-
我国是世界上最大的养猪国家,近十年来每年饲养超过5×109头猪,据统计2022年中国肉猪出栏量为近7×109头,所产生的废水量相当于49×109人产生的生活污水排放量[1-2]。大多数规模化养猪场的废水经过厌氧池、消化池等处理后产生的养猪沼液(digested piggery wastewater,DPW),具有碳氮比低、NH4+-N含量高、微生物降解能力差等特点[3]。此外,养殖过程中广泛使用的各种抗生素并不能被牲畜充分吸收利用,大约有75%的抗生素释放到环境中[4],导致养猪废水中高浓度的抗生素残留[5],使养猪废水的处理面临严峻挑战,对我国污水处理和生态环境造成严重压力。
曝气生物滤池(biological aerated filter, BAF)是一种集过滤、吸附、生物降解于一体的污水处理工艺,具有高效率、低成本等优点[5-6],已经被广泛应用于各种废水的处理。有研究表明,曝气生物滤池不仅可以高效去除氮、磷营养盐[5, 7],对重金属[8]、农药[9]、抗生素[5]、药物及个人护理品(pharmaceutical and personal care products, PPCPs)[10]等各种毒害污染物也表现出很好的去除效果。钟鸣扬[7]利用竹炭-陶粒组合填料的曝气生物滤池对养猪沼液进行处理,TP、COD和NH4+-N的去除率均达到80%以上。CHEN等[5]以弹性固体材料和砾石为填料构建曝气生物滤池,用其处理养猪废水,结果表明,曝气生物滤池对常规污染物的去除率超过80%,对9种抗生素的去除率达到82.1%~100%。填料是生物滤池的核心组成部分,能够吸附污染物,并为生物膜提供附着场所,其性能直接影响污染物的去除效果[11],常用的填料有陶粒[7, 9]、生物炭[6]、沸石[12]、聚氨酯泡沫[8]等,陶粒、沸石和砾石填料价格低廉,是多种水处理工艺的常用填料。ZHOU等[13]通过持续添加人工废水评估陶粒、沸石、砾石介质在累积生物量和渗流特性之间的相互作用,结果表明与沸石、砾石两种材料相比,陶粒的形状导致其水头损失大,但陶粒具有更高的水力效率,生物膜生长产生更小的死区和短路。需要进一步探究这3种填料在污染物去除效果及微生物组成的差异。
目前曝气生物滤池已经应用于养殖废水处理[5, 7],去除效果受碳源不足和缺氧区域不明显的影响[14]。已有研究表明,在人工湿地[15]、SBR系统[16]、MBBR系统[17]等污水处理系统中通过外部添加碳水化合物来调节进水C/N比可以强化微生物的反硝化能力以增强处理效果。本文以养猪沼液为处理对象,利用砾石、陶粒、沸石3组填料分别构建三级串联式曝气生物滤池,考察不同进水C/N比下对养猪沼液中氮、磷营养盐及抗生素的去除效果,并对填料生物膜上的微生物群落进行分析。研究结果可优化曝气生物滤池处理养猪废水的工艺和参数设计,为我国养殖废水的治理提供参考和借鉴。
-
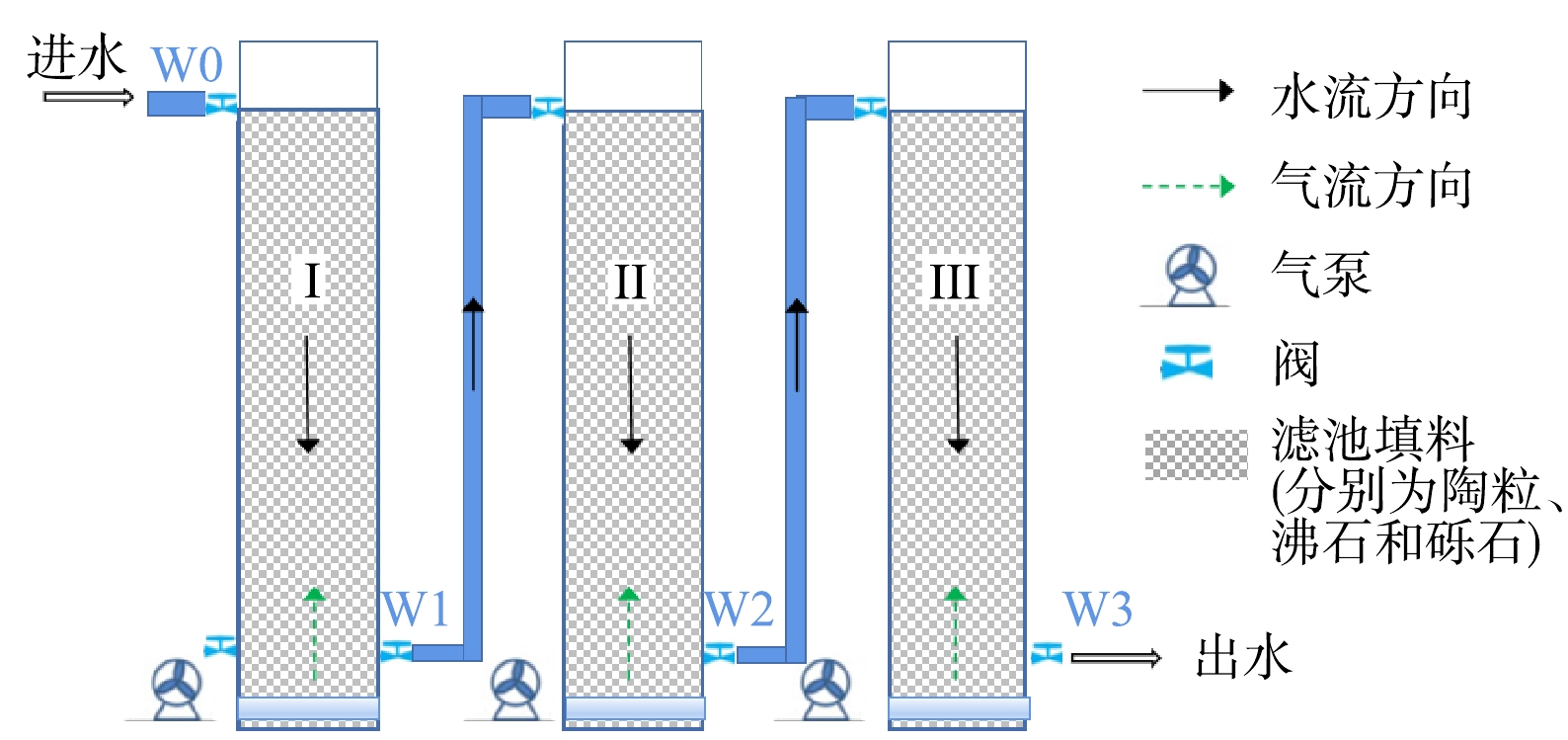
实验装置为3组三级串联曝气生物滤池,每组装置由3个体积为0.1 m×0.1 m×0.5 m(长×宽×高)的生物滤池单元串联而成(图1)。生物滤池单元为底部封口的PVC方管,顶部设进水口,底部设出水口和曝气口,内部填充高度为0.45 m填料,3组曝气生物滤池分别填充陶粒(TL, Φ=0.3~0.5 cm)、沸石(FS, Φ=0.4~0.8 cm)、砾石(LS, Φ=0.5~0.8 cm)。每个滤池单元的有效体积为1.2~1.7 L,3个单元之间用水管连通。
装置进水为广州市某养猪场的养猪沼液。每组滤池每隔8 h进水1.2 L,每天进水3次,废水以下行方式依次流经3个滤池单元,总的水力停留时间(hydraulic retention time, HRT)为24 h。利用气泵在滤池单元底部曝气,曝气流量为12 L·h−1。
-
为探究填料和进水碳氮比对BAF去除污染物效果及微生物群落结构的影响,实验过程分为4个阶段。阶段Ⅰ和阶段Ⅱ进水为稀释后的养猪沼液,阶段Ⅲ和阶段Ⅳ进水为养猪沼液原水。阶段Ⅰ进水C/N比为1.18,阶段Ⅱ进水投加葡萄糖至C/N比为6.17,阶段Ⅲ和阶段Ⅳ进水C/N比为4~6,阶段Ⅳ在每次进水时对第II级和第III级单元分别投加1 g葡萄糖。不同阶段进水的污染物质量浓度列于表1。
-
在每个实验阶段,对3组BAF的各个单元分别采集进、出水,每个位点取3个平行样,测定废水常规污染物和抗生素。在阶段Ⅳ对进水W0和BAF各单元填料进行采集,用于分析微生物群落结构。
1)常规水质指标测定。pH、DO和温度用便携式水质分析仪(YSI, USA)测定。水质指标总氮(TN)、氨氮(NH4+-N)、总磷(TP)和化学需氧量(COD)均采用国家标准水样化学分析方法测定[18],总氮(TN)采用碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度计法(HJ 636—2012)测定,氨氮(NH4+-N)采用纳氏试剂分光光度法(HJ 535—2009)测定,总磷(TP)采用钼酸铵分光光度法(GB 11893-89)测定,化学需氧量(COD)采用重铬酸盐法(HJ 828—2017)测定。
2)抗生素检测。本实验检测的目标抗生素为氧四环素(OTC)、四环素(TC)、磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SMZ2)、环丙沙星(CFX)、氧氟沙星(OFX)5种抗生素。水样收集后经0.7 μm滤膜过滤后,用于测定抗生素浓度。通过高效液相色谱仪HP 1100 LC(Agilent Technologies,US)和AB 4000QTRAP质谱仪(AB sciex,US)进行测定。上机方法与分析条件见参考文献[19]。
3)微生物群落分析。填料及水样滤膜用DNA提取试剂盒(PowerSoil TM DNA Isolation Kit,MOBIO)提取DNA,DNA样品送到上海美吉生物公司进行16S rRNA高通量测序。使用引物338F(5'-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3')和806R(5'-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3')扩增细菌16S rRNA基因的V3-V4区域。
将相似性大于97%的序列归为一个OTU,再利用RDP Classifier(http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/)与Sliva数据库进行比对,比对阈值设为70%,得到各OTU的物种注释信息。利用上海美吉生物公司的云平台开展样品微生物多样性和差异性的分析。
-
所有结果均由Microsoft Excel 2016进行统计分析,并由Origin 2021制图,采用SPSS 26.0软件进行统计差异,在显著性水平P<0.05或P<0.01下表示差异显著。水样数据及填料材料样品均在重复实验中取平均值与标准差。
-
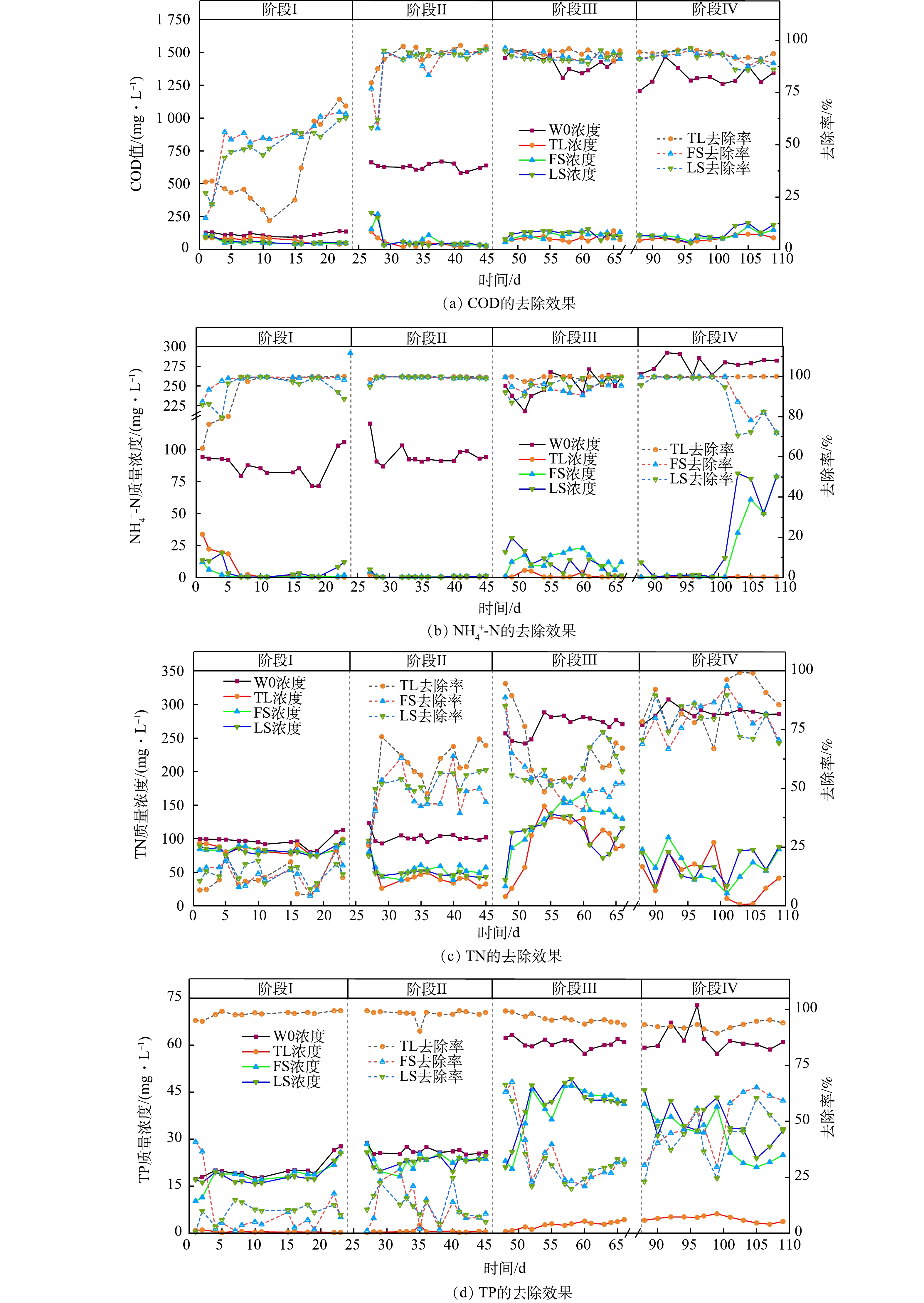
实验期间的4个阶段,3组曝气生物滤池进出水中COD、氨氮、总氮和总磷的质量浓度变化及去除效果如图2所示。在阶段Ⅰ,进水的COD平均值为(113.51±14.58) mg·L−1,TL、FS、LS组曝气生物滤池的去除率分别为37.89%、51.44%和48.25%;阶段Ⅱ提高进水碳氮比后,TL、FS、LS组曝气生物滤池对COD的去除率显著提升(P<0.01),去除率分别为92.82%、88.69%和88.85%。阶段III和阶段IV进水为沼液原液,3组装置对COD的去除率均超过90%,表明进水碳氮比和COD的提升有利于异养菌的增殖,可强化曝气生物滤池对有机物的降解和COD的去除,这与李冬等[20]、曾玉等[21]的研究结果一致。
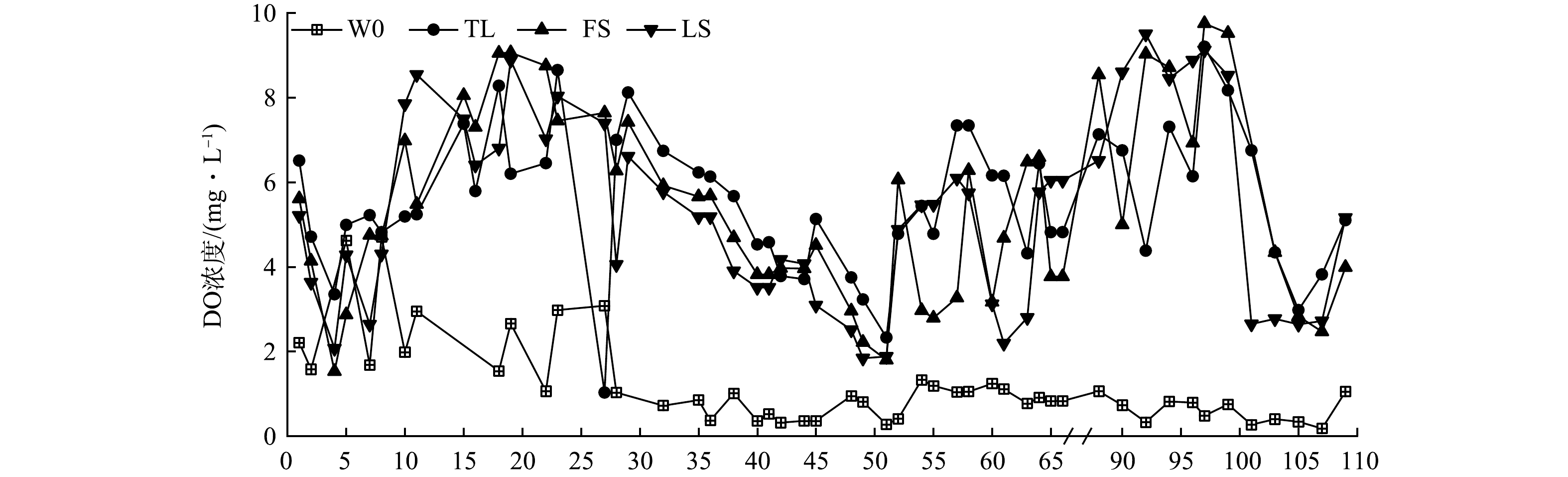
3组曝气生物滤池对NH4+-N的平均去除率超过90%。持续曝气使曝气生物滤池内部水体处于好氧环境,每个阶段3种填料的滤池出水DO的平均质量浓度均超过4 mg·L−1(图3),这有利于提升硝化菌和氨氧化菌的硝化作用,本研究结果与姜珊等[22]的研究结果一致。由于氨氧化菌为化能自养菌,且持续曝气有利于硝化菌的硝化作用,因此,提升进水碳氮比增加水体有机物浓度对NH4+-N去除无显著影响(P>0.05)。在阶段Ⅳ后期,曝气管可能发生堵塞,3组曝气生物滤池出水DO的浓度降低,而TL组滤池对NH4+-N的去除率不变,FS组和LS组装置的去除率降低,这可能是由于陶粒的多孔结构使其TL组曝气生物滤池高度富集具有脱氮除磷功能的细菌,即使DO下降,仍能保持TL组对NH4+-N优秀的去除效果。
不同阶段TN的去除率差异较大。阶段Ⅰ进水TN平均质量浓度为(96.58±8.39) mg·L−1,3组曝气生物滤池的TN平均去除率为11.55%~14.10%。阶段Ⅱ提高进水碳氮比后,TN平均去除率达到46.36%~58.00%,较阶段Ⅰ明显提高(P<0.01)。阶段Ⅲ和阶段Ⅳ过程TN的去除率也表现出相同的趋势,阶段Ⅳ添加葡萄糖后对TN的去除率(78.99%~85.23%)比阶段Ⅲ(53.63%~64.63%)显著提升(P<0.01)。脱氮过程的反硝化作用需要有机碳源充当电子供体,当进水碳氮比提高后,总氮的去除率提高[23]。董宝刚[24]利用间歇曝气序批式反应器处理养猪沼液得到了类似的结果。未稀释养猪沼液中含有更多的有机物,有利于反硝化菌等异养微生物的生长,进水有机负荷提高后,TN的去除率也提高[25-26]。
3组曝气生物滤池对TP的处理效果显示,TL组装置对TP的去除率再90%以上,而FS组和LS组曝气生物滤池对TP的平均去除率在9.36%~50.13%,TL组对TP的去除效果明显优于其他2组(P<0.01)。水体中的磷主要通过吸附、沉淀、吸收、离子交换、生物除磷等方式去除[27-28],填料吸附是TP去除的主要方式[29],填料比表面积、表面特征及化学组成元素
等对除磷效果有明显影响,陶粒表面积大、孔径结构多样、吸附力强[30],已有相关研究证明陶粒对磷的吸附要优于沸石和砾石[31-32]。本实验装置全程持续曝气,装置内水体处于好氧条件下,有利于聚磷菌对磷素的吸收和去除[33]。此外,碳氮比的提高对TP的去除效果影响不大(P>0.05),这可能是在生物除磷过程中,聚糖菌和聚磷菌之间的竞争影响除磷效果,外加葡萄糖提高碳氮比,聚糖菌比聚磷菌更具竞争优势,导致除磷性能没有显著变化[33-34]。
-
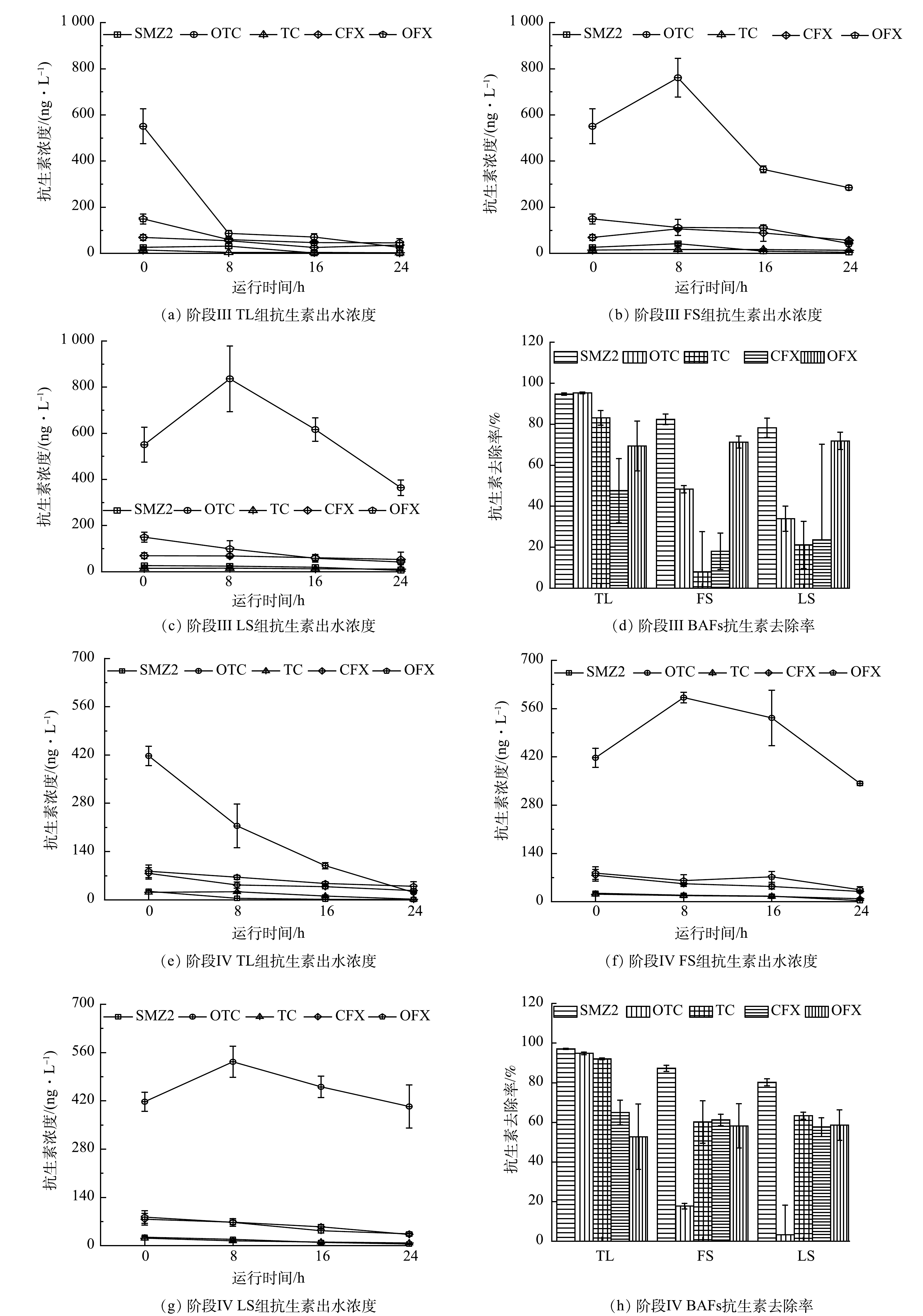
图4为3组曝气生物滤池运行期间5种抗生素质量浓度变化及去除率。养猪沼液中所检测的5种抗生素为SMZ2、OTC、TC、CFX和OFX,其平均质量浓度分别为25.52 ng·L−1、484.03 ng·L−1、18.18 ng·L−1、72.93 ng·L−1和116.19 ng·L−1,抗生素质量浓度大小为:OTC>OFX>CFX>SMZ2>TC,OTC的质量浓度远超其他4种抗生素。OTC和TC为四环素类广谱抗菌药物,是猪饲料主要添加抗生素,导致养猪沼液中OTC含量最高[35]。而常规污水处理工艺对四环素类抗生素去除效果有限[36]。在本研究的3组曝气生物滤池中,TL组对OTC和TC的平均去除率在80%以上,TL组对TC和OTC的去除效果明显优于其他2组(P<0.01)。有研究[37]表明,四环素类抗生素的去除以填料吸附为主,李佳泽等[38]以陶粒为填料的曝气生物滤池处理制药废水,对四环素类抗生素有较好的去除效果,这与本文的研究结果一致。
阶段Ⅳ在提升进水碳氮比后,3组曝气生物滤池对TC和CFX的去除率均有所提高。唐佳等[39]对抗生素在反硝化体系中去除特性进行了探究,也得到了类似结论,提升碳氮比有利于某些抗生素的去除。3组曝气生物滤池对SMZ2的去除率较好,其中TL组的去除率在90%以上。3组曝气生物滤池对OFX的去除率在52.76%~71.89%,去除效果良好。图中某些时刻出现抗生素的浓度比进水高的情况,这可能是由于填料上吸附的抗生素释放到水体中[5]。
-
样品中微生物群落的多样性和丰富度如表2所示。各组微生物样本覆盖率在98%以上,这表明测序足以覆盖样本中的大多数微生物。进水W0的Shannon指数最高,Simpson指数最低;而TL组的Shannon指数最低,Simpson指数最高,表明陶粒生物膜的细菌群落丰富度和多样性低。ZHOU等[13]研究发现,生物膜的生长会影响渗透系统(如人工湿地)的性能。随生物膜生长,最接近球形的陶粒虽然孔隙率低于其他2种材料,但陶粒的导水率变化小,表现出更高的水力效率。具有竞争优势的微生物更容易在陶粒填料上富集,使TL组的细菌群落多样性和均匀度都很低,而对污染物的去除效果优于其他两组填料。
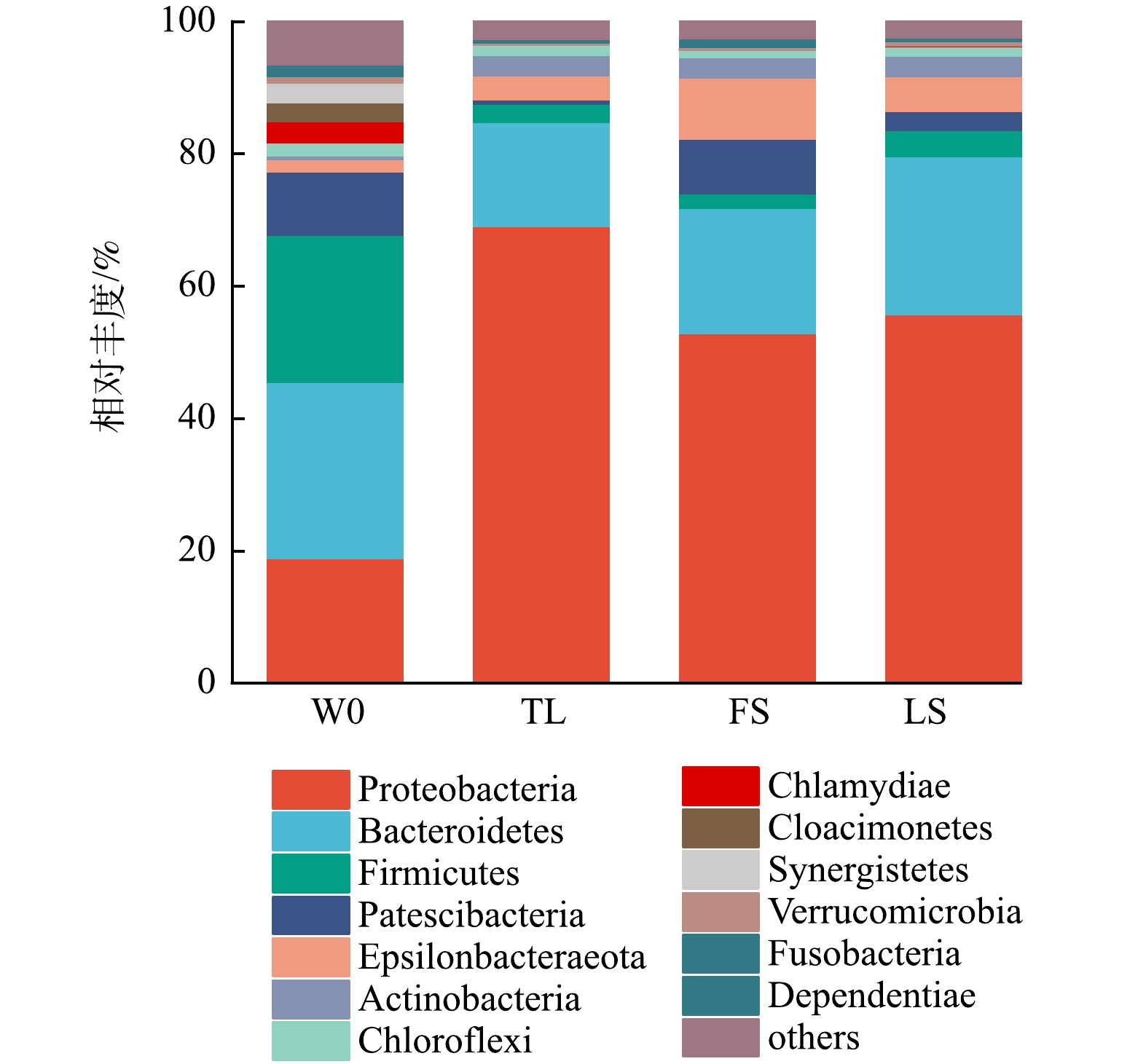
如图5所示,在生物膜样品中检测到主要门包括变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)和髌骨细菌门(Patescibacteria),在4组样品中的相对丰度之和均超过75%。养猪沼液W0样品中变形菌门(18.94%)、拟杆菌门(26.63%)和厚壁菌门(22.31%)的丰度较高,厚壁菌门是厌氧发酵过程中的优势菌门[40],其细胞壁较厚,有利于他们在恶劣环境中生存。填料生物膜样品中变形菌门的相对丰度提高到52.99%~69.15%,而拟杆菌门和厚壁菌门相对丰度有所降低,这是由于变形菌门细菌对环境的适应能力强,更容易在填料上定殖,且其具有良好的脱氮除磷能力[41-42],大多数脱氮微生物属于变形杆菌门[43]。Epsilonbacteraeota门和放线菌门(Actinobacteria)的相对丰度在填料生物膜中均有提高。LI等[44]研究发现Epsilonbacteraeota门细菌会选择性的附着在填料表面,而滤池填料为Epsilonbacteraeota门细菌提供附着位点使其相对丰度提高。放线菌门细菌降解能力强,且对恶劣环境适应能力强,其相对丰度在填料上有所提高[45]。本研究结果表明陶粒填料有利于变形杆菌门和拟杆菌门细菌富集,其中变形杆菌门的相对丰度达到69.15%,这可能与TL组曝气生物滤池污染物去除效果最佳有关。
属水平上微生物种群及其丰度如图6所示,养猪沼液W0中DMER64属和Smithella属相对丰度较高,DMER64属和Smithella属均与厌氧消化产甲烷有关[46],DMER64属是一类参与种间氢转移的功能微生物,能分解丙酸和丁酸产生氢气,与产甲烷菌同时共生,提高产甲烷速率[47]。Smithella属是丙酸盐氧化细菌,其可与产氢甲烷菌合作降解丙酸盐[48]。与养猪沼液相比,3组填料生物膜微生物群落的优势菌属相对丰度和组成发生了显著变化,Thauera属、Zoogloea属、Flavobacterium属和Arcobacter属为在3组填料生物膜的优势菌属,与污染物去除密切相关。Thauera属大多为兼性反硝化细菌,具有异养硝化-好氧反硝化功能[49-50],拥有与氮和磷代谢有关的基因[51],耦合异养硝化和好氧反硝化两个过程,使装置在曝气条件下同时具有硝化和反硝化功能,对氨氮和总氮维持较高的去除率。由于填料的不同,三组装置优势菌属的相对丰度存在差异。陶粒对微生物群落具有高度的优势筛选,其中Thauera属的相对丰度最高(36.27%),使得陶粒组装置去除效果最佳,但也导致其微生物多样性降低。沸石生物膜样品中Arcobacter属和Diaphorobacter属的相对丰度较高,Arcobacter属是脱硝脱硫系统中的核心菌属,具有氧化硫化物的功能[52]。Diaphorobacter属是活性污泥中常见菌属,具有反硝化能力[53]。Zoogloea属、Flavobacterium属和unclassified_f_Rhodocyclaceae属在砾石组(LS)的相对丰度高,Zoogloea属细菌具有絮凝能力,在废水处理过程中形成好氧颗粒状污泥[54]。Flavobacterium属细菌具有异养硝化能力及脱氮能力[55],可作为好氧颗粒污泥的丝状骨架[56],是好氧颗粒污泥中的常见菌属。unclassified_f_Rhodocyclaceae属与氮和磷的去除密切相关[57]。
-
1) 3组曝气生物滤池对养猪沼液中污染物有较好且稳定的去除性能,其中以陶粒为填料的曝气生物滤池装置对COD、NH4+-N、TN和TP均有良好的去除效果,去除率分别为93.77%~94.14%、99.44%~99.89%、64.63%~85.23%、92.68%~95.74%,提升进水碳氮比后,TN的去除效率显著提高(P<0.01)。
2) 以陶粒为填料的曝气生物滤池装置对抗生素去除效果表现好,对SMZ2、OTC、TC、CFX、OFX的平均去除率分别在94.72%~97.07%、94.85%~95.27%、83.17%~92.05%、47.62%~65.02%、52.76%~69.45%。3组曝气生物滤池对养猪沼液中SMZ2和OFX均有良好的去除效果;提升进水碳氮比后,SMZ2、TC和CFX的去除效率提高。
3) 微生物群落分析表明,3组滤池填料生物膜上的细菌中变形菌门(Proteobacteria)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)相对丰度高。Thauera属、Zoogloea属、Flavobacterium属和Arcobacter属为填料生物膜中的优势菌属,这些属是参与脱氮除磷的主要种群,其中陶粒组中Thauera属的相对丰度高达36.27%,使以陶粒为填料的曝气生物滤池具有良好的生态净化效果。
不同填料曝气生物滤池对养猪沼液的处理效果及微生物群落响应
Treatment effect of digested piggery wastewater by biological aerated filter with different fillers and microbial community response
-
摘要: 本文利用陶粒、沸石和砾石为填料分别构建3组三级串联式曝气生物滤池,考察不同进水碳氮比条件下生物滤池对养猪沼液(DPW)中COD、NH4+-N、TN、TP及抗生素的处理效果与差异,并通过16s rRNA高通量测序对填料生物膜进行分析。结果表明:以陶粒为填料的曝气生物滤池对污染物的去除效果最佳,对养猪沼液中COD、NH4+-N、TN、TP的平均去除率分别为93.77%~94.14%、99.44%~99.89%、64.63%~85.23%、92.68%~95.74%,对SMZ2、OTC、TC、CFX、OFX的平均去除率分别在94.72%~97.07%、94.85%~95.27%、83.17%~92.05%、47.62%~65.02%、52.76%~69.45%。进水碳氮比提高后,3组曝气生物滤池对TN的处理效率显著提高(P<0.01),对SMZ2、TC和CFX的去除效率也有所提高(P<0.05),但对NH4+-N和TP的去除无显著的提升;16S rRNA 高通量测序分析表明,3组滤池填料生物膜上的细菌中变形杆菌门(Proteobacteria)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)相对丰度较高;Thauera属、Zoogloea属、Flavobacterium属和Arcobacter属为优势属,其中以反硝化为主的Thauera属在陶粒组相对丰度最高,达到36.27%,使陶粒组有良好污染物去除效率。该研究结果可为利用生物滤池技术处理养殖废水提供参考和借鉴。
-
关键词:
- 曝气生物滤池(BAF) /
- 养猪沼液(DPW) /
- 抗生素 /
- 微生物群落
Abstract: In this study, three groups of three-stage and tandem biological aerated filters (BAFs) were constructed with ceramic, zeolites and gravels as fillers, respectively. Under the conditions with different C/N ratio in BAF influent, the treatment effects and differences of COD、NH4+-N、TN、TP and antibiotic in digested piggery wastewater (DPW) were investigated. The16s rRNA high-throughput sequencing was used to analyze the biofilms of BAFs. The results showed that the BAF with ceramic as filler had the best effect on removing pollutants, and the average removal rates of COD, NH4+-N, TN, and TP in DPW were 93.77%~94.14%, 99.44%~99.89%, 64.63%~85.23%, and 92.68%~95.74%, respectively; and the average removal rates of SMZ2, OTC, TC, CFX, and OFX ranged from 94.72% to 97.07%, 94.85% to 95.27%, 83.17% to 92.05%, 47.62% to 65.02%, and 52.76% to 69.45%, respectively. After the C/N ratio in BAF influent increased, the treatment efficiency of TN by the three groups of BAFs increased significantly ( P<0.01), and the removal rates of SMZ2, TC and CFX also increased ( P<0.05), while the removal rates of NH4+-N and TP increased insignificantly. According to the 16S rRNA sequence analysis, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes was high in the bacteria on the biofilm of the three groups of BAF; Thauera, Zoogloea, Flavobacterium and Arcobacter were the dominant bacteria in the bacteria on the biofilm of the three groups of BAF, of which the genus of Thauera, being mainly the denitrifying bacteria, had the highest relative abundance of 36.27% in the ceramic group, leading to its good removal efficiency of pollutant. This study can provide a reference for the treatment of aquaculture wastewater using biofilter technology. -
随着现代工业的快速发展,铬、镉、汞、铜等重金属的大规模开发和广泛应用,造成了严重的土壤地下水污染[1]。其中,铬是污染最为严重的重金属之一,在环境中主要以Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ) 2种形态存在,Cr(Ⅵ)的毒性是Cr(Ⅲ)的500倍[2-3],且在土壤地下水中的迁移扩散能力较强[4]。铬污染已经成为影响人类健康、生态环境及社会可持续发展的严重威胁[5]。用于Cr(Ⅵ)修复的还原剂有零价铁、二价铁和多硫化物等。其中,零价纳米铁是应用最为广泛的修复剂之一[6-7]。然而在实际修复工程中,由于零价纳米铁表面易氧化、颗粒易团聚,在很大程度上降低了其反应活性及其在环境介质中的迁移扩散能力[8-9]。
近年来,通过绿色合成法制备零价纳米铁逐渐成为研究热点[10],该方法是使用具有高还原能力的植物提取液替代硼氢化钠溶液。与传统方法相比,其优点在于:提取液中的多酚类物质既可作为还原剂又能包覆在纳米铁的表面,提高其抗氧化活性[11];具有更低的环境影响和制备成本[12];植物提取液中的有机质可为微生物提供养分,为利用微生物协同修复创造了条件[13]。MACHADO等[14]使用葡萄、红茶、葡萄藤叶提取液合成纳米铁,对布洛芬的去除率高达95%;ESSIEN等[15]将橄榄叶提取液作为还原剂制备绿色纳米铁,利用纳米铁静电吸附和表面络合去除水中的Ni2+,去除率最高可达97%;郭梦羽等[16]使用红背桂叶、菩提叶和龙眼叶的提取液制备纳米铁,其对亚甲基蓝的脱色率分别为99.2%、54.2%和20.8%。但是,由于绿色纳米铁对目标污染物的去除能力受到植物提取液性质的影响,在一些研究中,往往更多地关注修复剂对污染物的去除效果,而忽视了修复剂自身的悬浮稳定性和迁移扩散能力,而同时保持修复剂的反应活性和悬浮稳定性是修复技术发挥作用的关键。
本研究选取了富含植物多酚的绿茶、红茶、乌龙茶、桑树叶,以及成都市资源丰富的银杏叶、石榴树叶、枇杷叶、悬铃木、木芙蓉共9种样本植物。通过对不同植物提取液的抗氧化活性测试,初步筛选出3种还原能力较高的绿色纳米铁,并对其进行了较为深入的表征分析,通过考察不同绿色纳米铁对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除效果,比较了绿色纳米铁的反应活性,为绿色纳米铁制备技术应用于土壤地下水污染修复提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料与仪器
实验材料:四水合氯化亚铁(FeCl2·4H2O)、硫氰酸钾(KSCN)、二苯碳酰二肼(C13H14N4O)为分析纯,重铬酸钾(K2Cr2O7)为优级纯,均购于科隆化工试剂厂;三吡啶三吖嗪(TPTZ, C18H12N6)为分析纯,购于上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;银杏叶、石榴树叶、枇杷叶、悬铃木、木芙蓉采摘自成都理工大学校园,桑树叶、乌龙茶、绿茶及红茶在市场购买。
实验仪器:恒温水浴振荡器(KW-400,上虞佳星仪器厂);真空干燥箱(DZF-6 021,上海精宏实验设备有限公司);数显加热磁力搅拌器(HSC-19T,群安实验仪器有限公司);紫外-可见分光光度计(TU-1 901,北京谱析通用仪器有限责任公司);电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(DHG-9 240B,上海申贤恒温设备厂);马尔文激光粒度分析仪(Nano series 3 600,英国马尔文仪器有限公司)。
1.2 绿色纳米铁的制备及表征
在进行植物叶子提取液的制备时,将9种植物叶子(绿茶、红茶、乌龙茶、银杏叶、石榴叶、枇杷叶、悬铃木、木芙蓉和桑叶)洗净烘干,剪碎后过2 mm筛,各称取2 g,置于烧杯中。加入300 mL超纯水,在温度95 ℃,转速300 r·min−1的条件下磁力搅拌40 min,冷却至室温后过滤,即制得提取液。
利用铁离子抗氧化能力法(FRAP法)测试不同植物叶子提取液的抗氧化活性。FRAP试剂包括:0.3 mol·L−1 醋酸缓冲液(pH=3.6)、10 mmol·L−1 TPTZ溶液、20 mmol·L−1 FeCl3溶液,上述溶液以10∶1∶1的体积比例混合;在比色管中加入0.1 mL不同植物叶子提取液后,加入2.4 mL FRAP试剂,在37 ℃下水浴10 min,于593 nm处测定吸光度;以0.1~1.6 mmol·L−1的FeSO4标准液替代样品绘制标准曲线。
在进行绿色纳米铁的制备时,称取0.01 mol的FeCl2·4H2O,加300 mL超纯水在烧杯中搅拌溶解,配制成0.03 mol·L−1的Fe(Ⅱ)溶液。将新鲜制备的叶子提取液和Fe(Ⅱ)溶液以体积比2∶1的比例混合,采用恒速搅拌器搅拌,控制温度为(25±0.5) ℃,转速为(300±25) r·min−1,1 h后,得到纳米铁悬浊液并过滤,分别使用超纯水和无水乙醇进行清洗,所得的固体置于真空干燥箱中90 ℃干燥至恒重,即得到绿色纳米铁颗粒。
在进行绿色纳米铁的悬浮稳定性测试时,分别取650 mg·L−1绿色纳米铁的悬浊液,盛于50 mL的比色管中静置12 h。在不同的时间观察悬浊液的分层团聚情况,并取一定量的上清液,利用紫外可见分光光度计和硫氰酸盐比色法,在波长为510 nm处测定其中的绿色纳米铁浓度,并计算相对浓度(Ct/C0)。
1.3 绿色纳米铁去除Cr(Ⅵ)性能
配制不同浓度的纳米铁悬浊液10、20、30、40、70、100 mg·L−1,各取15 mL于50 mL锥形瓶内,分别加入15 mL Cr(Ⅵ)浓度为50 mg·L−1的 K2Cr2O7 溶液,在pH=4、温度25 ℃的条件下反应24 h。取1 mL反应后的悬浊液于10 mL的比色管中稀释10倍,采用二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法,在最大吸收波长540 nm下测定其吸光度,算出反应后的Cr(Ⅵ)浓度,根据式(1)计算Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率。
η=C0−CC0×100% (1) 式中:η为Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率;C0为悬浊液中Cr(Ⅵ)的初始浓度,mg·L−1;C为反应后悬浊液中Cr(Ⅵ)的浓度,mg·L−1。
绿色纳米铁去除Cr(Ⅵ)的动力学使用拟一级模型(pseudo first order model, PFOM)和双室一级模型(two-compartment first order model,2-PFOM)描述。拟一级模型和双室一级模型分别如式(2)和式(3)所示。
CtC0=e−k1⋅t (2) CtC0=ffast⋅e−kfast⋅t+fslow⋅e−kslow⋅t (3) 式中:Ct为t时刻Cr(Ⅵ)的浓度,mg·L−1;k1为拟一级模型去除速率常数,min−1;kfast和kslow分别为双室一级动力学去除速率常数,min−1;ffast和fslow分别为快、慢室去除的比例,并且ffast+fslow=1。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 零价纳米铁的抗氧化活性
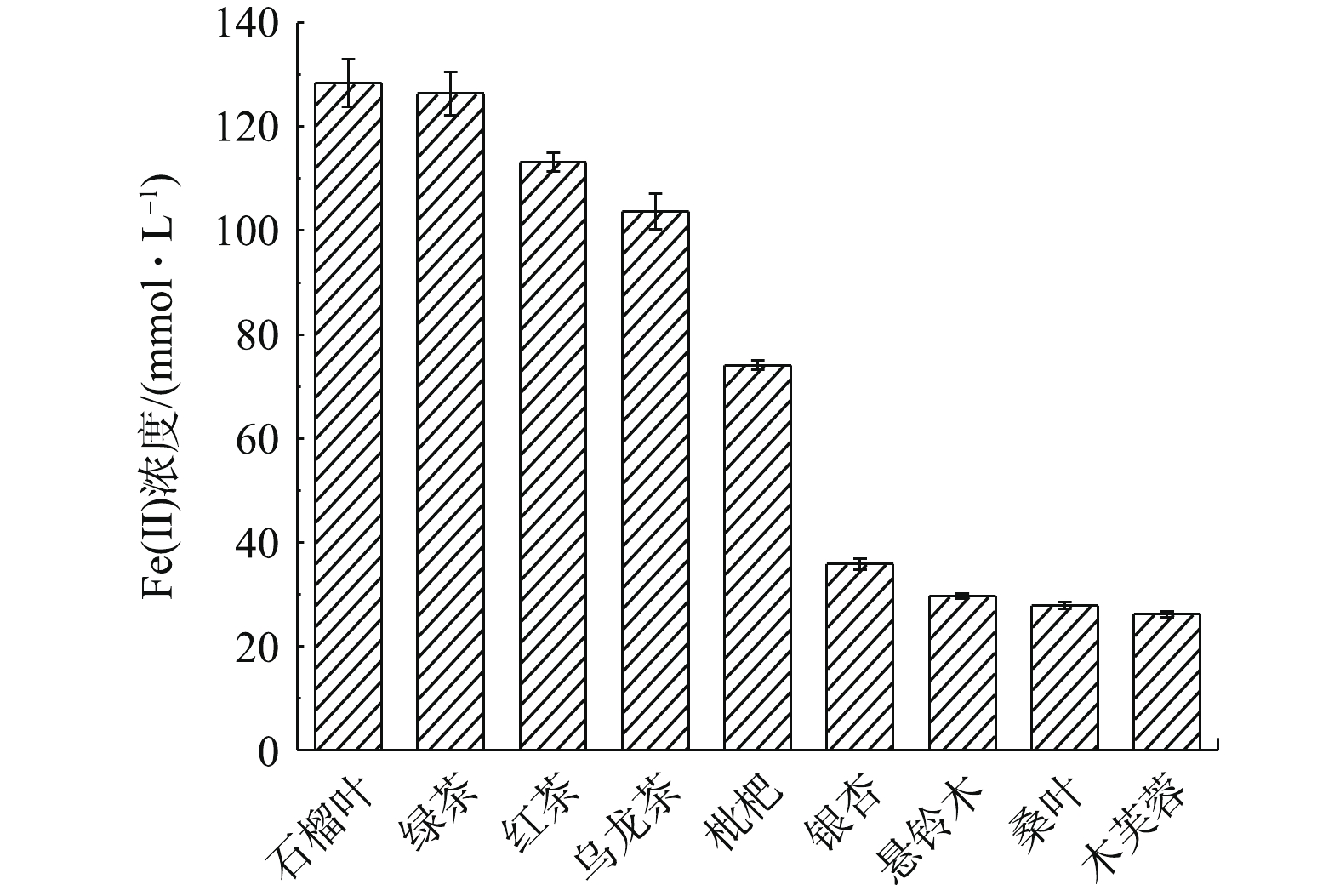
植物多酚是一类存在于植物体内的次生代谢物,具有抗菌、抗病毒和抗氧化的特性[17]。在制备零价纳米铁的过程中,植物多酚的抗氧化活性起到关键作用。利用FRAP法测定9种植物叶子提取液的抗氧化活性,结果如图1所示。
以还原产物Fe(Ⅱ)的浓度作为衡量标准,9种植物叶子提取液的抗氧化能力在25.67~133.48 mmol·L−1以内,其中绿茶、石榴叶提取液的抗氧化能力最强,红茶提取液次之,表明他们可能是作为绿色合成纳米铁最合适的原材料。多酚类物质首先与Fe(Ⅱ)络合,将其还原为Fe0,提取液中包括多酚在内的天然抗氧化有机分子具有多个极性原子和丰富的电子键,能够提供电子至铁原子d轨道的空位上,形成配位键,从而促进了抗氧化有机分子在铁表面的吸附[18],从而将生成的Fe0包裹,故混合液的颜色从黄绿色逐渐加深,最终转变为黑色,以此作为Fe0形成的初步指示,颜色越深则Fe0颗粒的生成率越高。
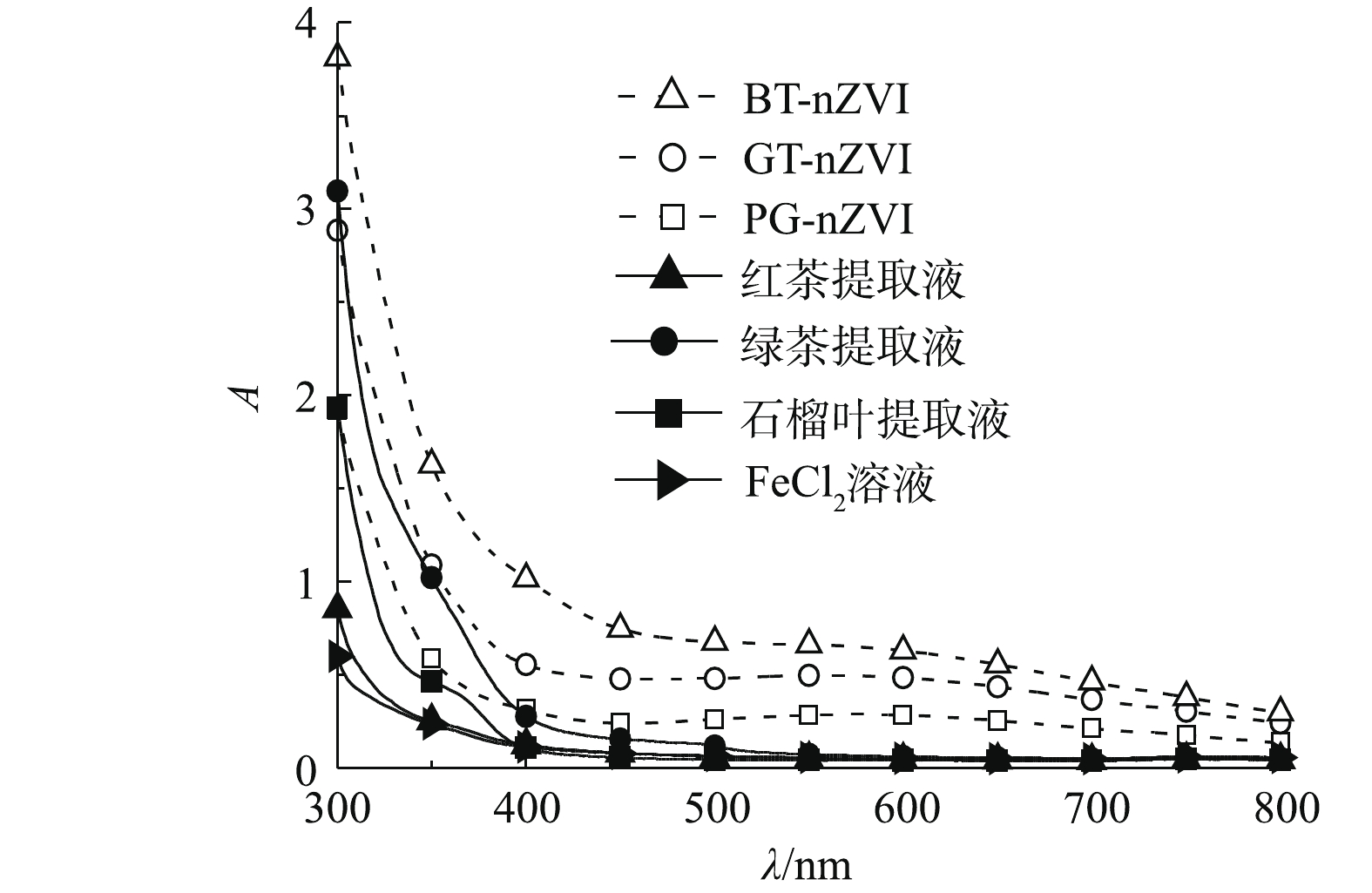
FeCl2溶液与不同植物提取液反应之后的颜色变化如图2所示。反应后颜色明显变黑的是绿茶、石榴叶和红茶提取液,乌龙茶提取液虽然在一定程度上变黑,但仍有明显的提取液原有颜色,这说明Fe0的生成量较少。其余的提取液反应后颜色变化并不明显,表明这些植物提取液对Fe(Ⅱ)的还原效果不佳。以上结果与FRAP法的测试结果一致,因此,在下一步研究中选取绿茶(GT)、石榴叶(PG)和红茶(BT)的提取液用于绿色纳米铁颗粒的合成,生成的纳米铁分别记为GT-nZVI、PG-nZVI及BT-nZVI。
对3种植物提取液、混合反应后的悬浊液及FeCl2溶液进行紫外-可见光谱扫描。全波长扫描结果如图3所示。绿茶(GT)、石榴叶(PG)及红茶(BT)提取液与FeCl2溶液在波长大于500 nm时,吸光度几乎为0,而反应之后的悬浊液在600 nm左右出现较宽的吸收峰,根据相关研究[19-21]表明,这是由于植物提取液与FeCl2溶液反应生成了新的产物,即Fe(Ⅱ)可能被还原为Fe0。
2.2 X射线衍射(XRD)分析
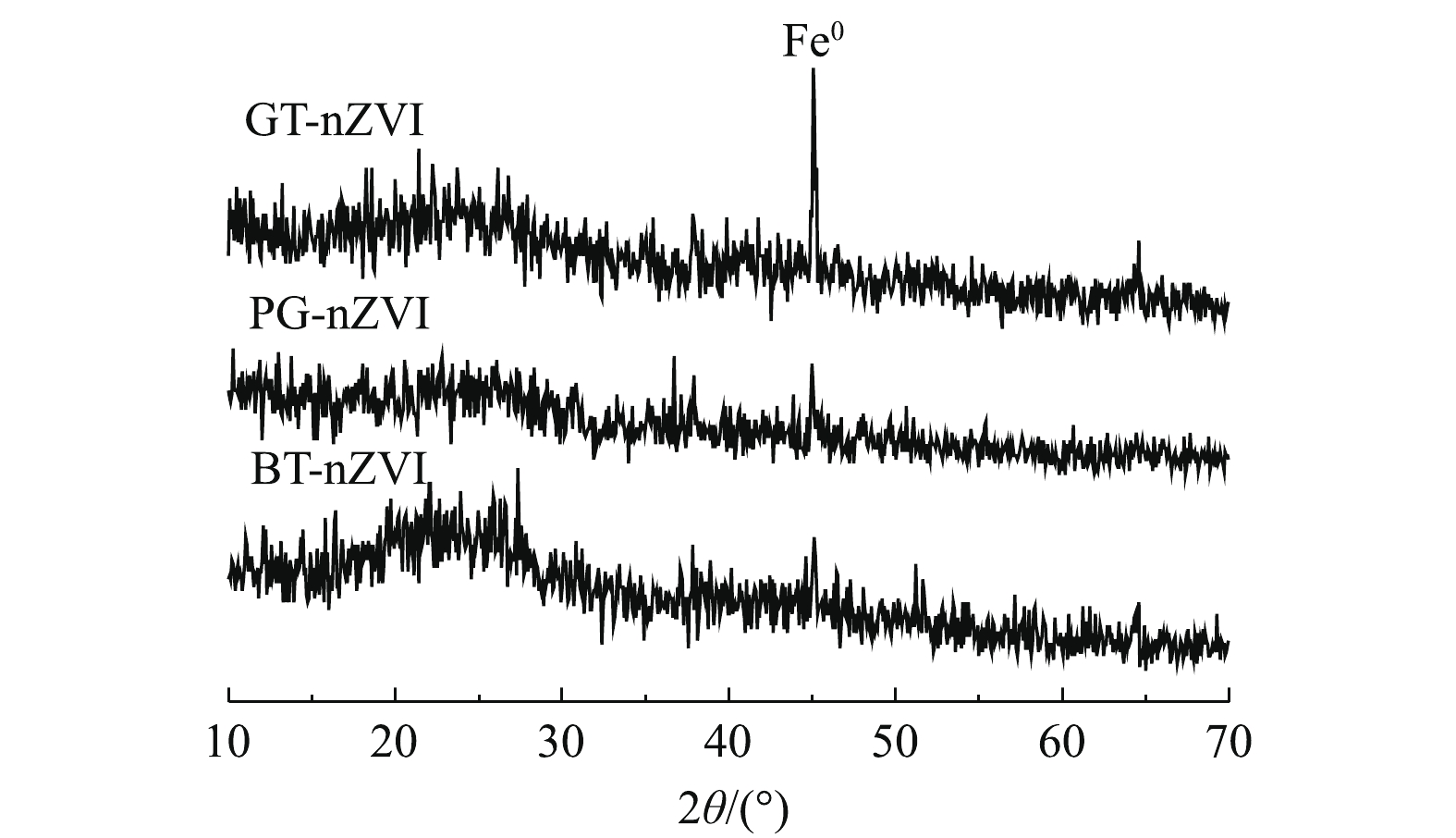
为进一步确认体系中纳米零价铁的生成,将制备的GT-nZVI、PG-nZVI和BT-nZVI进行了XRD测试,结果如图4所示。2θ = 44.9°为Fe0的特征峰[20, 22-23],这表明了纳米Fe0的成功制备。GT-nZVI的衍射峰比另外2种纳米铁更明显,BT-nZVI的衍射峰最微弱,这可能归因于生成的纳米铁颗粒为无定型态或者纳米铁表面包裹的不同有机成分。
2.3 绿色合成纳米铁的粒径与形貌
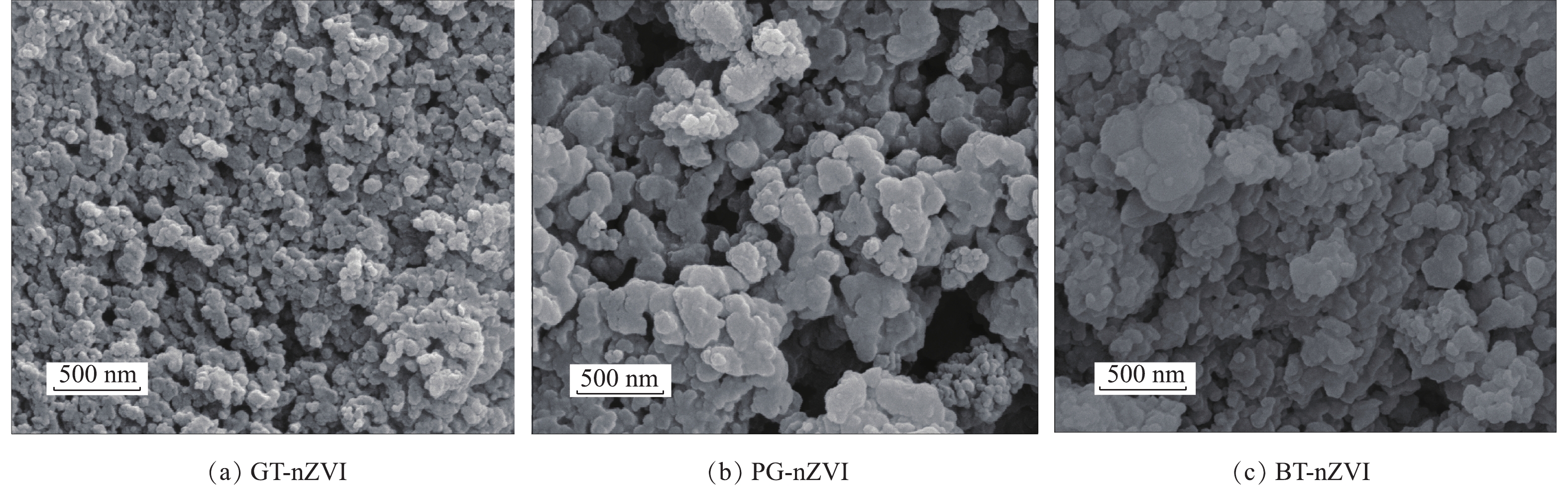
通过SEM对GT-nZVI、PG-nZVI和BT-nZVI的表面形态进行了观察,由图5(a)可以看出,经过干燥后的GT-nZVI整体为不规则的球状。由图5(b)和图5(c)可知,PG-nZVI、BT-nZVI在干燥后呈现出较明显的团聚,粒径增大,形貌上更接近片状堆叠物,GT-nZVI的粒径最小,分散性能最好。
利用马尔文激光粒度仪分析了GT-nZVI、PG-nZVI及BT-nZVI 3种纳米零价铁颗粒的粒径分布[24],其粒径分别为24~140、43~255、28~221 nm,平均尺寸为88、118、124 nm。一般来说,纳米铁颗粒粒径越小,比表面积则越大,代表其拥有更高的反应活性,因此,基于粒径分析结果可知,GT-nZVI的性能要优于PG-nZVI和BT-nZVI,这与污染物去除批实验结果一致。
2.4 纳米铁的悬浮稳定性
纳米铁具有较大的比表面积和本身具有的磁性,极易团聚,导致自身比表面积、反应活性以及迁移性降低,易在含水层中沉淀造成介质孔隙堵塞,进而降低含水层的渗透性[25]。而植物提取液制备纳米铁过程中,一些大分子物质包覆在Fe0的表面,能够有效控制纳米Fe0的粒径并减少团聚,从而增强了纳米Fe0悬浊液的悬浮稳定性。
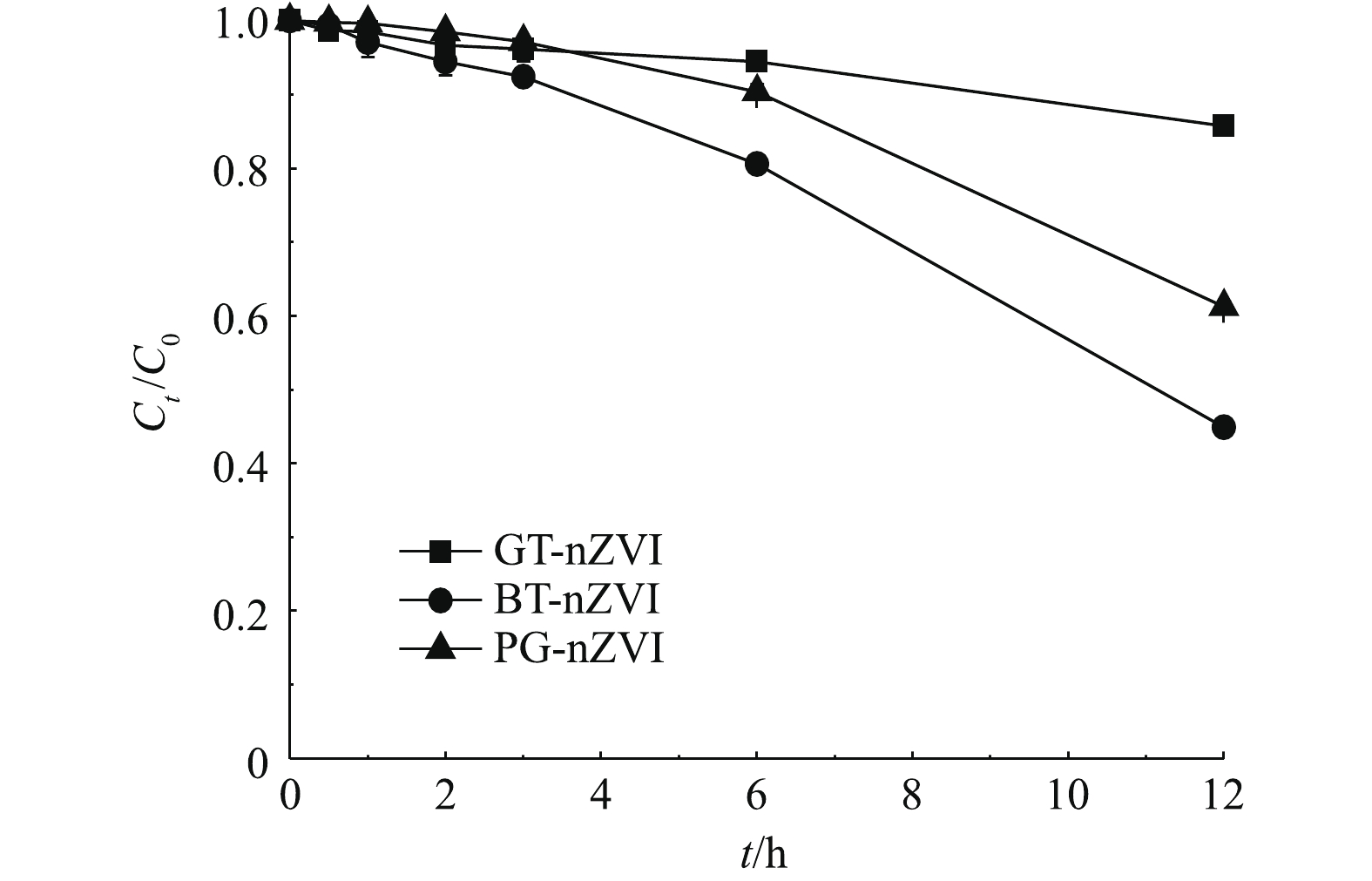
由图6可知,3种悬浊液均含650 mg·L−1的绿色纳米铁,在开始的4 h静置时间内,上清液中的铁含量一直保持在初始浓度的85%以上,在静置6 h后,BT-nZVI的上清液中铁含量约为初始浓度的80%,GT-nZVI与PG-nZVI的上清液中铁含量的比例在90%以上。在静置12 h后,BT-nZVI与PG-nZVI的上清液铁含量分别降至45%与60%,而GT-nZVI则在85%左右。这说明3种绿色纳米铁悬浊液在4 h以内均未出现明显的团聚,而之后的稳定性开始变差,其中,GT-nZVI的悬浮稳定性最好。
2.5 傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)分析
对绿色合成的纳米铁进行了FT-IR测定,以确定不同植物提取液还原FeCl2后潜在的生物分子官能团。图7为3种绿色纳米铁的FT-IR光谱。
红外光谱中3 422、3 416、2 356 cm−1处的峰表示绿色纳米铁和植物提取液存在多酚中的羟基,多酚是还原Fe(Ⅱ)的有效成分,以及纳米铁颗粒表面的覆盖层[22, 26-27]。通过对比提取液与纳米铁的峰强,3 422、3 416、2 356 cm−1处的峰强度明显降低,这表明提取物中的多酚参与了纳米铁的生成。1 642 cm−1和1 628 cm−1附近是C=C的振动吸收峰,当有C=C基团包覆在纳米铁表面时,能够减缓纳米铁的氧化,防止磁性团聚,进而保证了绿色纳米铁在长时间内较高的活性[19, 28],相较于另外2种绿色纳米铁,GT-nZVI在此处的峰强度更高,这说明表面覆盖了更多的C=C基团,故具有更好的稳定性和反应活性。1 404 cm−1附近是C—H键的伸缩振动吸收峰,1 385 cm−1和1 341 cm−1处的吸收峰则对应于芳香胺的C—N键,1 084 cm−1附近吸收峰是—NH的伸缩振动引起的,在约1 070 cm−1处可以看到由C—O键的伸缩振动吸收峰,这意味着酚类、脂肪族胺、氨基酸也可能是合成中的稳定剂[28-31]。
2.6 热重分析(TGA)
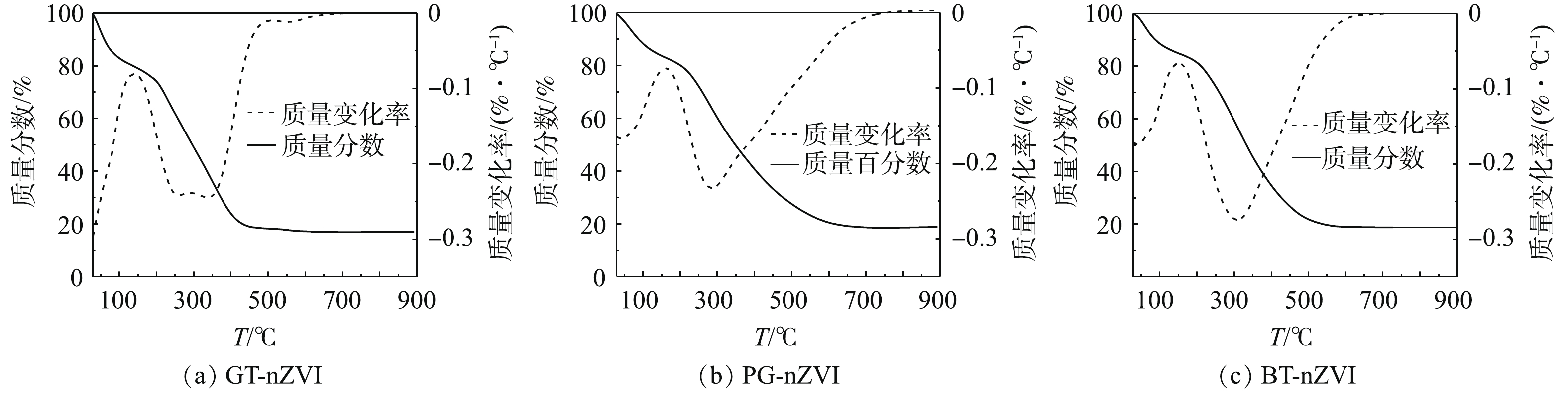
通过热重分析表征了3种绿色纳米铁的热力学效应。图8为GT-nZVI、PG-nZVI和BT-nZVI的热重曲线图,实验在氮气氛围中进行,起始温度29 ℃,终点温度900 ℃,升温速度为10 ℃·min−1。由热重分析曲线(图8)可知,合成的绿色纳米铁随着温度的升高出现了显著的质量损失。当温度从29 ℃升高至100 ℃时,3种绿色纳米铁的质量损失在15.0%左右[32],低于200 ℃的初始质量损失通常归因于残留水分和吸附水分的蒸发。在100~200 ℃的温度范围内,质量变化不明显,有机化合物在高达200 ℃的温度下表现出明显的热稳定性,当温度升到更高时,有机物会发生分解[33]。温度从200 ℃升至600 ℃和700 ℃时,3种绿色纳米铁的质量趋于稳定,包覆在纳米铁表面的有机物分解殆尽,残留物是其中的纳米铁颗粒。GT-nZVI的残留物大约有17.0%,PG-nZVI与BT-nZVI的残留物大约有18.8%。
以上结果表明,绿茶提取液中有更多的有机质包覆在纳米铁的表面,而包覆的厚度与空间位阻呈正相关关系,从而增强了对纳米铁颗粒之间磁力势能、范德华引力的抵抗[34]。结合粒径测试结果可知,3种绿色纳米铁中GT-nZVI的粒径最小,因此,颗粒之间的磁力势能也更弱,促使GT-nZVI的稳定性与分散性最好,与悬浮稳定性测试结果一致。
2.7 GT-nZVI、PG-nZVI和BT-nZVI对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除效果
本研究以Cr(Ⅵ)为目标污染物,考察了3种绿色纳米铁的反应活性。在已有研究中,刘勇等[35]以桉树叶提取液绿色合成纳米铁去除Cr(Ⅵ),并与商品化纳米铁的去除效果对比,发现以桉树叶提取液制备的绿色合成纳米铁对铬的去除率可达77.2%,而商品化纳米铁的去除率仅为37.3%。林国庆等[36]使用羊栖菜提取液绿色合成纳米铁去除Cr(Ⅵ),反应90 min后,去除率高达92.76%。赵玲子等[37]利用琼脂改性纳米铁,与水中Cr(Ⅵ)反应180 min后,去除率可达95%以上。
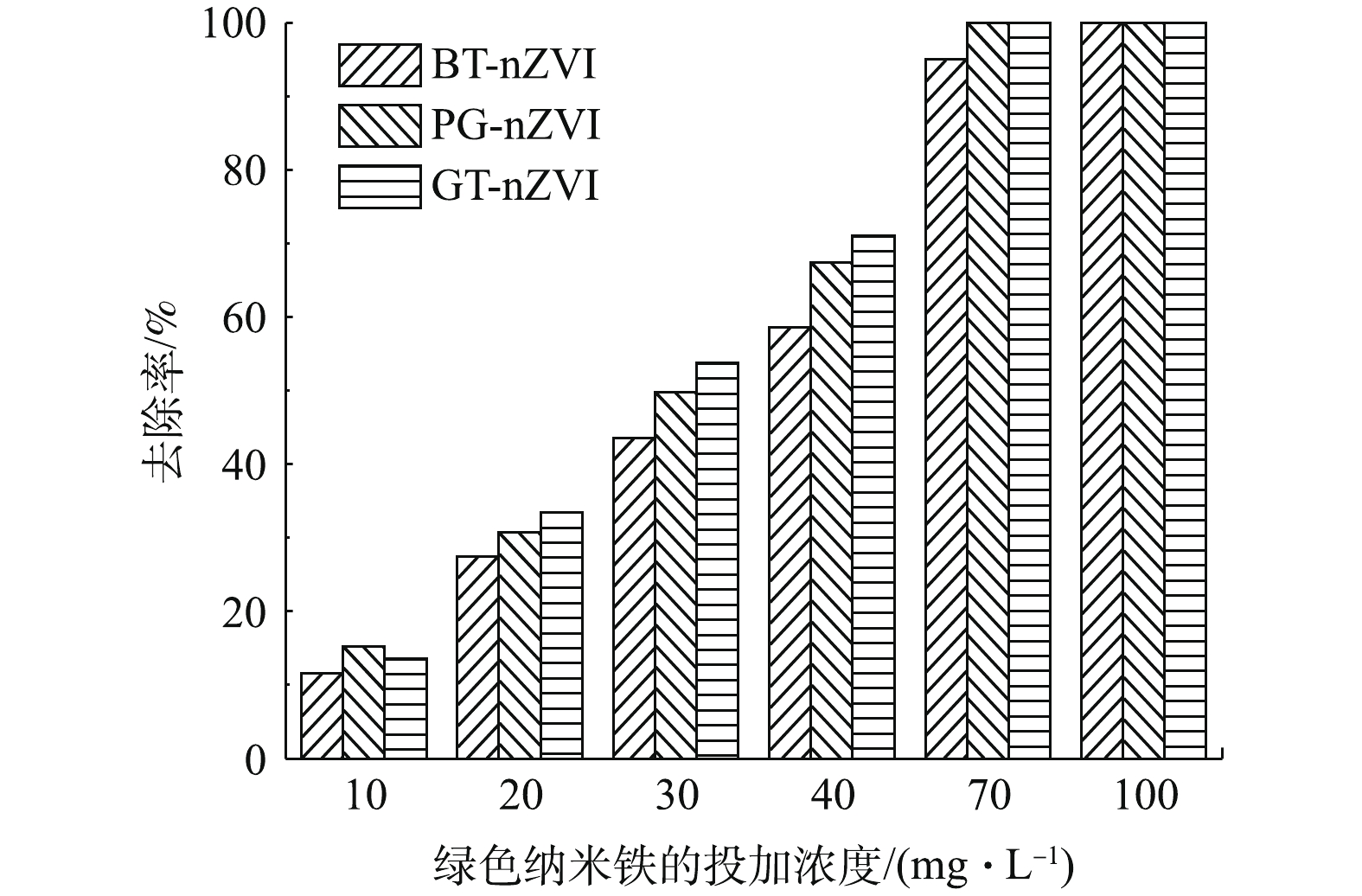
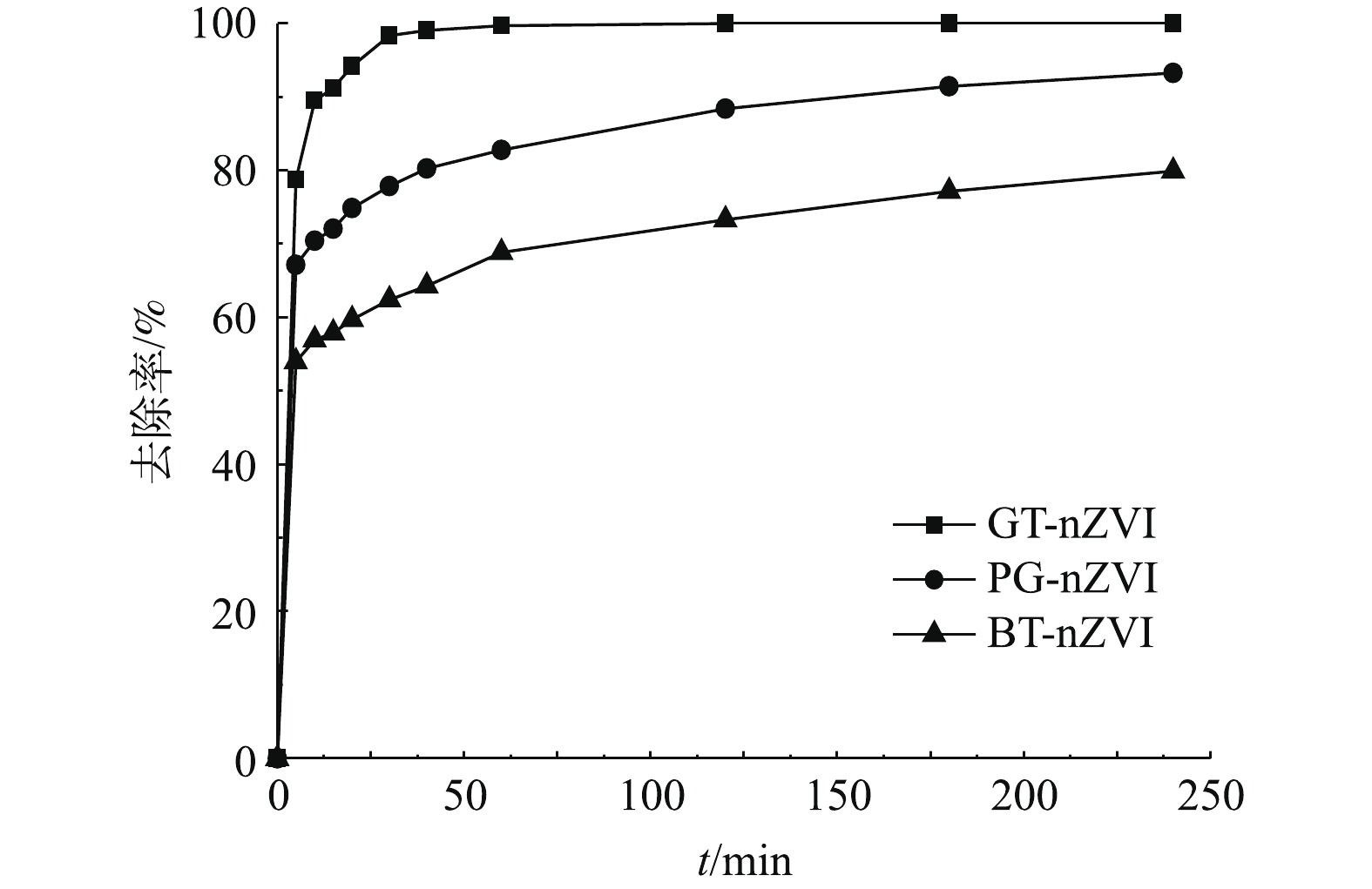
本实验中不同浓度GT-nZVI、PG-nZVI和BT-nZVI在24 h内对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率如图9所示,由图9可以看出,3种绿色纳米铁对Cr(Ⅵ)都有还原效果。在绿色纳米铁浓度低于70 mg·L−1时,GT-nZVI对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率最高,PG-nZVI的去除效果与之接近。在初始投加浓度在70 mg·L−1时,GT-nZVI与PG-nZVI对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率到达100%,BT-nZVI对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率到达94.9%,随着初始浓度到达100 mg·L−1,3种材料对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率均达到100%。图10为绿色纳米铁投加浓度为100 mg·L−1时对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率,反应约4 h达到平衡。其中GT-nZVI在反应时间为60 min时,去除率达到99.7%,可见GT-nZVI与Cr(Ⅵ)的反应速率较快,去除能力强。
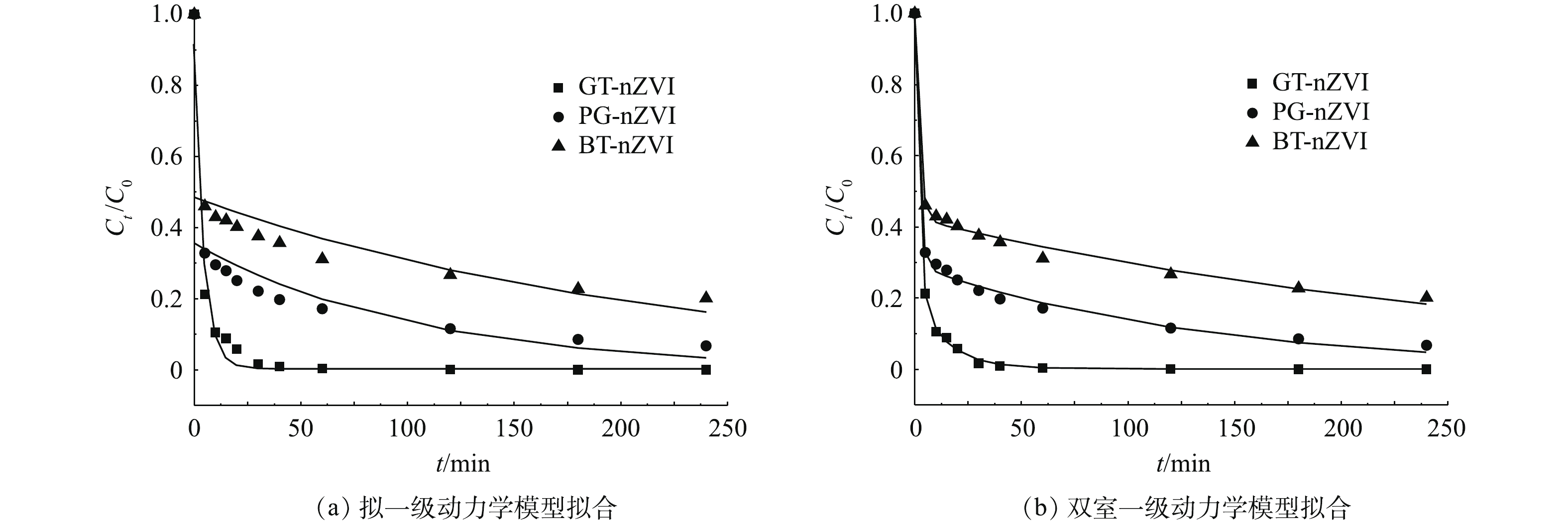
由于绿色纳米铁对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除速率表现出初始快速与随后较缓慢的2个阶段,本实验选用拟一级动力学模型和区分快、慢去除动力学的双室一级模型进行拟合,拟合结果见表1,动力学拟合曲线如图11(a)和图11(b)所示。双室一级模型具有更高的动力学曲线拟合度,其可调可决系数
R2adj 均大于拟一级动力学模型,因此,双室一级模型更适用于描述本实验中绿色纳米铁去除Cr(Ⅵ)的动力学过程。表 1 GT-nZVI、PG-nZVI和BT-nZVI对Cr(Ⅵ)去除反应动力学拟合结果Table 1. Kinetics fitting results of hexavalent chromium removal by GT-nZVI, PG-nZVI and BT-nZVI nanoparticles纳米铁类型 拟一级模型 双室一级模型 k1/min−1 标准误差 
ffast ffast标准误差 kfast/min−1 kfast标准误差 fslow fslow标准误差 kslow/min−1 kslow标准误差 
GT-nZVI 0.225 0.037 0.889 0.772 0.043 0.536 0.077 0.228 0.042 0.073 0.002 0.999 PG-nZVI 0.009 0.004 0.550 0.707 0.020 0.534 0.081 0.293 0.012 0.008 0.001 0.996 BT-nZVI 0.005 0.002 0.506 0.575 0.021 0.505 0.091 0.425 0.011 0.004 0.003 0.993 从双室一级模型拟合结果可以看出,绿色纳米铁对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除表现出明显的快室与慢室,其中GT-nZVI对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除反应表现出比其他2种绿色纳米铁更快的速率。具体而言,GT-nZVI的快、慢速去除速率常数(kfast和kslow)均大于PG-nZVI、BT-nZVI的快、慢速去除速率常数。此外,GT-nZVI快速去除约为总去除的0.77,高于PG-nZVI的0.70和BT-nZVI的0.58,表明GT-nZVI的还原反应对其总去除的贡献高于另外2种纳米铁。根据傅里叶红外光谱测试及热重测试结果推测,这是因为GT-nZVI中零价纳米铁表面被包覆了更多的有机质,且含有更多的C=C基团,因此,能够有效防止环境中的自由基对纳米铁的干扰,从而保持纳米铁较高的反应活性。
绿色纳米铁去除Cr(Ⅵ)主要存在还原反应和吸附作用2个方面。初始反应非常迅速,零价铁将重铬酸根还原为Cr(Ⅲ),反应生成的Fe(Ⅱ)可进一步还原Cr(Ⅵ),主要的反应如式(4)和式(5)所示,且零价铁还与混合液中的氢离子、溶解氧反应生成Fe(Ⅱ),继续充当还原剂,混合液中的Cr(Ⅵ)浓度快速降低,如式(6)和式(7)所示。随后的反应由吸附作用占主导,反应速率降低,由还原反应过程中生成Fe(Ⅲ)与Fe(Ⅱ)在混合液中发生水解反应,生成Fe(OH)3和Fe(OH)2,随着这2种沉淀的析出铬离子会被吸附,使得目标污染物进一步被去除[38-39]。
3Fe0+Cr2O2−7+14H+→Cr3++3Fe2++7H2O (4) Cr2O2−7+14H++6Fe2+→6Fe3++2Cr3++7H2O (5) Fe0+2H+→Fe2++H2 (6) 2Fe0+O2+2H2O→2Fe2++4OH− (7) 绿色纳米铁颗粒表面有机质含有特定作用的官能团,能够促进对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除,如氨基与羧基能够与Fe(Ⅲ)发生螯合作用,增强对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附[40];C=C、C—H、C—N等官能团通过吸附作用,增加绿色纳米铁表面Cr(Ⅵ)的浓度,同时还原反应也在进行,因此,绿色纳米铁对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除过程是吸附与还原的共同作用[41-42]。纳米铁的活性与植物提取液的抗氧化性强弱或多酚含量高低呈正相关[21],故结合上述的表征分析结果,与另外2种绿色纳米铁比,GT-nZVI粒径最小,分散稳定性最好,因此,能够更充分地与重金属污染物接触,且具有更快的反应速率和更强的抗氧化性,对地下水污染具有较好的修复效果。
3. 结论
1)筛选的3种绿色纳米铁的悬浮稳定性由高到低为GT-nZVI、PG-nZVI、BT-nZVI。其中,GT-nZVI能在12 h内保持上清液中铁含量在初始浓度的80%以上。
2)测试分析结果表明,GT-nZVI呈现椭球状,PG-nZVI和BT-nZVI形貌上更接近片状堆叠物,平均粒径分别为88、118、124 nm,表面被大量有机物包裹,其中GT-nZVI表面包裹的有机质含量最高。酚类化合物在还原Fe(Ⅱ)的反应中起到了主要作用,酚类、氨基酸、脂肪族胺可能在合成中起到了表面保护的作用。
3) 3种绿色纳米铁对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除过程中既有还原反应也有吸附作用,还原反应起主导作用。其中GT-nZVI具有更高的还原性,较小的粒径,对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除速率最快。
-
表 1 不同阶段进水的污染物质量浓度
Table 1. Pollutant concentrations in influent water at different stages
mg·L−1 阶段 TN NH4+-N TP COD 阶段Ⅰ 96.58±8.39 87.55±9.84 20.09±3.01 113.51±14.58 阶段Ⅱ 102.00±6.99 95.37±7.99 26.15±1.03 629.00±25.01 阶段Ⅲ 269.17±14.62 251.35±14.15 60.65±1.50 1426.63 ±62.29阶段Ⅳ 287.60±8.49 277.57±9.43 61.77±4.03 1315.92 ±67.57表 2 BAFs中微生物群落的多样性和丰富度估算
Table 2. Estimation of diversity and abundance of microbial communities in BAFs
样品 Shannon Simpson Ace Chao Coverage/% W0 4.99±0.03 0.03±0.002 1290.54 ±6.531267.19 ±14.1698.36 TL 3.45±0.23 0.14±0.05 735.13±66.80 688.84±56.22 99.09 FS 4.08±0.47 0.06±0.04 874.38±156.39 879.54±166.96 98.83 LS 4.38±0.07 0.04±0.01 967.67±153.27 940.47±87.00 98.79 -
[1] SUN X, ZHU B K, ZHANG S, et al. New indices system for quantifying the nexus between economic-social development, natural resources consumption, and environmental pollution in China during 1978–2018[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 804: 150180. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150180 [2] 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社. 2023. [3] WANG S, WANG L, DENG L W, et al. Performance of autotrophic nitrogen removal from digested piggery wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 241: 465-472. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.153 [4] ZHANG J M, XIA A, YAO D X, et al. Removal of oxytetracycline and ofloxacin in wastewater by microalgae-bacteria symbiosis for bioenergy production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 363: 127891. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127891 [5] CHEN J, LIU Y S, ZHANG J N, et al. Removal of antibiotics from piggery wastewater by biological aerated filter system: Treatment efficiency and biodegradation kinetics[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 238: 70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.023 [6] XIN X, LIU S Q, QIN J W, et al. Performances of simultaneous enhanced removal of nitrogen and phosphorus via biological aerated filter with biochar as fillers under low dissolved oxygen for digested swine wastewater treatment[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2021, 44(8): 1741-1753. doi: 10.1007/s00449-021-02557-z [7] 钟鸣扬. 竹炭-陶粒组合填料曝气生物滤池对养猪废水的处理性能研究[D]. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学, 2024. [8] 瞿艳芝, 李谦, 叶正芳, 等. 曝气生物滤池处理模拟选矿废水研究[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2018, 47(2): 79-83. [9] 朱乐辉, 邱俊, 徐星, 等. Fenton氧化/厌氧/好氧工艺处理苯胺农药废水[J]. 中国给水排水, 2009, 25(2): 58-61. [10] 董伟羊. 曝气生物滤池联合中性光Fenton降解水中典型医药品污染物的效果及机理研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2020. [11] WU Q D, CHEN C, ZHANG Y L, et al. Safe purification of rural drinking water by biological aerated filter coupled with ultrafiltration[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 868: 161632. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161632 [12] 郝添翼, 曲婷, 王海媚, 等. 曝气生物滤池滤料改进研究[J]. 应用化工, 2023, 52(7): 2112-2116. [13] ZHOU Y C, WENG S C, ZHANG Y P, et al. Experimental study of seepage flow properties with biofilm development in porous media with different filter morphologies[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 591: 125596. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125596 [14] 李怡, 朱恒亮. C/N对A~2O耦合生物曝气滤池脱氮除磷的影响[J]. 水处理技术, 2018, 44(9): 120-123. [15] LU S L, HU H Y, SUN Y X, et al. Effect of carbon source on the denitrification in constructed wetlands[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(8): 1036-1043. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62379-7 [16] 陈翠忠, 李俊峰, 刘生宝, 等. 间歇式活性污泥法(SBR)系统碳氮比对同步硝化反硝化微生物群落分布及脱氮效能的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(11): 3598-3607. [17] 曾锦涌, 柯水洲, 袁辉洲, 等. 碳氮比对MBBR系统脱氮性能及微生物群落的影响[J]. 环境工程, 2024, 42(4): 100-110. [18] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 132-284. [19] TSO J, DUTTA S, INAMDAR S, et al. Simultaneous analysis of free and conjugated estrogens, sulfonamides, and tetracyclines in runoff water and soils using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011, 59(6): 2213-2222. doi: 10.1021/jf104355x [20] 李冬, 郭跃洲, 劳会妹, 等. 进水碳氮比对缺氧/好氧SBR亚硝化系统的影响[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2019, 51(2): 1-7. [21] 曾玉, 曾敏静, 程媛媛, 等. 好氧颗粒污泥的培养及处理低碳氮比废水效果[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2021, 12(4): 104-111. [22] 姜姗, 黄锦楼, 阚凤玲, 等. 曝气条件对生态滤池处理农村生活污水的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(4): 1252-1262. [23] PANG Y M, WANG J L. Various electron donors for biological nitrate removal: A review[J]. The Science of the total environment, 2021, 794: 148699. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148699 [24] 董宝刚. 间歇曝气序批式反应器处理养猪沼液的特性研究[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2017. [25] 杨慎华, 李家麟, 王晓玲, 等. 进水碳氮比对生物膜微生物群落及系统脱氮性能的影响[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(11): 75-80. [26] MIQUELETO A P, DOLOSIC C C, POZZI E, et al. Influence of carbon sources and C/N ratio on EPS production in anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactors for wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(4): 1324-1330. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.026 [27] RAMASAHAYAM S K, GUZMAN L, GUNAWAN G, et al. A comprehensive review of phosphorus removal technologies and processes[J]. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part A - Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2014, 51(6): 538-545. doi: 10.1080/10601325.2014.906271 [28] BUNCE J T, NDAM E, OFITERU I D, et al. A review of phosphorus removal technologies and their applicability to small-scale domestic wastewater treatment systems[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2018, 6(8): 1-15. [29] 齐冉, 张灵, 杨帆, 等. 水力停留时间对潜流湿地净化效果影响及脱氮途径解析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(9): 4296-4303. [30] 王明玉, 朱琳, 王鹏. 净水除磷基质的综合筛选与长效建模预测[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2022, 12(1): 119-126. [31] 柯德峰. 人工湿地基质的筛选及其除磷机理研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2019. [32] 张海, 张旭, 梁军, 等. 处理含油地表水体的潜流湿地填料筛选及其性能评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2007(7): 1121-1126. [33] 巩有奎, 王一冰, 孙洪伟. 生物反应器电子受体反硝化聚磷PAOs-GAOs竞争及N_2O释放特性[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(23): 241-249. [34] 陶虎春, 佟浩, 王健, 等. 碳氮比对A/O-MBR工艺中污水脱氮除磷的影响研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(4): 680-686. [35] 李盟军, 申健, 姚建武, 等. 某规模化猪场废水中抗生素污染特征及生态风险评估[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(4): 884-893. [36] DAGHRIR R, DROGUI P. Tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: A review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2013, 11(3): 209-227. doi: 10.1007/s10311-013-0404-8 [37] SON H J, YOOM H S, RYU D C, et al. Characteristics of adsorption and biodegradation of tetracycline antibiotics by granular activated carbon and biofiltration process[J]. Journal of Environmental Science International, 2014, 23(3): 379-386. doi: 10.5322/JESI.2014.23.3.379 [38] 李佳泽, 吴宝利, 刘富荣, 等. BAF工艺深度处理四环素类制药废水研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(5): 24-31. [39] 唐佳, 陈茜, 覃牧川, 等. 4种典型抗生素在反硝化体系中的去除特性[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(6): 3204-3210. [40] 陆玉, 钟慧, 丑三涛, 等. 乙酸驯化对厌氧污泥微生物群落结构及发酵特性的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(5): 1835-1842. [41] XU L N, ZHANG B, PENG X W, et al. Dynamic variations of microbial community structure in myriophyllum aquaticum constructed wetlands in response to different NH4+-N concentrations[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2020, 93: 55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2020.02.028 [42] ZHANG M J, QIAO S, SHAO D H, et al. Simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal by combined anammox and denitrifying phosphorus removal process[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2018, 93(1): 94-104. doi: 10.1002/jctb.5326 [43] YANG X Y, HE Q, GUO F C, et al. Nanoplastics disturb nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands: Responses of microbes and macrophytes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(21): 14007-14016. [44] LI Y Q, ZHANG C M, YUAN Q Q, et al. New insight into the effect of microplastics on antibiotic resistance and bacterial community of biofilm[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 335: 139151. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139151 [45] ALVAREZ A, SAEZ J M, COSTA J S D, et al. Actinobacteria: Current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 166: 41-62. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.070 [46] 李静, 张宝刚, 刘青松, 等. 导电材料强化微生物直接种间电子传递产甲烷的研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 2021, 61(6): 1507-1524. [47] HU Y Y, WANG X F, ZHANG S H, et al. Microbial response behavior to powdered activated carbon in high-solids anaerobic digestion of kitchen waste: Metabolism and functional prediction analysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 337: 117756. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117756 [48] GUO B, ZHANG Y D, YU N, et al. Impacts of conductive materials on microbial community during syntrophic propionate oxidization for biomethane recovery[J]. Water Environment Research, 2021, 93(1): 84-93. doi: 10.1002/wer.1357 [49] ZHAO Y, HUANG J, ZHAO H, et al. Microbial community and N removal of aerobic granular sludge at high COD and N loading rates[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 143: 439-446. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.020 [50] 谭丰佚, 刘新颖, 党岩, 等. 有机碳源对异养硝化-好氧反硝化生物脱氮的影响及其优化[J]. 环境工程学报, 2024, 18(4): 1183-1191. [51] XIONG W, WANG S J, JIN Y, et al. Insights into nitrogen and phosphorus metabolic mechanisms of algal-bacterial aerobic granular sludge via metagenomics: Performance, microbial community and functional genes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 369: 128442. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128442 [52] HUANG C, LIU Q, LI Z L, et al. Relationship between functional bacteria in a denitrification desulfurization system under autotrophic, heterotrophic, and mixotrophic conditions[J]. Water Research, 2021, 188: 116526. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116526 [53] WANG J L, CHU L B. Biological nitrate removal from water and wastewater by solid-phase denitrification process[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2016, 34(6): 1103-1112. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.07.001 [54] XIE C H, YOKOTA A. Zoogloea oryzae sp nov. , a nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from rice paddy soil, and reclassification of the strain ATCC 19623 as Crabtreella saccharophila gen. nov. , sp nov[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2006, 56: 619-624. [55] 李龙山, 倪细炉, 李昌晓, 等. 生活污水对土壤及湿地植物根际细菌群落的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(11): 2163-2170. [56] LIU X Y, LI R J, CHEN R, et al. Formation of filamentous fungal pellets in aerobic granular sludge via reducing temperature and dissolved oxygen: Characteristics of filamentous fungi and denitrification performance[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 332: 339. [57] HUANG X, DONG W Y, WANG H J, et al. Sludge alkaline fermentation enhanced anaerobic- multistage anaerobic/oxic (A-MAO) process to treat low C/N municipal wastewater: Nutrients removal and microbial metabolic characteristics[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 302: 122583. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122583 期刊类型引用(8)
1. 杨毅,赵睿,郑振泽,舒麒麟,刘伟. 城市污水处理厂二级出水DOM的荧光组分、分子特性和来源. 环境工程. 2024(12): 66-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 马卫星,邹立航,李璇,李朝霞,马志强,杜洪秋,丁成,吴向阳. 光谱表征评价2种不同预处理工程对DOM去除特征. 环境工程. 2022(08): 150-158+61 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张国正,赵敏,李勇,应炎杰,路学军,潘继征. 水生植物腐解过程中溶解性有机质的释放特征. 中国给水排水. 2022(19): 93-101 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 周向军,齐婷,高茹霞. 玉米秸秆腐解释放溶解性有机质的光谱分析. 黑龙江农业科学. 2022(10): 76-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李晨璐,郭雅妮,郑利兵,焦赟仪,张鹤清,吴振军,黄国华,王哲晓,魏源送. 石英砂加载混凝工艺的DOM去除特征与混凝机理. 水资源保护. 2021(04): 148-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 田颖,郭婧,颜旭,席玥,刘保献,荆红卫. 紫外—可见指纹图谱溯源技术及应用研究. 环境污染与防治. 2021(07): 843-846+863 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 康赛,李清雪,张良长,艾为党,桂双林,郑利兵,李晨璐,魏源送. 预处理对尿液长期存储过程的影响及机理分析. 中国环境科学. 2021(10): 4597-4605 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 梁芊,郑海君. 基于光谱学的溶解性有机物与重金属作用机理研究. 济南大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(04): 390-394 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(10)
-






 下载:
下载: