-
四川盆地及其周缘油气田开采产出的卤水资源非常丰富[1],尤其是非常规天然气——页岩气逐渐成为我国主要的新型能源资源。目前,我国页岩气可开采资源总量达到12.85万×109 m3,2022年全年开采总量为238×109 m3[2]。在页岩气开采过程中,来自深地层水资源、人工注入的淡水和合成化学物质组成的大量混合液体会随着采气过程逐渐返排到地面,其成分具有高有机物含量、高浓度总溶解性固体和高悬浮物的特征,被统称为页岩气采出水[3]。此类废水中不仅含有钠、钾、镁、钡和钙等常规金属元素,还含有锂(Li+)、锶、镓和硼等具有回收价值高的金属元素[4],其中Li+质量浓度的中位数超过30 mg·L−1,且镁锂比<8[5-6]。相比于盐湖卤水的高镁锂比,页岩气采出水中镁锂比较低,锂资源开发价值潜力大。到2030年,四川每年页岩气采出水水量预计为5 000~5 500×104 m3,可开采锂资源量超过1 500 t[7]。在页岩气采出水深度处理过程中有效提取锂资源,可实现降本增效目的。
页岩气采出水与盐湖卤水的水质差异大,尤其是有机物含量高,并具有种类多但浓度低的特征[8-9],往往需要系列耦合工艺处理才能达到回用或外部排放的标准[10]。然而,耦合工艺的各工艺段会不可避免的损失部分Li+,导致出水中Li+的质量浓度值偏低。尽管某些耦合工艺中的浓缩液Li+的质量浓度较高,但溶解性有机物含量值和总盐度值远高于原水[11],可能使得Li+提取的经济效益难以平衡投资成本。适当的预处理工艺去除页岩气采出水中部分污染物同时保持Li+不损失,将有利于从此类卤水中最大限度提取锂资源。与膜分离法和电化学法提锂相比,吸附法是一种易操作、适应性强且高效率的方法,尤其是适用于低品位的卤水环境提取锂资源。本课题组前期开发的锰基炭气凝胶锂吸附剂材料成功从经过软化(碳酸钠沉淀-微滤膜)预处理后的页岩气采出水中原位选择性提取了Li+,但存在达到饱和吸附时间长和吸附剂材料制备工艺复杂的问题[12];同时,炭气凝胶的多孔结构容易吸附页岩气采出水中的溶解性有机物[13],不利于解吸液中Li+的进一步纯化,且溶解性有机物对吸附行为的影响不明确。铝基吸附剂材料已被证实在盐湖卤水中具有快速吸附性能,实现了Li+的快速获取[14-15],但像溶解性有机物含量高的页岩气采出水中的吸附能效研究甚少,且未见相关工艺路线报道。因此,探明铝基吸附剂在页岩气采出水中的吸附行为,了解溶解性有机物对Li+插层行为的影响,将有助于此类废水中锂资源工业化回收。
本研究通过沉淀法和沉析法分别制备铝基吸附剂粉体和颗粒,探讨从混凝-超滤膜耦合预处理后的页岩气采出水中回收锂资源的可行性。探究铝基吸附剂粉体和颗粒对页岩气采出水中Li+的吸附行为,并以不含溶解性有机物的模拟页岩气采出水作为对照组,探究了溶解性有机物对颗粒吸附剂吸附Li+行为的影响。本研究工作将为规模化从页岩气采出水中提取锂资源提供理论支撑。
-
无水氯化锂(分析纯,纯度 98%),氯化钾(分析纯,纯度 98%),六水氯化镁(分析纯,纯度 98%),六水氯化铝(分析纯,纯度 97%),氢氧化钠(分析纯,纯度 98%)和N,N-二甲基乙酰胺(分析纯,纯度 99%)均购买于成都科龙化工有限公司,聚氯乙烯购买于中国台湾塑料工业股份有限公司;氯化钠(分析纯,纯度 99%),二水氯化钙(分析纯,纯度 99%),二水氯化钡(分析纯,纯度 99%)和二水氯化锶(分析纯,纯度 99%)均购买于Sigma-Aldrich公司;聚偏氟乙烯超滤膜购买于深圳市立昇净水科技有限公司,聚合物氯化铝购买于自贡市利民化工厂。
-
实际页岩气采出水取自重庆铜梁某基地,总溶解性固体(total dissolved solids, TDS)为42.0 g·L−1,Li+质量浓度为31.1 mg·L−1,溶解性有机碳(dissolved organic carbon, DOC)值为26.6 mg·L−1,浊度为113 NTU。
所有实际页岩气采出水在吸附前需经过混凝-超滤膜组合的预处理工艺,以便去除大颗粒物质和部分有机物。混凝过程:取聚合物氯化铝质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的页岩气采出水,用六联搅拌仪以200 r·min−1快速搅拌3 min,之后转速降为60 r·min−1并持续搅拌30 min,之后静置30 min,取上清液。超滤膜过滤过程:将混合后的上清液通过错流中空纤维超滤膜系统中过滤,并收集过滤液体,膜滤系统的回收率为95%,操作压力为0.1 MPa,过滤液作为吸附实验原液。经过一些列表征检测混凝-膜滤组合工艺处理后的水样,其TDS值为42.0 g·L−1,Li+质量浓度为31.1 mg·L−1,TOC值为20.1 mg·L−1,浊度为0.64 NTU。
-
粉体吸附剂的制备:将氯化铝和氯化锂按照一定摩尔比溶解在75 ℃ 大约200 mL的去离子水中,并恒温搅拌1 h;之后用5 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液进行滴定实验,混合溶液逐渐形成LiCl·mAl(OH)3·nH2O白色颗粒,直到混合溶液pH为6.5时立刻停止滴定强碱溶液;此时混合溶液呈现白色浑浊液体,再经过抽滤实现固液分离,固体在80 ℃鼓风干燥箱中干燥24 h,即可得到铝基吸附剂粉体。氯化铝和氯化锂的摩尔比分别为1.2:1、1.3:1、1.6:1和2.0:1。
颗粒吸附剂的制备:首先,将取铝基吸附剂粉体8份、聚氯乙烯7份和N,N-二甲基乙酰胺85份混合放于三口烧瓶中,在60 ℃恒温水浴锅中以一定转速持续搅拌8 h,最终得到白色混合溶液。利用聚氯乙烯不溶于水相的特征,采用沉析法获得包埋有铝基锂吸附粉体的白色球形颗粒,其直径约2.4 mm。
-
X-射线衍射仪(丹东浩元仪器有限公司,DX-2700BH)被用于表征铝基吸附剂粉体的晶体结构,场发射扫描电子显微镜(日本Hitachi公司,Regulus
8230 )用于观察粉体和颗粒吸附剂的形貌,原子吸收仪(美国Perkin-Elmer公司,900T)被用于检测水样中Li+的质量浓度,离子色谱仪(美国赛默飞世尔科技公司,采用CS12A和AS11-HC色谱柱)被用于检测水样中各离子的种类和质量浓度,总有机碳仪(日本Shimadzu公司)被用于检测水样中DOC,三维荧光光度仪(日本Hitachi公司,F7100)被用于检测水样中溶解性有机物的种类及响应情况,便携式浊度仪(美国Hach公司,2100Q)被用于检测水样的浊度值,多功能水质检测仪(美国麦隆公司,Ultrameter II 6PFC)被用于检测水样中TDS。所有在表征前均用0.45 μm聚醚砜微滤膜(天津市津腾实验设备有限公司)过滤处理。 -
首先,称取一定量铝基吸附剂粉体或颗粒放入装有50 mL预处理后页岩气采出水的锥形瓶中,并将锥形瓶放于25 ℃恒温水浴摇床以150 r·min−1转速吸附一定时间。原子吸收仪用火焰法测定Li+的质量浓度值。铝基吸附剂粉体和颗粒的吸附容量根据式(1)进行计算,准一级和准二级吸附动力学模型如式(2)和(3)所示。
式中:Q为吸附容量,mg·g−1;C0和Ct分别为吸附前和t时刻页岩气采出水中Li+的质量浓度,mg·L−1;V为页岩气采出水的体积,L;m为铝基吸附剂的重量,g;Qt为t时刻的吸附量,mg·g−1;Qe为平衡吸附容量,mg·g−1;k1和k2分别为准一级和准二级的反应速率常数, g·(mg·min)−1。注:铝基颗粒吸附剂的重量为等量球形颗粒在50 ℃环境下干燥24 h得到恒定重量值,其含水率约为79%。
-
固定床吸附实验选用的吸附柱直径为1.5 cm,高度为30 cm,其有效床体积为30 cm3,空床体积为20 cm3,页岩气采出水进水速度为0.5 mL·min−1,流向为上向流。冲洗液(纯水)温度为5 ℃,流速为10 BV·h−1,水体积为2 BV;解吸液(纯水)温度为40 ℃,流速为3 BV·h−1,水体积为2 BV。
-
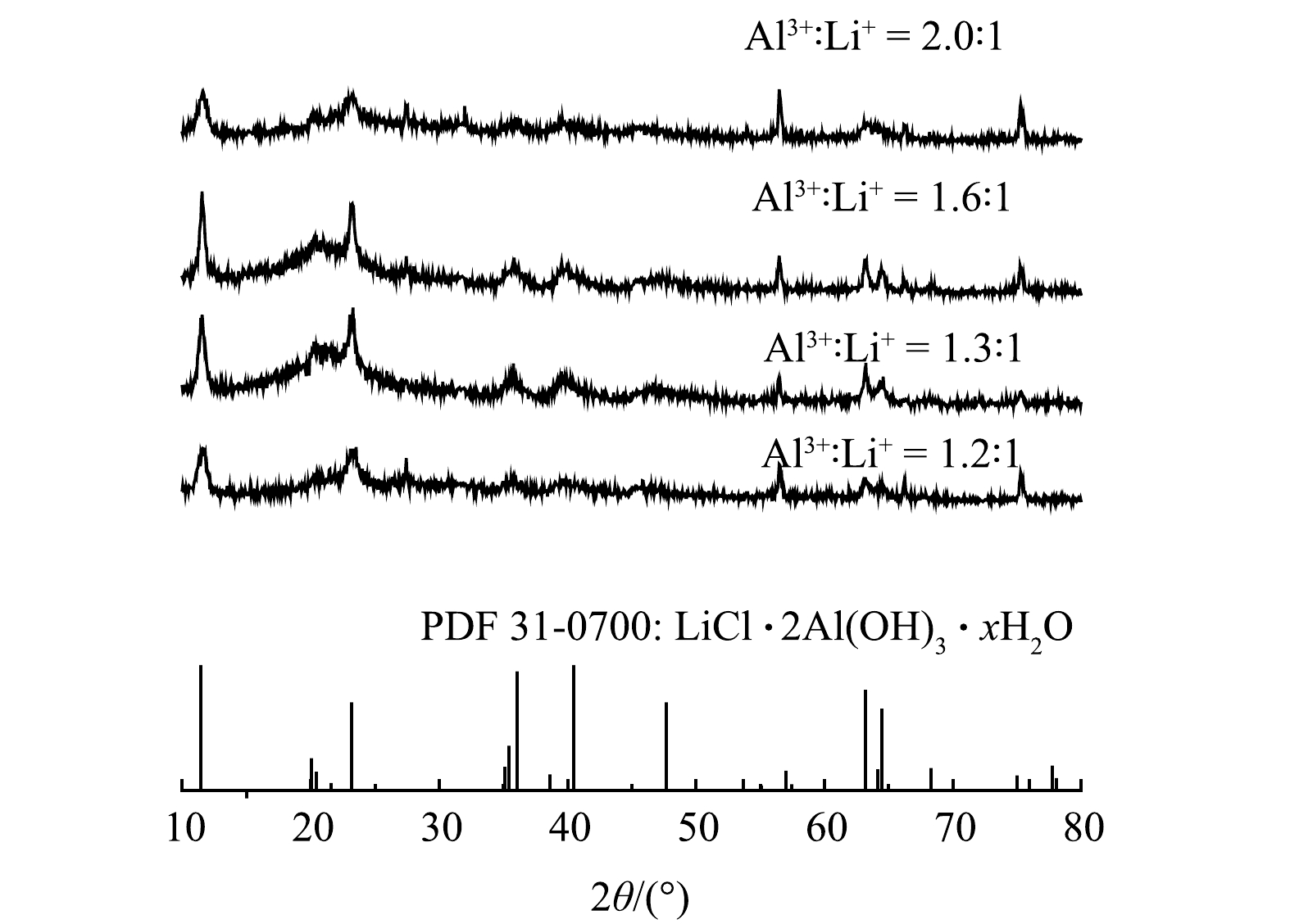
铝基吸附剂粉体晶体结构的XRD谱图如图1所示,通过与LiCl·2Al(OH)3·xH2O的标准卡片对比,发现合成的4种粉体的主要衍射图谱与其匹配吻合,表明成功合成了锂铝插层氧化物粉体。
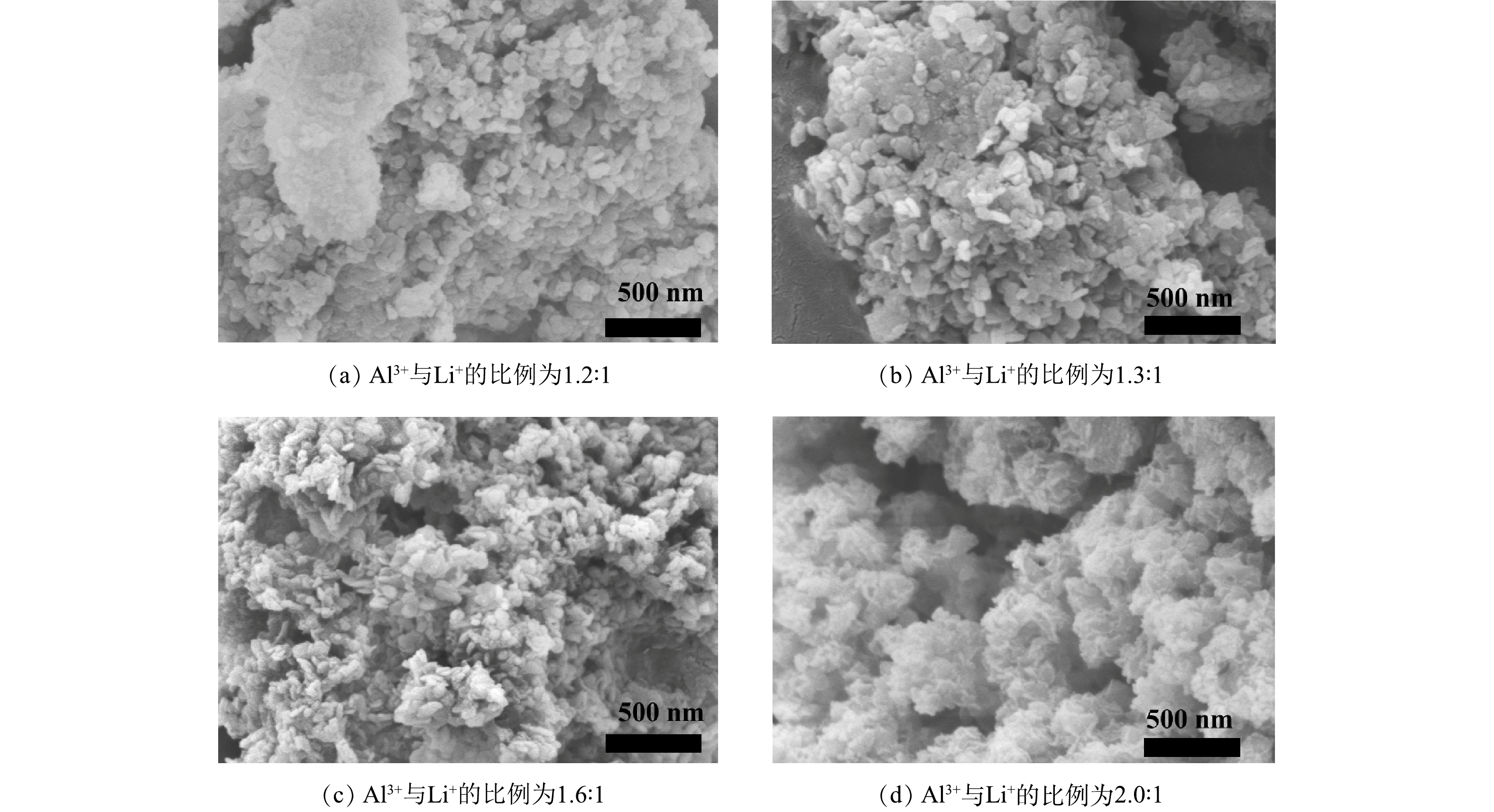
图2为不同Al3+与Li+比例合成的锂吸附剂粉体形态的SEM图。随着Al3+与Li+的比例从1.2:1增加到1.6:1,粉体吸附剂由片状结构堆积而成,说明成功合成了具有片状结构的铝基吸附剂粉体,与报道的文献结果相同[16]。
-
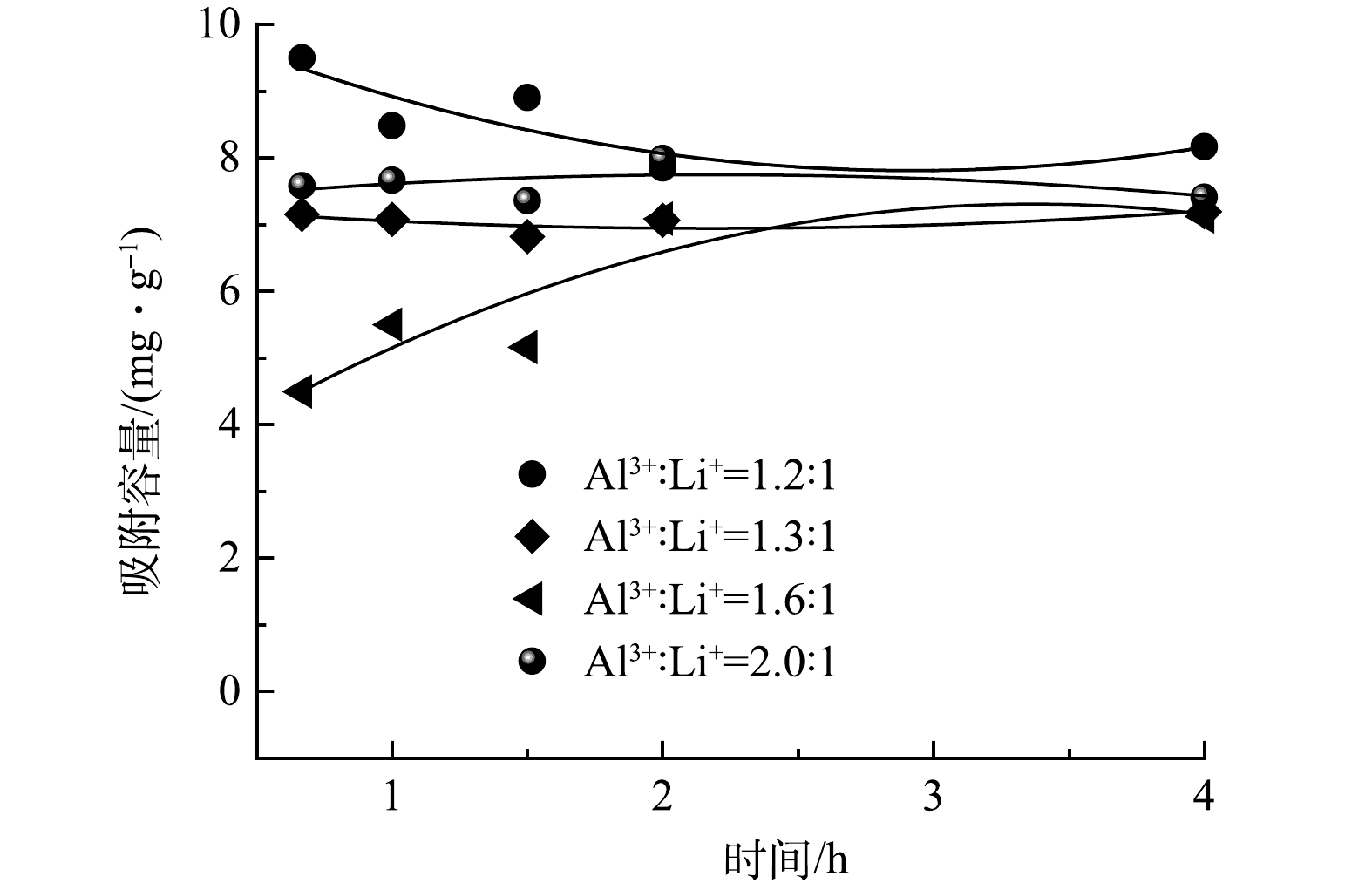
图3为铝基吸附剂粉体的吸收时间对吸附性能的影响。吸附2 h后,吸附剂达到吸附平衡,饱和吸附容量均超过了7.0 mg·g−1,表明铝基粉体吸附剂结构中Al(OH)3结构间隙空位快速被页岩气采出水中Li+占据,证明铝基吸附剂在页岩气采出水中具有快速吸附Li+的优势[13]。Al3+与Li+的比例为1.2:1合成的铝基吸附剂粉体的吸附容量先达到9.5 mg·g−1,之后吸附容量随着摇床吸附时间的延长而缓慢降低到8.1 mg·g−1,说明Al3+与Li+的比例为1.2:1制备的吸附剂粉体的锂插层结构不稳定,可能是制备的纳米片层容易在动态吸附过程中发生自解吸行为。在吸附容量相近条件下,考虑吸附剂制备成本,后续选择Al3+与Li+的比例为1.3:1制备的吸附剂粉体作为制备颗粒吸附剂的原料。
-
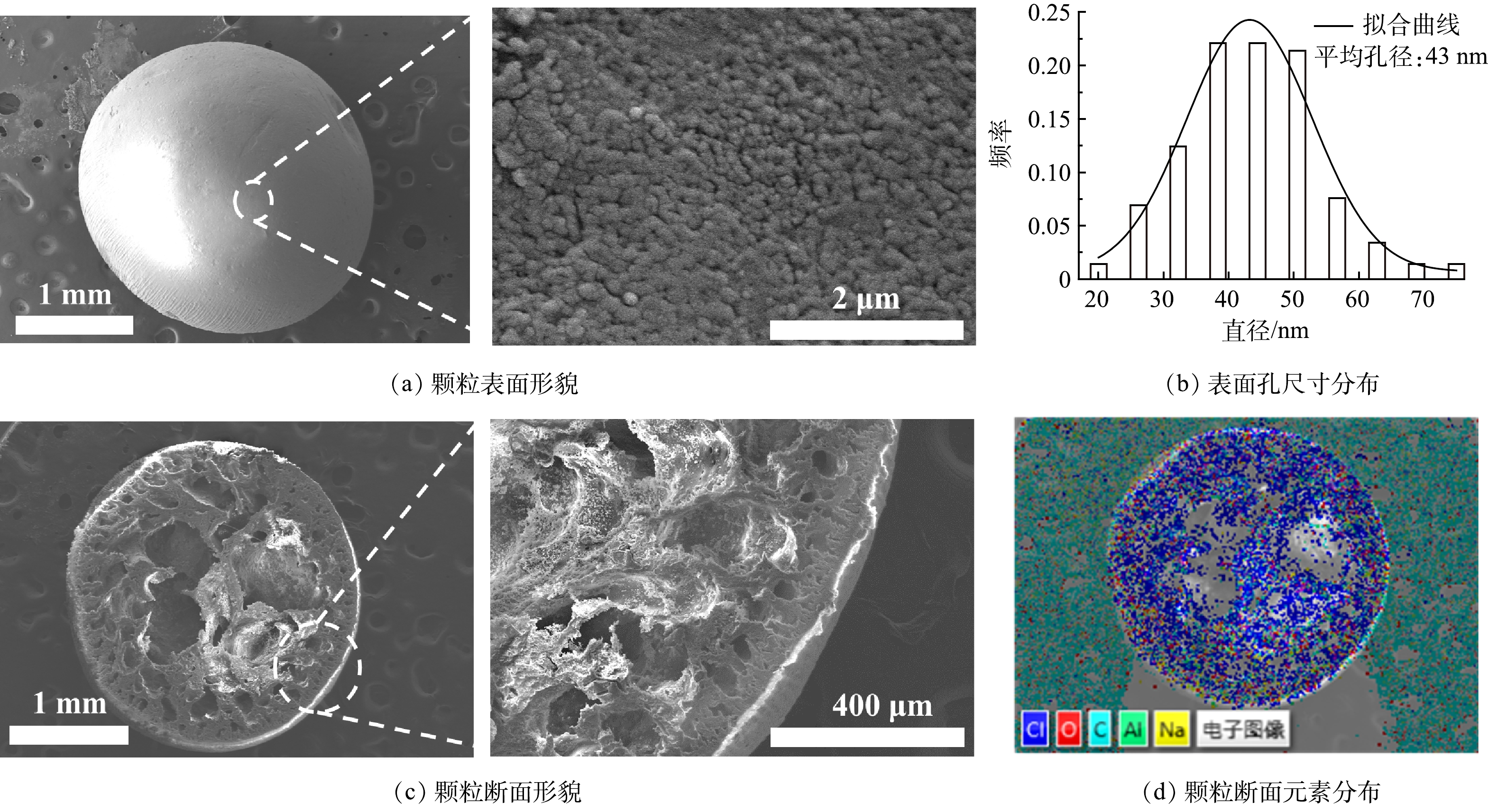
图4(a)~(c)为Al3+与Li+比例为1.3:1所制备的铝基颗粒吸附剂的表面形貌、表面孔尺寸分布和断面形貌。可见,球形颗粒表面孔形态由典型的非溶剂致相转换法所形成的无规则多孔结构[17],其平均孔尺寸约为43 nm。球形颗粒的断面随机分布着多孔结构,孔尺寸由外向里逐渐变大,并存在皮层小孔结构,这样的多孔球形颗粒将有利于离子溶液快速渗透。图4(d)为颗粒断面的元素分布情况,可以看到铝基吸附剂粉体被聚氯乙烯粘合在颗粒的骨架上。
-
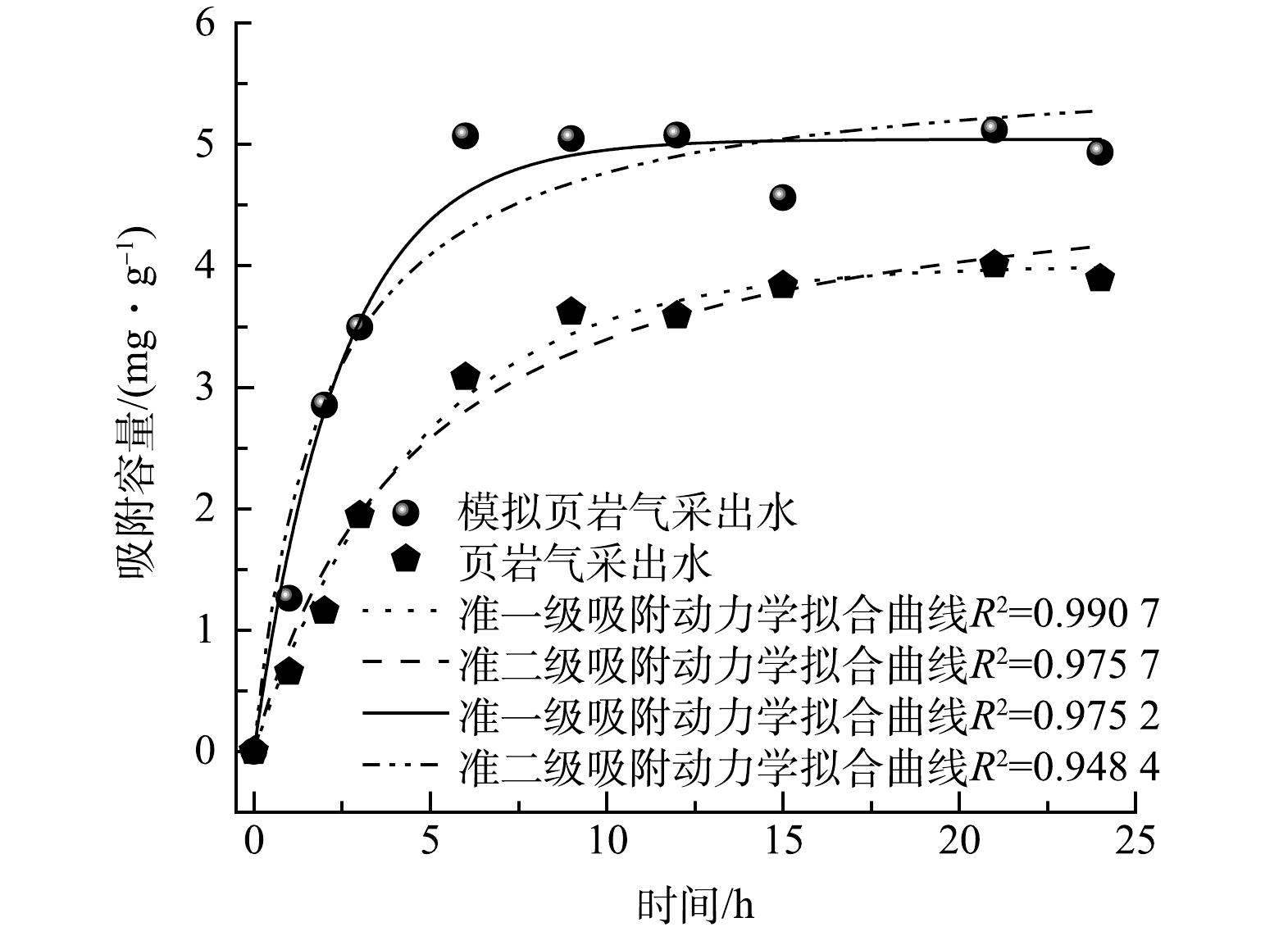
图5为铝基颗粒吸附剂分别在实际和模拟页岩气采出水中的吸附动力学。实际和模拟页岩气采出水的水质情况如表1所示。在2种水况条件下,颗粒吸附剂的吸附行为更符合准一级吸附动力学模型,实际页岩气采出水和模拟页岩气采出水的R2值分别为0.975 2和0.990 7,表明该吸附过程是以物理吸附为主[18-19]。然而,颗粒吸附剂在模拟页岩气采出水中饱和的吸附容量(4.9 mg·g−1)比真实页岩气采出水的吸附容量(3.9 mg·g−1)高出25.6%,出现饱和容量吸附点的时间从15 h缩短到6 h,可能的原因是实际页岩气采出水中存在的溶解性有机物会抑制Li+的插层行为。
不同区域的页岩气采出水水质情况差异大,吸附剂的适应性考察是推广应用的必要条件。表2为4种不同页岩气采出水的水质参数和颗粒吸附剂的吸附与解吸情况。解吸液为2倍颗粒吸附剂体积的纯水,在摇床中以100 r·min−1条件下解吸20 min。随着页岩气采出水中TDS值和Li+的质量浓度的增加,颗粒的吸附容量从3.0 mg·g−1逐渐增加到6.9 mg·g−1,解吸液中Li+的质量浓度从3.8 mg·L−1增加到48.2 mg·L−1,解吸液的TDS值由1.7 g·L−1增加到33.58 g·L−1。显然,页岩气采出水中Li+的质量浓度越高,颗粒吸附剂接触Li+的机会越大,其吸附容量越大,解吸液中Li+的质量浓度越高;同时,TDS越高,高渗透压也会加速Li+的吸附行为。以上实验结果表明颗粒吸附剂在页岩气采出水中适应性较强。
-
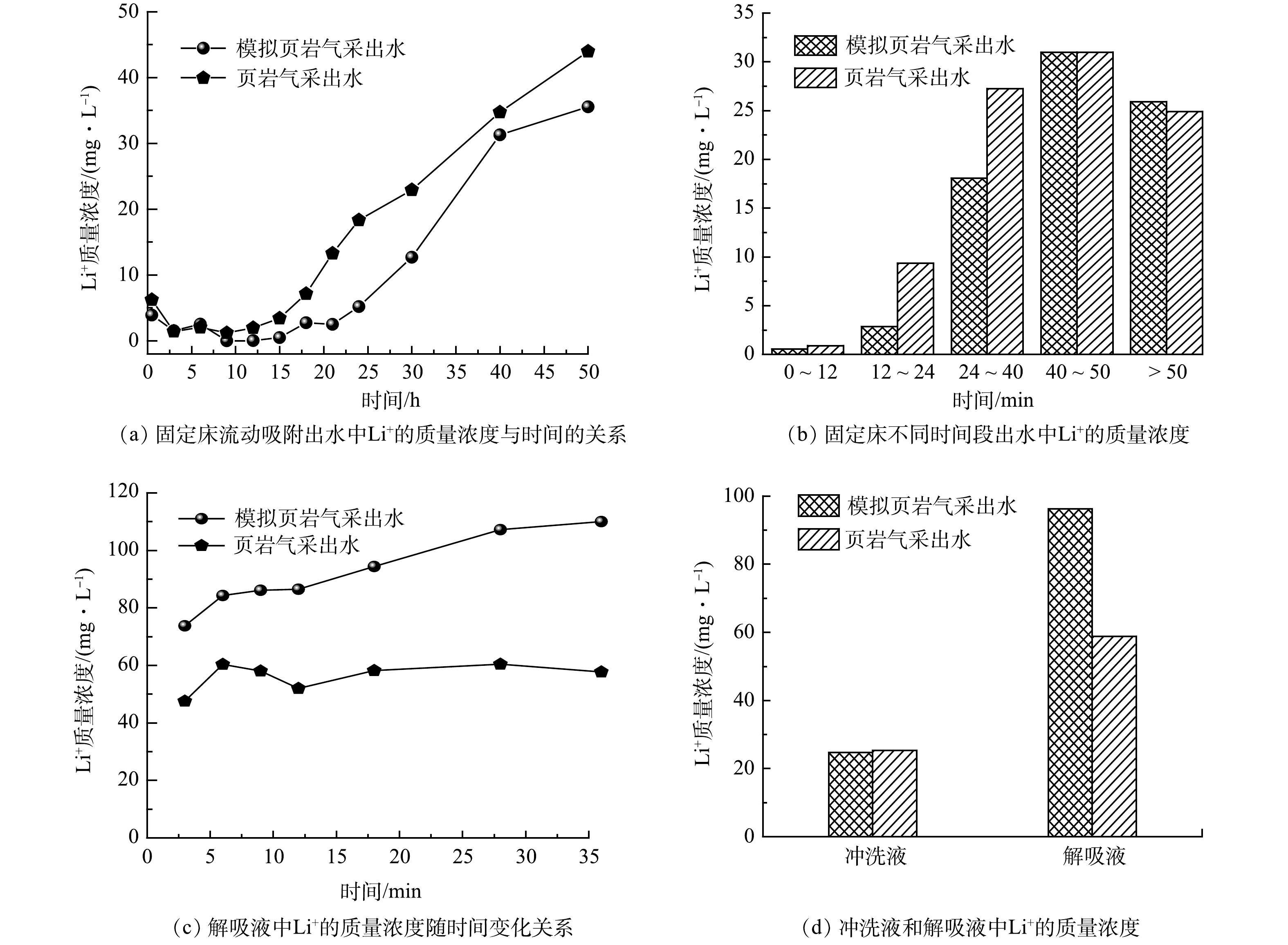
颗粒吸附剂对实际和模拟页岩气采出水的固定床动态吸附过程如图6(a)所示。在实际页岩气采出水中,固定床持续吸附12 h时,出水中Li+的质量浓度达到了2.0 mg·L−1,回收率达到93.5%,之后随着时间延长其浓度值呈现陡然上升趋势;然而,在模拟页岩气采出水中,固定床持续吸附15 h后,出水中Li+的质量浓度高于2.0 mg·L−1,之后随着吸附时间延长其浓度值呈现先缓慢增加(吸附时间为21 h)而后陡然增加的趋势。在模拟页岩气采出水中固定床出现穿透点的时间(40 h)比实际页岩气采出水(36 h)更长,且不同时间段出水溶液中Li+的质量浓度显著低于实际页岩气采出水(图6(b))。因此,可以推断当TDS和Li+的质量浓度相近时,页岩气采出水中的溶解性有机物会抑制颗粒吸附剂展现更好的吸附行为。此外,在流动吸附前40 h的出水中检测到实际页岩气采出水中Li+的质量浓度高于模拟页岩气采出水组,进一步说明颗粒吸附剂被限制释放部分吸附性能。
此外,观察到颗粒吸附剂的脱附和再吸附行为。当吸附时间超过40 h时,固定床出水中Li+的质量浓度高于原水浓度,说明存在吸附剂的脱附行为;当吸附时间超过50 h后,固定床出水中Li+的质量浓度值低于原水浓度,说明又发生了吸附剂的再吸附行为。这是由铝基吸附剂特殊结构决定的[14-20]。
图6(c)为解吸液中Li+的质量浓度值随时间变化情况。可见,随着解吸时间的延长,模拟页岩气采出水组解吸液中Li+的质量浓度值是实际页岩气采出水的1.6倍,最高可达110.0 mg·L−1;同时,最终解吸液中平均Li+的质量浓度值(96.2 mg·L−1)比实际页岩气采出水组高了37.4 mg·L−1,见图6(d)。该结果说明页岩气采出水中溶解性有机物也会影响颗粒吸附剂的解吸过程。
-
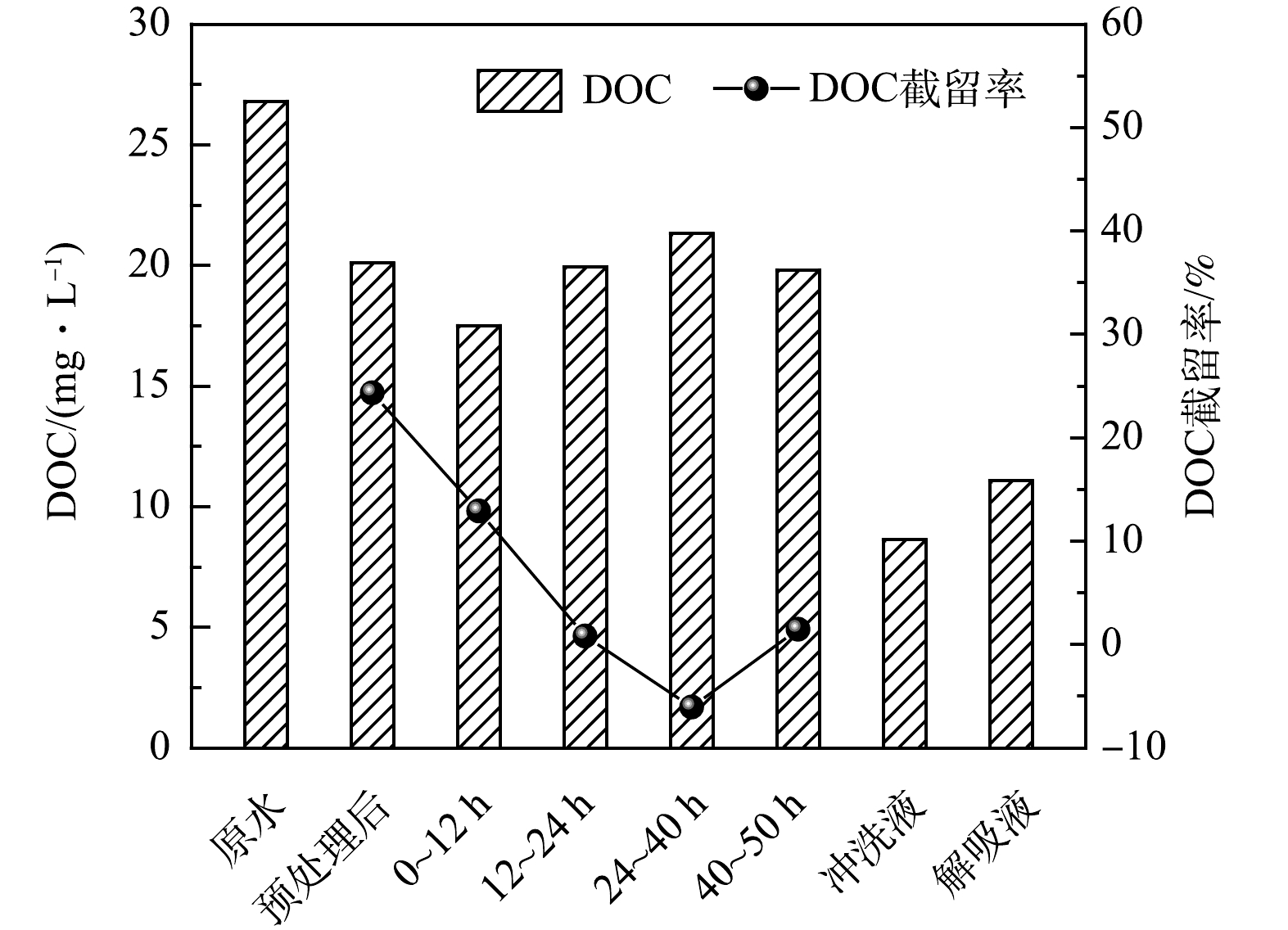
固定床不同处理阶段实际页岩气采出水中的溶解性有机物浓度变化如图7所示。混凝-膜滤组合工艺对溶解性有机物的去除率为24.3%。在0~12 h,固定床吸收的溶解性有机物含量为12.9%,之后随着流动吸附时间的延长,进水/出水的有机物浓度逐渐达到平衡,然而在24~40 h时间段的出水中有机物却比原水高了6.0%,表明颗粒出现了有机物的洗脱现象。冲洗液和解吸液中的有机物质量浓度分别为8.6 mg·L−1和11.1 mg·L−1,进一步证明了颗粒所吸附的有机物容易被水洗脱。
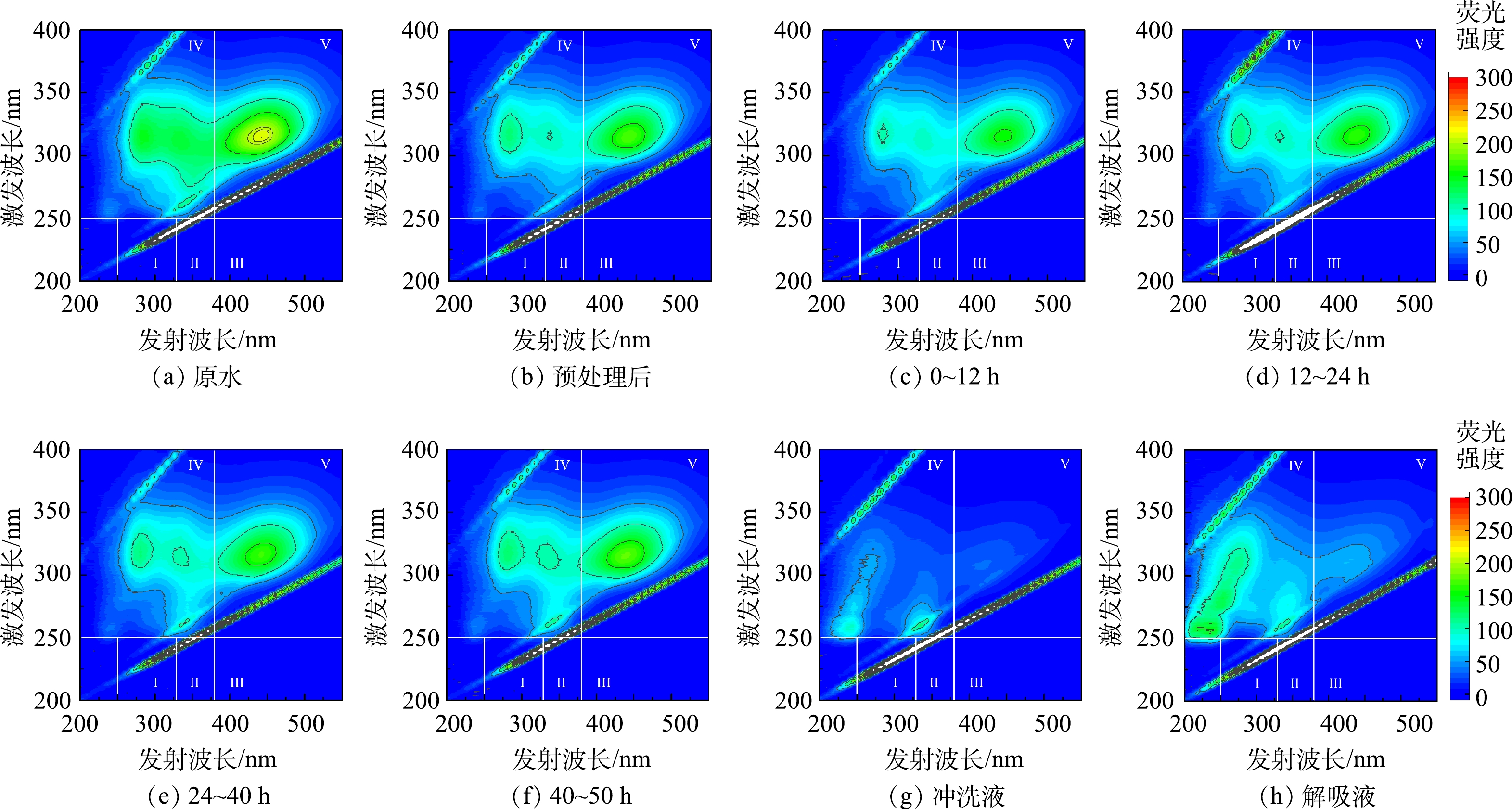
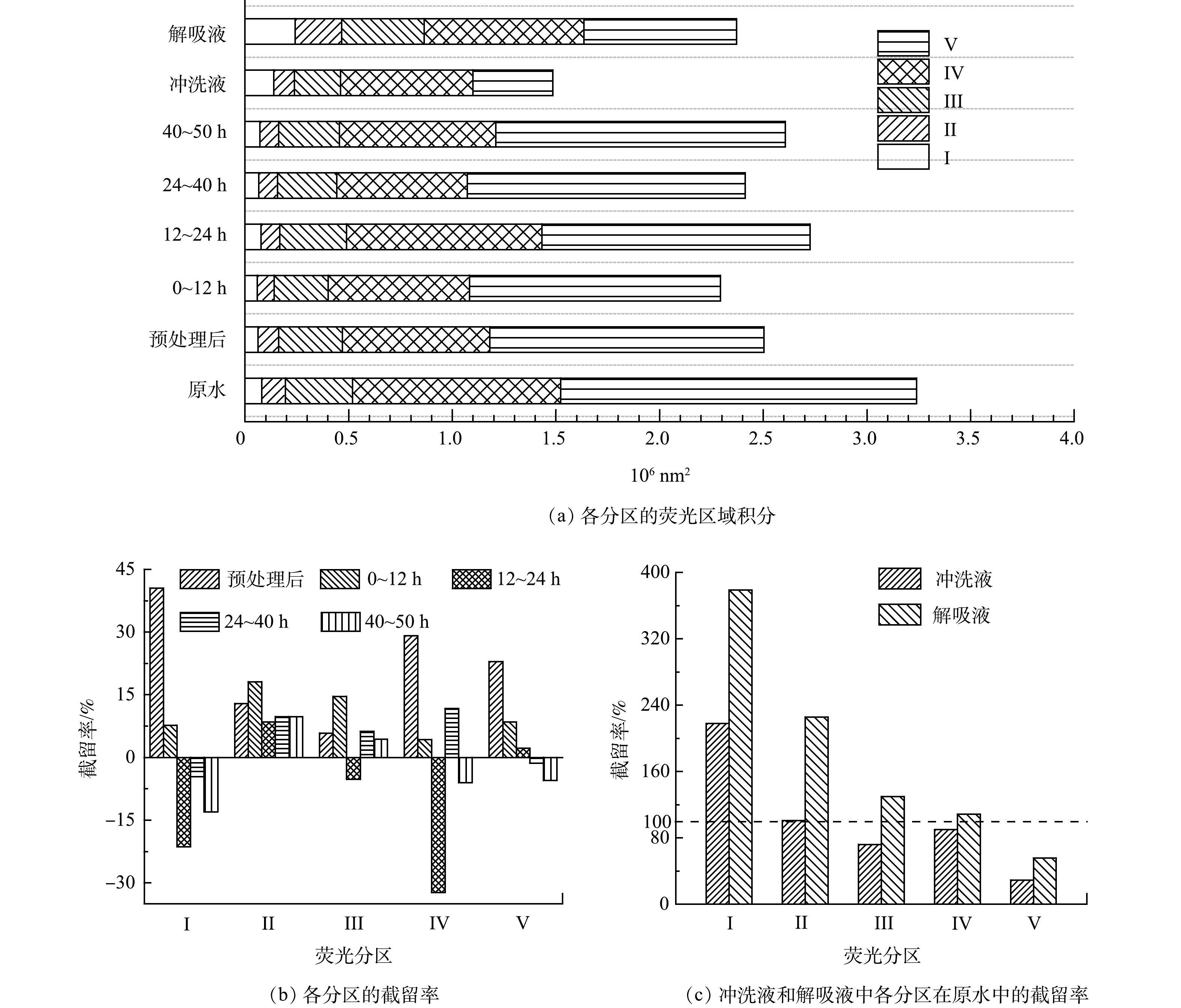
不同时段固定床出水中荧光响应有机物的三维荧光光谱如图8所示。首先,荧光谱图被分为芳香蛋白酪氨酸物质(I区)、芳香蛋白色氨酸物质(II区)、黄腐殖酸样(III区)、溶解性微生物副产物(IV区)和腐殖酸样(V区)共计5个区[21-22],各分区的荧光区域积分和截留率如图9所示。由图9(a)中可以看出,页岩气采出水中溶解性微生物副产物和腐殖酸样2种有机物含量远大于黄腐殖酸、芳香蛋白色氨酸和芳香蛋白酪氨酸的含量。预处理工艺(混凝-膜滤)对芳香蛋白酪氨酸物质、溶解性微生物副产物和腐殖酸3种类型有机物的去除率超过了20%,对芳香蛋白色氨酸物质和黄腐殖酸的去除率分别为12.9%和5.8%,表明预处理工艺对所有有机物均有部分去除效果,见图9(b)。
在流动吸附前12 h的过程中,颗粒吸附剂对5种有机物均有吸附,其截留值为正;并随着吸附时间延长会释放部分有机物,其I、III、IV和V区有机物的截留率为负,特别是12~24 h内固定床大量释放芳香蛋白酪氨酸、溶解性微生物副产物和黄腐殖酸物质。在24~40 h内固定床出现了重新吸附溶解性微生物副产物的现象,其次是吸附了黄腐殖酸物质,并开始释放腐殖酸物质;40~50 h内的出水中腐殖酸物质释放最多,超过原水含量。可以推断,固定床中颗粒吸附剂对有机物的吸附饱和容易顺序依次为芳香蛋白络氨酸、溶解性微生物副产物、黄腐殖酸、腐殖酸和芳香蛋白色氨酸。
由图9(a)和图(c)可看出,与固定床进水水样的成分相比,冲洗液和解吸液中芳香蛋白络氨酸物质和芳香蛋白色氨酸物质两种有机物的含量均远超过原水,解吸液中黄腐殖酸和微生物副产物物质的含量也超过了原水中黄腐殖酸物质和腐殖酸物质,说明这两类有机物被吸附,该结果表明颗粒吸附剂吸附积累蛋白类有机物能力比腐殖酸物质强。由图8(h)可见,解吸液中微生物副产物物质的荧光响应值更高证明了颗粒吸附剂解吸的蛋白类有机物量更多。
-
1)铝基颗粒吸附剂在页岩气采出水中对Li+的吸附行为符合准一级吸附动力学模型,成功从不同页岩气采出水水质中提取Li+资源。
2)固定床流动吸附实验,前12 h出水中Li+回收率为93.5%,模拟页岩气采出水组解吸液中Li+的质量浓度为96.2 mg·L−1,实际页岩气采出水组解吸液中Li+的质量浓度为58.8 mg·L−1
3)页岩气采出水中溶解性有机物会显著影响铝基吸附剂展现更好的吸附和解吸行为。
铝基吸附剂对页岩气采出水中Li+的吸附性能
Adsorption performance of aluminum-based adsorbent towards Li+ in shale gas produced water
-
摘要: 从页岩气采出水中有效回收锂(Li+)资源可实现降本增效的目的。本研究利用化学沉淀法和沉析法分别制备了铝基吸附剂粉体和颗粒,研究了吸附剂材料对页岩气采出水中Li+的吸附行为,剖析了页岩气采出水中溶解性有机物对吸附剂吸附行为的影响。结果表明,粉体吸附剂的饱和吸附容量达到7.0 mg·g−1,颗粒吸附剂的饱和吸附容量为3.8 mg·g−1,其吸附动力学符合准一级吸附动力学模型,对不同水质的页岩气采出水均有吸附效果;然而,颗粒吸附剂在不含溶解性有机物的模拟页岩气采出水中的饱和吸附容量为5.0 mg·g−1。在固定床吸附实验中,颗粒吸附剂能回收废水中93.5%的Li+,但是模拟页岩气采出水组的解吸液中Li+的质量浓度为96.2 mg·L−1高于实际页岩气采出水组(58.8 mg·L−1)。因此,实际页岩气采出水中的有机物会严重抑制铝基吸附剂的吸附和解吸行为。Abstract: Effective recovery of lithium (Li+) resources from shale gas produced water (SGW) may achieve the goals of saving costs and increasing benefits. In this study, an aluminum-based adsorbent powders and particulates were prepared by chemical deposition method and precipitation method, respectively. The adsorption behaviors of the adsorption material to Li+ in SGW were investigated, and the effects of dissolved organic substances in SGW on the adsorption behaviors of the adsorption material were analyzed. The results showed that the saturated adsorption capacity of the adsorbent powder reached 7.0 mg·g−1, and the saturated adsorption capacity of the adsorbent particulate was 3.8 mg·g−1, and its adsorption kinetics conformed to the quasi-primary adsorption kinetic model. It also had the adsorption capacity for SGW with different water qualities. However, the saturated adsorption capacity of the adsorbent particulate in the simulated SGW without dissolved organic matter was 5.0 mg·g−1. In the fixed-bed flow adsorption experiments, the adsorbent particulate was able to recover 93.5% of the Li+ in the SGW; however, but the Li+ concentration in the desorbed solution of the simulated shale gas wastewater group was 96.2 mg·L−1, which was higher than that of the actual SGW group(58.8 mg·L−1). Therefore, the organic matter in the shale gas wastewater can severely inhibit the adsorption and desorption behaviors of the aluminum-based adsorbent.
-
Key words:
- shale gas produced water /
- aluminum-based adsorbent /
- adsorption capacity /
- organic /
- Li+ adsorption
-
四川盆地及其周缘油气田开采产出的卤水资源非常丰富[1],尤其是非常规天然气——页岩气逐渐成为我国主要的新型能源资源。目前,我国页岩气可开采资源总量达到12.85万×109 m3,2022年全年开采总量为238×109 m3[2]。在页岩气开采过程中,来自深地层水资源、人工注入的淡水和合成化学物质组成的大量混合液体会随着采气过程逐渐返排到地面,其成分具有高有机物含量、高浓度总溶解性固体和高悬浮物的特征,被统称为页岩气采出水[3]。此类废水中不仅含有钠、钾、镁、钡和钙等常规金属元素,还含有锂(Li+)、锶、镓和硼等具有回收价值高的金属元素[4],其中Li+质量浓度的中位数超过30 mg·L−1,且镁锂比<8[5-6]。相比于盐湖卤水的高镁锂比,页岩气采出水中镁锂比较低,锂资源开发价值潜力大。到2030年,四川每年页岩气采出水水量预计为5 000~5 500×104 m3,可开采锂资源量超过1 500 t[7]。在页岩气采出水深度处理过程中有效提取锂资源,可实现降本增效目的。
页岩气采出水与盐湖卤水的水质差异大,尤其是有机物含量高,并具有种类多但浓度低的特征[8-9],往往需要系列耦合工艺处理才能达到回用或外部排放的标准[10]。然而,耦合工艺的各工艺段会不可避免的损失部分Li+,导致出水中Li+的质量浓度值偏低。尽管某些耦合工艺中的浓缩液Li+的质量浓度较高,但溶解性有机物含量值和总盐度值远高于原水[11],可能使得Li+提取的经济效益难以平衡投资成本。适当的预处理工艺去除页岩气采出水中部分污染物同时保持Li+不损失,将有利于从此类卤水中最大限度提取锂资源。与膜分离法和电化学法提锂相比,吸附法是一种易操作、适应性强且高效率的方法,尤其是适用于低品位的卤水环境提取锂资源。本课题组前期开发的锰基炭气凝胶锂吸附剂材料成功从经过软化(碳酸钠沉淀-微滤膜)预处理后的页岩气采出水中原位选择性提取了Li+,但存在达到饱和吸附时间长和吸附剂材料制备工艺复杂的问题[12];同时,炭气凝胶的多孔结构容易吸附页岩气采出水中的溶解性有机物[13],不利于解吸液中Li+的进一步纯化,且溶解性有机物对吸附行为的影响不明确。铝基吸附剂材料已被证实在盐湖卤水中具有快速吸附性能,实现了Li+的快速获取[14-15],但像溶解性有机物含量高的页岩气采出水中的吸附能效研究甚少,且未见相关工艺路线报道。因此,探明铝基吸附剂在页岩气采出水中的吸附行为,了解溶解性有机物对Li+插层行为的影响,将有助于此类废水中锂资源工业化回收。
本研究通过沉淀法和沉析法分别制备铝基吸附剂粉体和颗粒,探讨从混凝-超滤膜耦合预处理后的页岩气采出水中回收锂资源的可行性。探究铝基吸附剂粉体和颗粒对页岩气采出水中Li+的吸附行为,并以不含溶解性有机物的模拟页岩气采出水作为对照组,探究了溶解性有机物对颗粒吸附剂吸附Li+行为的影响。本研究工作将为规模化从页岩气采出水中提取锂资源提供理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 原材料
无水氯化锂(分析纯,纯度 98%),氯化钾(分析纯,纯度 98%),六水氯化镁(分析纯,纯度 98%),六水氯化铝(分析纯,纯度 97%),氢氧化钠(分析纯,纯度 98%)和N,N-二甲基乙酰胺(分析纯,纯度 99%)均购买于成都科龙化工有限公司,聚氯乙烯购买于中国台湾塑料工业股份有限公司;氯化钠(分析纯,纯度 99%),二水氯化钙(分析纯,纯度 99%),二水氯化钡(分析纯,纯度 99%)和二水氯化锶(分析纯,纯度 99%)均购买于Sigma-Aldrich公司;聚偏氟乙烯超滤膜购买于深圳市立昇净水科技有限公司,聚合物氯化铝购买于自贡市利民化工厂。
1.2 页岩气采出水预处理
实际页岩气采出水取自重庆铜梁某基地,总溶解性固体(total dissolved solids, TDS)为42.0 g·L−1,Li+质量浓度为31.1 mg·L−1,溶解性有机碳(dissolved organic carbon, DOC)值为26.6 mg·L−1,浊度为113 NTU。
所有实际页岩气采出水在吸附前需经过混凝-超滤膜组合的预处理工艺,以便去除大颗粒物质和部分有机物。混凝过程:取聚合物氯化铝质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的页岩气采出水,用六联搅拌仪以200 r·min−1快速搅拌3 min,之后转速降为60 r·min−1并持续搅拌30 min,之后静置30 min,取上清液。超滤膜过滤过程:将混合后的上清液通过错流中空纤维超滤膜系统中过滤,并收集过滤液体,膜滤系统的回收率为95%,操作压力为0.1 MPa,过滤液作为吸附实验原液。经过一些列表征检测混凝-膜滤组合工艺处理后的水样,其TDS值为42.0 g·L−1,Li+质量浓度为31.1 mg·L−1,TOC值为20.1 mg·L−1,浊度为0.64 NTU。
1.3 铝基吸附剂的制备
粉体吸附剂的制备:将氯化铝和氯化锂按照一定摩尔比溶解在75 ℃ 大约200 mL的去离子水中,并恒温搅拌1 h;之后用5 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液进行滴定实验,混合溶液逐渐形成LiCl·mAl(OH)3·nH2O白色颗粒,直到混合溶液pH为6.5时立刻停止滴定强碱溶液;此时混合溶液呈现白色浑浊液体,再经过抽滤实现固液分离,固体在80 ℃鼓风干燥箱中干燥24 h,即可得到铝基吸附剂粉体。氯化铝和氯化锂的摩尔比分别为1.2:1、1.3:1、1.6:1和2.0:1。
颗粒吸附剂的制备:首先,将取铝基吸附剂粉体8份、聚氯乙烯7份和N,N-二甲基乙酰胺85份混合放于三口烧瓶中,在60 ℃恒温水浴锅中以一定转速持续搅拌8 h,最终得到白色混合溶液。利用聚氯乙烯不溶于水相的特征,采用沉析法获得包埋有铝基锂吸附粉体的白色球形颗粒,其直径约2.4 mm。
1.4 铝基吸附剂的表征和水质分析
X-射线衍射仪(丹东浩元仪器有限公司,DX-2700BH)被用于表征铝基吸附剂粉体的晶体结构,场发射扫描电子显微镜(日本Hitachi公司,Regulus
8230 )用于观察粉体和颗粒吸附剂的形貌,原子吸收仪(美国Perkin-Elmer公司,900T)被用于检测水样中Li+的质量浓度,离子色谱仪(美国赛默飞世尔科技公司,采用CS12A和AS11-HC色谱柱)被用于检测水样中各离子的种类和质量浓度,总有机碳仪(日本Shimadzu公司)被用于检测水样中DOC,三维荧光光度仪(日本Hitachi公司,F7100)被用于检测水样中溶解性有机物的种类及响应情况,便携式浊度仪(美国Hach公司,2100Q)被用于检测水样的浊度值,多功能水质检测仪(美国麦隆公司,Ultrameter II 6PFC)被用于检测水样中TDS。所有在表征前均用0.45 μm聚醚砜微滤膜(天津市津腾实验设备有限公司)过滤处理。1.5 吸附容量计算及吸附动力学分析
首先,称取一定量铝基吸附剂粉体或颗粒放入装有50 mL预处理后页岩气采出水的锥形瓶中,并将锥形瓶放于25 ℃恒温水浴摇床以150 r·min−1转速吸附一定时间。原子吸收仪用火焰法测定Li+的质量浓度值。铝基吸附剂粉体和颗粒的吸附容量根据式(1)进行计算,准一级和准二级吸附动力学模型如式(2)和(3)所示。
Q=(C0−Ct)Vm (1) ln(Qe−Qt)=lnQe−k1t (2) tQ=1k2Q2e+tQe (3) 式中:Q为吸附容量,mg·g−1;C0和Ct分别为吸附前和t时刻页岩气采出水中Li+的质量浓度,mg·L−1;V为页岩气采出水的体积,L;m为铝基吸附剂的重量,g;Qt为t时刻的吸附量,mg·g−1;Qe为平衡吸附容量,mg·g−1;k1和k2分别为准一级和准二级的反应速率常数, g·(mg·min)−1。注:铝基颗粒吸附剂的重量为等量球形颗粒在50 ℃环境下干燥24 h得到恒定重量值,其含水率约为79%。
1.6 固定床吸附实验
固定床吸附实验选用的吸附柱直径为1.5 cm,高度为30 cm,其有效床体积为30 cm3,空床体积为20 cm3,页岩气采出水进水速度为0.5 mL·min−1,流向为上向流。冲洗液(纯水)温度为5 ℃,流速为10 BV·h−1,水体积为2 BV;解吸液(纯水)温度为40 ℃,流速为3 BV·h−1,水体积为2 BV。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 吸附剂粉体的结构表征
铝基吸附剂粉体晶体结构的XRD谱图如图1所示,通过与LiCl·2Al(OH)3·xH2O的标准卡片对比,发现合成的4种粉体的主要衍射图谱与其匹配吻合,表明成功合成了锂铝插层氧化物粉体。
图2为不同Al3+与Li+比例合成的锂吸附剂粉体形态的SEM图。随着Al3+与Li+的比例从1.2:1增加到1.6:1,粉体吸附剂由片状结构堆积而成,说明成功合成了具有片状结构的铝基吸附剂粉体,与报道的文献结果相同[16]。
2.2 吸附剂粉体的吸附性能
图3为铝基吸附剂粉体的吸收时间对吸附性能的影响。吸附2 h后,吸附剂达到吸附平衡,饱和吸附容量均超过了7.0 mg·g−1,表明铝基粉体吸附剂结构中Al(OH)3结构间隙空位快速被页岩气采出水中Li+占据,证明铝基吸附剂在页岩气采出水中具有快速吸附Li+的优势[13]。Al3+与Li+的比例为1.2:1合成的铝基吸附剂粉体的吸附容量先达到9.5 mg·g−1,之后吸附容量随着摇床吸附时间的延长而缓慢降低到8.1 mg·g−1,说明Al3+与Li+的比例为1.2:1制备的吸附剂粉体的锂插层结构不稳定,可能是制备的纳米片层容易在动态吸附过程中发生自解吸行为。在吸附容量相近条件下,考虑吸附剂制备成本,后续选择Al3+与Li+的比例为1.3:1制备的吸附剂粉体作为制备颗粒吸附剂的原料。
2.3 颗粒吸附剂的形貌
图4(a)~(c)为Al3+与Li+比例为1.3:1所制备的铝基颗粒吸附剂的表面形貌、表面孔尺寸分布和断面形貌。可见,球形颗粒表面孔形态由典型的非溶剂致相转换法所形成的无规则多孔结构[17],其平均孔尺寸约为43 nm。球形颗粒的断面随机分布着多孔结构,孔尺寸由外向里逐渐变大,并存在皮层小孔结构,这样的多孔球形颗粒将有利于离子溶液快速渗透。图4(d)为颗粒断面的元素分布情况,可以看到铝基吸附剂粉体被聚氯乙烯粘合在颗粒的骨架上。
2.4 颗粒吸附剂的吸附性能
图5为铝基颗粒吸附剂分别在实际和模拟页岩气采出水中的吸附动力学。实际和模拟页岩气采出水的水质情况如表1所示。在2种水况条件下,颗粒吸附剂的吸附行为更符合准一级吸附动力学模型,实际页岩气采出水和模拟页岩气采出水的R2值分别为0.975 2和0.990 7,表明该吸附过程是以物理吸附为主[18-19]。然而,颗粒吸附剂在模拟页岩气采出水中饱和的吸附容量(4.9 mg·g−1)比真实页岩气采出水的吸附容量(3.9 mg·g−1)高出25.6%,出现饱和容量吸附点的时间从15 h缩短到6 h,可能的原因是实际页岩气采出水中存在的溶解性有机物会抑制Li+的插层行为。
表 1 实际页岩气采出水和模拟页岩气采出水中各离子浓度Table 1. Concentration of ions in actual shale gas wastewater and simulated shale gas wastewater水样 离子质量浓度/(mg·L−1) Na+ K+ Li+ Mg2+ Ca2+ Ba2+ Sr2+ Cl‒ Br‒ DOC 页岩气采出水 11 700.0 483.0 31.0 158.0 1 219.0 1 264.0 619.0 2 5847.8 365.2 26.6 模拟页岩气采出水 11 376.2 297.5 29.6 293.7 1 184.1 1 104.9 557.4 2 5305.0 0.0 0.0 不同区域的页岩气采出水水质情况差异大,吸附剂的适应性考察是推广应用的必要条件。表2为4种不同页岩气采出水的水质参数和颗粒吸附剂的吸附与解吸情况。解吸液为2倍颗粒吸附剂体积的纯水,在摇床中以100 r·min−1条件下解吸20 min。随着页岩气采出水中TDS值和Li+的质量浓度的增加,颗粒的吸附容量从3.0 mg·g−1逐渐增加到6.9 mg·g−1,解吸液中Li+的质量浓度从3.8 mg·L−1增加到48.2 mg·L−1,解吸液的TDS值由1.7 g·L−1增加到33.58 g·L−1。显然,页岩气采出水中Li+的质量浓度越高,颗粒吸附剂接触Li+的机会越大,其吸附容量越大,解吸液中Li+的质量浓度越高;同时,TDS越高,高渗透压也会加速Li+的吸附行为。以上实验结果表明颗粒吸附剂在页岩气采出水中适应性较强。
表 2 4种不同来源实际页岩气采出水的水质参数和颗粒吸附剂的吸附容量Table 2. Water quality of four different actual SGW and adsorption capacity of adsorbent particulates样品 TDS/( mg·L−1) 浊度/NTU Li+质量浓度/(mg·L−1) DOC/(mg·L−1) 吸附容量/(mg·g−1) 解吸液中Li+质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 解吸液中TDS/(mg·L−1) 威远 10 363.0 0.73 9.9 10.2 3.0 3.8 1 775.0 重庆 36 420.0 0.48 71.8 92.9 5.9 12.4 4 796.0 铜梁 42 020.0 0.64 31.3 20.1 3.9 11.8 6 853.0 某浓缩液 231 400.0 0.27 101.0 45.8 6.9 48.2 3 5580.0 2.5 颗粒吸附剂的固定床吸附性能
颗粒吸附剂对实际和模拟页岩气采出水的固定床动态吸附过程如图6(a)所示。在实际页岩气采出水中,固定床持续吸附12 h时,出水中Li+的质量浓度达到了2.0 mg·L−1,回收率达到93.5%,之后随着时间延长其浓度值呈现陡然上升趋势;然而,在模拟页岩气采出水中,固定床持续吸附15 h后,出水中Li+的质量浓度高于2.0 mg·L−1,之后随着吸附时间延长其浓度值呈现先缓慢增加(吸附时间为21 h)而后陡然增加的趋势。在模拟页岩气采出水中固定床出现穿透点的时间(40 h)比实际页岩气采出水(36 h)更长,且不同时间段出水溶液中Li+的质量浓度显著低于实际页岩气采出水(图6(b))。因此,可以推断当TDS和Li+的质量浓度相近时,页岩气采出水中的溶解性有机物会抑制颗粒吸附剂展现更好的吸附行为。此外,在流动吸附前40 h的出水中检测到实际页岩气采出水中Li+的质量浓度高于模拟页岩气采出水组,进一步说明颗粒吸附剂被限制释放部分吸附性能。
此外,观察到颗粒吸附剂的脱附和再吸附行为。当吸附时间超过40 h时,固定床出水中Li+的质量浓度高于原水浓度,说明存在吸附剂的脱附行为;当吸附时间超过50 h后,固定床出水中Li+的质量浓度值低于原水浓度,说明又发生了吸附剂的再吸附行为。这是由铝基吸附剂特殊结构决定的[14-20]。
图6(c)为解吸液中Li+的质量浓度值随时间变化情况。可见,随着解吸时间的延长,模拟页岩气采出水组解吸液中Li+的质量浓度值是实际页岩气采出水的1.6倍,最高可达110.0 mg·L−1;同时,最终解吸液中平均Li+的质量浓度值(96.2 mg·L−1)比实际页岩气采出水组高了37.4 mg·L−1,见图6(d)。该结果说明页岩气采出水中溶解性有机物也会影响颗粒吸附剂的解吸过程。
2.6 页岩气采出水中溶解性有机物对铝基颗粒吸附剂吸附过程的影响
固定床不同处理阶段实际页岩气采出水中的溶解性有机物浓度变化如图7所示。混凝-膜滤组合工艺对溶解性有机物的去除率为24.3%。在0~12 h,固定床吸收的溶解性有机物含量为12.9%,之后随着流动吸附时间的延长,进水/出水的有机物浓度逐渐达到平衡,然而在24~40 h时间段的出水中有机物却比原水高了6.0%,表明颗粒出现了有机物的洗脱现象。冲洗液和解吸液中的有机物质量浓度分别为8.6 mg·L−1和11.1 mg·L−1,进一步证明了颗粒所吸附的有机物容易被水洗脱。
不同时段固定床出水中荧光响应有机物的三维荧光光谱如图8所示。首先,荧光谱图被分为芳香蛋白酪氨酸物质(I区)、芳香蛋白色氨酸物质(II区)、黄腐殖酸样(III区)、溶解性微生物副产物(IV区)和腐殖酸样(V区)共计5个区[21-22],各分区的荧光区域积分和截留率如图9所示。由图9(a)中可以看出,页岩气采出水中溶解性微生物副产物和腐殖酸样2种有机物含量远大于黄腐殖酸、芳香蛋白色氨酸和芳香蛋白酪氨酸的含量。预处理工艺(混凝-膜滤)对芳香蛋白酪氨酸物质、溶解性微生物副产物和腐殖酸3种类型有机物的去除率超过了20%,对芳香蛋白色氨酸物质和黄腐殖酸的去除率分别为12.9%和5.8%,表明预处理工艺对所有有机物均有部分去除效果,见图9(b)。
在流动吸附前12 h的过程中,颗粒吸附剂对5种有机物均有吸附,其截留值为正;并随着吸附时间延长会释放部分有机物,其I、III、IV和V区有机物的截留率为负,特别是12~24 h内固定床大量释放芳香蛋白酪氨酸、溶解性微生物副产物和黄腐殖酸物质。在24~40 h内固定床出现了重新吸附溶解性微生物副产物的现象,其次是吸附了黄腐殖酸物质,并开始释放腐殖酸物质;40~50 h内的出水中腐殖酸物质释放最多,超过原水含量。可以推断,固定床中颗粒吸附剂对有机物的吸附饱和容易顺序依次为芳香蛋白络氨酸、溶解性微生物副产物、黄腐殖酸、腐殖酸和芳香蛋白色氨酸。
由图9(a)和图(c)可看出,与固定床进水水样的成分相比,冲洗液和解吸液中芳香蛋白络氨酸物质和芳香蛋白色氨酸物质两种有机物的含量均远超过原水,解吸液中黄腐殖酸和微生物副产物物质的含量也超过了原水中黄腐殖酸物质和腐殖酸物质,说明这两类有机物被吸附,该结果表明颗粒吸附剂吸附积累蛋白类有机物能力比腐殖酸物质强。由图8(h)可见,解吸液中微生物副产物物质的荧光响应值更高证明了颗粒吸附剂解吸的蛋白类有机物量更多。
3. 结论
1)铝基颗粒吸附剂在页岩气采出水中对Li+的吸附行为符合准一级吸附动力学模型,成功从不同页岩气采出水水质中提取Li+资源。
2)固定床流动吸附实验,前12 h出水中Li+回收率为93.5%,模拟页岩气采出水组解吸液中Li+的质量浓度为96.2 mg·L−1,实际页岩气采出水组解吸液中Li+的质量浓度为58.8 mg·L−1
3)页岩气采出水中溶解性有机物会显著影响铝基吸附剂展现更好的吸附和解吸行为。
-
表 1 实际页岩气采出水和模拟页岩气采出水中各离子浓度
Table 1. Concentration of ions in actual shale gas wastewater and simulated shale gas wastewater
水样 离子质量浓度/(mg·L−1) Na+ K+ Li+ Mg2+ Ca2+ Ba2+ Sr2+ Cl‒ Br‒ DOC 页岩气采出水 11 700.0 483.0 31.0 158.0 1 219.0 1 264.0 619.0 2 5847.8 365.2 26.6 模拟页岩气采出水 11 376.2 297.5 29.6 293.7 1 184.1 1 104.9 557.4 2 5305.0 0.0 0.0 表 2 4种不同来源实际页岩气采出水的水质参数和颗粒吸附剂的吸附容量
Table 2. Water quality of four different actual SGW and adsorption capacity of adsorbent particulates
样品 TDS/( mg·L−1) 浊度/NTU Li+质量浓度/(mg·L−1) DOC/(mg·L−1) 吸附容量/(mg·g−1) 解吸液中Li+质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 解吸液中TDS/(mg·L−1) 威远 10 363.0 0.73 9.9 10.2 3.0 3.8 1 775.0 重庆 36 420.0 0.48 71.8 92.9 5.9 12.4 4 796.0 铜梁 42 020.0 0.64 31.3 20.1 3.9 11.8 6 853.0 某浓缩液 231 400.0 0.27 101.0 45.8 6.9 48.2 3 5580.0 -
[1] 张莉. 四川盆地典型富有机质页岩孔隙结构特征[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2021. [2] 马新华, 张晓伟, 熊伟, 等. 中国页岩气发展前景及挑战[J]. 石油科学通报, 2023, 8(4): 491-501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1693.2023.04.037 [3] CHANG H Q, LIU B C, WANG H Z, et al. Evaluating the performance of gravity-driven membrane filtration as desalination pretreatment of shale gas flowback and produced water[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 587: 117187. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117187 [4] XIE W C, TIAN L, TANG P, et al. Shale gas wastewater characterization: Comprehensive detection, evaluation of valuable metals, and environmental risks of heavy metals and radionuclides[J]. Water Research, 2022, 220: 118707. [5] 陈立, 胡永碧, 刘友权. 四川盆地含锂气田水资源调查分析[C]. 南宁: 第33届全国天然气学术年会论文集, 2023. [6] TIAN L, LIU Y H, TANG P, et al. Lithium extraction from shale gas flowback and produced water using H1.33Mn1.67O4 adsorbent[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 185: 106476. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106476 [7] 桑世华, 胡春桃, 岑雨秋, 等. 川南页岩气采出水伴生锂资源评价与开发利用前景[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 2023, 52(3): 41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3426.2023.03.007 [8] 卢培利, 邱哲, 张代钧, 等. 页岩气开采返排废水有机污染物研究进展与展望[J]. 化工进展, 2018, 37(3): 1161-1166. [9] JI X Y, TIRAFERRI A, ZHANG X F, et al. Dissolved organic matter in complex shale gas wastewater analyzed with ESI FT-ICR MS: Typical characteristics and potential of biological treatment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 447: 130823. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.130823 [10] 纪轩宇, 胡敏莉, 刘百仓. 磁分离-精细过滤-超滤-碟管式反渗透耦合工艺高效回用页岩气压裂返排液[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(9): 2928-2936. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202305028 [11] ZHAO P B, YAO B W, MENG J Q, et al. Studies on the fouling behavior and cleaning method of pervaporation desalination membranes for reclamation of reverse osmosis concentrated water[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 274: 119034. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119034 [12] TIAN L, YANG Y S, CHEN G J, et al. Efficient lithium extraction from shale gas wastewater using sodium alginate/H1.33Mn1.67O4 composite granular adsorbents[J]. ACS EST Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 1676-1685. [13] LIU Y H, TANG P, ZHU Y M, et al. Green aerogel adsorbent for removal of organic compounds in shale gas wastewater: High-performance tuning and adsorption mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 416: 129100. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129100 [14] 程鹏高, 黄传峰, 甘善甜, 等. 铝基锂吸附剂制备及其在泰和地下卤水提锂中的应用[J]. 无机盐工业, 2021, 53(6): 140-144. [15] 张瑞, 钟静, 林森, 等. 盐湖铝系提锂吸附剂成型条件的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 6291-6297. doi: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211079 [16] ZHONG J, LIN S, YU J G. Effects of excessive lithium deintercalation on Li+ adsorption performance and structural stability of lithium/aluminum layered double hydroxides[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 572: 107-113. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.081 [17] MOHAMMADIPOUR E, NABIAN N, DELAVAR M. Novel PVC-melamine mixed matrix membranes for the sirius red removal from aqueous solutions: Experimental study and RSM modeling[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 47: 102752. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102752 [18] 李坤权, 王艳锦, 杨美蓉, 等. 多胺功能化介孔碳对Pb(II)的吸附动力学与机制[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(8): 3198-3205. [19] 王岩, 周佳文, 孙培亮, 等. 磁性聚氨基噻唑吸附剂脱除水体Hg2+性能[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240134. [20] 钟静, 陆旗玮, 林森, 等. 锂铝层状吸附剂超低品位卤水提锂冲洗和解吸过程[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(8): 4638-4646. [21] LI W, LI X, HAN C X, et al. A new view into three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy for dissolved organic matter[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 855: 158963. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158963 [22] CHEN W, WESTERHOFF P, LEENHEER J A, et al. Fluorescence excitation emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(24): 5701-5710. -




 下载:
下载: