-
《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》[1]显示,全国土壤环境质量不容乐观,农田土壤环境质量更加令人堪忧。研究显示,我国粮食主产区耕地土壤重金属点位超标率达到21.49%[2]。土壤的可持续利用以及粮食安全与土壤中重金属污染水平息息相关[3],农田污染将直接影响农产品质量和粮食安全,最终影响人类健康[4-5]。小麦是世界三大粮食作物之一,也是我国主要粮食作物。国家统计局发布的数据显示,2019年全国小麦播种面积为2373万公顷,仅次于玉米和稻谷[6]。然而,众多研究显示,小麦主产区土壤存在不同程度的重金属污染[7-9],小麦籽粒重金属超标也较为严重[10-12]。张丙春等[13]对山东主产区小麦重金属污染进行调查,结果发现诸城、郯城、茌平、齐河、莱阳等地小麦籽粒Cd和Cr综合污染评价为警戒水平,个别样点达中度污染水平。康国华等[14]在黄河开封灌区采集122个小麦籽粒样品,发现小麦籽粒中Cd、Cr、Pb、Zn和Ni超标率分别为8.20%、0.82%、37.71%、94.26%和10.66%。雄安新区企业密集区周边农区调查结果显示,96.67%小麦根系土壤样品存在1种以上重金属含量超过《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险筛选值标准》(GB 15618—2018),分别有96.67%和16.67%的小麦籽粒样品中Pb、Cd含量超出《食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量》(GB 2762—2017)[15]。河南省某煤矿区周边小麦地Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn 和Cd的平均值分别为河南省土壤元素背景值的1.32、1.67、4.49、2.20、12.77倍,相应的超标点位所占比例分别为:80%、92%、92%、92%、100%[16]。
在农田土壤—作物系统中,土壤重金属与小麦吸收重金属的关系十分复杂[17],作物籽粒重金属累积程度与土壤理化性质、作物品种、气候条件等外界因素密切相关。赵科理等[18]认为,土壤理化性质对重金属的迁移转化起着重要作用,土壤低pH、有机质含量和电导率可促进重金属在土壤—水稻系统中迁移吸收,而高pH、电导率及粉粘质地均不利于土壤—水稻系统中重金属富集。刘克[19]也发现,土壤pH和可溶性有机质是制约小麦籽粒富集Pb和Cd的关键因子。利用多元回归方程构建小麦籽粒Cd累积方程显示,在土壤全Cd含量、 pH、 OM和CEC这4个因子的共同控制下,相关系数达到最大(R=81%)[20]。杨素勤等[21]在轻度污染条件下研究了20个小麦品种对Pb吸收差异,结果显示具有Pb低积累特性的有花培8号、平安8号、周麦20、同舟麦916和豫农201。翁南燕等[22]研究表明,随着温度升高,小麦幼苗生物量与对照相比没有显著差异,但小麦幼苗对Cu、Cd吸收量均显著增加。
农田土壤中的重金属可以通过多种暴露途径被人体摄入从而引起人体健康风险,最主要的为土壤-作物-食物暴露[23]。新乡市是国家商品粮基地和全国优质小麦生产基地,小麦种植面积达到618.9万hm2。以往文献对作物受污染程度研究较多,而由于污灌而对此地区周边土壤—农作物系统的重金属污染评价, 特别是植物重金属富集和健康风险评价方面研究鲜见报道。
本研究以河南省新乡市某冬小麦种植农田为研究对象,在田块尺度开展小麦与土壤样品点对点采集,分析土壤与小麦籽粒中Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Cr和Ni含量特征,小麦重金属含量的空间分布预测采用反距离权重插值法,探究土壤理化性质与小麦籽粒重金属含量的关系,应用综合目标危害商数法(TTHQ)对研究区小麦籽粒重金属健康风险进行综合评价,为受重金属污染农田小麦的安全生产提供可靠依据和科学指导。
-
河南省新乡县属暖温带大陆性季风气候,地处东经113°30′—115°30′,北纬34°55′—35°50′,地跨海河和黄河两大流域,主要由卫河、西孟姜女河两条天然河道以及人民胜利渠和共产主义渠两条人工河道组成[24]。姜玉玲等[25]调查共产主义渠支流两侧在土壤重金属分布特征,结果发现重金属Cd、Ni、Cr等呈现表聚性,其中Cd含量高于风险管制值。另调查发现西孟姜女河、卫河干流市区以下河段水质污染严重,主要污染因子为重金属等污染物,污染因子表征显示工业源为主要来源。本研究区域为河南省某污灌小麦农田作为研究区,土壤pH值范围在7.38—9.07之间,整体上属于弱碱性土壤,种植作物为冬小麦,一年一熟制。
-
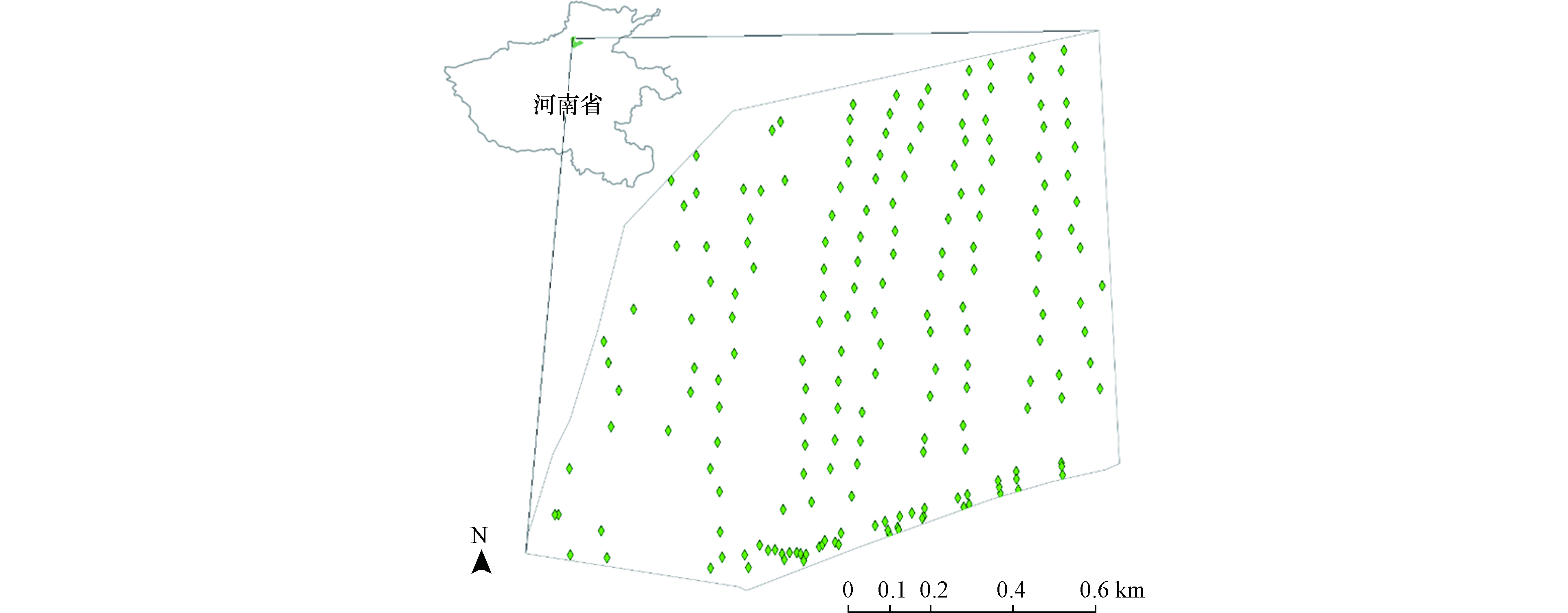
样品采集于2020年6月,采用梅花点法或对角线法,以点对点采集191份小麦籽粒(0—20 cm) 和作物根系土壤样品,采集3—4个样品混匀组成1个混合土壤和小麦籽粒样品,使用 GPS 记录采集点位的经纬度。采用四分法保留500 g土壤样品,除去植物根系及其他杂质并让其自然风干,用木槌及研钵对土壤样品进行研磨,过100和20目筛后备用;小麦籽粒自然晾干、脱壳后,研磨机碾成粉末,装入自封袋备用。采样点分布如图1所示。
-
土壤重金属全量采用HNO3-HF进行消解,称取0.25 g土壤样品,并使用标准物质SRM-2586进行控制。土壤重金属形态的测定采用Tessier连续提取法[26]。采用Sartorius PB-10 pH计测定土壤pH(水土比2.5∶1)。土壤有机质采用重铬酸钾容量法—外加热法进行测定[27],土壤阳离子交换量采用三氯化六氨合钴浸提—分光光度法测定[28],土壤电导率采用电导率仪(METTLER TOLEDO FE38)进行测定。小麦籽粒重金属全量的测定采用HNO3消解,称取0.25 g小麦籽粒样品,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS, Ultimate 3000-i CAP QC)测定重金属含量,使用标准物质SRM-1570a进行质量控制。
-
生物富集系数(bio-concentration factor, BCF)为作物中重金属含量与土壤中相应元素重金属含量的比值[29]。计算公式为:
式中,Cplant为作物籽粒部分重金属含量,Csoil为土壤中重金属总量,单位均为mg·kg−1,按照生物富集系数的大小,可将其分为4个等级:BCF>1时为强烈摄取,0.1<BCF≤1时为中等摄取,0.01<BCF≤0.10为微弱摄取,BCF<0.01时为极弱摄取[30-31]。
-
人体健康风险采用综合目标危害商数(TTHQ)和单一目标危害商数(THQ)进行评价(表1),此方法是2000年美国环保署创建的一种评价人类健康风险的方法,以污染物暴露剂量与参考剂量的比值来表征非致癌风险水平[32-33]。若THQ与TTHQ值小于1,则表示没有健康风险或健康风险较低,若THQ与TTHQ值大于1,则表明该污染对人体有一定的健康风险,值越大,风险越高。计算公式下:
重金属暴露参考剂量RfD中Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb取值分别为:3×10−3、2×10−2、4×10−2、3×10−2、1×10−3、4×10−3 mg·kg−1·d−1[34-35]。小麦日摄取速率取值375×103 mg·d−1(成人)和289.6×103 mg·d−1(儿童),其他参数参照国内外相关研究及中国人群饮食习惯等[13, 36-37]。
用Excel 2016进行数据计算,采用RStudio绘制相关性热图,ArcMap 10.6绘制反距离权重插值图及采样点分布图,其他相关图采用Origin 9进行绘制。
-
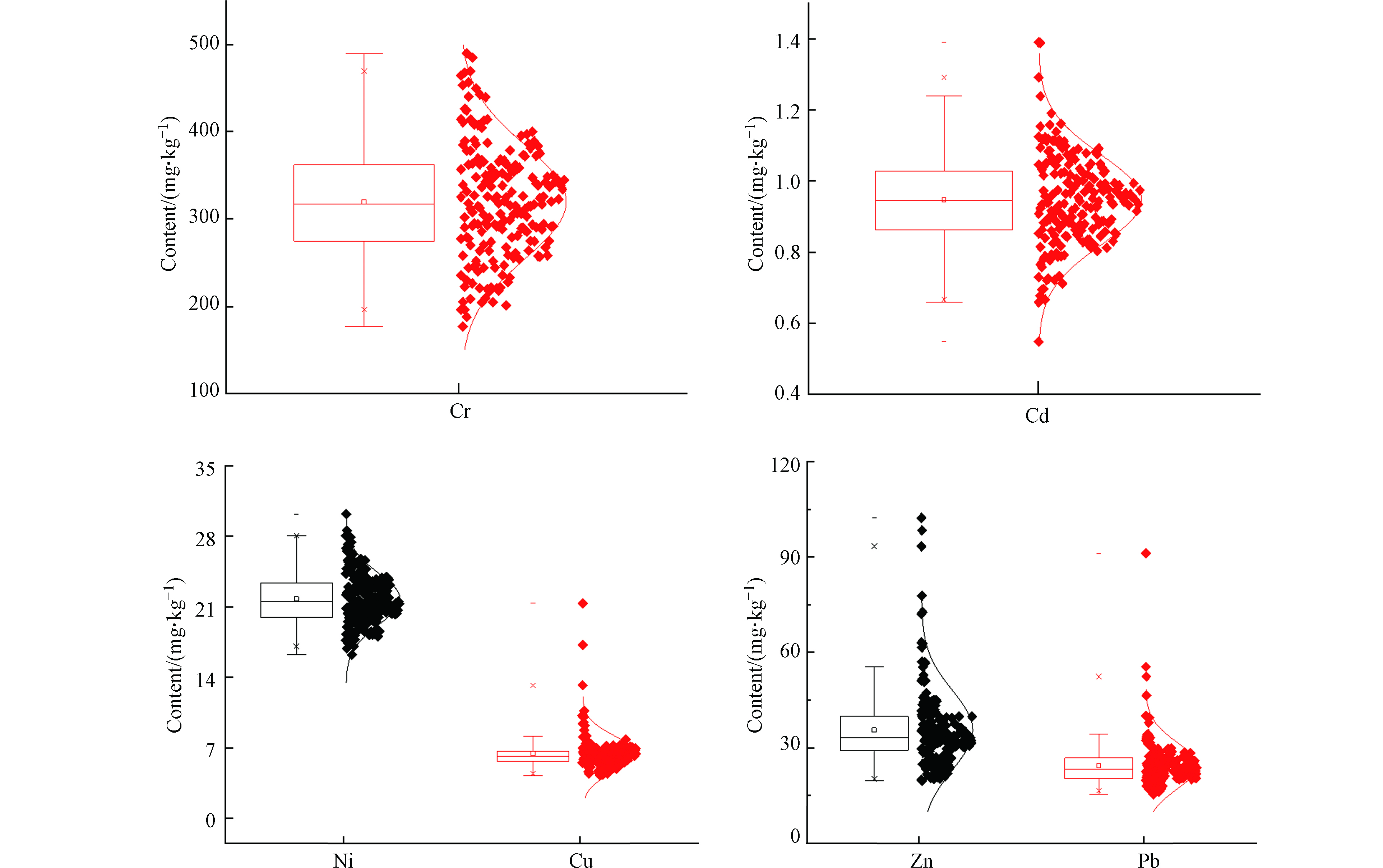
调查区土壤重金属含量如图2所示,Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb含量范围分别在489.70—176.98、30.21—16.23、21.33—4.25、102.24—19.60、1.39—0.55、91.14—15.36 mg·kg−1之间,均值分别为319.60、21.76、6.40、35.52、0.91、24.35 mg·kg−1,其中Cr、Cd、Pb含量超过河南省土壤重金属含量背景值[38]。Ni是6种重金属中元素变异系数最小的,为11.68%,变异系数最大的为Zn,可以达到35.09%,研究区土壤重金属元素变异系数按照大小排列为Zn>Pb>Cu>Cr>Cd>Ni。
研究区重金属的来源和生物有效性可被土壤中重金属的赋存形态特征反映[39],其迁移能力与赋存形态相关,其在自然界的循环及生态毒性会被重金属的赋存形态影响[15]。调查区土壤Cr、Ni、Cu和Pb主要以残渣态形式存在(图3),占比分别为97.18%、70.83%、55%和52.30%。Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb有机结合态占比分别为2.12%、9.47%、24.66%和7.50%,Cr的铁锰氧化物结合态与碳酸盐结合态所占比例的和不足1%,Cu、Ni、Pb铁锰氧化物结合态占比为17.21%、17.85%、32.14%;Cu、Ni、Pb碳酸盐结合态占比为1.80%、1.6%、 8.04%;Cr可交换态占比不足0.01%,可交换态含量极低,Ni、Cu、Pb可交换态占比分别为0.23%、1.32%、0.02%。土壤中Cd的赋存形态比例依次为:残渣态46.64%、碳酸盐结合态21.67%、铁锰氧化物结合态16.03%、可交换态14.19%、有机结合态7.50%;土壤中Zn的赋存形态比例依次为:残渣态45.92%、铁锰氧化物结合态39.62%、碳酸盐结合态8.33%、有机结合态5.41%、可交换态0.71%。在灌溉或者雨水作用下,可交换态易被植物吸收利用,迁移性较强。碳酸盐结合态在高pH环境中不易溶解,其迁移性稍次之。土壤氧化还原电位与pH值较高时易形成铁锰氧化物结合态。相对来讲,有机结合态较为稳定不易被吸收利用。
本调查区Cr在调查区主要以残渣态为主,具有较低的风险;Ni、Cu除残渣态外主要以有机结合态与铁锰氧化物结合态为主, Ni、Cu在该区域风险较低是因为该区域土壤pH较高,其铁锰氧化物结合态不易被吸收和利用;相对于Cr、Ni、Cu而言Zn、Pb对环境有一定的风险,这是由于Zn、Pb除有机结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态、残渣态外,还有8%左右的碳酸盐结合态;调查区可交换态占比14%,容易被吸收利用,迁移性较强,其风险较高。研究表明增加土壤pH值可降低土壤重金属的移动性与生物有效性[40],而该研究区土壤pH值较高,若选择增加土壤pH以降低土壤重金属活性的方法,可能会引发土壤板结、盐渍化等问题。
-
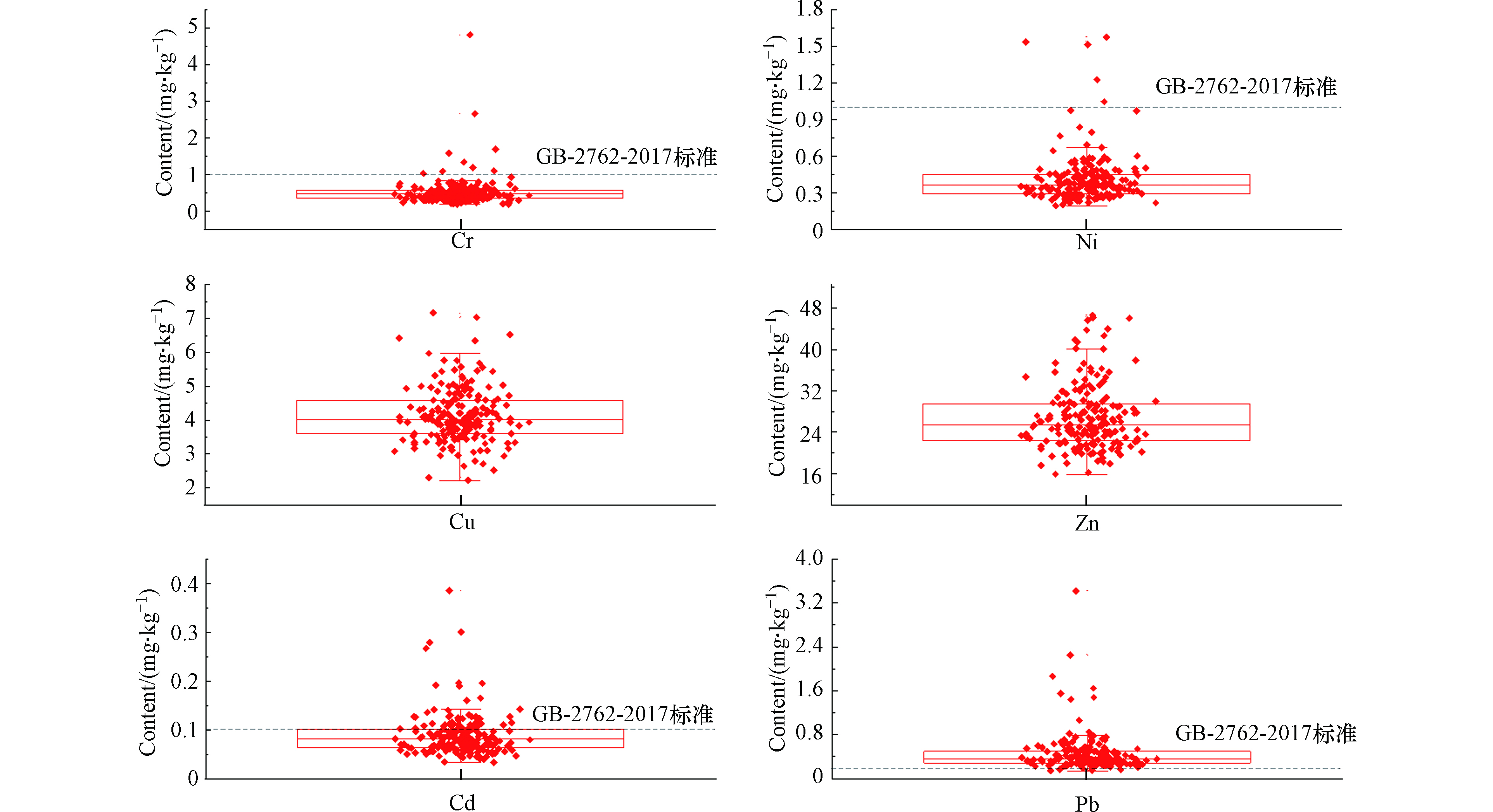
由图4可以看出,在小麦籽粒中Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Cr和Ni含量范围分别为2.22—7.17、16.40—48.80、0.03—0.39、0.15—3.42、0.19—4.81、0.20—1.58 mg·kg−1,平均值分别为4.14、28.07、0.09、0.45 0.54、0.42 mg·kg−1。小麦籽粒中Cd、Cr、Ni、Pb变异系数分别为49.48%、75.99%、49.31%和77.69%,说明这4种重金属受到人类活动的影响可能较大。分别有9、5、54和185份籽粒样品Cr、Ni、Cd和Pb含量超过食品安全标准(GB 2762—2017),超标率分别为4.71%、2.62%、28.27%和96.86%。王怡雯等[20]调查显示,保定、新乡冬小麦Pb含量为0.27—2.40 mg·kg−1,均值达到0.69 mg·kg−1。这可能来源于交通运输、电池厂等工业活动产生含Pb灰尘,沉降到小麦植株上被植物吸收[25]。李艳玲等[37]对济源市东部平原进行小麦籽粒重金属含量的测定,结果表明小麦籽粒Cd含量高于国家标准限值(GB2762—2017),超标率达61.3%。Salar等[41]对伊朗西北部阿塞拜疆省西部乌尔米亚市东南部污灌区小麦进行重金属含量测定,结果表明与淡水灌溉相比,小麦中Cu含量增幅178.2%为最大、Pb增幅40.9%为最小,小麦籽粒中重金属含量的顺序分别为Pb<Cd<Ni<Cu<Zn。
-
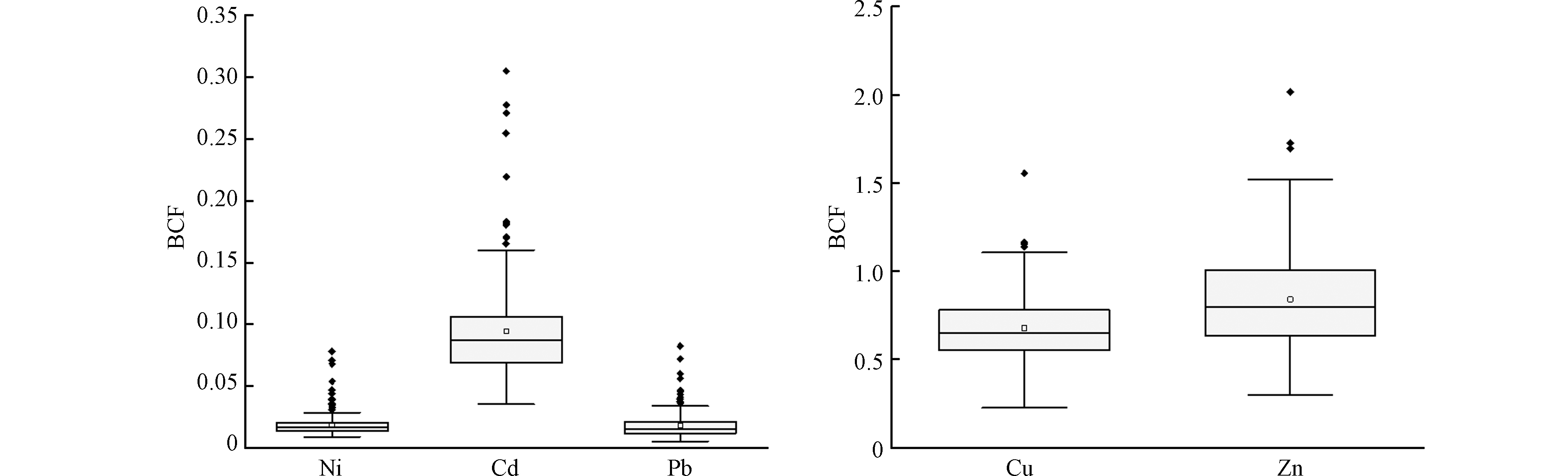
采用生物富集系数来分析小麦籽粒吸收土壤中重金属的状况,结果如图5所示,小麦籽粒对各个重金属富集能力不同,研究区Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb生物富集系数范围分别在8×10−4—0.02、0.01—0.08、0.33—1.55、0.30—2.02、0.04—0.30和0.01—0.08,均值分别为2×10−3、0.02、0.68、0.80、0.10和0.02,小麦籽粒样品重金属生物富集系数平均值由小到大关系依次为: Cr<Pb<Ni<Cd<Cu<Zn,其中Cr表现为极弱摄取,Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb变现为中等摄取。Zn、Cu作为作物生长的必要元素,相比较于其他重金属,表现出较强的迁移能力。研究区中Cr的生物富集系数与其他几种元素相比最低,主要是土壤Cr可交换态含量极低,大部分Cr以残渣态形式存在,较为稳定,不易向籽粒中迁移,故Cr生物富集系数较低。Cd可交换态占比较高,容易向籽粒中迁移,所以生物富集系数相对较高。Ni、Pb与其他几种元素相比富集能力相对居中,研究发现[18-19]Ni和Pb在作物中的富集与土壤理化性质相关。
-
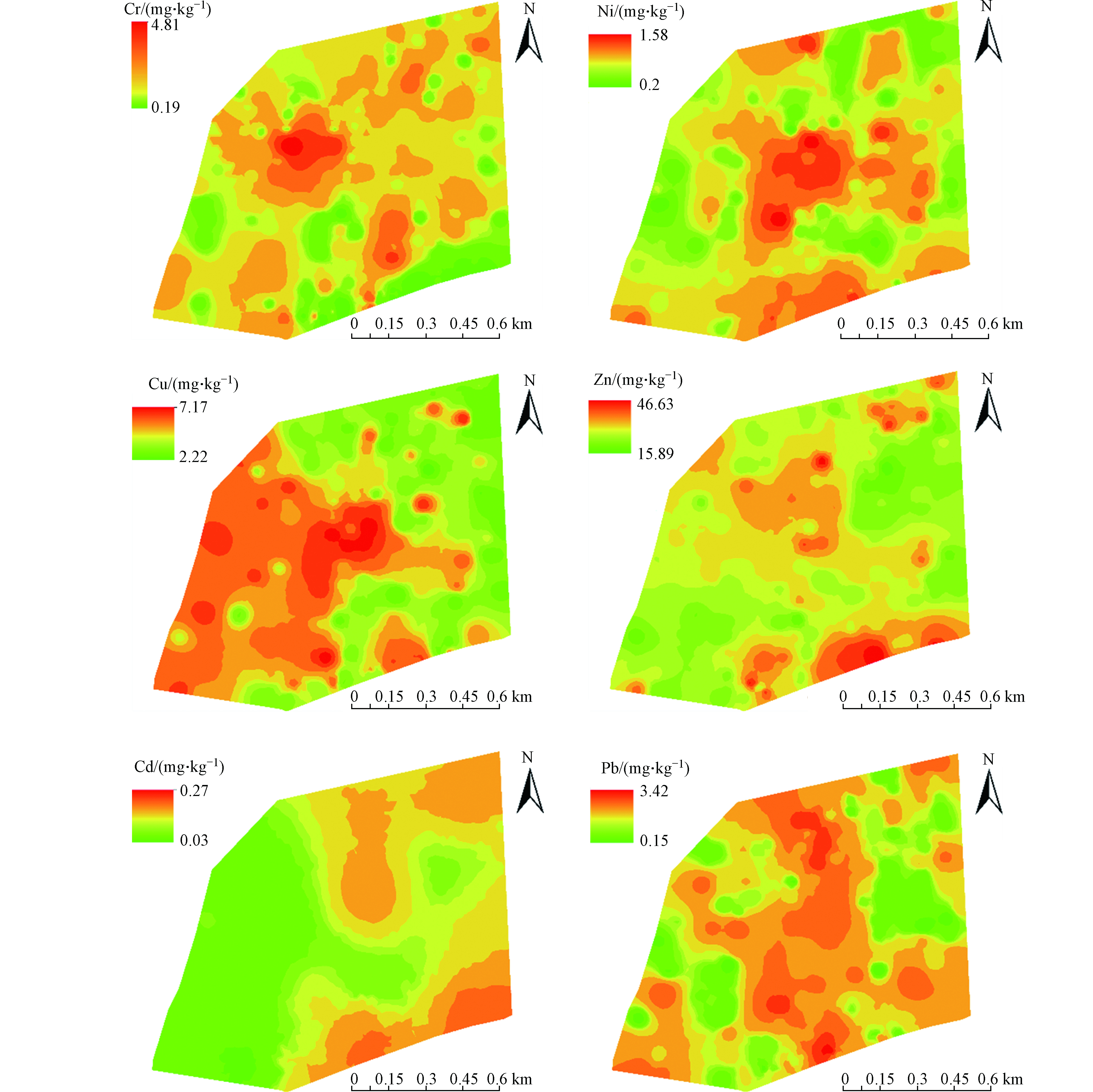
反距离权插值法以插值点与样本点间的距离为权重进行加权平均,离插值点越近的样本点赋予的权重越大[42]。如图6所示,根据小麦籽粒重金属的含量,利用ArcMap10.6中反距离权重插值法得到研究区小麦籽粒重金属含量空间分布图。
从图6可知,小麦籽粒重金属分布存在一定的规律,Cr在中部区域含量较高,其范围在0.57—4.81 mg·kg−1之间,而在南部区域含量较低,约在0.19—0.57 mg·kg−1之间;Ni在中部区域与南部区域含量较高,其范围约在0.36—1.58 mg·kg−1之间,在东北部和西部区域含量较低,范围在0.20—0.36 mg·kg−1之间;Cu在中部及西部区域含量较高。在东部区域含量较低;Zn在南部区域含量较高,其他区域含量较低;Cd含量在南部区域含量最高,其范围在0.13—0.27 mg·kg−1之间,北部含量稍次之,范围在0.07—0.13之间,其他区域含量较低,约在0.07—0.03 mg·kg−1之间;Pb在西部和东部小片区域含量较低,其他区域含量较高,其范围分别在0.15—0.34 mg·kg−1和0.34—3.42 mg·kg−1之间。不仅土壤本身重金属含量会导致重金属含量的空间分布存在差异,而且重金属来源、土壤理化性质以及人为活动也可能会对作物富集重金属产生影响。王爽等[43]研究表明,潼关县金矿开采区小麦、玉米籽粒中Hg含量与土壤中Hg含量表现出显著相关性。陆素芬等[44]调查发现,南丹县玉米与土壤中Cd、Zn和As含量存在显著相关性。周艳等[45]运用主成分分析对西南某铅锌矿区玉米籽粒重金属进行解析,其第一主成分主要支配Pb、Cd、Cr、Ni,来源于污水灌溉,第二主成分主要支配Zn,来源于大气沉降和污水灌溉。
-
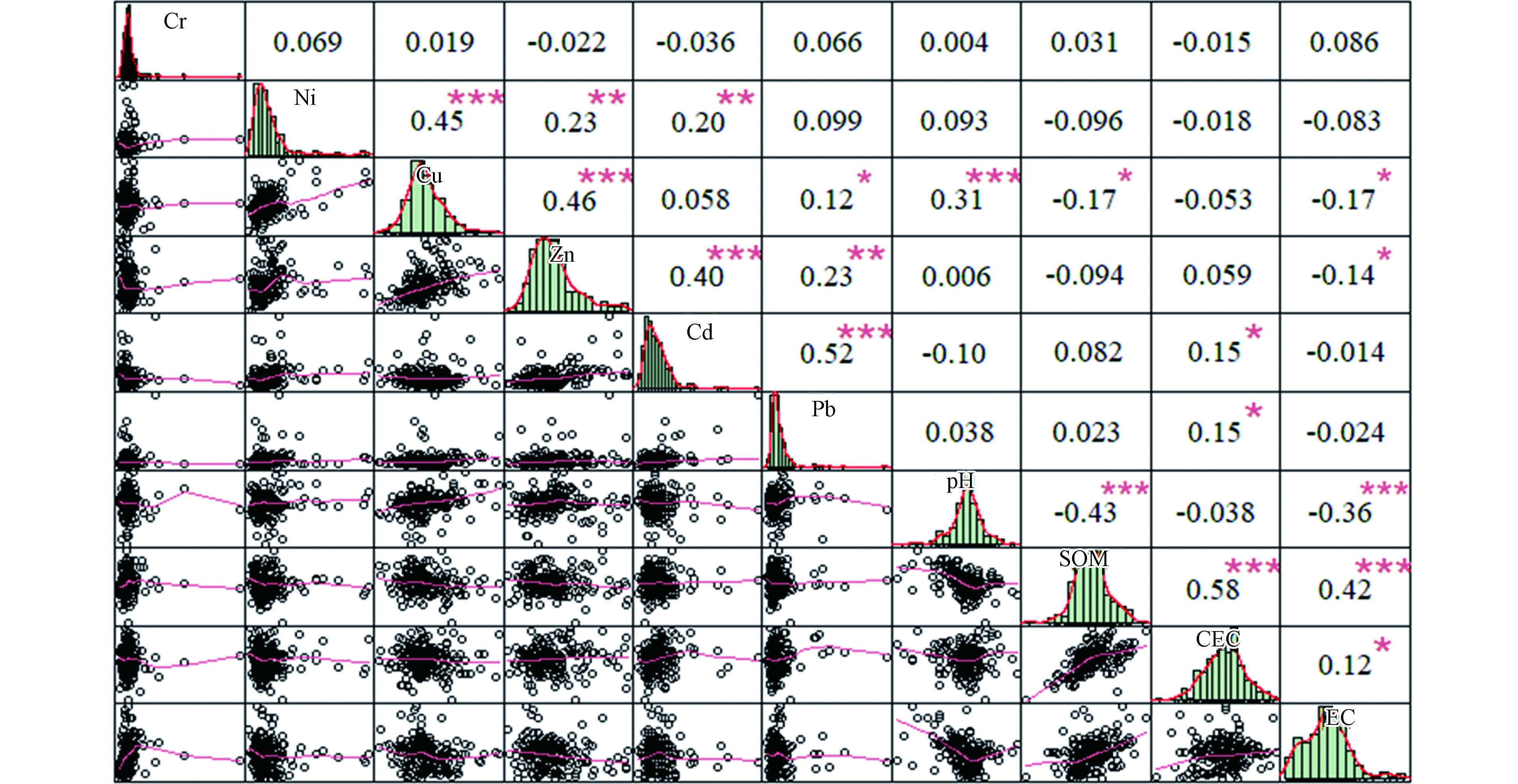
研究区土壤样品pH值、有机质、阳离子交换量、电导率范围分别为7.38—9.07、11.04—42.99 g·kg−1、5.80—14.81 cmol·kg−1和124.77—394.70 μS·cm−1,平均值分别为8.33、28.18 g·kg−1、10.77 cmol·kg−1和216.92 μS·cm−1。如图7为所示,小麦籽粒部分重金属与土壤理化性质的散点分布呈现出较高的非线性关系,分析可以看出,小麦籽粒中Cd和Pb与阳离子交换量呈显著正相关(P<0.05),相关系数为0.15;Zn与电导率呈显著负相关(P<0.05),相关系数为−0.14;Cr、Ni与土壤理化性质没有显著的相关性(P>0.05),Cu与土壤pH、有机质、电导率呈显著相关(P<0.05),相关系数分别为0.31、−0.17和−0.17。
土壤理化性质对作物中重金属的吸收富集有影响,李江遐等[46]研究表明,随着CEC的增加,土壤对重金属的吸附和螯合作用增加,从而减少了作物对重金属的吸收和积累。土壤有机质中可溶性小分子有机物如富里酸能和重金属形成稳定性弱的络合物,使重金属的生物有效性和移动性增强,促进作物对土壤重金属的吸收[47],而有机质中大分子有机物如胡敏酸等易与重金属形成稳定性强的螯合物,降低植物对土壤重金属的吸收[48, 40]。高智群等[49]研究表明,嵊州市土壤电导率与水稻籽粒Cd、Cu、Ni、Zn的生物富集系数呈显著负相关关系。刘克等[50]的研究认为,无论土壤是否受Cd污染,pH都是影响小麦籽粒吸收Cd的首要土壤因子,且与小麦籽粒Cd含量呈极显著性负相关,其他因素无明显效应。于灏等[51]选取土壤Cd含量、pH、阳离子交换量和有机质含量四个因子,利用多元回归分析构建小麦、水稻Cd含量预测模型,结果表明小麦、水稻模型的预测能力分别为83.8%与67.8%,显示出小麦、水稻Cd含量与土壤因子具有一定的关系。
-
采用单一目标危害商数(THQ)与综合目标危害商数(TTHQ)对研究区小麦籽粒重金属含量进行健康风险评价,若THQ与TTHQ值大于1,则表明该污染对人体有一定的健康风险。研究区小麦籽粒Ni在成人与儿童的THQ值均小于1,均值分别为0.11和0.19(表2),表明该研究区小麦籽粒中Ni在成人和儿童中均无人体健康风险;Cu和Zn成人THQ值均小于1,儿童中THQ分别有29.32%与17.28%,THQ>1,范围分别在0.50—1.62和0.49—1.47;Cr、Cd、Pb成人THQ值均小于1,其值范围分别在0.34—8.60、0.18—2.06和0.22—5.23,均值分别为0.96、0.48和0.69,成人THQ值大于1的比例分别为27.23%、4.19%和10.99%。
Cr、Cd、Pb儿童THQ值中,Cr与Pb大于1,Cd小于1,三者THQ值范围分别在0.57—14.53、0.30—3.49、0.38—8.84之间,儿童THQ值大于1的比例分别为82.72%、19.90%、43.46%。从综合目标危害商数来看,成人与儿童TTHQ均值分别为3.30和5.58,范围分别在1.38—18.15与2.34—30.66之间,TTHQ值大于1占比为100%。小麦籽粒健康风险评价结果表明,部分小麦籽粒中Cu、Zn对儿童有一定的健康风险,部分小麦籽粒中Cr、Cd、Pb不仅对儿童有一定的健康风险,对成人也有一定的健康风险,且相对于Cu、Zn健康风险更加严重,THQ>1所占比例更多,所有重金属中THQ与TTHQ风险值均儿童>成人。
-
(1)研究区土壤Pb、Cd、Cr含量超过河南省土壤背景值,其中Cd和Cr含量超过《土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》筛选值。土壤中Zn存在形态主要是和残渣态及铁锰氧化物结合态,Cd可交换态所占比例较高,Cu、Ni、Cr、Pb的存在形式主要是残渣态。
(2)调查区小麦籽粒Cr、Ni、Cd、Pb含量分别有9、5、54、185份样品超过食品安全限量标准(GB 2762—2017),Cr表现为极弱摄取,Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb变现为中等摄取。
(3)土壤pH、有机质、电导率与小麦籽粒中重金属Cu含量呈显著相关,Zn与电导率呈显著负相关,Cd和Pb与阳离子交换量呈显著正相关。
(4)小麦籽粒部分样品中重金属对儿童有一定的健康风险,重金属中THQ与TTHQ风险值均儿童>成人。
污灌区土壤—小麦系统中重金属富集特征及其对人体健康风险评价
Characteristics of heavy metals in the soil-wheat system of sewage irrigation area and its health risk assessment
-
摘要: 以河南省某污灌区小麦农田为研究对象,土壤与小麦籽粒点对点样品采集,分析土壤与小麦籽粒重金属含量特征和空间分布规律,探究影响小麦籽粒重金属累积的关键土壤理化因子,采用单一目标危害商数(THQ)与综合目标危害商数(TTHQ)评估研究区小麦籽粒重金属对人体健康风险。研究表明,研究区土壤Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Cr和Ni总量分别为6.40、35.52、0.95、24.35、319.60、21.71 mg·kg−1,其中Cd、Pb和Cr含量超过河南省土壤重金属含量背景值,而Cr和Cd含量超过《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB 15618—2018)筛选值。小麦籽粒中Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Cr和Ni含量分别为4.14、28.07、0.09、0.45、0.54和0.42 mg·kg−1,分别有54、18、59、5份籽粒样品Cd、Pb、Cr和Ni含量超过食品安全标准(GB 2762—2017)。小麦籽粒重金属含量与土壤理化性质呈现出较高的非线性关系。小麦籽粒重金属健康风险评价结果表明,儿童Cu和Zn的THQ值范围分别在0.50—1.62和0.49—1.47,其中>1%的样品占比分别为29.32%和17.28%,部分小麦籽粒中Cr、Cd、Pb同时对成人和儿童也有一定的健康风险;成人与儿童TTHQ均值分别为3.30和5.58,范围分别在1.38—18.15与2.30—30.66之间,TTHQ值>1的样品数为100%。THQ与TTHQ风险值均表现为儿童>成人。Abstract: Taking wheat farmland in a waster irrigation area of Henan Province as the research object, soil and wheat grain point-to-point samples were collected to determine the characteristics of heavy metal contents in soil and wheat grain, and then we explored the key factors of soil physio-chemical characteristics that affect uptake of heavy metals in wheat grain. Single target hazard quotient (THQ) and comprehensive target hazard quotient (TTHQ) were used to evaluate the health risk of heavy metals in wheat grains to human health in the study area. The contents of Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Cr and Ni in the study area were 6.40, 35.52, 0.95, 24.35, 319.60, and 21.71 mg·kg−1, Cd, Pb and Cr content exceeded the background value of heavy metal content in Henan Province, and Cr and Cd content exceed the screening value of soil pollution risk control standard of Soil Environmental Quality Control Standards for Soil Pollution Risk on Agricultural Land (GB 15618-2018). The concentrations of Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Cr and Ni in wheat grains were 4.14, 28.07, 0.09, 0.45, 0.54, and 0.42 mg·kg−1, and there were 54, 18, 59 and 5 wheat grain samples of Cd, Pb, Cr and Ni, respectively, exceeded the food safety standard (GB 2762—2017). Nonlinear results showed higher correlation between heavy metals in wheat grains and soil physical and chemical properties. Health risk evaluation showed that THQ of Cu, Zn was 0.50—1.62 and 0.49—1.47, respectively, and the samples of THQ>1 was 29.32% and 17.28% respectively. Cr, Cd, and Pb in some of wheat grain samples exhibited health risks to both adults and children. The mean values of TTHQ for adults and children were 3.30 and 5.58, ranging from 1.38 to 18.15 and 2.30 to 30.66, respectively. The samples of TTHQ > 1 was 100%. THQ and TTHQ risk values showed children > adults.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- wheat grain /
- heavy metal /
- health risk
-
近年来,全国90%以上的城市水域受污染严重,多种污染物并存成为水污染的新现状[1-2],当前氮磷已超过有机污染物成为主要污染物,控制污水中氮磷浓度成为水污染治理重点。纳米零价铁(nZVI)在环境修复中得到了广泛的研究[3-5],其具有还原性强、比表面积大和高反应活性等的特点,但单独使用易被氧化甚至自燃,或发生团聚形成链状或更大聚集体[6-7],从而降低其分散性和稳定性[8],限制了纳米零价铁的实际应用。为解决上述问题,在nZVI实际应用过程中常利用各类固定化手段,如负载法[9-10]等完成nZVI表面改性以克服其易团聚的缺陷性。
目前,常见的用于固定nZVI的材料有多孔材料(活性炭[11]、多孔碳板及浮石[12])和无机黏土矿物(蒙脱石[13]、膨润土[14])等,但利用这类材料进行nZVI改性存在成本高、制备工艺复杂的缺点[15],因此,在选取时考虑到实际工程应用的需要,应选择更节省成本且对环境友好的改性材料。高炉碱矿渣是高炉炼铁的副产物,属于固体废弃物类,露天堆放会侵占土地,污染大气和水环境,亦会造成明显或潜在的经济损失及资源浪费[16]。而碱矿渣材料具有比表面积大、孔隙率高,吸附能力强的特点,故可作为吸附剂、絮凝剂用于水处理[17]。鉴于nZVI和高炉碱矿渣两者在各自应用上的局限性,因此,本研究尝试将nZVI负载到高炉碱矿渣上,以探索解决两者应用缺陷性的有效途径。
实验中将nZVI负载高炉碱矿渣上,在不同质量比和不同投加量条件下,研究该负载材料对受污染地表水体中氮磷的去除效果,并通过改变温度条件和反应接触时间,研究其吸附机理。本研究在有效提高污水中氮磷去除率的同时,可提供一种价格低廉且安全绿色的新型环保材料。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试剂与仪器
硫酸亚铁、硼氢化钠、无水乙醇、葡萄糖、硝酸钾、硫酸铵、磷酸氢二钾均为分析纯级别,购自上海国药。高炉碱矿渣购自河南远恒环保工程有限公司,组成成分以CaO、MgO、SiO2、Al2O3、MnO、Fe2O3等为主(大于90%),还有部分CaS、MnS等(小于10%)。实验仪器有pH计(HACH-HQ40d)、溶氧仪(HACH-HQ40d)、电子天平(ME204TE/02)、数显控温加热磁力搅拌器(MPLK-701)、冷冻干燥机(FD-1A-50)、1 L双缸玻璃反应釜、卧式智能精密型摇床(BSD-WX2200)、紫外分光光度计(UV-2000)。
1.2 材料的制备
1)高炉碱矿渣负载纳米零价铁颗粒的制备。参考肖燕萍等[18]的研究,采用液相还原法制备碱矿渣-nZVI,分别取24.88 g七水合硫酸亚铁、20 g碱矿渣粉、50 mL硼氢化钠溶液于玻璃反应釜内,为保证新鲜制备的nZVI不被氧化,反应过程中持续通入氮气以保证厌氧环境,体系中的反应如式(1)所示。
Fe2++2BH4−+6H20→Fe0↓+2B(OH)3+7H2↑ (1) 2)实验设计。制备6种不同m矿渣粉:mFe2+比例(10∶1、8∶1、6∶1、4∶1、2∶1、1∶1)的碱矿渣-nZVI。以葡萄糖、硫酸铵、硝酸钾、磷酸氢二钾配制模拟污水,设计浓度分别为硝氮15 mg·L−1、氨氮15 mg·L−1、总磷2 mg·L−1。取100 mL配制的污水于各150 mL锥形瓶中,再向每个锥形瓶中分别加入0.1、0.2、0.5、1.0、2.0 g的碱矿渣和碱矿渣-nZVI材料做为对照组与实验组。在165 r∙min−1、25 ℃的卧式摇床中振荡24 h,取样,用国标法(GB 3838-2002)分别测定硝氮、氨氮、亚硝氮、总氮和总磷的出水浓度。
3)数据分析方法。吸附等温线反应在一定温度条件下,吸附达到平衡时吸附剂与吸附量的关系。吸附等温线的类型有很多种,其中Langmuir吸附模型是指恒温下均一表面的单层吸附平衡,Freundlich吸附模型则描述了发生在多分子层的吸附过程,这2种吸附模型(式(2)和式(3))被用来分析此次得出的实验数据[19]。
Ceqe=1qm+KL+Ceqm (2) lnqe=lnKF+1nlnCe (3) 式中:
Ce 为吸附平衡时的浓度,mg∙g−1;qe 为吸附反应平衡时的吸附量,mg∙g−1;qm 为最大吸附量,mg∙g−1;KL 为Langmuir吸附模型的吸附常数;KF 、1n 为Freundlich吸附模型的吸附常数。为了推断高炉碱矿渣的具体吸附过程,研究其脱氮除磷的吸附速率和机理,可采用不同动力学模型解释吸附过程中的行为。准一级动力学方程应用广泛,该方程假定吸附质的吸附去除变化速率与吸附量及平衡吸附量之间的差值呈线性关系;准二级动力学方程则与化学吸附作用密切相关,涉及吸附质与吸附剂之间的电子共用或电子转移[20]。准一级和准二级动力学方程分别如式(4)~(5)所示。
ln(qe−qt)=lnqe−K1t (4) tqt=12K2q2e+tqe (5) 式中:
qe 为吸附反应平衡时的吸附量,mg∙g−1;qt 为t时间下,吸附剂上的吸附量,mg∙g−1;K1 、K2 分别为准一级、准二级动力学的方程系数。为了能够进一步评估温度对高炉碱矿渣吸附氮磷元素的影响,可以采用式(6)~(8)计算出相关的热力学参数[21]。
Kd=qeCe (6) lnKd=ΔSR−ΔHRT (7) ΔG=ΔH−TΔS (8) 式中
:Kd 为吸附过程中的分配系数,mL∙g−1;R 为气体摩尔常数,8.314 J∙(mol∙K)−1;T 为热力学温度,K;ΔS 为吸附过程中的熵变,J∙(mol∙K)−1;ΔH 为吸附过程中的焓变,mg·L−1;ΔG 为吸附过程中的吉布斯自由能变,KJ∙mol−1。2. 结果与分析
2.1 材料表征
1)扫描电镜分析(SEM)和比表面积(BET)。为观察负载前后材料的外貌形态,对负载nZVI前后的高炉碱矿渣进行扫描电镜分析,结果如图1所示。高炉碱矿渣和碱矿渣-nZVI的比表面积测定结果如表1所示。由图1(a)可见,未负载nZVI的高炉碱矿渣呈不规则块粒状分布,表面平整,有空隙存在。图1(b)是负载nZVI后的碱矿渣-nZVI,与碱矿渣的电镜图相比,其表面明显附着大小均匀颗粒,且大部分颗粒能够独立存在,这表明高炉碱矿渣对nZVI具有较好的分散效果,可以减弱nZVI颗粒之间相互团聚的倾向[22]。
表 1 碱矿渣和碱矿渣-nZVI的比表面积Table 1. The surface area of alkali slag and alkali slag-nZVI材料 比表面积/(m2∙g−1) 孔容/(cm3∙g−1) 孔径/nm 碱矿渣 2.289 0.011 3.933 碱矿渣-nZVI 9.054 0.035 3.931 如表1所示,可见其孔径分别集中在3.933 nm和3.931 nm左右,差异不显著,这表明nZVI负载进了碱矿渣的空隙中;未负载nZVI的碱矿渣的比表面积仅为2.289 m2∙g−1,负载后其表面积提高至9.054 m2∙g−1,小于普通零价铁的比表面积(25~35 m2∙g−1)[23]。
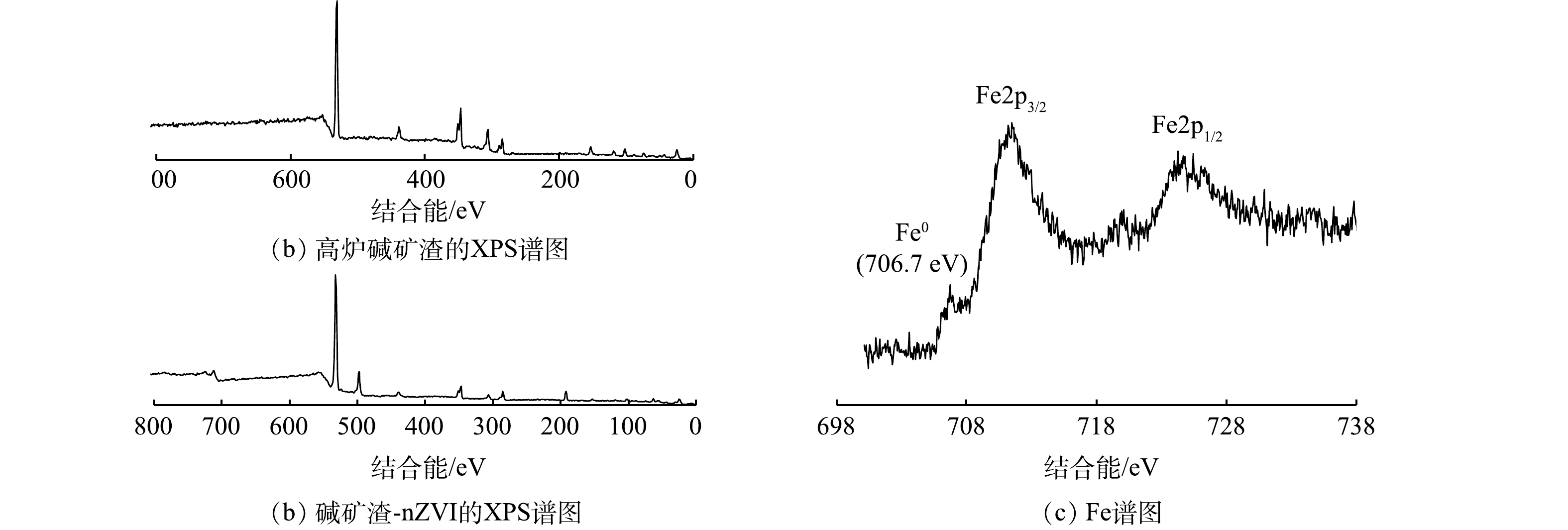
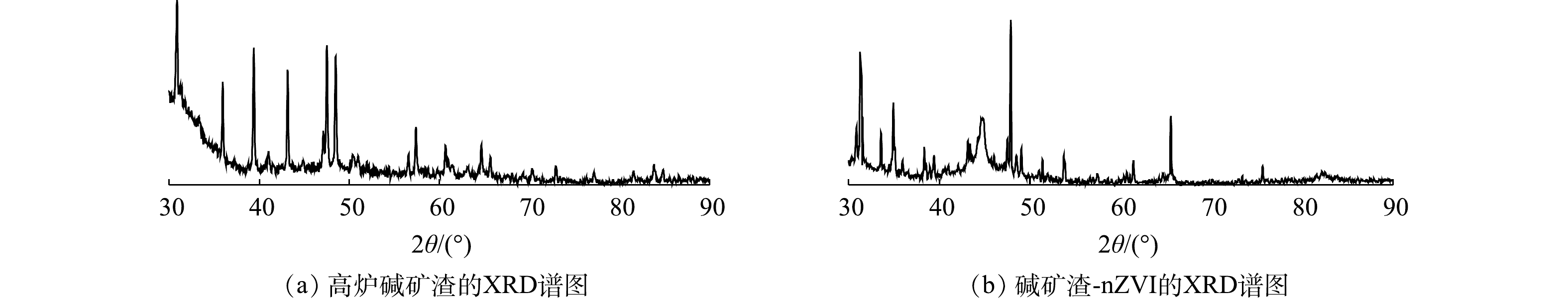
2) X射线光电子能谱(XPS)和X射线衍射分析(XRD)。为了直接得到负载材料内部nZVI颗粒存在的信息,本文利用X射线光电子能谱对碱矿渣-nZVI内部的Fe0进行分析,结果如图2和图3所示。由图2(c)可以看出,在706.7、711.8和724.8 eV处出现的特征峰分别对应Fe(0)2p3/2、Fe(Ⅲ)2p3/2、Fe(Ⅲ)2p1/2的结合能[24]。结果表明,在碱矿渣-nZVI内部确实存在Fe0,二价、三价铁氧化物的存在可能是因为部分Fe0裸露在碱矿渣表面被氧化形成的。图3为高炉碱矿渣和碱矿渣-nZVI颗粒的XRD图谱。由图3可知,碱矿渣-nZVI颗粒在2θ=44.56°处出现的衍射峰与体心立方晶格铁的(110)面的特征峰一致[23]。
2.2 污染物去除效果
1)不同碱矿渣与Fe2+质量比对氮磷去除率的影响。为了探究碱矿渣与Fe2+质量比对负载型纳米零价铁处理效果的影响,本实验制备出6种不同质量比例的碱矿渣-nZVI,并分别将其用于去除污水中的氮磷元素。实验结果如图4和图5所示。
图4表示的是在不同质量比例条件下,不同负载材料用量处理污水的出水pH。由图4可知,所有条件下的出水pH均高于8,呈碱性,其主要原因是负载材料中存在有铁元素,Fe0在被氧化过程中会消耗溶液中的H+,最终造成出水pH升高。
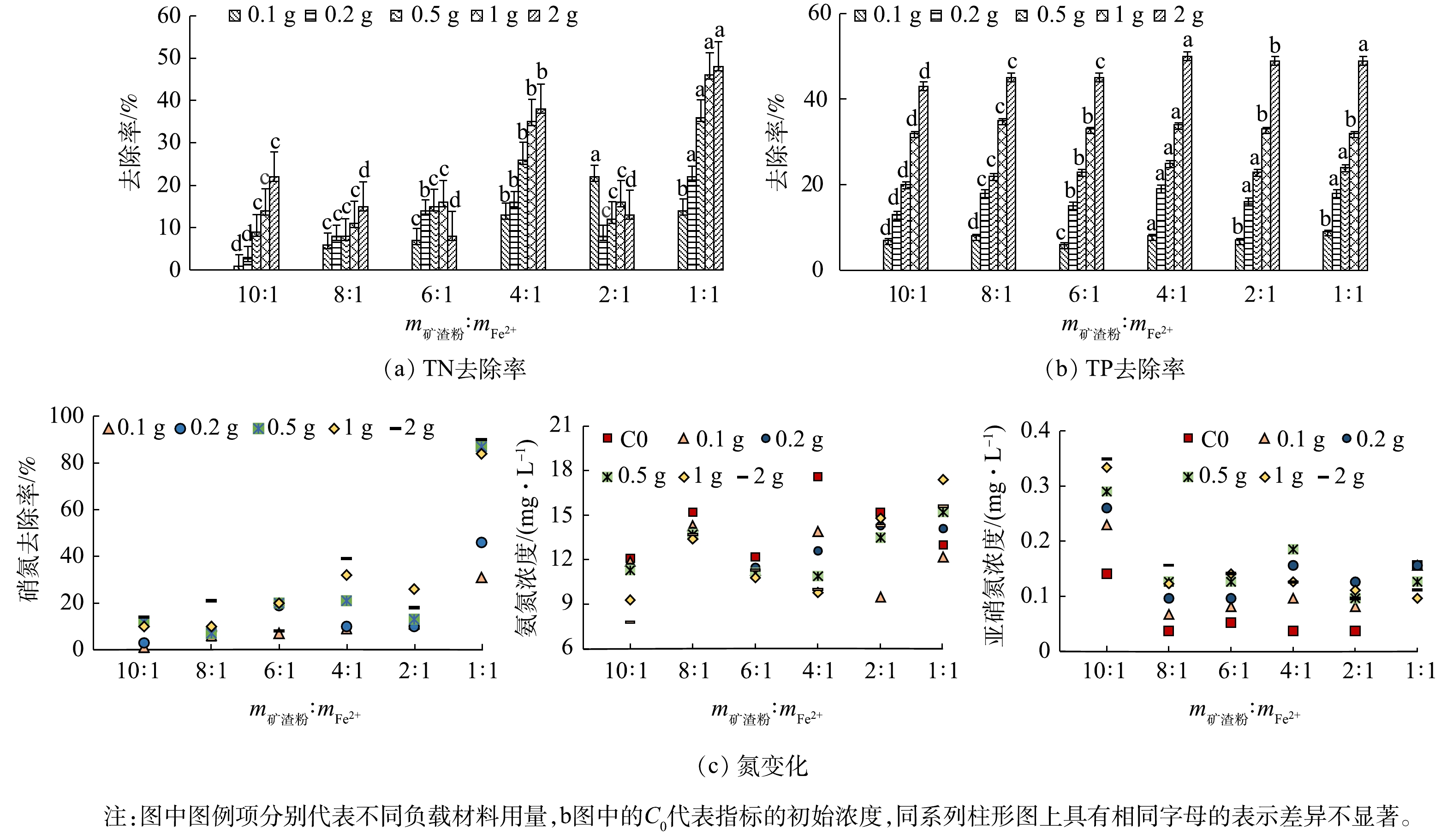
由图5(a)可见,当m矿渣粉∶mFe2+为1∶1时,负载材料用量0.1、0.2、0.5、1、2 g对总氮的去除率分别为14%、22%、36%、46%和48%。当两者比例增加时,负载型纳米零价铁对总氮的去除率显著降低(P<0.05),对比同等条件下只添加碱矿渣处理的出水总氮数据来看,负载材料的总氮去除率均高于对照组的总氮去除率9%、17%、20%、23%和26%,其原因是多方面的,具体可通过图5(c)中3种形态氮的变化来解释。
由图5(b)可见,碱矿渣负载纳米零价铁对总磷的去除效果明显,当m矿渣粉∶mFe2+从10∶1降至4∶1时,各不同用量下总磷的去除率显著增大(P<0.05),分别达到77%、68%、62%、79%和68%;当比例再降低时,总磷的去除率不升反降,即使在两者比例为1∶1时,去除率也只能分别达到62%、62%、68%、65%和65%。但对比同等条件下只添加碱矿渣处理后的出水总磷的去除率8%、17%、23%、33%和47%,所有比例条件下总磷去除率都相对较高,说明负载材料在去除磷酸盐时有沉淀作用发生。
由图5(c)可见,m矿渣粉∶mFe2+为1∶1时,各负载材料用量下的硝氮去除率分别为31%、46%、87%、84%和90%,当两者比例增加时,硝氮去除率显著降低(P<0.05)。其可能的原因是,负载材料中的Fe0含量减少,一方面使Fe0与硝酸盐的还原作用受到影响,另一方面Fe0被氧化后生成的Fe2+、Fe3+也相对减少,从而抑制反硝化过程的进行,最终导致硝氮去除率降低。在m矿渣粉∶mFe2+为4∶1时氨氮的去除效果好于在其他质量比的负载材料下的效果,而当m矿渣粉∶mFe2+为1∶1时,出水氨氮浓度高于进水氨氮浓度,且有随负载材料用量增加而升高的趋势。这可能是因为该质量比的负载材料中存在有足量的Fe0,能够在还原足够多硝氮的同时生成多于硝化过程可以反应掉的氨氮,最终表现为出水的氨氮浓度增加,其他质量比条件下的氨氮呈现被消耗的状态,以m矿渣粉∶mFe2+为4∶1时去除效果最佳;而亚硝氮存在有相反的变化趋势,当m矿渣粉∶mFe2+为1∶1时,亚硝氮开始被消耗,其它各质量比条件下出水的亚硝氮浓度均成升高趋势,以m矿渣粉∶mFe2+为4∶1时浓度增幅最大,这种现象也可以用负载材料中的Fe0含量解释。
以上结果表明,不同质量比例的碱矿渣与Fe2+对总氮和总磷的去除率有明显影响(P<0.05),其原因可能是碱矿渣投入量过多时会覆盖纳米零价铁颗粒,抑制硝化与反硝化过程的进行,从而降低去除率;而当碱矿渣投入量过少时,又不利于纳米零价铁的分散,造成其在使用过程中易发生团聚并堵塞矿渣粉表面空隙,导致材料自身吸附性能下降。因此,实际应用时应选取最合适质量比,结合实验数据,本文确定碱矿渣与Fe2+的最佳质量配比为4:1,最有效用量为1 g,以用于后续实验。
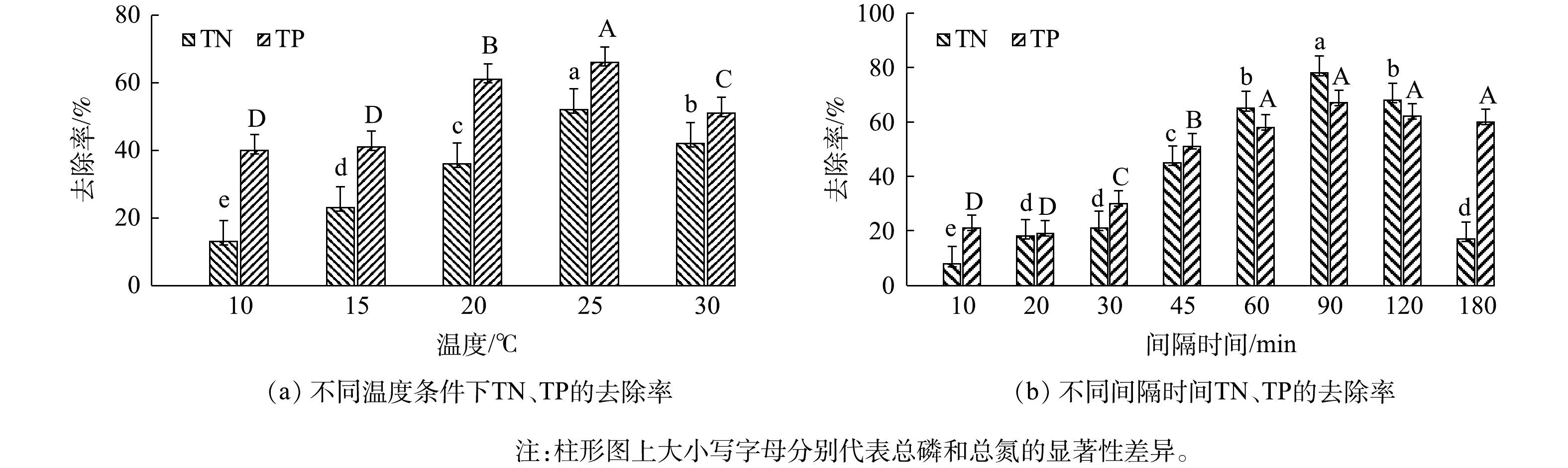
2)不同条件下碱矿渣-nZVI对总氮和总磷的去除效果。由上述实验得到最佳m矿渣粉∶mFe2+比例为4∶1,最佳用量为1 g后,为对比不同温度和间隔时间下负载材料对总氮和总磷的去除率,将1 g负载材料投加到总氮浓度为30 mg·L−1、总磷浓度为2 mg·L−1的水样中,在温度为10、15、20、25、30 ℃和间隔时间为10、20、30、45、60、90、120、180 min的条件下分别进行反应。实验结果如图6所示。由图6可知,随着温度的升高,总氮和总磷去除率在25 ℃分别达到最大值,为52%和66%,在30 ℃时两者去除率反而下降。间隔时间也会对总氮和总磷的去除率造成影响,具体表现为:在90 min前,负载材料对总氮和总磷的去除率呈显著提高趋势(P<0.05);在90 min时达到最大值,分别为78%和67%;在90 min后,总氮和总磷的去除率又有所下降。可见,不同的温度和间隔时间会影响总氮和总磷的去除率。结果表明,在温度为25 ℃、间隔时间为90 min的条件下,总氮和总磷的去除效果最佳。
2.3 吸附机理
1)等温吸附曲线。液-固界面的等温吸附行为通常采用Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型进行描述[25]。将上述实验所得数据用Langmuir和Freundlich 2种等温吸附模型进行拟合分析,具体相关参数见表2。拟合结果表明,总氮和总磷采用Langmuir等温吸附模型得到的相关系数R2均高于Freundlich模型,这表明吸附过程更符合Langmuir模型,说明总氮和总磷的吸附过程主要在单分子层进行,主要原因可能是活性吸附位点均匀分布在吸附材料上造成的。同时,拟合得到的KL较小,说明负载材料的吸附亲和力不大。Freundlich模型的拟合结果表明,总氮和总磷的1/n分别为0.094和0.108,均小于1。n指示的是吸附过程中的支持力,1/n越小吸附性能越好,一般认为当1/n为0.1~0.5时,吸附较易进行;当1/n>2时,吸附将难以进行[26]。
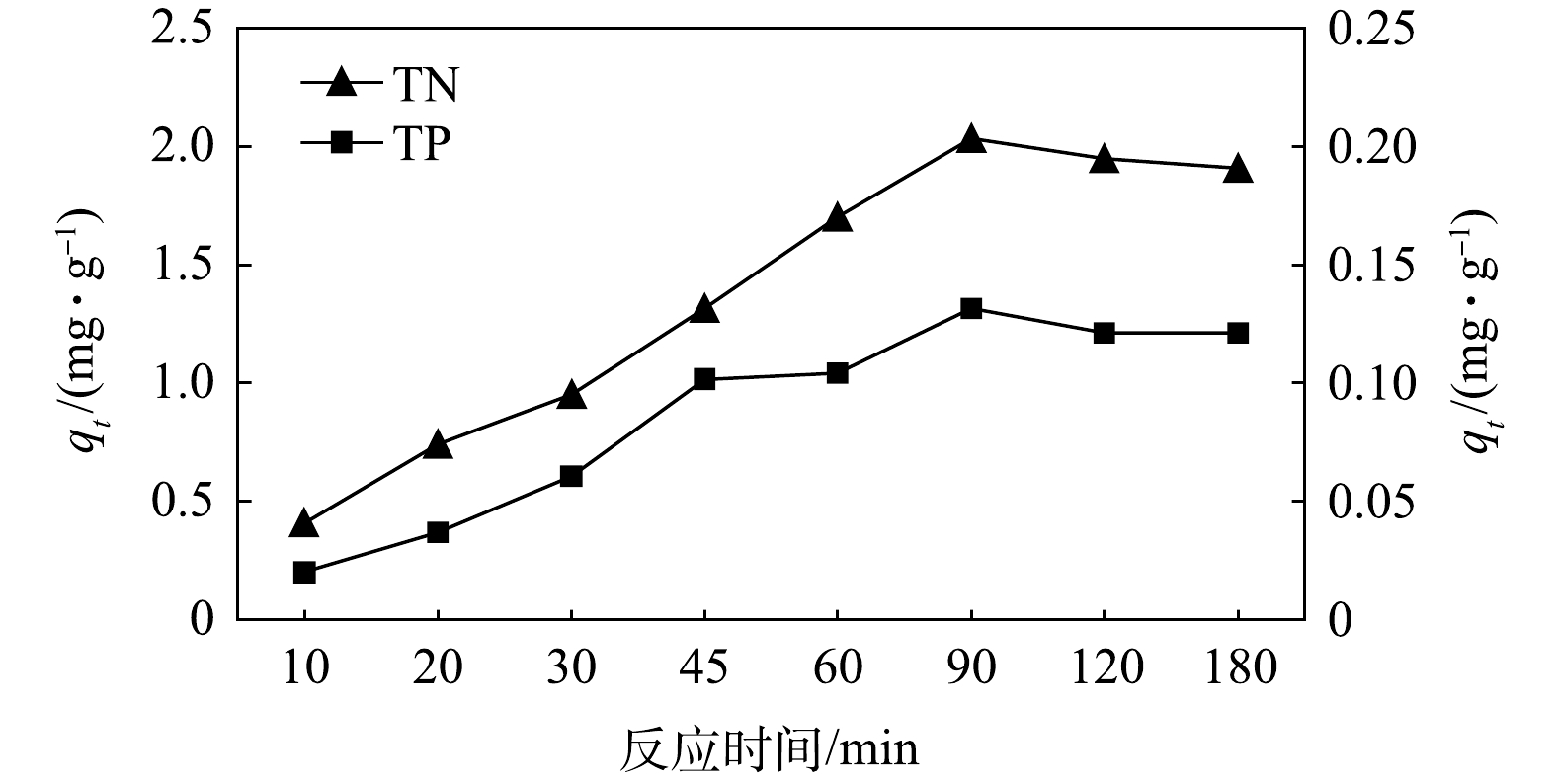
表 2 碱矿渣-nZVI去除TN、TP的Langmuir、Freundlich的方程参数及相关系数Table 2. Parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich equations for TN and TP removal by alkali slag-nZVI指标 Langmuir模型 Freundlich模型 KL Qm R2 KF 1/n R2 TN 0.050 12.469 0.902 0.714 0.094 0.853 TP 0.082 4.808 0.850 0.313 0.108 0.795 2)动力学特征。为获取负载材料在吸附过程中的动力学参数,本文研究了反应时间对初始浓度分别为30 mg·L−1和2 mg·L−1的总氮和总磷吸附量的影响,结果如图6所示,总氮和总磷在吸附反应进行90 min后吸附量达到最大值,分别为2.034 mg·L−1和0.131 mg·L−1。在吸附动力学实验中,碱矿渣-nZVI对总氮和总磷的吸附在90 min后基本达到平衡,参考姜侠等[27]的研究结果,为保证吸附反应充分进行,后续的吸附热力学实验中的反应时间确定为120 min。
根据2种不同吸附动力学模型计算并确定去除氮磷元素的斜率、截距、R2等动力学参数。如表3所示,可以看出准一级动力学方程能更好地描述m矿渣粉:mFe2+为4:1比例条件下总氮和总磷的吸附动力学过程。由图7可见,在吸附的初始阶段,总氮和总磷的吸附速率较快,这可能是因为氮磷元素附着在碱矿渣-nZVI材料表面和外部;随着吸附过程的进行,吸附效率降低,其可能的原因是氮磷元素沿负载材料的内部通道扩散吸附,阻力逐渐增大;到吸附后期,材料内的表面吸附成为主要吸附过程,吸附过程趋于平衡[28]。
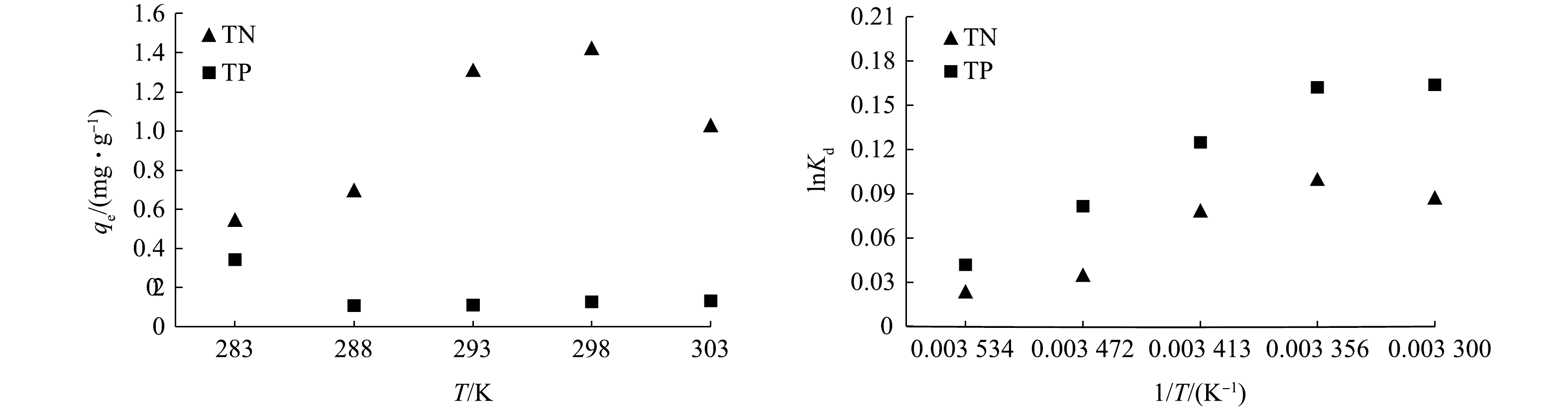
表 3 拟一级和拟二级动力学参数Table 3. Adsorption kinetic parameters of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order equations指标 qe.exp 准一级动力学方程 准二级动力学方程 qe K1 R2 qe K2 R2 TN 2.034 3.363 0.497 0.811 7.194 0.006 0.763 TP 0.131 0.165 0.271 0.880 0.511 0.261 0.651 3)热力学特征。温度对负载材料吸附氮磷元素的影响如图8所示。在10、15、20、25、30 ℃的条件下,总氮的吸附量随温度的升高而增加,而总磷的吸附量在温度升高时有下降的趋势。为了获得吸附过程中的热力学参数,本文对实验数据进行热力学拟合计算,结果如表4所示。当ΔG<0时,说明该过程是自发过程,升高温度将有利于吸附过程的进行;当时ΔH>0时,说明反应时吸热的,吸附量会随温度的升高而增加;当ΔS>0时,说明吸附过程在较强亲和力条件下自发完成的,也表明吸附质和吸附剂在吸附过程中发生了变化[29]。
表 4 TN和TP热力学参数Table 4. Thermodynamics parameters of TN and TP指标 ΔH /(KJ∙mol−1) ΔS/(J∙(K mol)−1) ΔG/(KJ∙mol−1) R2 283 K 288 K 293 K 298 K 303 K TN 0.019 0.061 −17.158 −17.462 −17.765 −18.069 −18.372 0.821 TP 0.033 0.146 −41.381 −42.113 −42.845 −43.576 −44.308 0.943 3. 结论
1)利用高炉碱矿渣的孔隙结构,采用液相还原法负载纳米零价铁得到碱矿渣-nZVI材料,这种材料表面附着大小均匀的颗粒,其具有比表面积大、孔隙率高的特点。
2)碱矿渣-nZVI材料具有高效吸附氮磷元素的特性,在25 ℃、1.5 h的反应条件下,总氮和总磷的去除效率可稳定到65%以上;氮磷的去除效率随着温度和碱矿渣与Fe2+质量比的变化发生显著变化(P<0.05);但考虑到工程应用问题,最终确定碱矿渣与Fe2+最佳质量比为4∶1,有效用量为1 g。
3)碱矿渣-nZVI材料吸附氮磷元素的过程属于熵增、吸热的自发过程,吸附平衡数据适合用Langmuir吸附等温线来描述,吸附动力学遵循准一级动力学模型。
-
表 1 综合目标危害商数各参数含义及参考值
Table 1. Meanings and reference values of parameters of integrated target hazard quotient
参数Parameter 含义Implications 成人参考值Adult reference value 儿童参考值Child reference values EF 暴露频率/(d·a−1) 365 ED 暴露年限/a 70 Ccrop 小麦籽粒重金属含量/(mg·kg−1) 实测值 IR 小麦日摄取速率/(g·d−1) 375 289.63 BW 体重/kg 70 32 AT 平均暴露天数/d ED×365 表 2 研究区小麦籽粒单一与综合目标危害商数
Table 2. Harm quotient of single and comprehensive target of wheat grain in study area
项目Project 元素Element 人群Crowd 最大值Maximum 最小值Minimum 均值Mean >1%占比/% 单一目标危害商数(THQ) Cr 成人 8.60 0.34 0.96 27.23 儿童 14.53 0.57 1.62 82.72 Ni 成人 0.42 0.05 0.11 0 儿童 0.71 0.09 0.19 0 Cu 成人 0.96 0.3 0.56 0 儿童 1.62 0.50 0.94 29.32 Zn 成人 0.87 0.29 0.50 0 儿童 1.47 0.49 0.85 17.28 Cd 成人 2.06 0.18 0.48 4.19 儿童 3.49 0.30 0.81 19.90 Pb 成人 5.23 0.23 0.69 10.99 儿童 8.84 0.38 1.17 43.46 综合目标危害商数(TTHQ) 成人 18.15 1.38 3.30 100.00 儿童 30.66 2.34 5.58 100.0 -
[1] 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[J]. 中国环保产业, 2014(5): 10-11. National Survey of Soil Pollution [J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2014(5): 10-11(in Chinese).
[2] 尚二萍, 许尔琪, 张红旗, 等. 中国粮食主产区耕地土壤重金属时空变化与污染源分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10): 4670-4683. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201802139 SHANG E P, XU E Q, ZHANG H Q, et al. Spatial-temporal trends and pollution source analysis for heavy metal contamination of cultivated soils in five major grain producing regions of China [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(10): 4670-4683(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201802139
[3] 梁捷, 孙宏飞, 葛成军, 等. 海南省主要农作物主产区土壤重金属含量分布及其健康风险评价 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2019, 40(11): 2285-2293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2019.11.026 LIANG J, SUN H F, GE C J, et al. Distribution of heavy metal contents in soils of main crop production areas in Hainan and the health risk assessment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2019, 40(11): 2285-2293(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2019.11.026
[4] ZHAO F J, MA Y B, ZHU Y G, et al. Soil contamination in China: Current status and mitigation strategies [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(2): 750-759. [5] RAI P K, LEE S S, ZHANG M, et al. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management [J]. Environment International, 2019, 125: 365-385. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.067 [6] 王晓君, 何亚萍, 蒋和平. “十四五”时期的我国粮食安全: 形势、问题与对策 [J]. 改革, 2020(9): 27-39. WANG X J, HE Y P, JIANG H P. China's food security during the 14th five-year plan period: Situation, problems and countermeasures [J]. Reform, 2020(9): 27-39(in Chinese).
[7] 贺新星, 魏芳, 范健, 等. 宁连高速两侧土壤及小麦重金属污染特征研究 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2020, 32(5): 28-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2020.05.007 HE X X, WEI F, FAN J, et al. Research of heavy metals pollution in soils and wheat on both sides of Lianyungang—Nanjing expressway [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2020, 32(5): 28-32(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2020.05.007
[8] 张江华, 徐友宁, 陈华清, 等. 小秦岭金矿区土壤-小麦重金属累积效应对比研究 [J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(3): 284-294. ZHANG J H, XU Y N, CHEN H Q, et al. Comparative study of the accumulated effect of heavy metals on soil and wheat in Xiaoqinling gold mining area [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(3): 284-294(in Chinese).
[9] WANG L H, YIN X X, GAO S L, et al. In vitro oral bioaccessibility investigation and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in wheat grains grown near the mines in North China [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 252: 126522. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126522 [10] 张洋. “小麦-土壤”系统耕地安全与小麦籽粒品质评估研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2019. ZHANG Y. Research on response rules of wheat-soil system from the perspective of agricultural product quality and safety[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019(in Chinese).
[11] LI L P, ZHANG Y Q, IPPOLITO J A, et al. Lead smelting alters wheat flour heavy metal concentrations and health risks [J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2021, 50(2): 454-464. doi: 10.1002/jeq2.20198 [12] ZHANG R, CHEN T, ZHANG Y, et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils and identification of main influencing factors in a typical industrial park in northwest China [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 252: 126591. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126591 [13] 张丙春, 范丽霞, 赵平娟, 等. 山东省主产区小麦镉和铬污染状况及评价 [J]. 麦类作物学报, 2016, 36(10): 1396-1401. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2016.10.19 ZHANG B C, FAN L X, ZHAO P J, et al. Contamination status and evaluation of cadmium and chromium in wheat grain in typical areas of Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2016, 36(10): 1396-1401(in Chinese). doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2016.10.19
[14] 康国华, 张鹏岩, 李颜颜, 等. 黄河下游开封段引黄灌区小麦中重金属污染特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(8): 3917-3926. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201709198 KANG G H, ZHANG P Y, LI Y Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in wheat grains cultivated in Kaifeng irrigation area of the Yellow River [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(8): 3917-3926(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201709198
[15] 周亚龙, 杨志斌, 王乔林, 等. 雄安新区农田土壤-农作物系统重金属潜在生态风险评估及其源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4): 2003-2015. ZHOU Y L, YANG Z B, WANG Q L, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in soil-crop system in Xiongan new district [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4): 2003-2015(in Chinese).
[16] 张成丽, 张伟平, 程红丹, 等. 禹州市煤矿区周边土壤和农作物重金属污染状况及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(4): 805-812. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018060502 ZHANG C L, ZHANG W P, CHENG H D, et al. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment of farmland soil around coal mines in Yuzhou City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(4): 805-812(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018060502
[17] 徐建明, 孟俊, 刘杏梅, 等. 我国农田土壤重金属污染防治与粮食安全保障 [J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(2): 153-159. XU J M, MENG J, LIU X M, et al. Control of heavy metal pollution in farmland of China in terms of food security [J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(2): 153-159(in Chinese).
[18] 赵科理, 傅伟军, 戴巍, 等. 浙江省典型水稻产区土壤?水稻系统重金属迁移特征及定量模型 [J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(2): 226-234. ZHAO K L, FU W J, DAI W, et al. Characteristics and quantitative model of heavy metal transfer in soil-rice systems in typical rice production areas of Zhejiang Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(2): 226-234(in Chinese).
[19] 刘克. 我国主要小麦产地土壤镉和铅的安全阈值研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. LIU K. Soil threshold of cadmium and lead in major Chinese wheat-producing areas[D]. Yangling, China: Northwest A & F University, 2016(in Chinese).
[20] 王怡雯, 芮玉奎, 李中阳, 等. 冬小麦吸收重金属特征及与影响因素的定量关系 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1482-1490. WANG Y W, RUI Y K, LI Z Y, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal absorption by winter wheat and its quantitative relationship with influencing factors [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1482-1490(in Chinese).
[21] 杨素勤, 程海宽, 张彪, 等. 不同品种小麦Pb积累差异性研究 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2014, 30(5): 646-651. YANG S Q, CHENG H K, ZHANG B, et al. Differences in Pb accumulation between wheat varieties [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2014, 30(5): 646-651(in Chinese).
[22] 翁南燕, 周东美, 武敬, 等. 铜镉复合胁迫下温度对小麦幼苗生长及其对铜、镉和矿质营养元素吸收与各元素在亚细胞分布的影响 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2011, 6(6): 607-616. WENG N Y, ZHOU D M, WU J, et al. Uptake, subcellular distributions of Cu, Cd and mineral elements, and plant growth for wheat seedlings under stress of Cu and Cd as affected by temperature [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2011, 6(6): 607-616(in Chinese).
[23] 邓海, 王锐, 严明书, 等. 矿区周边农田土壤重金属污染风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1127-1137. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020071601 DENG H, WANG R, YAN M S, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil around mining area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1127-1137(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020071601
[24] 周凯, 王智芳, 马玲玲, 等. 新乡市郊区大棚菜地土壤重金属Pb、Cd、Cr和Hg污染评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(12): 1962-1968. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2013.12.017 ZHOU K, WANG Z F, MA L L, et al. Pollution and assessment of soil heavy metal Cd, Cr, Pb and Hg in greenhouse vegetable fields of Xinxiang suburb, China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 22(12): 1962-1968(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2013.12.017
[25] 姜玉玲, 阮心玲, 马建华. 新乡市某电池厂附近污灌农田重金属污染特征与分类管理 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(2): 645-654. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0343 JIANG Y L, RUAN X L, MA J H. Heavy metal pollution and classification management of sewage irrigation farmland around a battery factory in Xinxiang, Henan Province [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(2): 645-654(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0343
[26] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [27] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. BAO S D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press, 2000(in Chinese).
[28] 陈桂华, 范芳, 林芷君. 三氯化六氨合钴浸提-分光光度法测定土壤阳离子交换量 [J]. 理化检验-化学分册, 2019, 55(12): 1448-1451. CHEN G H, FAN F, LIN Z J. Determination of cation exchange capacity of soil by spectrophotometry after extraction with [co(NH3)6]Cl3 [J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2019, 55(12): 1448-1451(in Chinese).
[29] HATTAB S, BOUGATTASS I, HASSINE R, et al. Metals and micronutrients in some edible crops and their cultivation soils in eastern-central region of Tunisia: A comparison between organic and conventional farming [J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 270: 293-298. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.029 [30] YANG Y, ZHOU X H, TIE B Q, et al. Comparison of three types of oil crop rotation systems for effective use and remediation of heavy metal contaminated agricultural soil [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 188: 148-156. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.140 [31] 孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 孙晓明, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿尾矿库复垦土地及周边土壤-玉米重金属迁移富集特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3): 1166-1176. SUN H Y, WEI X F, SUN X M, et al. Bioaccumulation and translocation characteristics of heavy metals in a soil-maize system in reclaimed land and surrounding areas of typical vanadium-titanium magnetite tailings [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3): 1166-1176(in Chinese).
[32] LIAO J B, WEN Z W, RU X, et al. Distribution and migration of heavy metals in soil and crops affected by acid mine drainage: Public health implications in Guangdong Province, China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 124: 460-469. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.11.023 [33] 曹春, 张松, 张鹏, 等. 大宝山污灌区土壤-蔬菜系统重金属污染现状及其风险评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(7): 1521-1531. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0001 CAO C, ZHANG S, ZHANG P, et al. Heavy metal contamination in soil–vegetable systems and its health risks in an area irrigated with acid mine drainage in Dabaoshan, Guangdong, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(7): 1521-1531(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0001
[34] 周涛, 苏小四, 宋铁军, 等. 三江平原典型农作区作物籽粒重金属健康风险评价 [J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2018, 35(10): 896-899. ZHOU T, SU X S, SONG T J, et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in seeds of different crops in typical agricultural area of Three River Plain [J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2018, 35(10): 896-899(in Chinese).
[35] LU Y L, SONG S, WANG R S, et al. Impacts of soil and water pollution on food safety and health risks in China [J]. Environment International, 2015, 77: 5-15. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.12.010 [36] 徐晶晶. 典型农耕区土壤—作物系统重金属污染及健康风险评估 : 以长丰县庄墓镇为例[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2014. XU J J. Pollution analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-crop systems: Case study of a typical agricultural area in zhuangmu town, Changfeng County[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2014(in Chinese).
[37] 李艳玲, 陈卫平, 杨阳, 等. 济源市平原区农田重金属污染特征及综合风险评估 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(6): 2229-2236. LI Y L, CHEN W P, YANG Y, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and comprehensive risk evaluation of farmland across the eastern plain of Jiyuan city [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(6): 2229-2236(in Chinese).
[38] LI L P, ZHANG Y Q, IPPOLITO J A, et al. Lead smelting effects heavy metal concentrations in soils, wheat, and potentially humans [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 257: 113641. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113641 [39] ADAMO P, IAVAZZO P, ALBANESE S, et al. Bioavailability and soil-to-plant transfer factors as indicators of potentially toxic element contamination in agricultural soils [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 500/501: 11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.085 [40] 杜彩艳, 祖艳群, 李元. pH和有机质对土壤中镉和锌生物有效性影响研究 [J]. 云南农业大学学报, 2005, 20(4): 539-543. DU C Y, ZU Y Q, LI Y. Effect of pH and organic matter on the bioavailability Cd and Zn in soil [J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 2005, 20(4): 539-543(in Chinese).
[41] REZAPOUR S, ATASHPAZ B, MOGHADDAM S S, et al. Heavy metal bioavailability and accumulation in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) irrigated with treated wastewater in calcareous soils [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 656: 261-269. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.288 [42] 汤国安, 杨昕. ArcGIS地理信息系统空间分析实验教程[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. TANG G A, YANG X. Geographic information system spatial analysis experiment tutorial. 2 Ed [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012(in Chinese).
[43] 王爽, 李荣华, 张增强, 等. 陕西潼关农田土壤及农作物重金属污染及潜在风险 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(9): 2313-2320. WANG S, LI R H, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Assessment of the heavy metal pollution and potential ecological hazardous in agricultural soils and crops of Tongguan, Shaanxi Province [J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(9): 2313-2320(in Chinese).
[44] 陆素芬, 张云霞, 余元元, 等. 广西南丹土壤-玉米重金属积累特征及其健康风险 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2017, 33(8): 706-714. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2017.08.005 LU S F, ZHANG Y X, YU Y Y, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal accumulation in soil-corn system contents and their health risks in Nandan, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2017, 33(8): 706-714(in Chinese). doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2017.08.005
[45] 周艳, 万金忠, 李群, 等. 铅锌矿区玉米中重金属污染特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(10): 4733-4739. ZHOU Y, WAN J Z, LI Q, et al. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment of corn grains from a Pb-Zn mining area [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(10): 4733-4739(in Chinese).
[46] 李江遐, 吴林春, 张军, 等. 生物炭修复土壤重金属污染的研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(12): 2075-2081. LI J X, WU L C, ZHANG J, et al. Research progresses in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(12): 2075-2081(in Chinese).
[47] 赵阿娟, 曾维爱, 蔡海林, 等. 长沙烟区烟叶重金属含量与土壤重金属含量及其性质的相关性分析 [J]. 中国烟草学报, 2020, 26(5): 90-97. ZHAO A J, ZENG W A, CAI H L, et al. Correlation analysis of heavy metal content in tobacco leaf and soil and physicochemical properties in Changsha tobacco growing area [J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2020, 26(5): 90-97(in Chinese).
[48] de SANTIAGO-MARTÍN A, VALVERDE-ASENJO I, QUINTANA J R, et al. Carbonate, organic and clay fractions determine metal bioavailability in periurban calcareous agricultural soils in the Mediterranean area [J]. Geoderma, 2014, 221/222: 103-112. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.01.009 [49] 高智群, 张美剑, 赵科理, 等. 土壤—水稻系统重金属空间异质性研究: 以浙江省嵊州市为例 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(1): 215-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.01.037 GAO Z Q, ZHANG M J, ZHAO K L, et al. Heavy metal contamination in soil-rice system and its spatial variation in Shengzhou City [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(1): 215-224(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.01.037
[50] 刘克, 和文祥, 张红, 等. 镉在小麦各部位的富集和转运及籽粒镉含量的预测模型 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(8): 1441-1448. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.08.002 LIU K, HE W X, ZHANG H, et al. Cadmium accumulation and translocation in wheat and grain Cd prediction [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(8): 1441-1448(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.08.002
[51] 于灏, 苏智杰, 祝培甜, 等. 水稻、小麦与土壤中重金属Cd含量的关系模拟研究 [J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(1): 438-445. YU H, SU Z J, ZHU P T, et al. Relationship between Cd contents in rice or wheat and soil: Insight from a simulation study [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(1): 438-445(in Chinese).
-





 下载:
下载: