-
随着我国社会和经济发展,农业生产过程中过量使用磷肥及城市大量排放含磷污水导致我国水体富营养化问题突显. 近年来,我国的滇池、太湖和巢湖等内陆湖泊不断发生水华现象[1]. 根据2019年中国海洋灾害公报显示,我国赤潮暴发频率自70年代开始每10年增长3倍,截止2018年我国有明确暴发时间及地点等基本信息的赤潮次数为1780次. 大量未经处理的含磷污水的直接排入是造成水体总磷超标的主要原因,包括城市、工业和农业中大量含磷水的排放. 控制磷污染,保障生态系统安全已刻不容缓.
吸附法除磷因具有操作简便、适用范围广、效果好、运行费用低等优点而得到高度关注[2]. 稀土元素镧(La)对磷酸盐具有强亲和力,可与磷酸根形成稳定不可溶的LaPO4,展现出优异的除磷性能[3]. 然而镧的氧化物通常以粉末形式存在,易流失、堵塞,且流体力学性能差,吸附磷后会沉入水体难以回收,造成了资源的浪费和污泥污染,从而限制了镧氧化物在水体除磷中的应用. 将La固定在多孔颗粒材料的表面或孔道中是减少La组分流失和提高除磷性能的有效方式. 目前常采用多孔的天然黏土材料(如沸石、蛭石、硅藻土等)、碳基材料(如活性炭、黑炭、碳纳米管等)、离子交换树脂高分子材料负载La,得到La改性的多孔无机或有机复合吸附材料,如La-负载多孔沸石、La-负载碳纳米管、La-离子交换树脂等含La吸附剂[4 − 6].
不同于以上载体硬模板方式固定La,钛(Ti)基多孔材料可通过原位自生模板法原位转化为介孔毫米球同步固载La[7],得到具有丰富的孔道(孔径2—50 nm)、高比表面积的球形颗粒,具有优异的流体力学与传质性能,有望实现高选择性除磷性能[8 − 9]. 而且,Ti载体本身也可通过静电吸附、配体交换、Ti—P化学键等作用吸附磷[10 − 11],起到协同La除磷作用. 故以Ti为载体通过溶胶-凝胶法制备镧钛双金属氧化物介孔毫米球,提高对磷的吸附能力,减少吸附过程中La的流失,同时大大增强吸附剂流体力学性能,实现吸附材料的分离与回收利用.
为此,本文以镧和钛金属盐为原料,海藻酸钠为交联剂,采用沉淀凝胶法制备了镧钛双金属氧化物介孔毫米球LaxTi1-xO2,利用N2吸附-脱附、XRD、SEM、TEM等对制备的LaxTi1-xO2进行了表征,根据镧钛物质的量比、煅烧温度对LaxTi1-xO2除磷性能的影响,优选出400 ℃煅烧制得的La0.5Ti0.5O2. 考察了La0.5Ti0.5O2投加量、溶液pH等因素对吸附的影响,并利用准一级和二级动力学模型及Langmuir和Freundlich模型对La0.5Ti0.5O2除磷过程进行了动力学与热力学研究. 通过除磷性能测定并结合零电荷点、FT-IR、XPS等表征手段提出了La0.5Ti0.5O2除磷机制.
-
实验过程中使用的试剂主要包括:LaN3O9·6H2O(AR,99%,麦克林)、TiOSO4·xH2SO4·xH2O(synthesis grade,阿拉丁)、尿素(AR,99%,阿拉丁)、海藻酸钠(AR,阿达丁)、磷酸二氢钾(AR,广东光华科技)、抗坏血酸(AR,西陇科学)、钼酸铵(AR,西陇科学)、酒石酸锑钾(AR,西陇科学)、硫酸(AR,中星化工),所有实验用水均为超纯水(Millipore,18.2 MΩ·cm).
-
镧钛金属氧化物制备是基于海藻酸钙凝胶球模板法和尿素沉淀法为基础并进行了改进和开发[12 − 13]. 制备具体步骤如下:将TiOSO4·xH2SO4·xH2O和LaN3O9·6H2O共15 mmol按照La占双金属元素物质的量比分别为0、2.5、5.0、7.5 mmol溶于80 mL去离子水中;将120 mL含有14.0 g尿素的水溶液加入到上述所得溶液中,500 r·min−1磁力搅拌并于90—95 ℃水浴锅中加热8 h;搅拌加热后,用去离子水将悬浊液离心清洗3次,得到高浓度金属氧化物前驱体悬浊液40 g,将0.4 g的海藻酸钠粉末加入到悬浊液中,在55 ℃水浴中高速磁力搅拌30 min预混合,静置30 min;利用蠕动泵将所得到的悬浊液滴入0.1 mol·L−1的LaN3O9·6H2O溶液中形成凝胶球,静置24 h后在60 ℃烘箱中烘干12 h;然后将烘干材料放入管式炉进行两段煅烧,先经氮气气氛下200 ℃预处理2 h后在空气气氛400 ℃下煅烧2 h,升温速度为5 ℃·min−1.
经过预实验后, LaN3O9·6H2O和TiOSO4·xH2SO4·xH2O共15 mmol分别按照La/Ti物质的量比1:1、2:1、3:1、1:3制备,其中La:Ti=2:1形成的球形形状不规范,故排除该物质的量比; La:Ti=3:1因过于黏稠无法成球,故也排除该物质的量比. 最终,制得3种不同物质的量比的小球材料,分别为:TiO2球、La:Ti=1:1(La0.5Ti0.5O2)、La:Ti=1:3(La0.25Ti0.75O2). 另外,为了探究煅烧温度的影响,在400 ℃和600 ℃两个不同的煅烧温度下制备了介孔毫米球.
-
通过测定ASAP2020HD88型比表面孔径测定仪(BET,中国,麦克默瑞提克)得到材料的比表面积和孔径. 通过JSM-6700F型扫描电子显微镜(SEM,日本,JEOL)分析介孔毫米球的表观形貌. 材料的微观结构通过JEM-2100F型透射电子显微镜/选区电子衍射(TEM/SAED,日本,JEOL)和D8ADVANCE型X射线衍射仪(XRD,美国,BRUKER)表征. 吸附剂中La含量采用6 mol·L−1硝酸消解后通过电感耦合等离子谱仪(ICP-OES, PerkinElmer,USA)测定.
-
用超纯水配制30 mg·L−1的KH2PO4溶液为初始磷溶液,取100 mL于150 mL三角烧瓶中. 用0.1 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液和0.1 mol·L−1的HCl溶液调节pH至7,温度为25 ℃,加入0.1 g吸附材料,振荡速率为150 r·min−1,在0、3、6、12、24、36、48、60、72 h分别取样测定,并用0.22 μm滤膜过滤,测定不同时间间隔下的磷浓度,水样中磷含量采用钼酸铵分光光度法(GB11893—89),并计算磷吸附量.
设置磷浓度为30 mg·L−1,溶液体积为100 mL,温度为25 ℃,振荡速率为150 r·min−1,通过改变溶液初始pH值(pH=3、5、7、9),介孔毫米球的投加量(投量为0.05、0.075、0.1、0.15、0.2 g)来探究对磷吸附效果的影响,同时选取水中常见阴离子Cl−、SO42−、NO3−和HCO3−(以钠盐形式存在)考察了共存离子的影响.
-
吸附剂投量为1 g·L−1,设置初始磷酸盐浓度为1—70 mg·L−1,pH为3,在25 ℃条件下以150 r·min−1速度振荡72 h.采用Langmuir和Freundlich模型进行拟合.
Langmuir等温吸附方程:
Freundlich等温吸附方程:
式中,qm为最大吸附量(mg·g−1);qe为吸附平衡时的磷酸盐吸附量(mg·g−1);Ce为吸附平衡时的磷酸盐浓度(mg·L−1);1/n为经验常数;KL和KF分别为Langmuir吸附模型和Freundlich吸附模型的吸附常数,代表吸附能力的强弱.
-
吸附动力学参数决定了磷酸盐回收时间,在水处理过程中至关重要. 吸附剂投加量为1 g·L−1,初始磷酸盐浓度为30 mg·L−1,pH为7,温度为25 ℃,置于恒温振荡器内以150 r·min−1速度振荡72 h,设置时间段测定磷酸盐浓度. 实验数据由准一级动力学模型和准二级动力学模型进行拟合.
准一级动力学模型:
准二级动力学模型:
式中,k1为准一级动力学速率常数(min−1);k2为准二级动力学速率常数(g·(mg·min)−1);t为反应时间(min);qe为反应平衡时的吸附量(mg·g−1);qt为反应时间t时的吸附量(mg·g−1).
-
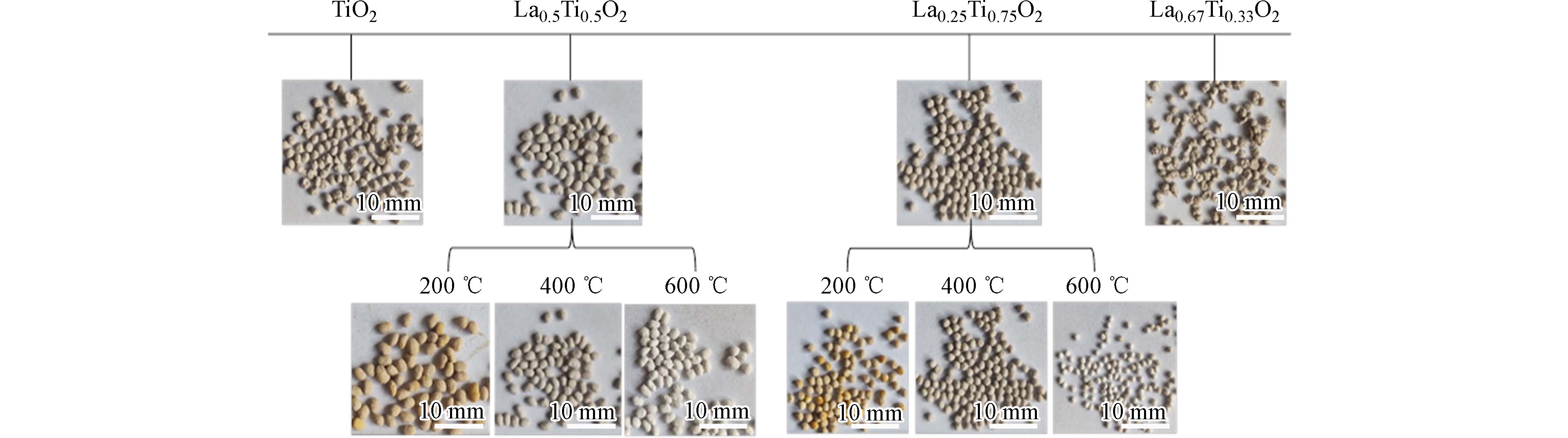
采用溶胶-凝胶模板法在不同煅烧温度下制备了不同La/Ti物质的量比的镧钛双金属氧化物介孔毫米球LaxTi1-xO2. 由图1可知,从宏观形貌上来看,随着煅烧温度的增加,LaxTi1-xO2的颜色由黄色逐渐变为灰白色,且通过吸附实验发现在200 ℃下煅烧制作的小球硬度不够,易碎成粉末,机械强度低,故舍弃该煅烧温度下制备的材料. 对比不同La/Ti物质的量比下制得的介孔毫米球发现,随着Ti含量增加,得到的毫米球球形变得更加规则,LaxTi1-xO2平均粒径为2—3 mm.
LaxTi1-xO2介孔毫米球的SEM图像如图2(a)所示,TiO2和La:Ti=1:3的LaxTi1-xO2颗粒外形均呈现球状且表面光滑,而La:Ti=1:1的LaxTi1-xO2颗粒外形均呈现棒状且互相黏集在一起,即随着La量的增加,介孔毫米球表面会形成褶皱而变得粗糙,这种形貌可有效增加吸附剂活性吸附位点,增强除磷性能. 类似的在负载La之后使得吸附剂表面呈条状褶皱的粗糙形态在其他研究中也有发现[14]. 为进一步探究材料的微观结构,对不同La/Ti物质的量比的LaxTi1-xO2介孔毫米球研磨制样进行了TEM和选区电子衍射(SAED)表征,结果如图2(b)所示. LaxTi1-xO2以纳米颗粒或纳米簇形式存在,且分散均匀,400 ℃和600 ℃下煅烧的Ti0.5La0.5O2球存在明显的晶格条纹,而400 ℃下煅烧的TiO2球与Ti0.75La0.25O2球未观测到晶格条纹. 400 ℃下煅烧的Ti0.5La0.5O2球和600 ℃下煅烧Ti0.75La0.25O2球存在明显的环状多晶衍射图样,而400 ℃下煅烧的Ti0.75La0.25O2球和600 ℃下煅烧Ti0.5La0.5O2球未观测到衍射图样,表明这两种金属氧化物球在微观尺度上依然保持无定形结构,这可能是因为La、Ti两种元素相互渗入对方氧化物晶格达到一定比例后造成明显的畸变和扭曲后,导致各自的周期性被破坏,形成了La—O—Ti键[15]. 以上结果说明, 控制La/Ti物质的量比和煅烧温度可以调控LaxTi1-xO2晶型和无定形两类结构的产生.
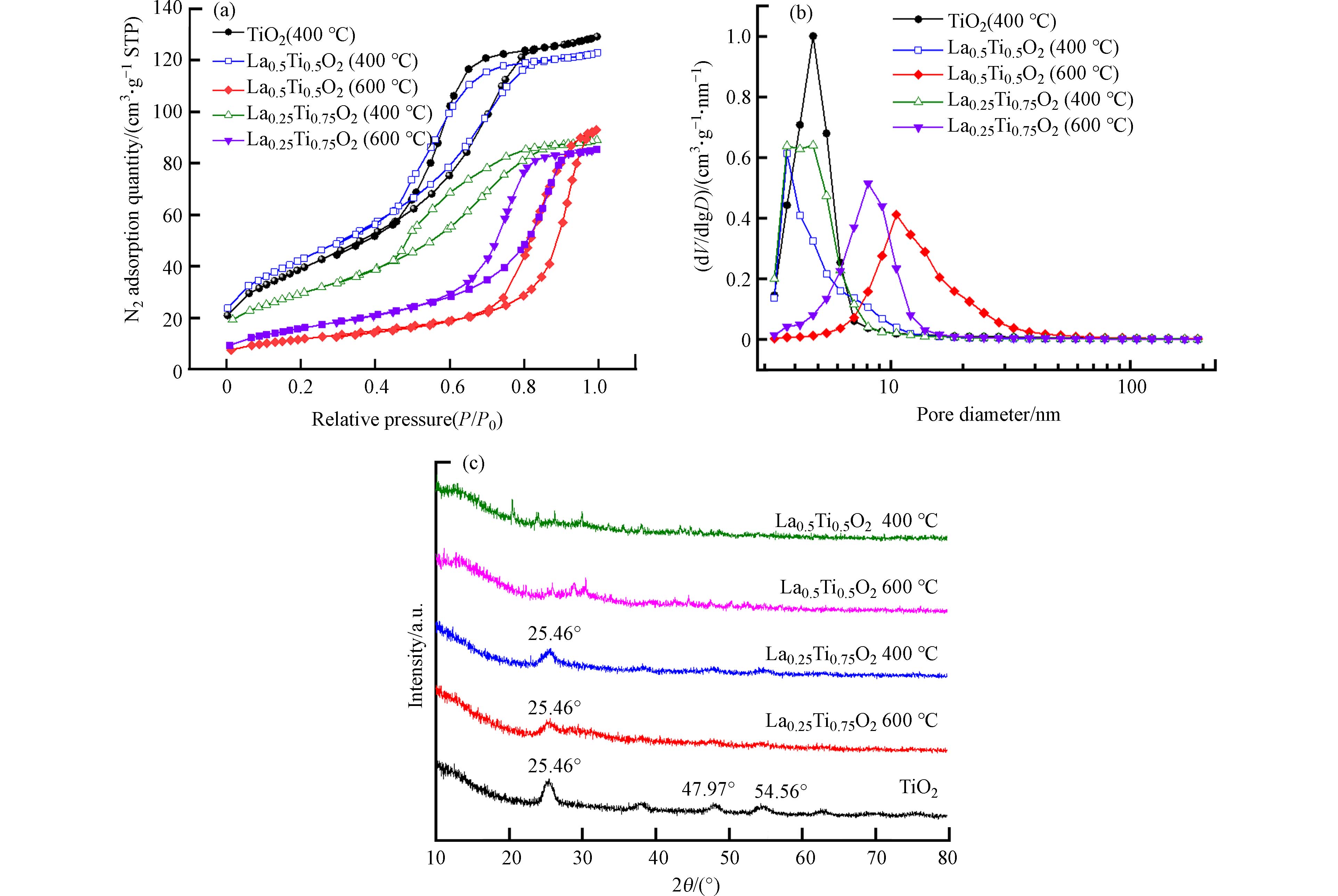
通过比表面积分析仪进一步测定了LaxTi1-xO2的孔结构. 根据国际纯粹与应用化学联合会(IUPAC)分类,LaxTi1-xO2的氮吸附-脱附等温线显示出“Ⅳ”型等温线(图3a),表明其孔结构主要是介孔,1—40 nm的孔径分布进一步证实了其介孔结构(图3b). 介孔毫米球LaxTi1-xO2的平均孔径和平均比表面积如表1所示,在不同的煅烧温度和La/Ti物质的量比下制备的材料的平均孔径和比表面积差别较大. 在400 ℃下煅烧LaxTi1-xO2平均孔径主要集中在3—5 nm;在600 ℃下煅烧LaxTi1-xO2平均孔径主要集中在8—10 nm. 由此可见,随着煅烧温度的增加,LaxTi1-xO2平均孔径有了明显的增加. 而在不同的煅烧温度下, LaxTi1-xO2介孔毫米球的比表面积也有不同程度的变化,其中在La:Ti=1:3时,400 ℃下煅烧的材料拥有最大的比表面积,为151 m2·g−1. 总体而言,在400 ℃下煅烧的材料的比表面积大于600 ℃下煅烧材料的比表面积. 综上,煅烧温度对LaxTi1-xO2比表面积影响较为显著,而La/Ti物质的量比对平均孔径和平均比表面积影响较小.
利用XRD谱图对LaxTi1-xO2的晶体结构特征进行了进一步分析,结果如图3(c)所示. TiO2的XRD谱图与锐钛矿标准谱图(PDF #21-1272)相符;对于La:Ti=1:3的两种LaxTi1-xO2,均在2θ=25.46°时出现了TiO2衍射峰,但是在特征峰处的衍射强度均有所减小,且经过改性后的LaxTi1-xO2的杂峰相较于TiO2有所减少,说明掺杂La之后的介孔材料和TiO2具有相似的结构特性[16]. 但是随着La量从La:Ti=1:3增加到La:Ti=1:1,TiO2特征峰逐渐消失,这表明LaxTi1-xO2中La含量增加会改变其晶形结构,使材料转变为无定形态[17 − 18]. 此外, LaxTi1-xO2的 XRD谱图中并没有出现明显的La相关衍射峰,谱图均表现为无定形特征,与SEAD和TEM结果一致,说明晶格周期性被完全破坏,形成了La—O—Ti键. 这与Ce—O—Ti破坏晶格周期性结构,形成无定型铈钛氧化物的结果一致[15 − 19].
-
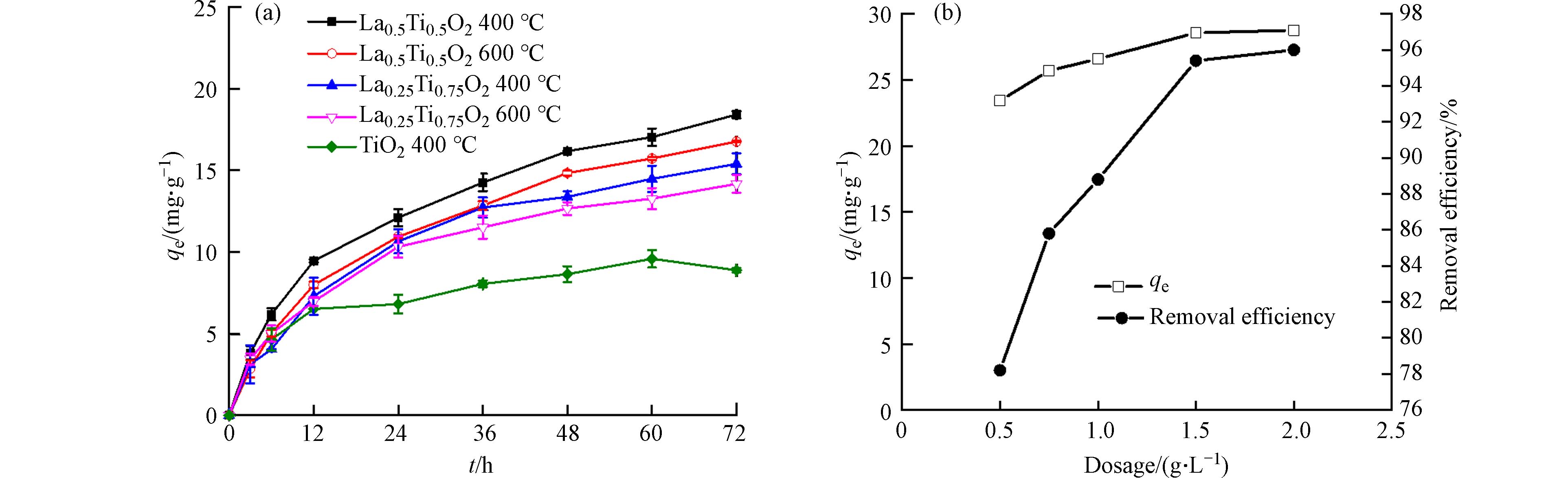
通过实验发现当La所占物质的量比过多时制备的吸附材料形状不规范甚至无法成球,因此选取了La:Ti=1:1、1:3的物质的量比条件下制备的LaxTi1-xO2介孔毫米球并探究其对磷酸盐的吸附性能. 如图4(a)所示,不管是La:Ti=1:1还是La:Ti=1:3的介孔毫米球,其对磷酸盐的吸附效果相较于TiO2球都有显著提高,TiO2对磷的吸附量仅为9 mg·g−1,而LaxTi1-xO2对磷的吸附量高达13—18 mg·g−1. 对比4种不同条件下制备的LaxTi1-xO2的吸附效果可知,煅烧温度由400 ℃升高至600 ℃,LaxTi1-xO2对磷的吸附量有一定下降. 400 ℃煅烧温度下La:Ti=1:1(La0.5Ti0.5O2)的介孔毫米球对磷的吸附量最大,为18.4 mg·g−1,是TiO2介孔毫米球的2倍. 故优选400 ℃下煅烧的La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球进行后续实验探究.
由图4(b)可以看出,在0.5 g·L−1到1.5 g·L−1范围内增加La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球的投加量,会提高对磷的吸附量和去除率,继续增加吸附剂投加量至2.0 g·L−1时对磷的吸附量和去除率趋于平缓. 尽管La0.5Ti0.5O2投加量为2.0 g·L−1时吸附量达到最大值28.76 mg·g−1,此时对磷的去除率达到96%,但当其投加量减少为1.0 g·L−1时其对磷的吸附量为26.59 mg·g−1,除磷率依然能够达到88.8%,因此本实验以磷的排放标准为基础,综合考虑吸附剂的吸附效果和经济成本,选用1.0 g·L−1 作为La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球最佳投加量.
-
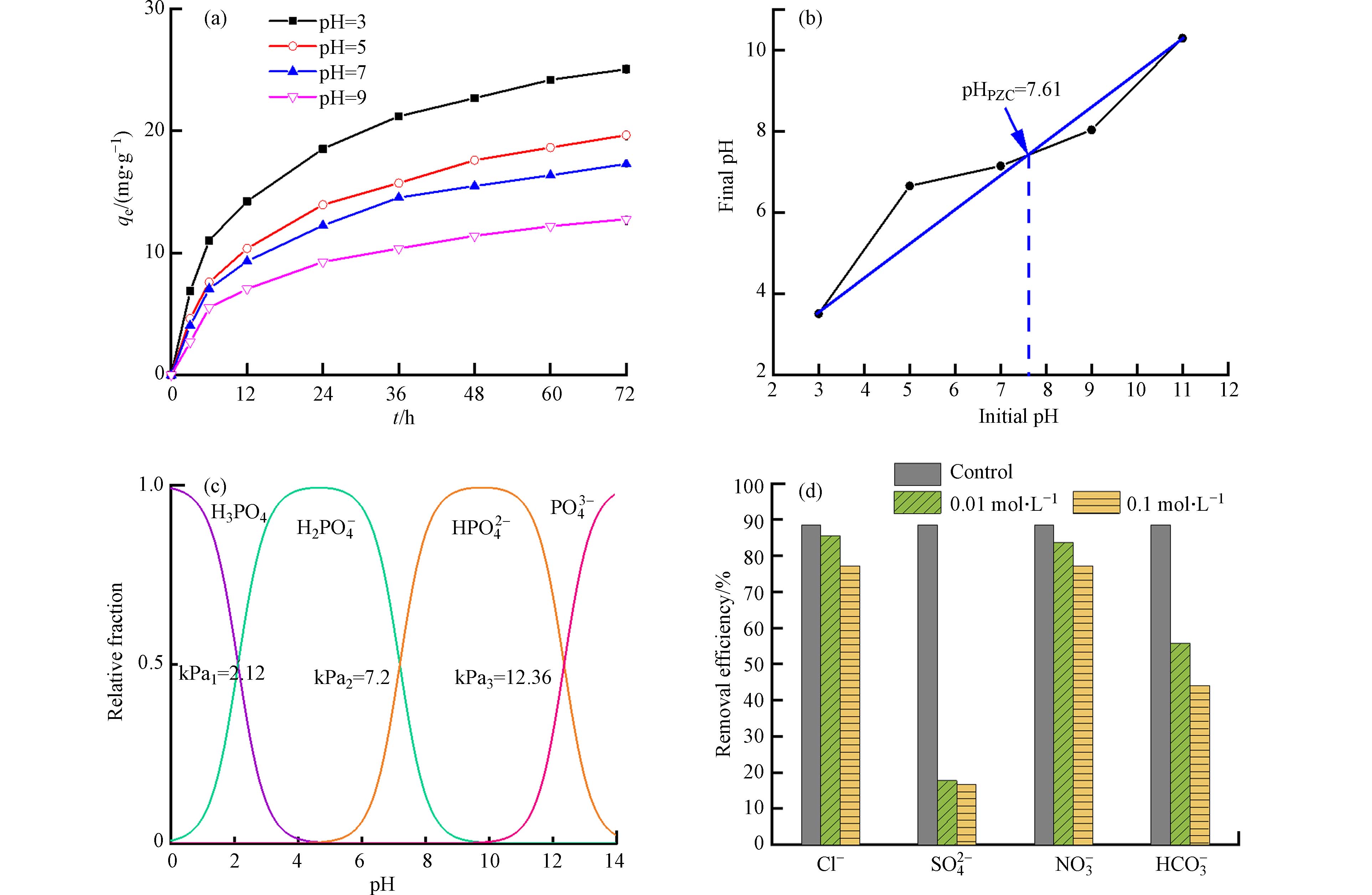
水体pH值是影响La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球吸附磷酸盐的重要影响因素,pH值既影响磷酸根在水体中的分布形态,又影响La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球的表面电荷[16]. 因此,实验通过改变溶液初始pH值,研究了其对La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球吸附磷酸盐的影响. 如图5(a)所示,La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷酸盐的吸附效果随着溶液初始pH的增加而削弱,当pH值为3时,吸附量达到最大值26.15 mg·g−1. 这主要归因于La是原子半径较大的带正电荷原子,主要吸附阴离子,当溶液中的OH−逐渐增多时,会与磷酸根产生竞争吸附作用从而不利于La0.5Ti0.5O2吸附磷的进行[20 − 22]. 如图5(b)所示,通过pH漂移法获得La0.5Ti0.5O2的零电荷点(pHpzc)为7.61,表明La0.5Ti0.5O2在pH<7.61时容易携带正电荷(H+),导致La0.5Ti0.5O2和磷酸盐之间产生静电吸引,有利于对磷的吸附. 相反,La0.5Ti0.5O2在pH>7.61时倾向于携带负电荷(OH−),导致其与磷酸盐之间产生静电排斥,不利于对磷的吸附. 此外,pH值的增加也导致H2PO4−转化为HPO42−和PO43−(图5c),并且它们的吸附亲和力弱于H2PO4−,从而进一步削弱La0.5Ti0.5O2对磷的吸附. 综上,La0.5Ti0.5O2在酸性水质条件下对磷的去除性能表现更好.
如图5(d)所示,考察了湖泊或河流中常见的阴离子(Cl−、NO3−、SO42−和HCO3−)对La0.5Ti0.5O2去除磷的影响. 所有阴离子对磷的去除都表现出一定的抑制作用. 其中,Cl−和NO3−对磷去除的抑制作用不大,而SO42−和HCO3−对磷去除的抑制作用较强. 与空白组相比,当添加0.01—0.1 mol·L−1 Cl−和NO3−时,磷的去除率仅下降了3%—10%,表明La0.5Ti0.5O2主要以化学吸附的形式去除磷,因此其对磷的去除几乎不受Cl−和NO3−离子强度的影响[23]. SO42−和HCO3−对磷去除的强烈抑制作用可能是由于这些阴离子会与La3+反应形成La2(SO4)3和La2(CO3)3[24 − 25],从而减少了对磷的有效吸附位点. 此外,SO42−和HCO3−还可以提高水环境的pH值,从而增强磷酸盐与La0.5Ti0.5O2之间的静电排斥,抑制La0.5Ti0.5O2对磷的吸附.
-
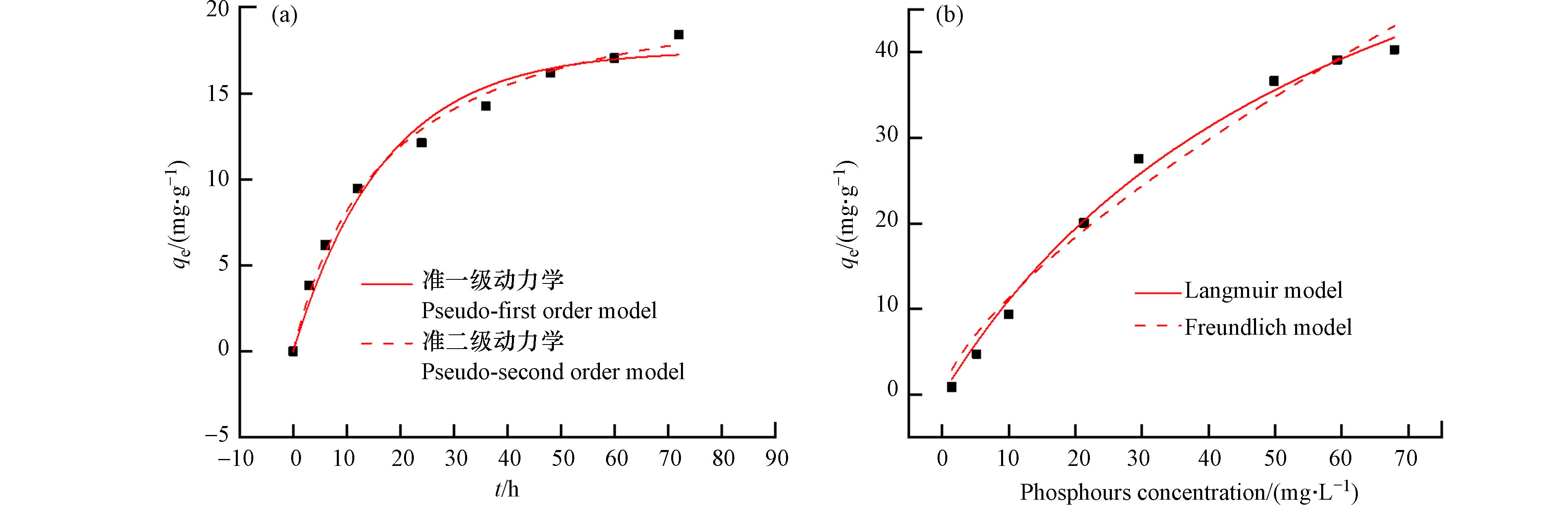
为了评估La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷吸附的快慢程度,考察了该材料对磷的吸附动力学,结果如图6(a)和表2所示. 由表2可知,准二级动力学模型的R2=0.994,高于准一级动力学模型的R2=0.978,说明La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷的吸附过程是以化学吸附为主的物理化学吸附过程. 图6(b)是La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷酸盐的吸附等温线,得到的拟合参数见表3. La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷的吸附量随着磷酸盐浓度的增加而逐渐增加,但增加速率逐渐变缓. 在低浓度磷酸盐溶液范围内的磷几乎被La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球完全吸附去除,这是因为在处理低浓度磷时,La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球吸附位点相对充足,可以足够吸附溶液中的磷. 但随着磷浓度的增加,吸附位点保持不变,La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球不能够完全吸附溶液中的磷,吸附量增加幅度随之变小,当吸附位点被占满后,吸附量几乎保持不变,从而吸附趋于饱和. 从拟合结果来看,两种模型均能较好地描述吸附过程,Freundlich模型的R2=0.974,Langmuir模型的R2=0.992,更接近于1. Langmuir模型更符合La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷的吸附过程,说明La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对于磷酸盐的吸附是单分子层吸附,这与已有报道的镧改性吸附剂一致[26 − 27]. La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球的理论最大磷吸附量为75.8 mg·g−1. 式(4)中的n值表示与吸附强度有关的常数,Freundlich模型得到的1/n小于1,表明磷易于吸附在La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球上[28]. 与其它含La吸附剂相比(表4), La0.5Ti0.5O2 表现出较好的磷吸附性能,磷的吸附量和P/La比(1.24)高于大多数含La吸附剂. 此外,La0.5Ti0.5O2对低浓度磷(<30 mg·L−1)的吸附能力明显强于其它含La吸附剂,这使其有望用于处理河流和湖泊的实际含磷水体治理.
-
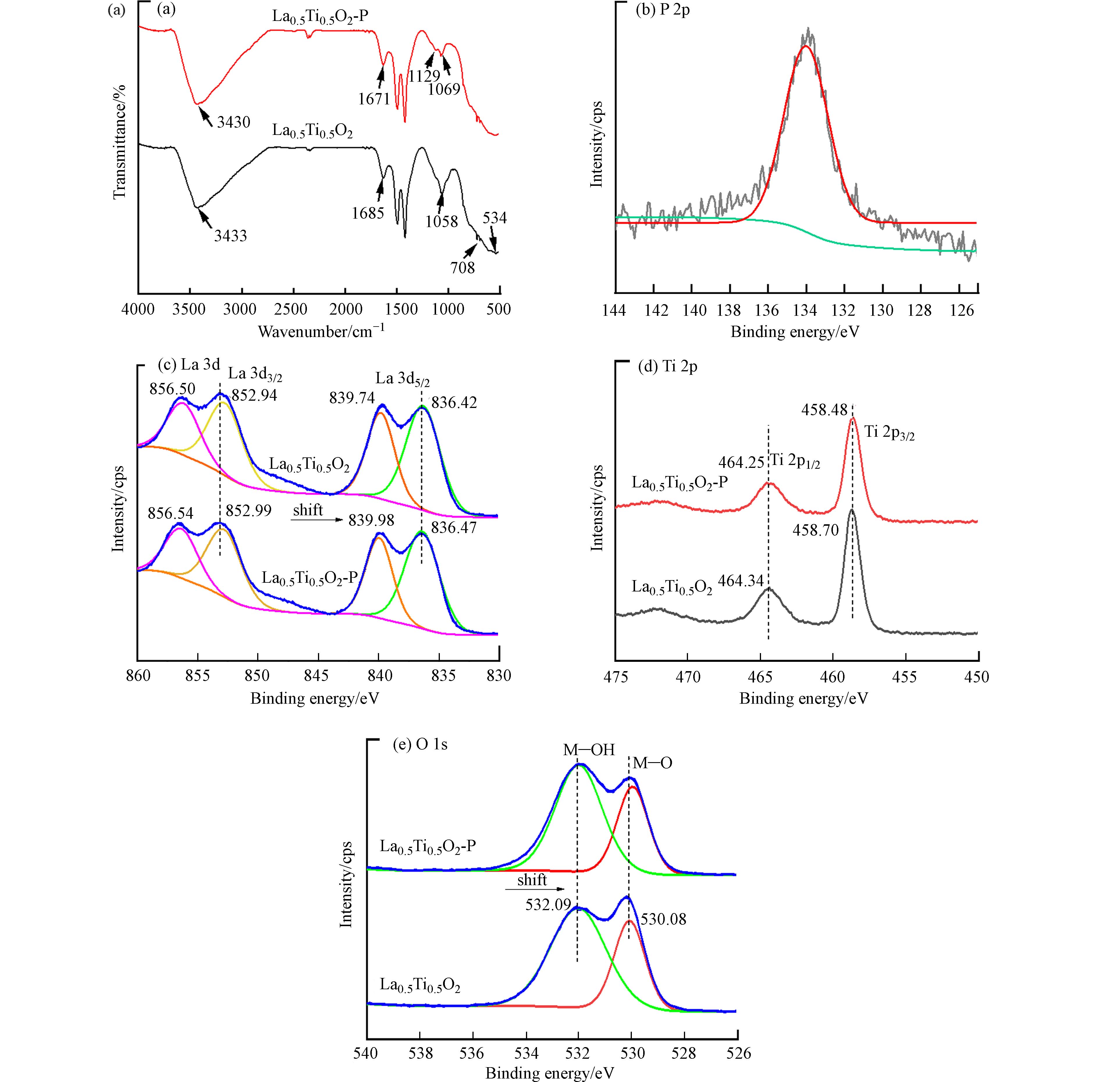
通过FR-IR谱图分析发现(图7a),在吸附磷的样品中检测到位于1129 cm−1处的P—O不对称拉伸振动[27]. La0.5Ti0.5O2吸附磷后,其位于534 cm−1处的特征峰消失,这是因为受到O—P—O的不对称拉伸振动影响. 此外,La0.5Ti0.5O2光谱中位于3433 cm−1和1685 cm−1处的O—H的拉伸和弯曲振动峰分别红移到3430 cm−1和1671 cm−1,表明La0.5Ti0.5O2表面的—OH参与了吸附磷过程,可能是由于La—OH中的—OH与部分磷酸盐发生了配体交换[29]. 为进一步探究La0.5Ti0.5O2与磷酸盐之间的相互作用,用XPS分析材料吸附磷酸盐前后结构变化,结果见图7(b)—(e). 吸附磷的La0.5Ti0.5O2样品的XPS光谱中检测到位于133.8 eV处的特征性P 2p峰(图7b),表明La0.5Ti0.5O2成功吸附了磷酸盐. 在吸附磷之前,在La 3d谱图中出现两特征峰(图7c),这两组峰分别是La 3d 3/2=856.50 eV、852.94 eV和La 3d 5/2=839.74 eV、83.42 eV. 在吸附磷之后,La 3d 3/2和La 3d 5/2的结合能移到较高的数值,分别为La 3d 3/2=856.54 eV、852.99 eV和La 3d 5/2=839.98 eV、836.47 eV,表明La价带上可能发生了电子转移且形成了La—O—P的内球络合物LaPO4[30]. 有研究表明P—O键具有强吸电子效应,其与镧(氢)氧化物结合后,导致镧电子密度降低,La 3d电子的结合能升高[38],这与本研究的现象一致. 此外,吸附后的La0.5Ti0.5O2的Ti 2p 2/3和Ti 2p 1/2也向较低的数值移动,在Ti 2p 2/3处的特征峰由458.70 eV移动到458.48 eV,在Ti 2p 1/2的特征峰由464.34 eV移动至464.25 eV(图7d),这可能是由于吸附剂表面的—OH键与磷酸盐之间发生了交换反应引起[31]. 由图5b可知,初始pH在零电荷点pHpzc=7.61以下,吸附稳定后的pH值均有一定程度的升高,进一步表明吸附过程表面-OH与磷酸盐发生配体交换反应. 吸附前,La0.5Ti0.5O2在532.09 eV和530.08 eV处出现了O 1s的两个特征峰(图7e),分别归属于La—OH和La—O[27]. 吸附后,532.09 eV处的特征峰强度增强,而530.08 eV处的特征峰强度减弱,进一步说明吸附的磷酸根形成了新的化学键La—O—P,改变了La—O键的化学环境. 结合文献报道和以上分析结果,La0.5Ti0.5O2通过配体交换吸附磷的过程可以表示如下[7, 29]:
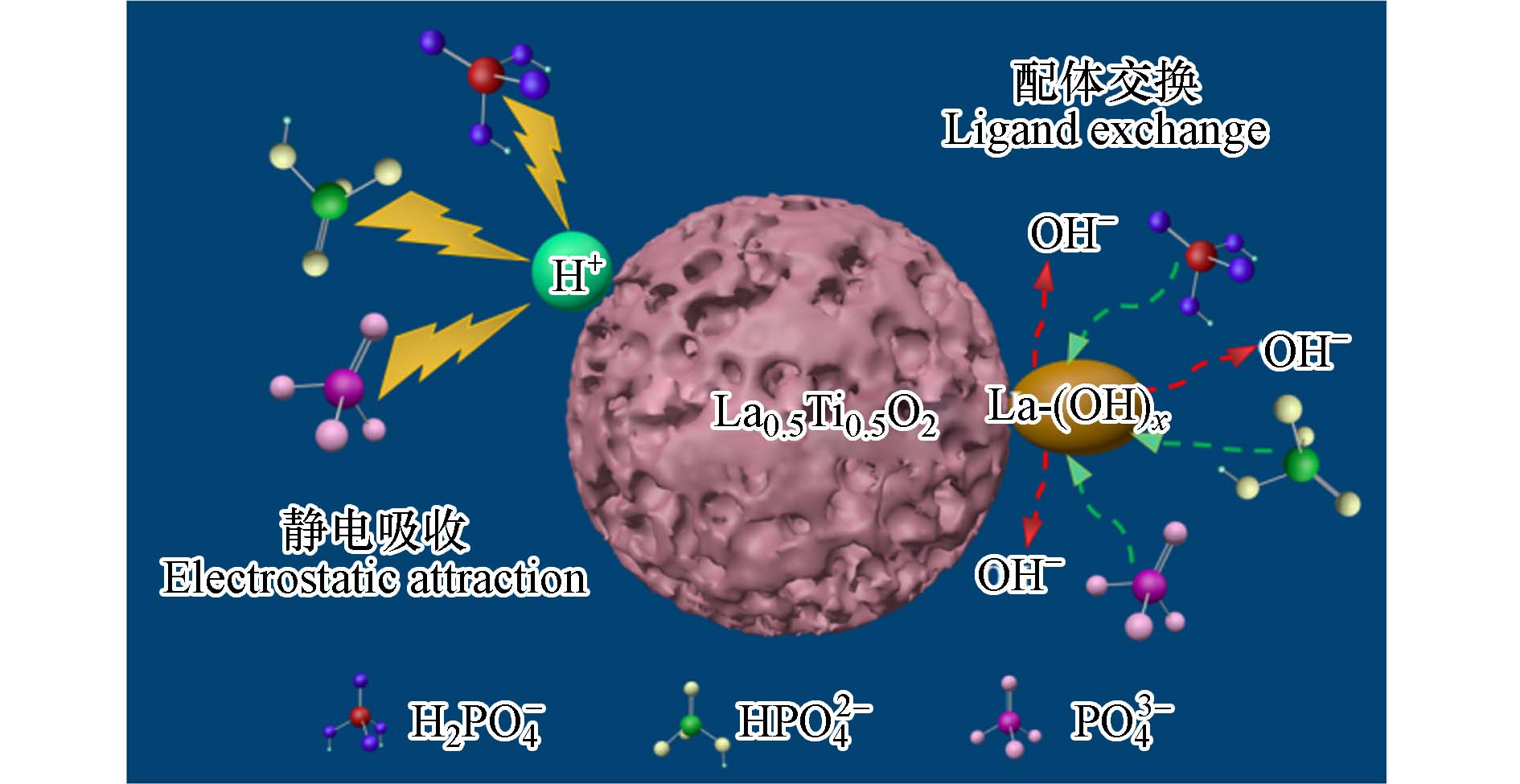
La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷酸盐的吸附过程如图8所示. 在吸附过程中,静电吸引(物理吸附)和配体交换(化学吸附)都起着重要作用. 静电吸引受到溶液pH值的显著影响. 当pH<pHpzc时,La0.5Ti0.5O2表面发生质子化,H+浓度增加,吸附位点与磷酸盐之间的吸附力增强. 当pH>pHpzc时,La0.5Ti0.5O2表面脱质子化,OH−浓度增加,吸附位点与磷酸盐之间的排斥力增强. 配体交换过程[式(5)—(7)]也受到水溶液pH的极大影响. 提高pH值会大幅提高OH−的浓度,这不利于吸附剂与磷酸盐的配体交换过程. 配体交换机制也可以解释La0.5Ti0.5O2对磷酸盐的高选择性,与常见的阴离子Cl−、NO3−、SO42−和HCO3−等相比,配体交换反应为磷酸盐与La0.5Ti0.5O2结合提供了非常强的驱动力.
-
(1) 本研究制备合成的介孔钛镧双金属氧化物毫米球,在La:Ti=1:1,煅烧温度为400 ℃时具有良好的吸附性能,其平均孔径为3.71 nm,具有丰富的孔结构、高比表面积,对磷酸根的吸附容量可以达到75.8 mg·g−1.
(2) 溶液pH的升高会抑制La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球的对磷的吸附性能;吸附除磷效果随着吸附剂投量的增加而增加,但投量为1.5 g·L−1之后,对磷去除效果提升较小;水体中常见的共存离子Cl−、NO3−对吸附除磷效果干扰不大,而SO42−和HCO3−对La0.5Ti0.5O2吸附除磷的抑制作用明显.
(3) La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷的吸附过程符合Langmuir模型和准一、准二级动力学模型,说明La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷酸盐的吸附是单分子层吸附,对磷酸盐吸附过程是物理化学吸附.
4) 静电吸附和配体交换反应共同决定了La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球对磷的吸附,两种作用机制均受pH值影响,pH值越低,吸附性能越好.
镧钛氧化物介孔毫米球除磷性能与机理
Performance and mechanism of mesoporous La-Ti oxide millispheres for efficient removal of phosphorus
-
摘要: 利用溶胶-凝胶模板法制备了镧钛双金属氧化物介孔毫米球LaxTi1-xO2,通过BET、XRD、SEM、TEM等方法对LaxTi1-xO2进行了系统表征,同时考察了镧钛物质的量比、煅烧温度、初始溶液pH等因素对LaxTi1-xO2除磷效果的影响. 结果表明,经400 ℃煅烧制得的La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球具有高比表面积(105 m2·g−1)、适宜的介孔结构(平均孔径3.71 nm)、优异的吸附磷酸盐能力,吸附容量达75.8 mg·g−1. La0.5Ti0.5O2除磷性能随La/Ti物质的量比和投量的增加而升高,随pH增加而下降. 共存Cl−和NO3−对La0.5Ti0.5O2吸附磷酸盐的影响较小,而SO42−和HCO3−对吸附过程有较大影响. 吸附等温线与Langmuir模型高度吻合(R2=0.992),表明La0.5Ti0.5O2对磷酸盐的吸附是单分子层吸附. La0.5Ti0.5O2对磷酸盐的吸附过程遵循准一级(R2=0.978)、准二级动力学模型(R2=0.994),表明其对磷酸盐吸附过程是以化学吸附为主的物理化学吸附. 零电荷点、FT-IR、XPS等表征结果表明,La0.5Ti0.5O2通过静电吸引与配体交换反应吸附去除磷.Abstract: A series of mesoporous LaxTi1-xO2 millispheres were prepared by sol-gel template method. The resultant adsorbents were systematically characterized by means of BET, XRD, SEM and TEM. Effects of La/Ti molar ratio, calcination temperature, initial solution pH on the performance of phosphorus removal by LaxTi1-xO2 millispheres were investigated. The results showed the optimized La0.5Ti0.5O2 prepared at 400 ℃ possessed high specific surface area (105 m2·g−1), suitable mesoporous structure (average pore size of 3.71 nm) and excellent adsorption capacity of 75.8 mg P·g−1. The removal of phosphorus by La0.5Ti0.5O2 increased with the increase of La/Ti molar ratio and La0.5Ti0.5O2 dosage, but decreased with the increase of pH. The coexisting Cl− and NO3− exhibited a little influence on the adsorption of phosphorus, while SO42− and HCO3− showed great effects on adsorption process. The adsorption isotherm was well in agreement with Langmuir model (R2=0.992), indicating that the adsorption of phosphorus by La0.5Ti0.5O2 obeyed monolayer adsorption. The adsorption kinetic of phosphorus followed pseudo-first-order (R2=0.978) and pseudo-second-order kinetic model (R2=0.994), suggesting that the removal of phosphorus by La0.5Ti0.5O2 belonged to a chemical adsorption-dominated physicochemical adsorption. The results of zero charge point measurement, FT-IR and XPS demonstrated the adsorption of phosphorus by La0.5Ti0.5O2 through electrostatic attraction and ligand exchange reaction.
-
Key words:
- mesoporous millisphere /
- La-Ti oxide /
- adsorption /
- phosphorus removal /
- ligand exchange.
-
全氟及多氟烷基物质(per and polyfluoroalkyl substances,PFAS)是一类由氟原子取代烷基链上每个或多个氢原子的人工合成有机氟化合物,化学结构末端包含带电荷、中性或者两性官能团,比如羧基、磺酸基、磷酸基等[1]. 碳氟链具有非极性、疏水性,末端官能团具有极性、亲水性,使得PFAS具有独特的两亲性[2]. 由于C—F键键能高(约536 kcal·mol−1),PFAS具有良好的化学稳定性和耐热性,适用于多种工业领域,如电镀、家纺、消防泡沫、炊具、农药等[3]. 近70多年来PFAS被广泛使用,造成全球范围内的普遍污染,在一些较偏远地区的河水、海水、雨水、瓶装水、大气以及土壤中均发现它们的存在,还包括野生生物和人群[4 − 5]. PFAS因其独特的化学性质,在生物体内难以代谢,具有生物累积性和毒性[6]. 在2009年、2019年和2022年,国际组织依次先后将全氟辛基磺酸(perfluorooctane sulfonic acid,PFOS)、全氟辛酸(perfluorooctanoic acid,PFOA)和全氟己基磺酸(perfluorohexane sulfonic acid,PFHxS)及其盐类列入《斯德哥尔摩》持久性有机污染物(persistent organic pollutants,POPs)公约清单中. 国内也在2019年颁布了全面禁止PFOS生产和使用的禁令. 为了限制人类暴露于PFAS,美国环境保护署(Environmental Protection Agency ,EPA)最新发布了一份关于PFOA和PFOS的饮用水健康咨询报告:将饮用水中PFOS和PFOA浓度(单个或综合浓度)的安全阈值规定为0.02 ng·L−1和0.004 ng·L−1,以此来保障人体健康.
依据美国洲际技术与管理委员会(Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council,ITRC)出台的文件,短链PFAS被定义为“含7个或更少碳的全氟烷基羧酸和含5个或更少碳的全氟烷基磺酸盐化合物”. 随着长链PFAS的管控,短链PFAS作为氟化表面活性剂而被大量生产[7],在1958年至2015年间,PFHxS的总排放量约为120—
1022 公吨[8],全氟丁酸(perfluorobutanoic acid,PFBA)、全氟丁基磺酸(perfluorobutane sulfonic acid,PFBS)和全氟己酸(perfluorohexanoic acid,PFHxA)等短链PFAS的生产或进口1—100吨,部分短链前体物质的生产甚至高达100吨以上. 短链PFAS可用于硬金属电镀中的铬雾抑制剂;由于绝缘和疏水性而用于电子工业;用于使产品具有疏水疏油性的化妆品;用于改善润湿性、光滑性和流动性的涂料和油墨、医疗器械和石油生产等. 不仅如此,用于扑灭易燃液体或气体的泡沫灭火剂中的表面活性剂从长链PFAS转变为短链PFAS. 短链PFAS因其具有较强的水溶性通常不被认为有与传统PFAS相当的生物积累潜力和生物放大效应,但其持久性与传统长链PFAS一致,因此短链PFAS在环境中的赋存仍值得关注[7]. 短链PFAS的C—F链较短,更加亲水,较难形成聚集体,在水体中的迁移率也会更高,且短链PFAS在底泥和土壤中的吸附性较差,更易远距离传输,增加了全球范围内生物和人群暴露于短链PFAS的可能性[9]. 2022年,EPA颁布了最新的饮用水健康建议,添加了短链PFBS和2,3,3,3-四氟-2-(1,1,2,2,3,3,3-七氟丙氧基)丙酸(2,3,3,3-tetrafluoro-2-(heptafluoro-propoxy)propanoic acid,GenX)的饮用水安全建议,其安全阈值分别为2000 ng·L−1和10 ng·L−1,并且后期将继续采取执法行动,扩大对环境中PFAS的监测,并通过开发新的分析方法和工具,加强解决PFAS问题的研究和科学基础.面对PFAS广泛污染的严峻现状,目前对传统长链PFAS的去除手段已较为成熟,包括吸附、氧化降解、光催化和电催化等方法. 然而关于短链PFAS污染赋存和处理技术的综述文献还较少,因此本文旨在总结水环境中短链PFAS污染水平和分布特征的最新研究进展,调研短链PFAS国际管控的最新消息,对已发表的与短链PFAS处理技术相关的研究进行综述,如吸附技术、膜分离、电催化及电催化技术、生物降解、热解和声解. 通过对比多种处理技术的优缺点,对当前研究的主要方向和目标进行展望,为有效处理和调控水环境中短链PFAS提供科学依据.
1. 短链PFAS的污染现状(Pollution of short chain PFAS)
1.1 水环境中短链PFAS的赋存情况
在1960年代末,人类血液中首次发现含氟化合物. 1999年,在受水成膜泡沫(aqueous film forming foam,AFFF)灭火剂影响的地下水中发现了6—8碳的全氟羧酸盐,总浓度范围为125 —
7090 μg·L−1[10]. 到2000年,PFOS和PFOA被明确鉴定,并发现几乎在科学家检测过的任何地方都存在. 因其对环境健康产生不利影响,从2002年开始,3M公司和许多其他主要的PFAS生产商开始用短链PFAS来取代长链PFAS. 随后由于短链PFAS的大量生产,在北欧地区的部分水域中发现PFHxA已占次要位置,并且在法罗群岛等地检测到微量PFBS. 在加拿大的Resolute湖[11]和中国的珠江、长江[12]等地也同样发现了相似的趋势:以PFOS、PFOA和5—7碳的短链羧酸占据水环境中的主导地位,含有较低浓度的PFBS. 随后4碳的短链PFAS逐渐被大量发现,2009年在德国海水中发现PFBS浓度水平达到3.38—17.7 ng·L−1,甚至高于PFOA的浓度水平(2.67—7.83 ng·L−1),占据主导地位[13]. 2010年,在莱茵河流域发现PFAS的分布以PFBS和PFBA(perfluorobutanoic acid,PFBA)为主,其浓度分别高达181 ng·L−1和335 ng·L−1[14],引起了学者的高度关注. 表1对近些年各种环境介质中短链PFAS的检测进行了总结,发现大部分环境介质中短链PFAS的浓度已显著超越了传统PFAS,并且其检测到的种类也越来越多[4, 15 − 16].表 1 PFAS在不同水环境中的污染现状Table 1. The pollution status of PFAS in different water environment来源Origin 地区Region 取样时间Sampling period PFAS 类别Category 平均浓度/(ng·L−1)Mean concentration 参考文献Reference 废水 美国市政污水处理厂 2020—2021 PFPrA 超短链 5.9—10.8 [15] PFHxA 短链 11.1—11.2 PFOA 长链 6.2—9.4 PFOS 长链 5.9—11.0 中国电镀废水处理厂 2019 PFHxS 长链 460 [25] PFOS 长链 1300 中国纺织废水处理厂 2019 PFHxS 长链 500 PFOS 长链 8.2 PFHxA 短链 21 PFOA 长链 52 河水 美国Haw河 2019—2020 PFBA 短链 189.9 [26] PFPeA 短链 274.1 PFHxA 短链 416.8 PFHpA 短链 235.9 PFOA 长链 133.3 PFOS 长链 110 河水 美国Truckee河 2019 PFPeA 短链 5.8 [27] PFHxA 短链 3.2—59.6 PFHpA 短链 1.7 PFOA 长链 1.6—19.2 PFBS 短链 2.3—11.4 PFPeS 短链 0.7 PFHxS 长链 6.4 PFOS 长链 2.2 PFDS 长链 7.3 美国Las Vegas河 2019 PFBA 短链 2.6 PFPeA 短链 2.3—170 PFHxA 短链 1.5—187 PFHpA 短链 11.6 PFOA 长链 27.3 PFUA 长链 0.5 PFBS 短链 17.7 PFPeS 短链 2.3 PFHxS 长链 11.2 PFOS 长链 12.9 PFDS 长链 4.3 中国山东小清河 2020 PFBA 短链 1051 —3930 [28] PFPeA 短链 770— 2966 PFHxA 短链 1200 —3787 PFHpA 短链 994— 3431 PFOA 长链 11565 —35352 PFNA 长链 5.3—18.1 PFDA 长链 0.6—2.4 PFBS 短链 2.0—114.9 PFHxS 长链 2.6—4.7 PFOS 长链 4.4—16.1 海水 南极海水 2013 PFBA 短链 0.072—0.137 [29] PFPeA 短链 0.032—0.064 PFHxA 短链 0.029—0.041 PFHpA 短链 0.022—0.049 PFOA 长链 0081—0.198 PFOS 长链 0.006—0.017 太平洋西北区域 2019—2020 PFBA 短链 0.032 [30] PFPeA 短链 0.013 PFHxA 短链 0.006 PFHpA 短链 0.027 PFOA 长链 0.108 PFBS 短链 0.013 海水 太平洋西北区域 2019—2020 PFHxS 长链 0.007 [30] PFOS 长链 0.007 中国台湾海峡西部 2019 PFBA 短链 0.102—0.660 [29] PFPeA 短链 0.014—0.148 PFHxA 短链 0.025—0.463 PFHpA 短链 0.013—0.167 PFOA 长链 0.075—0.94 PFBS 短链 0.023—0.983 PFHxS 长链 0.011—0.033 PFOS 长链 0.02—0.287 中国南海 2017—2018 PFBA 短链 0.018—0.270 [31] PFPeA 短链 0.008—0.129 PFHpA 短链 0.016—0.136 PFOA 长链 0.027—0.4 PFBS 短链 0.031—0.298 PFOS 长链 0.014—0.201 地下水 美国受AFFF影响地下水 2022 PFBA 短链 13000 [32] PFPeA 短链 40000 PFHxA 短链 75000 PFHpA 短链 19000 PFOA 长链 110000 PFBS 短链 23000 PFPeS 短链 32000 PFHxS 长链 380000 PFHpS 长链 15000 PFOS 长链 450000 中国广州垃圾处理厂地下水 2020 PFBA 短链 21.5 [33] PFPeA 短链 4.84 PFHxA 短链 5.59 PFHpA 短链 4.16 PFOA 长链 34.84 PFNA 长链 2.673 PFDA 长链 0.263 PFBS 短链 62.43 PFHxS 长链 1.013 PFOS 长链 1.043 短链PFAS不仅在水环境中的浓度大幅上升,在越来越多的环境介质中也都发现了它们的存在. Li等[4]综述了短链PFAS在水环境中的赋存和分布情况,在河水[17]、海水[18]、地下水[19]、地表水[20]、饮用水[21]等水质中均被检出. 另外, 有研究发现[22]发现在美国的瓶装水中全氟羧酸(perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids,PFCAs)(占比83%)和含有5个或更少CF2基团的短链全氟烷基酸(perfluoroalkyl acid,PFAA)(占比67%)在检测频率和浓度上分别比全氟磺酸(perfluoroalkane sulfonates,PFSAs)和长链PFAA更普遍,并首次在瓶装水中检测到超短链五氟丙酸(pentafluoropropionic acid,PFPrA)占总PFAS高达42%. Li等[23]报道了短链替代品已成为中国住宅土壤中主要PFAS污染物;在上海的污水、污泥样品[16]和青藏高原的大气样品[24]中均发现较高浓度的短链PFAS. 这些迹象都反映了全球PFAS的生产和应用从长链到短链PFAS的转变.
1.2 水环境中短链PFAS的迁移传输
短链PFAS的C—F链较短,亲水性更强,较难形成聚集体,在水体中的迁移率更高,通过饮用水摄入增加了人类暴露在PFAS化合物的可能性[8]. 短链PFAS已在公共饮用水供应站和与点源污染有关的地下水中被广泛检出,包括工业场所、使用AFFF的消防设施、垃圾填埋场和废水处理厂等[22]. 短链PFAS可通过点源或非点源释放[25]、大气沉积[34]、地下水渗透[35]等方式进行传输,在全球各个介质中均能检出. 此外,一些前体化合物或传统PFAS向短链PFAS的转化使他们在环境中的归趋更加复杂.
在荷兰一家氟聚合物制造工厂东北部3 km范围内采集的所有草和多种树叶样本中均检测到GenX,其含量分别为1—27 ng·g−1和4.3—86 ng·g−1,在25 km附近的自来水站内也检测到GenX[36]. 在美国卡罗来纳州一家氟化物制造厂产生的PFAS从地下水到Cape Fear河流附近5条支流迁移的研究中[35],每年约(32±7)kg的PFAS会从地下水排放到五条支流,最终到达Cape Fear河,导致地表水的长期污染,并影响下游饮用水供应. 南极菲尔德斯半岛的雪、湖水、海水和地表流径水中均发现了多种PFAS的存在[37],这些PFAS主要来源于南极站和游客的点源污染,但也受到非点源的影响,如PFBA在多介质中差异明显,其可被前体降解,大气粉尘是其主要污染途径. Cousins等[38]收集了全球多地雨水中PFOS、PFOA、PFNA和PFHxS的数据,发现雨水中PFOA和PFOS含量远超EPA的饮用水安全建议值,并且这4种PFAS随雨水落下会形成全球土壤和地表水的面源污染,在大气中的全球扩散也导致了全球化学污染的循环. 在过去的20年里,中国PFAS的产量急剧增加,已经成为了与PFAS相关产品生产和消费的新兴热点区域[39]. 短链类似物和新兴的替代品已在中国住宅土壤PFAS污染物中占主导[23]. 受工业和社会经济因素的影响,居住地土壤PFAS严重污染地区主要分布在中国东部沿海. 短链类似物(375±509)pg·g−1的浓度水平高于检测到的PFOS(193±502)pg·g−1,这表明短链PFAS用作替代品,其影响已经超过长链PFOS[23]. 最近的研究还发现,短链PFAS在青藏高原的大气、雪、冰川和地表水的PFAS污染中也占主导地位[24, 34, 40].
短链PFAS由于在环境中的稳定性和流动性,已显示出较高的全球污染潜力[41]. 它们在不同水环境中相互迁移和降解,在土壤中发生吸附与解吸附、渗滤和挥发,在大气中发生前体的转化和粉尘沉积,液固气三相中的相互传输使其在全球范围内相互循环,维持着一种质量平衡. 一方面,尽管短链PFAS的生物累积性低于长链同源物,但它们在环境中更易流动,不易被土壤或沉积物吸附,难以被环境降解;另一方面,仍有许多潜在的短链及其他替代品无法用现有分析技术检测到[42],阻碍了对这些化合物环境流动的清楚认知,因此,未来的研究仍需继续集中于确定环境中短链及其他替代品的赋存研究.
1.3 短链PFAS的生物毒性
随着短链PFAS的广泛应用,了解其生物累积性和毒性对人类生命健康至关重要. 不同链长PFAS灌胃大鼠研究发现,血浆中PFAS半衰期随氟碳链长度的增加而增加,在肝脏中长链PFOS占比最高,短链PFBS占比最低[43]. 雄性大鼠腹腔注射全氟庚酸(perfluoroheptanoic acid,PFHpA)120 h内,92%的剂量迅速通过尿液清除[44]. 在对中国济南地区老年人群5个月的评估发现,仅短链(C4—C7)PFCAs出现很大的浓度变化差异,长链PFAS(如PFOS、PFOA等)一直以较高浓度富集在血液中[45]. 以上研究均表明短链PFAS比长链化合物的半衰期更短,生物累积性较弱,这可能是因为较短的链长更快被吸收,在组织中累积、分布少,更容易从体内清除,从而导致更低的内暴露量[43].
流行病学研究表明,长期接触某些PFAS,包括一些相对较低浓度的短链PFAS,会对健康产生不利影响. 短链PFAS与长链PFAS具有相似的毒性,它们会导致生殖发育问题[46 − 47]、肝脏毒性[48]、免疫系统问题和良性肿瘤[49]等. Rericha等[50]利用斑马鱼胚胎研究了短链系列PFBS、全氟戊酸(perfluoropentanoic acid,PFPeA)、全氟丁基磺酰胺(perfluorobutylsulphonamide,FBSA)和4:2氟调磺酸(1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorohexanesulphonic acid,4:2 FTS)的发育毒性,所有化学品均导致幼鱼的行为异常,其影响程度分别为FBSA>PFBS>4:2 FTS>PFPeA. 在人群调查中发现,产前暴露于PFBS和PFHpA的水平与胎儿促性腺激素紊乱以及游离雄激素水平相关[51],与PFOA和PFOS相比,短链PFAS(PFBS和PFHpA)具有更高的胎盘转移效率,导致胎儿暴露量更高,从而影响胎儿的生长发育[52]. 此外,暴露于PFBS会导致体重下降、发育迟缓和对子代不利的生殖影响,以及甲状腺激素水平的变化和肾脏细胞的变化等生殖毒性和肝脏毒性. Weatherly等[48]通过暴露于PFBA的小鼠组织学、免疫表型和基因表达研究发现,PFBA诱导肝毒性、皮肤的组织病变和部分基因改变,持续性地皮肤接触PFBA甚至会引起全身效应.
关于短链PFAS的持久性、广泛传播性和毒性的研究强调了人类正面临短链PFAS的侵害,急需开发高效经济的适用于短链PFAS的水处理和修复技术.
2. 短链PFAS处理技术(Treatment of short chain PFAS)
本文重点关注短链PFAS的处理技术,同时也对比讨论了一些同源长链PFAS的处理技术,用以评估短链PFAS的可处理性. 此外,还概述了一些处理参数对水环境中PFAS去除效果的影响.
2.1 吸附去除
PFAS的C—F键能较高,化学性质稳定,吸附这项便捷且惠利的技术成为了去除PFAS的热门研究课题. 常用的吸附材料主要包括活性炭、树脂、生物材料和其他聚合材料等. 不同吸附剂对短链PFAS的吸附能力也各不相同.
2.1.1 碳质吸附剂
活性炭(AC)作为最经典的商用吸附剂之一,具有成本低廉、易获取且拥有较好吸附性能等优点[53],是水处理过程中最常用的吸附剂. AC的粒径会直接影响其对PFAS的吸附,粉末活性炭(PAC)往往比颗粒活性炭(GAC)具有更高的吸附容量和更快的吸附速率. Hansen等[54]利用GAC和PAC对短链PFAS进行批量吸附实验,发现在10 min内PAC的去除率约在60%—90%,而GAC仅为20%—40%. 活性炭的粒径越小,内部扩散距离越短且比表面积越大,使其暴露在外可与PFAS相互作用的活性位点越多,大颗粒的孔隙堵塞和空间位阻也更加明显[1],因此PAC的吸附速率快于GAC[53, 55 − 56]. 同时,前人发现AC的孔隙率也是一个重要因素,大孔的比例越高,吸附效果越佳[1]. Murray等[57]比较了超细粉末活性炭(SPAC,比表面积927 m2·g−1,大孔体积18.2%)和GAC(784 m2·g−1,大孔体积9.65%)在连续流动系统中去除PFAS(包括短链PFBS、PFPeA、PFHxA、PFHpA等),SPAC的吸附性能比GAC高480倍以上. AC在去除长链PFAS上效果显著,但对短链PFAS的去除仍存在缺陷. Mandu研究了木质生物炭去除PFBA和PFOA的吸附能力[58]. 吸附动力学实验结果表明,PFBA在硬木生物炭(HWC)上的吸附量比PFOA低3—4倍. 当使用GAC处理过滤废水时,对比PFOA和PFOS(约
60000 床体积),PFPrA和PFHxA很快就达到了100%突破体积(约10000 床体积),由此作者得出结论,短链PFAAs(PFBA、PFPrA或PFHxA)比长链的PFOS和PFOA更难用生物炭和GAC去除[58]. 为了提升吸附剂对短链PFAS的吸附能力,研究人员开展了一系列实验. Liu等[59]合成的芦苇衍生生物炭(RESCA),在环境相关的浓度(1 μg·L−1)下对短链PFAS表现出出色的去除效率(>92%),且吸附动力学显著高于GAC. RESCA填充过滤器在流速高达45 mL·min−1的情况下能够有效去除进水中3种短链和3种长链PFAS的混合物. 相比之下,填充GAC的过滤器在去除短链PFAAs方面的效率明显较低. 通过扫描电子显微镜和比表面积测试分析表明,高度疏水的表面和分散分布的中孔(直径2—10 nm)与短链PFAAs的快速吸附有关. 在处理含有超过8 mg·L−1溶解有机物的地下水样本时,RESCA 对短链PFAS的去除会受到负面影响.碳纳米管(CNTs)由于其独特的中空纳米结构和物理化学性质,具有较高的比表面积和较强的疏水性,对有机污染物具有良好的吸附能力,在环境修复中受到广泛关注[60]. Chen等[61]报道,碳纳米管可以快速吸附PFOS达到平衡(2 h),远比炭(384 h)和灰分(48 h)快得多. Deng等[62]发现单壁碳纳米管(SWCNTs,0.259 mmol·g−1)因其具有更大的比表面积和独特的物化特性,呈现出比多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs,0.028 mmol·g−1)更高的PFOA吸附容量;5 h后,95%以上的PFOA和PFOS被去除;而在48 h后,只有7.5%的PFBS被吸附在SWCNTs上. 平衡后,吸附量按PFOS > PFOA > PFHxS > PFHxA > PFBS > PFBA的顺序减少. 说明碳纳米管对PFAS的去除受链长影响极大. 此外,用不同官能团化的MWCNTs(MWCNTs-pri、MWCNTs-COOH和MWCNTs-OH)对PFBS进行去除测试[63],在去离子水中MWCNTs对PFBS的去除率约为30%,而当腐殖酸(HA)和苯酚共存时去除率低于20%. 由于PFBS相对较弱的疏水性,其去除率远低于长链PFAS.
碳质吸附剂对短链PFAS与长链PFAS的吸附作用一致,一般为静电和疏水相互作用. 一方面,碳质吸附剂表面的正电荷会通过静电相互作用吸引PFAS分子的阴离子官能团头部,反之其表面的负电荷则会与阴离子PFAS产生静电排斥[64]. 吸附剂在吸附PFAS分子后表面会携带更多的负电荷(即具有较低的pHPZC),从而排斥溶液中的PFAS分子或吸附在表面的阴离子PFAS分子,影响PFAS在吸附剂表面的吸附和分布. 同样,水体中的天然有机物(NOM)大多以负电荷态吸附在吸附剂表面,进而也会对PFAS分子产生静电斥力. 水中的阴离子会与PFAS分子的阴离子官能团竞争吸附位点,降低吸附效果. 相反地,二价阳离子可以被吸附剂表面的负电荷吸附,发生桥接效应,使吸附剂表面转为正电荷,对PFAS分子产生静电吸引. 此外,酸性条件有利于阴离子型PFAS的吸附,但在碱性条件下吸附剂表面的正电荷易受到干扰,静电相互作用减弱进而降低吸附效率[1].
另一方面,PFAS分子的C—F链是非极性疏水链,可以克服静电排斥,通过疏水相互作用吸附在带负电荷的吸附剂表面[65]. 疏水性强的PFAS分子的临界胶束浓度较低,更易在水中形成胶束和半胶束[66],通过胶束作用增加吸附剂的吸附容量. 短链PFAS的C—F链较短,疏水性较差,与吸附剂表面的疏水相互作用较弱,这也是碳质吸附剂对短链PFAS的吸附弱于长链PFAS的原因之一. 对于疏水材料而言,由于PFAS分子独特的疏水疏油性,有时简单的疏水作用并不能详细的对吸附机理进行解释,疏水碳质吸附剂表面的气泡有时也做出了贡献. Jiang等[67]对石墨烯脱气后对PFOS去除率有所下降,曝气后去除率又上升21.0%—29.2%. 同时还结合密度泛函理论和分子动力学计算验证了纳米气泡对石墨烯吸附PFAS所发挥的作用. 除此之外,PFAS分子上没有苯环和氢,因此在吸附过程中没有π-π和氢键相互作用[62]. 表2汇总了本文中碳质吸附剂对短链PFAS的吸附性能.
表 2 本文碳质吸附剂对短链PFAS吸附参数与结果汇总Table 2. Summary of short-chain PFAS adsorption parameters and results on carbonaceous adsorbents in this paper吸附剂Adsorbent 尺寸/(m2·g−1)Size 吸附剂浓度/(mg·L−1)Adsorbentconcentration 短链PFASShort-chain PFAS 初始浓度/(μg·L−1)Initialconcentration 水样基质Watermatrix 平衡时间/hEquilibriumtime 吸附容量/(μg·g−1)Adsorptioncapacity 参考文献Reference PAC 1200 125 PFBS 0.073 防水服厂的井水 — —22055 [54] PFHxA 0.28 PFHpA 0.32 ACs 854— 1270 10—60 20种混合PFAS 0.5 地下水 — — [56] SPAC 927 100—500 PFBS 0.0026 0.0144 0.0181 0.0086 地下水 — 0.043 [57] PFPeA 0.9 PFHxA 1.2 PFHpA 0.49 Calgon F400 GAC 784 PFBS 0.015 PFPeA 0.12 PFHxA 0.43 PFHpA 0.0033 松木生物炭 413 333 PFBA — 纯水、湖水、废水处理厂出水 24 — [58] HWC 453 24 — RESCA 730 200 PFBA 100 纯水 <24 — [59] PFBS PFHxA SWCNT 384.2 250 PFBS 150 纯水 <15 — [62] PFBA 107 PFHxA 157 MWCNTs-Pri 122.03 50 PFBS 150 纯水 — — [63] MWCNTs-COOH 127.95 HA MWCNTs-OH 139.09 苯酚 Filtrasorb 400® 1050 100000 PFBA 484100 纯水 — 25 [68] PFPeA PFHxA PFHpA PFBS F400 — — PFPeA 0.175 AFFF废水 — 3—6 [69] PFHxA 0.436 8—15 PFHpA 0.115 5—10 PFPrS 0.335 5—10 PFBS 0.715 13—25 PFPeS 0.925 60—80 2.1.2 聚合物树脂吸附剂
与AC相比,树脂的价格稍贵,但对PFAS的去除效率远高于GAC,已成为一种很有潜力且效果优良的吸附剂[69]. 离子交换(IX)树脂一般由聚苯乙烯或聚丙烯酸组成,同时携带电荷,可以与带电PFAS发生离子交换(式1). 相反,非离子交换(NIX)树脂则是中性聚合物,主要通过疏水和范德华相互作用去除PFAS[70]. 不同性质的树脂,对PFAS的去除效果也各不相同. Chularueangaksorn等报道了PFOA在阴离子交换树脂(PFA300)和非离子交换树脂(XAD4)上的吸附情况,结果表明PFA300的Kf值(Freundlich吸附常数)为117,而XAD4的Kf值为18,阴离子交换树脂PFA30对PFOA的吸附效果强于非离子交换树脂XAD4[71]. IX树脂用于去除短链PFAS的效果取决于聚合物材料的电荷、孔径和疏水性[72]. Deng等[73]发现PFBS在两种聚苯乙烯凝胶树脂上的去除率高于PFOS. 在另一项研究强碱性阴离子聚苯乙烯-DVB交联树脂的文献中,McCleav等[68]报道了在初始浓度为2.5 µg·L−1的情况下,短链PFAS(C4—C7)的去除率>80%. 此外,阴离子树脂对PFAS的吸附会受树脂孔隙度、基体和官能团的影响[3, 74]. 凝胶树脂的孔径小于大孔树脂,减缓了PFAS在其内部的扩散速度[73]. 不同的阴离子树脂基体导致不同的粒子扩散速率和吸附容量,与聚苯乙烯树脂相比,聚丙烯酸树脂的疏水性使其吸附速率更快,吸附容量更高[73, 75]. 其中,基体为主要影响因素,因为无论聚丙烯酸树脂的孔径大小如何,其吸附速率相差不大,而聚苯乙烯树脂孔径则会带来较大的变化. 正如前面所提起的,阴离子交换树脂主要是通过阴离子交换机制对PFAS进行吸附去除,同时疏水相互作用以及胶束或半胶束的形成也参与吸附过程[53, 73]. Zaggia等[3]利用3种强阴离子交换树脂去除水中的痕量PFOS、PFOA、PFBS和PFBA,证实了树脂的疏水性与PFAS的去除效率之间有很强相关性:高疏水性树脂(A532 E)对PFAS的吸附能力(52.3—260.5 mg·g−1)高于非疏水性树脂(A600E,19.1—186.2 mg·g−1)和疏水性树脂(A520E,29.5—210.4 mg·g−1). 然而,水中的阴离子和NOM会在阴离子交换树脂的吸附位点上与PFAS分子发生竞争,导致PFAS吸附能力的下降. 总的来说,阴离子交换树脂作为AC的可替代吸附剂,已被广泛研究生产.
[R4N+]Cl−+PFAS−→[R4N+]PFAS−+Cl− (1) [R3N]+H++PFAS−→[R3NH+]PFAS− (2) 2.1.3 其他吸附剂
考虑到原料的广泛可适用性,一些成本低廉的生物材料已被用于制备PFAS吸附剂. Deng等[76]以稻壳为原料用相同方法制得的胺化稻壳吸附剂,分别在5 h、3 h 和 9 h时达到了对PFOA、PFBA 和PFOS的吸附平衡,远快于活性炭颗粒,其平衡吸附容量分别为2.49、1.70、2.65 mmol·g−1,说明吸附剂表面的胺基有利于长链PFAS的吸附,而对短链PFAS的去除效果较差. 纤维素作为地球上最丰富的生物聚合物,来源广泛、便宜环保. Ateia等人利用聚乙亚胺来修饰纤维素微晶体,进而得到了聚乙烯亚胺功能化纤维素微晶(PEI-f-CMC)[77]. 在环境相关浓度(1 μg·L−1)的去离子水和真实湖水条件下分别开展吸附实验,发现PEI-f-CMC对长链PFAS的吸附能力相近,均可达到即时高效的去除. 然而,不足之处在于,在两种水质条件下PEI-f-CMC对短链PFAS的吸附效果均较差. β-环糊精(β-CD)是一种由7个葡萄糖单元组成的环状糖,与许多PFAS分子之间能产生独特的主-客体相互作用[78 − 79]. 并且,含胺的β-环糊精交联聚合物(CDP1)对短链PFAS展现出出色的吸附能力,甚至高于其他环糊精材料[79]. Weiss-Errico[80]报告了在β-CD 周边添加带电官能团对 β-CD与PFAS复合物的强度有明显影响,β-CD周边带正电荷的胺官能团能够显著增强其对传统和短链PFAS的络合. 作者将增强的络合作用归因于带负电荷的PFAS头部基团和带正电的β-CD衍生物之间的静电吸引力,带正电荷的β-CD似乎是修复短链PFAS的潜在络合剂.
此外,在模拟的环境条件下,人们对微塑料(HDPE、PS和PS-COOH)上的短链PFAS吸附进行了研究[81]. 由于离子强度的增加,PS-COOH对海水中短链羧酸盐化合物的去除效果比在淡水中更好. 而短链PFAS几乎没有被吸附在PS和HDPE上. Ji等[82]制备的胺功能化共价有机框架在PFAS初始浓度为1 µg·L−1的条件下,对短链PFBA和PFBS的去除分别可达60%和80%. 在关于由聚(N -(3 -(二甲胺基)丙基)丙烯酰胺为基体制成的阳离子吸附剂DMAPAA-Q研究中,Ateia等[83]发现,DMAPAA-Q 水凝胶对短链和长链PFAS的吸附性能大体相似,可达到80%的去除率且不受pH变化的影响. 然而,当使用树脂在较低浓度(<100 ng·L−1)下去除PFAS时,在早期突破体积时会观察到PFAS在吸附剂上的解吸现象. 在使用地下水进行的试点规模实验中,也观察到短链PFAS(C4—C7)类似趋势的解吸[3]. 同样地,在PEI-f-CMC[77]和胺功能化共价有机框架[82]中也观察到类似的结果. 根据它们的物理化学性质和在天然水体中相对较低的浓度,可以推测短链PFAS对吸附剂的吸附更依赖于开放活性位点的可用性. 因此,天然有机物(NOM)和其他更疏水的化合物,包括长链PFAS和水基质中的竞争离子的存在对短链PFAS去除速率有更大的影响[84]. 表3汇总了本文中树脂和其他吸附材料对短链PFAS的吸附性能.
表 3 本文树脂和其他吸附材料对短链PFAS吸附参数与结果汇总Table 3. Summary of short-chain PFAS adsorption parameters and results on resins and other adsorbents in this paper吸附剂Adsorbent 尺寸/μm /比表面积/(m2·g−1)Size/SSA 吸附剂浓度/(mg·L−1)Adsorbentconcentration 短链PFASShort-chain PFAS 初始浓度/(μg·L−1)Initialconcentration 水样基质Watermatrix 平衡时间/hEquilibriumtime 吸附容量/(μg·g−1)Adsorptioncapacity 参考文献Reference Purolite A-600 — 100000 PFBA 484100 纯水 — 44 [68] PFPeA PFHxA PFHpA PFBS A520E — 1000 PFBS 1000000 饮用水 70—80 53800 [3] PFBA 29500 A532E PFBS 50—60 109200 PFBA 52300 A600E PFBS 70—80 34600 PFBA 19100 CalRes 2301 — — PFPeA 0.175 AFFF废水 — 15—30 [69] PFHxA 0.436 70—100 PFHpA 0.115 20—40 PFPrS 0.335 75—120 PFBS 0.715 180—300 PFPeS 0.925 100—500 IRA400 300—1180/— 50 PFBS 200000 纯水 60 900000 [73] IRA410 300—850/— 1050000 胺化稻壳 500—800/— 100 PFBA 80000 纯水 5 364000 [76] PEI-f-CMC 10—50/7.8 25 22种PFAS 1 湖水 — — [77] CDP1 —/169 100 GenX 1000—200000 纯水 — 222000 [79] 10 GenX 1 — PFBA PFHxA PFHpA PFBS CDP2 —/78 100 GenX 10—1000 5000 10 GenX 1 — PFBA PFHxA PFHpA PFBS HDPE 3—16/— 5 PFBA 10 淡水、海水 — 0.26 [81] PFPeA 0.05 PFHxA 0.05 PFHpA 0.05 PFBS 0.05 PS 10/— 2 PFBA 0.01—0.34 PFPeA 0.09—0.12 PFHxA 0.16—0.21 PFHpA 0.07—0.1 PFBS 0.2 PS-COOH 10/— 2 PFBA 0.7 PFPeA 0.07—0.18 PFHxA 0.16—0.23 PFHpA 0.18—0.2 PFBS 0.05—0.33 28%[NH2]-COF 0.003/1900 10 GenX 1 纯水 <0.5 200000 [82] PFHpA — DMAPAA-Q 水凝胶 —/5.7 70 GenX 1 纯水 <2 — [83] PFBS PFBA 综上所述,尽管科学家们一直致力于研发能够有效去除短链PFAS的吸附材料,但短链PFAS本身的物化性质使其高效去除仍存在困难,且易受多种因素的影响.
2.2 膜分离工艺
在广泛应用于水处理工业的各种工艺中,高压膜工艺如纳米过滤(NF)和反渗透(RO)等已被探索可以有效分离水中PFAS[85]. Zeng等[86]使用反渗透膜(NTR-759 HR)从废水中去除100—300 ng·L−1的PFHxA,达到>99%的去除率. 同时,还比较了RO和NF的性能,发现纳滤膜比反渗透膜具有更大的纯水渗透性和NaCl传输能力,是去除饮用水中PFHxA的更好选择. Franke等[87]使用纳滤(NF270)来分离15种PFAS(包括PFBA、PFOA、PFDoDA、PFBS、PFOS、FOSA、6:2 FTS等),在初始浓度为6—110 ng·L−1时,平均去除率可达到99%,高于其他应用NF270膜处理含PFAS水样的研究. 另一种膜NF90在初始平均浓度160 ng·L−1条件下,对32种PFAS去除效率>98%[88]. 对比NF90和NF270发现,NF90对PFAS的分离能力更低,这可能是因为NF90分离的32种不同种类的PFAS主要是短链C3—C8,而NF270分离的15种不同类型的PFAS以长链C4—C12为主. 在膜处理过程中,长链的去除效果优于短链,PFAS的分子尺寸和结构被认为是影响去除的关键因素. Wang的报道中也有相似的结论[89],与PFBS相比,分子尺寸较大、疏水性较强的PFOS在所有水基质中均表现出较高的去除率. 除此之外,膜的电荷、疏水性、溶液的pH、离子强度和溶质浓度等也可能影响PFAS与膜的相互作用,从而影响对PFAS的消除. 膜的Zeta电位越低[86],亲水性越强[90],溶液pH的降低、离子强度和溶质浓度的增多都会增强对PFAS的去除效果[89, 91].
此外,膜污染和水流动性不足会降低膜的长期使用,在实际应用中,短链PFAS的分离极易受膜污染的影响. 尽管工业上可以对NF或RO工艺采用交叉流配置来减少溶质在膜表面的积累,或是运用高压操作来避免这些缺陷,但这可能需要频繁的系统停机来清洗或更换膜元件[85]. 不仅如此,通过膜分离产生的高浓度PFAS废水废料也给后续的处理带来了挑战. 因此,尽管纳滤和反渗透去除长链和短链PFAS的效果较好,但其较高的运营成本及维护限制了其在实际饮用水处理中的应用.
2.3 先进的氧化还原技术
先进的氧化技术已广泛用于PFAS的降解,不同于以上的物理分离方法,它可以产生活性物质,使PFAS的分子结构破裂,具有转化效率高和操作简单的优点,有些技术还可以实现对PFAS的完全矿化. 然而,目前这些技术通常用于长链PFAS效果显著,包括PFOA和PFOS,运用在短链PFAS上的研究仍较匮乏,已有研究表明对短链PFAS的去除效果并不明显. 本节总结了电化学氧化和光催化降解技术在短链PFAS降解中的应用.
2.3.1 电化学氧化
电化学氧化具有氧化强、能耗低、去除效率高的优点[92],是近年来一种新兴的先进氧化技术. 电化学氧化是指在直流电的作用下,借助具有电化学活性的阳极材料,夺取电子使有机物氧化分解为可生化的降解物质或完全矿化为CO2或碳酸盐等物质[93]. 因此,所选电极合适与否是保证持久性有机污染物在其表面附近进行顺利氧化的关键. 最常用的PFAS去除电极包括掺硼金刚石(BDD)薄膜、Ti/SnO2、Ce/PbO2和Ti/RuO2等. Barisci等[94]使用Ti/RuO2电极进行PFCAs和PFSAs的电化学降解,其中长链PFAS的降解在64%和91%之间,而短链PFAS的降解率仅在16%和67%之间,并且PFOS和PFOA的中间产物为对应的短链同系物,更加难以降解. 使用Ti/SnO2-Sb/PbO2-Ce电极降解PFHpA和PFBA,去除率分别为97.9%和31.8%[95]. 与SnO2或PbO2其他电极相比,BDD及其修饰电极展现出较好的效果. Liao等[96]用低电流密度和高PFBS浓度(>150 mg·L−1)能够在1 h内使用Si/BDD电极实现大于90%的去除效率. 然而,由于Si基底材料的弱导电性,限制了BDD电极的大规模应用.
有研究报道,PFAS的电化学氧化效果会随着链长的缩短而下降[92]. 短链PFAS的电化学氧化效果低于其长链同源物. 为了提高短链PFAS的降解效果,降低能耗,须使反应中产生大量·OH自由基,除了电极的改性外,电流密度越高、pH值越低、PFAS初始浓度越低和电极板间距越窄,越有利于PFAS的去除[97]. 这些因素也将直接影响电极的使用寿命和PFAS在电极上的传质速率.
2.3.2 光催化降解
光催化降解是另一种先进的技术,指的是利用紫外光与光催化剂一起分解/矿化目标化合物. 在紫外光照射下,水会产生水合电子(eaq−)、羟基自由基(·OH)和氢自由基(H·)等活性物质,PFAS会与之反应发生降解[98]. 然而,直接光解对PFAS分解的贡献几乎可以忽略不计[99],当使用紫外光(245 nm波长)处理PFOA 4 h仅消除33.5%[100 − 101]. 随着较短波长的加入(245 nm+185 nm),同样时间内去除率高达90%,但能耗也大大上升. 此外,短链PFAS的光解可能需要更多的能量,更难以去除. 在相同的光解条件下,直接光解消除了16.3%的PFBA和24.3%的PFPeA,去除率随着碳链的缩短而下降[102]. 总的来说,这一现象归因于直接光解对eaq−的产量较低,无法供应PFAS降解所需,因此利用催化剂促进活性物质的生成,来增强对PFAS的光降解势在必行.
一些半导体材料如二氧化钛(TiO2)、氧化铟(In2O3)等因其稳定的物化性质和经济无毒的特点经常被用作光催化剂,它们能够吸收光子,产生空穴和电子对(e−-h+),具有降解持久性有机污染物的能力. Xu等[103]综述了TiO2、In2O3、氧化镓(Ga2O3)及其改性材料的降解性能,发现以In2O3为催化剂,PFOA在紫外线照射下的光降解最有效,其次是Ga2O3和TiO2. 为了提高对PFAS的光催化性能,研究人员进行了一系列的尝试,如改变半导体催化材料的结构或用其他化合物进行修饰,具体降解性能见表4. 在二氧化钛上加入金属元素可以降低带隙能,从而增加e−-h+对的数量来降解PFOA[104]. 如Li等[105]制备了贵金属Pt、Pd和Ag改性TiO2光催化剂,结果表明3种M–TiO2样品对PFOA分解表现出极大的光活性,不同的金属具有不同程度的降解能力. Pt/Pd/Ag-TiO2的速率常数分别是TiO2的12.5、7.5、2.2倍,其中TiO2联合Pt是提高降解效率最显著的方法. 除上述原因外,贵金属纳米颗粒能够在导带中积累多余的电子来增强TiO2的光活性,降低e−-h+的重组合,从而充分降解PFAS. 此外,不同结构的In2O3材料(即多孔微球、纳米板和纳米立方体)[106]对PFOA的分解速率分别是TiO2的74.7、41.9、17.3倍,其中多孔微球具有最高的比表面积,可以提供更多的吸附和光催化反应中心,更有利于后续的分解.
表 4 本文光催化剂对PFAS降解参数与结果汇总Table 4. Summary of degradation parameters and results of PFAS by photocatalyst in this paper催化剂Catalyst 尺寸/nmSize 催化剂浓度/(g·L−1)Catalyst concentration PFAS 初始浓度/(mg·L−1)Initialconcentration 光照强度Lightintensity pH 去除率(反应周期/h)Removal rate(reaction period) 参考文献Reference TiO2 301 0.5 PFOA 50 400 Wλ=254 nm 5 22.4%(12 h) [113] Pb- TiO2 310 99.9%(12 h) Pt- TiO2 25.1 0.5 PFOA 60 125 W,λ=365 nm 3 100%(5 h) [105] Pd- TiO2 25.1 198%(7 h) Ag- TiO2 28 45%(7 h) In2O3(多孔微球) 180 0.5 PFOA 30 15 Wλ=254 nm 3.9 100%(17 min) [106] In2O3(纳米立方体) 50—180 100%(2 h) In2O3(纳米板) 40—150 100%(42 min) Na2SO3 — 2.52 PFOA 66.24 —λ=254 nm 10 >98%(30 min) [107] GenX 52.96 100%(2 h) K2S2O8 5.4 PFOA 66.24 >26%(3 h) GenX 52.96 <5%(3 h) Fe3+ — 0.28 PFPrA 11037.2 200 W, λ=200—310 nm 1.5 61.3% (24 h) [102] PFBA 14402.2 49.9% (24 h) PFPeA 17767.2 64.5% (24 h) Na2SO3 — 1.26 PFBS 7.5 18 Wλ=266 nm 12 48% (24 h) [109] Na2SO3 3.78 86% (16 h) Na2SO3+KI 1.26 >99% (24 h) 金刚石膜 — — PFOA 8.28 500 Wλ=254 nm — 100%(3 h) [110] Cu- TiO2 37 0.5 PFOA 50 400 Wλ=254 nm 5 91%(12 h) [113] Fe- TiO2 33 69%(12 h) 在一些无机盐的添加下,水合电子(eaq–)的还原降解/·OH的氧化诱导在降解PFAS方面各有不同. Bao等[107]对比了在UV/过硫酸盐(S2O82-)和UV/亚硫酸盐(SO32-)体系中,PFOA和GenX的降解差异. 在均相UV/SO32-体系中,SO32-会产生强还原eaq–,将PFOA和GenX在2 h内降解完全. 其中PFOA的降解速率比GenX快,但脱氟率却较低,这是因为GenX中醚基的存在增加了中间体的不稳定性,从而缩短了脱氟化过程. 相反地,S2O82-会产生的硫酸盐自由基(SO4−·)和·OH具有氧化性,但在3 h后仅<5%的GenX被氧化,长链PFOA的降解率也仅达到27%,对长链降解效果较差归因于体系的强碱环境. 在弱酸性条件下,约60%的PFOA可被去除[108]. 相比之下,GenX更容易被UV/SO32-系统生成的水合电子(eaq–)降解和脱氟,eaq–拥有更强的能力. Hori等[98]发现,在S2O82-的浓度为50 mmol·L−1时照射4 h后,PFOA在色谱图上消失但F−和CO2的浓度仍在上升,这表明PFOA降解产生的短链PFCAs中间体会继续被SO4−·氧化为CO2和F−. 该小组还发现Fe3+也是一种有效的光降解催化剂[102],由于PFAS与Fe3+络合的强光吸收,PFPrA、PFBA和PFPeA的光降解效率分别由原先的20%左右提高到61.3%、49.9%和64.5%. 为了进一步提高对短链PFAS的分解效果,Liu等[109]发现在UV/亚硫酸盐体系(UV/S)中添加(I−)显著加速了PFAS的降解. UV/S+I系统中PFAS衰变、脱氟和转化产物形成的动力学比UV/S中快3倍. I−对eaq–的高产率、SO32-对活性I−的快速恢复,使得UV/S+I中的eaq–寿命是单系统体系的数倍. 并且,优化的UV/S+I系统对短链PFBS拥有>70%的总脱氟率.
eaq–的获得往往是采用UV/亚硫酸盐光催化系统,但这同时也存在缺陷,造成潜在的二次环境污染,并且分解活性极依赖于水溶液的pH值[110]. 为了克服这一难题,Liu等[111]的研究证明了使用非均相的UV/金刚石催化体系在宽pH范围内产生eaq–对PFOA降解的可行性,PFOA通过逐步反应过程被分解成其他较短的小分子化合物(如PFHpA、PFHxA、PFPeA和PFBA). 与其他eaq–光催化剂(如亚硫酸盐和碘化物)不同,金刚石膜作为eaq–生成的负电子源,大大降低其对环境的不利影响. 在光催化体系中,pH可以调节H+和eaq−之间的相互转化,其中碱性条件有利于eaq−的产生. 此外,pH也会影响硫化物的分布,导致不同还原物种的形成;溶液中溶解氧的存在会降低光降解效果,这是因为eaq−会与O2快速反应;溶液中存在的阴离子(Cl−、 NO3−、SO42−和 HCO3−等)会限制降解效果,温度和光强与光降解呈正相关[112].
然而,目前还没有关于短链PFAS光催化降解的系统研究,光催化完全降解短链PFAS十分困难. 一般长链PFAS会转换为短链中间体,以此推断其降解效率. 如反应12 h后,UV/Cu–TiO2体系的PFOA分解和脱氟效率分别达到91%和19%. PFOA分解成氟化物离子(F−)以及较短的全氟羧酸PFCAs,例如PFHpA、PFHxA、PFPeA、PFBA和三氟乙酸(Trifluoroacetic acid,TFA)[113]. 由此可知,PFAS的光催化降解是CF2的逐渐裂解过程,断裂链的反应产生了短链中间体,但短链产物对光催化降解具有较强的抵抗性,分解效率与链长呈负相关. 表4总结了本文中不同光催化剂对降解PFAS的效率.
2.4 热解和声化学降解
热过程一般是利用热量形式的能量来转化材料. 在没有氧气或低于燃烧所需的温度下,材料暴露在高温下仍然会分解. 在化学反应中严格没有氧的情况下,热过程被称为热解[114]. Gabriele等[115]发现焚烧温度与总PFAS浓度呈负相关. 与较低的焚烧温度相比,较高的焚烧温度会使PFAS降解更完全,可能导致更多的PFAS向较短的C—F链物种转化. 这一结果与其他实验室结论一致,如Ellis等[116]发现含氟聚合物在500 ℃下分解并重排形成卤代有机酸,产生短链的多氟羧酸. García等[117]在850 ℃时,发现了C2F6和四氟化碳的形成. Krusic等[118]报道石英管中PFOA在温度低于300 ℃时热稳定,温度升高到370 ℃时PFOA在360 min内几乎完全降解,此时小分子物质不断生成,表明短链PFAS的抗性较高. 此外,将PFAS在GAC上预吸附可以提高矿化效率. 例如,将PFHxA(C6)预浓缩于GAC上,使热矿化率从46%(不含GAC吸附)增加到74%[119]. 在水处理过程中需要这种预浓缩,它不仅可以减少待处理的衬底体积,还可以防止PFAS从水中挥发释放,从而大大提高热效率和矿化率[4]. 然而,热解焚烧这个过程耗时耗能,存在产生额外的固体废物和对空气污染的担忧.
超声降解已被认为是处理PFAS的有效手段. 当声场作用于液体时,声波会以较低的压力和较高的压力相位传输. 在负压时形成微气泡,气泡在几个周期内振荡(稳定空化)并慢慢增大,直到在较高压力周期内变得不稳定并崩溃[120],此时从坍塌的水气泡内部释放出大量高达
5000 K的热能以及接近1000 bar的压力,并且形成一些溶剂化电子、自由基等活性物种[121]. 在气泡坍塌之前,PFAS被吸附在水气泡界面上,直到气泡破裂. 一方面,PFAS与活性物质反应被降解,另一方面,PFAS分子也被直接热解为其无机成分(氟化物F−、硫酸盐、CO和CO2)[122]. Sidnell等[123]综述了关于PFAS的超声降解的一些机制:1)降解机理始于羧酸基团或磺酸基团的裂解,然后形成全氟化碳中间产物,此过程在气泡蒸汽中进行热解,完全矿化形成不带任何短链副产物的F−;2)降解机制不涉及官能团的裂解,只从长链开始裂解,以全氟庚烷磺酸(perfluoroheptane sulfonic acid,PFHpS)和PFHxS为中间产物,以短链PFSA为最终降解产物. 由于这些实验是在不同的条件下进行,其拟议的机制有效性尚待进一步研究证实. 无论如何,PFAS成功降解的关键在于微气泡表面的吸附,因为氟化分子的声解被认为主要通过热解反应发生在水空化气泡界面,PFSAs和PFCAs具有非常低的蒸汽压,不易进入气泡的气相,亲水官能团溶解在液相中,而PFAS的疏水尾部倾向于聚集在气泡水间相上. 这种排列促进了PFAS的团聚,最大限度地增加了微气泡的表面积,从而达到更好的吸附降解效果[124].随后,科学家们在研究影响声化学降解的因素中发现PFAS的链长占重要地位. Moriwaki等[125]在声处理PFOA和PFOS时均检测到C2—C7短链PFCAs的存在,其中PFHpA和PFOS分别在15 min和30 min内被降解,短链PFAS在实验1 h内持续增加,并且表现出较高的抗性. 为了进一步确定短链PFAS对声降解的抵抗,Campbell[126]发现,在358 kHz时声化学降解速率遵循PFOA >PFHxA> PFBA和PFOS≈PFHxS> PFBS的顺序. 这可能是因为短链PFAS的表面活性较低,亲水性也较强,因此在气泡寿命期内难以在界面上形成稳定的表面薄膜. 同样地,Abad等[127]发现与之一致的规律,即声化学降解率会随着链长的缩短而降低. 这种碳链长度依赖性的降解归因于两个因素,一是具有高疏水性的长链PFAS更容易被吸附在气泡-水界面上进行热解或氧化降解(PFCAs和PFSAs的平衡气泡-水界面分配系数随着链长的增加而增加);二是短链PFAS比长链同源物更耐去氟化. 此外,他们还观察到全氟烷基化合物比多氟烷基化合物更容易声解,这可能是由于多氟烷基的分子尺寸较大,扩散速率缓慢所致. 除此之外,声化学气泡的降解速率还受声波频率的影响. 频率越高,去除效果越好[128]. 当频率范围为202—
1060 kHz时,0.23 μmol·L−1PFHxS和0.3 μmol·L−1PFBS的声化学降解率分别在358 kHz和610 kHz时达到最大[126].为了加速降解过程,学者发现可以将其与其他处理方法相结合,如与过硫酸盐等活性物质相结合,过硫酸盐形成SO4−·,有助于攻击PFAS,从而提高体系的降解性能[129]. Lei等[129]发现双频超声系统产生的合成波振幅大于单频超声系统,将双频US与过硫酸盐(PS)结合可协同降解PFAS. 对于双频US/PS反应,PFPeA出现在降解过程的早期,2 h后可以观察到PFBA,这应该是PFPeA进一步降解的产物. 在降解6 h后,脱氟百分比从高到低分别为PFOA(100%)> 6:2 FTS(86.9%)> PFOS(46.5%). 总的来说,声化学降解在去除短链PFAS上仍存在短板,并且在实际运用过程中产生的噪声污染也无法避免,因此尚未大规模地运用于实际污水的处理.
2.5 生物降解
不同于其他的物理化学降解方法,生物处理具有一些固定优势,如环境友好性和成本效益,不会进一步破坏土壤和水环境. 根据前人的研究,得知微生物可有效降解长链PFAS. Kwon等[130]通过培养铜绿假单胞菌,12 h对PFOS的去除率为67%. 酸性亚胺菌科菌株A6是一种厌氧自养细菌,与PFAS接触18 d后PFOA浓度显著降低[131]. 在另一篇文献中也观察到A6菌种对PFOS和PFOA高达60%的去除[132],但其孵化时间较长,需要100 d. 除此之外,研究人员还观察到在生物转化过程中短链PFAS的积累[133 − 134]. 然而,短链PFAS很难被生物降解,对各种活性污泥体系也具有较高程度的抗性[134]. Che等[135]研究了活性污泥群落对C3—C5不同结构(包括支链、氢原子取代、双键)的氟化羧酸(fluorinated carboxylic acids,FCAs)在好氧脱氟过程中结构与反应的关系,发现有4种结构的脱氟率>20%,其中3,3,3-三氟丙酸几乎完全脱氟. 含有类似于CF3(CH2)n−2COOH奇数链结构的氟化物的脱氟程度优于偶数链结构,并且氟化程度越高(氢原子取代越少),其脱氟效果越差,比如对五氟丙酸的脱氟效果几乎为0. 到目前为止,还没有关于微生物能有效降解短链PFAS的文献.
在植物体系中,一些PFAS有着明显的积累趋势,尤其是短链PFAS. 如PFOA的短链替代物GenX和4,8-二氧杂-3H-全氟壬酸铵(Ammonium 4,8-dioxa-3H-perfluorononanoate,ADONA)均不同程度地在植物枝条上被发现[136]. PFAS的吸收和影响在物种之间和物种内部都有所不同. 基于玉米对PFAS的摄取和分布的研究表明[137],植物对PFAs的吸附和分布依赖于链长、官能团和植物组织. PFAS分子的异位因子(TF)会随着链长的增加而减少,支链的TF较大,这归因于PFAS分子的疏水性. 因此,短链PFAS一般积累于植物的地上部分,而长链PFAS则主要集中于根茎.
总之,PFAS污染会对土壤微生物的数量和物种多样性产生不利影响. 随着短链PFAS的不断增加,有必要继续扩大在土地应用介质中量化PFAS清单,并评估其在植物中的积累潜力[138].
2.6 其他技术
2.6.1 等离子体技术
等离子体是带电粒子和中性粒子的集合,这些粒子包括电子、离子、自由基和质子等. 等离子体技术可以引发溶液中的多种物理和化学效应,包括冲击波、强紫外线辐射、高电场,以及产生强还原和氧化反应物种(·OH、HO2·、 O2 ·−、 H2O2和eaq−等)[139],这些活性物种进而再矿化污染物. 当使用等离子体技术处理PFAS时,先将母体PFAS还原成中间产物,进一步再氧化短链中间产物和全氟烷基自由基等成为氟离子和CO2[140]. 在相对较短的时间内(0.5 h),等离子体技术在受污染的地下水中有效解离PFAS,将约90% PFOA和PFOS进行了矿化,并且Cl−和 NO3−等共污染物的存在并不影响等离子体处理过程中PFAS的降解率[139]. 然而,在这过程中仍有部分降解成为短链PFAS,难以彻底消除. 总的来说,等离子体处理技术是一个可持续的过程,因为它排除了需要大量的化学品输入,并产生了广泛的活性物质.
2.6.2 泡沫分离技术
泡沫分离是一种基于无需固体型吸附剂的吸附分离方法. 当大量气泡从容器底部产生时,PFAS因趋向减少系统的吉布斯自由能而被吸附在气液界面[141]. 随后吸附了PFAS的气泡薄膜慢慢变得稳定,聚集在液体表面形成泡沫或浮渣[142]. McCleaf等[143]研究了泡沫分离技术在处理瑞典垃圾渗滤液中PFOS、PFOA、PFHxS、PFHpA、和6:2 FTS的有效性,发现其去除效率均超过90%,但废物流中存在的其他短链PFAS的去除效率仅在80%到20%之间. 为了提高对短链PFAS的去除效果,Burns等[141]报道了在澳大利亚陆军航空中心的一项实地研究. 在该地建立了一个由泡沫分离系统和阴离子交换树脂组成的水处理厂来修复受污染的地下水. 当仅通过泡沫分离过程,超过99.5%的PFAS(PFOS、PFOA和PFHxS)被去除. 然而只有当进水中短链PFAS较多时,才需要阴离子交换树脂,因为泡沫分离不能有效地去除它们. 同样地,利用泡沫分离技术和等离子体技术的协同效应也可以增强垃圾渗滤液中短链PFAS的去除[142]. 总之,泡沫分离是一个非常有吸引力的替代手段,拥有快速高速去除长链PFAS的特点,更重要的是,不需要制造和更换吸附剂,最大限度地减少固体废物的产生. 然而,对短链PFAS的去除效果十分微弱.
如前所述,各种工艺和技术已被用于处理水介质中的PFAS. 表5总结了对各工艺的总体比较,回顾了不同技术所用的材料、优势和劣势,并对其在实际应用的成熟度进行了评估.
表 5 短链PFAS处理技术的对比Table 5. Comparison of short chain PFAS processing technologies技术Technique 材料Materials 优点Advantage 缺点Disadvantage 成熟度Maturity 参考文献Reference 吸附 树脂、ACs 成本低、能耗低、操作方便;理化性质无变化;浓度宽,微量的短链PFAS可以处理 吸附时间长,吸附剂再生能力不佳;洗脱溶剂的二次污染 实际应用 [58] 膜分离 NF、RO 低碳和低能源消耗,其余杂质也被去除 膜的成本和易发生膜污染 实际应用 [144] 电化学氧化 SnO2、PbO2、BDD 能耗低,时间短,短链PFAS处理效果尚佳 昂贵的电极材料;不适合用于微量污染;容易发生二次污染和产生的中间体 实际应用 [145] 光催化降解 UV、S2O82−、Fe3+、TiO2 时间短,高脱氟率和矿化率 附加催化剂;低降解效率;复杂的副产品 中试 [146] 热解和声解 高温、超声波 矿化率高 时间长;能耗大 中试 [147] 生物降解 微生物、植物 低碳环保,可吸附部分PFAS 时间长;效率低;需专门培育 实际应用 [148] 等离子体 活性自由基 时间短 高能耗,矿化效率低;生成中间产物 实际应用 [145] 泡沫分离 气泡 能耗低,时间短 难以吸附短链 实际应用 [141] 3. 结论与展望(Conclusions and prospects)
短链PFAS具有持久性和远距离迁移能力,已形成了全球污染,严重影响人类的健康安全. 本文通过对各种处理手段的比较,主要发现如下:(1)物理去除如吸附、膜过滤等方法可以去除部分短链PFAS,成本低,耗能少,操作方法简便,对处理浓度宽泛,且无理化性质的改变. 吸附是目前有效去除短链PFAS中最广泛的应用技术,已投入工厂实际运用许多年,满足低碳经济策略. 但其效果不如长链同源物,处理时间长,材料再生效率差,工艺废料和洗脱溶剂仍需二次处理. (2)热解和声化学降解可以实现对短链PFAS的有效矿化,但其处理时间较长,且耗能高,成本消耗大,产生环境和噪音污染. (3)光催化和电化学催化可以完全降解长链PFAS,处理时间短,但其产生的短链中间体难以降解,并且还会产生其他丰富的有机副产物和CO2,尤其不适合消除微量的短链PFAS. 目前为止,实际应用最广泛、最有效的方法是吸附,其次是高级氧化/还原技术. 但无论何种技术,在C1—C4的PFAS去除上仍存在局限,尤其是存在复杂背景基质干扰的情况下. 这是因为在物理去除手段中,长链PFAS可通过静电吸引、疏水作用、胶束作用和气泡吸附等多种手段进行去除,而短链PFAS因疏水性较差,很难突破固液界面,一般只能通过静电吸引进行去除;在化学降解技术中,短链PFAS比长链更稳定,可克服外来能量对它们的作用,难以去除. 因此,希望可以根据不同水域的特性来选择合适的处理技术,探索新的吸附材料、电极材料和催化剂,开发具有成本效益优势且有效的短链PFAS处理技术,以提高对环境中短链PFAS污染的修复.
-
表 1 不同煅烧温度下LaxTi1-xO2介孔毫米球的基本性质
Table 1. Basic properties of LaxTi1-xO2 mesoporous millispheres
LaxTi1-xO2介孔毫米球 TiO2(400 ℃) La0.5Ti0.5O2 (400 ℃) La0.5Ti0.5O2 (600 ℃) La0.25Ti0.75O2 (400 ℃) La0.25Ti0.75O2 (600 ℃) 平均孔径/nm平均比表面积/(m2·g−1) 4.76140 3.71105 10.641.3 4.76151 8.0656.9 表 2 La0.5Ti0.5O2介孔毫米球吸附磷的动力学参数
Table 2. Kinetic parameters of phosphorus adsorption by LaxTi1-xO2 mesoporous millispheres
温度/℃Temperature 准一级动力学Pseudo-first order model 准二级动力学Pseudo-second order model qe/(mg·g−1) k1 R2 qe/(mg·g−1) k2 R2 25 ℃ 17.5 6.25×10−2 0.978 22.1 2.74×10−3 0.994 表 3 Langmuir和Freundlich模型拟合参数
Table 3. Fitting related parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich
温度/℃Temperature Langmuir模型Langmuir model Freundlich模型Freundlich model qm/(mg·g−1) R2 KL/(L·mg−1) KF/(mg·g−1) 1/n R2 25 75.8 0.992 0.0176 2.49 0.671 0.974 表 4 吸附剂吸附性能对比
Table 4. Comparation of adsorption capacity of adsorbents
吸附剂Adsorbents 初始浓度/(mg ·L−1P)Initial concentration pH 投加量/(g·L−1)Dosage 比表面积/(m2·g−1)Specific surface area 吸附容量/(mg ·g−1P)Adsorption capacity 磷镧比P/La 参考文献References La-多孔沸石 5—60 7.02 2.0 52.75 14.8 0.95 [29] La(OH)3 5—500 11.3 12.5 153 107.5 0.84 [30] Fe3O4/50%-La(OH)3 1—10 7.0 0.1 190 52.7 0.68 [31] FeOOH/La-磁铁矿 2—120 6.8 1.0 85.8 44.8 1.30 [32] La-功能化SiO2气凝胶 10—120 5.0 1.0 192 69.4 0.85 [33] La(OH)3-改性蛭石 1—100 7.0 1.0 39.1 79.6 0.85 [27] La-介孔硅小球 5—80 6.0 0.5 67.4 44.8 0.67 [34] La(OH)3-改性硅藻石 10—100 6.8 0.5 74.1 58.7 2.39 [35] 沸石-氢氧化镧复合吸附剂 10—500 7.74 0.1 55.7 71.9 1.48 [6] 碳酸镧-阴离子交换树脂 5—60 7.0 0.5 — 77.4 0.73 [5] La-碳纳米管 0—100 12.0 0.2 — 96.3 — [4] LaOH-活性炭纤维 10—70 2.0 0.25 — 15.3 1.30 [36] LaFe-活性炭纤维 5—60 4.0 1.0 — 29.4 — [37] La0.5Ti0.5O2 1—70 3.0 1.0 105 75.8 1.24 本研究 -
[1] 杨桂山, 徐昔保. 长江经济带“共抓大保护、不搞大开发” 的基础与策略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(8): 940-950. YANG G S, XU X B. Foundation and strategy of well-coordinated environmental conservation and avoiding excessive development in the Yangtze River economic belt[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 35(8): 940-950 (in Chinese).
[2] 张亦南, 丁佳锋, 张小芳, 等. 镧负载沸石壳聚糖复合吸附剂高效除磷性能研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(2): 557-565. ZHANG Y N, DING J F, ZHANG X F, et al. Adsorption properties of high efficient lanthanum-loaded zeolite-chitosan composite absorbent for phosphorus removal[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(2): 557-565 (in Chinese).
[3] ZHANG Y Y, KONG B, SHEN Z Y, et al. Phosphorus binding by lanthanum modified pyroaurite-like clay: Performance and mechanisms[J]. ACS ES& T Engineering, 2021, 1(11): 1565-1575. [4] LIU B H, DAI S Y, ZHANG X T, et al. Highly efficient and reusable lanthanum-carbon nanotube films for enhanced phosphate removal[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 299: 121710. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121710 [5] TEE K A, BADSHA M A H, KHAN M, et al. Lanthanum carbonate nanoparticles confined within anion exchange resin for phosphate removal from river water: Batch and fixed-bed column study[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 159: 640-651. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.01.008 [6] XIE J, WANG Z, FANG D, et al. Green synthesis of a novel hybrid sorbent of zeolite/lanthanum hydroxide and its application in the removal and recovery of phosphate from water[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2014, 423: 13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2014.02.020 [7] 魏小兰, 赵靖华, 丁静, 等. 介孔吸附剂SiO2-TiO2的合成及其水蒸气吸附性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 40(9): 14-19. WEI X L, ZHAO J H, DING J, et al. Synthesis and water vapor adsorption property of meso-porous adsorbent SiO2-TiO2[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(9): 14-19 (in Chinese).
[8] YIN X J, LI X, PETROPOULOS E, et al. Phosphate removal from actual wastewater via La(OH)3-C3N4 adsorption: Performance, mechanisms and applicability[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 814: 152791. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152791 [9] FENG Y Y, LUO Y, HE Q P, et al. Performance and mechanism of a biochar-based Ca-La composite for the adsorption of phosphate from water[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(3): 105267. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105267 [10] LI X C, YAN L, ZHONG W, et al. Competitive arsenate and phosphate adsorption on α-FeOOH, LaOOH, and nano-TiO2: Two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy study[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 414: 125512. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125512 [11] CONNOR P A, McQUILLAN A J. Phosphate adsorption onto TiO2 from aqueous solutions: an in situ internal reflection infrared spectroscopic study[J]. Langmuir, 1999, 15(8): 2916-2921 doi: 10.1021/la980894p [12] KIMLING M C, CARUSO R A. Sol–gel synthesis of hierarchically porous TiO2 beads using calcium alginate beads as sacrificial templates[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(9): 4073-4082. doi: 10.1039/c2jm15720a [13] WATANABE S, MA X L, SONG C S. Characterization of structural and surface properties of nanocrystalline TiO2–CeO2 mixed oxides by XRD, XPS, TPR, and TPD[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(32): 14249-14257. doi: 10.1021/jp8110309 [14] 许润, 石程好, 唐倩, 等. 氢氧化镧改性介孔稻壳生物炭除磷性能[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(4): 1834-1841. XU R, SHI C H, TANG Q, et al. Phosphate removal using rice husk biochars modified with lanthanum hydroxide[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(4): 1834-1841 (in Chinese).
[15] FEI Z Y, YANG Y R, WANG M H, et al. Precisely fabricating Ce-O-Ti structure to enhance performance of Ce-Ti based catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 353: 930-939. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.198 [16] 王羽. 镧改性除磷剂的制备及其性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2021. WANG Y. Preparation and properties of lantanum-modified adsorbents for phosphorus removal[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2021 (in Chinese).
[17] ZHAN W C, LU G Z, GUO Y L, et al. Synthesis of Ln-doped MCM-41 mesoporous materials and their catalytic performance in oxidation of styrene[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2008, 26(1): 59-65. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(08)60038-1 [18] YANG J P, CHEN W Y, SHEN D K, et al. Controllable fabrication of dendritic mesoporous silica–carbon nanospheres for anthracene removal[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(29): 11045-11048. doi: 10.1039/c4ta01516a [19] 周冬, 单超, 高冠道, 等. 铈钛氧化物介孔毫米球的制备及其催化臭氧氧化特性与机理[J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 2019, 49(5): 565-578. doi: 10.1360/N092018-00418 ZHOU D, SHAN C, GAO G D, et al. Preparation of mesoporous Ce-Ti oxide millispheres for efficient catalytic ozonation: Performance and mechanism[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2019, 49(5): 565-578 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N092018-00418
[20] ZAMPARAS M, GIANNI A, STATHI P, et al. Removal of phosphate from natural waters using innovative modified bentonites[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2012, 62/63: 101-106. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2012.04.020 [21] LIU S J, LI J, YANG Y K, et al. Influence of environmental factors on the phosphorus adsorption of lanthanum-modified bentonite in eutrophic water and sediment[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(3): 2487-2494. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5453-z [22] 司静, 卢少勇, 金相灿, 等. pH值和光照对镧改性膨润土吸附水中氮和磷的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2009, 29(9): 946-950. SI J, LU S Y, JIN X C, et al. Effect of pH value and light on La-modified bentonite adsorption of phosphorus and nitrogen in water[J]. China Environmental Science, 2009, 29(9): 946-950 (in Chinese).
[23] 林建伟, 王虹, 詹艳慧, 等. 氢氧化镧-天然沸石复合材料对水中低浓度磷酸盐的吸附作用[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(1): 208-219. LIN J W, WANG H, ZHAN Y H, et al. Adsorption of phosphate by lanthanum hydroxide/natural zeolite composites from low concentration phosphate solution[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(1): 208-219 (in Chinese).
[24] 戴敏, 王建国, 巢军委, 等. 镧生物质炭对磷酸根离子的吸附特性[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2015, 31(3): 372-379. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2015.03.016 DAI M, WANG J G, CHAO J W, et al. Phosphate adsorption characteristics of La-containing biochar[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2015, 31(3): 372-379 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2015.03.016
[25] WANG D, CHEN N, YU Y, et al. Investigation on the adsorption of phosphorus by Fe-loaded ceramic adsorbent[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 464: 277-284. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.11.039 [26] WANG Z H, SHEN D K, SHEN F, et al. Phosphate adsorption on lanthanum loaded biochar[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 150: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.004 [27] HUANG W Y, LI D, LIU Z Q, et al. Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic, and adsorption mechanism studies of La(OH)3-modified exfoliated vermiculites as highly efficient phosphate adsorbents[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 236: 191-201. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.077 [28] ISMAIL Z Z, AbdelKAREEM H N. Sustainable approach for recycling waste lamb and chicken bones for fluoride removal from water followed by reusing fluoride-bearing waste in concrete[J]. Waste Management, 2015, 45: 66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.039 [29] HE Y H, LIN H, DONG Y B, et al. Preferable adsorption of phosphate using lanthanum-incorporated porous zeolite: Characteristics and mechanism[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 426: 995-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.272 [30] XIE J, WANG Z, LU S Y, et al. Removal and recovery of phosphate from water by lanthanum hydroxide materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 254: 163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.113 [31] FANG L P, LIU R, LI J, et al. Magnetite/Lanthanum hydroxide for phosphate sequestration and recovery from lake and the attenuation effects of sediment particles[J]. Water Research, 2018, 130: 243-254. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.008 [32] FU H Y, YANG Y X, ZHU R L, et al. Superior adsorption of phosphate by ferrihydrite-coated and lanthanum-decorated magnetite[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 530: 704-713. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.07.025 [33] EMMANUELAWATI I, YANG J, ZHANG J, et al. Low-cost and large-scale synthesis of functional porous materials for phosphate removal with high performance[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(13): 6173-6180. doi: 10.1039/c3nr01574b [34] HUANG W Y, YU X, TANG J P, et al. Enhanced adsorption of phosphate by flower-like mesoporous silica spheres loaded with lanthanum[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2015, 217: 225-232. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.06.031 [35] WU Y, LI X M, YANG Q, et al. Hydrated lanthanum oxide-modified diatomite as highly efficient adsorbent for low-concentration phosphate removal from secondary effluents[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 231: 370-379. [36] ZHANG L, ZHOU Q, LIU J Y, et al. Phosphate adsorption on lanthanum hydroxide-doped activated carbon fiber[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 185/186: 160-167. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.066 [37] LIU J Y, ZHOU Q, CHEN J H, et al. Phosphate adsorption on hydroxyl–iron–lanthanum doped activated carbon fiber[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 215/216: 859-867. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.067 [38] YANG J, DAI Y, ZHU X Y, et al. Metal-organic frameworks with inherent recognition sites for selective phosphate sensing through their coordination-induced fluorescence enhancement effect[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(14): 7445-7452. doi: 10.1039/C5TA00077G -






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: