-
硝酸盐污染正在成为全球性的环境问题,水体中过量的硝酸盐可导致水体富营养化,对水生生态系统和人类健康造成威胁[1 − 2]. 生物反硝化法处理硝酸盐污水以其经济性好、处理效率高等优点,已成为水处理中采用的主流方法[3]. 生物反硝化是通过反硝化微生物进行的. 自然界中最常见的反硝化菌是以有机碳为碳源的异养反硝化菌[4]. 异养反硝化菌利用硝酸盐作为电子受体,有机碳作为电子供体和能源来维持生长,并将硝态氮最终转化为氮气从而完成反硝化脱氮.
在异养反硝化中,有机碳是不可或缺的关键要素. 当水体碳氮比(C/N)较低时,外加碳源的作用就变得尤为重要[5]. 可溶性的甲醇、乙醇、葡萄糖、乙酸钠等物质通常作为外加碳源,但由于其快速溶解而随出水流出生物处理系统,易造成二次污染,需要复杂的连续监测和过程控制系统而导致运行成本高昂[6]. 天然植物类有机碳源(木屑、稻壳、秸秆、玉米芯、花生壳等)虽然价格低廉、材料易得,但存在释碳不稳定、出水色度偏高、含有大量难以被微生物降解成分、易造成系统堵塞等弊端,限制了其广泛使用[7 − 8].
可生物降解聚合物(biodegradable polymers, BDPs)作为固相反硝化缓释碳源的同时,可充当生物膜载体,这种新型材料近年来逐渐在利用生物膜进行反硝化研究中受到重视. BDPs通过微生物分泌的胞外酶被降解,转化成可溶性小分子有机物,这些小分子有机物能为异养反硝化菌提供能源和反硝化必需的电子[9]. BDPs只在微生物作用下分解,这一特性能够避免或减轻上述可溶性碳源投加不足或过量导致的水质问题[10]. BDPs长期释碳速率稳定、易于挂膜、维护简单,与天然植物类碳源相比,能获得更高的反硝化速率[11 − 12],利用BDPs处理低C/N污水已成为研究热点. 已有文章综述了不同类型碳源的作用机制[13]及其在不同目标水体中的应用[3,7]. 目前尚缺乏针对BDPs反硝化碳源的系统性综述.
本文从BDPs缓释碳源类型、反硝化性能、影响因素、脱氮机制、微生物群落、脱氮成本评价以及共存污染物去除等多方面展开综述和讨论,并对未来研究方向提出展望,以期为BDPs反硝化技术研究和应用提供参考和依据.
-
BDPs是一类人工合成的高分子材料,具有较好的生物相容性、生物降解性以及无生物毒性等许多优良特性[14 − 15]. 目前,作为反硝化碳源研究较多的主要有PHBV(poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate),聚羟基丁酸戊酸酯)[9,16]、PCL(polycaprolactone,聚己内酯)[17 − 18]、PBS(poly(butylene succinate),聚丁二酸丁二醇酯)[19]、PLA(polylactic acid,聚乳酸)[20]、PHB(polyhydroxybutyrate,聚羟基丁酸酯)[21]以及混合碳源[22]等.
已报道的部分BDPs及混合碳源体系的NO3−-N去除速率与可溶性有机碳(DOC)、总有机碳 (TOC)总结见表1. BDPs的反硝化性能与其物理、化学特性息息相关. 一般来说,同一碳源,分子量越低越易于水解,反硝化性能越好;含有C—O或C=O等亲水基团更多的碳源更容易被微生物降解利用;碳源比表面积越大、表面越粗糙越易于生物膜附着生长. 2.1节详细介绍了BDPs理化性能对反硝化的影响. 总的来说,作为固相碳源,反硝化性能最优异的为PHBV,其次是PCL、PBS等. 近年来,将PHBV及其混合物如PHBV/PLA[30]、PHBV/零价铁/木屑[31]作为反硝化基质的研究逐渐增多,显示出PHBV应用于反硝化领域的巨大潜力. 吴为中等[32]采用PHBV为碳源和生物膜载体的反应器去除硝酸盐,水力停留时间(hydraulic retention time,HRT)为2 h,总氮(TN)平均去除率达98.39%(进水NO3−-N约14.9 mg·L−1). Yi等[33]构建的PHBV反硝化系统,在HRT为0.5、1、2、5 h条件下,NO3−-N(约18 mg·L−1)去除率均高于96%. PHBV反硝化系统可以高效去除高浓度硝酸盐,在HRT为7.25 h时,NO3−-N(100 mg·L−1)去除率达到99%,同时不积累NO2−-N和NH4+-N[34]. PHBV用于反硝化时水处理系统启动时间短. Yi等[33]以PHBV为碳源,NO3−-N浓度从第1 天开始急剧下降,第5 天便降到1.0 mg·L−1以下. 其他研究亦表明,PHBV反硝化启动时间快于PCL和PLA(PHBV 11 d、PCL 20 d、PLA 40 d)[35 − 36]. PHBV是一种由微生物合成的聚酯,具有较好的生物降解性和生物相容性,所以能够较快地被微生物降解释放出有机碳供异养反硝化菌利用,从而快速启动反硝化作用[15].
DOC是评估固相反硝化体系有机碳释放性能的重要指标. 反硝化系统中,碳源不足时反硝化受到抑制,也会因反硝化不彻底而导致NO2−-N积累[33,37]. NO2−-N的毒性大于NO3−-N,会进一步抑制反硝化菌的生长从而影响反硝化速率[38]. 另一方面,当碳源降解速率超过利用速率时,会造成DOC积累[11,35]. 多余的DOC如果不经处理随废水排放易污染环境,同时也浪费碳源、增加处理成本. 理想的碳源应以适当的速率释放DOC,在保证足以完全反硝化的同时,不产生过量的DOC[38 − 39]. 大部分BDPs在HRT为5 h左右及5 h以下时出水DOC在10—100 mg·L−1(表1),混合碳源PHBV/PLA[12,27]、PBS/竹粉[29]稳定期的出水DOC可以达到15 mg·L−1以下,PHBV/木屑系统出水DOC和NH4+-N(DOC(9.00±4.16) mg·L−1、NH4+-N (0.37±0.32) mg·L−1)都远低于单一PHBV系统(DOC (33.70±20.79) mg·L−1、NH4+-N(1.14±0.37) mg·L−1)[11],显示出了混合碳源控制碳释放方面的优势. BDPs的碳释放还与水质条件有关. 例如使用PBS做碳源,处理合成废水与真实的养殖废水进行对比,真实养殖废水出水DOC的增加量(出水DOC与进水DOC的差值)明显超过合成废水,说明复杂的进水成分能刺激微生物的降解活性[19]. 盐度的存在也会使微生物的生物降解更活跃进而增加出水的DOC[19]. 此外,对碳源材料进行预处理或改性可以改善释碳性能. 李加伟[40]将PBS/竹粉在-10℃条件下冷冻处理1 d后研究释碳规律,发现经过冷冻处理后的释碳速率远低于未经处理的对照组.
Luo等[41]发现,尽管PCL反硝化系统的硝酸盐去除率接近100%,但会释放大量的DOC,也就是说在反硝化结束时,碳释放仍在进行. 因此,他们认为PCL系统反硝化和碳释放在一定程度上是两个相互独立的过程. 与此结果有所不同,Luo等[42]研究表明,在不同的进水硝酸盐浓度条件下,PCL系统反硝化速率与DOC释放速率呈显著的正相关,并将这一特性称之为“自适应”(Self-adaptation). 而该系统之所以具有“自适应”特性,可能是因为优势菌Acidovorax_sp同时具有反硝化和PCL降解功能,可以根据一定范围内硝酸盐负荷的变化,动态调整PCL的碳释放速率,以使得碳源的供应能够满足反硝化过程的实际需求. 这个研究结果为通过优化微生物群落结构和功能来平衡DOC释放速率与硝酸盐去除速率的关系提供了崭新的思路.
由于单独使用BDPs成本较高,将BDPs与其他低价BDPs或廉价的天然材料混合,制备低成本碳源材料成为研究者们关注的焦点. Xiong等[43]以PCL和花生壳为碳源,聚乙烯醇和海藻酸钠为骨架制备的混合碳源PPP,当投加量为40 g时,NO3−-N去除率达99.92%. Chu和Wang等[44]分别用PHBV、PHBV/淀粉和PHBV/竹粉等3种材料在填充床反应器中进行反硝化用于去除地下水中的硝酸盐. 在自然挂膜条件下,两个混合碳源反应器30—40 d完成启动(NO3−-N去除率60%以上),而单一PHBV反应器则需要3个月以上才能达到相同水平,且PHBV混合碳源比单一PHBV具有更好的硝酸盐去除性能. 这是因为启动初期混合碳源系统DOC显著高于单一PHBV系统,高的DOC有利于生物膜的形成和生长. 将BDPs与其他物质混合使用不仅可降低成本,还可以同时或分段处理多种污染物. Sun等[10]用20%PHBV、20%PLA、30%木屑、30%零价铁高温混合制成的复合材料,实现了同时去除92.6%的NO3−-N和99%的总磷(TP)的效果. Yi等[33]发现PHBV与活性炭串联使用可以去除95%的NO3−-N和80%的药品和个人护理品(PPCPs). 由于水体中硝酸盐经常与农药、重金属、含氯化合物等污染物共存,同时去除硝酸盐和这些污染物不仅减少了处理设施,而且节约成本[38].
-
BDPs反硝化的影响因素不同于可溶性碳源. 可溶性碳源的投加量是可控的,C/N是主要的影响因素. 而BDPs固相反硝化最重要的影响因素是HRT. 在其他因素一定的条件下,可以通过调整HRT来提高反硝化效率. 讨论了BDPs理化性能、温度、溶解氧、HRT、pH等对反硝化性能的影响,最佳的运行条件可使系统脱氮效率达到最高.
-
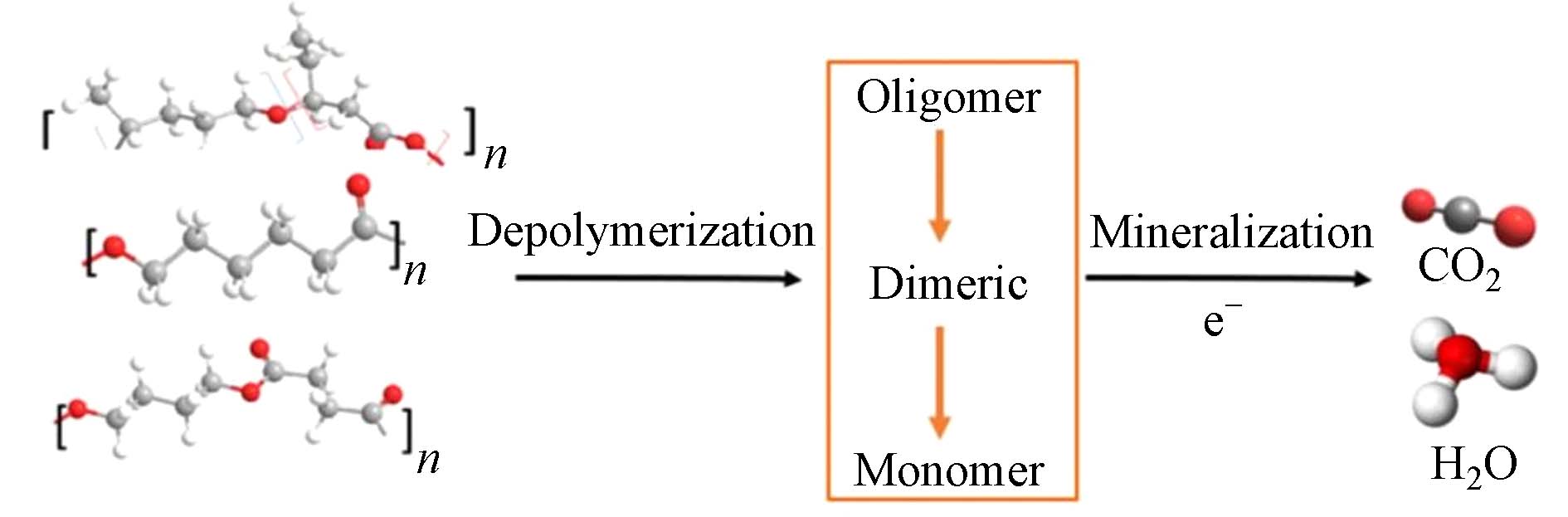
BDPs的可生物降解性(释碳能力)是影响氮还原速率和反硝化效果的关键因素[45 − 46]. BDPs可被真菌、细菌和藻类产生的酶分解. 首先,BDPs被降解为低分子量的低聚体、二聚体和单体. 接着,降解产物被微生物作为碳源转化为能量、生物量和各种代谢产物,最终被矿化为二氧化碳、水等,从而实现有效的生物地球化学碳循环[13] (图1). 不同化学组成的BDPs可生物降解性不尽相同[7,30]. 有报道称,PHBV比其他BDPs具有更高的可生物降解性[5]. PHBV降解可产生乙酸、丁酸等酸性物质,而乙酸是小分子化合物中微生物最容易利用的水解产物[13,26],这也可能是PHBV系统具有较高反硝化性能的原因之一. 另有研究发现PHB和PHBV的可生物降解性较高,其次为PCL,最后为PLA[47]. PLA的可生物降解性远低于PBS和PCL,原因可能是PLA中烷基的含量过低[20].
BDPs作为反硝化碳源时,为了获得足够的有机物进行代谢和生理活动,微生物倾向于附着在碳源的表面[11]. 因此,表面特性如比表面积、粗糙度、孔隙率、亲水性/疏水性等都关系到BDPs作为生物膜载体的优劣[35,48 − 49]. 易成豪等[35]发现PHBV相较于PCL具有更加稳定持续的反硝化性能,因为PHBV表面粗糙且有大量孔洞,生物膜中富集多种异养反硝化菌. 相比之下,PCL表面较光滑且无孔隙,易造成附着生物量低且生物膜不牢固,在水流冲刷下脱落的现象[50]. 随着降解微生物的利用,碳源表面粗糙度增加,孔隙变大,分子量变低,化学结构发生变化等,会对BDPs碳源产生各种影响. Zhang等[48]研究了分子量分别为60000、80000和140000的PCL反硝化性能,发现PCL的可生物降解性和反硝化速率随着分子量的增加而降低. 然而,当降低HRT,水流剪切力增加时,分子量最大表面最粗糙的圆柱形PCL-4反而表现出最高的反硝化速率. 结果表明,载体形状和表面粗糙度(物理特性)在反硝化过程中可能起着比分子量(化学特性)更重要的作用. 粗糙的表面不仅增加了微生物的附着面积,还在高水流剪切力条件下为生物膜提供了庇护所,使其不易脱落[48]. 因此,BDPs载体表面粗糙和高孔隙率是增强微生物附着性的必要条件.
-
BDPs反硝化效能不仅与其理化性能有关,还受到运行条件等因素的影响.
温度能够显著影响BDPs碳源的释放率、微生物活性和代谢,从而影响污染物的去除率[51]. 在一定温度范围内,NO3−-N的去除率随温度上升而提高[52]. 淀粉/PCL混合碳源15 ℃时NO3−-N去除率只有33.1%,远远低于30 ℃时的88.0%[6]. PHBV/PLA/稻壳混合碳源[49]随着温度从15 ℃增加到35 ℃,7 h内硝酸盐去除率从53.3%快速提高到100%. 低温抑制了酶和功能微生物的活性[4], 温度的提高促进了水解菌和反硝化菌的活性,加速了BDPs的降解和反硝化过程,从而提高了硝酸盐的去除率. 较高温度能促进碳源释放有利于微生物生长[52],但也会导致总有机碳(TOC)的积累[15]. 过高的温度反而会抑制反硝化菌的活性,从而导致反硝化效率迅速下降[38].
溶解氧(DO)是BDPs反硝化过程的另一个重要的环境因子. 反硝化菌在缺氧条件下利用NO3−-N作为电子受体[53]. DO可能会抑制反硝化过程,因为DO是比NO3−-N活性更高的电子受体[12],DO与NO3−-N同时存在时,DO更容易被利用,从而阻碍了反硝化反应. 另外,DO会降低亚硝酸盐还原酶的活性,导致中间产物NO2−-N积累[41]. BDPs作为碳源与生物膜载体不同于可溶性碳源,生物膜阻碍DO扩散从而在生物膜内部形成缺氧区,这种缺氧区加上BDPs的碳供应促进了反硝化作用,从而减少了DO对BDPs反硝化的负面影响[41]. Gutierrez-Wing等[54]评估了循环水养殖系统中DO对PHB为碳源的反硝化性能的影响,发现NO3−-N去除速率随DO浓度的增加而降低,当DO达到4—5 mg·L−1时,反硝化最终停止. 与PHB不同,Luo等[41]发现,PCL作为碳源可有效地减少DO对反硝化过程的抑制. 与缺氧条件相比,PCL在有氧时DOC释放量更高. 低氧(3.83±0.22) mg·L−1、中氧(6.12±0.50) mg·L−1条件下NO3−-N去除率高于缺氧(0.44±0.01) mg·L−1、高氧(10.45±0.65) mg·L−1条件. Luo等[55]的研究表明,DO可以促进PBS的生物降解以及好氧反硝化菌的富集,从而使得曝气组脱氮率高于低氧组和缺氧组. 关于DO对BDPs体系反硝化作用影响的解释,大多研究倾向归因于BDPs材料间形成的厌氧微环境、生物膜生成的厌氧微环境促进了反硝化发生. 实际上,好氧反硝化作用已被发现并进行了广泛的研究[56],但关于BDPs反硝化体系中好氧反硝化的作用我们还知之甚少.
硝酸盐负荷对BDPs反硝化的影响通过水力停留时间(HRT)和进水硝酸盐浓度两个条件来进行研究. HRT影响污水与生物膜接触时间以及水流对生物膜的冲击力,过高或过低的HRT均不利于反硝化过程. Zhang等[57]的研究显示,PCL系统HRT小于2.7 h时,NO3−-N去除效率随HRT的增加而提高,HRT为2.7 h时,NO3−-N去除效率达到最高93%,而HRT进一步增加对NO3−-N去除效率影响不大. 降低HRT导致硝酸盐负荷增加以及水体与生物膜接触时间变短都可能导致脱氮效率下降[48]. Jiang等[58]测定了PCL在不同NO3−-N浓度条件下,完全去除NO3−-N(出水TN<5 mg·L−1)所需的HRT. 进水NO3−-N浓度为15、25、35、45、55 mg·L−1时,PCL反应器完全去除NO3−-N(平均出水TN (2.06±1.14) mg·L−1)的HRT分别为42、64、87、129、202 min,HRT与进水NO3−-N浓度呈线性关系. Xia等[49]发现,降低HRT出水DOC浓度会下降. 这可能是由于降低HRT导致的高硝酸盐负荷会消耗更多的DOC,同时,在较短的HRT条件下较高的水负荷也可能稀释了DOC. 一般来说,较长的HRT为反硝化提供了足够的时间从而会提高反硝化性能,但同时也降低了污水处理效率. 另一方面,较短的HRT可能会因为反应不充分而导致NO2−-N的积累[59]. 适宜的HRT应兼顾反硝化效果和污水处理效率. 有研究者[3]认为BDPs碳源释碳性能优异,很多情况下2 h的HRT足以完全去除NO3−-N. Luo等[42]对比了HRT和进水硝酸盐浓度两个条件下PCL系统的脱氮性能. 结果显示,反硝化速率与HRT引起的硝酸盐负荷呈正相关,而进水硝酸盐浓度变化对反硝化性能影响不大,系统依旧保持较高的反硝化效率. 结果表明,PCL系统对不断变化的进水硝酸盐浓度具有较强的耐受性,而HRT对硝酸盐去除效率的影响要大于进水硝酸盐浓度.
除以上因素外,还有很多条件影响BDPs反硝化系统的性能. 相较于水溶性碳源,BDPs反硝化系统中pH的变化和影响更为复杂. 例如,PHBV在反硝化过程中会生物降解生成有机酸等酸性物质,从而中和反硝化产生的碱度[49]. 以PHBV/PLA为反硝化碳源,酸性条件下,硝酸盐去除效率明显降低. 进水pH为5.68时,硝酸盐去除效率只有中性或碱性条件下的34%,而进水pH为9.57—10.38强碱性时,不影响硝酸盐去除效率[60]. 另外,盐度可以提高PBS反硝化系统硝酸盐去除效率和稳定性[61].
-
BDPs反硝化体系本质上是功能微生物在发挥作用. 反硝化系统中微生物群落与所使用的碳源类型密切相关[40]. 以BDPs为碳源和生物膜载体,门水平微生物主要为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)、绿菌门(Chlorobi)、绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)[29,62 − 63]. 其中,变形菌门和拟杆菌门被广泛报道为反硝化菌的两个主要门. 变形菌门是生物反硝化系统中最重要的门,其包括多种好氧菌和厌氧菌,它们可以降解多种有机物,并参与多种代谢类型的反硝化作用[64]. 很多研究已经确定变形菌门是BDPs为碳源的固相反硝化系统中的优势门[17,35,61,65]. 变形菌门在PCL、PHBV生物膜中的相对丰度可达60%以上[17,35]. 考虑到变形菌门在除氮过程中的关键作用,Yang等[11]专门分析了PHBV、PHBV/稻壳、PHBV/木屑三个中试系统变形菌门亚群中β-变形菌亚门(Betaproteobacteria)、α-变形菌亚门(Alphaproteobacteria)、δ-变形菌亚门(Deltaproteobacteria) 、γ-变形菌亚门(Gammaproteobacteria)的丰度结构和功能. 在他们的研究中,β-变形菌亚门在所有样品中占优势,在PHBV系统中的相对丰度最高. 与PHBV系统相比,PHBV/稻壳、PHBV/木屑系统中,γ-变形菌亚门的相对丰度显著增加. 由此可见,不同碳源的微生物群落结构是有差异的. 拟杆菌门在高分子有机物的水解和发酵中发挥重要作用,其中Lentimicrobium属是以强大的反硝化能力而闻名[31]. 绿菌门、绿弯菌门可降解生物膜中凋亡细胞产生的有机物[62]. 厚壁菌门可以产生降解纤维素、蛋白质和脂质必不可少的胞外酶[66].
多个研究发现,BDPs表面生物膜中微生物群落多样性低于初始接种活性污泥[17,58,62],表明BDPs对附着微生物具有选择性. 由于碳源的选择压力,最适者实现了富集[58],这使得微生物功能更倾向于专门化[62]. 如PCL生物膜变形菌门丰度达到了83.98%,远远高于初始接种污泥的32.42%[58]. 易成豪等[35]的研究显示,PHBV对微生物的选择限制作用相比于PCL较弱,这也从微生物角度验证了此研究中PHBV比PCL具有更好的促进反硝化性能. 最近,网络分析不断被用于BDPs反硝化微生物群落相关性研究[29,31,61 − 63]. 有结果显示,变形菌门、拟杆菌门和绿弯菌门呈显著的正相关关系[62],这些微生物的共存可能是BDPs系统中微生物协同关系的典型反映. 另有研究[11,67]表明,BDPs混合碳源较单一BDPs微生物群落结构更复杂、功能微生物更丰富,有利于系统稳定性、抗逆性以及脱氮性能的提高.
-
对于BDPs反硝化体系运行机制的研究,大多文献还是沿用传统反硝化机制的研究方法,从脱氮基因或脱氮酶系着手. 对于脱氮基因,研究较多的主要有amoA(编码氨单加氧酶)、napA/narG(编码硝酸盐还原酶)、nirS/nirK(编码亚硝酸盐还原酶)、nosZ(编码氧化亚氮还原酶),以及编码催化硝酸盐异化还原为铵(dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium,DNRA)的硝酸盐异化还原酶nrfA. 这些传统反硝化(硝化)相关的基因在BDPs体系中大多可以检测到[9,11,61,66,68]. 在脱氮基因研究方法的基础上,Yang等[39]还从碳源降解相关基因的角度,探讨了PHBV、PHBV/木屑作为固体碳源对糖酵解代谢途径的影响. 他们发现,编码甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶(GAPDH,EC 1.2.1.59)的基因丰度在PHBV/木屑系统显著高于PHBV系统,促使PHBV/木屑系统产生更多的电子供体从而具有更好的反硝化性能. 而编码葡萄糖激酶(GK,EC 2.7.1.2)的基因丰度在PHBV系统更高,这可能是PHBV系统出水DOC高于PHBV/木屑系统的原因. 还有研究证明了BDPs可调节反硝化功能酶的表达. Wu等[69]通过转录组学、蛋白组学、免疫印迹技术,从关键反硝化酶的角度对PHA影响施氏假单胞菌(Pseudomonas stutzeri)脱氮的内部机制进行了研究. 结果显示,PHA促进硝酸盐还原酶NapB和NapA的表达量分别提高了10倍和20倍,加速了电子转移过程,从而使得NO3−-N去除率从32.8%(乙酸钠)增加到45.8%(PHA),证明了PHA可以促进反硝化脱氮. Jiang等[58]发现PCL反应器的反硝化性能不如乙酸钠的一个重要原因是PCL解聚酶不足,导致PCL降解速度慢,因而需要较长的时间产生电子来还原硝酸盐.
目前,关于BDPs用于反硝化碳源的研究多集中在反硝化性能、影响因素、微生物群落结构等方面,对于机制方面的研究尚缺乏广度和深度. 如BDPs如何参与微生物代谢、如何影响微生物生长、如何调节反硝化作用、BDPs反硝化功能基因(BDPs降解、反硝化)的表达条件、表达过程中各种基因的调控、与传统反硝化基因表达的异同点等问题尚不明晰. 阐明BDPs脱氮机制有助于研制适合不同处理水体的碳源材料、开发反硝化工艺. 今后可通过多组学技术如基因组学、转录组学、蛋白组学、代谢组学等进行联合研究.
-
脱氮成本是工程应用需要考虑的重要问题. BDPs作为碳源具有较好的反硝化效果,但是相对较高的成本限制了此类材料在实际工程中的广泛应用. 不同碳源去除单位NO3−-N成本评价见表2. 处理1 kg NO3−-N,PHB的使用成本是其他BDPs的2—7倍[48]. 使用PHBV、PCL、PLA的成本是甲醇的5—13倍. 混合碳源较纯BDPs脱氮成本显著降低. Zhang等[3]对多个研究的数据进行统计分析发现,混合碳源较纯BDPs的NO3−-N去除效果没有显著差异,这意味着成本更低的混合碳源值得更进一步研究. 值得一提的是,水溶性碳源工艺除了原材料成本之外,还有生物膜载体(填料)成本、监测控制等设备成本. 由此综合来看,BDPs碳源还是具有一定的竞争力.
-
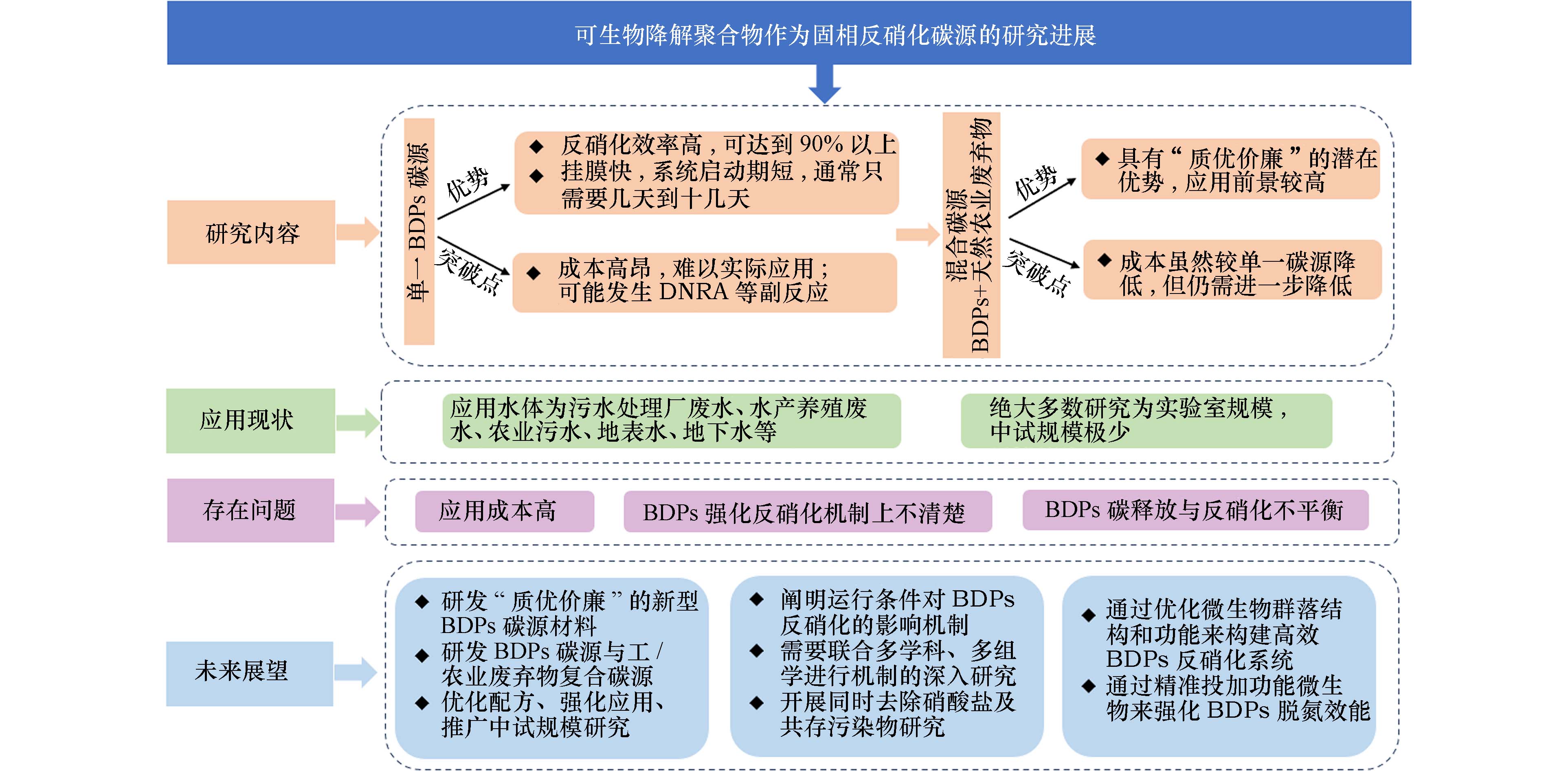
基于BDPs为碳源的反硝化脱氮技术具有反硝化效率高、操作简单、环境友好等优点,在对水质量要求高的低C/N水处理中显示出很大的应用潜力,如污水处理厂废水、地下水、饮用水、循环养殖废水等. 在以往的研究中,多种BDPs被证明具有良好的反硝化性能,且对影响因素和微生物群落结构等方面进行了较多探索并取得了一定的研究成果. 但是,该领域仍然面临很大挑战,对未来研究和应用提出展望(图2).
(1)研发“质优价廉”的新型BDPs碳源材料应该是未来研究的重点. 质优:从反硝化效果来看,理想的BDPs碳源应具有合适的反硝化速率和有机碳释放速率. 在保证完全反硝化的同时出水中不应含有过多的有机碳. 价廉:从经济因素来看,BDPs碳源将继续在废弃物利用方向发展. 比如BDPs工业废弃物的再利用,或将BDPs与廉价的农业废弃物混合制成复合碳源. 现有研究结果表明,BDPs复合碳源具有“质优价廉”的潜在优势,应用前景较高,但目前相关研究还很有限. 今后应在优化配方、强化应用以及进一步推进中试以上规模研究等方面进行更加广泛深入的尝试与探索.
(2)阐明运行条件对BDPs反硝化的影响机制. BDPs体系的反硝化效率和中间产物(副产物)的产生很大程度上取决于系统的运行条件. 而生物体主要依靠体内生化反应的调节来适应环境. 因此,未来需要联合多学科、多组学进行深入研究.
(3)通过优化微生物群落结构和功能来构建高效BDPs反硝化系统是今后研究的重要课题. BDPs反硝化系统能够高效地脱氮,关键在于BDPs降解菌和反硝化菌有一个合适的比例. 以往的多数研究并未对接种活性污泥的功能和比例进行设计,这也可能是碳源不能完全利用或反硝化效果不理想的原因. 通过精准投加功能微生物来强化BDPs脱氮效能,这一方向值得深入探索.
(4)应重视同时去除硝酸盐及其共存污染物这一方面的研究. 各种污染物与硝酸盐在污水中普遍共存,BDPs反硝化系统具有去除这些共存污染物的巨大潜力.
可生物降解聚合物作为固相反硝化碳源的研究进展
Research progress in biodegradable polymers as the carbon sources of solid-phase denitrification process
-
摘要: 碳源是生物反硝化法处理低碳氮比硝酸盐污水的必要物质. 传统的水溶性碳源投加量难以控制,易导致出水水质恶化,需要寻找一种释碳稳定、安全高效的替代碳源. 可生物降解聚合物(biodegradable polymers,BDPs)是一类人工合成的高分子有机物,已被证实可作为新型的反硝化缓释碳源. 其具有反硝化效率高、安全稳定、操作简单等优点,近年来被广泛报道. 归纳总结了BDPs碳源类型及其体系的反硝化性能和影响因素,讨论了BDPs体系脱氮机制及生物膜群落结构与功能,评价了BDPs反硝化脱氮的成本. 提出发展成本相对低廉的BDPs复合碳源、阐明运行条件对BDPs反硝化的影响机制、通过优化微生物群落来构建高效BDPs反硝化系统以及加强共存污染物去除等未来重点研究方向,以期为可生物降解聚合物的反硝化脱氮研究和应用提供参考和依据.Abstract: Carbon source is essential for biological denitrification of the nitrate wastewater with low carbon/nitrogen ratio. However, it is difficult to control the dosage of traditional water-soluble carbon source, and overdose will easily cause deterioration of effluent water quality. Thus, it is necessary to develop slow-release, safe, and efficient alternative carbon source. Synthetic biodegradable polymers (BDPs), a kind of high molecular organic compound, has been proven to be the potential carbon source meeting these demands. With the advantages of high denitrification efficiency, safety, stability, and simple operation, BDPs has been extensively studied as slow-release carbon source of denitrification. In this study, the carbon source types of BDPs, the denitrification performance and influencing factors of BDPs system were summarized. The denitrification mechanism of BDPs system, the structure and function of microbial community were discussed. The cost of BDPs for denitrification was evaluated. Several key directions for future research, such as developing low-cost composite BDPs carbon sources, elucidating the influence mechanism of operating conditions on BDPs denitrification, building efficient BDPs denitrification systems by optimizing microbial community, and enhancing the co-existing pollutants removal, were proposed to provide reference and basis for the research and application for denitrification using biodegradable polymers.
-
Key words:
- biological nitrogen removal /
- sewage treatment /
- solid carbon source /
- mixed carbon sources /
- nitrate
-
贻贝是一种常见的海洋生物,它们可以强力附着在水体环境中有机或无机基底材料的表面[1]。研究发现,贻贝黏液中的黏附蛋白(mussel adhesive proteins,MAPs)是贻贝能够迅速在潮湿环境中附着在各种材料表面的主要成分[2]。而黏附蛋白中起到黏附作用的关键物质是3,4-二羟基苯丙氨酸(3,4-dihydroxylphenylalanine,L-多巴或L-DOPA)和含赖氨酸蛋白质[3]。2007年,Lee等的研究团队在表面化学的研究中发现,多巴胺(dopamine,DA)在含氧碱性水溶液中会发生自聚反应,并利用共价和非共价键作用在材料表面生成具有极强黏附性的聚多巴胺包覆层,该涂层拓宽了材料表面功能化的新途径[4]。聚多巴胺包覆层拥有大量的邻苯二酚和胺基等功能基团,为吸附结合目标物提供了大量活性位点。目前,聚多巴胺功能材料已广泛运用在生产生活的多个领域[5]。在环境护方面,聚多巴胺功能材料凭借着优异的吸附催化性能,成为净化去除水体中重金属离子和有机污染物的研究热点[6-7]。
1. 聚多巴胺的形成-附着机理(Formation-adhesion mechanism of polydopamine)
1.1 多巴胺的结构性质
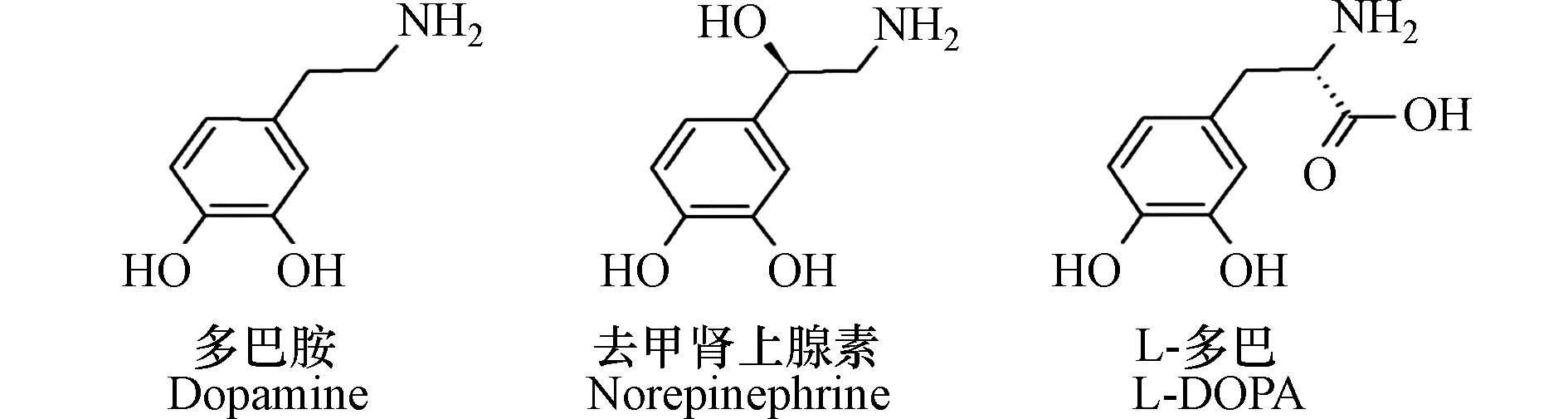
多巴胺是一种生物神经递质,它的化学名称为4-(2-乙氨基)-苯-1,2-二酚(4-(2-aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol),属于儿茶酚胺类物质[8]。在脱羧酶的作用下,L-多巴可转化形成多巴胺[9]。作为L-多巴的衍生物,多巴胺的化学结构中的邻苯二酚和氨基官能团为后续实现材料的修饰奠定了基础[10]。
儿茶酚胺类的不同结构(引自Barclay等[10])如下:
1.2 聚多巴胺的形成-附着机理
多巴胺在氧气的参与作用下,能够在弱碱性水溶液中自发反应生成聚合物—聚多巴胺(polydopamine,PDA)[11]。目前,关于聚多巴胺形成机理的研究众说纷纭,尚没有定论。主流的聚多巴胺形成理论包括 “氧化-聚合”机理、“真黑色素”形成理论和“共价-非共价”共同作用机理等[12-18]。
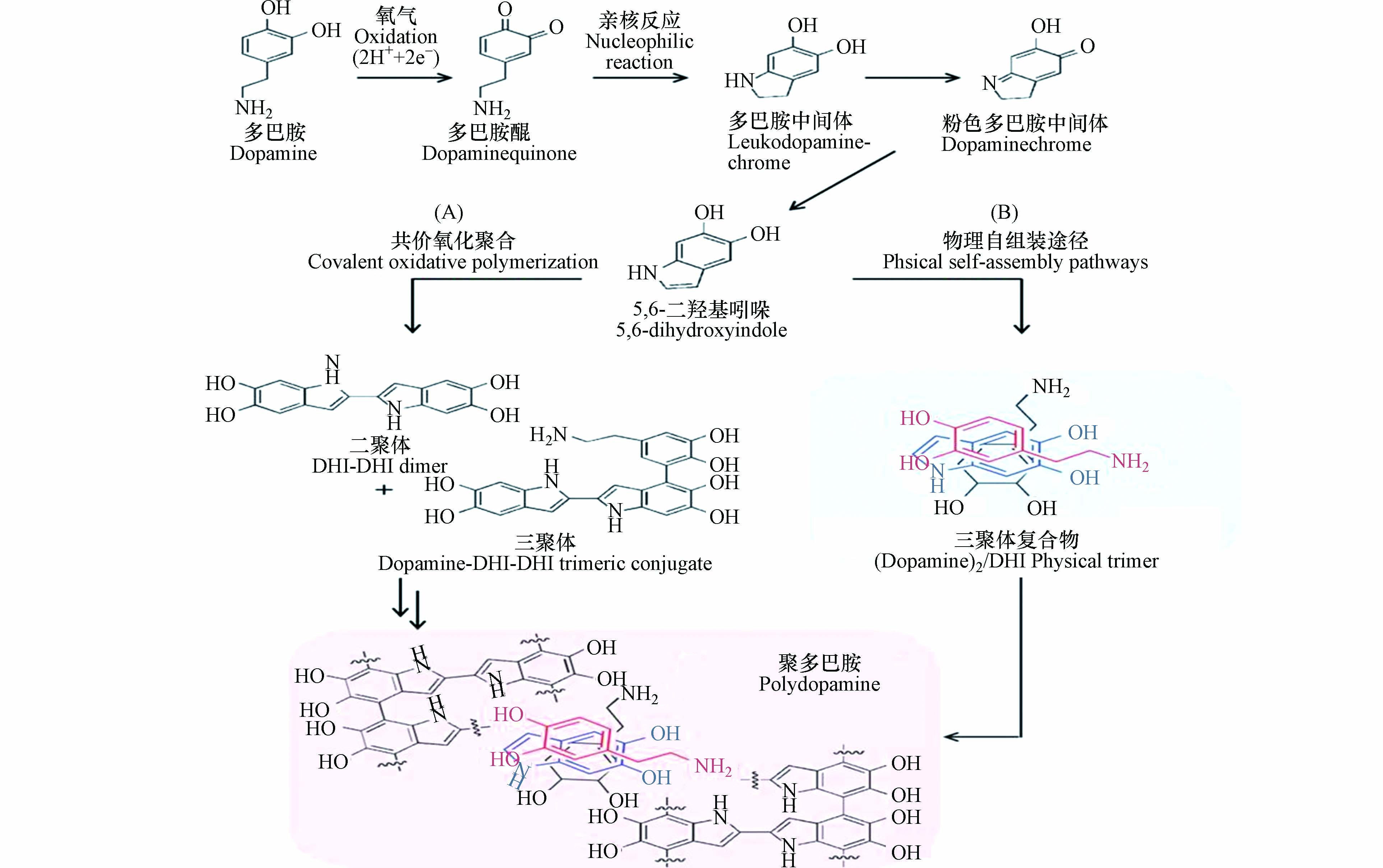
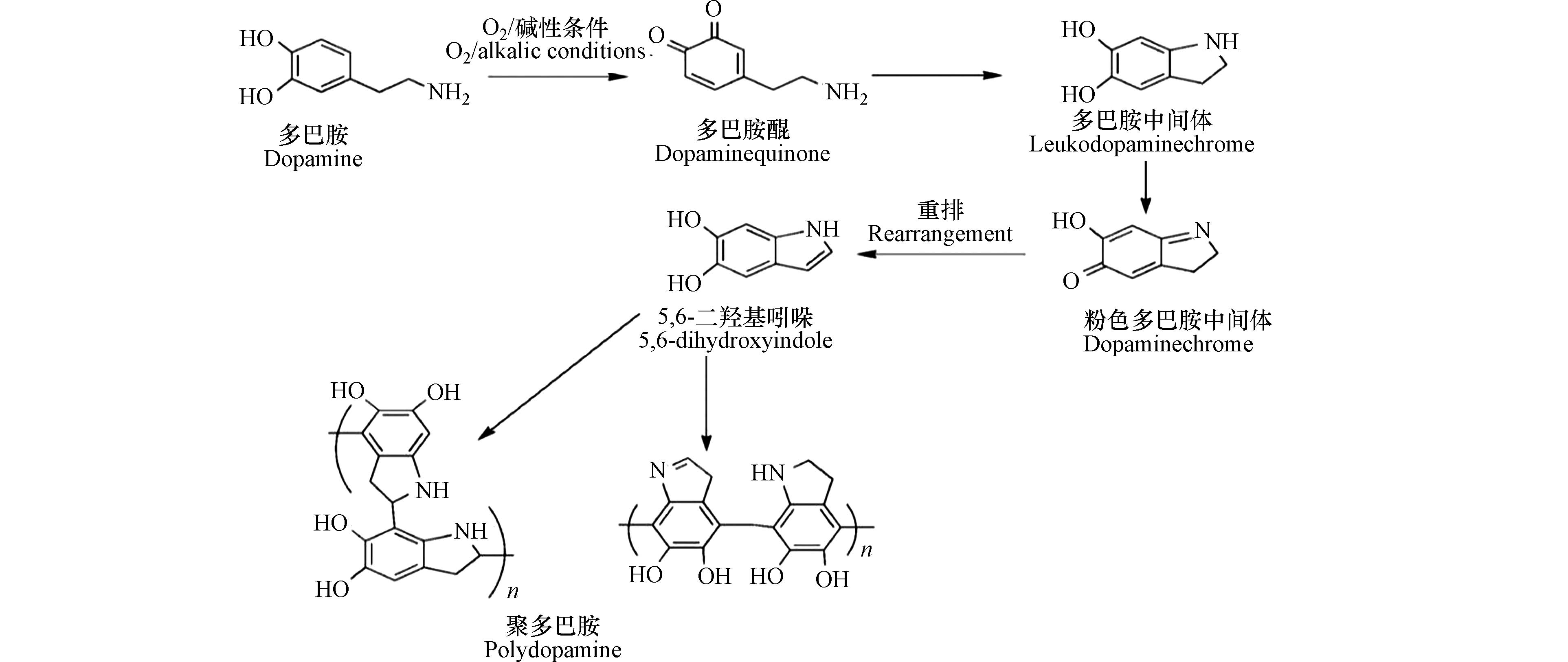
如图1所示,学者们提出了“氧化-聚合”机理:在反应过程中,多巴胺单体的邻苯二酚基团首先被氧化,生成结构性质不稳定的多巴胺醌(dopaminequinone)。多巴胺醌会发生内环化反应生成无色的多巴胺中间体(leukodopaminechrome)。该中间体发生氧化形成粉红色的多巴胺中间体(dopaminechrome),粉色中间体继续发生氧化重排生成5,6-二羟基吲哚(5,6-dihydroxyindole,DHI);5,6-二羟基吲哚与其产物5,6-醌再发生支化反应形成二聚体或其他低聚体,这些低聚体最后通过交联形成聚多巴胺包覆层[12-13]。多巴胺在溶液中的自聚反应伴随着颜色的变化,溶液颜色随着时间的延长由无色变为棕色,最终变为黑色[14]。针对该现象,科研人员通过模拟分析大量的分子数据,提出聚多巴胺的形成主要是依赖反应前期生成的低聚物,且这些受共价键束缚的低聚物以 π-π 键的相互作用堆积在一起,形成类似石墨结构的层状聚集体[15]。
Dreyer等也证明了聚多巴胺的形成与非共价键力(π-π 键、氢键和电荷转移)的作用密切相关,并且赋予了聚多巴胺在水溶液中较强的稳定性[16]。因此,大部分学者认为聚多巴胺的形成是非共价键和共价键共同作用的产物。如图2所示,Hong等[17]提出了“共价-非共价”共同作用机理:聚多巴胺是由共价聚合和非共价自组装共同作用形成的;反应前期生成的5,6-二羟基吲哚之间发生氧化聚合形成二聚体,二聚体再和一个多巴胺单体分子结合生成三聚体(DA-DHI-DHI);同时,两个多巴胺分子与5,6-二羟基吲哚通过自组装形成三聚体复合物(DA2/DHI)。DA2/DHI具有一定的生物毒性,但因其大部分被固定在聚多巴胺中,使得聚多巴胺具有较好的生物相容性。同时DA2/DHI也是聚多巴胺的形成过程中黑色沉淀产生的原因[18]。
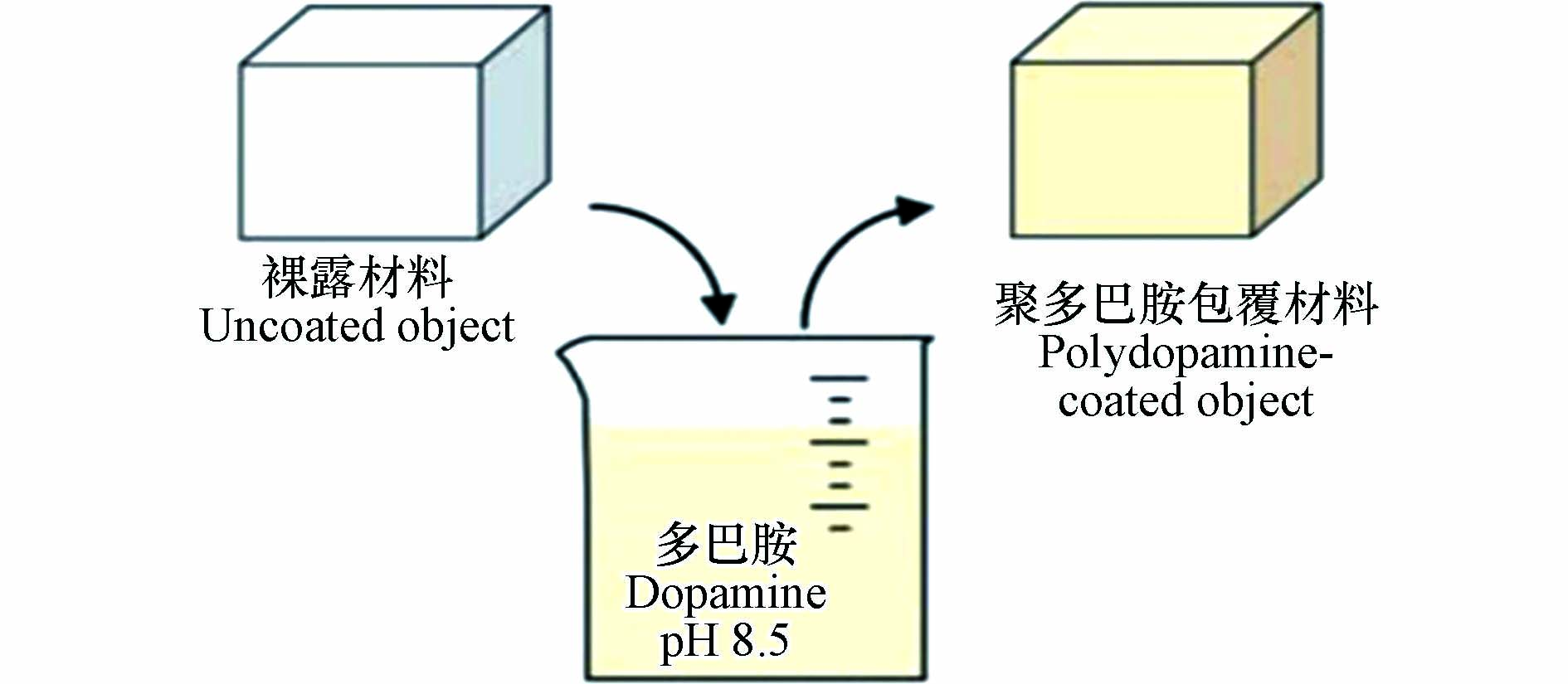
如图3所示,在避光有氧的环境条件下,基体材料置于三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris)的缓冲溶液(pH=8.5)中,多巴胺可以在其表面通过自聚反应生成聚多巴胺包覆层[4]。包覆层的厚度随反应时间的推移而增加。当反应时间为24 h时,厚度达到最大,为50 nm。因此在合适的反应条件下,多巴胺能够通过非共价和共价键力的相互作用,与不同的基底材料表面进行聚合附着来实现对材料的包覆[19-20]。在非共价作用方面,聚多巴胺利用非共价键力(π-π 堆积、氢键、金属离子螯合或配位等)在基底材料表面进行聚合包覆;而在共价作用方面,聚多巴胺不仅可以利用共价键的结合作用与一些表面含有硫醇基和胺基等官能团的材料发生迈克尔加成反应或碱性条件下的希夫反应,而且通过这些反应也可在聚多巴胺包覆层上接枝功能分子,实现复合材料进一步的功能化[21-22]。
1.3 影响聚多巴胺形成-附着的因素
影响聚多巴胺形成-附着过程的因素主要包括多巴胺单体浓度、溶液pH及沉积时间/温度等。多巴胺单体浓度会影响到聚多巴胺包覆层的厚度和表面粗糙度。一般包覆层的厚度和表面粗糙度会随着多巴胺浓度的提高而增加,但超出一定范围后,浓度基本不影响包覆层的沉积[23]。通常聚多巴胺的沉积发生在弱碱性溶液中,这是因为弱碱性环境有助于多巴胺自聚反应前驱体的形成,但Wei等研究发现,在反应溶液中加入一些氧化剂(Cu2+、过硫酸铵等)后也能实现酸性条件下的自聚反应[24]。此外,沉积时间/温度也是影响反应速率的重要因素,当沉积时间或温度适当增加,包覆层沉积的速率同样会提高[25]。
2. 聚多巴胺功能材料在去除水中重金属和有机物污染物方面的应用(Applications ofpolydopamine-functional materials in the removal of heavy metals and organic pollutants in water)
随着当代社会的高速发展,人类的生产生活已严重影响到水体生态环境的稳定,水污染问题日益突出。水体污染物主要来源于工业废水、生活污水及农业污水,而污染物的种类一般分为有机物、无机物和微生物三大类[26]。目前,应用于水污染控制领域的处理技术有物理法、化学法、物理化学法及生物法。在水污染处理方面,聚多巴胺功能材料结合了基底材料的优良特性和聚多巴胺包覆层丰富的功能基团,通过吸附或催化等方法对水中重金属离子和有机污染物进行有效的去除[27]。
2.1 聚多巴胺功能材料在水中重金属去除方面的应用
作为一种利用吸附材料的高比表面积和特殊吸附位点等优势来去除水中重金属的方法,吸附法因材料廉价易得和操作简单的优势而被广泛使用[28]。聚多巴胺功能材料凭借着聚多巴胺层丰富的功能基团(邻苯二酚、胺基和亚胺基等),为与水中重金属离子结合提供了大量的吸附位点[29]。
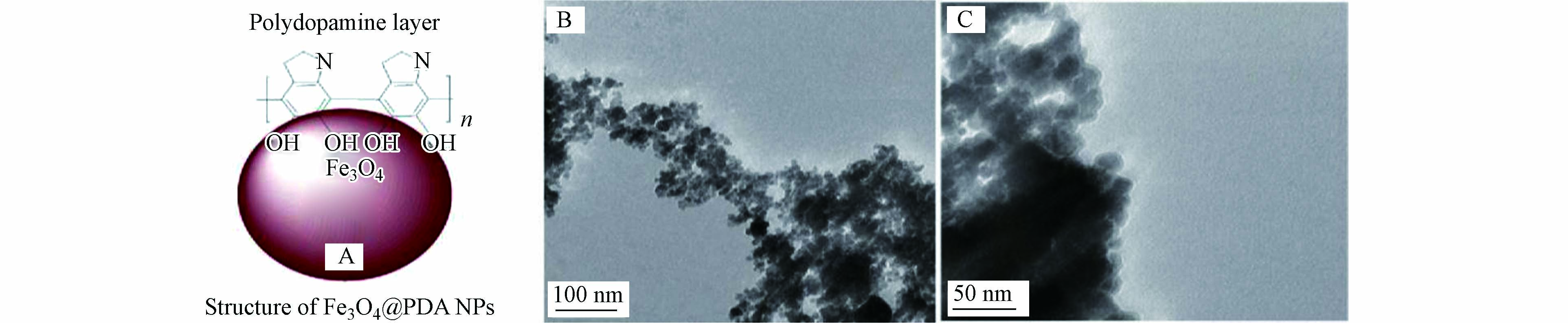
目前,研究人员在努力开发新型的基底材料和聚多巴胺表面改性手段以提高复合材料吸附去除重金属离子的效率。马玉荣等利用共沉淀法合成的聚多巴胺包覆的Fe3O4(Fe3O4@PDA NPs),通过利用聚多巴胺具有丰富吸附位点和磁性材料易于分离回收的特点,用来吸附去除模拟废水中的Pb2+[30]。由电镜表征可以看出,聚多巴胺通过羟基-铁化学作用包覆在在Fe3O4 NPs表面,形成了具有核壳结构的Fe3O4@PDA NPs(图4C)。实验表明,在最佳条件下,Fe3O4@PDA NPs对Pb2+的最大吸附量约为20.68 mg∙g−1。作为石墨烯的衍生物,氧化石墨烯(GO)具有高比表面积、丰富功能基团和优秀力学性能等特点,因此可对GO进行表面改性来调控表面性质,以提升其吸附性能[31-32]。Dong等通过控制聚多巴胺的质量分数,合成了一系列亚纳米级厚的聚多巴胺包覆的GO复合材料(PDA/GO)[33]。PDA/GO对Pb2+、Cu2+、Cd2+及Hg2+等重金属离子的最大吸附量分别为53.6、24.4、33.3、15.2 mg∙g−1,吸附性能均优于单纯的GO和PDA,体现了复合材料中PDA和GO的协同作用。Ali等同样利用共沉淀法合成了磁性氧化石墨烯(GO/Fe3O4),然后通过聚多巴胺包覆GO/Fe3O4制备出 rGO/Fe3O4@PDA,作为吸附水中Pb2+的新型磁性吸附剂[34]。由于吸附材料存在丰富的胺基和羟基等官能团,rGO/Fe3O4@PDA对Pb2+的吸附能力可达35.2 mg∙g−1,吸附性能明显优于未修饰的GO/Fe3O4。碳纳米管也是一类具有较高比表面积的碳基材料,但因表面带有的官能团较少、水分散性较差等缺点导致其在实际运用过程中存在短板[35]。刘杏红等通过将多巴胺氧化自聚到磁性碳纳米管(mMWNTs)上,合成了聚多巴胺包覆的磁性碳纳米管材料(mMWNTs@PDA)[36]。实验结果证明,mMWNTs@PDA对水中Ni2+的吸附过程符合Freundlich等温吸附和准二级动力学模型,且在最优条件下,mMWNTs@PDA对Ni2+最大吸附量可达27.9788 mg∙g−1。针对一些特殊重金属离子污染水体的治理,Yang等通过采用多巴胺聚合沉积工艺和温和水热法合成了层状双氢氧化物(LDH)原位生长修饰的Fe3O4@PDA(Fe3O4@PDA@LDH)微球,对核工业产生的含U(Ⅵ)的废水进行吸附净化[37]。在实验过程中,通过控制PDA和LDH的用量制备了不同PDA厚度和LDH含量的复合材料微球(MP2L1、MP2L2、MP2L3、ML2及MP2等)。在pH=5.0和T=298.15 K的条件下,材料对U(Ⅵ)的最大吸附容量分别为MP2L2(344 mg∙g−1)> MP2L3(291 mg∙g−1)> MP3L2(245 mg∙g−1)> MP2L1(211 mg∙g−1)> ML2(142 mg∙g−1)> MP1L2(141 mg∙g−1)> MP2(71 mg∙g−1)> Fe3O4(34 mg∙g−1),其中MP2L2具有较高的吸附容量,处理效果在含铀废水的净化方面是较为可观的。
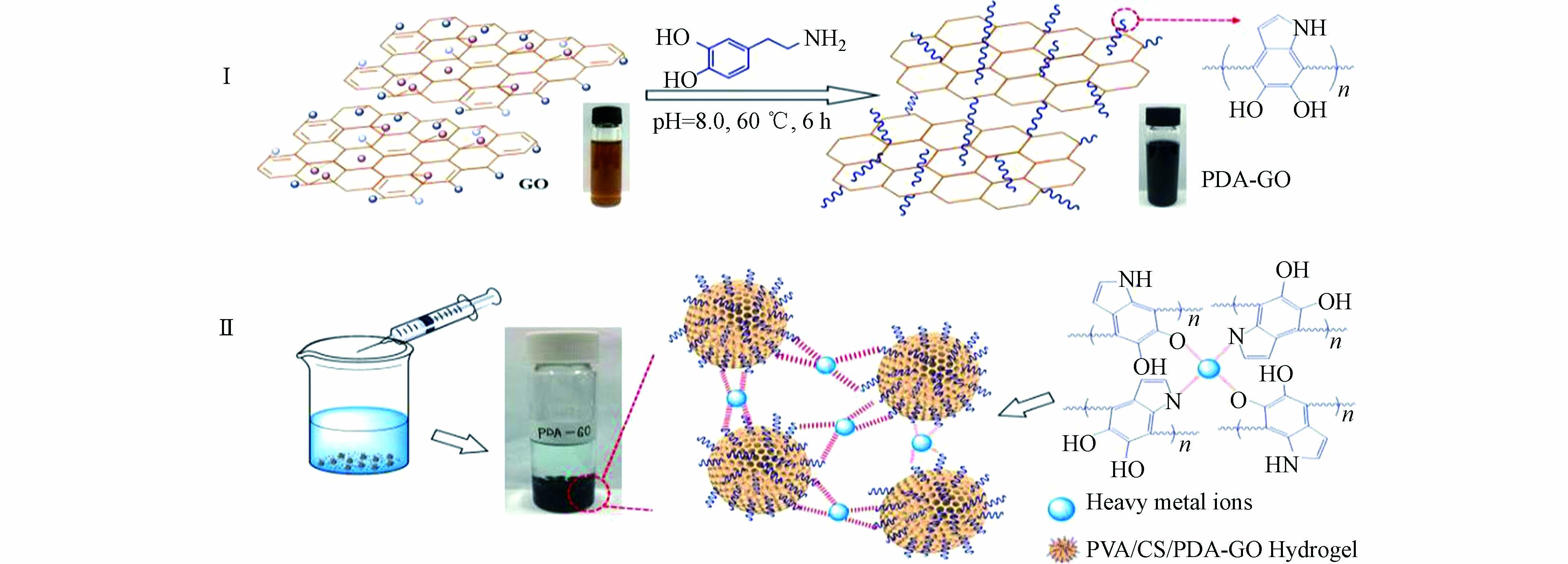
Zeng等通过将聚多巴胺掺入到支链淀粉水凝胶基质中,合成了具有高机械强度和可生物降解特性的支链淀粉/聚多巴胺(Pu/PDA)生物水凝胶吸附剂[38]。实验表明,通过调节预凝胶溶液中的聚多巴胺的浓度,可很好地控制该吸附剂的吸水率、机械强度及孔径。Pu/PDA对重金属离子具有较高的吸附能力,对Cu2+的吸附容量最高可达到100 mg∙g−1 。而Li等首先将聚多巴胺引入氧化石墨烯中合成了PDA-GO(图5-Ⅰ),然后通过瞬时凝胶法制备出聚乙烯醇/壳聚糖功能化的PDA-GO(PVA/CS/PDA-GO)水凝胶珠,用于吸附水中的Pb2+、Cu2+及Cd2+[39]。PDA-GO的存在不仅增强了水凝胶珠体系的稳定性,而且大量的活性基团的引入提高了吸附性能(图5-Ⅱ)。在最优条件下,通过Langmuir等温线对实验数据的拟合可知,PVA/CS/PDA-GO对Pb2+、Cu2+及Cd2+的最大吸附量分别为236.20、210.94、214.98 mg∙g−1。为解决实际水体环境中重金属离子共存污染的问题,Wang等采用水溶法快速制备了氨基水杨酸/聚多巴胺改性的PP无纺布吸附剂(PP/PDA/ASA)[40]。交联在聚合物末端的水杨酸分子增加了官能团的类型,有效地解决了因多组分体系中重金属离子的竞争吸附效应引起去除效率低的问题。在含有5 mg∙L−1的Cu(Ⅱ)/Cd(Ⅱ)/Pb(Ⅱ) 混合体系溶液中,由于表面氨基、羟基及羧基等官能团参与了重金属离子的吸附,PP/PDA/ASA可去除90%的Cu2+和Pb2+及80%的Cd2+。
2.2 聚多巴胺功能材料在水中有机污染物去除方面的应用
有机污染是造成水污染的重要原因之一。水中有机污染物的来源主要有生活污水、工业废水及大气污染,污染水体一旦不进行净化处理,便会对自然环境造成严重破坏并威胁到人体生命健康[41]。聚多巴胺功能材料因聚多巴胺包覆层上邻苯二酚、胺基及芳香族基团的存在,为有机污染物的去除提供了大量的活性位点。聚多巴胺功能材料可通过静电相互作用、配位或螯合作用、氢键或 π-π 键堆积相互作用对有机染料和硝基苯酚等进行吸附或催化降解,因此在水中有机污染物的净化方面具有广阔前景[42-43]。
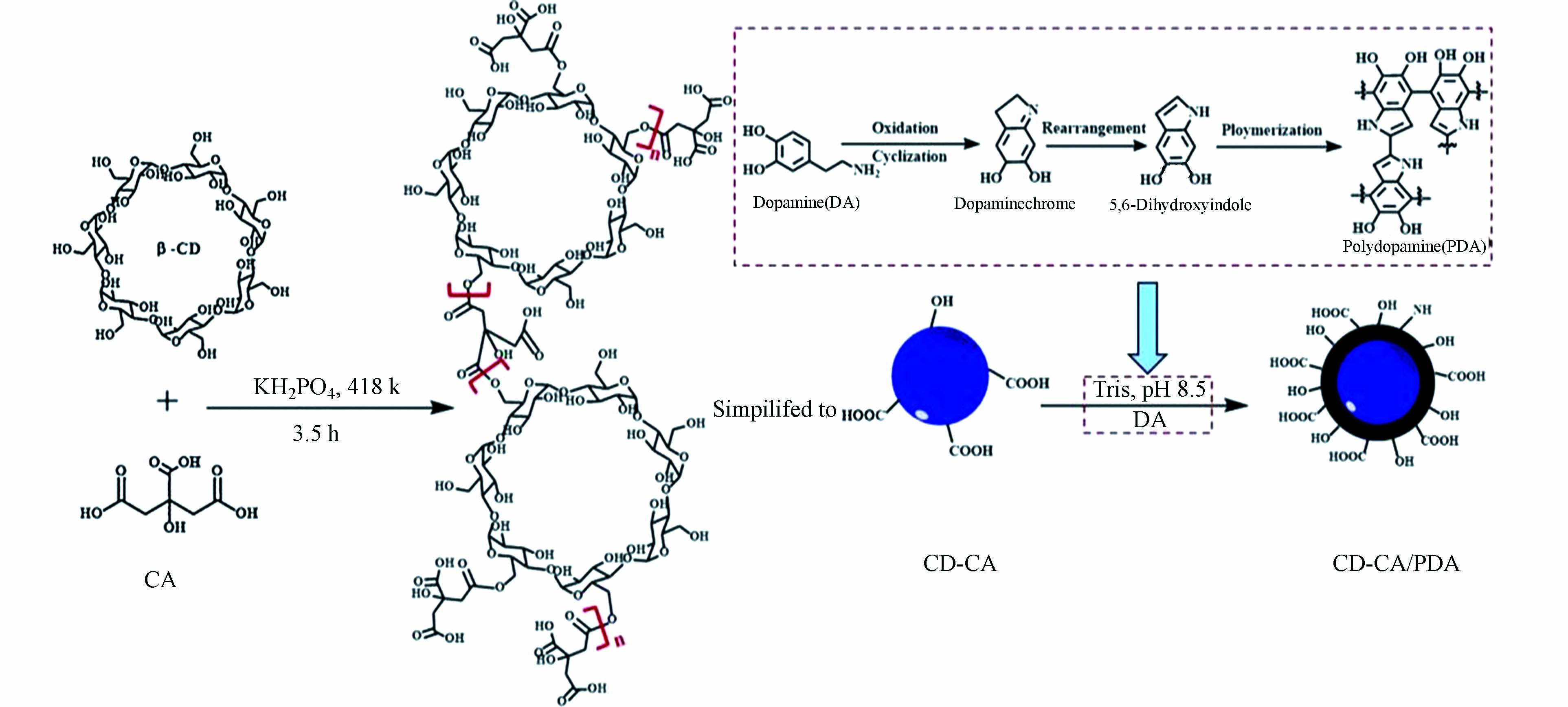
在污水中有机染料的吸附去除方面,Li等利用聚多巴胺为原料,通过将聚多巴胺包覆的CoFe2O4亚微球包裹在海藻酸钠微球中,合成了具有多孔结构和大量官能团的复合微球材料(SA@CoFe2O4-PDA),用来吸附去除亚甲基蓝(MB)、孔雀石绿(MG)及晶体紫(CV)等有机染料[44]。实验表明,SA@CoFe2O4-PDA对MB、CV及MG的最大吸附容量分别为466.60、456.52、248.78 mg∙g−1。Chen等首先将β-环糊精(β-CD)和柠檬酸(CA)酯化交联生成CD-CA,然后CD-CA与聚多巴胺结合,制备出聚多巴胺改性的环糊精聚合物(CD-CA/PDA)(如图6所示),用于MB、MG及CV等染料的吸附去除[45]。CD-CA/PDA对染料的吸附呈现出从单层吸附向多层吸附过渡的趋势,且对MB、MG及CV的吸附容量分别为582.95、1174.67、473.01 mg∙g−1。刘怡虹等将多巴胺和氧化石墨烯(GO)混合,通过聚多巴胺提供的强大粘合力,辅助GO自组装形成具有三维多孔网状结构的GO水凝胶,经水合肼对其进行还原后,生成了聚多巴胺交联的还原性石墨烯气凝胶(DA-rGA),以对MG、藏红T(ST)和罗丹明B(RhB)等阳离子染料进行吸附研究[46]。实验结果表明,DA-rGA的三维孔隙利于吸附分子在内部的快速扩散,因此对有机染料具有优异的吸附性能。Fu等通过合成的聚多巴胺微球对亚甲基蓝的吸附研究进一步证实,聚多巴胺在反应体系中会释放质子而带有负电荷,因此聚多巴胺功能材料可通过静电作用对水中阳离子染料进行吸附结合,而对阴离子染料的吸附效果就不如人意[47]。而何雪梅等利用双醛壳聚糖作为交联剂,通过在聚多巴胺修饰的羊毛织物表面上接枝季铵盐阳离子进行二次功能化,巧妙地得到了PDA/季铵盐阳离子改性的羊毛织物,用于吸附去除阴离子染料酸性大红G[48]。相较于未经处理的羊毛,羊毛织物的表面经改性后拥有更多的活性基团,大大提高了染料扩散进入纤维内部的速率。在pH值为2、染色时间为60 min等最佳实验条件下,PDA/季铵盐阳离子改性的羊毛织物对酸性大红G具有较高的吸附率。Zhan等通过将多巴胺聚合到多孔柚皮表面,成功制备了一种环保的生物吸附剂(PP-PDA)[49]。PP-PDA对水中阳离子染料表现出较高吸附能力,MB、MG和中性红(NR)的最大吸附容量分别为434.78、143.88、208.33 mg∙g−1。且PP-PDA的再生能力较强,经过20次循环后也可保持较高的吸附能力。
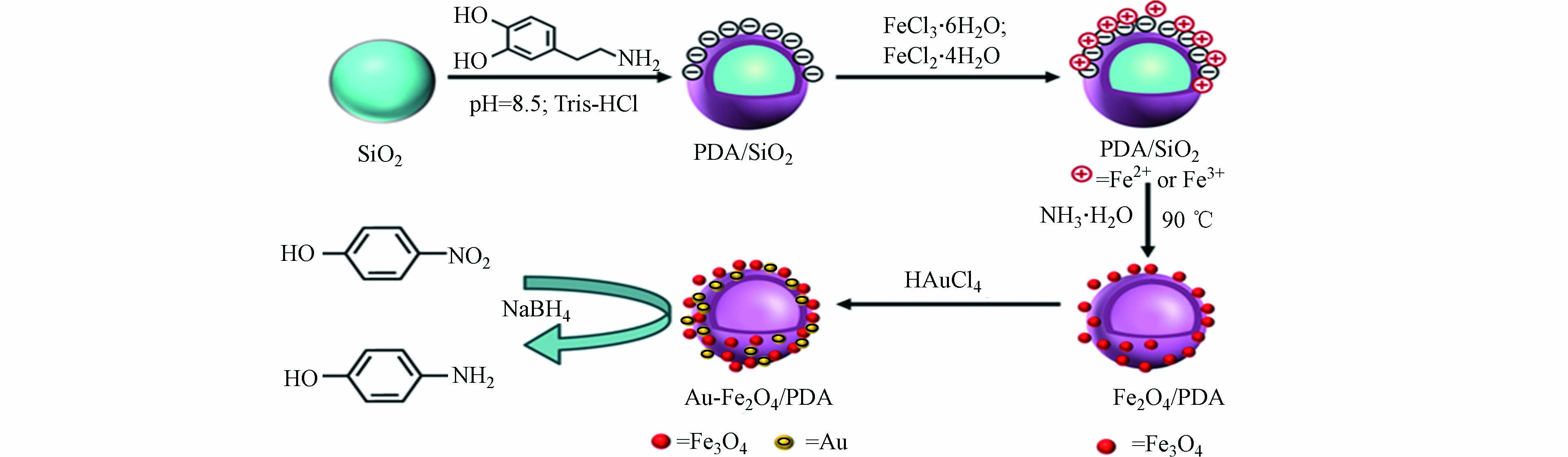
聚多巴胺功能材料也可利用催化法对水中有机染料和芳香族化合物进行去除。Ma等首次通过原位自聚反应合成了具有核壳结构的聚多巴胺包覆的CuFe2O4磁性纳米粒子(CuFe2O4@PDA MNPs),且该产品的PDA涂层厚度可通过调节制备过程中多巴胺的浓度来控制[7]。在H2O2的存在下,CuFe2O4@PDA MNPs表面吸附MB,H2O2分子被CuFe2O4@PDA激活产生的·OH可有效降解MB,最优条件下的催化降解效率可达97%以上。如图7所示,Niu等首先制备出PDA包覆的SiO2颗粒,接着利用PDA涂层作为交联剂和还原剂,在其表面接枝Fe3O4 NPs和Au NPs,合成了具有中空结构的Au-Fe3O4/PDA纳米颗粒[50]。在优化实验材料用量后,Au-Fe3O4/PDA利用金属纳米颗粒的催化性能,能够将溶液体系中的4-硝基苯酚完全还原为4-氨基苯酚,且复合材料具有较优异的可回收性。MASSARO等通过将铜离子螯合在PDA包覆的沙子表面,制备出低成本的砂载铜催化剂(Cu-PDA@Sand),对MB、CR及4-硝基苯酚进行催化还原[51]。实验表明,由于负载铜离子的存在,复合材料有效地对有机染料进行了催化降解。Cu-PDA@Sand不仅能够通过自沉淀法进行简单地回收,而且可重复使用来实现长期稳定的催化性能。而在聚多巴胺对膜材料表面的改性方面,张娇娇等利用DA作为涂层材料,聚丙烯腈(PAN)静电纺纳米纤维膜为基底材料,制备出PDA/PAN纳米纤维复合膜材料[52]。在保证较高纯水通量的前提下,经聚多巴胺涂覆后的PAN纤维膜对乳化油的截留率高达96.1%,大幅提升了处理含油废水的效果。
3. 结论与展望(Conclusions and prospects)
多巴胺在弱碱条件下可通过自聚反应生成聚多巴胺,涂覆在各种基底材料表面形成聚多巴胺功能材料。目前,社会的高速发展已经对环境造成严重破坏,尤其在水体环境方面,水污染问题日益严峻。不同于一般的水污染修复材料,聚多巴胺功能材料不仅可利用邻苯二酚和胺基等丰富的功能基团,与水中重金属离子和有机污染物通过氢键、静电相互作用、π-π 键堆积及配位螯合作用进行结合,而且可利用共价和非共价键力在聚多巴胺包覆层接枝功能分子来提升复合材料的功能特性。聚多巴胺功能材料凭借着优异的吸附和催化还原性能、简单环保的制备方法、良好的生物相容性及可二次修饰等优势,对水中的重金属离子和有机污染物具有较高的去除效率且处理后不易对水体环境造成二次污染。本篇文章首先从多巴胺的结构性质入手,介绍了目前表面化学研究中主流的聚多巴胺形成和附着机理,然后从去除水中重金属离子和有机污染物这两个方面,总结了多种聚多巴胺功能材料在水污染处理方面的具体应用。
通过上述聚多巴胺功能材料在水体污染物去除方面的应用可以看出,基底材料经聚多巴胺修饰或在聚多巴胺涂层表面进行二次修饰后,吸附和催化还原性能均有大幅度的提升。但将这些复合材料从实验室的研究运用到实际生产生活中时,却存在一些关键问题需要解决。一方面,多巴胺的自聚过程、中间产物的组成及聚多巴胺的精确分子结构尚无定论,在缩短多巴胺聚合时间和调控聚多巴胺涂层的厚度等问题上仍需要摸索实验条件。另一方面,在实际污染水样的处理中,由于较难控制的水体含氧量和流速、复杂的污染物质及过酸或过碱的水体环境等多种因素的制约,导致聚多巴胺功能材料的使用场景受到严重限制且处理效率大幅降低。因此,需要针对聚多巴胺的形成机理做进一步的研究,探究限制多巴胺自聚反应的形成过程的限制因素(例如单次反应涂层的最大厚度不会超过50 nm、酸性条件下需要特定氧化剂的帮助等)[42]。此外,还需要通过优化聚多巴胺功能材料的制备过程来提高其在各种污染水体中的稳定性和高效性,并减少复合材料对水体的二次污染。目前,研究人员正努力开发制备简单、成本较低及环境友好的新型聚多巴胺功能材料,挖掘其在医学、光学及电化学等新领域的应用潜力。未来,相信聚多巴胺功能材料凭借其优异的性能会在水污染领域中具有更广阔的前景,也定会在更广泛的领域做出更大的贡献。
-
表 1 不同BDPs碳源类型及其在反硝化系统中反硝化性能
Table 1. Denitrification performance of different BDPs as carbon source in denitrification system
碳源类型Carbon sources 进水NO3−-N/(mg·L−1)Influent NO3−-N NO3−-N去除速率/(mg·L−1·h−1)NO3−-N removal rate 可溶性有机碳DOC,总有机碳TOC/(mg·L−1)Dissolved organic carbon,total organic carbon 水力停留时间/hHRT 文献References PCL 81.1—132.75 11.25 进水与出水DOC差值:-2.8—63.43 5 [23] PCL 200 30.3 出水DOC:(26.12±3.12)—(53.06±5.93) 5.5 [24] PCL 60—80 7.92—23.33 出水比进水TOC增加1.7—5.2 3—6 [25] PHBV 15 32.08 出水DOC:39.75—82.42 0.5 [26] PHBV/PLA 10 9.58 稳定期出水DOC:9±3.4 2 [12] PHBV/PLA 15 13.95 稳定期出水DOC:10以下 1 [27] PHBV/木纤维素 15 14.02 稳定期出水DOC:60以下 1 [27] PBS 146 22.08±7.92(盐度0‰)27.5±5(盐度25‰) 出水DOC:(136.11±49.52)(盐度0‰),(202.51±118.90)(盐度25‰) 2 [19] PBS 100—150 26.67—5.83 未见明显的DOC积累 5 [28] PBS/竹粉 100 28.33—34.58 进水约80—115,出水约90—160 2 [22] PBS/竹粉 75 5.42±1.25(盐度0‰)2.92±0.83(盐度25‰) 两个盐度条件下出水DOC均低于15 4 [29] 表 2 不同碳源处理硝酸盐的成本评价
Table 2. Cost evaluation of different carbon sources for nitrate removal
碳源类型Carbon sources 碳源单价/(元·kg−1)Carbon source unit-price 碳源消耗/ (kg·kg−1 NO3−-N)Carbon source consumption 反硝化成本(元·kg−1 NO3−-N)Denitrification cost/ 文献References PHB — — 145.5—257.8 [48] PLA 28.8 1.5—1.9 43.2—54.7 [7] PHBV/PLA 21.3 1.4 29.8 [12] PHBV 31.9 1.5—1.7 47.9—54.2 [4] PHBV/淀粉 17.3 2.08—2.60 36.0—45.0 [4] PHBV/竹粉 16.6 1.69—1.86 28.1—30.9 [4] PBS/竹粉 15.2 1.3—1.5 19.8—22.8 [7] PCL 28.4—34.7 1.3—1.8 36.9—62.5 [70] PCL/淀粉 16.8 2.0—3.1 33.6—52.1 [7] 乙酸 9.6 3.5 33.6 [7] 乙醇 5.9 2.0—3.3 11.8—19.5 [12] 甲醇 2.3 2.0—3.2 4.6—7.4 [12] -
[1] LIU Y, ZHANG X M, WANG J L. A critical review of various adsorbents for selective removal of nitrate from water: Structure, performance and mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 291(Pt 1): 132728. [2] 袁世红, 宋新山, 曹新, 等. 几种可作固相碳源的硝酸根吸附剂的制备及其性能[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(3): 589-598. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018042707 YUAN S H, SONG X S, CAO X, et al. Preparation and characterization of nitrate adsorbents with slow-releasing carbon capacity[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(3): 589-598 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018042707
[3] ZHANG F F, MA C J, HUANG X F, et al. Research progress in solid carbon source-based denitrification technologies for different target water bodies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 782: 146669. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146669 [4] WANG J L, CHU L B. Biological nitrate removal from water and wastewater by solid-phase denitrification process[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2016, 34(6): 1103-1112. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.07.001 [5] YANG Z C, YANG L H, WEI C J, et al. Enhanced nitrogen removal using solid carbon source in constructed wetland with limited aeration[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 248: 98-103. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.188 [6] JIANG L, WU A Q, FANG D X, et al. Denitrification performance and microbial diversity using starch-polycaprolactone blends as external solid carbon source and biofilm carriers for advanced treatment[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 255: 126901. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126901 [7] FU X R, HOU R R, YANG P, et al. Application of external carbon source in heterotrophic denitrification of domestic sewage: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 817: 153061. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153061 [8] 徐玉金, 汤映莹, 高依林, 等. 新型LDHs基缓释碳源的制备及应用[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(12): 3840-3854. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021080908 XU Y J, TANG Y Y, GAO Y L, et al. Preparation and application of a novel LDHs-based slow-release carbon source[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(12): 3840-3854 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021080908
[9] SUN H M, YANG Z C, WEI C J, et al. Nitrogen removal performance and functional genes distribution patterns in solid-phase denitrification sub-surface constructed wetland with micro aeration[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 263: 223-231. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.078 [10] SUN H M, ZHOU Q, ZHAO L, et al. Enhanced simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate using novel solid carbon source/zero-valent iron composite[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 289: 125757. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125757 [11] YANG Z C, SUN H M, ZHOU Q, et al. Nitrogen removal performance in pilot-scale solid-phase denitrification systems using novel biodegradable blends for treatment of waste water treatment plants effluent[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 305: 122994. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122994 [12] SUN H M, YANG Z C, YANG F F, et al. Enhanced simultaneous nitrification and denitrification performance in a fixed-bed system packed with PHBV/PLA blends[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2020, 146: 104810. [13] WANG H S, CHEN N, FENG C P, et al. Insights into heterotrophic denitrification diversity in wastewater treatment systems: Progress and future prospects based on different carbon sources[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 780: 146521. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146521 [14] WU W Z, YANG F F, YANG L H. Biological denitrification with a novel biodegradable polymer as carbon source and biofilm carrier[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 118: 136-140. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.066 [15] 杨飞飞, 吴为中. 以PHBV为碳源和生物膜载体的生物反硝化研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(7): 1703-1708. YANG F F, WU W Z. Biological denitrification using PHBV as carbon source and biofilm carrier[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(7): 1703-1708 (in Chinese).
[16] ZHANG S S, SUN X B, FAN Y T, et al. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by Diaphorobacter polyhydroxybutyrativorans SL-205 using poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) as the sole carbon source[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 241: 500-507. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.185 [17] LI P, ZUO J E, WANG Y J, et al. Tertiary nitrogen removal for municipal wastewater using a solid-phase denitrifying biofilter with polycaprolactone as the carbon source and filtration medium[J]. Water Research, 2016, 93: 74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.02.009 [18] YANG L, GUO L K, REN Y X, et al. Denitrification performance, biofilm formation and microbial diversity during startup of slow sand filter using powdery polycaprolactone as solid carbon source[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(4): 105561. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105561 [19] ZHU S M, DENG Y L, RUAN Y J, et al. Biological denitrification using poly(butylene succinate) as carbon source and biofilm carrier for recirculating aquaculture system effluent treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 192: 603-610. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.021 [20] 范振兴, 王建龙. 利用聚乳酸作为反硝化固体碳源的研究[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(8): 2315-2319. FAN Z X, WANG J L. Denitrification using polylactic acid as solid carbon source[J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(8): 2315-2319 (in Chinese).
[21] BOLEY A, MÜLLER W R, HAIDER G. Biodegradable polymers as solid substrate and biofilm carrier for denitrification in recirculated aquaculture systems[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 2000, 22(1/2): 75-85. [22] LIU D Z, LI J W, LI C W, et al. Poly(butylene succinate)/bamboo powder blends as solid-phase carbon source and biofilm carrier for denitrifying biofilters treating wastewater from recirculating aquaculture system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 3289. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21702-5 [23] LUO G Z, HOU Z W, TIAN L Q, et al. Comparison of nitrate-removal efficiency and bacterial properties using PCL and PHBV polymers as a carbon source to treat aquaculture water[J]. Aquaculture and Fisheries, 2020, 5(2): 92-98. doi: 10.1016/j.aaf.2019.04.002 [24] LUO G Z, XU G M, GAO J F, et al. Effect of dissolved oxygen on nitrate removal using polycaprolactone as an organic carbon source and biofilm carrier in fixed-film denitrifying reactors[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 43: 147-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2015.10.022 [25] CHU L B, WANG J L. Denitrification performance and biofilm characteristics using biodegradable polymers PCL as carriers and carbon source[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 91(9): 1310-1316. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.064 [26] XU Z S, DAI X H, CHAI X L. Biological denitrification using PHBV polymer as solid carbon source and biofilm carrier[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 146: 186-193. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2019.03.019 [27] 朱擎, 杨飞飞, 赵兰, 等. 两种共混BDPs作为生物膜载体和碳源的脱氮研究比较[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(3): 525-530. ZHU Q, YANG F F, ZHAO L, et al. Comparison of two biodegradable polymer blends as biofilm carrier and carbon source for nitrogen removal[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2015, 51(3): 525-530 (in Chinese).
[28] RUAN Y J, DENG Y L, GUO X S, et al. Simultaneous ammonia and nitrate removal in an airlift reactor using poly(butylene succinate) as carbon source and biofilm carrier[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 216: 1004-1013. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.056 [29] QI W H, TAHERZADEH M J, RUAN Y J, et al. Denitrification performance and microbial communities of solid-phase denitrifying reactors using poly (butylene succinate)/bamboo powder composite[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 305: 123033. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123033 [30] XU Z S, DAI X H, CHAI X L. Effect of different carbon sources on denitrification performance, microbial community structure and denitrification genes[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 634: 195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.348 [31] ZHOU Q, SUN H M, JIA L X, et al. Simultaneously advanced removal of nitrogen and phosphorus in a biofilter packed with ZVI/PHBV/sawdust composite: Deciphering the succession of dominant bacteria and keystone species[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 347: 126724. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126724 [32] 吴为中, 赵柳, 周琦, 等. 基于黄铁矿与PHBV协同自养-异养反硝化试验研究[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2022, 30(2): 282-294. WU W Z, ZHAO L, ZHOU Q, et al. Laboratory-scale study on combined autotrophic-heterotrophic denitrification based on pyrite and PHBV[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2022, 30(2): 282-294 (in Chinese).
[33] YI C H, QIN W, WEN X H. Renovated filter filled with poly-3-hydroxybutyrateco-hydroxyvalerate and granular activated carbon for simultaneous removal of nitrate and PPCPs from the secondary effluent[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 749: 141494. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141494 [34] XU Z S, SONG L Y, DAI X H, et al. PHBV polymer supported denitrification system efficiently treated high nitrate concentration wastewater: Denitrification performance, microbial community structure evolution and key denitrifying bacteria[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 197: 96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.023 [35] 易成豪, 秦伟, 陈湛, 等. 聚己内酯与聚羟基丁酸戊酸酯的脱氮性能对比[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9): 4143-4151. YI C H, QIN W, CHEN Z, et al. Comparison of polycaprolactone and poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate for nitrogen removal[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(9): 4143-4151 (in Chinese).
[36] SI Z H, SONG X S, WANG Y H, et al. Intensified heterotrophic denitrification in constructed wetlands using four solid carbon sources: Denitrification efficiency and bacterial community structure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 267: 416-425. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.029 [37] SHAHABI Z A, NAEIMPOOR F. Enhanced heterotrophic denitrification: Effect of dairy industry sludge acclimatization and operating conditions[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2014, 173(3): 741-752. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-0884-4 [38] ZHONG H, CHENG Y, AHMAD Z, et al. Solid-phase denitrification for water remediation: Processes, limitations, and new aspects[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2020, 40(8): 1113-1130. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1805720 [39] YANG Z C, ZHOU Q, SUN H M, et al. Metagenomic analyses of microbial structure and metabolic pathway in solid-phase denitrification systems for advanced nitrogen removal of wastewater treatment plant effluent: A pilot-scale study[J]. Water Research, 2021, 196: 117067. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117067 [40] 李加伟. 基于可生物降解聚合物的循环水养殖废水生物脱氮技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. LI J W. Study on biological nitrogen removal by using BDPs for RAS wastewater treatment[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019 (in Chinese).
[41] LUO G Z, XU G M, TAN H X, et al. Effect of dissolved oxygen on denitrification using polycaprolactone as both the organic carbon source and the biofilm carrier[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2016, 110: 155-162. [42] LUO F Z, ZHANG J S, WEI Q, et al. Insights into the relationship between denitrification and organic carbon release of solid-phase denitrification systems: Mechanism and microbial characteristics[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 364: 128044. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128044 [43] XIONG R, YU X X, YU L J, et al. Biological denitrification using polycaprolactone-peanut shell as slow-release carbon source treating drainage of municipal WWTP[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 235: 434-439. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.198 [44] CHU L B, WANG J L. Denitrification of groundwater using PHBV blends in packed bed reactors and the microbial diversity[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 155: 463-470. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.090 [45] TAKAHASHI M, YAMADA T, TANNO M, et al. Nitrate removal efficiency and bacterial community dynamics in denitrification processes using poly (L-lactic acid) as the solid substrate[J]. Microbes and Environments, 2011, 26(3): 212-219. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME11107 [46] HANG Q Y, WANG H Y, CHU Z S, et al. Application of plant carbon source for denitrification by constructed wetland and bioreactor: Review of recent development[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(9): 8260-8274. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6324-y [47] HIRAISHI A, KHAN S T. Application of polyhydroxyalkanoates for denitrification in water and wastewater treatment[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2003, 61(2): 103-109. doi: 10.1007/s00253-002-1198-y [48] ZHANG Q, JI F Y, XU X Y. Effects of physicochemical properties of poly-ε-caprolactone on nitrate removal efficiency during solid-phase denitrification[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 283: 604-613. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.07.085 [49] XIA L, LI X M, FAN W H, et al. Denitrification performance and microbial community of bioreactor packed with PHBV/PLA/rice hulls composite[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 803: 150033. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150033 [50] CHU L B, WANG J L. Comparison of polyurethane foam and biodegradable polymer as carriers in moving bed biofilm reactor for treating wastewater with a low C/N ratio[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 83(1): 63-68. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.077 [51] HE Q L, WANG H Y, CHEN L, et al. Robustness of an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor for low strength and salinity wastewater treatment at ambient to winter temperatures[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121454. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121454 [52] FENG L, PI S, ZHU W, et al. Nitrification and aerobic denitrification in solid phase denitrification systems with various biodegradable carriers for ammonium-contaminated water purification[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2019, 94(11): 3569-3577. [53] van RIJN J, TAL Y, SCHREIER H J. Denitrification in recirculating systems: Theory and applications[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 2006, 34(3): 364-376. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaeng.2005.04.004 [54] GUTIERREZ-WING M T, MALONE R F, RUSCH K A. Evaluation of polyhydroxybutyrate as a carbon source for recirculating aquaculture water denitrification[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 2012, 51: 36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaeng.2012.07.002 [55] LUO G Z, LI L, LIU Q, et al. Effect of dissolved oxygen on heterotrophic denitrification using poly(butylene succinate) as the carbon source and biofilm carrier[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 171: 152-158. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.055 [56] HAO Z L, ALI A, REN Y, et al. A mechanistic review on aerobic denitrification for nitrogen removal in water treatment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 847: 157452. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157452 [57] ZHANG Q, JI F Y, XU X Y. Optimization of nitrate removal from wastewater with a low C/N ratio using solid-phase denitrification[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(1): 698-708. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5308-7 [58] JIANG L, ZHANG Y F, SHEN Q S, et al. The metabolic patterns of the complete nitrates removal in the biofilm denitrification systems supported by polymer and water-soluble carbon sources as the electron donors[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 342: 126002. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126002 [59] 罗国芝, 侯志伟, 高锦芳, 等. 不同水力停留时间条件下PCL为碳源去除水产养殖水体硝酸盐的效率及微生物群落分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(2): 572-580. LUO G Z, HOU Z W, GAO J F, et al. Nitrate removal efficiency and microbial community analysis of polycaprolactone-packed bioreactors with PCL as carbon source treating aquaculture water under different hydraulic retention time[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2018, 12(2): 572-580 (in Chinese).
[60] XU Z S, DAI X H, CHAI X L. Effect of influent pH on biological denitrification using biodegradable PHBV/PLA blends as electron donor[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 131: 24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2017.12.008 [61] ZHU S M, ZHANG L P, YE Z Y, et al. Denitrification performance and bacterial ecological network of a reactor using biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) as an electron donor for nitrate removal from aquaculture wastewater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 857: 159637. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159637 [62] FANG D X, WU A Q, HUANG L P, et al. Polymer substrate reshapes the microbial assemblage and metabolic patterns within a biofilm denitrification system[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 387: 124128. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124128 [63] HAN F, LI X, ZHANG M R, et al. Solid-phase denitrification in high salinity and low-temperature wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 341: 125801. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125801 [64] MIAO Y, LIAO R H, ZHANG X X, et al. Metagenomic insights into Cr(VI) effect on microbial communities and functional genes of an expanded granular sludge bed reactor treating high-nitrate wastewater[J]. Water Research, 2015, 76: 43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.042 [65] SHEN Q S, JI F Y, WEI J Z, et al. The influence mechanism of temperature on solid phase denitrification based on denitrification performance, carbon balance, and microbial analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 732: 139333. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139333 [66] JIA L X, SUN H M, ZHOU Q, et al. Pilot-scale two-stage constructed wetlands based on novel solid carbon for rural wastewater treatment in Southern China: Enhanced nitrogen removal and mechanism[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 292: 112750. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112750 [67] 杨惠兰, 张丹, 兰书焕, 等. 聚己内酯复合固体碳源的制备及其深度脱氮性能研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(5): 263-273. YANG H L, ZHANG D, LAN S H, et al. Preparation of polycaprolactone composite solid carbon source and its tertiary nitrogen removal[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2022, 42(5): 263-273 (in Chinese).
[68] WANG X J, WANG W Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification by a novel isolated Pseudomonas sp. JQ-H3 using polycaprolactone as carbon source[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 288: 121506. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121506 [69] WU B R, ZHOU M, SONG L Y, et al. Mechanism insights into polyhydroxyalkanoate-regulated denitrification from the perspective of pericytoplasmic nitrate reductase expression[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 754: 142083. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142083 [70] LI C Y, WANG H Y, YAN G K, et al. Initial carbon release characteristics, mechanisms and denitrification performance of a novel slow release carbon source[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 118: 32-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2021.08.045 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李霞,李惠娟,王理明,高敏,梅若晨,张典奥. PN-ANAMMOX两段法处理污泥消化液. 环境化学. 2024(11): 3921-3934 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载: