-
传统城镇污水厂在污水处理过程中会消耗大量电能和药剂,导致处理成本增加。同步硝化反硝化(simultaneous nitrification and denitrification,SND)在同一个反应池内实现硝化和反硝化,可显著缩短反应时间、降低曝气能耗。SND在各种结构的处理工艺中均可实现,其反应机理包括:利用活性污泥絮体内部缺氧环境、利用生物膜[1-3]或颗粒污泥[4-6]内缺氧环境,或者利用异养硝化-好氧反硝化菌(heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification,HD-AN)[7-8]等。
实现SND的关键在于通过控制DO创造合适的微氧或缺氧环境,同时提供充足的碳源。其控制策略包括:将好氧池DO控制在较低水平(一般为0.3~1.0 mg·L−1)[9-10],或者间歇曝气[11],缩短好氧水力停留时间(hydrolic retention time,HRT)[12],以及分段进水等。利用聚磷菌(phosphate accumulating organisms,PAOs)和聚糖菌(glycogen accumulating organisms,GAOs)等菌种储存聚羟基链烷酸(poly-hydroxyalkanoates,PHAs)的特性,可实现内碳源反硝化;通过延长厌氧HRT、缩短好氧HRT,可以强化厌氧阶段PHAs的合成,改善好氧阶段SND效果[11-12]。SND工艺可与多种工艺进行优化组合。比如,SND可与短程硝化工艺组合,实现同步短程硝化-反硝化[6, 11, 13-14]。SND也可与强化生物除磷工艺(enhanced biological phosphorus removal,EBPR)结合,实现同步硝化反硝化除磷(simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal process,SNDPR)[5-6, 9-13]。但现有研究大多基于序批式反应器(sequencing batch reactor,SBR),对于连续流工艺的SND强化策略和最佳工艺参数等方面研究较少,缺乏相关工艺优化和运行经验。
本研究通过对A2O-MBR工艺进行改造建立梯度曝气A2O2-MBR工艺,设置单独的低氧池和好氧池,进行分级梯度曝气,通过逐步降低DO浓度强化SND效果,考察了对低C/N比污水的处理效果,在改善TN去除效果的同时降低曝气能耗,为污水厂提质增效提供技术参考。
-
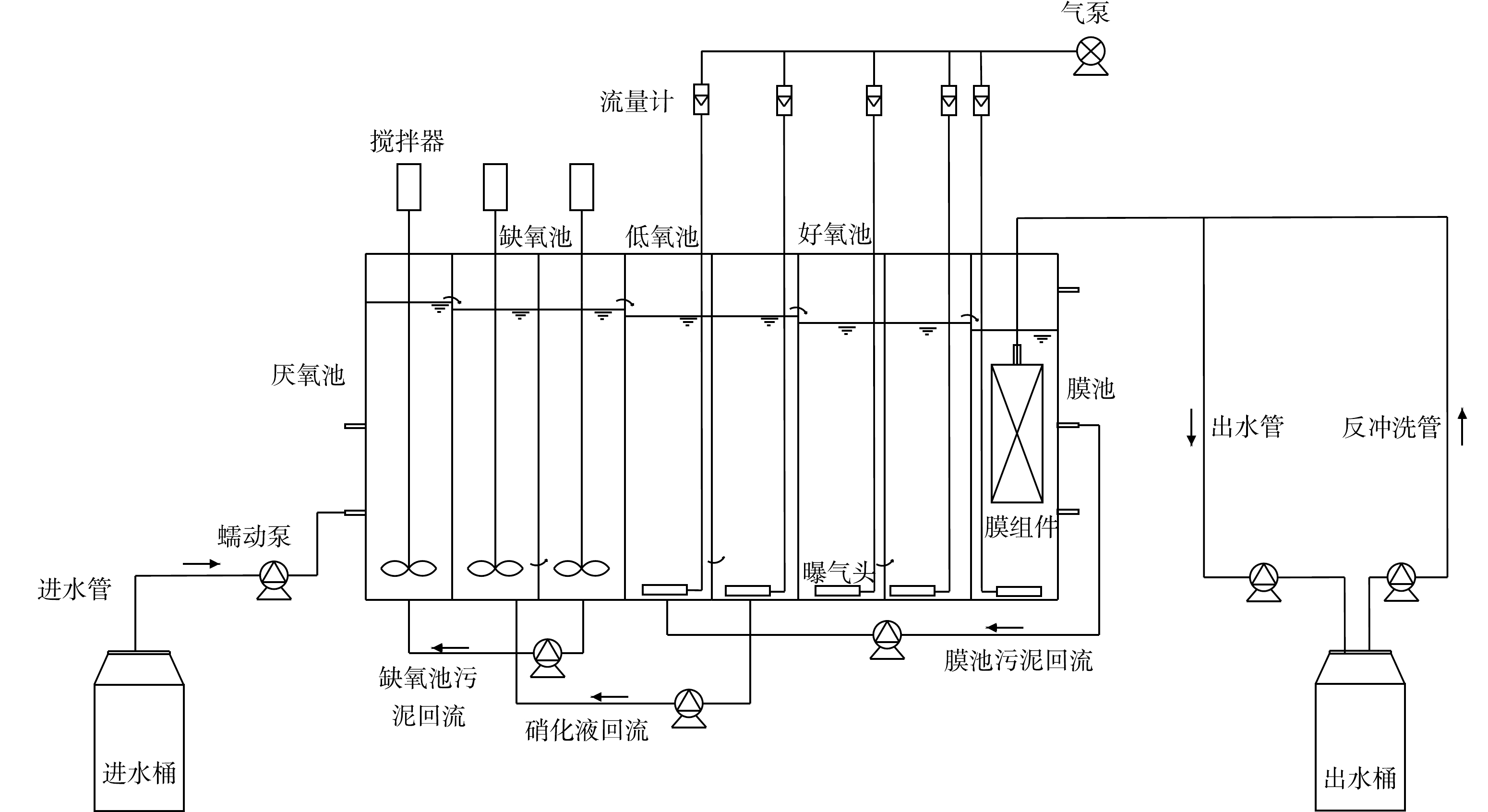
A2O2-MBR工艺装置如图1所示,反应器为折流式,共分为8格,包括厌氧池、缺氧池、低氧池(O1池)、好氧池(O2池)和膜池,体积比为1:2:2:2:1,生化池总有效体积50 L。厌氧池、缺氧池和低氧池安装了机械搅拌器。气泵通过曝气头为低氧池、好氧池和膜池曝气,由气体流量计控制曝气量。膜池安装了聚偏氟乙烯(polyvinylidene fluoride,PVDF)中空纤维膜组件,膜孔径0.1 μm,有效过滤面积0.3 m2,设计流量5 L·h−1。采用间歇负压出水方式,出水5 min,反冲洗1 min。系统HRT控制在12 h,泥龄(sludge retention time, SRT)为50 d。膜池混合液回流至低氧池第一格,回流比200%;低氧池第2格混合液回流至缺氧池,回流比200%;缺氧池合液回流至厌氧池,回流比100%。水温为25~31 oC。
-
进水采用模拟生活污水,根据实验需要投加CH3COONa、NH4Cl和KH2PO4,使进水NH4+-N质量浓度为50 mg·L−1,PO43--P质量浓度为5 mg·L−1;进水耗氧有机污染物的浓度(以COD计)最初为300 mg·L−1,之后逐步降低至250 mg·L−1和200 mg·L−1。其他组分包括:90 mg·L−1 MgSO4 7H2O,10 mg·L−1 CaCl2,1 mL·L−1微量元素。进水pH在7.5左右。本研究在前期研究基础上进行[15-16],污泥为前期培养的污泥,前期实验接种污泥为广州市猎德污水厂好氧池污泥。
-
A2O2-MBR工艺连续运行1 a以上。启动阶段进水COD值为300 mg·L−1,进水C/N为6.0;在TN去除效果有所改善后,将进水COD值逐步降至250 mg·L−1和200 mg·L−1,进水C/N比降至5.0和4.0,考察对低C/N比污水的处理效果。单个低氧池曝气量从400 mL·min−1逐步降至80 mL·min−1,低氧池DO质量浓度由3 mg·L−1逐步降至0.6 mg·L−1左右;单个好氧池曝气量从640 mL·min−1逐步降至500 mL·min−1,好氧池DO质量浓度由4 mg·L−1逐步降至1.7 mg·L−1左右,考察低DO条件对SND效果的强化作用。厌氧池DO质量浓度0.3~0.4 mg·L−1,缺氧池DO质量浓度0.4~0.5 mg·L−1。各阶段工艺参数如表1所示。
-
每天取进水和出水水样,一周左右取一次各池体样品,经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后测定COD、NH4+-N、NO2−-N、NO3−-N等指标,分析方法参见《水和废水监测分析方法(第四版)》。TN为NH4+-N、NO2−-N、NO3−-N总和。
-
选取接种污泥和工艺运行不同阶段的6个样品(表2),委托百迈克生物科技有限公司,开展微生物高通量测序分析。采用TGuide S96 Magnetic Soil/Stool DNA试剂盒,提取高质量的细菌16S rRNA基因序列,以分析污泥中微生物群落结构变化;同时提取氨氧化菌(AOB)功能基因amoA、反硝化菌功能基因nirS和narG,分析硝化和反硝化功能菌组成和变化情况。通过Illumina NovaSeq 6000测序平台,利用双末端测序(Paired-End)的方法,构建小片段文库进行测序。通过对Reads拼接过滤,聚类或去噪,利用QIIME2软件进行物种注释及丰度分析。
-
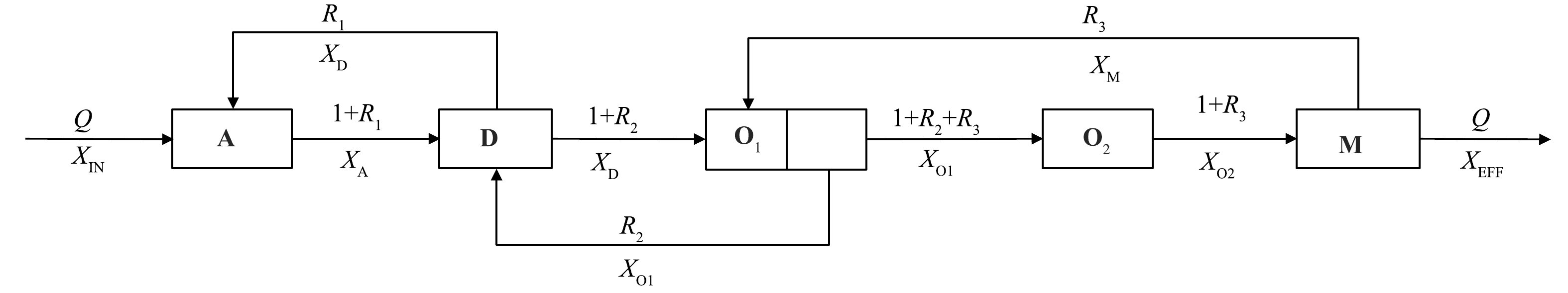
为了分析A2O2-MBR工艺各处理单元对TN去除的贡献情况,建立物质平衡模型(图2)。各单元TN去除量根据式(1)~式(4)计算,COD去除量的公式与之类似。
式中:RTN,A、RTN,D、RTN,O、RTN,M为厌氧池、缺氧池、好氧池、膜池的TN去除量,g·d−1;XIN、XA、XD、XO1、XO2、XM、XEFF为进水、厌氧池、缺氧池、低氧池、好氧池、膜池和出水TN质量浓度,mg·L−1;Q为进水流量,L·d−1;R1、R2、R3为缺氧池到厌氧池、低氧池到缺氧池、膜池到低氧池的回流比。
忽略反应过程中微生物的同化作用和细胞死亡对NH4+-N含量的影响,SND率的计算公式如式(5)[17]所示。
式中:ESND为SND效率,%;CNOx,produced为系统曝气前后NOx−(NO2−-N+NO3−-N)的增加量,mg·L−1;CNH4,removal为系统曝气前后NH4+-N的减少量,mg·L−1。
-
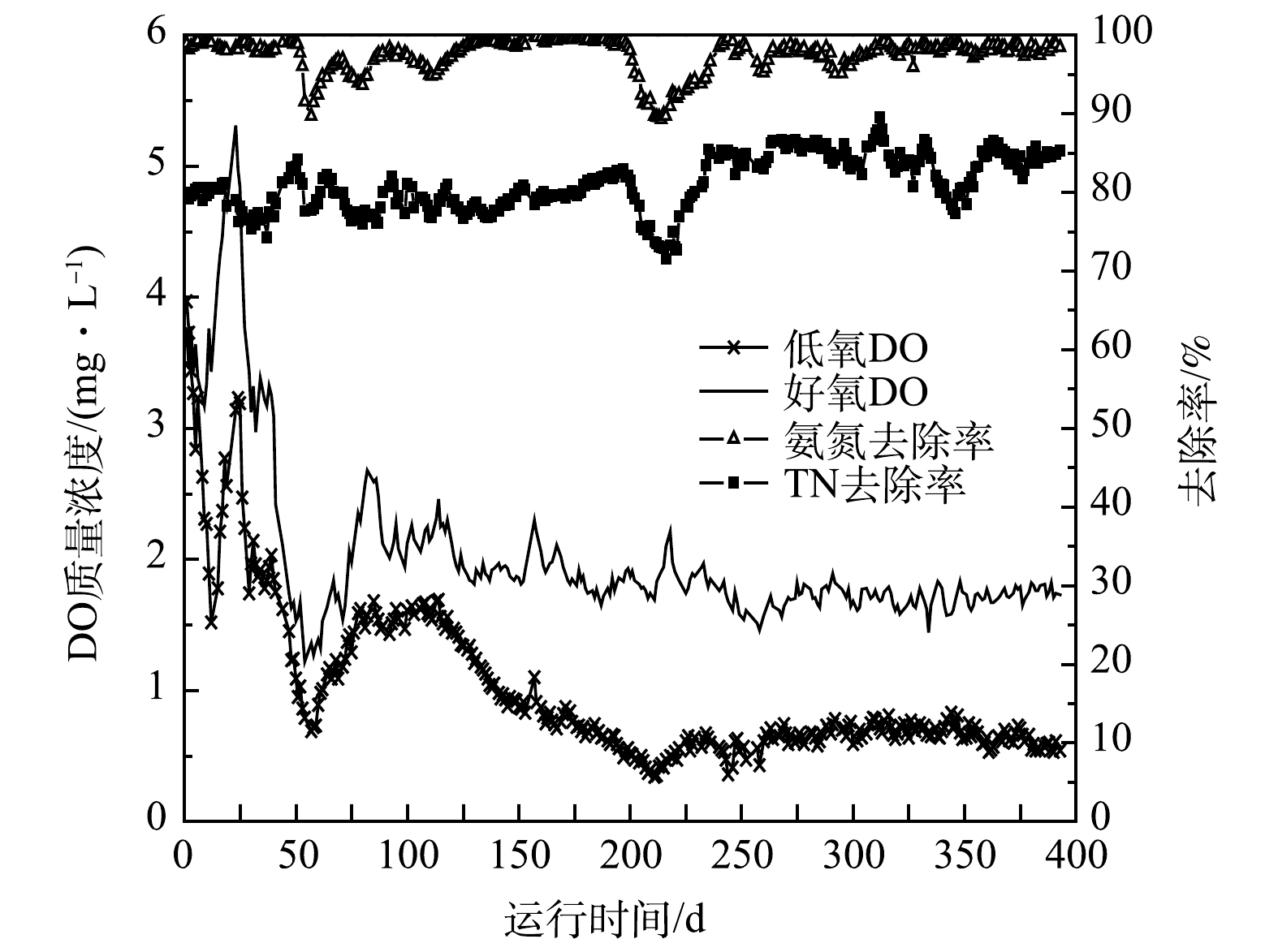
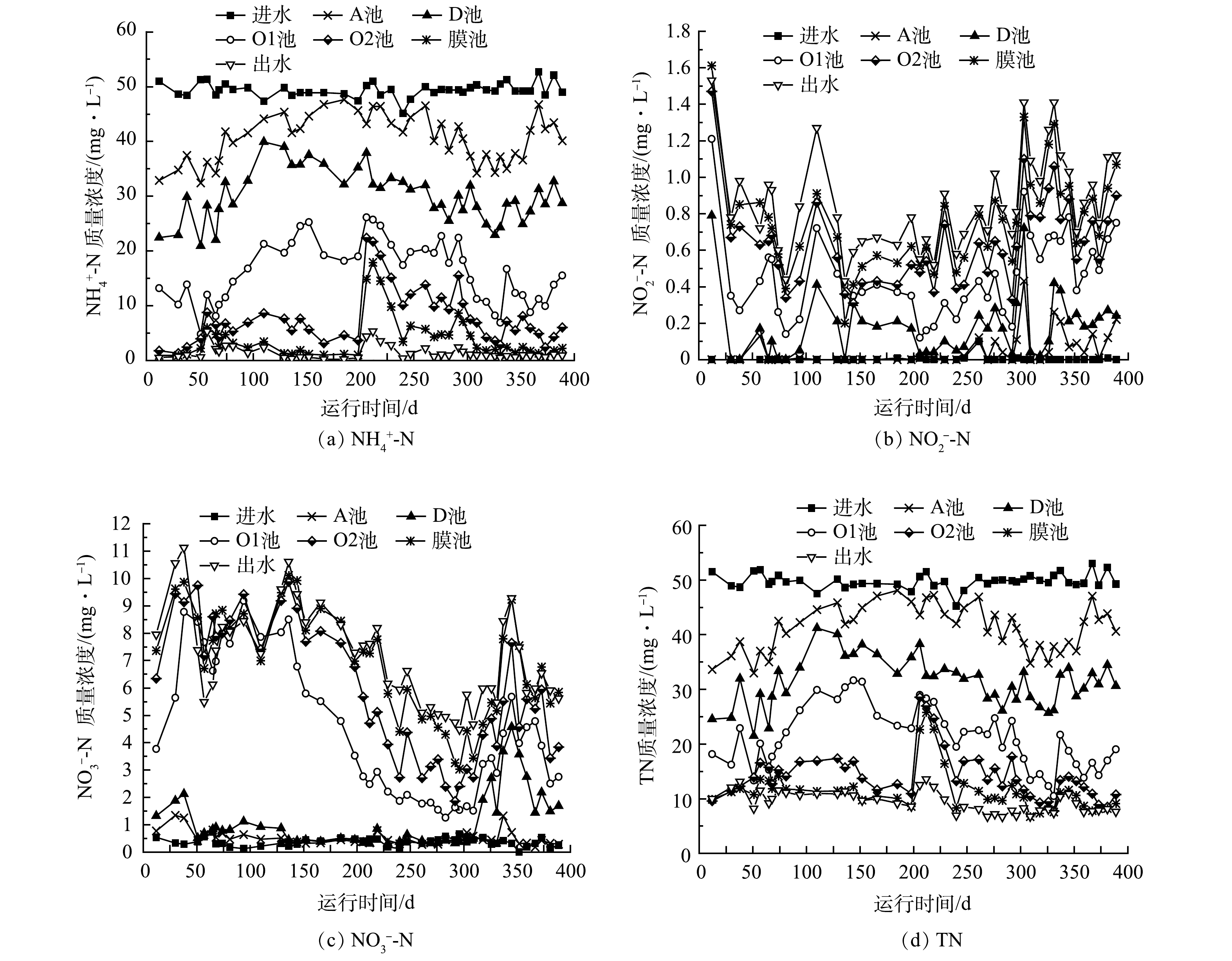
1)氨氮去除效果。A2O2-MBR工艺连续运行393d,其中氨氮去除效果如图3所示。可见氨氮去除效果总体保持稳定,平均进水氨氮质量浓度为49.4 mg·L−1,出水质量浓度1.3 mg·L−1,平均去除率97.3%。但在运行过程中由于DO浓度过低,出现了2次氨氮去除率下降。其中,41 d时低氧池和好氧池的曝气量同步下调,结果41~58 d低氧池DO质量浓度由1.75 mg·L−1降至0.72 mg·L−1,好氧池DO质量浓度由2.42 mg·L−1降至1.27 mg·L−1,DO浓度快速降低导致氨氮去除效果下降,54~58 d出水氨氮质量浓度升高到4.0 mg·L−1以上;之后好氧池的曝气量增大,DO浓度升高,氨氮去除效果得到恢复。88 d和144 d时好氧池曝气量调小,DO浓度略有降低,但对处理效果影响不大。202 d低氧池DO质量浓度降至0.5 mg·L−1以下,好氧池DO质量浓度降至1.7 mg·L−1左右,结果出水氨氮质量浓度升高到2.0 mg·L−1以上;之后随着DO浓度升高,氨氮去除效果得到恢复。235 d后,氨氮去除率保持在98%左右,出水氨氮质量浓度在1.0 mg·L−1左右。可见,虽然低DO条件有利于实现SND作用,从而改善TN去除效果[9-13],但在工艺启动和调试过程中,应首先富集足够的AOB等功能菌,确保氨氮处理效果保持稳定,然后逐步降低DO浓度,强化适应低DO条件的功能菌富集;如果曝气量或曝气时间的调整速度过快,可能会导致氨氮去除效果恶化[13,18-19]。此外,曝气量和DO的调整还应该考虑进水氨氮负荷和温度的变化[20]。
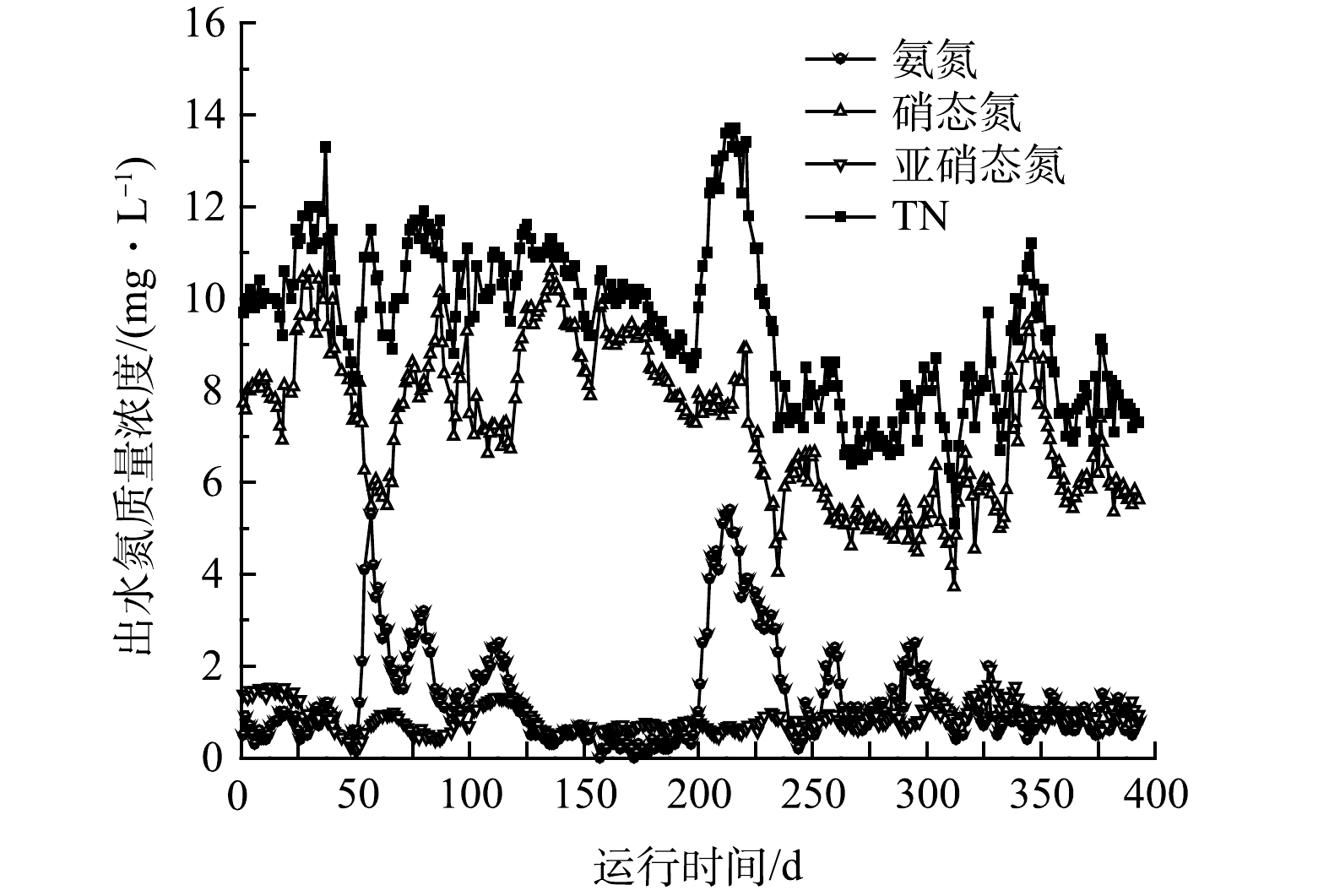
2) TN去除效果。不同阶段氨氮和TN去除效果如表3所示,氨氮和TN去除效果与DO浓度变化的关系如图4所示,出水各氮素浓度变化如图5所示。A2O2-MBR工艺启动时进水C/N比为6.0。1~23 d时TN去除效果比较稳定,出水TN在10 mg·L−1左右。24~40 d出水硝氮和TN升高,可能是由于这期间低氧池和好氧池DO质量浓度较高(分别为3.0 mg·L−1和5.0 mg·L−1左右)。41~53 d随着DO浓度下降,出水硝氮和TN有所降低。54~60 d由于DO浓度快速降低,出水氨氮和TN浓度升高。61~87 d随着DO浓度的回调,出水氨氮浓度下降,但出水硝氮浓度略有上升,出水TN稳定在11.5 mg·L−1左右。88~201 d,低氧池和好氧池曝气量连续7次下调,DO浓度逐步降低。由图5可以看出,出水TN浓度总体呈先升高后降低趋势,178~201 d时TN平均去除率为81.7%,出水TN平均质量浓度为9.1 mg·L−1。202~214 d,DO浓度过低导致氨氮去除效果再次恶化,TN去除率也随之下降;215~234 d,低氧池曝气量回调,DO浓度升高,出水氨氮浓度下降,同时出水硝氮浓度也在下降,导致TN去除率回升至80%以上。235~283 d,低氧池和好氧池DO质量浓度分别稳定在0.60 mg·L−1和1.68 mg·L−1,TN平均去除率达85.0%,平均出水TN质量浓度为7.4 mg·L−1。可见,与第Ⅰ阶段相比,TN去除率由78.9%提升至85.0%。284~333 d进水C/N比降至5.0,但TN去除效果基本未受影响,TN平均去除率84.9%,出水TN平均质量浓度为7.5 mg·L−1;期间曝气量未调整,但低氧池DO质量浓度升至0.7 mg·L−1。334 d进水C/N比进一步降至4.0,出水TN浓度略有升高;357 d后低氧池曝气量进一步降低,DO平均质量浓度降至0.61 mg·L−1,之后TN去除效果改善,平均去除率达84.7%。常规A2O工艺的TN去除率一般不超过75%[21-22],与之相比,本工艺经过对DO的优化后TN去除效果明显提升。
3) 影响TN去除效果的主要因素。一般认为,进水C/N比对生物脱氮效果影响显著,随着C/N比的降低,TN去除效果会逐步下降[10, 23-24]。在本研究中,虽然进水C/N比从6.0降为5.0和4.0,但通过调控低氧池和好氧池的DO浓度,可改善系统TN去除效果,使TN去除率保持在85%左右。推测其原因是在低DO条件下污泥絮体内部的缺氧区域增加,有利于反硝化作用进行,强化了低氧池和好氧池的SND作用。为了强化SND效果,好氧池的DO质量浓度一般控制在0.3~2.0 mg·L−1 [12-13, 25],或者通过缩短好氧HRT[26-27],减少好氧阶段碳源的过快消耗,使污水中碳源或内碳源更多为反硝化菌所利用,从而强化SND作用,改善低C/N比污水TN去除效果。JIANG等[25]将A2O-MBR工艺膜池中DO质量浓度由2.4 mg·L−1降至0.5~1.0 mg·L−1,TN去除效果明显提升。值得注意的是,DO浓度过低或下降速度过快容易造成氨氮去除效果恶化。由于活性污泥系统的复杂性,从曝气量的调整到DO浓度的稳定有一定滞后期,从DO浓度变化到处理效果变化也存在一定的滞后[28]。因此,在工艺调试过程中,曝气量的下降不应过快,而应小幅度逐步调整。
-
1)各池体浓度变化。工艺运行过程中,一周左右测一次各池体浓度变化情况,如图6所示。由图6(a)可见,1~152 d随着DO浓度的下降,低氧池(O1池)的氨氮质量浓度呈逐步升高趋势,由10 mg·L−1左右升至25.2 mg·L−1,同时好氧池(O2池)氨氮浓度保持在较低水平,膜池氨氮浓度进一步降低,确保了出水氨氮稳定达标。206 d时低氧池的DO质量浓度降至0.46 mg·L−1,其氨氮质量浓度进一步升至26.1 mg·L−1,同时好氧池氨氮质量浓度急剧上升至22.4 mg·L−1,导致出水氨氮升至4.4 mg·L−1。206~234 d低氧池DO质量浓度提高到0.6 mg·L−1左右,低氧池和好氧池的硝化效果很快得到恢复,此后基本保持稳定。284 d和334 d进水C/N比降为5.0和4.0,低氧池、好氧池的氨氮浓度先略有升高,然后逐步降低。可见,从低氧池到好氧池采用梯度曝气,一般情况下可保证稳定的硝化效果;但如果低氧池DO过低,氨氮去除效果持续下降,会导致进入好氧池的氨氮浓度升高,超过好氧池的处理能力,导致好氧池硝化效果恶化。
由图6(b)可见,各池体亚硝氮浓度总体呈先升高后降低趋势,283~333 d期间在C/N为5.0条件下亚硝氮浓度升高,之后再次下降。可能由于NOB对氧的亲和力较弱,低DO条件下NOB受到一定抑制,亚硝氮氧化速率较慢[11, 29];同时在低C/N比条件下,硝氮反硝化不完全也可能导致亚硝氮发生一定的积累[30]。由图6(c)和图6(d)可见,1~136 d,各池体硝氮浓度有一定波动但基本稳定,136~283 d低氧池和好氧池硝氮浓度逐步下降,促进了出水硝氮和TN的下降,推测在低DO条件下SND得到强化。284~331 d进水C/N比降至5.0,好氧池和低氧池的硝氮浓度有所升高,但膜池和出水硝氮变化不大,说明膜池起到一定作用。334 d后进水C/N比降至4.0,好氧池和低氧池的硝氮快速升高,358 d后有所降低。其原因可能是在低C/N比条件下,污水中碳源不足,SND作用受到限制[10,23];之后随着低氧池DO降低,碳源消耗速度下降,反硝化菌对碳源的利用率提高,导致SND效果改善[13,31],各池体硝氮和TN浓度随之下降。
不同工况下各池体COD和氮素变化如图7所示。由图7(a)可以看出,在工艺运行初期(68~81 d),COD值在厌氧池和缺氧池快速降低,进入低氧池时COD值已降至100 mg·L−1以下;氨氮浓度在低氧池和好氧池中快速下降,硝氮浓度明显升高,出水硝氮质量浓度为7.89 mg·L−1。从图7(b)可见,在进水C/N比为6.0的稳定运行阶段(269~283 d),COD值下降速度减慢,低氧池COD值仍达137.6 mg·L−1,且COD与TN的变化趋势基本一致,有利于反硝化作用的进行;氨氮和TN浓度在低氧池、好氧池和膜池同步下降,硝氮保持在较低水平,出水硝氮质量浓度仅为5.09 mg·L−1。如图7(c)所示,在进水C/N比降至5.0后,虽然进水中碳源减少,但低氧池COD值仍达132.67 mg·L−1,低氧池TN质量浓度已降至12.41 mg·L−1,好氧池进一步降至8.81 mg·L−1,低氧池和好氧池对TN的去除效果进一步改善。如图7(d)所示,在进水C/N比降至4.0后,低氧池COD值降至76.50 mg·L−1,低氧池TN浓度比之前有所升高,但好氧池和膜池去除效果显著,出水TN仍保持在8 mg·L−1以下。此外,从膜池到出水的COD、氨氮和TN等指标均有所下降,尤其是在膜池TN浓度较高时效果更为明显,推测膜组件表面的生物膜发生了SND作用。有研究表明,MBR工艺膜池污泥浓度较高,污泥颗粒较大,且膜材料表面附着有生物膜,在适当的DO浓度条件下,膜池内部形成缺氧微环境,有利于强化SND作用。
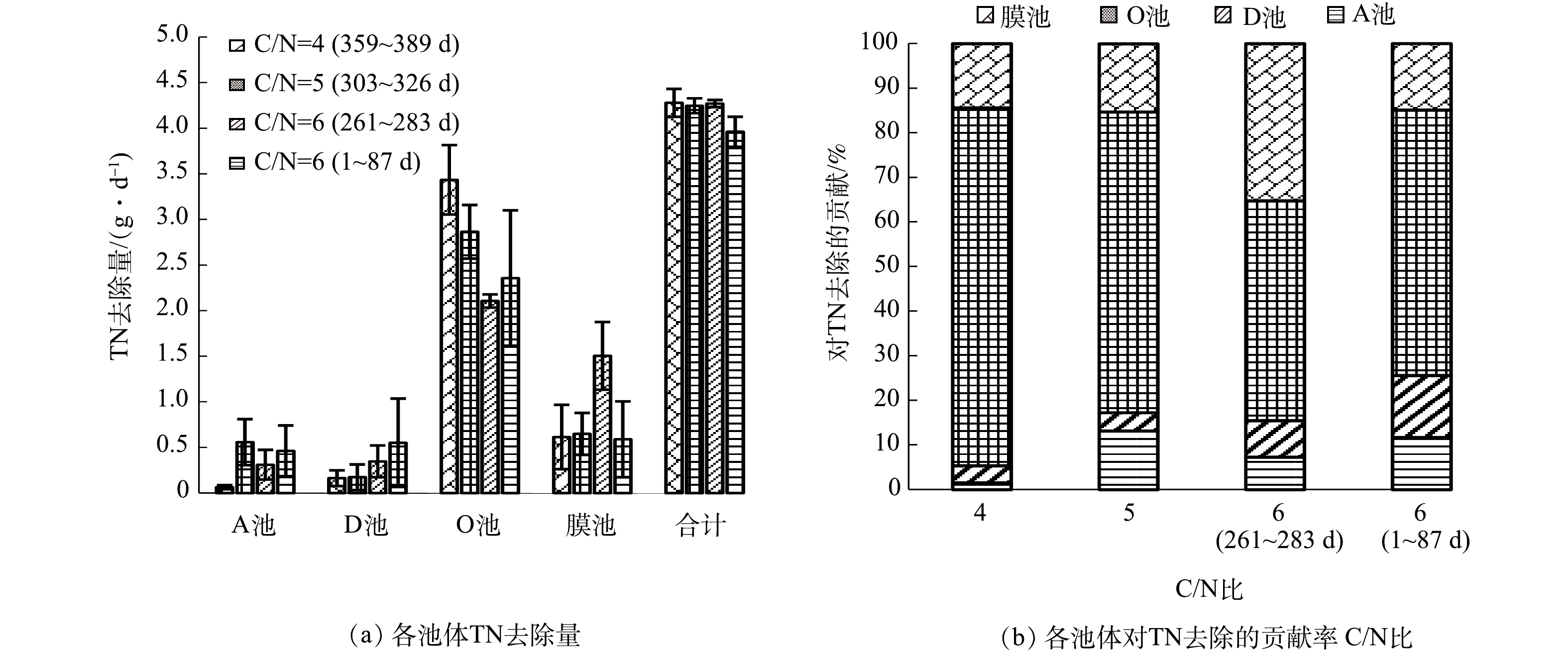
2)物质平衡和SND效率分析。不同阶段各池体TN去除量和所占比例如图8所示,各池体对COD的去除量和贡献如图9所示。可见,1~87 d整个工艺的TN去除量为3.96 g·d−1,比后续几个阶段略低;其中O池(包括O1和O2池)去除的TN占59.5%,膜池占14.9%,合计74.4%;这一阶段厌氧池去除的COD较高,占总去除量的45.44%(图9),同时去除的硝氮和亚硝氮(NOx-N)很少,说明COD主要被DPAOs和DGAOs吸收并转化为PHAs储存起来。261~283 d,系统TN去除量增加到4.27 g·d−1,这一阶段膜池的TN去除量明显增加,O池和膜池对TN去除的贡献率分别为49.3%和35.2%,合计达84.5%,O池和膜池的总贡献明显提高;同时厌氧和缺氧池去除COD减少,O池和膜池去除的COD增加,说明有机碳源主要在O池和膜池得到利用。进水C/N降至5.0时,TN总去除量保持稳定,O池去除量回升,膜池去除量下降,二者对TN去除的贡献分别为67.4%和15.3%,合计82.7%;在COD去除方面,厌氧池的贡献进一步减少,O池和膜池进一步增加,贡献达到83.2%。进水C/N降为4.0时,系统TN总去除量略有降低,O池去除量略有提高,O池对TN去除的贡献进一步增加,O池和膜池对TN去除的贡献分别为80.3%和14.4%,合计94.7%;在COD去除方面,缺氧池贡献有所增加,其原因是在低C/N比条件下O1池的NOx-N升高,导致进入缺氧池的NOx-N增加;另外由于进水碳源浓度降低,O2池出水COD值下降,导致膜池对COD去除的贡献显著降低。可见,本工艺稳定阶段O池和膜池对TN去除的贡献在82.7%以上,SND效果稳定;同时COD主要在O池和膜池得到去除,为SND作用提供了充足的碳源。
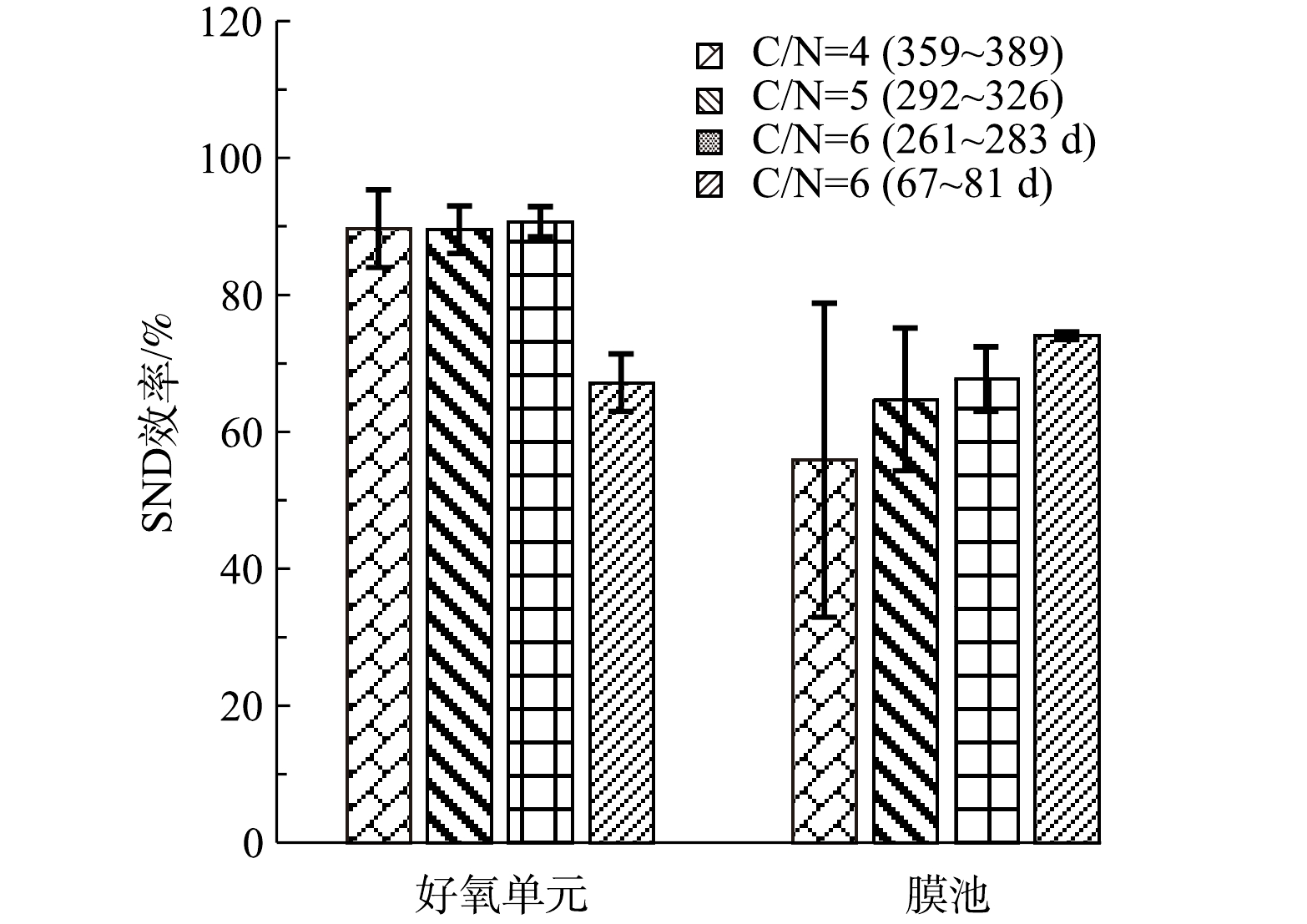
SND效率计算结果如图10所示。可见O池的SND效率呈升高趋势,67~81 d时SND效率为67.2%,到261~287 d时已升至90.7%。此后,C/N比从6.0降至5.0和4.0,但O池SND效率基本保持稳定,仍有89.5%和89.7%。膜池SND效率总体略低于好氧单元,随着C/N比降低呈现逐步降低趋势,同时膜池对TN去除的贡献也呈下降趋势(图8)。可能随着O池去除效果的改善,好氧池进入膜池TN浓度降低;同时随着C/N降低,进入膜池的碳源较少,导致膜池处理效果下降。对比表3可知,O池SND效率与系统TN去除效率的变化规律高度一致,说明SND作用对系统TN去除效果具有重要的影响。
3) SND工艺处理效能对比分析。对比SND工艺相关研究(表4)可知,现有研究在低C/N比条件下的SND效率大多在80%以下,只有少数报道的SND效率达到85%以上[10, 32],但其进水C/N比一般在5.0以上。已有研究一般利用PHAs内碳源[12-13, 31]、培养颗粒污泥[6, 33-34]、投加生物填料[1, 17, 27]等方式强化SND作用。此外,陈均利等[35]将富集培养的HN-AD菌种投加到好氧/微氧固定床反应器中,提高了TN去除效果,TN去除率达97.6%。与之相比,本研究通过设置低氧池和好氧池,逐步降低曝气量,并对DO浓度进行准确控制,使O池SND效率达到90%,同时TN去除率达85%左右。且该工艺操作简便,处理效果稳定,适用于采用A2O和MBR工艺的污水厂进行升级改造。
-
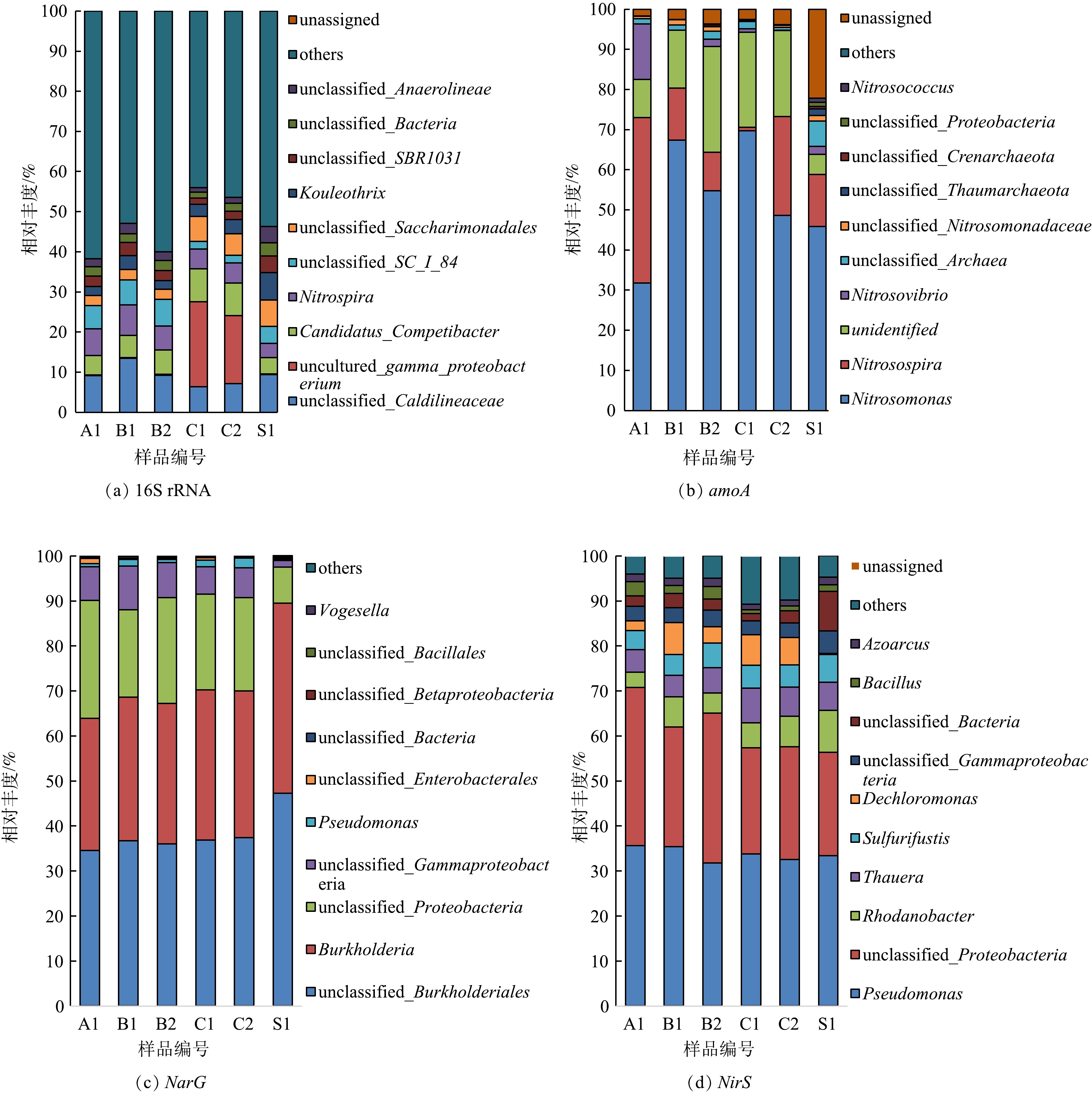
16S rRNA以及amoA、nirS和narG功能基因高通量测序得到的柱状图如图11所示。其中,由16S rRNA的柱状图可以看出,C1和C2的菌群结构与其他污泥样品存在明显差别,有一种未知的γ-变形菌丰度显著增加,从之前的0.2%增至最高21.17%(C1);亚硝化螺菌Nitrospira(属于NOB)的丰度由最高7.53%(B1)降至5.00%(C1),Candidatus_Competibacter(属于反硝化聚糖菌,DGAOs)的丰度从接种污泥的4.1%(S1)增加到最高8.17%(C1)。其中,NOB的减少主要与DO浓度下降有关,200 d后低氧池DO质量浓度保持在0.5~0.7 mg·L−1,好氧池DO质量浓度也低于2 mg·L−1,不利于NOB的生长,更有利于AOB的生长。DGAOs可将进水中碳源转化为PHA等内碳源,然后利用内碳源进行反硝化,从而改善低C/N比污水TN去除效果[6,11-13,26-27]。C1和C2污泥中DGAOs增加,说明低C/N比条件有利于DGAOs的富集。有研究指出,在有机碳源有限(低C/N比)的条件下,DGAOs可在厌氧条件下将污水中碳源吸收并转化为PHA在体内储存起来,导致常规异养菌可利用碳源减少,竞争力减弱[39-40]。
amoA测序结果表明,系统中主要AOB菌种为亚硝化单胞菌(Nitrosomonas)和亚硝化螺菌(Nitrosospira),占所有检出菌种的70%左右。其中亚硝化单胞菌丰度更高也更稳定,亚硝化螺菌的丰度先减少,最后又有所增加,可能是前期在低氧环境下生长受到抑制,后期逐渐适应了低氧环境,生长繁殖得到恢复。narG基因测序检出的菌种类别比较有限,主要为Burkholderia和假单胞菌(Pseudomonas)。nirS基因测序检出了多种反硝化菌,主要包括Pseudomonas、Thauera、Dechloromonas、Paracoccus、Zoogloea、Azoarcus、Candidatus_Accumulibacter和Bacillus,其中部分菌种属于反硝化除磷菌(DPAOs)。其中,Pseudomonas的丰度最高,占30%以上,且保持稳定。Thauera和Zoogloea两个菌种在C1和C2样品中丰度明显增加,说明其更适应低C/N比的条件。基于非加权平均算法(UPGMA)的Beta多样性分析结果表明,C1和C2样品的微生物群落结构比较接近,而这2个样品与其他样品的差异比较明显(图12)。可见,在低C/N比和低DO条件下,系统中富集了DGAOs、DPAOs和常规异养反硝化菌(DNB)等多种反硝化菌,从而有利于反硝化的进行,强化了低DO条件下低氧池和好氧池的SND作用。结合COD去除特征可知,厌氧池去除的COD很少,COD主要在O池和膜池去除(图9),说明TN主要通过常规DNB去除,DGAOs和DPAOs的贡献较小。可能由于本研究中厌氧池DO质量浓度仍达0.3~0.4 mg·L−1,不利于DGAOs和DPAOs对碳源的吸收和利用。
-
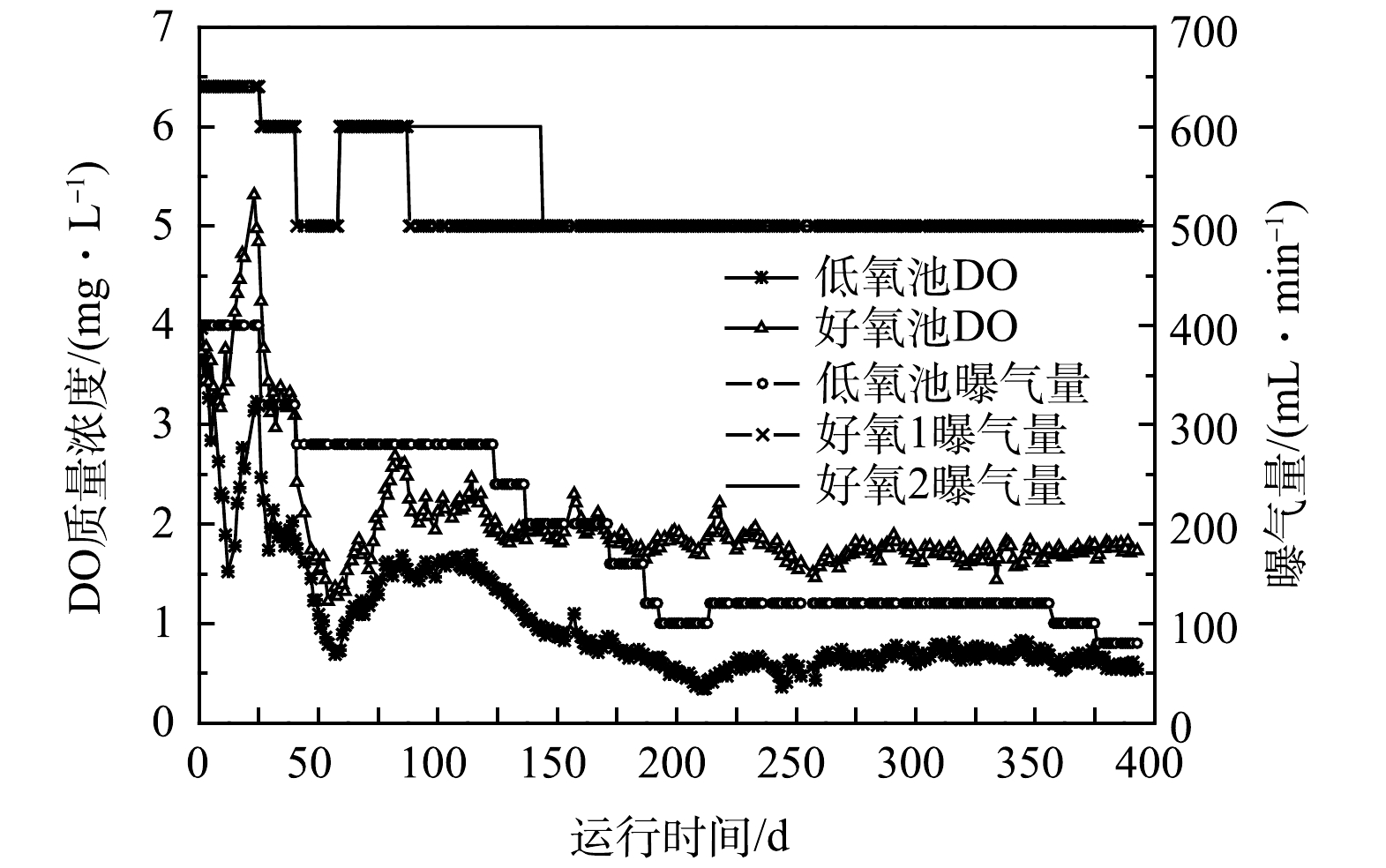
在系统启动时低氧池和好氧池DO质量浓度在2~4 mg·L−1,与常规A2O工艺接近。在系统运行过程中,逐步降低低氧池和好氧池的曝气量,从而降低DO浓度,低氧池和好氧池曝气量和DO浓度变化如图13所示。2个低氧池的曝气量最初均为400 mL·min−1,经过多次调整,376 d后降至80 mL·min−1。与启动阶段相比,低氧池曝气量减少了80%,低氧池DO质量浓度由2.76 mg·L−1降至0.6 mg·L−1。2个好氧池曝气量最初为640 mL·min−1,经过多次调整,144 d后均保持在500 mL·min−1。与启动阶段相比,好氧池曝气量减少了21.9%,好氧池DO质量浓度由3.99 mg·L−1降至1.7 mg·L−1。低氧池和好氧池总曝气量从启动阶段的2 080 mL·min−1降至1 160 mL·min−1,下降了44.2%,使系统曝气能耗明显降低。该工艺启动时按常规A2O工艺运行,经过改造为梯度曝气A2O2工艺后,总曝气量和DO浓度降低了40%以上,说明该工艺比常规A2O工艺的曝气能耗明显降低。在其他基于低DO条件的SND或SNDPR工艺中,曝气量也实现大幅下降。ZAMAN等[10]研究表明,将SBR工艺好氧段的DO质量浓度控制在0.3 mg·L−1,可实现SNDPR,且曝气能耗降低了35%。WANG等[12]把SBR工艺好氧段DO质量浓度控制在1.0 mg·L−1,实现了基于内碳源的SNDPR工艺,使曝气能耗降低了65%。
由图13中可以看出,曝气量调整以后,DO浓度的变化有一定滞后性。比如41 d低氧池和好氧池曝气量降低后,经过15 d左右的时间,低氧池DO质量浓度由1.75 mg·L−1缓慢降低至0.69 mg·L−1,好氧池DO质量浓度由2.42 mg·L−1缓慢降低至1.22 mg·L−1。59 d好氧池曝气量再次调高,低氧池和好氧池DO质量浓度缓慢升高,经过20 d左右才分别稳定在1.5 mg·L−1和2.5 mg·L−1。124~213 d低氧池曝气量多次降低,低氧池DO浓度出现连续下降,202~213 d时DO质量浓度降至0.5 mg·L−1以下,导致出水氨氮升高。DO浓度变化的滞后性为污水厂好氧池DO浓度的精确控制带来一定挑战,其具体机理尚不清晰,可能与污泥絮体对氧的缓冲作用有关。在工程实践中应高度关注DO变化的滞后性问题,在曝气量调整后密切观察DO浓度变化,必要时及时进行调整,防止DO浓度过低或过高影响处理效果。
-
1)本研究对传统的A2O-MBR工艺进行改造,构建了梯度曝气A2O2-MBR工艺,优化了工艺参数,提出了从传统工艺改造为新工艺的调试策略。在硝化效果稳定后,通过逐步下降低氧池和好氧池DO浓度,强化了SND作用,改善了TN去除效果。低氧池最佳DO质量浓度为0.6~0.7 mg·L−1,好氧池为1.7 mg·L−1。进水C/N比从6.0下降至5.0和4.0,TN去除效果基本保持稳定,TN去除率在85%左右,出水TN质量浓度在7.5 mg·L−1左右。
2)为了分析A2O2-MBR工艺脱氮机理,开展了物质平衡分析,结果表明,稳定运行阶段O池(低氧池和好氧池)和膜池对TN去除的贡献达80%以上,对COD去除的贡献为64.9%~83.2%;虽然进水C/N比从6.0降至4.0,但O池SND效率保持在90%左右,与文献报道相比处于较高水平。可见,该工艺通过强化SND作用,使TN去除效果得到改善。
3) 16S rRNA以及amoA、nirS和narG功能基因高通量测序结果表明,在低DO低C/N比条件下,系统中NOB丰度下降,DGAOs、Thauera和Zoogloea等反硝化菌丰度增加;反硝化菌类群丰富,其中Pseudomonas的丰度最高。说明经过工艺条件的优化,多种脱氮功能菌得到富集,有利于TN去除效果的改善,其中常规DNB对TN去除贡献较大,DGAOs和DPAOs的贡献较小。
4)与启动阶段(接近常规A2O-MBR工艺)相比,低氧池曝气量减少80%,好氧池曝气量减少21.9%,总曝气量下降了44.2%,表明梯度曝气A2O2-MBR工艺不仅使去除效果得到改善,而且曝气能耗明显降低。曝气量调整后,DO浓度的变化存在一定的滞后期,经过15~20 d后DO浓度才能稳定,因此曝气量的调整不应过快,防止DO浓度过低或过高。
梯度曝气A2O2-MBR工艺强化同步硝化反硝化效能
Enhanced SND performance of step-wise aeration A2O2-MBR process
-
摘要: 针对城镇污水厂对低C/N比污水脱氮效果差、能耗高的问题,研发了梯度曝气A2O2-MBR工艺,设置单独的低氧池(O1池)和好氧池(O2池),O1和O2池DO质量浓度逐步降至0.6 mg·L−1和1.7 mg·L−1。进水碳氮比(C/N)从6.0逐步降至5.0和4.0,总氮(TN)去除率保持在85%左右。O1和O2池同步硝化反硝化效率保持在90%左右,O池(O1池+O2池)和膜池对TN去除的贡献在82.5%以上,对COD去除的贡献在64.9%~83.2%。高通量测序结果表明,在低DO低C/N比条件下,系统中亚硝酸盐氧化菌(nitrite-oxidizing bacteria,NOB)丰度下降,反硝化聚糖菌(denitrifying glycogen accumulating organisms,DGAOs)丰度增加;反硝化菌类群丰富,其中Pseudomonas的丰度最高,Thauera和Zoogloea在低C/N比条件下丰度增加。大部分TN通过常规异养反硝化菌(denitrifying bacteria,DNB)去除,DGAOs的贡献较小。与启动阶段相比,O1池和O2池总曝气量下降了44.2%。结果表明,通过采用梯度曝气方式,并逐步降低DO浓度,可促进功能菌的富集,强化SND作用,改善TN去除效果,并降低能耗。Abstract: Aiming at poor denitrification effect and high energy consumption when treating the wastewater with the low C/N ratio in wastewater treatment plant (WWTPs), a step-wise aeration A2O2-MBR process was developed. The separated low-oxic zone(O1) and oxic zone(O2) were design with the DO concentrations decreased gradually to 0.6 mg·L−1 and 1.7 mg·L−1, respectively. When the influent C/N ratio decreased from 6.0 to 5.0 and 4.0, the total nitrogen (TN) removal efficiency maintained at around 85%. The simultaneous nitrification and denitrification (SND) efficiency of the O1 and O2 zones kept at around 90%. Both O zones (O1+O2) and membrane zones contributed to above 82.5% of TN removal, and 64.9%~83.2% of COD removal. High-throughput gene sequencing showed that, under low DO and low C/N ratio conditions, the abundance of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) decreased, while the abundance of denitrifying glycogen accumulating organisms (DGAOs) increased. Rich denitrifiers occurrred, of which the abundance of Pseudomonas was highest. Besides, the abundance of Thauera and Zoogloea increased under low C/N ratio condition. Most of TN was removed by ordinary denitrifying bacteria (DNB), rather than DGAOs. Compared with the startup stage, the total aeration rate of the O1 and O2 zones decreased by 44.2%. The results showed that the step-wise aeration mode could gradually lower the DO concentrations, enrich the functional bacteria, then enhance the SND effect, increase TN removal, save the energy consumption.
-
环丙沙星(ciprofloxacin,CIP)是一种典型的喹诺酮类抗生素,其具有喹诺酮和哌嗪环结构[1]。CIP在医学上有抗菌性强,能用来预防畜禽疾病和感染引起的人为性疾病[2],其广泛使用对微生物、植物、动物和人类健康构成潜在威胁,破坏原有环境的生态平衡[3-4]。目前,抗生素类废水处理技术主要有生物法、物理法,化学法等[5]。但由于抗生素类废水具有杀菌性强的特点,不易被生物降解,故物理法也只能对污染物进行转移,不能对其彻底去除[6]。因而,寻求高效彻底的治理工艺成为研究热点。
传统Fenton法在处理难降解、有毒有害有机物方面具有独特优势[7],但其在发挥优势的同时,自身也存在许多缺陷:需在较低pH值下(<4.0)反应,催化剂难分离而无法重复利用;反应体系中外加铁离子会造成溶液色度的增加,且反应后要重新调节pH。这不仅增加了处理成本,还会生成铁泥,给污水处理造成不便[8]。为了能在更宽的pH范围下提升Fenton活性,充分分离、回收和循环利用催化剂,众多研究已趋于非均相Fenton反应[9]。非均相Fenton反应体系具有反应条件温和,操作简单,对降解物无选择性,且有处理效率高等优点而被广泛使用[10]。但非均相铁基芬顿体系在非酸性条件下具有易丧失芬顿活性的缺陷[11],故诸多研究者已开始关注其他具有芬顿活性的金属离子。有研究发现,金属离子在pH为5.5~9.5时,类芬顿活性顺序为Cu(Ⅱ)>Cr(Ⅲ)>Co(Ⅱ)>Fe(Ⅲ)>Mn(Ⅱ)>Ni(Ⅱ),Cu(Ⅱ)/H2O2体系产生羟基自由基(·OH)能力最强[12]。Zn2+与Cu2+有相近离子尺寸和电子环境,且具有Fenton催化活性,因此,添加Zn2+与Cu2+发挥双金属间协同作用,可以提高催化剂的活性,同时可减少金属离子溶出[13]。
本研究采用化学共沉淀法制备以Cu为核心元素、掺杂Zn元素的非均相铜基催化剂,通过正交实验研究了Cu/Zn金属盐投加比例、模板剂葡萄糖添加量、反应液pH、焙烧温度等因素对催化剂催化降解CIP的影响;利用XRD、SEM、BET、XPS等表征手段对优选出的Cu/Zn催化剂进行分析表征,探讨了Zn掺杂元素对Cu/Zn催化剂的催化性能影响;考察了Cu/Zn催化剂投加量、H2O2投加量、溶液初始pH等对CIP的最优条件,同时研究了反应体系的H2O2消耗量和·OH生成量,最后探讨了非均相铜基催化剂对CIP的降解机理。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试剂与仪器
CIP标准品,购自阿拉丁;乙腈(HPLC)、甲酸(HPLC)、无水乙醇(AR)均购自天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;硝酸铜、硝酸锌、硫酸钛、硫酸、邻苯二甲酸氢钾、香豆素、磷酸二氢钾、氢氧化钠、30%H2O2、无水葡萄糖均为分析纯,购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
高效液相色谱仪(LC1100,美国安捷伦);扫描电子显微镜(SU-8010,日本日立);X射线衍射仪(XRD-6100,日本岛津);BET(Quantachrome Instruments Quadrasorb EVO,美国);XPS(ESCALAB 250Xi,美国赛默飞世尔科技公司);ICP-MS(ThermoFisher X SERIESⅡ,美国);LC-MS(waters 2996,waters micromass-ZQ,美国);马弗炉(德国Nabertherm);电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(DHG-92468,上海精宏实验设备有限公司);原子荧光光谱仪(AF-640);pH计(STARTER5000,美国奥豪斯);多头磁力加热搅拌器(HJ-4,常州国华电器有限公司);三频数控超声波清洗器(KQ-500VDE,昆山市超声仪器有限公司)。
1.2 非均相铜基催化剂的制备
1)非均相铜基催化剂的制备。分别称取一定量Cu(NO3)2·3H2O和Zn(NO3)2·6H2O,溶解到100 mL蒸馏水中,将双金属盐混合液搅拌10 min至其溶解均匀,加入模板剂无水葡萄糖。持续搅拌的同时,将3.33 mol·L−1的NaOH逐滴加到混合液中,控制悬浊液pH,将得到的沉淀液继续搅拌20 min后超声10 min,在室温下静置3 h,使用无水乙醇和蒸馏水离心洗涤至上清液为中性,将离心洗涤后的样品在60 ℃下干燥12 h。最后将烘干研磨后的样品分别在300、500、700 ℃的马弗炉里煅烧2 h,制得的非均相铜基催化剂。
2)正交实验方案设计。实验过程中发现制备出催化性能较优的催化剂受到多种实验条件的影响。因此,利用正交实验探讨了非均相铜基催化剂制备过程中的Cu/Zn金属盐摩尔比、模板剂葡萄糖添加量、反应液pH值、焙烧温度等条件对制备出的催化剂催化降解CIP的影响,正交实验条件如表1所示。
表 1 正交实验因素及水平Table 1. Factors and levels of orthogonal experiment水平 因素 A(Cu/Zn金属盐摩尔比) B(模板剂添加量)/(mol·L−1) C(反应液pH) D(焙烧温度)/℃ 1 10∶1 0.01 3.5 300 2 10∶2 0.02 5.0 500 3 10∶3 0.03 7.0 700 1.3 实验方法
以优选出的Cu/Zn催化剂与30%H2O2进行非均相Fenton反应降解CIP。在室温下,准确移取浓度为20 mg·L−1的CIP溶液100 mL至250 mL锥形瓶中,用NaOH溶液或稀H2SO4调节pH。加入适量Cu/Zn催化剂,吸附平衡后加入30%H2O2,控制搅拌速度为250 r·min−1,每隔15 min取样,经0.22 µm滤膜过滤后,用HPLC测定反应液中CIP的剩余浓度。实验结果均通过3次平行实验取平均值。
1.4 分析方法
1) CIP的HPLC分析。CIP浓度检测采用LC1100高效液相色谱仪。色谱分离条件为Promosil C18色谱柱(4.6×150 mm,5 μm),流动相为乙腈:0.2%甲酸水溶液=17:83,检测波长为277 nm,流速为1 mL·min−1,色谱柱温度为30 ℃,进样量设定为20 µL。
2) H2O2消耗量测定。取经0.22 μm滤膜过滤后的上清液1 mL置于25 mL具塞比色管中,将1 mL的0.1 mol·L−1的Ti(SO4)2溶液、1 mL的2 mol·L−1的H2SO4溶液依次加入比色管中,然后准确加入去离子水10 mL,充分振荡,显色5 min后在400 nm处测其吸光度[14],得到H2O2浓度与吸光度的标准曲线为y=0.011 5x+0.7088(R2=0.998 6),其中x为H2O2浓度,y为吸光度。
3) ·OH产生量测定。采用荧光光谱法测定。以香豆素作为探针分子,捕获·OH生成具有强大荧光特性的7-羟基香豆素。将pH为7.2的缓冲液0.5 mL和0.1 mol·L−1香豆素溶液50 mL混合均匀,分别取不同时刻反应液5 mL与上述溶液混合,置于封闭空间中,用紫外灯照射及磁力搅拌5 min后,置于荧光光谱仪测量其荧光度,由标准曲线得出反应体系·OH的浓度(C·OH=1.58×I460 mmol·L−1[10])。荧光检测的激发波长为345 nm,发射波长为460 nm,积分时间为1 s。
4) LC-MS分析。采用LC-MS检测中间产物:C18色谱柱(安捷仑poroshell 120 EC-C18 2.7 μm 4.6×100 mm)。流动相为乙腈/0.2%甲酸水溶液=17:83,离子源是大气压电离源,流速1 mL·min−1,进样杆温度为35 ℃,DAD检测器,高分辨质谱为ESI源(Q-Exactive Thermofishe)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 正交实验
表2显示了正交实验结果。在室温下,当CIP浓度为20 mg·L−1、溶液初始pH为5.0、催化剂投加量为3.0 g·L−1时,在吸附平衡30 min后投加H2O2为149.55 mmol·L−1条件下反应60 min。由表2可知,A是影响催化降解CIP的主要因素,其次是B,再次是C,而D影响最小,制备非均相铜基催化剂的最佳方案:A为10:3、B为0.02 mol、C为5.0、D为700 ℃。后续所有实验的催化剂均采用此条件下所制备,并命名为Cu/Zn催化剂。
表 2 正交实验结果与极差分析Table 2. Results of the orthogonal experiment and range analysis实验号 因素 CIP降解率/% A B C D 1 1 1 1 1 82.3 2 1 2 2 2 91.0 3 1 3 3 3 65.4 4 2 1 2 3 77.2 5 2 2 3 1 56.6 6 2 3 1 2 22.1 7 3 1 3 2 69.3 8 3 2 1 3 87.4 9 3 3 2 1 84.5 K1j 79.57 76.27 63.93 74.47 K2j 51.97 78.33 84.23 60.80 K3j 80.4 57.33 63.77 76.67 Rj 28.43 21.00 20.46 15.87 2.2 催化剂的表征
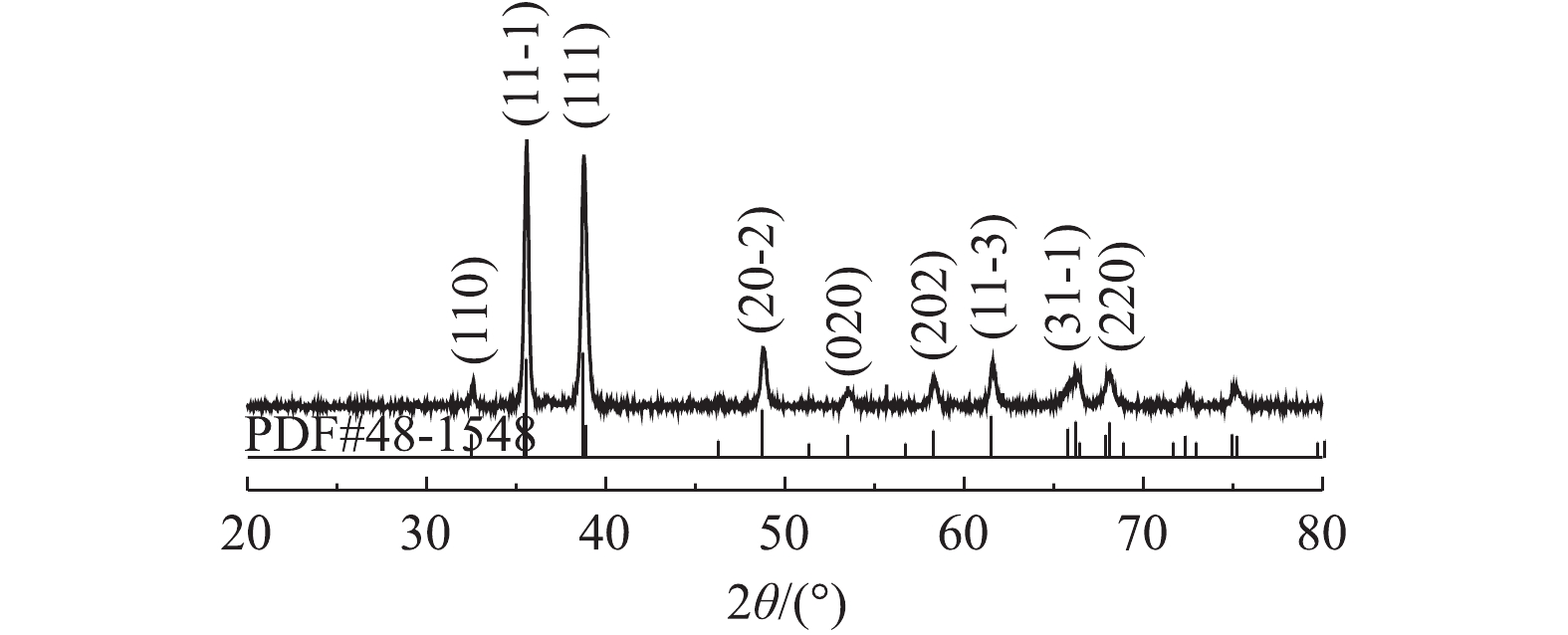
1) XRD分析。图1为化学共沉淀法制备Cu/Zn催化剂的XRD图。由图1可知,催化剂在2θ为32.508°、35.543°、38.708°、48.716°、53.49°、58.27°、61.35°、66.57°、68.12°等位置出现的特征衍射峰与CuO(PDF NO.48-1548)相一致,分别对应CuO的(110)、(11-1)、(111)、(20-2)、(020)、(202)、(11-3)、(31-1)、(220)晶面[15],这表明所制备的Cu/Zn催化剂主要成分为CuO。
2) SEM分析。图2为Cu/Zn催化剂的SEM图。由图2可见,催化剂大部分是由直径约50 nm的小椭圆形颗粒构成,也有小部分颗粒粒径达到200 nm,整个样品颗粒均匀分布。由图2(a)可知,当放大倍数为15 000时催化剂出现小部分片状团聚,小颗粒之间连接不紧密,狭缝孔明显。由图2(b)可知,当放大倍数为60 000时催化剂表面附着有小白点形式的微小纳米颗粒。分析其可能原因是在模板剂葡萄糖作用下,形成了良好的胶束,使添加的元素Zn能够附着于材料表面[16],加速了铜基催化剂的协同作用。
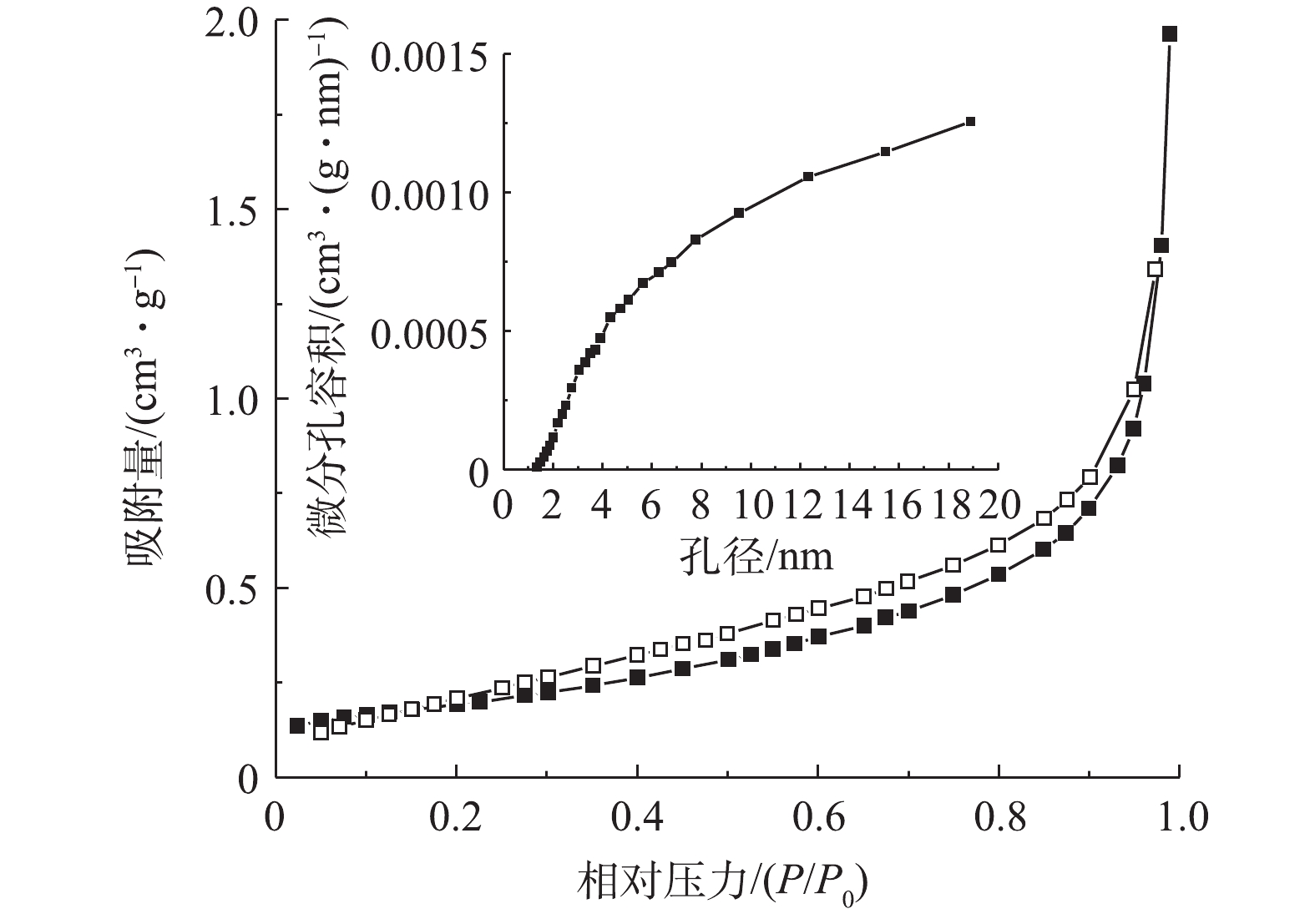
3) BET分析。图3为Cu/Zn催化剂的N2吸附-脱附等温线和孔结构分布图。根据国际纯粹与应用化学联合会的分类标准,Cu/Zn催化剂的吸附等温线属于Ⅲ类,吸附等温线显示了催化剂具有介孔结构。由图还可以看到,催化剂的N2吸附-脱附等温线出现了明显的狭长H3型滞后环。滞后环的吸附分支在相对高压力下没有明显的极限吸附量,且吸附量随压力增加而呈递增趋势,可能是裂隙孔或堆积孔,而这多出现在有狭长裂口孔状结构的片层材料里,即颗粒堆积而形成的狭缝孔,这与催化剂的SEM图(图2(a))相吻合[17]。Cu/Zn催化剂孔径分布曲线图进一步说明了材料是均匀的介孔材料,孔径大小大部分位于2~8 nm。
Cu/Zn催化剂的比表面积为0.739 m2·g−1、总孔容为0.003 cm3·g−1、中孔孔容为0.0029 cm3·g−1、平均孔径为3.414 nm,属于中孔。
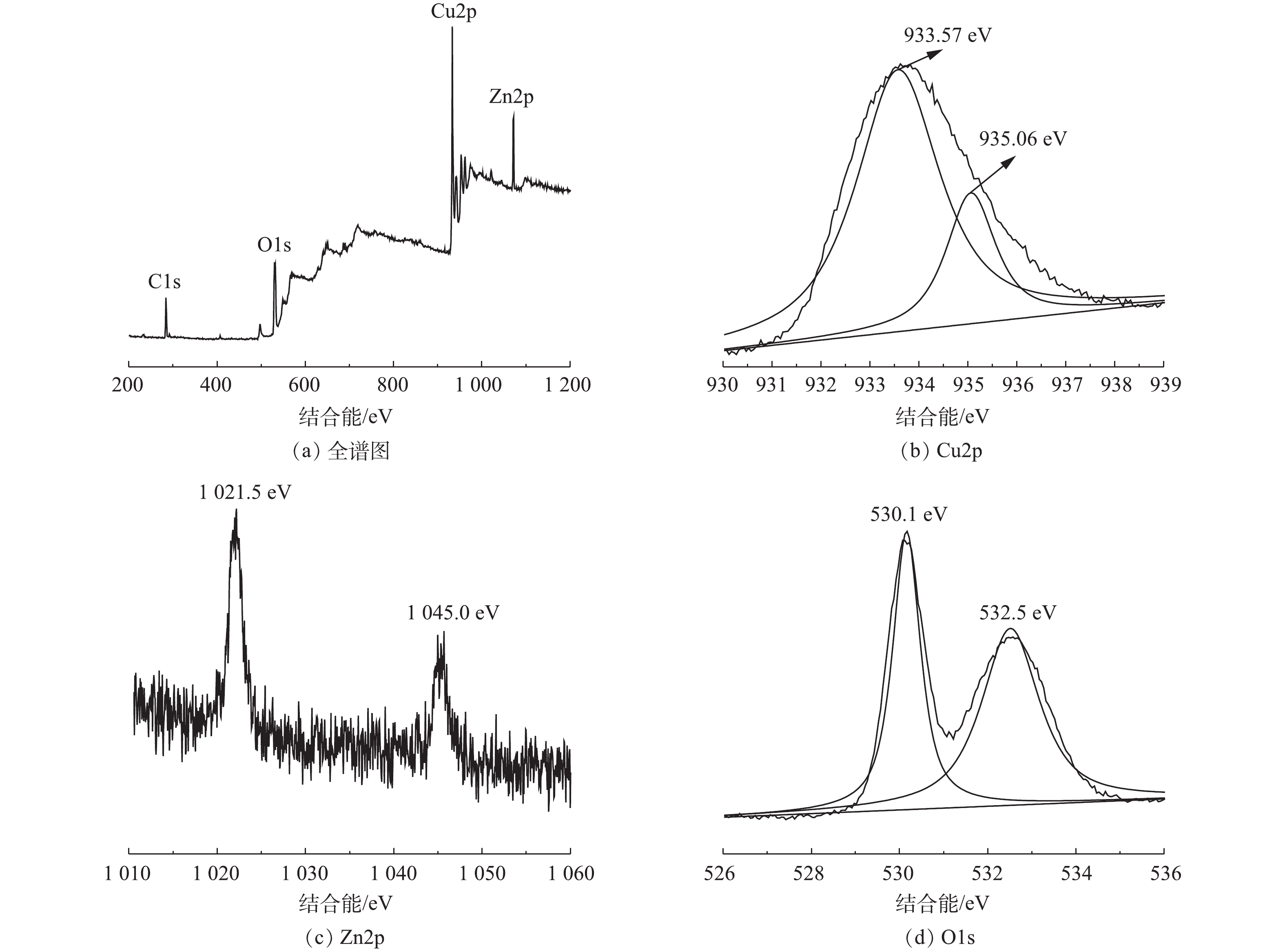
4) XPS分析。图4为Cu/Zn催化剂的XPS图。图4(a)为Cu/Zn催化剂全谱扫描图,说明了催化剂中存在Cu、Zn、O、C的4种元素。其中,图4(b)在结合能为934 eV的Cu2p3/2轨道峰拟合成结合能为933.57 eV的还原态Cu+和结合能为935.06 eV的氧化态Cu2+,通过计算可得,Cu+/Cu2+的比值为3.39[18]。这说明催化剂中含量较多的Cu+可催化H2O2分解产生·OH,而存在的Cu2+可与H2O2反应生成Cu+,达到Cu+/Cu2+高效循环,其反应方程如式(1)~(3)所示。
Cu++H2O2→Cu2++⋅OH (1) H2O2+⋅OH→HO2⋅+H2O (2) Cu2++HO2⋅→Cu++H++O2 (3) 图4(c)为Zn元素在结合能为1 021.5 eV和1 045.0 eV位置出现的2个峰,分别对应Zn2p3/2和Zn2p1/2,表明锌元素以Zn2+形式与O结合,在催化剂表面有ZnO存在,少量的Zn掺杂能够调控表面氧空穴从而间接影响·OH的产生[19-20]。图4(d)为O1s轨道峰,结合能为530.1 eV为晶格氧,其能够使金属氧化物被还原较高价态,从而促进氧化还原反应进行;532.5 eV处的峰为表面氧,表面氧可以吸附氧气从而捕捉电子产生更多的·OH,达到降解CIP的目的[19]。
2.3 Cu/Zn催化剂与Cu催化剂降解效果对比
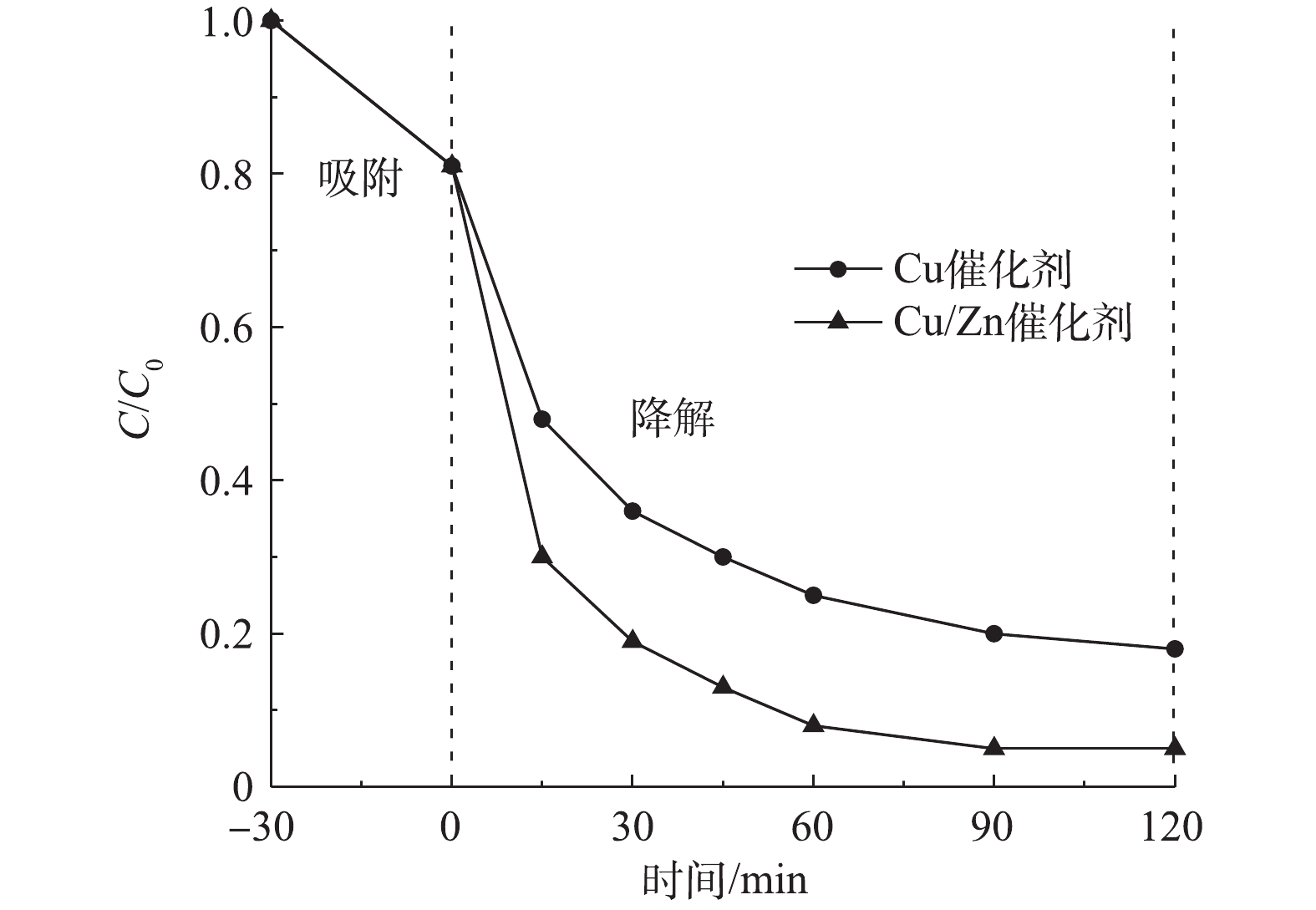
图5为相同条件下制备的Cu/Zn催化剂和Cu催化剂对CIP催化降解效果对比。实验条件:室温下,当CIP浓度为20 mg·L−1、溶液初始pH为5.0、催化剂投加量为3.0 g·L−1时,在吸附平衡30 min后投加H2O2为149.55 mmol·L−1。由图5可知,反应120 min时,Cu/Zn催化剂和Cu催化剂对CIP的降解趋于缓慢,降解率分别为95.0%和81.9%;从整个反应过程看,反应进行30 min时,Cu/Zn催化剂对CIP的降解率为80.6%,而Cu催化剂仅降解63.7%的CIP。结果表明,与Cu催化剂相比,在掺杂Zn元素后的Cu/Zn催化剂不仅引入了新的活性位点,且双金属可协同活化H2O2会产生更多的·OH,可显著提高对CIP的催化性能。
2.4 Cu/Zn催化剂催化降解CIP的影响因素
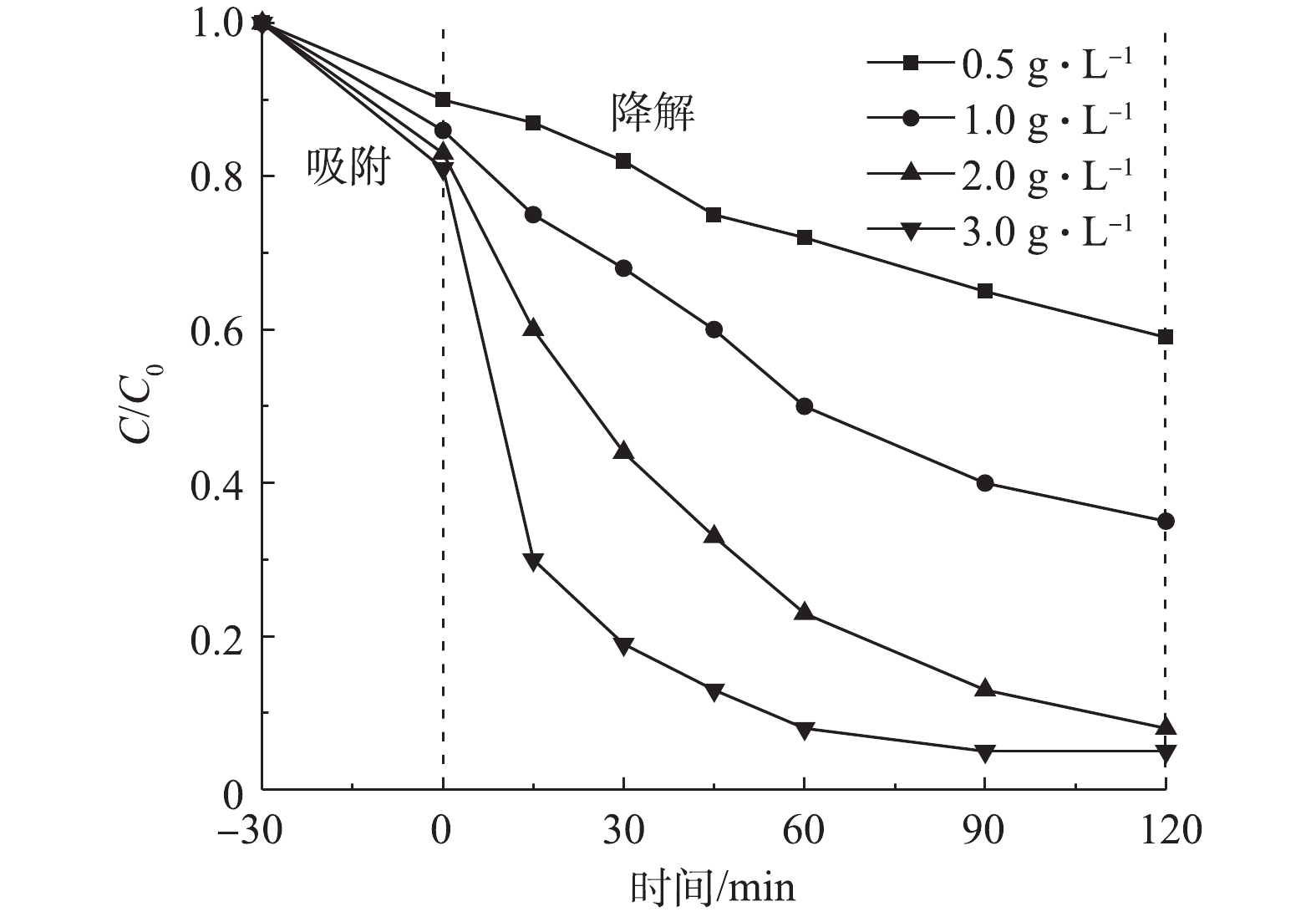
1) Cu/Zn催化剂投加量的影响。在室温下,当CIP浓度为20 mg·L−1、溶液初始pH为5.0时,Cu/Zn催化剂投加量分别为0.5、1.0、2.0、3.0 g·L−1,吸附平衡后投加H2O2为149.55 mmol·L−1,在此条件下考察催化剂投加量对CIP降解效果(图6)。由图6可知,催化剂吸附量在10.0%~20.0%,反应体系中CIP的降解率随着催化剂投加量的增加而呈递增趋势。当反应时间为15 min时,明显发现催化剂投加量为3.0 g·L−1对CIP的降解效果最佳(70.5%),其降解率约为投加量0.5 g·L−1的7倍,投加量1 g·L−1的2.8倍,投加量2 g·L−1的1.75倍;当反应时间为60 min时,催化剂投加量为3.0 g·L−1时对CIP的降解率达92.0%,而当其投加量为2.0、1.0、0.5 g·L−1时的降解率分别为77.6%、48.5%、24.6%;当反应时间为90 min时,催化剂投加量为3.0 g·L−1和2.0 g·L−1时,其对CIP的降解率分别为95.0%和87.0%,而投加量为1.0 g·L−1和0.5 g·L−1时对CIP的降解率为60.0%和35.0%。这说明随着催化剂投加量的增加,提供了更多的表面活性成分,可以在短时间内与H2O2反应生成更多的·OH,加速了氧化降解CIP。此后继续增加反应时间,催化剂投加量为3.0 g·L−1对CIP的降解率不变。因此,选择催化剂投加量为3.0 g·L−1时,在90 min内CIP可完成催化降解。
2) H2O2投加量的影响。非均相Fenton反应的基本原理是催化剂与H2O2产生·OH来对目标污染物进行氧化降解,因此,H2O2投加量将会直接影响到·OH的产生速率,进而影响降解CIP的效率[21]。在室温下,反应器中CIP浓度为20 mg·L−1,调节溶液初始pH为5.0,投加Cu/Zn催化剂为3.0 g·L−1,吸附平衡后H2O2投加量分别为49.85、99.70、149.55、199.40 mmol·L−1,在此条件下考察H2O2投加量对CIP降解效果(图7)。由图7可知,CIP的降解率在30 min内随H2O2投加量的增加而增大;但随着反应时间继续增加(>30 min),投加量为199.40 mmol·L−1对CIP的降解率迅速放缓,低于投加量为149.55 mmol·L−1的降解率。反应体系在30 min内均能大部分的降解CIP是由于催化剂能与足量的H2O2反应,短时间内产生大量的·OH来降解CIP;但当投加量提高到199.40 mmol·L−1且反应时间大于30 min后,因H2O2浓度过大会与·OH反应生成氧化能力小得多的HO2·,甚至还会使H2O2无效分解为H2O和O2[22]。因此,本实验选择H2O2投加量为149.55 mmol·L−1。
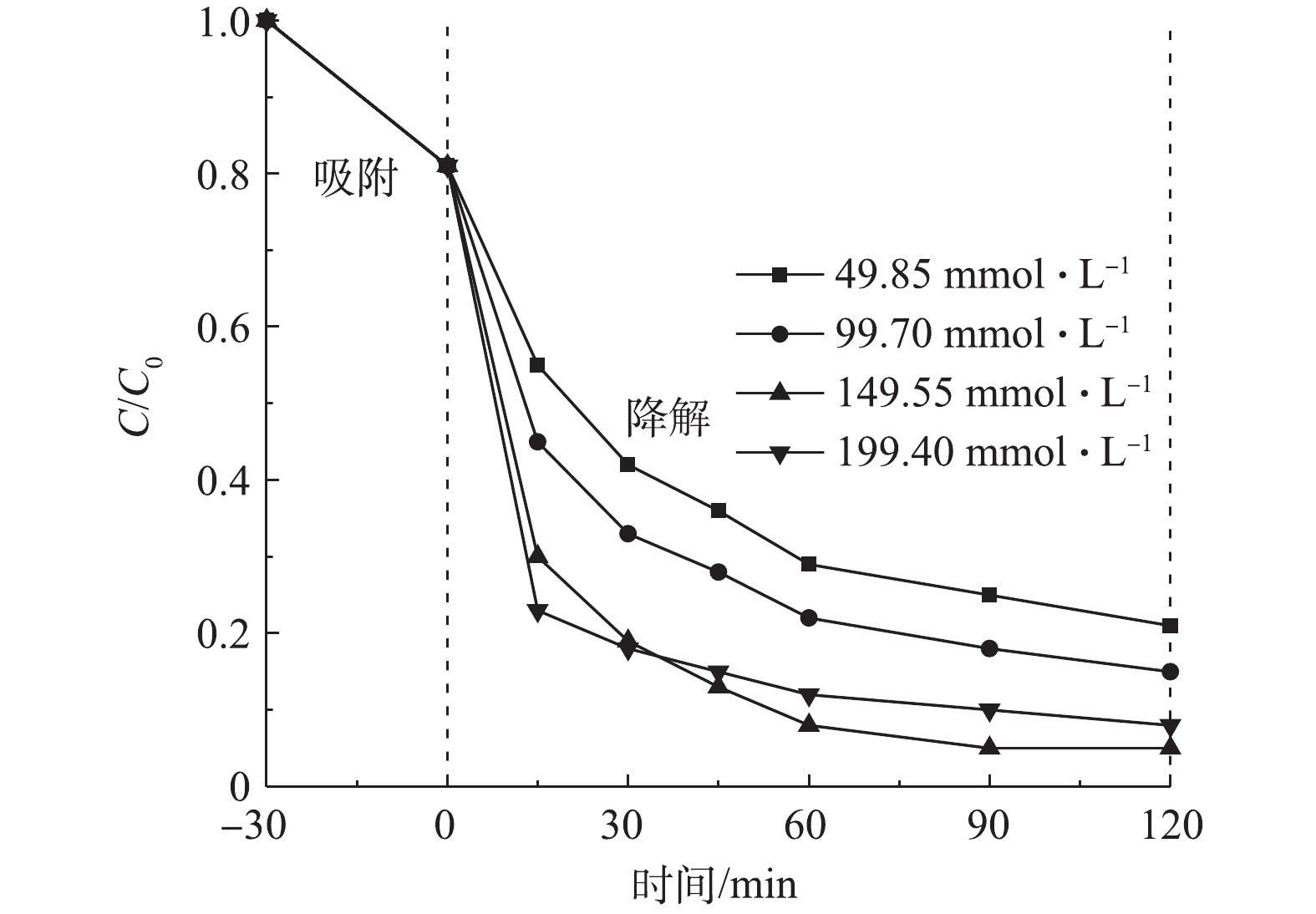
3)溶液初始pH的影响。在室温下,反应器中CIP浓度为20 mg·L−1,调节溶液初始pH分别为3.0、5.0、7.0、9.0、11.0,Cu/Zn催化剂投加量为3.0 g·L−1,吸附平衡后分别投加H2O2为149.55 mmol·L−1,在此条件下考察溶液初始pH对CIP降解效果(图8)。由图8可知,pH为3.0、5.0的反应体系时,CIP降解曲线差异较小,说明这2种反应体系中CIP降解率较为一致。但由图8中也可以看出,随着pH增大,CIP的降解率呈降低趋势。当反应时间为90 min时,pH为3.0、5.0、7.0、9.0和11.0各反应体系对CIP降解率分别为93.2%、95.0、82.3%、69.4%、45.2%。这是因为反应体系pH>7.0时影响了CIP的水解形态,导致其降解率会显著降低,且H2O2也容易分解成O2和H2O,导致其生成·OH速率降低[23];继续增加反应时间,pH为3.0、5.0的反应体系对CIP降解率趋于不变,而pH为7.0、9.0和11.0反应体系的降解率分别为86.4%、76.2%、50.6%。由于不同的目标污染物降解有各自特定的pH,但与传统Fenton法相比,本实验结果说明了Cu/Zn催化剂能在pH为3.0~7.0时达到较好降解率。考虑到实际应用,选择溶液初始pH为5.0。
2.5 降解过程H2O2的消耗量与·OH产生量
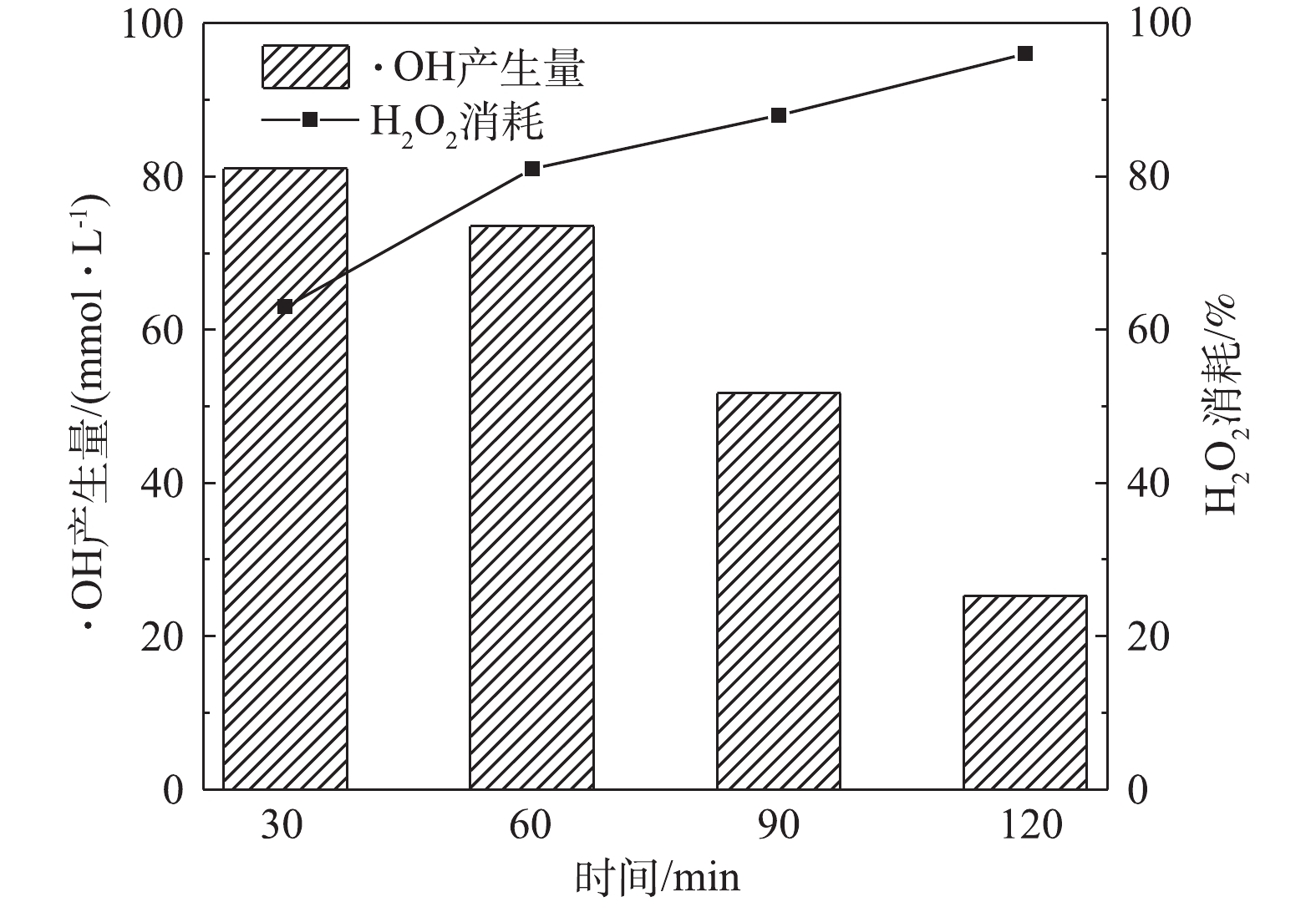
为了分析反应体系中H2O2消耗量及·OH产生量,采用钛盐分光光度法测定了反应体系H2O2消耗量,以香豆素作为探针,使用荧光光度法测定了体系中·OH的产生量。在室温下,CIP浓度为20 mg·L−1、溶液初始pH为5.0、催化剂Cu/Zn投加量为3.0 g·L−1、吸附平衡后H2O2投加量为149.55 mmol·L−1的条件下,分析降解过程H2O2的消耗量和·OH产生量(图9)。由图9可知,反应30 min时,H2O2实际消耗了63.0%,即消耗了94.2 mmol·L−1的H2O2,此刻产生了81.0 mmol·L−1的·OH,H2O2利用率达到86.0%;反应60 min时,H2O2实际消耗了81.0%,即消耗了121.1 mmol·L−1的H2O2,此刻产生了74.0 mmol·L−1的·OH,H2O2利用率达到了61.1%。由图7可知,当反应体系进行到60 min时,CIP的降解率已达92.0%,即此时反应体系中H2O2消耗81.0%就能去除大部分的CIP,而反应体系继续进行时(>60 min)还有H2O2消耗及·OH产生是为了降解CIP的中间产物,使其最终降解为CO2和H2O等。传统Fenton反应体系能达到10%~60%的H2O2利用率,而本实验最大能达到86.0%的H2O2利用率,说明了本研究制备的Cu/Zn催化剂在反应体系中能高效催化H2O2产生·OH,从而快速地降解CIP。
2.6 Cu/Zn催化剂的稳定性
反应过程中金属离子的溶出是评价催化剂稳定性的一个重要因素。通过ICP-MS分析反应进行到30、60、90、120 min时体系中金属离子溶出浓度,不同反应时溶出总铜浓度几乎保持不变,稳定在2.6~2.9 mg·L−1,这显著低于文献[24]中高达17~200 mg·L−1的总铜浓度;溶出锌离子浓度未检出。这可能是因为Cu/Zn催化剂经过高温焙烧后晶粒粒径变小,其比表面积增大,CuO与ZnO协同作用增强,使催化剂的稳定性提高,故不易于溶出[25]。上述结果表明,Cu/Zn催化剂具有良好的稳定性,在反应过程中金属离子的溶出量较低。
2.7 CIP降解机理
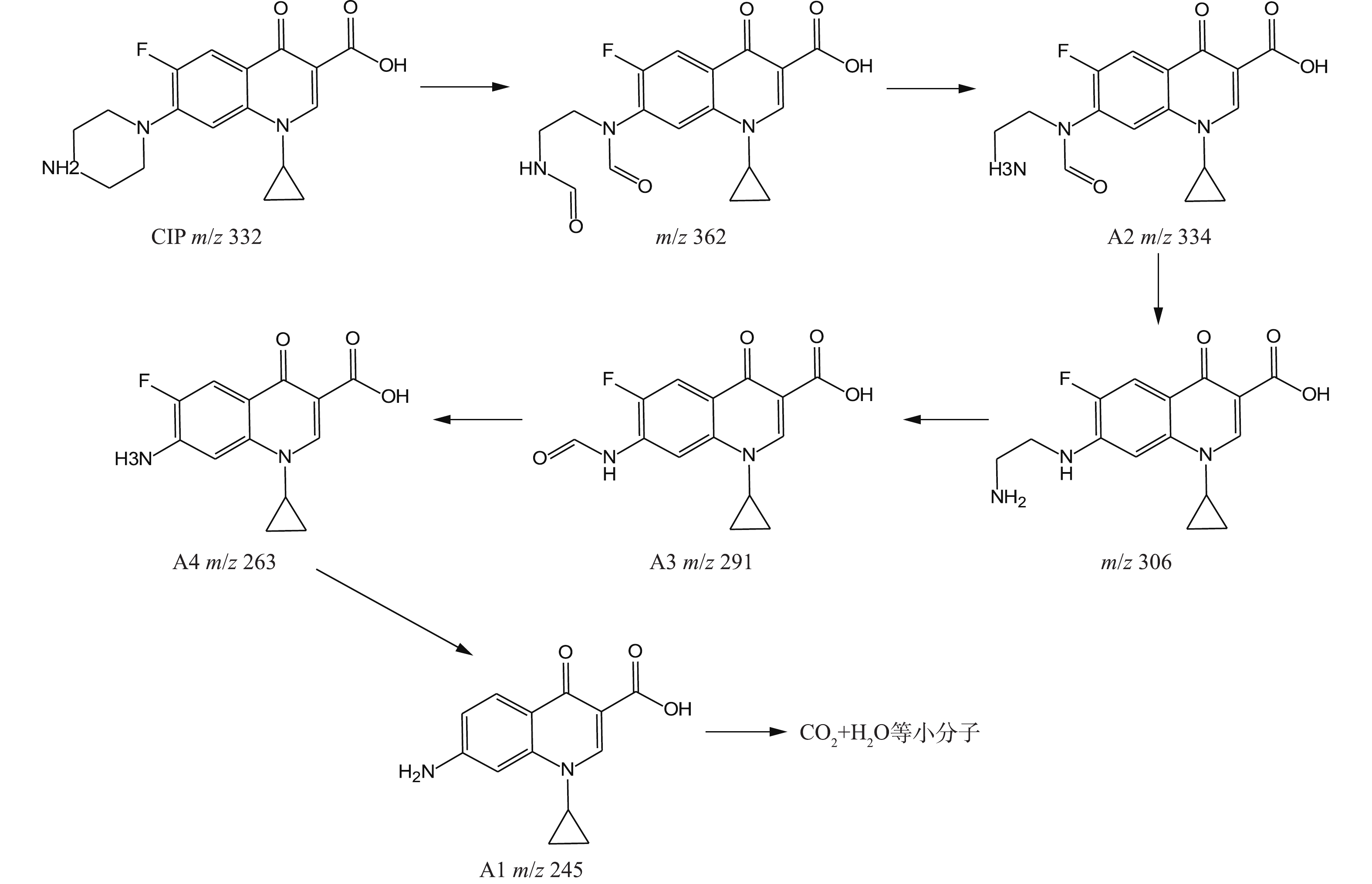
Cu/Zn催化剂与H2O2反应产生具有强氧化性的·OH,通过攻击CIP导致化学键断裂,生成短链羧酸,最终降解为CO2、H2O、
NO−3 、NH+4 等。在CIP氧化过程中,通过LC-MS谱图(30 min)检测出4种降解产物(A1、A2、A3、A4),其详细检测结果见表3。根据HPLC实验可知,CIP出峰时间tR为1.68 min,m/z为332,其主要质谱特征碎片为m/z=314(对应于CIP的1个H2O损失)、m/z=288(对应于CIP的COO—损失)、且还出现了含量较少的m/z=245(对应于CIP的哌嗪环断裂)和m/z=231(对应于环丙基环脱落)[26]。表 3 CIP降解产物LC-MS检测结果Table 3. LC-MS detection results of CIP degradation products可能物质 出峰时间/min m/z 化学式 CIP 1.680 [332]: 314, 288, 245 
A1 1.462 [236]: 218, 364, 258 C13H12N2O3 A2 3.382 [334]: 316, 268, 242 
A3 3.556 [291]: 273, 263, 245 C14H11FN2O4 A4 3.731 [263]: 245, 227, 205 
基于表3提出的合理降解路径是:官能团的可氧化次序为哌嗪环>苯环>吡啶酮环[27],结合AN等[28]对CIP分子前线电子密度的计算,且哌嗪环是CIP分子结构的活性中心,因此,CIP的氧化分解主要发生在哌嗪环上;CIP的哌嗪环被·OH攻击导致C—C键断裂,即哌嗪环开环,之后继续被·OH氧化并醛基化,生成双醛基衍生物,该物质上的醛基易被·OH氧化,损失一个甲醛后生成A2[29-30];A2的N1在损失了仲胺氮基后生成A3;产物A4为CIP中哌嗪环侧链被完全氧化,最后只剩下氨基,是被·OH多次攻击的结果[31];A4经过C—F键的断裂和进一步氧化转化成A1,最终A1在持续攻击下而被完全矿化成CO2和H2O等小分子物质,CHONG等[32]也报道了相似的CIP降解路径。
根据以上结果,在Cu/Zn与H2O2反应体系中CIP可能存在的降解路径如图10所示。
3. 结论
1) Cu/Zn催化剂主要是由CuO组成的介孔材料,具有较好的结晶度及均匀的颗粒状表面形貌,比表面积为0.739 m2·g−1、总孔容为0.003 cm3·g−1、中孔孔容为0.0029 cm3·g−1、平均孔径为3.414 nm。
2)采用浓度为20 mg·L−1的CIP作为目标污染物,在初始溶液pH为5.0、催化剂投加量为3.0 g·L−1、H2O2投加量为149.55 mmol·L−1最适条件下,Cu/Zn催化剂具有良好的催化性能;在反应进行到30 min时,产生了81.0 mmol·L−1的·OH,H2O2利用率可达86.0%;当反应时间为90 min时对CIP的降解率为95.0%;Cu/Zn催化剂具有良好的稳定性。
3) Cu/Zn催化剂能在pH为3.0~7.0时保持较好的非均相Fenton反应效果,解决了传统Fenton催化剂在非酸性条件下催化活性较低的局限。
4)在CIP氧化30 min时,通过LC-MS检测出4种降解产物(A1、A2、A3、A4),其出峰时间分别为1.462、3.382、3.556、3.731 min,其对应的化合物分子式分别为C13H12N2O3、
C16H17FN3O+4 、C14H11FN2O4、C13H12FN2O+3 。 -
表 1 A2O2-MBR工艺各阶段工艺参数
Table 1. Operation parameters of the A2O2-MBR process at each stage
运行时间/d 进水COD/(mg·L−1) C/N比 DO质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 曝气量/(mL·min−1) 低氧池 好氧池 低氧池 好氧池1 好氧池2 1~25 300 6.0 2.76 3.99 400 640 640 26~40 300 6.0 1.98 3.34 320 600 600 41~58 300 6.0 1.12 1.64 280 500 500 59~87 300 6.0 1.29 1.96 280 600 600 88~136 300 6.0 1.46 2.08 240~280 500 600 137~171 300 6.0 0.89 1.95 200 500 500~600 172~192 300 6.0 0.70 1.79 120~160 500 500 193~213 300 6.0 0.48 1.82 100 500 500 214~283 300 6.0 0.58 1.76 120 500 500 284~333 250 5.0 0.70 1.71 120 500 500 334~356 200 4.0 0.70 1.69 120 500 500 357~375 200 4.0 0.63 1.73 100 500 500 376~393 200 4.0 0.58 1.75 80 500 500 表 2 高通量测序污泥样品信息
Table 2. The activated sludge samples used for high-throughput gene sequencing analysis
样品编号 取样时间/d C/N 低氧池DO浓度/(mg·L−1) TN去除率/% S1 — — — — A1 26 6 2.47 77.5 B1 194 6 0.59 82.8 B2 278 6 0.59 86.1 C1 333 5 0.66 86.3 C2 375 4 0.71 84.6 表 3 A2O2-MBR工艺不同阶段氨氮和TN去除效果
Table 3. Ammonia and TN removal effects at various stages of the A2O2-MBR process
时间/d 进水C/N比 平均DO质量浓度/(mg·L−1) NH4+-N平均去除率/% TN平均去除率/% 低氧池 好氧池 1~87 6.0 1.80±0.61 2.73±0.93 97.0±1.8 78.9±1.8 88~201 6.0 1.06±0.33 1.96±0.14 98.4±1.0 79.6±1.3 202~234 6.0 0.50±0.08 1.87±0.08 92.2±1.5 76.3±2.8 235~283 6.0 0.60±0.07 1.68±0.08 97.8±0.9 85.0±1.1 284~333 5.0 0.70±0.05 1.71±0.06 97.6±0.9 84.9±1.4 334~356 4.0 0.70±0.05 1.69±0.08 98.2±0.4 80.9±1.5 357~393 4.0 0.61±0.05 1.74±0.04 98.3±0.4 84.7±0.7 表 4 不同SND工艺参数和处理效果比较
Table 4. The operating parameters and removal effects of various SND process
工艺 进水C/N HRT/h 好氧HRT/h DO/(mg·L−1) SND效率/% TN去除率/% 参考文献 SBR 5~10 16 7 0.3 60~88 70~91 [10] SBR 6 12 8 1~2 79.2 89.6 [31] SBR 3.5 14.6 6.7 1.0 49.3 77.7 [12] AOA-SBR 3.5 20 8 0.5 59.6 92.1 [13] AOA-SBR 5 15 5~10 0.3 100 98.9 [32] SBR-AGS 3.4 14~18 10~14 0.1~0.7 73.1 81.4 [6] SBR-AGS 6.7 5.2 3.3 1.8 75 80~90 [33] SBR-AGS 3~4 24 12 0.5~1.0 / 77 [34] 好氧/微氧固定床 4 12 12 4/0.5 / 97.6 [35] SBBR 2.6~4.1 15 11 2.5 70.57 82.95 [17] AOA+膜 4.4 14 3.9 1~2 / 92.2 [18] MUCT 5~7 / / 1.2~2 35.3 85.5 [36] UCT-MBR 7.3 15.5 / 0.9 / 90.27 [37] OOA-MBR 10.9 4.8 2.4 1.2~1.6 83.67 77.7 [1] 氧化沟-MABR 1.5~2.3 24 / 1~4 51~71 85.7 [38] A2O2-MBR 4 12 6 0.6 90 84.7 本文 -
[1] 李宁, 钟为章, 苗志加, 等. 两段进水生物膜法OOA-MBR工艺强化生物脱氮[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(9): 4849-4894. [2] JIA Y, ZHOU M, CHEN Y, et al. Insight into short-cut of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification process in moving bed biofilm reactor: Effects of carbon to nitrogen ratio[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 400: 25905. [3] IANNACONE F, CAPUA FD, GRANATA F, et al. Effect of carbon-to-nitrogen ratio on simultaneous nitrification denitrification and phosphorus removal in a microaerobic moving bed biofilm reactor[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 250: 109518. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109518 [4] 王景峰, 王暄, 季民, 等. 颗粒污泥膜生物反应器同步硝化反硝化[J]. 中国环境科学, 2006, 26(4): 436-440. [5] HE Q, ZHANG W, ZHANG S, et al. Enhanced nitrogen removal in an aerobic granular sequencing batch reactor performing simultaneous nitrification, endogenous denitrification and phosphorus removal with low superficial gas velocity[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 326: 1223-1231. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.071 [6] YUAN C, WANG B, PENG Y, et al. Enhanced nutrient removal of simultaneous partial nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal (SPNDPR) in a single-stage anaerobic/micro-aerobic sequencing batch reactor for treating real sewage with low carbon/nitrogen[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 257: 127097. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127097 [7] 闫苗苗, 张海涵, 钊珍芳, 等. 生物脱氮技术中好氧反硝化细菌的代谢及应用研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(3): 668-676. [8] XI H, ZHOU X, ARSLAN M, et al. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification process: Promising but a long way to go in the wastewater treatment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 805: 150212. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150212 [9] BAI X, MCKNIGHT MM, NEUFELD J D, et al. Nitrogen removal pathways during simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal under low temperature and dissolved oxygen conditions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 354: 127177. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127177 [10] ZAMAN M, KIM M, NAKHLA G. Simultaneous nitrification-denitrifying phosphorus removal (SNDPR) at low DO for treating carbon-limited municipal wastewater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 760: 143387. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143387 [11] HU T, PENG Y, YUAN C, et al. Enhanced nutrient removal and facilitating granulation via intermittent aeration in simultaneous partial nitrification endogenous denitrification and phosphorus removal (SPNEDpr) process[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 285: 131443. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131443 [12] WANG X, WANG S, XUE T, al. Treating low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) wastewater in simultaneous nitrification-endogenous denitrification and phosphorous removal (SNDPR) systems by strengthening anaerobic intracellular carbon storage[J]. Water Research, 2015, 77: 191-200. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.03.019 [13] WANG X, WANG S, ZHAO J, et al. Combining simultaneous nitrification-endogenous denitrification and phosphorus removal with post-denitrification for low carbon/nitrogen wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 220: 17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.132 [14] 张郅昊, 张群, 孙郁聪, 等. 低温同步短程硝化反硝化可行性研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2022, 42(5): 83-88. [15] 陈明月, 刘丽红, 温榛煌, 等. 折流式A2O-MBR工艺启动过程及影响因素研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2023, 49(4): 120-124. [16] 刘钢, 温榛煌, 刘丽红, 等. A2O-MBR工艺短程硝化和SND影响因素研究[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41: 88-91. [17] 张建华, 彭永臻, 张淼, 等. 同步硝化反硝化SBBR处理低C/N比生活污水的启动与稳定运行[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(11): 4817-4824. [18] ZHAO J, WANG X, LI X, et al. Combining partial nitrification and post endogenous denitrification in an EBPR system for deep-level nutrient removal from low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) domestic wastewater[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 210: 19-28. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.135 [19] GAO X, ZHANG T, WANG B, et al. Advanced nitrogen removal of low C/N ratio sewage in an anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic process through enhanced post-endogenous denitrification[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 252: 126624. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126624 [20] WU Y, PENG Z, WANG H, et al. Hydraulic retention time optimization achieved unexpectedly high nitrogen removal rate in pilot-scale anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic system for low-strength municipal wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 393: 130128. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.130128 [21] GAO X, XUR X, LI L, et al. Balance nitrogen and phosphorus efficient removal under carbon limitation in pilot-scale demonstration of a novel anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic process[J]. Water Research, 2022, 223: 118991. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118991 [22] VIEIRA A, GALINHA CF, OEHMEN A, et al. The link between nitrous oxide emissions, microbial community profile and function from three full-scale WWTPs[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 651: 2460-2472. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.132 [23] 赵冰怡, 陈英文, 沈树宝. C/N比和曝气量影响MBR同步硝化反硝化的研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(3): 400-404. [24] WU T, YANG S-S, ZHONG L, et al. Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal: What have we done so far and how do we need to do in the future?[J] Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 856: 158977. [25] JIANG L, LIU Y, GUO F, et al. Evaluation of nutrient removal performance and resource recovery potential of anaerobic/anoxic/ aerobic membrane bioreactor with limited aeration[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 340: 125728. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125728 [26] HE Q, YAN X, FU Z, et al. Rapid start-up and stable operation of an aerobic/oxic/anoxic simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal reactor with no sludge discharge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 362: 127777. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127777 [27] ZHAO W, HUANG Y, WANG M, et al. Post-endogenous denitrification and phosphorus removal in an alternating anaerobic/oxic/ anoxic (AOA) system treating low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) domestic wastewater[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 339: 450-458. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.096 [28] 张晓辉, 谢俊浩, 曹奇光, 等. 智慧污水处理自控系统设计及应用研究[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2021, 16(1): 27-31. [29] ZHENG Z, HUANG S, BIAN W, et al. Enhanced nitrogen removal of the simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) biofilm reactor for treating mainstream wastewater under low dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 283: 213-220. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.148 [30] 孙盼, 张萌, 郭磊艳, 等. 短程反硝化生物过程及工艺研究进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2023, 39(6): 9-17. [31] LI C, LIU S, MA T, et al. Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) under low temperature[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 229: 132-141. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.185 [32] XIE S, ZHAO J, ZHANG Q, et al. Improvement of the performance of simultaneous nitrification denitrification and phosphorus removal(SNDPR)system by nitrite stress[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 788: 147825. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147825 [33] BASSIN JP, KLEEREBEZEM R, DEZOTTI M, et al. Simultaneous nitrogen and phosphate removal in aerobic granular sludge reactors operated at different temperatures[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46: 3805-3816. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.04.015 [34] 冷璐, 信欣, 鲁航, 等. 同步硝化反硝化耦合除磷工艺的快速启动及其运行特征[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 35(11): 4180-4188. [35] 陈均利, 张树楠, 戴桂金, 等. 同步硝化反硝化菌(Alcaligenes faecalis WT14)养殖污水脱氮效果研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(8): 1811-1817. [36] GE S, PENG Y, LU C, et al. Practical consideration for design and optimization of the step feed process[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science and Engineering in China, 2013, 7(1): 135-142. doi: 10.1007/s11783-012-0454-3 [37] 王朝朝, 李军, 高金华, 等. 进水碳氮比对UCT-MBR工艺运行效能及膜污染的影响[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2014, 40(4): 619-626. [38] 茹凌宇, 刘恒毅, 李蕾, 等. 两级同步硝化反硝化工艺处理低碳氮比壤中流[J]. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(21): 84-91. [39] WANG H, SONG Q, WANG J, et al. Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal in an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor with high dissolved oxygen: effects of carbon to nitrogen ratios[J]. Science of Total Environment, 2018, 642: 1145-1152. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.081 [40] MA J, JI Y, FU Z, et al. Performance of anaerobic/oxic/anoxic simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal system overwhelmingly dominated by Candidatus_Competibacter: Effect of aeration time[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 384: 129312. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129312 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 汤凯,宋灿辉,曹茜斐,安天一,刘洋,周钒,杜桂泉,孙法迁,陈重军. 低耗往复式膜生物反应器系统的中试应用研究. 中国环境科学. 2025(02): 727-735 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 韩奕彤,罗育池,王刚,刘畅,宋宝德,秘昭旭,王先稳. 典型离子型稀土矿区氮污染地下水原位微生物修复技术研究. 环境科学研究. 2024(11): 2391-2400 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨春玉,董战峰,顾湘,汪俊峰. 中国公众空气质量感知的时空演化及其驱动因素分析. 环境科学研究. 2024(12): 2653-2664 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: