-
当前全球人口不断增长,但土壤质量却不断下降,现代文明再次面临粮食危机[1]。过去几十年,污水灌溉、采矿、冶炼、废弃物处理、以及农药、化肥大量使用等人类活动导致土壤重金属积累与超标[2-3],继而影响着农产品安全,威胁着人类健康。土壤治理方法中原位稳定化技术因其具有成本低、见效快、操作简便、对污染点位扰动较小等优势而得到了广泛应用 [4]。但该技术使用的常见修复剂大多存在一定的缺陷,如石灰类材料碱性太强,易造成土壤板结;含磷矿物材料使用不当会间接造成水体污染;黏土矿物成分单一、有效活性组分较低,存在施用量过大等问题 [5]。因此合理选择或开发高效、经济、环境友好的修复剂是原位稳定化技术的关键[6]。
近年来,水铁矿-腐殖酸(Fh-HA)复合材料的制备及应用受到了广大学者的研究[7-9]。相较于单一修复剂而言,复合材料更能满足各种不同要求[10]。多种材料在性能上相互取长补短, 产生协同效应,使复合材料的综合性能往往优于原组成材料[11]。腐殖酸的引入,增加了水铁矿的官能团种类,改变了比表面积,并增大了孔径尺寸;此外,水铁矿在此过程中晶格结构不变,没有向其他铁氧化物转变[12]。腐殖酸仅存在于水铁矿的晶格夹缝间,阻碍水铁矿结晶转化,同时也减缓自身在土壤中的矿化降解[13],因此Fh-HA在稳定土壤重金属方面具有优越的性能。但是腐殖酸在一定条件下,具有较高的溶解性 [14-15],重金属离子在Fh-HA复合物表面的吸附也受到腐殖酸溶解性的影响[16]。自然环境下的酸雨、水淹等现象都可能导致腐殖酸溶解,引起复合材料结构破坏,吸附的重金属再次活化。溶解性腐殖酸与水铁矿的相互作用也会明显增强水铁矿中重金属的释放[17]。若对腐殖酸进行高温改性可使其羟基和羧基等官能团发生脱水反应,增强疏水性,达到不溶的目的[18],从而提高复合材料的稳定性。虽然改性过程减少了腐殖酸可用于吸附重金属的酸性基团,但对于酸性基团的金属络合常数并没有影响[19]。马明广[20]、陈荣平[21]等制备热改性腐殖酸吸附水中重金属,均展现出了高吸附效率,并且不易损失、可以重复利用。由此本文提出一种将腐殖酸高温改性形成不溶性腐殖酸,再与水铁矿结合成更稳定的Fh-IHA复合材料的思路。
目前Fh-IHA对自然环境下碱性土壤重金属的吸附性能以及土壤基本理化性质的影响鲜有研究。然而评价修复材料稳定污染土壤重金属的效果时,不仅要关注重金属有效性,还要关注其本身对土壤基本理化性质的影响。因此本研究以甘肃白银某Cd、Pb污染农田为试验区,进行田间稳定化试验,旨在为重金属污染防控提供一种环境友好的修复材料。主要内容如下:(1)采用高温改性腐殖酸与水铁矿制备成Fh-IHA复合材料,并通过扫描电子显微镜、X射线衍射、傅里叶红外光谱、比表面积与Fh-HA进行表面性能对比分析;(2)经田间稳定化试验,分析Fh-IHA对土壤pH值,有机质,铵态氮、速效磷、有效钾的影响;(3)根据改进BCR法,探讨处理后污染土壤中Cd、Pb的形态变化特征,掌握Fh-IHA对重金属Cd、Pb的稳定规律。
-
不溶性腐殖酸:腐殖酸购买于山东西亚化学股份有限公司(C含量为52.9%),将其置于马弗炉,在400 ℃温度下加热1 h,待其自然冷却后用2 mol·L−1 CaCl2溶液浸泡处理,然后抽滤,再用1 mol·L−1 NaNO3溶液和蒸馏水反复洗涤,烘干。最终所得固体为不溶性腐殖酸,储存在密封玻璃瓶中待用[22]。
Fh-HA复合材料(C/Fe=0.5,物质的量比):将FeCl3·6H2O、腐殖酸分别溶于水、NaOH溶液,再将二者混合,然后通过NaOH溶液快速将混合溶液pH调节至7.5。搅拌2 h后,将混合物静置分层后虹吸除去上清液,沉淀物用去离子水清洗离心,最后用真空冷冻干燥机冷冻干燥48 h后密封冷藏于4 ℃条件下备用。
Fh-IHA复合材料(C/Fe=0.5,物质的量比):采用不溶性腐殖酸,其余步骤与制备Fh-HA复合材料相同。
-
试验田位于甘肃白银某Cd、Pb污染农田,土壤呈碱性,气温低、温差大、降水量少,其基本理化性质见表1。全铅含量为95.47 mg·kg−1,全镉含量为 10.93 mg·kg−1,与《土壤环境质量 农用地污染镉污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 15618—2018)相比,该农田属于重度Cd污染、轻微Pb污染。稳定试验在田间进行,分别处理3处半径为0.3 m、深0.6 m的土壤。空白对照(CK)为不添加钝化剂的混合土壤,#1、#2、#3为添加 3 % (W/W)Fh-IHA处理的不同点位土壤。土壤充分混匀后装于Ф10 cm×60 cm的有机玻璃土柱中置于田间稳定化 90 d,土柱上覆盖塑料膜(扎孔通气)进行保湿,期间分别在10、20、30、60、90 d采样,各处理一式三份,密封装袋带回实验室分析。
-
Fh-HA与Fh-IHA的微观形貌通过低真空扫描电子显微镜(JSM-5600LV)在6000倍下观察;比表面积是以N2吸附/脱附的BET法用比表面积分析仪(ASAP 2020)测定;傅里叶变换红外光谱在扫描范围为400—4000 cm−1之间,分辨率为8 cm−1下用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(NEXUS 670)分析;X射线衍射是将样品用玛瑙研钵研磨并过筛后放入药瓶槽内,以(2θ)0.02° 为增量,从(2θ)10° 到80° 用粉末X射线衍射仪(JSM-5600LV)扫描。
土壤pH值采用电位法(HJ 962—2018)以水土比为1:2.5(W/V),室温下剧烈振荡2 min,静止30 min后用pH计测定;土壤有机质采用重铬酸钾滴定法(NY/T 1121.6—2006),以过量重铬酸钾-硫酸溶液氧化0.5 g土壤有机碳,然后用硫酸亚铁滴定消耗量计算;土壤铵态氮、有效磷、速效钾采用联合浸提比色法(NY/T 1848—2010),称取2.5 g风干土样,加入无磷活性炭与土壤联合浸提剂,在25 ℃、220 r·min−1下振荡 10 min过滤,滤液用于测定;土壤Cd和Pb总量是通过向土壤中按体积比5:1:1添加HNO3、HF和H2O2后用微波消解仪(MARS6)消解,然后将消解液用火焰原子吸收光谱仪(ZEEnitt700P)测定;土壤Cd、Pb酸可溶态、可还原态、可氧化态以及残渣态的测定是通过称取1 g风干土样按照改进BCR连续浸提法[23]分步提取。
-
3次重复试验结果的平均值和标准偏差由Microsoft Office Excel 2010计算,并用Origin 2018进行作图。使用SPSS25.0软件进行单因素方差分析,当两组数据间存在显著性差异(P<0.05)时,采用最小显著性差异检验进行多重比较。
-
Fh-IHA与Fh-HA的X射线衍射(XRD)图谱如图1所示。两种材料在2θ为35° 和62°附近显示出两个宽峰,与2-线水铁矿的标准衍射卡片(PDF 29—0712)基本一致,表明实验室制备的Fh-IHA与Fh-HA的晶体结构与2-线水铁矿的晶体结构相同,是一种低序的铁(氢)氧化物[24]。由图可以发现,制备的材料没有出现尖锐的衍射峰,峰型相对宽化,表明材料的结晶度较低,这也说明水铁矿没有发生结晶转化,腐殖酸与水铁矿成功复合。对比Fh-HA,Fh-IHA的衍射峰没有明显变化,也没有出现新的峰,说明热改性腐殖酸不会影响复合材料的晶体结构。该结果也得到了Shimizu [25]、Liang 等[26]的证实。经比表面积分析测定,Fh-HA的比表面积为258.9 m2·g−1,经过腐殖酸改性后Fh-IHA的比表面积增加到288.5 m2·g−1。观察扫描电子显微镜(SEM)图(图2)可以看出,比表面积的不同是由于两种复合材料的表面形貌具有明显差异导致。Fh-HA表面呈现出相对规则、光滑的形貌;而Fh-IHA表面更为粗糙,附着有不规则的细小颗粒,因此具有更大的比表面积。优化腐殖酸使复合材料具有更为优越的表面性质,相比凹凸棒石/纳米铁、沸石/纳米零价铁镍、腐殖酸/海泡石等复合材料[27-29],Fh-IHA的比表面积也更大。高比表面积可以使Fh-IHA复合材料暴露更多的功能基团,为重金属提供更多的物理吸附空间和化学吸附活性位点,从而增强吸附重金属的能力[30]。
-
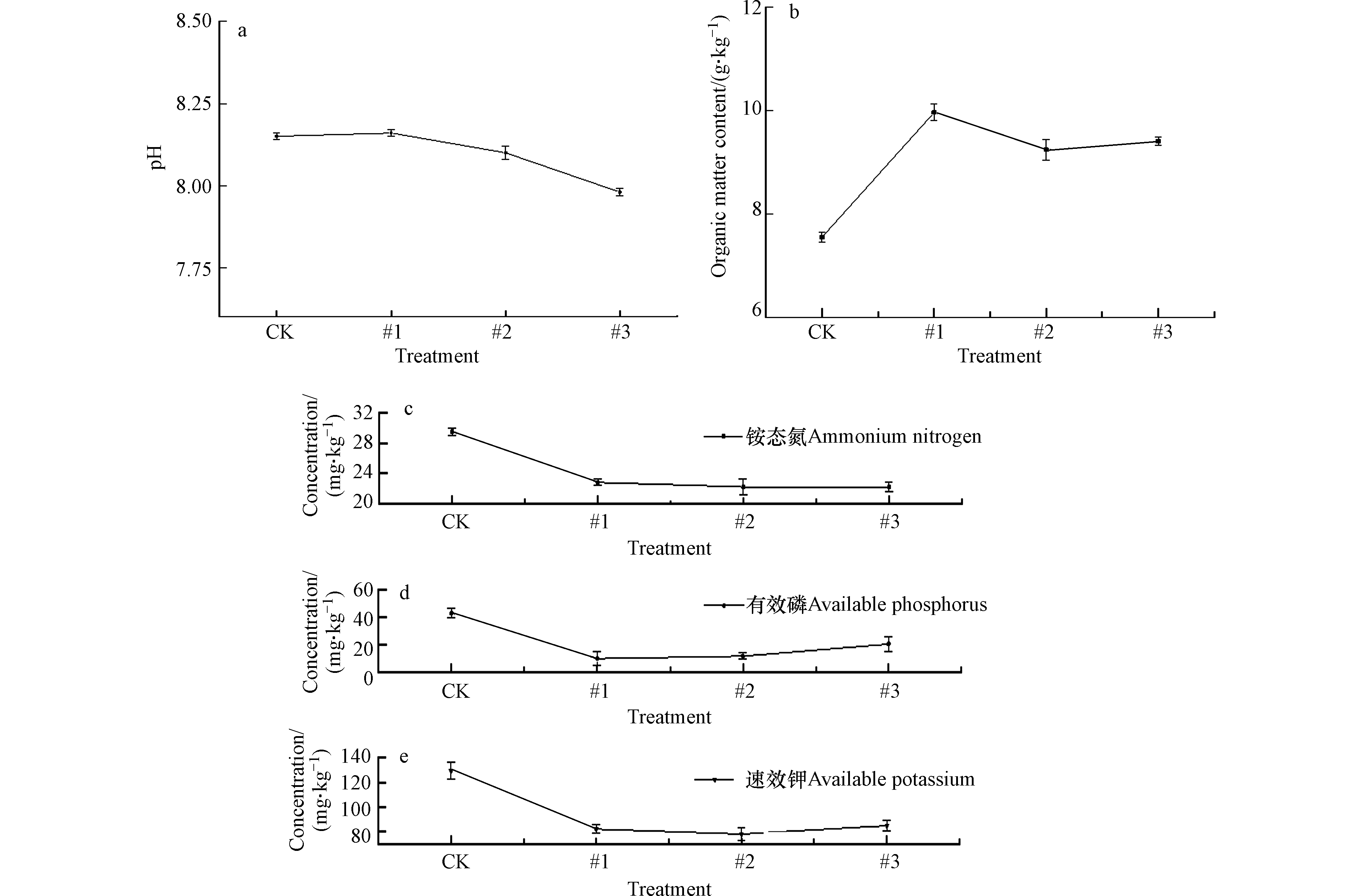
土壤的基本理化性质对重金属的活性及植物生长发育起着至关重要的作用[31-32]。在酸性土壤中,常通过添加材料提高土壤pH值,来降低重金属的活性;而对于碱性土壤,pH提高过大会造成土壤过碱,不利于植物生长[33]。本研究中添加Fh-IHA复合材料处理 90 d后,3个土柱中土壤pH值总体上轻微降低。结果如图3a所示,稳定后3个土柱中土壤pH仍为碱性,相比土壤初始pH值,#1号土柱仅微弱变化了0.01个单位(P<0.05),#2、#3号土柱分别降低了0.06和0.16个单位(P<0.05),3个土柱中土壤pH值总体上呈现降低的趋势,但降低幅度相对较小。这一方面可能是由于土壤本身具有一定的酸碱缓冲性[34] ,另一方面主要是水铁矿对H+具有亲和力,而腐殖酸是一种带负电荷的胶体粒子,二者相互作用下一定程度上抵消了对土壤pH的影响[7],因此在碱性土壤中Fh-IHA复合材料不会因为改变土壤的酸碱环境而影响重金属的活性。
有机质是反映土壤肥力的重要特征。图3b显示了添加Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后,土壤中有机质含量的变化。与空白对照相比,#1、#2、#3土柱中土壤有机质含量显著变化(P<0.05), 从7.55 g·kg−1分别升高到了9.96、9.24、9.39 g·kg−1。这是因为不溶性腐殖酸本身属于有机物质,材料的添加增加了土壤中有机碳的含量;另一方面Fh-IHA特殊的表面性质可以吸附有机分子胶结土壤粘粒形成团聚体,减少微生物与有机质的接触,起到减缓土壤有机质的降解作用[35]。
Fh-IHA复合材料处理 90 d后,土壤中铵态氮、速效磷、有效钾含量的变化由图3c所示。与空白对照相比,3种养分均呈现出显著降低(P<0.05),3个土柱土壤中铵态氮分别从 29.57 mg·kg−1 降低为22.82、22.21、22.22 mg·kg−1,有效磷含量从42.70 mg·kg−1 降低为9.84、11.60、20.31 mg·kg−1,速效钾含量则由129.42 mg·kg−1 分别降低到82.11、78.08、84.80 mg·kg−1。铵态氮、速效钾中NH4+、K+能与Fh-IHA形成的土壤胶体进行阳离子交换,而有效磷在土壤中多以H2PO4−形式存在,H2PO4−也可通过取代-OH的配体交换而与腐殖酸-铁络合物结合,从而导致3种速效养分变成移动性较小、不易流失的缓效养分[36-37]。因此添加Fh-IHA后土壤中铵态氮、有效磷、速效钾含量呈现出了显著降低。但同时有研究显示在分泌有机酸的植物根系作用以及微生物的活动下,部分缓效养分又可被活化释放[38],表明添加Fh-IHA复合材料有利于土壤中养分的高效利用,促进植物的生长发育。
-
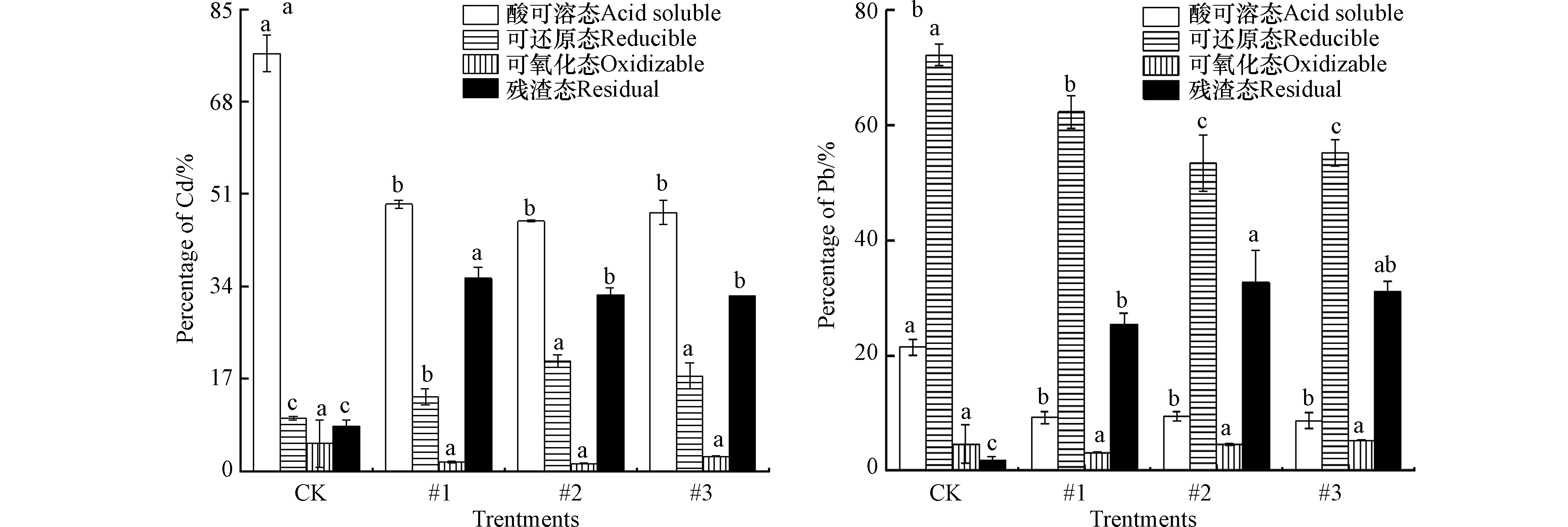
土壤中重金属所赋存的化学形态影响着其迁移能力和生物活性,酸可溶态具有较高活性,容易被植物吸收,而残渣态则已经进入土壤晶体物质的晶格中,即使环境改变一般也难以活化[39],可氧化态与可还原态重金属往往只有在土壤性质发生重大变化时才能在土壤中释放 [40]。本试验研究区域位于西北干旱地区,土壤呈碱性,生物活性较低,自然环境相对稳定,由此本研究将可还原态、可氧化态与残渣态统一归为稳定态,以酸可溶态为活性态。添加Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后土壤中活性态Cd百分比含量明显降低,稳定态Cd含量升高,稳定效果显著(P<0.05)。具体结果如图4a所示,与空白对照相比,3个土柱中土壤活性态Cd百分比含量分别为45.2%、45.1%、51.1%,显著降低了25.9%—31.9%,降幅达到33.6%—41%;稳定态Cd百分比含量显著增加了22.1%—34.0%,增幅达到96%—148%。具体而言,未经处理情况下土壤中Cd化学形态主要集中在酸可溶态,占总Cd含量的77.0%。经Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后,各土柱Cd赋存形态具体表现为酸可溶态与可氧化态转化为可还原态与残渣态,可氧化态Cd由5.1%降低到了0.9%—1.4%,可还原态与残渣态Cd分别由9.7%、8.3%增加到了18.7%—19.2%与34.4%—38.5%。温鑫[41]研究了腐殖酸、有机肥、沸石、海泡石、硅藻土等多种材料单一以及组合添加处理Cd污染土壤,最佳效果为活性态Cd降低2.01%—3.35%,其中腐殖酸单一添加甚至对土壤Cd产生了活化作用。相比之下,Fh-IHA复合材料对土壤中Cd展现出更好的稳定效果,这可能是因为复合材料同时具有多重稳定机制,并且可以弥补单一或组配添加下材料本身存在的缺陷。而腐殖酸既能促进也能抑制土壤Cd的活性[14],这是因为腐殖酸含有多种活性官能团,可与重金属结合,但同时自然环境下腐殖酸不够稳定,容易被矿化分解为有机酸,即使在高pH下也能促进土壤中Cd的释放[42],这也正是腐殖酸需要进行改性的原因之一。
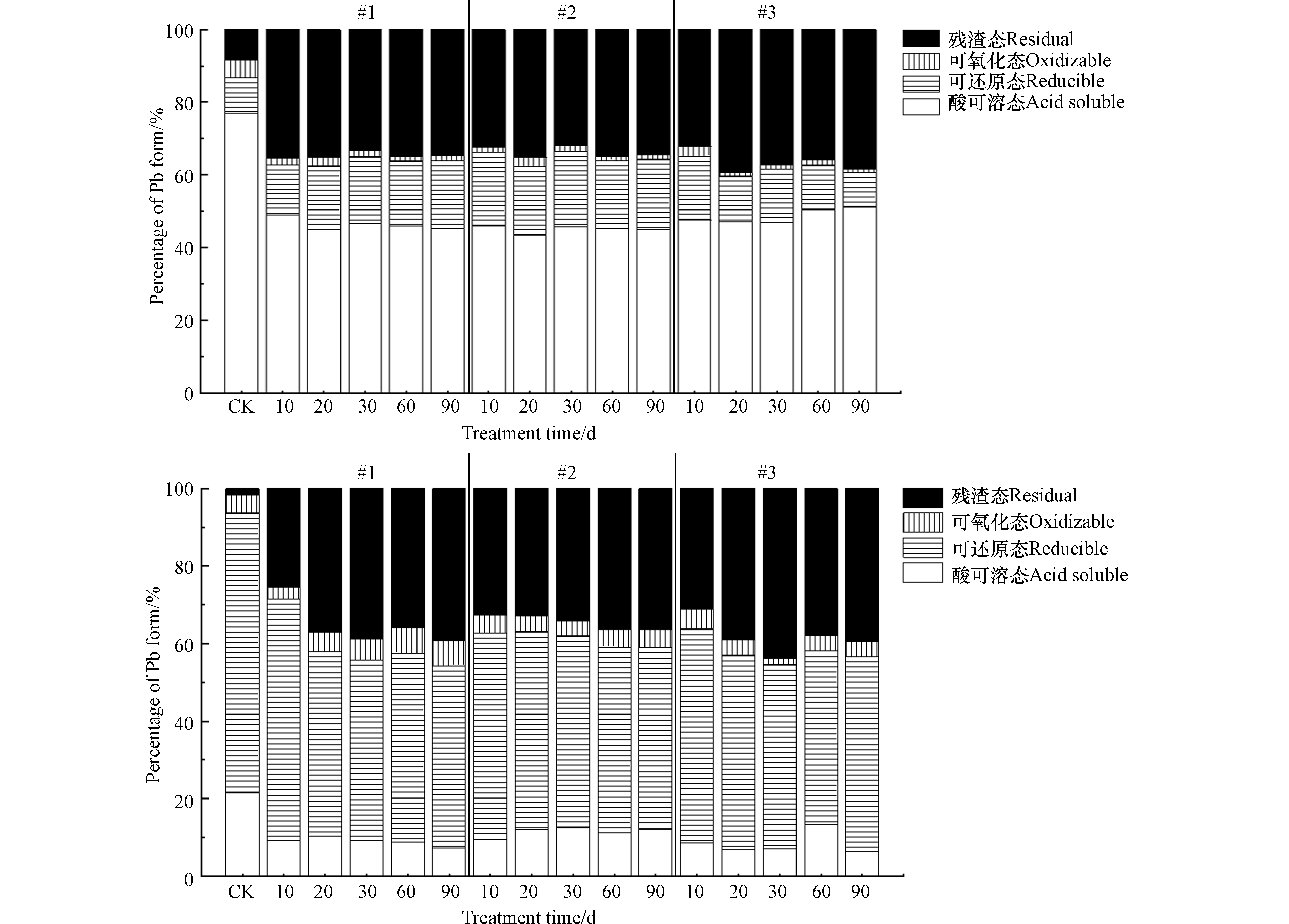
Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后土壤中活性态Pb百分比含量明显降低,稳定态Pb含量明显升高,稳定效果显著(P<0.05)。结果如图4b所示,与空白对照相比,3个土柱中活性态Pb百分比含量分别降低为7.4%、12.2%、6.4%,显著降低了9.2%—15%,降幅达到43.0%—70.1%;稳定态Pb百分比含量显著增加了15.6%—21.4%,增幅达到19.8—27.2%。具体而言,土壤中Pb各形态百分比含量与Cd展现出了不同的情形,在未经处理情况下,Pb主要集中在可还原态,占总含量的72.2%,而酸可溶态Pb仅占总含量的21.4%。经Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后,3个土柱具体表现为由酸可溶态与可还原态Pb转化为可氧化态与残渣态Pb,可还原态Pb由72.2%降低至46.8%—50.4%,可氧化态Pb呈现不规律的变化,残渣态Pb由1.8% 增加到了36.5%—39.4%。在土壤Pb稳定化方面,袁兴超等[43]分别在大田与盆栽环境下研究了钙镁磷肥、生物炭、石灰、腐殖酸、海泡石对Pb形态的影响,结果表明对残渣态Pb稳定效果较好的石灰与生物炭分别增加23.7%、20.8%。而本研究在Fh-IHA处理下残渣态Pb由1.8%显著增加到了36.5%—39.4%,表明Fh-IHA对Pb也同样具有较好的稳定效果,可同时应用于治理Cd、Pb复合污染土壤。Fh-IHA复合材料处理10 d后土壤Cd、Pb的各化学形态变化就基本稳定(图5),之后在长达90 d的监测中土壤Cd浓度保持不变,土壤Pb呈现出由活性态Pb向稳定态Pb轻微转化的趋势。 Cd、Pb均未见活化迹象,三个土柱表现基本一致。现阶段大量的重金属稳定研究监测时间在60 d以内[44-46],庞瑜[8]、赵立芳[47]分别在30和60 d的监测下验证了Fh-HA对土壤Cd、Pb的钝化效果,但部分处理出现了活化现象。这证明优化后的Fh-IHA复合材料具有较高的稳定性,充分表明了Fh-IHA可作为一种固定土壤中Cd、Pb重金属的理想稳定剂。
-
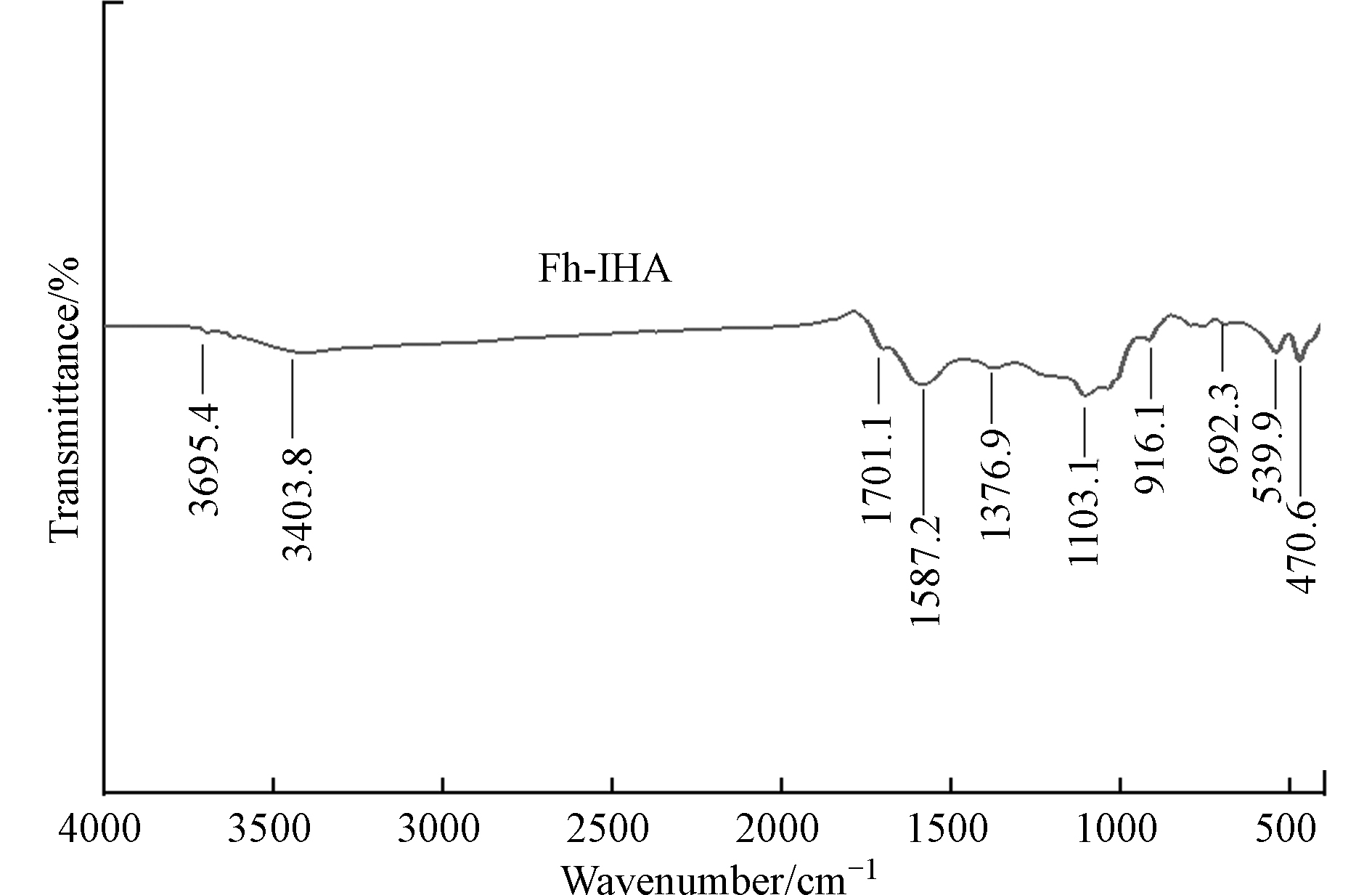
傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)可用来显示物质中涉及的主要键的特征吸收带,Fh-IHA复合材料的分析结果如图6所示。通过对比红外特征谱图库中化学键的特征波数,Fh-IHA在916.1 cm−1与692.3 cm−1处出现特征峰,这归因于Fe—OH和Fe—O键的伸缩振动,对应水铁矿表面羟基及氧配位根[48],而 539.9 cm−1 和 470.6cm−1处特征峰,则表明存在芳族C—H的平面外弯曲振动,1103.1 cm−1为羟基的C—O振动,1376.9 cm−1处为醇O—H的弯曲振动、1587.2 cm−1处为C=C伸缩振动,1701.1 cm−1处为羧基中的C=O伸缩振动,3403.8 cm−1、3695.4 cm−1处主要为O—H与N—H的伸缩振动。Fh-IHA复合材料相比水铁矿的红外光谱图[49]具有更多的特征峰,增加的特征峰主要由不溶性腐殖酸结构中羧基、醇羟基、酚羟基以及氨基等官能团结构上的特殊化学键产生,而活性官能团可通过吸附、络合等作用与环境中的重金属离子形成配位化合物[16]。不同的官能团与金属离子之间的结合能力不同,腐殖酸与重金属离子之间的作用基团,最主要的是酚羟基和羧基[50]。此外,铁(氢)化物表面大量的两性基团通过去质子化作用形成的可变电荷也可与重金属离子发生表面配合,产生吸附[16]。Fh-IHA复合材料由不溶性腐殖酸与水铁矿复合而成,因此能够实现两种交互作用方式,水铁矿、不溶性腐殖酸通过表面络合、静电吸附作用结合Cd2+、Pb2+,从而达到有效降低土壤中活性态Cd、Pb的目的。其可能的稳定作用过程由图7所示。
-
(1)Fh-IHA复合材料表面性质优越,是良好的重金属稳定材料。优化后的Fh-IHA仍保持2-线水铁矿的晶体特征,结构稳定。与Fh-HA相比,Fh-IHA具有更粗糙的表面和更大的比表面积,可以提供更多的吸附空间和活性位点,有利于稳定Cd、Pb重金属。
(2)Fh-IHA复合材料添加到碱性重金属污染土壤中,有利于改善土壤理化性质。经田间试验显示,添加Fh-IHA后土壤pH轻微降低,土壤有机质含量显著提高,并促进土壤中铵态氮、有效磷、速效钾的固存,减少了土壤中速效养分的流失。
(3)Fh-IHA复合材料能有效降低土壤中Cd、Pb重金属的活性,且见效快、稳定性高。Fh-IHA通过丰富的活性官能团与土壤中Cd2+、Pb2+发生表面络合、静电吸附作用,使得土壤中稳定态Cd、Pb百分比含量显著升高了22.1%—34.0%、15.6%—21.4%,可作为一种环境友好的土壤重金属污染修复材料。
优化水铁矿-腐殖酸复合材料对镉、铅污染土壤的稳定化
Study on stabilization of soil contaminated with cadmium and lead by optimization of carbon and iron composites
-
摘要: 为解决土壤重金属污染问题,用高温改性腐殖酸制备出水铁矿-不溶性腐殖酸(Fh-IHA)复合材料,通过扫描电镜(SEM)、比表面积(BET)、X射线衍射(XRD)、傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)分析Fh-IHA的表面特性,结合田间稳定试验研究施加Fh-IHA对土壤pH,有机质(OM),铵态氮(A-N)、有效磷(A-P)、速效钾(A-K)和镉、铅形态的影响。结果表明,Fh-IHA表面粗糙、比表面积大、含有多种官能团,可通过表面络合、静电吸附结合镉、铅离子;稳定化修复后土壤pH轻微降低,有机质升高,铵态氮、有效磷、速效钾转变为缓效养分;稳定态镉、铅百分比含量分别升高22.1%—34.0%、15.6%—21.4%,且经90 d监测未出现活化现象。研究表明,Fh-IHA对土壤中重金属镉、铅稳定效果显著,可作为一种环境友好的土壤重金属污染修复材料。Abstract: To solve contaminated soil by heavy metals, A synthesis of ferrihydrite-insoluble humic acid composite was prepared using high temperature modified humic acid and ferrihydrite. The composite was characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), specific surface area (BET), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR) to explore surface characteristics. The effects of introduced Fh-IHA to soil on soil pH, organic matter(OM), ammonium nitrogen(A-N), available phosphorus(A-P), available potassium(A-K), and speciation of cadmium and lead were researched combined with field plot test. The results discovered that Fh-IHA is featured with rough surface, large specific area and abundant functional groups, can complex with cadmium ions and lead ions by surface complexation and electrostatic absorption. After immobilization remediation, soil pH lowered, the content of organic matter increased, and A-N, A-P, A-K were transformed to slow release fertilizers. The percentage of stable cadimium and stable lead in soil increased 22.1%—34.0% and 15.6%—21.4% respectively. Furtherly, the reactivation of cadmium and lead was not detected after 90 days of monitoring. The paper showed that Fh-IHA delivered superior results in immobilizing heavy metal ions, it can be used as an environment-friendly materials for remediation for contaminated soil by heavy metals.
-
Key words:
- ferrihydrite /
- insoluble humic acid /
- cadmium, lead pollution /
- soil remediation
-
当前全球人口不断增长,但土壤质量却不断下降,现代文明再次面临粮食危机[1]。过去几十年,污水灌溉、采矿、冶炼、废弃物处理、以及农药、化肥大量使用等人类活动导致土壤重金属积累与超标[2-3],继而影响着农产品安全,威胁着人类健康。土壤治理方法中原位稳定化技术因其具有成本低、见效快、操作简便、对污染点位扰动较小等优势而得到了广泛应用 [4]。但该技术使用的常见修复剂大多存在一定的缺陷,如石灰类材料碱性太强,易造成土壤板结;含磷矿物材料使用不当会间接造成水体污染;黏土矿物成分单一、有效活性组分较低,存在施用量过大等问题 [5]。因此合理选择或开发高效、经济、环境友好的修复剂是原位稳定化技术的关键[6]。
近年来,水铁矿-腐殖酸(Fh-HA)复合材料的制备及应用受到了广大学者的研究[7-9]。相较于单一修复剂而言,复合材料更能满足各种不同要求[10]。多种材料在性能上相互取长补短, 产生协同效应,使复合材料的综合性能往往优于原组成材料[11]。腐殖酸的引入,增加了水铁矿的官能团种类,改变了比表面积,并增大了孔径尺寸;此外,水铁矿在此过程中晶格结构不变,没有向其他铁氧化物转变[12]。腐殖酸仅存在于水铁矿的晶格夹缝间,阻碍水铁矿结晶转化,同时也减缓自身在土壤中的矿化降解[13],因此Fh-HA在稳定土壤重金属方面具有优越的性能。但是腐殖酸在一定条件下,具有较高的溶解性 [14-15],重金属离子在Fh-HA复合物表面的吸附也受到腐殖酸溶解性的影响[16]。自然环境下的酸雨、水淹等现象都可能导致腐殖酸溶解,引起复合材料结构破坏,吸附的重金属再次活化。溶解性腐殖酸与水铁矿的相互作用也会明显增强水铁矿中重金属的释放[17]。若对腐殖酸进行高温改性可使其羟基和羧基等官能团发生脱水反应,增强疏水性,达到不溶的目的[18],从而提高复合材料的稳定性。虽然改性过程减少了腐殖酸可用于吸附重金属的酸性基团,但对于酸性基团的金属络合常数并没有影响[19]。马明广[20]、陈荣平[21]等制备热改性腐殖酸吸附水中重金属,均展现出了高吸附效率,并且不易损失、可以重复利用。由此本文提出一种将腐殖酸高温改性形成不溶性腐殖酸,再与水铁矿结合成更稳定的Fh-IHA复合材料的思路。
目前Fh-IHA对自然环境下碱性土壤重金属的吸附性能以及土壤基本理化性质的影响鲜有研究。然而评价修复材料稳定污染土壤重金属的效果时,不仅要关注重金属有效性,还要关注其本身对土壤基本理化性质的影响。因此本研究以甘肃白银某Cd、Pb污染农田为试验区,进行田间稳定化试验,旨在为重金属污染防控提供一种环境友好的修复材料。主要内容如下:(1)采用高温改性腐殖酸与水铁矿制备成Fh-IHA复合材料,并通过扫描电子显微镜、X射线衍射、傅里叶红外光谱、比表面积与Fh-HA进行表面性能对比分析;(2)经田间稳定化试验,分析Fh-IHA对土壤pH值,有机质,铵态氮、速效磷、有效钾的影响;(3)根据改进BCR法,探讨处理后污染土壤中Cd、Pb的形态变化特征,掌握Fh-IHA对重金属Cd、Pb的稳定规律。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and Methods)
1.1 材料的制备
不溶性腐殖酸:腐殖酸购买于山东西亚化学股份有限公司(C含量为52.9%),将其置于马弗炉,在400 ℃温度下加热1 h,待其自然冷却后用2 mol·L−1 CaCl2溶液浸泡处理,然后抽滤,再用1 mol·L−1 NaNO3溶液和蒸馏水反复洗涤,烘干。最终所得固体为不溶性腐殖酸,储存在密封玻璃瓶中待用[22]。
Fh-HA复合材料(C/Fe=0.5,物质的量比):将FeCl3·6H2O、腐殖酸分别溶于水、NaOH溶液,再将二者混合,然后通过NaOH溶液快速将混合溶液pH调节至7.5。搅拌2 h后,将混合物静置分层后虹吸除去上清液,沉淀物用去离子水清洗离心,最后用真空冷冻干燥机冷冻干燥48 h后密封冷藏于4 ℃条件下备用。
Fh-IHA复合材料(C/Fe=0.5,物质的量比):采用不溶性腐殖酸,其余步骤与制备Fh-HA复合材料相同。
1.2 试验设计
试验田位于甘肃白银某Cd、Pb污染农田,土壤呈碱性,气温低、温差大、降水量少,其基本理化性质见表1。全铅含量为95.47 mg·kg−1,全镉含量为 10.93 mg·kg−1,与《土壤环境质量 农用地污染镉污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 15618—2018)相比,该农田属于重度Cd污染、轻微Pb污染。稳定试验在田间进行,分别处理3处半径为0.3 m、深0.6 m的土壤。空白对照(CK)为不添加钝化剂的混合土壤,#1、#2、#3为添加 3 % (W/W)Fh-IHA处理的不同点位土壤。土壤充分混匀后装于Ф10 cm×60 cm的有机玻璃土柱中置于田间稳定化 90 d,土柱上覆盖塑料膜(扎孔通气)进行保湿,期间分别在10、20、30、60、90 d采样,各处理一式三份,密封装袋带回实验室分析。
表 1 土壤基本理化性质Table 1. Basic physical and chemical properties of soilpH 阳离子交换量/(cmol·kg-1)CEC 有机质/(g·kg−1) OM 铵态氮/(mg·kg−1)A-N 有效磷/(mg·kg−1)A-P 速效钾/(mg·kg−1)A-K 镉/(mg·kg-1)Cd 铅/(mg·kg-1)Pb 8.15 8.83 7.55 29.57 42.70 129.42 10.93 95.47 1.3 指标测定方法
Fh-HA与Fh-IHA的微观形貌通过低真空扫描电子显微镜(JSM-5600LV)在6000倍下观察;比表面积是以N2吸附/脱附的BET法用比表面积分析仪(ASAP 2020)测定;傅里叶变换红外光谱在扫描范围为400—4000 cm−1之间,分辨率为8 cm−1下用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(NEXUS 670)分析;X射线衍射是将样品用玛瑙研钵研磨并过筛后放入药瓶槽内,以(2θ)0.02° 为增量,从(2θ)10° 到80° 用粉末X射线衍射仪(JSM-5600LV)扫描。
土壤pH值采用电位法(HJ 962—2018)以水土比为1:2.5(W/V),室温下剧烈振荡2 min,静止30 min后用pH计测定;土壤有机质采用重铬酸钾滴定法(NY/T 1121.6—2006),以过量重铬酸钾-硫酸溶液氧化0.5 g土壤有机碳,然后用硫酸亚铁滴定消耗量计算;土壤铵态氮、有效磷、速效钾采用联合浸提比色法(NY/T 1848—2010),称取2.5 g风干土样,加入无磷活性炭与土壤联合浸提剂,在25 ℃、220 r·min−1下振荡 10 min过滤,滤液用于测定;土壤Cd和Pb总量是通过向土壤中按体积比5:1:1添加HNO3、HF和H2O2后用微波消解仪(MARS6)消解,然后将消解液用火焰原子吸收光谱仪(ZEEnitt700P)测定;土壤Cd、Pb酸可溶态、可还原态、可氧化态以及残渣态的测定是通过称取1 g风干土样按照改进BCR连续浸提法[23]分步提取。
1.4 数据统计分析
3次重复试验结果的平均值和标准偏差由Microsoft Office Excel 2010计算,并用Origin 2018进行作图。使用SPSS25.0软件进行单因素方差分析,当两组数据间存在显著性差异(P<0.05)时,采用最小显著性差异检验进行多重比较。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and Discussion)
2.1 Fh-IHA与Fh-HA表面性质对比分析
Fh-IHA与Fh-HA的X射线衍射(XRD)图谱如图1所示。两种材料在2θ为35° 和62°附近显示出两个宽峰,与2-线水铁矿的标准衍射卡片(PDF 29—0712)基本一致,表明实验室制备的Fh-IHA与Fh-HA的晶体结构与2-线水铁矿的晶体结构相同,是一种低序的铁(氢)氧化物[24]。由图可以发现,制备的材料没有出现尖锐的衍射峰,峰型相对宽化,表明材料的结晶度较低,这也说明水铁矿没有发生结晶转化,腐殖酸与水铁矿成功复合。对比Fh-HA,Fh-IHA的衍射峰没有明显变化,也没有出现新的峰,说明热改性腐殖酸不会影响复合材料的晶体结构。该结果也得到了Shimizu [25]、Liang 等[26]的证实。经比表面积分析测定,Fh-HA的比表面积为258.9 m2·g−1,经过腐殖酸改性后Fh-IHA的比表面积增加到288.5 m2·g−1。观察扫描电子显微镜(SEM)图(图2)可以看出,比表面积的不同是由于两种复合材料的表面形貌具有明显差异导致。Fh-HA表面呈现出相对规则、光滑的形貌;而Fh-IHA表面更为粗糙,附着有不规则的细小颗粒,因此具有更大的比表面积。优化腐殖酸使复合材料具有更为优越的表面性质,相比凹凸棒石/纳米铁、沸石/纳米零价铁镍、腐殖酸/海泡石等复合材料[27-29],Fh-IHA的比表面积也更大。高比表面积可以使Fh-IHA复合材料暴露更多的功能基团,为重金属提供更多的物理吸附空间和化学吸附活性位点,从而增强吸附重金属的能力[30]。
2.2 Fh-IHA复合材料对实地修复土壤理化性质的影响
土壤的基本理化性质对重金属的活性及植物生长发育起着至关重要的作用[31-32]。在酸性土壤中,常通过添加材料提高土壤pH值,来降低重金属的活性;而对于碱性土壤,pH提高过大会造成土壤过碱,不利于植物生长[33]。本研究中添加Fh-IHA复合材料处理 90 d后,3个土柱中土壤pH值总体上轻微降低。结果如图3a所示,稳定后3个土柱中土壤pH仍为碱性,相比土壤初始pH值,#1号土柱仅微弱变化了0.01个单位(P<0.05),#2、#3号土柱分别降低了0.06和0.16个单位(P<0.05),3个土柱中土壤pH值总体上呈现降低的趋势,但降低幅度相对较小。这一方面可能是由于土壤本身具有一定的酸碱缓冲性[34] ,另一方面主要是水铁矿对H+具有亲和力,而腐殖酸是一种带负电荷的胶体粒子,二者相互作用下一定程度上抵消了对土壤pH的影响[7],因此在碱性土壤中Fh-IHA复合材料不会因为改变土壤的酸碱环境而影响重金属的活性。
有机质是反映土壤肥力的重要特征。图3b显示了添加Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后,土壤中有机质含量的变化。与空白对照相比,#1、#2、#3土柱中土壤有机质含量显著变化(P<0.05), 从7.55 g·kg−1分别升高到了9.96、9.24、9.39 g·kg−1。这是因为不溶性腐殖酸本身属于有机物质,材料的添加增加了土壤中有机碳的含量;另一方面Fh-IHA特殊的表面性质可以吸附有机分子胶结土壤粘粒形成团聚体,减少微生物与有机质的接触,起到减缓土壤有机质的降解作用[35]。
Fh-IHA复合材料处理 90 d后,土壤中铵态氮、速效磷、有效钾含量的变化由图3c所示。与空白对照相比,3种养分均呈现出显著降低(P<0.05),3个土柱土壤中铵态氮分别从 29.57 mg·kg−1 降低为22.82、22.21、22.22 mg·kg−1,有效磷含量从42.70 mg·kg−1 降低为9.84、11.60、20.31 mg·kg−1,速效钾含量则由129.42 mg·kg−1 分别降低到82.11、78.08、84.80 mg·kg−1。铵态氮、速效钾中NH4+、K+能与Fh-IHA形成的土壤胶体进行阳离子交换,而有效磷在土壤中多以H2PO4−形式存在,H2PO4−也可通过取代-OH的配体交换而与腐殖酸-铁络合物结合,从而导致3种速效养分变成移动性较小、不易流失的缓效养分[36-37]。因此添加Fh-IHA后土壤中铵态氮、有效磷、速效钾含量呈现出了显著降低。但同时有研究显示在分泌有机酸的植物根系作用以及微生物的活动下,部分缓效养分又可被活化释放[38],表明添加Fh-IHA复合材料有利于土壤中养分的高效利用,促进植物的生长发育。
2.3 Fh-IHA复合材料对实地修复土壤重金属的固定效果分析
2.3.1 Fh-IHA复合材料对Cd、Pb的固定效果
土壤中重金属所赋存的化学形态影响着其迁移能力和生物活性,酸可溶态具有较高活性,容易被植物吸收,而残渣态则已经进入土壤晶体物质的晶格中,即使环境改变一般也难以活化[39],可氧化态与可还原态重金属往往只有在土壤性质发生重大变化时才能在土壤中释放 [40]。本试验研究区域位于西北干旱地区,土壤呈碱性,生物活性较低,自然环境相对稳定,由此本研究将可还原态、可氧化态与残渣态统一归为稳定态,以酸可溶态为活性态。添加Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后土壤中活性态Cd百分比含量明显降低,稳定态Cd含量升高,稳定效果显著(P<0.05)。具体结果如图4a所示,与空白对照相比,3个土柱中土壤活性态Cd百分比含量分别为45.2%、45.1%、51.1%,显著降低了25.9%—31.9%,降幅达到33.6%—41%;稳定态Cd百分比含量显著增加了22.1%—34.0%,增幅达到96%—148%。具体而言,未经处理情况下土壤中Cd化学形态主要集中在酸可溶态,占总Cd含量的77.0%。经Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后,各土柱Cd赋存形态具体表现为酸可溶态与可氧化态转化为可还原态与残渣态,可氧化态Cd由5.1%降低到了0.9%—1.4%,可还原态与残渣态Cd分别由9.7%、8.3%增加到了18.7%—19.2%与34.4%—38.5%。温鑫[41]研究了腐殖酸、有机肥、沸石、海泡石、硅藻土等多种材料单一以及组合添加处理Cd污染土壤,最佳效果为活性态Cd降低2.01%—3.35%,其中腐殖酸单一添加甚至对土壤Cd产生了活化作用。相比之下,Fh-IHA复合材料对土壤中Cd展现出更好的稳定效果,这可能是因为复合材料同时具有多重稳定机制,并且可以弥补单一或组配添加下材料本身存在的缺陷。而腐殖酸既能促进也能抑制土壤Cd的活性[14],这是因为腐殖酸含有多种活性官能团,可与重金属结合,但同时自然环境下腐殖酸不够稳定,容易被矿化分解为有机酸,即使在高pH下也能促进土壤中Cd的释放[42],这也正是腐殖酸需要进行改性的原因之一。
Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后土壤中活性态Pb百分比含量明显降低,稳定态Pb含量明显升高,稳定效果显著(P<0.05)。结果如图4b所示,与空白对照相比,3个土柱中活性态Pb百分比含量分别降低为7.4%、12.2%、6.4%,显著降低了9.2%—15%,降幅达到43.0%—70.1%;稳定态Pb百分比含量显著增加了15.6%—21.4%,增幅达到19.8—27.2%。具体而言,土壤中Pb各形态百分比含量与Cd展现出了不同的情形,在未经处理情况下,Pb主要集中在可还原态,占总含量的72.2%,而酸可溶态Pb仅占总含量的21.4%。经Fh-IHA复合材料处理90 d后,3个土柱具体表现为由酸可溶态与可还原态Pb转化为可氧化态与残渣态Pb,可还原态Pb由72.2%降低至46.8%—50.4%,可氧化态Pb呈现不规律的变化,残渣态Pb由1.8% 增加到了36.5%—39.4%。在土壤Pb稳定化方面,袁兴超等[43]分别在大田与盆栽环境下研究了钙镁磷肥、生物炭、石灰、腐殖酸、海泡石对Pb形态的影响,结果表明对残渣态Pb稳定效果较好的石灰与生物炭分别增加23.7%、20.8%。而本研究在Fh-IHA处理下残渣态Pb由1.8%显著增加到了36.5%—39.4%,表明Fh-IHA对Pb也同样具有较好的稳定效果,可同时应用于治理Cd、Pb复合污染土壤。Fh-IHA复合材料处理10 d后土壤Cd、Pb的各化学形态变化就基本稳定(图5),之后在长达90 d的监测中土壤Cd浓度保持不变,土壤Pb呈现出由活性态Pb向稳定态Pb轻微转化的趋势。 Cd、Pb均未见活化迹象,三个土柱表现基本一致。现阶段大量的重金属稳定研究监测时间在60 d以内[44-46],庞瑜[8]、赵立芳[47]分别在30和60 d的监测下验证了Fh-HA对土壤Cd、Pb的钝化效果,但部分处理出现了活化现象。这证明优化后的Fh-IHA复合材料具有较高的稳定性,充分表明了Fh-IHA可作为一种固定土壤中Cd、Pb重金属的理想稳定剂。
2.3.2 Fh-IHA复合材料对Cd、Pb的稳定作用
傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)可用来显示物质中涉及的主要键的特征吸收带,Fh-IHA复合材料的分析结果如图6所示。通过对比红外特征谱图库中化学键的特征波数,Fh-IHA在916.1 cm−1与692.3 cm−1处出现特征峰,这归因于Fe—OH和Fe—O键的伸缩振动,对应水铁矿表面羟基及氧配位根[48],而 539.9 cm−1 和 470.6cm−1处特征峰,则表明存在芳族C—H的平面外弯曲振动,1103.1 cm−1为羟基的C—O振动,1376.9 cm−1处为醇O—H的弯曲振动、1587.2 cm−1处为C=C伸缩振动,1701.1 cm−1处为羧基中的C=O伸缩振动,3403.8 cm−1、3695.4 cm−1处主要为O—H与N—H的伸缩振动。Fh-IHA复合材料相比水铁矿的红外光谱图[49]具有更多的特征峰,增加的特征峰主要由不溶性腐殖酸结构中羧基、醇羟基、酚羟基以及氨基等官能团结构上的特殊化学键产生,而活性官能团可通过吸附、络合等作用与环境中的重金属离子形成配位化合物[16]。不同的官能团与金属离子之间的结合能力不同,腐殖酸与重金属离子之间的作用基团,最主要的是酚羟基和羧基[50]。此外,铁(氢)化物表面大量的两性基团通过去质子化作用形成的可变电荷也可与重金属离子发生表面配合,产生吸附[16]。Fh-IHA复合材料由不溶性腐殖酸与水铁矿复合而成,因此能够实现两种交互作用方式,水铁矿、不溶性腐殖酸通过表面络合、静电吸附作用结合Cd2+、Pb2+,从而达到有效降低土壤中活性态Cd、Pb的目的。其可能的稳定作用过程由图7所示。
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)Fh-IHA复合材料表面性质优越,是良好的重金属稳定材料。优化后的Fh-IHA仍保持2-线水铁矿的晶体特征,结构稳定。与Fh-HA相比,Fh-IHA具有更粗糙的表面和更大的比表面积,可以提供更多的吸附空间和活性位点,有利于稳定Cd、Pb重金属。
(2)Fh-IHA复合材料添加到碱性重金属污染土壤中,有利于改善土壤理化性质。经田间试验显示,添加Fh-IHA后土壤pH轻微降低,土壤有机质含量显著提高,并促进土壤中铵态氮、有效磷、速效钾的固存,减少了土壤中速效养分的流失。
(3)Fh-IHA复合材料能有效降低土壤中Cd、Pb重金属的活性,且见效快、稳定性高。Fh-IHA通过丰富的活性官能团与土壤中Cd2+、Pb2+发生表面络合、静电吸附作用,使得土壤中稳定态Cd、Pb百分比含量显著升高了22.1%—34.0%、15.6%—21.4%,可作为一种环境友好的土壤重金属污染修复材料。
-
表 1 土壤基本理化性质
Table 1. Basic physical and chemical properties of soil
pH 阳离子交换量/(cmol·kg-1)CEC 有机质/(g·kg−1) OM 铵态氮/(mg·kg−1)A-N 有效磷/(mg·kg−1)A-P 速效钾/(mg·kg−1)A-K 镉/(mg·kg-1)Cd 铅/(mg·kg-1)Pb 8.15 8.83 7.55 29.57 42.70 129.42 10.93 95.47 -
[1] 戴维·蒙哥马利. 张甘霖等译. 耕作革命: 让土壤焕发生机[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2019. DAVID R M. Translated by ZHANG G L, et al. Farming revolution: Revitalization of soil [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2019(in Chinese).
[2] 王玉婷, 王紫玥, 刘田田, 等. 钝化剂对镉污染土壤修复效果及青菜生理效应影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(9): 2395-2403. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020032505 WANG Y T, WANG Z Y, LIU T T, et al. Effects of amendments on remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil and physiological characteristics of pakchoi [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(9): 2395-2403(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020032505
[3] SHI W Y, SHAO H B, LI H, et al. Progress in the remediation of hazardous heavy metal-polluted soils by natural zeolite [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 170(1): 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.097 [4] 张迪, 吴晓霞, 丁爱芳, 等. 生物炭和熟石灰对土壤镉铅生物有效性和微生物活性的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(11): 2526-2534. ZHANG D, WU X X, DING A F, et al. Effects of hydrated lime and biochar on the bioavailability of Cd and Pb and microbial activity in a contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(11): 2526-2534(in Chinese).
[5] 陈功宁. 矿物质钝化剂对重金属污染红壤的修复效应及机理研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. CHEN G N. Mechanism and remediation effect of mineral amendment on heavy metals contaminated red soil[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017(in Chinese).
[6] XIANG Y L, KANG F R, XIANG Y X, et al. Effects of humic acid-modified magnetic Fe3O4/MgAl-layered double hydroxide on the plant growth, soil enzyme activity, and metal availability [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 182: 109424. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109424 [7] XU M M, ZHAO Z J, SHI M, et al. Effect of humic acid on the stabilization of cadmium in soil by coprecipitating with ferrihydrite [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(26): 27330-27337. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05893-6 [8] 庞瑜. 腐植酸、水铁矿及其共沉物对土壤Pb形态及生物有效性的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017. PANG Y. Effects of coal humic acid and ferrihydrite and their coprecipitate on lead's speciation and bioavailability in soil[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017(in Chinese).
[9] 李梦婕. 腐殖酸、铁氧化物及其共存时对土壤汞赋存状态及生物活性的影响[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2012. LI M J. The effects of humic acid, iron oxides and their combinations on the occurrence state and biological activity of mercury in soils[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2012(in Chinese).
[10] 肖康, 胡杰, 崔岩山. 复合药剂对不同类型重金属污染土壤的固化修复 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(2): 660-664. XIAO K, HU J, CUI Y S. Immobilization and remediation of the heavy metal contaminated soils via the composite agents [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(2): 660-664(in Chinese).
[11] 徐婧婧, 赵科理, 叶正钱. 重金属污染土壤原位钝化修复材料的最新研究进展 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(7): 852-855. XU J J, ZHAO K L, YE Z Q. The latest research progress of in situ passivation remediation materials for heavy metal contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2019, 41(7): 852-855(in Chinese).
[12] 赵转军, 杨艳艳, 庞瑜, 等. 铁碳共沉作用对土壤重金属的吸附性能研究进展 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(8): 867-874. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.08.0867 ZHAO Z J, YANG Y Y, PANG Y, et al. A review of study on Fe-C interaction and their adsorption properties to soil heavy metal [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(8): 867-874(in Chinese). doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.08.0867
[13] 张兆虎. 碳铁共沉物对Cd、Pb复合污染农田土壤修复试验研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. ZHANG Z H. Experimental study on soil remediation of Cd & Pb contaminated farmland by iron-carbon co-precipitate[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019(in Chinese).
[14] YANG Y H, KOOPAL L K. Immobilisation of humic acids and binding of nitrophenol to immobilised humics [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1999, 151(1/2): 201-212. [15] ANIRUDHAN T S, SUCHITHRA P S. Adsorption characteristics of humic acid-immobilized amine modified polyacrylamide/bentonite composite for cationic dyesin aqueous solutions [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(7): 884-891. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62358-X [16] 王龙, 马杰, 邓迎璇, 等. 金属离子在铁(氢)氧化物与腐殖质微界面上的吸附机理和模型研究进展 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2017, 34(5): 405-413. WANG L, MA J, DENG Y X, et al. Micro-interfacial mechanism and model of metal ions adsorption on the iron(hydr) oxides and humic substances: A review [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2017, 34(5): 405-413(in Chinese).
[17] 张磊, 宋柳霆, 郑晓笛, 等. 溶解有机质与铁氧化物相互作用过程对重金属再迁移的影响 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(8): 2193-2198. ZHANG L, SONG L T, ZHENG X D, et al. The remobilization of heavy metals influenced by interaction of DOM and iron oxides [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(8): 2193-2198(in Chinese).
[18] 蒋海燕, 周书葵, 曾光明, 等. 不溶性腐殖酸对U(Ⅵ)的吸附动力学和吸附热力学 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(1): 193-198. JIANG H Y, ZHOU S K, ZENG G M, et al. Thermodynamics and kinetics of the adsorption of insolubilized humic acid to uranium(Ⅵ) ions [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(1): 193-198(in Chinese).
[19] SEKI H, SUZUKI A. Adsorption of heavy metal ions onto insolubilized humic acid [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1995, 171(2): 490-494. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1995.1207 [20] 马明广, 周敏, 蒋煜峰, 等. 不溶性腐殖酸对重金属离子的吸附研究 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2006, 6(3): 68-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2006.03.021 MA M G, ZHOU M, JIANG Y F, et al. Study on adsorption of heavy metal ions onto insolublized humic acid [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2006, 6(3): 68-71(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2006.03.021
[21] 陈荣平, 张银龙, 马爱军, 等. 腐殖酸改性及其对镉的吸附特性 [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(4): 102-106. CHEN R P, ZHANG Y L, MA A J, et al. Study on the modification of humic acid and its adsorption to cadmium [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2014, 38(4): 102-106(in Chinese).
[22] BAKER H, KHALILI F. Analysis of the removal of lead(II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto insolubilized humic acid: Temperature and pH dependence [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2004, 516(1/2): 179-186. [23] BEESLEY L, MORENO-JIMÉNEZ E, GOMEZ-EYLES J L. Effects of biochar and greenwaste compost amendments on mobility, bioavailability and toxicity of inorganic and organic contaminants in a multi-element polluted soil [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(6): 2282-2287. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.02.003 [24] YANG R, LI Z W, HUANG B, et al. Effects of Fe(Ⅲ)-fulvic acid on Cu removal via adsorption versus coprecipitation [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 197: 291-298. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.042 [25] SHIMIZU M, ZHOU J H, SCHRÖDER C, et al. Dissimilatory reduction and transformation of ferrihydrite-humic acid coprecipitates [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(23): 13375-13384. [26] LIANG Y Z, TIAN L, LU Y, et al. Kinetics of Cd(ii) adsorption and desorption on ferrihydrite: Experiments and modeling [J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2018, 20(6): 934-942. [27] 王虹. 凹凸棒石/纳米铁复合材料的制备及去除亚甲基蓝的研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020. WANG H. Preparation of attapulgite/nano-iron composite and its removal application to methylene blue[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2020(in Chinese).
[28] ANGARU G K R, CHOI Y L, LINGAMDINNE L P, et al. Facile synthesis of economical feasible fly ash-based zeolite-supported nano zerovalent iron and nickel bimetallic composite for the potential removal of heavy metals from industrial effluents [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 267: 128889. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128889 [29] 胡冬雪, 张飞杰, 周燕, 等. 腐殖酸负载羟基磷灰石对废水中Cd2+吸附性能的影响 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(12): 4022-4030. HU D X, ZHANG F J, ZHOU Y, et al. Effect of humic acid load hydroxyapatite on the adsorption of Cd2+ in wastewater [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(12): 4022-4030(in Chinese).
[30] 闫成成, 贾永堂, 曾显华, 等. 静电纺纳米纤维膜用于重金属离子吸附的研究进展 [J]. 材料导报, 2014, 28(9): 139-143. YAN C C, JIA Y T, ZENG X H, et al. Research development of electrospinning nanofiber mats for heavy metal ions adsorption [J]. Materials Review, 2014, 28(9): 139-143(in Chinese).
[31] 潘胜强, 王铎, 吴山, 等. 土壤理化性质对重金属污染土壤改良的影响分析[J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(增刊1): 600-603, 633. PAN S Q, WANG D, WU S, et al. Impact of soil properties on improvement of heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 32(Sup 1): 600-603, 633(in Chinese).
[32] 唐琨, 朱伟文, 周文新, 等. 土壤pH对植物生长发育影响的研究进展 [J]. 作物研究, 2013, 27(2): 207-212. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5280.2013.02.25 TANG K, ZHU W W, ZHOU W X, et al. Research progress on effects of soil pH on plant growth and development [J]. Crop Research, 2013, 27(2): 207-212(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5280.2013.02.25
[33] 王宏鹏. 石灰性土壤镉污染原位钝化修复材料研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. WANG H P. Study on in situ passivation materials for remediation of calcareous cadmium contaminated soil[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2020(in Chinese).
[34] 戴树桂. 环境化学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006: 277-278. DAI S G. Environmental Chemistry [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006: 277-278(in Chinese).
[35] BRONICK C J, LAL R. Soil structure and management: A review [J]. Geoderma, 2005, 124(1/2): 3-22. [36] GERKE J, HERMANN R. Adsorption of orthophosphate to humic-Fe-complexes and to amorphous Fe-oxide [J]. Zeitschrift Für Pflanzenernä hrung Und Bodenkunde, 1992, 155(3): 233-236. [37] 赵义涛, 姜佰文, 梁运江. 土壤肥料学[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009: 163-180. ZHAO Y T, JIANG B W, LIANG Y J. Soil and Fertilizer Science [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009: 163-180(in Chinese).
[38] 高晓玲. 有机-矿物缓释材料对土壤养分及玉米产量的影响[D]. 太谷: 山西农业大学, 2005. GAO X L. The effect of organic- minerals of slowly-release material on soil nutrition and maize yields[D]. Taigu, China: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2005(in Chinese).
[39] 刘丹丹, 刘菲, 缪德仁. 土壤重金属连续提取方法的优化 [J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(2): 390-396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.024 LIU D D, LIU F, MIAO D R. Optimization of soil heavy metal sequential extraction procedures [J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(2): 390-396(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.024
[40] JUHASZ A L, WEBER J, NAIDU R, et al. Determination of cadmium relative bioavailability in contaminated soils and its prediction using in vitro methodologies [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(13): 5240-5247. [41] 温鑫. 有机-无机复合钝化剂修复镉污染土壤研究[D]. 成都: 西华大学, 2020. WEN X. Study on the remediation of cadmium polluted soil by organic-inorganic compound passivator[D]. Chengdu: Xihua University, 2020(in Chinese).
[42] 余贵芬, 蒋新, 孙磊, 等. 有机物质对土壤镉有效性的影响研究综述 [J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(5): 770-776. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.05.021 YU G F, JIANG X, SUN L, et al. A review for effect of organic substances on the availability of cadmium in soils [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(5): 770-776(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.05.021
[43] 袁兴超, 李博, 朱仁凤, 等. 不同钝化剂对铅锌矿区周边农田镉铅污染钝化修复研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(4): 807-817. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0672 YUAN X C, LI B, ZHU R F, et al. Immobilization of Cd and Pb using different amendments of cultivated soils around lead-zinc mines [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(4): 807-817(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0672
[44] XU C B, QI J, YANG W J, et al. Immobilization of heavy metals in vegetable-growing soils using nano zero-valent iron modified attapulgite clay [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 686: 476-483. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.330 [45] 陶玲, 管天成, 刘瑞珍, 等. 热改性坡缕石对土壤Cd污染的钝化修复研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(4): 782-790. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1115 TAO L, GUAN T C, LIU R Z, et al. Stabilization remediation of cadmium contaminated soil by using heat-modified palygorskite [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(4): 782-790(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1115
[46] 武晓微, 翟文珺, 高超, 等. 钝化剂对土壤性质及镉生物有效性的影响研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(3): 562-569. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0826 WU X W, ZHAI W J, GAO C, et al. Influence of passivation on soil properties and bioavailability of cadmium in soils [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(3): 562-569(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0826
[47] 赵立芳. 腐植酸、水铁矿及其共沉物对土壤镉的钝化效果研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. ZHAO L F. Study on the passivation effect of humic acid, ferrihydrite and their coprecipitates on cadmium in soils[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019(in Chinese).
[48] BARGAR J R, BROWN G E Jr, PARKS G A Jr. Surface complexation of Pb(II) at oxide-water interfaces: I. XAFS and bond-valence determination of mononuclear and polynuclear Pb(II) sorption products on aluminum oxides [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(13): 2617-2637. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00124-5 [49] WANG H W, TSANG Y F, WANG Y N, et al. Adsorption capacities of poorly crystalline Fe minerals for antimonate and arsenate removal from water: Adsorption properties and effects of environmental and chemical conditions [J]. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 2018, 20(10): 2169-2179. doi: 10.1007/s10098-018-1552-0 [50] 刘保峰. 土壤腐殖酸及其对重金属化学与生物行为的影响[C]//全国耕地土壤污染监测与评价技术研讨会论文集. 海拉尔, 2006: 191-196. LIU B F. Soil humic acid and its effects on the chemical and biological behavior of heavy metals[C]//. National Workshop on Monitoring and Evaluation Technology of Soil Pollution in Arable Land, 2006: 191-196 (in Chinese).
[51] LIU H B, CHEN T H, FROST R L. An overview of the role of goethite surfaces in the environment [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 103: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.11.065 -






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: