似结构的颗粒污泥。在较低的温度下,厌氧消化颗粒污泥会因丝状古菌的消失而分解[24]。而本研究结果表明,无机磷酸盐矿物核的形成增强了颗粒的强度并改善了生物质在反应器中的存在条件,使颗粒即使在低温下也能保持稳定。同时,在管道或反应器壁上并未观察到明显沉淀。这也进一步表明厌氧氨氧化生物膜与HAP形成之间存在共反应机制,HAP内核的形成高度依赖于anammox生物膜的存在。
-
颗粒的粒径、密度、几何形状、表面电荷和亲水性/疏水性与沉降性均呈现出一定的相关性[25-26]。另外,根据斯托克斯定律,球体落入流体中的终端速度会受到球形颗粒半径和流体粘度的影响,同时颗粒和流体的质量密度也起着重要作用。此外,较低的温度条件下,水的密度及粘性均较大,会降低颗粒的沉降速度。在本研究中,同一运行温度条件下,流体的质量密度和粘度保持恒定,故颗粒的质量密度对相同尺寸颗粒的沉降速度起关键作用。
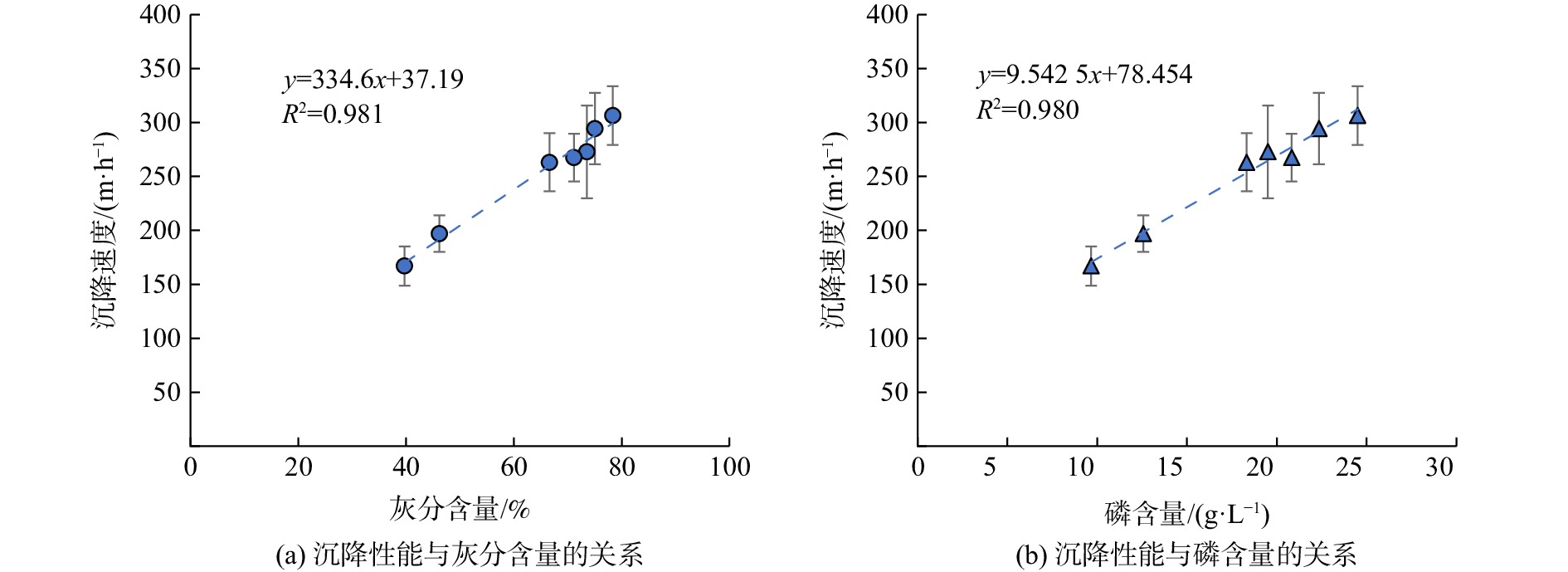
以R1的颗粒污泥沉降性能为例,在连续实验过程中,随着流入反应器的N/P增加,污泥平均VSS从(49.8±6.8) g·L−1增加到(62.1±1.1) g·L−1,平均TSS从(230.0±14.6) g·L−1降至(106.1±33.3) g·L−1。同时,污泥中的平均灰分含量从78.35%降低到39.72%,污泥中的平均磷含量从24.50 g·L−1逐渐降至9.67 g·L−1。随着颗粒污泥中灰分含量及磷含量的降低,颗粒的沉降速度也逐渐降低,如图6所示。灰分及磷含量与颗粒污泥的平均沉降速度之间呈明显的线性关系(R2>0.98)。
随着磷含量的减少,尽管颗粒的平均沉降速度从(306±27) m·h−1降至(167±18) m·h−1,但仍明显高于其他报道中50~110 m·h−1的沉降速度[25-26]。anammox-HAP颗粒污泥优良的沉降性能明显提高了反应器的生物量截留能力,进而保证了反应器稳定高效的脱氮性能。
-
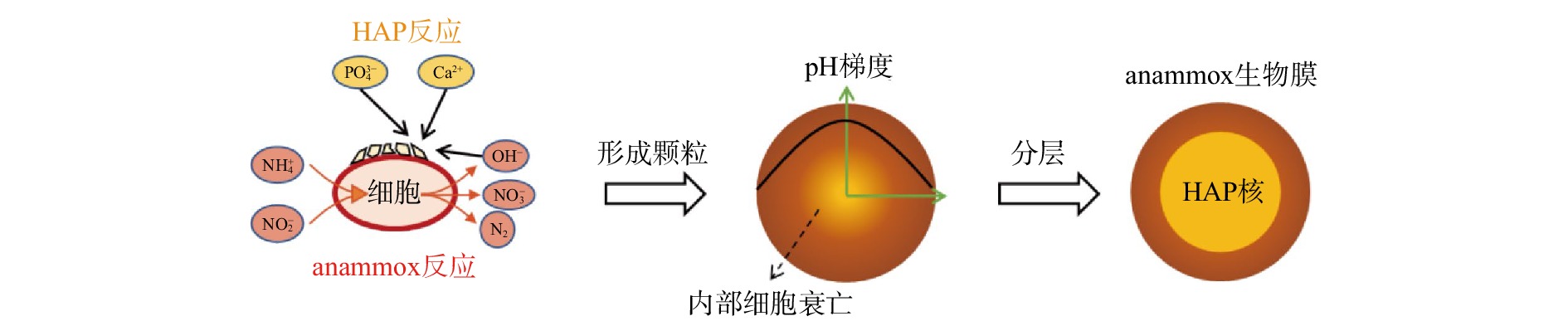
常规厌氧颗粒污泥的造粒被认为大致分为2个阶段:由于细菌粘附而形成前体,以及由前体逐渐形成颗粒。从胚胎颗粒形成到颗粒成熟的过程中,细菌分泌的胞外聚合物可保护颗粒免受剪切应力,并逐渐形成由不同细菌主导的多层结构[27]。本研究中无机物含量非常高的复合颗粒污泥含有较高含量的HAP,与常规厌氧颗粒污泥有明显差异,导致在这种情况下颗粒的形成机制与厌氧颗粒污泥的形成有所不同。根据颗粒的切面结构和微观形貌特征梳理出结合了生物矿物形成过程和常规厌氧颗粒形成过程的机制,过程如图7所示。
随着anammox细菌的代谢活动的进行,细胞附近会形成较高的pH。在具有高浓度Ca2+和
PO3−4 另外,由于氨氮和亚硝氮进入anammox外层的生物膜时被anammox细菌利用,浓度会逐渐降低[31],而且anammox反应会导致整个颗粒污泥核心的pH高于外部[4]。颗粒内侧较高的pH和底物浓度较低的环境会促进颗粒核心部位沉淀的生成以及厌氧氨氧化细胞的衰亡。在本研究中的颗粒横截面SEM图像中可观察到明显的蜂窝状结构,表明在细胞表面产生了生物诱导矿物,这也进一步应证了在颗粒形成过程中核心部位细胞逐渐衰亡的推测(见图5(a))。随着对环境条件的长期适应,反应器内最终会形成具有致密HAP内核和附着在外层的anammox生物膜的成熟颗粒。
-
1) Anammox-HAP颗粒污泥型膨胀床反应器可在35、25、15 ℃时实现高负荷条件下的高效率脱氮,脱氮效率未受温度影响。
2)在不同温度条件下培养的anammox-HAP颗粒的活性最适温度为35~40 ℃,脱氮能力与温度之间的关系遵循Arrhenius方程。
3) Anammox-HAP颗粒污泥呈现明显的anammox生物膜附着于HAP内核的内外结构,且HAP的形成依赖于anammox生物膜的存在。Anammox-HAP颗粒污泥的沉降性能明显高于一般的厌氧以及anammox颗粒污泥,且与颗粒中所含磷含量呈线性关系。




 下载:
下载: