-
矿山开发导致硫化矿物暴露于氧化环境中,产生大量的酸性矿山废水(acid mine drainage,AMD),AMD具有低pH、高重金属和硫酸盐的特点[1-3],会对矿区周围水生和土壤生态系统造成严重污染。传统处理方法为化学沉淀法[4],如石灰中和,但其存在废渣产量大、重金属含量高、金属资源浪费等问题,故限制了其大规模的应用。
硫酸盐还原菌(sulfate reducing bacteria,SRB)生物处理技术是一种有效治理AMD的方法,其主要反应过程为:SRB在还原氛围中将
SO2−4 还原为S2−,代谢产物S2−与AMD中重金属离子形成硫化矿物[5-7]。但SRB活性易受AMD (酸、重金属)、代谢产物S2−等毒性抑制,从而导致其处理AMD效率降低。周立祥[8]和狄军贞等[9]发现,SRB最适pH为中性,在pH<5的AMD中,其处理活性较差。UTGIKAR等[10]、GUO等[11]、曹恒恒等[12]发现,Zn2+、Cu2+(≥20 mg·L−1)等重金属对SRB具有毒性抑制作用,且金属硫化物(金属离子与生物硫化物反应形成)是阻碍硫酸盐、有机物进入生物体系的屏障。LEWIS等[13]将SRB生化出水直接与AMD混合反应,发现水相中多硫化物络合物不利于金属去除,且金属沉淀物中包含未知复合物。BIJMANS等[14]报道,硫化物会抑制SRB生长,硫化物的去除可提高SRB活性。汪琦[15]采用两级循环气提工艺,有效解除了H2S对菌群(SRB、产酸菌、产甲烷菌)的毒性抑制。任立人等[16]采用两相厌氧-气提生化法,有效地解除了H2S对高含硫抗生素有机废水内SRB、产甲烷菌的毒性抑制。上述研究仅提出了对SRB活性抑制因素和单一因素的解除,鲜少涉及全面解除SRB(处理AMD)的多重毒性抑制和有效促进SRB活性的研究。本研究采用气提内循环反应器对AMD进行了处理,考察了反应器内涉硫组分的演变、产碱效率、微生物群落结构、重金属的去除,并对重金属沉淀物的纯度进行了分析;综合评估了气提内循环反应器内毒性抑制的解除效果及重金属回收,为AMD的SRB处理及有价金属回收提供应用指导和参考。
-
SRB菌种由课题组前期驯化所得。培养基的组成为 0.06 g·L−1 CaCl2·6H2O、1.0 g·L−1 NH4Cl、0.5 g·L−1 K2HPO4、0.738 g·L−1 MgSO4·7H2O、0.8 g·L−1 Na2SO4、1 g·L−1 FeSO4·7H2O、6 mL·L−1 乳酸钠(COD为2 000 mg·L−1)。SRB反应器运行控制参数为温度(25±2) ℃、pH 6.7~7.0。酸性矿山废水的水质参数为pH 3.01、21 mg·L−1 Cu2+、199 mg·L−1 Fe2+、30 mg·L−1 Zn2+、28.5 mg·L−1 Mn2+、1 098 mg·L−1
SO2−4 。 -
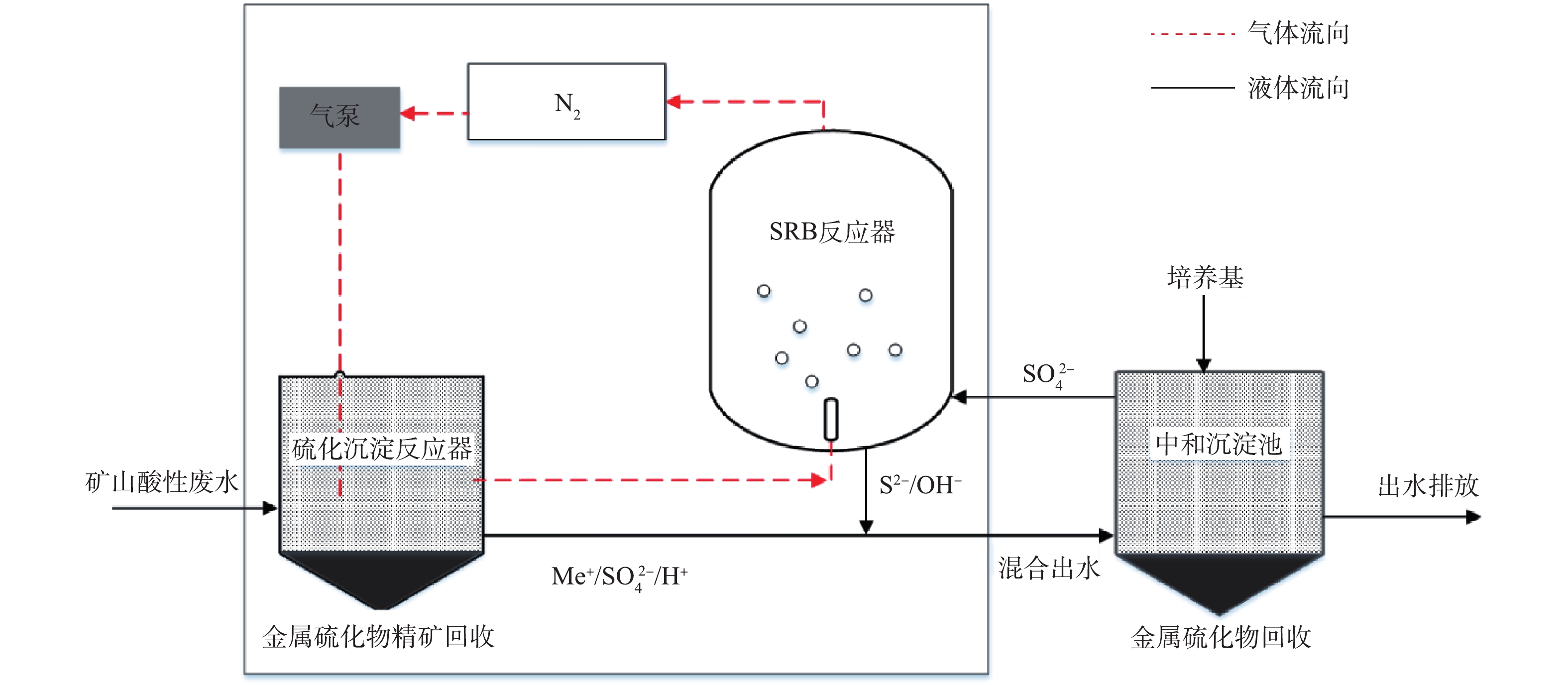
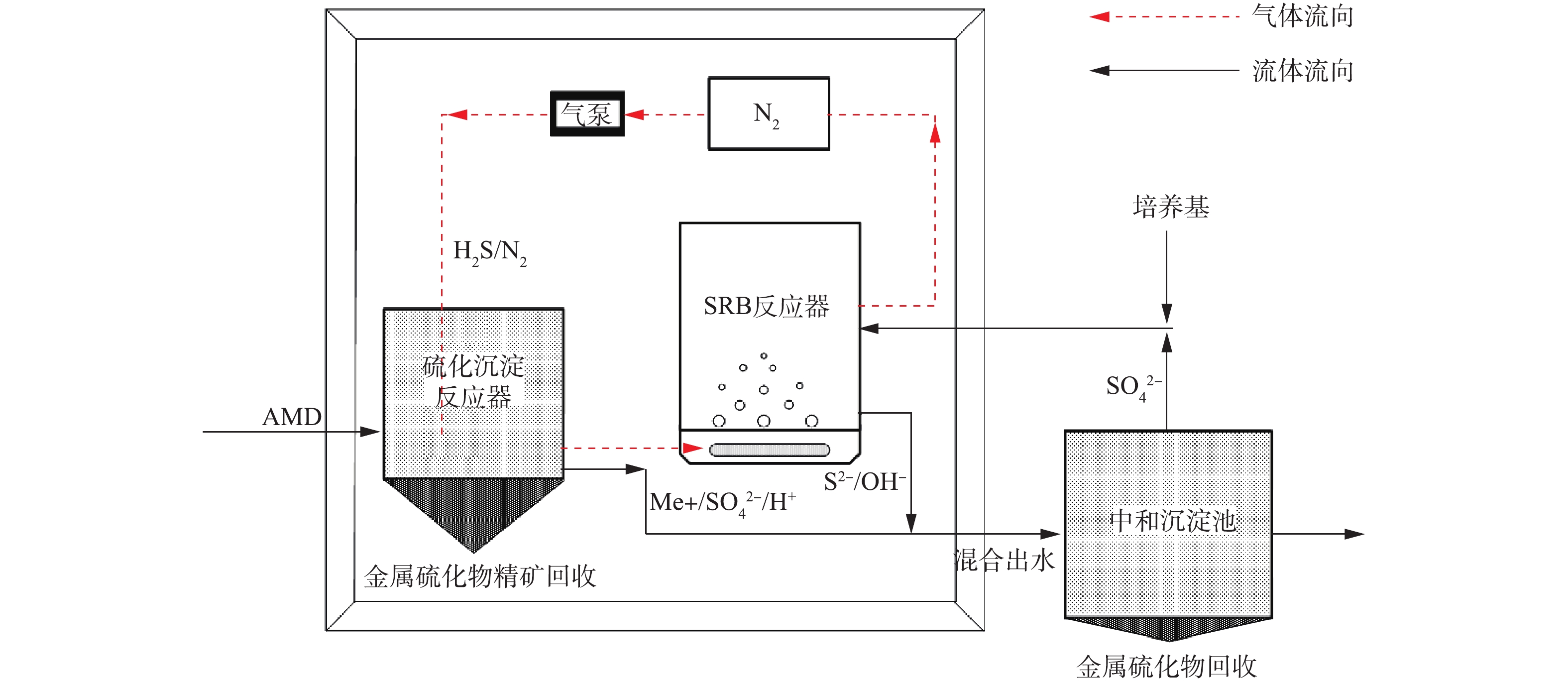
实验装置如图1所示。主要由SRB反应器(总体积4 L,其底部设有曝气装置)、硫化沉淀反应器(总体积3 L)、气泵、中和沉淀池组成;反应装置制备材料均为有机玻璃;反应器中AMD的进水量为3 L·d−1,中和排水量为3 L·d−1;在反应器运行过程中,采用气泵将循环N2(气体流量为0.005 L·min−1)引入SRB反应器,SRB代谢过程中产生的H2S被吹脱至硫化沉淀反应器;将中和沉淀池的上清液与培养基混合作为物料引入SRB反应器。传统反应器为有机玻璃SRB反应器(总体积4 L),将AMD(进水量为3 L·d−1)和培养基混合,直接引入该SRB反应器,反应过程中不进行吹脱,反应后排水量为3 L·d−1。
-
气提内循环反应器(SRB反应器)、传统反应器中菌液接种量均为20%。每隔2 h,对气提内循环反应器(SRB反应器)、传统反应器内涉硫组分(
SO2−4 、SO2−3 、H2S、S2−)进行检测;每隔3 h,对气提内循环反应器(SRB反应器)、传统反应器内pH和ORP进行测定。在10、20、30、40、50、60 min和24 h时,在气提内循环反应器(硫化沉淀反应器)、传统反应器中取样,测定废水中金属离子的浓度。 -
使用pH计(上海雷磁,PHS-3C)测定pH;采用自动电位滴定仪(上海雷磁,ZD-2)测定ORP;使用硫离子浓度计(上海般特,Bante931-S)测定S2−;采用吹脱-金属离子吸收法和火焰原子吸收光谱仪(普析通用,TAS-990)测定H2S;选用 16S rDNA技术进行微生物群落结构分析;采用火焰原子吸收光谱仪(普析通用,TAS-990)测定重金属离子。
SO2−3 、S2O2−3 、SO2−4 的样品预处理在4 000 r·min−1离心10 min,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤后,使用离子色谱分析仪(北京东西分析,IC-2800)并搭配色谱柱(美国Dionex,IonPacTMAS23 4×250 mm)进行测定,淋洗液配比为4.5 mmol·L−1 Na2CO3和0.8 mmol·L−1 NaHCO3,抑制电流为30 mA,淋洗液泵流速为1.0 mL·min−1。 -
从气提内循环反应器(SRB反应器)、传统反应器中取3组平行菌液,离心收集菌体,采用CTAB方法对样本的基因组DNA进行提取,之后利用琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA的纯度和浓度。取适量的样本DNA于离心管中,使用无菌水稀释样本至1 ng·μL−1。以稀释后的基因组DNA为模板,引物对应区域:16S V4区引物(515F和806R)鉴定细菌多样性,使用带Barcode的特异引物、New England Biolabs公司的Phusion®带有GC缓冲液的高保真PCR预混液、高效高保真酶进行PCR。
PCR产物使用2%浓度的琼脂糖凝胶进行电泳检测;根据PCR产物浓度进行等量混样,充分混匀后,使用1×TAE浓度2%的琼脂糖胶电泳,纯化PCR产物,剪切回收目标条带。使用Thermo Scientific公司GeneJET胶回收试剂盒回收产物。
使用Thermofisher公司的Ion Plus Fragment Library Kit 48 rxns建库试剂盒进行文库的构建,构建好的文库经过Qubit定量和文库检测合格后,使用Thermofisher的Ion S5TMXL进行上机测序。
-
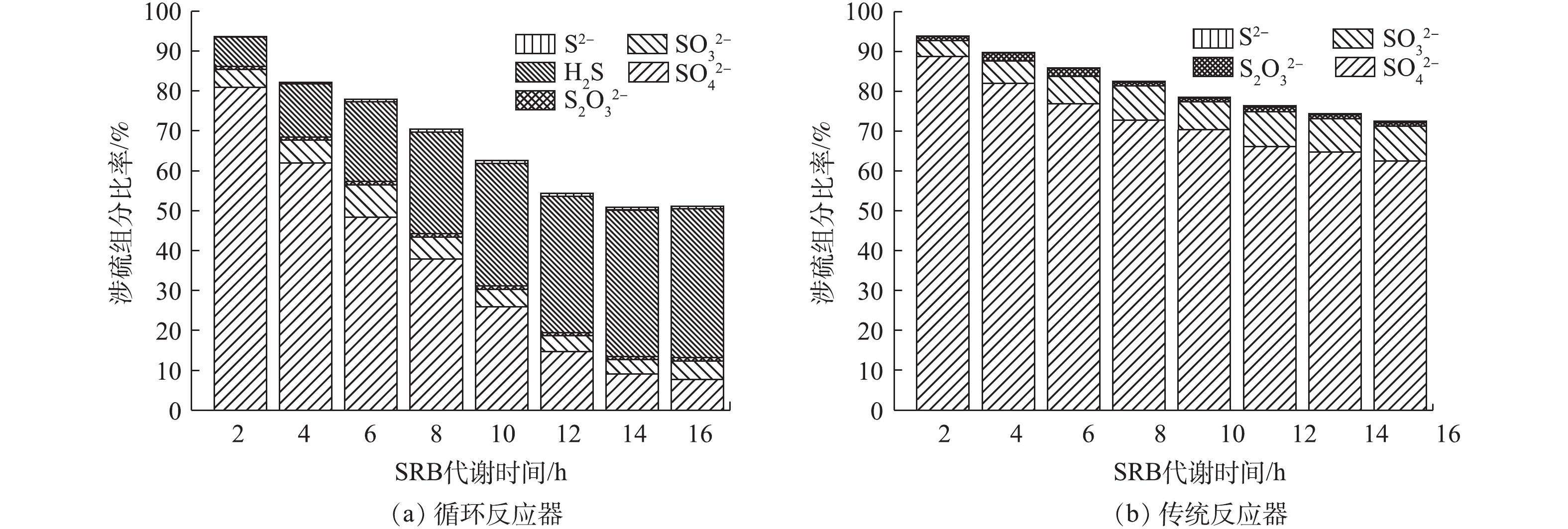
气提内循环反应器可有效解除代谢产物H2S对SRB的毒性抑制,并提高
SO2−4 的去除率。气提内循环反应器与传统反应器的涉硫组分比率变化如图2所示。由图2可知,气提内循环反应器中SO2−4 去除率为91.24%;传统反应器因不能及时排出H2S(S2−),其SO2−4 去除率仅为36.5%。在气提内循环反应器中,SO2−4 主要转化为SO2−3 和H2S(图2(a)),随着H2S的产率增加,SO2−3 逐渐降低,SO2−3 作为SO2−4 和H2S的中间产物,成为代谢转化的限速因素。H2S作为SO2−4 还原的最终产物,其浓度较高时会对SRB产生毒性抑制。FIRMINO等[17]、ZHAO等[18]发现H2S会导致反应器中微生物活性和硫酸盐降解率的下降。BIJMANS等[14]对生物反应器内硫化物进行了去除,发现微生物代谢活性可由13 mmol·(L·d)−1上升至51 mmol·(L·d)−1。气提内循环反应器的SO2−4 去除率较传统反应器高,其原因是气提内循环反应器及时去除反应产物H2S,从而促进反应的进行,且解除S2−累积富集对SRB的毒性抑制。 -
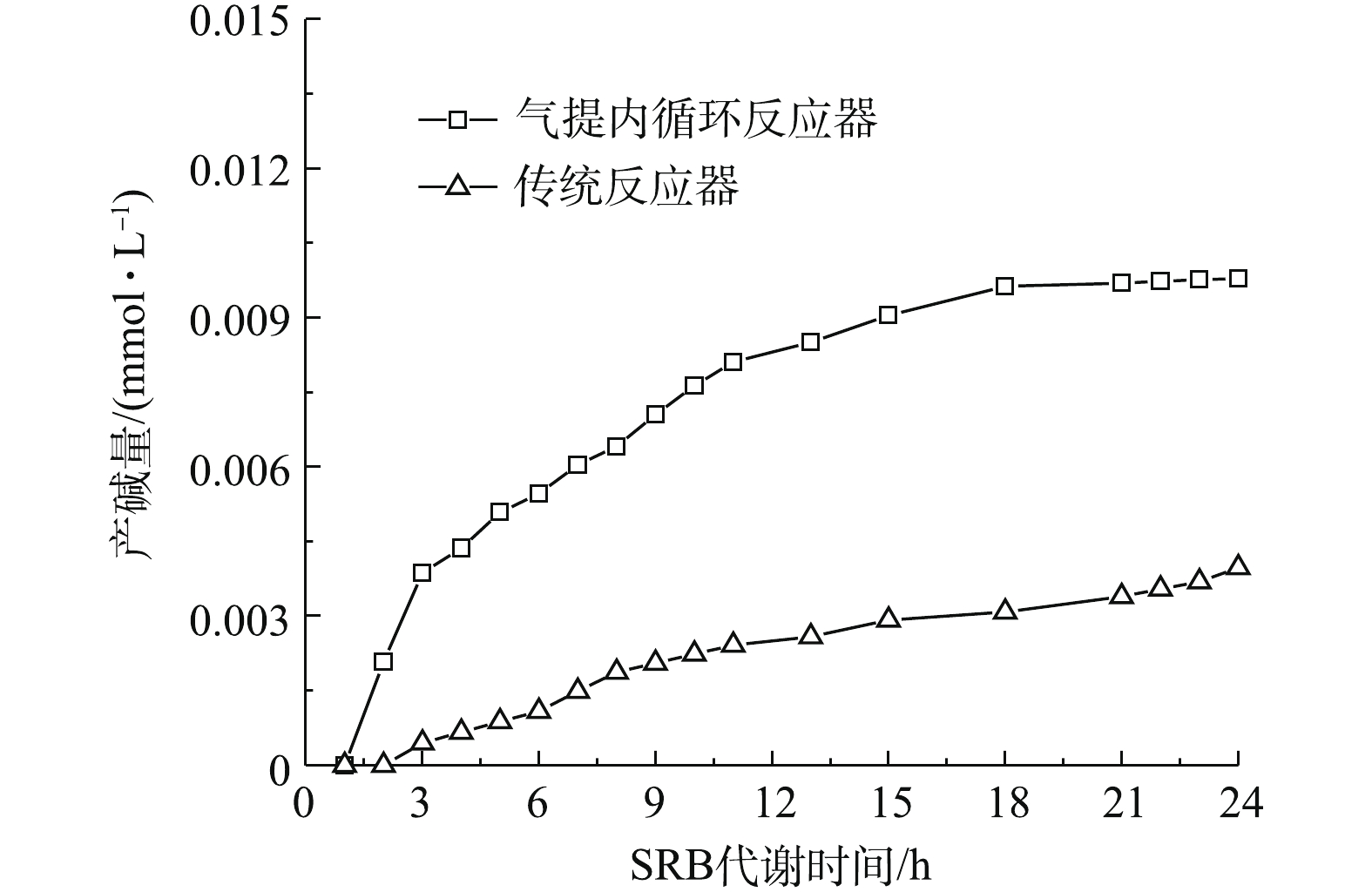
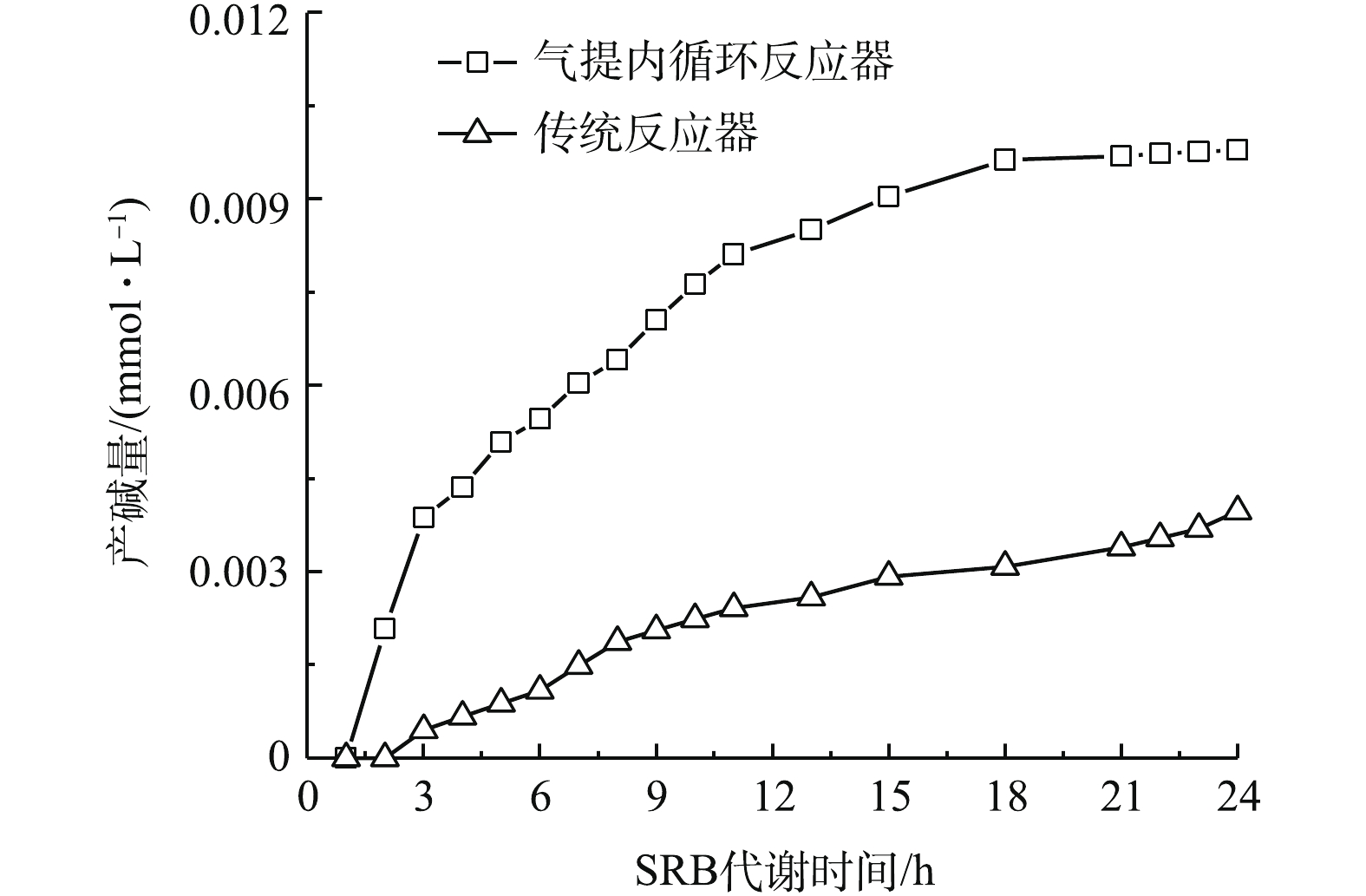
气提内循环反应器可避免AMD与SRB的直接接触所造成的毒性抑制与冲击,可实现较高的产碱效率。气提内循环反应器的产碱量变化情况如图3所示。由图3可知,气提内循环反应器的产碱量是传统反应器的3倍。在SRB代谢乳酸盐过程中会产生
HCO−3 ,使得反应器内碱度逐渐增加[19],其反应机理[20]如式(1)和式(2)所示。系统中存在的Fe2+能促进各种酶的合成,缩短反应迟滞,促进SRB还原反应的进行[21-23],导致pH上升。随着反应的进行,
SO2−4 逐渐转化为H2S,气提内循环反应器将H2S去除,不仅能使水体中OH−增加,还能避免S2−积累对SRB的毒性抑制。 -
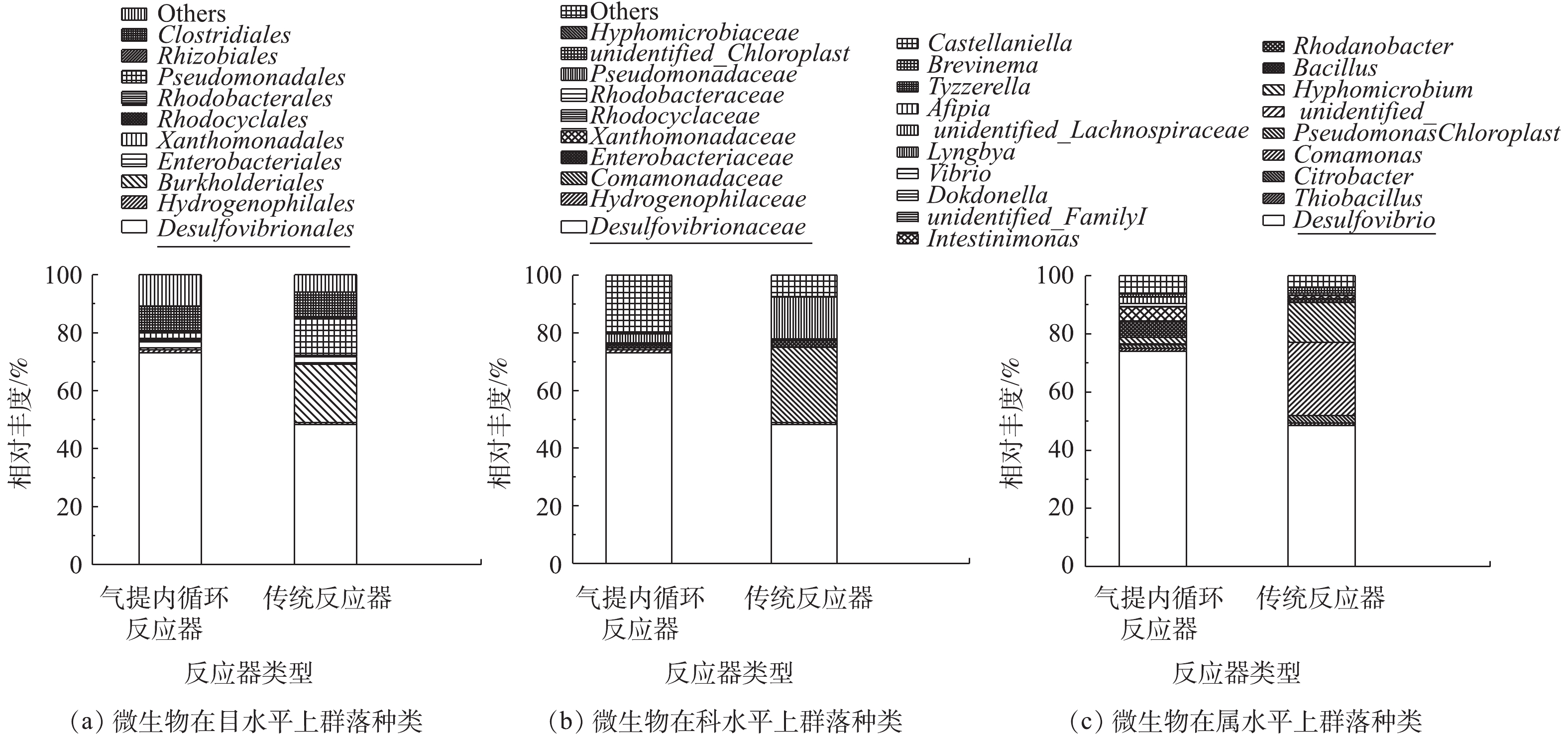
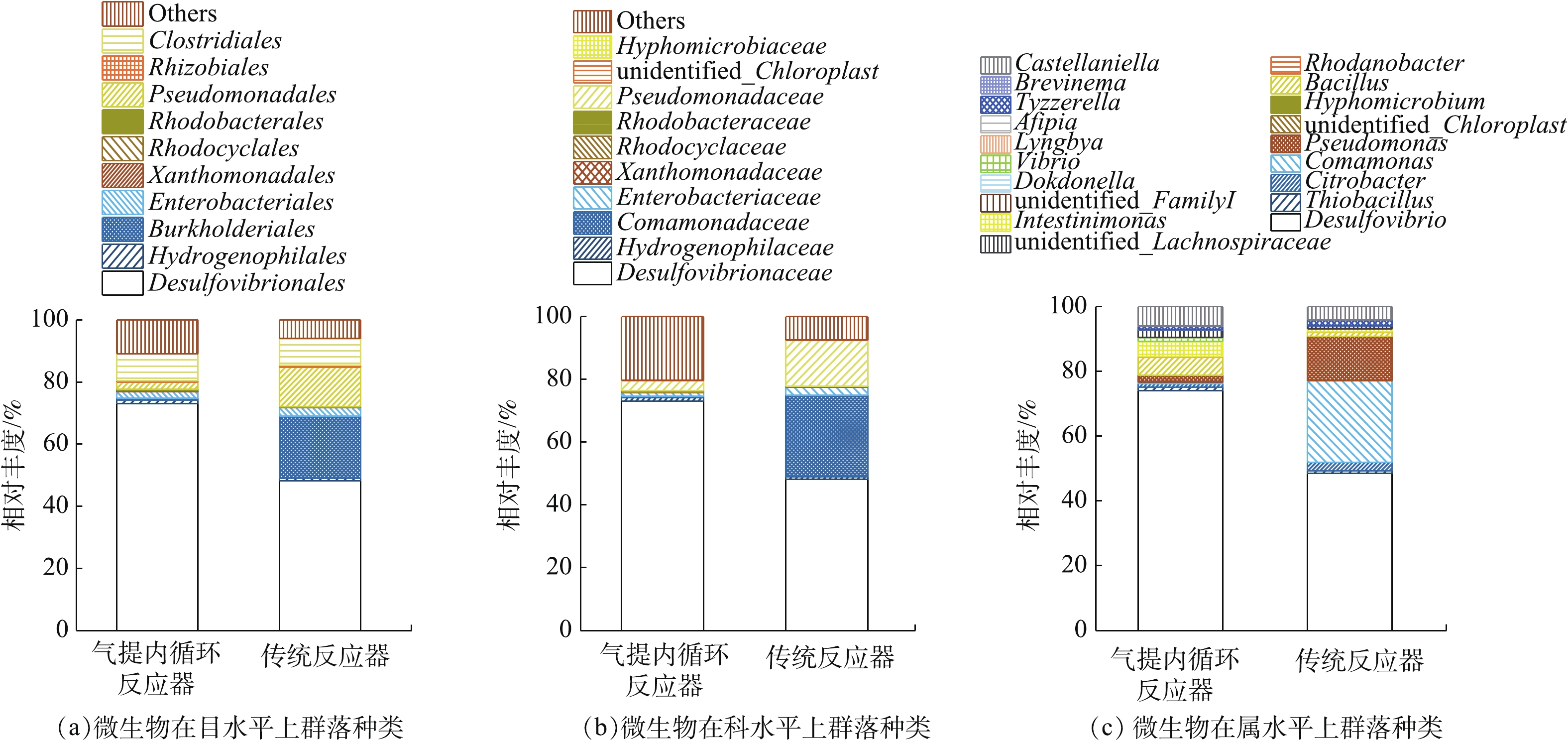
根据Barcode处理数据得到有效数据,再利用Uparse软件对所有样品的有效数据进行聚类,筛选出OTUs(operational taxonomic units,默认以97%的一致性序列聚类),并利用SSUrRNA数据库对OTUs进行物种注释分析,获得目、科、属群落组成(图4)。由图4可知,气提内循环反应器中脱硫弧菌(Desulfovibrio)在目、科、属水平上的相对丰度均为73%,传统反应器中脱硫弧菌的相对丰度仅为48%,对比2个反应器中菌属丰度,传统反应器中丛毛单胞菌(Comamonas)、柠檬酸杆菌属(Citrobacter)、假单胞菌(Pseudomonas)的相对丰度较气提内循环反应器明显增多。在适宜的环境条件下,SRB生长速度最快,能竞争到更多的营养物,使其在体系中的相对丰度较其他微生物高;当环境因素(pH、毒性物质的产生及含量等)改变时,SRB会对环境条件做出快速反应(调节体内代谢过程或改变细胞结构等),其内在生长速率也会发生变化[24]。传统反应器中pH(3.01)较低、代谢S2−积累和重金属离子的毒性抑制,均会导致SRB的竞争能力变弱、数量减少,而气提内循环反应器可解除酸、重金属及代谢S2−对SRB活性的多重抑制,充分发挥系统内优势菌属脱硫弧菌的还原能力。
-
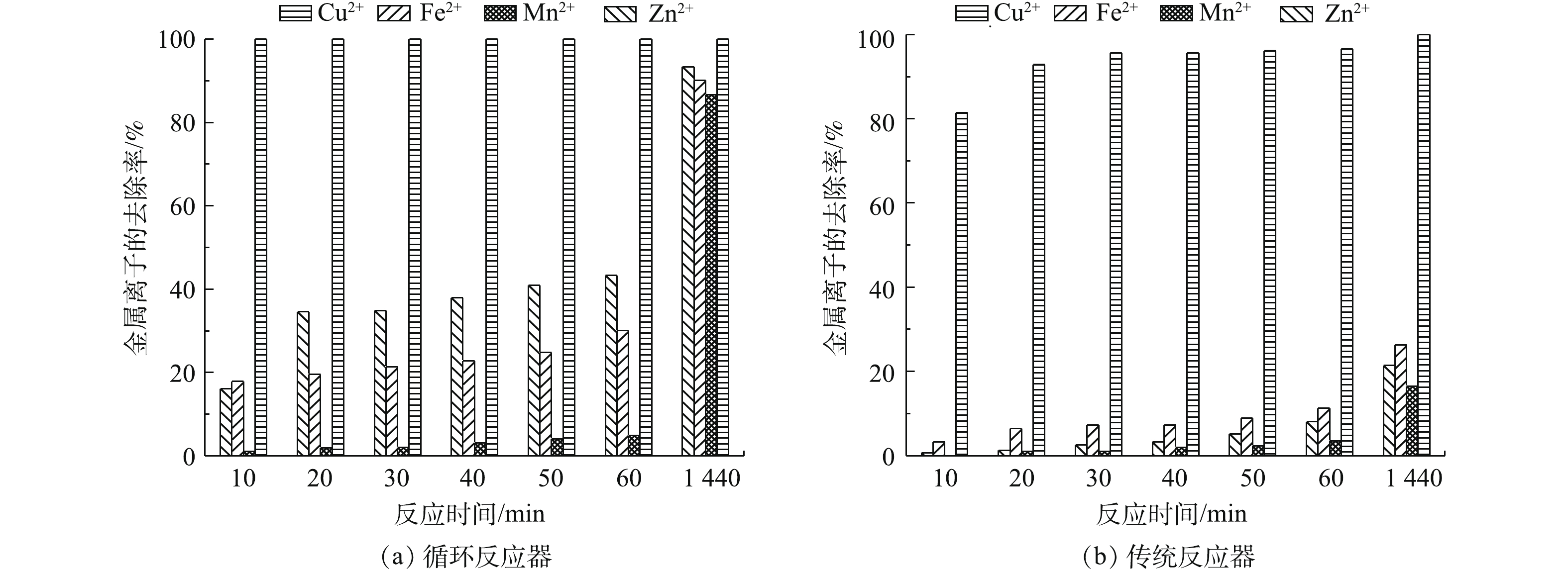
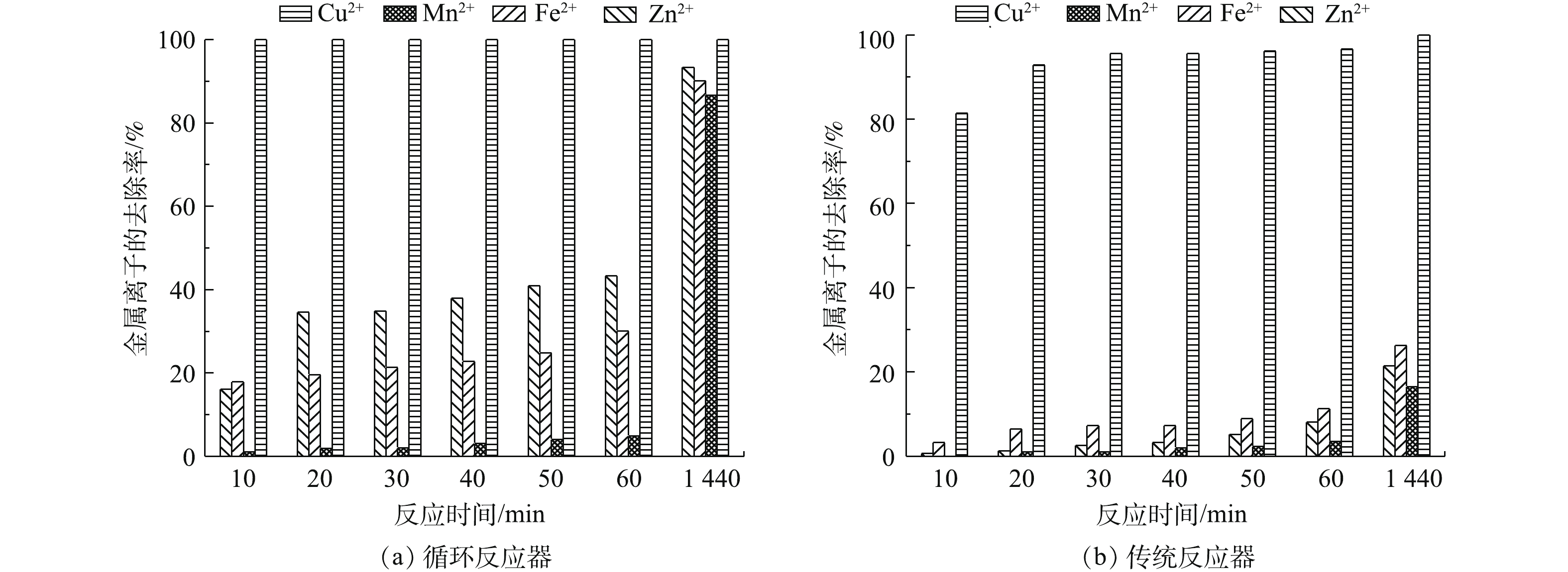
气提内循环反应器对AMD中重金属离子的去除效果较传统反应器好。气提内循环反应器和传统反应器对金属离子的去除效果如图5(a)和图5(b)所示。气提内循环反应器内Cu2+、Mn2+、Zn2+、Fe2+的去除率分别为100%、86.67%、93.34%、90.14%,Cu2+和Zn2+的出水浓度分别为0 mg·L−1和2 mg·L−1(表1),可达到《污水综合排放标准》二级标准;而在传统反应器内,Cu2+、Mn2+、Zn2+、Fe2+的去除率分别仅为96.6%、16.5%、21.4%、26.3%。反应器中Cu2+较其他金属离子容易去除的原因是,CuS的Ksp相较于ZnS、MnS、FeS等金属硫化物低,其溶度积常数顺序为MnS>FeS>ZnS>CuS[25-26];气提内循环反应器的金属去除率较传统反应器高,在气体内循环反应器中各金属的去除率为Cu2+>Zn2+>Fe2+>Mn2+,但在传统反应器中Fe2+的去除率较Zn2+高,产生该结果的原因是传统反应器内SRB酶的合成需要消耗大量的Fe2+[21]。
传统SRB反应器采用生化出水直接与重金属混合沉淀,但生化出水中除S2−外,还含有大量无效组分(如硫代硫酸根以及溶解性微生物产物、胞外多聚物等[1]),导致沉淀物中除金属硫化物外还含有其他复合物。气提内循环反应器运用目标代谢产物H2S与重金属沉淀,反应结束后,对该反应器中的沉淀物进行了XRF分析。结果表明,沉淀物中含有3.9% Cu、4.27% Zn、5.28% Mn、35.78% Fe、48.89% S,这说明目标代谢产物H2S与重金属产生的金属硫化物不含其他复合组分,且该金属硫化物的纯度可达98.12%。
-
1) H2S作为
SO2−4 还原的最终产物,会对SRB产生毒性抑制;气提内循环反应器可有效解除H2S对SRB的毒性抑制,SO2−4 去除率由36.5%(传统反应器)提升至91.24%。2)气提内循环反应器可避免AMD与SRB直接接触所造成的毒性抑制和冲击,实现较高的产碱效率,产碱效率是传统反应器的3倍。
3)体系中环境条件会影响脱硫弧菌属与丛毛单胞菌、柠檬酸杆菌属、假单胞菌之间的竞争;气提内循环反应器解除了多重抑制对脱硫弧菌属的活性影响,其相对丰度由传统反应器的48%提升至73%。
4)气提内循环反应器对AMD中重金属离子去除效果优于传统反应器。气提内循环反应器中Mn2+、Zn2+、Fe2+的去除率为86.67%、93.07%、90.14%,其金属硫化物的纯度可达98.12%,出水Cu2+和Zn2+浓度分别为0和2 mg·L−1,可达到《污水综合排放标准》二级标准。




 下载:
下载: