-
自然环境中氨氮最初主要由雷电产生的硝酸盐和动植物分解产生,而磷酸盐来自雨水对矿物的溶解和动物的粪便。但随着经济社会发展,人类活动对生态环境的影响逐步加大,水环境不断恶化[1]。农业生产中使用的大量化肥、城市生活中洗涤剂、水产养殖业排放的废水中通常都含有大量氮磷[2]。过量的氮磷进入水体后,极易造成水体富营养化,藻类大量繁殖,对水体表面形成覆盖,大大降低水体含氧量和透光率,造成水质污染[3]。我国主要河流湖泊水体富营养化问题日益严峻[4-5]。水体中氮磷的去除一直是解决水体富营养化问题的关键。
生物炭是由有机原料在一定的有限氧气热燃烧下产生的富碳材料[6]。因其具备较高的阳离子交换能力、比表面积大和结构稳定等优点,可利用吸附作用去除重金属和有机污染物,在水处理和土壤防治领域具有很好的应用前景[7]。生物炭吸附能力与本身的理化性质相关,而理化性质随制备条件的不同而不同[8]。由高温直接裂解的生物炭存在着吸附量较低的缺点,因此需要添加改性剂进行改性提高其吸附量[9]。常用的改性方法包括使用酸、碱、氧化剂和金属离子等[10-13],均可增强生物炭对各类污染物的吸附效果。
玉米芯是一种年产量很大的农业副产物,在我国其年产量约为4 000×104 t,每年都有大量玉米芯被丢弃,或在田间被焚烧,既浪费了资源又污染了环境[14]。玉米芯具有碳含量高、天然纤维结构、产量大等特点[15],合理利用将会是良好的绿色环保资源。
本实验对玉米芯材料进行高温煅烧处理得到生物炭,通过使用CaCl2溶液作为改性剂对玉米芯生物炭进行改性,分析其形态和结构变化,并进一步研究改性玉米芯生物炭对于模拟水体中氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附性能及其吸附机理,为生物炭处理水环境中氮磷污染物的研究提供相关实验依据。
-
玉米芯(来源于天津市河北区)作为烧制生物炭的原材料。磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)、氯化铵(NH4Cl)均为优级纯,无水氯化钙(CaCl2)为分析纯,分别购于天津市光复精细化工研究所,天津市大茂化学试剂厂,天津市风船化学试剂科技有限公司。实验用水均为去离子水。
-
1)生物炭制备。玉米芯原材料用清水洗干净,干燥后磨碎,记录热解前材料质量,随后放入坩埚中并封盖,然后置于SX-12-10箱式电阻炉(北京中山伟业仪器有限公司)内, 500 ℃条件下裂解1.5 h,裂解结束后,待温度降至室温,取出坩埚并除去表面灰分后将生物炭研磨过筛,取60~100目生物炭于密封袋内,置于干燥器中保存。
2)生物炭清洗。未经处理的生物炭在纯水溶液中可释放少量氮磷,且在氮磷溶液中吸附效果较差,因此,对生物炭进行清洗处理。将烧制后的生物炭(BC0)放入足量去离子水中(2 g炭用250 mL水),在室温条件下用去离子水搅拌清洗多次至清洗液透明无色,使用0.45 um滤膜过滤,得到清洗后的生物炭,置于120 ℃烘箱中干燥2 h后,放置于干燥器中保存待用,清洗后生物炭记为BC。
3)生物炭改性。采用常温处理法对热解制备的玉米芯生物炭进行改性。配制2 mg·L−1的CaCl2改性剂溶液,取0.3 g BC0放入20 mL样品瓶中后,加入3 mLCaCl2溶液,充分摇匀后放入25 ℃的恒温振荡器中,转速200 r·min−1条件下振荡24 h,然后用去离子水反复多次清洗后0.45 µm滤膜过滤分离,在120 ℃烘箱中干燥2 h后放置于干燥器中保存待用。改性生物炭用Ca-BC表示。
-
对改性前后生物炭表面形态进行理化性质分析。采用扫描电子显微镜(JSM-IT300LV,日本)研究样品表面形态,X射线能谱(EDS)对生物炭进行元素分析;全自动比表面积分析仪BET(Micromeritics ASAP2460,美国)测定样品比表面积与孔隙结构;FT-IR傅里叶红外光谱仪(IS50,美国)分析生物炭吸附官能团,X射线衍射仪(XRD,Rigaku Ultima IV,日本)对生物炭进行物相分析;X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,PHI 5000 Versaprobe Ш,日本)研究其官能团种类与含量。
-
1)不同固液比实验。取不同量的生物炭放入250 mL锥形瓶中,设定固液比分别为0.1,0.5、1、2、5,分别加入50 mL质量浓度为50 mg·L−1的KH2PO4和100 mg·L−1的NH4Cl溶液,混合均匀,然后放入25 ℃恒温水浴振荡器中以180 r·min−1振荡24 h,溶液经0.45 µm滤膜过滤,测定滤出液中剩余KH2PO4和NH4Cl质量浓度,得出不同固液比下生物炭对氨氮和磷的吸附效果,确定最佳固液比。
2)吸附动力学实验。将一定量生物炭加入到50 mL含50 mg·L−1的KH2PO4和100 mg·L−1的NH4Cl溶液中混合均匀,置于250 mL锥形瓶内,然后在25 ℃恒温水浴振荡器中以180 r·min−1分别振荡10、30、75、120、180、240、300、480、720、1 440 min后取出,经0.45 µm滤膜过滤,测定滤出液中剩余的KH2PO4和NH4Cl质量浓度,测定不同时间下生物炭对氮磷的吸附量,使用动力学模型进行拟合分析生物炭的吸附动力学特征。
3) 等温吸附实验。设置NH4Cl质量浓度(以N计)梯度为:1、2、5、10、20、50、100 mg·L−1;设置KH2PO4质量浓度(以P计)梯度为:0.5、1、2、5、10、20、50 mg·L−1。其余操作同吸附动力学实验。
4)NH4+-N 质量浓度的测定采用纳氏试剂分光光度法,吸收波长为420 nm;PO43--P质量浓度的测定采用钼锑抗分光光度法,吸收波长为700 nm。生物炭对氮磷的吸附效果使用Qe表示,计算公式如式(1)所示,采用准一级动力学模型(式(2))、准二级动力学模型(式(3))、Freundlich模型(式(4))、Langmuir模型(式(5))等对实验数据进行拟合。
式中:C0为初始氮磷的质量浓度,mg·L−1;Ce为吸附平衡时氮磷的质量浓度,mg·L−1;V为溶液体积,L;m为吸附剂质量,g; Qe为吸附量,mg·g−1;Qt为反应t时间的吸附量,mg·g−1;t为反应时间,min;K1为准一级动力学反应速率常数,min−1;K2为准二级动力学模型的速率常数,g·(mg·h) -1;KF为Freundlich模型的平衡常数;
1n 为异质性因子;b为最大吸附量,mg·g−1;KL为Langmuir模型的平衡常数。 -
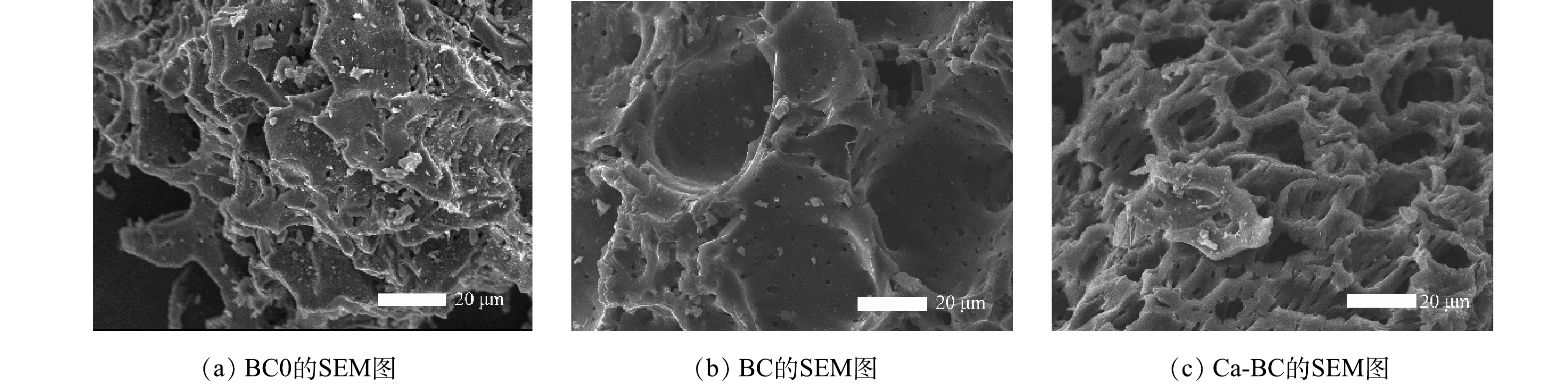
1) SEM电镜分析。采用场发射电镜观察BC0、BC和Ca-BC的微观形态如图1(a)~(c)所示。可以看到玉米芯生物炭具有大量蜂窝孔洞结构,比表面积大,这是有机物经高温热分解开孔作用形成,数量庞大。未经清洗的原始生物炭(BC0)孔洞结构中可见有大量碎屑杂质颗粒物,可能是经高温裂解产生的灰分,而清洗后的生物炭(BC)孔洞结构表面明显光滑,说明生物炭孔洞表面灰分经过清洗后大部分被清除,孔洞结构明显;Ca-BC更是在原有基础上出现更为细密的小型孔洞,生物炭上形成了发达的碳骨架和蜂窝结构等,使生物炭对水中氮和磷的吸附位点大大增多。
2) EDS分析。X射线能谱对生物炭的元素分析结果如图2(a)~(c)所示,表1为BC0、BC、Ca-BC材料元素含量分析。可以看到,C、O元素是生物炭的主要元素,同时含有微量的K元素。玉米芯生物炭在经过清洗和改性后表面元素含量百分比发生变化,清洗过程会去除材料表面部分化学物质,C占比降低,对材料元素含量产生影响, 而O、K元素含量随之相对增加;Ca-BC材料中出现Ca、Cl元素,C、K元素占比相应下降,而Ca、Cl元素含量百分比为1∶1.63,换算为摩尔比例为1∶1.84,接近1∶2,说明CaCl2改性剂材料成功附着在生物炭上。
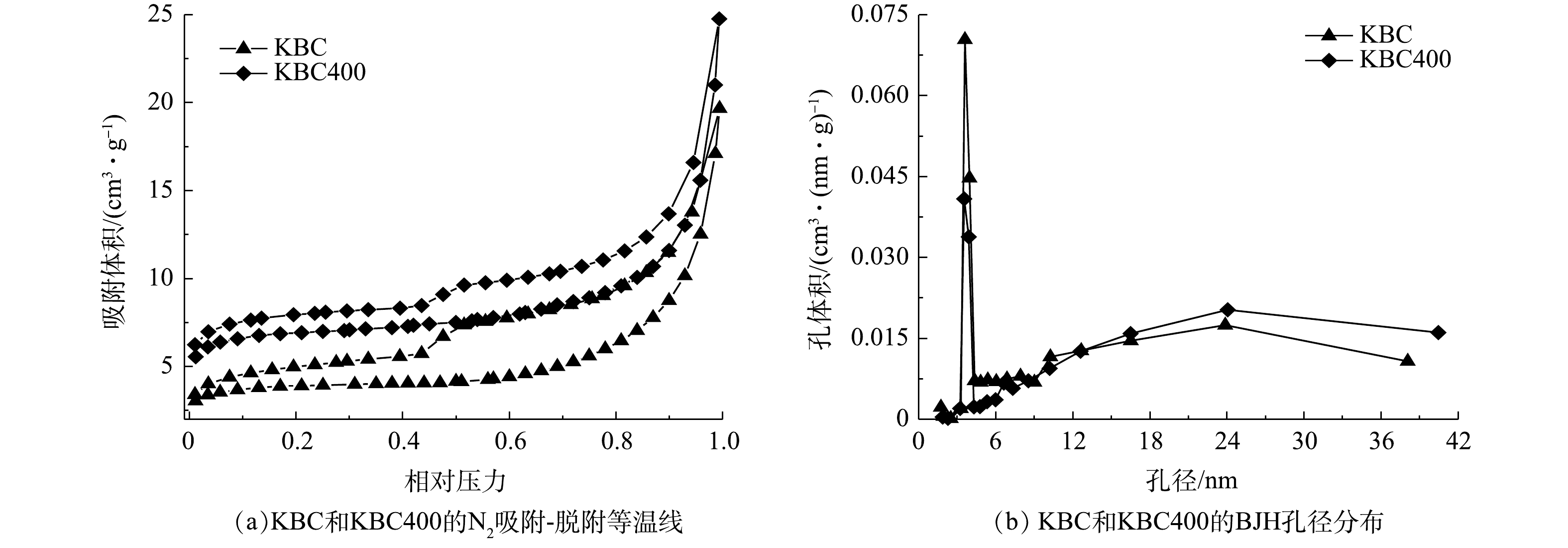
3)比表面积、孔径、孔容分析。吸附剂的孔隙结构及比表面积极大地影响着吸附剂的吸附性能。观察BC和Ca-BC的N2吸附-脱附曲线(图3)均符合Ⅳ型等温线的特征,说明这2种生物炭材料具有狭窄微孔,2种生物炭的微孔和介孔结构同时共存[16-17]。一般孔宽小于1 nm,其吸附很快达到饱和,观察2种材料吸脱附曲线符合这一情况。在低P/P0区时,BC和Ca-BC吸附量很高,表明两类生物炭充满着丰富的微孔结构;在高P/P0区时,N2吸附-脱附曲线没有重合,说明 MBC的孔内表面积远大于外表面积,除微孔外也存在着许多中孔结构。两类生物炭吸附-脱附曲线均出现了明显的回滞环,说明2种生物炭均为介孔材料[18],在P/P0>0.9时,N2吸附-脱附曲线仍在上升,说明两类生物炭中也存在着一部分大孔[19]。
为了进一步明确生物炭孔径大小,基于Barrett-Joyner-Halenda(BJH)法与Horvath-Kawazoe(HK)微孔分布计算法对生物炭孔径进行检测,得到BC和Ca-BC孔径分布图(图4和图5),可见BC与Ca-BC孔径分布类似,主要集中整在0.8~1.5 nm,均是介孔材料,与N2吸附-脱附曲线结果一致。BC微孔孔径主要集中在1.1~1.3 nm,微孔较多,中孔较少,随着孔径增大,孔径分布量先小幅增加后逐渐减少,;Ca-BC的中孔孔径主要集中在0.8~1.2 nm,0.8 nm处出现峰值,随着孔径增大,孔径分布量在1.2 nm处再次出现峰值后逐渐减少。与BC相比,Ca-BC材料的0.8 nm孔和1.2 nm孔明显增多,累计孔隙体积成倍增长,说明BC在经过改性后出现了大量微孔结构,CaCl2对玉米芯生物炭进行改性可以促进其孔结构的形成与发展。
具有高比表面积和孔隙结构的生物碳材料由于具有明显的孔隙填充作用,会促进有机质的吸附[20]。Ca-BC具有发达的孔隙结构和更大的比表面积,由表2可以看到,经过改性后,生物炭比表面积(SBET)从66.37 m2·g−1增加到157.68 m2·g−1,增加了137.58%。微孔比表面积(SMicro)从53.58 m2·g−1增加到124.05 m2·g−1。生物炭孔容从(VTotal)0.040 cm3·g−1增长到0.090 cm3·g−1,而其中微孔孔容(VMicro)从0.027 cm3·g−1增长到0.065 cm3·g−1。Ca-BC的SBET,微孔结构孔容体积等相关数据均大于BC,与N2吸附-脱附曲线结果一致,说明CaCl2溶液对于生物炭的改性通过离子反应、附着等方式,显著增加了玉米芯生物炭的比表面积和微孔结构。高质量浓度氯化钙本身具有强腐蚀性,随着与生物炭接触时间的增加,孔结构也在不断丰富发展,同时也会导致孔结构坍塌,形成更多的中孔和大孔[21],从Ca-BC的结构变化可以看出,CaCl2溶液改性处理促进了玉米芯生物炭微孔和介孔结构的发育。
4) FT-IR傅里叶红外谱图分析。BC0、BC、Ca-BC以及吸附24 h氮磷后的改性炭Ca-BC1的傅里叶红外光谱图如图6所示。4种生物炭在3 426 cm−1都出现了宽大明显峰值,说明生物炭表面主要以-NH4(氨基)和-OH(羟基)为主,可以观察到经过清洗后的生物炭对比原始生物炭在该区域峰强度小幅度下降,而经过改性和吸附氮磷后生物炭该峰的峰强度均明显增强,说明清洗、改性和长时间氮磷吸附均可导致生物炭表面-NH4(氨基)和-OH(羟基)含量发生变化。所有生物炭均在2 927 cm−1和2 847 cm−1处出现吸收峰,说明生物炭表面存在烷烃的-CH2键,4种生物炭该峰峰强度变化不大,说明生物炭的清洗和改性并未改变其表面的-CH2基团,氮磷吸附对于生物炭表面的烷烃基团数量有一定增强。
1 580 cm−1为苯(C=C)代表峰,4种生物炭在该处峰强度变化较小,Ca-BC和Ca-BC1峰强小幅度增强,说明改性和氮磷吸附会使生物炭表面苯C=C基团含量增加。1 693 cm−1处为C=O羰基代表峰区间(1 680~1 720 cm−1),羰基是典型的含氧基团代表,与BC0和BC相比,Ca-BC和Ca-BC1在此处明显出峰,说明改性和吸附使生物炭表面含氧基团含量增加。1 255 cm−1处存在的吸收峰表示生物炭可能存在醇,醚,酯类的C—O或C—O—C键伸缩振动,870 cm−1附近出现碳酸钙C—O特征吸收峰[22],说明生物炭表面存在少量碳酸钙成分,802 cm−1处为芳环上的C—H弯曲振动峰。745 cm−1附近出现氯化物特征峰区。改性生物炭此处峰强度小幅度增强,说明CaCl2改性后生物炭表面出现氯化物附着[23]。观察改性生物炭在500~1 600 cm−1范围内的谱峰可见,与未改性生物炭相比,此区间的各类基团物质峰强度均有所增加,说明CaCl2改性增加了生物炭表面多种有机物质和基团的数量。氮磷吸附后该范围内所有出现的峰峰强度都有小幅降低甚至降低回改性前,说明氮磷吸附过程可能对生物炭表面的有机物,各类基团和碳酸钙有一定消耗。
5) XRD结果分析。图7为BC和Ca-BC的XRD谱图。可见,BC与Ca-BC均具有晶体结构,BC与Ca-BC均在2θ=28.22º出现了尖锐衍射峰,说明2种生物炭均具有炭化结晶化合物以及碳酸盐类[24],Ca-BC在该处的衍射峰强度比BC明显增加,且出现CaCl2(29.28º)衍射峰,碳酸盐聚乙烯醇聚合物(40.37º)衍射峰以及碳酸钙类盐(45º~50º)微小尖锐衍射峰出现,说明Ca-BC相较于BC,生物炭表面附着产生碳酸盐和CaCl2晶体结构,并改变了生物炭表面化合物组分,CaCl2改性后的生物炭结构表面可能会产生碳酸钙有机聚合物[25]。进一步说明CaCl2对玉米芯生物炭改性改变了其表面组分构成并产生了离子附着和化学反应。
6) XPS结果分析。图8所示为BC与Ca-BC的XPS总谱图。可以看出, 改性前的玉米芯生物炭表面主要是C1s和O1s的电子能谱峰,说明C和O是玉米芯的主要组成成分,而CaCl2改性过后的玉米芯生物炭出现新元素Ca和Cl,表面出现CaCl2附着,与EDS分析结果一致;O含量增高,说明生物炭经过改性,有利于提高含氧官能团的含量[26],与傅里叶红外谱图分析中含氧基团羰基含量增加结果相符。
-
在不同固液比下对Ca-BC和BC进行氨氮和磷酸盐吸附实验,吸附效果如图9(a)~(b)所示。对比改性前后生物炭对氮磷的吸附效果可见,随着固液比增大,BC和Ca-BC对氮磷的吸附效果呈现先增强后减弱趋势,且均在0.5固液比条件下达到峰值。在固液比为0.5时,BC对氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附量分别为18.47 mg·g−1和3.25 mg·g−1;而经过CaCl2改性后,Ca-BC对氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附量分别增加至28.03 mg·g−1和8.96 mg·g−1,说明CaCl2改性能有效增加玉米芯生物炭对于水中氮磷的吸附效果。
-
1)改性生物炭吸附氮磷动力学结果分析。分别对BC和Ca-BC 2种生物炭进行了吸附氮磷的动力学实验,并使用准一级和准二级动力学方程进行拟合,吸附动力学拟合曲线见图10(a)~(d),得到的拟合参数见表3。
由图10可见,改性前后的生物炭对氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附量都随着吸附时间的增加而增加,生物炭对于氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附过程分为2个阶段:快速吸附阶段和慢速吸附阶段。观察图10(a)~(b),300 min前,BC对氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附处于快速吸附阶段,300~600 min内,吸附逐渐减缓,进入慢速阶段,在600 min之后趋于稳定,达到吸附平衡。图10(c)~(d)为Ca-BC对于氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附过程,可以看到180 min内,Ca-BC对于氮磷的吸附处于快速吸附阶段,在180~420 min内迅速减缓进入慢速吸附阶段,并在420 min后逐渐趋于稳定达到吸附平衡。结合SEM和孔径孔容分析,改性后的生物炭比表面积增大,蜂窝表面吸附位点增多,Ca-BC对氮磷的吸附能够更快达到吸附稳定,快速吸附阶段耗时更短,平衡吸附量更大。
观察动力学拟合方程计算出的平衡吸附量Qe可以看出,生物炭在经过改性后对氮磷污染物的吸附量明显增加,其中氨氮平衡吸附量由改性前的19.36 mg·g−1增加到28.39 mg·g−1,磷酸盐平衡吸附量由5.46 mg·g−1增加到9.74 mg·g−1,分别增加了46.6%和78.4%,说明生物炭经改性处理后对氮磷污染物的吸附增强效果明显,且吸附过程更加复杂。对Ca-BC和BC的吸附数据进行动力学拟合可以看出,BC对氨氮(图10(a))和磷酸盐(图10(b))的吸附能用准一级动力学模型更好的表达,相关系数分别达到了0.860和0.779,高于准二级动力学模型的拟合相关系数,说明BC对氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附过程以物理扩散为主,生物炭表面的范德华力对吸附起关键作用,吸附行为受离子浓度差影响[27]。Ca-BC对氨氮(图10(c))和磷酸盐(图10(d))的吸附与准一级动力学和准二级动力学均能较好的拟合,但准二级动力学拟合相关度更好,相关系数R2分别达到了0.912和0.904。准二级动力学可以描述孔填充,共价键形成和离子交换等作用,表明吸附与物理吸附和化学吸附密切相关[28],说明BC经CaCl2改性后,与未改性前的生物炭对氮磷污染物的吸附机制不同,Ca-BC与水中氮磷之间的交换或共享电子可能会产生共价键或新化合物[29]。金属离子和 NH4+在含氧官能团上的离子交换是金属改性生物炭去除水中NH4+-N 的主要机制之一[30], Ca-BC的FT-IR、XPS和XRD谱图均检测到含氧官能团的增加以及Ca2+的大量存在,说明Ca-BC对氨氮的化学吸附主要表现为离子交换作用;LIU等[31]研究发现水溶液中的Ca2+能与OH−和磷酸盐结合形成羟基磷灰石 (HAP) 沉淀去除磷酸盐,说明Ca-BC去除磷酸盐的化学过程主要为化学沉淀作用。
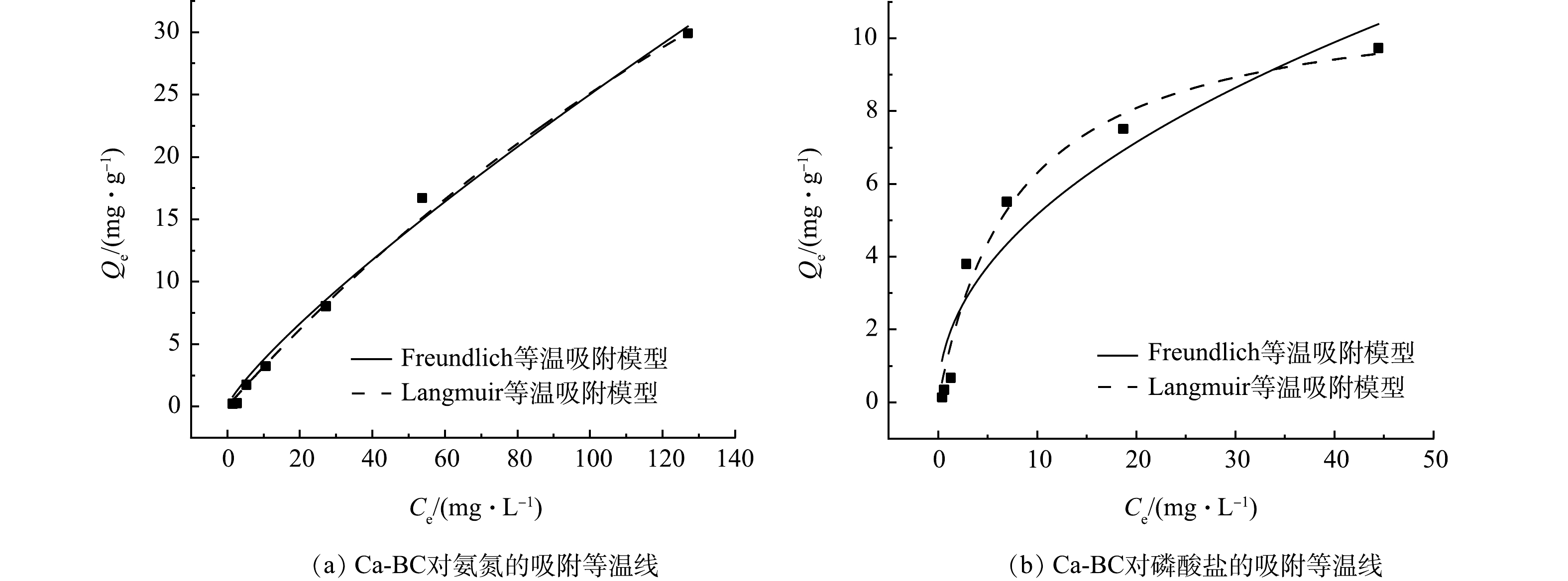
2)改性生物炭吸附氮磷等温吸附模型拟合分析。根据等温吸附实验结果,分别使用Freundlich和Langmuir等温吸附方程进行拟合,等温吸附拟合曲线见图11(a)~(b),拟合参数见表4。如图11(a)~(b)所示,氮磷溶液初始质量浓度是生物炭吸附氮磷的重要影响因素,氮磷溶液初始质量浓度越高,Ca-BC对于氮磷的吸附效果越好。Ca-BC对氮磷的等温吸附拟合结果可见Freundlich方程和Langmuir方程都有很好的拟合效果,相关系数R2都达到了0.9以上,相比之下,Langmuir等温吸附模型拟合效果更佳,对氨氮和磷酸盐的等温吸附拟合相关系数R2分别达到了0.999和0.971,说明Ca-BC对于水中氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附主要为单分子层吸附,材料为均质表面,表面点位均匀分布[32],吸附过程以物理吸附为主。根据Langmuir等温吸附模型可得到Ca-BC对水中氨氮和磷酸盐的最大吸附量分别为107.68 mg·g−1和11.28 mg·g−1。
-
生物炭原材料不同以及改性剂和改性方法的不同,对氮磷的吸附能力也会有所不同,通常可以用最大吸附量来大致评判不同生物炭的吸附性能。如表5所示,同种原材料生物炭,采用不同的改性剂和改性方法进行改性后,对氮磷的吸附性能相差较大。以芦苇为原材料,同样以MgCl2作为改性剂,共热解改性后对磷酸盐的最大吸附量为109.57 mg·g−1[33],而经浸渍+共热解改性后,对磷酸盐的最大吸附量可达到317.09 mg·g−1 [34]。使用不同的改性剂对玉米芯进行浸渍改性后,对氨氮的吸附量有所不同,本研究和李廷梅等[35]采用不同改性方法均对玉米芯进行了改性研究,结果表明,CaCl2和H3PO4改性玉米芯对氨氮的吸附量分别107.68 mg·g−1和3.97 mg·g−1,CaCl2改性更能促进玉米芯对氨氮的吸附。同一种改性剂对不同材料生物炭进行改性后,对氮磷的吸附性能也均有不同,如MgCl2改性芦苇[33]、香蕉秸秆[36]、玉米芯[37]对氨氮和磷酸盐的吸附量各有差异。除去改性方法,改性剂、原材料、改性剂质量浓度、共热解改性温度等也均会对生物炭的吸附性能产生影响,所以实际不同改性生物炭的吸附性能差异均不能绝对而言。
本研究采用的CaCl2浸渍法改性玉米芯,相较共热解法操作简单,且处理后的生物炭比其他浸渍生物炭甚至是其他改性方法的生物炭,对氨氮的吸附效果更好,Qe达到了107.68 mg·g−1,但对于磷酸盐的吸很低,仍待优化,说明使用CaCl2改性玉米芯对氨氮的吸附优化更为突出。Ca2+离子为生物所需微量元素,少量浸出甚至能提高植物的生长,如增加茎和根的长度,促进新陈代谢[40],Cl−为环境水体中常见元素,不会造成污染,环境风险很小。
对于实际水体,多种离子之间的竞争吸附也会影响吸附效果。周成赟等[41]研究了实际水体中共存阴离子对Ce-BDC-400(A)吸附氟过程的影响,发现CO32−会对生物炭吸附有一定的抑制作用,Ca-BC在实际水体中的应用有待进一步深入研究。
-
1) CaCl2改性可以改善玉米芯生物炭孔隙结构并产生有效离子附着,CaCl2在生物炭表面产生附着且发生化学变化,可以检测到CaCO3类物质。清洗、改性和吸附并没有在材料表面产生新的官能团,只是导致材料表面原有官能团的含量发生变化。
2)随着吸附时间和氮磷溶液质量浓度的增加,生物炭对氮磷的吸附效果明显增强;在固液比为0.5时BC对氮磷的吸附效果最好,经过改性后,生物炭对于氮磷的吸附效果明显增强,氨氮平衡吸附量由改性前的19.36 mg·g−1增加到28.39 mg·g−1,磷酸盐平衡吸附量由5.46 mg·g−1增加到9.74 mg·g−1,分别增加了46.6%和78.4%。
3) BC对水中氮磷吸附特征更符合准一级动力学,吸附过程主要为范德华力主导的物理吸附;Ca-BC吸附特征更符合准二级动力学,使生物炭对氮磷的吸附过程变得更为复杂,同时存在物理吸附和化学吸附,除物理吸附外,离子交换是去除水中NH4+-N 的主要化学吸附机制之一,而离子交换游离出来的Ca2+能够与磷酸盐结合产生化学沉淀去除磷酸盐。Ca-BC对氨氮和磷酸盐的等温吸附平衡规律更符合Langmuir等温吸附模型,吸附过程更接近单分子层吸附,说明Ca-BC对氮磷的吸附以物理吸附为主,化学吸附为辅。
钙改性玉米芯生物炭对水中氮磷吸附特性
Adsorption characteristics of calcium-modified corncob biochar for nitrogen and phosphorus in water
-
摘要: 以玉米芯为原材料,在500 ℃条件下高温热解制备生物炭,使用CaCl2对其进行改性,通过SEM、EDS、BET-N2、FTIR、XPS等手段对生物炭结构与组成进行了测定。通过吸附实验研究了改性生物炭对水中氮磷的吸附性能和影响因素,分析探讨其吸附机理,为生物炭在水处理中的应用提供参考依据。结果表明:CaCl2改性使玉米芯生物炭比表面积提高了137.57%,微孔和介孔数增加,并产生Ca2+、Cl−离子有效附着。氮磷初始溶液质量浓度、固液比、吸附时间均会对生物炭的吸附性能产生影响。CaCl2改性后的生物炭对氮磷吸附量分别提高了46.6%和78.4%。改性后的生物炭(Ca-BC)对水中氮磷的吸附更符合准二级动力学;Ca-BC对氨氮和磷酸盐的等温吸附更符合Langmuir模型,吸附过程更接近物理吸附为主,化学吸附为辅的单分子层吸附。Ca-BC通过范德华力静电相互作用、离子交换和化学沉淀过程去除水中氮磷。Abstract: Biochar was prepared by pyrolysis of corn cob at 500 ℃. The biochar was modified by CaCl2. The structure and composition of biochar were determined by SEM、EDS、BET-N2、FTIR and XPS. The adsorption properties and influencing factors of modified biochar toward nitrogen and phosphorus in water were studied through the adsorption experiments, and the adsorption mechanism was analyzed, which will provide a reference for the application of biochar in water treatment. The results showed that the specific surface area of corncob biochar increased by 137.57%, the number of micro- and meso-pores increased, and Ca2+ and Cl− ions were effectively attached. All the initial solution concentration of nitrogen and phosphorus, the ratio of solid to liquid and the adsorption time affected the adsorption performance of biochar. The adsorption capacities of nitrogen and phosphorus of biochar modified by CaCl2 increased by 46.6% and 78.4%, respectively. The adsorption kinetic behaviors of nitrogen and phosphorus in water by modified biochar (Ca-BC) were consistent with the quasi-second-order kinetic model. The adsorption isotherms of ammonia nitrogen and phosphate by Ca-BC could be consistent with the Langmuir model, and the adsorption processes were close to the single molecular layer adsorption with physical adsorption as the main one and chemical adsorption as the auxiliary one. Ca-BC removed nitrogen and phosphorus from water through van der Waals electrostatic interaction, ion exchange and chemical precipitation processes.
-
Key words:
- corn cob /
- biochar /
- nitrogen and phosphorus /
- adsorption
-
水体重金属污染是严重威胁生态、环境和人类健康的全球性问题之一[1]。镉是І类致癌物,具有生物积蓄性大、迁移能力强、半衰期长等特点[2]。其主要来源于人为活动(如采矿、电镀、颜料、电池等行业和冶炼排放的废渣、废气等),其排放造成水污染,严重影响陆地生态系统[3-4]。因此,迫切需要安全高效去除水体中的镉。
吸附法因其简单易操作被认为是去除水中镉污染的有效方法之一。其中,生物炭作为吸附剂具有廉价易得、物理化学性质稳定、官能团较多等特点,常被应用在重金属污染土壤和水体修复中[5-6]。但原始生物炭的分散性差、吸附能力有限,需通过活化或负载等手段提高吸附能力[7]。活化的制备工艺相对简单,可分为物理活化和化学活化。物理活化一般以CO2、H2O为活化剂,其操作简单,但活化后孔道分布不均,且能耗高。化学活化以ZnCl2[8]、KOH[9-10]、H3PO4[11]等为常用活化剂,其能耗低,但有些活化剂(如ZnCl2)会产生有毒气体。采用KOH活化可以有效改善炭材料孔道结构和比表面积,并且能够形成碳的官能团[12-13],不易产生二次污染。2步KOH活化法是利用已经炭化的前驱体与KOH混合均匀后共同热解制备得到的炭材料,其相对于1步活化法的优势在于能更好改善炭材料孔隙结构。目前大部分生物炭主要由小麦、玉米、水稻等秸秆制备而成,关于蚕沙生物炭吸附去除水体中镉的研究相对较少。2步KOH(浸渍-热解)活化法中每步对于炭材料的理化性质的影响及吸附贡献率也鲜见报道。
蚕沙是农业废弃物,其来源广泛,富含氨基酸、粗蛋白质和叶绿素等有机化合物,因此,在炭化后其可能含有较多活性基团。本研究以蚕沙生物炭为原料,以KOH为活化剂制备蚕沙基生物炭,分步探究了浸渍-热解活化法对炭材料理化性质的影响,并通过一系列的单因素实验考察了其对重金属Cd2+的吸附性能,以期为利用蚕沙制备高吸附性能生物炭提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与试剂
蚕沙来自于广西农业技术推广所(5龄蚕沙),氢氧化钾(KOH)、硝酸镉(Cd(NO3)2·4H2O)、硝酸钙(Ca(NO3)2·4H2O)、硝酸镁(Mg(NO3)2·6H2O)、氯化钾(KCl)、氯化钠(NaCl)等试剂均为分析纯;实验用水为超纯水。主要仪器包括管式炉(KGF1600-80,河南酷斯特仪器科技有限公司)、原子吸收分光光度计(AA-7000,日本岛津SHIMADZU株式会社)、水浴恒温振荡器(SHA-BA,常州国华仪器有限公司)。
1.2 生物炭的制备与表征
将蚕沙中的杂质挑除干净,烘干后用粉碎机粉碎,过60目筛,放置于刚玉舟中压实并密封,通入N2,于真空管式炉中缓慢升温(5 ℃·min−1)至500 ºC,保温2 h,用去离子水洗涤至中性,标记为BC。待冷却后取出样品,并将生物炭进行研磨、过100目筛,放入干燥器中备用。
1)浸渍活化炭材料的制备。BC和KOH按照质量比1∶1的比例置于烧杯中混合搅拌5 h,用超纯水洗至中性,于105 ℃下烘干12 h,将得到的生物炭进行研磨、过100目筛,储存在干燥器中。标记为KBC。
2)浸渍-热解活化炭材料的制备。浸渍步骤同上,于105 ℃下烘干12 h,再置于25 mL的刚玉舟中压实,密封,在N2氛围下于真空管式炉中升温至400 ºC,保温1 h。热解完成后用水洗至中性,于105 ℃下烘干12 h。将得到的生物炭进行研磨、过100目筛,储存在干燥器中。标记为KBC400。
采用Sigma300型场发射扫描电镜SEM-EDS(卡尔蔡司公司,德国)分析样品的表面形貌。采用ASAP 2460型多站全自动比表面积分析仪BET(麦克默瑞提克公司,美国)分析样品的比表面积。采用inVia Reflex型激光拉曼光谱仪(雷绍尼公司,英国)分析样品晶格振动。采用IRTracer-100型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(岛津公司,日本)对样品进行表面官能团分析。采用NanoBrook Omni型多角度粒度及高灵敏Zeta电位分析仪(布鲁克海文公司,美国)对样品所带电负性分析。
1.3 吸附实验
本实验所用溶液均使用去离子水配制,用硝酸镉(Cd(NO3)2·4H2O)配制1 g·L−1的Cd2+标准储备液,以0.01 mol·L−1 NaNO3作为溶液背景电解质。后续实验所需Cd2+溶液通过稀释储备液制得。每组实验设置3个重复和1个空白对照。
蚕沙基生物炭投加量对溶液Cd2+吸附的影响。取50 mL质量浓度为30 mg·L−1 Cd2+溶液置于100 mL离心管中,调节pH为5.0,分别称取BC、KBC、KBC400样品0.01、0.015、0.02、0.025、0.03、0.04、0.05 g加入其中,在25 ℃水浴中,以200 r·min−1振荡24 h后取样,使用0.45 μm聚醚砜针筒滤器过滤,采用原子吸收分光光度计(AAS)测定滤液中Cd2+的浓度。
不同pH对Cd2+吸附效果影响。取50 mL质量浓度为30 mg·L−1 Cd2+溶液置于100 mL离心管中,用0.1 mol·L−1 NaOH或HCl调节pH为2.0、3.0、4.0、5.0、6.0,称取BC、KBC、KBC400样品0.02 g加入其中,在25 ℃、200 r·min−1下振荡24 h,测定滤液中Cd2+的浓度。
共存离子对Cd2+吸附效果影响。取50 mL浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1 Cd2+溶液置于100 mL离心管中,分别配制0.1 mmol·L−1的K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+溶液作为背景液,pH为5.0,加入BC、KBC、KBC400样品0.02 g,在25 ℃、200 r·min−1下振荡24 h,测定滤液中Cd2+的浓度。
吸附平衡实验。1)动力学实验:取50 mL质量浓度为30 mg·L−1 Cd2+溶液置于100 mL离心管中,调节pH为5.0,称取BC、KBC、KBC400样品0.02 g加入其中,在预定的反应时间(5、10、30、60、120、360、720、1 440、2 880 min)取样,测定滤液中Cd2+的浓度。2)吸附等温线:分别称取BC、KBC、KBC400样品0.02 g,设置一系列Cd2+溶液质量浓度梯度(5、10、20、30、40、60、80、100 mg·L−1),调节pH为5.0,振荡24 h取样,测定滤液中Cd2+的浓度。
1.4 分析方法
蚕沙基生物炭的吸附量(qe)和去除率(η)通过式(1)和式(2)计算。
qe=(C0−Ce)Vm (1) η=(C0−Ce)C0×100\text{%} (2) 式中:C0为镉溶液的初始质量浓度,mg·L−1;Ce为镉溶液吸附平衡时的质量浓度,mg·L−1;V是镉溶液的体积,L;m是吸附剂的质量,g。
吸附动力学通过拟合准一级动力学、准二级动力学和Weber-Morris颗粒内扩散模型来分析镉离子的吸附过程。计算模型如式(3)~式(5)所示。
ln(qe−qe)=lnqe−k1t (3) tqt=1k2qe2+tqe (4) qt=Kdit12+Ci (5) 式中:qt和qe分别为t时刻和吸附平衡时的吸附量,mg·g−1;k1和k2表示准一级和准二级动力学的速率常数,min−1和g·(mg·min)−1;Kdi是粒子内扩散的速率常数,g·(min·mg1/2)−1;Ci是与边界层厚度相关常数,mg·g−1。
吸附等温线通过拟合Langmuir模型和Freundlich模型分析镉离子的吸附机理,具体如式(6)和式(7)所示。
qe=CeqmKL1+CeKL (6) qe=KFCe1n (7) 式中:qm是最大吸附量,mg·g−1;Ce是吸附平衡时镉溶液质量浓度,mg·L−1;KL是Langmuir等温吸附常数,L·mg−1;KF是Freundlich吸附常数;n是与Freundlich等温模型有关的吸附剂表面作用强度;qe是平衡吸附量,mg·g−1。
活化步骤贡献率根据式(8)和式(9)进行计算。
QI=QKBC−QBC (8) QP=QKBC400−QKBC (9) 式中:QKBC是KBC吸附Cd2+的吸附量,mg·g−1;QBC是BC吸附Cd2+的吸附量,mg·g−1;QI是浸渍活化处理的吸附量,mg·g−1;QP是热解活化处理的吸附量,mg·g−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 生物炭的基本性质
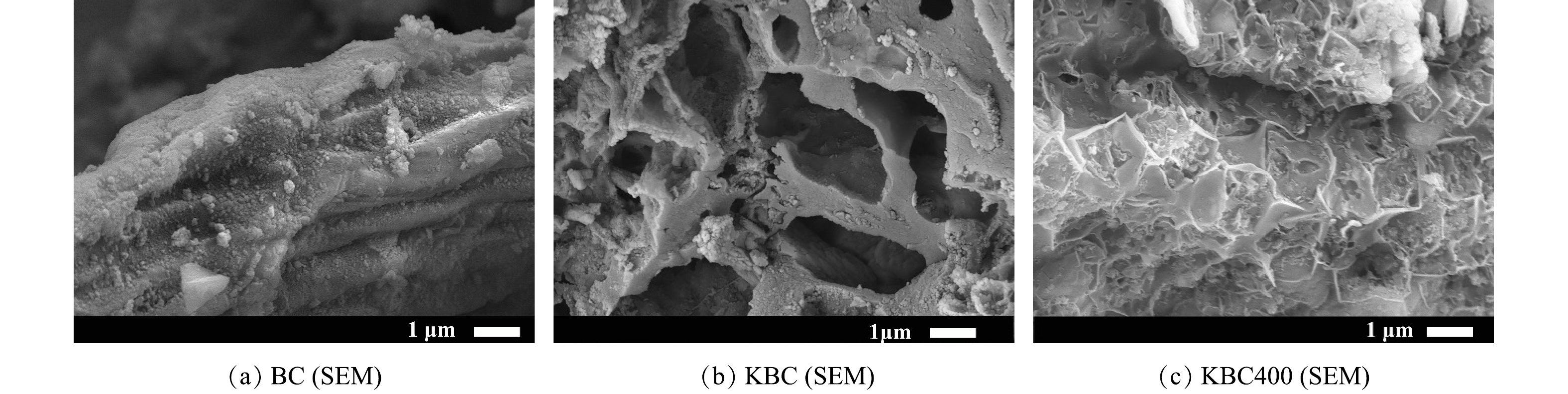
1)表面形貌(SEM)与比表面积(BET)分析。活化前后生物炭的微观表面形貌如图1所示。未经KOH活化的BC具有粗糙、致密的表面特征,且观察不到明显的孔结构(图1(a)),说明仅500 ℃碳化对生物炭的造孔能力有限。经过KOH浸渍的KBC表面变得孔隙结构丰富起来,主要以中孔为主,并具有较为清晰的纤维状结构(图1(b))。这是由于浸渍KOH可以去除一部分灰分以及促进孔结构膨胀,说明KOH在孔结构的形成中起着重要作用[14-15]。加入活化剂KOH浸渍并再次热解后,KBC400的表面出现了许多不均匀的凹陷(图1(c))。这可能是KOH在400 ℃下与碳原子反应并转化为易溶于水的K2CO3,形成大量孔隙[16-17]。其具体反应过程如式(10)~式(13)所示[18]。
2KOH⟶K2O+H2O (10) C+H2O⟶CO+H2 (11) CO+H2O⟶CO2+H2 (12) CO2+K2O⟶K2CO3 (13) 在浸渍-热解活化过程中,浸渍时KOH进入生物炭内部,K+起到支撑作用,随后K+在孔隙中刻蚀掉不稳定的C、N、H等原子,不稳定的C原子会变成CO、CO2等气体挥发掉。但当热解温度较低(≤600 ℃)时,生物炭内部的K+没有释放出来,导致不能形成致密的孔结构。
活化后的生物炭比表面积和孔隙结构如表1和图2所示。KBC400的比表面积比KBC增加了1倍,孔容和微孔面积也有所增加。经过KOH活化的炭材料平均孔径位10~14 nm,主要以中孔为主。从孔径分布(图2(b))可以发现,浸渍-热解活化生物炭中一部分中孔是由微孔裂变而来的。这些丰富的中孔结构有利于吸附质的扩散。
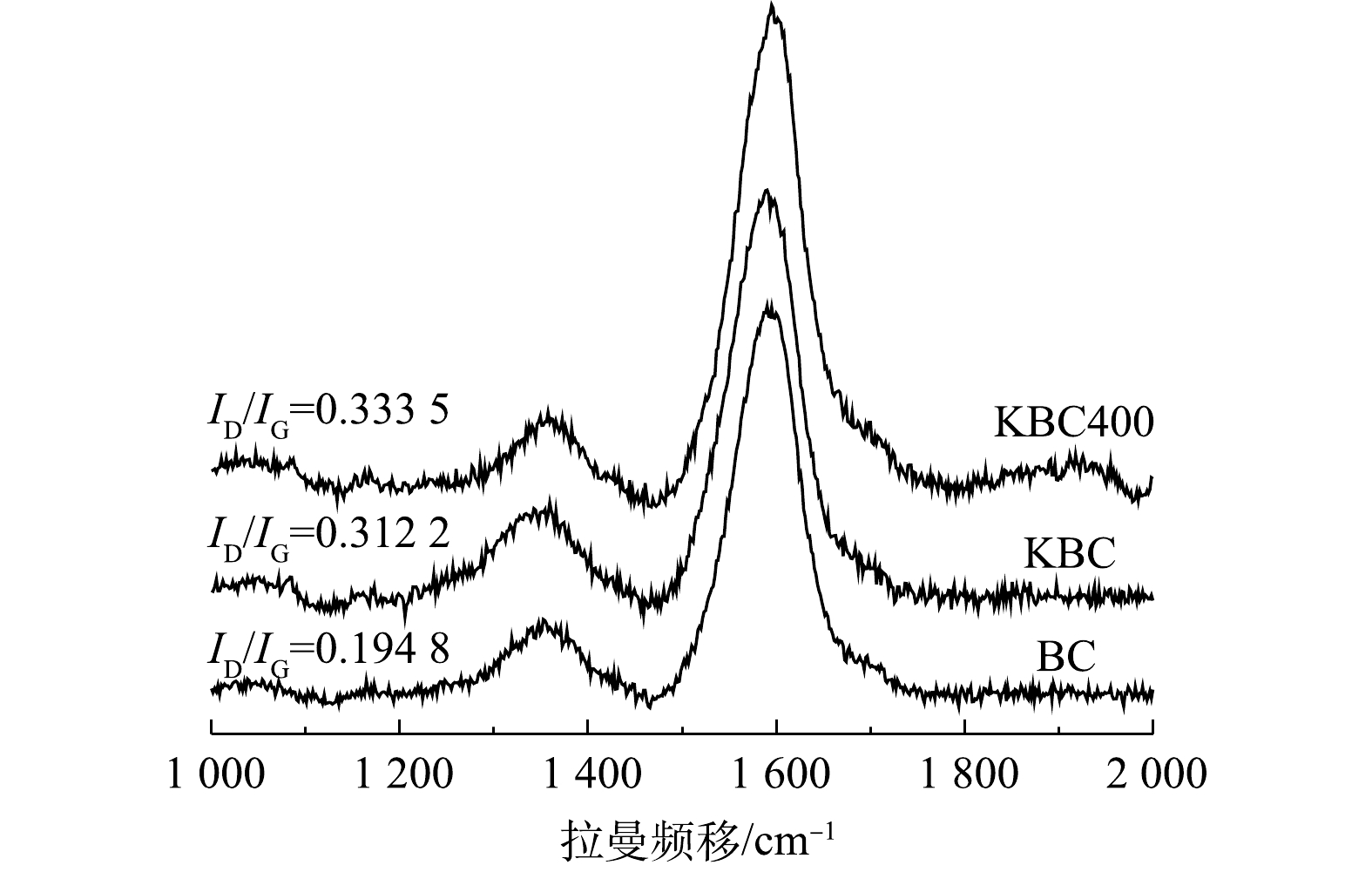
表 1 KBC和KBC400的孔隙信息Table 1. Pore parameters of KBC and KBC400材料 SBET/(m2·g−1) Vt/(cm3·g−1) Smic/(m2·g−1) dp/nm KBC 12.858 2 0.030 4 9.069 8 10.34 KBC400 21.769 1 0.038 3 16.367 9 14.25 2)拉曼(Raman)分析。图3为活化前后生物炭的拉曼光谱图。可见,在1 359 cm−1和1 593 cm−1有2个明显的吸收峰,分别代表D峰和G峰。D峰表示炭材料的面内缺陷结构(SP3杂化碳原子)[19],与无序化程度有关;G峰表示炭材料的类石墨微晶的面内振动以及稠芳环结构(芳香结构骨架中SP2碳原子)[20],与内部结晶度和对称性相关(石墨化程度)。D峰和G峰的强度表明,蚕沙基生物炭是包括SP2和SP3杂化的不同碳结构的混合体,且G峰强度较高,表明其内部的结晶度和对称性较好,且表明其可以形成π电子供体,有利于形成重金属Cd2+-π键[21](图3)。基于D峰和G峰的物理意义,可以用R来表示炭材料的无序化度,即R=ID/IG[22-23]。对比R值可以得出生物炭的无序化程度,即BC<KBC<KBC400,表明KOH活化可以增加材料的无序化程度,且浸渍-热解方式更能增加无序化程度,这可能是由比表面积和孔体积增大导致的,有利于提高Cd2+的吸附量[24]。
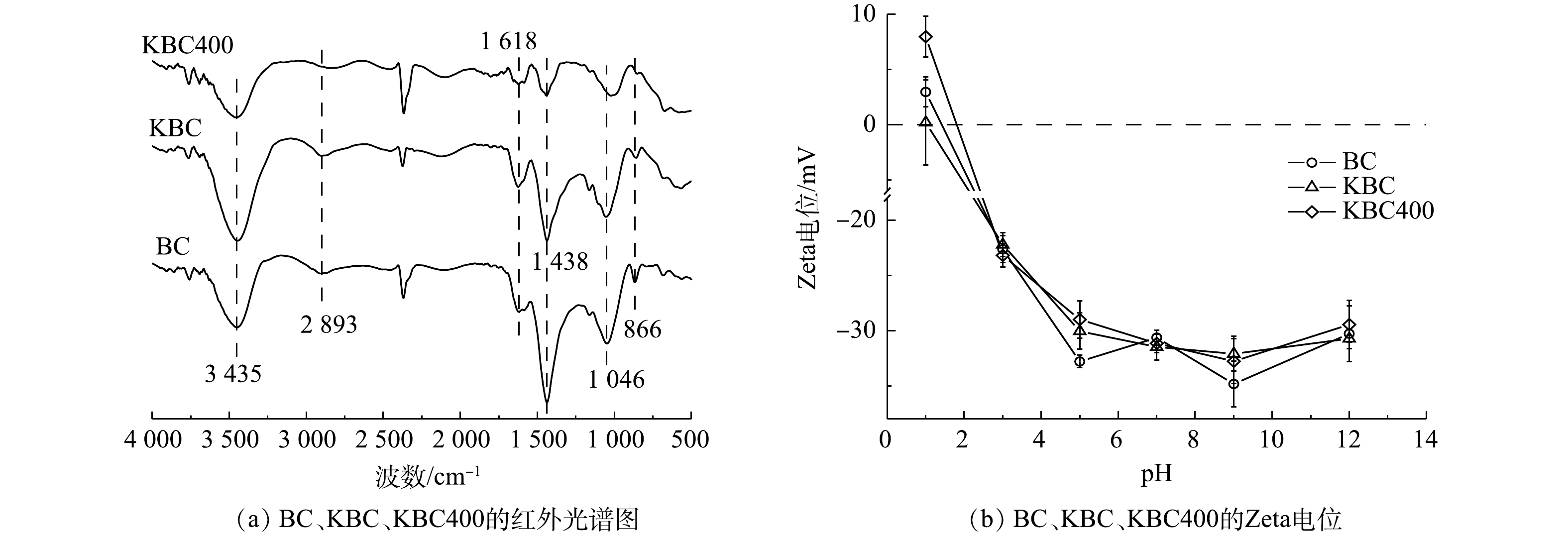
3)傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)分析。炭材料在500~4 000 cm−1内的傅里叶红外光谱图如图4(a)所示。3 452 cm−1附近出现的特征峰对应于醇类、酚类或者水的分子间的O—H的伸缩振动[25]。在此区域由生物炭的O—H伸缩振动引起的吸收峰强度为KBC>BC>KBC400。这说明在KOH浸渍的过程中,氢氧根会结合到生物炭表面形成羟基,但随着裂解温度的升高,O—H峰的振动强度逐渐减弱[26]。2 893 cm−1处出现的峰为脂肪族的(甲基(—CH3)或者次甲基(—CH))C—H键伸缩振动引起的[13];1 046、1 438和1 618 cm−1附近出现的峰分别表示C—O—C的伸缩振动、—O—CH3(甲氧基)和芳香族的C=C骨架振动或C=O键分子面的伸缩振动,是原料木质素最典型的红外特征带[27]。此区域生物炭的吸收峰强弱为KBC>BC>KBC400。其中KBC400在1 046 cm−1处的峰有所偏移,说明KOH能够影响碳骨架;1 618 cm−1处的峰强度有所减弱,可能是KOH在高温下的脱水作用[28-30]。866 cm−1处出现的峰为芳香族的C—H键面外弯曲振动引起的[31]。综上所述,可能发生如式(14)所示的反应[32]。
OH−+C(缺陷)⟶(C= =O)+(—OH)+C—O+(O—C= =O)+(—COOH) (14) 由此可见,KBC和KBC400主要含有羟基、羧基等含氧官能团,能与Cd2+结合,有利于吸附的进行。
4) Zeta电位分析。Zeta电位分析结果表明(图4(b)),蚕沙基生物炭的等电点(PZC)均在1~1.5,且Zeta电位均随着pH的升高而降低。这是由于生物炭表面的含氧官能团(羧基、羟基等)在不同H+浓度的溶液中发生的电离作用引起的[33]。BC与2种活化生物炭对比显示Zeta电位变化不大,说明不同的KOH活化方式对生物炭表面的电负性影响较小[34]。
2.2 投加量对吸附效果的影响
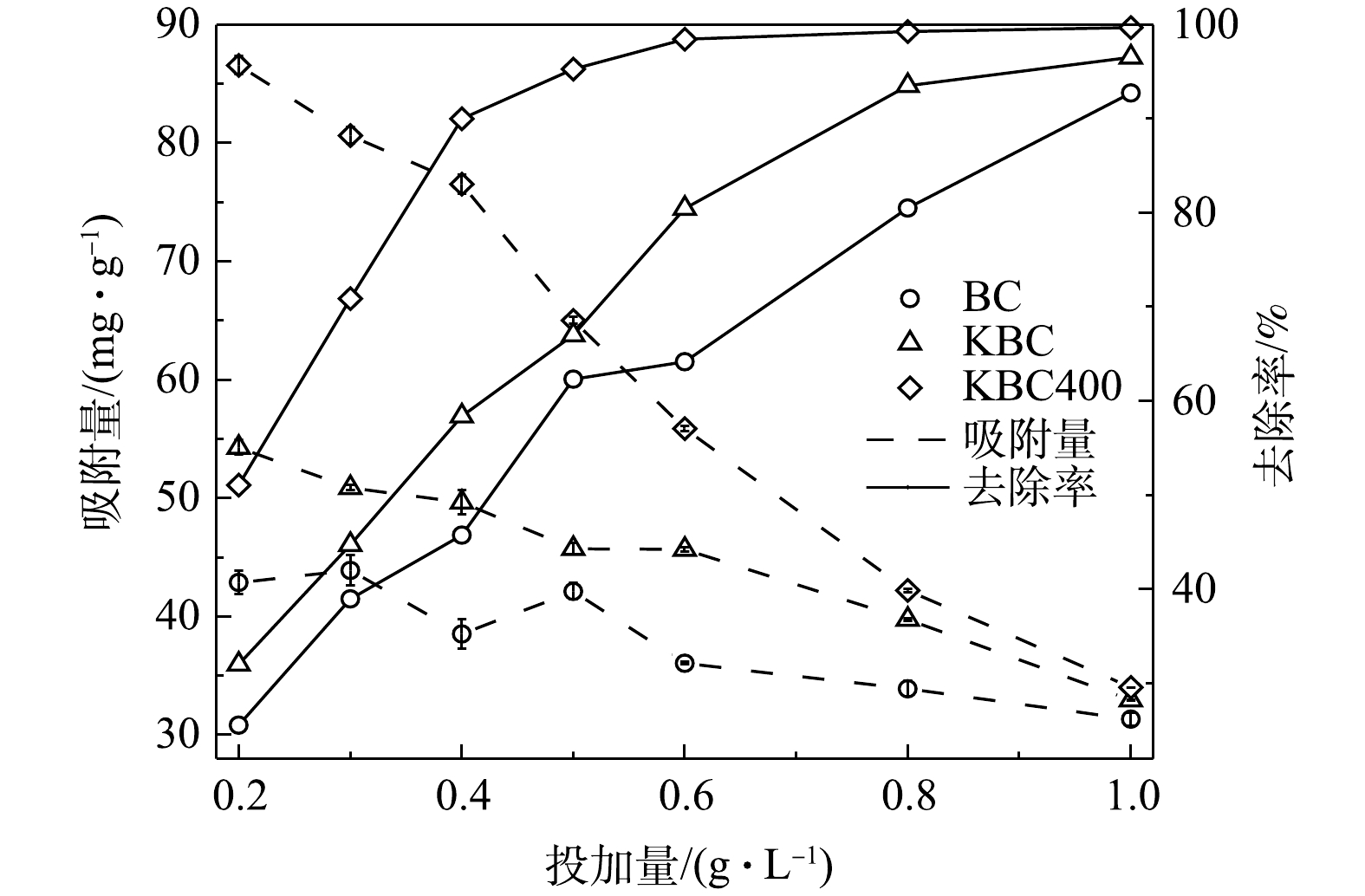
活化前后生物炭的投加量对吸附Cd2+的影响(图5)。在本研究条件下,BC、KBC和KBC400对Cd2+的最大去除率分别为92.73%、96.54%和99.68%,可见,在同等条件下KBC400去除率最高。其中,KBC400投加量由0.2 g·L−1增加至0.4 g·L−1,对Cd2+的去除率增加显著,去除率由51.06%增加至90.00%;之后再增大投加量,去除率变化不大。KBC投加量由0.2 g·L−1增加至0.8 g·L−1时,Cd2+的去除率从由32.02%增加至93.50%。BC在投加量由0.2 g·L−1增加至1 g·L−1时,Cd2+的去除率仅由25.54%增加至92.73%。各材料的吸附量随着投加量的增加而减少。在投加量为0.4 g·L−1时,BC、KBC、KBC400的吸附量分别为38.53、49.65、76.53 mg·g−1,而投加量超过0.4 g·L−1,其吸附量分别降低至31.33、32.94、34.01 mg·g−1。这是因为生物炭投加量增加时,生物炭表面的吸附位点和Cd2+的去除率均呈增加趋势,由于溶液中的Cd2+数量有限,其表面的吸附位点未达到饱和,所以对Cd2+的吸附量降低。考虑到去除效果、经济和一致性原则,在后续研究中选择0.4 g·L−1作为的生物炭最优投加量。
2.3 溶液pH对吸附效果的影响
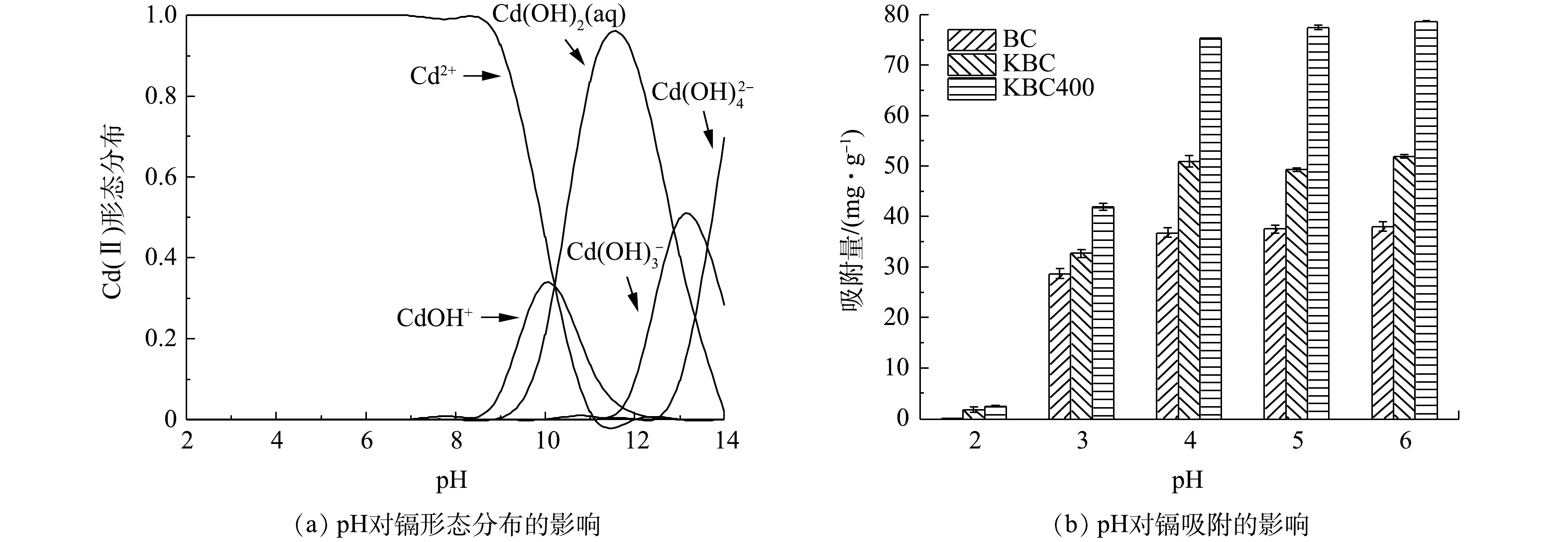
初始pH对重金属的存在形态和吸附剂表面的电荷情况来说意义重大[35],会直接影响吸附剂对水中重金属的吸附。由Visual MINTEQ 3.1计算得到纯水中Cd2+在不同pH下的水解情况(有效质量浓度为30 mg·L−1)如图6(a)所示。Cd(Ⅱ)在水中主要以Cd2+、Cd(OH)+、Cd(OH)2(aq)、Cd(OH)3−和Cd(OH)42−4种形态存在。在pH<8.0时,镉在水中的存在形态以Cd2+为主;在pH为8.0~10.0时,有部分少量的水解产物(CdOH+)和沉淀Cd(OH)2;在pH为10.0~14.0时,Cd2+形成的水解产物组成比较复杂,但主要以沉淀形式存在。因此,在pH<8.0的环境中,水中Cd2+的去除几乎均由生物炭的吸附作用完成,而不是水解形成的难溶产物的沉淀。
由图6(b)可以观察到,BC、KBC、KBC400对Cd2+去除率和吸附容量随着pH的增加呈现先迅速增大后趋于平缓。由于BC所含的碱性矿物较多,会显著提高溶液pH,若pH≥8.0,Cd2+有聚沉的趋势,故只考察吸附剂pH在2.0~6.0内对Cd2+吸附的影响。在pH=3.0时,BC、KBC和KBC400对Cd2+的吸附量提高最显著,分别由低于3 mg·g−1提高至28.64、33.20和41.90 mg·g−1。在弱酸性条件下(pH=4.0~6.0),与BC相比,KBC和KBC400对Cd2+的吸附容量由33.20 mg·g−1和41.90 mg·g−1提高至51.90 mg·g−1和78.76 mg·g−1,分别提高了56.33%和87.97%。综合上述结果可知,浸渍-热解活化制备的炭材料(KBC400)能适用于较广的pH范围,且吸附量也显著高于浸渍活化制备的生物炭。
蚕沙基生物炭表面都含有丰富的—OH等官能团,电离后使其表面带有负电荷,Cd2+在生物炭表面发生吸附主要是静电引力的作用,与其本身的电负性密不可分。当pH较低时,溶液中存在大量H+、H3O+离子会占据生物炭表面的吸附位点,使得Cd2+的吸附受到抑制。同时,生物炭表面的—OH也会与溶剂中的H+发生质子化反应[36],抑制炭材料表面的—COOH等官能团解离,从而阻碍Cd2+与官能团结合。此外,若溶剂中存在大量的质子,则会导致炭材料表面带正电荷,使带正电荷的Cd2+难以与之结合。随着pH的增加,生物炭表面官能团(—COOH、—OH)等开始去质子化,所带的负电荷数量的增加能提高与Cd2+间的静电引力,利于发生离子交换作用,所以Cd2+的去除率逐渐增加[37]。
2.4 共存离子对吸附的影响
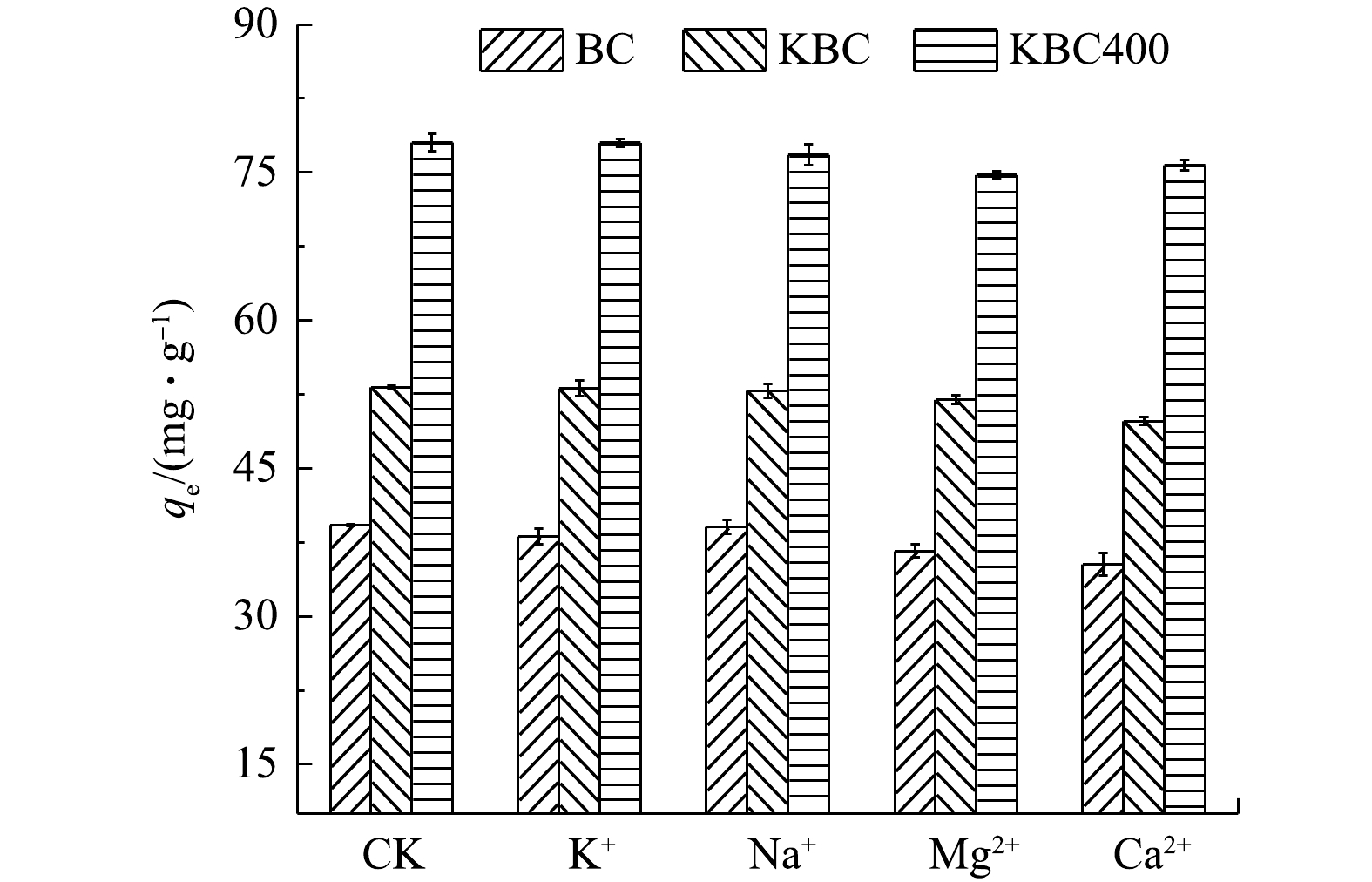
除了溶液pH外,吸附介质中的共存离子也会影响吸附剂的吸附效果,因此,本实验探讨了溶液中存在不同的碱金属离子(K+、Na+、Mg2+和Ca2+)对吸附效果的影响(图7)。其中,CK为未添加碱金属离子时BC、KBC和KBC400对Cd2+的吸附情况。对吸附影响较小的是Na+、K+;对吸附影响影响较大的是Mg2+,BC、KBC和KBC400对Cd2+的吸附量分别下降了25.16%、10.96%、3.08%。同时,Ca2+也会抑制BC、KBC和KBC400对Cd2+的吸附,吸附量分别下降了30.42%、12.29%和2.24%。出现这种现象可能是由于Mg2+、Ca2+较弱的共价性质,导致其水化程度较低,从而增强它们与吸附剂表面的相互作用[38-39]。以上结果表明,KBC400具有较好的抗离子干扰能力,其次是KBC。
2.5 吸附动力学
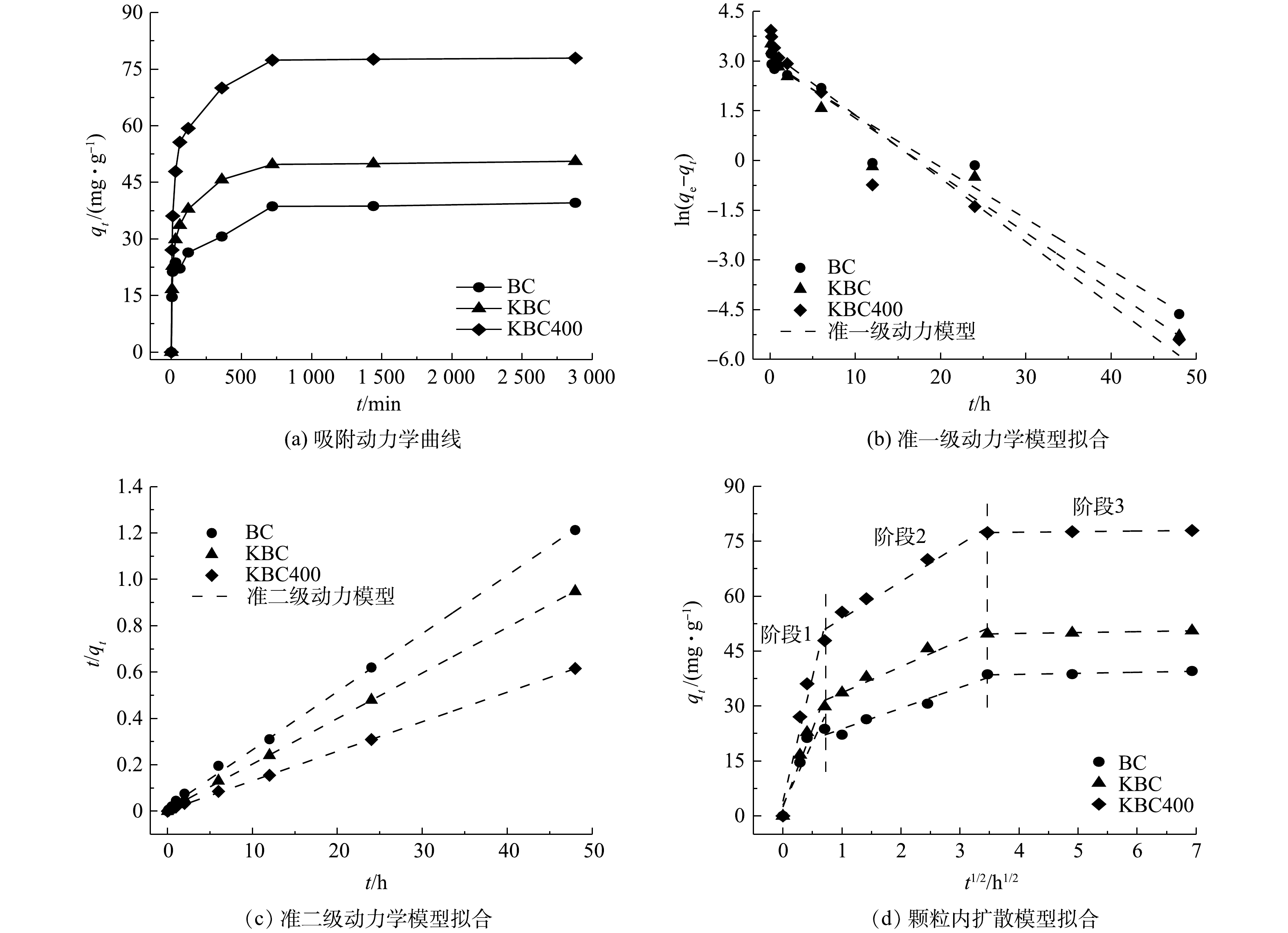
吸附时间对蚕沙基生物炭吸附Cd2+的影响如图8所示。在不同时间下,比较生物炭的吸附量大小为KBC400>KBC>BC。在12 h内,生物炭对Cd2+的吸附容量迅速增大。这是因为生物炭表面的活性位点丰富,能与Cd2+迅速结合。之后生物炭表面的活性位点渐渐饱和(即达到吸附平衡),即使吸附时间增加,吸附容量也变化不大。其中,浸渍-热解活化方式能够更快速的吸附Cd2+。因为KOH热解后提高了生物炭的比表面积,导致与Cd2+的接触面积有所增加。
Weber-Morris颗粒内扩散模型拟合结果如图8(d)所示。该模型假设吸附主要可分为3个阶段:首先,吸附质通过水膜层从外部流体介质中向吸附剂的外表面扩散,即外扩散过程;然后,吸附质由材料外表面进一步向孔隙中活性位点扩散,即内扩散过程;最后是吸附质被活性位点吸附的过程,该阶段可能涉及化学反应,此模型能直观地反映吸附剂在吸附的各个阶段的吸附速率大小,且一般主要由前2个阶段控制[38]。Cd2+在KBC、KBC400上的快速吸附阶段发生在6 h内,而初始快速去除阶段则发生在0.5 h内。此外,与BC相比,KBC和KBC400具有良好的吸附性能,0.5 h吸附容量分别达29.88 mg·g−1、47.89 mg·g−1,占其总吸附量的59.06%和61.43%。而BC在1 h内吸附量才达到22.17 mg·g−1,占其总吸附量的56.01%。初始快速吸附可归因于溶液扩散、表面静电吸引和离子交换等过程。对比Weber-Morris模型的斜率可知,浸渍-热解(KBC400)活化方式能够更快速的吸附镉离子。
由表2中的准一级、二级动力学模型的拟合结果可知,BC、KBC和KBC400的吸附过程都更加符合准二级动力学模型(R2≥0.99),说明发生在生物炭表面的Cd2+的吸附行为主要以化学过程为主,即吸附过程可能存在吸附质与吸附剂之间的电子共用或化学成键作用[40]。此外,KBC和KBC400的准一级和准二级动力学模型的R2皆大于0.9,说明经过KOH活化后的生物炭的吸附可能同时存在物理和化学吸附过程[35, 41]。
表 2 BC、KBC、KBC400的动力学拟合参数Table 2. Parameters of kinetic models of BC, KBC and KBC400吸附剂 准一级动力学模型 准二级动力学模型 Weber-Morris模型 qe/(mg·g−1) K1/h−1 R2 K2/(g·(mg·h)−1) R2 R2 BC 39.58 0.155 5 0.958 0.043 7 0.998 0.742~0.938 KBC 50.59 0.172 9 0.965 0.054 6 0.999 0.920~0.951 KBC400 77.96 0.190 9 0.943 0.039 6 0.999 0.922~0.999 2.6 吸附等温线
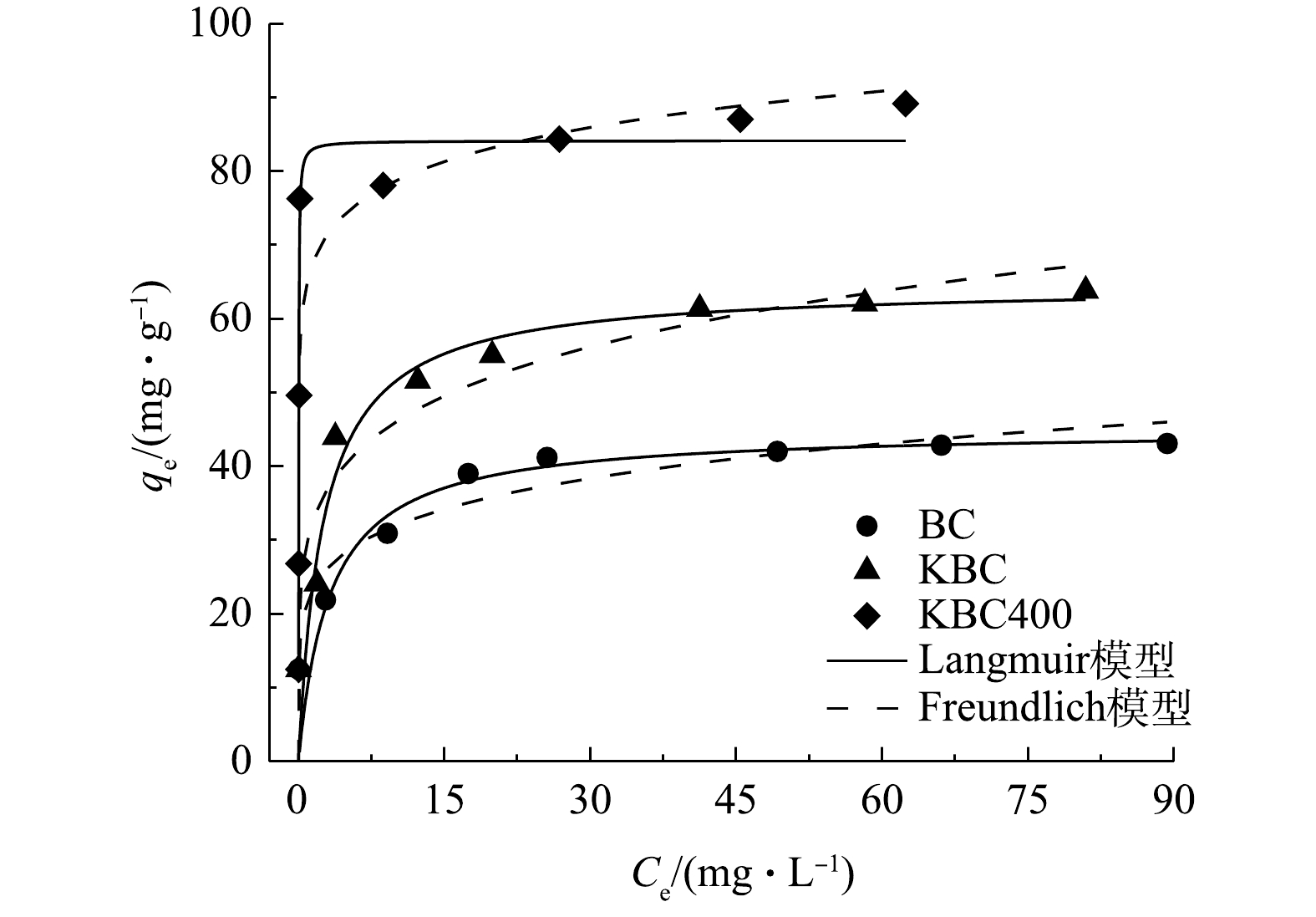
不同Cd2+浓度溶液对蚕沙基生物炭吸附的影响以及等温模型拟合曲线如图9所示。在不同浓度下,对比吸附量可得出对应关系为KBC400>KBC>BC。在Cd2+质量浓度低于30 mg·L−1时,生物炭的吸附容量快速增加。这是因为污染物浓度较低,生物炭表面结合位点充足,可迅速与之结合。之后结合位点渐渐饱和,虽然污染物浓度增加但吸附量趋于平缓。BC、KBC和KBC400实际测量最大吸附量分别为43.09、63.80和89.15 mg·g−1。
本研究采用Langmuir和Freundlich 2种等温模型对数据进行拟合(表3),Langmuir等温模型代表均质的单层吸附,BC、KBC和KBC400的拟合结果显示R2值为0.874~0.971,说明Langmuir模型能够更好的描述生物炭材料在不同Cd2+浓度下的吸附行为。
表 3 BC、KBC、KBC400的等温吸附拟合参数Table 3. Parameters of isothermal adsorption model of BC, KBC and KBC400吸附剂 Langmuir模型 Freundlich模型 qm/(mg·g−1) KL/(L·mg−1) R2 KF/(mg·g−1) n R2 BC 44.99 0.31 0.971 21.80 0.17 0.805 KBC 64.54 0.39 0.948 30.23 0.18 0.865 KBC400 84.12 48.73 0.874 65.43 0.08 0.842 通过Langmuir等温线模型拟合可知,BC、KBC和KBC400的理论最大吸附量分别为44.99、64.54和84.12 mg·g−1,与实际吸附量相近。通过KOH活化能提高蚕沙基生物炭的吸附容量,相比于BC分别提高了43%、99%。同时,在本研究条件下,浸渍-热解活化方式制备的生物炭对Cd2+的吸附量提升最多,表明KBC400在去除Cd2+污染具有一定应用潜力。
3. 结论
1)本研究通过2种KOH活化法制备了高吸附性能的蚕沙基生物炭。KOH活化改善了生物炭的表面特征。浸渍活化的生物炭(KBC)比表面积小于浸渍-热解活化的生物炭(KBC400),分别为12.86 m2·g−1和21.77 m2·g−1。KBC的无序化程度低于KBC400,两者官能团种类基本一致,说明KOH浸渍-热解活化方式制备的生物炭具有更优异的孔隙结构,有利于对污染物的吸附与去除。
2) 2种KOH活化法均可增加生物炭的吸附量,但KBC400的吸附能力高于KBC。在投加量为0.4 g·L−1和pH为5.0的条件下,KBC和KBC400最大吸附量分别为63.80 mg·g−1和89.15 mg·g−1。两者的吸附过程更符合准二级动力学模型和Langmuir等温线吸附模型,说明该吸附过程主要由化学反应控制,属于单层均质吸附。
3)蚕沙基生物炭主要通过静电引力和Cd2+-π结合作用吸附去除水体中Cd2+。2步KOH(热解-浸渍)活化法制备蚕沙基生物炭,第1步(浸渍)和第2步(热解)对吸附Cd2+的相对贡献率分别为28.69%和71.31%。
-
表 1 BC0,BC,Ca-BC元素含量分析
Table 1. Element content analysis of BC0, BC and Ca-BC %
样品 C O K Ca Cl BC0 90.14 8.53 1.33 — — BC 89.26 9.30 1.44 — — Ca-BC 87.19 9.50 0.65 1.01 1.63 注:“—”表示含量为0。 表 2 生物炭结构参数
Table 2. Structural parameters of biochar
生物炭 SBET/(m2·g−1) SMicro/(m2·g−1) VTotal/(cm3·g−1) VMicro/(cm3·g−1) BC 66.37 53.59 0.040 0.027 Ca-BC 157.68 124.05 0.090 0.065 表 3 BC和Ca-BC吸附动力学特性
Table 3. Adsorption kinetic characteristics of BC and Ca-BC
生物炭类型 准一级动力学方程 准二级动力学方程 Qe/(mg·g−1) K1 R2 Qe/ mg·g−1) K2 R2 Ca-BC-N 27.49 0.027 0.874 28.456 0.001 9 0.912 Ca-BC-P 10.03 0.030 4 0.864 10.353 0.005 8 0.904 BC-N 19.34 61.6×10−4 0.860 22.80 3.0×10−4 0.826 BC-P 5.46 0.012 9 0.779 6.00 0.003 1 0.727 表 4 Ca-BC对氮磷等温吸附特性
Table 4. Isothermal adsorption characteristics of Ca-BC to nitrogen and phosphorus
生物炭类型 Freundlich方程 Langmuir方程 KF 1/n R2 b/( mg·g−1) KL R2 Ca-BC-N 0.559 8 0.825 0.991 107.68 0.003 0.999 Ca-BC-P 1.745 8 0.47 0.906 11.28 0.126 0.971 表 5 与其他改性生物炭对比
Table 5. Comparison with other modified biochar
-
[1] 孔维芳. 富营养化水体生态修复中水生植物的应用研究[J]. 皮革制作与环保科技, 2021, 2(7): 59-60. [2] 文秋红, 李丹凤, 田望舒, 等. 地表水的氮磷污染及其检测方法研究[J]. 绿色科技, 2015(6): 255-257. [3] 王书锦, 刘云, 张超, 等. 洱海流域入湖河口湿地沉积物氮、磷、有机质分布及污染风险评价[J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(1): 69-77. [4] QI F J, CHEN L, MA J R. Current situation and prospect of reclaimed water reuse[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 2301: 295-298. [5] KUMAR S, JHA P, BAIER K, et al. Pollution of Ganga River due to urbanization of Varanasi: Adverse conditions faced by the slum population[J]. Environment and Urbanization Asia, 2012, 3(2): 343-352. doi: 10.1177/0975425312473229 [6] SEPEHRI A, SARRAFZADEH M. Effect of nitrifiers community on fouling mitigation and nitrification efficiency in a membrane bioreactor[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2018, 128: 10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2018.04.006 [7] 孙耀胜, 么强, 刘竞依, 等. 生物炭材料在水体有机污染治理中的研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(01): 170-180. [8] AHMAD M, LEE S S, DOU X, et al. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soybean stover- and peanut shell-derived biochar properties and TCE adsorption in water[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 118: 536-544. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.042 [9] CHA S J, PARK H S, JUNG S, et al. Production and utilization of biochar: A review[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2016, 40: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2016.06.002 [10] 林冰峰, 陈志豪, 杨芳俐, 等. 锰铁氧体改性生物炭对四环素的吸附性能研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2023, 42(7): 1585-1596. [11] 梁欣冉, 郭光光, 甄静, 等. 铁改性生物炭的制备及水体修复应用综述[J]. 河南科学, 2023, 41(1): 55-63. [12] 张田田, 杨英, 李卫华, 等. 碱改性生物炭对四环素的吸附研究[J]. 宜春学院学报, 2022, 44(12): 6-12. [13] 江汝清, 余广炜, 王玉, 等. 酸改性猪粪生物炭的制备及其对直接红23染料的吸附性能[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(12): 6489-6499. [14] 张茂林, 李领川, 沈晓武, 等. 玉米芯糖化水解及发酵法生物产氢[J]. 化工学报, 2009, 60(2): 465-470. [15] YUAN Q, LI X, YI C, et al. Efficient toluene adsorption/desorption on biochar derived from in situ acid-treated sugarcane bagasse[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021, 28(44): 62616-62627. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15128-2 [16] 杨奇亮, 吴平霄. 改性多孔生物炭的制备及其对水中四环素的吸附性能研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(12): 3973-3984. [17] 郭明帅, 王菲, 张学良, 等. 改性生物炭活化过硫酸盐对水中苯和氯苯的去除机制[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(12): 5280-5289. [18] 张智霖, 丁磊, 周强, 等. 响应曲面法优化木薯酒精污泥基活性炭制备及对没食子酸的吸附性能[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(7): 794-806. [19] 马锋锋, 赵保卫, 刁静茹, 等. 磁性生物炭对水体中对硝基苯酚的吸附特性[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(1): 170-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.01.019 [20] ZHU X, LIU Y, ZHOU C, et al. A novel porous carbon derived from hydrothermal carbon for efficient adsorption of tetracycline[J]. Carbon, 2014, 77: 627-636. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2014.05.067 [21] LI Q, MU J, ZHOU J, et al. Avoiding the use of corrosive activator to produce nitrogen-doped hierarchical porous carbon materials for high-performance supercapacitor electrode[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 832: 284-292. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.11.013 [22] 唐艳军, 李友明, 宋晶, 等. 纳米/微米碳酸钙的结构表征和热分解行为[J]. 物理化学学报, 2007(5): 717-722. [23] 段漓童, 刘正猛. 红外光谱图的分区[J]. 华北煤炭医学院学报, 2006(3): 336-337. [24] 王亮, 田伟君, 乔凯丽, 等. 改性大豆秸秆生物炭对咪唑乙烟酸的吸附[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(10): 4488-4495. [25] 郑庆福, 王志民, 陈保国, 等. 制备生物炭的结构特征及炭化机理的XRD光谱分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(10): 3355-3359. [26] 史月月, 单锐, 袁浩然. 改性稻壳生物炭对水溶液中甲基橙的吸附效果与机制[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6): 2783-2792. [27] 余剑, 丁恒, 张智霖, 等. 改性菱角壳生物炭吸附水中土霉素性能与机理[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(12): 5688-5700. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.12.025 [28] 王菁姣. 生物炭对重金属的吸附作用及腐殖酸的影响[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. [29] DENG W D, ZHANG D Q, ZHENG X X, et al. Adsorption recovery of phosphate from waste streams by Ca/Mg-biochar synthesis from marble waste, calcium-rich sepiolite and bagasse[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 288: 125638. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125638 [30] YIN Q, LIU M, REN H. Biochar produced from the co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and walnut shell for ammonium and phosphate adsorption from water[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 249(C): 109410. [31] LIU X, SHEN F, QI X. Adsorption recovery of phosphate from aqueous solution by CaO-biochar composites prepared from eggshell and rice straw [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 666 694-702. [32] 赵志伟, 陈晨, 梁志杰, 等. 锰氧化物改性生物炭对水中四环素的强化吸附[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(1): 194-201. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0803 [33] GONG Y P, NI Z Y, XIONG Z Z, et al. Phosphate and ammonium adsorption of the modified biochar based on Phragmites australis after phytoremediation.[J]. Environmental science and pollution research international, 2017, 24(9): 8326-8335. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-8499-2 [34] 丁玉琴, 李大鹏, 张帅, 等. 镁改性芦苇生物炭控磷效果及其对水体修复[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(4): 1692-1699. [35] 李廷梅, 于鲁冀, 叶露阳, 等. 改性玉米芯表面特征及其对氨氮的吸附作用研究[J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(1): 42-46. [36] JIANG Y, LI A, DENG H, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus adsorption by Mg-loaded biochar from different feedstocks[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 276: 183-189. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.12.079 [37] 邓玉, 刘斌, 晏琪涵, 等. 一步法制备Mg改性玉米芯生物炭吸附磷酸盐研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2021, 47(4): 35-39. [38] 宋格. 芦苇生物炭吸附水中氨氮的作用及机制[D]. 杭州: 中国计量大学, 2020. [39] 戴田池. 改性秸秆生物炭吸附水中磷酸盐和四环素效能及机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. [40] 范沾涛, 刘寒, 黄媛, 等. 钙离子对药用植物生长和次生代谢产物积累作用的研究进展[J]. 中国现代中药, 2023, 25(8): 1789-1798. [41] 周成赟, 唐小峰, 渠晓琳, 等. Ce-BDC衍生碳的除氟性能与机理[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(10): 1-10. -





 下载:
下载: