-
我国大部分油田已进入高含水开采期。油田在生产开发过程中产生大量的采出水,而热采工艺需要消耗大量的蒸汽,蒸汽的水源主要是自来水,导致采出水处理量和回注量逐年增加[1],同时也消耗了大量的淡水资源。为了解决这一难题,近年来对采出水资源化进行了较多的研究[2]。
资源化利用的关键是解决采出水中含油量、悬浮物、矿化度、硬度过高的问题[3]。目前,较为成熟的技术是MVR[4-5]和反渗透工艺。MVR工艺的优点是产水率高,适用于高矿化度水质,但由于其成本较高、核心技术不易掌握,限制了推广范围,而反渗透工艺在一定程度上克服了这些缺点。反渗透膜不仅能有效去除有机物、降低COD,而且具有优异的脱盐效果[6]。采出水进行反渗透处理前通常需要利用超滤工艺进行预处理,超滤的主要作用是为了去除水中的悬浮物和细菌,以达到保护反渗透膜的目的。超滤工艺之前也需要进行预处理,主要是为了减轻采出水中原油对超滤膜的污染问题,以延长超滤膜的使用寿命。常用的超滤预处理工艺有混凝沉降、多介质过滤、生化,其中生化工艺对原油的去除较为彻底,能耗较低,是一种较为理想的超滤预处理工艺。油田采出水利用生化双膜工艺制备锅炉用水技术尚未大规模推广,笔者[7-8]通过近2年的生化超滤工艺和7个月的生化双膜工艺研究发现,油田采出水利用生化双膜工艺制备锅炉用水,实现采出水的资源化利用是非常有前景的,既具有经济效益,又具有社会效益。
在之前的研究[9]中已对预处理及生化工艺进行了详细介绍。本研究重点研究了超滤进水悬浮物与超滤膜污染之间的关系,分别考察了反渗透进水压力、进水温度对产水率、膜通量和透盐率的影响。
全文HTML
-
对采出水的水质进行了多次检测,水质较为稳定:pH=7.55、温度为48 ℃、SS为50 mg∙L−1、含油量为127 mg∙L−1、COD为376 mg∙L−1、BOD为125 mg∙L−1、
HCO−3 为614 mg∙L−1、总硬度为1 400 mg∙L−1、TDS为18 100 mg∙L−1、电导率为30 348 μs∙cm−1。以上结果表明,采出水具有高含油、高矿化度、高COD的特点,将采出水用于锅炉给水必须进行脱盐,脱盐采用的工艺为反渗透,反渗透对进水水质有一定的要求,因此,需要对采出水进行降温、除油、降COD、降悬浮物等预处理。 -
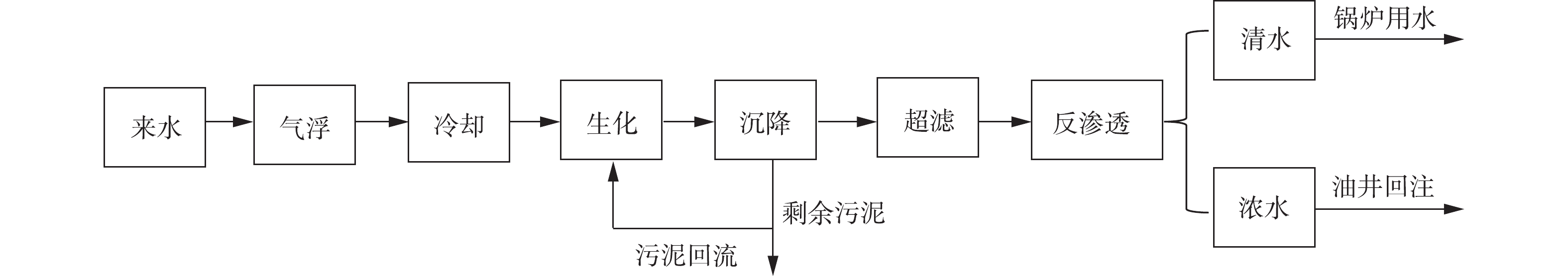
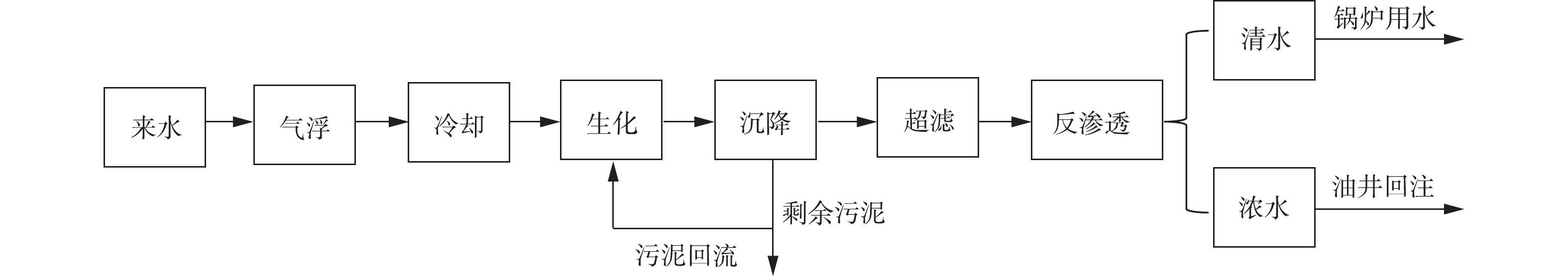
整套流程包括预处理、生化、超滤、反渗透4个部分,超滤前部分自2018年6月开始运行,2019年10月接入反渗透流程,整套工艺流程如图1所示。
1)预处理包括气浮和降温2个单元。来水首先进行气浮工艺,处理能力为10 m3∙h−1,可去除大部分含油和悬浮物,降低生化部分负荷。风式冷却塔将来水的温度由48 ℃降低到35 ℃以下,为微生物提供合适的生长温度。生化采用的是MBBR工艺,生化池的有效体积为100 m3。加入填料40 m3,材质为HDPE,直径为25 mm,高为10 mm。活性污泥为2 000 mg∙L−1,功能菌种的发酵液为6 m3,初期加入碳源、氮源,7 d后生化运行正常,不再加入碳氮等营养物质。生化曝气采用的是罗茨风机,风量为4 m3∙min−1,沉降采用拉美兰沉降池,停留时间为2 h。连续检测生化后采出水的含油量,并与来水和气浮后对比。
2)超滤采用PVDF管式中空纤维膜,过滤精度为30 nm,过滤方式采用的是死端过滤,超滤综合产水率大于97%。在线检测超滤进水压力、浓水压力、产水压力,并计算跨膜压差。每2 d人工检测1次超滤进水悬浮物,记录同一时间的跨膜压差,分析悬浮物对膜污染的影响。不定期检测超滤产水含油量、悬浮物和pH。
跨膜压差根据式(1)进行计算。
式中:ΔP为跨膜压差,MPa;P1为进水压力,MPa;P2为浓水压力,MPa;P3为产水压力,MPa。
3)反渗透采用的是陶氏提供的专用反渗透膜。进水泵为固定频率,最高可提供2.3 MPa的进水压力,通过控制浓水阀门调节进水压力。通过调节风式冷却塔和系统进水量调节整个系统水温。在线检测系统的进水压力、进水量、产水量、浓水量、温度、电导率,并计算产水率和膜通量。分析进水压力、进水温度与产水率、膜通量、透盐率的关系。不定期检测反渗透产水的含油量、悬浮物、矿化度、硬度和pH。
反渗透过程中膜通量根据式(2)进行计算。产水率根据式(3)进行计算。
式中:Jw为膜通量,L·(m2·h)−1;A 为纯水渗透系数;ΔP为膜两侧压力差,MPa;ΔPs为膜两侧渗透压差,MPa。
式中:K为产水率;Jw为膜通量,L·(m2·h)−1;S为膜面积,m2;Q为进水量,m3·h−1。
1.1. 水质分析
1.2. 工艺流程
-
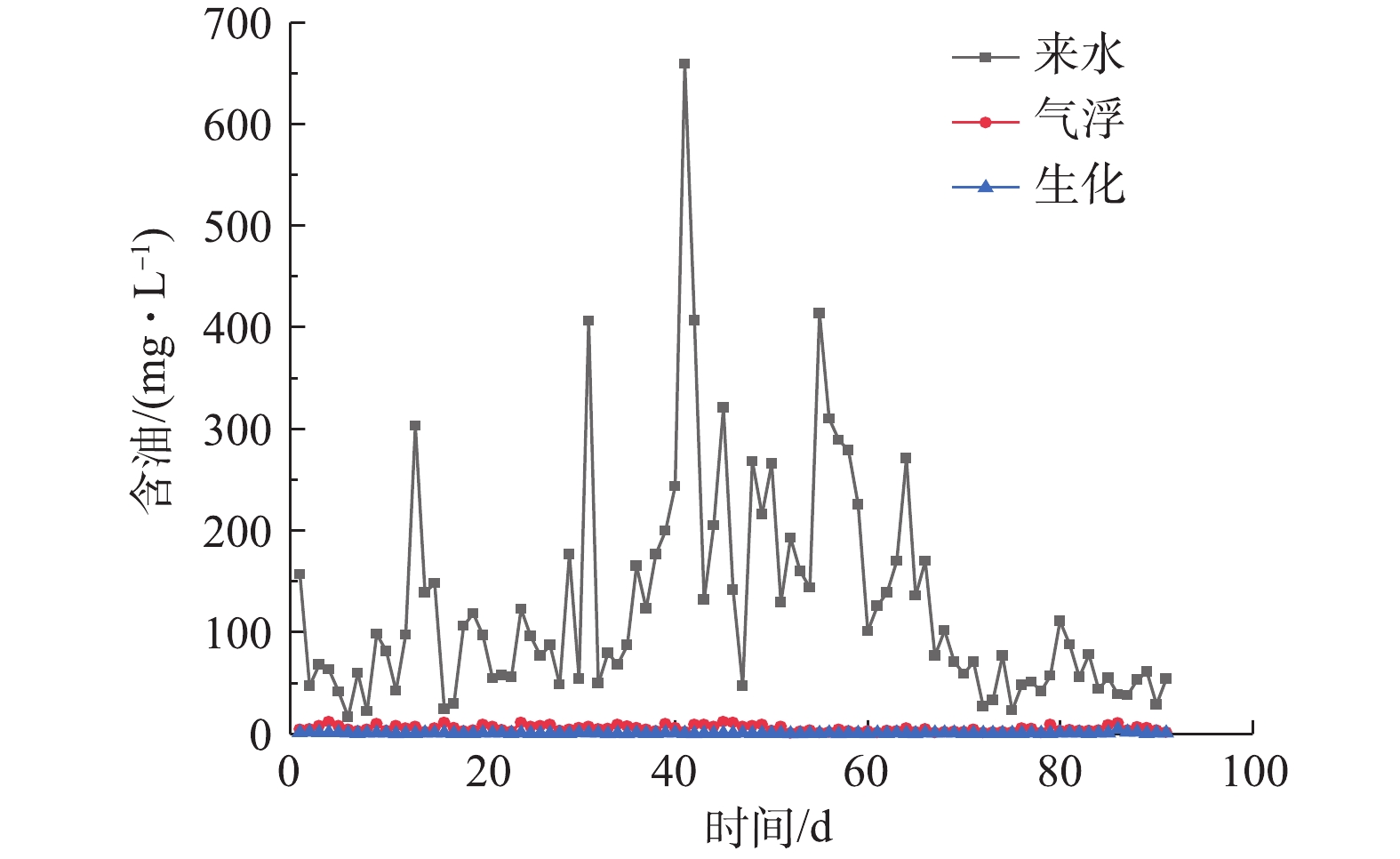
采出水经过气浮和生化后的含油量指标变化如图2所示。来水平均含油量为127 mg∙L−1;气浮出水平均含油量为5.14 mg∙L−1;生化出水平均含油量为0.63 mg∙L−1。
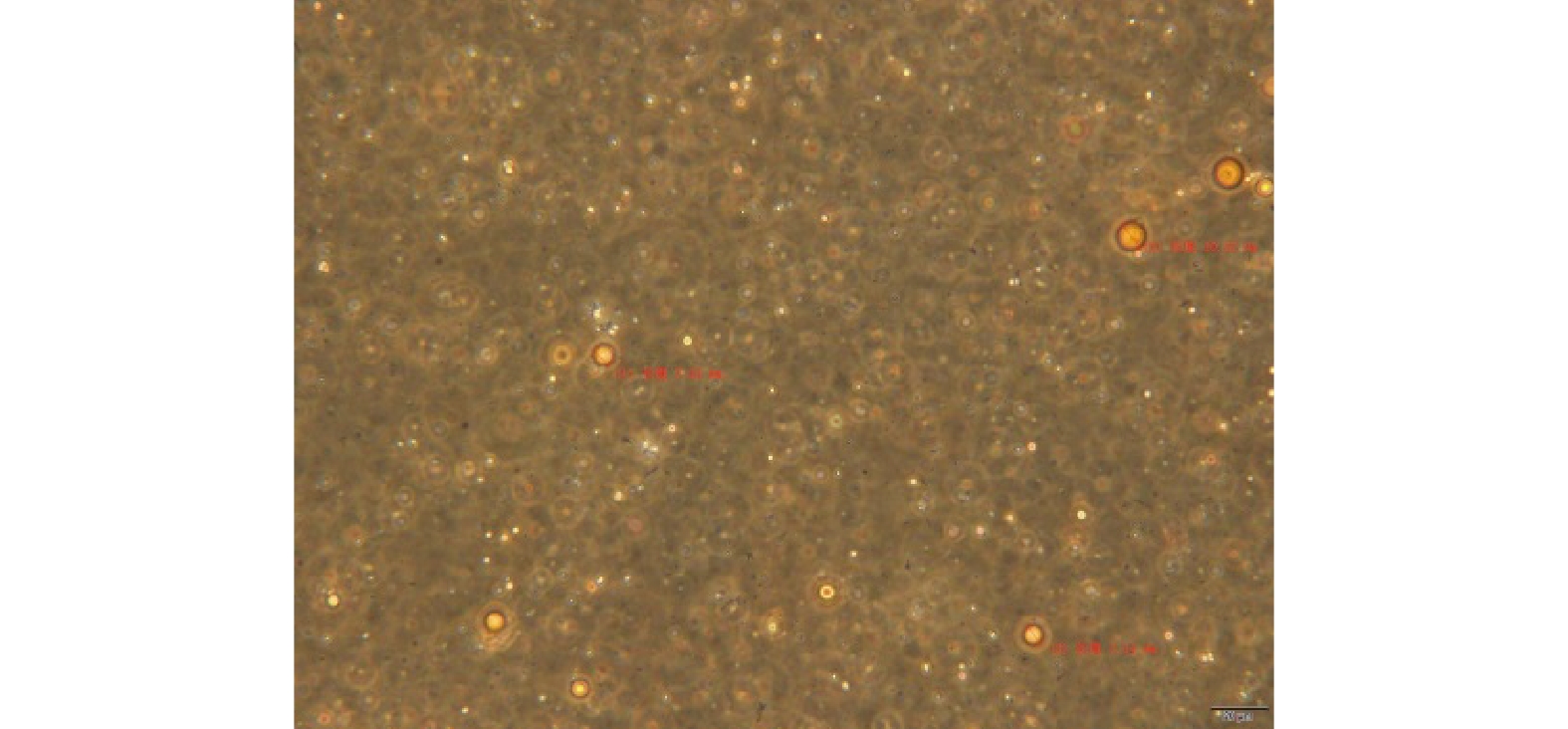
气浮可以去除大部分原油,去除率为96.0%,剩余的4%原油为乳化油和溶解油,均匀分布在采出水中,原油直径小于10 µm,如图3所示。这部分原油利用絮凝和其他常规的方法难以去除,而功能性菌种具有较高的浓度和较大的比表面积,可以比较彻底地降解这部分剩余原油,降解率为3.6%。
-
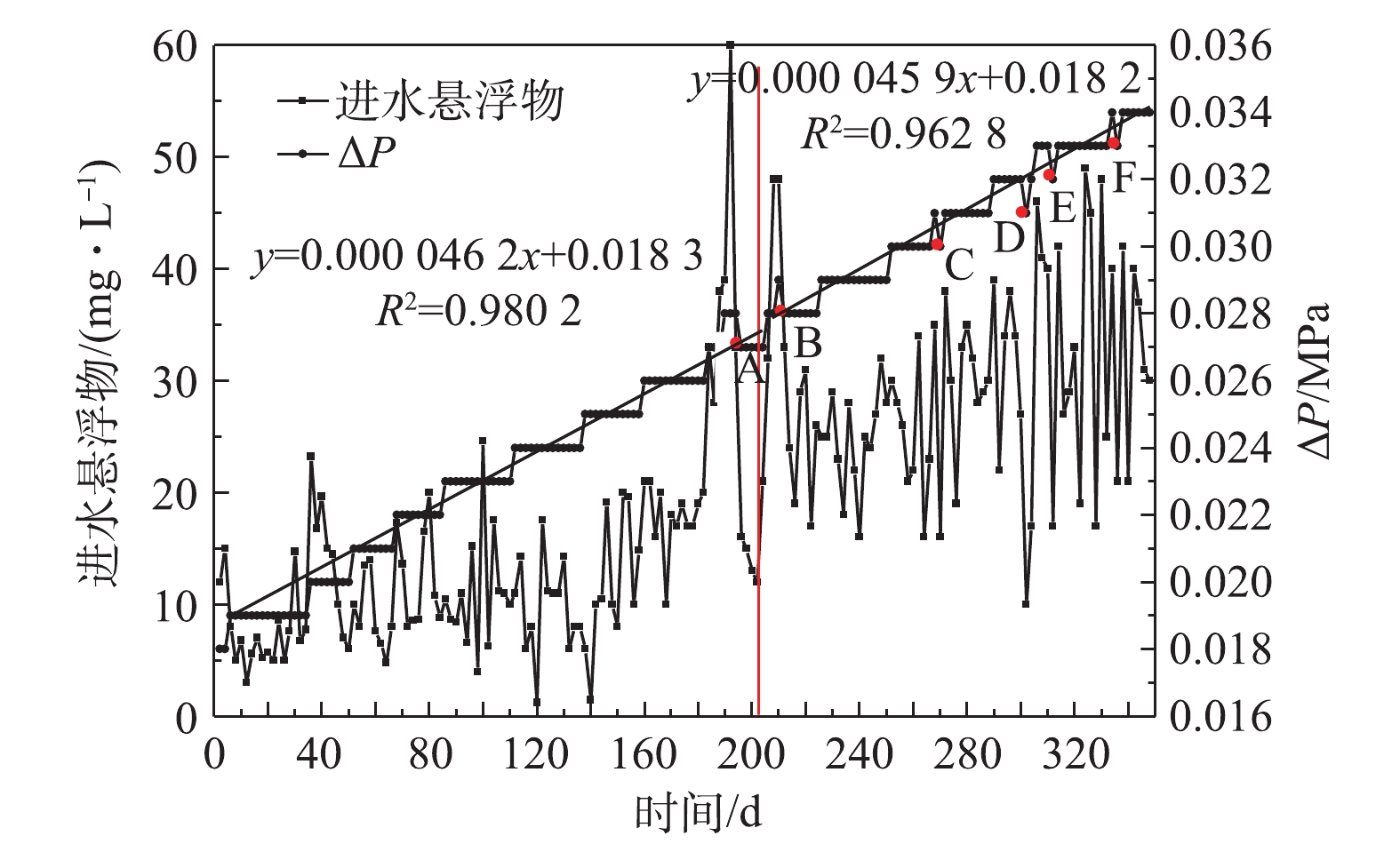
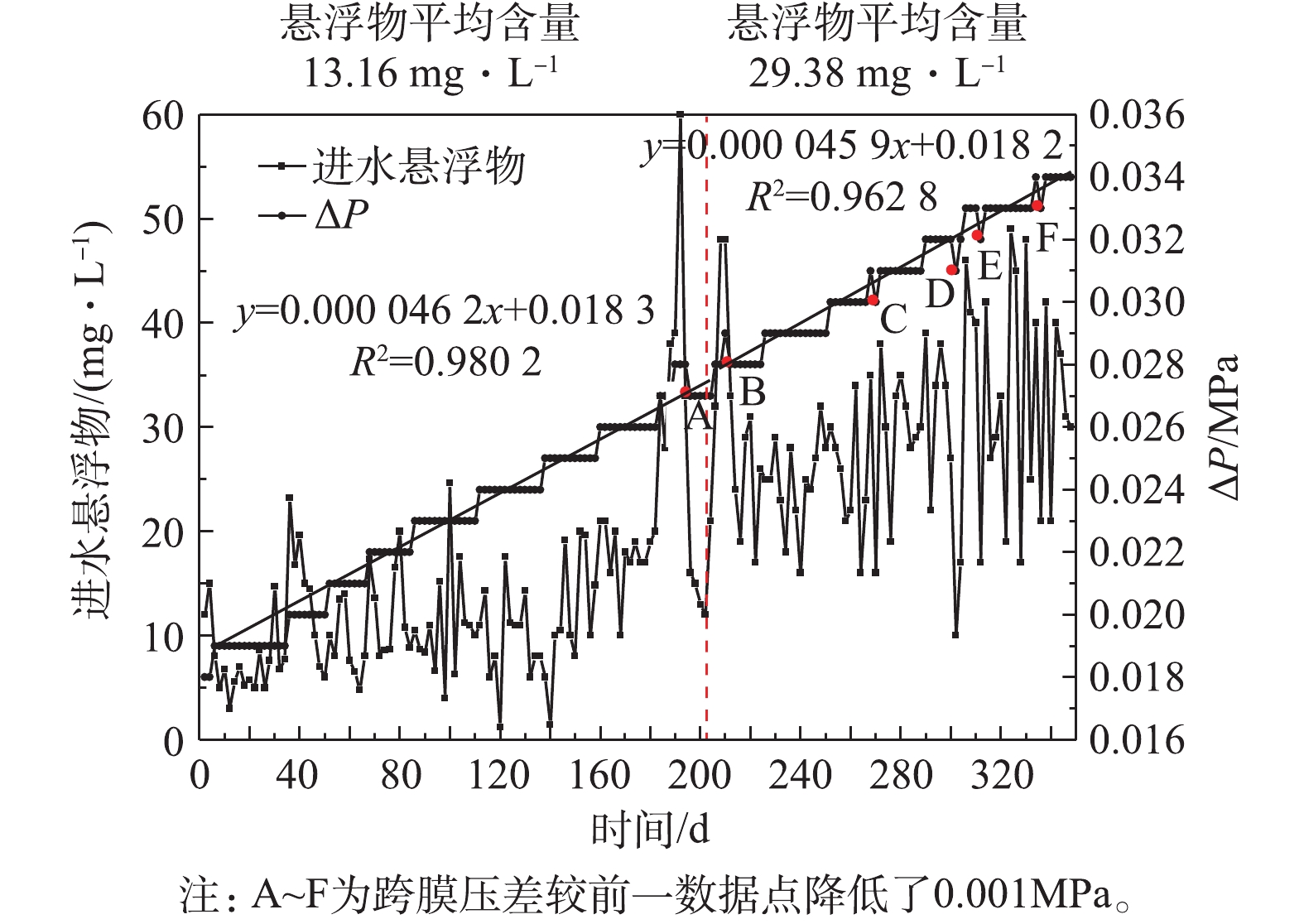
每2 d取一组跨膜压差,跨膜压差的变化如图4所示。实验总共选取了174组数据,由于来水水源某些参数的变化,导致生化后采出水的悬浮物含量增加。前102组数据为来水水源变化前数据,进水悬浮物平均为13.16 mg∙L−1,ΔP的增加速度为0.000 046 2 MPa·d−1,即每年增加0.016 9 MPa,后72组数据为来水水源变化后数据,悬浮物平均为29.38 mg∙L−1,ΔP的增加速度为0.000 045 9 MPa·d−1,即每年增加0.016 8 MPa。对于生化处理后的油田采出水,超滤进水中悬浮物的数量与ΔP的增加速度无关。即在一定范围内,超滤膜的污染速度与进水悬浮物的数量无关。
跨膜压差为超滤膜运行的重要指标之一,其增大速度主要表征超滤膜污染的程度,一般跨膜压差达到0.06 MPa需要对超滤膜进行化学清洗,那么第1次化学清洗,需要的时间为(0.06-0.018 2)/0.016 8 = 2.5 a。由此可见,经过生化处理后的采出水悬浮物虽然较高,但是对超滤膜污染程度较小。
在运行过程中,跨膜压差A、B、C、D、E、F等6个点较前一数据降低了0.001 MPa,原因是由于这6个点对应的悬浮物较前一数据均有较大幅度的波动。由此可见,进水悬浮物数值短时间较大波动会引起跨膜压差暂时增高或降低,当悬浮物数值正常后,跨膜压差可以恢复到前期水平。
-
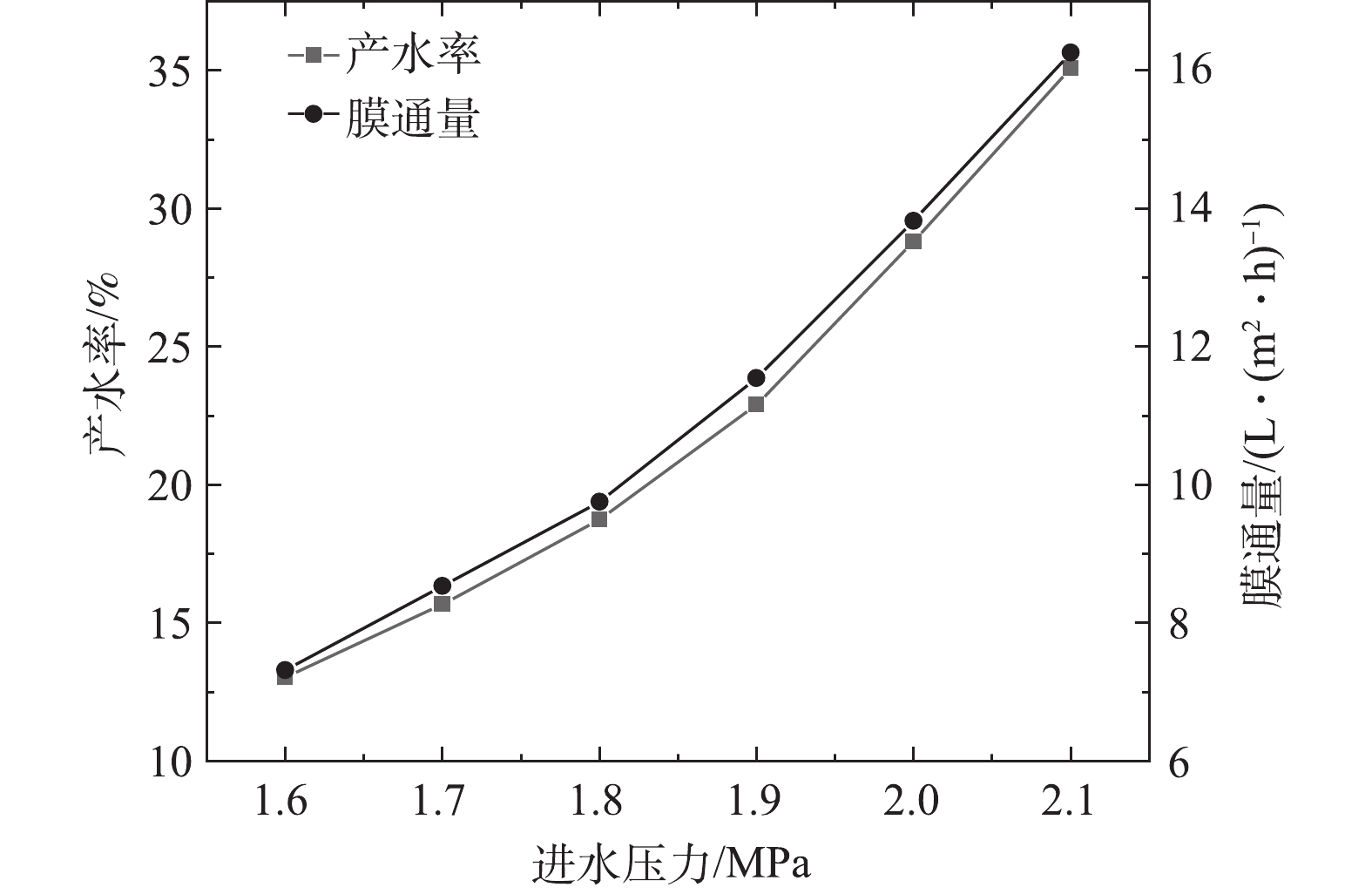
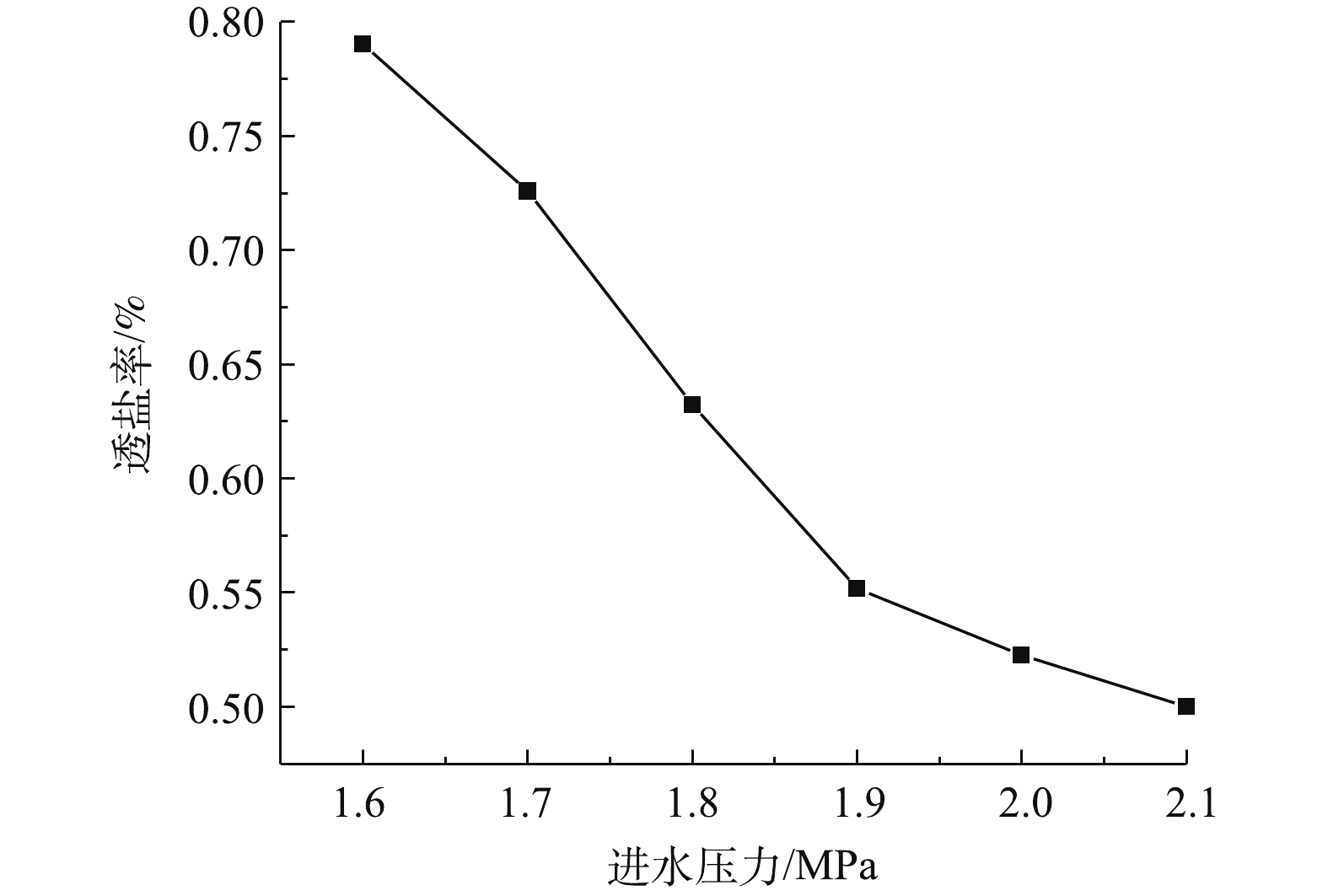
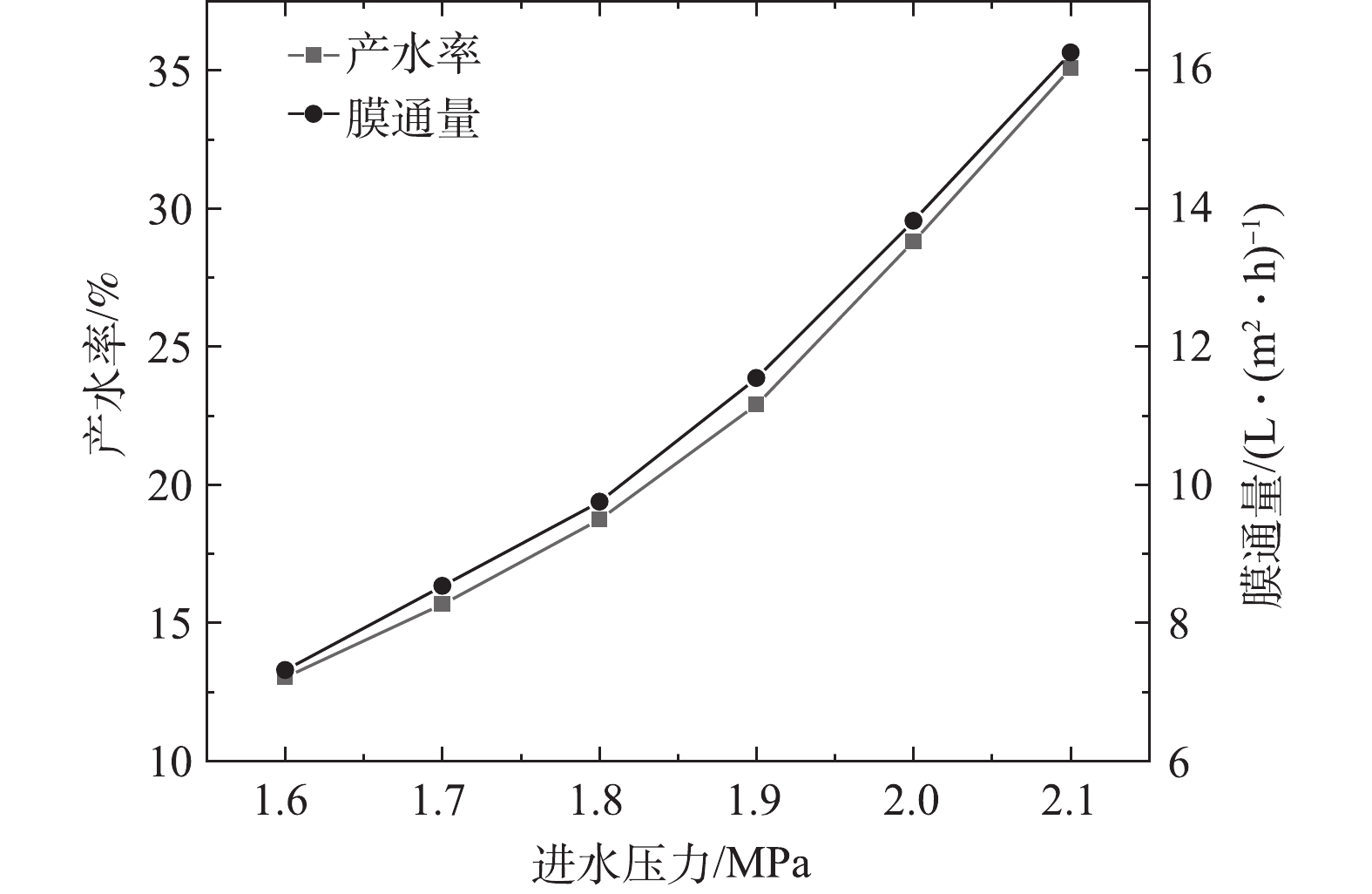
1)通过调节浓水阀调节进水压力,产水率及膜通量的变化如图5所示,透盐率的变化如图6所示。产水率随着进水压力的增大而增加,进水压力每增加0.1 MPa,产水率增加13%~37%,膜通量增加9%~33%。根据溶解-扩散模型[10],进水压力增加的同时,跨膜压差增加,导致Jw增大。在膜通量Jw增加的同时,Q减小,K增大,并且K增大的速度大于Jw增大的速度。透盐率随着进水压力的增大而减小,进水压力每增加0.1 MPa,透盐率减小3%~14%。
增加进水压力的方式有2种:方式A,调节浓水阀,减小浓水流量;方式B,增加进水泵频次。进水压力增加的同时可以带来其他参数的变化,结果如表1所示。本研究采用方式A提高进水压力。
有研究[11]表明,采用方式A增加进水压力可以提高透盐率,与本实验结果相反,文献中关于浓差极化变化的观点无法解释本实验的现象。有研究[12-17]表明,采用方式B增加进水压力,进水量、浓水量和产水率随之增加,浓水量的增加导致了膜表面浓差极化现象减弱,因此进水侧膜表面离子浓度减小,从而导致产水的离子浓度降低,即透盐率降低。但方式B增加进水压力导致浓差极化减小的结论需要论证,浓差极化的变化取决于膜表面水流的径向速度和纵向速度,径向速度变大可增强浓差极化现象,纵向速度变大可减弱浓差极化现象。如表2所示,2种方式的产水率均有所增大,因此,V径/V纵值均增大。在方式A和方式B中,提高进水压力均会导致浓差极化现象增强。
笔者认为,根据选择吸附毛细管理论,RO膜表面的浓差极化现象增加导致膜表面的各种离子浓度增加,相互排斥作用加强,因此,各种离子透过RO膜难度增大。随着进水压力的增大,膜通量和透盐量同时增加,而透盐量增加的速度小于膜通量增加的速度,因此,产水的含盐量减小,透盐率减小。本研究结果表明,在一定范围内,如果只考虑透盐率因素,增加反渗透工艺的浓差极化可以降低透盐率。综上所述,在一定范围内,提高进水压力既可以增加产水率,又可以降低透盐率,有利于整套系统的运行。
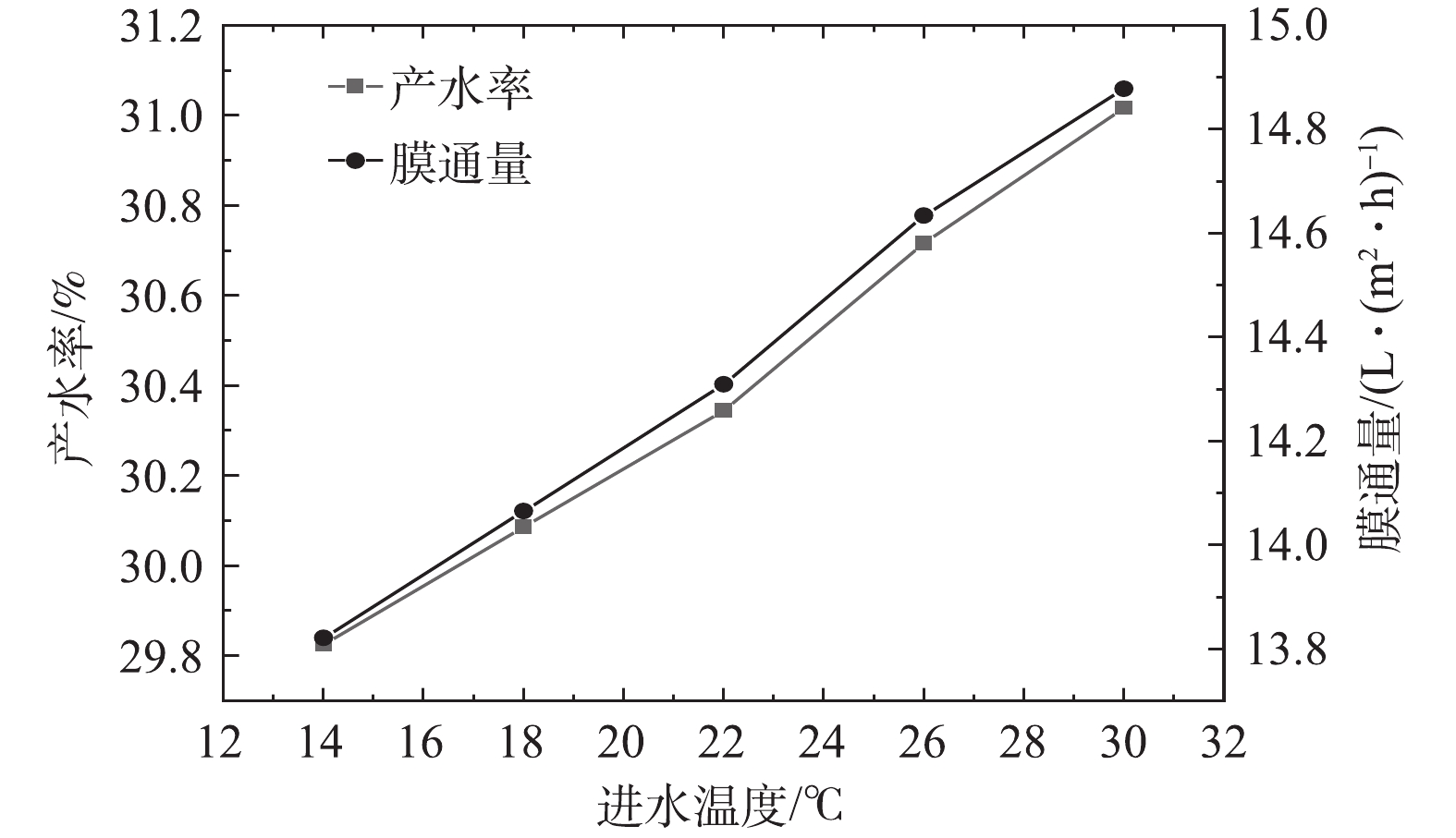
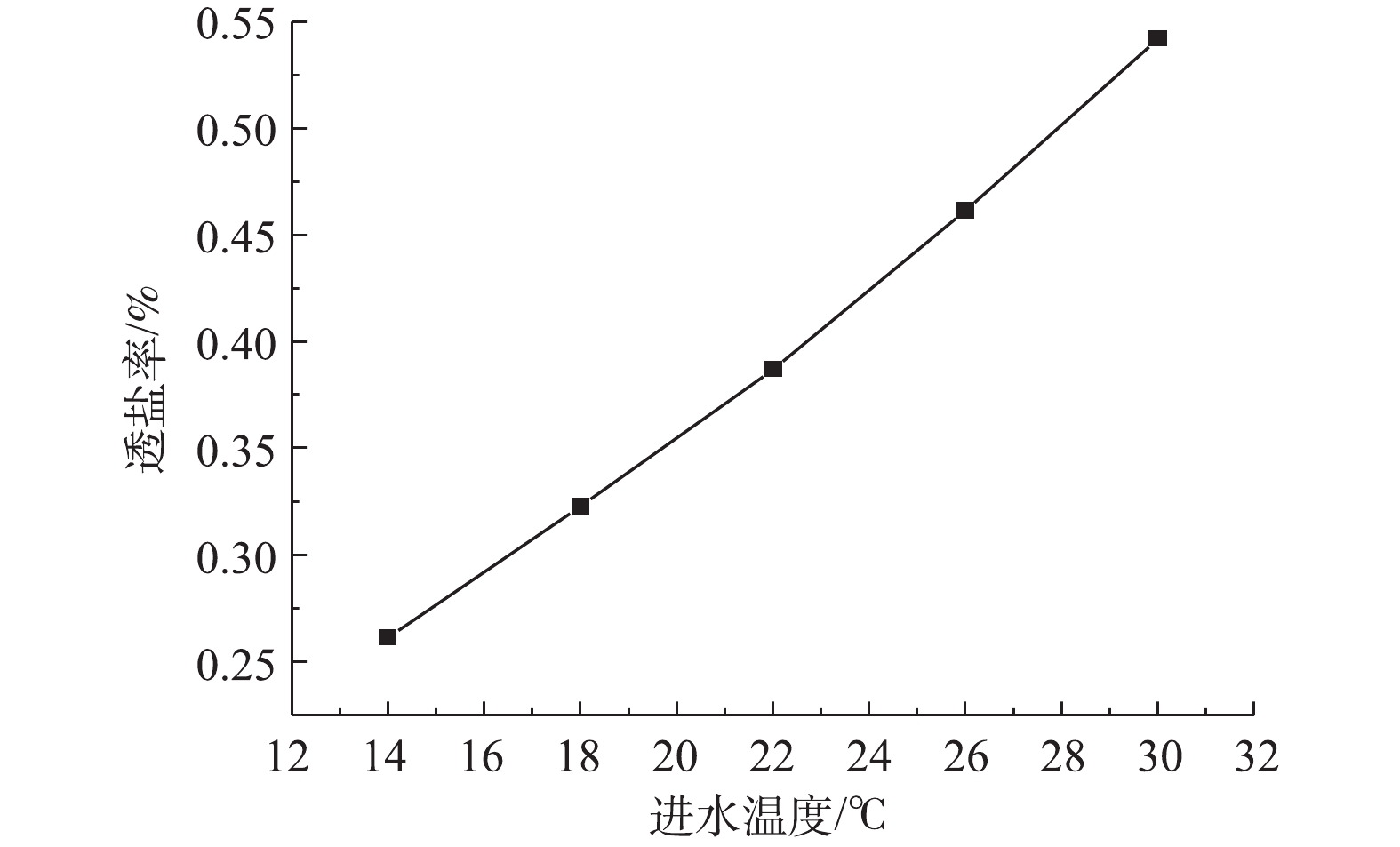
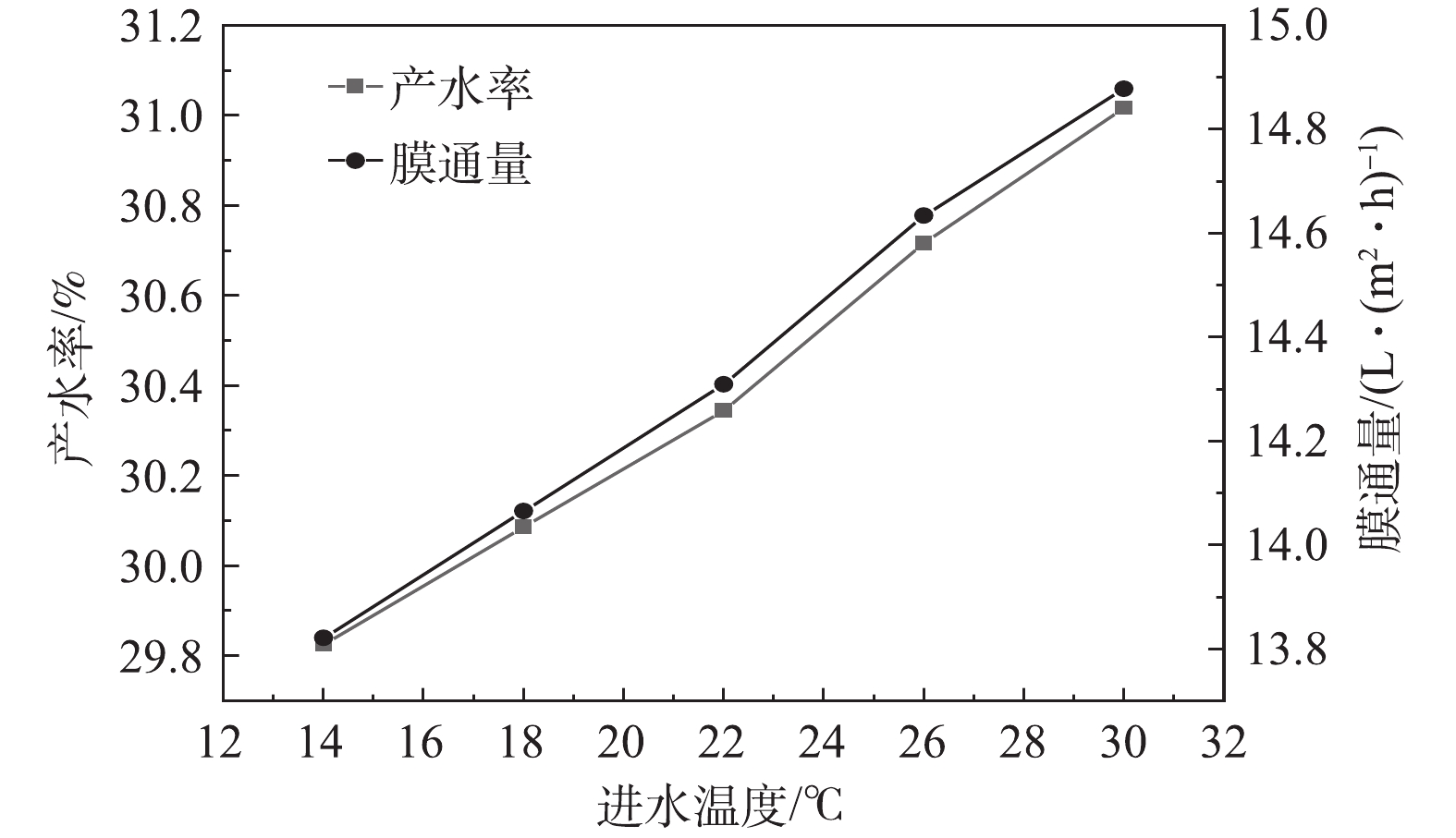
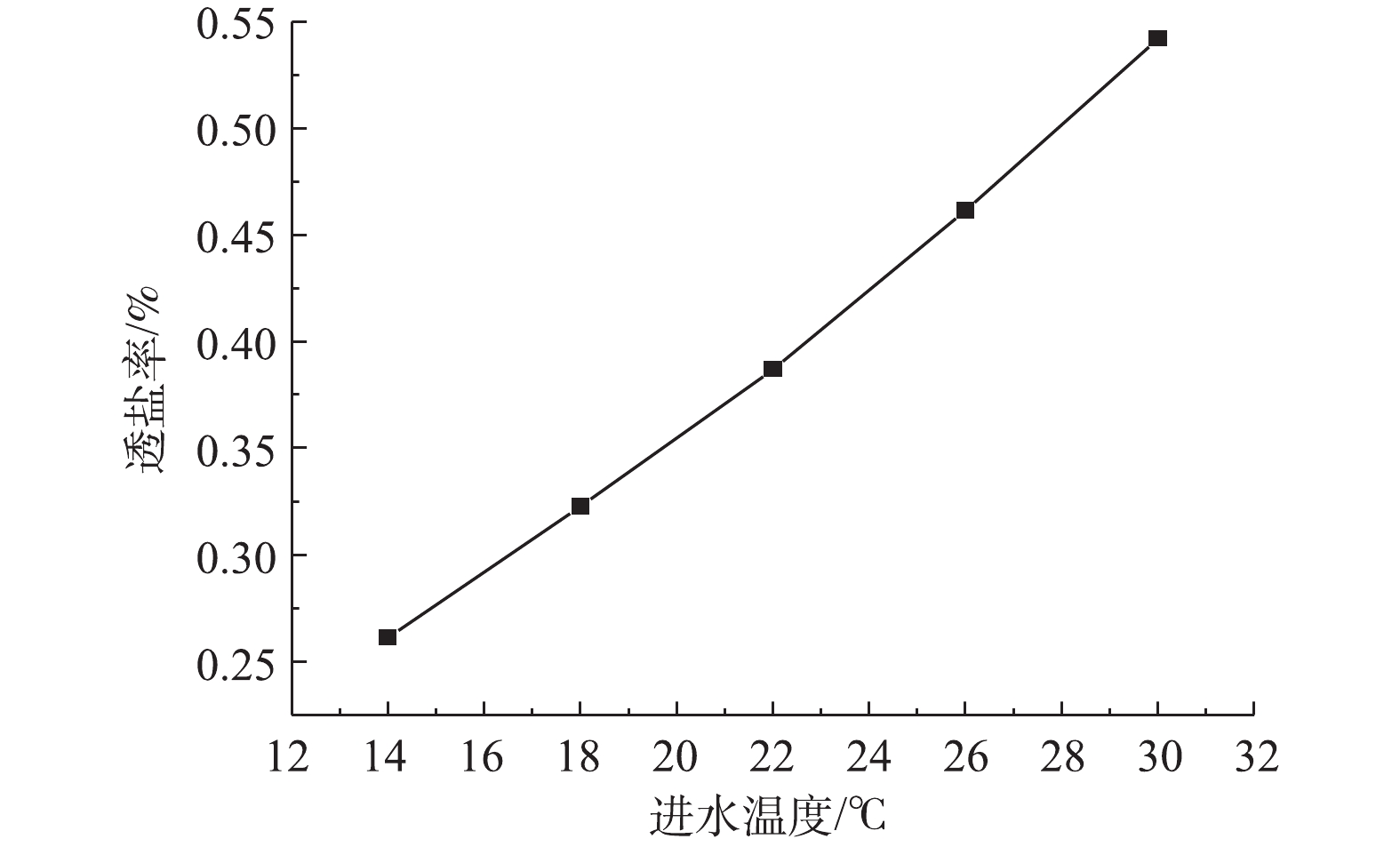
2)通过调节风式冷却塔和系统进水量改变RO进水温度,产水率及膜通量的变化如图7所示,透盐率的变化如图8所示。在压力不变的情况下,产水率随着水温的升高而增加,进水温度每升高1 ℃,产水率增加约0.25%,膜通量增加约0.47%,随着温度升高,水的黏度变小,因此,膜通量和进水量均有增加。根据式(3)可知,进水量Q随着温度的增加而升高,因此,膜通量Jw增加的速度大于产水率K增加的速度。在压力不变的情况下,透盐率随着水温的升高而升高,进水温度每升高1 ℃,透盐率增加约6.7%。水温的升高同样会导致透盐率的增大,这主要是因为盐分透过膜的扩散速度会因水温的升高而加快[18]。
综上所述,在一定范围内,提高RO系统进水温度可以增加产水率和透盐率,整套系统可以根据产水水质和水量的要求以调节进水温度。
-
对整个流程各个节点的指标进行检测,并与锅炉给水(SY/T 0097-2016)指标进行对比,结果如表3所示。含油量、悬浮物和矿化度等指标完全满足锅炉给水的要求。
pH由7.31下降到6.86,这是因为RO膜可以脱除溶解性的离子而不能脱除溶解性的气体,产水中的CO2和进水中CO2的基本相等,而产水中
HCO−3 大幅度减少,由于水中的CO2和HCO−3 存在平衡方程(式(4)),因此,原有的平衡被打破,平衡方程式向右移动,导致H+浓度增加,故导致pH下降。RO水中的硬度和pH未达到锅炉给水的标准,使用常规的树脂交换可以除掉残余硬度,用液碱可以调节pH,在此不做深入研究。
2.1. 采出水经过预处理和生化后含油量的变化
2.2. 超滤跨膜压差的变化
2.3. 进水压力、进水温度与产水率、膜通量、透盐率的关系
2.4. 生化双膜工艺各个节点的指标变化
-
1)油田采出水经过气浮后,剩余的原油以乳化油和溶解油的形态存在,直径小于10 µm,经过生化处理后,水中的剩余原油为0.63 mg∙L−1,满足超滤膜的进水要求。
2)生化处理后的油田采出水,对超滤膜的污染程度很小,在一定范围内,水中的悬浮物含量与膜污染速度无关,跨膜压差ΔP的增加速度为0.000 046 2 MPa·d−1;进水悬浮物数值短时间较大波动会引起跨膜压差的暂时升高或降低,当悬浮物数值恢复正常后,跨膜压差可以恢复到前期水平。
3)增大反渗透进水压力会导致产水率增加、膜通量增加、透盐率降低,产水率和膜通量增加是膜两侧压力差增大的结果,透盐率降低,是浓差极化加强导致的结果;升高进水温度会导致产水率增加、膜通量增加、透盐率增加,产水率和膜通量增加是水粘度变小的结果,透盐率升高,是水中的离子扩散速度变大的结果。
4)油田采出水利用生化双膜工艺制备锅炉用水的方法是可行的。处理后的水质含油量为0 mg∙L−1、悬浮物为0 mg∙L−1、矿化度为81 mg∙L−1,可以达到锅炉给水的要求;而硬度和pH达不到锅炉给水的标准,需要进一步处理。



 下载:
下载: