-
传统活性污泥法是污水生物脱氮除磷工艺中的主流技术,其中反硝化除磷技术证明了聚磷不仅能在好氧条件下实现,也能在缺氧条件下利用硝酸盐作为电子受体氧化细胞内提前储存的聚-β-羟基丁酸,实现反硝化的同时完成过量吸磷。此工艺实现了同步脱氮除磷和降解有机物,节省碳源,不需曝气,低污泥产量,适合处理污水氮磷含量高且COD浓度低的污水[1]。然而我国北方城镇污水处理厂普遍存在冬季低温条件下脱氮除磷效果差的问题[2],如何提高低温条件下的脱氮除磷效率一直是污水处理的难点之一。
在氧化还原反应中,电子传递速率是制约反应进行快慢的一个重要因素[3]。有研究[4]表明,氧化还原介体能够加速电子从初级电子供体传递到最终电子受体,从而使反应速率提升一至几个数量级,其能够催化反硝化过程、增强硝基芳香族化合物的厌氧生物转化、对偶氮染料脱色具有促进作用[5-8]。笔者所在的课题组前期将氧化还原介体引入反硝化研究中,发现低温投加介体可以使硝态氮去除率相对空白提高1.5倍[9],但氧化还原介体是否会对污水低温生物反硝化除磷效率产生影响仍然未知。因此,本研究考察了介体对污水低温生物反硝化除磷影响及磷形态的变化,以期为解决低温条件下脱氮除磷效果差的问题寻找新的途径。
全文HTML
-
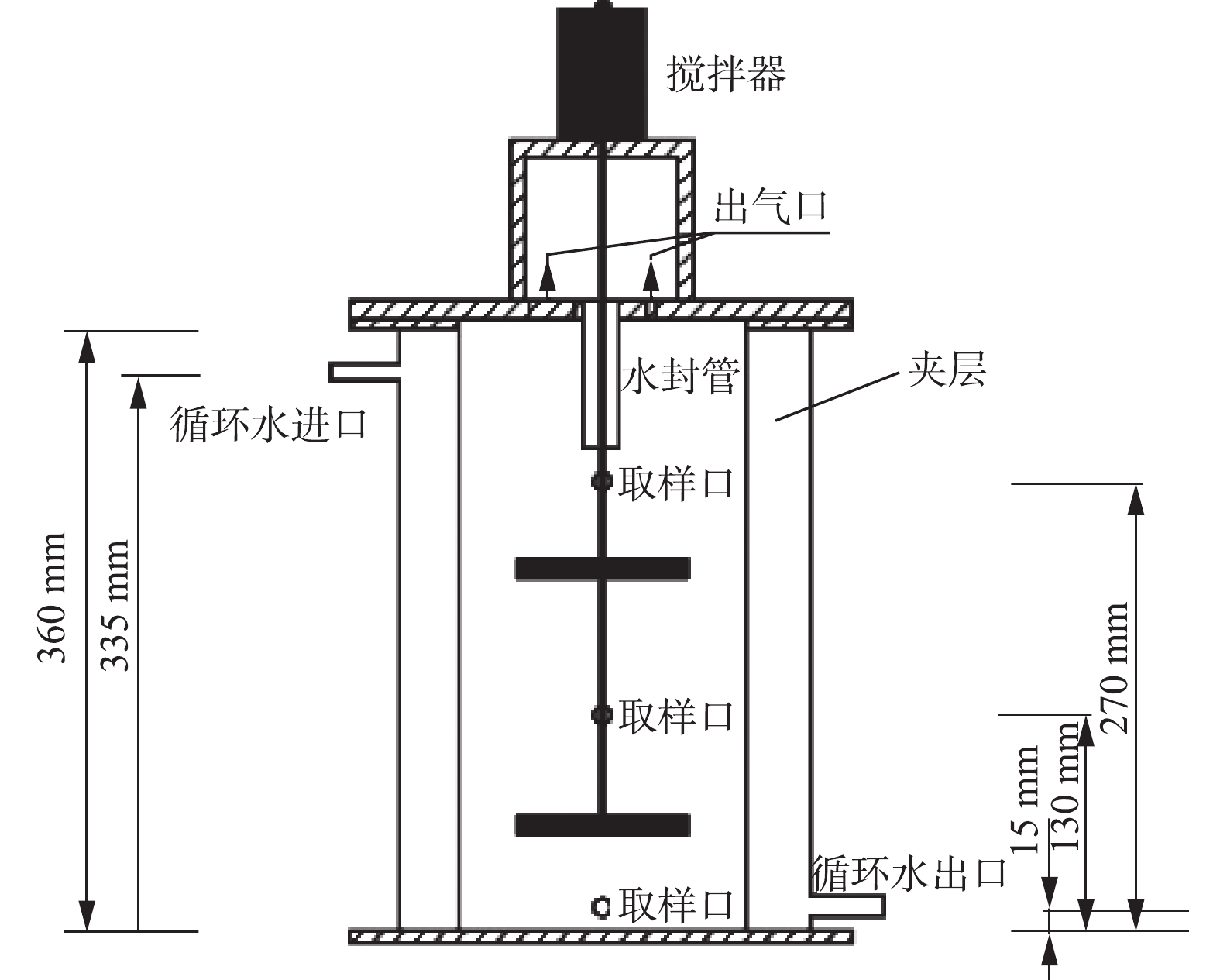
SBR实验装置如图1所示,高360 mm,内径170 mm,总有效容积为7.6 L。反应器外部留有充水夹层,水温由冷却水循环器(上海施都凯仪器设备有限公司,1L-008-02,可控温度为−20~20 ℃)控制。
-
2个反应器分别编为1#(空白对照)、2#(投加介体),水温控制为(10±1) ℃,搅拌速度控制在100~120 r∙min−1,进水由计量泵调节控制,反应时间由计时器控制。反应器的工作周期为12 h,每个周期的设定为进水15 min、厌氧反应1.5 h、缺氧反应5.5 h、排水15 min、待机4.5 h。采用多次均匀投加的方式,每周期向2#反应器投加介体NQS(浓度为100 µmol∙L−1)。
厌氧结束时为投加人工配置的硝酸盐溶液营造缺氧环境,浓度为(40±5) mg·L−1。进水的pH用HCl和NaOH调到7.0左右,防止生成磷酸盐沉淀。每天9点定时(取样时间点为0、5、10、20、30、60、90、95、100、110、120、150、210、300、420 min)从2个反应器的出水口取样,测其pH、总氮、总磷、磷酸盐等指标。
进水为人工配置的模拟生活污水,为了使配水尽量接近常规废水,在配水中投加10 mg·L−1的氯化铵。丙酸钠、硝酸钾、磷酸二氢钾提供微生物代谢所需的碳源、氮源和磷源。进水水质指标:COD为385 mg·L−1、TN为(70±5) mg·L−1、TP约为15 mg·L−1。配水其他成分:167 mg·L−1 MgSO4、70 mg·L−1 CaCl2·5H2O、4 mg·L−1 FeSO4。微量元素的组成:0.24 mg·L−1 CoCl2·6H2O、1.5 mg·L−1乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)、0.43 mg·L−1 ZnSO4、0.99 mg·L−1 MnSO4、0.22 mg·L−1 Na2MoO4·2H2O、0.25 mg·L−1 CuSO4·5H2O。
-
1)实验中常规指标的分析方法[10]:
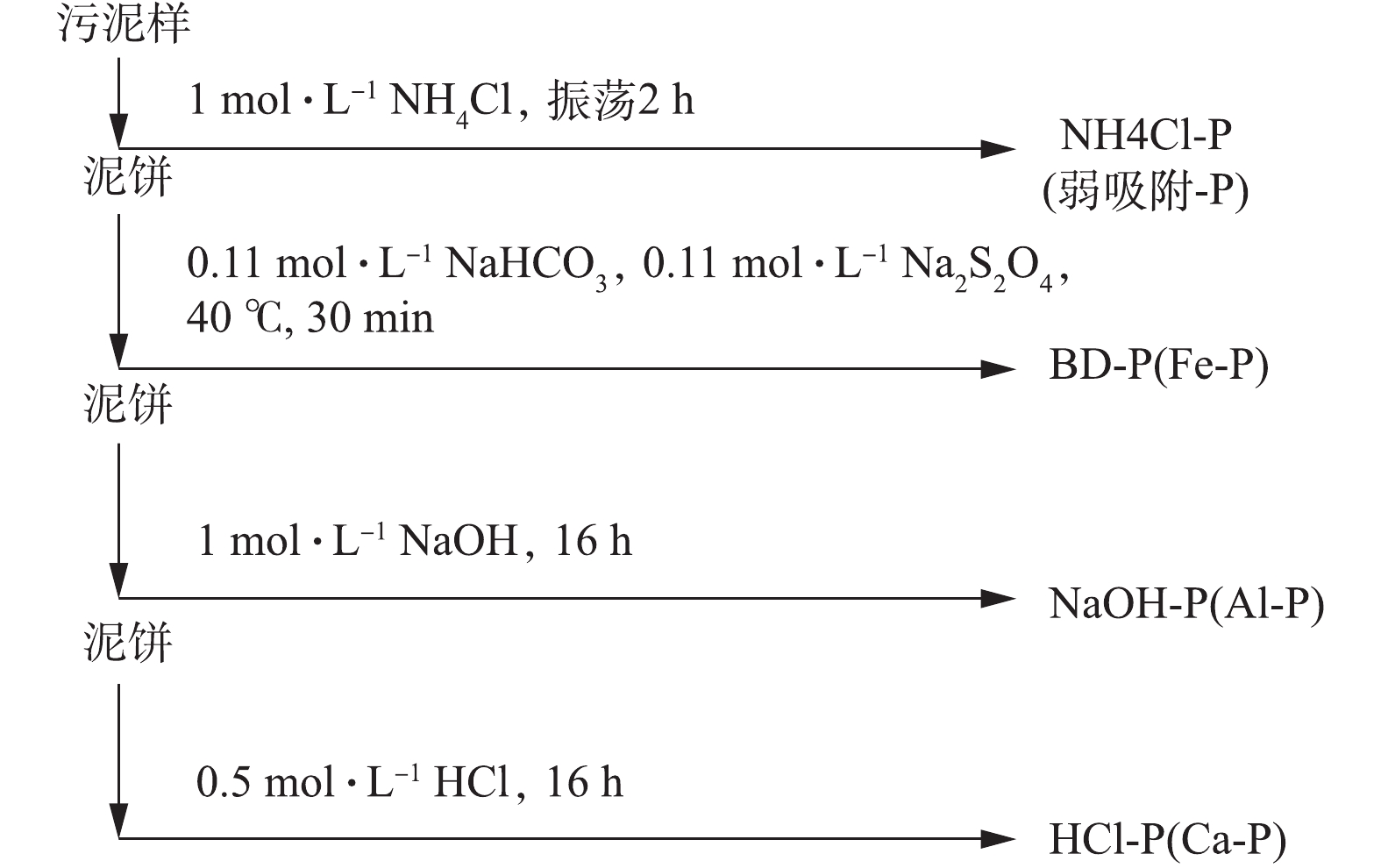
NO−2 -N采用N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺光度法;NO−3 -N采用紫外分光光度法;TN采用过硫酸钾氧化紫外分光光度法;TP采用过硫酸钾消解法;PO3−4 采用钼锑抗分光光度法。2)磷的形态分析。将污泥中的磷分为SRP、弱吸附态磷(NH4Cl-P)、可还原态磷(BD-P)、金属氧化物结合态磷(NaOH-P)、钙结合态磷(HCl-P)、有机磷(Org-P)。参考Hupfter改进的Psenner连续提取法[11-12],具体步骤见图2。每步提取多次重复, 提取液经5 000 r∙min−1离心30 min, 上清液用0.45 μm滤膜过滤后测可溶性磷;最后所得泥饼在105 ℃下干燥至恒重,520 ℃灼烧2 h,加入3.5 mol∙L−1的盐酸,振荡提取16 h,然后测定可溶性磷含量。有机磷用灼烧法(450 ℃,2 h)测定。
-
反应系统接种天津市某污水处理厂的活性污泥后,采用三段式驯化反硝化聚磷菌(DPAOs)。第1阶段中的活性污泥在常温25 ℃厌氧/好氧条件下培养约20 d,2个反应器中总磷的去除率稳定在85%左右,使聚磷菌成为优势菌群;第2阶段中的活性污泥在常温25 ℃厌氧/缺氧条件下驯化约30 d,2个反应器中总磷的去除率稳定在85%左右,硝酸盐氮的去除率稳定在50%以上,驯化出具有反硝化除磷的活性污泥;第3阶段中的活性污泥在低温(10±1) ℃厌氧/缺氧条件下驯化约55 d,总磷、硝酸盐氮的去除率分别稳定在85%和50%以上,驯化出适应低温的反硝化聚磷菌。
1.1. 实验装置
1.2. 运行条件及实验用水水质
1.3. 分析方法
1.4. 活性污泥的驯化
-
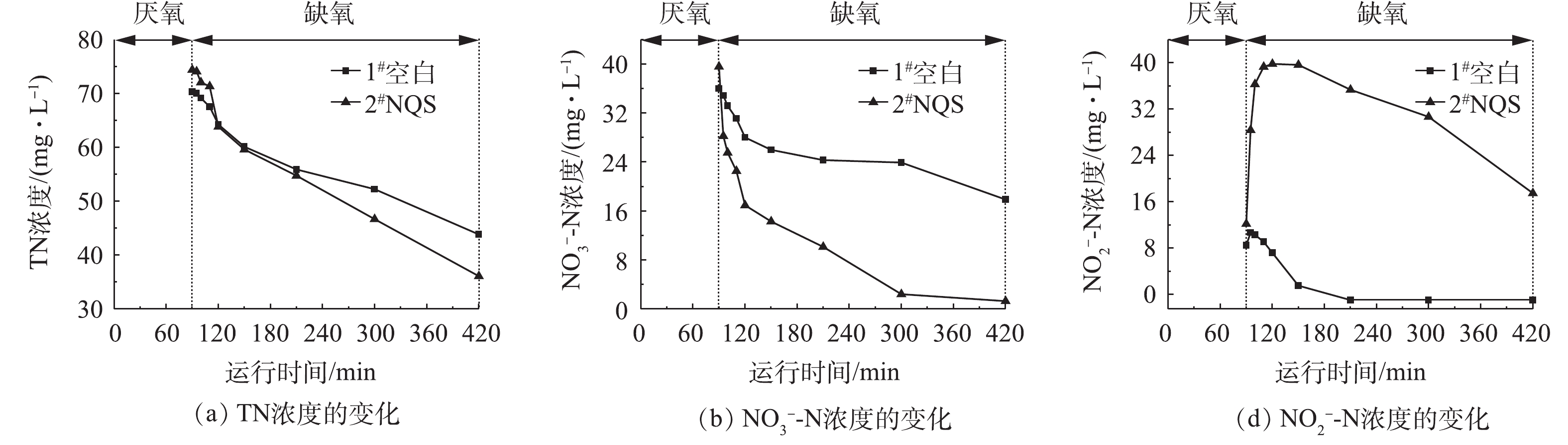
低温(10±1) ℃条件下,随着反应的进行,反应器中总氮、硝态氮、亚硝态氮浓度的变化如图3所示。由图3(a)可以观察到,在缺氧阶段2个反应器的总氮浓度均呈下降趋势,并以持平的反硝化速率进行,直至60 min后,空白对照中的脱氮速率开始逐渐减缓,而投加介体NQS的系统仍以较快速率降解总氮,直至反应结束2个反应器中总氮去除速率分别为4.82 mg∙(L∙h)−1和6.96 mg∙(L∙h)−1,介体NQS使总氮去除速率大幅度提高。缺氧结束时1#和2#中总氮的浓度分别为43.84 mg∙L−1和36.10 mg∙L−1,脱氮效率分别为37.67%和51.47%,2#反应器的脱氮率较1#提高了1.37倍。图3(b)也显示出2#反应器中硝酸盐氮的降解速率持续以高于1#空白的速率进行直至第300 min,反应结束时2个系统中硝酸盐氮去除速率分别为3.29 mg∙(L∙h)−1和6.96 mg∙(L∙h)−1,介体NQS的投加明显促进了硝酸盐氮的降解速率。2个反应器中硝态氮起始浓度分别为35.98 mg∙L−1和39.57 mg∙L−1,反应结束时硝态氮的浓度降为17.88 mg∙L−1和1.28 mg∙L−1,去除率分别为50.31%和96.77%,2#反应器中硝态氮去除率是空白的1.92倍。
YIN等[13]也在研究不同氧化还原介体对反硝化脱氮性能影响的过程中,发现35 ℃时投加蒽醌(AQ)、2-甲基-1,4-萘醌(ME)、2-羟基-1,4-萘醌(LAW)3种介体,浓度分别为75、25、75 μmol∙L−1,相比空白实验,总氮去除率可分别提高了1.60、1.25、2.08倍,与本实验具有相似的脱氮效果。由此可见,投加NQS为解决冬季低温脱氮效果差的问题提供了新的思路。
亚硝态氮的含量在2个反应器中的变化趋势差异明显,结果如图3(c)所示。2#亚硝态氮快速积累,经过30 min达到最大量,为39.78 mg∙L−1,因为在此阶段内,2#反应器中对应的硝态氮含量急剧下降,硝态氮被还原,导致亚硝态氮快速生成。随着反硝化脱氮的进行,亚硝态氮逐渐被还原,反应结束时仍剩余17.48 mg∙L−1的亚硝态氮。1#中亚硝态氮在缺氧阶段初期时少量增加后迅速下降,反应结束时没有亚硝态氮的积累。
氧化还原介体对硝酸还原酶、亚硝酸还原酶活性影响的不平衡可能是亚硝酸盐氮积累的主要原因[13]。硝酸还原酶是一种氧化还原酶,可催化硝态氮还原成亚硝态氮,从而提高反硝化速率。YIN等[13]的研究表明,在空白系统中亚硝酸还原酶活性相比硝酸还原酶活性较高,亚硝酸还原酶将亚硝酸盐降解为NO或NH3,从而减少污水中亚硝态氮的积累;而ME的投加使硝酸还原酶活性增强了1.97倍,使硝态氮迅速转化为亚硝态氮,造成亚硝态氮的积累。因此,本实验中介体NQS很可能使硝酸还原酶活性提高,从而促进了亚硝态氮的生成过程。
-
在低温(10±1) ℃条件下,反应系统中总磷、磷酸盐浓度随时间的变化结果如图4所示。由图4可以看出,随着反应时间的进行,总磷和磷酸盐的浓度先升高后下降,2#反应器对总磷、磷酸盐的去除效果优于1#。
在1#和2#反应器中的起始总磷浓度分别为15.36 mg∙L−1和14.29 mg∙L−1,经过厌氧释磷后磷浓度分别达到23.52 mg∙L−1和20.29 mg∙L−1,释磷量分别为8.16 mg∙L−1和6.00 mg∙L−1。厌氧反应结束后,通过蠕动泵抽入人工配置的硝酸盐废水形成缺氧条件,反应器中的DPAOs由厌氧释磷转变为缺氧吸磷。2个反应器以相同速率吸磷,直至150 min时,2#反应器开始以高于1#的速率进行反应,在结束时1#和2#反应器出水总磷已降至7.15 mg∙L−1和0.50 mg∙L−1,去除率分别达到了53.45%和96.50%,投加介体NQS反应器相对于空白对照提高了1.81倍。在缺氧吸磷阶段,1#和2#反应器中的总磷降解速率分别为1.49 mg∙(L∙h)−1和2.51 mg∙(L∙h)−1,这说明介体的投加对除磷具有很强的促进作用。磷酸盐浓度随时间的变化趋势与总磷变化一致,结果如图4(b)所示。1#和2#反应器中的磷酸盐的去除率分别为50.07%和97.32%,与空白对照相比,投加介体NQS反应器的除磷率提高了1.94倍。
根据物料平衡计算,1#反应器中缺氧初始
NO−3 -N和PO3−4 -P分别为35.98 mg∙L−1和23.95 mg∙L−1,缺氧末端NO−3 -N和PO3−4 -P分别为17.88 mg∙L−1和6.74 mg∙L−1,缺氧脱氮量/缺氧吸磷量为1.05,即吸收1 mg的PO3−4 -P大约需要1.05 mg的NO−3 -N;2#反应器中缺氧初始NO−3 -N及PO3−4 -P分别为39.57 mg∙L−1和20.52 mg∙L−1,缺氧末端NO−3 -N及PO3−4 -P分别为1.28 mg∙L−1和0.38 mg∙L−1,缺氧脱氮量/缺氧吸磷量为1.90。可见,低温(10±1) ℃时,投加NQS的反应系统中反硝化除磷率是空白对照组的1.81倍。ZHOU等[14]利用A/O-SBR反应系统研究不同电子受体对DPAOs缺氧吸磷能力的影响时,验证了当NO−3 -N为电子受体且初始浓度为30 mg∙L−1时,反硝化除磷率是0.89,本实验中的空白对照结果略高于上述报道。在介体NQS的强化下,系统的反硝化除磷率明显增强。介体NQS促进低温污水反硝化除磷的原因可能是:醌类介体参与反硝化除磷过程的呼吸链,通过NADH脱氢酶和泛醌加速电子从NADH向硝酸还原酶的转移,从而增加反应效率[15]。醌类介体根据被氧化还原状态的程度分为氧化态醌、还原态氢醌和位于两者之间的半醌,DPAOs能利用NQS作为其电子传递链中的电子受体进行醌呼吸,将其还原成氢醌,氢醌又可被氧化成醌类将电子传递给电子受体
NO−3 ,电子在醌、半醌、氢醌之间的转移是完全可逆的,这种可持续的连续氧化还原循环加速了DPAOs反硝化除磷过程中的电子传递[5,16-17]。氧化还原反应速率与其活化能的大小密切相关,降低活化能会有效地促进反应的进行。DOS SANTOS等[18]研究发现,空白对照、蒽醌二磺酸钠(AQS)体系的反应活化能分别为27.9 kJ∙mol−1和22.9 kJ∙mol−1,AQS的添加使得反应活化能降低了1.2倍。由此可见,氧化还原介体可能降低了反应过程所需的活化能,从而加速DPAOs的代谢过程。 -
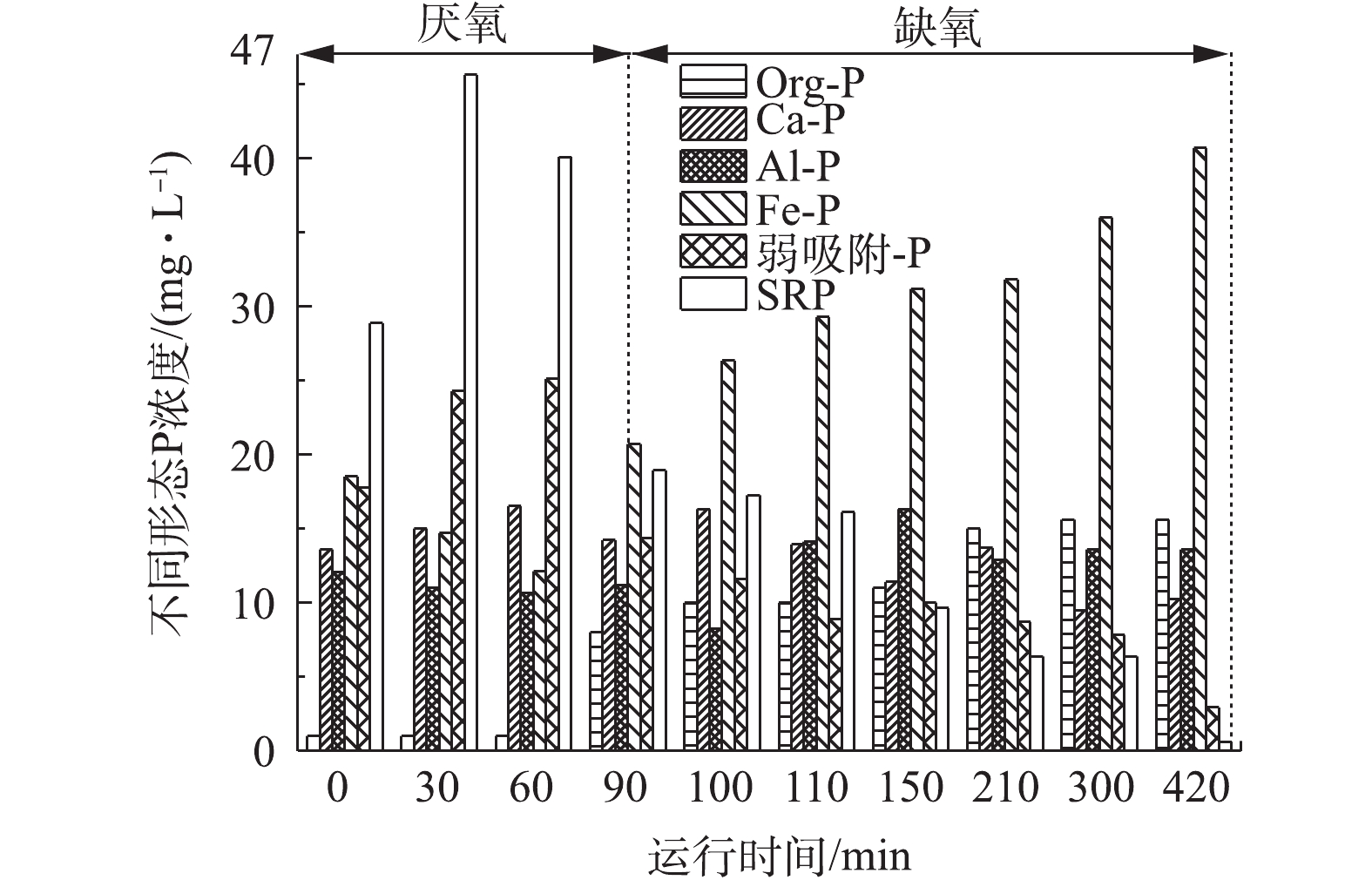
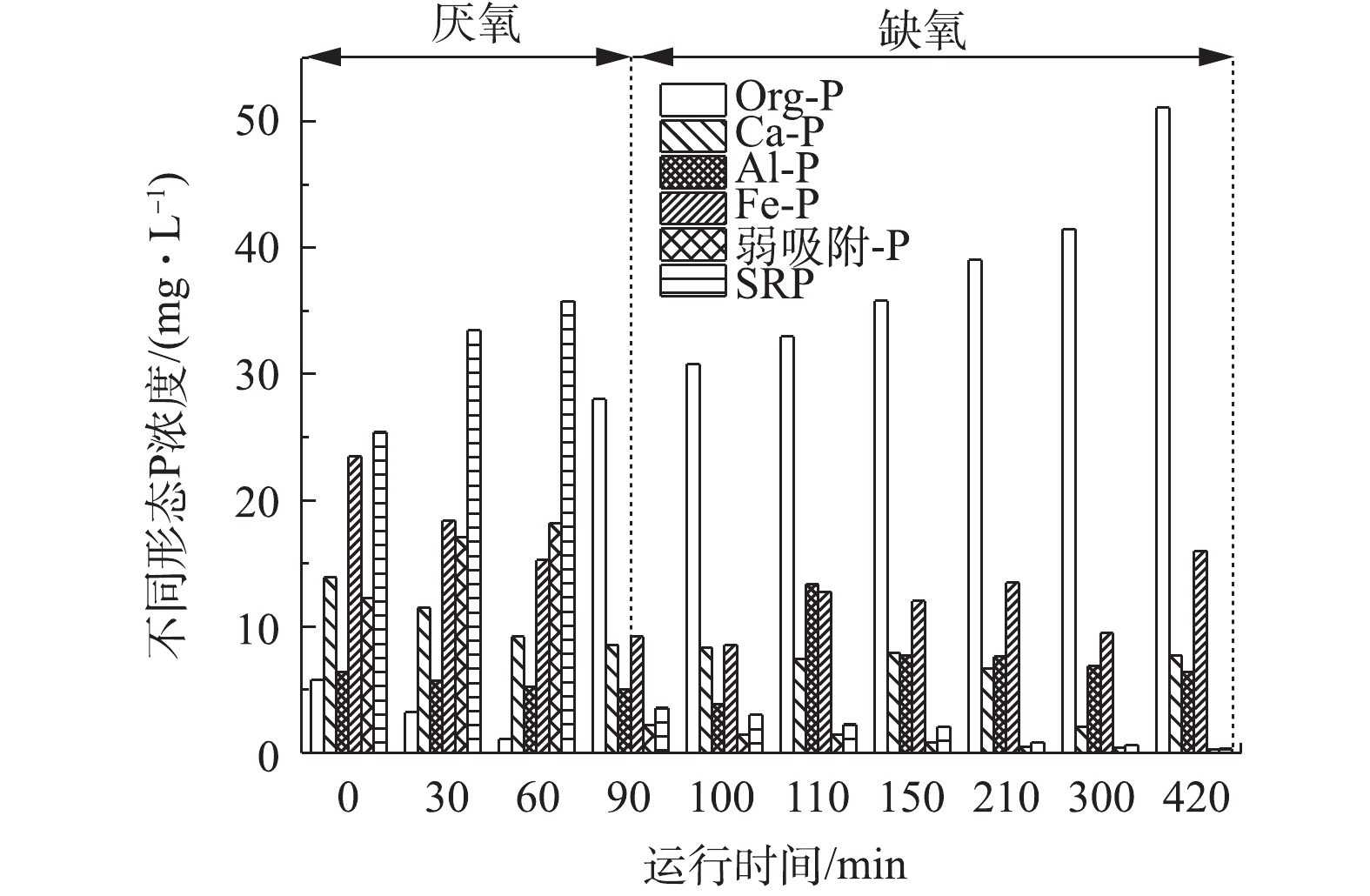
定时取1#和2#反应器中的泥水混合物,测试样品中磷形态的迁移转化过程,其结果如图5和图6所示。由图5可明显看出,各反应器中均以SRP和Fe-P居多,成为磷的主要赋存形态。
在1#空白反应器中,SRP和Fe-P的含量波动较大,结果如图5所示。SRP在厌氧阶段被释放,浓度增高,在缺氧阶段被吸收,浓度不断减少,Fe-P的变化则相反。Ca-P、弱吸附-P在厌氧阶段的浓度略大于缺氧阶段,Org-P、Al-P则相反。随着反应的进行,SRP在厌氧阶段的0~60 min内迅速增加,浓度达到最大值45.61 mg∙L−1。在90 min时,SRP开始大幅度下降,直至反应结束降至0.62 mg∙L−1。而Fe-P在系统运行前期缓慢下降至12.13 mg∙L−1,从90 min时浓度才开始增加,直至反应结束浓度增加至40.67 mg∙L−1。pH对缺氧吸磷也会产生一定的影响作用,尤其当pH大于8时,污水中磷浓度会因为化学沉淀作用而大幅下降[19]。在1#反应器中,pH的升高十分迅速,在反应进行至120 min后,pH到达8.50且持续快速上升,直至反应结束,pH达到9.05,所以pH过大的环境导致污水中的磷酸盐主要与铁盐发生结合形成沉淀。Ca-P、Al-P与弱吸附-P的含量变化不大。Org-P在缺氧阶段浓度升高,说明缺氧阶段微生物细胞内也有一些聚磷的合成。
由图6可以看出,2#反应器中变化幅度最大的是SRP和Org-P。SRP在厌氧阶段浓度很高,缺氧阶段迅速下降,Org-P的变化则呈相反的趋势。Ca-P、Fe-P和弱吸附-P在厌氧阶段的含量大于缺氧阶段的含量,Al-P则相反。
在厌氧阶段的0~60 min内释放磷,SRP迅速富集,60 min时浓度达到最大值,为35.78 mg∙L−1。在缺氧阶段前10 min时,SRP的剩余量骤降,直至反应结束降至0.33 mg∙L−1,这说明在缺氧阶段反应器中的SRP被微生物细胞吸收或在污泥中形成沉淀,从而导致其浓度下降。而Org-P的变化趋势与SRP恰恰相反,在厌氧反应的0~60 min内,Org-P含量从6.00 mg∙L−1降解到1.10 mg∙L−1,在90 min时Org-P迅速积累至28.01 mg∙L−1。在整个缺氧阶段,Org-P浓度呈现上升趋势,反应结束时浓度达到最高为51.09 mg∙L−1。在生物除磷过程中,Fe-P基本呈现出厌氧阶段减少,缺氧阶段略有升高,可能是由于缺氧阶段pH不断上升,导致少量的磷以与铁盐结合的方式赋存。随着反应的进行,Ca-P缓慢下降,Al-P波动不大,弱吸附-P在厌氧阶段含量较高,缺氧阶段下降至0.31 mg∙L−1。
聚羟基脂肪酸酯(PHA)是微生物在不平衡生长时细胞内储存能量、碳源的聚合物,反硝化除磷过程中积累聚磷与PHA的合成密切相关。厌氧时,DPAOs利用分解聚磷、部分糖原释放的能量来摄取有机物,并以储存PHA及糖原等的形式储存于细胞内;缺氧时,微生物进行氧化磷酸化作用,以体内储存的PHA及污水中可利用的有机物作为能源,供细菌生长、合成糖原及积累聚磷[20]。介体NQS的投加很可能使反应器中的PHA含量远远大于空白对照组中的含量。在2#反应器中,厌氧条件下合成的PHA越多,缺氧条件下降解的PHA越多,即有机磷合成量越大,生物除磷的效果越好[21-22]。
综上所述,介体NQS防止了磷酸盐以沉淀的形式在水中去除,促进了水中磷酸盐向有机磷的转化,进而为微生物生长代谢提供能量,达到了出水磷浓度低、除磷效率高、无需通过排泥除磷的效果。
2.1. 生物脱氮效率的变化
2.2. 生物除磷效率的变化
2.3. 污泥中磷形态的变化
-
1)在缺氧阶段,1#和2#反应器中总氮降解速率分别为4.82 mg∙(L∙h)−1和6.96 mg∙(L∙h)−1,总磷降解速率分别为1.49 mg∙(L∙h)−1和2.51 mg∙(L∙h)−1,低温时介体NQS使总氮、总磷去除速率大幅度提高。
2)在1#反应器中,缺氧脱氮量/缺氧吸磷量为1.05;在2#反应器中,缺氧脱氮量/缺氧吸磷量为1.90。在低温(10±1) ℃时,介体NQS使系统的反硝化除磷率明显增强。
3)在磷形态的迁移转化过程中,介体NQS使污泥中更多的磷酸盐以有机磷的形式赋存,更有利于生物除磷。




 下载:
下载: