-
社会经济的快速发展和城市化进程加速推动了污泥体量的增加,2022年我国干污泥产量已达到1300万吨以上[1 − 2]. 同时,污泥富含丰富的磷、矿物质和有机质,具有较高的资源化前景[3 − 4]. 污泥热解是指在缺氧或者无氧条件下,将污泥加热至一定温度使得污泥发生有机质裂解、水分挥发、小分子聚合等热化学反应,最终转化为气态、液态和固态(生物炭)[5 − 7]. 在热解过程中,随着有机物的裂解和小分子物质的挥发,污泥中的磷(P)、钾(K)等营养元素得到有效的富集,并且重金属可以生成硅铝结合态化合物,从而实现重金属的惰性转变[8 − 12].
污泥单独热解生成的生物炭具有比表面积较小、孔隙结构不完善、对土壤的改良效益不明显的问题,通过添加共热解物质、调整污泥热解参数等方法可以优化污泥基生物炭的土壤改良特性[13 − 15]. 污泥共热解的添加物包括生物质、碱土金属、塑料等,调节热解参数例如温度、时间和气氛[16 − 18]. 以秸秆为代表的生物质添加物可以提高混合物有机质含量、增强生成的污泥基生物炭的芳香结构,并且污泥中重金属可通过与生物质中的矿物成分结合、惰性转变等方式降低其生物活性[19]. 以氧化钙为代表的碱土金属与污泥共热解,可促使污泥中的磷转化为羟基磷酸钙的形式从而提高其有效磷的转化效率[20]. 以聚氯乙烯(PVC)为代表的塑料添加物,会促使污泥中重金属转变为金属氯化物的形态,使其在热解过程更容易挥发[21 − 22]. 以上污泥共热解方法以不同的机制有效提高了污泥基生物炭的物化特性使得其具备一定的土壤改良特性[23].
我国土壤污染严重,酸性土壤主要分布于中国南方、约占陆域面积的30%以上[24],有机污染土壤和重金属污染土壤主要与制药厂、工厂和农用地相关,总体呈现南方污染高于北方、东部发达地区高于中部地区,且二者呈现出明显的复合污染特征[25]. 污泥基生物炭可以从多方面对污染土壤起到改良作用,一方面污泥的碱性可有效中和土壤中的酸性、稳定土壤中的活性金属/重金属[26];另一方面,污泥基生物炭的多孔性质可改善污染土壤的结构和持水能力并为微生物的生长提供寄居场所. 最重要的,P是一种不可再生资源,污泥基生物炭中富含以P为代表的植物和微生物生长必须的矿物营养成分,不仅可提高土壤肥力、改善土壤品质也可以实现不可再生资源的回收利用[27]. 因此,污泥基生物炭应用于土壤改良具有良好的发展前景.
现有的对生物炭土壤改良的综述文章大多是技术成熟且已经投入市场应用的生物质类等生物炭,而对污泥基生物炭作为改良剂的相关机理探究还不够充足,缺乏对污泥定向热解和污泥基生物炭对土壤修复作用机制的分析和研究. 具体来说,一方面,污泥与不同物质在共热解过程中的相互作用机制,共热解条件因素对污泥重金属以及P的迁移转化影响还不够清晰;另一方面,污泥基生物炭的物化性质对土壤肥力、pH、微生物以及碳平衡等的作用效应还需要进行系统的分析评估. 因此,本综述拟基于国内外污泥的热解方法、污泥基生物炭物化性质演变及其土壤回用效果的最新研究进行深入的探讨与分析. 通过分析污泥基生物炭的热解制备及土壤回用效应的研究现状,明确不同热解工艺对重金属、P迁移转化的影响机制以及土壤回用过程中的增益作用,指导和丰富污泥基生物炭的定向热解和土壤改良机制的研究,为我国污泥资源化处置提供基础研究数据.
-
为了提高污泥基生物炭对污染土壤的改良特性,有必要在热解过程控制热解条件以实现污泥基生物炭有效磷的强化和重金属固化并降低以多环芳烃为首的有机污染物,一般来说,可采用添加共热解添加剂、控制热解温度以及酸碱、浸渍、蒸汽等的改性强化方法[28 − 29]. 目前污泥共热解物质主要有生物质、碱土金属、磷酸盐类、塑料等,可在污泥热解过程产生协同/拮抗作用,不仅影响污泥基生物炭中P和重金属的存在形态,还对产率有一定的影响.
如表1所示,生物质类添加剂主要包括食物残渣、木屑、秸秆等,生物质添加剂可通过芳香结构螯合污泥重金属、活性基团络合重金属、增加重金属挥发比例等方式降低污泥基生物炭的活性重金属. Wang等[30]将食物残渣与污泥共热解,促进了高岭石(Al2Si2O5(OH)4)和金属磷酸盐结晶化合物的形成,重金属结合在该复杂晶体化合物中大大降低了其重金属的风险指数. Yang等[31]将稻壳与污泥共热解明显降低了Pb和Cd的含量,并且其形态分别转变为更加稳定的PbAl2O4和CdAl2O4,污泥基生物炭生态风险降低了1—2级. Wang等[32]将污泥和棉花秸秆共热解,棉花秸秆在热解过程产生的以羧基、羟基、酚羟基等为首的丰富有机官能团与重金属发生络合反应从而起到稳定重金属的效应.
碱金属也是一种常用的污泥共热解添加剂,Tang等[33]将CaO添加于污泥,在700 ℃共热解发现污泥中的重金属得到有效固定,且P以羟基磷灰石的形态富集. Han等[34]将CaO/Fe2O3与污泥共热解,发现CaO能与污泥中的As2O3、As2S3和NaAsO2反应生成Ca(AsO2)2稳定形态物质. 田[35]还在污泥中添加K3PO4,发现相比不添加共热解物质时产物中出现了磷酸金属盐等结合态,分析发现PO43-的添加可以促进污泥中金属氧化物与之作用形成结合态. 此外,一些塑料添加物也证实可有效固化污泥的重金属[36]. Li等[37]将污泥与载金属聚氯乙烯共热解可有效固定除Pb外的重金属,且随着载金属聚氯乙烯热解占比越大,重金属稳定态分数增加,对Pb的消极效果是载金属聚氯乙烯中PbSO4的释放导致. 李志远等[21]同样的采用污泥与聚氯乙烯进行共热解,发现加入PVC使得重金属转化为容易挥发的金属氯化物形态,降低了生物炭中As、Zn等的残留量.
综上分析,污泥与生物质共热解更容易生成孔隙结构丰富的污泥基生物炭,且Pb等重金属常与铝化合物结合形成稳定化合物;污泥与碱土金属共热解,可以对As等重金属起到较好的固定作用;而当污泥与塑料共热解降低重金属残留量的同时塑料中原本还有的金属化合物还会对某些金属固定带来负面作用.
-
热解气氛,尤其是氧气的存在比例会影响污泥在热解中的氧化还原反应,从而决定污泥基生物炭的性质. 氮气是热解常用的惰性保护气,Tang等[33]的研究采用N2作为保护气研究CaO与污泥共热解,还有研究采用CO2作为热解气体[38]. 相比N2,CO2气氛可以在热解过程为污泥中的还原物质(如C原子)提供氧原子,进而影响污泥基生物炭的O/C. 另外,研究还发现相比 N2气氛,CO2气氛条件下会抑制甲烷的生成,这是因为在高温条件下会促使CH4与H2O(g)作用生成CO反应的进行,而CO在排出过程中遇到氧气又会被还原成为CO2[39]. Huang等[40]将污泥与水葫芦在CO2/O2气体条件下共热解,当二者比值为7/3时热解产物在1000 ℃减重最少,结构最稳定,且此气体比例下热解过程活化能最低反应易于进行. 分析发现,在有氧气存在的热解气氛条件下,Ca的赋存形态会发生变化,N2气氛下主要以CaCO3形态存在,低氧条件下CaO为主要存在形态,这也是低氧条件下生物炭pH较高的原因. 氧气的存在还会导致产生大量飞灰颗粒,不易挥发的金属以氧化物形态留存在飞灰中从而被带走,降低生物炭中重金属的留存率[41]. CO2气氛还能降低热解污泥的活化能并减少酸类化合物的生成[42],当有生物质参与热解时,氧气的存在会影响CO2和CO的产生量,进而影响生物炭孔径结构[43]. CO2气氛在热解反应的最初有增大热解混合物比表面积和孔体积的效用,但在更高的温度条件下(>500 ℃),CO2会导致大孔数量增多、比表面积减小.
惰性气氛有助于调控污泥混合物的定向发展,而CO2气氛不仅能促进污泥基生物炭孔隙结构的完善,形成丰富的芳香烃结构,促进金属形成稳定形态,还能通过控制氧气比例调控混合物活化能,调控生物炭pH以及重金属的留存率.
-
热解温度是决定产物生物炭结构的主要因素. 表2可以看出,污泥单独热解时随着热解温度的增大,污泥基生物炭的比表面积也逐渐增大[44].
但是,共热解物质添加后,尤其是柳木与污泥共热解相比污泥单独热解时比表面积明显增大,此时温度对污泥基生物炭孔隙结构的影响变得不明显[45]. 在相同热解温度条件下,停留时间的长短也影响着生物炭的比表面积,这是因为污泥与共热解物质泥中含有的半纤维素、纤维素、木质素在不同温度阶段分解状态不同. 例如,在400 ℃时停留时间的增大促进有机质的继续分解;当温度升高有机质分解完全(500 ℃),此时停留时间的增大会使生物炭基体呈熔融态,部分灰分可能会堵住孔隙结构;温度继续升高(700 ℃),生物炭中的碳酸盐分解出CO2等气体迫使生物炭重新形成孔径结构.
热解升温速率对生物炭的性质也有一定影响,Zhu等[46]改变升温速率分别为10、20、30 ℃·min−1,发现升温速率越低污泥随温度升高减重更快,这是因为介质扩散和传热需要一定的时间,升温速率过高会延迟热解反应,增大整个热解过程的时长. 升温速率越高生物炭产率越低,气体产量越高. Wang等[47]改变升温速率分别为10、20、30 ℃·min−1,发现随着升温速率的改变,热解产物的总失重相同,表明升温速率不影响有机物的分解效率,只是达到热解终温的快慢不同. Huang等[40]改变升温速率分别为10、20、40 ℃·min−1,发现随着热解升温速率的提升,污泥随温度热解减重速率减小,这是因为增大加热速率不利于热解物质的燃尽,增大了热解时长,但有利于挥发分的分离和燃烧.
-
污泥中含有4%—9%的P[49 − 50],其主要存在形态包括有机磷(OP)和无机磷(IP),有机磷一般以核酸、磷脂、含磷蛋白等形式存在,而无机磷包括磷灰石无机磷(AP)和非磷灰石无机磷(NAIP).
热解温度、添加剂是影响污泥P转化的关键因素,而热解气氛对P的迁移转化影响很小[51]. OP沸点较低,在热解过程中会随着温度的升高而逐渐分解转化为其他含磷化合物,即OP在热解过程中发生脱水、脱羧、聚合等反应,一个或多个与磷酸基团相连的有机官能团丢失并释放正磷酸盐及焦磷酸盐[49, 52 − 53],原来被这些有机官能团占据的位置会被金属阳离子(Ca2+、Fe3+和Al3+)重新占据,即OP释放的正磷酸盐与金属离子一起形成矿物或立即吸附到其他固相表面. 因此,提高温度或低灰分、高挥发性的污泥有利于OP向IP的转化,促进IP的富集. 污泥单独热解时P主要与铁、铝等结合生成难以分解的磷酸铁盐、磷酸铝盐等. 以CaO为首的碱金属添加剂,已经被证实可促进NAIP向AP转化,且P与其他金属离子的反应顺序为: Ca2+> Mg2+> Al3+> Fe3+[54 − 57]. 当添加CaO等共热解物质后污泥中的非磷灰石IP逐渐转化为钙磷酸盐等磷灰石IP,但是羟基磷灰石的形成取决于Ca/P. 通常Ca/P比值控制在1.50—1.67,热解温度控制在600—900 ℃更有利于羟基磷灰石的形成[58]. Tang等[33]采用添加CaO、控制热解温度定向调控污泥热解过程促使P转化为羟基磷酸钙物相(P targeted transformation to hydroxyapatite),简称“P2THAP”,并且通过玉米盆栽实验证实该污泥基生物炭再生P肥养分供给效果媲美甚至超越传统化学P肥. 另外有研究指出,随着热解温度的提高,制出的生物炭对P具有更高吸附能力且解吸量也在逐渐降低,从而在生物炭上形成较稳定的磷酸盐化合物并能实现对P的缓慢释放[59].
-
污泥在热解富集P资源的同时,污泥中携带的重金属也同时被富集,不利于污泥基生物炭的土壤回用. 重金属在污泥基生物炭中的存在与热解过程的挥发度和物质流分配密切相关,Hg、Se等高挥发性重金属在低温热解阶段易挥发存在于气态产物中,Ba、Cr、Co、Cu、Ni等低挥发性重金属主要留存在污泥基生物炭中,Pb、Cd、Zn、As、Sn、Ti等中等挥发性重金属通过挥发冷凝富集于生物油中[60]. 因此,降低污泥基生物炭中的重金属生态风险可以通过提高热解温度将易挥发重金属减量、中挥发性和低挥发性重金属形成稳定态重金属固定来实现. 但是,过高热解温度会破坏生物炭的孔隙结构,促使芳香族化合物分解形成C=C稳定结构.
刘菲菲等[61]采用微波热解发现,随着热解温度的提升,生物炭中的稳定态重金属占比逐渐增大,对几种重金属的固定效果由好到差依次为Cr>Pb>Ni>Cu>Zn,这可能与重金属氧化物的可挥发性和稳定性相关. Xu等[62]分别添加CaO和MgO与污泥共热解,相比原污泥热解污泥基生物炭中残渣态重金属比例最高可以达到99%,并且通过浸出毒性研究发现MgO与污泥共热解制备生物炭对重金属的固定效果更优. 添加CaO对重金属固定效果由好到次依次为Pb>Cu>Cr>Cd,添加改为MgO时重金属固定效果依次为Pb>Cu>Cd>Cr. 分析发现,吸附差异主要取决于共热解添加物所能提供的吸附位点以及各吸附位点与重金属之间的吸附次序. 共热解添加物可以促进重金属的固定,张进等[63]将稻壳与污泥等比例共热解,相比原污泥中Mn、Ni、Cr、Zn、Pb、Cu的有效态含量下降百分比分别为85.94%、79.83%、76.83%、63.41%、31.74%、30.76%,这是由于稻壳含有丰富的Si元素并且在热解过程中含Si化合物与重金属结合固定降低了重金属的生物有效性. 汪刚等[64]研究了添加不同塑料对污泥定向热解产物的影响,发现塑料在热解过程中产生的自由氯易与重金属发生结合生成高挥发性的重金属氯化物. 以上研究中污泥与各物质共热解制备的污泥基生物炭中重金属存在形态如图1所示,发现重金属在迁移转化过程中有一部分与P发生耦合作用,可以在固定重金属的同时实现P富集. 但是,二者之间的耦合机制还有待进一步探究,且结合态的稳定性以及分解后的存在形态也是制约污泥基生物炭应用的一大问题.
-
污泥通过定向热解生成含有官能团和芳香结构的生物炭,可以很好的削减有机污染物,例如降低多环芳烃(polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, PAHs)、全氟及多氟化合物(per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances,PFAS)、多氯联苯(polychlorinated biphenyls,PCBs)等的浓度. 当采用柳木和污泥按照4:6的比例混合,在温度为700 ℃、气氛为CO2条件下定向热解制得生物炭[45],能够有效降低3—6环的PAHs,使其占比低至9.0%. PFAS通常在热解温度450 ℃以下就可以被分解挥发,且在500 ℃以上全氟辛烷磺酰基化合物(PFOS)和全氟辛酸(PFOA)的去除率就可以达到90.0%以上[65]. MOŠKO等[66]对污泥热解发现700 ℃及以上且保留足够停留时间(>30 min)PAHs、PCBs等大多数可以挥发到气相,去除效率可达99.8%以上,污泥中含有的抗生素等药物大多也挥发或者分解. ALIPOUR等 [67]发现了同样的规律,并且Brown等 [68]对木炭热解也发现随着温度升高产物毒性和PAHs浓度显著降低. Buss[69]对污泥热解有机污染物的综述也表明,当温度高于500 ℃对药物等有机物的削减率达到99.0%以上. 因此,挥发性和热降解是去除PAHs、PCBs、药物等有机污染物的最重要手段,但是需要对其热解保持中高温条件并维持一定时间.
综合以上分析,污泥热解想同时达到P固定与缓释、重金属低生物有效性、有毒物质含量降低可以通过调节热解气氛、热解温度以及共热解添加物来实现. 从污泥基生物炭的孔隙结构以及生物产气的角度考虑,CO2可以作为较优的热解气氛选择,在降低活化能促进反应进行的同时完善污泥基生物炭的孔隙结构. 在中高温度条件下控制热解速率可以实现对有机物的大部分降解,还能实现重金属的固定. 但是,高温会影响热解气氛对孔径结构的调控,而共热解添加物的引入会让热解气氛对孔径结构的影响减弱,同时共热解添加物可以为重金属的固定提供不同的吸附位点. 高温(700 ℃)条件下的污泥基生物炭对P有较强的吸附能力且解吸率低. 因此,保持较高的热解终温并且调控CO2/O2热解配比能有效富集P、固定重金属以及去除有机污染物,而对特定重金属的固定则取决于共热解添加物所能提供的吸附位点.
-
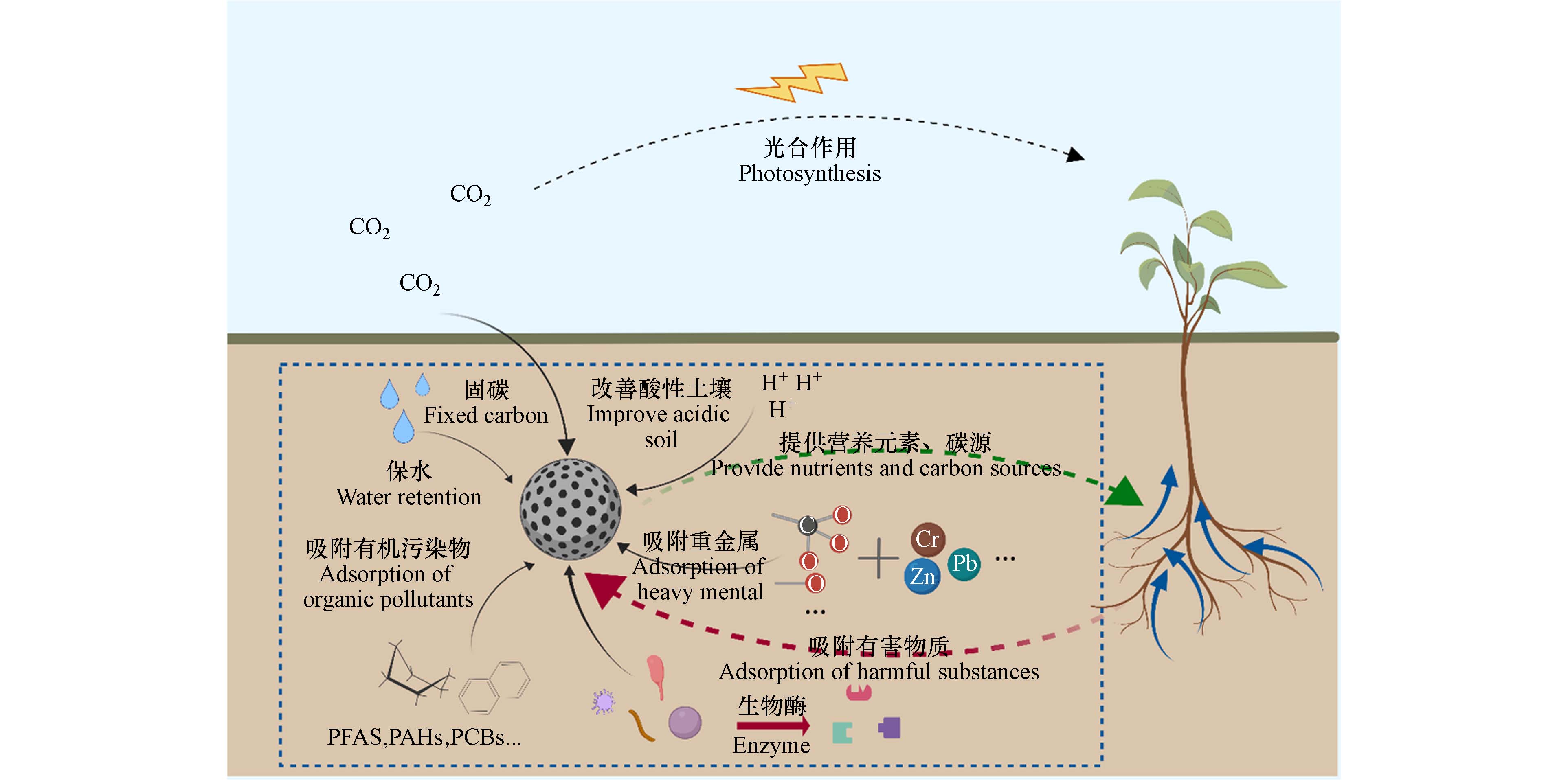
我国鼓励将处理后的污泥作为土壤改良剂用于土壤改良,而污泥基生物炭已经被大量的科学研究证明具有良好的土壤改良效果,对土壤的各种改良效果如图2所示.
污泥基生物炭修复酸性土壤是一种比较温和的方法,可以促进土壤生物活性、改善土壤理化性质并降低污染物的毒性[70 − 72]. 污泥基生物炭改善酸性土壤主要通过与酸性土壤中的H+发生中和反应以及生物炭中的阳离子释放与土壤H+交换,降低土壤H+含量,提高土壤的pH值,但是硝化作用释放质子会让土壤酸度逐渐恢复原来状态[73]. 因此,污泥基生物炭改善土壤pH与污泥中无机氮的存在形态有关,当以NH4+-N形态存在时,回用至土壤会降低土壤的pH,而当以游离氨的形态存在时则能提高土壤pH[74]. 卢再亮等[73]发现在500 ℃定向热解制备的污泥基生物炭相比低温热解生物炭对酸性土壤的改良效果更好,这是由于污泥基生物炭中的盐基阳离子与土壤中的交换性Al3+和H+发生离子交换. 王秋利等[75]将污泥与木屑按照2:1的比例在500 ℃热解2 h制备生物炭,回用至酸性土壤中经过培养发现,土壤的pH由4.37增长至6.69. 另外,酸性土壤相比其他土壤Cd含量较高,将污泥与木屑定向热解的生物炭添加土壤后能很好地固定并降低酸性土壤Cd含量,Cd含量降低约46%,对Hg和Pb也有同样的作用.
污泥基生物炭可以通过吸附土壤中的重金属和有机污染物达到修复受污染的土壤的目的,其稳定的碳质结构还能进一步促进土壤恢复. 污泥基生物炭的高表面积和孔隙结构使其具有较强的吸附能力,而其内部富含阳离子和氧化物的羟基可以以氢键和离子键结合有害物质. 周佳丽等[76]研究发现KOH改性后的污泥基生物炭对Pb2+有明显的吸附作用,吸附后的污泥基生物炭Pb2+含量由4.28%增加到19.05%,而镁离子和钙离子的含量下降,可能是Pb2+与其发生了离子交换. 另外,红外光谱发现Pb以—CO3自由基及Pb—O的形式负载在生物炭表面,即吸附Pb2+的方式主要是通过矿物沉淀、离子交换、含氧官能团络合及ᴨ键结合. 污泥基生物炭对有机污染物的吸附效果也较好,ZIELIŃSKA等[44]将700 ℃下热解污泥得到的生物炭加5%至富含PAHs的土壤中,使得改良后的土壤对菲的吸收率从8.3%提高到20.3%,芘从14.5%提高到31.7%,但是土壤中含有的溶解有机碳(DOC)和黏土矿物会影响生物炭的吸附效果. KRAHN等[77]的研究发现污泥基生物炭可以作为PFAS的有效吸附剂,这是因为污泥基生物炭拥有较低的C/N,因此生物炭碳结构外围有更多带正电的官能团,有助于与PFAS的带负电荷的羧酸头基进行阴离子交换从而实现对PFAS吸附[78 − 80]. 污泥基生物炭还可以有效吸附土壤中的抗生素等,污泥基生物炭C—O—Fe结构中的Fe是活化过二硫酸盐降解四环素的反应位点[81 − 82]. 因此,污泥生物炭界面结构可以有效活化过二硫酸盐有效吸附降解四环素[83 − 84].
污泥与生物质定向热解的产物生物炭还可以被用来改善盐碱土壤,例如韩剑宏等[85]将污泥和玉米秸秆按照5:2的比例混合在500 ℃定向热解制备生物炭并将其回用至盐碱土壤中,有机碳和可交换阳离子量相比原土壤增长了约9倍,大大提高了土壤的肥力和缓冲能力,而水溶性盐的含量降低约45%,消除了高盐含量对土壤肥力的不利影响.
-
生物炭的高比表面积和负电荷表面可以改善土壤结构,并增加土壤团聚体的稳定性. 生物炭的大量孔隙不仅可以作为微生物依附的结构,还可以增加土壤的保水性和通透性,提高土壤的水分和养分供应能力,更有利于土壤微生物的生长. 污泥基生物炭中含有的水溶性有机物主要由氨基酸和小分子碳水化物等组成,也可以被土壤中的微生物分解利用[75]. Tang等[86]的研究表明生物炭大孔(>50 nm)可以为微生物提供栖息的空间,而中孔(2—50 nm)和介孔(<2 nm)可以为微生物储存所需营养物质. 污泥热解制得的生物炭回用土壤对生物多样性也有影响,例如王秋利等[75]在500 ℃将木屑与污泥按照1:2的比例混合热解2 h,将制得的生物炭回用至土壤中. 经过培养,回用生物炭土壤对比原土壤Shannon指数变大,即生物群落多样性增大;Chao指数也增大,即物种总数增多. 在同样的条件下,将热解温度升至800 ℃,发现两种指数反而下降,即对土壤微生物群落的多样性和物种数有相反的作用. 另外,有研究发现PAHs苯环数决定其对土壤微生物的正/负影响[87],低环PAHs(苯环数≤4)可以被土壤微生物分解利用,高环PAHs(苯环数>4)则能与细胞表面的膜磷脂结合破坏细胞膜的功能. 因此,可以通过定向热解调控污泥基生物炭中活性成分,在土壤回用时起到促进土壤微生物的生长繁殖的作用[88 − 89].
生物炭添加至土壤中对土壤中酶活性的影响有两种不同的观点:一是认为,生物炭表面的羧基、羟基等会与土壤酶的氨基发生脱水缩合,改变土壤酶的活性位点及官能团结构从而降低土壤酶的活性. 土壤中脲酶和脱氢酶的活性是表征土壤氮素供应强度的重要指标,而污泥基生物炭的添加能明显增大这两种酶的活性[29]. 有机质可以通过离子键、氢键、共价键以及离子交换等方式固定土壤中酶分子,以此降低酶活性. 污泥基生物炭释放出的溶解性有机质还会抑制土壤中酸性磷酸酶的活性,降低土壤中有效磷的浓度[90];二是认为,生物炭对酶吸附的同时也会吸附底物,从而增大酶与底物的接触概率,促进酶促反应的进行[91]. 有研究总结发现,污泥在热解过程中可能会产生环境持久性自由基(environmentally persistent free radicals,EFPRs)[92],而EFPRs会氧化酶活性位点,对酶结构造成损害,从而抑制生物酶活性[93].
-
污泥基生物炭一方面在热解过程相较于燃烧可减少碳的释放量,另一方面将其应用于土壤可增大土壤的碳固存量. PARIYAR等[94]的研究表明,由于脱水和脱羧反应,较高热解温度能获得O/C、H/C较低的生物炭,550 ℃和600 ℃热解得到的生物炭更适于土壤碳固存,当生物炭中O/C<0.6时,半衰期最少可达100年[95]. Gusiatin等[96]将污水污泥、木屑、秸秆等物质共热解制备生物炭发现随着热解温度上升,生物炭的固定碳含量升至20%以上,将生物炭添加至土壤中发现土壤中溶解性碳含量随时间推移在不断下降,例如Hu等[97]将生物炭加入土壤中减少了50%的二氧化碳排放. 另外,有研究者从猪粪、污水污泥和小麦秸秆中提取的生物炭研究生物炭对二氧化碳的吸附行为,发现提高吸附温度和含水量可促进二氧化碳的吸收从物理过程转变为化学过程. 生物炭中的Mg、Ca、Fe、K 等矿物成分通过矿物反应可以诱导CO2的化学吸附,占总吸附量的17.7%—50.9%. 污泥基生物炭中的FeOOH被吸附的CO2转化为Fe(OH)2CO3[98],而猪粪生物炭中吸附的CO2则沉淀为K2Ca(CO3)2和CaMg(CO3)2,这导致两种生物炭中的不溶性无机碳显著增加,可以在土壤应用中形成稳定碳库. 对于小麦秸秆生物炭,吸附的二氧化碳诱导CaCO3转化为可溶性Ca(HCO3)2,从而导致可溶性无机碳的增加[99].
另外,污泥基生物炭的添加会通过影响土壤微生物群落进而影响土壤碳封存. Schwander等[100]报道了一种非天然的酶催化固碳途径,而这些固碳作用酶大多来自异养微生物等,而污泥基生物炭不仅可以为异养微生物提供寄居场所,还能为其提供营养物质,形成高效固碳循环[101]. 污泥基生物炭不仅可以抑制土壤中CO2的释放,对CH4也有吸收作用从而实现碳固定. 例如土壤中含有产CH4菌和 CH4氧化菌,添加生物炭可以改善土壤的通透性和保水性. 土壤孔隙度增大促使氧气含量增大抑制产CH4菌的活性,较高的含水率能增强CH4氧化菌的活性,从而减少CH4释放实现碳封存[102]. 综合以上分析,污泥基生物炭影响土壤碳封存主要包括以下几种途径. 污泥基生物炭施加到土壤中会影响土壤中有机碳库的矿化,进而导致CO2排放增加;污泥基生物炭可以吸附土壤中释放的CO2;污泥基生物炭可以显著影响参与二氧化碳代谢的土壤微生物活性和多样性,从而在很大程度上影响土壤碳释放[103 − 104].
目前,污泥基生物炭应用于实际土壤改良还相对较少,一方面原因是受其本身重金属毒性限制,另一方面经济成本也是需要考虑的一大问题. 其中,热解温度、停留时间和升温速率是影响热解过程能耗的关键因素,这些因素决定了污泥基生物炭的成本. 有研究将热解成本与市面商品做了对比,Wang等[47]将棉花秸秆与污泥共热解,制备1 t生物炭的成本约为350元,而市场上腐殖酸和生石灰每吨的成本分别为700元、1100元,制备生物炭的成本远低于市场具有相同肥效的商品肥. 因此,明确所需土壤改良剂的性质之后对污泥进行定向热解不仅可以实现污泥的无害化处理,还能降低原本处理成本节约资源.
-
本文综述了污泥热解条件变化对污泥基生物炭物化性质和土壤改良效益的影响. 碱土金属、生物质与污泥共热解能使磷转化为土壤有效磷,还能通过与正磷酸盐、羟基化合物、金属氧化物等结合的方式固定污泥本身含有的重金属,并且污泥中含有的多环芳烃、全氟化合物等物质经过热解去除率可以达到90%及以上. 热解的温度会影响污泥基生物炭的pH、孔径大小和比表面积,而通过调控共热解添加物不仅可以定向调配污泥基生物炭中磷和重金属的存在形态还能增大其比表面积,优化孔隙结构. 热解一般采用氮气为主的惰性气氛以实现污泥的定向热解,而采用CO2热解气氛相比氮气能形成更丰富和优化的孔隙结构且降低反应的活化能. 因此,通过调控热解条件可调控污泥基生物炭的特性以应用不同场景,例如污泥与生物质的共热解能用来改良盐碱地;提高热解温度,可以增大污泥基生物炭的pH用来改善土壤酸化;而碱土金属共热解制备的污泥基生物炭具有缓释磷肥的功效同时还能吸附重金属及有机污染物,降低土壤生态风险修复受污染土壤.
污泥定向热解富集磷的机理目前已经研究较多,且对污泥基生物炭重金属最终形态也有所了解,但是在污泥热解过程中重金属的迁移转化机制还有待进一步明确,关于磷和重金属在热解过程中存在的关联机制也尚不清楚,还需要进一步研究. 另外,将污泥热解产物转化为增值产品仍然存在实际运行困难. 基于此,本综述提出以下展望:明确重金属在污泥热解过程中的动力学过程,以及P与重金属之间的关联转化机制对其安全土壤回用尤为重要;热解产物生物气、生物油也应该实现同步回收,它们也应该被进一步加工利用,可以代替普通肥料、气体燃料及交通燃料. 因此,需要对热解工艺进一步研究和创新,明确重点元素迁移转化机制指导实现生物炭的定向制备,降低污泥处理成本并将其转化为可增值产品,使污泥在资源回收利用中由小规模向大规模发展.
污泥共热解制备污泥基生物炭及其在土壤回用中的改良效益
Directional pyrolysis of sludge to prepare sludge-based biochar with soil improvement function
-
摘要: 随着全球污泥产量的快速增长,对其的资源化处置是亟待解决的现实问题. 相较于传统的填埋以及新型的焚烧工艺,污泥热解可实现污泥的无害化、减量化并生成具有土壤改良潜力的污泥基生物炭,是污泥处理的一种较优选择. 本文以市政污泥为研究对象,全面综述了污泥不同热解方法对生成污泥基生物炭的物化性质和其对土壤改良效应的影响,重点介绍了污泥中磷和重金属在不同热解工艺中的迁移转化机制,污泥基生物炭对土壤物化性质的影响机理、对污染土壤的修复机制、对土壤中微生物和微生物酶等的作用机制. 通过以上分析,能够以此为理论支撑指导制备具有定向改良土壤功能的污泥基生物炭. 本综述将有助于污泥定向热解制备污泥基生物炭的进一步发展,为污泥基生物炭土壤改良提供理论参考和支持.Abstract: With the rapid growth of global sludge production, how to recycle it into resource is an urgent realistic problem. Compared with traditional direct landfill disposal and incineration, pyrolysis of sewage sludge is a superior disposal method not only because it can realize the harmlessness and reduction of sludge, but also can generate sludge biochar, which has potential value for soil improvement. In this paper, the effects of different pyrolysis methods on sludge properties and soil improvement effects were comprehensively reviewed. The migration and transformation mechanisms of phosphorus and heavy metals in pyrolysis of sewage sludge, the effects of sewage sludge biochar on soil characteristics, the remediation mechanisms of sewage sludge biochar on heavy metal and organic contaminated soil, and the effects of sewage sludge biochar on soil microorganisms and microbial enzymes were mainly introduced. Through the above analysis, this can be used as a theoretical support to guide the preparation of sludge-based biochar with the function of directional soil improvement. This review will contribute to the further studies of tailored pyrolysis of sewage sludge, and provide theoretical reference and support for using sewage sludge biochar in soil improvement.
-
生态滤坝是指用砾石或碎石在河道中垒筑坝体,通过砾石碎石等的拦截吸附作用以及其表面形成生物膜的降解作用以降解水体氮、磷等营养物质。同时,滤坝还可以调节透过坝体径流量,从而实现径流拦截[1]和控制雨水径流等作用。滤坝技术作为一种新型的污染物拦截和水体生态修复技术,已成功应用于微污染水体[2-3]、山溪性河流[4-5]、雨水[6]和二级生化尾水[7]等不同水体的拦截净化。此外,水质跟踪监测结果表明,滤坝应用于水体治理均具有较为明显的净化效果[4,7-8]。传统的原位拦截技术,如人工湿地、生物滞留池、缓冲带等,虽具有技术成熟、去除效率高、运行稳定等优势,但对于人口和河网较为密集的区域存在工程量大和占地面积大[4]等局限性。滤坝则因具备占地面积小、操作简单、人工投入少等特点[9-11],在河网和人口密集区域有较好的应用潜力。
与人工湿地依靠水力负荷和基质孔隙率进行设计不同,滤坝理论设计主要依赖于渗流力学中的渗流方程和达西定律[1,8]。而滤坝基质的选择目前主要以人工湿地基质研究为基础,通常选择疏松多孔、有生物亲和性、廉价易得的材料[2,12],如沸石、火山石、炉渣和钢渣等。滤坝一方面可通过基质的挡隔作用减缓水流,促进营养物质发生沉降;另一方面,其基质可吸附水体营养物并在表面形成的生物膜,进而降解营养物质[13-16],从而达到净化水体的作用。此外,被修复水体还可利用滤坝前后的水位差增加水体扰动[4,8,17],促进水体复氧[18],提高水体自我修复能力[19]。
影响滤坝净化效果的主要因素有基质材料、坝体坡度、坝体厚度、基质组合配置等。基质材料一般选择疏松多孔、具有生物亲和性的材料。此外,在滤坝中构建原电池可显著提升净化效率。李阳阳[2]通过在普通滤坝中添加铁屑和活性炭,显著提升了滤坝的净化效果,尤其是微污染水体中化学需氧量去除率由20%提升至39%。坝体坡度可通过直接影响微生物载体基质量和渗流量而影响其净化效果。张文生等[19]通过构建3个坡度梯度的生态滤坝发现,20°坡度滤坝的基质量最多,其净化效率也最高;而25°坡度滤坝由于渗流量过大,生物膜容易脱落,因此净化效果最差。刘露等[20]通过构筑不同厚度的滤坝发现,基质厚度越大,基质量越多,其吸附能力和生物挂膜量也越多,因此,净化效果越好,防堵性能最佳。基质组合配置方式通常有2种:基质均匀混合模式和上下分层模式。于鲁冀等[3]通过构筑分层滤坝和普通混合滤坝净化清潩河河水,结果表明,基质均匀混合的模式显著地提高了滤坝净化效率。
在滤坝中,水流几乎与河道平行,但以往在大多数滤坝的研究中,基质多采用均匀混合[3,6,19]或上下分层[2]的模式,鲜有研究沿水流方向先后分布不同的基质对水质净化效果的影响。因此,本文通过构建3个室内滤坝小试系统,选用常用的且已被证实具有较好氨氮吸附效果的火山石[21-22]和具有较好总磷吸附效果的炉渣[2,23]为填料,采用水平方向进出水来探究了基质排布模式对滤坝净化效果的影响,并基于不同污染物的去除效果,提出了相应的基质组合建议。此外,基于对基质细菌群落的分析,初步探讨了相应的污染物净化机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置和基质材料
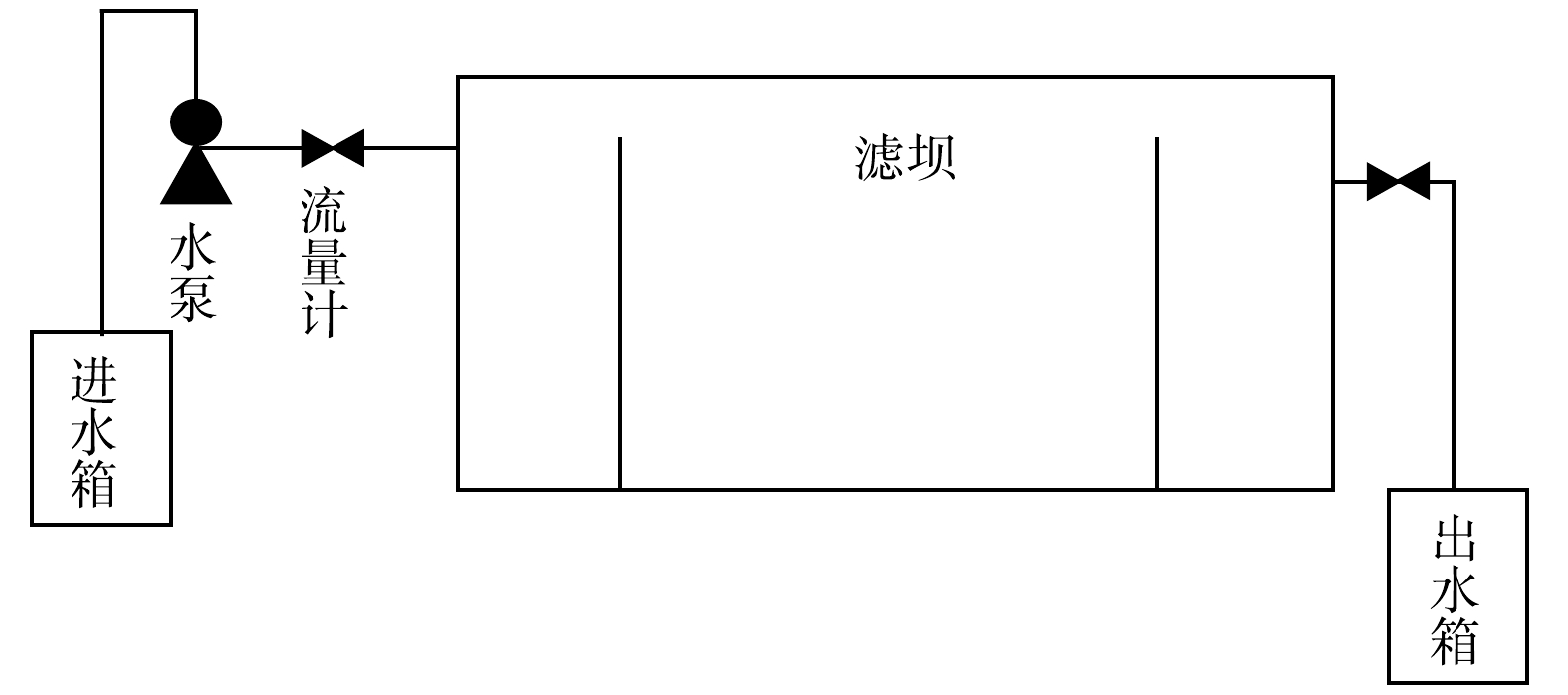
实验装置由 10 mm 厚的有机玻璃制成,装置尺寸的长、宽、高分别为60、20、30 cm。装置内设配水区、基质区和出水区,3个区域的体积之比为 1∶4∶1,配水区与基质区和基质区与出水区均采用穿孔挡板分开,穿孔挡板为每隔1 cm2 分布1个孔,圆孔直径为 4 mm。滤坝装置尺寸与基质区如图1所示。
基质区填料火山石和炉渣均购自巩义市紫荆龙腾滤材经销部,粒径均为 10~20 mm,用去离子水清洗并浸泡 24 h,再用无水乙醇清洗并浸泡 24 h,用去离子水清洗后,于60 ℃烘干备用。滤坝基质区基质的排布方式分别为沿水流方向火山石和炉渣均匀混合(HL)、沿水流方向先火山石后炉渣(H-L)和沿水流方向先炉渣后火山石(L-H)。
1.2 实验配水
实验所用水为模拟《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级标准A标准排水,自来水中加入分析纯级的葡萄糖(C6H12O6·H2O)、氯化铵(NH4Cl)、硝酸钠(NaNO3)和磷酸氢二钾(K2HPO4·3H2O),所得水样的目标质量浓度及实际质量浓度如表1所示。
表 1 配制进水目标质量浓度及实际质量浓度Table 1. Target and actual concentration of influent watermg·L−1 配水 COD TN TP NH3-N 目标配水 50 15 0.5 5 实际配水 39.4~55.6 11.3~19.0 0.474~0.700 4.79~6.97 1.3 装置运行
运行方式为连续进水,参照以往研究,该实验水力停留时间设为8 h[8]。实验装置利用水泵、流量计控制滤坝进出水的流量和流速,由水泵抽取进水箱中的水进入进水区,经过基质区后,由出水区流出至出水箱中,滤坝装置的构建示意图如图2所示。实验期间,每隔48 h 清洗进出水管、进出水区和水箱,防止生物膜堵塞和污染。预运行时间为2019-12-03—2019-12-09,此期间实验用水为自来水,水力停留时间为8 h,目的是清洗填料以及装置中的有机物和氮磷等。正式运行时间为2019-12-10—2020-01-17,每2 d取1次进水水样和出水水样,进水水样采自进水水箱,出水水样采自出水水管。取样时间为当天9:00—11:00,水样用500 mL聚乙烯瓶收集,在24 h内进行分析。实验结束时共取样20次。
1.4 样品采集与分析
测定指标为总氮(total nitrogen, TN)、总磷(total phosphorus, TP)和氨氮(ammonium nitrogen, NH3-N)、重铬酸盐指数(dichromate oxidizability, COD)。TN采用碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法(HJ 626-2012);TP采用过硫酸钾消解一钼酸铵分光光度法(GB 11893-1989);NH3-N采用纳氏试剂分光光度法(HJ 636-2012);三者测定仪器均为多波长紫外可见分光光度计(GENESYS-180型,赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司)。COD采用快速消解分光光度法(HJ/T 399-2007),消解仪器为COD消解仪(DRB200-30型,哈希水质分析仪器上海有限公司),测定仪器为紫外分光光度计(UV-1200型,上海美谱达仪器有限公司)。实验结束时,分别从3个滤坝中距离水面0~5 cm处采集炉渣和火山石,每个滤坝均采用梅花点法采集5个点,混合均匀后放入−80 ℃冰箱保存。HL滤坝中所采集的炉渣和火山石样品标记为HL_L和HL_H,H-L滤坝中所采集的炉渣和火山石分别标记H-L_L和H-L_H,L-H滤坝中所采集样品的炉渣和火山石分别标记为L-H_L和L-H_H,将此6个样品送往生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行微生物宏基因组测序及微生物多样性分析。实验数据的处理使用Microsoft Excel 2019,图表的绘制使用Origin 2018、Microsoft PowerPoint 2019和Microsoft Word 2019,方差分析采用SPSS 24。去除率根据式(1)和式(2)进行计算。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) 式中:
Ri ¯R C C0 n i 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 基质排布方式对TN去除效果的影响
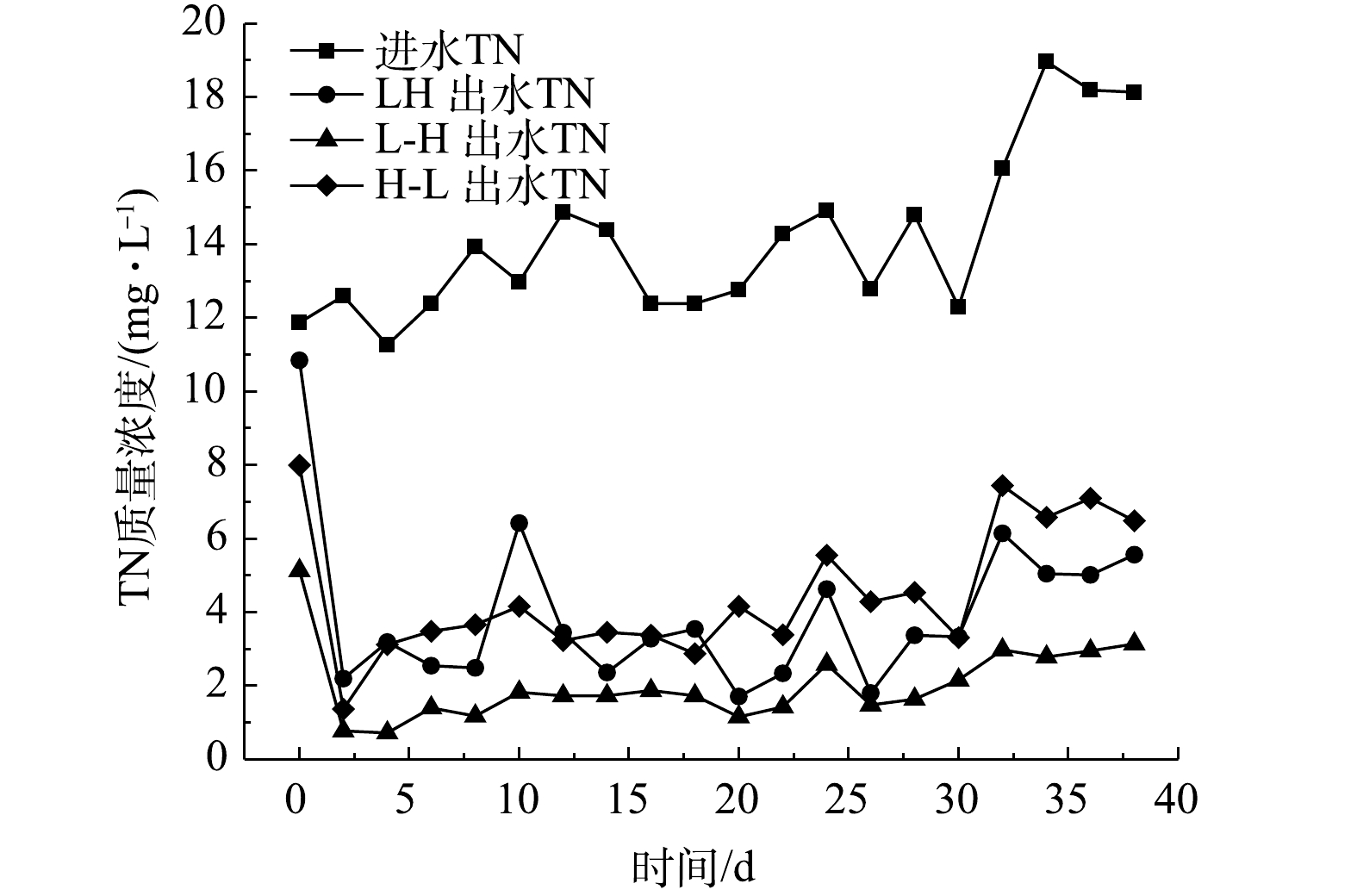
3个滤坝装置进出水的TN质量浓度变化见图3。由图3可知,TN进水质量浓度为11.3~19.0 mg·L−1时,HL、H-L和L-H系统的出水质量浓度分别为(3.96±2.10)、(2.02±1.00)和(4.48±1.73) mg·L−1。系统运行前2 d,TN的出水质量浓度迅速降低。在20 ℃下,生物膜的形成至少需要5 d,因此,此时系统对无机氮(氨氮和硝态氮)的去除主要依靠填料的吸附作用[24-26]。在运行14 d以后,出水质量浓度趋于稳定,且对TN具有良好的去除效果,表明此时系统已经形成生物膜。当系统运行至第6周时,进出水质量浓度均有所升高,这可能是因为生物膜累积过厚,老旧生物膜脱落,释放污染物造成二次污染水体。在柴宏祥等[17]的研究中,也观察到类似情况。此外,TN出水质量浓度会随着进水质量浓度升高而升高。在实验的前5周,L-H滤坝TN平均去除率高达85.7%,显著高于其他2组(P < 0.05);而HL滤坝和H-L滤坝无显著差异,TN去除率分别为70.3%和69.3%。这表明基质的排布方式可显著影响滤坝对TN的去除效果,且L-H排布模式优于其他2种排布模式。因此,对于TN质量浓度较高的水体,可优先采用L-H排布模式。但需要注意的是,在HL排布模式中,TN的出水质量浓度波动比其他2组要大,出水质量浓度不太稳定。此外,本实验中TN的去除率高于以往的研究结果[3-5,8,19,27-28]。其原因可归为2点:首先,滤坝内水体流速极为缓慢,而且滤坝中基质区较厚, 基质的堆积有利于扩充系统内的缺氧区[20],硝态氮的去除依赖于系统中反硝化菌在缺氧环境中的反硝化作用以及系统填料的吸附作用,从而可促进反硝化菌大量繁殖和硝态氮的去除;其次,系统的水力停留时间比较长,也使得反硝化进行地比较充分。
2.2 基质排布方式对TP去除效果的影响
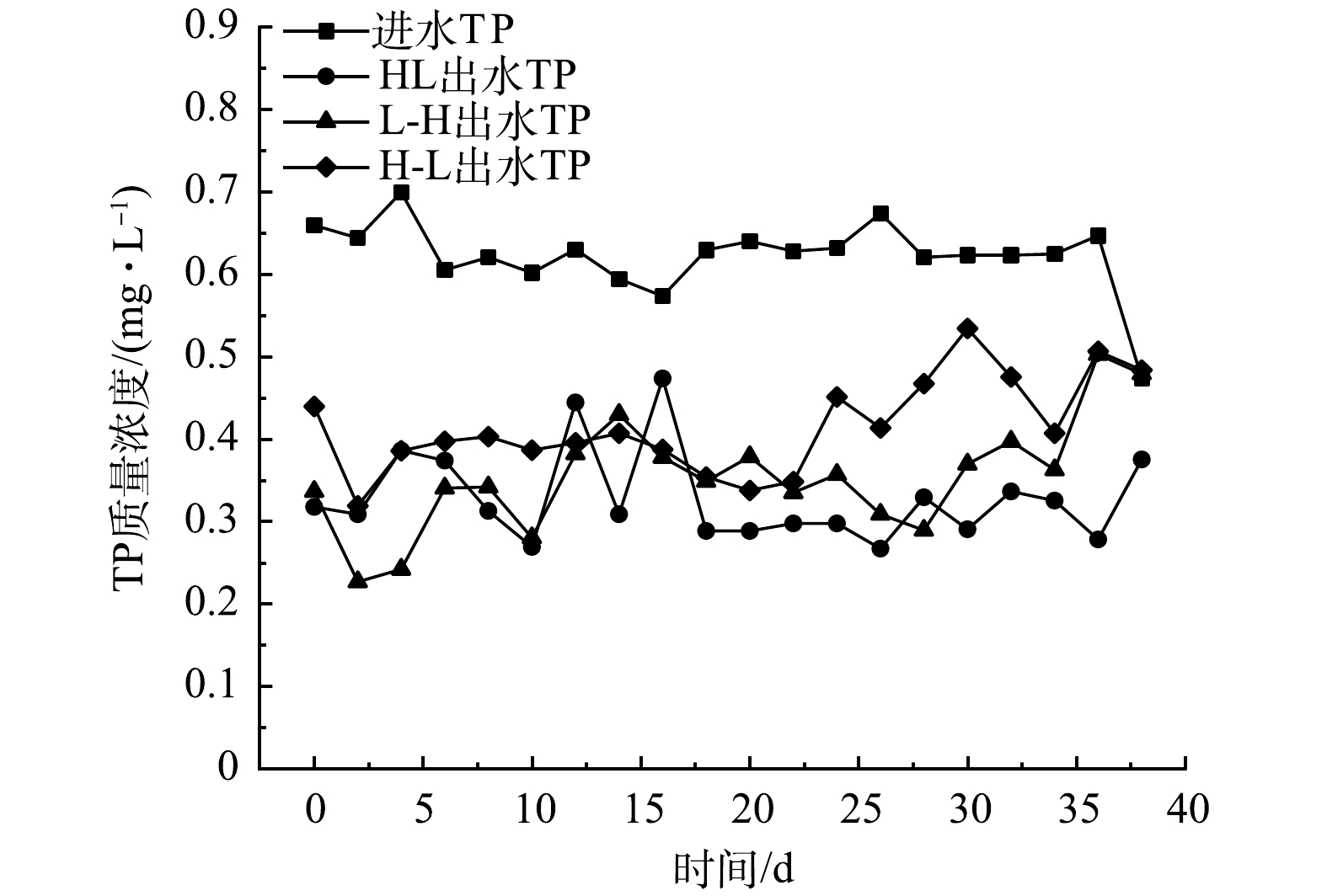
3个滤坝装置进出水的TP质量浓度变化见图4。由图4可知,TP进水质量浓度为0.474~0.700 mg·L−1,HL、H-L和L-H系统的出水质量浓度分别为(0.328±0.0546)、(0.354±0.0667)和(0.415±0.0558) mg·L−1。滤坝中TP的去除主要依赖于微生物除磷和填料的吸附作用[29],TP的出水质量浓度在前2 d迅速降低主要是依赖于火山石和炉渣对TP的吸附作用,而当填料达到吸附饱和之后,则去除能力缓慢降低。第5周时,TP去除率缓慢提升,此时微生物膜形成且稳定,有利于TP的去除。SPSS数据统计结果表明,在HL系统中,TP平均去除率高达46.7%,显著高于另外2组(P < 0.05),其余2组的去除率分别为42.3%(HL)和32.7%(L-H)。以上结果表明,基质的排布方式可显著影响滤坝对TP的去除效果,且HL排布模式比其他2种模式更有优势。因此,对于TP浓度较高的水体时,可优先采用HL排布模式。但HL系统出水质量浓度相较于其他2个系统波动较大,且稳定期较长。第12天时,H-L滤坝和L-H滤坝达到稳定,但在第18天时,HL滤坝才达到稳定。
2.3 基质排布方式对NH3-N去除效果的影响
3个滤坝装置进出水的NH3-N质量浓度变化见图5。由图5可知,NH3-N进水质量浓度为4.79~6.97 mg·L−1,HL、H-L和L-H系统的出水质量浓度分别为(2.88±0.474)、(3.02±0.807)、(3.37±0.823) mg·L−1。NH3-N的平均去除率分别为47.2%(HL)>44.6%(H-L)>38.8%(L-H),但3种排布模式下的NH3-N去除率差异不显著 (P<0.05)。以上结果表明,基质的排布方式不会影响滤坝对NH3-N的去除效果,因此,若针对氨氮含量较高的水体,采用3种基质排布模式并无显著差异。装置运行第2天时,NH3-N出水质量浓度迅速降低至整个运行期间的最小值,由于此时还未形成成熟的生物膜,由此可推测,此时系统以基质的吸附为主要作用。而后,由于基质中的铵根离子不断向水体中释放,NH3-N出水质量浓度不断升高,由于系统中微生物的繁殖,生物膜不断形成,NH3-N去除率则不断升高,并在运行第18天后,NH3-N出水质量浓度趋于稳定,并且维持较高的去除率。此外,在HL排布系统中,整个阶段的NH3-N平均去除效率最高,出水质量浓度也相较于其他2个系统稳定。整体而言,3个滤坝装置的NH3-N去除率呈现先逐渐升高后缓慢降低的趋势。因为基质上的吸附位点随着系统的运行而不断减少,故吸附速率变缓,导致出水中NH3-N的浓度缓慢上升[30-31]。另外,装置内水体流动较为缓慢,水体中溶解氧有限,因此也限制了NH3-N向亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐转化,造成了出水质量浓度在后期缓慢上升。
2.4 基质排布方式对COD去除效果的影响
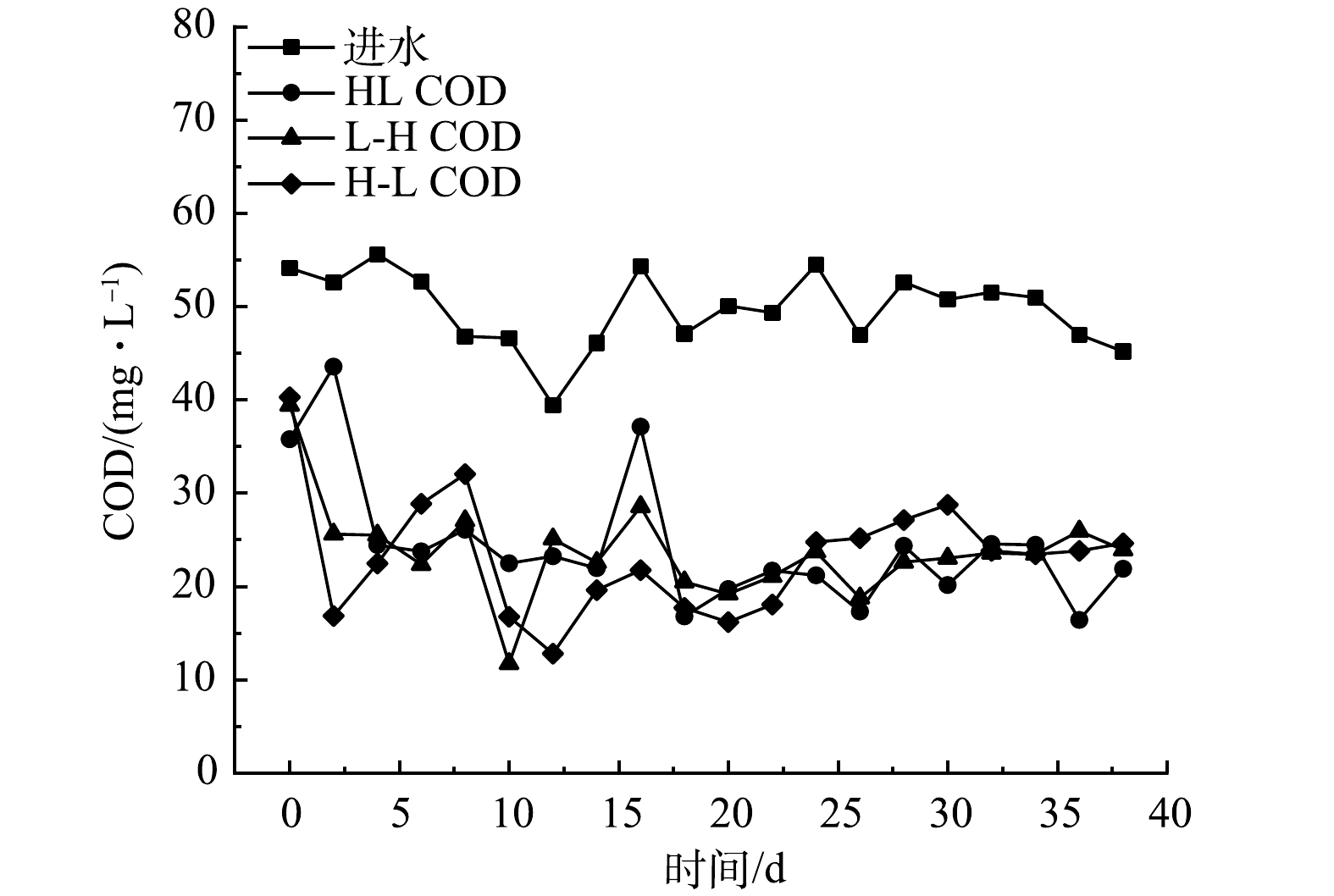
3个滤坝装置进出水的耗氧有机污染物的质量浓度(以COD计)变化情况见图6。由图6可知,3个滤坝系统进水COD值为39.4~55.6 mg·L−1,HL、H-L和L-H系统的出水COD值分别为(24.3±6.74)、(23.7±5.03)和(23.2±6.20) mg·L−1。在整个正式运行期间,3个滤坝系统对COD的平均去除率分别为53.4%(L-H)>52.3%(H-L)>51.2%(HL),但系统间差异不显著(P<0.05)。此结果表明,对于COD较高的水体,3种排布模式下净化效率无明显差异。实验结束时,3个系统的出水COD均值均达到了《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838-2002)Ⅳ类水。滤坝正式运行第1周,出水COD值迅速降低;第8天时,H-L滤坝出水COD值高于运行刚开始阶段,这可能是因为填料吸附的有机物向水体释放导致水体耗氧有机污染物质量浓度升高。在3个系统运行到第18天时,出水COD值均趋于稳定,表明此时3个滤坝系统已经稳定运行。以往统计结果[32]表明,滤坝对COD的去除率为10%~20%。而本研究的COD去除率远高于这一值,这是因为相对于实际可生化性较低的水体,本实验水体中耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)来源为葡萄糖,更有利于微生物降解。
2.5 基质微生物群落及多样性分析
滤坝排布方式对细菌多样性并没有显著的影响,但改变了细菌在属水平上的相对丰度,细菌在属水平上的丰度见图7。由图7可知,在HL滤坝中,火山石和炉渣的微生物优势菌种均为气单胞菌属(Aeromonas),占比分别为53.8%和51.4%。周岳溪等[33]的研究表明,气单胞菌属为除磷微生物的优势种属。在HL滤坝中,TP的去除效率明显高于其他2个系统,可能与该系统中气单胞菌属的相对丰度较高有关。H-L滤坝和L-H滤坝优势种均发生了改变,4个样品的优势菌均为肠杆菌属(Enterobacter)。在H-L滤坝中,火山石(H-L_H)的肠杆菌属占比为66.6%,其次为假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas),占比为8.83%;炉渣(H-L_L)的肠杆菌属占比为49.9%,气单胞菌属占比为8.1%。在L-H滤坝中,火山石(L-H_H)的肠杆菌属占比为64.3%,气单胞菌属占比为9.69%;炉渣(L-H_L)的肠杆菌属占比为53.9%,其次假单胞菌属占比为18.8%。肠杆菌属可发酵葡萄糖,产酸产气,可将硝酸盐还原至亚硝酸盐[34],最后产生N2[35],这可能是L-H滤坝TN的去除率明显高于HL滤坝的原因。此外,这2个系统中接触进水端的基质(H-L_H、L-H_L)假单胞菌属的相对丰度均较高。这与本研究中进水端的进水管和水面之间有7 cm距离有关,水位差造成了一定的扰动,增加进水区的溶解氧,因为假单胞菌是一类具有硝化和反硝化、可降解多种有机物的能力的严格好氧细菌[36-40],溶解氧浓度越高,越有利于假单胞菌属的繁殖。
3. 结论
1)当水力停留时间为8 h时,采用水平方向进出水的火山石和炉渣填料滤坝对TN、TP、NH3-N、COD具有良好的去除效果,但在不同的基质排布模式间仅TN和TP的去除率差异显著。
2)对于TN污染程度相对较高的水体,可优先采取沿水流方向先炉渣后火山石的排布模式;而对于TP指标较高的水体来说,炉渣和火山石均匀混合的模式更有利于TP的去除。
3)沿水流方向炉渣火山石均匀混合滤坝的优势菌种为气单胞菌属,这可能是导致该系统TP去除效果较好的原因;而沿水流方向先炉渣后火山石的滤坝TN去除效果相对较好,这与该系统的优势菌种为可反硝化产N2的肠杆菌属有关。此外,在沿水流方向先后排布炉渣和火山石的2个系统中,进水端基质中好氧菌-假单胞菌属相对丰度比出水端高,主要是因为水体扰动造成进水端溶解氧浓度较高。
-
表 1 不同添加物对磷、重金属形态以及产率的影响
Table 1. Effects of different additives on phosphorus and heavy metal speciation and yield
共热解添加物Co-pyrolysis additives 污泥/生物质Sludge/biomass 热解温度/℃Pyrolysis temperature 升温速率/(℃·min−1)Heating rate 热解时长/hSoaking time H/C O/C pH 产率/%Yield 磷、重金属存在形态Forms of phosphorus and heavy metals 比表面积/(m2·g−1)Specific surface area 参考文献Reference 生物质 食物残渣 3:1 550 10 1 0.06 0.41 8.70 65.70 — 18.95 [30] 2:2 0.05 0.56 8.60 69.50 18.74 1:3 0.08 1.00 8.70 73.10 21.99 木屑 9:1 500 — 2 0.21 0.30 9.30 60.10 PbAl2O4、CdAl2O4 — [31] 7:3 0.09 0.09 9.20 50.70 — 5:5 0.08 0.03 9.10 44.10 — 棉花秸秆 9:1 650 — 2 0.86 — 9.40 57.50 — 23.75 [32] 7:3 0.69 — 9.30 51.00 25.50 5:5 0.60 — 9.20 45.00 31.25 3:7 0.55 — 9.10 38.00 31.75 1:9 0.48 — 9.00 32.50 33.75 碱土金属 CaO Ca/P=1.41 700 10 2 — — — — Ca5(PO4)3OH — [33] Ca/P=1.67 Ca/P=1.91 CaO/Fe2O3 Fe2O3/CaO=4:1 450 — — — — — — Ca(AsO2)2 — [34] 650 — 850 8.97 磷酸盐 K3PO4 1:5 500 10 3 0.11 — 11.10 49.70 KMgPO4、K4P2O7、KCaPO4 — [36] 塑料 聚氯乙烯 19:1 400 10 2 0.88 0.53 4.00 70.70 金属氯化物 — [37] 3:1 0.73 0.37 2.90 62.00 1:3 0.99 0.22 2.90 36.40 载金属聚氯乙烯 19:1 0.90 0.61 7.00 72.40 — 3:1 1.84 0.84 7.20 73.30 1:3 2.76 0.91 10.90 73.80 表 2 热解温度对污泥基生物炭孔隙结构的影响
Table 2. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on the pore structure of sludge-based biochar
热解物质Pyrolysis material 热解温度/℃Pyrolysis temperature 升温速率/(℃·min−1)Heating rate 热解时长/hSoaking time pH 孔隙结构Pore structure 参考文献Reference 污泥 700 25 5 — 平均孔径 6.61 nm比表面积 54.05 m2·g−1 [44] 污泥 500 25 5 — 平均孔径 9.28 nm比表面积 31.81 m2·g−1 污泥/柳木=8:2 700 10 3 12.5 比表面积 99.0 m2·g−1 [45] 污泥/柳木=6:4 700 10 3 12.5 比表面积 104.1 m2·g−1 污泥/棉花秸秆=1:9 650 — 2 9 平均孔径为3—4 nm比表面 ~33 m2·g−1总孔体积 ~0.071 m3·g−1 [48] 污泥/棉花秸秆=3:7 650 — 2 9 平均孔径为3—4 nm比表面 ~33 m2·g−1总孔体积 ~0.065 m3·g−1 -
[1] 丁洪, 余居华, 郑祥洲, 等. 中国城市污泥应用对作物产量、品质和土壤质量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1933-1942. DING H, YU J H, ZHENG X Z, et al. Review on effect of municipal sewage sludge application on yield and quality of crops and soil quality in China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(9): 1933-1942 (in Chinese).
[2] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 2022年城乡建设统计年鉴[EB/OL]. [2023-11-16]. [3] FANG L, WANG Q M, LI J S, et al. Feasibility of wet-extraction of phosphorus from incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) for phosphate fertilizer production: A critical review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 51(9): 939-971. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2020.1740545 [4] CHU X, NI Y, WANG X, et al. A win-win situation for environment and economy: Analysis of maximizing benefits in municipal sludge treatment plants[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 419: 138271. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138271 [5] 肖懿, 王理明, 李东阳, 等. 市政污泥热解特性及含碳官能团演化过程分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(5): 1589-1598. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202211170 XIAO Y, WANG L M, LI D Y, et al. Pyrolysis characteristics of municipal sludge and transformation of carbon-containing functional groups during pyrolysis process[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2023, 17(5): 1589-1598 (in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202211170
[6] HU A B, ZHENG Y L, WANG Z, et al. Tracking the transformation pathway of dissolved organic matters (DOMs) in biochars under sludge pyrolysis via reactomics and molecular network analysis[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 342: 140149. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.140149 [7] 张吉琛, 刘婷然, 董志强, 等. 污泥生物炭的催化机理及应用研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(6): 2018-2031. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022120203 ZHANG J C, LIU T R, DONG Z Q, et al. Mechanism and application for removal of contaminants by sludge-derived biochar catalyst: A review[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(6): 2018-2031 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022120203
[8] FANG L, YAN F, CHEN J J, et al. Novel recovered compound phosphate fertilizer produced from sewage sludge and its incinerated ash[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(17): 6611-6621. [9] ZHANG W Q, HE Y H, XING X X, et al. In-depth insight into the effects of intrinsic calcium compounds on the pyrolysis of hazardous petrochemical sludge[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 455: 131593. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131593 [10] LI J, PAN L J, LI Z W, et al. Unveiling the migration of Cr and Cd to biochar from pyrolysis of manure and sludge using machine learning[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 885: 163895. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163895 [11] FANG L, LI J S, DONATELLO S, et al. Recovery of phosphorus from incinerated sewage sludge ash by combined two-step extraction and selective precipitation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 348: 74-83. [12] 张洁, 张少逸, 梁学峰, 等. 污泥热解生物炭中重金属化学形态分布的影响因素研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(10): 3254-3266. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021070402 ZHANG J, ZHANG S Y, LIANG X F, et al. Research progress on influence factors on heavy metals chemical speciation distribution in sludge pyrolysis biochar[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(10): 3254-3266 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021070402
[13] FANG L, LI J S, DONATELLO S, et al. Use of Mg/Ca modified biochars to take up phosphorus from acid-extract of incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) for fertilizer application[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 244: 118853. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118853 [14] MA C W, ZHANG F X, HU J H, et al. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and waste tobacco stem: Gas products analysis, pyrolysis kinetics, artificial neural network modeling, and synergistic effects[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 389: 129816. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129816 [15] 卢欢亮, 叶向东, 汪永红, 等. 热解温度对污泥生物炭的表面特性及重金属安全性的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(3): 1433-1439. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150373 LU H L, YE X D, WANG Y H, et al. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on surface properties and heavy metal safety of sludge-derived biochar[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2015, 9(3): 1433-1439 (in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150373
[16] 赵佳琪, 黄亚继, 李志远, 等. 污泥和聚氯乙烯共热解三相产物特性[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(4): 2122-2129. ZHAO J Q, HUANG Y J, LI Z Y, et al. Characteristics of three-phase products from co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and PVC[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(4): 2122-2129 (in Chinese).
[17] 王玉, 余广炜, 汪刚, 等. 污泥与不同添加剂共热解对重金属的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2022, 45(3): 163-170. WANG Y, YU G W, WANG G, et al. Effects of co-pyrolysis of sludge and different additives on heavy metals in biochar[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 45(3): 163-170 (in Chinese).
[18] 郭江山, 顾卫华, 白建峰, 等. 污泥与磷酸二氢钙共热解对残渣特性及Cr稳定性的影响[J]. 环境工程, 2022, 40(3): 45-50,88. GUO J S, GU W H, BAI J F, et al. Effect of co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and ca(h2po4)2 on residue characteristic and chromium stability[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2022, 40(3): 45-50,88 (in Chinese).
[19] HUANG C, MOHAMED B A, LI L Y. Comparative life-cycle energy and environmental analysis of sewage sludge and biomass co-pyrolysis for biofuel and biochar production[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal , 2023, 457: 141284. [20] MENG J T, WANG J, YANG F L, et al. Study on the multiple roles of CaO on nitrogen evolution mechanism of protein inside sewage sludge pyrolysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 458: 141039. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.141039 [21] 李志远, 黄亚继, 赵佳琪, 等. 污泥与聚氯乙烯共热解重金属特性[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(9): 4947-4956. LI Z Y, HUANG Y J, ZHAO J Q, et al. Characterization of heavy metals during co-pyrolysis of sludge with PVC[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(9): 4947-4956 (in Chinese).
[22] LING C C Y, LI S F Y. Synergistic interactions between sewage sludge, polypropylene, and high-density polyethylene during co-pyrolysis: An investigation based on iso-conversional model-free methods and master plot analysis[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 455: 131600. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131600 [23] 李娜, 张惠民, 孟记朋, 等. 污泥与不同生物质共热解制备生物炭及生物炭的土地应用[J]. 可再生能源, 2018, 36(10): 1423-1430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5292.2018.10.001 LI N, ZHANG H M, MENG J P, et al. Preparation of biochar from sewage sludge with different biomass by co-pyrolysis and its land application[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2018, 36(10): 1423-1430 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5292.2018.10.001
[24] 赵学强, 潘贤章, 马海艺, 等. 中国酸性土壤利用的科学问题与策略[J]. 土壤学报, 2023, 60(5): 1248-1263. ZHAO X Q, PAN X Z, MA H Y, et al. Scientific issues and strategies of acid soil use in China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2023, 60(5): 1248-1263 (in Chinese).
[25] 葛锋, 张转霞, 扶恒, 等. 我国有机污染场地现状分析及展望[J]. 土壤, 2021, 53(6): 1132-1141. GE F, ZHANG Z X, FU H, et al. Distribution of organic contaminated sites in China: Statu quo and prospect[J]. Soils, 2021, 53(6): 1132-1141 (in Chinese).
[26] 苏加强, 汪淼, 曲自超, 等. 污泥/凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对土壤重金属的钝化效果研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2023, 48(9): 88-93. SU J Q, WANG M, QU Z C, et al. Stabilization efficiency of biochar prepared by co-pyrosis with sludge and attapulgite on heavy metals in soils[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2023, 48(9): 88-93 (in Chinese).
[27] FANG L, LI J S, GUO M Z, et al. Phosphorus recovery and leaching of trace elements from incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA)[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 193: 278-287. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.023 [28] 王旭东, 任雪冰, 汤舒, 等. 污泥生物炭在土壤改良中的应用研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 165-173. WANG X D, REN X B, TANG S, et al. Application of sludge biochar in soil improvement[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 165-173 (in Chinese).
[29] 曹秀芹, 刘丰, 柴莲莲, 等. 污泥生物炭制备与其对土壤环境影响的研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2022, 40(3): 203-211. CAO X Q, LIU F, CHAI L L, et al. Research progress on preparation of sludge based biochar and its effect on soil environment[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2022, 40(3): 203-211 (in Chinese).
[30] WANG X D, CHANG V W C, LI Z W, et al. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and food waste digestate to synergistically improve biochar characteristics and heavy metals immobilization[J]. Waste Management, 2022, 141: 231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2022.02.001 [31] YANG Y Q, CUI M H, REN Y G, et al. Towards understanding the mechanism of heavy metals immobilization in biochar derived from co-pyrolysis of sawdust and sewage sludge[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2020, 104(4): 489-496. doi: 10.1007/s00128-020-02801-4 [32] WANG Z P, SHU X Q, ZHU H N, et al. Characteristics of biochars prepared by co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and cotton stalk intended for use as soil amendments[J]. Environmental Technology, 2020, 41(11): 1347-1357. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2018.1534891 [33] TANG S Q, LIANG J M, XU X M, et al. Targeting phosphorus transformation to hydroxyapatite through sewage sludge pyrolysis boosted by quicklime toward phosphorus fertilizer alternative with toxic metals compromised[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 183: 113474. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113474 [34] HAN H D, HU S, LU C F, et al. Inhibitory effects of CaO/Fe2O3 on arsenic emission during sewage sludge pyrolysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 218: 134-139. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.075 [35] 田天. 磷酸盐共热解污泥基生物炭的理化性质研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021. TIAN T. Study on the Physicochemical Properties of Phosphate Copyrolyzed Sewage Sludge-based Biochar[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2021 (in Chinese).
[36] HUANG H J, YANG T, LAI F Y, et al. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and sawdust/rice straw for the production of biochar[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2017, 125: 61-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2017.04.018 [37] LI W J, MENG J, ZHANG Y L, et al. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and metal-free/metal-loaded polyvinyl chloride (PVC) microplastics improved biochar properties and reduced environmental risk of heavy metals[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 302: 119092. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119092 [38] JINDAROM C, MEEYOO V, RIRKSOMBOON T, et al. Thermochemical decomposition of sewage sludge in CO2 and N2 atmosphere[J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 67(8): 1477-1484. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.066 [39] 蔡旭, 黄群星, 王飞, 等. 污泥在CO2气氛下热解CO与CH4的生成特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(7): 3779-3786. CAI X, HUANG Q X, WANG F, et al. CO and CH4 emission characteristics during sewage sludge pyrolysis in CO2 atmosphere[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(7): 3779-3786 (in Chinese).
[40] HUANG L M, LIU J Y, HE Y, et al. Thermodynamics and kinetics parameters of co-combustion between sewage sludge and water hyacinth in CO2/O2 atmosphere as biomass to solid biofuel[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 218: 631-642. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.133 [41] 徐智, 郭朝晖, 徐锐, 等. 控氧热解过程中污染稻草生物炭的组分特性及其重金属累积特征[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(2): 1051-1062. XU Z, GUO Z H, XU R, et al. Component properties and heavy metal accumulation characteristics of contaminated rice straw biochar during oxygen-controlled pyrolysis[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(2): 1051-1062 (in Chinese).
[42] CHEN J C, ZHANG J H, LIU J Y, et al. Co-pyrolytic mechanisms, kinetics, emissions and products of biomass and sewage sludge in N2, CO2 and mixed atmospheres[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 397: 125372. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125372 [43] 张琳, 姚锡文, 刘清华, 等. 热解温度和气氛对松木屑热解气化特性的影响研究[J]. 能源与节能, 2022(5): 24-26,49. ZHANG L, YAO X W, LIU Q H, et al. Effects of pyrolysis temperature and atmosphere on pyrolysis and gasification characteristics of pine sawdust[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation, 2022(5): 24-26,49 (in Chinese).
[44] ZIELIŃSKA A, OLESZCZUK P. Attenuation of phenanthrene and pyrene adsorption by sewage sludge-derived biochar in biochar-amended soils[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(21): 21822-21832. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7382-x [45] KOŃCZAK M, GAO Y Z, OLESZCZUK P. Carbon dioxide as a carrier gas and biomass addition decrease the total and bioavailable polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in biochar produced from sewage sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 228: 26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.029 [46] ZHU X F, ZHAO L, FU F Y, et al. Pyrolysis of pre-dried dewatered sewage sludge under different heating rates: Characteristics and kinetics study[J]. Fuel, 2019, 255: 115591. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.05.174 [47] WANG X H, JIA J C. Effect of heating rate on the municipal sewage sludge pyrolysis character[J]. Energy Procedia, 2012, 14: 1648-1652. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2011.12.1146 [48] WANG Z P, XIE L K, LIU K, et al. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and cotton stalks[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 89: 430-438. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.04.033 [49] QIAN T T, JIANG H. Migration of phosphorus in sewage sludge during different thermal treatment processes[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2014, 2(6): 1411-1419. [50] WESTERHOFF P, LEE S, YANG Y, et al. Characterization, recovery opportunities, and valuation of metals in municipal sludges from U. S. wastewater treatment plants nationwide[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(16): 9479-9488. [51] 钱婷婷. 磷在固体废物热处理过程中的迁移转化及再利用[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2014. QIAN T T. Transformation Behavior of Phosphorus during the Thermal Treatment of Solid Wastes and Its Utilization[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2014 (in Chinese).
[52] SUN D Q, HALE L, KAR G, et al. Phosphorus recovery and reuse by pyrolysis: Applications for agriculture and environment[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 194: 682-691. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.035 [53] HUANG R X, TANG Y Z. Speciation dynamics of phosphorus during (hydro)thermal treatments of sewage sludge[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(24): 14466-14474. [54] CHEN J J, TANG S Q, YAN F, et al. Efficient recovery of phosphorus in sewage sludge through hydroxylapatite enhancement formation aided by calcium-based additives[J]. Water Research, 2020, 171: 115450. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115450 [55] CHEN J J, AIHEMAITI A, XIA Y, et al. The effect of soil amendment derived from P-enhanced sludge pyrochar on ryegrass growth and soil microbial diversity[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 813: 152526. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152526 [56] LI J S, LI Y L, LIU F F, et al. Pyrolysis of sewage sludge to biochar: Transformation mechanism of phosphorus[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2023, 173: 106065. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2023.106065 [57] FANG Z Q, ZHUANG X Z, ZHANG X H, et al. Influence of paraments on the transformation behaviors and directional adjustment strategies of phosphorus forms during different thermochemical treatments of sludge[J]. Fuel, 2023, 333: 126544. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126544 [58] 孟详东, 黄群星, 严建华, 等. 磷在污泥热解过程中的迁移转化[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(7): 3208-3215. MENG X D, HUANG Q X, YAN J H, et al. Migration and transformation of phosphorus during pyrolysis process of sewage sludge[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(7): 3208-3215 (in Chinese).
[59] 施川, 张盼月, 郭建斌, 等. 污泥生物炭的磷吸附特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(12): 7202-7208. SHI C, ZHANG P Y, GUO J B, et al. Phosphorus adsorption performance onto sewage sludge biochar[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(12): 7202-7208 (in Chinese).
[60] LI D N, SHAN R, JIANG L X, et al. A review on the migration and transformation of heavy metals in the process of sludge pyrolysis[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 185: 106452. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106452 [61] 刘菲菲, 李京书, 李彦龙, 等. 污泥微波热解过程中磷和重金属共富集特性研究[C]//中国环境科学学会2022年科学技术年会--环境工程技术创新与应用分会场论文集(四). 沈阳航空航天大学, 2022: 6. LIU F F, LI J S, LI Y L, et al. Study on the co-enrichment characteristics of phosphorus and heavy metals in the process of sludge microwave pyrolysis [C]//2022 Annual Meeting of Science and Technology of Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences-Environmental Engineering Technology Innovation and Application Branch (4). Shenyang Aerospace University, 2022: 6(in Chinese).
[62] XU G R, ZOU J L, LI G B. Stabilization/solidification of heavy metals in sludge ceramsite and leachability affected by oxide substances[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(15): 5902-5907. [63] 张进, 刁韩杰, 王敏艳, 等. 稻壳与污泥共热解对污泥炭特性及其重金属生态风险的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(4): 1250-1256. ZHANG J, DIAO H J, WANG M Y, et al. Effects of rice husk and sewage sludge co-pyrolysis on characteristics of the sludge biochar and its ecological risk of heavy metals[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(4): 1250-1256 (in Chinese).
[64] 汪刚, 余广炜, 谢胜禹, 等. 添加不同塑料与污泥混合热解对生物炭中重金属的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(5): 611-620. WANG G, YU G W, XIE S Y, et al. Effect of co-pyrolysis of different plastics with sewage sludge on heavy metals in the biochar[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2019, 47(5): 611-620 (in Chinese).
[65] LONGENDYKE G K, KATEL S, WANG Y X. PFAS fate and destruction mechanisms during thermal treatment: A comprehensive review[J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2022, 24(2): 196-208. [66] MOŠKO J, POHOŘELÝ M, CAJTHAML T, et al. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on removal of organic pollutants present in anaerobically stabilized sewage sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 265: 129082. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129082 [67] ALIPOUR M, ASADI H, CHEN C R, et al. Fate of organic pollutants in sewage sludge during thermal treatments: Elimination of PCBs, PAHs, and PPCPs[J]. Fuel, 2022, 319: 123864. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123864 [68] BROWN R A, KERCHER A K, NGUYEN T H, et al. Production and characterization of synthetic wood chars for use as surrogates for natural sorbents[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 37(3): 321-333. [69] BUSS W. Pyrolysis solves the issue of organic contaminants in sewage sludge while retaining carbon—Making the case for sewage sludge treatment via pyrolysis[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(30): 10048-10053. [70] JONES S, BARDOS R P, KIDD P S, et al. Biochar and compost amendments enhance copper immobilisation and support plant growth in contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 171: 101-112. [71] SHEIKH L, YOUNIS U, SHAHZAD A S, et al. Evaluating the effects of cadmium under saline conditions on leafy vegetables by using acidified biochar[J]. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2023, 55: 33-39. [72] DENG Y, HUANG Q, GU W H, et al. Application of sludge-based biochar generated by pyrolysis: A mini review[J]. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 2020: 1-10. [73] 卢再亮, 李九玉, 姜军, 等. 生活污水污泥制备的生物质炭对红壤酸度的改良效果及其环境风险[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(10): 3585-3591. LU Z L, LI J Y, JIANG J, et al. Amelioration effects of wastewater sludge biochars on red soil acidity and their environmental risk[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(10): 3585-3591 (in Chinese).
[74] 张丛光, 尚高原, 邱凌, 等. 污泥—生物炭耦合还田技术研究进展[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2017, 32(3): 84-90. ZHANG C G, SHANG G Y, QIU L, et al. Research progress of the application technology of sludge and biochar[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2017, 32(3): 84-90 (in Chinese).
[75] 王秋利, 韩勇. 污泥基生物炭在矿区土壤重金属污染治理中的应用[J]. 能源与环保, 2023, 45(5): 43-48. WANG Q L, HAN Y. Application of sludge-based biochar on treatment of heavy metal pollution in mining area soil[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2023, 45(5): 43-48 (in Chinese).
[76] 周佳丽, 林伟雄, 关智杰, 等. 响应曲面法优化KOH改性污泥生物炭的制备及其强化去除Pb(Ⅱ)的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(8): 194-207. ZHOU J L, LIN W X, GUAN Z J, et al. Optimization of preparation of KOH-modified sludge biochar by response surface method and its enhanced Pb(Ⅱ)removal[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2022, 42(8): 194-207 (in Chinese).
[77] KRAHN K M, CORNELISSEN G, CASTRO G, et al. Sewage sludge biochars as effective PFAS-sorbents[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 445: 130449. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130449 [78] FABREGAT-PALAU J, VIDAL M, RIGOL A. Modelling the sorption behaviour of perfluoroalkyl carboxylates and perfluoroalkane sulfonates in soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 801: 149343. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149343 [79] GAGLIANO E, SGROI M, FALCIGLIA P P, et al. Removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water by adsorption: Role of PFAS chain length, effect of organic matter and challenges in adsorbent regeneration[J]. Water Research, 2020, 171: 115381. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115381 [80] DENG S B, YU Q, HUANG J, et al. Removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate from wastewater by anion exchange resins: Effects of resin properties and solution chemistry[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(18): 5188-5195. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.038 [81] WANG H Z, GUO W Q, LIU B H, et al. Sludge-derived biochar as efficient persulfate activators: Sulfurization-induced electronic structure modulation and disparate nonradical mechanisms[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 279: 119361. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119361 [82] 李韬略, 袁雪红, 陈传胜, 等. Fe2+耦合热活化过硫酸盐降解土壤中四溴双酚A[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(8): 2730-2739. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022031501 LI T L, YUAN X H, CHEN C S, et al. Degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by ferrous coupling thermally activated persulfate in soil[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(8): 2730-2739 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022031501
[83] PREMARATHNA K S D, RAJAPAKSHA A U, SARKAR B, et al. Biochar-based engineered composites for sorptive decontamination of water: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 372: 536-550. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.097 [84] KANG X D, ZHANG Q Y, LIU X F, et al. The interface mechanism of sludge biochar activating persulfate to remove tetracycline: The role of the C-O-Fe bridge at the carbon surface[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 384: 135514. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135514 [85] 韩剑宏, 李艳伟, 姚卫华, 等. 玉米秸秆和污泥共热解制备的生物质炭及其对盐碱土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2017, 37(4): 92-98,105. HAN J H, LI Y W, YAO W H, et al. Co-pyrolysis preparing biochar with corn straw and sewage sludge and its effects on saline soil improvement[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 37(4): 92-98,105 (in Chinese).
[86] TANG J Y, ZHANG L H, ZHANG J C, et al. Physicochemical features, metal availability and enzyme activity in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by biochar and compost[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 701: 134751. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134751 [87] FERNÁNDEZ-LUQUEÑO F, VALENZUELA-ENCINAS C, MARSCH R, et al. Microbial communities to mitigate contamination of PAHs in soil: Possibilities and challenges: A review[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2011, 18(1): 12-30. doi: 10.1007/s11356-010-0371-6 [88] BARAN S, BIELIŃSKA J E, OLESZCZUK P. Enzymatic activity in an airfield soil polluted with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Geoderma, 2004, 118(3/4): 221-232. [89] 张晶, 张惠文, 丛峰, 等. 长期灌溉含多环芳烃污水对稻田土壤酶活性与微生物种群数量的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2007, 26(8): 1193-1198. ZHANG J, ZHANG H W, CONG F, et al. Effects of long-term PAHs-containing wastewater irrigation on lowland rice soil enzyme activities and microbial populations[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2007, 26(8): 1193-1198 (in Chinese).
[90] ALLISON S D. Soil minerals and humic acids alter enzyme stability: Implications for ecosystem processes[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2006, 81(3): 361-373. doi: 10.1007/s10533-006-9046-2 [91] TAVOLARO P, TAVOLARO A, MARTINO G. Influence of zeolite PZC and pH on the immobilization of cytochrome c: A preliminary study regarding the preparation of new biomaterials[J]. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 2009, 70(1): 98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2008.12.019 [92] YUAN Z H, HUANG Q J, WANG Z Q, et al. Medium-low temperature conditions induce the formation of environmentally persistent free radicals in microplastics with conjugated aromatic-ring structures during sewage sludge pyrolysis[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(22): 16209-16220. [93] LIU Y, DAI Q Y, JIN X Q, et al. Negative impacts of biochars on urease activity: High pH, heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, or free radicals?[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(21): 12740-12747. [94] PARIYAR P, KUMARI K, JAIN M K, et al. Evaluation of change in biochar properties derived from different feedstock and pyrolysis temperature for environmental and agricultural application[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 713: 136433. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136433 [95] CHEN J F, DING L S, WANG P Y, et al. The estimation of the higher heating value of biochar by data-driven modeling[J]. Journal of Renewable Materials, 2022, 10(6): 1555-1574. doi: 10.32604/jrm.2022.018625 [96] GUSIATIN Z M, KURKOWSKI R, BRYM S, et al. Properties of biochars from conventional and alternative feedstocks and their suitability for metal immobilization in industrial soil[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(21): 21249-21261. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7335-4 [97] HU Y H, THOMSEN T P, FENTON O, et al. Effects of dairy processing sludge and derived biochar on greenhouse gas emissions from Danish and Irish soils[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 216(Pt 2): 114543. [98] XU X Y, KAN Y, ZHAO L, et al. Chemical transformation of CO2 during its capture by waste biomass derived biochars[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 213: 533-540. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.013 [99] ZHAO L, SUN Z F, PAN X W, et al. Sewage sludge derived biochar for environmental improvement: Advances, challenges, and solutions[J]. Water Research X, 2023, 18: 100167. doi: 10.1016/j.wroa.2023.100167 [100] SCHWANDER T, SCHADA von BORZYSKOWSKI L, BURGENER S, et al. A synthetic pathway for the fixation of carbon dioxide in vitro[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 900-904. doi: 10.1126/science.aah5237 [101] GONG F Y, LI Y. Fixing carbon, unnaturally[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 830-831. doi: 10.1126/science.aal1559 [102] 程功, 刘廷玺, 李东方, 等. 生物炭和秸秆还田对干旱区玉米农田土壤温室气体通量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(7): 1004-1014. CHENG G, LIU T X, LI D F, et al. Effects of biochar and straw on greenhouse gas fluxes of corn fields in arid regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(7): 1004-1014 (in Chinese).
[103] KAZEMI SHARIAT PANAHI H, DEHHAGHI M, OK Y S, et al. A comprehensive review of engineered biochar: Production, characteristics, and environmental applications[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 270: 122462. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122462 [104] KUZYAKOV Y, BOGOMOLOVA I, GLASER B. Biochar stability in soil: Decomposition during eight years and transformation as assessed by compound-specific 14C analysis[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 70: 229-236. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.12.021 -





 下载:
下载: