-
我国西北干旱地区水资源短缺,生活污水再生回用农业技术应用广泛,但污水处理厂的生活污泥缺乏合理的处置方式。目前,污泥处置方法主要有物理填埋、焚烧和污泥堆肥,填埋和焚烧均对生态环境有一定的污染,而污泥堆肥可以在高温发酵过程中杀死病原菌,其最终产品可以作为有机肥料或土壤改良剂[1]。这既解决了城市污泥处置难的问题,又可为农业生产、城市绿化、苗圃育苗等提供肥料[2]。因此,污泥堆肥处置是有机物循环再利用的有效途径。我国西北干旱地区生活污泥利用离心技术脱水后的含水率在90%左右,而经过压滤板压滤后的含水率仍高达65%~75%,高含水率导致污泥在堆肥过程中存在升温和腐熟慢,养分损失多,而且还容易产生有毒有害气体的问题。因此,西北干旱地区污泥堆肥过程中亟需解决高含水率污泥升温速度慢的问题。
污泥好氧堆肥的升温速度和成品质量受添加辅料因素的影响。研究表明,污泥好氧堆肥辅料为稻草和秸秆时升温快,为锯末时氮素损失小[3-6]。秸秆小粒径比大粒径更有利于保存堆肥产品的养分;污泥与秸秆体积比1∶2时升温速度和腐熟度较好,堆肥产品中养分含量随着污泥和秸秆比例升高而增大,污泥堆肥处理成本也随之升高[7-9]。MAZDAK等[10]和ZHANG等[11]发现,适宜的翻抛工艺可以解决堆肥升温慢、效率低、成品质量差的问题。可见,污泥与辅料的配比、粒径及翻抛工艺是影响污泥堆肥升温速率和堆肥产品质量的重要因素。在我国,已有研究多集中于不同辅料的选择、配比和粒径等单因素对污泥堆肥升温速率和堆肥产品质量的影响方面,而综合这些因素对西北干旱地区污泥好氧堆肥过程中各项指标动态变化规律影响的研究相对较少。
本研究在我国西北干旱区通过开展3因素3水平的正交实验,研究玉米秸秆比例、粒径及翻抛工艺对污泥堆肥堆体内部温度、pH、电导率及水分的影响,筛选适宜该地区污泥堆肥的玉米秸秆添加比例、粒径及翻抛工艺,以期为我国西北干旱地区生活污泥高效堆肥提供参考。
-
供试材料为生活污泥、玉米秸秆和微生物菌剂。生活污泥取自银川某公司污泥脱水车间,该污泥有机质含量高,5种重金属含量均小于国家标准限值,可以作为污泥堆肥原料。微生物菌剂为商用试剂,成分有芽孢杆菌、乳酸菌、解磷真菌、酵母菌、木霉菌、嗜热球菌等复合微生物及载体,复合微生物活菌量>2×1010 个·g−1。污泥和玉米秸秆初始基本成分如表1所示。
-
采用3因素3水平正交实验,3因素分别为玉米秸秆配比、秸秆粒径、翻抛工艺。每因素设置3水平,秸秆配比(质量)分别为5%(A1)、10%(A2)、15%(A3);秸秆粒径分别为5 cm(B1)、3 cm(B2)、(15~20) cm(B3);翻抛工艺分别为静置6 d后翻抛(C1,堆肥后前2周先静置1周厌氧发酵,第2周的翻堆频率为2 次∙周−1,后3周翻堆频率为1 次∙周−1)、常规翻抛(C2,堆肥后前2周翻堆频率为2 次∙周−1,后3周翻堆频率为1 次∙周−1)、常规翻抛曝气处理(C3,在常规翻抛的基础上通过在堆体内埋设打孔的PVC管道进行间歇式通气,每天分别在9:00和15:00进行通气,通气时间为30 min,通风量为10 m3∙min−1)。
实验时间为2020年8—10月,堆肥实验设置9个处理(见表2),堆垛污泥的重量固定为3 t,添加不同比例、不同粒径的玉米秸秆,按堆肥总质量添加0.2%的有机肥发酵菌剂。
-
如图1所示,将物料充分混合后堆成长6 m、宽1.5 m、高1.2 m的条垛,横截面积为梯形,以机械翻堆的方式进行翻堆。堆肥期间采用不同翻抛方式处理,堆肥周期为35 d,堆肥完成后进一步陈化10 d,总周期45 d。在堆肥后第 1、3、5、7、10、14、18、23、28、32、35、45 d进行分层采样,如图1(b)所示,取堆体垂直剖面的上、中、下层,3个部位采样。每次采集不少于200 g 的多点混合样。剔除大小碎石块等杂质后作为新鲜样品放入密封容器中带回实验室,并尽快分析测定堆肥中的含水率、pH、电导率。在堆体的中心深度放置60 cm酒精温度计记录温度,每天9:00和15:00人工读取温度计读数,取其算术平均值作为当天的堆体温度,同时读取悬挂式温湿度计记录环境温度。
-
有机质含量的测定参考《土壤检测 第6部分》(NY/T1121.6-2006)中土壤有机质的测定方法[12];全氮的测定参考《土壤质量 土壤全氮测定 凯氏法》(HJ717-2014)中全氮(HJ717-2014)测定方法[13];总汞、总砷、总铅的测定参考《土壤质量 原子荧光法》(GB/T22105-2008)[14];总铬的测定参考《土壤和沉积物 火焰原子吸收分光光度法》(HJ491-2019)[15];总镉的测定参考《土壤质量 石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法》 (GB/T17141-1997)[16];pH和电导率的测定方法分别用酸度计(哈纳HI2221pH/ORP测定仪)和电导率仪(雷磁DDS-307A 电导率仪)测定;堆肥含水率采用烘干法测定。
-
堆体温度直接反映了堆肥效率和微生物活性,进而影响堆肥产品质量高低,故堆体温度的变化是衡量污泥好氧堆肥是否正常的关键指标[17]。由图2可以看出,各处理堆体温度均经历了升温、高温和降温3个阶段。由图2(a)可看出,不同玉米秸秆配比之间在升温期温度变化曲线存在明显差异。15%秸秆配比处理的堆体温度在第3 d即达到最高温度70 ℃,升温速率最快,为17.3 ℃∙d−1。10%秸秆配比的堆体温度在第5 d达到最高温度70 ℃,升温速率次之,为10.4 ℃∙d−1。5%秸秆配比堆体温度在第14 d才达到最高温度70 ℃,升温速率最慢,仅4 ℃∙d−1。这说明,玉米秸秆配比显著影响堆体的升温速率。秸秆添加量越高,堆体孔隙率越大,可以给好氧微生物提供较多的空气,促进微生物繁殖和堆体升温发酵。玉米秸秆配比不同各处理的最高温度均能达到70 ℃,高温持续时间均超过10 d,满足《粪便无害化卫生标准》(GB 7959-2012)[18]中要求的高温持续时间。但秸秆配比显著影响高温持续时间。其中,15%秸秆配比堆体温度大于55 ℃的时间持续了15 d,10%秸秆配比的持续18 d,而5%秸秆配比的只有10 d。由图2(b)可看出,不同粒径的升温速率相同,降温期曲线基本一致。但5 cm粒径秸秆处理的堆体最高温度相比其他处理更高且高温持续时间更长,有利于堆肥发酵反应的顺利进行。秸秆粒径为5、3和(15~20) cm的高温持续时间分别为22、20和19 d,粉碎的玉米秸秆处理的堆体温度更高,高温持续时间更长。但3 cm粒径处理的堆体最高温和高温持续时间小于5 cm粒径的。这是因为,玉米秸秆粒径小、堆体空间结构致密,影响堆体内部氧气输送,造成微生物因氧气不足,故导致堆肥温度低和高温持续时间短。由图2(c)可看出,先静置6 d常规翻抛堆体温度升温速率快于其他2种翻抛工艺;曝气翻抛由于曝气会带走堆体温度,在前期堆体升温速率较慢。3种翻抛工艺之间在最高温度和高温持续时间方面无明显差异。堆肥降温期表现为静置6 d翻抛的降温速率大于常规翻抛和曝气翻抛,而常规翻抛和曝气翻抛无明显差异。不同操作工艺会影响堆肥周期,常规翻抛和翻抛曝气处理堆肥周期长,不利于污泥堆肥生产实际运行。静置6 d翻抛堆体降温快,可以缩短堆肥周期和提高生产效率。
-
引用有效积温来分析条垛污泥堆肥反应的温度效应,用式(1)计算污泥好氧堆肥堆体有效积温。
式中:Ti为堆肥i时刻的堆体温度,取当天平均温度,℃;T0为堆肥中微生物大量繁殖时的起始温度(生物学零度)。本研究中参考了陈同斌等[19]建议的生物学零度将T0取15 ℃;∆t为Ti持续的时间,h。
各处理堆肥期间的有效积温结果见图3。各处理堆肥过程中的有效积温均值为2.97×104 ℃·h。其中,T7堆体积温高于有效积温平均值,且最接近有效积温平均值。
极差分析(表3)表明,影响好氧堆肥堆体有效积温因素的大小顺序为,玉米秸秆粒径>翻抛工艺>玉米秸秆配比,即玉米秸秆的粒径大小对堆体的有效积温影响最大,其次是翻抛工艺,最小的是污泥与玉米秸秆的比例。
-
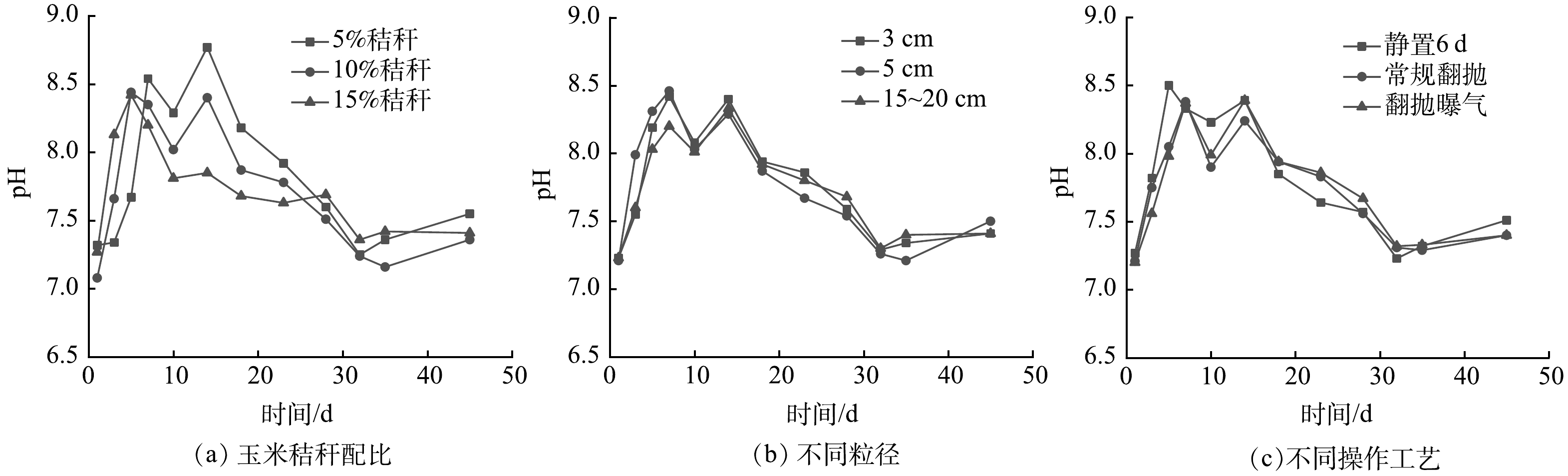
堆体pH是评估堆肥过程中微生物生存环境变化的重要参数,适宜的 pH 是微生物良好生存环境的保障[20],还可以有效减少氨气的挥发,从而降低铵态氮损失[21]。由图4可看出,各处理堆体堆肥过程中pH变化过程总体趋势一致,均呈现先升高后减低的趋势,与温度变化趋势相似。这是因为,堆体在升温阶段,微生物菌群快速分解堆体中的有机质,铵态氮含量增高,氨气在堆体中不断积累使pH升高,之后由于氨气的挥发和硝化作用以及有机物分解产生的低分子有机酸使 pH下降[22]。各处理最终pH稳定在7~8,符合《城镇污水处理厂污泥处置农用泥质》(CJ/T 309-2009)[23]标准要求。有研究表明[24],堆肥结束时pH稳定在中性或偏碱性的范围内,说明堆体达到腐熟。
由图4(a)可看出,不同玉米秸秆配比之间堆体pH有明显差异。其中,5%玉米秸秆配比处理的pH达到最大值8.8,且达到最高值的时间相对其他配比的时间延后。堆肥15 d后pH随着玉米秸秆比例增加而降低,这是因为,玉米秸秆比例增大,升温速度快,好氧微生物数量多,氨气产生少,低分子脂肪酸少,所以造成pH降低[25]。达到最高值后pH变化随着堆肥时间延长而降低,但最终pH无明显差异,均在7.36~7.51。由图4(b)可看出,不同粒径处理的pH变化过程基本一致,且后期pH无明显差异,前期粒径为15~20 cm的堆体pH低于粒径为3和5 cm的堆体pH。这是因为,15~20 cm秸秆块状物大,不利于微生物分解。由图4(c)可看出,不同翻抛工艺下pH变化曲线趋于一致,各处理之间无明显差异。但静置6 d翻抛的pH先达到最大值。这是因为,静置6 d时堆体内部缺少空气,一直处于厌氧发酵的状态,大量产生氨气使得堆体的pH提升较快。
-
由图5可看出,各处理堆体的电导率(EC)在堆肥过程中均随时间变化呈升高的趋势。这是因为,在堆肥发酵过程中,微生物将有机物分解为无机小分子物质,小分子物质溶于水从而提高了堆体的电导率。后期部分无机离子在弱碱性条件下形成沉淀而使离子浓度降低[26],堆肥结束时,电导率稳定在2.27~2.86 mS·cm−1。一般认为,当EC<4 mS·cm−1不会对植物产生毒害作用[27-28]。整个时期各处理的电导率EC值均低于4 mS·cm−1。
由图5(a)可看出,不同玉米秸秆配比之间堆体电导率有明显差异。随着玉米秸秆配比的增加,堆体电导率呈增加的趋势;堆肥结束后堆体电导率的大小顺序为:15%秸秆配比>10%秸秆配比>5%秸秆配比。由图5(b)可知,不同玉米秸秆粒径堆体电导率变化过程趋于一致。不粉碎处理的电导率在后期高于3和5 cm粒径的。由图5(c)可知拿出,不同翻抛工艺之间堆体电导率变化过程无明显差异,静置6 d翻抛处理的后期堆体电导率较常规翻抛和翻抛曝气的稍高。
-
堆肥含水率是影响堆肥周期长短和堆肥质量的关键性因素[29]。堆体含水率过高会妨碍气体输送,严重影响微生物有氧代谢,堆体含水率过低则会抑制堆体中微生物的活动和代谢[30]。由图6可看出,不同处理堆体含水率随堆肥时间延长均呈现下降趋势,但堆体含水率减少量上存在较大差异。由图6(a)可看出,不同玉米秸秆配比之间堆体含水率变化过程存在明显差异。堆体含水率随着玉米秸秆配比增加而降低;15%玉米秸秆配比处理孔隙度大,堆体升温速度快,加速了堆体水分散发,堆体含水率下降快,从刚开始70%到堆肥结束时的40%左右,减少了30%。5%玉米秸秆配比的处理堆体初始含水率高,孔隙度小,堆体升温慢,从开始到堆肥结束堆体含水率减少了18%;由图6(b)可看出,不同粒径之间堆体含水率变化曲线差异不大。在堆肥中后期,15~20 cm的含水率低于3和5 cm粒径的。这是因为,15~20 cm的玉米芯具吸水性强、含水率下降快。中后期3 cm粒径含水率下降较快。这是因为,玉米秸秆粒径小,增加了玉米秸秆与污泥接触的面积,为微生物菌群提供了更多的生存环境。由图6(c)可看出,不同操作工艺之间堆体含水率变化过程线差异也不大。从堆肥开始到结束,堆体含水率减少了20%。后期静置6 d翻抛的堆体含水率值先达到最小值。这是因为,堆体翻堆次数少,堆体热量散失少,增加了水分的损失量。
从图7可看出,不同操作工艺对堆体上中下层含水率有明显差异。由图7(a)可看出,静置6 d翻抛的堆体前期未翻堆,温度散失少,而高于其他2种操作工艺。这是因为,堆体内部气体温、湿度高,堆体外部空气温、湿度低,高温和低温气体产生密度差形成向上的浮力,使得堆体中的水汽被输送到堆体的上部,从而形成独特堆体含水率的垂直空间分布。 10 d后,上层含水率高出中层6%,下层由于氧气含量少,且接触地面,温度较低,含水率下降速度慢。 堆肥30 d后,由于后期的翻抛操作各层含水率逐渐趋于一致。堆肥结束时,堆体下层含水率高于上、中层的。由图7(b)可看出,常规翻抛的堆体前期各层含水率无明显差异,随着堆肥时间延长,在堆肥15 d后各层含水率呈现下层>上层>中层的空间分布。由图7(c)可看出,翻堆曝气堆体各层含水层分层效果明显,表现为下层>中层>上层。这是因为,曝气会给上层提供充足氧气,堆体微生物分解剧烈,故上层含水率下降较快。
极差分析(表4)表明,各技术参数对堆体含水率减量的影响大小顺序为:玉米秸秆配比>玉米秸秆粒径>操作工艺。这与堆体温度变化规律一致。其原因是,堆体温度的高低决定堆体含水率的高低,温度高的堆体水分蒸发快,微生物分解剧烈,对水分消耗较大。
-
1)玉米秸秆配比对堆体升温速率影响最大。其中,15%配比升温速率快。秸秆粒径为5 cm的高温持续时间最长,粒径对堆体的有效积温影响最大,静置6 d翻抛的堆体温度前期升温速率更快。
2) 5%玉米秸秆配比处理的pH最高,15~20 cm玉米秸秆的pH在前期低于3和5 cm粒径的;堆体电导率随着秸秆配比的增加有增加的趋势,堆肥结束后15%秸秆配比电导率值最大。
3)堆体含水率降低程度随着玉米秸秆配比的增加而增大;不同操作工艺对堆肥过程中堆体各层含水率垂直分布有显著影响。玉米秸秆比例15%、秸秆粒径5 cm、先静置6 d翻抛是适合我国西北干旱地区污泥条垛式堆肥系统的技术参数。
Effects of auxiliary materials and pile-turning technique on the dynamical changes of some physical index of sludge composite in northwest arid region
- Received Date: 15/11/2021
- Available Online: 31/08/2022
-
Key words:
- northwest drought district /
- domestic sludge /
- aerobic composting /
- ratio of auxiliary materials /
- double cast process
Abstract: The objectives of this research were to clarify the influence of auxiliary materials and pile-turning technique on the dynamic change of physical index of sludge composting in northwest arid region, and to provide suitable technical parameters for organic fertilizer production with domestic sludge. The temperature, pH value, electrical conductivity, moisture content and its dynamic change in the upper, middle and lower layers of the windrow were studied by a large windrow composting system with an orthogonal experiment of 9 strips including 3 factors (ratio of auxiliary materials, particle size of auxiliary materials and turning-over process) and 3 levels. Results showed that the rate of temperature increase of compost was as fast as 17.3 ℃·d−1 and the highest temperature reached over 75 ℃ with 15% straw ratio. The duration of high temperature period got 22 days with the straw particle size of 5 cm. The electrical conductivity (EC) of the compost increased with the increase of the straw ratio, and the maximum value of EC at the end of experiment was achieved with 15% straw ratio. The moisture content at upper layer was higher with the treatment of conventional turning-over after standing for 6 d within composting 10 days and then gradually tended to be consistent among different layers after composting 30 days. However, the moisture content of each layer showed a vertical gradient of lower layer > upper layer > middle layer with conventional turning-over after composting 15 days. The maximum affecting factor on sludge composting temperature was corn straw particle size, while the maximum affecting factor on sludge composting moisture content was corn straw ratio during sludge composting. In a word, the optimal composting parameters for the sludge composting system in the northwest arid region are 15% corn stalks, 5 cm particle size of the stalks, and conventional turning-over after standing for 6 days. The results of this study can provide a reference for sludge window composting in the arid region of northwest China.











 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
