-
磷(P)是现代农业和化学工业中广泛使用的重要资源,通常以磷酸盐的形式存在于水溶液中[1]. 然而,在磷化工的快速发展和过量施用磷肥下导致磷大量向淡水资源转移,水体磷浓度超标,藻类过度生长,引起水体富营养化,造成磷资源损失和环境污染[2 − 3]. 此外,磷是一种不可再生资源,由于每年对磷的需求不断增长[4],预计在未来100—400年内将完全消耗掉[5]. 因此,废水中磷的去除和回收对于缓解富营养化染和磷资源危机至关重要[6].
迄今为止,化学沉淀[7]、膜分离工艺[8]、生物处理[9]、阴离子交换[10]和吸附[11]等多种技术已被证明可以用于去除水体中磷酸盐. 而吸附法因其操作简单、效率高成本低、应用方便等优点,吸引了众多研究人员的关注. 已经发现多种吸附材料,如水和氧化铁[12]、多孔二氧化硅[13]和碳基材料[14]等,它们具有良好的吸附性,用于去除废水磷酸盐的吸附剂. 但相对而言,这些吸附剂多为粉末形式很难在水中回收,这可能会造成二次污染问题[15]. 并且一些材料存在苛刻的问题制备条件好,成本高,去除能力低,难以分离等缺点. 制备高效稳定、绿色环保可循环利用的新型磷酸盐吸附材料吸附和回收水体磷酸盐,这是近年来的研究热点之一[16].
近年来,合成纤维作为催化剂和吸附剂载体受到研究者的广泛关注. 其中,腈纶纤维(PANF)含有丰富的氰基和酯基等化学性质活泼的基团,在一定条件下可以进行特定的化学反应,并可以转化为具有多种官能团的新型功能化纤维,是一种优秀的载体材料. 腈纶纤维具有成本低、易获得、密度低、柔韧性好等特点,其在大规模机械化加工和环境保护方面也具有一定的优势[17]. 腈纶纤维可以在一定条件进行灵活改性,构建富含氨基、羟基、羧基、季铵盐等组分[18]. 例如,Xu等[19]通过简单的化学接枝反应合成了一种可回收的载铁胺化聚丙烯腈纤维(PANAF-Fe)去除废水中的磷酸盐;Zheng等[20]合成了富含氯离子的功能化聚丙烯腈纤维(PANAF-Cl),对废水中磷酸盐的去除率高达90%以上,最大吸附容量为15.49 mg·g−1. 丁天琦[21]以聚丙烯腈(PAN)作为基体,制备出多孔碳纳米纤维膜,对磷酸盐最大去除量可达131 mg·g−1.
铁、铜、镧等金属和磷酸盐具有较强的结合能力,其在水体磷酸盐的去除获得较多的应用. 然而,使用固载铜离子的胺化纤维对水中磷酸盐的吸附尚缺乏研究. 本研究以腈纶纤维为原料,将Cu2+固载在胺化改性腈纶纤维表面,制备了新型磷酸盐吸附剂(PANAF-Cu),探究了该吸附剂对水体中磷酸盐的吸附性能,为废水中磷的回收提供理论依据.
-
腈纶纤维(抚顺石化公司,中国),使用前将其剪成长度约10 cm备用. 实验中所有化学试剂均为国内市售分析纯试剂,且未进一步纯化. 本实验中所用化学试剂:乙二胺、磷酸二氢钾(上海阿拉丁试剂有限公司)、三水合硝酸铜(上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司);盐酸、硝酸、硫酸(西陇科技有限公司);碳酸钾、氢氧化钠、碳酸氢钠(上海素艺化学试剂有限公司);氯化钾、硫酸钾、硝酸钾、一水合柠檬酸(国药集团化学试剂有限公司)、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA,上海苏懿化学试剂有限公司)、氯化钠(上海中试化工有限公司). 本研究中的所有实验使用的皆为去离子水.
实验中主要用到的仪器为:集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器(DF-101S),巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;磁力搅拌器(84-1A),金坛区西城新瑞仪器厂;鼓风干燥箱(DHG-9070A型),常州海博仪器设备有限公司;pH计(FE20~standard),梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;循环水式多用真空泵(SHB-Ⅲ),郑州长城科工贸有限公司;分光光度计(722G),上海仪电分析仪器有限公司.
-
将600 mg干燥的腈纶纤维(PANF)、20 mL乙二胺和20 mL去离子水(DI)先在室温条件下混合搅拌,然后加入到高压反应釜中125°C反应100 min.反应结束后,将纤维从溶液中分离出来,后用70—80℃去离子水反复洗涤,再将纤维置于60℃烘箱中干燥过夜,得到淡黄色的胺化纤维(PANAF),即胺化腈纶纤维.
-
准备好50 mL 10 mmol·L−1的三水合硝酸铜(Cu(NO3)2·3H2O)配制的硝酸铜溶液,将50 mg干燥过夜后的胺化纤维加入到溶液中,室温下搅拌30 min,过滤后,进一步洗涤,反复冲洗,后将纤维放置在60 ℃的烘箱中干燥6 h,即可得到载铜的功能化纤维PANAF-Cu.
-
扫描电子显微镜(SEM,德国蔡司Sigma 300),傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(FTIR,美国PerkinElmer Spectrum One),全自动元素分析仪(EA,德国Vario EL Cube),X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,美国Thermo Scientific K-Alpha),X射线衍射仪(XRD,德国Bruker D8 Advance),pH计(METTLER TOLEDO,FE20),可见分光光度计(722G,Shanghai).
-
利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、元素分析(EA)、傅里叶红外光谱仪(FTIR)、X射线衍射光谱(XRD)和能量色散X射线谱仪(XPS)等表征功能化纤维的表面形貌、化学结构及内部晶体结构等,从而根据表征结果检验改性纤维是否初步制备成功.
-
分别探究不同吸附时间、不同pH值、不同温度以及不同初始磷酸盐浓度下PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附能力. 纤维吸附饱和后,用镊子将纤维吸附剂从溶液中分离出来,从剩余溶液中吸取1 mL溶液放入50 mL容量瓶中,后按钼酸铵分光光度法测定不同条件下待测液中磷酸盐的浓度,测定低浓度磷酸盐时,要先将剩余溶液用0.22 μm滤膜过滤,后使用ICP-OES测定. 所有吸附实验均进行3次重复. 计算吸附量和吸附率公式如下:
式中,η为吸附率,%;qe为吸附P的量,mg·g−1;C0和Ce分别为无机磷初始质量浓度和平衡浓度,mg·L−1;V为溶液体积,L;W为吸附剂添加量,g.
-
吸附动力学是用来描述吸附剂吸附溶质速率快慢的方式,采用拟一级动力学和拟二级动力学模型探究正在进行的吸附过程,以便讨论其合适的吸附机理. 不同动力学模型如下:
其中, qt和qe为t时刻和平衡时的吸附量(mg·g−1)K1和K2依次为拟一级动力学和拟二级动力学的吸附速率常数.
-
吸附等温线是描述在一定温度下吸附剂达到吸附平衡状态时吸附量(qe)和吸附质浓度(Ce)之间关系的曲线,常见的模型有Freundlich模型、Langmuir模型、Temkin 模型和D-R方程,本文采用Langmuir和Freundlich模型探究PANAF-Cu对无机磷的吸附方式,拟合方程如下:
其中,qm为Langmuir模型估算的理论最大吸附量,KL为Langmuir常数,KF和n分别是Freundlich常数和均匀性系数.
-
固载铜离子的功能化腈纶纤维(PANAF-Cu)的合成由两步法完成,首先腈纶纤维和乙二胺发生胺化反应,纤维表面富含伯氨功能基的胺化纤维(PANAF),进一步利用氮和铜的配位作用,成功构建铜离子螯合的胺化纤维(PANAF-Cu). 胺化纤维的改性程度可以通过增重法来计算,胺化后的纤维对比腈纶纤维质量增加地较为明显,增重为10%,且纤维颜色也发生了变化,说明乙二胺被成功接枝到纤维表面. 胺化的程度可以通过控制反应时间或者乙二胺的浓度,过低的胺化程度不利于铜离子的螯合,然而过高的胺化程度导致纤维机械强度的下降,因此本文选择增重为10%的PANAF作进一步研究.
此外,本文研究了胺化纤维与不同浓度硝酸铜溶液制备得到的PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附能力, PANAF-Cu功能化纤维在Cu(NO3)2浓度增加的同时,其对磷酸盐的去除能力也不断增加,并且在Cu(NO3)2浓度为10 mmol·L−1时达到最高值,最大吸附量为35.29 mg·g−1. 然而,随着硝酸铜浓度的继续增加,PANAF-Cu中铜的含量达到饱和,导致其对磷酸盐的吸附能力趋势放缓至平衡,这是因为PANAF对铜的固载量是有限的,表明当铜离子浓度大于10 mmol·L−1时,PANAF对铜离子的固载量达到饱和. 因此,选择浓度为10 mmol·L−1的硝酸铜溶液制备PANAF-Cu.
-
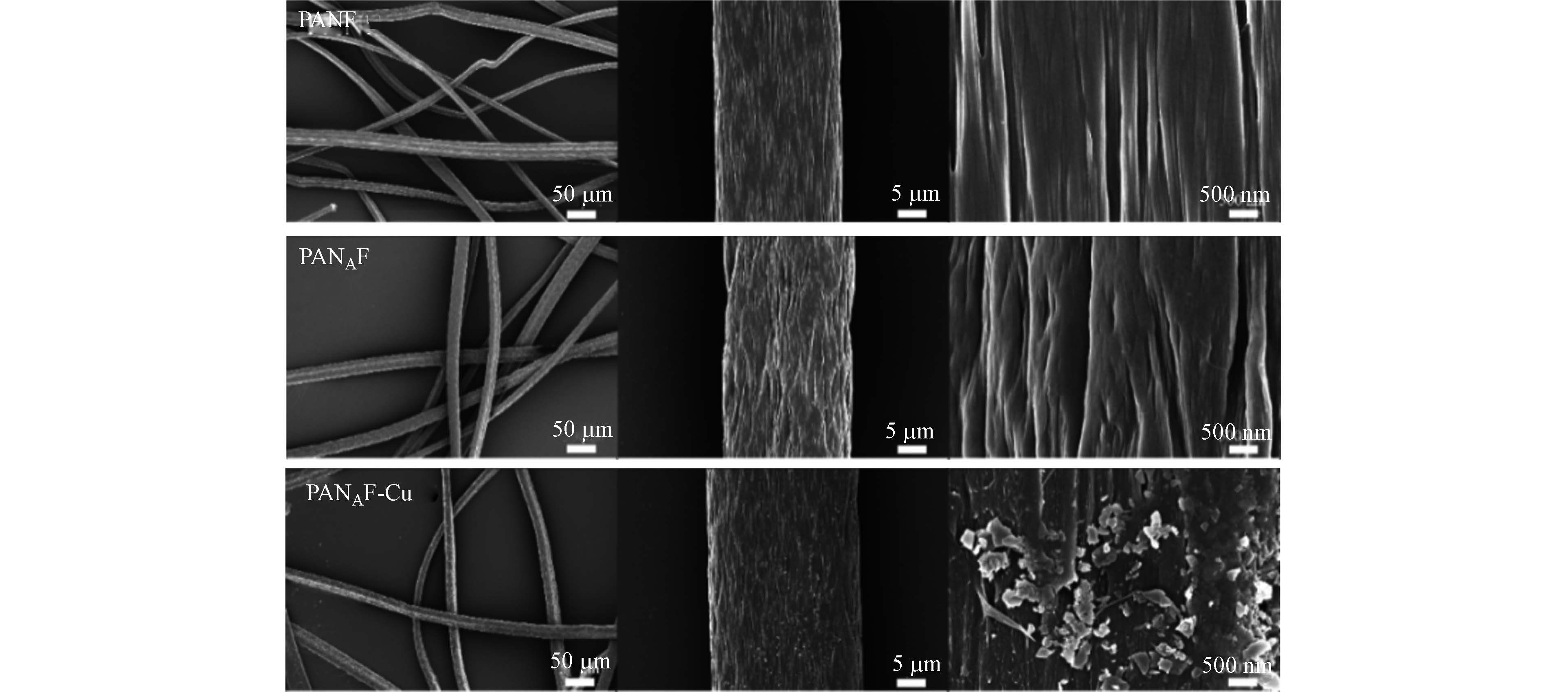
如图1可知,样品都呈连续完整的纤维状,表明纤维在改性前后及使用过程中,其完整性得到了良好的保持,未遭受到破坏. 放大2000倍的电子显微镜图像看到,随着改性反应的进行,纤维表面出现了若干裂纹,可能是因为氨基的进入和增溶作用导致纤维直径增加,出现裂纹,在一定程度上增加了纤维的表面积. 放大20000倍后,在胺化反应和螯合Cu2+后,可以清楚地观察到纤维不同程度的变形和溶胀,纤维表面明显变得粗糙,同时还被一层颗粒状物所覆盖,这可能是因为纤维表面的薄膜形成了由若干Cu-N配位产生的片晶.
-
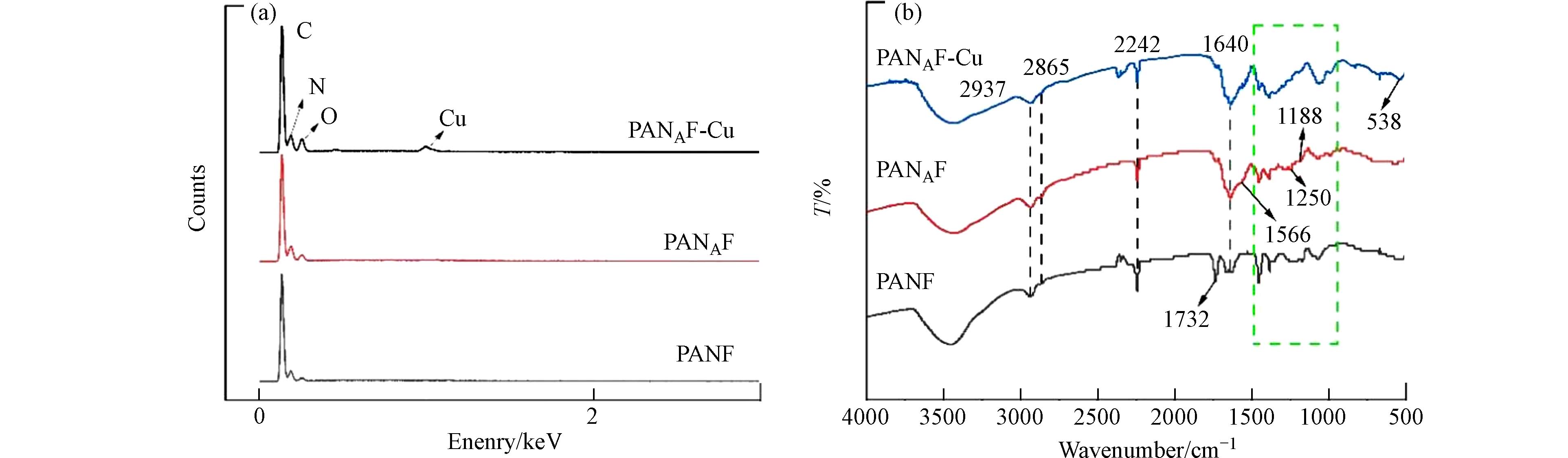
为进一步明确纤维结构,利用傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)和能谱图[22]分析了纤维改性前后的纤维表面组分. 图2(a)显示了每个阶段纤维的EDS能谱图,发现与PANAF相比,PANAF-Cu出现了新的Cu元素的峰,这表明Cu2+成功的固载到了胺化纤维上. 图2(b)显示了每个阶段纤维的红外光谱,PANF在2242 cm−1处的吸收峰和在1732 cm−1处的吸收峰分别为腈纶纤维第一单体丙烯腈的C≡N的伸缩振动和第二单体丙烯酸甲酯的C=O伸缩振动[17]. 由于胺化反应消耗了PANF上的氰基,胺化反应后2242 cm−1处的吸收峰强度下降. 此外,由于PANF中的C≡N在强碱性EDA溶液中被水解,与EDA中的NH2基团在1640 cm−1处形成了酰胺C=O双键的伸缩震动峰,说明了胺基基团的成功接枝[23]. 在胺化改性纤维吸附Cu2+后,在538 cm−1处新峰的出现,可能归因为Cu-N的配位结构,表明Cu已被-NH所固化[24]. 上述结果表明了胺基的成功接枝,以及Cu2+在纤维上的固载.
-
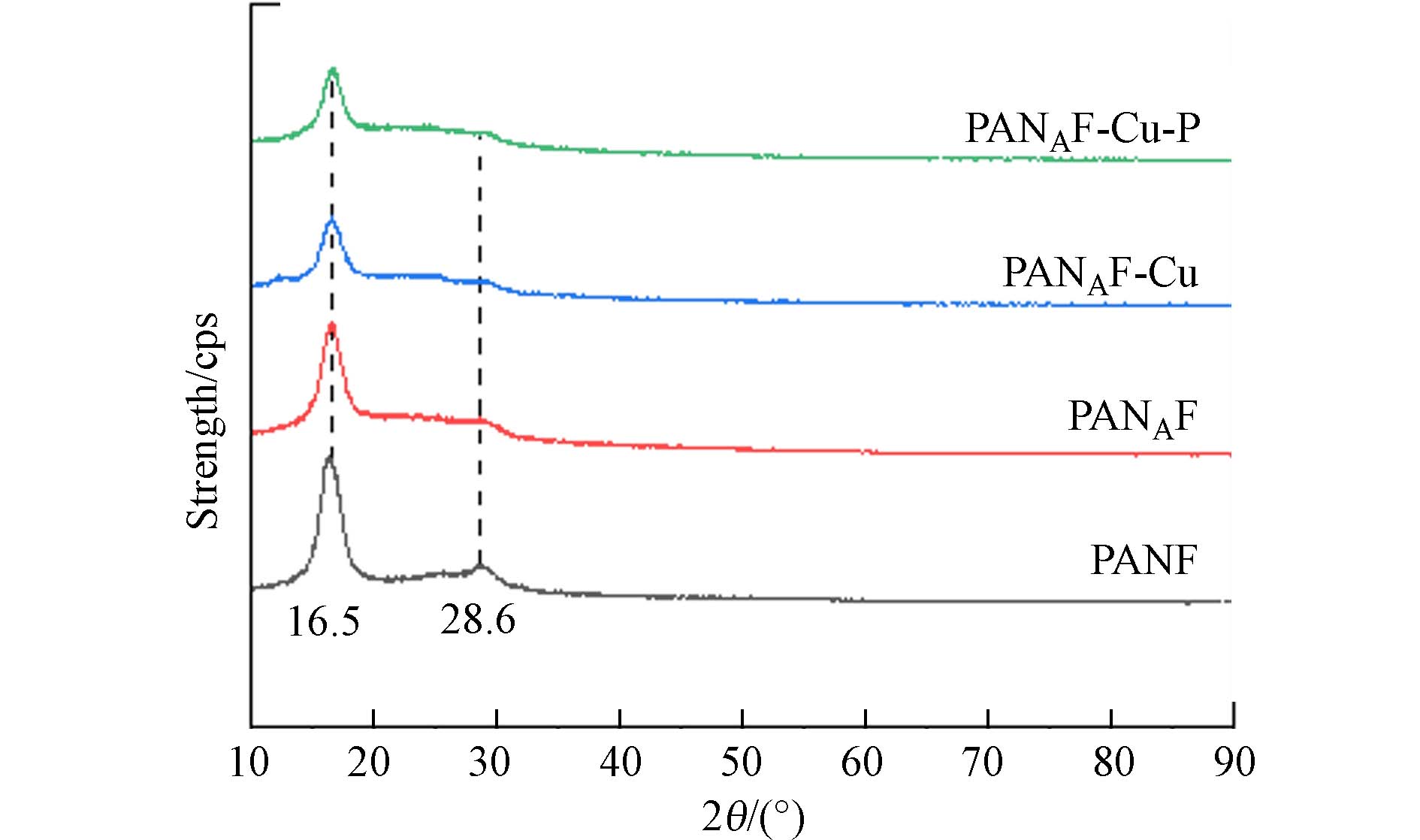
通过X射线衍射(XRD)表征了不同纤维的晶体结构. 图3显示了不同阶段的纤维的XRD图像,每个纤维都在2θ为16.5°处有一个共同的衍射峰,2θ = 28.6°处有一个不太强烈的衍射峰,表明PANAF、PANAF-Cu和PANAF-Cu-P与PANF具有相似的特征峰,表明纤维改性后仍保持了腈纶纤维原有的晶体结构,未被破坏,依然保持良好. 此外,PANAF、PANAF-Cu和PANAF-Cu-P较弱的衍射峰的强度明显降低,表明聚丙烯腈的聚合物链结构已经被胺分子部分溶解. 进一步固载Cu2+后,XRD光谱中并没有观察到结晶的Cu,这表明加载在纤维表面的固体Cu处于无定形状态,并可能通过Cu—N键与纤维骨架结合.
-
通过元素分析分析了不同阶段纤维的元素组成,相关数据见表1. 与PANF相比,PANAF中的C含量降低,H含量增加,因为乙二胺比原始腈纶纤维具有更少的C和更多的H,表明乙二胺被成功接枝到PANF上. 此外,N的存在也证实了不是所有的C≡N基团都被水解,参与EDA的官能化,所以改性过程可能仅发生在表面. 引入Cu元素后,PANAF-Cu中C、H含量的降低表明—NH2直接参与了Cu2+的吸附. 引入P元素后,相对于PANAF-Cu,PANAF-Cu-P中N含量的下降表明Cu与N形成配位键,被封存在纤维上,以上实验结果证明PANAF-Cu的成功改性.
-
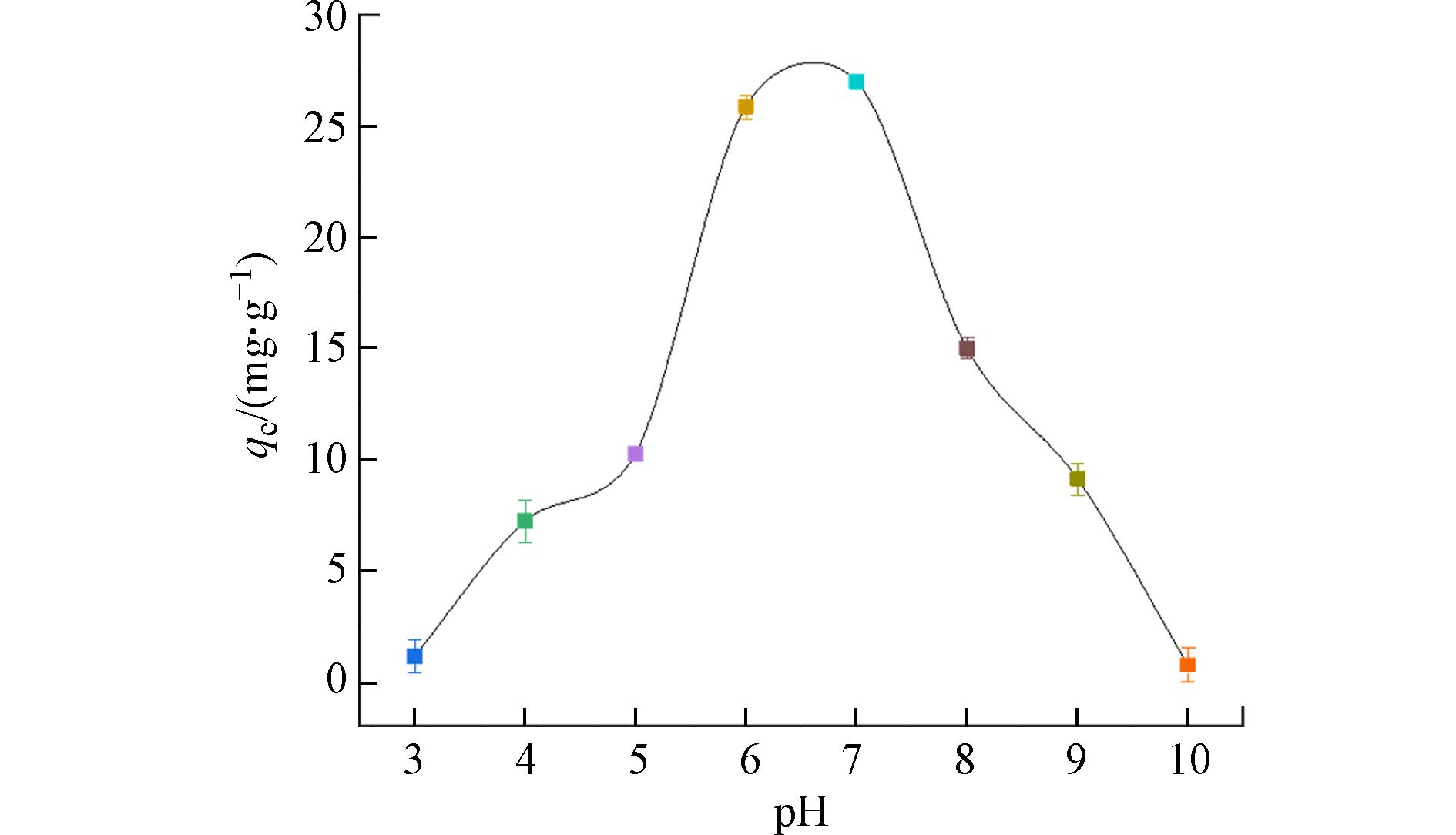
pH值是决定吸附效果的关键因素. 图4表明,pH值在3—7时,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附量随着pH的升高而迅速增大,并在pH=7时达到最大值26.99 mg·g−1. 聚丙烯腈纤维的氨基的非选择性吸附是以静电作用形式产生的,因此,带正电的表面可以增强带负电的磷酸根阴离子的吸附. 其后通过配体的交换让表面负载的Cu2+对磷的进行选择性吸附. 在pH值在5—8的条件下,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附量都能维持在较好的水平,吸附量仍能保持到10 mg·g−1以上. 表明固载铜离子的胺化改性纤维具有较高且稳定的磷酸盐去除效率.
-
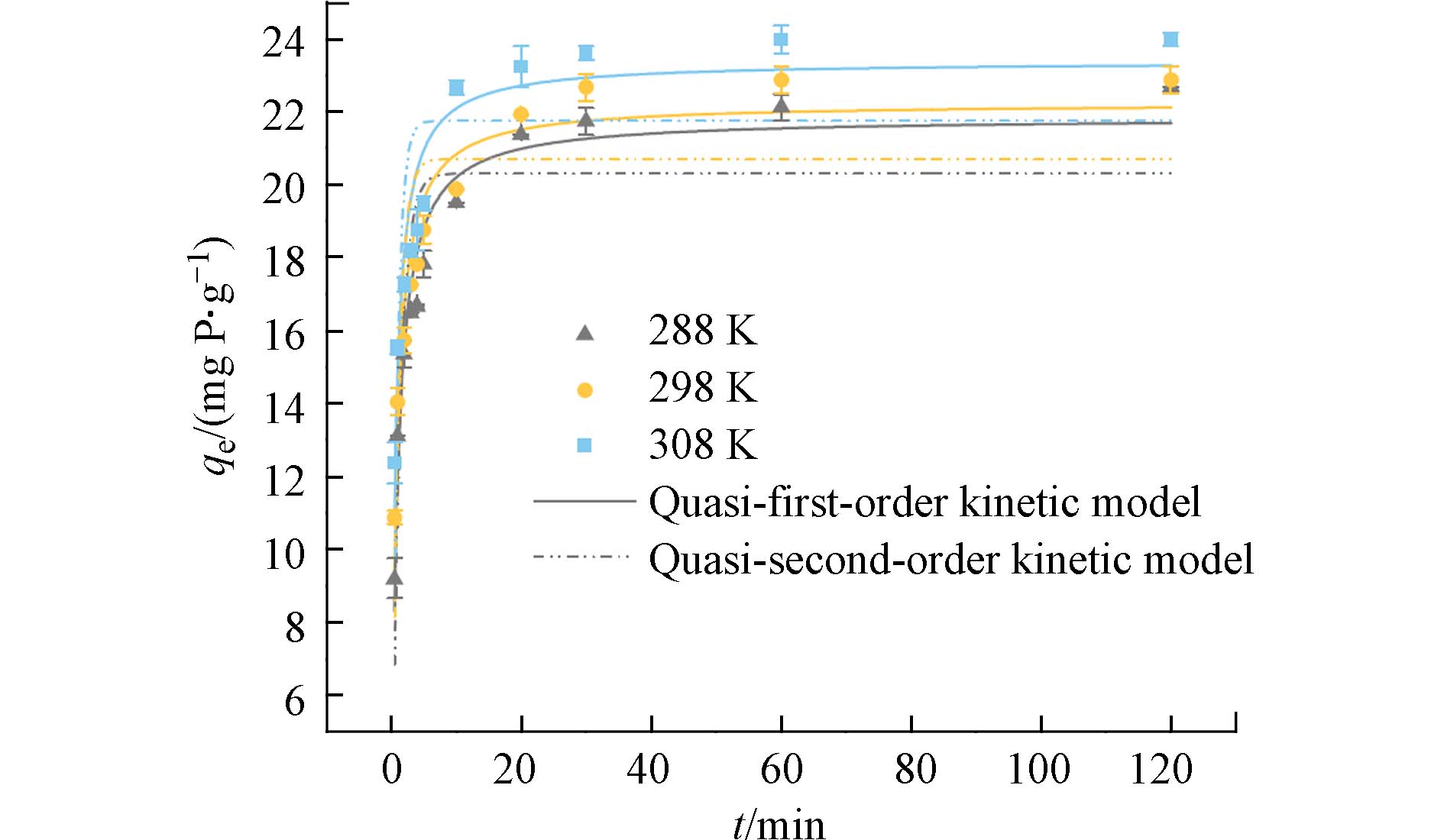
分别研究了在288、298 、308 K 的3种温度条件下,纤维吸附剂随时间改变对磷酸盐的吸附量的变化. 3条曲线的变化趋势大致相同,前10分钟内吸附速度较快,随后吸附速率减缓,在30 min左右基本达到吸附平衡. 这表明,在刚开始吸附阶段,吸附剂表面暴露的大量活性位点可以很迅速地捕获水中的磷酸盐. 随着时间的推移,吸附剂的表面吸附活性位点逐渐达到饱和,吸附过程随之减慢. 为深入了解PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附过程,分别通过拟一级动力学和拟二级动力学对吸附数据进行拟合. 拟合图和动力学参数分别如图5和表2所示,在288、298、308 K等3种温度下,拟二级动力学模型的R2均高于拟一级动力学模型;而且,用拟二级动力学模型拟合的qe值也更贴近于实际的吸附量. 因此,该吸附剂对磷酸盐的吸附过程更加倾向于化学吸附[25].
-
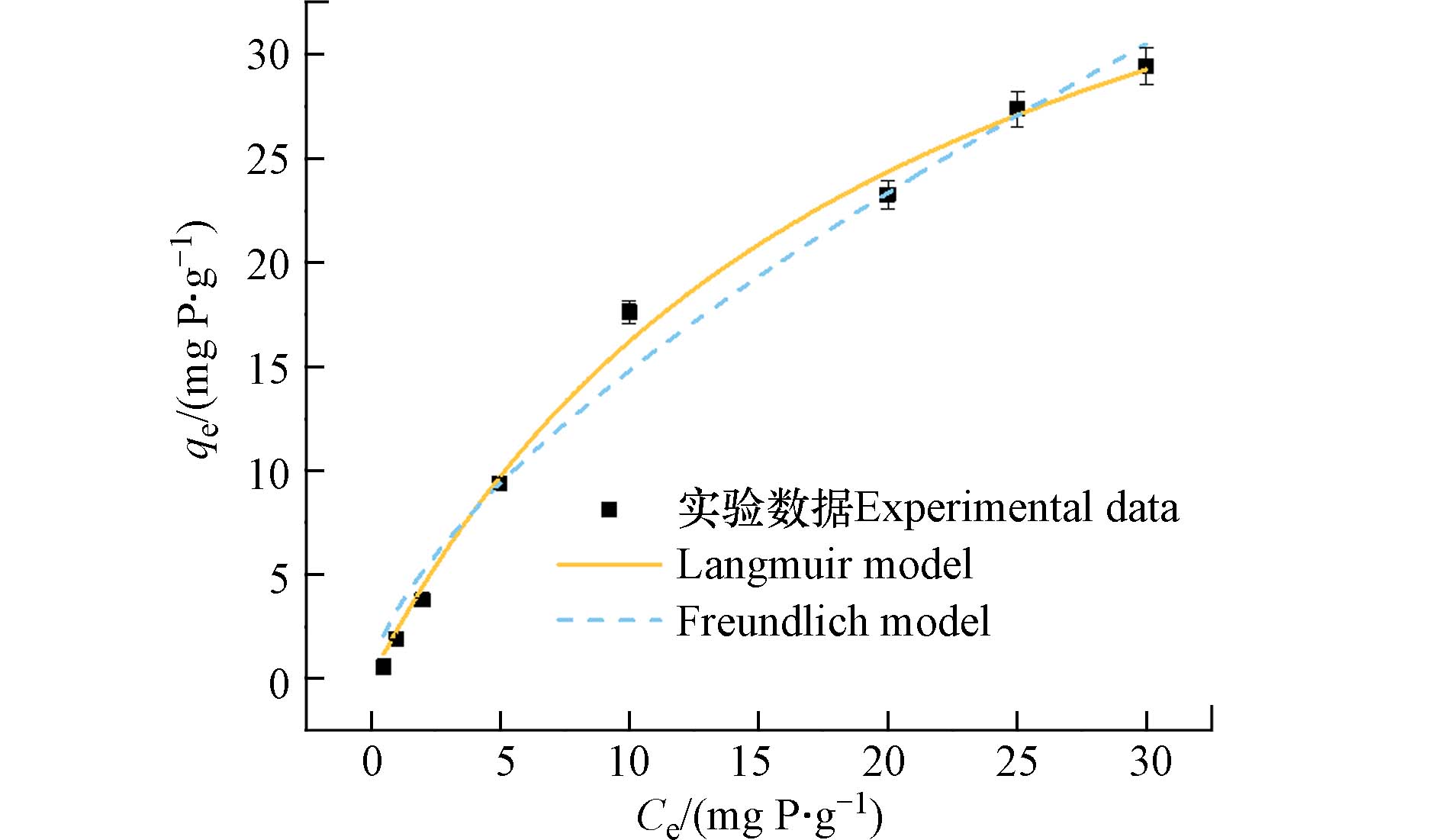
为了阐明PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附模式和吸附性能,在室温下,对不同初始磷酸盐浓度下进行了吸附等温实验. 实验发现,吸附剂对磷酸盐的吸附能力伴随着磷酸盐初始浓度的升高而增强,直至吸附饱和. 这可能是因为在较低的磷酸盐浓度下,磷的配位位点更多,随着磷浓度的提高,活性吸附位点也逐渐达到饱和,吸附量不再升高. 利用Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温线模型对数据进行拟合,通过拟合得到的图和相关数据分别位于图6和表3.
从表3可以看出,Langmuir模型拟合曲线的回归参数大于Freundlich模型,说明PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附更适合于Langmuir模型. 因此,吸附剂对磷酸盐的吸附更趋向于均匀的单分子层化学吸附. 通过Langmuir模型估算PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的最大吸附量为49.03 mg·g−1.
-
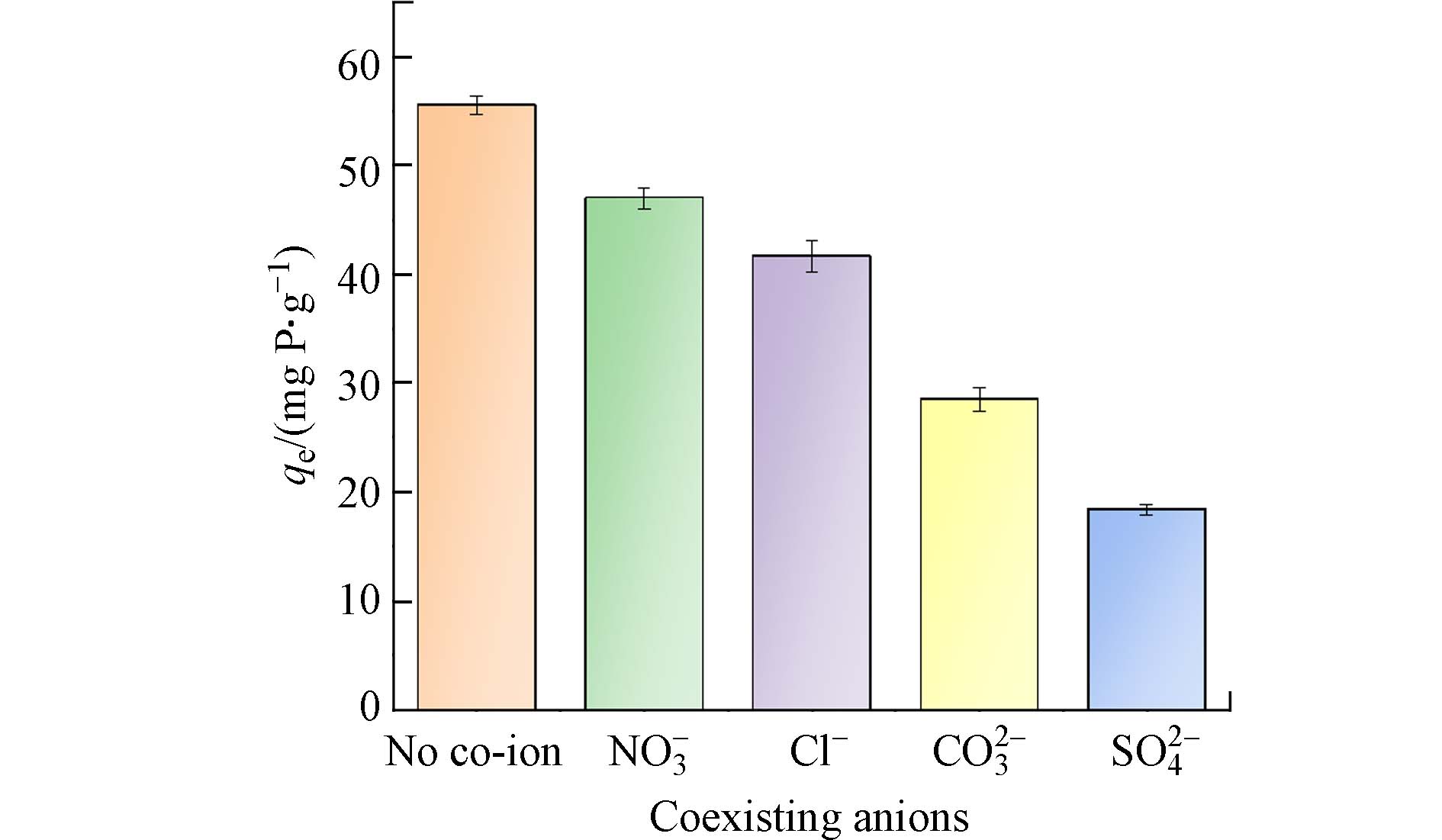
为测定PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐去除的选择性,选定硫酸盐、氯化物、硝酸盐和碳酸盐为代表性的共存阴离子. 在浓度为1×10−3 mol·L−1的磷酸盐中分别加入同等浓度的Cl−、NO3−、CO32-以及SO42-等共存离子溶液,探究PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附能力,结果见图7. 结果表明, 4种共存离子对PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐的影响如下:SO42-﹥CO32-﹥Cl−﹥NO3−. 其中NO3−对磷酸盐的吸附影响最小. SO42-和CO32-比Cl−和NO3−更有竞争力,可能是因为硫酸盐和碳酸盐作为二价离子具有更高的电荷密度,比单价阴离子能更迅速地被吸附. 以上实验说明PANAF-Cu在实际水体中也能在较多阴离子的影响下具有很好的除磷效果.
-
XPS分析进一步揭示了吸附剂的化学状态和元素组成. 图8显示了吸附前后PANAF-Cu纤维的XPS光谱,与PANAF相比,PANAF-Cu出现了新的Cu元素的峰(图8a),这表明Cu2+成功的固载到了胺化纤维上,吸附后的纤维中出现了一个133.5 eV的信号峰,这是由P 2p轨道引起的,表明磷酸盐被纤维成功捕获(图8b). Cu2+对磷酸盐吸附的贡献由纤维吸附后Cu元素的高分辨率光谱证明(图8 c-d),对比吸附前的纤维,Cu的高分辨率光谱发现,PANAF-Cu-P的高分辨率Cu 2p光谱被分解成两个峰,最初位于934.73 eV的Cu—N键结合能下降到932.61 eV,这可以归因于来自磷酸盐的P原子为Cu提供了额外的电子,形成了新的N-Cu-P配位键,从而增加了Cu元素电子云密度,降低了结合能,这证实了改性纤维表面的Cu2+通过配位吸收起到了对P的固化作用. 即表明络合-配体相互作用是该吸附过程的主要机制[26]. 根据N的吸附前后的高分辨率光谱(图8 e-f)发现原本位于400.62 eV 的—NH2(—NH)键结合能下降到399.93 eV,氨基与Cu离子形成Cu-N的配位结构,纤维表面的Cu2+通过和磷酸盐中P—O键作用形成新的N-Cu-P配位去除磷酸盐,该基团的移动表明含氮官能团在PANAF-Cu对废水中的磷酸盐的吸附中起着重要作用. 因此根据上述结果,可以推断PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的有效吸附主要依赖于纤维表面的Cu-N配位结构,从而形成新的N-Cu-P配位结构.
-
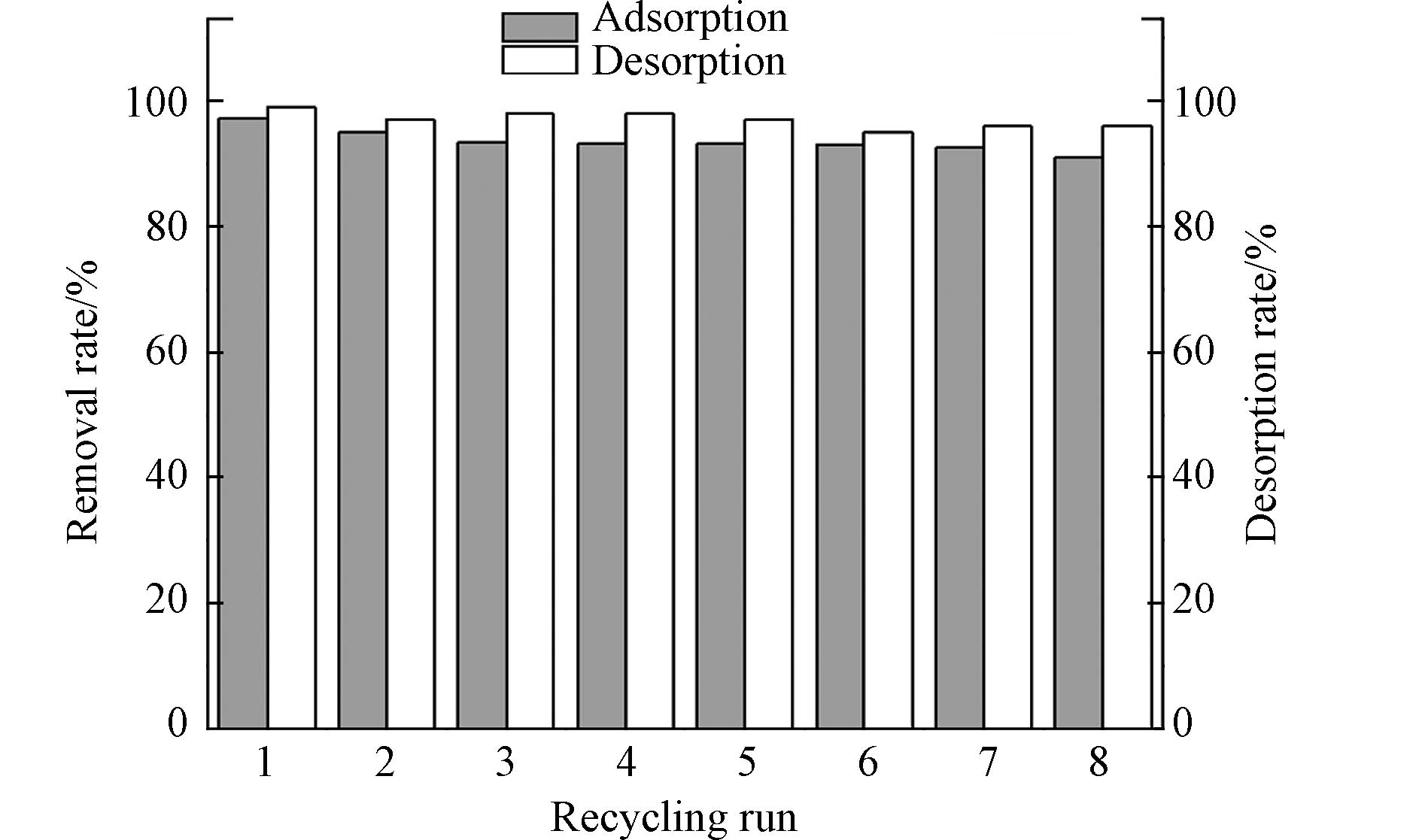
为探究不同解吸剂对磷酸盐的解吸率影响,进行对比实验(表4),发现HCl、NaCl、C6H8O7(柠檬酸)和EDTA(乙二胺四乙酸二钠)对磷酸盐的解吸率分别为52.50%、2.50%、87.50%和97.50%,EDTA的解吸率最高为97.5%. 从图9可以看出,经过8次循环后,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的解吸率基本稳定在90%以上,相应的解吸率也保持在95%以上,表明PANAF-Cu具有多重吸附和再生的优良特性.
-
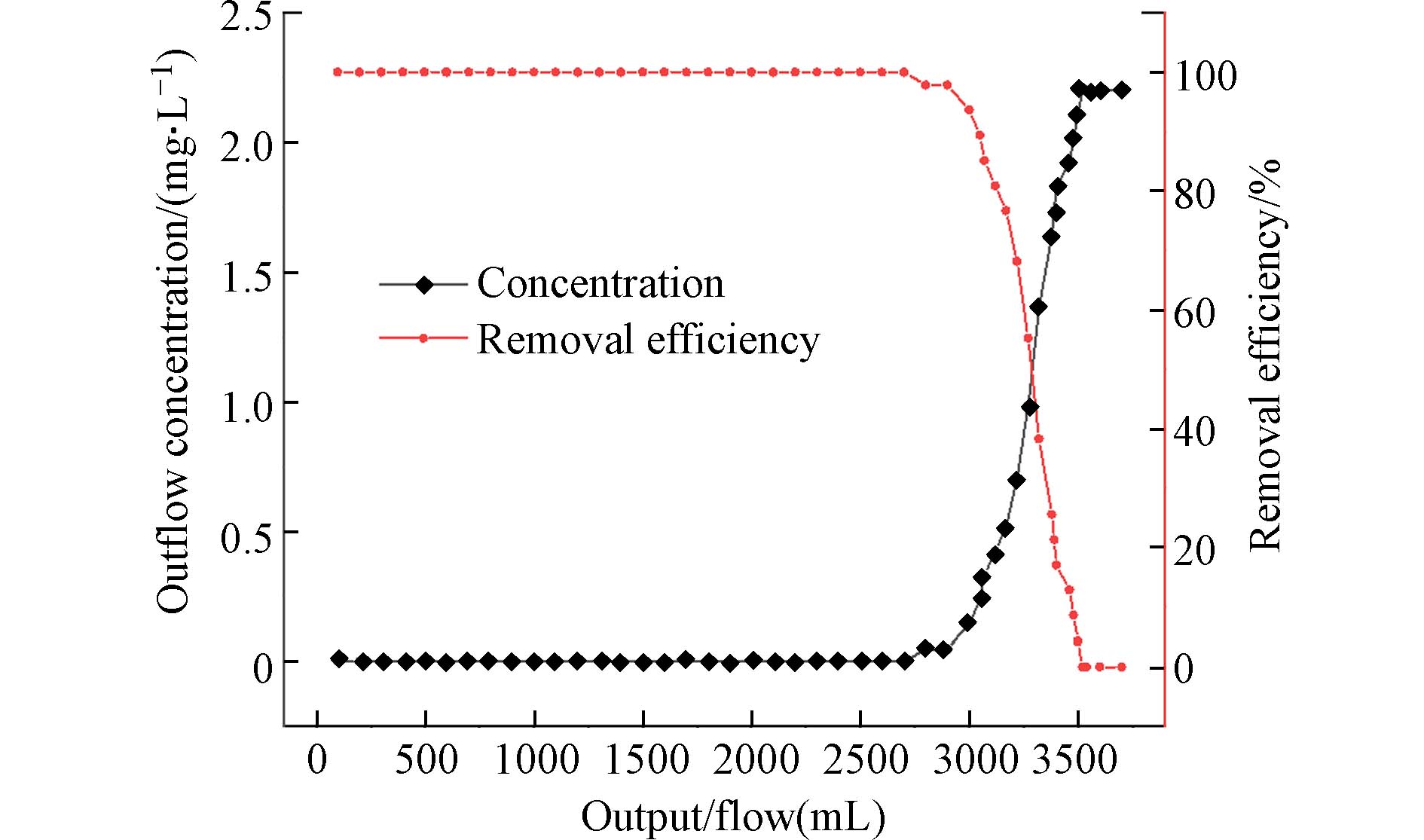
用初始浓度为2 mg·L−1的磷酸盐溶液利用恒流泵以0.5 mL·min−1的速率进行连续流动实验. 每隔50 mL测试出水中的磷酸盐浓度,就可以绘制出磷酸盐的穿透曲线,如图10所示. 实验发现,随着出水量的增加,出水中的磷酸盐浓度也随之增加. 当出水量小于2700 mL时,磷酸盐去除率维持在99%以上,大于2700 mL后,对硫酸盐的去除率大幅度下降. 这些结果皆说明PANAF-Cu在模拟自然水体和流动的水体条件下的具有优异除磷效果.
-
本研究进一步探究PANAF-Cu在实际水体的应用效果,测试了PANAF-Cu对巢湖(自然水体)磷污染水体中对磷的吸附能力. 为了更好地说明问题,将采集的水样的磷酸盐浓度调整为1000 µg· L−1 P. 分别将0、5、10、20、40、60 mg的PANAF-Cu置于10 mL上述水样中搅拌24h,利用ICP测定剩余磷酸盐浓度,测定结果见表5. 实验表明,当PANAF-Cu添加量超过20 mg时,磷酸盐浓度即可降至100 µg·L−1以下,已低于湖泊富营养化的最小磷浓度200 µg·L−1. 可见,本研究制备得到的少量PANAF-Cu在实际水体中也可以有效的降低水体的富营养化程度.
-
为了评估功能纤维吸附剂的吸附效果,表6列出了近年来报道的一些用于去除废水P的吸附剂材料. 值得注意的是,本工作中合成的铜胺负载纤维可以在较温和的反应条件下就可以获得较高的吸附能力. 此外,与表中列举的其他吸附剂有限的P吸附能力相比,接枝了Cu-N配体结构的功能化纤维表现出了更高的P容量和更快的吸附速率. 这可以归因于配位中心的铜离子和-NH2中的N原子之间的配位模式所引起的铜离子的高反应性以及形成的N-Cu-P之间的独特结合机制. 此外,PANAF-Cu在循环使用8次以后依然能够有效地去除磷酸盐. 总的来说,与目前报道的磷酸盐选择性吸附材料相比,本课题中报道的功能纤维吸附剂在常温下具有更高的反应活性和更好的选择性吸附性能.
-
以聚丙烯腈纤维为原料,通过胺化改性使得聚丙烯腈纤维表面固载胺基,在通过胺基与铜的配位作用,成功合成具有Cu-N配位结构的新型吸附剂(PANAF-Cu). 在pH=7时达到吸附量最大值26.99 mg·g−1,pH值在5—8的条件下,吸附量仍能保持到10 mg·g−1以上. 表明固载铜离子的胺化改性纤维具有较高且稳定的磷酸盐去除效率. PANAF-Cu的吸附过程更符合伪二级动力学吸附模型,吸附等温学拟合结果更适合Langmuir等温模型,表明P在PANAF-Cu属单分子层吸附,在一定温度内,对磷酸盐的去除效果随着温度升高而增加. 通过吸/脱附循环性能试验,经过8次循环后,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附率基本稳定在90%以上,相应的解吸度效率也保持在95%以上,PANAF-Cu良好的除磷可循环性;吸附极限试验表明当出水量达到2700 mL时,对磷酸盐的去除率仍达到99%,具有较高的实际应用能力. XPS解析表明,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附机理主要为纤维表面形成新的N-Cu-P配位结. PANAF-Cu对治理磷污染的废水具有很大的应用优势,是一种高效净化与回收水体磷酸盐的吸附材料.
铜离子固载腈纶纤维的制备及其对水体磷酸盐的去除
Preparation of copper ion supported polyacrylonitrile fiber and its removal of phosphate in water
-
摘要: 为缓解过量磷对水体的富营养化影响,本研究以聚丙烯腈纤维为原料,通过胺化、配位反应,成功制备出一种新型磷酸盐吸附剂(PANAF-Cu),对水体中过量的磷进行回收再利用,同时实现对磷的高资源化利用. 扫描电镜(SEM)、元素分析(EA)、X射线衍射(XRD)、傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)结果表明,胺基成功接枝,Cu2+在纤维上固载,并通过Cu—N键与纤维骨架结合. 吸附性能实验表明,PANAF-Cu具广泛的pH适应性,其中pH在5—8范围吸附能力较高. 通过对实验数据进行模型拟合,发现PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附过程更接近于化学吸附,且PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附更趋向于均匀的单分子层吸附,其对磷的最大理论吸附量为49.03 mg·g−1. PANAF-Cu最优异的循环能力,8次吸-脱附循环后,去除率仍可达到90%以上. 在连续流动实验中发现,当出水量小于2700 mL时,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐去除率可维持在99 %以上,PANAF-Cu在水体磷酸盐的去除和回收领域拥有良好的应用前景.Abstract: To alleviate the influence of phosphorus on water eutrophication, It is successfully prepared a new phosphate adsorbent (PANAF-Cu) using polyacrylonitrile fiber as raw material through amination and coordination reaction. It can be recovered and reused excess phosphorus in water and realized high resource utilization of phosphorus. The results of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), elemental analysis (EA), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) were showed that the amine group was successfully grafted on the fiber, and Cu2+ supported on the fiber skeleton by Cu-N bond. The adsorption performance experiments is showed that the PANAF-Cu had a wide range of pH adaptability. The adsorption capacity was higher in the range of pH 5—8. It can be found that the adsorption process of phosphate by PANAF-Cu was closer to chemical adsorption through model fitting of the experimental data. The adsorption of phosphate by PANAF-Cu was more homogeneous monolayer adsorption. The maximum theoretical adsorption capacity of phosphorus was 49.02 mg·g−1. The PANAF-Cu was had the best circulation ability. The removal rate can still reach to more than 90% after eight times sorption-desorption cycles. It was found that when the water yield was less than 2700 mL in the continuous flow experiment. The phosphate removal rate of the PANAF-Cu could be maintained above 99%. The PANAF-Cu will have a good application prospect in the field of phosphate removal and recovery in water bodies.
-
磷(P)是现代农业和化学工业中广泛使用的重要资源,通常以磷酸盐的形式存在于水溶液中[1]. 然而,在磷化工的快速发展和过量施用磷肥下导致磷大量向淡水资源转移,水体磷浓度超标,藻类过度生长,引起水体富营养化,造成磷资源损失和环境污染[2 − 3]. 此外,磷是一种不可再生资源,由于每年对磷的需求不断增长[4],预计在未来100—400年内将完全消耗掉[5]. 因此,废水中磷的去除和回收对于缓解富营养化染和磷资源危机至关重要[6].
迄今为止,化学沉淀[7]、膜分离工艺[8]、生物处理[9]、阴离子交换[10]和吸附[11]等多种技术已被证明可以用于去除水体中磷酸盐. 而吸附法因其操作简单、效率高成本低、应用方便等优点,吸引了众多研究人员的关注. 已经发现多种吸附材料,如水和氧化铁[12]、多孔二氧化硅[13]和碳基材料[14]等,它们具有良好的吸附性,用于去除废水磷酸盐的吸附剂. 但相对而言,这些吸附剂多为粉末形式很难在水中回收,这可能会造成二次污染问题[15]. 并且一些材料存在苛刻的问题制备条件好,成本高,去除能力低,难以分离等缺点. 制备高效稳定、绿色环保可循环利用的新型磷酸盐吸附材料吸附和回收水体磷酸盐,这是近年来的研究热点之一[16].
近年来,合成纤维作为催化剂和吸附剂载体受到研究者的广泛关注. 其中,腈纶纤维(PANF)含有丰富的氰基和酯基等化学性质活泼的基团,在一定条件下可以进行特定的化学反应,并可以转化为具有多种官能团的新型功能化纤维,是一种优秀的载体材料. 腈纶纤维具有成本低、易获得、密度低、柔韧性好等特点,其在大规模机械化加工和环境保护方面也具有一定的优势[17]. 腈纶纤维可以在一定条件进行灵活改性,构建富含氨基、羟基、羧基、季铵盐等组分[18]. 例如,Xu等[19]通过简单的化学接枝反应合成了一种可回收的载铁胺化聚丙烯腈纤维(PANAF-Fe)去除废水中的磷酸盐;Zheng等[20]合成了富含氯离子的功能化聚丙烯腈纤维(PANAF-Cl),对废水中磷酸盐的去除率高达90%以上,最大吸附容量为15.49 mg·g−1. 丁天琦[21]以聚丙烯腈(PAN)作为基体,制备出多孔碳纳米纤维膜,对磷酸盐最大去除量可达131 mg·g−1.
铁、铜、镧等金属和磷酸盐具有较强的结合能力,其在水体磷酸盐的去除获得较多的应用. 然而,使用固载铜离子的胺化纤维对水中磷酸盐的吸附尚缺乏研究. 本研究以腈纶纤维为原料,将Cu2+固载在胺化改性腈纶纤维表面,制备了新型磷酸盐吸附剂(PANAF-Cu),探究了该吸附剂对水体中磷酸盐的吸附性能,为废水中磷的回收提供理论依据.
1. 实验部分(Experimental section)
1.1 试剂与仪器
腈纶纤维(抚顺石化公司,中国),使用前将其剪成长度约10 cm备用. 实验中所有化学试剂均为国内市售分析纯试剂,且未进一步纯化. 本实验中所用化学试剂:乙二胺、磷酸二氢钾(上海阿拉丁试剂有限公司)、三水合硝酸铜(上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司);盐酸、硝酸、硫酸(西陇科技有限公司);碳酸钾、氢氧化钠、碳酸氢钠(上海素艺化学试剂有限公司);氯化钾、硫酸钾、硝酸钾、一水合柠檬酸(国药集团化学试剂有限公司)、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA,上海苏懿化学试剂有限公司)、氯化钠(上海中试化工有限公司). 本研究中的所有实验使用的皆为去离子水.
实验中主要用到的仪器为:集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器(DF-101S),巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;磁力搅拌器(84-1A),金坛区西城新瑞仪器厂;鼓风干燥箱(DHG-9070A型),常州海博仪器设备有限公司;pH计(FE20~standard),梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;循环水式多用真空泵(SHB-Ⅲ),郑州长城科工贸有限公司;分光光度计(722G),上海仪电分析仪器有限公司.
1.2 胺化腈纶纤维的合成
将600 mg干燥的腈纶纤维(PANF)、20 mL乙二胺和20 mL去离子水(DI)先在室温条件下混合搅拌,然后加入到高压反应釜中125°C反应100 min.反应结束后,将纤维从溶液中分离出来,后用70—80℃去离子水反复洗涤,再将纤维置于60℃烘箱中干燥过夜,得到淡黄色的胺化纤维(PANAF),即胺化腈纶纤维.
1.3 铜离子固载胺化腈纶纤维的设计合成
准备好50 mL 10 mmol·L−1的三水合硝酸铜(Cu(NO3)2·3H2O)配制的硝酸铜溶液,将50 mg干燥过夜后的胺化纤维加入到溶液中,室温下搅拌30 min,过滤后,进一步洗涤,反复冲洗,后将纤维放置在60 ℃的烘箱中干燥6 h,即可得到载铜的功能化纤维PANAF-Cu.
1.4 材料的表征
扫描电子显微镜(SEM,德国蔡司Sigma 300),傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(FTIR,美国PerkinElmer Spectrum One),全自动元素分析仪(EA,德国Vario EL Cube),X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,美国Thermo Scientific K-Alpha),X射线衍射仪(XRD,德国Bruker D8 Advance),pH计(METTLER TOLEDO,FE20),可见分光光度计(722G,Shanghai).
1.5 铜离子固载腈纶纤维(PANAF-Cu)的表征
利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、元素分析(EA)、傅里叶红外光谱仪(FTIR)、X射线衍射光谱(XRD)和能量色散X射线谱仪(XPS)等表征功能化纤维的表面形貌、化学结构及内部晶体结构等,从而根据表征结果检验改性纤维是否初步制备成功.
1.6 吸附实验
分别探究不同吸附时间、不同pH值、不同温度以及不同初始磷酸盐浓度下PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附能力. 纤维吸附饱和后,用镊子将纤维吸附剂从溶液中分离出来,从剩余溶液中吸取1 mL溶液放入50 mL容量瓶中,后按钼酸铵分光光度法测定不同条件下待测液中磷酸盐的浓度,测定低浓度磷酸盐时,要先将剩余溶液用0.22 μm滤膜过滤,后使用ICP-OES测定. 所有吸附实验均进行3次重复. 计算吸附量和吸附率公式如下:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) 式中,η为吸附率,%;qe为吸附P的量,mg·g−1;C0和Ce分别为无机磷初始质量浓度和平衡浓度,mg·L−1;V为溶液体积,L;W为吸附剂添加量,g.
1.7 吸附动力学
吸附动力学是用来描述吸附剂吸附溶质速率快慢的方式,采用拟一级动力学和拟二级动力学模型探究正在进行的吸附过程,以便讨论其合适的吸附机理. 不同动力学模型如下:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (3) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (4) 其中, qt和qe为t时刻和平衡时的吸附量(mg·g−1)K1和K2依次为拟一级动力学和拟二级动力学的吸附速率常数.
1.8 吸附等温学
吸附等温线是描述在一定温度下吸附剂达到吸附平衡状态时吸附量(qe)和吸附质浓度(Ce)之间关系的曲线,常见的模型有Freundlich模型、Langmuir模型、Temkin 模型和D-R方程,本文采用Langmuir和Freundlich模型探究PANAF-Cu对无机磷的吸附方式,拟合方程如下:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (5) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (6) 其中,qm为Langmuir模型估算的理论最大吸附量,KL为Langmuir常数,KF和n分别是Freundlich常数和均匀性系数.
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 功能化纤维(PANAF-Cu)的制备
固载铜离子的功能化腈纶纤维(PANAF-Cu)的合成由两步法完成,首先腈纶纤维和乙二胺发生胺化反应,纤维表面富含伯氨功能基的胺化纤维(PANAF),进一步利用氮和铜的配位作用,成功构建铜离子螯合的胺化纤维(PANAF-Cu). 胺化纤维的改性程度可以通过增重法来计算,胺化后的纤维对比腈纶纤维质量增加地较为明显,增重为10%,且纤维颜色也发生了变化,说明乙二胺被成功接枝到纤维表面. 胺化的程度可以通过控制反应时间或者乙二胺的浓度,过低的胺化程度不利于铜离子的螯合,然而过高的胺化程度导致纤维机械强度的下降,因此本文选择增重为10%的PANAF作进一步研究.
此外,本文研究了胺化纤维与不同浓度硝酸铜溶液制备得到的PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附能力, PANAF-Cu功能化纤维在Cu(NO3)2浓度增加的同时,其对磷酸盐的去除能力也不断增加,并且在Cu(NO3)2浓度为10 mmol·L−1时达到最高值,最大吸附量为35.29 mg·g−1. 然而,随着硝酸铜浓度的继续增加,PANAF-Cu中铜的含量达到饱和,导致其对磷酸盐的吸附能力趋势放缓至平衡,这是因为PANAF对铜的固载量是有限的,表明当铜离子浓度大于10 mmol·L−1时,PANAF对铜离子的固载量达到饱和. 因此,选择浓度为10 mmol·L−1的硝酸铜溶液制备PANAF-Cu.
2.2 功能化纤维(PANAF-Cu)的表征
2.2.1 纤维微观形貌分析
如图1可知,样品都呈连续完整的纤维状,表明纤维在改性前后及使用过程中,其完整性得到了良好的保持,未遭受到破坏. 放大2000倍的电子显微镜图像看到,随着改性反应的进行,纤维表面出现了若干裂纹,可能是因为氨基的进入和增溶作用导致纤维直径增加,出现裂纹,在一定程度上增加了纤维的表面积. 放大20000倍后,在胺化反应和螯合Cu2+后,可以清楚地观察到纤维不同程度的变形和溶胀,纤维表面明显变得粗糙,同时还被一层颗粒状物所覆盖,这可能是因为纤维表面的薄膜形成了由若干Cu-N配位产生的片晶.
2.2.2 纤维表面组分分析
为进一步明确纤维结构,利用傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)和能谱图[22]分析了纤维改性前后的纤维表面组分. 图2(a)显示了每个阶段纤维的EDS能谱图,发现与PANAF相比,PANAF-Cu出现了新的Cu元素的峰,这表明Cu2+成功的固载到了胺化纤维上. 图2(b)显示了每个阶段纤维的红外光谱,PANF在2242 cm−1处的吸收峰和在1732 cm−1处的吸收峰分别为腈纶纤维第一单体丙烯腈的C≡N的伸缩振动和第二单体丙烯酸甲酯的C=O伸缩振动[17]. 由于胺化反应消耗了PANF上的氰基,胺化反应后2242 cm−1处的吸收峰强度下降. 此外,由于PANF中的C≡N在强碱性EDA溶液中被水解,与EDA中的NH2基团在1640 cm−1处形成了酰胺C=O双键的伸缩震动峰,说明了胺基基团的成功接枝[23]. 在胺化改性纤维吸附Cu2+后,在538 cm−1处新峰的出现,可能归因为Cu-N的配位结构,表明Cu已被-NH所固化[24]. 上述结果表明了胺基的成功接枝,以及Cu2+在纤维上的固载.
2.2.3 纤维表面晶体分析
通过X射线衍射(XRD)表征了不同纤维的晶体结构. 图3显示了不同阶段的纤维的XRD图像,每个纤维都在2θ为16.5°处有一个共同的衍射峰,2θ = 28.6°处有一个不太强烈的衍射峰,表明PANAF、PANAF-Cu和PANAF-Cu-P与PANF具有相似的特征峰,表明纤维改性后仍保持了腈纶纤维原有的晶体结构,未被破坏,依然保持良好. 此外,PANAF、PANAF-Cu和PANAF-Cu-P较弱的衍射峰的强度明显降低,表明聚丙烯腈的聚合物链结构已经被胺分子部分溶解. 进一步固载Cu2+后,XRD光谱中并没有观察到结晶的Cu,这表明加载在纤维表面的固体Cu处于无定形状态,并可能通过Cu—N键与纤维骨架结合.
2.2.4 纤维元素含量分析
通过元素分析分析了不同阶段纤维的元素组成,相关数据见表1. 与PANF相比,PANAF中的C含量降低,H含量增加,因为乙二胺比原始腈纶纤维具有更少的C和更多的H,表明乙二胺被成功接枝到PANF上. 此外,N的存在也证实了不是所有的C≡N基团都被水解,参与EDA的官能化,所以改性过程可能仅发生在表面. 引入Cu元素后,PANAF-Cu中C、H含量的降低表明—NH2直接参与了Cu2+的吸附. 引入P元素后,相对于PANAF-Cu,PANAF-Cu-P中N含量的下降表明Cu与N形成配位键,被封存在纤维上,以上实验结果证明PANAF-Cu的成功改性.
表 1 不同纤维的元素分析数据Table 1. Elemental analysis data of different fibers样品Sample C/% H/% N/% 1 PANF 66.11 4.86 23.91 2 PANAF 60.30 5.89 22.77 3 PANAF-Cu 55.28 5.49 22.57 4 PANAF-Cu-P 55.76 5.65 21.91 2.3 PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附性能研究
2.3.1 pH对 PANAF-Cu吸附磷性能的影响
pH值是决定吸附效果的关键因素. 图4表明,pH值在3—7时,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附量随着pH的升高而迅速增大,并在pH=7时达到最大值26.99 mg·g−1. 聚丙烯腈纤维的氨基的非选择性吸附是以静电作用形式产生的,因此,带正电的表面可以增强带负电的磷酸根阴离子的吸附. 其后通过配体的交换让表面负载的Cu2+对磷的进行选择性吸附. 在pH值在5—8的条件下,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附量都能维持在较好的水平,吸附量仍能保持到10 mg·g−1以上. 表明固载铜离子的胺化改性纤维具有较高且稳定的磷酸盐去除效率.
2.3.2 吸附动力学分析
分别研究了在288、298 、308 K 的3种温度条件下,纤维吸附剂随时间改变对磷酸盐的吸附量的变化. 3条曲线的变化趋势大致相同,前10分钟内吸附速度较快,随后吸附速率减缓,在30 min左右基本达到吸附平衡. 这表明,在刚开始吸附阶段,吸附剂表面暴露的大量活性位点可以很迅速地捕获水中的磷酸盐. 随着时间的推移,吸附剂的表面吸附活性位点逐渐达到饱和,吸附过程随之减慢. 为深入了解PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附过程,分别通过拟一级动力学和拟二级动力学对吸附数据进行拟合. 拟合图和动力学参数分别如图5和表2所示,在288、298、308 K等3种温度下,拟二级动力学模型的R2均高于拟一级动力学模型;而且,用拟二级动力学模型拟合的qe值也更贴近于实际的吸附量. 因此,该吸附剂对磷酸盐的吸附过程更加倾向于化学吸附[25].
表 2 PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的动力学参数Table 2. Kinetic parameters of PANAF-Cu on phosphateT/K 拟一级动力学模型Quasi-first-order kinetic model 拟二级动力学模型Quasi-second-order kinetic model K1/ min qe /(mg·g−1) R2 K2 /min−1 qe/ (mg·g−1) R2 288 0.824 19.781 0.754 0.056 21.533 0.952 298 0.999 20.700 0.688 0.066 22.237 0.931 308 0.927 21.754 0.627 0.073 23.379 0.906 2.3.3 吸附等温线分析
为了阐明PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附模式和吸附性能,在室温下,对不同初始磷酸盐浓度下进行了吸附等温实验. 实验发现,吸附剂对磷酸盐的吸附能力伴随着磷酸盐初始浓度的升高而增强,直至吸附饱和. 这可能是因为在较低的磷酸盐浓度下,磷的配位位点更多,随着磷浓度的提高,活性吸附位点也逐渐达到饱和,吸附量不再升高. 利用Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温线模型对数据进行拟合,通过拟合得到的图和相关数据分别位于图6和表3.
从表3可以看出,Langmuir模型拟合曲线的回归参数大于Freundlich模型,说明PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附更适合于Langmuir模型. 因此,吸附剂对磷酸盐的吸附更趋向于均匀的单分子层化学吸附. 通过Langmuir模型估算PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的最大吸附量为49.03 mg·g−1.
表 3 PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的等温学参数Table 3. Isothermal parameters of PANAF-Cu on phosphateLangmuir Freundlich qe /(mg·g−1) KL/(L·mg−1) R2 KF /(mg·g−1·(L·mg−1)1/n) 1/n R2 49.026 20.258 0.995 3.242 0.659 0.982 2.3.4 共存阴离子影响
为测定PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐去除的选择性,选定硫酸盐、氯化物、硝酸盐和碳酸盐为代表性的共存阴离子. 在浓度为1×10−3 mol·L−1的磷酸盐中分别加入同等浓度的Cl−、NO3−、CO32-以及SO42-等共存离子溶液,探究PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附能力,结果见图7. 结果表明, 4种共存离子对PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐的影响如下:SO42-﹥CO32-﹥Cl−﹥NO3−. 其中NO3−对磷酸盐的吸附影响最小. SO42-和CO32-比Cl−和NO3−更有竞争力,可能是因为硫酸盐和碳酸盐作为二价离子具有更高的电荷密度,比单价阴离子能更迅速地被吸附. 以上实验说明PANAF-Cu在实际水体中也能在较多阴离子的影响下具有很好的除磷效果.
2.3.5 吸附机理
XPS分析进一步揭示了吸附剂的化学状态和元素组成. 图8显示了吸附前后PANAF-Cu纤维的XPS光谱,与PANAF相比,PANAF-Cu出现了新的Cu元素的峰(图8a),这表明Cu2+成功的固载到了胺化纤维上,吸附后的纤维中出现了一个133.5 eV的信号峰,这是由P 2p轨道引起的,表明磷酸盐被纤维成功捕获(图8b). Cu2+对磷酸盐吸附的贡献由纤维吸附后Cu元素的高分辨率光谱证明(图8 c-d),对比吸附前的纤维,Cu的高分辨率光谱发现,PANAF-Cu-P的高分辨率Cu 2p光谱被分解成两个峰,最初位于934.73 eV的Cu—N键结合能下降到932.61 eV,这可以归因于来自磷酸盐的P原子为Cu提供了额外的电子,形成了新的N-Cu-P配位键,从而增加了Cu元素电子云密度,降低了结合能,这证实了改性纤维表面的Cu2+通过配位吸收起到了对P的固化作用. 即表明络合-配体相互作用是该吸附过程的主要机制[26]. 根据N的吸附前后的高分辨率光谱(图8 e-f)发现原本位于400.62 eV 的—NH2(—NH)键结合能下降到399.93 eV,氨基与Cu离子形成Cu-N的配位结构,纤维表面的Cu2+通过和磷酸盐中P—O键作用形成新的N-Cu-P配位去除磷酸盐,该基团的移动表明含氮官能团在PANAF-Cu对废水中的磷酸盐的吸附中起着重要作用. 因此根据上述结果,可以推断PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的有效吸附主要依赖于纤维表面的Cu-N配位结构,从而形成新的N-Cu-P配位结构.
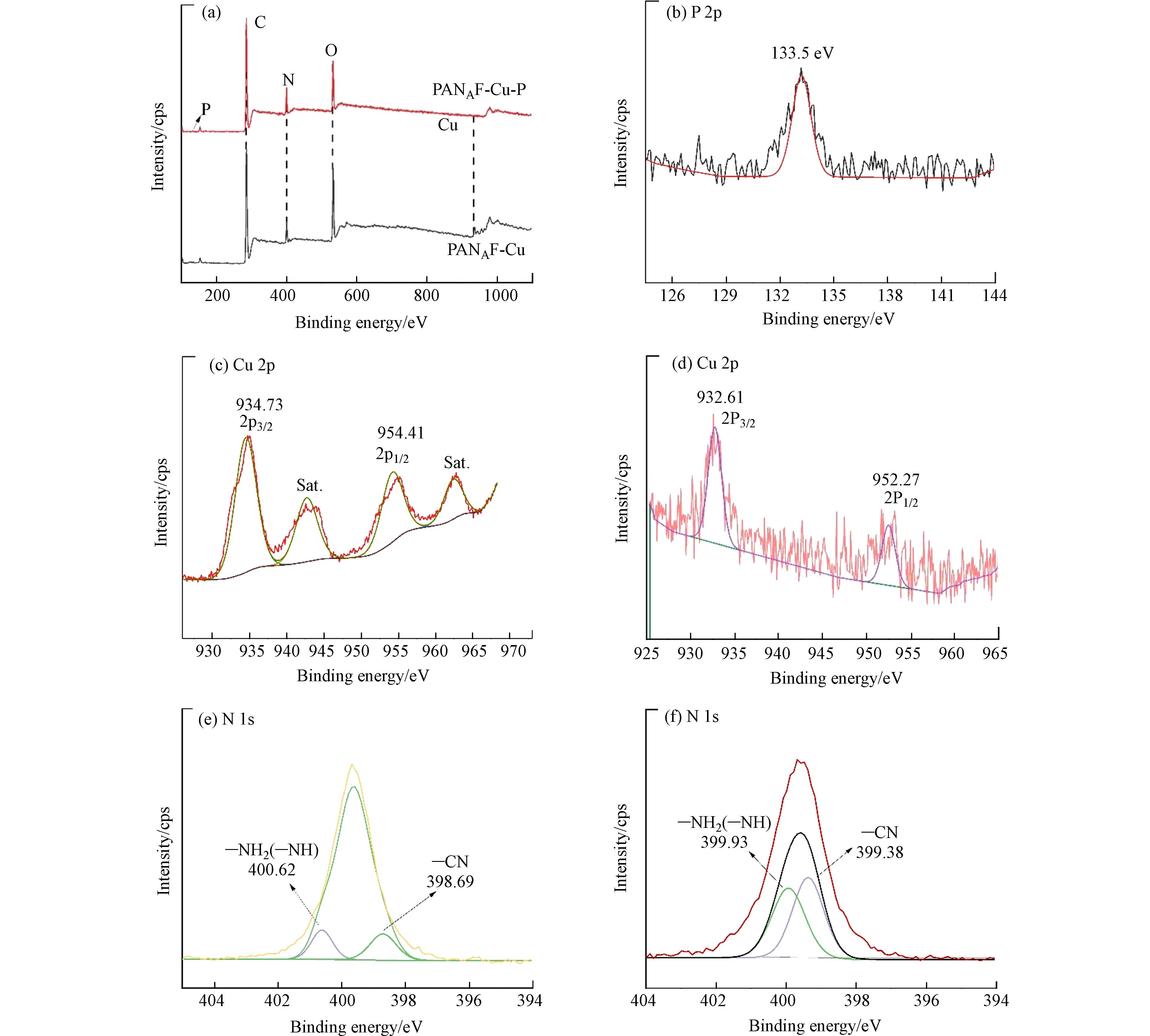 图 8 功能化纤维吸附磷酸盐前后的XPS谱图Figure 8. XPS spectra of functionalized fibers before and after phosphate adsorption(a)PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐前后的XPS总谱图,(b)P 2p的高分辨光谱图,(c-d)PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐前、后的Cu 2p的高分辨光谱图,(e-f)PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐前、后的N 1s的高分辨光谱图(a) XPS survey spectra of PANAF-Cu before and after phosphate adsorption, (b) High resolution XPS spectrum of P2p, (c-d) High resolution XPS spectrum of Cu2p before and after phosphate adsorption, (e-f) High resolution XPS spectrum of N1s before and after phosphate adsorption
图 8 功能化纤维吸附磷酸盐前后的XPS谱图Figure 8. XPS spectra of functionalized fibers before and after phosphate adsorption(a)PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐前后的XPS总谱图,(b)P 2p的高分辨光谱图,(c-d)PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐前、后的Cu 2p的高分辨光谱图,(e-f)PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐前、后的N 1s的高分辨光谱图(a) XPS survey spectra of PANAF-Cu before and after phosphate adsorption, (b) High resolution XPS spectrum of P2p, (c-d) High resolution XPS spectrum of Cu2p before and after phosphate adsorption, (e-f) High resolution XPS spectrum of N1s before and after phosphate adsorption2.3.6 循环性能实验
为探究不同解吸剂对磷酸盐的解吸率影响,进行对比实验(表4),发现HCl、NaCl、C6H8O7(柠檬酸)和EDTA(乙二胺四乙酸二钠)对磷酸盐的解吸率分别为52.50%、2.50%、87.50%和97.50%,EDTA的解吸率最高为97.5%. 从图9可以看出,经过8次循环后,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的解吸率基本稳定在90%以上,相应的解吸率也保持在95%以上,表明PANAF-Cu具有多重吸附和再生的优良特性.
表 4 不同洗脱液对PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐后的解吸率Table 4. Desorption rate of phosphate adsorbed by different eluents to PANAF-Cu洗脱剂Eluent 浓度/(mmol·L−1)Concentration V/mL T/ h 解吸率/%Desorption rate HCl 1 50 1 52.5 NaCl 1 50 1 2.5 C6H3O7 1 50 1 87.5 EDTA 1 50 1 97.5 2.3.7 改性纤维在连续流动实验中的应用
用初始浓度为2 mg·L−1的磷酸盐溶液利用恒流泵以0.5 mL·min−1的速率进行连续流动实验. 每隔50 mL测试出水中的磷酸盐浓度,就可以绘制出磷酸盐的穿透曲线,如图10所示. 实验发现,随着出水量的增加,出水中的磷酸盐浓度也随之增加. 当出水量小于2700 mL时,磷酸盐去除率维持在99%以上,大于2700 mL后,对硫酸盐的去除率大幅度下降. 这些结果皆说明PANAF-Cu在模拟自然水体和流动的水体条件下的具有优异除磷效果.
2.3.8 PANAF-Cu在实际废水中除磷性能研究
本研究进一步探究PANAF-Cu在实际水体的应用效果,测试了PANAF-Cu对巢湖(自然水体)磷污染水体中对磷的吸附能力. 为了更好地说明问题,将采集的水样的磷酸盐浓度调整为1000 µg· L−1 P. 分别将0、5、10、20、40、60 mg的PANAF-Cu置于10 mL上述水样中搅拌24h,利用ICP测定剩余磷酸盐浓度,测定结果见表5. 实验表明,当PANAF-Cu添加量超过20 mg时,磷酸盐浓度即可降至100 µg·L−1以下,已低于湖泊富营养化的最小磷浓度200 µg·L−1. 可见,本研究制备得到的少量PANAF-Cu在实际水体中也可以有效的降低水体的富营养化程度.
表 5 PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附极限测试Table 5. Adsorption limit test of phosphate by PANAF-CuPANAF-Cu的质量Quality of PANAF-Cu 体积/ mLVolume 时间/ hTime 磷酸盐浓度/(µg·L−1 P)Phosphate concentration 0 10 24 1113 5 10 24 759 10 10 24 393 20 10 24 98 40 10 24 92 60 10 24 90 2.3.9 与其他除磷吸附剂的比较
为了评估功能纤维吸附剂的吸附效果,表6列出了近年来报道的一些用于去除废水P的吸附剂材料. 值得注意的是,本工作中合成的铜胺负载纤维可以在较温和的反应条件下就可以获得较高的吸附能力. 此外,与表中列举的其他吸附剂有限的P吸附能力相比,接枝了Cu-N配体结构的功能化纤维表现出了更高的P容量和更快的吸附速率. 这可以归因于配位中心的铜离子和-NH2中的N原子之间的配位模式所引起的铜离子的高反应性以及形成的N-Cu-P之间的独特结合机制. 此外,PANAF-Cu在循环使用8次以后依然能够有效地去除磷酸盐. 总的来说,与目前报道的磷酸盐选择性吸附材料相比,本课题中报道的功能纤维吸附剂在常温下具有更高的反应活性和更好的选择性吸附性能.
表 6 与其他除磷吸附剂的比较Table 6. Comparison with other phosphorus removal adsorbent吸附剂Adsorbent 吸附时间Adsorption time 最大吸附量(mg·g−1)Maximum adsorption capacity 循环次数Number of cycles 参考文献 黏土-牡蛎壳复合吸附材料 7 d 10 — [27] 鸟蛤壳粉 20 min 7.1 — [28] 掺杂淀粉的磷石膏和磷矿浮选尾矿 60 min 31.28 — [29] 淀粉包裹的Fe3O4纳米颗粒 90 min 7.73 3 [30] 磁性淀粉基Fe3O4黏土聚合物(CIONP) 2 h 3.12 3 [31] 炼钢渣 72 h 10.21 — [32] 掺杂SiO2的活性炭 1 h 0.65 — [33] 固载Fe2+的活性炭 4 h 14.12 — [34] 固载铜离子的功能化腈纶纤维(PANAF-Cu) 24 h 26.99 8 本研究 3. 结论(Conclusion)
以聚丙烯腈纤维为原料,通过胺化改性使得聚丙烯腈纤维表面固载胺基,在通过胺基与铜的配位作用,成功合成具有Cu-N配位结构的新型吸附剂(PANAF-Cu). 在pH=7时达到吸附量最大值26.99 mg·g−1,pH值在5—8的条件下,吸附量仍能保持到10 mg·g−1以上. 表明固载铜离子的胺化改性纤维具有较高且稳定的磷酸盐去除效率. PANAF-Cu的吸附过程更符合伪二级动力学吸附模型,吸附等温学拟合结果更适合Langmuir等温模型,表明P在PANAF-Cu属单分子层吸附,在一定温度内,对磷酸盐的去除效果随着温度升高而增加. 通过吸/脱附循环性能试验,经过8次循环后,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附率基本稳定在90%以上,相应的解吸度效率也保持在95%以上,PANAF-Cu良好的除磷可循环性;吸附极限试验表明当出水量达到2700 mL时,对磷酸盐的去除率仍达到99%,具有较高的实际应用能力. XPS解析表明,PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附机理主要为纤维表面形成新的N-Cu-P配位结. PANAF-Cu对治理磷污染的废水具有很大的应用优势,是一种高效净化与回收水体磷酸盐的吸附材料.
-
表 1 不同纤维的元素分析数据
Table 1. Elemental analysis data of different fibers
样品Sample C/% H/% N/% 1 PANF 66.11 4.86 23.91 2 PANAF 60.30 5.89 22.77 3 PANAF-Cu 55.28 5.49 22.57 4 PANAF-Cu-P 55.76 5.65 21.91 表 2 PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的动力学参数
Table 2. Kinetic parameters of PANAF-Cu on phosphate
T/K 拟一级动力学模型Quasi-first-order kinetic model 拟二级动力学模型Quasi-second-order kinetic model K1/ min qe /(mg·g−1) R2 K2 /min−1 qe/ (mg·g−1) R2 288 0.824 19.781 0.754 0.056 21.533 0.952 298 0.999 20.700 0.688 0.066 22.237 0.931 308 0.927 21.754 0.627 0.073 23.379 0.906 表 3 PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的等温学参数
Table 3. Isothermal parameters of PANAF-Cu on phosphate
Langmuir Freundlich qe /(mg·g−1) KL/(L·mg−1) R2 KF /(mg·g−1·(L·mg−1)1/n) 1/n R2 49.026 20.258 0.995 3.242 0.659 0.982 表 4 不同洗脱液对PANAF-Cu吸附磷酸盐后的解吸率
Table 4. Desorption rate of phosphate adsorbed by different eluents to PANAF-Cu
洗脱剂Eluent 浓度/(mmol·L−1)Concentration V/mL T/ h 解吸率/%Desorption rate HCl 1 50 1 52.5 NaCl 1 50 1 2.5 C6H3O7 1 50 1 87.5 EDTA 1 50 1 97.5 表 5 PANAF-Cu对磷酸盐的吸附极限测试
Table 5. Adsorption limit test of phosphate by PANAF-Cu
PANAF-Cu的质量Quality of PANAF-Cu 体积/ mLVolume 时间/ hTime 磷酸盐浓度/(µg·L−1 P)Phosphate concentration 0 10 24 1113 5 10 24 759 10 10 24 393 20 10 24 98 40 10 24 92 60 10 24 90 表 6 与其他除磷吸附剂的比较
Table 6. Comparison with other phosphorus removal adsorbent
吸附剂Adsorbent 吸附时间Adsorption time 最大吸附量(mg·g−1)Maximum adsorption capacity 循环次数Number of cycles 参考文献 黏土-牡蛎壳复合吸附材料 7 d 10 — [27] 鸟蛤壳粉 20 min 7.1 — [28] 掺杂淀粉的磷石膏和磷矿浮选尾矿 60 min 31.28 — [29] 淀粉包裹的Fe3O4纳米颗粒 90 min 7.73 3 [30] 磁性淀粉基Fe3O4黏土聚合物(CIONP) 2 h 3.12 3 [31] 炼钢渣 72 h 10.21 — [32] 掺杂SiO2的活性炭 1 h 0.65 — [33] 固载Fe2+的活性炭 4 h 14.12 — [34] 固载铜离子的功能化腈纶纤维(PANAF-Cu) 24 h 26.99 8 本研究 -
[1] 葛文书. 钙铝层状双氢氧化物/粉煤灰复合物用于磷吸附[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2022. GE W S. Phosphorus removal by composite of calcium-aluminum layered double hydroxides and fly ash[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2022 (in Chinese).
[2] 郝强州. 复合金属氧化物掺杂沸石对水中氨氮和磷酸根的吸附特性研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. HAO Q Z. Study on the adsorption characteristics of ammonia nitrogen and phosphate in water by zeolite doped with composite metal oxides[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2022 (in Chinese).
[3] 张小宇, 张世熔, 王新月, 等. 镧改性农业废弃秸秆对养殖废水中磷的去除[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1274-1284. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020072802 ZHANG X Y, ZHANG S R, WANG X Y, et al. Removal of phosphorus from wastewater by lanthanum modified straws[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1274-1284 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020072802
[4] 刘欣. 中国磷循环格局演变及其资源与环境效应[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2017. LIU X. Dynamics of phosphorus cycling in China and the impacts on resources and the environment[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2017 (in Chinese).
[5] SCHOLZ R W, ULRICH A E, EILITTÄ M, et al. Sustainable use of phosphorus: A finite resource[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 461/462: 799-803. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.043 [6] 冯鑫, 周剑, 潘杨. 蓝铁矿法回收生物膜富集的城市污水中的磷[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(5): 1787-1795. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021011004 FENG X, ZHOU J, PAN Y. Vivianite crystallization method to recover phosphorus in municipal sewage enriched by biofilm method[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(5): 1787-1795 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021011004
[7] LACSON C F Z, LU M C, HUANG Y H. Calcium-based seeded precipitation for simultaneous removal of fluoride and phosphate: Its optimization using BBD-RSM and defluoridation mechanism[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 47: 102658. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102658 [8] 康为清, 时历杰, 赵有璟, 等. 水处理中膜分离技术的应用[J]. 无机盐工业, 2014, 46(5): 6-9. KANG W Q, SHI L J, ZHAO Y J, et al. Application of membrane separation technique in water treatment[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2014, 46(5): 6-9 (in Chinese).
[9] SUN S F, GAO M C, WANG Y, et al. Phosphate removal via biological process coupling with hydroxyapatite crystallization in alternating anaerobic/aerobic biofilter reactor[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 326: 124728. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124728 [10] DONG H, WEI L Z, TARPEH W A. Electro-assisted regeneration of pH-sensitive ion exchangers for sustainable phosphate removal and recovery[J]. Water Research, 2020, 184: 116167. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116167 [11] 韩飞超. 聚苯乙烯球体基水合氧化锰复合材料的研制及其强化除磷性能[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2014. HAN F C. Preparation of polystyrene anion exchanger-based Hydrous manganese oxide nanocomposite for preferable phosphate removal from water[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2014 (in Chinese).
[12] LIU Y Q, CHEN Z H, YIN X S, et al. Selective and efficient removal of As(V) and As(III) from water by resin-based hydrated iron oxide[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2023, 1273: 134361. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134361 [13] CHEN L, LI Y Z, SUN Y B, et al. La(OH)3 loaded magnetic mesoporous nanospheres with highly efficient phosphate removal properties and superior pH stability[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 360: 342-348. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.234 [14] BRAUN J C A, BORBA C E, GODINHO M, et al. Phosphorus adsorption in Fe-loaded activated carbon: Two-site monolayer equilibrium model and phenomenological kinetic description[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 361: 751-763. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.073 [15] 吴语潇, 杨甜, 徐武松, 等. 极性可调功能化纤维的构建及其对废水磷酸盐的去除[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(12): 3898-3908. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021051007 WU Y X, YANG T, XU W S, et al. The construction of polarity regulable functionalized fibers and its removal of phosphate in wastewater[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(12): 3898-3908 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021051007
[16] 崔婉莹, 艾恒雨, 张世豪, 等. 改性吸附剂去除废水中磷的应用研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(10): 4210-4226. CUI W Y, AI H Y, ZHANG S H , et al. Research status on application of modified adsorbents in phosphorus removal from wastewater[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(10): 4210-4226 (in Chinese).
[17] XU G, CAO J, ZHAO Y. et al. Phosphorylated Polyacrylonitrile Fibers as an Efficient and Greener Acetalization Catalystr[J]. Chemistry –An Asian Journal, 2017, 12(19): 2565-2575. doi: 10.1002/asia.201700846 [18] NATARAJ S K, YANG K S, AMINABHAVI T M. Polyacrylonitrile-based nanofibers—a state-of-the-art review[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2012, 37(3): 487-513. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.07.001 [19] XU W S, ZHENG W J, WANG F J, et al. Using iron ion-loaded aminated polyacrylonitrile fiber to efficiently remove wastewater phosphate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 403: 126349. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126349 [20] ZHENG W, WU Q, XU W. et al. Efficient capture of phosphate from wastewater by a recyclable Environmental Science-Water Research & Technology, 2022, 8(3): 607-618. [21] 丁天琦. 基于静电纺丝制备聚丙烯腈基多孔纤维膜及其吸附性能研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽建筑大学, 2023. DING T Q. Preparation and adsorption properties of polyacrylonitrile based porous fiber membranes based on electrospinning technique[D]. Hefei: Anhui Jianzhu University, 2023 (in Chinese).
[22] MEEDS J A, MARTY KRANABETTER J, ZIGG I, et al. Phosphorus deficiencies invoke optimal allocation of exoenzymes by ectomycorrhizas[J]. The ISME Journal, 2021, 15: 1478-1489. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-00864-z [23] KUANG Y Z, HE H, CHEN S X, et al. Adsorption behavior of CO2 on amine-functionalized polyacrylonitrile fiber[J]. Adsorption, 2019, 25(4): 693-701. doi: 10.1007/s10450-019-00070-0 [24] DANON A, STAIR P C, WEITZ E. FTIR study of CO2 adsorption on amine-grafted SBA-15: Elucidation of adsorbed species[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(23): 11540-11549. doi: 10.1021/jp200914v [25] LIU R T, CHI L N, WANG X Z, et al. Effective and selective adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution via trivalent-metals-based amino-MIL-101 MOFs[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 357: 159-168. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.122 [26] ZHOU S L, HE H, WANG L, et al. The structural design of polyacrylonitrile fibre-based colorimetric sensors and their synergistic interaction mechanism for Cu2+ detection[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(35): 16806-16821. doi: 10.1007/s10853-020-05217-x [27] ZHOU Z J, XU Q L, WU Z J, et al. Preparation and characterization of clay-oyster shell composite adsorption material and its application in phosphorus removal from wastewater[J]. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 2023, 32: 101023. doi: 10.1016/j.scp.2023.101023 [28] NAYEEM A, MIZI F, ALI M F, et al. Utilization of cockle shell powder as an adsorbent to remove phosphorus-containing wastewater[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 216: 114514. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114514 [29] JIANG W, JIANG Y S, LI P Y, et al. Reuse of phosphogypsum and phosphorus ore flotation tailings as adsorbent: The adsorption performance and mechanism of phosphate[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2023, 178: 111313. doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2023.111313 [30] ATNAFU T, LETA S. Plasticized magnetic starch-based Fe3O4 clay polymer nanocomposites for phosphate adsorption from aqueous solution[J]. Heliyon, 2021, 7(9): e07973. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07973 [31] 丁程程, 潘纲, 张美一. 淀粉改性纳米四氧化三铁的制备及其除磷效能的研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(10): 2167-2172. DING C C, PAN G, ZHANG M Y. Study on preparation of starch-coated Fe3O4 and its phosphate removal properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011, 5(10): 2167-2172 (in Chinese).
[32] VU M T, NGUYEN L N, ABU HASAN JOHIR M, et al. Phosphorus removal from aqueous solution by steel making slag–Mechanisms and performance optimisation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 284: 124753. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124753 [33] MEHRABI N, SOLEIMANI M, SHARIFIFARD H, et al. Optimization of phosphate removal from drinking water with activated carbon using response surface methodology (RSM)[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2016, 57(33): 15613-15618. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2015.1070763 [34] WANG Z F, SHI M, LI J H, et al. Influence of moderate pre-oxidation treatment on the physical, chemical and phosphate adsorption properties of iron-containing activated carbon[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(3): 519-528. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60440-4 -




 下载:
下载: