-
厌氧氨氧化(anaerobic ammonium oxidation, anammox)指在缺氧条件下anammox菌以亚硝酸盐(NO2−−N)为电子供体,将氨氮(NH4+ −N)氧化为氮气(N2)的过程。该过程无需有机碳源,其需氧量仅为传统硝化反硝化工艺的1/3,为自养低耗脱氮提供了新途径[1]。然而,anammox菌生长速率慢、倍增时间长,在实际应用中易因污泥流失而难以快速培养。颗粒污泥具有优良的沉降性能,其内部物种非常多样,微生物系统更加稳定,可在一定程度解决反应器内污泥流失和难以适应复杂环境条件的问题[2]。因此,厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的培养及其稳定化运行,是该工艺走向大规模应用的重要环节。
胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances,EPS)在颗粒污泥的形成和保持结构完整性方面起到关键作用,其主要成分包括多糖、蛋白质、核酸和腐殖酸等[3]。EPS的理化性质和空间分布结构会影响微生物聚集体的结构和功能。比如,EPS中的蛋白质、腐殖酸和糖醛酸有助于污泥的疏水性,而碳水化合物则有助于亲水性[4];某些蛋白质二级结构促进了生物絮凝聚集、吸附和生物膜形成[5- 6];处理工艺、运行条件和水质等诸多因素均会影响EPS的组分、结构、组成等特性[7]。
近年来,研究者在EPS对anammox颗粒污泥形成及稳定运行过程中的作用、EPS成分特征、影响其特性的主要因素等方面开展了广泛研究,积累了大量有益成果。本文梳理了近年来关于anammox颗粒污泥中EPS的最新研究进展,以期明确EPS的特性在anammox颗粒污泥形成及运行过程中的作用,为anammox颗粒污泥的实际工程化应用提供参考。
-
关于anammox菌聚集及颗粒污泥形成有多种假说,EPS在这些过程中均起到重要作用。
JIA等 [4]认为,anammox微生物的聚集过程可能包括3个步骤,如图1所示。1) 第1阶段中游离的anammox菌游走在固体表面,直到找到适宜生态点位,通过分泌少量糖醛酸黏附在固体表面。2) 第2阶段中anammox菌停留在固体表面并通过蹭动互相接触,并开始分泌大量糖醛酸;由于糖醛酸的凝胶特性形成了网状结构,其网捕作用可防止微生物脱落,使anammox菌更加牢靠地黏附于固体表面。3) 在第3阶段,anammox菌的生长繁殖过程中会产生更多EPS紧密包裹在细胞表面,其胞外蛋白展现的β折叠结构使内部疏水基团很容易被暴露,使得细胞表面疏水性增强并有助于细胞间的聚集,从而形成了结构牢固的群落结构。
MANONMANI等[8]认为,anammox颗粒污泥形成的常见途径为2种。第1种途径是最容易被学者接受的EPS粘附说。即采用好氧或厌氧颗粒污泥作为接种物,在启动初期因培养环境急剧变化,接种颗粒污泥逐渐解体;解体的细小颗粒污泥作为内核,EPS作为黏附剂黏附AnAOB菌;AnAOB菌生长繁殖形成菌胶团,多个菌胶团在EPS 和丝状菌的粘接下形成亚单元;多个亚单元再团聚成anammox颗粒污泥。而第2种途径为采用非颗粒性接种物,以钙镁铁等阳离子作为粘附剂和内核,形成anammox颗粒污泥。
EPS是污泥颗粒化的重要物质,主要分布于细胞外,作为黏结剂促使细胞团聚,从而使得细胞与细胞、细胞与颗粒之间黏连在一起,最终实现聚集[9]。然而,目前仅能证明EPS的存在促进了anammox颗粒污泥的形成,尚未对EPS直接影响AnAOB菌聚集能力的内在机制提出较为清晰的解释。在限氧自养硝化反硝化(oxygen-limited autotrophic nitrification-denitrification,OLAND)工艺中培养的anammox颗粒污泥中,颗粒污泥的自养空间大约50%被EPS所占据,与异养型厌氧颗粒污泥相比,EPS含量相对较高,表明EPS在anammox颗粒污泥聚集方面产生了更重要的作用[10]。
-
在不同类型anammox颗粒污泥中,EPS各成分含量存在较大差异(表1)。这可能与反应器类型、接种污泥及培养策略有关,但对差异存在的内在机制还缺乏强有力的证明。EPS主要由蛋白质、核酸、多糖、脂质和存在于各种微生物聚集体内部的其他聚合化合物组成。其中,多糖(polysaccharide, PS)是EPS的主要成分,其次是腐殖质和蛋白质(protein, PN)。
由微生物分泌产生的EPS中含有大量胞外多糖。胞外多糖通过形成聚合物来促进微生物间的黏附从而增强颗粒污泥的稳定性。同时,多糖交联形成的水凝胶是维持颗粒污泥稳定的重要因素。凝胶可通过氢键、疏水性作用保持颗粒污泥的稳定性[11]。胞外多糖长主链之间的缠结以及丰富的结合位点桥接形成骨架,增强了微生物之间的黏附,有利于维持颗粒污泥的稳定状态[12]。PN含氨基并带正电荷,导致污泥表面负电荷减少,微生物间的静电斥力降低,细胞表面的疏水性增加,从而使微生物细胞更易于从水相中脱离出来并互相聚集。这说明PN含量的增加、PN/PS的增高可促进污泥颗粒化[13]。
胞外多糖可分为结合型胞外多糖和可溶性胞外多糖[14]。EPS具有多层空间结构,根据其结构特点一般分为固着性(bound-EPS,B-EPS)和溶解性(soluble-EPS,S-EPS)2种。其中,B-EPS的内层由紧密结合型(tightly bound-EPS,TB-EPS)组成,与细胞表面结合稳定;外层由松散附着(loosely bound-EPS,LB-EPS)组成,松散可分散[15]。自养anammox颗粒会比好氧/厌氧颗粒物分泌更多的EPS,而高基质浓度下培养的anammox颗粒具有更高EPS含量,且颗粒中EPS的分布存在较大差异[16]。JIA等[4]对比了18种不同条件下生成的anammox颗粒污泥,发现其中的TB-EPS与颗粒污泥形态密切相关,可作为厌氧氨氧化微生物存活能力和微生物聚集体形态的表征指标,且TB-EPS 含有的大量蛋白质疏水基团可促进微生物的聚集。有研究者采用可酶解多糖的淀粉酶对anammox颗粒污泥进行酶解,发现α-淀粉酶处理组颗粒污泥外边缘出现溶胀,而β-淀粉酶处理组颗粒污泥表面无明显变化,但出现破碎且稳定性明显下降[12]。β-D-呋喃葡萄糖集中分布在颗粒污泥最外层,蛋白质、脂类、α-呋喃葡萄糖和α-甘露糖则分布于整个颗粒污泥,主要集中在颗粒污泥外侧。蛋白质和脂类构成了厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的骨架,anammox菌则分布在蛋白质和脂类中间[17]。HOU等18]发现,EPS含量与化学组成主要受细菌的代谢作用影响,细菌的代谢性质也决定了EPS的聚集能力[18]。
Anammox颗粒污泥的粒径直接影响EPS含量及成分[19]。EPS的3层结构(S-EPS,TB-EPS和LB-EPS)会随粒径变化而变化。当粒径<0.5 mm时,S-EPS的含量(以每克VSS含有EPS质量计)占总EPS的48%以上,为121.0~302.3 mg·g−1,并随着粒径的增大而减小,在粒径为2.5 mm时占总EPS的35%。而TB-EPS含量随粒径增大而增大,由粒径< 0.2 mm时的95.6 mg·g−1增至粒径为2.5 mm时的334.1 mg·g−1,且随着anammox颗粒污泥粒径的增大,TB-EPS逐步取代S-EPS成为EPS的主要组分。而LB-EPS含量随粒径变化波动较小,保持在总EPS含量的24%以下[20]。粒径不同还会造成EPS中各组分含量的差异,粒径从0.5~1.4 mm增至> 2.8 mm,PN含量从(56.88±0.86) mg·g−1增至(98.59±2.10)mg·g−1,总EPS量从(68.05±0.97)mg·g−1 增至(94.26±2.20)mg·g−1 [21]。因此,控制反应器运行条件、调控适宜粒径、强化anammox颗粒污泥EPS的分泌,可增强颗粒污泥的运行稳定性。
-
EPS中PN和PS两大组分在anammox颗粒污泥的形成、运行中发挥重要作用。在不同反应器类型及脱氮负荷条件下,anammox颗粒污泥的EPS含量与PN/PS存在显著差异。较高的脱氮负荷往往PN/PS较大,但二者并无线性相关性,这可能与运行环境条件有直接关系。当脱氮负荷为0~1 kg·(m3·d)−1时, anammox颗粒污泥在不同反应器运行条件下的EPS总量(以每克VSS含有EPS质量计)为13.35~850 mg ·g−1,PN/PS为0.54~7.66。同种接种污泥形成的anammox颗粒污泥PN/PS较为接近[17],而不同接种污泥和培养策略会对颗粒污泥PN/PS产生较大影响[16],但迄今为止的研究尚未对EPS的组分差异作出合理解释,还需进一步深入探究。
颗粒污泥EPS的PN/PS可用于表征其稳定性能和沉降性能。PN/PS为0.5~5时,颗粒污泥的稳定性和沉降性随比值增大而增强[22]。PN/PS大小与污泥表面疏水性、带电性及颗粒污泥的形成直接相关,污泥的相对疏水性会随着PN/PS的提高逐渐增强,从而促进anammox颗粒污泥的聚集,且随着颗粒污泥的形成PN/PS有较大幅度的增加[23]。anammox颗粒污泥EPS中的蛋白质是决定疏水性的主要成分,因此,随着PN/PS的升高,蛋白质占比越高,细胞电负性越强,微生物表面疏水性越好,颗粒化程度更强[24-25]。虽然EPS含量与颗粒污泥粒径无明显关联,但PN/PS受粒径影响变化较大。CHEN等[20]研究了4种不同粒径anammox颗粒污泥的EPS含量,发现小粒径(1.0~1.5 mm)颗粒污泥的PN/PS达3.81,厌氧氨氧化活性较大,EPS分泌量较高。粒径为300~500 μm的PN/PS随粒径增大而呈上升趋势,但粒径增大到一定程度时(>500 μm),颗粒污泥向胞外分泌较少的EPS,PN/PS也会随之降低,小颗粒间的聚集作用减弱,亲和力降低,沉降能力下降[26]。掌握这种变化规律有利于调整条件以促进颗粒污泥的聚集并维持颗粒间的稳定性。PN/PS是颗粒结构稳定性的重要调控因素,较高的PN/PS有利于颗粒污泥造粒并增加颗粒污泥强度和相对疏水性,促进anammox颗粒污泥的聚集,故可作为颗粒形成指标。
-
对 anammox 颗粒污泥的元素组成分析表明,C、H、N、O、S元素的组成分别占总量的44.4%、6.6%、9.0%、35.7%和1.4%[41]。除了主要成分外,颗粒污泥的EPS提取物中还有Na、K、Ca、Mg、Al、Fe、Mn、P、Si、S等元素组成的矿物颗粒。其中,Na、K、Ca、Mg占主要成分,其含量大小为K>Na>Ca>Mg[42]。Anammox颗粒污泥EPS中K、Ca、Mg有离子和非离子2种存在形式,但绝大多是以离子形式存在。K、Ca的金属离子形式占比分别为68.6%、56.2%,Mg的离子形态比例最高,可达94.7%。在非离子存在形态中,K和Mg占比分别为31.4%和5.3%。在金属元素中,Ca的非离子存在形式占比最高,为43.8%。随着粒径的增大,厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥EPS中PN的含量随之增大,从而可结合更多金属元素,使得金属元素含量增大,Ca2+的含量亦增大,进而中和细菌表面和多糖分子上的负电荷,提升多糖水平并显著缩短颗粒的形成时间,加速颗粒污泥形成并维持其稳定性[28, 43-44]。金属离子在颗粒污泥聚集中发挥的作用不同,如EPS中的Na+会通过压缩双电层作用促进颗粒污泥的聚集,而Na+、K+会通过离子交换作用与Ca2+竞争EPS中的结合位点。因此,Na+与Ca2+和Mg2+含量的变化趋势相反[45]。还有研究者认为,EPS中的Ca、K、Mg、Na、Al、Fe等金属元素会影响厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的表面特性[46]。如Ca可诱导形成CaCO3和Ca5OH(PO4)3沉淀,作为anammox颗粒污泥初期的晶核并促成颗粒污泥的形成[43, 47]。而其他金属元素在anammox颗粒污泥的形成及EPS成分结构方面的作用尚有待进一步研究。
-
Anammox颗粒污泥属于自养脱氮颗粒污泥,主体功能菌为anammox菌,其生长缓慢、倍增时间长[1]。当废水中含有有机物时,异养菌如反硝化菌会快速增殖,与anammox菌争夺反应基质NO2−−N,导致anammox菌的生长被抑制,从而影响anammox颗粒污泥的性能甚至使之解体[2]。范丹等[13]发现,较低的有机物质量浓度(<100 mg·L−1)会使同步亚硝化厌氧氨氧化反硝化(simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification,SNAD)反应器内的功能微生物更易于相互聚集黏附,加快污泥快速颗粒化,增大颗粒粒径,最大粒径达到1 103 μm;经过约140 d的培养,最大EPS含量达到140 mg·g−1(以每克VSS含有的EPS质量计)。同样,当COD为100 mg·L−1时,EPS含量达到最大值(482.69 ± 9.83) mg·g−1;而随着COD增至150 mg·L−1,EPS含量降至 (451.80 ± 9.79) mg·g−1;当COD持续增至200 mg·L−1,EPS含量开始急剧下降[48]。LI等[49]发现,COD为200 mg·L−1的条件可促进anammox颗粒污泥EPS的分泌,其含量从33 mg·g−1升至181 mg·g−1,但当COD升至300 mg·L−1时,EPS含量降至155 mg·g−1。从共聚焦激光扫描图像可发现,在有机物存在的条件下,PN显著增加,但PS有所下降。适量的有机碳源(<130 mg·L−1)可提高厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的EPS含量,PN、PS含量分别由最初的63、45.1 mg·g−1增至140、60 mg·g−1(以每克MLSS中PN或PS质量计)。此时,污泥的沉降性能明显提高。然而,COD高于130 mg·L−1时,EPS含量则下降。这可能是由于有机物过多会导致部分anammox颗粒污泥解体,进而造成EPS的释放[50]。
-
氮作为厌氧氨氧化过程的主要基质,其浓度和负荷直接影响着anammox颗粒污泥的形成及EPS分泌[51]。ZHANG等[52]发现,当氮负荷由4.8 g·(L·d)−1增至10.0 g·(L·d)−1时,anammox颗粒污泥的EPS含量增加了约60%;当氮负荷达到最大值20.0 g·(L·d)−1时,EPS总量增至77.2 mg·g−1(以每克VSS含有的EPS质量计),但anammox颗粒污泥因密度降低而大量解体。WANG等[53]亦发现随着氮负荷增大(由0.09 ~ 0.26 kg·(m3·d)−1增至0.21 ~ 0.97 kg·(m3·d)−1),anammox颗粒污泥EPS含量由11.09 mg·g −1 增至83.38 mg·g−1,且PN/PS 增大,由5.09增至8.84。NI等[16]通过设置不同停留时间(HRT)调控反应器的氮负荷,发现:EPS在不同氮负荷运行条件下的特征存在差异,低HRT(22 h)高氮负荷anammox颗粒污泥的PN/PS为0.8,而高HRT(36 h)低氮的PN/PS为2.1。在低氮条件下,PN为胞外多糖的主要成分;在高氮条件下,EPS含量更高且PS为主要成分。金慧磊[54]发现,高氮负荷下(4.97 kg·(m3·d)−1),anammox颗粒污泥的EPS含量为529.13 mg·g−1;随着氮负荷降至1.01 kg·(m3·d)−1),EPS含量降至256.52 mg·g−1。唐崇俭等[34]发现,随着厌氧氨氧化反应器容积基质氮去除速率的提升,anammox颗粒污泥EPS中多糖和蛋白质含量(以每克MLSS中PN或PS的质量计)均增大;当脱氮负荷达到(50.75 ±0.18) kg ·(m3·d)−1时,多糖含量为45.50 mg·g−1、蛋白质含量为97.50 mg·g−1,而EPS 总量高达143.00 mg·g−1;随着脱氮负荷的增大,蛋白质含量增加更快,蛋白质的“超量产生”致使颗粒污泥的PN/ PS 增大。因此,氮负荷的提升总体上会促进anammox颗粒污泥产生更多EPS,但氮负荷过高会导致EPS分泌过量,造成颗粒污泥孔隙率增加、团聚性降低,甚至解体。
-
外加介体的加入会直接促进anammox菌活性或其强化电子传递等功能,也会直接影响anammox颗粒污泥中EPS的分泌[55]。FTIR分析结果表明,石墨烯纳米片(graphene nanosheets,GNs)的加入可使anammox颗粒污泥EPS中PN和PS含量增大,并增强其疏水性,促进颗粒污泥的形成,而磁赤铁矿(γ-Fe2O3 NPs)的加入会导致PN峰完全消失[56]。XU等[57]发现当MnO2纳米颗粒(MnO2 NPs)的投加量逐步增至200 mg·L−1时,为抵御NPs的侵扰,anammox颗粒污泥中EPS含量增至(481.5 ± 13.4) mg·g−1(以每克VSS含有的EPS质量计)。然而,添加过量外加介体也会抑制EPS分泌。anammox颗粒污泥在低浓度(5 mg·L−1)的La(Ⅲ)胁迫下,EPS分泌量由(292.9 ± 17.5) mg·g−1增至(398.3±26.8) mg·g−1。而随着La(Ⅲ)质量浓度增至50 mg·L−1,大量La(Ⅲ)经EPS吸附和跨膜运输后抑制相关代谢酶活性,导致EPS分泌量下降[58]。CHENG等[59]在探究铜纳米粒子(CuNPs)与土霉素(OTC)双重影响下anammox颗粒污泥EPS的变化时发现:低质量浓度(CuNPs和OTC质量浓度均为0.5 mg·L−1)下,EPS含量较初始水平增加18.7%;而将CuNPs和OTC质量浓度增至1 mg·L−1时,EPS含量则增加21.4%;而在高浓度(CuNPs和OTC质量浓度分别为2.5 mg·L−1 和 2.0 mg·L−1)下,EPS含量又急速降低,仅为初始水平的77%。在外加介体浓度较低时,为抵御外加介体侵扰,anammox颗粒污泥中PN大量分泌会造成EPS含量增大。而当外加介体浓度过高时,EPS分泌饱和,在外加介体长期影响下介体经跨膜运输进入细胞内,导致相关酶代谢功能被抑制,并可能造成外层EPS的脱落(PS分离)[58-59]。
-
除粒径、有机物和氮的浓度、外加介体之外,盐度、脉冲电场和信号分子等的作用对anammox颗粒污泥的EPS分泌量亦存在影响。有研究表明,添加一定盐度能够刺激颗粒污泥分泌EPS以避免细胞脱水而失活[60]。分析不同盐度(质量浓度为0、15、30 g·L−1的NaCl)条件下,anammox颗粒污泥的EPS特性,发现不同盐度胁迫下EPS含量存在变化。随着盐度(NaCl质量浓度由0 g·L−1增至30 g·L−1)的增大,PN含量(以每克MLSS含有的EPS质量计)由(30.58 ± 2.50) mg·g−1降至(18.11 ± 2.1) mg·g−1 ,而PS则由(1.48 ± 0.09) mg·g−1 增至(10.52 ± 0.50) mg·g−1 [61]。在盐度的胁迫下,颗粒污泥EPS的多糖C—O基团增加,并影响合成酶活性及代谢通量重组[62]。另外,ZHANG等[63]发现,在中频脉冲电压(1 000 Hz,1.5 V)条件下,anammox颗粒污泥的PN/PS分别比低频和高频两种条件下分别增加了28.46%和54.20%。ZHANG等[64]通过投加外源信号分子(C8-HSL, N-octanoyl-DL-homoserinelactone)抑制了高氮负荷下anammox颗粒污泥EPS的过量分泌,与无信号分子添加的空白组对比,PN/PS由4.09降至2.14,外源信号分子的添加直接影响到颗粒污泥的沉降性能。
-
在碳达峰碳中和背景下,以anammox颗粒污泥为主体的处理工艺在废水零碳源自养脱氮领域具有重要实践意义。促进EPS分泌并优化其结构成分以快速形成anammox颗粒污泥,并通过调控粒径、水质和运行条件,维持和优化颗粒污泥的结构稳定,提升处理效能,将推进anammox颗粒污泥的工程化应用进程。尽管研究者们对anammox颗粒污泥EPS功能的研究日益增多,但对EPS的主要组成和结构特征的认识还远远不够。尤其是在实际废水处理的复杂条件下,如何促进EPS分泌,并明确其成分和结构的变化具有重要现实意义。
在未来还应在以下方面开展进一步研究:1) 通过外界条件和环境因素的刺激,强化anammox颗粒污泥的EPS分泌,优化PN/PS比例,以促进颗粒污泥快速形成;2) 在明晰anammox颗粒污泥EPS主要成分与含量的基础上,进一步关注EPS在anammox颗粒污泥内的空间分布;3) 强化anammox颗粒污泥EPS微观结构和特殊成分的解析,优化anammox颗粒污泥结构和活性;4) 进一步深化环境因素对anammox颗粒污泥EPS的影响研究,阐明实际应用过程中环境因子波动与结构成分之间的响应关系。
厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥EPS的作用、成分及影响因素研究进展
Review on function, composition and influencing factors of EPS in anammox granular sludge
-
摘要: 厌氧氨氧化是一种新型自养生物脱氮反应,具有节能、脱氮负荷高、无需外加碳源、污泥产生量小等优势,因而对低碳高氮废水的处理具有应用价值。然而,厌氧氨氧化菌生长速率低,常通过污泥颗粒化提升反应器的生物量。胞外聚合物(EPS)在颗粒污泥的形成和稳定方面起着至关重要的作用。为此,综述了EPS在anammox颗粒形成过程中,促进污泥聚集和维持稳定的作用,并阐明了EPS主次要成分及作用,分析了anammox颗粒污泥自身粒径大小、水质条件(有机物、氮浓度和负荷),以及外加介体(矿物质或金属离子等)对EPS含量及成分的影响,并提出未来应在anammox颗粒污泥EPS结构和成分的微观解析、强化EPS分泌以促进颗粒污泥快速形成等方面进一步开展研究,旨在为anammox颗粒污泥的大规模工程化应用提供参考。Abstract: Anaerobic ammonia oxidation (anammox) is a lithoautotrophic biological nitrogen removal process with inherent advantages of low energy consumption, high nitrogen removal loading rate, no external carbon source and low sludge generation, which can be applied for treating wastewater with low C/N ratios. However, due to the slow growth rate of anammox bacteria, biomass is commonly increased by sludge granulation in the anammox reactor. The extracellular polymer substances (EPS) play a vital role in the formation and stabilization of anammox granular sludge. Here, we reviewed the role of EPS in promoting sludge aggregation and maintaining stability during formation of anammox granular sludge, and clarified the major components and functions of EPS. In addition, the particle size of anammox particle sludge, the water quality such as organic matter, nitrogen concentration and nitrogen loading, and the additional mediators such as minerals or metal ions were evaluated on the concentration and composition of EPS of anammox granular sludge. Future research is needed in the field of the micro-analysis of the EPS structure and composition of anammox granular sludge and the enhancement of EPS secretion to promote the rapid formation of granular sludge should be carried out. The ultimate goal of this review is to provide a reference for applying anammox granular sludge technology at large scale.
-
厌氧氨氧化(anaerobic ammonium oxidation, anammox)指在缺氧条件下anammox菌以亚硝酸盐(NO2−−N)为电子供体,将氨氮(NH4+ −N)氧化为氮气(N2)的过程。该过程无需有机碳源,其需氧量仅为传统硝化反硝化工艺的1/3,为自养低耗脱氮提供了新途径[1]。然而,anammox菌生长速率慢、倍增时间长,在实际应用中易因污泥流失而难以快速培养。颗粒污泥具有优良的沉降性能,其内部物种非常多样,微生物系统更加稳定,可在一定程度解决反应器内污泥流失和难以适应复杂环境条件的问题[2]。因此,厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的培养及其稳定化运行,是该工艺走向大规模应用的重要环节。
胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances,EPS)在颗粒污泥的形成和保持结构完整性方面起到关键作用,其主要成分包括多糖、蛋白质、核酸和腐殖酸等[3]。EPS的理化性质和空间分布结构会影响微生物聚集体的结构和功能。比如,EPS中的蛋白质、腐殖酸和糖醛酸有助于污泥的疏水性,而碳水化合物则有助于亲水性[4];某些蛋白质二级结构促进了生物絮凝聚集、吸附和生物膜形成[5- 6];处理工艺、运行条件和水质等诸多因素均会影响EPS的组分、结构、组成等特性[7]。
近年来,研究者在EPS对anammox颗粒污泥形成及稳定运行过程中的作用、EPS成分特征、影响其特性的主要因素等方面开展了广泛研究,积累了大量有益成果。本文梳理了近年来关于anammox颗粒污泥中EPS的最新研究进展,以期明确EPS的特性在anammox颗粒污泥形成及运行过程中的作用,为anammox颗粒污泥的实际工程化应用提供参考。
1. EPS在颗粒污泥的形成及稳定中的重要作用
关于anammox菌聚集及颗粒污泥形成有多种假说,EPS在这些过程中均起到重要作用。
JIA等 [4]认为,anammox微生物的聚集过程可能包括3个步骤,如图1所示。1) 第1阶段中游离的anammox菌游走在固体表面,直到找到适宜生态点位,通过分泌少量糖醛酸黏附在固体表面。2) 第2阶段中anammox菌停留在固体表面并通过蹭动互相接触,并开始分泌大量糖醛酸;由于糖醛酸的凝胶特性形成了网状结构,其网捕作用可防止微生物脱落,使anammox菌更加牢靠地黏附于固体表面。3) 在第3阶段,anammox菌的生长繁殖过程中会产生更多EPS紧密包裹在细胞表面,其胞外蛋白展现的β折叠结构使内部疏水基团很容易被暴露,使得细胞表面疏水性增强并有助于细胞间的聚集,从而形成了结构牢固的群落结构。
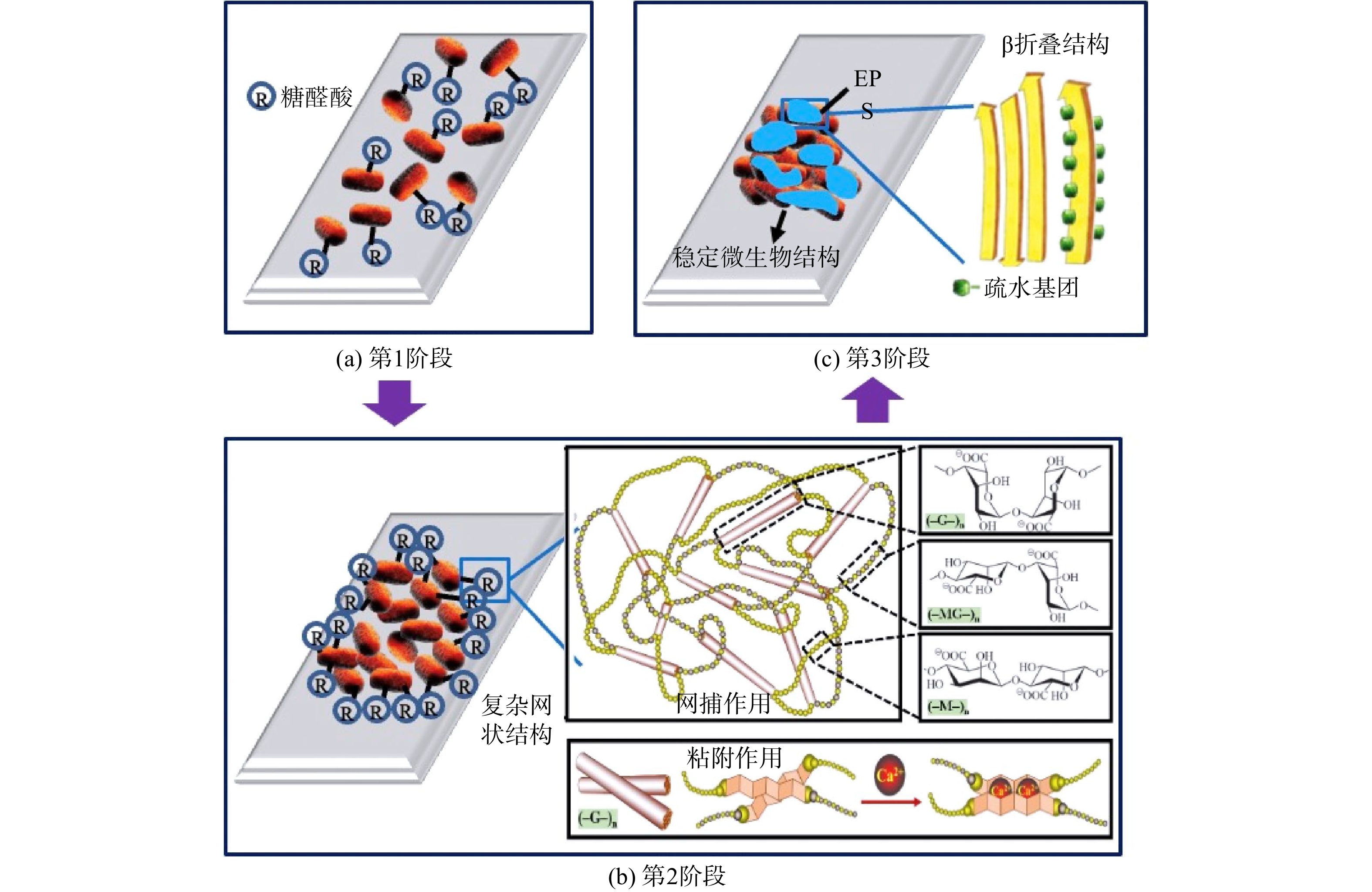 图 1 厌氧氨氧化菌聚集过程的假说[4]Figure 1. Hypothesis of Anammox Bacterial Aggregation Process
图 1 厌氧氨氧化菌聚集过程的假说[4]Figure 1. Hypothesis of Anammox Bacterial Aggregation ProcessMANONMANI等[8]认为,anammox颗粒污泥形成的常见途径为2种。第1种途径是最容易被学者接受的EPS粘附说。即采用好氧或厌氧颗粒污泥作为接种物,在启动初期因培养环境急剧变化,接种颗粒污泥逐渐解体;解体的细小颗粒污泥作为内核,EPS作为黏附剂黏附AnAOB菌;AnAOB菌生长繁殖形成菌胶团,多个菌胶团在EPS 和丝状菌的粘接下形成亚单元;多个亚单元再团聚成anammox颗粒污泥。而第2种途径为采用非颗粒性接种物,以钙镁铁等阳离子作为粘附剂和内核,形成anammox颗粒污泥。
EPS是污泥颗粒化的重要物质,主要分布于细胞外,作为黏结剂促使细胞团聚,从而使得细胞与细胞、细胞与颗粒之间黏连在一起,最终实现聚集[9]。然而,目前仅能证明EPS的存在促进了anammox颗粒污泥的形成,尚未对EPS直接影响AnAOB菌聚集能力的内在机制提出较为清晰的解释。在限氧自养硝化反硝化(oxygen-limited autotrophic nitrification-denitrification,OLAND)工艺中培养的anammox颗粒污泥中,颗粒污泥的自养空间大约50%被EPS所占据,与异养型厌氧颗粒污泥相比,EPS含量相对较高,表明EPS在anammox颗粒污泥聚集方面产生了更重要的作用[10]。
2. Anammox颗粒污泥EPS的成分特征
2.1 EPS主要成分及其对EPS结构和稳定性的影响
在不同类型anammox颗粒污泥中,EPS各成分含量存在较大差异(表1)。这可能与反应器类型、接种污泥及培养策略有关,但对差异存在的内在机制还缺乏强有力的证明。EPS主要由蛋白质、核酸、多糖、脂质和存在于各种微生物聚集体内部的其他聚合化合物组成。其中,多糖(polysaccharide, PS)是EPS的主要成分,其次是腐殖质和蛋白质(protein, PN)。
表 1 不同运行条件下厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥EPS主要成分Table 1. The main components of anammox granular sludge EPS under different operating conditions反应器类型 脱氮负荷/ (kg ·(m3·d)−1) EPS总量/( mg·g−1) EPS成分含量/( mg·g−1) PN/PS 参考文献 PN PS UASB 0.24 387.23 226.9 140 1.62 [27] UASB 0.14 105.15±6.63 93.01±6.23 12.15±0.40 7.66 [28] UASB 0.17 265.2±4.6 164.4±9.3 71.8±2.3 2.29 [29] UASB 0.30 850 500 350 1.43 [30] UASB 0.06 174.2 49.2 91.1 0.54 [19] UASB 0.40 13.35 11.61 1.74 6.67 [31] UASB 0.19 220.20 114.66 99.71 1.15 [32] UASB 0.36 334.1 162.37 158.36 1.03 [20] UASB / 133.7 55.6±3.2 70.8±6.5 0.79 [16] UASB 5.64 ± 0.2 275.4 171.5 103.9 1.65 [33] EGSB 1.55 143 97.5 45.5 2.14 [34] EGSB 0.17 333.03 234.25 90.78 2.58 [35] SBR 1.12 131.82 94.01 37.81 2.49 [36] SBR 0.24±0.02 165 140 25 5.60 [37] SBR 0.125 200 140 60 2.33 [38] SBBR 0.19 290.92 132.05 106.32 1.24 [39] A2O 1.01 146.69 90 23 3.91 [40] 注:EPS各成分的含量以每克VSS含有的该成分质量计。 由微生物分泌产生的EPS中含有大量胞外多糖。胞外多糖通过形成聚合物来促进微生物间的黏附从而增强颗粒污泥的稳定性。同时,多糖交联形成的水凝胶是维持颗粒污泥稳定的重要因素。凝胶可通过氢键、疏水性作用保持颗粒污泥的稳定性[11]。胞外多糖长主链之间的缠结以及丰富的结合位点桥接形成骨架,增强了微生物之间的黏附,有利于维持颗粒污泥的稳定状态[12]。PN含氨基并带正电荷,导致污泥表面负电荷减少,微生物间的静电斥力降低,细胞表面的疏水性增加,从而使微生物细胞更易于从水相中脱离出来并互相聚集。这说明PN含量的增加、PN/PS的增高可促进污泥颗粒化[13]。
胞外多糖可分为结合型胞外多糖和可溶性胞外多糖[14]。EPS具有多层空间结构,根据其结构特点一般分为固着性(bound-EPS,B-EPS)和溶解性(soluble-EPS,S-EPS)2种。其中,B-EPS的内层由紧密结合型(tightly bound-EPS,TB-EPS)组成,与细胞表面结合稳定;外层由松散附着(loosely bound-EPS,LB-EPS)组成,松散可分散[15]。自养anammox颗粒会比好氧/厌氧颗粒物分泌更多的EPS,而高基质浓度下培养的anammox颗粒具有更高EPS含量,且颗粒中EPS的分布存在较大差异[16]。JIA等[4]对比了18种不同条件下生成的anammox颗粒污泥,发现其中的TB-EPS与颗粒污泥形态密切相关,可作为厌氧氨氧化微生物存活能力和微生物聚集体形态的表征指标,且TB-EPS 含有的大量蛋白质疏水基团可促进微生物的聚集。有研究者采用可酶解多糖的淀粉酶对anammox颗粒污泥进行酶解,发现α-淀粉酶处理组颗粒污泥外边缘出现溶胀,而β-淀粉酶处理组颗粒污泥表面无明显变化,但出现破碎且稳定性明显下降[12]。β-D-呋喃葡萄糖集中分布在颗粒污泥最外层,蛋白质、脂类、α-呋喃葡萄糖和α-甘露糖则分布于整个颗粒污泥,主要集中在颗粒污泥外侧。蛋白质和脂类构成了厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的骨架,anammox菌则分布在蛋白质和脂类中间[17]。HOU等18]发现,EPS含量与化学组成主要受细菌的代谢作用影响,细菌的代谢性质也决定了EPS的聚集能力[18]。
Anammox颗粒污泥的粒径直接影响EPS含量及成分[19]。EPS的3层结构(S-EPS,TB-EPS和LB-EPS)会随粒径变化而变化。当粒径<0.5 mm时,S-EPS的含量(以每克VSS含有EPS质量计)占总EPS的48%以上,为121.0~302.3 mg·g−1,并随着粒径的增大而减小,在粒径为2.5 mm时占总EPS的35%。而TB-EPS含量随粒径增大而增大,由粒径< 0.2 mm时的95.6 mg·g−1增至粒径为2.5 mm时的334.1 mg·g−1,且随着anammox颗粒污泥粒径的增大,TB-EPS逐步取代S-EPS成为EPS的主要组分。而LB-EPS含量随粒径变化波动较小,保持在总EPS含量的24%以下[20]。粒径不同还会造成EPS中各组分含量的差异,粒径从0.5~1.4 mm增至> 2.8 mm,PN含量从(56.88±0.86) mg·g−1增至(98.59±2.10)mg·g−1,总EPS量从(68.05±0.97)mg·g−1 增至(94.26±2.20)mg·g−1 [21]。因此,控制反应器运行条件、调控适宜粒径、强化anammox颗粒污泥EPS的分泌,可增强颗粒污泥的运行稳定性。
2.2 EPS中的PN/PS对其稳定性的影响
EPS中PN和PS两大组分在anammox颗粒污泥的形成、运行中发挥重要作用。在不同反应器类型及脱氮负荷条件下,anammox颗粒污泥的EPS含量与PN/PS存在显著差异。较高的脱氮负荷往往PN/PS较大,但二者并无线性相关性,这可能与运行环境条件有直接关系。当脱氮负荷为0~1 kg·(m3·d)−1时, anammox颗粒污泥在不同反应器运行条件下的EPS总量(以每克VSS含有EPS质量计)为13.35~850 mg ·g−1,PN/PS为0.54~7.66。同种接种污泥形成的anammox颗粒污泥PN/PS较为接近[17],而不同接种污泥和培养策略会对颗粒污泥PN/PS产生较大影响[16],但迄今为止的研究尚未对EPS的组分差异作出合理解释,还需进一步深入探究。
颗粒污泥EPS的PN/PS可用于表征其稳定性能和沉降性能。PN/PS为0.5~5时,颗粒污泥的稳定性和沉降性随比值增大而增强[22]。PN/PS大小与污泥表面疏水性、带电性及颗粒污泥的形成直接相关,污泥的相对疏水性会随着PN/PS的提高逐渐增强,从而促进anammox颗粒污泥的聚集,且随着颗粒污泥的形成PN/PS有较大幅度的增加[23]。anammox颗粒污泥EPS中的蛋白质是决定疏水性的主要成分,因此,随着PN/PS的升高,蛋白质占比越高,细胞电负性越强,微生物表面疏水性越好,颗粒化程度更强[24-25]。虽然EPS含量与颗粒污泥粒径无明显关联,但PN/PS受粒径影响变化较大。CHEN等[20]研究了4种不同粒径anammox颗粒污泥的EPS含量,发现小粒径(1.0~1.5 mm)颗粒污泥的PN/PS达3.81,厌氧氨氧化活性较大,EPS分泌量较高。粒径为300~500 μm的PN/PS随粒径增大而呈上升趋势,但粒径增大到一定程度时(>500 μm),颗粒污泥向胞外分泌较少的EPS,PN/PS也会随之降低,小颗粒间的聚集作用减弱,亲和力降低,沉降能力下降[26]。掌握这种变化规律有利于调整条件以促进颗粒污泥的聚集并维持颗粒间的稳定性。PN/PS是颗粒结构稳定性的重要调控因素,较高的PN/PS有利于颗粒污泥造粒并增加颗粒污泥强度和相对疏水性,促进anammox颗粒污泥的聚集,故可作为颗粒形成指标。
2.3 EPS中其他成分对颗粒污泥特性的影响
对 anammox 颗粒污泥的元素组成分析表明,C、H、N、O、S元素的组成分别占总量的44.4%、6.6%、9.0%、35.7%和1.4%[41]。除了主要成分外,颗粒污泥的EPS提取物中还有Na、K、Ca、Mg、Al、Fe、Mn、P、Si、S等元素组成的矿物颗粒。其中,Na、K、Ca、Mg占主要成分,其含量大小为K>Na>Ca>Mg[42]。Anammox颗粒污泥EPS中K、Ca、Mg有离子和非离子2种存在形式,但绝大多是以离子形式存在。K、Ca的金属离子形式占比分别为68.6%、56.2%,Mg的离子形态比例最高,可达94.7%。在非离子存在形态中,K和Mg占比分别为31.4%和5.3%。在金属元素中,Ca的非离子存在形式占比最高,为43.8%。随着粒径的增大,厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥EPS中PN的含量随之增大,从而可结合更多金属元素,使得金属元素含量增大,Ca2+的含量亦增大,进而中和细菌表面和多糖分子上的负电荷,提升多糖水平并显著缩短颗粒的形成时间,加速颗粒污泥形成并维持其稳定性[28, 43-44]。金属离子在颗粒污泥聚集中发挥的作用不同,如EPS中的Na+会通过压缩双电层作用促进颗粒污泥的聚集,而Na+、K+会通过离子交换作用与Ca2+竞争EPS中的结合位点。因此,Na+与Ca2+和Mg2+含量的变化趋势相反[45]。还有研究者认为,EPS中的Ca、K、Mg、Na、Al、Fe等金属元素会影响厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的表面特性[46]。如Ca可诱导形成CaCO3和Ca5OH(PO4)3沉淀,作为anammox颗粒污泥初期的晶核并促成颗粒污泥的形成[43, 47]。而其他金属元素在anammox颗粒污泥的形成及EPS成分结构方面的作用尚有待进一步研究。
3. 影响EPS分泌和污泥颗粒化的主要因素
3.1 废水中有机物的浓度
Anammox颗粒污泥属于自养脱氮颗粒污泥,主体功能菌为anammox菌,其生长缓慢、倍增时间长[1]。当废水中含有有机物时,异养菌如反硝化菌会快速增殖,与anammox菌争夺反应基质NO2−−N,导致anammox菌的生长被抑制,从而影响anammox颗粒污泥的性能甚至使之解体[2]。范丹等[13]发现,较低的有机物质量浓度(<100 mg·L−1)会使同步亚硝化厌氧氨氧化反硝化(simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification,SNAD)反应器内的功能微生物更易于相互聚集黏附,加快污泥快速颗粒化,增大颗粒粒径,最大粒径达到1 103 μm;经过约140 d的培养,最大EPS含量达到140 mg·g−1(以每克VSS含有的EPS质量计)。同样,当COD为100 mg·L−1时,EPS含量达到最大值(482.69 ± 9.83) mg·g−1;而随着COD增至150 mg·L−1,EPS含量降至 (451.80 ± 9.79) mg·g−1;当COD持续增至200 mg·L−1,EPS含量开始急剧下降[48]。LI等[49]发现,COD为200 mg·L−1的条件可促进anammox颗粒污泥EPS的分泌,其含量从33 mg·g−1升至181 mg·g−1,但当COD升至300 mg·L−1时,EPS含量降至155 mg·g−1。从共聚焦激光扫描图像可发现,在有机物存在的条件下,PN显著增加,但PS有所下降。适量的有机碳源(<130 mg·L−1)可提高厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的EPS含量,PN、PS含量分别由最初的63、45.1 mg·g−1增至140、60 mg·g−1(以每克MLSS中PN或PS质量计)。此时,污泥的沉降性能明显提高。然而,COD高于130 mg·L−1时,EPS含量则下降。这可能是由于有机物过多会导致部分anammox颗粒污泥解体,进而造成EPS的释放[50]。
3.2 反应体系中的氮浓度及负荷
氮作为厌氧氨氧化过程的主要基质,其浓度和负荷直接影响着anammox颗粒污泥的形成及EPS分泌[51]。ZHANG等[52]发现,当氮负荷由4.8 g·(L·d)−1增至10.0 g·(L·d)−1时,anammox颗粒污泥的EPS含量增加了约60%;当氮负荷达到最大值20.0 g·(L·d)−1时,EPS总量增至77.2 mg·g−1(以每克VSS含有的EPS质量计),但anammox颗粒污泥因密度降低而大量解体。WANG等[53]亦发现随着氮负荷增大(由0.09 ~ 0.26 kg·(m3·d)−1增至0.21 ~ 0.97 kg·(m3·d)−1),anammox颗粒污泥EPS含量由11.09 mg·g −1 增至83.38 mg·g−1,且PN/PS 增大,由5.09增至8.84。NI等[16]通过设置不同停留时间(HRT)调控反应器的氮负荷,发现:EPS在不同氮负荷运行条件下的特征存在差异,低HRT(22 h)高氮负荷anammox颗粒污泥的PN/PS为0.8,而高HRT(36 h)低氮的PN/PS为2.1。在低氮条件下,PN为胞外多糖的主要成分;在高氮条件下,EPS含量更高且PS为主要成分。金慧磊[54]发现,高氮负荷下(4.97 kg·(m3·d)−1),anammox颗粒污泥的EPS含量为529.13 mg·g−1;随着氮负荷降至1.01 kg·(m3·d)−1),EPS含量降至256.52 mg·g−1。唐崇俭等[34]发现,随着厌氧氨氧化反应器容积基质氮去除速率的提升,anammox颗粒污泥EPS中多糖和蛋白质含量(以每克MLSS中PN或PS的质量计)均增大;当脱氮负荷达到(50.75 ±0.18) kg ·(m3·d)−1时,多糖含量为45.50 mg·g−1、蛋白质含量为97.50 mg·g−1,而EPS 总量高达143.00 mg·g−1;随着脱氮负荷的增大,蛋白质含量增加更快,蛋白质的“超量产生”致使颗粒污泥的PN/ PS 增大。因此,氮负荷的提升总体上会促进anammox颗粒污泥产生更多EPS,但氮负荷过高会导致EPS分泌过量,造成颗粒污泥孔隙率增加、团聚性降低,甚至解体。
3.3 外加介体
外加介体的加入会直接促进anammox菌活性或其强化电子传递等功能,也会直接影响anammox颗粒污泥中EPS的分泌[55]。FTIR分析结果表明,石墨烯纳米片(graphene nanosheets,GNs)的加入可使anammox颗粒污泥EPS中PN和PS含量增大,并增强其疏水性,促进颗粒污泥的形成,而磁赤铁矿(γ-Fe2O3 NPs)的加入会导致PN峰完全消失[56]。XU等[57]发现当MnO2纳米颗粒(MnO2 NPs)的投加量逐步增至200 mg·L−1时,为抵御NPs的侵扰,anammox颗粒污泥中EPS含量增至(481.5 ± 13.4) mg·g−1(以每克VSS含有的EPS质量计)。然而,添加过量外加介体也会抑制EPS分泌。anammox颗粒污泥在低浓度(5 mg·L−1)的La(Ⅲ)胁迫下,EPS分泌量由(292.9 ± 17.5) mg·g−1增至(398.3±26.8) mg·g−1。而随着La(Ⅲ)质量浓度增至50 mg·L−1,大量La(Ⅲ)经EPS吸附和跨膜运输后抑制相关代谢酶活性,导致EPS分泌量下降[58]。CHENG等[59]在探究铜纳米粒子(CuNPs)与土霉素(OTC)双重影响下anammox颗粒污泥EPS的变化时发现:低质量浓度(CuNPs和OTC质量浓度均为0.5 mg·L−1)下,EPS含量较初始水平增加18.7%;而将CuNPs和OTC质量浓度增至1 mg·L−1时,EPS含量则增加21.4%;而在高浓度(CuNPs和OTC质量浓度分别为2.5 mg·L−1 和 2.0 mg·L−1)下,EPS含量又急速降低,仅为初始水平的77%。在外加介体浓度较低时,为抵御外加介体侵扰,anammox颗粒污泥中PN大量分泌会造成EPS含量增大。而当外加介体浓度过高时,EPS分泌饱和,在外加介体长期影响下介体经跨膜运输进入细胞内,导致相关酶代谢功能被抑制,并可能造成外层EPS的脱落(PS分离)[58-59]。
3.4 其他影响因素
除粒径、有机物和氮的浓度、外加介体之外,盐度、脉冲电场和信号分子等的作用对anammox颗粒污泥的EPS分泌量亦存在影响。有研究表明,添加一定盐度能够刺激颗粒污泥分泌EPS以避免细胞脱水而失活[60]。分析不同盐度(质量浓度为0、15、30 g·L−1的NaCl)条件下,anammox颗粒污泥的EPS特性,发现不同盐度胁迫下EPS含量存在变化。随着盐度(NaCl质量浓度由0 g·L−1增至30 g·L−1)的增大,PN含量(以每克MLSS含有的EPS质量计)由(30.58 ± 2.50) mg·g−1降至(18.11 ± 2.1) mg·g−1 ,而PS则由(1.48 ± 0.09) mg·g−1 增至(10.52 ± 0.50) mg·g−1 [61]。在盐度的胁迫下,颗粒污泥EPS的多糖C—O基团增加,并影响合成酶活性及代谢通量重组[62]。另外,ZHANG等[63]发现,在中频脉冲电压(1 000 Hz,1.5 V)条件下,anammox颗粒污泥的PN/PS分别比低频和高频两种条件下分别增加了28.46%和54.20%。ZHANG等[64]通过投加外源信号分子(C8-HSL, N-octanoyl-DL-homoserinelactone)抑制了高氮负荷下anammox颗粒污泥EPS的过量分泌,与无信号分子添加的空白组对比,PN/PS由4.09降至2.14,外源信号分子的添加直接影响到颗粒污泥的沉降性能。
4. 建议与展望
在碳达峰碳中和背景下,以anammox颗粒污泥为主体的处理工艺在废水零碳源自养脱氮领域具有重要实践意义。促进EPS分泌并优化其结构成分以快速形成anammox颗粒污泥,并通过调控粒径、水质和运行条件,维持和优化颗粒污泥的结构稳定,提升处理效能,将推进anammox颗粒污泥的工程化应用进程。尽管研究者们对anammox颗粒污泥EPS功能的研究日益增多,但对EPS的主要组成和结构特征的认识还远远不够。尤其是在实际废水处理的复杂条件下,如何促进EPS分泌,并明确其成分和结构的变化具有重要现实意义。
在未来还应在以下方面开展进一步研究:1) 通过外界条件和环境因素的刺激,强化anammox颗粒污泥的EPS分泌,优化PN/PS比例,以促进颗粒污泥快速形成;2) 在明晰anammox颗粒污泥EPS主要成分与含量的基础上,进一步关注EPS在anammox颗粒污泥内的空间分布;3) 强化anammox颗粒污泥EPS微观结构和特殊成分的解析,优化anammox颗粒污泥结构和活性;4) 进一步深化环境因素对anammox颗粒污泥EPS的影响研究,阐明实际应用过程中环境因子波动与结构成分之间的响应关系。
-
图 1 厌氧氨氧化菌聚集过程的假说[4]
Figure 1. Hypothesis of Anammox Bacterial Aggregation Process
表 1 不同运行条件下厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥EPS主要成分
Table 1. The main components of anammox granular sludge EPS under different operating conditions
反应器类型 脱氮负荷/ (kg ·(m3·d)−1) EPS总量/( mg·g−1) EPS成分含量/( mg·g−1) PN/PS 参考文献 PN PS UASB 0.24 387.23 226.9 140 1.62 [27] UASB 0.14 105.15±6.63 93.01±6.23 12.15±0.40 7.66 [28] UASB 0.17 265.2±4.6 164.4±9.3 71.8±2.3 2.29 [29] UASB 0.30 850 500 350 1.43 [30] UASB 0.06 174.2 49.2 91.1 0.54 [19] UASB 0.40 13.35 11.61 1.74 6.67 [31] UASB 0.19 220.20 114.66 99.71 1.15 [32] UASB 0.36 334.1 162.37 158.36 1.03 [20] UASB / 133.7 55.6±3.2 70.8±6.5 0.79 [16] UASB 5.64 ± 0.2 275.4 171.5 103.9 1.65 [33] EGSB 1.55 143 97.5 45.5 2.14 [34] EGSB 0.17 333.03 234.25 90.78 2.58 [35] SBR 1.12 131.82 94.01 37.81 2.49 [36] SBR 0.24±0.02 165 140 25 5.60 [37] SBR 0.125 200 140 60 2.33 [38] SBBR 0.19 290.92 132.05 106.32 1.24 [39] A2O 1.01 146.69 90 23 3.91 [40] 注:EPS各成分的含量以每克VSS含有的该成分质量计。 -
[1] 谢军祥, 姜滢, 常尧枫, 等. 城镇生活污水厌氧氨氧化处理的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(10): 4175-4184. [2] ADAMS M, XIE J X, KABORE A W J, et al. Research advances in anammox granular sludge: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2020: 1-44. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2020.1831358 [3] LIU X W, SHENG G P, YU H Q. Physicochemical characteristics of microbial granules[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2009, 27(6): 1061-1070. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.05.020 [4] JIA F, YANG Q, LIU X, et al. Stratification of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) for aggregated anammox microorganisms[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(6): 3260-3268. [5] BADIREDDY A R, CHELLAM S, GASSMAN P L, et al. Role of extracellular polymeric substances in bioflocculation of activated sludge microorganisms under glucose-controlled conditions[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(15): 4505-4516. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.024 [6] YIN C, MENG F, CHEN G H. Spectroscopic characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from a mixed culture dominated by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Water Research, 2015, 68: 740-749. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.046 [7] SHENG G P, YU H-Q, LI X Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review[J]. Biotechnology advances, 2010, 28(6): 882-894. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.08.001 [8] Manonmani U, Joseph K, et al. Granulation of anammox microorganisms for autotrophic nitrogen removal from wastewater[J]. Environmental Chemistry Lethers, 2018, 16(4): 881-901. [9] 杨敏, 胡学伟, 宁平, 等. 废水生物处理中胞外聚合物(EPS)的研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2011, 31(7): 7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2011.07.002 [10] VLAEMINCK S E, TERADA A, SMETS B F, et al. Aggregate size and architecture determine microbial activity balance for one-stage partial nitritation and anammox[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(3): 900-999. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02337-09 [11] SEVIOUR T, YUAN Z, LOOSDRECHT M, et al. Aerobic sludge granulation: A tale of two polysaccharides?[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(15): 4803-4813. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.06.018 [12] 杨帆 王帅, 龙曼, 等. 胞外多糖酶解对Anammox颗粒污泥稳定性的影响[J]. 土木与环境工程学报, 2021, 16(7): 1-9. [13] 范丹, 李冬, 梁瑜海, 等. 生活污水SNAD颗粒污泥快速启动及脱氮性能研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(11): 3321-3328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.11.015 [14] NEILSEN P. Extraction of EPS[J]. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1999: 47-72. [15] LI X Y, YANG S F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(5): 1022-1030. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.037 [16] NI S-Q, SUN N, YANG H, et al. Distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in anammox granules and their important roles during anammox granulation[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 101(1): 126-133. [17] 李惠娟, 彭党聪, 陈国燕, 等. ANAMMOX的快速启动及EPS在ANAMMOX颗粒污泥中的空间分布[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(7): 2931-2940. [18] HOU X, LIU S, ZHANG Z. Role of extracellular polymeric substance in determining the high aggregation ability of anammox sludge[J]. Water Research, 2015, 75(15): 51-62. [19] CHEN C, JIANG Y, ZOU X, et al. Insight into the influence of particle sizes on characteristics and microbial community in the anammox granular sludge[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 39: 101883. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101883 [20] ZHU G, WANG S, MA B, et al. Anammox granular sludge in low-ammonium sewage treatment: Not bigger size driving better performance[J]. Water Research, 2018, 142(1): 147-158. [21] 杨明明. 厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥胞外聚合物(EPS)及表面特性研究 [D]; 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019. [22] 王衫允, 贾方旭, 靳鹏飞, 等. 高效厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥脱氮特征及EPS分层特性[J]. 中国给水排水, 2016, 32(11): 35-39. [23] 杨明明, 党超军, 张爱余, 等. 厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥胞外聚合物金属元素特性[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(11): 4728-4734. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.011 [24] TANG C J. Performance of high-loaded ANAMMOX UASB reactors containing granular sludge[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(1): 135-144. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.018 [25] 刘云曼. 胞外多聚物对厌氧氨氧化污泥脱氮性能的影响研究 [D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2018. [26] 张倩, 刘晓朋, 张旭, 等. 盐胁迫对厌氧氨氧化污泥脱氮性能及其胞外聚合物特性的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(7): 117-126. [27] 张亚超, 张晶, 侯爱月, 等. 胞外聚合物和信号分子对厌氧氨氧化污泥活性的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(10): 4133-4140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.10.012 [28] BOLEIJ M, SEVIOUR T, WONG L L, et al. Solubilization and characterization of extracellular proteins from anammox granular sludge[J]. Water Research, 2019, 164(1): 114952. [29] 唐崇俭, 郑平, 汪彩华, 等. 高负荷厌氧氨氧化EGSB反应器的运行及其颗粒污泥的ECP特性[J]. 化工学报, 2010, 061(3): 732-739. [30] CHEN J, JI Q, ZHENG P, et al. Floatation and control of granular sludge in a high-rate anammox reactor[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(11): 3321-3328. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.03.016 [31] 李冬, 田海成, 梁瑜海, 等. 水质条件对厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥EPS含量的影响[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2017, 49(2): 6-12. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2017.02.002 [32] 宋成康, 王亚宜, 韩海成, 等. 温度降低对厌氧氨氧化脱氮效能及污泥胞外聚合物的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(7): 2006-2013. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.07.015 [33] 李冬, 王艳菊, 吕育锋, 等. 有机碳源对厌氧氨氧化污泥颗粒化的影响[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2018, 50(9): 116-1122. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201704033 [34] MIAO L, ZHANG Q, WANG S, et al. Characterization of EPS compositions and microbial community in an Anammox SBBR system treating landfill leachate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 249(2): 108-116. [35] 郭静. 胞外聚合物对厌氧氨氧化污泥性能的影响研究 [D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017. [36] FRANCO A, ROCA E, LEMA J M. Granulation in high-load denitrifying upflow sludge bed (USB) pulsed reactors[J]. Water Research, 2006, 40(5): 871-80. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2005.11.044 [37] 吴昌永, 王然登, 彭永臻. 污水处理颗粒污泥技术原理与应用 [M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011. [38] 顾澄伟. 厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥培养及其颗粒特性研究 [D]. 苏州: 苏州科技大学, 2019. [39] 陈方敏, 顾澄伟, 胡羽婷, 等. 厌氧氨氧化污泥恢复过程中的颗粒特性[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(12): 5605-5611. [40] 王洋. 厌氧氨氧化污泥EPS功能解析及对氮、硫的耦合转化研究 [D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2019. [41] IZADI P, IZADI P, ELDYASTI A. Holistic insights into extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) in anammosx bacterial matrix and the potential sustainable biopolymer recovery: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 274: 129703. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129703 [42] BOURVEN I, JOUSSEIN E, GUIBAUD G. Characterisation of the mineral fraction in extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from activated sludges extracted by eight different methods[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(14): 7124-7130. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.058 [43] YAN L, LIU Y, WEN Y, et al. Role and significance of extracellular polymeric substances from granular sludge for simultaneous removal of organic matter and ammonia nitrogen[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 179(1): 460-466. [44] JIANG H L, TAY J H, YU L, et al. Ca2+ augmentation for enhancement of aerobically grown microbial granules in sludge blanket reactors[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2003, 25(2): 95-99. doi: 10.1023/A:1021967914544 [45] PEVERE A, GUIBAUD G, HULLEBUSCH E, et al. Effect of Na+ and Ca2+ on the aggregation properties of sieved anaerobic granular sludge[J]. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects, 2007, 306(1/2/3): 142-149. [46] D'ABZ AC P, BORDAS F, JOUSSEIN E, et al. Characterization of the mineral fraction associated to extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in anaerobic granular sludges[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(1): 412. [47] 许冬冬, 康达, 郭磊艳, 等. 厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(8): 1988-1997. [48] ZHANG X, LIU Y, LI Z R, et al. Impact of COD/N on anammox granular sludge with different biological carriers[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 728: 138557. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138557 [49] LI Y, HUANG Z, RUAN W, et al. ANAMMOX performance, granulation, and microbial response under COD disturbance[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2015, 90(1): 139-148. [50] 林志福, 伍健东, 周兴求, 等. 厌氧颗粒污泥胞外聚合物的影响因素研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(7): 1311-1315. [51] YANG S F, LI X Y. Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the characteristics of activated sludge under non-steady-state conditions[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2009, 44(1): 91-96. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2008.09.010 [52] ZHANG Y, MA H, NIU Q, et al. Effects of substrate shock on extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) excretion and characteristics of attached biofilm anammox granules[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(114): 113289-113297. doi: 10.1039/C6RA20097D [53] WANG W, LI D, LI S, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of hollow Anammox granular sludge in low-strength ammonia sewage treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 421: 127766. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127766 [54] 金慧磊. 厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的培养及其脱氮性能研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. [55] WANG H, GUO W, LIU B, et al. Edge-nitrogenated biochar for efficient peroxydisulfate activation: An electron transfer mechanism[J]. Water Research, 2019, 160(1): 405-414. [56] ELREEDY A, ISMAIL S, ALI M, et al. Unraveling the capability of graphene nanosheets and γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles to stimulate anammox granular sludge[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 277: 111495. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111495 [57] XU J-J, CHENG Y-F, XU L Z J, et al. The performance and microbial community in response to MnO2 nanoparticles in anammox granular sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 233(10): 625-632. [58] 黄双蕾. 稀土元素对厌氧氨氧化脱氮性能的影响研究 [D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2020. [59] CHENG Y F, LI G F, MA W-J, et al. Resistance of anammox granular sludge to copper nanoparticles and oxytetracycline and restoration of performance[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 307: 123264. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123264 [60] SHENG G P, YU H Q, YUE Z. Factors influencing the production of extracellular polymeric substances by Rhodopseudomonas acidophila[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2006, 58(2): 89-93. [61] FANG F, YANG M-M, WANG H, et al. Effect of high salinity in wastewater on surface properties of anammox granular sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 210: 366-375. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.038 [62] WANG Z, GAO M, WANG Z, et al. Effect of salinity on extracellular polymeric substances of activated sludge from an anoxic–aerobic sequencing batch reactor[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 93(11): 2789-2795. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.09.038 [63] ZHANG C, LI L, WANG Y, et al. Enhancement of the ANAMMOX bacteria activity and granule stability through pulsed electric field at a lower temperature (16 ± 1 °C)[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 292: 121960. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121960 [64] ZHANG J, LI J, ZHAO B H, et al. Long-term effects of N-acyl-homoserine lactone-based quorum sensing on the characteristics of ANAMMOX granules in high-loaded reactors[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 218(3): 632-642. -




 下载:
下载:

