-
人类社会正处在人工智能跨越式发展的关键节点,人工智能及其应用是环境工程领域未来创新发展的关键方向之一。习近平总书记2023年7月17日在全国生态环境保护大会上的重要讲话指出:“深化人工智能等数字技术应用,构建美丽中国数字化治理体系,建设绿色智慧的数字生态文明”。中共中央、国务院印发的《数字中国建设整体布局规划》也将“推动生态环境智慧治理,加快构建智慧高效的生态环境信息化体系”确定为数字中国赋能经济社会发展的关键内容之一。探索新型人工智能技术在环境工程领域的赋能形态、拓展其应用边界,是环境工程学科发展的必经过程,更是响应国家“建设绿色智慧的数字生态文明”重大需求的关键任务。
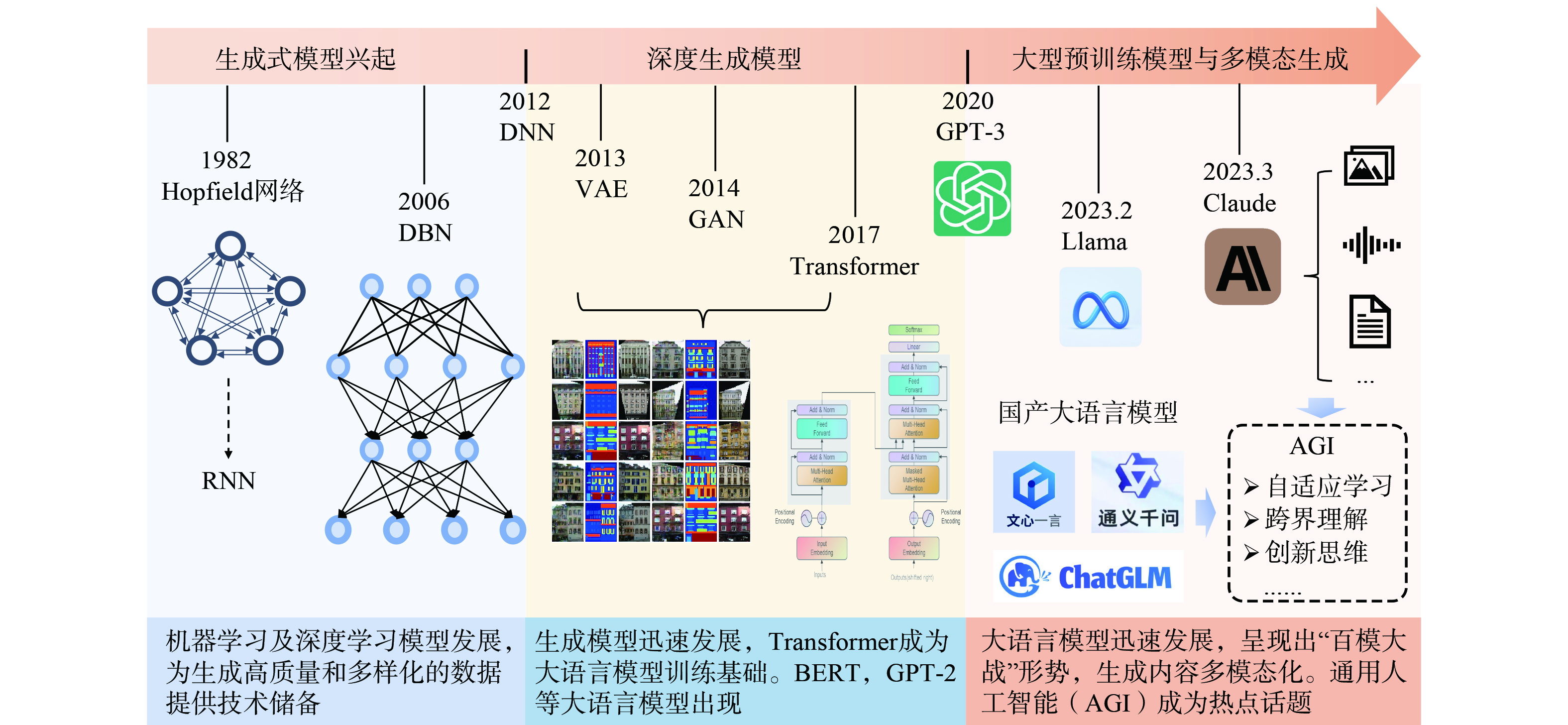
生成式人工智能 (generative artificial intelligence) 是指一类能够创造新内容的人工智能系统,它们能够基于大量的学习理解内容模式,以生成新的内容,包括但不限于文字、图像、视频、音频等,并且具备理解、分析、规划和一定的泛化能力。近两年,以ChatGPT为代表的“大语言模型”井喷式发展,大语言模型背后的生成式人工智能技术被公认为是当前最具有应用前景的人工智能技术,越来越丰富的新应用形态迅速涌现。2023年5月23日国家互联网信息办公室审议通过了《生成式人工智能服务暂行管理办法》,提出鼓励生成式人工智能技术在各行业、各领域的创新应用,探索优化应用场景,构建应用生态体系等,为我国生成式人工智能发展和应用指引方向。
生成式人工智能发展为人工智能在环境工程领域的应用带来新的机遇。借助生成式人工智能技术高效的信息处理与分析能力和强大的多模态信息处理能力,环境工程领域发展可基于“AI for Science”[1]的理念,在高复杂度、高知识密度、高重复性等研究工作场景下助力科学家做出更快、更准确的决策,推动科学进步和创新。
-
机器学习是人工智能的子集,生成式模型和判别式模型是机器学习的主要方法。其中,判别式模型专注于直接学习输入数据与输出标签之间的映射关系,用于分类和回归任务,如支持向量机、神经网络等传统机器学习模型。而生成式模型不仅能进行分类或回归,还可以生成与训练数据具有相似分布的新样本,如变分自编码器[2] (variational auto-encoders,VAE) 、生成对抗网络[3] (generative adversarial networks,GAN) 等。生成式模型具有更强的无监督学习、多模态生成及数据增强和创造能力,具有更广泛的应用潜力。其中生成式预训练Transformer (GPT) 是生成式人工智能领域的最新突破,以GPT-4、Claude-3等为代表的生成式大语言模型在文本生成与处理、信息抽取等多个领域提供了强力支撑。
当前生成式人工智能在特定领域当中展现出强大能力,然而其与通用人工智能 (artificial general intelligence,AGI) [4]相比仍有较大差距,当前研究者将实现通用人工智能作为生成式人工智能发展的重要目标之一。理想的通用人工智能具备广泛的理解、学习、推理和解决问题能力,具备持续学习与自我进化、抽象推理和创造等特性[5]。生成式人工智能发展为科学研究、社会治理、工业生产等各个方面带来了变革性影响,并有望随未来通用人工智能发展重构科学研究范式。
-
随着生态环境保护要求的发展及环境工程研究内容的不断深入,新时代环境工程学科发展呈现出多学科交叉融合增加、知识边界日益扩展、信息量爆炸增长以及复杂系统性环境问题凸显等趋势,研究人员面临多学科知识汇聚融合、大批量信息处理与分析以及综合性复杂场景分析与决策等挑战。当前亟需基于生成式人工智能技术开发一系列智能研究方法与应用,以应对复杂挑战、全面提升研究效率和水平。
-
环境工程学科交叉属性明显,研究内容跨越化学、生物、物理、地理等领域,近年来随着环境问题研究不断深入,与新兴材料科学、管理学和信息科学等学科融合日渐紧密,并发展出新的研究方向,如新型污染物行为研究、气候变化、可持续发展与循环经济等[6]。随着环境工程研究领域不断扩展,知识边界也日益扩展,复杂来源信息获取及多学科知识汇聚融合成为挑战。生成式人工智能多模态学习和适应能力使得其可以理解和整合不同学科知识,并且学习不同领域知识的关联,从而支持和促进知识深度融合。通过生成式人工智能构建知识获取管道,助力多学科知识汇聚融合,从而为研究人员提供更加快捷的知识获取通道,同时通过构建专业知识库与可信度验证数据集,为生成式人工智能在环境工程领域应用开发提供数据基础。
-
环境监测技术的进步以及自动化、物联网、大数据等技术的发展为文字、图片、视频等多模态环境数据获取、处理和存储提供了便利[7]。此外,多学科交叉融合带来的数据量、信息量提升使得环境工程研究当中对于大批量、多模态数据的分析需求不断增加,亟需智能化工具辅助提升效率[8]。近年来,机器学习 (包括深度学习) 等典型人工智能技术在水污染控制、固废管理、污染物迁移转化分析等众多场景中发挥了重要作用[9-10]。随着环境工程学科信息种类和数量迅速增长、应用场景逐步扩展,大规模数据处理需求增多,对环境工程信息化提出了新的要求。生成式人工智能自动化与扩展性,灵活性与适应性以及多模态能力等特点使得其在大规模、多模态、跨领域的数据处理与分析任务中具有显著优势,并且在复合多层次任务当中可与传统机器学习方法联合使用,全面提升环境工程研究的智能化水平。基于生成式人工智能开发面向多种场景的智能应用系统,可以辅助研究人员提高工作效率,增强理解、预测和决策能力。
-
随着人类社会的不断发展,过度的资源开发与废弃物排放对环境造成巨大压力,复杂系统性环境问题凸显。以气候变化[11]、生态系统退化[12]、多介质污染[13]等为代表的复杂环境问题引起广泛关注,成为环境工程领域的严峻挑战。复杂系统性环境问题涉及到经济发展、社会公平、环境保护等多个领域,且多个领域相互联系,大大增加了分析和决策难度,亟需智能化模拟和分析手段辅助研究,为分析和决策提供参考。传统基于主体建模 (agent based modeling,ABM) 方法在多主体参与的环境行为模拟方面应用广泛,然而其适用性有限且学习能力有限,在更多主体参与、行为模式更复杂的场景下无法适应。生成式人工智能驱动的代理建模,通过使用生成式人工智能模型为各主体提供基于自然语言的理解和交互能力、分析评估能力和自定义工具调用能力、形成智能体,突破传统ABM方法规则化和参数化的局限性,具有更强的理解和响应复杂场景能力。通过刻画多样化的智能体,可构建涵盖社会经济等多个要素的复杂模拟系统[14],从而为复杂系统性环境问题的模拟、分析和解决提供实现路径。
-
当前国内外已经对生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的应用进行了初步探索,主要包括大语言模型专业知识拓展、专用任务智能体开发等场景。如何进行多学科知识的汇聚融合以及大语言模型专业化,并以此为基础进行智能应用开发和综合智能体系统构建,探索生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的潜在应用形态、扩展其应用边界仍然是当前面临的重要挑战。
-
目前全球各国、各行业都在探索生成式人工智能的应用场景、方法和技术,在环境工程领域也处于探索和起步阶段。国外部分研究者探索了大语言模型在气候数据获取[15]和环境多维数据模拟预测[16]等任务当中的应用,但是应用场景相对单一,未能充分挖掘生成式人工智能潜力。国内百度智能云发布了《百度智能云水行业大模型白皮书》,提出了水业大模型建设的总体架构,旨在打造水利“2+N”、供水保障、排水防涝、水环境综合治理、绿色低碳等业务场景的大模型创新应用。科大讯飞发布的生态环境大模型通过环保领域的政策法规、行业知识、历史案例进行检索增强生成 (retrieval-augmented generation,RAG) ,为企业和执法人员构建了快速的知识获取通道。然而以上工作目前还停留在理论研究和初步的模型专业化阶段,未对生成式人工智能的智能应用形态进行探索。
清华大学领衔开发的“天工AI”探索了生成式人工智能在环境、生态和可持续发展领域应用的新形态,初步形成了以检索增强生成、智能应用开发、多智能体模拟等多个层面递进的生成式人工智能应用开发框架,然而当前仍存在专业知识覆盖领域不够广、模型专业化不足以及智能应用场景相对单一等问题。随着生成式人工智能的持续发展和全球气候变化、环境污染等议题日益重要,生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的应用势必成为全球热点。国内外研究人员仍需拓展生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的应用范围,构建全面赋能环境工程研究的智能应用体系。
-
当前环境工程领域的生成式人工智能应用尚处于探索阶段,难以匹配应用需求。其主要瓶颈在于生成式人工智能专业领域能力不足、智能应用场景不明、智能体自主潜力有待挖掘等。因此,未来生成式人工智能在环境工程领域应用将面临环境工程领域的生成式人工智能模型专业化、生成式人工智能场景下环境工程领域人机边界划分以及面向通用人工智能的环境工程复杂任务智能体构建等挑战。此外,随着生成式人工智能技术的不断发展,通用人工智能等新形态人工智能技术将带来更多潜在的应用场景,如何适应技术发展,拓展其在环境工程领域的应用边界也亟待研究。
1) 环境工程领域的生成式人工智能模型专业化。生成式人工智能模型一般由广泛获取的信息训练,具有通识知识和一定的泛化能力,但由于专业信息无法全面覆盖导致专业领域知识不足、难以避免生成式人工智能广泛存在的“幻觉”现象。同时,环境工程涉及化学、生物、地理等多个复杂知识体系,如何构建、优化和强化基座模型生成能力以满足科学研究“准确、高质量、高时效性”要求,将成为基础性研究问题。
2) 生成式人工智能场景下环境工程领域人机边界划分。生成式人工智能相较于基于机器学习等传统人工智能技术具有更多元的能力,并已衍生出全新的人工智能应用体系 (如对话式助手、代码生成与执行器、专业工作领航和复杂任务智能体等) ,具有更大的创新应用可能性。如何根据生成式人工智能的能力、特性和潜力,发掘其在环境工程领域的应用场景并划分新的人机边界,构建符合环境工程领域需要的人工智能应用,将成为重大挑战。
3) 面向通用人工智能的环境工程复杂任务智能体构建。传统人工智能技术通常被应用于解决特定问题,而通用人工智能是指可以执行跨领域多元复杂任务并展现超越人类水平的能力,且能够像人类一样理解、学习和适应新情境的人工智能系统,是生成式人工智能发展的下一阶段目标。环境工程问题具有系统性、复杂性和多样性特征,如何针对复杂专业任务设计面向通用人工智能的智能体,突破方法瓶颈、形成技术体系,将成为环境工程领域人工智能应用的重大问题。
-
立足环境工程学科生成式人工智能需求、应用现状及重要挑战,我国环境工程学科在生成式人工智能应用领域需要在生成式人工智能技术快速发展和全球性、系统性复杂环境问题日益突出的背景下,基于生成式人工智能技术的本质、特点和发展路径,更新、迭代和扩展环境工程相关全量知识系统,界定各研究方向通用场景人机边界,构建专业任务智能应用、形成面向通用人工智能的新一代智能应用体系,全面重构环境工程研究工作方式、模式和范式,引领全球环境工程领域的智能化革命。
在未来5到10年,本领域的具体学科目标包括:
1) 构建面向生成式人工智能的环境工程跨领域知识汇聚方法和技术体系。基于高效、高度可用和高度可成长的架构,形成广泛覆盖、可信可靠、及时更新的基础知识库。
2) 构建环境工程通用及典型场景的智能应用。设计生成式人工智能相关数据安全机制,在保护数据产权和安全的前提下,确定和调整人机边界,探索其在环境工程相关研究中的应用潜力,从而在科学研究、工程实施和管理决策中实现智能化辅助和支持、显著提升效率。
3) 构建环境工程领域的生成式人工智能应用体系。针对环境工程各细分领域复杂任务构建系列智能体,形成环境工程领域的生成式人工智能应用体系,完成生成式人工智能应用对传统工作方法和工具的替代,为科研、工程和管理提供实际支撑。
-
针对当前生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的应用现状和发展目标,基座模型专业化、场景辅助应用和复杂任务智能体是生成式人工智能在环境工程学科应用主要的战略方向,我国需要在3个层次上逐层递进开展工作,提升环境工程研究智能化水平。
-
构建环境工程领域相关学科知识库并进行生成式人工智能模型在专业领域的适应研究,是构建环境工程领域的生成式人工智能应用的前提和必要条件。其中重点方向包括面向生成式人工智能的环境工程跨学科信息集成;生成式人工智能基座模型的环境工程领域专业延伸;环境工程领域专业信息置信度验证。
1) 面向生成式人工智能的环境工程跨学科信息集成。面向化学、生物、地理等环境工程领域涉及的学科,识别高质量、集中且持续更新的优质信息来源,并针对主要信息来源分别构建数据管道,实现多模态数据动态实时/近实时获取;并且面向生成式人工智能模型特点,设计数据集成流程和技术架构,应用向量数据库等新一代数据服务支撑专业知识库构建。
2) 生成式人工智能基座模型的环境工程领域专业延伸。根据专业场景需求、基于专业知识对生成式人工智能模型进行训练和/或精调,构建具有环境工程领域专业知识的生成式人工智能基座模型。
3) 环境工程领域专业信息置信度验证。基于环境工程信息学科基本知识和研究重点,构建环境工程学科典型问题数据集,结合生成式人工智能模型自动判断和专家辅助判定方法,建立生成式人工智能模型在环境工程领域的专业能力评价框架,量化评价生成内容的准确性、一致性和可信度,并建立有效的验证机制。
-
面向环境数据分析与模拟预测、工程设计与优化、环境监测与预警等典型场景,根据持续演进的生成式人工智能模型专业能力,适时调整其和人类在分析与解释、设计与审核、模拟与决策等任务当中的人机边界和权重,构建面向典型场景的环境工程领域生成式人工智能应用。其中重点研究方向包括:面向环境工程专业的新型搜索引擎;基于生成式人工智能的专业数据智能解析;面向环境工程典型场景的智能辅助应用。
1) 面向环境工程专业的新型搜索引擎。构建基于专业知识库的检索增强生成框架,形成基于专业知识的内容检索和生成能力,构建覆盖环境工程领域涉及学科专业知识的新型搜索引擎,并持续优化检索效果。
2) 面向环境工程专业数据的智能、安全解析。基于生成式人工智能具备的文件解析、数据指标识别、代码生成等能力,形成覆盖数据文件解析、指标含义分析、数据格式处理、可视化和数据解析内容生成的全流程智能化环境工程专业多模态数据处理能力。同时,建立数据访问控制、数据安全审计、数据去标识等机制,明确数据权属,保障数据安全。
3) 面向环境工程典型场景的智能辅助应用。在土地利用规划、城市布局设计、水资源管理等典型设计和规划场景,实现基于专业知识和最佳实践的智能化建议及方案初步设计;在项目、产品、组织等维度环境影响评价和优化场景,实现快速评估及环境影响和风险识别,并生成决策建议和依据;在环境污染治理、气候变化应对等复杂系统性环境问题分析场景,根据持续更新的数据、技术及政策等相关信息,解析现状并提出方案和优化建议,以增强理解、预测和决策能力。
-
面向通用人工智能研发环境工程领域智能体及基于智能体的复杂系统模拟推演,可通过实现对重复性、高人力成本复杂任务的智能化替代和升级,进一步提升环境工程研究效能,为环境工程领域研究提供新一代智能化基础设施和成套工具。其中重点研究方向包括:面向通用人工智能的环境工程领域复杂任务解构;面向通用人工智能的复杂场景专业模型集成;环境工程领域基于智能体的多场景、多层次、多角色模拟推演。
1) 面向通用人工智能的环境工程领域复杂任务解构。面向通用人工智能、深入理解环境工程领域复杂任务工作流,基于人工智能的特性和能力重构原生任务流程,形成专业任务智能体构建理论和技术框架。
2) 面向通用人工智能的复杂场景专业模型集成。在环境工程领域内各研究方向识别智能体应用场景并进行设计、编排和构建,包括但不限于减污降碳领域,实现多维度生命周期自动建模、评价、热点识别、优化建议并形成解析内容,环境监测、资源能源管理等领域,实现基于数据、规则和专业模型的智能判断、模拟、预警和决策,物质与微生物分析领域,实现生成式人工智能对相关定量分析及机器学习预测算法模型的集成,实现自动化特征提取、分析和物质行为模拟,环境功能材料设计领域,基于化学、材料等专业数据和模型,实现材料性能智能预测和模拟等。
3) 环境工程领域基于智能体的多场景、多尺度、多介质模拟推演。面向环境水污染治理、气候变化应对等单介质环境问题,基于大语言模型实现跨多个传统环境模型的深度融合与协同决策,形成具备高级综合分析能力的专家智能体,增强对相关场景和尺度的系统理解和预测决策能力。针对大尺度、跨介质的复杂环境问题,构建混合专家智能体驱动的环境系统模拟器,实现对环境系统的全面模拟和智能评估。
-
生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的应用经过探索,初步产生了大语言模型专业化及智能体应用开发等应用形态,在提升研究效率、助力环境治理方面展现出应用潜力。对于环境工程领域的研究人员,生成式人工智能除了助力科研效率提升外,还将带来新的研究契机,为复杂综合性环境问题解决提供实现路径。未来研究人员需要积极适应新兴技术的发展,进一步探索生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的应用形态,扩展其应用边界,在已有的研究基础上不断推进模型专业化、丰富智能应用体系,构建面向复杂任务的智能体。全面提升生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的应用水平,助力模拟、分析、决策等多个过程,为环境工程学科智能化水平提升和国家绿色智慧的数字生态文明建设提供技术支撑。
生成式人工智能在环境工程中的应用前瞻
Prospective applications of generative artificial intelligence in Environmental Engineering
-
摘要: 人类社会正处在人工智能跨越式发展的关键节点,以大语言模型为代表的新型生成式人工智能技术为科学研究和社会治理带来新的机遇。与此同时,系统性复杂环境问题日益凸显,使得环境工程学科亟需更加智能化的研究方式、模式和范式。探索新型生成式人工智能技术在环境工程领域的赋能形态、拓展其应用边界,是环境工程学科发展的必经过程,更是响应国家“建设绿色智慧的数字生态文明”重大需求的关键任务。本研究旨在通过分析环境工程智能化需求变化、挖掘人工智能环境工程领域应用现状和趋势,从而探索新型生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的应用场景、方法和技术,从专业基座模型构建与适应研究、需求场景导向的多功能智能辅助应用和基于复合工作流理解与重构的复杂任务智能体三个层次逐层递进,提出我国环境工程的智能化发展关键战略方向。本研究为我国加快推动生成式人工智能在环境工程领域的应用研究,成为该方向的先行者和领导者而助力。Abstract: Human society is currently at a critical juncture in the revolutionary development of artificial intelligence (AI), with new generative AI technologies, represented by large language models, bringing new opportunities for scientific research and social governance. Concurrently, the increasingly prominent issues of systemic complexity in environmental contexts necessitate a more intelligent approach to research, methodologies, and paradigms within the field of Environmental Engineering. Exploring the empowering forms and expanding the application boundaries of new generative AI technologies in Environmental Engineering is an essential process for the development of the discipline and a key task in responding to the national demand for building a “green and intelligent digital ecological civilization.” This paper aimed to analyze changes in the intelligent demands of Environmental Engineering, explore the current status and trends of AI applications in this field, and investigate the application scenarios, methods, and technologies of new generative AI in Environmental Engineering. It progressed through three levels: constructing and adapting foundational models, developing multifunctional intelligent support applications driven by demand scenarios, and understanding and reconstructing complex tasks based on combined workflows. The study proposes key strategic directions for the intelligent evolution of Environmental Engineering in China, aiming to accelerate the country's research into applying generative AI in this field and establish its leadership and pioneering status.
-
[1] 杨小康, 许岩岩, 陈露, 等. AI for science: 智能化科学设施变革基础研究[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2024, 39(1): 59-69. [2] KINGMA D P, WELLING M. Auto-encoding variational bayes[M/OL]. arXiv, 2022. [2024-04-08]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6114. [3] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[M/OL]. arXiv, 2014. [2024-04-08]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2661. [4] MITCHELL M. Debates on the nature of artificial general intelligence[J]. Science, 2024, 383(6689): eado7069. doi: 10.1126/science.ado7069 [5] TRIGUERO I, MOLINA D, POYATOS J, et al. General purpose artificial intelligence systems (GPAIS): Properties, definition, taxonomy, societal implications and responsible governance[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 103: 102135. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102135 [6] 王旭, 董欣. 数据融合驱动学科交叉, 赋能环境工程管理与研究创新——“环境工程基础数据与模型”专刊[J]. 环境工程, 2022, 40(6): 3-4. [7] 关琳, 王让会, 刘春伟, 等. 祁连山自然保护区生态环境大数据管理模式的探讨[J]. 测绘通报, 2023(7): 97-106. [8] 叶林, 吴兵, 蒋丽娟, 等. 融合大数据分析的环境工程微生物学教学改革探索[J]. 高等工程教育研究, 2024(1): 54-57. [9] 程婉清, 袁定波, 熊鹏, 等. 基于多种机器学习算法的水质指数预测模型构建与评估[J]. 环境科学学报, 2023, 43(11): 144-152. [10] 侯俊雄, 李琦, 朱亚杰, 等. 融机器学习与WRF大气模式的PM2.5预报方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2018, 43(2): 114-120+141. [11] 赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 全球气候指标、气候影响驱动因子与全球变暖[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(3): 1-5. [12] 王柯, 张建军, 邢哲, 等. 我国生态问题鉴定与国土空间生态保护修复方向[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(18): 7685-7696. [13] 滕应, 骆永明, 沈仁芳, 等. 场地土壤-地下水污染物多介质界面过程与调控研究进展与展望[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(6): 1333-1340. [14] QI J, GUO J, WANG P, et al. Incorporating generative AI agents into socio-economic metabolism modelling: The next frontier[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2024, 207: 107670. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2024.107670 [15] KOLDUNOV N, JUNG T. Local climate services for all, courtesy of large language models[J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2024, 5(1): 1-4. [16] LI H, LIU J, WANG Z, et al. LITE: Modeling environmental ecosystems with multimodal large language models[M/OL]. arXiv, 2024. [2024-04-06]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2404.01165. -




 下载:
下载:


