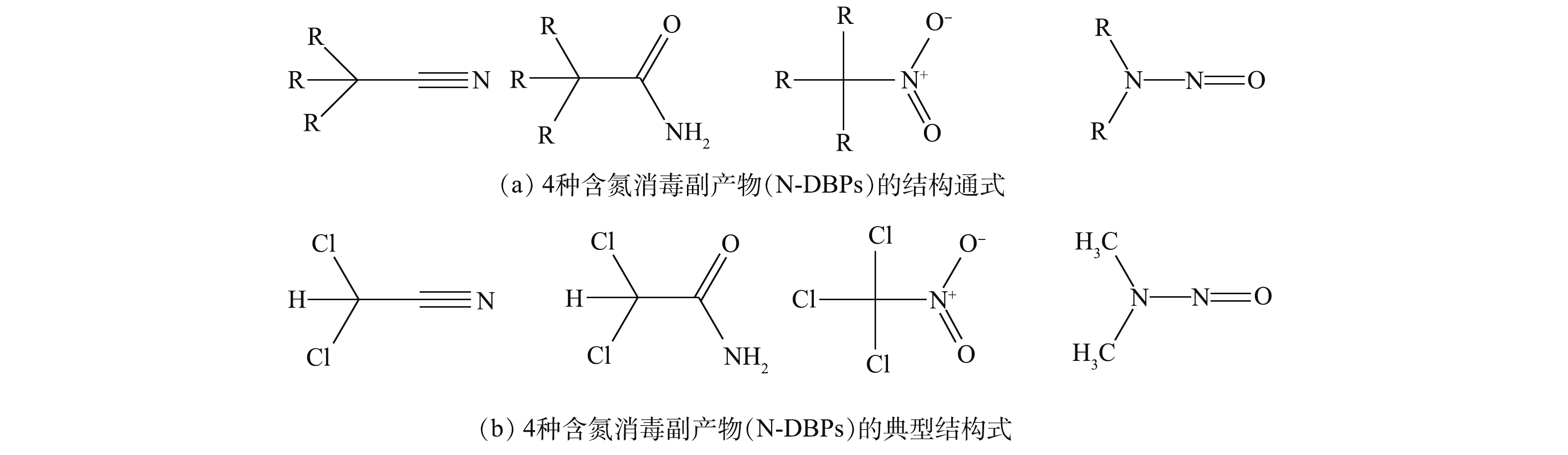
-
近年来,我国自然水体中砷和磷复合污染案例屡见不鲜。砷(As)及其化合物主要通过人类工农业生产及地球化学循环而进入地表及地下水中。长期饮用高砷水会对人类的生理健康造成严重的危害,故地表水砷污染导致的饮用水健康风险问题受到人们的广泛关注[1-2]。因此,世界卫生组织(WHO)、美国环境保护署(EPA)等众多组织将饮用水中的砷含量限定为10 μg·L−1以下[3-5]。此外,水体富营养化也对我国各类水体(主要是湖泊、水库及河流城市河段)造成了严重威胁,而磷是引起水体富营养化的主要因子之一[6-8]。有研究表明,环境中磷和砷存在着竞争关系,砷容易置换出磷,从而被细胞吸收导致中毒[9-10]。因此,从环境治理、资源回收等角度考虑,有必要对污染水体中的砷和磷进行控制。
在现有砷、磷去除技术中,吸附法作为较成熟的除砷及除磷方法之一,具有处理效果好、经济安全、操作简单等特点,在小城镇及农村等分散供水地区水处理技术中具有明显优势[11-12]。近年来,新型吸附剂的开发成为国内外学者的研究重点。其中,介孔材料具有均一的孔径、较大的比表面积、稳定的骨架结构和易于修饰等优点,在环境治理领域已得到广泛的运用[13-15]。目前,已有研究报道吸附法单独去除水中的磷或砷时均有良好的效果[16-17],但是,对于砷、磷共存情况下对吸附剂性能的研究还较少。因此,本研究通过镧金属掺杂对介孔材料进行改性,合成了La-MCM-41吸附剂,考察了其同步去除砷、磷复合污染的性能,以期为同步去除环境水体中砷和磷提供参考。
-
十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(C19H42BrN, CTAB)、正硅酸乙酯(C8H20O4Si, TEOS)、硝酸镧(La(NO3)3·xH2O)、磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)、钼酸铵((NH4)6Mo7O24)、L-抗坏血酸(C6H8O6)、酒石酸氧锑钾(C4H4KO7Sb·0.5H2O)、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(C10H14N2O8Na2)、甲酸(CH2O2)、硫脲(CH4N2S)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)均为分析纯。
-
本研究模板剂采用十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB),硅源采用正硅酸乙酯(TEOS),并按照TEOS∶CTAB∶NaOH∶H2O = 1∶0.1∶0.24∶100的摩尔配比进行实验。具体步骤:将NaOH溶于去离子水中,加入相应量的CTAB,36 ℃下磁力搅拌至溶液澄清,剧烈搅拌下逐滴加入TEOS;调节溶液pH = 9~11,混合体系剧烈搅拌2 h,将所得乳白色凝胶转入聚四氟乙烯晶化反应釜中,120 ℃下晶化24 h;取出冷却至室温,过滤、洗涤、干燥,得MCM-41原粉;将其置于马弗炉中,升温至550 ℃,焙烧6 h,制得MCM-41介孔材料。
-
本研究模板剂采用十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB),硅源采用正硅酸乙酯(TEOS),硝酸镧为镧源,以La/Si = 0.03的量掺杂金属离子。具体步骤同MCM-41的制备。
-
采用X射线衍射(德国布鲁克公司D8ADVANCE型,Cu靶,扫描角度为1°~10°)对介孔材料晶体结构进行测定;采用比表面积与孔隙度吸附仪测定介孔材料改性前后比表面积、孔容及孔径分布(美国麦克公司ASAP2460型);采用扫描电子显微镜观察介孔材料改性前后微观形貌(FEI公司NANO SEM430型)。
-
分别配制As(V)、
PO3−4 -P(以下简称P)浓度均为20 mg·L−1的溶液,取50 mL As(V)或P溶液倒入具塞锥形瓶中,吸附剂投加量为0.01 g,调节溶液pH为5.0。将各锥形瓶置于恒温振荡箱中,调节温度为15、25、35、45 ℃,在转速为150 r·min−1条件下,振荡24 h,反应过程中保持pH稳定。在反应结束后,取水样,过0.45 μm滤膜,采用氢化物发生-原子荧光分光光度法测定As(V)浓度,钼酸铵-抗坏血酸比色法测定P浓度 -
配制As(V)、P浓度均为20 mg·L−1的混合溶液[18-19],取50 mL混合溶液倒入具塞锥形瓶中,吸附剂投加量为0.01 g,调节溶液pH为5.0。将锥形瓶置于恒温振荡箱中,调节温度为15、25、35、45 ℃,在转速为150 r·min−1条件下,振荡24 h,反应过程中保持pH稳定。反应结束后,取水样,过0.45 μm滤膜,采用日本岛津公司ICPS-7510 PLUS电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱仪分别测定As(V)和P的浓度。
-
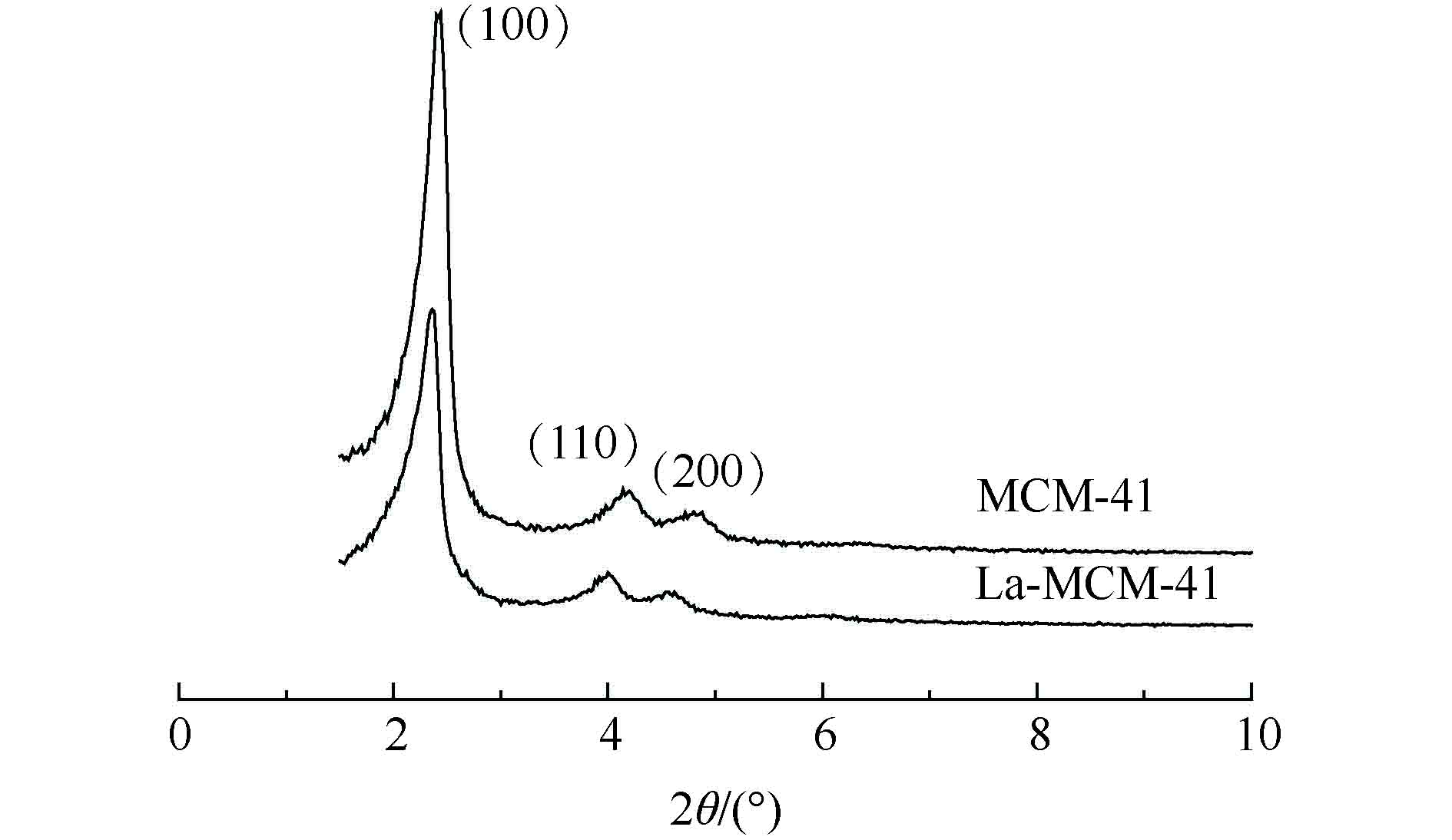
图1是MCM-41及La-MCM-41的XRD衍射图。由图1可见,2组材料在小角范围内都有3个明显的衍射峰。其中,在2θ=2.2°附近有1个较强的衍射峰,对应于介孔分子筛(100)晶面;在2θ=4.0°、4.3°附近出现2个强度相对较弱的衍射峰,分别对应于介孔分子筛(110)、(200)晶面。这与已有报道[20-21]中关于介孔材料的结构特征峰位置的结果一致,说明本研究制备的MCM-41和La-MCM-41都具有长程有序的六方相介孔结构特征,掺杂镧之后的介孔材料和MCM-41具有相似的结构特性。经La改性后的MCM-41的特征峰强度有明显的减弱,而且相应衍射峰2θ角向低角度偏移,这表明,骨架中镧的引入会改变分子筛的表面结构,从而降低了材料的有序性。
-
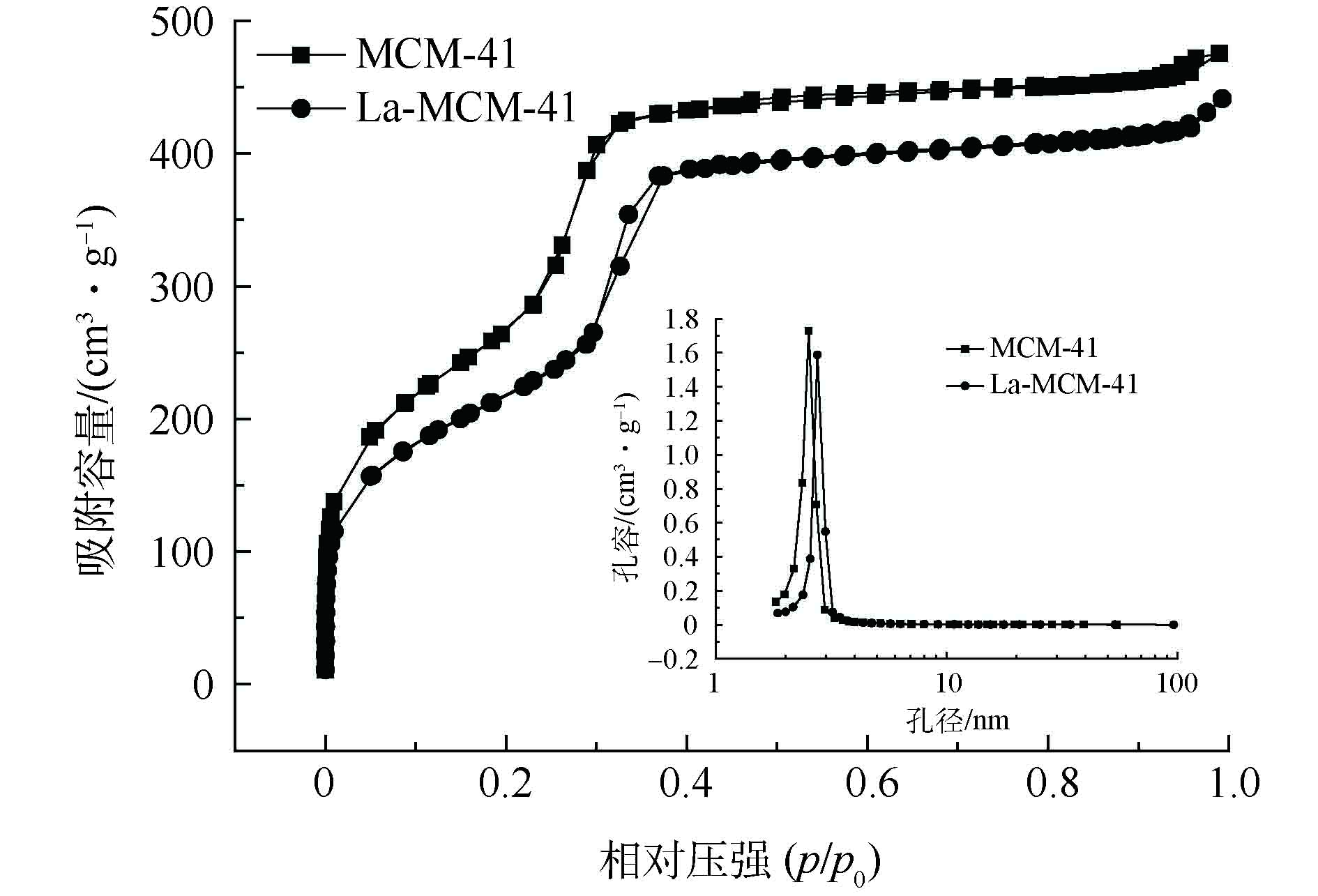
通过N2-吸脱附测试,可以表征多孔材料孔道结构等信息。MCM-41和La-MCM-41的N2吸脱附曲线和孔径分布如图2所示。2种材料的N2吸脱附等温线均为Ⅳ型[22],属于典型的介孔材料吸附曲线,镧掺杂后也没有明显改变介孔材料的结构特征,但La-MCM-41的比表面积和孔容积都有所减小,而孔径有所增加。其中比表面积从1 193.68 m2·g−1减小到812.27 m2·g−1,孔容从0.71 cm3·g−1减小到0.64 cm3·g−1,孔径从2.38 nm增加到3.18 nm,这是因为镧掺杂后占据了部分孔道,影响了原有孔道结构[23]。
-
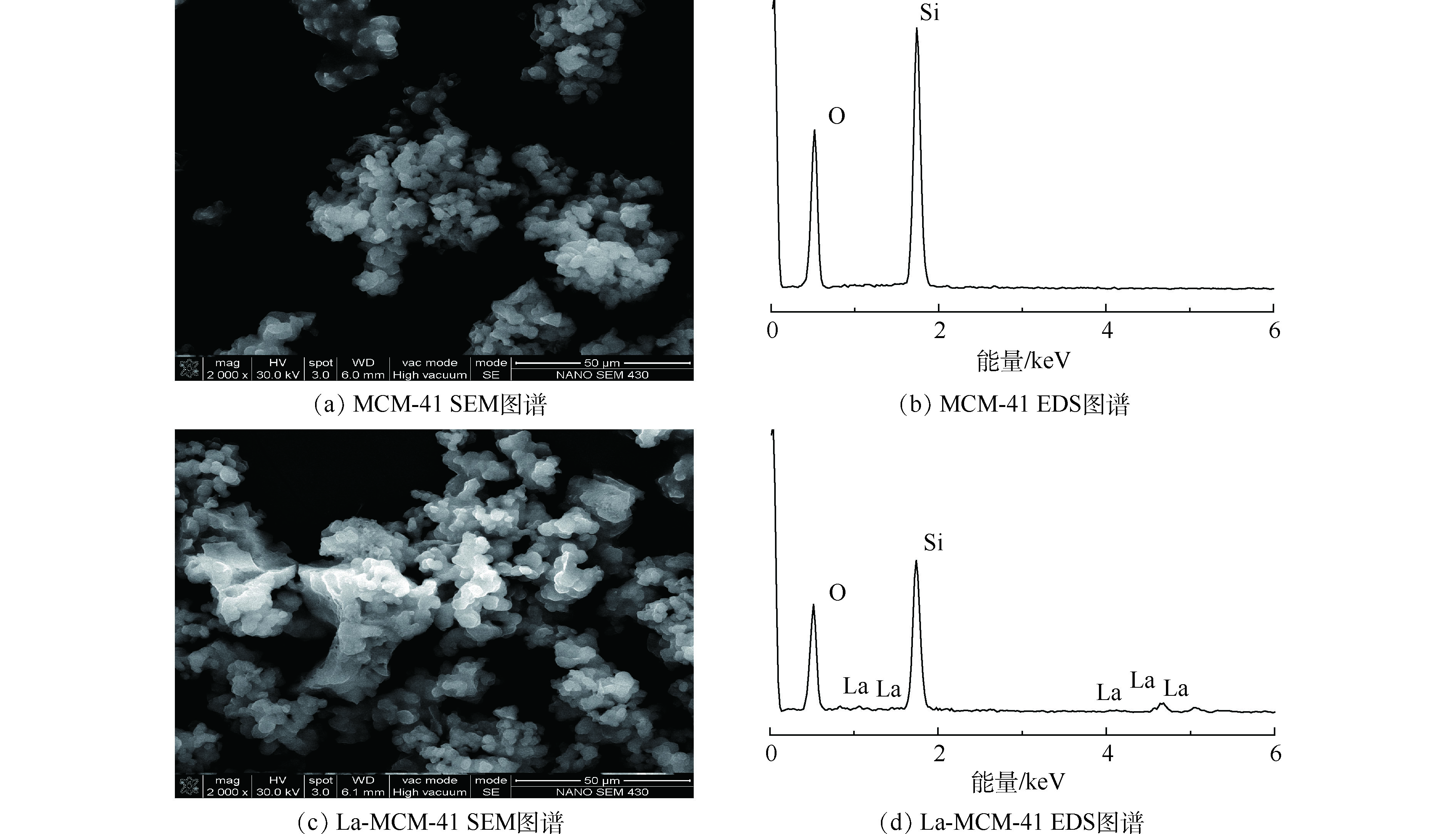
图3为MCM-41和La-MCM-41的扫描电镜(SEM)和X射线能谱分析图(EDS)。从图3中可以看出,MCM-41和La-MCM-41的颗粒外形均呈现颗粒状,改性并未改变介孔材料的形貌特征。对比二者发现,MCM-41介孔吸附材料颗粒粒径较小,团聚后呈现一些不规则的形状结构。La-MCM-41介孔分子筛外形轮廓粗糙,并出现了团聚后的大颗粒。改性前后EDS图也呈现出差别,改性后的吸附剂硅含量减少,同时出现镧元素,说明镧成功取代硅,掺杂到介孔材料中。
-
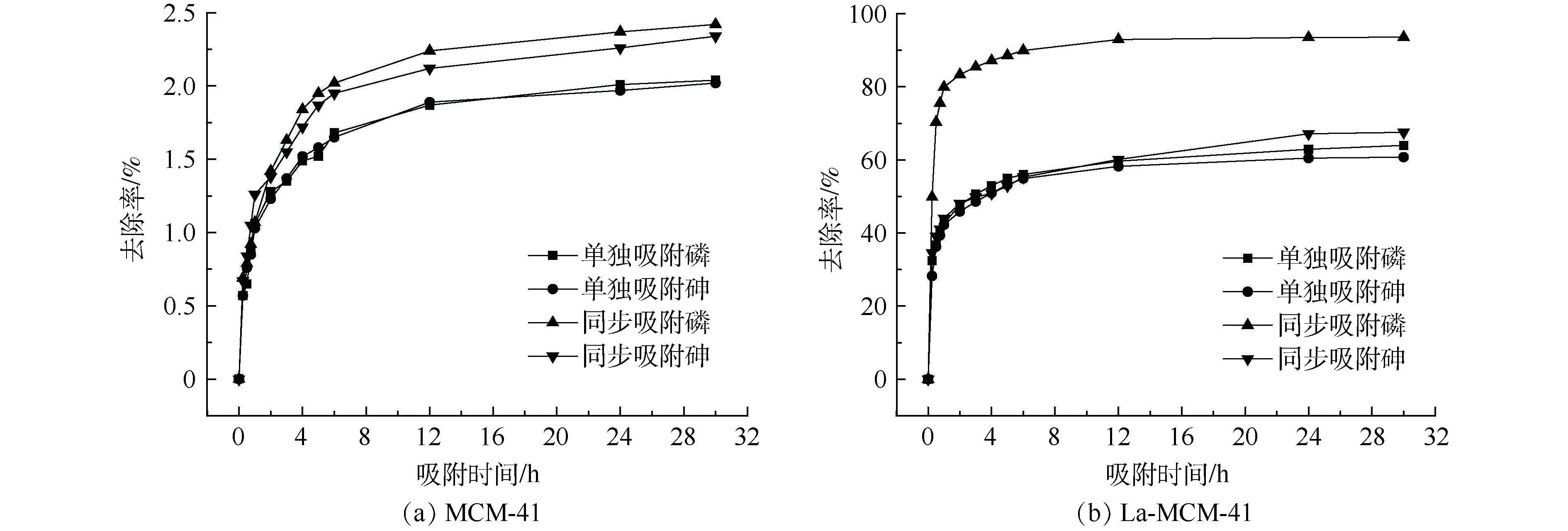
本研究考察了吸附剂改性前后对砷、磷吸附效果的影响,结果如图4所示。未经过改性的介孔吸附剂MCM-41对溶液中的砷、磷几乎没有吸附作用,单一吸附和同步吸附体系中砷、磷的去除率均低于2.5%。这主要是因为,未经过改性的MCM-41本身几乎不含活性位点;而经过改性的La-MCM-41吸附剂对砷、磷具有良好的吸附效果,吸附去除率大大提高。由此可见,介孔吸附材料对砷、磷吸附效果的提升是由于La元素的加入,La的加入使得吸附剂上活性吸附位点增加,故对砷、磷的去除率也提高。且与其他常用吸附剂相比(见表1),本研究的La-MCM-41对砷、磷的吸附效果更突出[24-28],表明La-MCM-41是一种能够同步去除砷、磷的良好吸附剂。
-
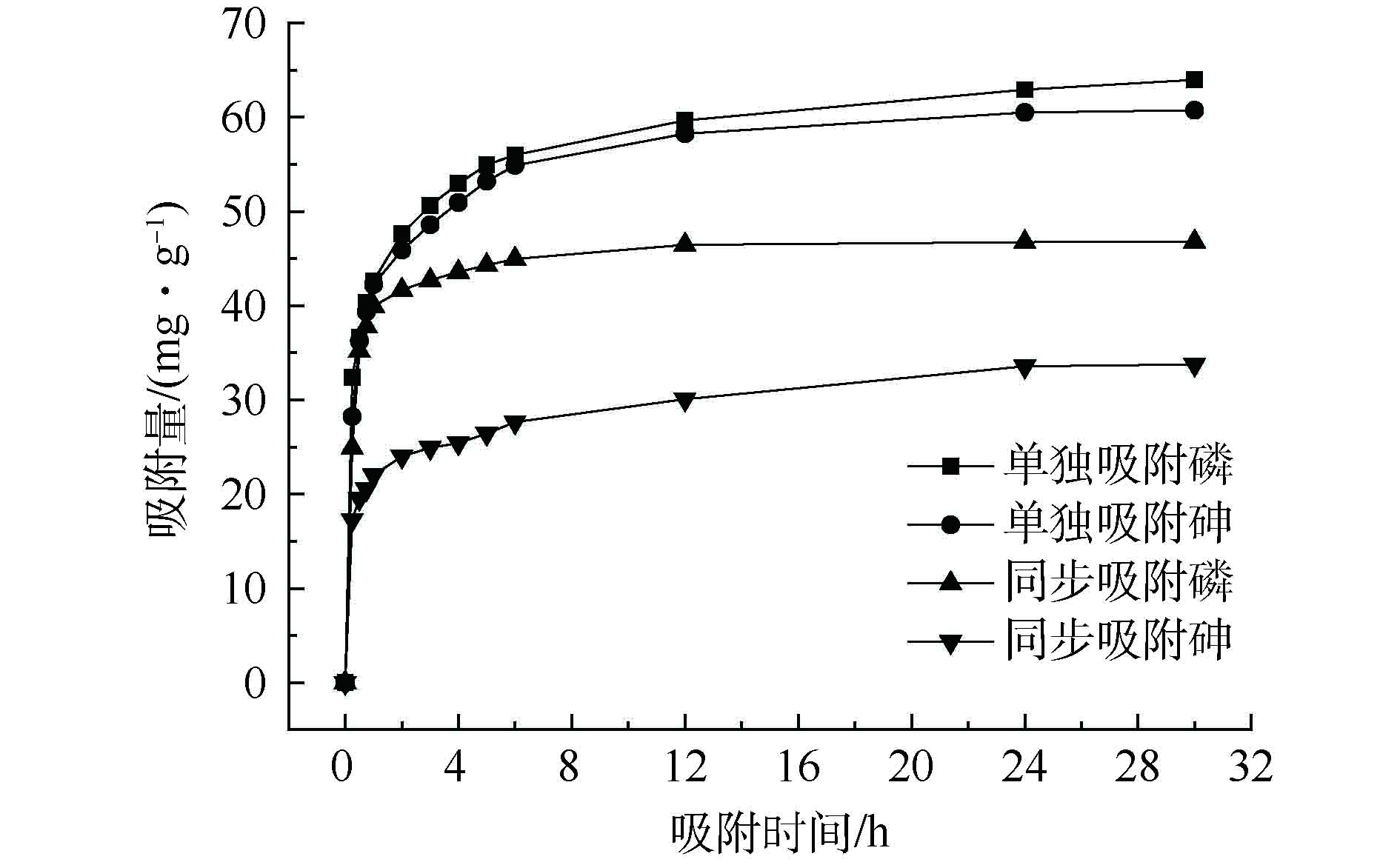
图5是在25 ℃条件下La-MCM-41对目标污染物的动力学吸附结果。La-MCM-41对目标污染物的吸附过程可分为2个阶段:快速反应阶段,由于溶液与吸附剂表面的浓度梯度较大,吸附剂对目标污染物的吸附量快速上升;慢速反应阶段,由于吸附剂表面位点被大量占据,目标污染物吸附量升高速度缓慢,到24 h基本达到平衡,随着平衡随着吸附时间的增加,吸附剂上的吸附点位被不断占用,吸附速率减慢从而达到平衡。从图5中还可发现,单一吸附体系中的吸附量均要高于同步吸附体系,其中,P的吸附量高于As(V)。
采用准一级和准二级动力学吸附模型对实验数据进行了拟合[29]。准一级和准二级动力学模型的数学方程如式(1)和式(2)所示。
式中:k1为准一级动力学速率常数,min−1;k2为准二级动力学速率常数,g·(mg·min)−1;t为反应时间,min;Qe为反应平衡时吸附剂对吸附质的吸附量,mg·g−1;Qt为反应时间t时吸附剂对吸附质的吸附量,mg·g−1。
结合表2及图5可看出,准一级动力学方程R2 > 0.9,准二级动力学方程R2 > 0.99,准二级动力学方程的拟合性更好,并且准二级动力学方程模拟得到的平衡吸附量更加接近于实际测定值,综合来看,La-MCM-41对As(V)、P的吸附更加符合准二级动力学模型。
采用阿累尼乌斯方程计算反应活化能[30],阿累尼乌斯方程如式(3)所示。
两边取对数改写为式(4)。
式中:K为温度为T时的反应速度常数,min−1;Ea为反应活化能,kJ·mol−1;T为热力学温度,K;R为摩尔气体常数,8.314 J·(mol·K)−1;A为指前因子。
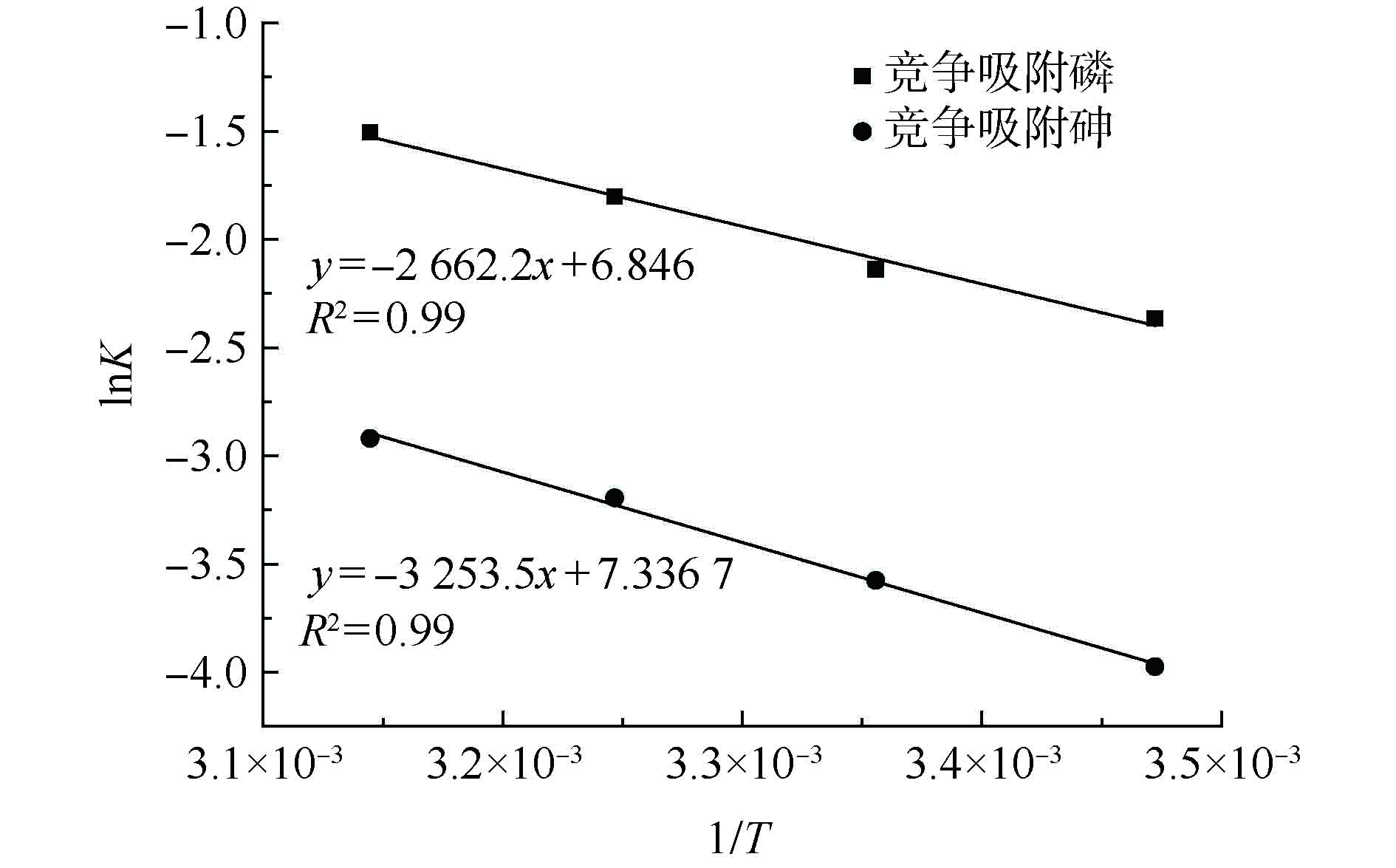
图6是同步吸附条件下La-MCM-41对P、As(V)吸附的阿累尼乌斯方程的拟合情况。根据图6中拟合曲线的直线方程,得出活化能Ea,La-MCM-41对砷和磷的同步吸附活化能分别为27.05 kJ·mol−1和22.68 kJ·mol−1。对比二者可发现,在同步吸附条件下,La-MCM-41对As(V)的吸附活化能稍高于对P的吸附活化能。这说明La-MCM-41对As(V)的吸附需要更多的能量来越过能垒,而对P的吸附相对更容易发生。因此,在同步吸附条件下,磷更容易被吸附在La-MCM-41的位点上,在同步吸附体系中占据优势地位。
-
图7考察了25 ℃下La-MCM-41分别对不同初始浓度的As(V)、P的吸附效果。由图7可知,La-MCM-41对As(V)、P的等温吸附线呈现类似的变化过程,吸附量随着初始浓度的增加而增加,当初始浓度增大到一定程度时,吸附曲线增长速率减缓;达到平衡时,同步吸附时P的最大吸附容量可达到160.07 mg·g−1,As(V)的最大吸附容量为126.75 mg·g−1。两者吸附量的差异可能是因为砷酸根离子的分子大小比磷酸根离子大,砷酸根比磷酸根离子的直径大,因此,单位表面积的砷酸根离子的吸附量会低于磷酸根离子。上述结果与茹春云[30]的报道结果相似。
分别采用Langmuir方程和Freundlich方程[31-32]对吸附等温线进行拟合,拟合所得参数如表3所示。
式中:Ce为平衡时溶液浓度,mg·L−1;qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;qm为吸附剂最大吸附量,mg·g−1;KL为Langmuir平衡常数,L·mg−1;KF为Freundlich吸附常数;1/n为浓度常数,其值越接近1,说明吸附等温线的线性程度越高,1/n值小于1,说明吸附过程属于优惠吸附。
La-MCM-41对As(V)、P的等温吸附数据拟合结果均能较好地符合Langmuir方程和Freundlich方程,除单独吸附P,吸附对Freundlich方程的拟合性更好,故推测La-MCM-41对As(V)和P的吸附介于单分子层和多分子层吸附。同时根据公式(7)可知,RL值均介于0与1之间,说明此吸附过程为有利吸附,且RL值随着浓度的增加而减小,更加说明提高砷和磷的浓度有利于吸附的进行。
式中:C0为起始砷(磷)浓度,mg·L−1;KL为Langmuir平衡常数,L·mg−1。
从表3可以看出,单一吸附体系和同步吸附体系下P的最大吸附量和KF值均大于As(V)的最大吸附量和KF值,说明La-MCM-41对P的吸附能力优于对As(V)的吸附能力。
-
1)采用水热合成法成功制备了吸附容量大,选择性较好的除砷、磷吸附剂La-MCM-41,吸附剂具有稳定的二维六方介孔结构,比表面积为812.27 m2·g−1、孔容为0.64 cm3·g−1、平均孔径为3.18 nm。
2)La-MCM-41对砷、磷的吸附能够在12 h内达到平衡。通过动力学研究分析可发现,在同步吸附体系中,La-MCM-41对2种污染物质的吸附能力具有一定的差距,其对磷的吸附能力比砷强,磷在同步吸附中占据优势,该过程符合准二级动力学模型。
3)采用Langmuir和Frreundlich方程对等温吸附数据进行拟合分析发现,La-MCM-41对磷、砷的吸附过程介于单分子层与多分子层之间,且在2种体系中n值均大于1,说明La-MCM-41对磷、砷的吸附均为优惠型吸附。相比单一吸附体系,同步吸附体系中La-MCM-41对2种离子的饱和吸附量均有不同程度的降低,其中As(V)吸附量下降较多。
镧改性介孔材料对砷、磷的吸附
Adsorption of phosphorus and arsenic on La-modified mesoporous materials
-
摘要: 为探究在复合污染条件下介孔吸附材料对砷、磷的去除效果,通过水热合成法制备镧金属改性介孔吸附材料(La-MCM-41),采用X-射线衍射(XRD)、比表面积测定(BET)、扫描电镜(SEM)等分析方法对改性前后的介孔吸附剂进行了表征;研究了介孔吸附剂在不同吸附体系中对砷、磷的降解效果、等温线及动力学。结果表明:La-MCM-41仍具有长程有序的六方相介孔结构,BET比表面积、总孔容均减小,平均孔径有所增加;介孔吸附剂在单独吸附体系下对砷、磷的吸附量大于同步吸附体系,且均符合二级反应动力学。通过分析可知,在2种体系下,改性后的介孔吸附剂极大地提高了对砷、磷的吸附量,是一种经济高效的吸附材料。Abstract: In this study, La doped mesoporous material (La-MCM-41) was synthesized through the hydrothermal method and used to remove arsenic and phosphorus under combined pollution conditions. The X-ray diffraction (XRD), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), and scanning electron microscope (SEM) were employed to characterize the pristine mesoporous absorbent and La-MCM-41. In different systems, the arsenic and phosphorus adsorption capacity, isotherm and kinetics of by La-MCM-41 were studied. The results show that compared with pristine mesoporous absorbent, La-MCM-41 maintained a long range-ordered hexagonal mesoporous structure, and its BET specific surface area and total pore volume decreased, while its average pore diameter increased. Moreover, the adsorption capacity of arsenic or phosphorus in adsorption single system by La-MCM-41 was greater than that in the synchronous adsorption system, and both adsorption systems could be well described by the second order kinetics. As a cost-effective adsorbent of the modified mesoporous material, its adsorption capacity of arsenic and phosphorus was greatly improved under two systems.
-
Key words:
- mesoporous materials /
- arsenic /
- phosphorus /
- synchronous adsorption
-
消毒是保障饮用水安全的重要工艺,但消毒过程中产生的各类消毒副产物(disinfection by-products,DBPs)会严重危害人体健康。根据消毒副产物结构中是否含N,可将其分为含氮消毒副产物(N-DBPs)和含碳消毒副产物(C-DBPs,只含C而不含N)[1]。毒理学研究表明,相比于C-DBPs,N-DBPs的遗传毒性、细胞毒性和致癌性更强[2]。已知的典型N-DBPs及其结构[3]见表1,其对应结构如图1所示。MUELLNER等[4]研究了卤乙腈(HANs)对仓鼠卵巢细胞的细胞毒性,表明HANs细胞毒性、遗传毒性远高于三卤甲烷(THMs)和卤乙酸(HAAs),其中细胞毒性最高可达THMs的150倍。KANCHANAMAYOON[5]概括了3种HANs的癌症级别(表2),由表2可知,其在低浓度下就会对生命健康造成损害。研究N-DBPs的生成机制、控制和高效去除方法,对保障饮水安全、保护生命健康具有重要意义。
表 1 典型含氮消毒副产物(N-DBPs)的种类Table 1. Species of typical nitrogenous disinfection by-products (N-DBPs)名称或化学式 结构 典型种类 典型结构 卤乙腈(HANs)R3CCN 
二氯乙腈(DCAN) 
溴氯乙腈(BCAN) 二溴乙腈(DBAN) 三氯乙腈(TCAN) 三溴乙腈(TBAN) 卤乙酰胺(HAcAms)R3CCONH2 
二氯乙酰胺(DCAcAm) 
二溴乙酰胺(DBAcAm) 三氯乙酰胺(TCAcAm) 卤代硝基甲烷(HNMs)R3CNO2 
三氯硝基甲烷(TCNM) 
三溴硝基甲烷(TBNM) 二氯一溴硝基甲烷(DCBNM) 二溴一氯硝基甲烷(DBCNM) 亚硝胺(NMs)R2NNO 
N-亚硝基二甲胺(NDMA) 
N-亚硝基吡咯烷(NPYR) N-亚硝基吗啡胆碱(NMOR) N-亚硝基二乙胺(NDEA) 注:R通常是Cl、Br、I、H或烷基,也可以是脂肪族或芳香族基团。 表 2 3种卤乙腈在定量条件下的毒性Table 2. Toxicity of three kinds of haloacetonitrile under quantitative conditions物质 癌症级别 参考剂量/(mg·(kg·d)−1) 饮用水当量/(mg·L−1) 定性目标水平/(μg·L−1) 毒性 TCAN C — — 1 致癌、致突变 DCAN C 0.008 0.300 90 细菌分析种致突变 DBAN C 0.020 0.800 100 小鼠致癌致突变 1. N-DBPs的生成机制
在DBPs的众多前驱物中,水体天然有机物(nature organic matter,NOM)占比最大。其中,腐殖质具有较高的芳香含碳量、比紫外吸收率及较高的N-DBPs生成潜能[6]。N-DBPs的主要前驱物溶解性有机氮(dissolved organic nitrogen,DON)的来源为腐殖质中微生物活动的代谢产物、藻类释放的有机物[7]、土壤侵蚀和生活废水中的氨基酸、蛋白质、氨基糖等[8]。在沿海地区,由于受潮汐侵扰影响,水中溴、碘离子浓度增加,溴碘离子取代次氯酸中的氯离子形成氧化性更强的次溴酸和次碘酸,进而促使二卤乙腈(DHAN)转化为溴氯乙腈(BCAN),最终生成毒性更强的二溴乙腈(DBAN)[9]。
宝露尔等[10]总结了卤乙腈(HANs)生成的2种主要机制:1)脱羧途径,即自由氯或氯胺与α-胺基发生卤代反应;2)醛途径,即氯胺的孤电子对与醛类发生亲核反应生成氯化氨和甲醇,再进行脱水反应消去HCl生成HANs。
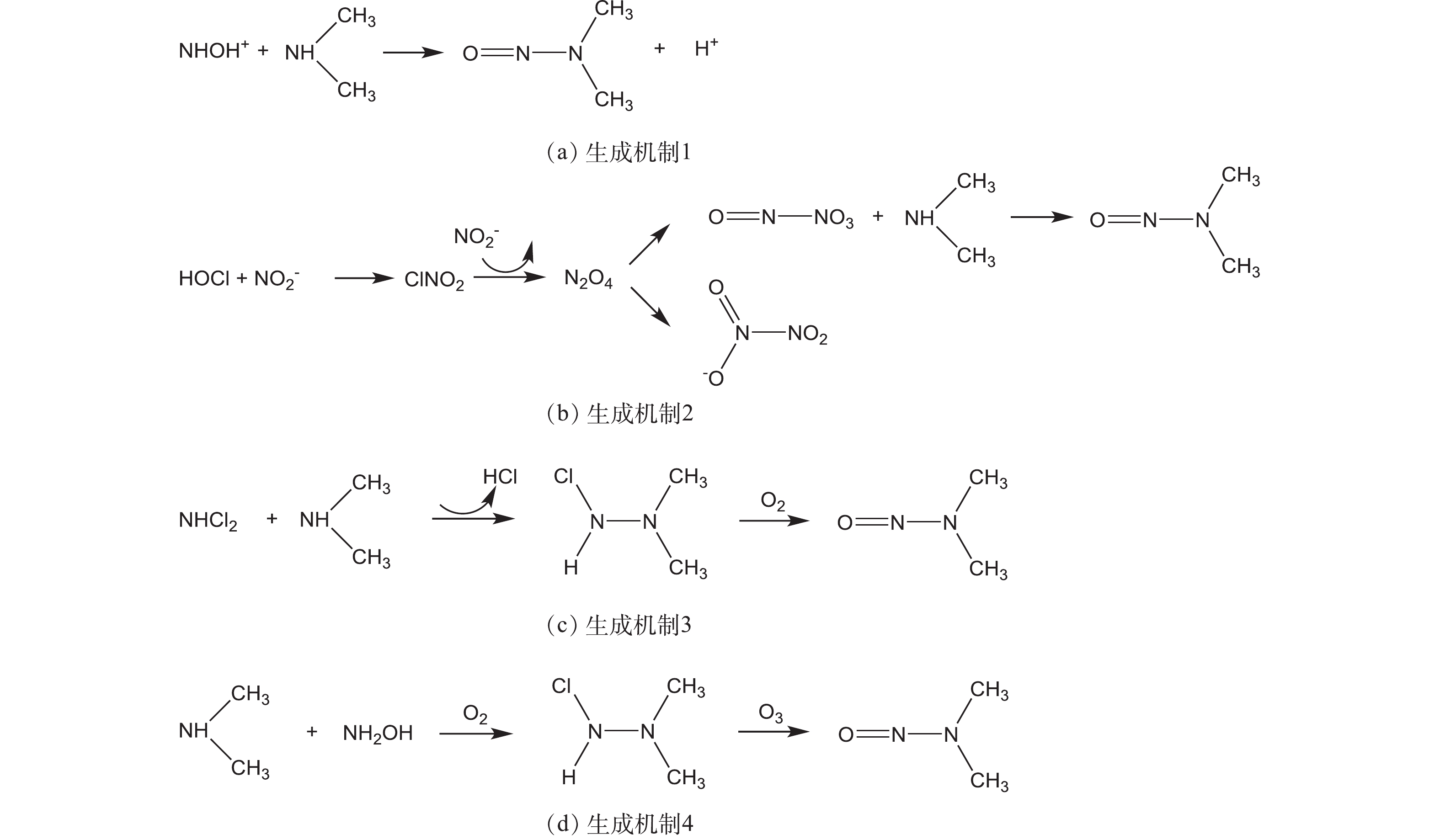
饮用水中检出频率较高的亚硝胺类N-DBPs主要是N-亚硝基二甲胺(NDMA)。SGROI等[11]根据不同的消毒方式,总结NDMA的4种生成机制(见图2):1)通过亚硝酸盐(亚硝化)作用,如二甲胺(DMA)与亚硝基阳离子或类似含氮物种反应生成NDMA;2)亚硝酸盐与次氯酸盐生成ClNO2,进一步与亚硝酸盐反应生成高活性亚硝化中间体N2O4,与DMA反应生成NDMA;3)NH2Cl与仲胺前体如DMA发生亲核取代反应,形成不对称的氯化中间体,之后被溶解氧氧化为NDMA;4)在臭氧条件下,NH2OH与DMA反应生成NDMA。
学者们目前主要关注卤代硝基甲烷(HNMs)中的三氯硝基甲烷(TCNM),高乃云等[12]总结了TCNM的3种生成机制:1)前驱物首先生成硝基甲烷,硝基增强了C—H键的酸性,使α碳位发生卤化反应形成TCNM;2)亚硝酸盐和次氯酸通过两步反应分别生成硝化产物ClNO2和N2O4,它们和芳香结构有机物进行硝化,随后氯化反应使苯环裂解,形成TCNM;3)UV预处理使亚硝酸盐、硝酸盐分解产生N2O4、
NO⋅2 和ONOOH等硝化剂,并与NOM进行硝化反应后再发生氯化反应生成TCNM。DENG等[13]以色氨酸作为氨基酸的代表,提出氨基酸在紫外/氯作用下生成TCNM的可能机制如图3所示。此外,SHAH等[14]补充了溴化物存在下,预臭氧处理会促进溴代硝基甲烷的形成。卤乙酰胺(HAcAms)是一类新发现的N-DBPs,其生成途径有:1)HANs的顺序水解生成HAcAms[15];2)氨基酸氯化生成HAcAms[16]。HAcAms的生成潜能与氨基酸侧链结构上的官能团有关,组氨酸、色氨酸侧链上含有杂环结构,容易发生亲电取代反应和开环,表现出HAcAms生成潜能[17-18];天冬氨酸侧链含有羧基官能团,易发生脱羧和进一步氯取代反应,从而表现出HAcAms生成潜能[16]。目前,对其生成机理的研究报道尚不全面,还需要进一步探索。
2. N-DBPs的控制及去除
由前文可知,在现有净水工艺下,各类N-DBPs的产生不可避免,对人体健康构成威胁。为保障饮用水安全,学者们开展了大量控制及去除水中N-DBPs的研究。目前,对N-DBPs的控制及去除的研究分为3个方面:1)前驱物的去除,主要是去除水中DON;2)优化消毒工艺,包括控制消毒剂用量、更换消毒剂、消毒工艺优化组合等方法;3)对N-DBPs本身的去除。
2.1 前驱物的去除
去除N-DBPs前驱物即去除水中的DON。水中DON来源广泛、成分复杂,对各类N-DBPs生成潜能的影响不同。N-DBPs主要由DON与消毒剂反应生成,现有研究集中于3类物质:1)氨基酸类:DON中结合性和游离性氨基酸,是卤乙腈(HANs)、卤代硝基甲烷(HNMs)和卤乙酰胺(HAcAMs)的重要前驱物[15-16, 19];2)胺类:已确定二甲胺(DMA)是N-亚硝基二甲胺(NDMA)的有效前驱物,一些复杂胺类和含胺化合物也可能是NDMA的前驱物[20];3)藻类:在衰亡期藻细胞大量死亡,其含氮内含物释放到水中,增加水中DON浓度[21]。由于DON分子量较小,含有亲水性含氮官能团,易和水分子形成氢键[22],传统工艺较难去除。目前,常采用强化混凝工艺、深度处理和高级氧化技术去除水中的DON。
传统工艺如混凝法能够有效去除高分子质量、疏水性和芳香性有机物,但较难去除低分子量和亲水性有机物[23];过滤法只能去除一些不溶性有机物[24]。刘冰等[25]研究了预氧化和混凝联用对二级出水DON的影响,在分别采用O3、KMnO4和NaClO作为预氧化剂处理后,混凝对DON的去除率最高可达36.8%。使用粉末活性炭和聚合氯化铝联用进行混凝处理,粉末活性炭对低分子质量和不带电的有机物有较好吸附作用,且与聚合氯化铝形成的颗粒絮体能够中和吸附带负电的官能团,对原水中DON去除效率最高可达71%[26]。采用混凝-超滤联用技术,投加混凝剂形成的絮体吸附包裹有机物形成滤饼层,能够有效被超滤膜过滤[27];混凝还能有效阻止有机物直接通过超滤膜,减少膜污染,因此,该工艺对水中C-NBPs和N-DBPs前驱物都有较好的去除效果。
深度处理工艺采用O3-生物联用和膜过滤这2种技术。O3氧化能够改变有机物的分子特性,使低分子质量和亲水性有机物更容易被生物降解[28]。膜是一种选择性屏障,通过筛分和扩散机制将颗粒和分子分开,可根据不同N-DBPs前驱物的组分特性,选择合适的膜进行处理[29]。TAN等[30]对比了自来水厂中传统水处理工艺和O3/生物活性碳(biological activated carbon,BAC)工艺对二氯乙腈(DCAN)生成潜能的控制作用,常规水处理工艺对DCAN前驱物的去除率为21.89%,经O3/BAC深度处理后,DCAN前驱物的去除率提高到50.58%。分析表明,在增加O3/BAC处理的组合工艺中,黄腐酸和腐殖酸主要通过常规处理工艺去除,而芳香蛋白和可溶性生物副产物则通过O3/BAC的氧化、降解和吸附去除。ERSAN等[31]用3种不同的平板聚酰胺薄膜复合纳滤(nanofiltration,NF)膜去除地表水、受废水影响的地表水及城市和工业废水处理出水中NDMA、HNMs的前驱物,其前驱物的总去除率分别为57%~83%、48%~87%。FAN等[28]采用混凝-O3-陶瓷超滤-生物活性碳组合工艺,对微污染地表水中DCAN和TCAN前驱物的去除率分别达到77%和51%。当O3与陶瓷超滤结合时,膜池中的部分O3会随有机物一起进入膜孔,O3和有机物会在膜孔内发生反应,极大减小传质时间和反应时间。此外,O3与膜孔内的有机物会发生反应,减小膜污染影响。
高级氧化技术(advanced oxidation processes,AOPs)是一类以产生具有强氧化性的·OH为主的新型氧化技术,具有反应速度快、降解彻底等优点。SRITHEP等[32]研究了高级氧化技术去除二氯乙腈(DCAN)前驱物的动力学特征,采用拟一阶动力学模型拟合UV/H2O2、UV/O3、UV/H2O2/O3 3种工艺对DCAN前驱物的降解过程。这3种工艺的
k′DON (去除DON的一级反应常数)均大于k′DCAN⋅FP (去除DCAN前体的一级反应常数),原因可能是在对高DOC/DON的水进行消毒时,有部分无机氮参与DCAN的形成增加降解难度,UV/O3工艺的k′DON 和k′DCAN⋅FP 值最小,降解速度缓慢。DING等[33]研究了UV/H2O2氧化后消毒方法对DBPs生成的影响,UV既能直接光解部分有机物,又能激活H2O2产生·OH,进一步氧化有机物。经UV/H2O2处理后,水中DON浓度可降低70%左右,经氯或氯胺消毒后卤乙腈(HAN)、卤代硝基甲烷(HNM)去除率最高可达83.6%和87.3%。2.2 优化消毒工艺
从目前研究来看,去除前驱物能减少后续N-DBPs生成。由于传统工艺的局限性,多种工艺联用已成为解决N-DBPs前驱物问题的主要手段,以克服单独方法的不足,如活性炭滤池中微生物的泄漏、膜组件的堵塞、高级氧化技术运行成本高等问题。在实际应用中,应根据原水水质、主要前驱物、处理效果等条件选择合适的组合工艺或优化消毒工艺,保证饮用水水质安全。
优化消毒工艺是指根据水源和出厂水的实际情况,针对某类易生成、超标且难去除的N-DBPs,在保证消毒杀菌效果的前提下,通过调节消毒工艺参数、更换消毒剂、采用组合消毒工艺等方法,实现对N-DBPs的有效控制,以保障出水水质达标,同时减少运行成本。
纪瑶瑶等[34]采用游离氯转氯胺消毒的顺序氯化消毒工艺处理微污染原水,研究反应时间、加氨转化时间、氨氮质量比和pH对处理效果的影响,结果显示在加氨转化时间为30 min、氯氮质量比为(5∶1)~(3∶1)、与消毒剂接触24 h后,二氯乙腈(DCAN)、三氯硝基甲烷(TCNM)和1,1,1-三氯丙酮的生成量分别减少了72.08%、70.37%和82.61%。LIU等[35]比较了氯和氯胺消毒,KMnO4和K2FeO4预氧化、紫外线/过氧化氢(UV/H2O2)和紫外线/过硫酸盐(UV/PS)工艺对水中DBPs的控制,发现氯胺消毒能有效控制C-DBPs的生成,但不能控制N-DBPs的生成;与KMnO4预氧化相比,K2FeO4预氧化能更好的控制DBPs的生成,4种处理工艺均能使水样的细胞毒性指数、遗传毒性指数明显降低。因此,在使用氯胺作为替代消毒剂时,可以通过有效去除N-DBPs前驱物来降低后续氯胺消毒过程中N-DBPs的生成潜能,从而实现同步削减C-DBPs和N-DBPs。HU等[36]对比混凝-沉淀-过滤(CSF)、KMnO4/O3/K2FeO4/ClO2预氧化+CSF以及KMnO4/O3/K2FeO4/ClO2预氧化+CSF+O3/GAC这3种深度处理组合工艺对N-DBPs生成的影响;采用预氧化处理使DCAN生成潜能分别降低26.8%(KMnO4)、31.9%(O3)、30.2%(K2FeO4)、24.0%(ClO2),而采用O3/GAC深度处理使DCAN去除效率分别提高到48.6%、53.0%、51.0%、48.5%。
2.3 直接去除N-DBPs
实际工程应用中,在确保饮用水水质安全的前提下,降低运行成本是选择水处理方案的关键因素。通过去除前驱物和优化消毒工艺对水中N-DBPs均有一定控制效果,但现有方法仍存在不足之处。应用各种工艺时必须考虑原水水质、处理规模和投资等因素,将去除前驱物和优化消毒工艺有机结合,通过有效去除前驱物降低后续消毒处理负荷,通过优化整体消毒工艺保证水质,降低成本。对于经过整个净水消毒流程后仍存在的N-DBPs,可通过一些方法将其直接去除。因此,研究N-DBPs的直接去除也很关键。基于不同N-DBPs的理化特性差异,学者们进行了有关去除方法和机理方面的研究,主要方法可分为三类:物理法、高级氧化法和还原降解法。
根据N-DBPs分子大小、极性、电荷和官能团等特点,采用活性炭吸附和膜滤的方法直接去除。曹中琦等[37]研究了活性炭对卤乙酰胺(HAcAMs)的去除,发现HAcAMs的去除主要依靠自身水解和活性炭吸附双重作用,活性炭对极性较弱的三氯乙酰胺(TCAcAM)吸附效果较好。丁春生等[38]研究了改性活性炭对三氯硝基甲烷(TCNM)的吸附作用。通过氢氧化钠改性,能清除附着在活性炭孔道内的杂质,在其表面能削减酸性基团,增加非极性,提高对TCNM的吸附效果,去除率可达87%。FUJIOKA等[39]通过热处理原型反渗透膜,使膜的聚合结构发生改变,降低了膜的电导截留率和渗透率,提高对N-亚硝基二甲胺(NDMA)的排斥效果,使NDMA的去除率达到92%。
员建等[40]研究了紫外光(UV)在不同条件下对二氯乙腈(DCAN)和二溴乙腈(DBAN)的去除效果。随着反应条件的改变,UV几乎能去除所有的DBAN,远高于对DCAN的总去除率。推测机理是UV既能直接光解大部分N-DBPs,同时释放的光子也能激活水分子,水中的OH−会吸收UV转变为·OH,进一步降解有机物,由于DBAN中的C—Br键能较小,容易被破坏,去除率较高。HOU等[41]采用拟一级动力学模型拟合UV/PS法去除氯化消毒产生HANs的过程发现,随着氯化程度增加,UV/PS法产生的·OH会将更多有机物的C—Cl键转化为键能较小的C—H键,使k0降低,反应速度逐渐下降。
近年来,学者们广泛关注零价铁(zero-valent iron,ZVI)对N-DBPs的还原降解作用。丁春生等[42]利用溶液中的Fe/Cu微电池,通过电化学法还原降解水中的溴氯乙腈(BCAN)。由于Cu具有很好的催化性能,其含量越高,降解速率越快。反应体系中原电池数量随Fe/Cu投加量的增大而增加,活化分子数随温度升高而增加,从而提高对BCAN的去除效率,最高可达91.6%。韩莹等[43]探究了CuO催化ZVI对水中N-亚硝基二甲胺(NDMA)的去除效果,研究发现反应18 h后NDMA基本全部被去除,推测去除机理为ZVI通过催化加氢生成活性氢原子,活性氢原子还原NDMA生成二甲胺(DMA)。这类研究从新的角度揭示了N-DBPs还原降解的机理,但目前对ZVI的应用研究还处于起步阶段,还不能用于实际水处理,仍需深入探索。
3. 结语与展望
在实际水净化工程中去除N-DBPs,应根据原水水质特点,优先考虑去除N-DBPs的前驱物,并选择经济有效的去除前驱物方法。选择的工艺既能减小后续处理过程中N-DBPs的生成潜能,又能降低后续工艺的处理负荷;进一步优化消毒工艺,可实现同步削减C-DBPs和N-DBPs,保障出水的安全性,同时降低处理成本。综合前文所述,应加强以下2个方面的研究:1)明确DON中特定组分对N-DBPs生成潜能的影响,进一步探索不同N-DBPs的生成机理;2)优化现有的处理工艺,建立N-DBPs在不同处理工艺中的生成潜能模型,以便根据实际条件制定最佳处理方案。
近年来,新型纳米功能材料成为众多学者们关注的热点,广泛应用于水处理、环境修复、能源等领域。纳米材料具有可调变性、大比表面积和高催化活性等特性,通过改性或复合等手段制备的新型纳米功能材料在吸附、光电催化、氧化还原降解N-DBPs方面表现出很大潜力。电化学催化氧化技术是一种重要的高级氧化技术,具有无需外加药剂、可避免二次污染、反应条件温和、设备操作简单及占地面积小等优点。电化学反应一般发生在电极表面和附近的紧密层区域,而三维电化学体系中的粒子电极大大缩短污染物到电极表面的传质距离,更有利于去除低浓度的有机物。由于电化学体系的灵活性,能将装置缩小到适配家用输水装置,避免管网输水过程产生的次生污染影响水质,实现龙头的水污染控制。因此,新型纳米功能材料耦合电化学技术用于处理饮用水中的N-DBPs将会是未来一个重要的研究方向。
-
表 1 不同吸附剂去除As(V)和P性能的比较
Table 1. Comparison of As(V) and P adsorption by different adsorbents
表 2 La-MCM-41同步去除As(V)和P的动力学参数
Table 2. Kinetic models parameters for simultaneous removal of As(V) and P by La-MCM-41
温度/℃ 吸附类型 准一级动力学 准二级动力学 Qe/(mg·g−1) k1 R2 Qe/(mg·g−1) k2 R2 15 同步吸附P 10.38 0.160 3 0.965 46.08 0.094 0.997 15 同步吸附As 18.87 0.175 4 0.962 34.36 0.018 0.997 25 同步吸附P 12.08 0.252 8 0.903 47.17 0.118 0.999 25 同步吸附As 17.73 0.177 7 0.945 34.48 0.028 0.997 35 同步吸附P 13.57 0.363 3 0.992 48.31 0.165 0.999 35 同步吸附As 16.07 0.179 7 0.949 34.72 0.041 0.998 45 同步吸附P 14.11 0.695 2 0.991 50 0.222 0.999 45 同步吸附As 13.77 0.180 4 0.926 34.72 0.054 0.998 表 3 La-MCM-41吸附As(V)和P的等温吸附模型参数
Table 3. Isotherm parameters for As(V) and P adsorption onto La-MCM-41
吸附类型 Langmuir Freundlich Qm/(mg·g−1) KL/(L·mg−1) R2 n KF/(mg·g−1) R2 单独吸附P 192.3 0.09 0.99 2.39 26.66 0.989 单独吸附As 163.93 0.14 0.982 2.73 24.75 0.988 同步吸附P 188.68 0.075 0.983 2.39 24.61 0.993 同步吸附As 133.33 0.075 0.979 2.38 17.3 0.987 -
[1] ZHOU Q, XI S H. A review on arsenic carcinogenesis: Epidemiology, metabolism, genotoxicity and epigenetic changes[J]. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2018, 99: 78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.09.010 [2] HOMERO H F, PARIONA N, MARTIN H T, et al. Concrete/maghemite nanocomposites as novel adsorbents for arsenic removal[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2018, 1171: 9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.05.078 [3] KARDIA R M, FATIMA P R, RANGEL M R. Adsorption of arsenic onto an environmental friendly goethite-polyacrylamide composite[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 264: 253-260. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.05.063 [4] KOILRAJ P, TAKAKI Y, SASAKI K. Adsorption characteristics of arsenate on colloidal nanosheets of layered double hydroxide[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2016, 134: 110-119. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2016.06.002 [5] ANTELO J, ARCE F, FIOL S. Arsenate and phosphate adsorption on ferrihydrite nanoparticles: Synergetic interaction with calcium ions[J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 410(2): 53-62. [6] GOSCIANSKA J, PTASZKOWSKA-KONIARZ M, FRANKOWSKI M, et al. Removal of phosphate from water by lanthanum-modified zeolites obtained from fly ash[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 513: 72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.11.003 [7] ZHANG M, GAO B, YAO Y, et al. Phosphate removal ability of biochar/MgAl-LDH ultra-fine composites prepared by liquid-phase deposition[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(8): 1042-1047. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.050 [8] BOUJELBEN N. phosphorus removal from aqueous solution using iron coated natural and engineered sorbents[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 151(1): 103-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.057 [9] REDFIELD R J. Comment on " A bacterium that can grow by using arsenic instead of phosphorus”[J]. Science, 2011, 332(1): 1163-1166. [10] 邹强, 刘芳, 杨剑虹. 紫色土中砷、磷的吸附-解吸和竞争吸附[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(6): 1383-1389. [11] LOGANATHAN P, VIGNESWARAN S, KANDASAMY J, et al. Removal and recovery of phosphate from water using sorption[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2014, 44(8): 847-907. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2012.741311 [12] DUENAS J F, AlONSO J R, REY F, et al. Characterisation of phosphorous forms in wastewater treatment plants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2003, 97(1/2/3): 193-205. [13] TENG W, WU Z X, FAN J W, et al. Ordered mesoporous earbons and their corresponding column for highly efficient removal of microcystin-LR[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(9): 2765-2776. [14] HUANG W, ZHANG Y, LI D. Adsorptive removal of phosphate from water using mesoporous materials: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 193: 470-482. [15] SUBHAN F, LIU B S, ZHANG Y, et al. High desulfurization characteristic of lanthanum loaded mesoporous MCM-41 sorbents for diesel fuel[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2012, 97(3): 71-78. [16] CHUTIA P, KATO S, KOJIMA T, et al. Arsenic adsorption from aqueous solution on synthetic zeolites[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(1): 440-447. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.061 [17] VASUDEVAN S, LAKSHMI J. The adsorption of phosphate by graphene from aqueous solution[J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(12): 5234. doi: 10.1039/c2ra20270k [18] 何素芳. 铝改性SBA-15介孔材料在砷吸附去除中的应用及吸附机理[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2015. [19] ZHANG J, SHEN Z, SHAN W, et al. Adsorption behavior of phosphate on lanthanum(III)-coordinated diamino-functionalized 3D hybrid mesoporous silicates material[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(1): 76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.076 [20] ZHAN W C, LU G Z, GUO Y L, et al. Synthesis of Ln-doped MCM-41 mesoporous materials and their catalytic performance in oxidation of styrene[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2008, 26(1): 59-65. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(08)60038-1 [21] YANG J P, CHEN W Y, SHEN D K, et al. Controllable fabrication of dendritic mesoporous silica-carbon nanospheres for anthracene removal[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(29): 11045-11048. doi: 10.1039/c4ta01516a [22] 王宇红, 袁联群, 俞磊, 等. 镧、钒取代MCM-41分子筛的结构表征及其在苯酚羟基化反应中的催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2010, 61(10): 2565-2572. [23] LI X, LI B, XU J, et al. Synthesis and characterization of Ln-ZSM-5/MCM-41 (Ln = La, Ce) by using kaolin as raw material[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2010, 50(1): 81-86. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.07.006 [24] 张芙蓉. 砷磷在铁锰/铝锰复合氧化物表面的同步吸附特性及竞争作用规律[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2017. [25] ZHU N, YAN T, QIAO J, et al. Adsorption of arsenic, phosphorus and chromium by bismuth impregnated biochar: Adsorption mechanism and depleted adsorbent utilization[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 164: 32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.036 [26] 曹秉帝, 徐绪筝, 王东升, 等. 三价铁改性活性炭对水中微量砷的吸附特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(5): 2321-2328. [27] LEDUC J F, LEDUC R, CABANA H. Phosphate adsorption onto chitosan-based hydrogel microspheres[J]. Adsorption Science & Technology, 2014, 32(7): 557-570. [28] LIU J, QI Z, CHEN J, et al. Phosphate adsorption on hydroxyl-iron-lanthanum doped activated carbon fiber[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 215(2): 859-867. [29] 王宇, 高宝玉, 岳文文, 等. 改性玉米秸秆对水中磷酸根的吸附动力学研究[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(3): 703-708. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.03.027 [30] 茹春云. 典型阴离子在纳米铁表面的竞争吸附模型研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2013. [31] MALEKIAN R, ABEDI-KOUPAI J, ESLAMIAN S S, et al. Ion-exchange process for ammonium removal and release using natural Iranian zeolite[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2011, 51(3): 323-329. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.12.020 [32] TANG D, ZHANG G. Efficient removal of fluoride by hierarchical Ce-Fe bimetal oxides adsorbent: Thermodynamics, kinetics and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 283: 721-729. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.019 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: