-
炼油行业是我国的支柱产业,据统计,我国每加工1 t原油会产生0.7~3.5 t污水[1]。炼油污水中有机污染物种类多,浓度高,且多为难降解有机物。污水中的溶解性有机物(dissolved organic matters, DOM)的组成及其在水处理过程中的迁移转化一直是水处理研究过程中的重点和难点。DOM成分复杂,其会对体系中金属、胶体等物质在体系中的形成和变化产生影响[2],排入天然水体的DOM会对自然生态产生影响[3]。因此,了解炼化污水中DOM的组成和性质对污水处理和水资源保护有重要的作用[4-5]。
大孔树脂吸附和固相萃取是2种最常用的DOM化学分级分离方法[6]。大孔树脂吸附法一般使用XAD树脂根据DOM的极性和酸碱性将DOM分成不同组分[7-8],但XAD树脂自身有机碳杂质溶出较高,使用前需要进行清洗预处理,操作繁琐耗时长。固相萃取法采用商品化的固相萃取柱对DOM进行分离富集,是近年来快速发展的DOM分离富集方法。与XAD树脂吸附法相比,固相萃取法采用高纯度商品化萃取填料,萃取柱背景溶出低,操作简单,耗时短,同时可供选择的萃取填料种类多,可将DOM分级分离成不同性质的组分。WANG等[9]比较了不同固相萃取填料对城市生活污水处理厂二沉出水中DOM分离的效果,发现不同固相萃取填料对DOM组分选择性不同。单独使用1种SPE材料能分离富集特定性质的DOM组分,但不适于对DOM中不同性质的组分进行全面表征。FANG等[10]将利用Waters Oasis MCX和MAX固相萃取柱串联,将炼油厂污水中DOM分为疏水酸性组分(HOA)、疏水碱性组分(HOB)、疏水中性组分(HON)和亲水物质(HIS)4个组分,该方法所需样品量少,操作简单快捷,可以对DOM中不同性质组分进行全面表征,适合于对DOM组成分离分析。三维荧光光谱(EEM)和傅里叶离子回旋共振质谱(FTICR MS)是DOM组成分析常用的2种高分辨分析方法,三维荧光光谱(EEM)可将水中有机物的进行光谱和组成性质的整体分析,并根据水样特征峰区域将DOM分为不同组分,已经广泛用于水中DOM的组成分析[11];傅里叶离子回旋共振质谱(FT-ICR MS)具有超高质量分辨率和超高质量精确度,可明确DOM的分子式,是分析DOM分子组成的重要手段[12-13],常用于炼油污水中DOM分子组成和转化的表征[14-15]。
本研究利用MCX和MAX固相萃取柱串联的分离提取方法将炼油污水处理厂二沉出水中的DOM分为疏水酸性组分 (hydrophobic acid, HOA) 、疏水碱性组分(hydrophobic base, HOB)、疏水中性组分(hydrophobic neutral, HON)和亲水物质(hydrophilic substance, HIS)4种亚组分,并应用EEM和FT-ICR MS对其进行了组成分析,为炼油污水处理工艺优化和外排水环境影响评估提供科学支撑。
-
水样取自济南某炼油污水处理厂二沉池出水,水样经过0.45 μm混合醋酸纤维素滤膜过滤,过滤后的水样保存于4 ℃冰箱保存。
-
MCX柱和MAX柱使用前分别用10 mL乙腈和10 mL超纯水依次活化。经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后的水样,用1 mol·L−1的NaOH调pH至12,水样过MCX柱并收集流出液备用。用10 mL含 2%甲酸的超纯水淋洗MCX柱,然后用氮气吹干柱子中水分,再用10 mL乙腈洗脱MCX柱,得到HON-1组分;继续用10 mL含5%氨水的乙腈洗脱MCX柱,得到HOB组分;将水样过MCX柱的流出液用用1 mol·L−1的HCl调pH至2,过MAX柱萃取,收集流过MAX柱的水样即为HIS组分,上样后使用10 mL 5%氨水淋洗,用氮气吹干MAX柱子中水分,用10 mL乙腈洗脱MAX柱,得到HON-2组分,继续用10 mL含2%甲酸的乙腈洗脱MAX柱,得到HOA组分。
-
三维荧光光谱由日立F-7000荧光光谱仪测定。测试条件为:PMT电压700 V;扫描速度30 000 nm·min−1;扫描范围:激发波长Ex为200~550 nm,发射波长Em为200~600 nm;扫描间隔为5 nm;狭缝宽带为5 nm;响应时间为0.002 s。测试时以超纯水为空白,样品经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后上机测试。
-
采用Apex-Ultra 9.4T FT-ICR MS(Bruker,德国)对DOM分子组成进行分析,电离源为Apollo ESI负离子,实验样品用乙腈配制成100 mg·L−1的溶液,进样速度为250 μL·h−1。
电离源条件为:毛细管发射电压3 000 V,引入电压3 500 V;毛细管出口电压-320 V。离子在源六级杆中的存储时间为1 ms,碰撞累计时间0.02 s,飞行时间为1 ms。质量采集范围为100~700 Da,平均扫描64次,采样点数4 M,仪器校准和数据处理参考以往研究[16]。
-
使用日本岛津TOC-L对TOC进行测定,以高纯氧做载气,采用680 ℃催化氧化法将有机物氧化成二氧化碳,再由非色散红外检测器对产生的二氧化碳进行定量。
-
水样经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后使用紫外可见分光光度计(岛津UVmini-1280)在254 nm波长下测试,测试时以超纯水为空白,于10 mm石英比色皿中进行测定。
-
遗传毒性测试采用SOS/umu改进方法[17],受试菌株为鼠伤寒沙门氏菌Salmonella typhimurium TA 1535/pSK1002。
-
对炼油污水处理厂二沉出水进行常规水质指标和溶解性有机物特征指标以及遗传毒性指标分析,各水质指标结果为:pH为7.46,SS为28 mg·L−1,COD为91.80 mg·L−1,TOC为28.21 mg·L−1,TN为48.49 mg·L−1,UV254为0.438 6 AU·cm−1,SUVA254为1.520 8 L ·(mg·m)−1,TEQ4-NQO为146.95 μg·L−1。
由水质指标测试分析结果可知,二沉池出水中仍存在较多的溶解性有机物,COD和TOC指标较高,UV254和SUVA254指标分别为0.438 6 AU·cm−1和1.520 8 L ·(mg·m)−1,说明水中可能存在较多的含芳香环的难降解有机物。遗传毒性指标4-NQO当量浓度达到146.95 μg·L−1,出水中的溶解性有机物具有较高的遗传毒性。
-
4种组分在DOM中的TOC分布见表1。炼油污水二沉出水的TOC为28.21 mg·L−1,DOM由67.4%的疏水组分组成(基于TOC值),其中HOA、HOB和HON分别占17.8%、16.95%和32.65%,亲水分HIS为17.23%,剩余未测出的DOM可能残余吸附在萃取柱中。该结果与FANG等[10]应用此分离方法得到的的焦化废水二沉出水4组分分布的研究相似。
-
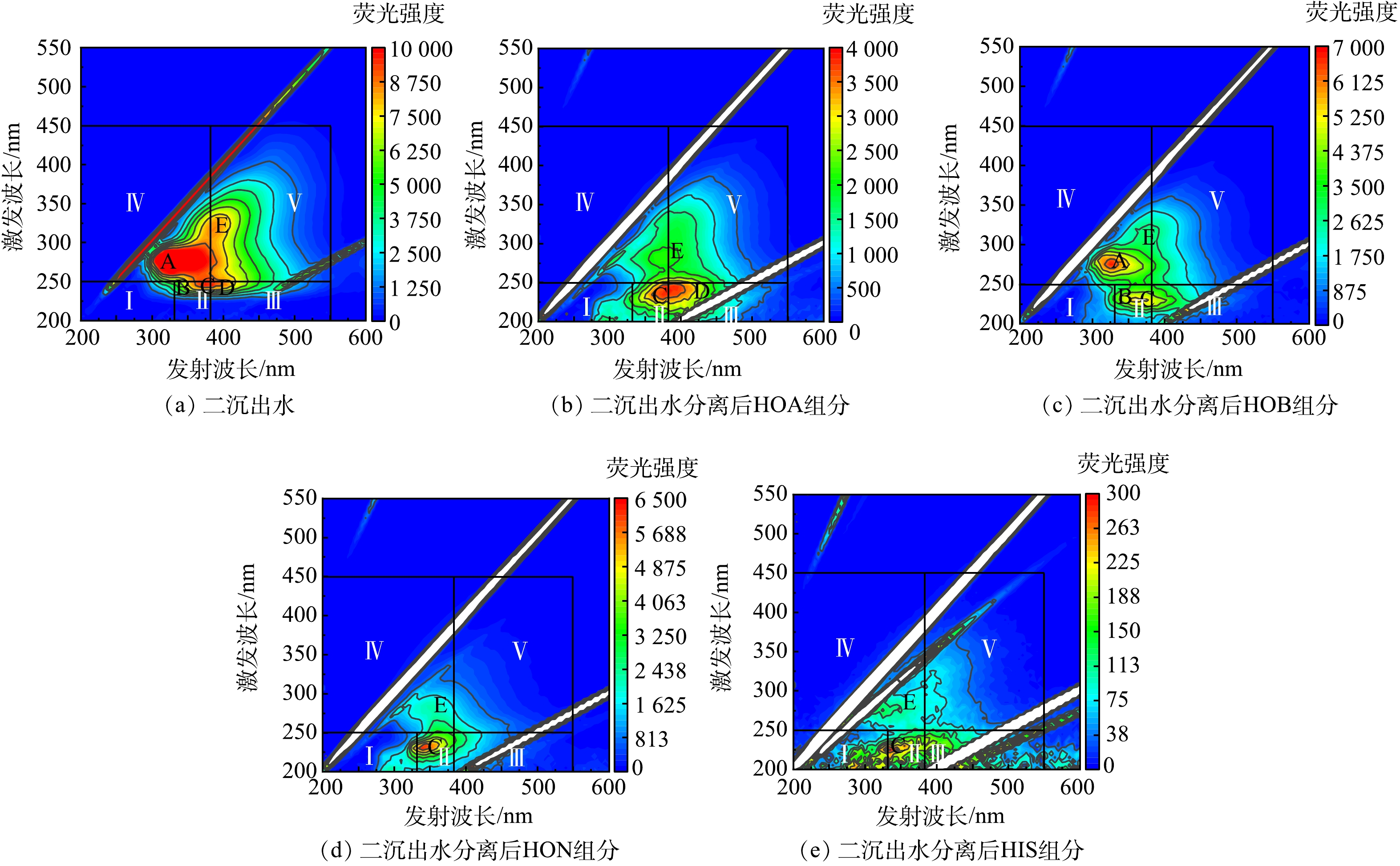
炼油污水处理厂二沉池出水及其四组分的三维荧光光谱结果见图1。以往的研究一般将三维荧光谱图划分为五个特征荧光峰区域,其中Ⅰ区(Ex/Em=200~250 nm/280~330 nm)为酪氨酸类似物,发光物质与低激发类酪氨酸有关;Ⅱ区(Ex/Em=200~250 nm/330~380 nm)为色氨酸类似物区,发光物质与低激发类色氨酸有关;Ⅲ区(Ex/Em=200~250 nm/380~550nm)的发光物质与富里酸、类富里酸、类胡敏酸、疏水性酸有关,简称富里酸类物质;Ⅳ区(Ex/Em=200~450 nm/200~380nm)为可溶性微生物副产物区,发光物质与类蛋白物质、和微生物代谢产物相关的酪氨酸、高激发类酪氨酸、高激发类色氨酸、含苯环蛋白类物质有关;Ⅴ区(Ex/Em=250~450 nm/380~550nm)的发光物质与胡敏酸、类胡敏酸、海洋类富里酸和疏水性酸有关[18-20]。由二沉出水的三维荧光分区积分结果可知,二沉出水中Ⅰ区荧光区域积分体积占1.21%,Ⅱ区占4.31%,Ⅲ区占4.22%,Ⅳ区占31.81%,Ⅴ区占55.45%, V区腐殖酸类物质和IV区微生物代谢物在二沉出水DOM中所占比例超过50%。由各组分的三位荧光光谱图1可知,HOA组分主要是Ⅴ区的腐殖酸类物质,占比达到49.69%,另外Ⅲ区和Ⅳ区占比也较高,占比分别为22%和17.02%。HOB组分主要是Ⅳ和Ⅴ区的微生物代谢蛋白物质和腐殖酸类物质,占比分别为32.84%和37.26%,Ⅰ区占3.07%,Ⅱ区占10.08%,Ⅲ区占16.75%。HON组分主要是Ⅴ区的腐殖酸类物质,区域积分体积占比达到35.02%,Ⅱ区占16.96%,Ⅲ区占20.49%,Ⅳ区占22.66%,与二沉出水中各组分占比最为相似。HIS组分主要是V区腐殖酸类物质和Ⅲ区富里酸类物质,占比分别为46.78%和35.71%,而二沉出水中Ⅲ区富里酸类物质仅占4.22%。
采用吸光度比特征峰法分析方法对二沉出水中DOM的三维荧光光谱进行分析,光谱图显示水样共有5个物质特征峰,其中A(Ex/Em=270 nm/300 nm)、B(Ex/Em=220 nm/300 nm)附近是酚类物质的特征峰;C(Ex/Em=230 nm/345 nm)、D(Ex/Em=250 nm/425 nm)、E(Ex/Em=280 nm/345 nm)附近为石油类的特征峰[21-22],其中E峰为一环和二环芳烃化合物的特征峰,C为三环芳烃化合物的特征峰,D为三环和四环芳烃化合物的特征峰。二沉出水中主要含有酚类物质、多环芳烃化合物;HOA组分中主要是石油类物质,其中三环和四环芳烃化合物占主导;HOB组分中含有酚类物质,此外还含有一、二、三环芳烃化合物;HON组分与HIS组分主要是三环芳烃化合物,HIS谱图较为杂乱,可能含有较多其它类型化合物。
-
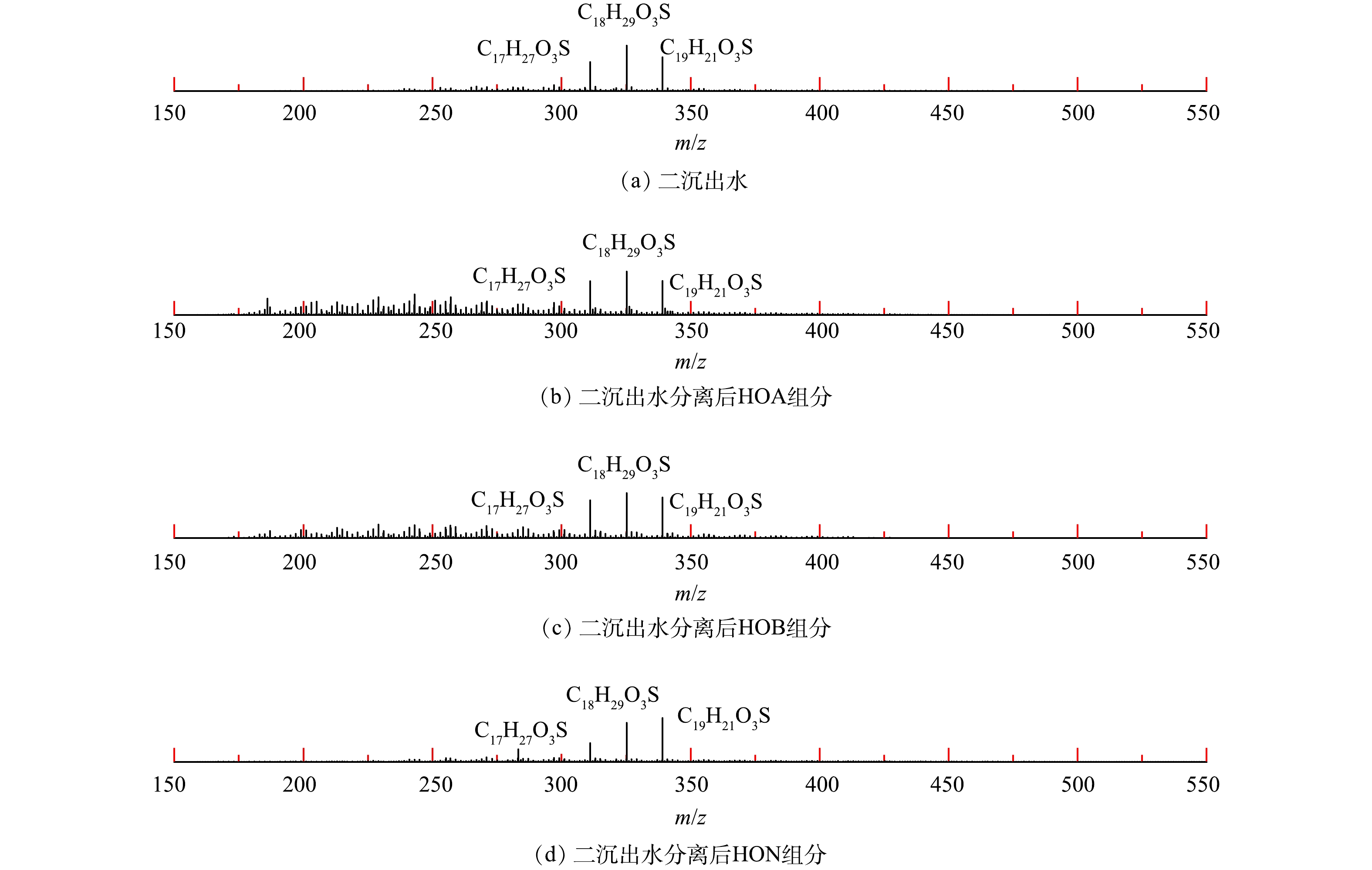
HIS组分中有大量的无机盐,不适合用负离子ESI FT ICR MS检测,对炼油污水处理厂二沉出水和HOA、HOB、HON组分进行了负离子ESI FT ICR MS检测分析。图2为DOM样品在负离子ESI FT ICR MS下的原始谱图。可见,二沉出水、HOA和HON组分的响应较好,HOB 组分响应较差。通过数据分析可知,二沉出水、HOA、HOB、HON分别检测到6 585、2 900、533、1 924个DOM分子,HOA组分中含有的分子个数和化合物类型最多,这是因为负离子ESI模式下会选择性地电离酸性化合物和非碱性氮化物,而HOB组分主要是疏水碱性物质,难以被电离。二沉出水、HOA、HON的分子质量主要分布在200~600 Da。HOB组分有2个质量中心,分别在320 Da和470 Da左右。质谱图中m/z 297、311、325处有较高的质谱峰,为DBE为4的O3S1类化合物,可能是污水中烷基苯磺酸表面活性剂[23-24]。
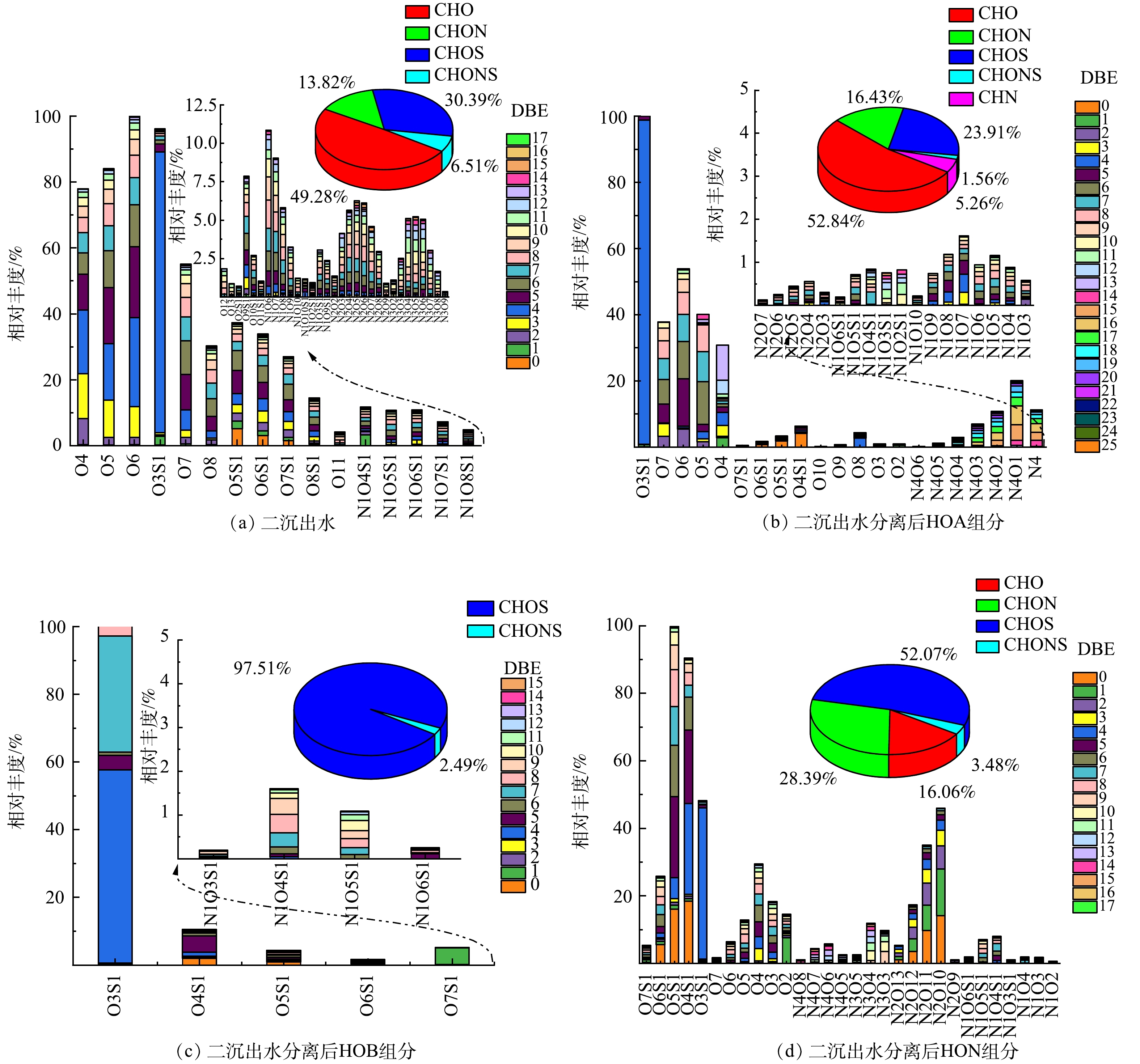
在二沉出水、HOA、HOB和HON中分别鉴别出56、39、9、30种杂原子类型,主要包括CHO、CHON、CHOS和CHONS 4类化合物,杂原子化合物及其相对丰度见图3。二沉出水中的DOM类型主要包括CHO、CHON、CHOS和CHONS类物质,其中CHO类化合物的相对丰度最高,为49.28%,主要集中在O4~O8。其次是CHOS类化合物,主要集中在O3S1~O8S1。CHON类物质以N1O3~N1O8为主,CHONS类物质以N1O4S~N1O8S为主;双键当量DBE(double bond equivalents) = (2C+2 - H+N) / 2代表化合物分子中含有的双键和环数之和,DBE越高,不饱和度越高,二沉出水中主要的CHO类化合物DBE 大多小于6,代表含CHO3S类化合物DBE主要为4,二沉出水中主要化合物的不饱和程度较低。HOA组分与二沉出水组成相似,以CHO类物质为主,相对丰度达到52.84%,主要集中在O4~O7,这是由于负离子ESI电离源选择性电离酸性物质决定的;其次为CHOS类物质,以O3S1为主,CHON类物质以N4、N4O1~N4O4为主。负离子ESI模式下HOB组分响应较差,检测出来的物质较少,但HOB组分仍以CHOS类物质为主,主要是O3S1。HON中以CHOS类物质为主,主要集中在O3S1~O6S1,其次是CHON类物质,以N2O10~N2O13、N3O3~N3O4为主,CHO类物质以O2~O6为主,CHONS类物质以N1O4S1~N1O5S1为主。因此,二沉出水中存在的N1O3~N1O8类CHON物质主要存在于HIS亲水组分中。
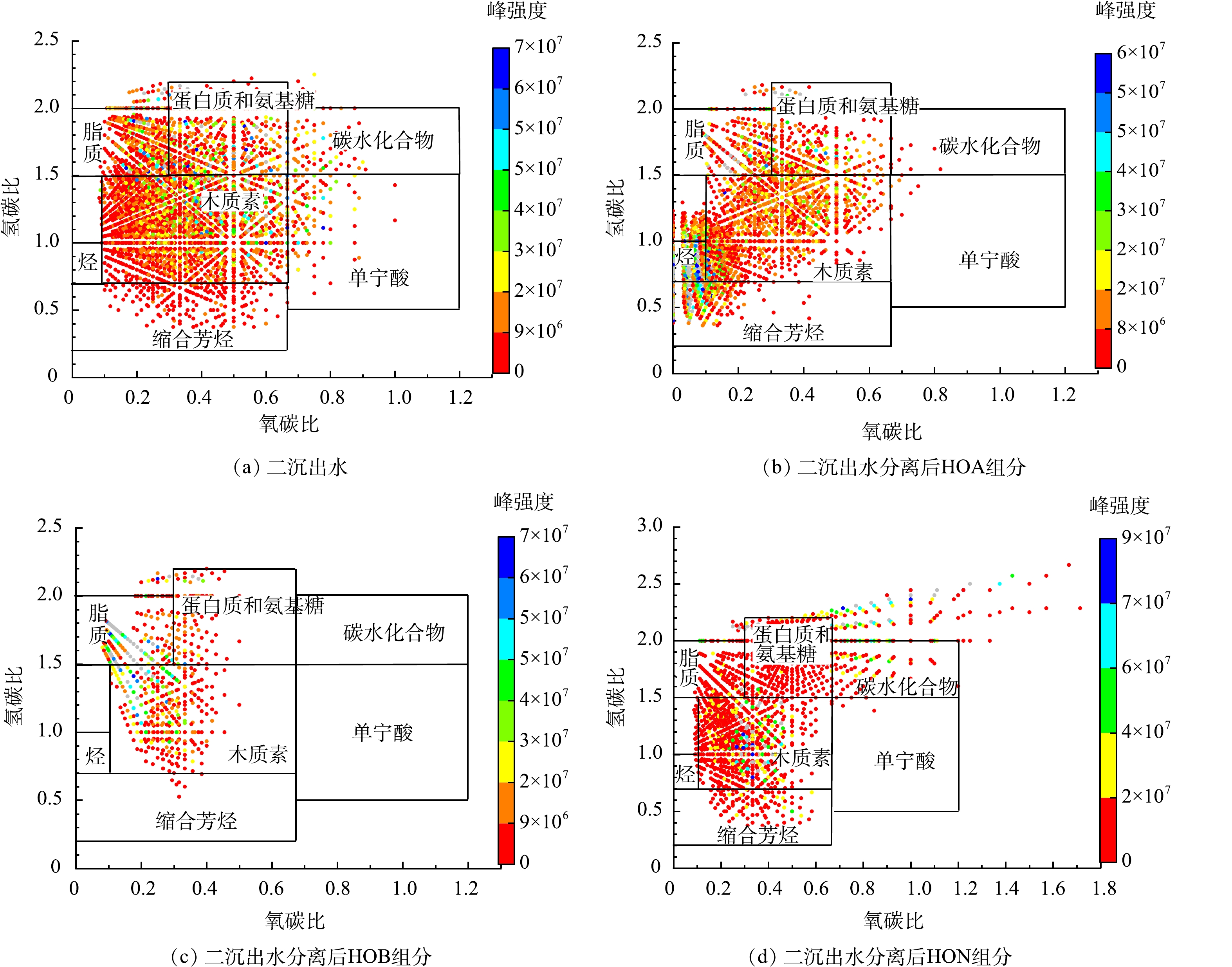
由于DOM不同类型化合物有特定的H/C和O/C,因此,在Van Krevelen图中特定区域对DOM进行归类分析。以往研究主要将VK图划分为7个区域,分别为:脂质 (O/C=0~0.30,H/C=1.50~2.00) ;蛋白质和氨基糖(O/C=0.30~0.67,H/C=1.50~2.20);碳水化合物(O/C=0.67~1.20,H/C=1.50~2.00);不饱和烃(O/C=0~0.10,H/C= 0.70~1.00);木质素(O/C=0.10~0.67,H/C=0.70~1.50);单宁酸(O/C=0.67~1.20,H/C=0.50~1.50);缩合芳烃(O/C=0~0.67,H/C=0.20~0.70) [25-28]。炼油污水处理厂二沉出水DOM的7类化合物在位置均以序号的形式在Van Krevelen图(图4)中标出。由图4可以看出,二沉出水和HOA组分的化合物分布最为相似,主要为脂质、蛋白质和氨基糖、木质素和缩合芳烃类化合物。HOA、HOB组分O/C较低,说明这2个组分中保留了较多的低氧数化合物,而HON组分有更高的O/C,即碳水化合物,说明HON组分中保留了更多氧化程度较高的化合物。此外与HOB组分相比,HOA和HON组分保留了一些H/C较低,缩合度较高的化合物(缩合芳烃类化合物),HOB组分H/C较高,其中化合物的缩合度相对较低。HOA组分含有较多的不饱和烃和缩合芳烃;HOB组分以脂质,蛋白质和氨基糖和木质素为主,缩合芳烃含量较少;HON组分保留了一些H/C较低的缩合芳烃类化合物。
-
1)使用MAX/MCX萃取柱将炼油污水处理厂二沉出水分为HOA、HOB、HON和HIS 4种组分,HON组分的TOC最高,为32.65%,二沉出水中的DOM主要为疏水中性化合物。
2)二沉出水中主要为V区腐殖酸类物质和IV区微生物代谢蛋白物质,HON组分与二沉出水组成最为相似。二沉出水中主要含有酚类物质和多环芳烃化合物;HOA组分主要以三环和四环芳烃化合物占主导;HOB组分含有酚类物质,此外,还含有一环、二环、三环芳烃化合物;HON组分与HIS组分主要是三环芳烃化合物。
3) HOA组分组成与二沉出水最为接近,主要为脂质、蛋白质和氨基糖、木质素和缩合芳烃类化合物,主要化合物类型为CHO,以O4~O7为主,CHOS次之,以O3S1为主,HOA组分含有较多的不饱和烃和缩合芳烃,有较多低氧数化合物;HOB组分主要是CHOS类物质,以脂质,蛋白质和氨基糖和木质素为主;HOB组分中缩合芳烃含量较少且H/C较高; HON中主要的化合物类型为CHOS和CHON,保留了一些H/C较低的缩合芳烃类化合物,且具有更多的高O/C的化合物。
炼油污水处理厂二沉出水中溶解性有机物组分分析
Characterization of four fractions of dissolved organic matters in secondary effluent of refinery wastewater treatment plant
-
摘要: 使用MCX/MAX萃取柱对炼油污水处理厂二沉池出水中的溶解性有机物(DOM)进行分离,获得疏水酸性组分(HOA)、疏水碱性组分(HOB)、疏水中性组分(HON)和亲水物质(HIS)4种亚组分。使用三维荧光光谱和电喷雾-傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱对各组分进行了组成表征,结果表明:二沉出水中存在酚类物质和石油类物质的特征荧光峰;HOA组分中化合物类型较多,主要为CHOS类物质;HOB组分中检测到的物质较少,主要为O3S1物质;HON组分中有较多的CHOS、CHON和CHO类物质。以上研究结果可为炼油污水处理工艺优化和外排水环境影响评估提供参考。Abstract: The dissolved organic matter (DOM) in the effluent from the secondary effluent of a refinery wastewater treatment plant was separated by MCX/MAX extraction column, and four sub-components including hydrophobic acidic component (HOA), hydrophobic alkaline component (HOB), hydrophobic neutral component (HON) and hydrophilic substance (HIS) were obtained. 3D-EEM and ESI FT-ICR MS were used to analyze each component. The results showed that specific fluorescence peaks of phenolic substances and petroleum substances existed in the refined wastewater, there were more compounds in HOA component, which mainly was CHOS substances; less substances were detected in HOB component, which mainly was O3S1 substances, and more CHOS, CHON and CHO substances were observed in HON component. This study makes an in-depth analysis of DOM in the effluent of refined wastewater, providing a reference for treatment process optimization and environmental impact assessment of external drainage of refinery wastewater.
-
Key words:
- refinery wastewater /
- secondary effluent /
- 3D-EEM /
- molecular composition
-
炼油行业是我国的支柱产业,据统计,我国每加工1 t原油会产生0.7~3.5 t污水[1]。炼油污水中有机污染物种类多,浓度高,且多为难降解有机物。污水中的溶解性有机物(dissolved organic matters, DOM)的组成及其在水处理过程中的迁移转化一直是水处理研究过程中的重点和难点。DOM成分复杂,其会对体系中金属、胶体等物质在体系中的形成和变化产生影响[2],排入天然水体的DOM会对自然生态产生影响[3]。因此,了解炼化污水中DOM的组成和性质对污水处理和水资源保护有重要的作用[4-5]。
大孔树脂吸附和固相萃取是2种最常用的DOM化学分级分离方法[6]。大孔树脂吸附法一般使用XAD树脂根据DOM的极性和酸碱性将DOM分成不同组分[7-8],但XAD树脂自身有机碳杂质溶出较高,使用前需要进行清洗预处理,操作繁琐耗时长。固相萃取法采用商品化的固相萃取柱对DOM进行分离富集,是近年来快速发展的DOM分离富集方法。与XAD树脂吸附法相比,固相萃取法采用高纯度商品化萃取填料,萃取柱背景溶出低,操作简单,耗时短,同时可供选择的萃取填料种类多,可将DOM分级分离成不同性质的组分。WANG等[9]比较了不同固相萃取填料对城市生活污水处理厂二沉出水中DOM分离的效果,发现不同固相萃取填料对DOM组分选择性不同。单独使用1种SPE材料能分离富集特定性质的DOM组分,但不适于对DOM中不同性质的组分进行全面表征。FANG等[10]将利用Waters Oasis MCX和MAX固相萃取柱串联,将炼油厂污水中DOM分为疏水酸性组分(HOA)、疏水碱性组分(HOB)、疏水中性组分(HON)和亲水物质(HIS)4个组分,该方法所需样品量少,操作简单快捷,可以对DOM中不同性质组分进行全面表征,适合于对DOM组成分离分析。三维荧光光谱(EEM)和傅里叶离子回旋共振质谱(FTICR MS)是DOM组成分析常用的2种高分辨分析方法,三维荧光光谱(EEM)可将水中有机物的进行光谱和组成性质的整体分析,并根据水样特征峰区域将DOM分为不同组分,已经广泛用于水中DOM的组成分析[11];傅里叶离子回旋共振质谱(FT-ICR MS)具有超高质量分辨率和超高质量精确度,可明确DOM的分子式,是分析DOM分子组成的重要手段[12-13],常用于炼油污水中DOM分子组成和转化的表征[14-15]。
本研究利用MCX和MAX固相萃取柱串联的分离提取方法将炼油污水处理厂二沉出水中的DOM分为疏水酸性组分 (hydrophobic acid, HOA) 、疏水碱性组分(hydrophobic base, HOB)、疏水中性组分(hydrophobic neutral, HON)和亲水物质(hydrophilic substance, HIS)4种亚组分,并应用EEM和FT-ICR MS对其进行了组成分析,为炼油污水处理工艺优化和外排水环境影响评估提供科学支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 水样信息
水样取自济南某炼油污水处理厂二沉池出水,水样经过0.45 μm混合醋酸纤维素滤膜过滤,过滤后的水样保存于4 ℃冰箱保存。
1.2 MCX/MAX串联萃取
MCX柱和MAX柱使用前分别用10 mL乙腈和10 mL超纯水依次活化。经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后的水样,用1 mol·L−1的NaOH调pH至12,水样过MCX柱并收集流出液备用。用10 mL含 2%甲酸的超纯水淋洗MCX柱,然后用氮气吹干柱子中水分,再用10 mL乙腈洗脱MCX柱,得到HON-1组分;继续用10 mL含5%氨水的乙腈洗脱MCX柱,得到HOB组分;将水样过MCX柱的流出液用用1 mol·L−1的HCl调pH至2,过MAX柱萃取,收集流过MAX柱的水样即为HIS组分,上样后使用10 mL 5%氨水淋洗,用氮气吹干MAX柱子中水分,用10 mL乙腈洗脱MAX柱,得到HON-2组分,继续用10 mL含2%甲酸的乙腈洗脱MAX柱,得到HOA组分。
1.3 三维荧光测定方法
三维荧光光谱由日立F-7000荧光光谱仪测定。测试条件为:PMT电压700 V;扫描速度30 000 nm·min−1;扫描范围:激发波长Ex为200~550 nm,发射波长Em为200~600 nm;扫描间隔为5 nm;狭缝宽带为5 nm;响应时间为0.002 s。测试时以超纯水为空白,样品经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后上机测试。
1.4 FT-ICR MS测定方法
采用Apex-Ultra 9.4T FT-ICR MS(Bruker,德国)对DOM分子组成进行分析,电离源为Apollo ESI负离子,实验样品用乙腈配制成100 mg·L−1的溶液,进样速度为250 μL·h−1。
电离源条件为:毛细管发射电压3 000 V,引入电压3 500 V;毛细管出口电压-320 V。离子在源六级杆中的存储时间为1 ms,碰撞累计时间0.02 s,飞行时间为1 ms。质量采集范围为100~700 Da,平均扫描64次,采样点数4 M,仪器校准和数据处理参考以往研究[16]。
1.5 TOC测定方法
使用日本岛津TOC-L对TOC进行测定,以高纯氧做载气,采用680 ℃催化氧化法将有机物氧化成二氧化碳,再由非色散红外检测器对产生的二氧化碳进行定量。
1.6 UV254测定方法
水样经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后使用紫外可见分光光度计(岛津UVmini-1280)在254 nm波长下测试,测试时以超纯水为空白,于10 mm石英比色皿中进行测定。
1.7 遗传毒性测定方法
遗传毒性测试采用SOS/umu改进方法[17],受试菌株为鼠伤寒沙门氏菌Salmonella typhimurium TA 1535/pSK1002。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 炼油污水处理厂二沉出水水质指标
对炼油污水处理厂二沉出水进行常规水质指标和溶解性有机物特征指标以及遗传毒性指标分析,各水质指标结果为:pH为7.46,SS为28 mg·L−1,COD为91.80 mg·L−1,TOC为28.21 mg·L−1,TN为48.49 mg·L−1,UV254为0.438 6 AU·cm−1,SUVA254为1.520 8 L ·(mg·m)−1,TEQ4-NQO为146.95 μg·L−1。
由水质指标测试分析结果可知,二沉池出水中仍存在较多的溶解性有机物,COD和TOC指标较高,UV254和SUVA254指标分别为0.438 6 AU·cm−1和1.520 8 L ·(mg·m)−1,说明水中可能存在较多的含芳香环的难降解有机物。遗传毒性指标4-NQO当量浓度达到146.95 μg·L−1,出水中的溶解性有机物具有较高的遗传毒性。
2.2 DOM的组分分布
4种组分在DOM中的TOC分布见表1。炼油污水二沉出水的TOC为28.21 mg·L−1,DOM由67.4%的疏水组分组成(基于TOC值),其中HOA、HOB和HON分别占17.8%、16.95%和32.65%,亲水分HIS为17.23%,剩余未测出的DOM可能残余吸附在萃取柱中。该结果与FANG等[10]应用此分离方法得到的的焦化废水二沉出水4组分分布的研究相似。
表 1 二沉出水中4种DOM组分占比Table 1. The proportion of four components of DOM in the secondary effluent组分 TOC/(mg·L−1) 组分占比/% HOA 5.02 17.8 HOB 4.78 16.95 HON 9.21 32.65 HIS 4.86 17.23 2.3 三维荧光光谱
炼油污水处理厂二沉池出水及其四组分的三维荧光光谱结果见图1。以往的研究一般将三维荧光谱图划分为五个特征荧光峰区域,其中Ⅰ区(Ex/Em=200~250 nm/280~330 nm)为酪氨酸类似物,发光物质与低激发类酪氨酸有关;Ⅱ区(Ex/Em=200~250 nm/330~380 nm)为色氨酸类似物区,发光物质与低激发类色氨酸有关;Ⅲ区(Ex/Em=200~250 nm/380~550nm)的发光物质与富里酸、类富里酸、类胡敏酸、疏水性酸有关,简称富里酸类物质;Ⅳ区(Ex/Em=200~450 nm/200~380nm)为可溶性微生物副产物区,发光物质与类蛋白物质、和微生物代谢产物相关的酪氨酸、高激发类酪氨酸、高激发类色氨酸、含苯环蛋白类物质有关;Ⅴ区(Ex/Em=250~450 nm/380~550nm)的发光物质与胡敏酸、类胡敏酸、海洋类富里酸和疏水性酸有关[18-20]。由二沉出水的三维荧光分区积分结果可知,二沉出水中Ⅰ区荧光区域积分体积占1.21%,Ⅱ区占4.31%,Ⅲ区占4.22%,Ⅳ区占31.81%,Ⅴ区占55.45%, V区腐殖酸类物质和IV区微生物代谢物在二沉出水DOM中所占比例超过50%。由各组分的三位荧光光谱图1可知,HOA组分主要是Ⅴ区的腐殖酸类物质,占比达到49.69%,另外Ⅲ区和Ⅳ区占比也较高,占比分别为22%和17.02%。HOB组分主要是Ⅳ和Ⅴ区的微生物代谢蛋白物质和腐殖酸类物质,占比分别为32.84%和37.26%,Ⅰ区占3.07%,Ⅱ区占10.08%,Ⅲ区占16.75%。HON组分主要是Ⅴ区的腐殖酸类物质,区域积分体积占比达到35.02%,Ⅱ区占16.96%,Ⅲ区占20.49%,Ⅳ区占22.66%,与二沉出水中各组分占比最为相似。HIS组分主要是V区腐殖酸类物质和Ⅲ区富里酸类物质,占比分别为46.78%和35.71%,而二沉出水中Ⅲ区富里酸类物质仅占4.22%。
采用吸光度比特征峰法分析方法对二沉出水中DOM的三维荧光光谱进行分析,光谱图显示水样共有5个物质特征峰,其中A(Ex/Em=270 nm/300 nm)、B(Ex/Em=220 nm/300 nm)附近是酚类物质的特征峰;C(Ex/Em=230 nm/345 nm)、D(Ex/Em=250 nm/425 nm)、E(Ex/Em=280 nm/345 nm)附近为石油类的特征峰[21-22],其中E峰为一环和二环芳烃化合物的特征峰,C为三环芳烃化合物的特征峰,D为三环和四环芳烃化合物的特征峰。二沉出水中主要含有酚类物质、多环芳烃化合物;HOA组分中主要是石油类物质,其中三环和四环芳烃化合物占主导;HOB组分中含有酚类物质,此外还含有一、二、三环芳烃化合物;HON组分与HIS组分主要是三环芳烃化合物,HIS谱图较为杂乱,可能含有较多其它类型化合物。
2.4 基于负离子ESI电离源条件下的 FT-ICR MS的分子组成分析
HIS组分中有大量的无机盐,不适合用负离子ESI FT ICR MS检测,对炼油污水处理厂二沉出水和HOA、HOB、HON组分进行了负离子ESI FT ICR MS检测分析。图2为DOM样品在负离子ESI FT ICR MS下的原始谱图。可见,二沉出水、HOA和HON组分的响应较好,HOB 组分响应较差。通过数据分析可知,二沉出水、HOA、HOB、HON分别检测到6 585、2 900、533、1 924个DOM分子,HOA组分中含有的分子个数和化合物类型最多,这是因为负离子ESI模式下会选择性地电离酸性化合物和非碱性氮化物,而HOB组分主要是疏水碱性物质,难以被电离。二沉出水、HOA、HON的分子质量主要分布在200~600 Da。HOB组分有2个质量中心,分别在320 Da和470 Da左右。质谱图中m/z 297、311、325处有较高的质谱峰,为DBE为4的O3S1类化合物,可能是污水中烷基苯磺酸表面活性剂[23-24]。
在二沉出水、HOA、HOB和HON中分别鉴别出56、39、9、30种杂原子类型,主要包括CHO、CHON、CHOS和CHONS 4类化合物,杂原子化合物及其相对丰度见图3。二沉出水中的DOM类型主要包括CHO、CHON、CHOS和CHONS类物质,其中CHO类化合物的相对丰度最高,为49.28%,主要集中在O4~O8。其次是CHOS类化合物,主要集中在O3S1~O8S1。CHON类物质以N1O3~N1O8为主,CHONS类物质以N1O4S~N1O8S为主;双键当量DBE(double bond equivalents) = (2C+2 - H+N) / 2代表化合物分子中含有的双键和环数之和,DBE越高,不饱和度越高,二沉出水中主要的CHO类化合物DBE 大多小于6,代表含CHO3S类化合物DBE主要为4,二沉出水中主要化合物的不饱和程度较低。HOA组分与二沉出水组成相似,以CHO类物质为主,相对丰度达到52.84%,主要集中在O4~O7,这是由于负离子ESI电离源选择性电离酸性物质决定的;其次为CHOS类物质,以O3S1为主,CHON类物质以N4、N4O1~N4O4为主。负离子ESI模式下HOB组分响应较差,检测出来的物质较少,但HOB组分仍以CHOS类物质为主,主要是O3S1。HON中以CHOS类物质为主,主要集中在O3S1~O6S1,其次是CHON类物质,以N2O10~N2O13、N3O3~N3O4为主,CHO类物质以O2~O6为主,CHONS类物质以N1O4S1~N1O5S1为主。因此,二沉出水中存在的N1O3~N1O8类CHON物质主要存在于HIS亲水组分中。
由于DOM不同类型化合物有特定的H/C和O/C,因此,在Van Krevelen图中特定区域对DOM进行归类分析。以往研究主要将VK图划分为7个区域,分别为:脂质 (O/C=0~0.30,H/C=1.50~2.00) ;蛋白质和氨基糖(O/C=0.30~0.67,H/C=1.50~2.20);碳水化合物(O/C=0.67~1.20,H/C=1.50~2.00);不饱和烃(O/C=0~0.10,H/C= 0.70~1.00);木质素(O/C=0.10~0.67,H/C=0.70~1.50);单宁酸(O/C=0.67~1.20,H/C=0.50~1.50);缩合芳烃(O/C=0~0.67,H/C=0.20~0.70) [25-28]。炼油污水处理厂二沉出水DOM的7类化合物在位置均以序号的形式在Van Krevelen图(图4)中标出。由图4可以看出,二沉出水和HOA组分的化合物分布最为相似,主要为脂质、蛋白质和氨基糖、木质素和缩合芳烃类化合物。HOA、HOB组分O/C较低,说明这2个组分中保留了较多的低氧数化合物,而HON组分有更高的O/C,即碳水化合物,说明HON组分中保留了更多氧化程度较高的化合物。此外与HOB组分相比,HOA和HON组分保留了一些H/C较低,缩合度较高的化合物(缩合芳烃类化合物),HOB组分H/C较高,其中化合物的缩合度相对较低。HOA组分含有较多的不饱和烃和缩合芳烃;HOB组分以脂质,蛋白质和氨基糖和木质素为主,缩合芳烃含量较少;HON组分保留了一些H/C较低的缩合芳烃类化合物。
3. 结论
1)使用MAX/MCX萃取柱将炼油污水处理厂二沉出水分为HOA、HOB、HON和HIS 4种组分,HON组分的TOC最高,为32.65%,二沉出水中的DOM主要为疏水中性化合物。
2)二沉出水中主要为V区腐殖酸类物质和IV区微生物代谢蛋白物质,HON组分与二沉出水组成最为相似。二沉出水中主要含有酚类物质和多环芳烃化合物;HOA组分主要以三环和四环芳烃化合物占主导;HOB组分含有酚类物质,此外,还含有一环、二环、三环芳烃化合物;HON组分与HIS组分主要是三环芳烃化合物。
3) HOA组分组成与二沉出水最为接近,主要为脂质、蛋白质和氨基糖、木质素和缩合芳烃类化合物,主要化合物类型为CHO,以O4~O7为主,CHOS次之,以O3S1为主,HOA组分含有较多的不饱和烃和缩合芳烃,有较多低氧数化合物;HOB组分主要是CHOS类物质,以脂质,蛋白质和氨基糖和木质素为主;HOB组分中缩合芳烃含量较少且H/C较高; HON中主要的化合物类型为CHOS和CHON,保留了一些H/C较低的缩合芳烃类化合物,且具有更多的高O/C的化合物。
-
表 1 二沉出水中4种DOM组分占比
Table 1. The proportion of four components of DOM in the secondary effluent
组分 TOC/(mg·L−1) 组分占比/% HOA 5.02 17.8 HOB 4.78 16.95 HON 9.21 32.65 HIS 4.86 17.23 -
[1] 张帆. 炼化行业废水处理浅析[J]. 化工管理, 2020, 20: 44-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4800.2020.05.029 [2] 于婷. 炼厂二沉出水DOM特性及光催化降解规律研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2014. [3] PENG Y K, LI J, LU J L, et al. Characteristics of microbial community involved in early biofilms formation under the influence of wastewater treatment plant effluent[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 66: 113-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.05.015 [4] ZHANG B L, SHAN C, HAO Z N, et al. Transformation of dissolved organic matter during full-scale treatment of integrated chemical wastewater: molecular composition correlated with spectral indexes and acute toxicity[J]. Water Research, 2019, 157: 472-482. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.04.002 [5] KOU Y, JIANG J T, YANG B Y, et al. Transformation of dissolved organic matter at a full-scale petrochemical wastewater treatment plant[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 329: 117021. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117021 [6] DITTMAR T, KOCH B, HERTKORN N, et al. A simple and efficient method for the solid-phase extraction of dissolved organic matter (SPE-DOM) from seawater[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods, 2008, 6(6): 230-235. doi: 10.4319/lom.2008.6.230 [7] 王立英, 吴丰昌, 张润宇. 应用XAD系列树脂分离和富集天然水体中溶解性有机质的研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 2006, 34(1): 90-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2006.01.015 [8] SHI Q, PAN N, LONG H Y, et al. Characterization of middle-temperature gasification coal tar. Part 3: molecular composition of acidic compounds[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(1): 108-117. [9] WANG X, JI Y Y, SHI Q, et al. Characterization of wastewater effluent organic matter with different solid phase extraction sorbents[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 257: 127235. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127235 [10] FANG Z, HE C, LI Y Y, et al. Fractionation and characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in refinery wastewater by revised phase retention and ion-exchange adsorption solid phase extraction followed by ESI FT-ICR MS[J]. Talanta, 2017, 162: 466-473. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.10.064 [11] 栗则, 张晓飞, 吴百春, 等. 三维荧光光谱技术在石油炼化行业的应用[J]. 分析试验室, 2018, 37(7): 863-868. [12] HEADLEY J V, PERU K M, BARROW M P, et al. Mass spectrometric characterization of naphthenic acids in environmental samples: a review[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2009, 28(1): 121-134. [13] QI Y L, FU P Q, VOLMER D A. Analysis of natural organic matter via fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry: an overview of recent non-petroleum applications[J]. Mass Spectrometry reviews, 2022, 41(5): 647-661. doi: 10.1002/mas.21634 [14] HE C, CHEN W M, CHEN C M, et al. Molecular transformation of dissolved organic matter in refinery wastewaters: Characterized by FT-ICR MS coupled with electrospray ionization and atmospheric pressure photoionization[J]. Petroleum Science, 2022, 20(1): 590-599. [15] 吴百春, 李玉果, 聂凡, 等. 某炼化污水处理厂水中可溶有机物的转化规律研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2022, 42(1): 133-142. [16] LI Y Y, XU C M, CHUNG K H, et al. Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter and its subfractions in refinery process water by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuel, 2015, 29(5): 2923-2930. [17] YAN Y, JIANG W W, LI N, et al. Assessing of genotoxicity of 16 centralized source-waters in China by means of the SOS/umu assay and the micronucleus test: Initial identification of the potential genotoxicants by use of a GC/MS method and the QSAR Toolbox 3.0[J]. Mutation Research, 2014, 763: 36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.11.003 [18] CHEN W, WESTERHOFF P, LEENHEER J A, et al. Fluorescence excitation− emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental science & technology, 2003, 37(24): 5701-5710. [19] CHEN M, PRICE R M, YAMASHITA Y, et al. Comparative study of dissolved organic matter from groundwater and surface water in the Florida coastal Everglades using multi-dimensional spectrofluorometry combined with multivariate statistics[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2010, 25(6): 872-880. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.03.005 [20] COBLE P G. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy[J]. Marine chemistry, 1996, 51(4): 325-346. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(95)00062-3 [21] 吴静, 曹知平, 谢超波, 等. 石化废水的三维荧光光谱特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2011, 31(9): 2437-2441. [22] 吴静, 谢超波, 曹知平, 等. 炼油废水的荧光指纹特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(2): 415-419. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)02-0415-05 [23] GENG C, CAO N, XU W, et al. Molecular Characterization of organics removed by a covalently bound inorganic-organic hybrid coagulant for advanced treatment of municipal sewage[J]. Environment Science & Technology, 2018, 52(21): 12642-12648. [24] BAHRI M, MAHDAVI A, MIRZAEI A, et al. Integrated oxidation process and biological treatment for highly concentrated petrochemical effluents: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 2018, 125: 183-196. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2018.02.002 [25] ANTONY R, GRANNAS A M, WILLOUGHBY A S, et al. Origin and sources of dissolved organic matter in snow on the East Antarctic ice sheet[J]. Environment Science & Technology, 2014, 48(11): 6151-6159. [26] HOCKADAY W C, PURCELL J M, MARSHALL A G, et al. Electrospray and photoionization mass spectrometry for the characterization of organic matter in natural waters: A qualitative assessment[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods, 2009, 7(1): 81-95. doi: 10.4319/lom.2009.7.81 [27] LU Y H, LI X P, MESFIOUI R, et al. Use of ESI-FTICR MS to characterization dissolved organic matter in headwater streams draining forest-dominated and pasture-dominated watersheds[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(12): 145639. [28] FENG L, XU J Z, KANG S C, et al. Chemical composition of microbe-derived dissolved organic matter in cryoconite in Tibetan plateau glaciers: Insights from Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry analysis[J]. Environment Science & Technology, 2016, 50(24): 13215-13223. -






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: