-
城市污水中的有机物、氮和磷等物质是污水处理厂需要去除的主要污染物[1]。实际上,这些物质亦是能源和资源,若能实现资源化利用,则可解决污水处理厂能耗和成本较高的问题,确保其可持续性发展。因此,城市污水处理需由达标处理向能源回收、资源回收和低碳处理方向转型[2]。大量有机物、氮磷等物质在污水处理过程中进入污泥,故污泥的资源化处理亦成为研究热点[3]。利用厌氧消化技术对其中的有机物进行能源高效回收,再利用厌氧氨氧化(anaerobic ammonium oxidation, anammox)技术对污泥厌氧消化液进行低碳脱氮处理被认为是较为有效的方法[4]。
污泥厌氧消化过程会释放高浓度的磷,产生高含磷的污泥厌氧消化液。LIN等[5]成功开发了厌氧氨氧化-羟基磷酸钙(anammox-hydroxyapatite, anammox-HAP)颗粒污泥技术,实现了高负荷厌氧氨氧化脱氮同步高效磷回收[6]。污泥厌氧消化液的磷酸盐浓度与污水处理厂的除磷工艺密切相关。对于采用化学除磷方法的污水处理厂,其出水中磷酸盐质量浓度一般低于10 mg·L−1;而采用生物除磷方法的污水处理厂,则出水中磷酸盐的质量浓度相对较高[7]。anammox-HAP颗粒污泥技术可实现污泥厌氧消化液的高效脱氮和磷回收[8]。然而,污泥消化液水质差异对anammox-HAP系统磷回收效率会产生影响。MA等[9]通过批次实验研究发现,对于不同磷含量的废水,最适宜的钙投加量是不同的,磷的回收效率亦不相同。
现有研究在探索anammox-HAP系统的脱氮性能和磷回收效率时,主要集中在磷质量浓度较低时(<100 mg·L−1)的性能与表现,而实际污泥厌氧消化液中,磷的质量浓度可超过200 mg ·L−1[8]。本课题组在连续流膨胀颗粒污泥床(expanded granular sludge bed,EGSB)反应器中建立anammox-HAP系统并观察其长期运行特征,考察不同进水磷质量浓度、反应器pH、进水钙磷比(Ca/P)对反应器磷回收效率及污泥特性的影响,以期实现高效脱氮和磷回收,为anammox-HAP工艺应用于污泥厌氧消化液的低碳处理和资源回收提供参考。
-
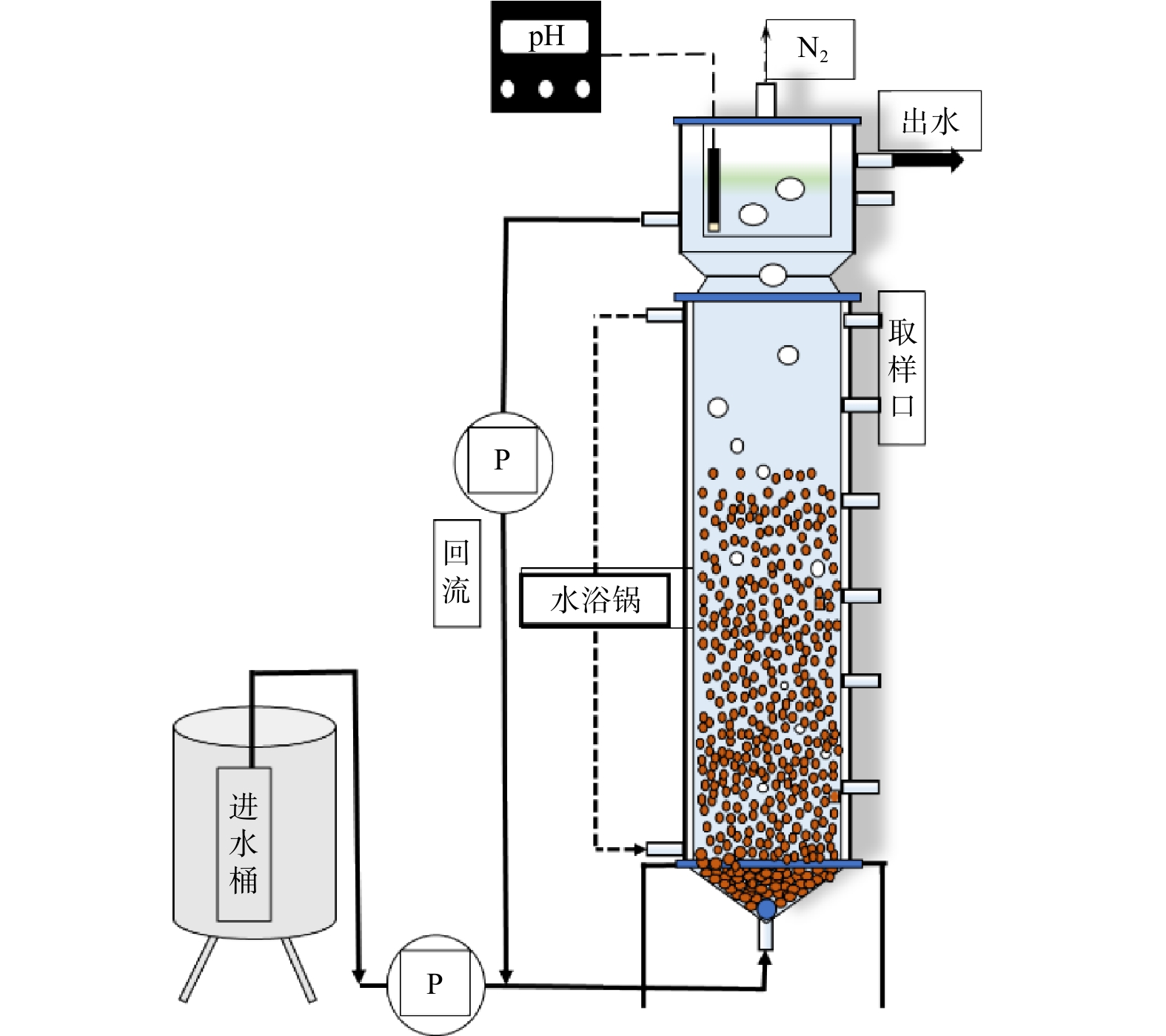
实验反应器为EGSB反应器,结构如图1所示。反应器由有机玻璃制成,有效容积为6 L。在反应器的顶端设有三相分离器,用于固液气三相的分离,从而防止反应器运行过程中絮状污泥的流失。
-
接种污泥取自实验室长期稳定运行的anammox反应器。anammox-HAP颗粒污泥的质量浓度为51.5 g·L−1,接种体积为1 L。
反应器的进水均为人工配水。氯化铵(NH4Cl)与亚硝酸钠(NaNO2)为进水中的基质。配水中用1.25 g·L−1的KHCO3提供无机碳源和碱度,并添加质量浓度为0.1 g·L−1的MgSO4·7H2O、0.017 g·L−1的FeSO4·7H2O、0.024 g·L−1的Na2EDTA和0.4 mL·L−1等微量元素。EGSB反应器中磷质量浓度的控制通过投加不同浓度的KH2PO4来实现,Ca2+的质量浓度根据磷变化而变化。另外,为避免过高的游离氨(free ammonia, FA)或者游离亚硝酸硝酸盐(free nitrous acid, FNA)对厌氧氨氧化菌(anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacterium, AnAOB)产生抑制作用,向反应器中添加HCl和NaOH以调节系统pH,从而保证反应器的正常运行。
-
每天定时取反应器出水水样进行分析。水样先经过0.45 μm滤膜过滤后,再进行水质分析。水质分析指标包括氨氮、亚硝态氮、硝态氮、正磷酸盐和pH。分析方法按照《水和废水分析监测方法》(第4版)[10]进行。
颗粒污泥的特性分析方法包括:颗粒污泥粒径分布(筛分法)、颗粒污泥沉降速度(重量沉降法)、颗粒污泥VSS和TSS含量(重量法)、颗粒污泥固相总磷(钼酸铵分光光度法)。
-
通过逐步提高总氮(由50 mg·L−1升至1 000 mg·L−1)和降低HRT(由4.8 h降至3.2 h),调节反应器的氮负荷(nitrogen loading rate, NLR)(由0.3 g·(L·d)−1提升至7.5 g·(L·d)−1)。为避免因出水中基质的质量浓度过高而影响回流的稀释效果,反应器进水[
NO−2 -N]/NH+4 -N]可设定为1.2~1.3。在研究后期,为避免因磷的质量浓度提高导致反应器内pH过低、造成FNA抑制,向基质桶里添加NaOH以调节反应器内的pH,确保FNA的质量浓度不大于10 μg·L−1。表1为反应器的运行条件。初始阶段设置的进水磷质量浓度为40 mg·L−1,反应器稳定运行过程中,进水磷的质量浓度逐步升至250 mg·L−1。此外,通过调节反应器内pH与Ca/P,以考察磷回收效率的变化。
-
不同磷质量浓度对anammox-HAP系统的进、出水氮质量浓度及去除率的影响如图2所示。磷的质量浓度变化对anammox-HAP系统脱氮性能并没有明显影响。反应器运行前5 d,出水的氮质量浓度较高,主要是由于反应器刚启动时污泥的状态不太稳定。在第6~108天,进水磷的质量浓度提升至150 mg·L−1,反应器稳定运行,出水氨氮和亚硝态氮均小于5 mg·L−1。在第109天,反应器回流管出现破裂导致反应器直接进入高浓度基质状态,此时AnAOB受FA和FNA的抑制,且回流泵一直处于工作状态,较多空气被带入反应器中,从而使得AnAOB被进一步抑制。为恢复系统正常运行,降低了进水总氮。7 d后,反应器恢复正常运行。在第118~133天,磷的质量浓度提升至200 mg·L−1,反应器仍然保持稳定运行,出水氨氮和亚硝态氮均小于5 mg·L−1。从第134 天开始,反应器出水氮的质量浓度逐渐升高。其原因有2个:1)磷浓度的提升导致更多HAP生成,消耗更多碱[11],反应器内pH出于较低水平,导致FNA抑制AnAOB,反应系统失稳;2)从反应器长期运行条件来看,由于回流使得颗粒污泥的多次被取出导致反应器内无机组分含量占比较大,此时反应器内微生物含量无法使反应器维持之前的运行负荷。在第161天后,总氮最终稳定在800 mg·L−1。当磷的质量浓度提升至250 mg·L−1后,向进水桶中添加NaOH调节合适的pH,以维持反应器稳定运行。
反应器进水的磷质量浓度为40~250 mg·L−1。在整个运行过程中,发生过一次由于回流泵的蠕动管未及时更换,导致回流管破裂,AnAOB被抑制的意外状况。除此之外,反应器运行均很稳定,反应器总氮的平均去除率达到88.5%。反应器的氮去除负荷(nitrogen removal rate, NRR)最高达到6.8 g·(L·d)−1。因此,此反应过程对应的磷质量浓度范围对anammox-HAP系统的脱氮性能并无明显影响。然而,周正等[12]发现,在长期研究获得的结果中,磷酸盐质量浓度在70~90 mg·L−1时,SAA开始受到明显影响。不同研究得到的抑制浓度差异较大,这可能是由于在高负荷水平下培养的anammox-HAP颗粒污泥具有较高活性,抗冲击能力更强,故磷质量浓度对anammox的抑制阈值也会更高。此外,反应器的类型及操作条件也会影响AnAOB,导致抑制浓度存在差异。综上所述,污泥厌氧消化液中磷质量浓度对EGSB反应器中anammox-HAP系统的脱氮性能无明显的不利影响。
-
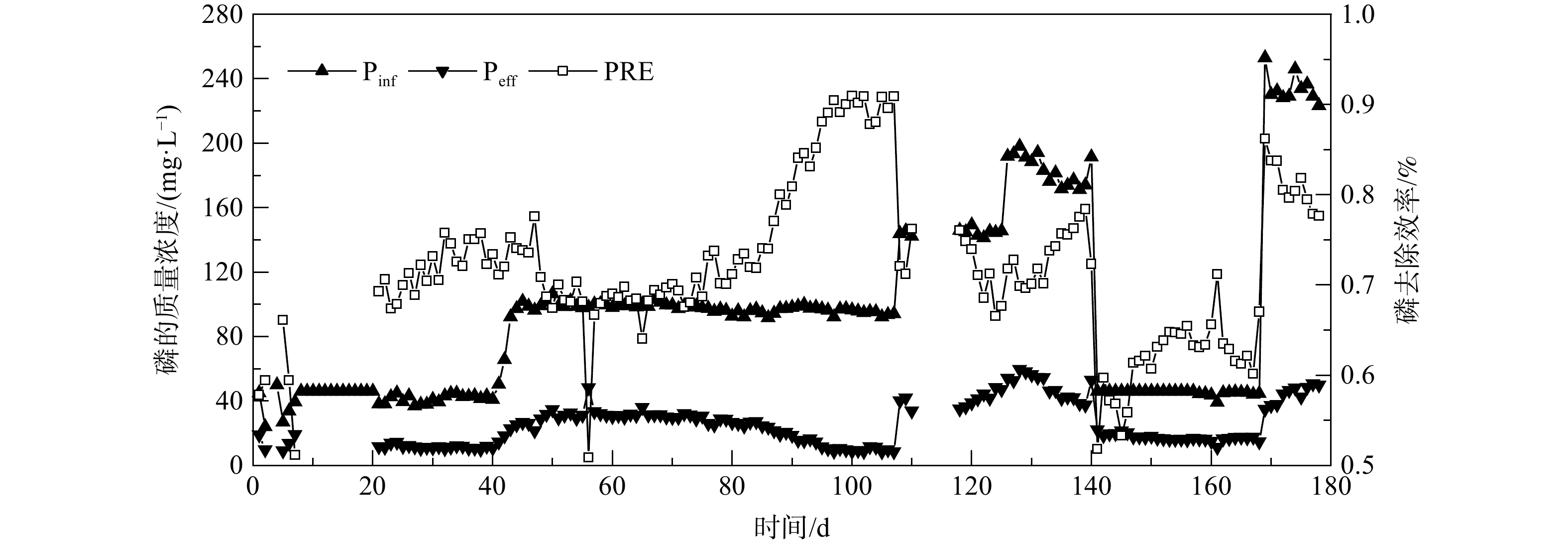
EGSB反应器长期进出水磷质量浓度及anammox-HAP系统磷回收效率的变化如图3所示。在反应器运行的第55~73 天和第169~178天,磷的质量浓度分别为100 mg·L−1和250 mg·L−1。维持反应器中pH和Ca/P不变,磷的回收效率会随着进水磷质量浓度的升高而升高,分别为69%和80%。因此,在未改变其他影响因素的条件下,进水磷的质量浓度越高,anammox-HAP系统的磷回收效率越高。这与LIN等[13]的研究结果一致。
-
pH是影响anammox-HAP系统磷回收效率的关键因素。在反应器运行的第133~140天,通过向基质桶里加NaOH将pH从6.7调节至8.0~8.1。此时,氮和磷的质量浓度不变,磷的平均回收效率明显从70.9%提高至75.5%,结果如图3所示。此外,在第20~40天,将氮的质量浓度从600 mg·L−1升至700 mg·L−1,磷的平均回收效率从69.3%提升至73.2%。这是由于anammox过程是个消耗H+的过程,氮质量浓度的提升导致pH升高。因此,在HAP结晶过程中,pH会对磷酸钙的沉淀起到重要作用,pH的升高促进了结晶的形成[14]。在第141~168 天,由于反应器中FNA抑制AnAOB,脱氮效率降低。同时,磷的回收效率也明显降低,最低时降至51.8%。anammox的高效脱氮特性可为HAP的形成提供较好的pH条件[15]。因此,AnAOB被FNA或FA抑制也会减弱生物诱导HAP矿化作用,进而影响磷的回收效率。
在第80 ~106天,反应器进水总氮维持在1 000 mg·L−1,进水磷的质量浓度约为100 mg·L−1,pH不变。当进水Ca/P从1.5提升至3,anammox-HAP系统磷的回收效率明显提升,从70.6%提高到89.7%。在运行过程中,反应器内极易出现白色沉淀导致管道堵塞。而对于不同的磷质量浓度,最佳Ca/P也不一样[9]。因此,在实际污泥厌氧消化液处理中,可通过控制anammox-HAP系统的最佳Ca/P,以提高污泥厌氧消化液中磷的回收效率。
-
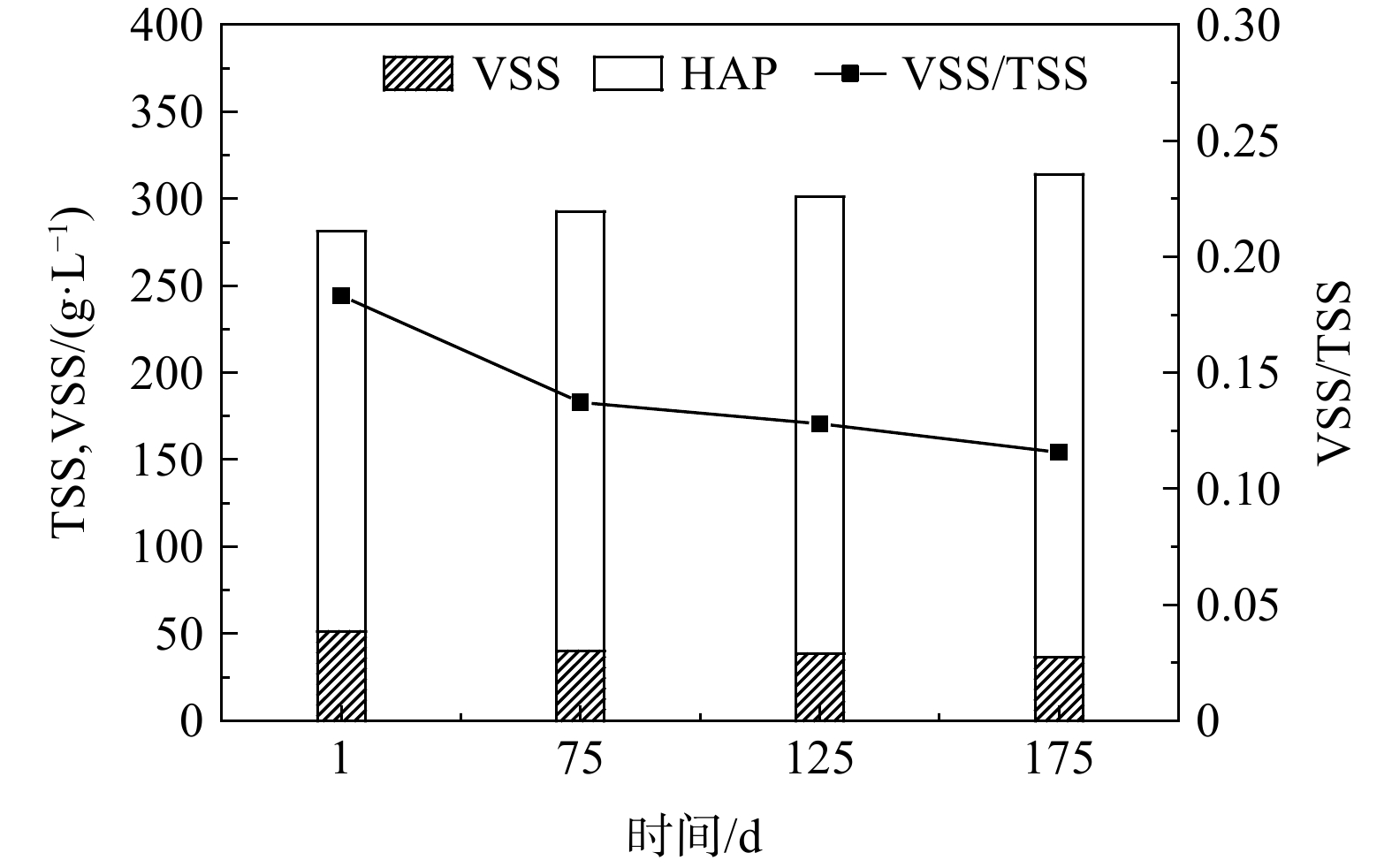
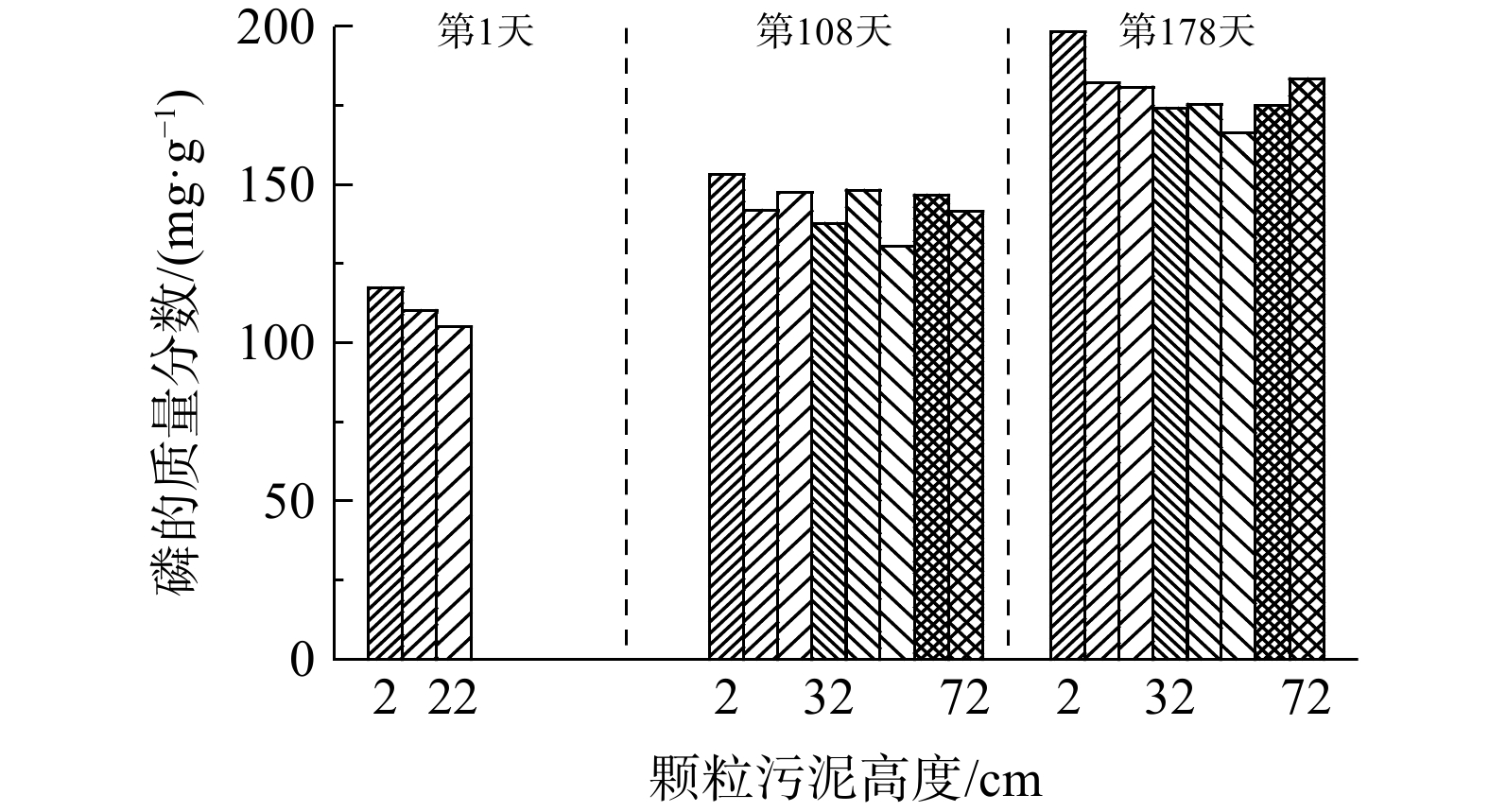
高磷浓度下形成高度矿化的颗粒污泥有助于实现系统对污泥厌氧消化液中磷的回收。不同时期EGSB反应器内VSS和HAP的分布如图4所示。反应器启动初期,接种污泥的泥层高度为12 cm,生物量质量浓度为51.5 g·L−1。运行至第103天,反应器内泥层高度为80 cm。此后,不定期的排泥使得反应器内泥层高度保持在约80 cm。随着反应器的运行,反应器内颗粒污泥的平均污泥浓度变化不大,为281.1~314.1 g·L−1。然而,污泥中平均VSS在明显减小,从51.5 g·L−1减至36.4 g·L−1;而反应器内平均HAP的含量在逐渐增大,从229.6 g·L−1增至277.8 g·L−1;VSS占TSS的比值从18%降至12%。由于EGSB反应器的升流式特性,反应器中形成的颗粒污泥无机组分含量从底部到上部逐渐减少。因此,需要不定期地从反应器底部取泥,以保证反应器中微生物量的充足,维持反应器的稳定运行。如表2和图5所示,反应器底部的颗粒污泥生物量占比较低,无机组分占比较高,且底部颗粒污泥的磷质量浓度高,因此,从反应器底部取出的高度矿化的颗粒污泥可成为有利用价值的磷资源。
-
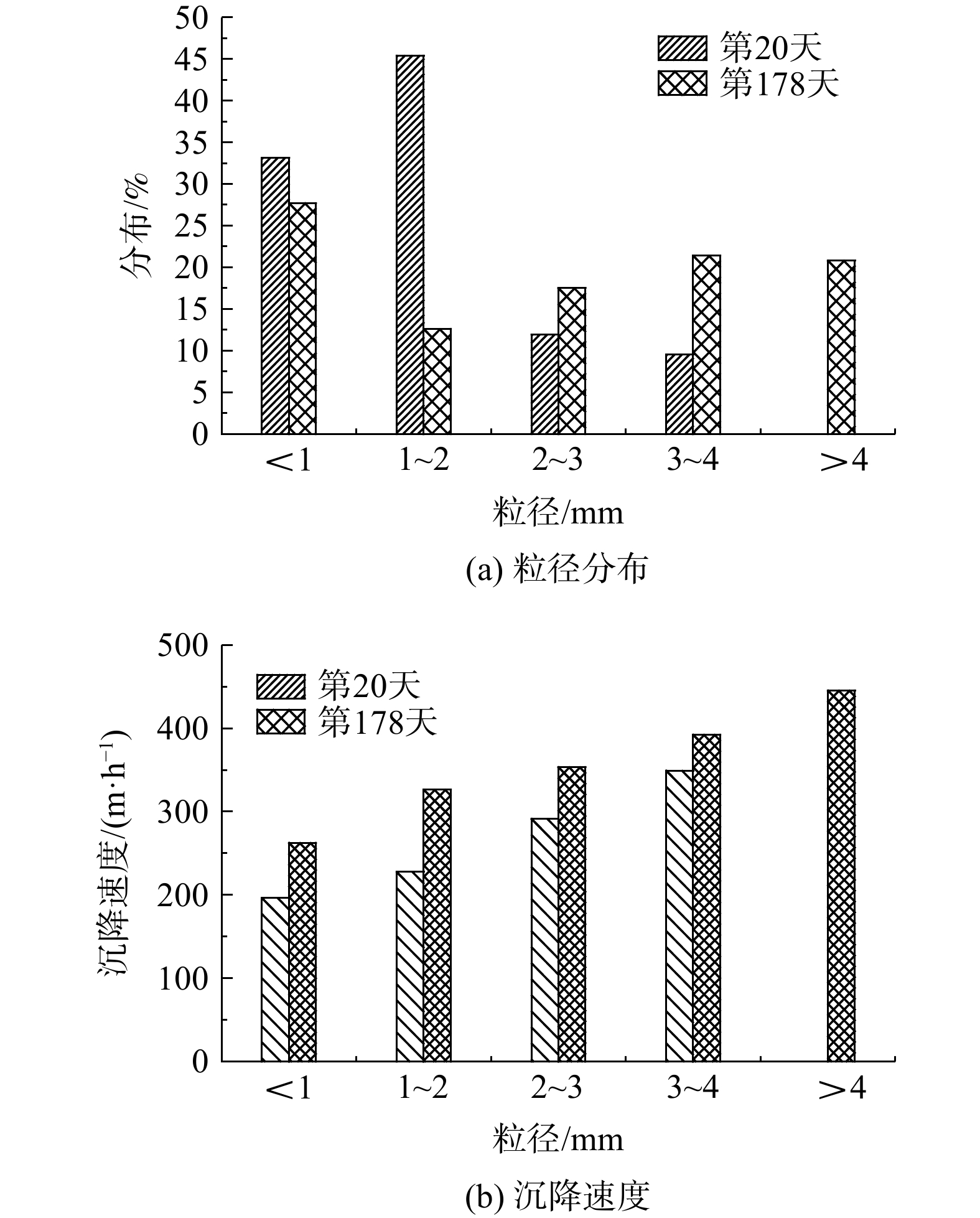
颗粒污泥的粒径分布和沉降速度分别体现了anammox-HAP颗粒污泥的生长情况和颗粒污泥的沉降性能。根据粒径大小,本研究将颗粒污泥分为5类:<1 、1~2、2~3、3~4 和>4 mm。由图6(a)可知,反应器运行至第20 天时,反应器内颗粒污泥主要以粒径<2 mm的为主;运行至第178 天时,颗粒污泥的粒径明显增大,大于2 mm的颗粒污泥的占比明显提高,占到50%以上。这也映证了反应器内的颗粒污泥会由小颗粒变成大颗粒。大粒径的颗粒污泥具有发育更为成熟的外膜内核结构[16]。然而,在本系统内磷质量浓度较高的条件下,形成的大颗粒污泥结构松散且不稳定,这可能是由于之前AnAOB活性受抑制,使得微生物新陈代谢能力下降,在不利于其凝聚的条件下形成了颗粒污泥。这也解释了在第178天反应器内小于1 mm的颗粒污泥占比仍达到27.2%。
HAP作为内核时anammox-HAP颗粒污泥具有较好的沉降性能[17]。由图(b)可知,反应器运行期间,颗粒污泥的沉降速度整体呈变大趋势。反应器内产生的高度矿化的污泥有利于污泥的沉降。在较高磷浓度下形成的颗粒污泥沉降速度为262.5~445.5 m·h−1,明显高于刚接种时anammox-HAP颗粒污泥的沉降速度。Anammox-HAP颗粒污泥的沉降速度明显高于其他研究中颗粒污泥的沉降速度[18-19],使其更易实现反应器内厌氧氨氧化菌的有效持留。然而,AnAOB的抑制会影响颗粒污泥的形成,导致反应器内存在一定的絮状污泥。反应器内的絮状污泥仍会因较大的上升流速随出水一起流出反应器。因此,在实验研究或者工程应用的过程中,应保证反应器的稳定运行,促进颗粒污泥形成较紧密的结构,以维持反应器内充足的生物量。
-
1)进水磷浓度在40~250 mg·L−1时,基于anammox-HAP工艺的EGSB反应器脱氮性能稳定,平均总氮去除率为88.5%,氮去除负荷为6.8 g·(L·d)−1。
2) Anammox-HAP系统磷回收效率与进水磷质量浓度、反应器pH及进水Ca/P密切相关。在保证反应器稳定运行的前提下,进水磷质量浓度、pH和Ca/P越高,越有利于磷的回收。磷回收效率最高可达89.7%。
3)由于EGSB反应器的升流式特性,反应器中形成的anammox-HAP颗粒污泥无机组分含量会沿反应器高度从上到下逐渐增大。通过定期从反应器底部排泥,既可实现高效优质的磷回收,又能保证anammox-HAP系统颗粒污泥的厌氧氨氧化活性,保持反应器的高效脱氮性能。
污泥消化液的磷浓度对anammox-HAP系统磷回收的影响
Effect of phosphorus concentration in sludge digestion liquid on phosphorus recovery by anammox-HAP
-
摘要: 厌氧氨氧化-羟基磷酸钙(anammox-hydroxyapatite, anammox-HAP)技术可实现污泥厌氧消化液高效自养脱氮同步磷回收。污泥厌氧消化液中磷的浓度与污泥性质、厌氧消化过程相关,变化范围很大。为探索anammox-HAP系统中的磷回收效率,通过基于anammox-HAP长期运行的膨胀颗粒污泥床反应器,考察了不同进水磷浓度、pH和钙磷质量比(Ca/P)对磷回收效率及污泥特性的影响。结果表明:进水磷浓度在40~250 mg·L−1时,膨胀颗粒污泥床反应器脱氮性能稳定,总氮去除率可达88.5%;磷回收效率与进水磷浓度、反应器内pH及进水Ca/P密切相关,磷回收效率最高为89.7%;高磷浓度下形成的颗粒污泥,有望实现高效的磷资源利用。本研究可为利用anammox-HAP系统实现磷回收提供参考。Abstract: Anammox-hydroxyapatite (anammox-HAP) process was developed to effectively remove nitrogen and recover phosphorus at the same time from municipal sludge digestion liquid. However, phosphorus concentration in sludge digestion liquid varies greatly with the characteristics of sludge and the digestion process. In this study, the effects of different influent phosphorus concentration, pH value and calcium phosphorus ratio on phosphorus recovery efficiency and granular sludge characteristics were investigated through long-term operation of a continuous flow expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactor. Results showed that the nitrogen removal performance of the continuous flow EGSB reactor was stable when the influent phosphorus concentration is in the range of 40~250 mg·L−1, and the average total nitrogen removal rate of the reactor reached 88.5%. The recovery efficiency of phosphorus was closely correlated with the influent concentration of phosphorus, the pH value in the reactor and the ratio of calcium to phosphorus. The maximum recovery efficiency of phosphorus was up to 89.7%. Granular sludge formed under high phosphorus concentration is expected to realize efficient recovery of phosphorus. This study can provide reference for phosphorus recovery using the anammox-HAP system.
-
Key words:
- sludge digestion liquid /
- phosphorus concentration /
- anammox /
- hydroxyapatite /
- granular sludge
-
经济快速增长背景下,人们对生产生活的空间需求日益增加,长江中下游的巢湖、太湖、洞庭湖和鄱阳湖等滨湖区域开展了大规模的围湖造田活动[1]。围垦区是滨湖低地生态系统的一种主要地理单元,在荷兰和中国,围垦区是滨湖区主要农业分布区,XIE等[2]调查发现长江中下游围垦导致湖泊面积减少13.80%,鄱阳湖滨湖围垦区面积达到4 180 km2[3]。
围垦区是一个较为封闭的生产生活区域,通常采用圈圩筑堤的方式建设,其水文管理需要通过电排灌站调控。围垦区中密集的农业生产活动产生大量的氮磷等营养物质,通过人工设施(如涵洞、电排灌站等)被排放至受纳水体,导致周边水生态环境质量的改变[4]。因此,研究人员认为围垦区的排水量及排水形式对受纳水体的影响值得关注[5]。YAN等[6]模拟了太湖流域低地圩田与泵站的水文过程与排水磷负荷的关系,发现与自然排水相比,电排灌站管控下的年均排水量减少了8.6%。电排灌站排水运行初时会引起沟渠表层沉积物再悬浮,导致沟渠水中TP和浊度骤然上升[7]。HUANG等[8]利用氮动态模型对太湖流域低地圩田和非圩田进行了模拟,发现圩田排放的氮负荷高于非圩田。汛期电排灌站排水是引起下游国控断面TP超标的主要原因[9],其已成为受纳水体汛期水质超标的潜在风险源[10]。此外,围垦区由于人类活动密集,过量的营养物质输出导致受纳水体富营养化[11]。因此,持续关注低地圩田\围垦区内人为控制电排灌站排水水量水质特征,有利于精细刻画其对受纳水体的影响并提出相对有效的管控措施。
鄱阳湖是长江流域最大的“吞吐型”通江湖泊,入湖面源污染及其控制日益得到关注。已有研究[12]表明,赣江、抚河等五河入湖水质中的TN和TP是引起鄱阳湖水质下降的主要因子,模型模拟估算结果表明农业源和城镇生活源的TP入湖负荷贡献率分别为56.4%和30.6%[13]。本研究以鄱阳湖流域南昌湖区典型围垦区——蒋巷联圩为主要研究区,该区域地势低洼平坦,是四面环水的独立岛镇,全域排灌水均通过联圩内电排灌站调控。收集与整理电排灌站2021年、2023年全年运维数据,并于2023年开展现场水质监测调研,明确围垦区电排灌站排水的水量水质时空分布特征,并估算全域排水污染负荷,以期为鄱阳湖围垦区农业面源污染防控提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
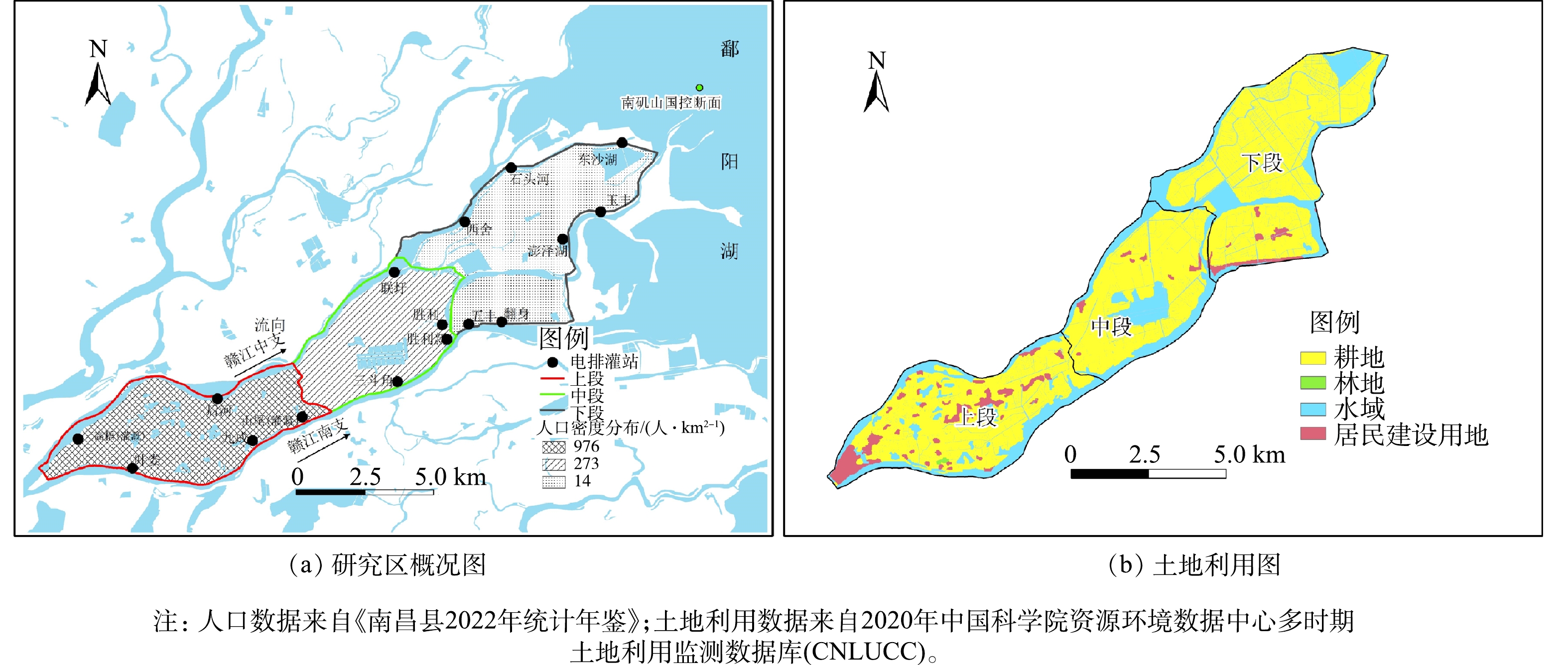
蒋巷联圩地处赣江三角洲下游,是赣江南支和中支所夹区域,属于典型赣江-鄱阳湖河湖交错带围垦区[14](图1)。全域总面积241 km2,根据土地利用类型及人口分布,可将全域分为上、中、下3段,其中上段面积为76.71 km2,人口约7.49×104人,农田面积为23.14 km2;中段面积为67.33 km2,人口约1.84×104人,农田面积为24.78 km2;下段为黄湖蓄滞洪区,面积为96.96 km2,人口约0.14×104人,农田面积为55.61 km2。蒋巷联圩内共建有16座电排灌站,排水去向是赣江南支(9座)、赣江中支(5座),其中高梧和山尾仅灌不排。上段共有高梧、叶娄、后河、九成和山尾5个电排灌站;中段共有联圩、三斗角、胜利新和胜利4个电排灌站;下段共有五丰、翻身、西舍、澎泽湖、玉丰、石头河和东沙湖7个电排灌站。
1.2 数据来源
电排灌站排水量数据来源于2021年和2023年完整的电排灌站的运维资料,2022年因特大干旱,记录不完整。根据式(1)核算该电排灌站的年度总排放量。
Q=∑miQ=∑mi(ntq) (1) 式中:Q为年度总排放量,m3;t运行时间,h;n该电排灌站开泵台数;q结合泵站流量,m3·h−1。
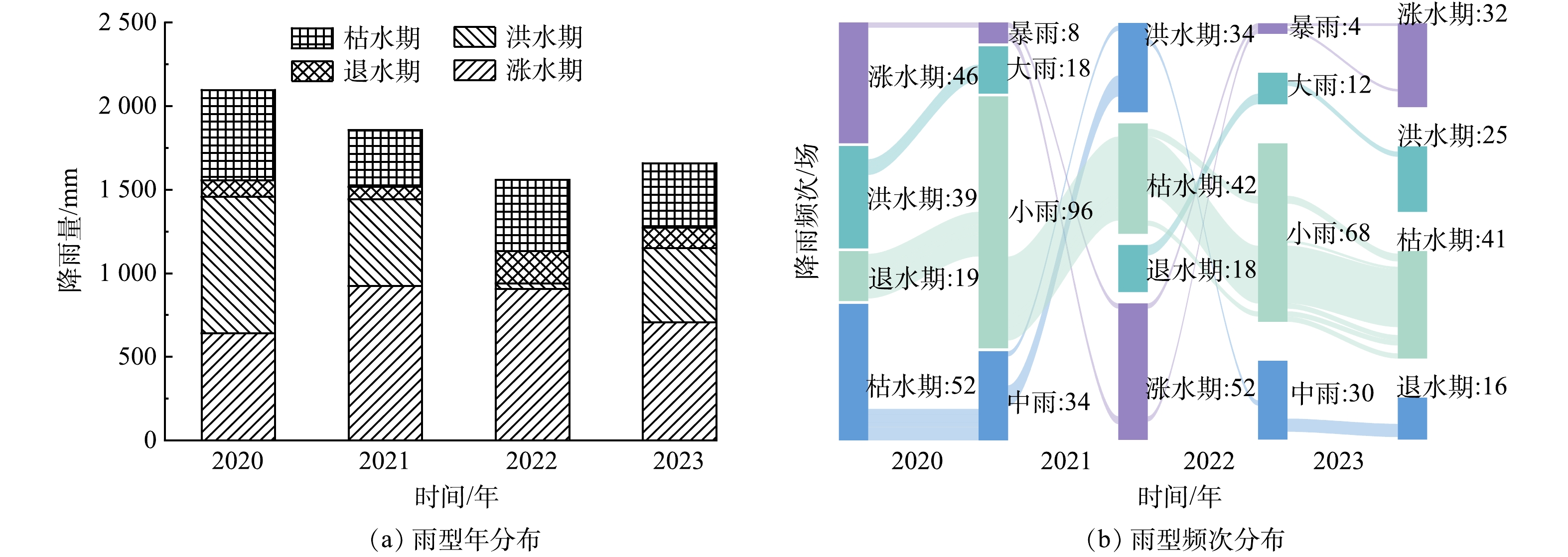
降雨量数据来源于中国气象科学数据共享服务网(气象数据共享网(mlogcn.com))南昌气象站2020—2023年逐日数据,并按照《降雨量等级(GB/T 28592—2012)》划分为小雨(0.1~9.9 mm)、中雨(10~24.9 mm)、大雨(25~49.9 mm)和暴雨(>50 mm)4种类型。前期研究发现,退水期、枯水期是鄱阳湖水质超标的主要时期,其中典型国控断面——南矶山断面在枯水期TP超标达2.28倍[15]。蒋巷联圩围垦区是南矶山断面的主要汇水区域,电排灌站排水水质直接影响南矶山断面水环境质量,因此,本研究中电排灌站排水水量及水质分析将按照鄱阳湖水期进行划分,即涨水期(4—6月)、洪水期(7—9月)、退水期(10—11月)和枯水期(12—翌年3月)。
1.3 样品采集与水质指标分析
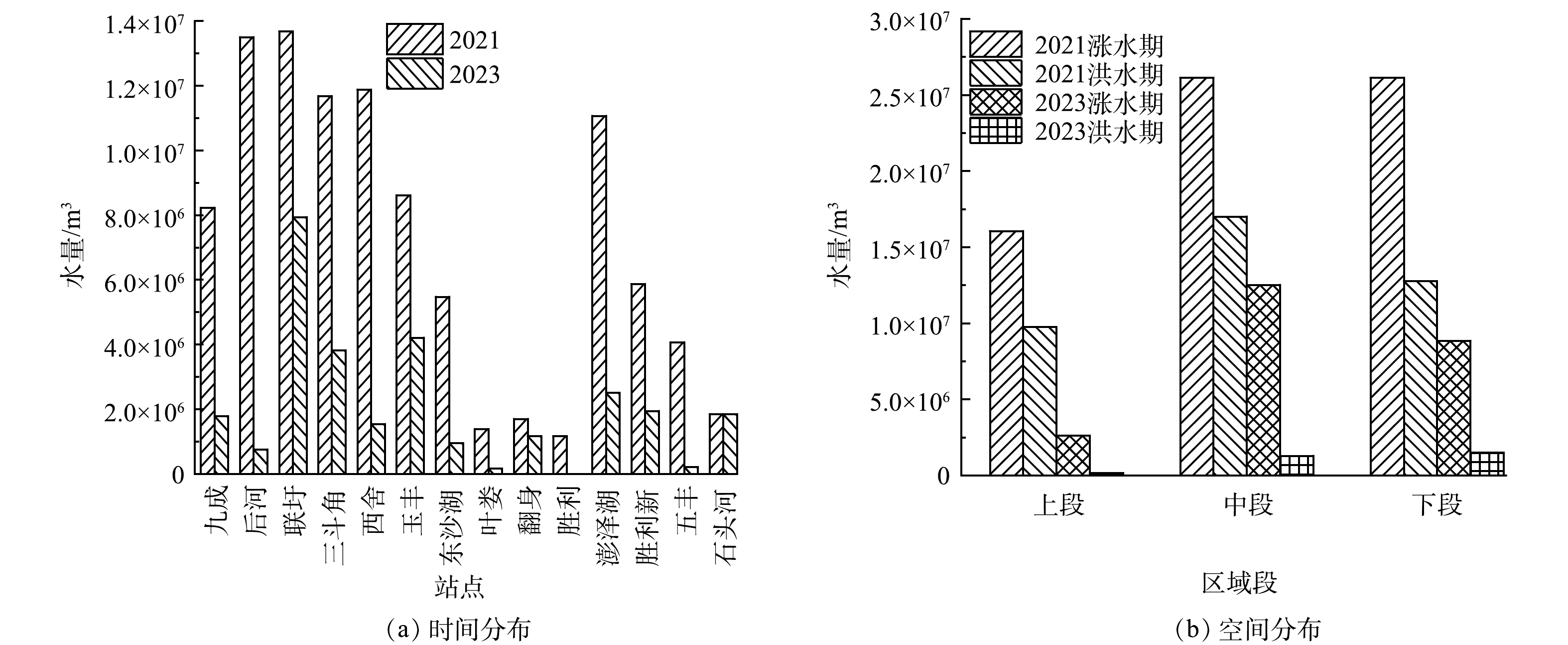
基于运维记录整理和分析发现,蒋巷联圩电排灌站排水发生在4—9月份,即涨水期和洪水期。为明确降雨和人类活动强度对电排灌站排水水量和水质的影响,根据2021年总排水量分析,分别在蒋巷联圩上、中、下段选择排水量最大、排水去向分别为赣江南支、中支的2个电排灌站进行排水水质样品采集,其中上段为九成和后河;中段选择三斗角和联圩;下段选择玉丰和西舍(图1)。采样时间为2023年4—9月,每月采集1次排水水样,采用干净的聚乙烯塑料瓶(1 L)于电排灌站排口处各采集1瓶,共采集36个样品。采集现场使用便携式浊度计(WZB-175,中国)测定浊度后,样品当天带回实验室且于4 ℃保存,并在7 d内完成相关指标测定。水质测定指标包括化学需氧量(COD)、总氮(TN)、氨氮(NH4+-N)、硝态氮(
NO−3 采用SPSS 23.0(IBM,USA)进行数据统计分析,Origin 2023(OriginLab,USA)和ArcMap10.8(ESRI,USA)进行可视化表达。
1.4 污染物排放负荷估算
经调研发现,围垦区地表径流主要通过电排灌站进行内外水力交换,且排放时间集中在涨水期和洪水期。基于区域独特的水文特性及文献调研[18-19],围垦区污染负荷排放主要受排水的排放量及污染物质量浓度影响。故本研究的电排灌站排放污染负荷根据式(2)估算。
W=∑QCi×10−6 (2) 式中:W为围垦区电排灌站灌排的污染物负荷量,t·a−1;Q为排水量,m3·a−1;Ci为第i种污染物质量浓度,mg·L−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 电排灌站的排水量时空分布特征
1)降雨量变化特征。土壤N、P流失特征与降雨量显著相关,较大降雨量条件下对土壤的冲刷力度加大,易携带较多N、P[20]。平原圩区水网密布,水系联通,降雨是影响电排灌站排水量和水质的重要因子[21]。由图2(a)可知,2020—2023年的年降雨量分别为2 096.2、1 856.7、1 559.0和1 658.4 mm,其中2022年降雨量最低,长江中下游区域遭遇罕见的大旱,鄱阳湖流域出现了1949年以来最严重的干旱[22]。由图2(b)可知,小雨频次最高,年降雨量的平均贡献为13.98%;而暴雨频次最低,但年降雨量的平均贡献占33.65%,其中2022年暴雨贡献占比最低(24.21%),2023年最高(41.84%)。在各个水期中,小雨虽然发生频次最高,但其对各个水期的降雨量影响不显著(P>0.05)。暴雨是各水期降雨量增加的主要降雨类型,尤其在涨水期和洪水期,例如,2020年洪水期暴雨发生5次,降雨量占比为51.10%;2021年涨水期暴雨发生了6次,占该水期降雨量的54.58%;2022年涨水期暴雨发生了4次,降雨量占比为41.67%;2023年涨水期暴雨发生了5次,降雨量占比为48.92%
2)排水量时空分布特征。由图3(a)可知,2021和2023年蒋巷联圩电排灌站总排水量分别为1.08×108 m3和2.69×107 m3,其中2023年排水量降低了75.04%,这可能与2022年极端干旱天气影响下,地下水储量下降有关[23]。曹思佳等[24]研究发现2022年鄱阳湖极端干旱导致地下水迅速外泄,是正常年份地下水排泄量的14.5倍。2023年总降雨量虽与2021年相差不大,但基于2022年的极端干旱,2023年降雨在较大程度上用于地下水补给,导致2023年电排灌站排水量大幅下降。由图3(b)可知,涨水期电排灌站排水量大于洪水期,占总排水量的63.36%(2021年)和89.08%(2023年)。鄱阳湖汛期气候变化对径流深度变化的影响相较于非汛期显著增加[25],同时长江中下游地区洪涝集中在5—7月,受涝次数占全年的80%[26],因此,受汛期降雨影响,涨水期电排灌站排水量占比增加。
在排水方向上,由于赣江南支的电排灌站布设数量大于赣江中支,因此赣江南支排水方向的排水量大于赣江中支,其中南支排水量占总排水量的54.82%(2021年)和53.81%(2023年)。在排水区域分布上,电排灌站排水量为中段>下段>上段。这与实际调研发现蒋巷联圩中段地势最低且分布有大面积水域有关(图1)。Pearson分析结果表明,电排灌站的排水量与降雨量和降雨类型呈显著正相关(P<0.05),暴雨雨型下电排灌站日均排水量最大,为6.33×105 m3。有研究[27]表明,在下垫面类型不变的条件下,降雨强度越大,则地表径流形成时间越短,径流强度越大。本研究结果表明暴雨后的7 d内,围垦区内电排灌站排水总量占年总排水量的61.99%。
2.2 电排灌站排水水质的时空分布特征
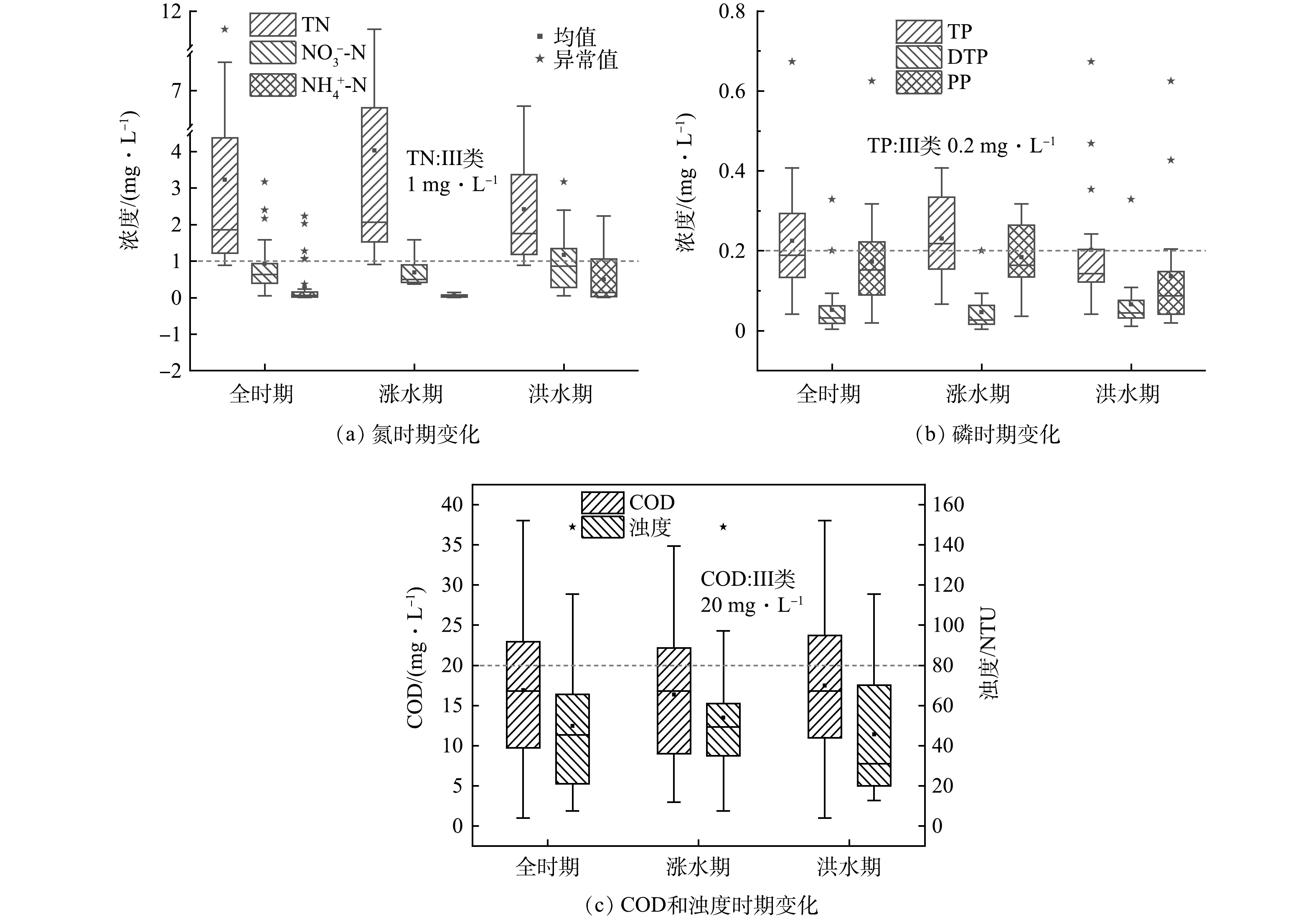
1)排水水质的时间分布特征。如图4所示,2023年电排灌站排水的TN、TP质量浓度均值和COD值分别为(3.22±2.73)、(0.22±0.13)和(16.92±8.98) mg·L−1,超过地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838-2002)III类限值,超标倍数均值分别为2.23、0.29和0.12。HUANG等[28]发现太湖低地圩区排水TP质量浓度均值0.14 mg·L−1;储茵等[29]调研巢湖低地圩区排水TN、TP质量浓度分别为0.8~6.5 mg·L−1、0.05~0.6 mg·L−1;HUA等[30]调研发现汉江平原农业地表径流TP质量浓度均值为0.14 mg·L−1。太湖、巢湖圩区、汉江平原和鄱阳湖流域位于长江中下游地区,属于亚热带季风气候,降雨量差异较小;土地利用类型以农田为主,主要作物类型为水稻,研究发现地表径流氮磷浓度相似。
不同水期下电排灌站排水水质分析结果表明(图4),涨水期排水TN、TP质量浓度高于洪水期;涨水期排水TN、TP质量浓度均值和COD值分别为(4.03±1.61)、(0.23±0.15)和(16.36±9.92) mg·L−1,其超标倍数均值分别是3.03、0.31和0.09;洪水期排水TN、TP质量浓度均值和COD值分别为(2.42±1.61)、(0.20±0.15)和(17.47±9.92) mg·L−1,其超标倍数均值分别是1.43、0.26和0.15,这与围垦区农事活动有关[31]。现场调研结果表明,围垦区沟渠、坑塘密集,在4—6月(涨水期)的早稻生长季,稻田分别施加尿素和有机氮肥作为基肥和分蘖期追肥,随着高频次暴雨和大雨(图2b)导致溢流出来的田面水汇入沟渠和坑塘中,水体氮以有机氮为主[32],洪水期围垦区内沟渠和坑塘的水体停留时间长,沟渠植被硝化速率高[33],排水水体以
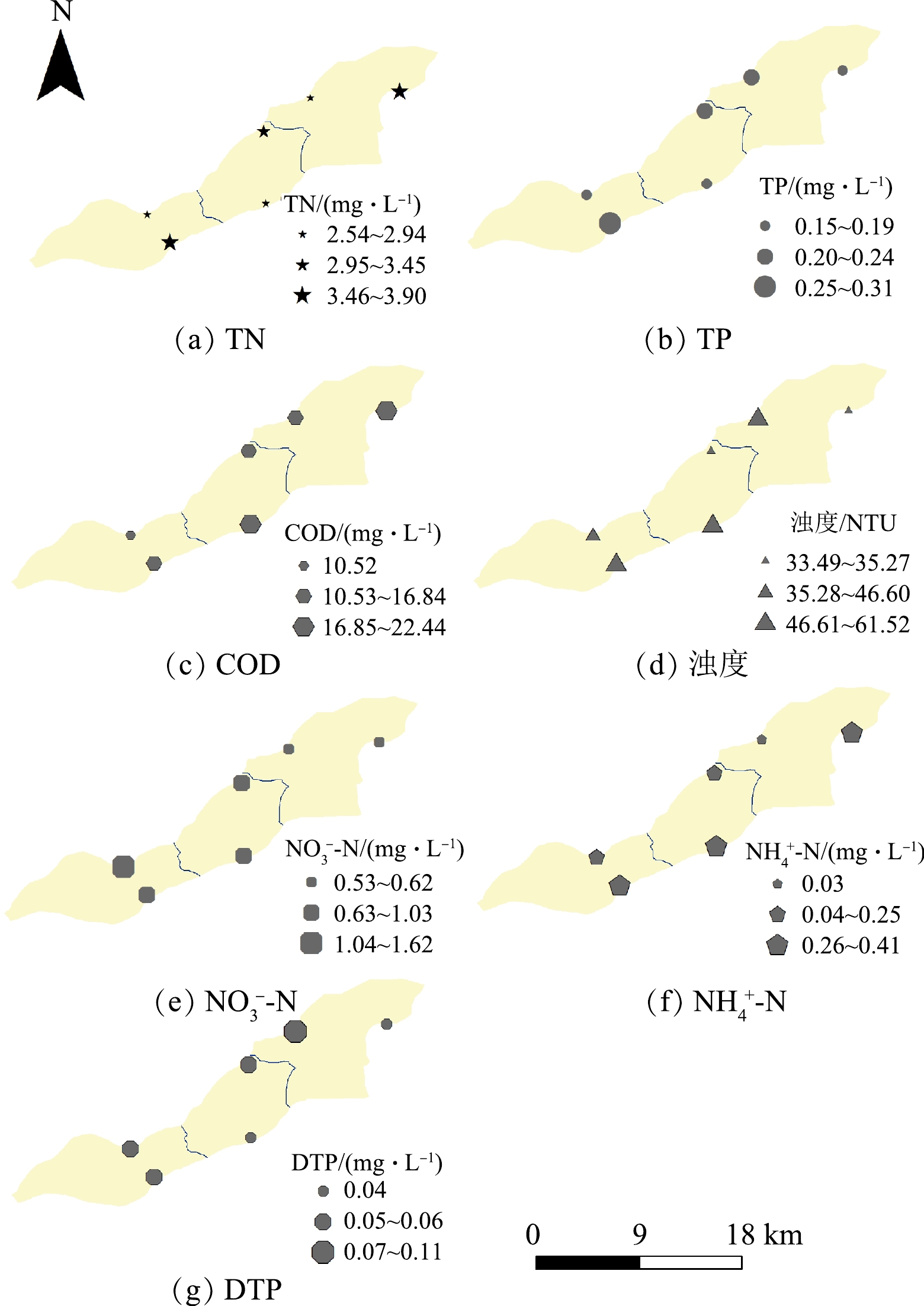
NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 2)排水水质的空间分布特征。如图5所示,排水TN、TP平均质量浓度和浊度为上段>下段>中段,排水
NO−3 在排水方向上,排往南支的排水TN、TP质量浓度均值和COD值高于排往中支,其值分别为(3.41±2.9)、(19.18±9.29)、(0.21±0.15) mg·L−1,超标倍数均值分别为2.03、0.17、0.28。王朔月等[41]的研究表明,2017—2018年赣江上游流向鄱阳湖湖区的氮磷浓度呈阶梯状递增,其中赣江(下游)污染物浓度显著高于香溪河和架竹河(上游)。刘文强等[42]研究赣江中支周坊断面TP超标规律,发现其主要发生在涨水期,而电排灌站在涨水期的大量排水加剧了断面TP超标的风险。
2.3 电排灌站排水的主要污染物负荷量
由表1可知,2023年蒋巷联圩电排灌站年排放的TN、TP和COD负荷分别为111.07、6.14和501.95 t·a−1,其中涨水期排水TN、TP和COD负荷分别占全年93.01%、90.20%和86.57%。从区域分布看,中段排放的TN、TP和COD负荷量最高,分别占全区域47.50%、52.67%和49.13%;虽然中段排水的氮磷质量浓度低(图5(a)和图5(b)),但其排水量最大(图3(b)),占比超过年总排水量50%以上。从电排灌站排水去向看,排往南支方向的TN、TP和COD负荷大于排往中支方向,分别占总负荷的51.57%、57.69%和56.89%。围垦区TN负荷年排放量是TP负荷的18.07倍,这与高田田等[43]对巢湖流域农业面源氮磷负荷输出结果一致;在中低强度的降雨下,排放的农田尾水会留存在沟渠和池塘中[44]。沟渠和池塘能够有效阻断农田氮磷输出过程,增加水力停留时间,且沟渠坑塘内大量水生植物能够充分吸收氮磷[45-46]。蒋巷联圩土地利用以农田为主,区内河网密布,沟渠坑塘众多,研究发现暴雨7 d内的排放水量占总降水量的61.99%,因此,建议将电排灌站作为鄱阳湖流域围垦区内农业面源污染控制的重要节点,统筹电排灌站的运行管理,结合天气预报,充分利用围垦区内沟渠池塘缓滞作用,减少农业面源污染物排放,降低对受纳水体水环境质量的影响。
表 1 蒋巷联圩电排灌站排水的主要污染物负荷估算表Table 1. Estimated loading of drainage main pollutants from electric drainage and irrigation stations in Jiangxiang Lianwei水期 位置 排水去向(赣江) 排放负荷/(t·a−1) 负荷占比/% TN TP COD TN TP COD 涨水期 上段 中支 2.39 0.19 9.09 2.15 3.05 1.81 上段 南支 9.58 0.56 30.63 8.62 9.11 6.10 中段 中支 33.30 1.53 112.89 29.98 24.84 22.49 中段 南支 16.16 1.49 106.12 14.55 24.22 21.14 下段 中支 16.05 0.70 79.11 14.45 11.33 15.76 下段 南支 25.83 1.08 96.70 23.26 17.64 19.27 洪水期 上段 中支 0.04 0.01 0.15 0.03 0.16 0.03 上段 南支 0.23 0.03 1.23 0.21 0.45 0.25 中段 中支 1.41 0.11 10.62 1.27 1.78 2.12 中段 南支 1.89 0.11 16.98 1.70 1.82 3.38 下段 中支 0.61 0.07 4.51 0.55 1.13 0.90 下段 南支 3.59 0.27 33.91 3.23 4.45 6.76 合计 111.07 6.14 501.95 100 100 100 3. 结论
1) 2023年排水量(2.69×107 m3)较2021年减少了75.04%,涨水期因暴雨频率增加引起排水量占比增加,由2021年的63.36%增加到2023年的89.08%。年总排水量为中段>下段>上段;赣江南支排水方向的排水量大于赣江中支。
2) 2023年电排灌站排水中TN、TP的质量浓度年均值超过地表III水,其中涨水期TN和TP质量浓度最高,平均值分别为(4.03±1.61) mg·L−1和(0.23±0.15) mg·L−1,其平均超标倍数分别为3.03、0.31;蒋巷联圩上段电排灌站排水中TN、TP质量浓度最高。
3) 2023年电排灌站排水中TN、TP、COD负荷分别为111.07、6.14和501.95 t·a−1,涨水期其对应的占比分别为93.01%、90.20%和86.57%。中段TN、TP、COD负荷量占比最高,分别为47.50%、52.67%和49.13%;赣江南支排水方向排水TN、TP、COD负荷大于赣江中支。
-
表 1 反应器运行条件
Table 1. Operational conditions of the reactor
时间/d P/(mg·L-1) Ca/(mg·L-1) Ca/P pH 1~42 40 60 1.5 7.2~8.2 43~87 100 150 1.5 7.3~7.7 88~91 100 200 2 7.4~7.7 92~95 100 250 2.5 7.3~7.4 96~108 100 300 3 7.2~7.4 109~126 150 225 1.5 7.1~7.4 127~141 200 300 1.5 7.0~7.7 170~179 250 375 1.5 7.0~7.3 表 2 不同高度EGSB反应器内颗粒污泥的组分特征(第178天)
Table 2. Distribution of VSS and HAP in the EGSB reactor at different heights (178th day)
反应器高度/cm TSS/(g·L-1) VSS /(g·L-1) VSS/TSS 2 350.3 38.17 0.11 12 272.34 35.35 0.13 22 253.71 32.29 0.13 32 237.96 31.74 0.13 42 259.5 32.73 0.13 52 240.91 25.76 0.11 62 220.83 31 0.14 72 209.87 28.59 0.14 -
[1] MIAO J, YIN Q, HORI T, et al. Nitrifiers activity and community characteristics under stress conditions in partial nitrification systems treating ammonium-rich wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 73: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.12.020 [2] 蔡碧婧. 反硝化脱氮补充碳源选择与研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2008. [3] GU J, ZHANG M, LIU Y. A review on mainstream deammonification of municipal wastewater: Novel dual step process[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 299: 122674. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122674 [4] MULDER A, GRAAF A A V D, ROBERTSON L A, et al. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 1995, 16(3): 177-184. [5] LIN Y M, LOTTI T, SHARMA P K, et al. Apatite accumulation enhances the mechanical property of anammox granules[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(13): 4556-66. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.061 [6] GUO Y, LI Y. Hydroxyapatite crystallization-based phosphorus recovery coupling with the nitrogen removal through partial nitritation/anammox in a single reactor[J]. Water Research, 2020, 187: 116444. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116444 [7] 梅翔, 成慧灵, 张寅丞. 离子交换法选择性回收污泥厌氧消化液中的磷[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(9): 3319-3326. [8] MA H, XUE Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Simultaneous nitrogen removal and phosphorus recovery using an anammox expanded reactor operated at 25 degrees C[J]. Water Research, 2020, 172: 115510. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115510 [9] MA H, ZHANG Y, XUE Y, et al. A new process for simultaneous nitrogen removal and phosphorus recovery using an anammox expanded bed reactor[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 267: 201-208. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.044 [10] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[J]. 4版. 北京:中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 258-282. [11] XUE Y, MA H, KONG Z, et al. Formation mechanism of hydroxyapatite encapsulation in Anammox-HAP Coupled Granular Sludge[J]. Water Research, 2021, 193: 116861. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.116861 [12] 周正, 刘凯, 王凡. 磷酸盐对厌氧氨氧化活性污泥脱氮效能的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(6): 2453-2460. [13] LIN L, ZHANG Y, BECKMAN M, et al. Process optimization of anammox-driven hydroxyapatite crystallization for simultaneous nitrogen removal and phosphorus recovery[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 290: 121779. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121779 [14] MAURER M, ABRAMOVICH D, SIEGRIST H, et al. Kinetics of biologically induced phosphorus precipitation in waste-water treatment[J]. Water Research, 1999, 33(2): 484-493. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00221-8 [15] ZHANG Z Z, XU J J, HU H Y, et al. Insight into the short- and long-term effects of inorganic phosphate on anammox granule property[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 208: 161-169. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.02.097 [16] ZHANG Y, MA H, LIN L, et al. Enhanced simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal performance by anammox–HAP symbiotic granules in the attached film expanded bed reactor[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(8): 10989-10998. [17] GUO Y, CHEN Y, WEBECK E, et al. Towards more efficient nitrogen removal and phosphorus recovery from digestion effluent: Latest developments in the anammox-based process from the application perspective[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 299: 122560. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122560 [18] WU D L, QIAN H F, MAHMOOD Q, et al. Cultivation, granulation and characteristics of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing sludge in sequencing batch reactor[J]. Water Science & Technology:Water Supply, 2006, 6(6): 71-79. [19] TANG C, ZHENG P, WANG C, et al. Performance of high-loaded ANAMMOX UASB reactors containing granular sludge[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(1): 135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.018 -




 下载:
下载: