-
邻苯二甲酸酯(PAEs)作为增塑剂广泛用于制造和加工塑料产品。PAEs的生产始于20世纪20年代,其用量一直在增长[1-3]。PAEs在制造、使用和处置过程中可以直接或间接地释放到环境中。PAEs普遍存在于大气气溶胶[4-5]、污水和废水处理的污泥[6]、河流和海水/沉积物[7]、饮用水[8]、生物群和空气[9]中。据报道,人类对 PAEs的摄入量可高达70 μg·(kg·d)−1;PAEs对生态系统功能和公共健康存在潜在影响,因而PAEs已引起广泛的关注[10]。短链酯(如邻苯二甲酸二甲酯(DMP))是不同环境介质中最常见的PAEs,作为一种内分泌干扰化学物质,其可能导致人类白细胞的染色体损伤,干扰动物和人类的生殖系统和正常生长发育[11]。因此,研发一种可用于从水域和废水中去除这种污染物的处理技术十分必要。
去除DMP的方法包括催化臭氧法[12],γ-辐射/ H2O2工艺[13],紫外光催化法[14],生物降解处理法[15]等。在众多处理方法中,光催化技术已被证明能够有效处理各种水体污染物。高铁酸钾作为一种高效的电子受体可有效抑制e−/h+重组,其还原产物为Fe3+或Fe(OH)3, 具有絮凝、吸附、共沉淀等功能,是一种绿色氧化剂,但目前关于高铁酸盐和光催化组合降解有机水污染物的研究相对较少。
本研究利用高铁酸钾与TiO2光催化的协同氧化效应降解水中DMP,建立了DMP降解方法,并探究了不同参数对DMP降解效果的影响以及反应过程中在催化剂表面产生Fe—O—(有机)络合物对降解效果的影响。
HTML
-
邻苯二甲酸二甲酯(DMP)、二氧化钛(TiO2)、高铁酸钾(K2FeO4)、磷酸氢二钠(Na2HPO4)、四硼酸钠(Na2B4O7·10H2O)、亚硫酸钠(Na2SO3)均为分析纯;甲醇(CH3OH)为色谱纯。
紫外-可见分光光度计(TU-1810,北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司);紫外灯(8 W,荷兰皇家飞利浦公司);pH计(UB-10,美国Denver Instrument公司);高效液相色谱仪(UltiMate3000,美国Dionex公司);X射线衍射仪(Ultima IV,日本Rigaku公司);磁力搅拌器(78-1,常州国华电器有限公司)。
-
实验采用自制光催化反应器,它是由石英装置、高压汞灯、磁力搅拌器组成的开放式反应器,实验装置见图1。紫外灯(8 W,365 nm)作为光源,石英反应器放置于磁力搅拌器上距光源8 cm处,反应开始时,开启磁力搅拌器,溶液在搅拌器搅拌下混合均匀。在室温下进行实验,整套实验装置外加紫外线防护装置。
-
用0.005 mol·L−1 Na2HPO4和0.001 mol·L−1 Na2B4O7·10H2O调节DMP溶液pH为9,目的在于维持高铁酸盐的水溶液稳定性和消除铁酸盐分析中Fe3+的干扰。在光催化实验中,向DMP水溶液中加入一定量的TiO2催化剂;光反应之前,先进行30 min暗反应,以达到吸附/解吸平衡。在反应期间,以不同的时间间隔取样,加入亚硫酸钠[16]终止反应,然后通过0.22 μm 有机滤膜,除去固体颗粒,所有实验均在室温下进行。
-
采用高效液相色谱仪(HPLC)测量DMP浓度。色谱条件:尖峰II C18柱(5 μm粒度,250 mm×4.6 mm),柱温为30 ℃,使用甲醇/水(70∶30)的流动相,流速为1 mL·min−1,进样量为10 μL,UV检测器波长230 nm。采用紫外-可见分光光度法在505 nm波长下测量高铁酸盐浓度;采用X射线衍射(XRD)仪分析TiO2催化剂反应前后的晶体结构。
1.1. 试剂与仪器
1.2. 实验装置
1.3. 实验方法
1.4. 分析方法
-
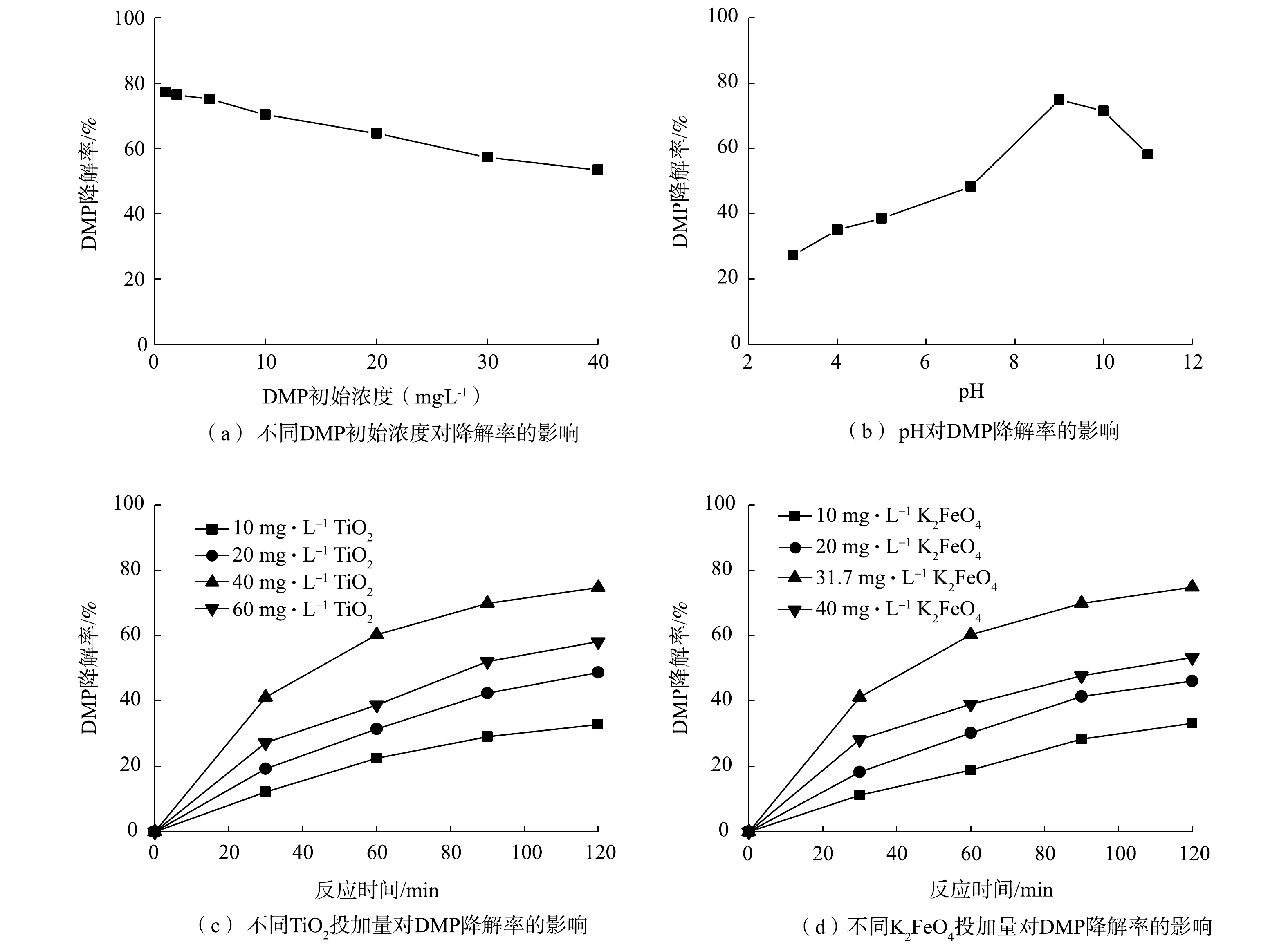
不同因素对DMP降解率的影响见图2。
-
DMP初始浓度对光降解率的影响如图2(a)所示。可以看出,随着DMP初始浓度的增加,DMP的光降解率逐渐降低。水溶液中TiO2的量是恒定的,故催化剂的活性位点数也是恒定的,较高的DMP初始浓度导致分子竞争催化剂的活性位点,使降解速率降低。DMP的初始浓度越高,导致越多的DMP分子被吸附在催化剂的表面上,从而抑制TiO2表面产生光生空穴和光生电子。因此,DMP的最佳初始浓度确定为5 mg·L−1,并在此条件下进行后续的研究。
-
Fe(Ⅵ)在整个pH范围内都是强氧化剂,从式(1)和式(2)中看出,Fe(Ⅵ)在酸性和碱性溶液中的还原电位分别为2.2 V和0.7 V。从图2(b)中可以看出,随着pH的增加,DMP降解率也随之增加,但当pH为9时,降解率随pH的增加开始降低。其原因可能是:在酸性条件下,K2FeO4分解生成的OH−与水溶液中H+发生中和反应,使OH−浓度降低[17];另外,H+使得 K2FeO4在水溶液中不稳定,高铁酸钾的分解速度非常快,还未来得及与DMP反应,自身就已经分解,导致DMP降解率降低。反之,在碱性条件下,反应体系中OH−浓度增加,高铁酸钾自分解速度较缓慢,稳定性增强,DMP降解率较高。综合考虑,在酸性条件下,高铁酸盐稳定性很差,随着pH的升高,高铁酸盐稳定性逐渐加强(碱性>中性>酸性),K2FeO4在pH为9~10的水溶液中稳定性最好[18],故本研究的最佳pH确定为9。
-
从图2(c)中看出,TiO2投加量较少时,溶液中催化剂的活性位点较少,导致DMP降解率不高;TiO2投加量逐渐增加,催化剂的活性位点也增加,降解率也随之提高。TiO2投加量为40 mg·L−1时,DMP降解率最高可达到75%;当TiO2投加量超过40 mg·L−1后,进入溶液中可被吸收的光子全部被催化剂吸收,导致催化剂表面产生的活性基团数目保持恒定;继续加大TiO2,投加量不但会造成光散射,而且溶液浑浊度增加,阻碍了紫外光的有效照射,光的吸收效率和反应活性都会下降[19]。
-
高铁酸钾投加量对DMP降解效果的影响也较大。由图2(d)中可以看出, 随着高铁酸钾投加量的增加, DMP的降解率先升高后降低。当高铁酸钾投加量达到31.7 mg·L−1时,DMP的降解率最高可达75%。由于高铁酸钾自身会有一定分解, 并且随着高铁酸钾投加量的增大, 高铁酸钾自分解随之加快,可能影响降解效果。若投加过量的铁,会直接影响光照强度,从而降低光催化效率[20]。因此,确定最佳高铁酸钾投加量为31.7 mg·L−1。
-
在光催化体系中,存在某些金属离子或氧化剂可以作为电子受体来防止e−和h+电子的快速复合,从而增强目标化合物的光催化降解。从图3中可以看出,高铁酸盐对DMP没有显著的降解效果,DMP降解率只有5%左右,表明高铁酸盐对有机基质的氧化有特定的选择性。在紫外光照和高铁酸盐存在的情况下,DMP的降解效果也较差,表明在没有TiO2的情况下,高铁酸盐和单纯的紫外光照没有明显的协同作用。TiO2光催化氧化降解DMP的效果也不理想,120 min后,DMP只降低15%。然而,与之形成鲜明对比的是,用Fe(VI)-TiO2-UV体系降解DMP的效果是显著的,120 min时,DMP降解率约75%,这表明光催化与高铁酸盐的组合可对DMP的降解产生明显的协同效应。由于高铁酸盐比其他电子受体(如高锰酸盐或过氧化物)具有更高的氧化能力,并且可能还原为高度活性的Fe(Ⅴ),因此,高铁酸盐可以通过电子清除从而起到增强光氧化和有机氧化的作用。
-
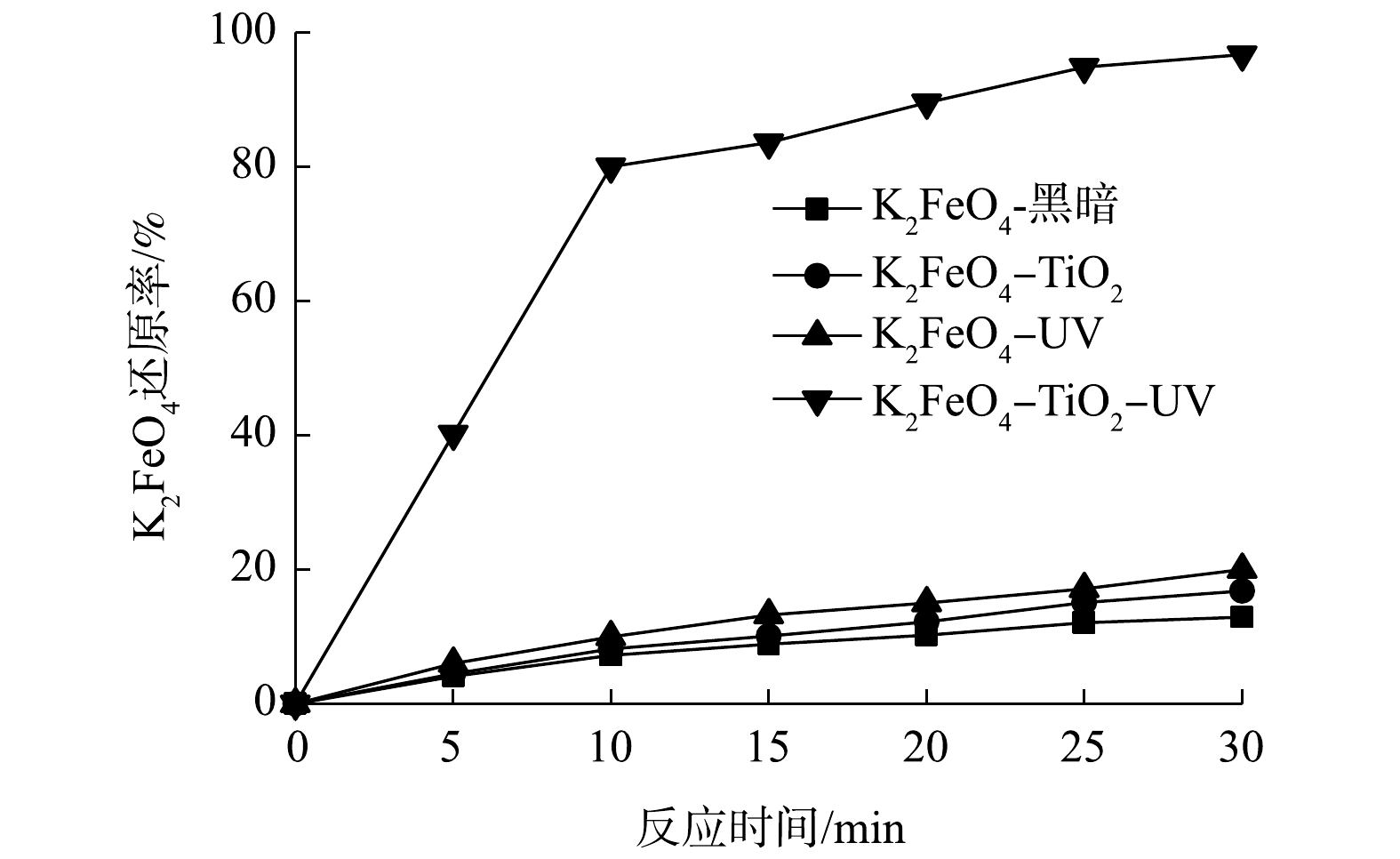
由图4中可以看出,Fe(Ⅵ)在黑暗中减少地非常缓慢,在单独的UV照射下或者在具有TiO2悬浮液但没有UV照射的情况下仅略快。然而,相比之下,在紫外光照下,二氧化钛悬浮液存在的情况下发生了快速的Fe(Ⅵ)还原。很显然,Fe(Ⅵ)的快速还原是由于它从TiO2催化剂上清除了激发的导带电子。Fe(Ⅵ)还原对催化剂的电子清除大大减少了导带电子(e−)和价带空穴(h+)的复合,从而提高了TiO2光催化反应过程中的量子效率。
-
1)TiO2催化剂的失活。使用不同的TiO2催化剂光降解DMP的效果见图5。对采用Fe(Ⅵ)-TiO2-UV工艺降解DMP后的TiO2进行回收利用。由图5可知,回收后的TiO2经水洗后,降解DMP的效果很差;但经1% HCl洗涤后的TiO2在120 min后可降解70%的DMP,类似于新二氧化钛的降解效果。上述结果表明,在对DMP的降解反应过程中,催化剂表面上会形成Fe—O—(有机)络合物,其能够抑制DMP的降解,故可用1% HCl溶液洗涤失活的TiO2催化剂将其再活化。本研究对反复使用后的催化剂的催化降解性能进行了分析。在Fe(Ⅵ)浓度为 31.7 mg·L−1、TiO2为 40 mg·L−1、pH 为 9、反应时间为 120 min的条件下,对5 mg·L−1 的 DMP 进行催化氧化。反应后过滤回收催化剂用1% HCl清洗烘干,在相同反应条件下,对 DMP 进行降解,如此反复使用4次。实验结果表明,第 1 次使用催化剂时,DMP降解率达到了70%;第 2、3、4次重复使用,其降解率依次降低,分别为63.22%、58. 92%、53.33%。这说明催化剂的降解稳定性较好。
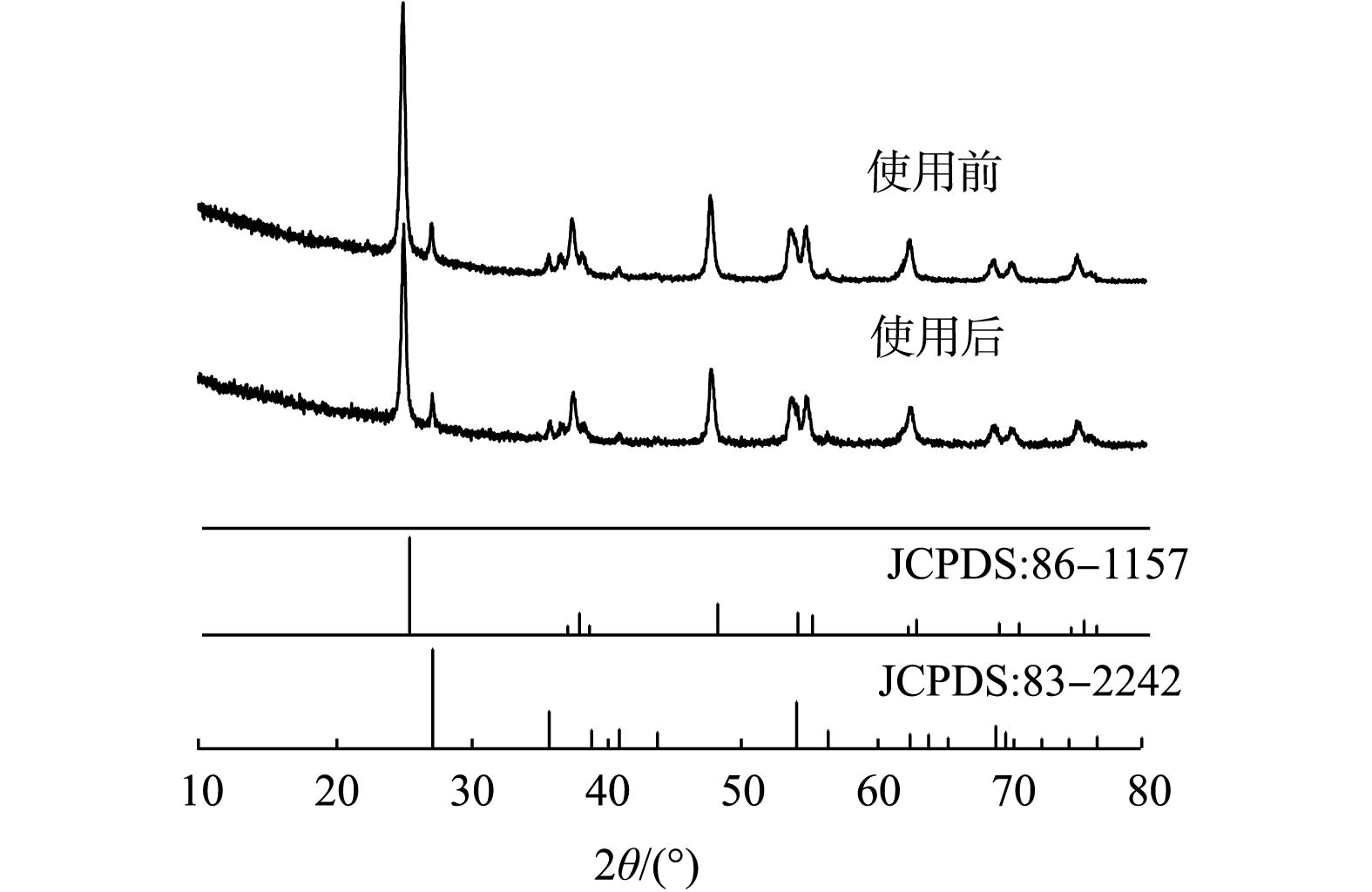
2)未使用和使用过的二氧化钛催化剂的比较。图6是使用前、后TiO2的XRD图谱。由图6可知,XRD特征峰发生在2θ=25.32°、37.86°、48.06°、53.97°、55.08°、62.75°、68.87°、70.33°、75.14°和82.75°,分别对应于锐钛矿TiO2的(101)、(004)、(200)、(105)、(211)、(204)、(116)、(220)、(215)和(224)晶面(JCPDS,No.86-1157);在27.46°,36.08°,41.24°,56.67°这4个特征峰处,分别对应于金红石TiO2的(110)、(101)、(111)和(220)晶面(JCPDS,No.83-2242)[21]。上述结果表明, TiO2催化剂由锐钛矿和金红石的混合相组成。使用前、后TiO2的衍射峰证实了在反应后TiO2催化剂的晶体结构没有发生显著变化。
-
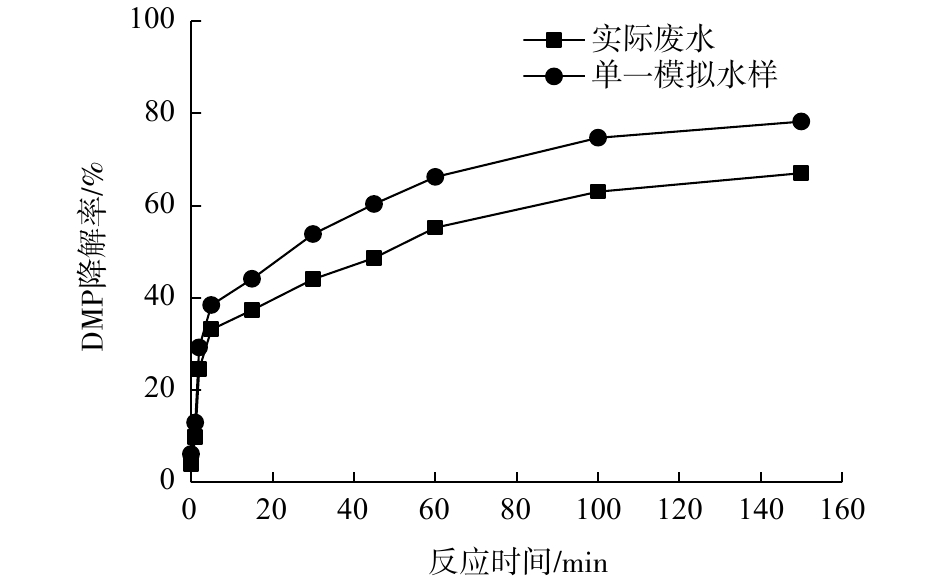
Fe(Ⅵ)-TiO2-UV工艺降解实际含DMP废水与浓度为0.32 mg·L−1的DMP模拟水样的结果见图7。模拟水样DMP配置浓度0.32 mg·L−1是基于实际生产废水中DMP的检出浓度,实验中调节水样pH=7,TiO2投加量为40 mg·L−1,K2FeO4投加量为31.7 mg·L−1。结果表明,DMP实际废水和模拟水样在Fe(Ⅵ)-TiO2-UV体系中的降解率分别为67%和78.2%,说明Fe(Ⅵ)-TiO2-UV工艺对实际废水中的DMP降解效果良好,具有实用意义。
-
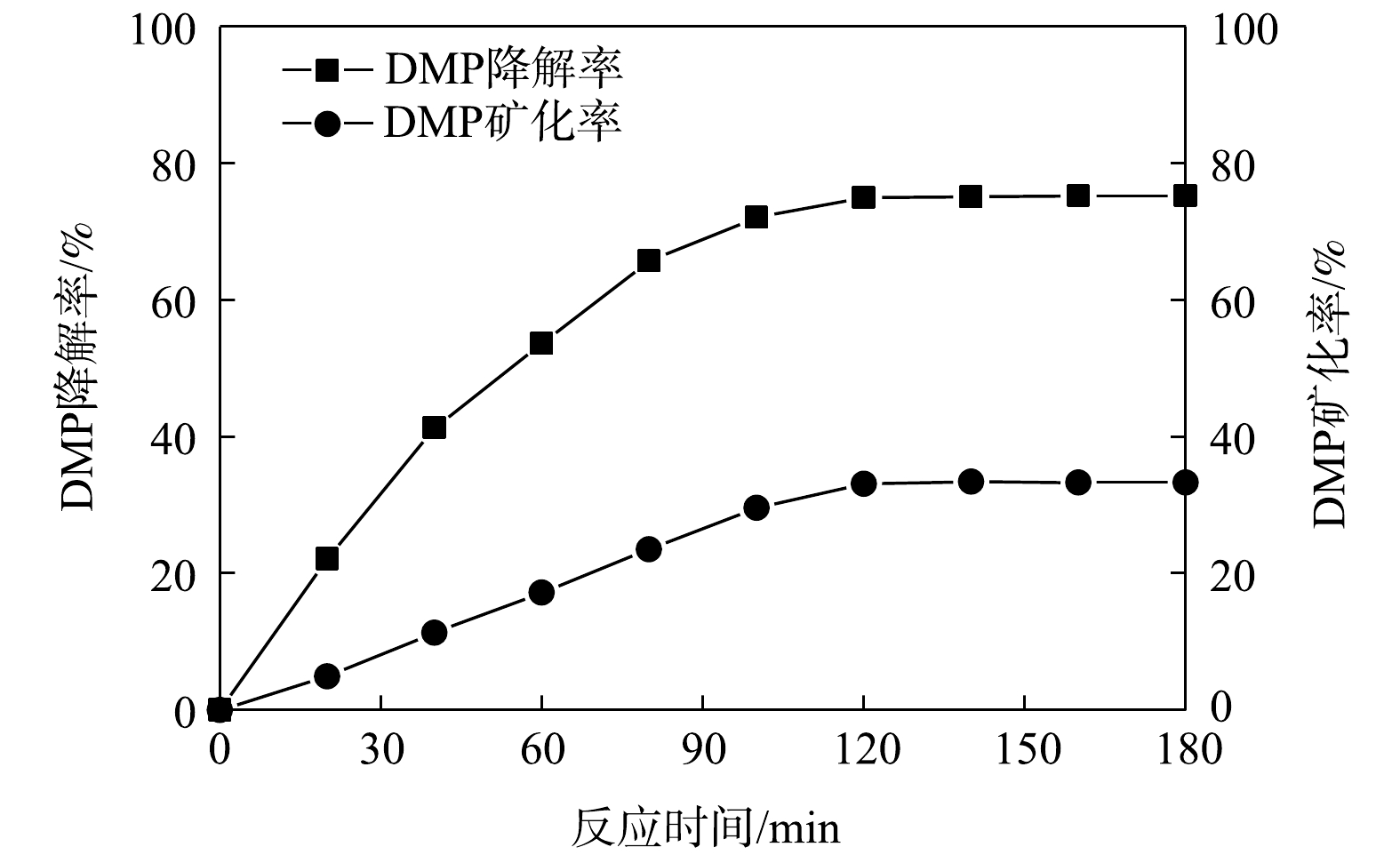
由图8可以看出,当反应时间在120 min内,DMP 降解率和矿化率均随反应时间的增加而增大。已知在 120 min 时, DMP 的降解率可达75%,DMP的矿化率仅达到 33. 1% 左右。继续延长反应时间,DMP 降解率和矿化率都趋于平缓。这表明反应体系中紫外光激发 TiO2催化剂所产生的·OH 在反应过程中的协同作用显著,大部分的 DMP 已被转换为较难矿化的有机中间产物。
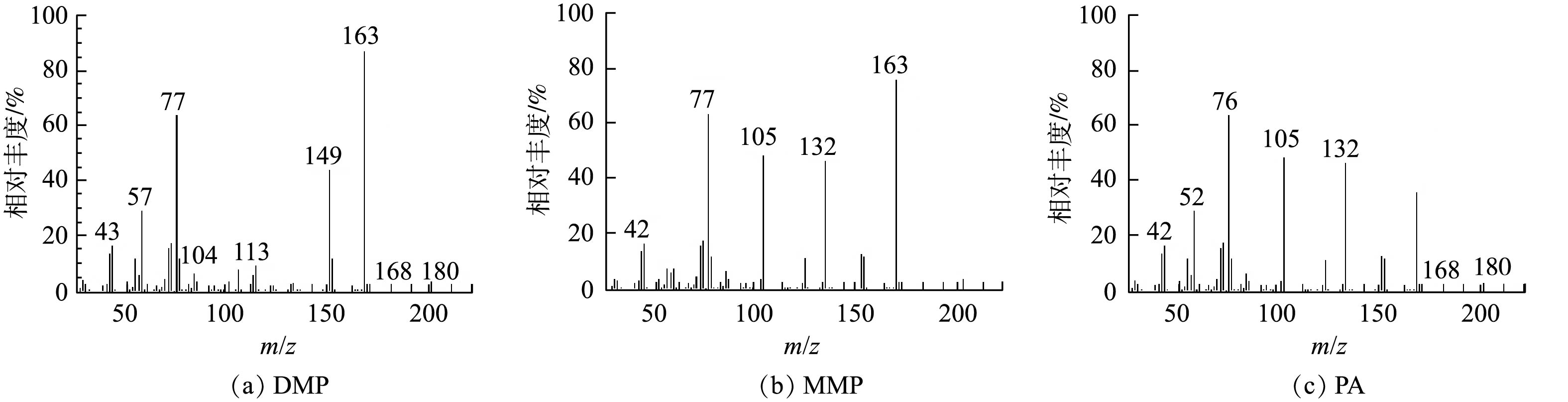
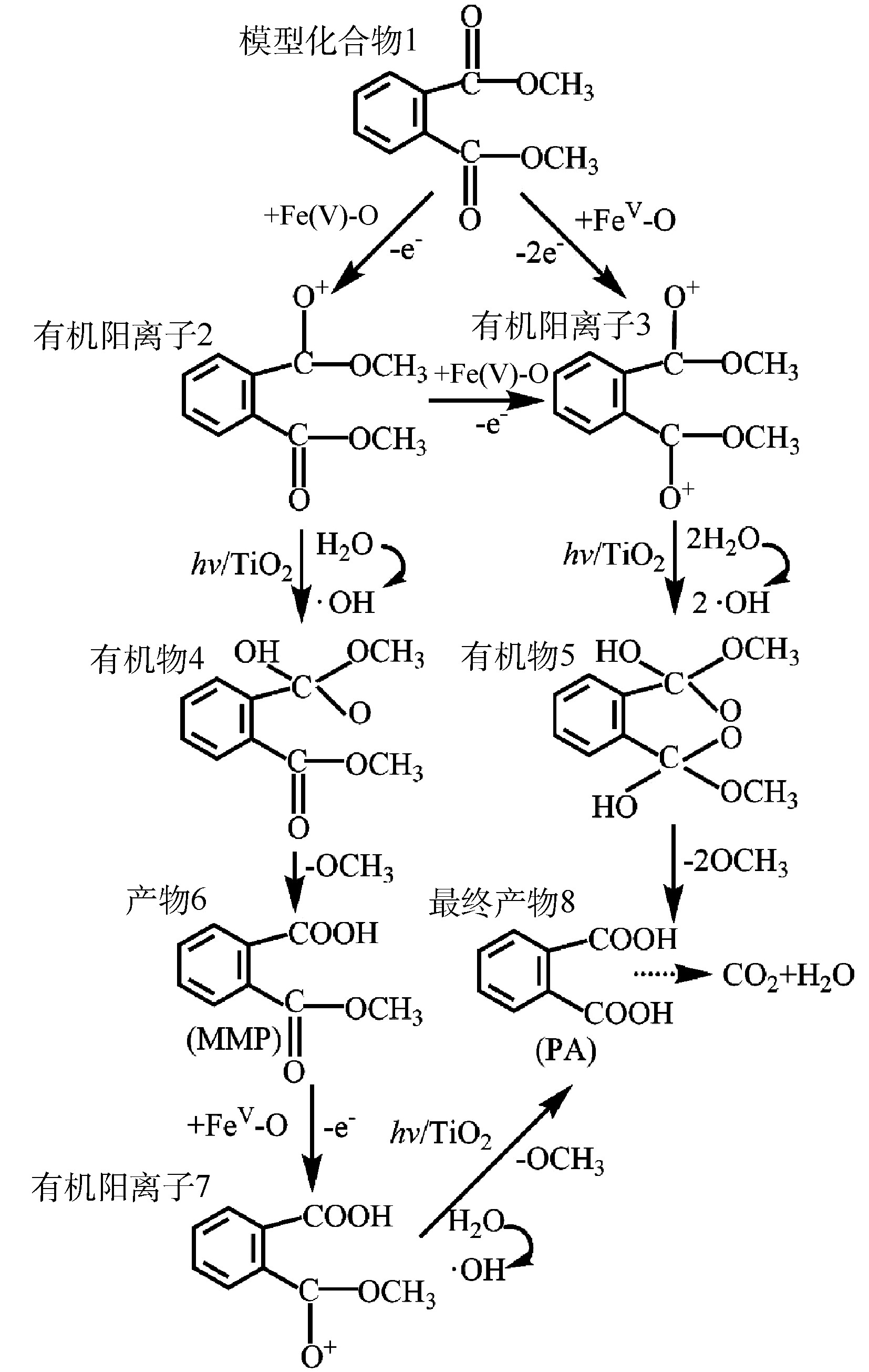
TiO2光催化生成的·OH如何氧化DMP是一个复杂问题,至今未有定论[22]。有研究[23]认为,·OH是从侧链进攻,最终把 DMP 氧化为邻苯二甲酸等。如图9所示,本研究使用GC-MS方法检测了DMP光催化降解中间产物DMP、邻苯二甲酸单甲酯(MMP)和邻苯二甲酸(PA),并在此基础上,推测了Fe(VI)-TiO2-UV体系中可能存在的DMP光催化降解途径(图10)。由图9可知,DMP降解的主要中间产物为PA,其由DMP的电子转移反应和与·OH的反应产生。一旦Fe(Ⅴ)反应失去1个电子或2个电子时,模型化合物1可以分别形成有机阳离子2和3,有机阳离子2可被·OH氧化生成有机物4,有机阳离子3可被·OH氧化生成有机物5,然后再进一步发生反应。有机物4失去一个甲氧基后将生成产物6(MMP),其在Fe(Ⅴ)氧化之后,进一步失去电子生成有机阳离子7,有机阳离子7加入一个羟基,然后失去一个甲氧基,生成最终产物8(PA);或者,有机物5在失去2个甲氧基后,直接生成最终产物8(PA)。最后,在紫外光和·OH的作用下,DMP 及其苯环中间产物发生开环反应,生成小分子有机酸,最后进一步矿化为 CO2和H2O。
2.1. DMP初始浓度对DMP降解率的影响
2.2. 溶液pH对DMP降解率的影响
2.3. TiO2催化剂量对DMP降解率的影响
2.4. 高铁酸钾浓度对DMP降解率的影响
2.5. 不同体系对DMP降解率的影响
2.6. 二氧化钛-高铁酸盐反应体系中的高铁酸盐还原
2.7. TiO2催化剂的失活与再生
2.8. Fe(Ⅵ)-TiO2-UV光催化氧化降解实际生产废水中的DMP
2.9. 矿化度的分析和降解机制的讨论
-
1) Fe(Ⅵ)-TiO2-UV工艺对DMP的降解效果优于单独的高铁酸钾和单独的二氧化钛光催化,说明高铁酸钾与TiO2光催化之间存在协同效应。最佳降解条件是DMP初始浓度为5 mg·L−1、pH=9、高铁酸钾和TiO2投加量分别为31.7 mg·L−1和40 mg·L−1,DMP降解效果达到最优。
2) DMP降解过程产生Fe—O—(有机)络合物,造成光催化活性降低,导致DMP降解受到抑制,失活的TiO2催化剂可以用1% HCl溶液再活化。
3)采用Fe(Ⅵ)-TiO2-UV工艺降解实际废水和模拟水样,DMP降解率分别为67%和78.2%,表明K2FeO4协同TiO2光催化降解实际废水中的DMP效果良好,具有实用意义。
4)利用 GC/MS 检测分析,推测Fe(Ⅵ)-TiO2-UV体系光催化降解DMP中生成的自由基首先攻击DMP的侧链,生成中间产物MMP和最终产物PA,然后PA继续分解为小分子有机酸,最后矿化为 CO2和H2O。








 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
