-
复配农药的出现,解决了现有作物病虫害对农药产生的交叉抗性及多抗性问题[1],主要遵循复配农药有效成分不应发生化学反应[2],不改变其理化性质的原则,以达到农药增药效、减药害的效果[3]。目前,农药污染土壤修复技术主要包括物理修复、化学修复以及生物修复。其中,物理修复和化学修复两种技术同时具备周期短、效率高等优异特性,但也存在工程量大、费用高、容易产生二次污染等缺点。基于以上特征,物理修复与化学修复更适合用于高农药残留浓度的土壤修复,如农药现场污染修复。生物修复虽然修复周期相对较长,但由于其经济环保,对生态系统友好等优点,更适合于中低残留浓度农药污染土壤的修复,如农田土壤。目前应用较多的农田土壤生物修复主要包括微生物修复、植物修复、菌根修复等。基于此,本文综述了近年来主要复配农药在土壤环境中主要降解方式及重要环境行为,旨在为复配农药在土壤环境修复中的研究提供有价值的参考。
-
农药的合理复配不仅可以增强药效,克服和缓解抗药性,还可以加强兼治病虫害的作用,减少用药次数进而节约防治成本[4]。复配农药虽在使用过程中有很多好处,但不可随意复配混用。复配农药不合理不仅无益,而且会产生相反的效果。因此,农药在复配使用时应注意以下几点[5]:
(1)物理性状不变原则:复配农药不能出现分层、悬浮率降低、絮结、沉淀或变色,也不能出现发热、产生气泡等现象。
(2)无化学反应原则:复配农药在选择原药剂的情况下,关注药剂酸碱性及其结构特性和其他化学性质,避免在复配过程中发生化学反应,而产生药害,降低药效。
(3)交互抗性农药不复配原则:具有交互抗性的药剂,制成复配农药后会加速作物病虫害抗药性的产生,故不能混用。
(4)生物农药不与杀菌剂混用原则:农药杀菌剂大多对生物农药有害,使得生物农药不能发挥作用,复配农药没有意义。
-
近年来,随着农田杂草群落的演变,化学除草剂得到广泛的发展,单一除草剂的施用已无法解决多种杂草产生的危害,多种除草剂的配合使用得到人们越来越多的重视。除草剂的复配一般将持效期长、短不同的除草剂,或将内吸传导性与触杀性除草剂进行混合搭配使用;根据杀虫谱互补,杀单子叶杂草的除草剂与杀双子叶杂草的除草剂混用[6]。其目的在于扩大除草范围、延长除草持效性、减少药害、降低成本,了解分析发现代表性复配除草剂具有以下特点,如表1所示。
-
目前,许多害虫对农药单一制剂均产生有不同程度的抗性,研究发现,将具有不同作用机制的农药配合使用是延缓抗药性发展的最有效方法之一[7]。杀虫剂之间的复配就是将不同类型、不同作用方式的杀虫剂复配,目前主要有有机磷类和有机磷类复配、有机磷与拟菊酯类复配、有机磷与氨基甲酸酯类复配、有机氮与氨基甲酸酯类复配,有机氮与拟菊酯类复配等方式,表2是复配杀虫剂典型特点。
-
杀菌剂在世界农药市场、国际作物解决方案中的作用日益凸显,科学复配杀菌剂的合理开发及利用已经成为杀菌剂在实际病害管理中的主要潮流及趋势,是延缓病原菌抗药性的最佳方式,也是发挥杀菌剂最大增效性能的途径,复配杀菌剂是兼具保护和治疗的高效药剂[8]。复配杀菌剂的主要作用效果表现在降低产品的有效成分含量、降低单位面积用药量,从而减低成本,进而达到保护环境节约资源的目的。如表3所示,列出目前使用效果较好的一些复配杀菌剂。
-
根据1985—2012年间除草剂登记情况可知,现有421个除草剂品种中,复配除草剂有255个[37],占比60.6%。除草剂的混用已经是除草剂的大趋势,但是复配除草剂对土壤的污染不容忽视,针对不同复配除草剂在土壤中的降解情况,现今已有很多成就。
-
磺酰脲类除草剂是目前最大类除草剂,具有适用范围广、持效期长,低毒性、作物安全性、用量低等优异特点[38]。喹啉羧酸类除草剂是一类激素类除草剂,在土壤中残留量较大,对后茬作物易产生药害[39]。苄嘧磺隆与二氯喹啉酸除草剂复配作为此类复配的代表在的土壤中的降解研究已有一定的进展。
桑丽雅[40]利用从二氯喹啉酸、苄嘧磺隆污染土壤中筛选出苍白杆菌属LS菌株(Ochrobactrum sp. LS),研究苍白杆菌LS菌株对二氯喹啉酸、苄嘧磺隆及其复配农药苄·二氯的降解,实验结果显示,苍白杆菌LS菌株恒温培养8 d时对二氯喹啉酸的降解率可达到73.9%,恒温培养15 d时降解率达到90%;苍白杆菌LS菌株培养3 d和7 d时对苄嘧磺隆的降解率分别为50%、67%;而对于苄·二氯,苍白杆菌LS菌株以苄·二氯为唯一碳源,恒温培养9 d时,对复配剂中二氯喹啉酸和苄嘧磺隆的降解率分别为90.4%和50.9%,恒温培养15 d时,对两者的降解率可分别达到95.2%、67.5%,均较单一除草剂的降解率有所升高。
-
酰胺类除草剂在除草剂市场占有重要地位,是一种高效、高选择性除草剂,全世界酰胺类除草剂销量前三分别为乙草胺、丙草胺、甲草胺,主要用于防治一年生禾本科杂草和部分阔叶杂草[41-42]。磺酰脲类除草剂与酰胺类除草剂混配,可使除草剂具有杀草谱广、成本低、使用方便等优异特点,
据了解丁草胺与苄嘧磺隆除草剂的复配农药是目前稻田使用最广泛的除草剂之一[43],长期大量使用导致这种复配除草剂已严重污染了植物、土壤和水,可能破坏土壤微生物群落结构,降低土壤肥力[44],故针对苄嘧磺隆与丁草胺的复配现已有许多研究成果。刘军和霍光华[45]通过富集纯化得到两株能同时降解丁草胺和苄嘧磺隆的真菌菌株Dx9和Dx12,经测定菌种分别为青霉属(Penicillium expansum)Y2-08和曲霉属(Aspergillus fumigatus)Dx12,两者均能以丁·苄复配除草剂为唯一碳源生长,恒温培养3 d时,Dx9和Dx12降解菌对丁草胺的降解率分别为87.3%和92.1%,对苄嘧磺隆的降解率分别为95.6%和88.5%,是十分可观的降解能力。李春艳等[46]利用筛选出来的苄嘧磺隆高效降解菌(Rhodococcus sp.)BX2和丁草胺高效降解菌(Acinetobacter sp.)LYC-1通过原生质体融合技术进行原生质体融合及再生,获得融合菌F1,并进行降解分析实验,发现菌株在培养7 d时,单菌株BX2对苄嘧磺隆的降解率为73.52%、单菌株LYC-1对丁草胺的降解率为50.63%,而融合菌F1对苄嘧磺隆和丁草胺的降解率可分别达到65.35%和62.41%。
-
三嗪类除草剂早在在上世纪中期就已得到广泛应用,具有很长的应用历史,使用量较大,但其残留时间较长。三嗪类除草剂通过光合系统Ⅱ(PSⅡ)以D1蛋白为作用靶标,抑制植物的光合作用而发挥作用,用于控制一年生草本科植物及阔叶杂草的生长。在实际应用过程中,常与其他类除草剂混配使用,以磺酰脲类除草剂与其复配为代表。
王磊[47]在复配农药使用的土壤中,经过多次划线分离得多株降解菌,分别测定恒温培养7 d时,菌株对烟嘧磺隆和莠去津的降解率,发现烟嘧磺隆最优降解菌为YU6,降解率为17.68%,莠去津最佳降解菌为YU5,降解率为14.9%,两菌株分别为弗氏柠檬酸杆菌(Citrobacter freundii)YU6和苍白杆菌(Ochrobactrum anthropi)U4,将YU6和U4按2∶1体积比例进行混合制备复合菌,此时复合菌对烟嘧磺隆降解率可达75.56%,对莠去津的降解率可达35.61%。王平平[48]研究了蒙脱土复合生物炭和磷酸改性生物炭对莠去津和烟嘧磺隆在土壤中消解的影响,实验结果显示,蒙脱土-花生壳复合生物炭(MMT/BC)和磷酸改性花生壳生物炭(H3PO4-BC)都抑制了莠去津在土壤中的消解,而MMT/BC加速了烟嘧磺隆在土壤中的化学消解,H3PO4-BC通过刺激微生物的活性加速了烟嘧磺隆的微生物降解。
-
杀虫剂是一类对有害昆虫基体有毒或通过其他途径可控制其种群形成或减轻、消除危害的药剂,在我国的使用历史非常久远,用量十分庞大,且品种十分丰富,近年来随着我国农业生物快速发展,杀虫剂的产量也出现了大幅上升。但由于单一农药的长期大量的使用,导致有害生物抗药性增强且环境污染日益严重,为应对这种问题,高效、低毒、环境友好的除草剂研发是现今农药研发的热点和重点,而农药复配是一种十分有效的研究手段[49]。
李惠娟和刘守庆等[50]研究了氯氰菊酯,毒死蜱及其复配剂在土壤中的降解,实验发现与两种单一农药降解相比,复配剂在土壤中的降解分为前后两个阶段,降解前期氯氰菊酯和毒死蜱的降解半衰期分别为33.0 d和63.0 d, 降解后期两者的降解半衰期分别为53.3 d和86.6 d。
啶虫脒作为氯化烟碱吡啶类化合物是一种广谱性杀虫剂,具有用量少、活性高、持效时间长等特点,常做混配剂使用[51]。赖作旺[52]研究了两种啶虫脒复配剂在土壤中的降解情况。其中啶虫脒和阿维菌素复配杀虫剂在土壤中的降解受两者浓度的影响,阿维菌素的降解不受啶虫脒浓度的影响,而啶虫脒的降解随着阿维菌素浓度升高而抑制情况加剧;此外发现啶虫脒和毒死蜱复配剂在土壤中的降解与两者在土壤中单独作用的降解无明显差异。
-
当作物同时出现由病原微生物引起的植物病害和害虫危害时,可将杀菌剂和杀虫剂进行混配使用[53],以发挥杀虫、杀菌的兼治作用。
百菌清是目前世界上最常用的广谱保护性杀菌剂之一,是由氯化苯腈组成的合成化合物[54]。百菌清在土壤中的半衰期属于中度残效期,其半衰期最高可达6个月,容易在土壤中积累残留,易富集到食物链对人体造成伤害[55-57]。硫丹作为内吸性广谱有机氯杀虫剂,在我国应用范围较广,但存在急性毒性、潜在的生物蓄积性、持久性等问题[58]。在农业应用过程中,硫丹可以与百菌清进行复合使用。目前对于硫丹单独在土壤中的微生物降解已有很多研究,Bilgin等[59]将阿菲彼亚杆菌(Afipia geno sp.),嗜酸单胞菌Q1(Sphingomonas yanoikuyae Q1)和罗得西亚甲基杆菌(Methylobacterium rhodesianum)的3种菌制成联合体,实验发现在pH6.5时该联合体对硫丹的降解率为59%(63%α-硫丹和57%β-硫丹);在pH8.4时该联合体对硫丹的降解率为98%(96%α-硫丹和97%β-硫丹)实验发现在没有额外碳源的情况下博代氏杆菌属(Bordetella sp. B9)能降解80%的α-硫丹和86%的β-硫丹。郝乙杰[60]通过实验研究了硫丹、百菌清复合农药在土壤中降解的相互影响,结果显示硫丹与百菌清在土壤中的降解是相互抑制的作用,且作用效果与两者的浓度呈正相关;在整个测量过程中发现复配农药在土壤中的降解半衰期普遍比单一农药在土壤中的降解半衰期长。
-
复配杀菌剂的应用一定程度上能够减轻病害造成的作物影响,复配药剂的合理应用可提高药剂药效、降低病害抗药性,有利于新型杀菌剂的开发应用,可在施用过程中做到一药多防[61]。
毛江胜等[62]通过田间试验,利用高效液相色谱分析了40%吡唑醚菌酯·戊唑醇悬浮剂在山东及安徽土壤中降解规律。实验结果显示吡唑醚菌酯在土壤中残留量为0.96—3.80 mg·kg−1,其3 d消解率超过50%,5 d消解率超80%,7 d时达到90%,42 d时在土壤中未检出,其半衰期为5.2—10.8 d。戊唑醇在山东土壤中残留量为3.54 mg·kg−1,其5 d消解率达到80%,14 d时达到90%,半衰期为12.1 d;安徽土壤中残留量为17.36 mg·kg−1,其5 d消解率即可达到90%,半衰期为6.6 d,受环境影响较大。
-
为了解我国土壤修复和农药污染问题,本文分析了土壤环境中的复配农药降解情况,就目前研究现状来看,单一农药在土壤中的修复问题已被广泛研究,但是大多数复配农药的使用仍然是土壤修复过程中的一个重大问题。通过对现有复配农药在土壤环境中降解方法的研究,可以发现微生物降解是复配农药的主要降解方法。由于农药在土壤中的微生物降解受土壤环境温度、pH、含水量、营养组成以及其他微生物相互作用引起的竞争性抑制的影响,所以如何从土壤中筛选针对复配农药降解的高效降解菌是复配农药在微生物修复污染土壤过程中的首要问题。通过调查研究发现,在微生物修复复配农药污染土壤这一领域,复配除草剂的微生物降解方法研究相对较多,而缺乏对复配杀虫剂的研究,针对其他农药复配,如:杀虫剂与杀菌剂复配、杀虫剂与除草剂复配、杀菌剂复配等,在土壤中的微生物降情况的研究少之更少。
因此,对于农药污染土壤的微生物修复研究不应只关注单一药剂的降解综合方法,还应关注复配农药残留及其在土壤环境中的降解方法。微生物修复农药污染土壤的研究方向应主要有以下几方面:1. 复配农药在土壤中的降解;2. 土壤中农药高效降解菌的分离筛选;3. 高效降解农药的复合菌系的培养;4. 农药在土壤环境中的生物降解的模型定量化研究;5. 微生物修复污染土壤的新型技术的开发等。在整个微生物修复复配农药污染土壤的领域中,有待进一步研究解决的问题还有很多,这些问题一经解决,必将推动复配农药在土壤修复中的研究进入更高的层次,有助于更好地解决土壤环境中的复配农药污染问题。
复配农药污染土壤的微生物修复研究进展
Research progress of microbial remediation of soil contaminated by compound pesticide
-
摘要: 随着农药使用量的急剧增加以及农药种类的发展,农药在土壤中的残留累积情况越来越严重,引起了社会广泛的关注,但以往对农药污染的研究主要集中在农药单体上,而复配农药作为现今的使用热点,没有得到足够的重视。本文以现有复配农药在土壤环境中的研究情况为基础,针对目前应用较多的除草剂、杀虫剂、杀菌剂之间的复配情况进行分析,以典型复配农药在土壤环境中的降解情况及环境行为为研究对象,介绍复配农药在土壤环境修复中的研究进展,为农药污染处理方面提供参考。Abstract: With the rapid increase of pesticide application and the development of pesticide types, the accumulation of pesticide residues in soil is becoming more and more serious, which has aroused widespread concern in the society. However, the research on pesticide pollution at present mainly focuses on single pesticide, while combine pesticides, as a hot topic in the present, have not been paid enough attention. Based on the research of existing compound pesticides in soil environment, this paper analyzed the combined situation among herbicides, insecticides and fungicides which were widely used at present. In addition, the degradation and environmental behavior of typical combined pesticides in soil environment were taken as the research object, and the research progress of compound pesticides in soil environmental remediation was also introduced, which provided reference for pesticide pollution treatment.
-
Key words:
- combined pesticide /
- soil environment /
- remediation method /
- environmental behavior
-

-
表 1 复配除草剂特点及用途
Table 1. Characteristics and application of compound herbicide
复配除草剂
Herbicide mixture药剂
Herbicide结构式
Structural formula单剂性质
Herbicide properties单剂用途
Applicability降解菌
Degrading bacteria复配农药作用
Herbicide mixture action苄·二氯 苄嘧
磺隆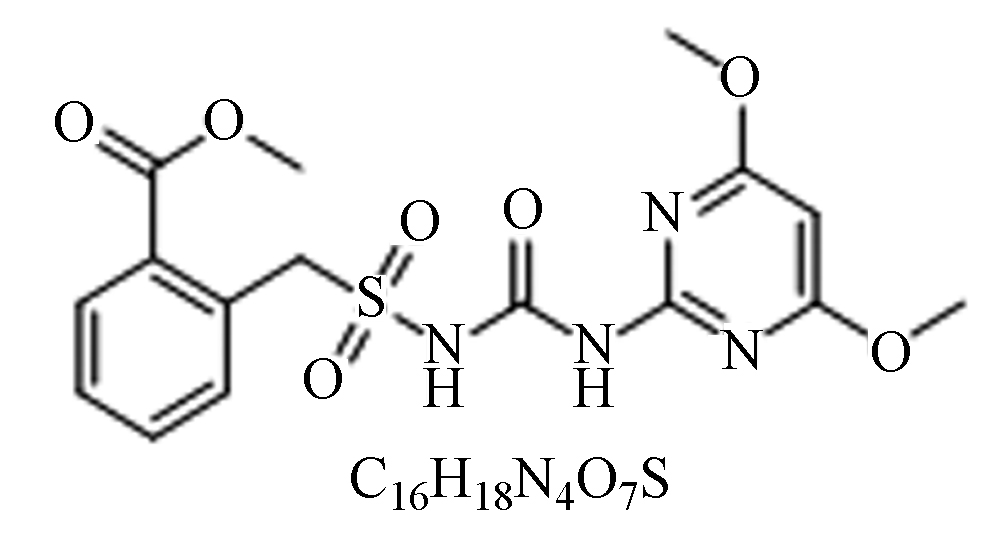
纯品:白色、无臭、固体;
性质:水溶液中稳定,酸性中分解缓慢,土壤移动性小;
毒性:低毒。择性内吸传导型除草剂,可防除水稻田莎草和阔叶杂草,麦田阔叶杂草,但是对稗草处理效果较差。 短杆菌[9]、巨大芽孢杆菌[10]、无色杆菌[11]。 扩大除草谱,适用于稻田等的不同杂草类型。 苄·二氯 二氯喹
啉酸
纯品:白色、晶体,
性质:稳定,不易降解,生物累积性;
毒性:高。选择性激素除草剂,对水稻田单子叶杂草和稗草可有效防除,对莎草和阔叶杂草的防除效果较差。 克雷伯氏菌[12]、蒙氏假单胞菌[13]。 苄·乙 乙草胺 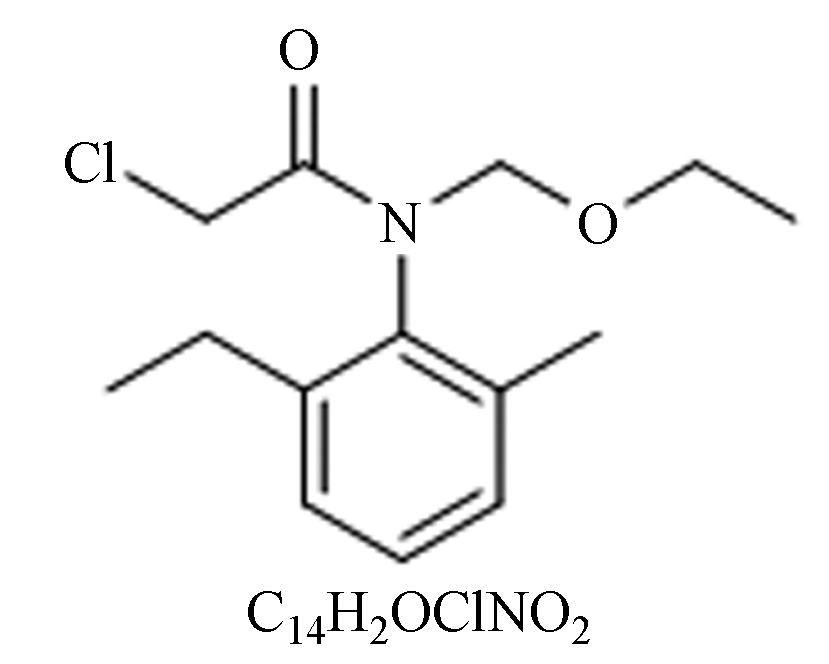
纯品:浅棕色、液体;
性质:稳定,不易挥发与光解,持久性好,土壤移动性小;
毒性:中。选择性除草剂,对棉田、玉米田、大豆田等一年生禾本科杂草和部分一年生阔叶杂草均有去除作用。 鞘氨醇单胞菌[14]、红球菌[15]、枯草芽孢杆菌[16]。 扩大杀草谱,适用于稻田和大苗移栽田。 苄·丁 丁草胺 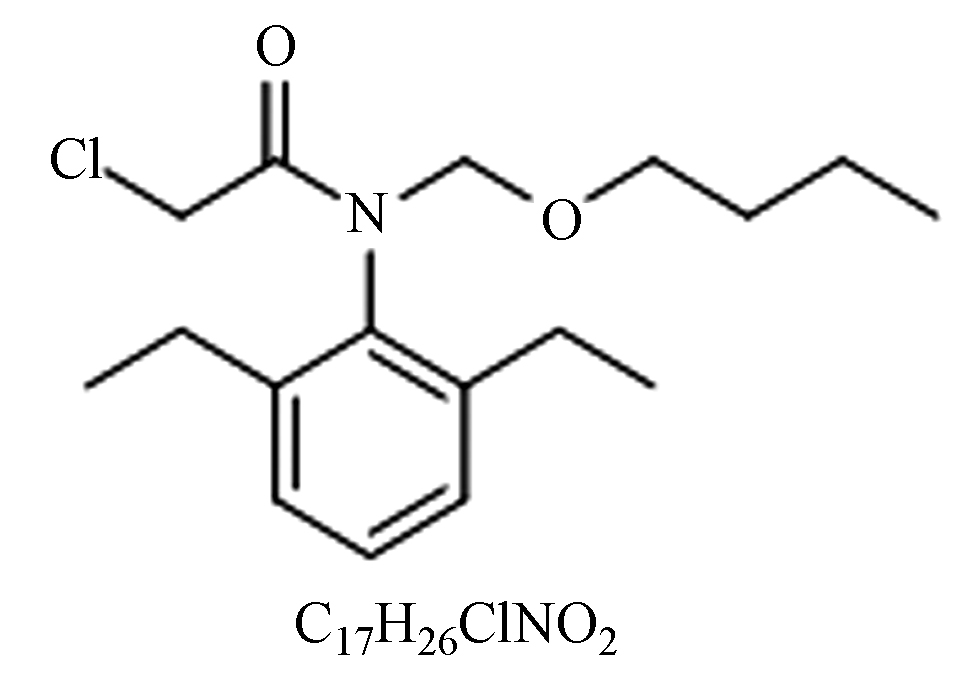
纯品:淡黄色、油状液体;
性质:常温中性、弱碱性条件下稳定,强酸加速分解,难溶于水,土壤中可降解;
毒性:对人、畜低毒。选择性内吸传导型芽前除草剂,用于防除稻田、小麦、大麦等作物田的杂草、莎草和一些阔叶杂草。 克雷伯氏杆菌[17]、代尔夫特菌[18]、恶臭假单胞菌[19]。 提高农药持效性,扩大杀草谱,可用于水稻抛秧田和移栽田。 烟·莠 莠去津 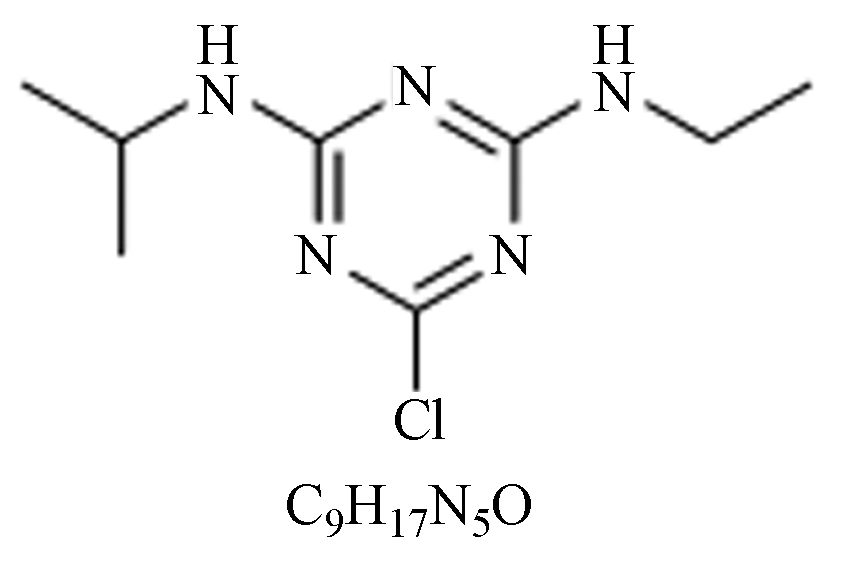
纯品:无色、结晶固体;
性质:中性、碱性、微酸性下稳定,强酸、强碱较高温度下使其水解,残效期短;
毒性:对人、畜低毒。选择内吸性传导型除草剂,防治一年生禾本科杂草和阔叶杂草,及某些多年生杂草,适用于玉米、高粱田等。 金色节杆菌、假单胞菌以及微杆菌[20]。 用于去除玉米田一年生和多年生禾本科杂草、一些阔叶杂草。 烟嘧磺隆 
纯品:白色、结晶;
性质:稀水溶液、土壤环境中易分解,残留期长。内吸性传导型除草剂,主治玉米田内一年、多年生阔叶杂草、莎草科杂草,及稗草。 黑曲霉[21]、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌[22]、枯草芽孢杆菌[23]。 烟·硝·莠 硝磺草酮 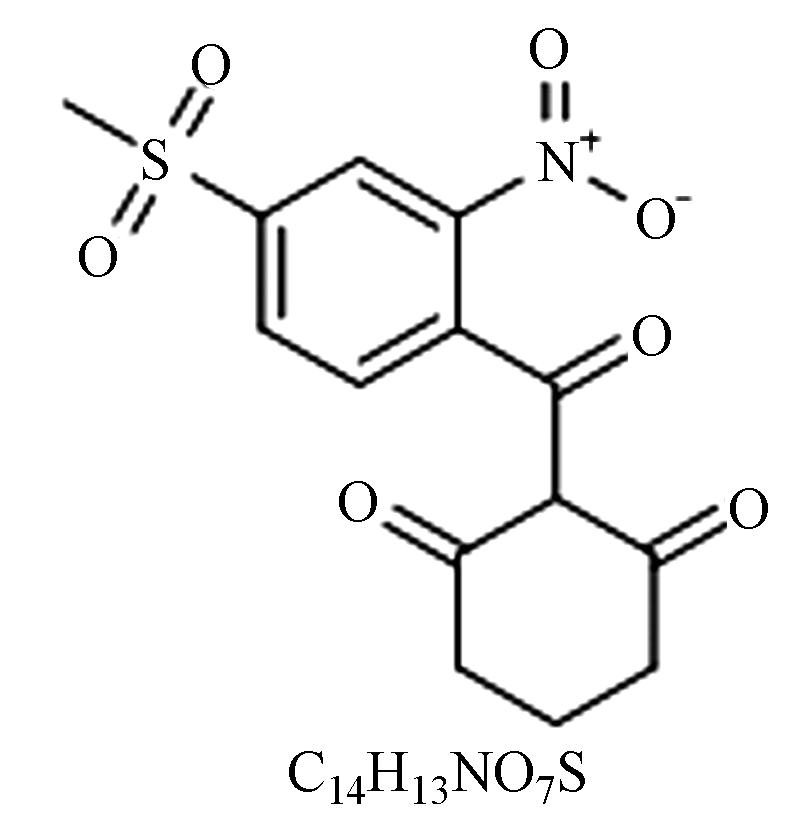
纯品:褐色、淡黄色固体;
性质:对环境无影响。广谱内吸选择性触杀型除草剂,可除玉米田里一年生阔叶杂草。 短小芽孢杆菌[24]。 属于选择性除草剂,除草迅速安全,杀草谱广,防除大部分禾、阔、莎杂草。 表 2 复配杀虫剂特点及用途
Table 2. Characteristics and application of compound insecticide
复配杀虫剂
Insecticide mixture药剂
Insecticide结构式
Pesticide properties单剂性质
Pesticide properties单剂用途
Applicability降解菌
Degrading bacteria复配作用
Insecticide mixture action氯氰·
毒死蜱毒死蜱 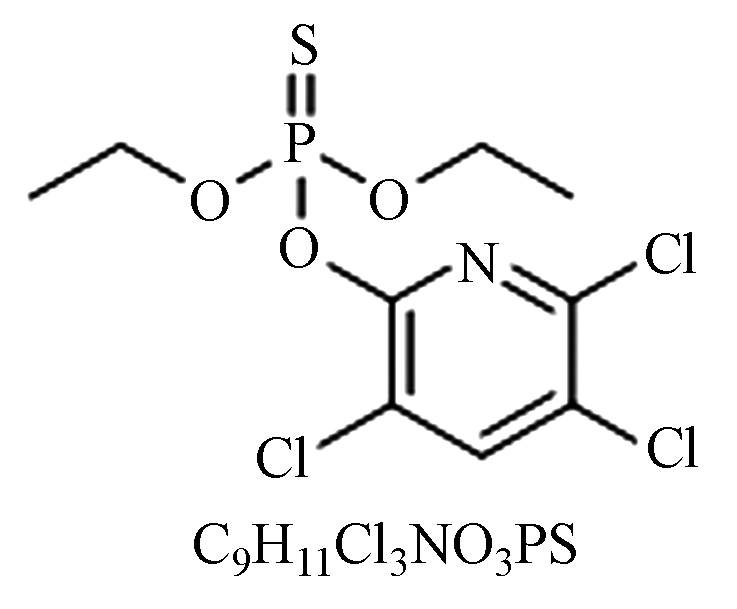
纯品:白色结晶固体;
性质:土壤残留期较长,挥发性较高。去除水稻、小麦、棉花、果蔬、茶树等,多种咀嚼式和刺吸式口器害虫。 枯黄假单胞菌[25]、苍白杆菌、硝基还原假单胞菌[26]、芽孢杆菌[27]。 增强药效,具有触杀、内吸、熏蒸、胃毒四种特效杀虫功能。适用于水稻、玉米、豆类等作物。 氯氰·
毒死蜱氯氰
菊酯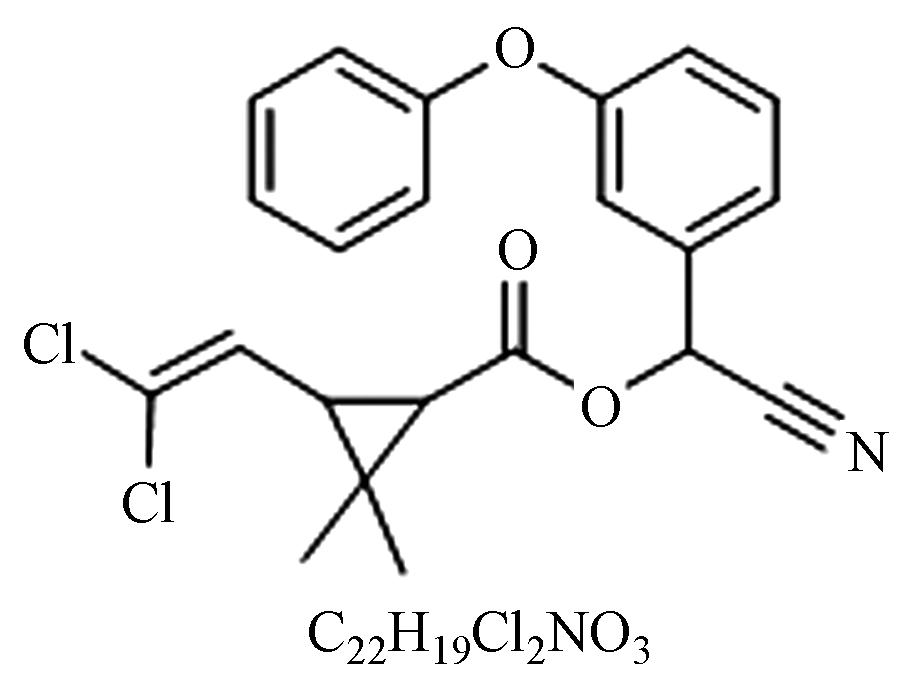
工业品:黄色至棕色、黏稠固体;
性质:对光稳定,弱酸、中性下稳定,碱性分解;
毒性:中等。对鳞翅目害虫活性极高。用于棉花、水稻、蔬菜、果树和茶叶等作物的去除,适合做土壤杀虫剂。 米曲霉[28]、鲁氏不动杆菌[29]、苏云金杆菌[30]. 毒死蜱·
吡虫啉吡虫啉 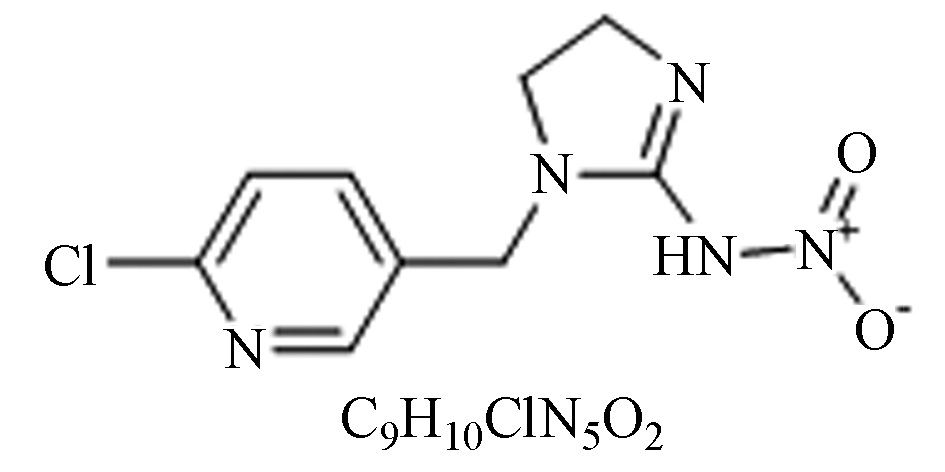
纯品:白色、晶体;
性质:土壤中稳定性高,高效、残留性低;
毒性:低毒。具有内吸、胃毒、拒食、驱避等除草作用,可防除刺吸式口器害虫及其抗性品系。 碱腈芽孢杆菌[31]、嗜麦芽寡养单胞菌[32]. 有胃毒、内吸和触杀等作用。用量少,药效高,可防除水稻、小麦、棉花等作物田的刺吸式口器害虫。 联苯·
噻虫胺联苯菊酯 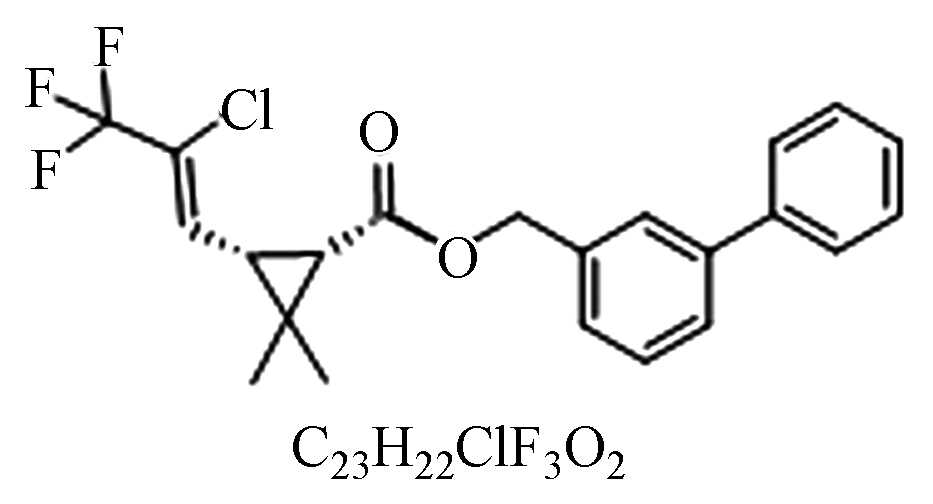
纯品:白色、固体;
性质:杀虫谱广,作用迅速,残效期长;
毒性:剧毒。杀虫、螨,防除棉花、蔬菜、果树、茶树等害虫。 醋酸钙不动杆菌[33]、代尔夫特菌[34]、寡养单胞菌[35]。 具有触杀、胃毒、熏蒸作用;且活性高、具有强内吸性。适用于防治蚜虫、跳甲、飞虱等害虫。 噻虫胺 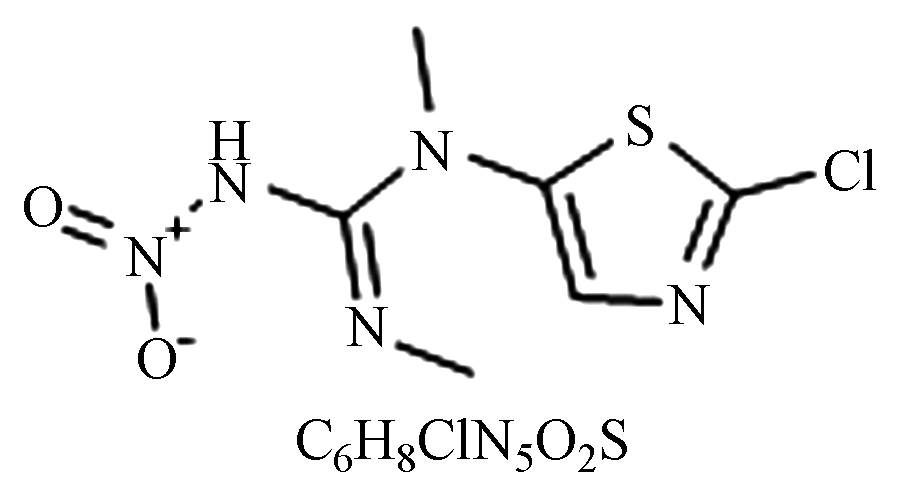
纯品:白色、结晶粉末;
性质:活性高、内吸活性好、广谱高效;
毒性:低毒。去除水稻、 果树、 蔬菜、 茶叶、 棉花等作物田的同翅目。 苍白杆菌、肠杆菌、不动杆菌、单胞菌、寡养单胞菌[36]. 表 3 复配杀菌剂特点及用途
Table 3. Characteristics and application of compound fungicide
复配杀菌剂
Bactericide
mixture药剂
Bactericide结构式
Structural formula单剂作用
Bactericide properties适用作物
Applicability复配作用
Bactericide
mixture action唑醚·
代森联吡唑醚菌酯 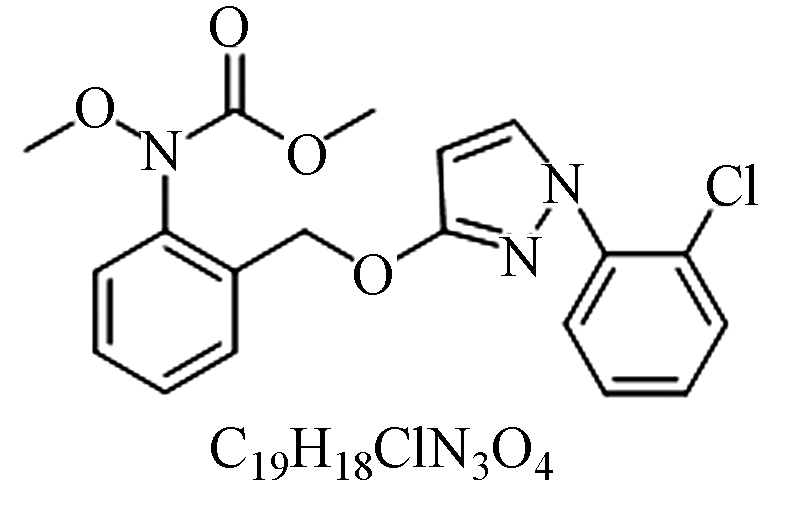
纯品:白色至浅米色、无味、结晶体;
性质:广谱杀菌,高效、广谱;
毒性:低毒。从谷物、柑橘、葡萄、香蕉、大豆、蔬菜和草坪中去除多种病原体和种子处理。 可阻碍病菌入侵、病菌传播和清除体内病菌。具有见效快、疗效可靠、药效持久、对农作物安全等优点。 代森联 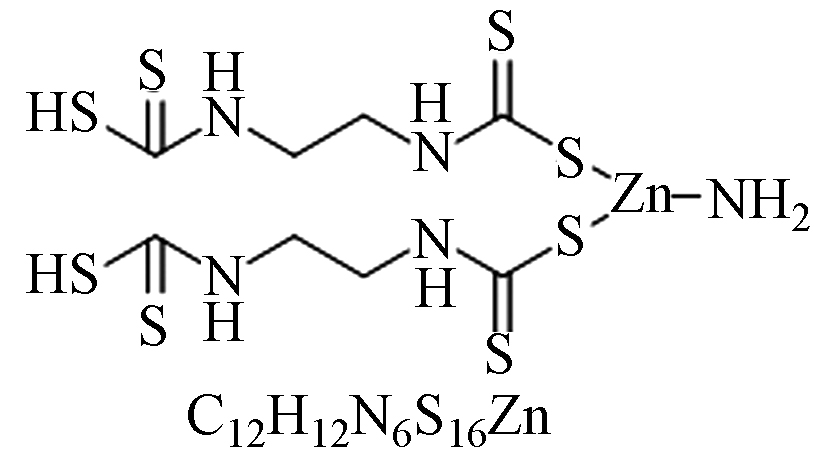
纯品:白色、粉末;
工业品:灰白色或淡黄色、粉末;
性质:保护性杀菌剂;
毒性:低毒。主要防治梨黑星病、霜霉病、瓜菜疫病、田间作物锈病等,适用于梨、苹果、香蕉、蔬菜、花卉及粮食作物。 甲霜·
霜霉威甲霜灵 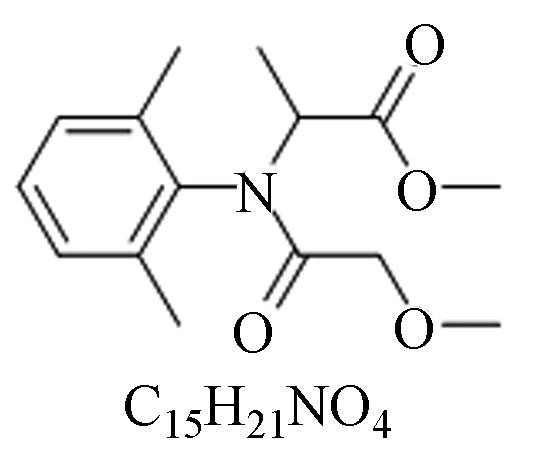
纯品:白色、晶体;
性质:在酸性、中性中稳定,高效内吸性杀菌剂,低残留,药效长;
毒性:低毒。可作为烟草、橡胶树、葡萄、啤酒花、水果、蔬菜等的杀菌剂,尤其是卵菌引起的疾病。 内吸保护性杀菌剂,适用于霜霉菌、疫霉菌、腐霉菌引起作物病害。 霜霉威盐酸盐 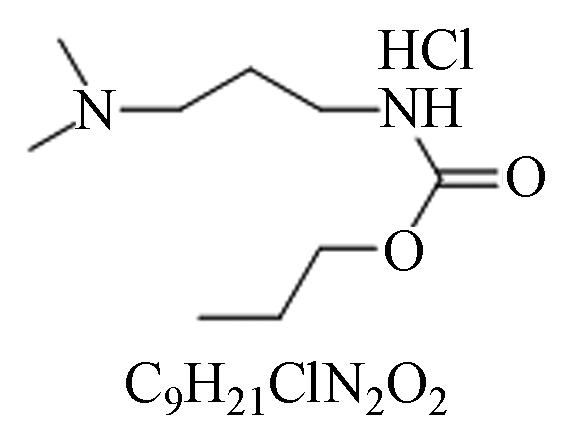
纯品:白色、晶体;
性质:土壤中稳定性高,高效、低残留;
毒性:低毒,对人、畜、植物安全等。防治霜霉病、疫病、猝倒病等病害,适用于黄瓜、西瓜、茄子、葡萄、萝卜、烟草等多种作物。 多·锰锌 多菌灵 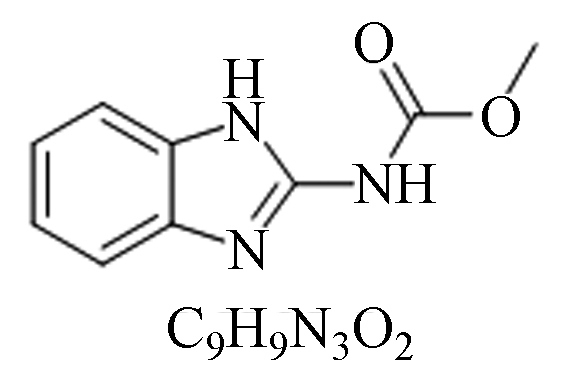
纯品:白色、结晶;
工业品:淡黄褐色、粉末;
性质:热稳定,对酸碱不稳定,高效广谱,持效期长;
毒性:低毒。内吸性杀菌剂,适用于麦类及瓜果蔬菜等,对许多子囊菌、半知菌及各种担子菌有效,可防治三麦赤霉病等。 内吸性杀菌剂,防治谱广,不易产生耐药性,持续时间长,同时具备保护和治疗作用。适用于果树、蔬菜、烟草等作物的多种真菌性病害。 代森锰锌 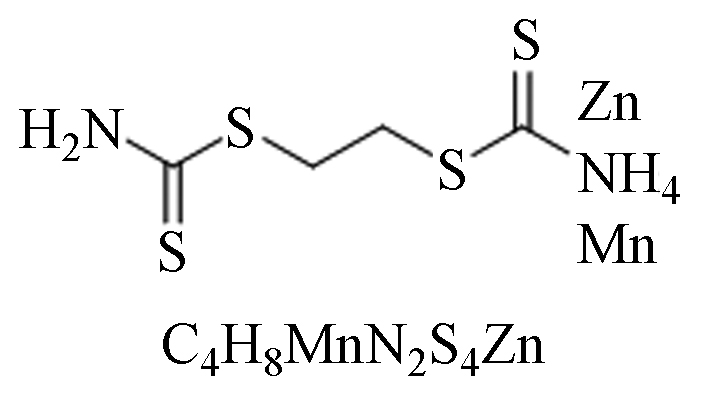
纯品:白色、粉末;
工业品:灰白色或淡黄色、粉末;
性质:广谱、低残留、高效、多作用位点;
毒性:低毒。叶面保护广谱性杀菌剂,可防治多种叶部真菌病害,可施用于果树、蔬菜以及大田作物等。 -
[1] 顾中言, 林郁. 复配农药的作用及复配原则 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 1987, 15(11): 25-26. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.1987.11.011 GU Z Y, LIN Y. Function and principle of compound pesticide [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 1987, 15(11): 25-26(in Chinese). doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.1987.11.011
[2] 王永洲. 农药的混配原则与禁忌 [J]. 科学种养, 2008(7): 62. doi: 10.13270/j.cnki.kxzh.2008.07.019 WANG Y Z. Principle and contraindication of pesticide mixture [J]. Scientific Farming, 2008(7): 62(in Chinese). doi: 10.13270/j.cnki.kxzh.2008.07.019
[3] 冯雪. 农药复配要知类型 守原则 [J]. 农村农业农民(B版), 2011(5): 42. FENG X. Pesticide mixture should know the type and abide by the principle [J]. Country Agriculture Farmers, 2011(5): 42(in Chinese).
[4] 以琴. 农药复配要科学 [J]. 北京农业, 2009(4): 44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6966.2009.04.047 YI Q. Pesticide compounding needs science [J]. Beijing Agriculture, 2009(4): 44(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6966.2009.04.047
[5] 王大海. 农药混配原则及注意事项[N]. 河南科技报, 2020-04-07(B02). WANG D H. Pesticide mixture principle and matters needing attention[N]. Henan Science and Technology News, 2020-04-07(B02) (in Chinese).
[6] 曹立耘. 农药不能盲目复配混用 [J]. 山东农药信息, 2018(2): 42. CAO L Y. Pesticides should not be mixed and used blindly [J]. Pesticide Information in Shandong, 2018(2): 42(in Chinese).
[7] 张婧, 黄治强, 王丹婷, 等. 苯甲酰脲类杀虫剂在农药复配物中的应用进展 [J]. 农药, 2015, 54(10): 703-708,723. doi: 10.16820/j.cnki.1006-0413.2015.10.001 ZHANG J, HUANG Z Q, WANG D T, et al. Application of benzoylurea insecticides in pesticidal composition [J]. Agrochemicals, 2015, 54(10): 703-708,723(in Chinese). doi: 10.16820/j.cnki.1006-0413.2015.10.001
[8] 周明国. 杀菌剂的复配及其增效与拮抗作用//第二届中国植物病害化学防治学术研讨会[C]. 2000. ZHOU M G. Compound of fungicide and its synergistic and antagonistic effects//The 2nd Chinese Symposium on Chemical Control of Plant Diseases[C]. 2000 (in Chinese).
[9] LIN X Y, YANG Y Y, ZHAO Y H, et al. Biodegradation of bensulfuron-methyl and its effect on bacterial community in paddy soils [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2012, 21(5): 1281-1290. doi: 10.1007/s10646-012-0882-7 [10] 林晓燕. 苄嘧磺隆降解菌的分离鉴定特性研究及生态学研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2008. LIN X Y. Isolation, identification and characteristics of bensulfuron-methyl-degrading bacteria and effects of bensulfuron-methyl on soil microbial ecology[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2008(in Chinese).
[11] 李阳阳. 苄嘧磺隆降解菌株的分离、降解特性及降解途径研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2013. LI Y Y. Isolation and characterization of a bensulfuron-methyl-degrading strain and its degradation pathway[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2013(in Chinese).
[12] 贺亚斐, 张来星, 曹子敬, 等. 1株二氯喹啉酸降解菌的分离、鉴定及降解特性研究 [J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2020, 54(4): 657-663. doi: 10.16445/j.cnki.1000-2340.2020.04.014 HE Y F, ZHANG L X, CAO Z J, et al. Study on the isolation, identification and degradation characteristics of a strain of quinclorac degrading bacteria [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2020, 54(4): 657-663(in Chinese). doi: 10.16445/j.cnki.1000-2340.2020.04.014
[13] 俞程. 二氯喹啉酸降解菌的筛选及其对油菜苗期的修复效应[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2018. YU C. Screening of quinclorac degrading bacteria and its remediation effect on rape seedlings[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2018(in Chinese).
[14] 陈青, 姚利, 王成红, 等. 乙草胺降解菌Sphingomonas sp. DC-6的分离鉴定及其代谢途径的初步研究 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2013, 15(5): 67-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0864.2013.05.10 CHEN Q, YAO L, WANG C H, et al. Isolation and characterization of acetochlor-degrading strain Sphingomonas sp. DC-6 and preliminary studies on its metabolic pathway [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013, 15(5): 67-74(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0864.2013.05.10
[15] 周庆新, 王军华, 陈蕾蕾, 等. 乙草胺降解菌株Rhodococcus sp. AC-1的分离及降解特性研究 [J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(4): 662-669. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2016.04.0662 ZHOU Q X, WANG J H, CHEN L L, et al. Isolation of acetochlor-degrading bacterium Rhodococcus sp. AC-1 and its degradability [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(4): 662-669(in Chinese). doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2016.04.0662
[16] 闫志宇, 翟蓓蓓, 张娟, 等. 乙草胺降解菌Bacillus subtilis L3的土壤修复效果研究 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(2): 65-71. YAN Z Y, ZHAI B B, ZHANG J, et al. Research on the soil restoration effect of an acetochlor-degrading strain Bacillus subtilis L3 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(2): 65-71(in Chinese).
[17] 彭亚军. 丁草胺降解菌的筛选及其对水稻的生物修复作用[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2012. PENG Y J. Screening of butachlor-degrading strain and its bioremediation to rice[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2012(in Chinese).
[18] 程小梅. 丁草胺降解细菌C-5的降解特性研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2013. CHENG X M. Research on characteristics of a butachlor degrading bacterium C-5[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2013(in Chinese).
[19] WANG J H, LU Y T, CHEN Y Y. Comparative proteome analysis of butachlor-degrading bacteria [J]. Environmental Geology, 2008, 53(6): 1339-1344. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-0742-6 [20] 王娅丽, 朱姗姗, 杨峰山, 等. 莠去津降解菌泛基因组测序及比较基因组分析 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2019, 35(7): 90-99. WANG Y L, ZHU S S, YANG F S, et al. Pan-genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of atrazine-degrading bacteria [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2019, 35(7): 90-99(in Chinese).
[21] 王佳颖, 郑宇, 王振梅, 等. 黑曲霉YF1菌株固体菌剂对烟嘧磺隆降解效果研究 [J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2020, 43(6): 95-100. WANG J Y, ZHENG Y, WANG Z M, et al. Study on degradation of nicosulfuron by Aspergillus niger YF1 strain solid inoculum [J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2020, 43(6): 95-100(in Chinese).
[22] 张晨芳. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)降解烟嘧磺隆的作用机制研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2020. ZHANG C F. Study on the degradation mechanism of nicosulfuron by Bacillus velezensis[D]. Baoding, China: Hebei Agricultural University, 2020(in Chinese).
[23] KANG Z H, REN C C, ZHANG J L, et al. Purification and cloning of nicosulfuron-degrading enzymes from Bacillus subtilis YB1 [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 2014, 50(1): 30-34. doi: 10.1134/S0003683814010049 [24] 韩海涛, 刘婕, 高云飞, 等. 硝磺草酮降解菌的分离鉴定及其降解特性 [J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2013, 32(3): 62-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2421.2013.03.012 HAN H T, LIU J, GAO Y F, et al. Isolation, identification and characterization of a mesotrione-degrading bacterial strain [J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2013, 32(3): 62-66(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2421.2013.03.012
[25] 蒋秋悦. 毒死蜱降解菌的分离、鉴定以及联合植物促生菌对土壤的改良[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2015. JIANG Q Y. The isolation and identification of chlorpyrifos degrading bacteria and its effect on soil amendment with PGPR[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2015(in Chinese).
[26] 李文华. 毒死蜱降解菌的分离、筛选及其降解条件的优化[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2013. LI W H. Isolation, identification of chlorpyrifos degradation bacteria and optimization of degradation conditions[D]. Taian, China: Shandong Agricultural University, 2013(in Chinese).
[27] 杜晓敏, 王金花, 朱鲁生, 等. 毒死蜱降解菌降解特性及其降解条件优化 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(10): 2437-2445. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0212 DU X M, WANG J H, ZHU L S, et al. Characteristics of a chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterial strain and optimization of its degradation conditions by response surface methodology [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(10): 2437-2445(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0212
[28] 陈锐, 门欣, 瞿佳, 等. 高效氯氰菊酯降解菌米曲霉SSCL-3的分离筛选及降解能力研究 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(10): 2274-2280. CHEN R, MEN X, QU J, et al. Biodegradation of β-cypermethrin by newly isololate strain, Aspergillus oryzae SSCL-3 [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(10): 2274-2280(in Chinese).
[29] 陈春琳, 张莉, 龙娜娜, 等. 鲁氏不动杆菌降解高效氯氰菊酯条件的响应面优化 [J]. 成都医学院学报, 2020, 15(5): 557-562. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2257.2020.05.003 CHEN C L, ZHANG L, LONG N N, et al. Response surface optimization of the degradation conditions of beta-cypermethrin by Acinetobacter lwoffii [J]. Journal of Chengdu Medical College, 2020, 15(5): 557-562(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2257.2020.05.003
[30] PANKAJ, NEGI G, GANGOLA S, et al. Differential expression and characterization of cypermethrin-degrading potential proteins in Bacillus thuringiensis strain, SG4 [J]. 3 Biotech, 2016, 6(2): 1-13. [31] SHARMA S, SINGH B, GUPTA V K. Assessment of imidacloprid degradation by soil-isolated Bacillus alkalinitrilicus [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 186(11): 7183-7193. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-3919-y [32] 宋贵珍, 孙永亮, 苏斌, 等. 吡虫啉降解菌BCL-1的分离鉴定及对桑园污染土壤的修复//中国蚕学会2018年学术年会论文集[C]. 咸阳, 2018. SONG G Z, SUN Y L, SU B, et al. Isolation and identification of imidacloprid degrading bacterium BCL-1 and remediation of polluted mulberry orchard soil//Chinese Silkworm Society. Proceedings of the 2018 Academic Annual Meeting of Chinese Silkworm Society [C]. Chinese Silkworm Society: 2018 (in Chinese).
[33] 刘婷婷, 董昆明, 缪莉, 等. 联苯菊酯降解菌的筛选、鉴定及降解特性研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(6): 1147-1152. LIU T T, DONG K M, MIAO L, et al. Isolation, identification and biodegradation characteristics of a bacterial strain able to degrade bifenthrin [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(6): 1147-1152(in Chinese).
[34] 景岳龙, 朱凤晓, 王军玲, 等. 联苯菊酯降解菌的筛选、鉴定及其降解特性 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(10): 98-102. JING Y L, ZHU F X, WANG J L, et al. Isolation, identification and degradation characteristics of a Bifenthrin-degrading strain Delftia tsuruhatensis [J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(10): 98-102(in Chinese).
[35] 张群, 马晨, 张月, 等. 一株可同时降解毒死蜱和联苯菊酯降解菌的筛选鉴定及其降解特性初探 [J]. 农药, 2017, 56(10): 733-738. ZHANG Q, MA C, ZHANG Y, et al. Isolation, identification and degradation characteristics of Stenotrophomonas sp. strain able to simultaneous degrade chlorpyrifos and bifenthrin [J]. Agrochemicals, 2017, 56(10): 733-738(in Chinese).
[36] 王霞. 噻虫胺降解菌株的分离、鉴定及其在土壤污染修复中的应用基础[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2019. WANG X. Isolation and identification of clothianidin degrading strain and its application basis in soil pollution remediation[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiatong University, 2019(in Chinese).
[37] 张静. 我国除草剂的登记现状及其发展趋势分析[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2013. ZHANG J. The analysis of herbicide registration status and development trend in China[D]. Baoding, China: Hebei Agricultural University, 2013(in Chinese).
[38] 邓金保. 磺酰脲类除草剂综述 [J]. 世界农药, 2003, 25(3): 24-29,32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6485.2003.03.006 DENG J B. A review of sulfonylurea herbicides [J]. World Pesticide, 2003, 25(3): 24-29,32(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6485.2003.03.006
[39] 徐磊. 激素类除草剂发展评析 [J]. 市场信息, 2020(6): 22-23. XU L. Review on development of hormonal herbicides [J]. Pesticide Market Information, 2020(6): 22-23(in Chinese).
[40] 桑丽雅. 二氯喹啉酸、苄嘧磺隆及其复配制剂的微生物毒理和降解研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2007. SANG L Y. Studies on microbial toxicology and degradation of herbicides quinclorac, bensulfuron-methyl and their mixture[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2007(in Chinese).
[41] 李瑾, 刘秀, 金晨钟, 等. 酰胺类除草剂安全剂作用机理及研究应用进展 [J]. 现代农业科技, 2016(21): 107-109,114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2016.21.065 LI J, LIU X, JIN C Z, et al. Research progress of mechanism and application of amide herbicide safener [J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016(21): 107-109,114(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2016.21.065
[42] 丁丽, 付颖, 叶非. 酰胺类除草剂的研究和应用进展 [J]. 农药科学与管理, 2011, 32(9): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5480.2011.09.011 DING L, FU Y, YE F. Progress in research and application of amide herbicides [J]. Pesticide Science and Administration, 2011, 32(9): 22-26(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5480.2011.09.011
[43] 《新编农药商品手册》[J]. 农药, 2010, 49(7): 477. Vegetable common fungicide mixed and mixed agent [J]. Agrochemicals , 2010, 49(7): 477(in Chinese).
[44] AIDA M, IKEDA H, ITOH K, et al. Effects of five rice herbicides on the growth of two threatened aquatic ferns [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2006, 63(3): 463-468. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.02.010 [45] 刘军, 霍光华. 两株分解除草剂丁·苄的双效菌株筛选、鉴定及其降解特性研究 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2011, 33(6): 1212-1218. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2011.06.033 LIU J, HUO G H. A study on screening, identification and degradation characteristics of two strains with double effects on butachlor and bensulfuron methyl [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2011, 33(6): 1212-1218(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2011.06.033
[46] 李春艳, 吴志洋, 冯丽萍, 等. 苄嘧磺隆和丁草胺降解菌原生质体融合条件优化 [J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2014, 45(3): 79-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2014.03.014 LI C Y, WU Z Y, FENG L P, et al. Optimization of protoplast fusion conditions of bacteria able to degrade bensulfuron-methyl and butachlor [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2014, 45(3): 79-84(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2014.03.014
[47] 王磊. 烟嘧磺隆、莠去津降解菌的筛选及降解特性研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2013. WANG L. Study on bacteria mixtures of Nicosulfuron·Atrazine isolation and degradation characteristics[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2013(in Chinese).
[48] 王平平. 改性生物炭对莠去津和烟嘧磺隆的吸附机理及环境行为影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020. WANG P P. Studies on the sorption mechanism and environmental fate of atrazine and nicosulfuron by modified biochar materials[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020(in Chinese).
[49] 米凤玉. 几种复配杀虫剂的杀虫作用及机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2011. MI F Y. Studies on insecticidal activity and mechanisms of several insecticidal mixtures[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2011(in Chinese).
[50] 李惠娟, 刘守庆, 杨发忠, 等. 两种环境激素类农药及其混合剂在土壤中的降解研究 [J]. 土壤通报, 2019, 50(4): 946-951. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2019.04.26 LI H J, LIU S Q, YANG F Z, et al. Research about bout degradation characteristics of the individual and mixed treatments of two environ-hormone pesticides in the soil [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 50(4): 946-951(in Chinese). doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2019.04.26
[51] 刘少伟, 阮赞林. 啶虫脒超标青菜 [J]. 质量与标准化, 2018(3): 40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0918.2018.03.015 LIU S W, RUAN Z L. Acetamiprid exceeds the standard for vegetables [J]. Quality and Standardization, 2018(3): 40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0918.2018.03.015
[52] 赖作旺. 两种啶虫脒复配剂在土壤中的环境行为研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2010. LAI Z W. The environmental behavior of two acetamiprid mixed-pesticides in soils[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2010(in Chinese).
[53] 王文桥. 蔬菜常用杀菌剂的混用及混剂 [J]. 中国蔬菜, 2011(7): 27-29. WANG W Q. Vegetable common fungicide mixed and mixed agent [J]. China Vegetables, 2011(7): 27-29(in Chinese).
[54] BAĆMAGA M, WYSZKOWSKA J, KUCHARSKI J. The influence of chlorothalonil on the activity of soil microorganisms and enzymes [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2018, 27(9): 1188-1202. doi: 10.1007/s10646-018-1968-7 [55] 曲军辉. 人工湿地对三种农药去除效果的研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2018. QU J H. Study on removal effect of three kinds of pesticides by constructed wetlands[D]. Suzhou, China: Soochow University, 2018(in Chinese).
[56] 张晓菲. 一株百菌清降解菌株的分离鉴定及其对土壤中百菌清污染的修复研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2013. ZHANG X F. Isolation and identification of a chlororthalonil-degrading strain and its bioremediation of chlororthalonil-contaminated soil[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2013(in Chinese).
[57] YANG X B, YING G G, KOOKANA R S. Rapid multiresidue determination for currently used pesticides in agricultural drainage waters and soils using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 2010, 45(2): 152-161. doi: 10.1080/03601230903472165 [58] SHAMEEMA K, ANAND P P, VARDHANAN Y S. Protective effect of Catharanthus roseus plant extracts against endosulfan and its isomers induced impacts on non-targeted insect model, Drosophila melanogaster and live brain cell imaging [J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C:Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2021, 240: 108916. [59] BILGIN A, SANIN S L. Isolation and identification of endosulfan degrading native bacterial consortium from agricultural soils [J]. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 2020, 11(7): 3303-3313. doi: 10.1007/s12649-019-00662-5 [60] 郝乙杰. 百菌清、硫丹在土壤中的降解动态及对土壤微生物群落多样性的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2007. HAO Y J. Degradation dynamics of chlorothalonil and endosulfan in soil and their effects on soil microbial community diversity[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2007.
[61] 毕秋艳, 马志强. 杀菌剂复配存在的主要问题及发展趋势 [J]. 河北农业科学, 2010, 14(8): 64-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1088-1631.2010.08.015 BI Q Y, MA Z Q. Main problems and development trend of compound fungicide [J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 14(8): 64-66(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1088-1631.2010.08.015
[62] 毛江胜, 邵其霞, 郭长英, 等. 40%吡唑醚菌酯·戊唑醇悬浮剂在玉米及土壤中的残留与降解 [J]. 农药, 2017, 56(11): 832-835. MAO J S, SHAO Q X, GUO C Y, et al. Residue and degradation of Pyraclostrobin·Tebuconazole 40% SC in corn and soil [J]. Agrochemicals, 2017, 56(11): 832-835(in Chinese).
-










 下载:
下载: 











