-
基于羟基自由基反应的高级氧化技术(AOPs)已被广泛应用于去除持久性有机污染物[1]。然而,均相催化体系有许多缺点,且所生成的铁泥会对环境造成二次污染[2]。与均相类芬顿催化剂相比,非均相类芬顿催化技术越来越受到青睐,特别是纳米磁铁矿(Fe3O4)被认为是一种有潜力的催化剂[3-4]。为了克服Fe3O4磁性纳米粒子的团聚,提高催化降解性能,有研究学者将Fe3O4磁性纳米粒子与多孔载体材料,如沸石[5]、石墨烯[6]、多壁碳纳米管[7]、活性炭[8]等进行结合。
凹凸棒土(ATP)是一种天然的水合铝镁硅酸盐矿物,具有棒状形态以及较大的比表面积和较强的吸附性能[9]。尽管ATP对水中的金属和有机污染物有良好的吸附能力[10],但却不具备催化性能。本课题组已成功地将Fe3O4与ATP结合制备出ATP@Fe3O4复合材料,并证实其是H2O2强有力的催化剂,不仅同时具有吸附和催化性能,且因其具有磁性,从而便于从溶液中分离回收[11]。
随着高级氧化技术的不断发展,硫酸根自由基(
SO⋅−4 )有替代羟基自由基(·OH)的趋势,其主要由过硫酸盐(PS)分解而来,因此,简便易得。相比于·OH,SO⋅−4 具有更高的氧化还原电位,且SO⋅−4 与难降解的有机物之间发生的是电子转移反应,所以在体系中的寿命比·OH更长[12]。到目前为止,有关ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系降解有机污染物的研究鲜见报道。由于我国医药行业和养殖业中四环素类抗生素的大量使用,造成水体中四环素含量较高,增加了环境的生态风险。本研究选择四环素(tetracycline)作为目标污染物,探讨了ATP@Fe3O4复合材料的制备及其催化过硫酸盐(persulfate)降解四环素的效果及其相关机理,以期为催化材料的应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
凹凸棒土(ATP)购自中国江苏省盱眙黏土技术有限公司;六水合氯化铁(FeCl3·6H2O)、七水合硫酸亚铁(FeSO4·7H2O)、盐酸(HCl)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、甲醇、过硫酸钠(NaS2O8)、高纯度压缩氮气(N2)、乙腈和草酸均购自扬州试剂有限公司;四环素(TC)购自上海阿拉丁生物化学技术有限公司。实验中所有试剂均为分析纯。
-
将ATP(2.0 g)加入到盛有去离子水的锥形瓶中,搅拌6~12 h,然后滴加NaOH,调节悬浮液的pH至8,再通入N2气流鼓泡30 min,以除去溶解的O2。将20 mL 0.6 mol·L−1 FeSO4溶液和20 mL 0.8 mol·L−1 FeCl3溶液依次逐滴加入烧瓶中,超声处理30 min后,调节溶液pH至10,再在70 ℃水浴中继续搅拌2 h。最后,用去离子水和乙醇交替洗涤沉淀,以除去游离的离子,在70 ℃真空干燥24 h,即得到ATP@Fe3O4复合材料,室温储存于干燥器中备用。
-
通过催化PS降解TC的效果来评价材料的催化性能。由于ATP具有吸附性能,因此,在降解之前,进行如下吸附平衡实验:取50 mL 80 mg·L−1 TC溶液置于150 mL锥形瓶中,向其中加入1.5 g·L−1催化材料后,放置在25 ℃恒温振荡器中,以150 r·min−1摇动,开始吸附实验。每隔一段时间取一定的反应液,经0.1 μm滤膜过滤后,测定滤液中TC的浓度。每次实验重复3次。
在进行批量催化降解TC实验时,将50 mL 80 mg·L−1 TC溶液置于一系列锥形瓶中,向其中加入不同质量(25~100 mg)的ATP@Fe3O4,并调节pH至 3.0~9.0,放置在25 ℃恒温振荡器中,以150 r·min−1摇动。反应达到吸附平衡后,将不同浓度(2~20 mmol·L−1)的PS溶液加入到反应体系中,开始降解反应,并将此时视为初始时间t0,初始浓度C0。在降解反应5、10、20、40、60、90 min时取样,样品经0.1 μm滤膜后,测定滤液中TC的浓度。所有实验均重复3次。
-
微观形貌采用日本日立S-4800 II场发射SEM(扫描电子显微镜)和美国FEI Tecnai G2 F30场发射HTEM(透射电镜)进行观察。材料结构采用德国Bruker AXS D8 Advance多晶X射线衍射仪(Cu Kα radiation at 40 kV and 40 mA)获得XRD(X射线衍射)数据。使用X射线能量色散光谱仪(Thermo Electron Corporation)以AlKα辐射作为激发源测量EDX。采用美国ESCALAB 250 Xi X光电子能谱仪进行XPS(X射线光电子能谱)分析。材料的磁化强度采用VSM-EV7振动样品磁强计进行测定。使用高效液相色谱法(HPLC,Hitachi L-2455)测定四环素(TC)浓度。采用日本TOC-LCPN分析仪来测定催化反应过程中四环素(TC)矿化成CO2和H2O的效率。采用邻菲啰啉分子吸收光谱法和原子吸收光谱测定反应过程中Fe2+和溶出铁的浓度。
-
根据高效液相色谱峰面积所对应的四环素浓度计算去除率,计算方法如式(1)所示。
式中:α为去除率;C0为初始四环素溶液的浓度,mg·L−1;C为吸附或降解后四环素溶液的浓度,mg·L−1。
1.1. 试剂
1.2. ATP@Fe3O4复合材料的制备
1.3. 材料的催化性能测试
1.4. 材料的表征及其测定方法
1.5. 数据分析方法
-
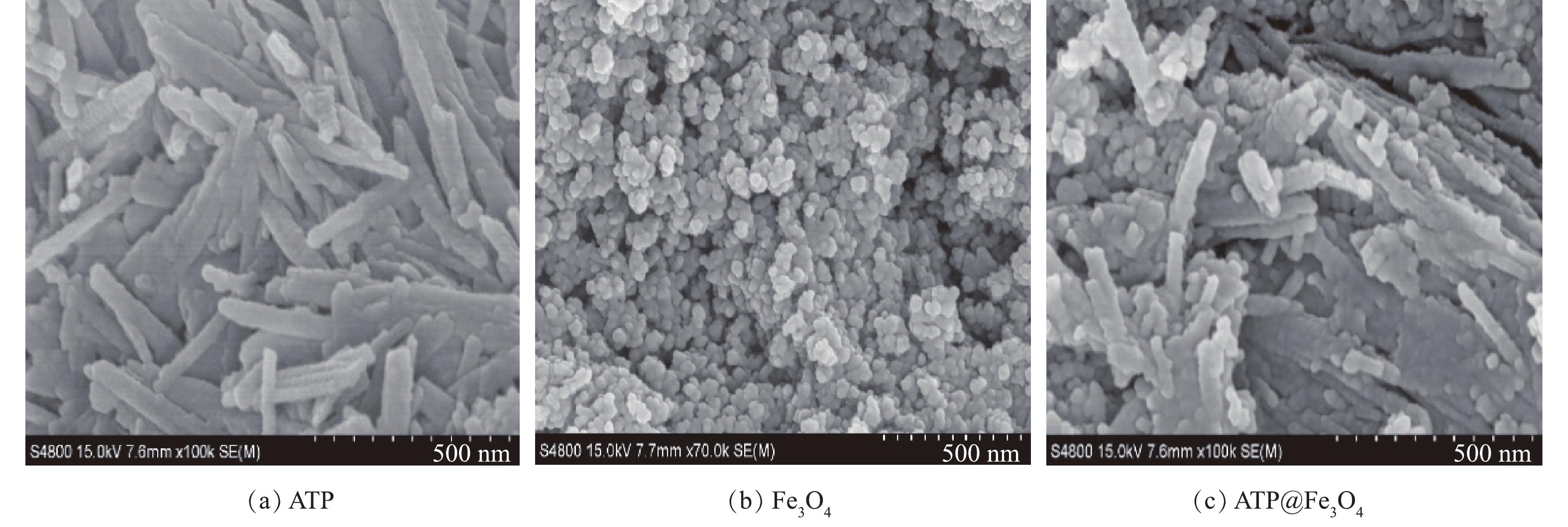
1)扫描电子显微镜分析。由图1可见,ATP为长约200 nm,直径约30 nm的棒状结构,表面较光滑;Fe3O4粒子的粒径约为20 nm,呈现团聚的状态;ATP@Fe3O4复合材料中ATP表面粗糙,凸起明显,这表明Fe3O4纳米粒子成功负载于ATP表面,与此同时,也减少了Fe3O4纳米粒子团聚的现象。
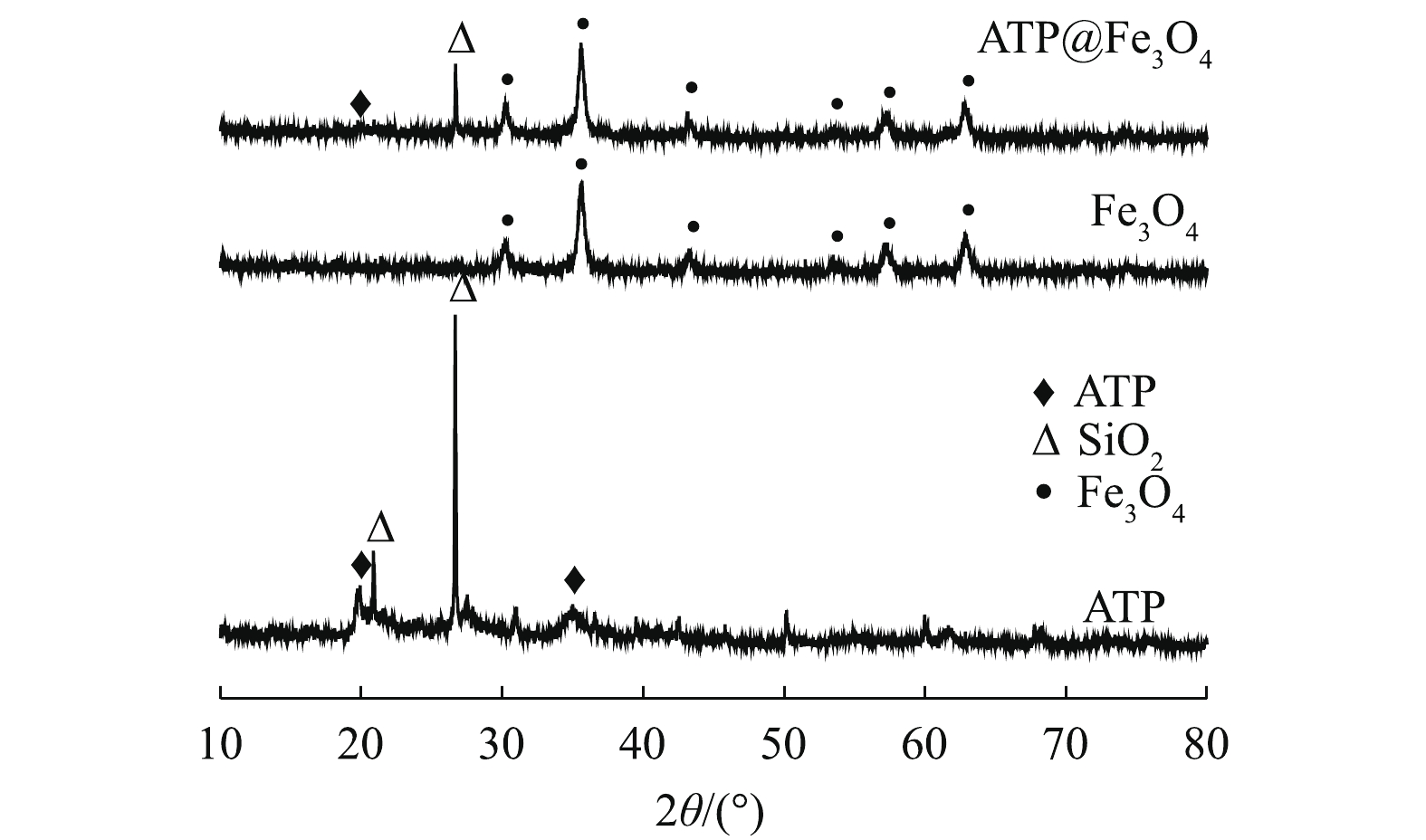
2) X射线衍射分析。图2为ATP、Fe3O4和ATP@Fe3O4的XRD图谱。2θ=19.8°处的峰对应于ATP的特征峰[13];2θ为30.1° (220)、35.5° (311)、43.1° (400)、54.6° (422)、56.9° (511) 和62.6° (440) 处的尖峰对应于立方相Fe3O4的特征峰[14]。在ATP@Fe3O4中,既保留了ATP的特征峰,又观察到Fe3O4的特征峰,这表明Fe3O4纳米粒子成功负载到ATP上,且负载过程中没有破坏ATP的特征结构,这与SEM结果一致。
3)透射电镜分析。由图3(a)可见,ATP@Fe3O4的结构及粒径大小与SEM表征结果一致。由ATP@Fe3O4的元素组成分析结果(图3(b)~图3(f))可知,ATP@Fe3O4材料中含有Fe、O、Si、Al和Mg 元素,相应的含量分别为29.51%、45.34%、16.86%、4.24%和3.09%。综上可知,Fe3O4成功地负载在ATP表面。
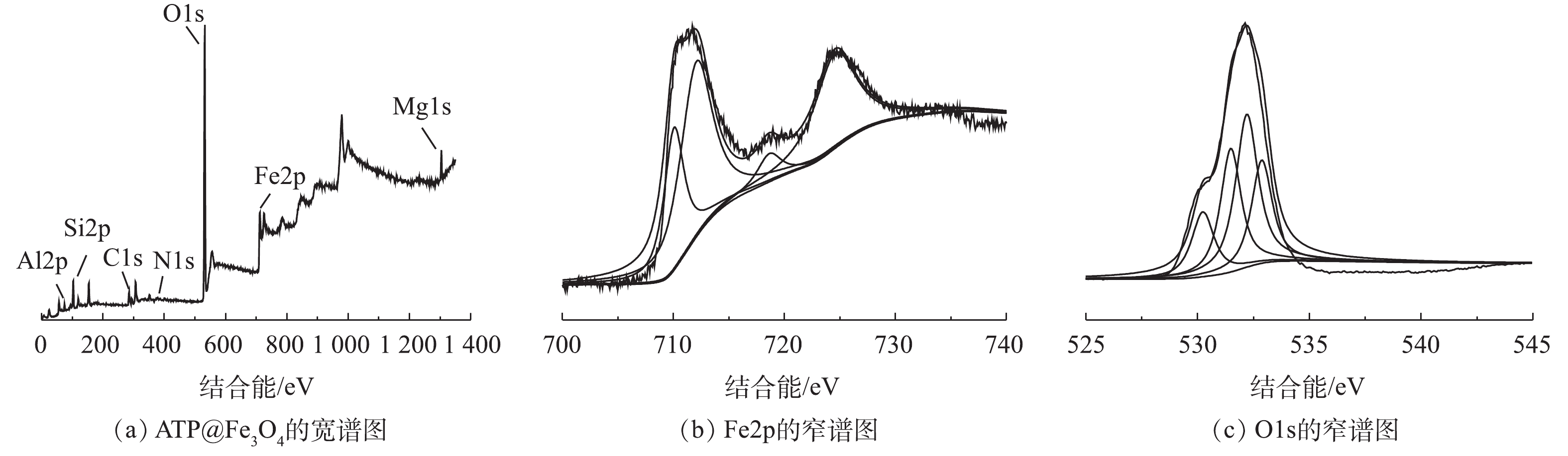
4) X射线光电子能谱分析。由图4(a)可见,Al2p、Si2p、O1s、Fe2p、Mg1s分别在85.08、110.08、537.58、738.58、1 309.08 eV处出峰。由Fe2p结合能的分峰拟合(图4(b))可见,出现在结合能710.04 eV和724.58 eV处的XPS峰分别代表八面体Fe3+和八面体配位的Fe2+[15]。在结合能712.06 eV处出现的峰代表Fe3+,且在718.62 eV处产生相应Fe3+的卫星峰,这也进一步论证了Fe3+和Fe2+负载于ATP表面。由O1s结合能的分峰拟合(图4(c))可见,XPS峰分别出现在530.23、531.48、532.2和533.07 eV处。530.23 eV处对应于Fe3O4的晶格氧[16],531.48 eV和532.2 eV的峰分别对应于单氧原子(H—O)以及单齿和双齿氧(Si—O—Si)[17],533.07 eV处的峰对应的是存在于双齿配位键(O—C=O)中的氧[18],其在氧化反应中起着重要的作用。
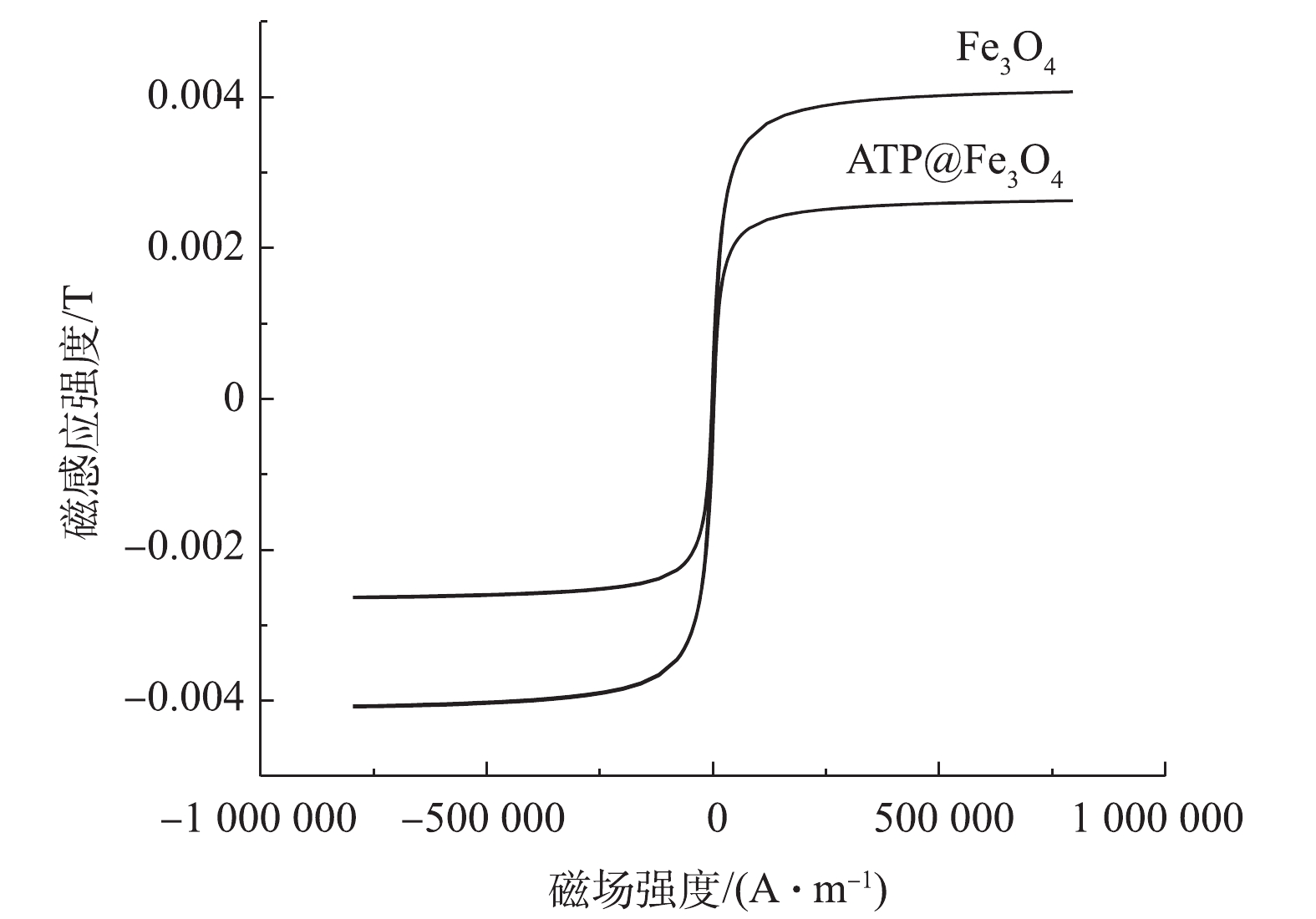
5)磁滞曲线分析。如图5所示,Fe3O4和ATP@Fe3O4对应的2条磁化曲线均表现出几乎为零的剩磁和矫顽力,这说明ATP@Fe3O4和Fe3O4一样具有超顺磁性[19]。而ATP@Fe3O4的最大磁感应强度为2.6×10−3 T,小于Fe3O4的最大磁感应强度4.0×10−3 T,这归因于复合材料中ATP的“稀释”作用[20]。ATP@Fe3O4具有磁性的这一特性也表明了其具有回收利用的潜质。
-
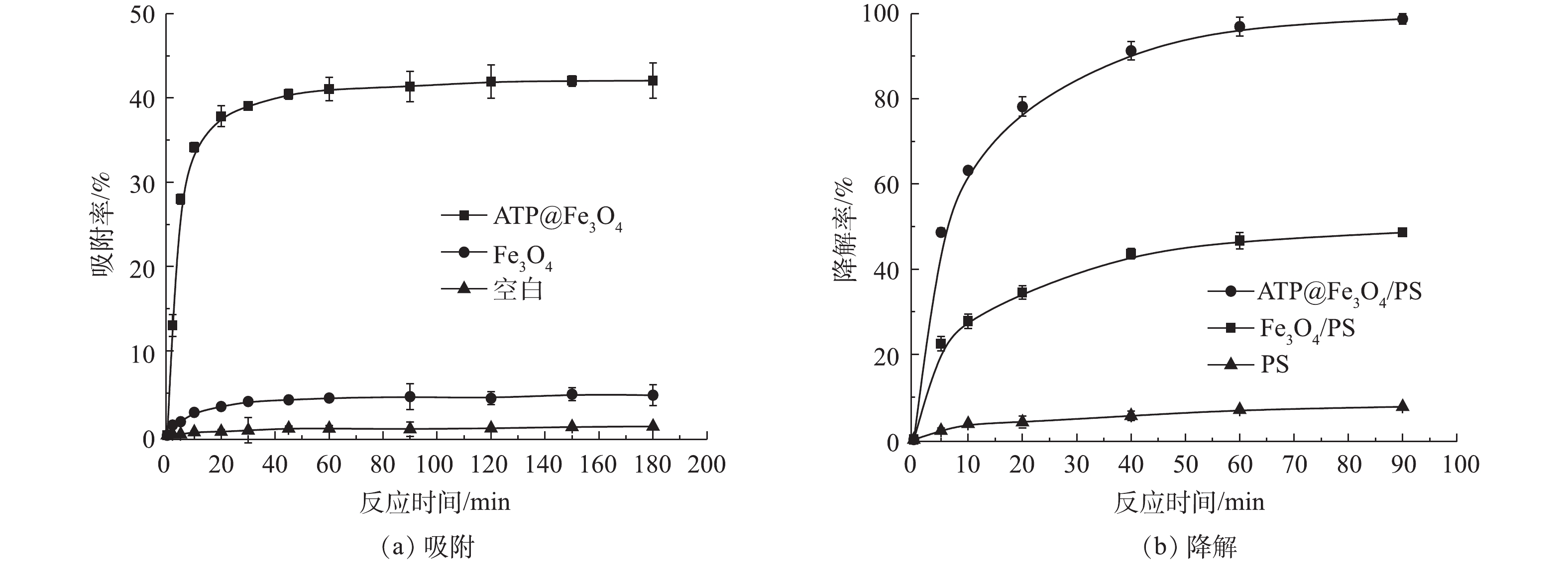
ATP@Fe3O4复合材料对TC吸附和降解的影响如图6所示。ATP@Fe3O4复合材料对TC的吸附效果如图6(a)所示。在实验的前30 min内吸附较快,30 min后吸附缓慢,在60 min时基本达到吸附平衡,这主要是由于ATP表面的吸附位点逐渐被占据,吸附容量逐渐达到平稳,最终吸附达到饱和状态时,吸附量便不再增加[21],此时ATP@Fe3O4对TC的吸附率为41%。而Fe3O4 对TC的吸附影响较小,TC自然降解率可以忽略不计。因此,60 min可以被认为是本实验条件下的最佳吸附时间。
ATP@Fe3O4催化PS降解TC的结果如图6(b)所示,90 min后在ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系中TC的降解效率达到98.75%,显著高于Fe3O4/PS体系对应的48.61%,这是由于在类芬顿反应中,非均相催化剂所释放的Fe2+的量是催化PS产生
SO⋅−4 的关键[22]。ATP@Fe3O4中ATP的存在减小了Fe3O4粒子间的相互作用,从而更好地释放Fe2+,相反地,对于纯Fe3O4,由于粒子间的相互作用而团聚,阻碍了Fe2+的产生。除此之外,PS本身对TC的降解率仅为7.72%,这表明ATP@Fe3O4复合材料是活化PS强有力的催化剂。 -
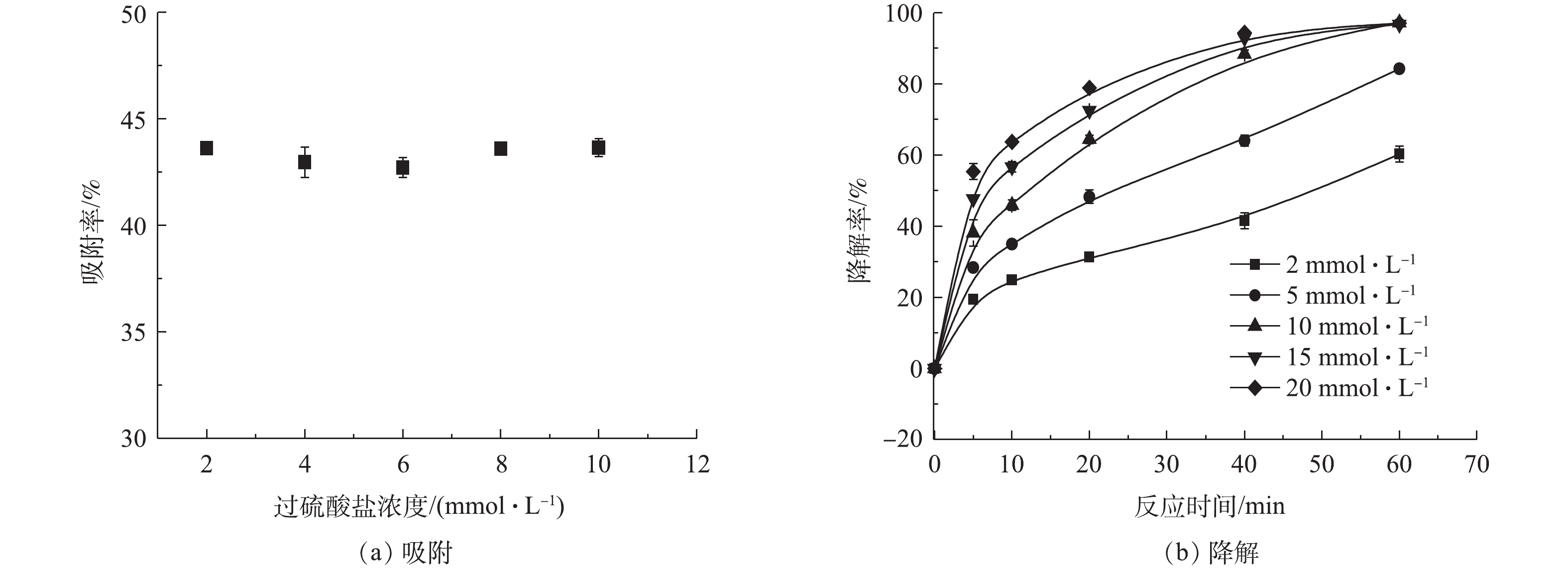
1)初始pH对ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系去除四环素的影响。溶液的初始pH是影响类芬顿氧化反应的重要因素之一[23]。由图7(a)和图7(b)中可以看到,无论在吸附还是降解阶段,ATP@Fe3O4对TC的去除率均是随着pH的增加而下降(四环素原液的pH=3.9)。溶液的pH会影响Fe3O4中Fe2+的释放以及氧化剂的活性和稳定性,进而影响有机污染物的去除率。在pH=3.0的TC溶液中,复合材料中Fe2+更容易活化PS产生
SO⋅−4 ;而在较高pH条件下的低降解率可归因于Fe3+沉淀物在催化剂表面上的吸附所致。总体来看,当降解反应进行60 min时,即使是pH=9.0的溶液中,TC的降解率也接近80%,这表明ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系对TC具有良好的降解能力。反应后溶液pH如图7(c)所示,初始溶液为酸性时,反应后溶液的pH略有升高,是由于存在的凹凸棒土表面带负电荷中和了部分H+;初始溶液为碱性时,反应后溶液的pH略有降低,这归因于Fe3+形成沉淀物消耗了OH−。尽管如此,反应前后溶液pH变化不大。此外,TC溶液本身的pH=3.9,与pH=3.0时系统的降解效率相接近,因此无需预先调节TC溶液的pH,这也为实际应用中调节废水的pH提供理论依据和参考。2)过硫酸盐浓度对ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系去除四环素的影响。由图8(a)可知,由于在不同过硫酸盐浓度的体系中,复合材料的投加量是固定的,所以达到吸附平衡时TC的吸附率基本相同。而在降解反应中(图8(b)),TC的降解率随着PS浓度的增加而逐步提高,这是由于在较高的PS浓度下,会产生更多的
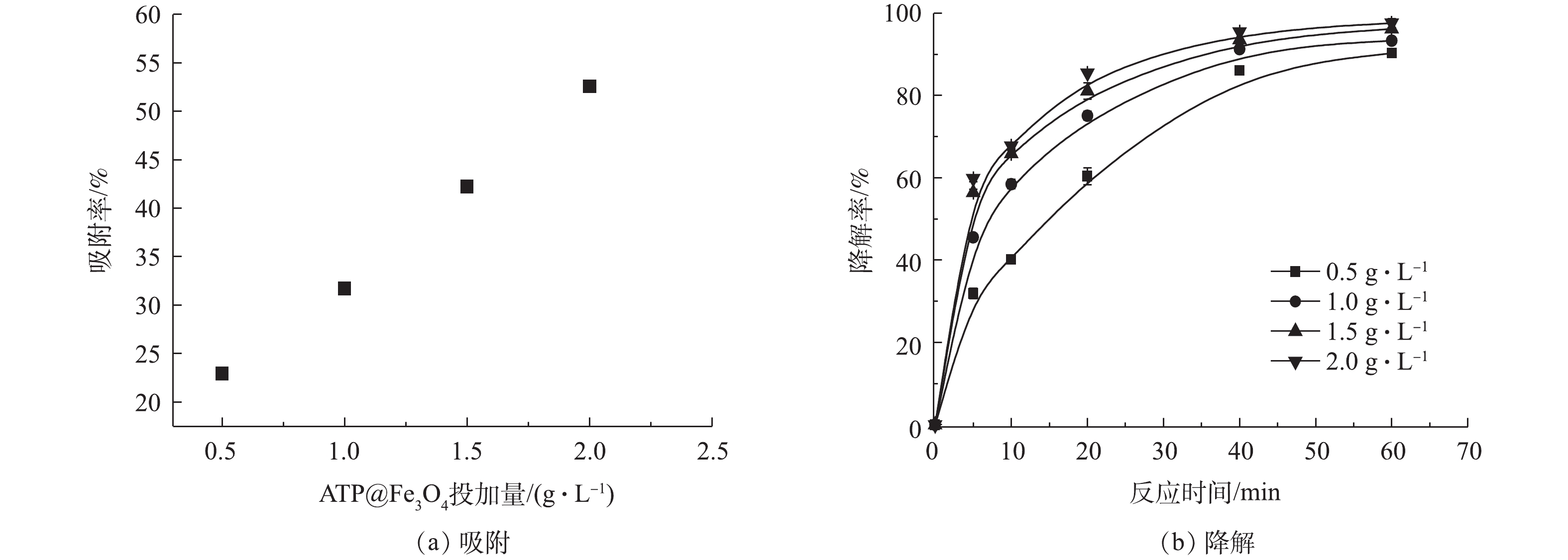
SO⋅−4 来降解TC。降解反应60 min后,在15 mmol·L−1和20 mmol·L−1 PS体系中,TC的降解率与10 mmol·L−1 PS体系大致相同,这归因于溶液中过量的PS充当了自由基的清除剂,从而抑制了TC的降解[24]。综上所述,过硫酸盐的最佳浓度应为10 mmol·L−1。3)催化剂投加量对ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系去除四环素的影响。由图9(a)可知,在前60 min的吸附中,ATP@Fe3O4材料投加量越大,对TC的吸附效果越好。由图9(b)可知, TC的降解率随降解时间的延长而增加。当降解反应60 min时,复合材料投加量从0.5 g·L−1增加到2.0 g·L−1,相应的四环素降解率由89.3%提高到97.6%,这是由于催化剂表面积的增加,为PS提供了更多的活性位点,从而产生了更多的
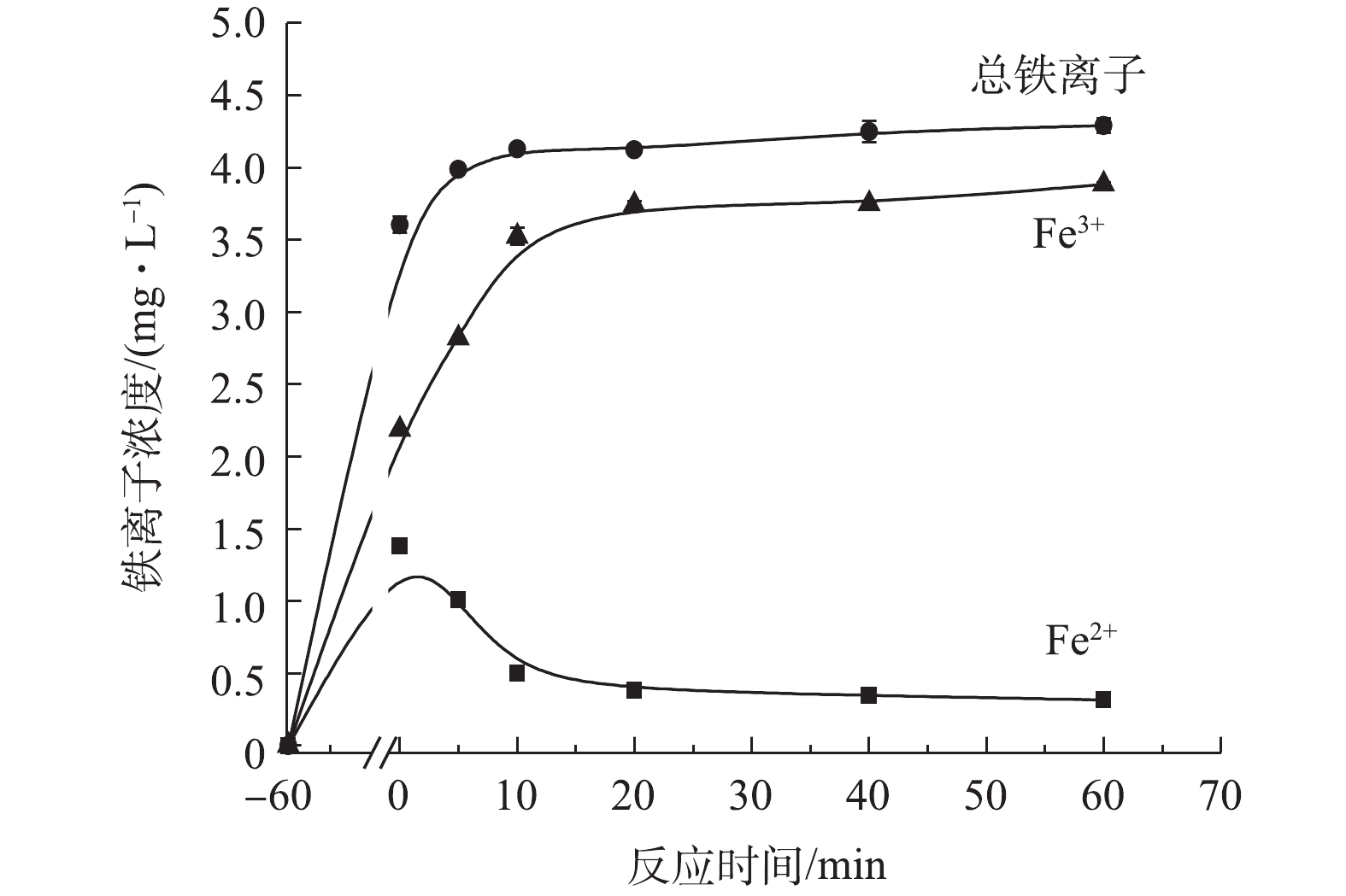
SO⋅−4 。但是催化剂的进一步增加(1.5 g·L−1增加到2.0 g·L−1)没有显著提高TC的降解率,是因为过量的PS充当了自由基清除剂[25]。综上所述,并结合经济角度考虑,复合材料的最佳投加量为1.5 g·L−1。4) ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系吸附降解四环素过程中铁离子的溶出。如图10所示,在材料吸附降解四环素过程中,随着反应时间的增加,Fe2+的浓度呈现先升高后降低的趋势,总铁离子和Fe3+则是逐渐升高。在前60 min的吸附中,Fe2+浓度不断升高并达到峰值1.38 mg·L−1。当PS加入后,Fe2+被PS消耗产生SO4·−和Fe3+,从而导致Fe2+不断地减少和Fe3+浓度不断升高。随着催化降解反应的结束,Fe2+和Fe3+的浓度均趋于平缓。在降解过程中,尽管溶液中总铁离子浓度逐渐上升,但是溶出的铁离子为4.29 mg·L−1,仅仅占1.5 g·L−1复合材料所铁含量的0.94%,这说明该复合材料较稳定,具有重复利用的潜质。
-
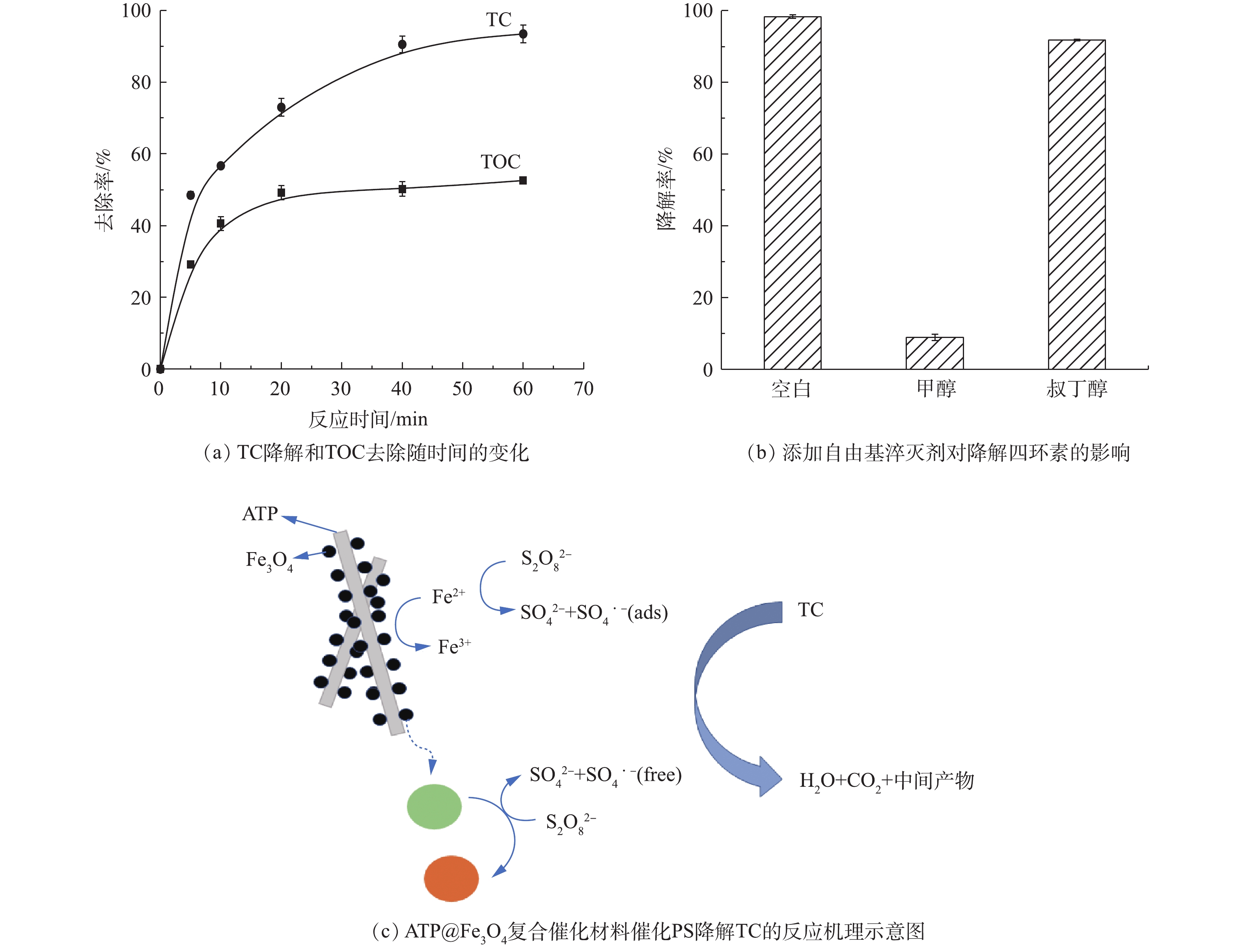
硫酸根自由基(
SO⋅−4 )可以将四环素(TC)氧化为CO2和H2O,因此,TOC在一定程度上反映了TC的降解过程[26]。ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系降解四环素的反应机制见图11。由图11(a)可知,在降解60 min后,TC的降解率高达97%,同时TOC的去除率约为50%,表明50%的TC被活性自由基氧化为CO2和H2O[27],一部分四环素被自由基攻击后产生了中间体,这还需要进一步的研究确定。众所周知,高级氧化技术(AOP)是基于自由基与有机污染物的反应[28]。为了研究ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系中的活性物质,向体系中加入自由基清除剂进行淬灭实验。由于甲醇(MeOH)可与硫酸根自由基(
SO⋅−4 )和羟基自由基(·OH)快速反应,而叔丁醇 (TBA)与·OH反应比SO⋅−4 快,可选择性地淬灭体系中的·OH,因此,采用MeOH和TBA分别作为SO⋅−4 和·OH的淬灭剂。结果如图11(b)所示,在添加甲醇、叔丁醇的体系中,四环素降解率分别为8.92%、91.80%,表明系统中的起主要作用的自由基是SO⋅−4 。而存在的少量羟基自由基·OH是由于SO⋅−4 的存在使自由基相互转化而生成·OH,该·OH的氧化电位比SO⋅−4 稍高[29]。反应如式(2)所示。根据上述结论,提出了ATP@Fe3O4活化PS的反应机理。如图11(c)所示,当最初的
S2O2−8 分子被吸附在ATP@Fe3O4的表面上时,负载于ATP表面的Fe3O4粒子和部分溶解于水中的Fe2+共同催化PS生成SO⋅−4 ,由此TC被SO⋅−4 氧化为CO2、H2O和中间体。
2.1. 表征分析
2.2. ATP@Fe3O4对TC的吸附和降解
2.3. 单因素影响分析
2.4. ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系降解四环素的反应机制
-
1)采用共沉淀法将Fe3O4纳米粒子与ATP结合,成功合成了同时具备吸附与催化性能的非均相类芬顿催化剂ATP@Fe3O4。制备的ATP@Fe3O4具有超顺磁性,有回收利用的潜质。
2) ATP@Fe3O4是活化过硫酸盐(PS)生成硫酸根自由基(
SO⋅−4 )强有力的催化剂,且ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系显示出良好的去除水溶液中四环素(TC)的能力,该体系的去除机理为:负载于ATP表面的Fe3O4粒子和部分溶解于水中的Fe2+共同催化PS生成SO⋅−4 ,将TC氧化为CO2、H2O和中间体。3)溶液的pH、过硫酸盐浓度以及催化剂投加量均影响ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系对四环素的去除效果。当PS浓度为10 mmol·L−1、ATP@Fe3O4投加量为1.5 g·L−1、四环素溶液pH为3.9时,ATP@Fe3O4/PS体系去除四环素的效果最佳,去除率可达98.75%。









 下载:
下载:


 百度学术
百度学术






