-
随着时代不断发展,城市内涝频繁发生,排水管网淤堵问题备受人们关注。排水管道沉积物是污水中的可沉降颗粒物,在排水管网运行过程中,这些颗粒物在适当条件下发生沉降并逐渐积累,形成底层沉淀物沉积在排水管道中[1]。沉积堵塞排水管网的物质主要包括有机物、无机物以及固体垃圾[2]。管网沉积物中所含的有机质一般是复杂的高分子物质,如脂类、糖类、蛋白质、动植物腐殖质以及微生物等[3]。也有研究将管网沉积物分为3类:底层粗颗粒沉积物、有机层和生物膜[4]。其中,生物膜通常形成于水面附近的管壁,或受扰动作用较小的沉积物表面上,由覆盖在有机质上的微生物构成[5]。胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances, EPS)作为微生物的重要组成部分,其主要成分为多糖、蛋白质、核酸、脂肪、胞外 DNA 等[6],具有粘性和吸附性,对排水管道的淤积及冲刷具有重要影响。传统的管网机械清淤方法均存在人工消耗量大,施工过程中影响道路交通等问题。因此,探究生物或化学方法来减缓管网中沉积物的沉积速率,降低管网清淤与维护频率是解决排水管网淤堵问题新的研究方向。
相关研究表明,利用纤维素酶或蛋白酶可破坏污泥EPS,促使污泥颗粒变得细小分散,污泥颗粒比表面积增大,酶与细胞接触面积增加,并且EPS 的分解还降低了其对污泥细胞的保护作用,进而提高了酶对污泥的水解效率[7]。YANG等[8]研究发现经酶解后,污泥细胞破解,胞内物质流出,大大提高了污泥后续厌氧消化的效率并缩短了污泥消化时间。此外,LU等[9]报道了酸性处理过程中污泥内部酶(蛋白酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶)的释放也可以增强厌氧发酵污泥的破解。
同时,在污泥处理方面,表面活性剂也有其不可或缺的作用。表面活性剂的增溶作用和分散作用[10]使胞外聚合物脱离污泥溶于液相[11];而表面活性剂结构中自带的疏水烷基可与细胞壁相互作用,导致细胞溶解,破坏细胞结构和EPS[12]。王怡等[13]研究表明,添加SDS(十二烷基硫酸钠)可以促进剩余污泥水解,EPS中溶解性蛋白质和多聚糖含量大幅增加,污泥的粒径变小、比阻变大。WANG等[14]研究发现阴离子表面活性剂SDS可以增加体系中的负电荷,EPS与SDS之间的静电排斥和疏水相互作用使污泥中的EPS大量释放。LUO等[15]研究了SDS与酶制剂联合作用对剩余污泥水解酸化的影响,结果表明,组合体系比单一SDS和单一酶体系更能有效促进污泥水解,SDS和复配酶体系优于SDS和单一酶体系的水解性能。由于表面活性剂联合生物酶技术不仅反应条件温和,对管道无腐蚀和破坏性,并且两者联合对管网中有机沉积物具有较好的水解作用,有利于降低沉积物间的黏性,促进有机质从固相向液相转移,强化其冲刷性能,从而为解决排水管网淤堵问题提供新的解决方法,但目前尚未有关于该方面的报道。
基于对排水管网中沉积物的性质分析,根据课题组前期研究结果,本研究在确定复配酶(α-淀粉酶∶中性蛋白酶=2∶3)投加量的质量百分比为8%的条件下,探究不同SDS投加量、反应温度、初始pH(7.28±0.3)和反应时间对SDS+复配酶体系对沉积物水解效果的影响,根据反应前后沉积物EPS、三维荧光、粒径和SEM(scanning electron microscope)表征结果对其水解沉积物的机理进行了深入分析;采用高通量测序技术对经复配酶(α-淀粉酶∶中性蛋白酶=2∶3)、SDS+复配酶(α-淀粉酶∶中性蛋白酶=2∶3)水解后的排水管网沉积物中微生物群落结构与功能菌群的影响进行了分析,探讨了不同方法对微生物群落结构的影响。
-
实验所用管网沉积物取自天津市某排水管道检查井,取回的污泥样品封装于样品袋中,存放在4 ℃冰箱内里冷藏待用。该沉积物样品的相关特性指标为:有机质含量为 (56.39±0.81)%,pH=7.28±0.3;沉积物上清液中SCOD(soluble chemical oxygen demand)值为 (206.9±16.9) mg·L−1、氨氮为 (85.03±2.53) mg·L−1、多糖为 (18.14±2.16) mg·L−1、蛋白质为 (0.08±0.01) mg·mL−1。
-
所用试剂主要包括中性蛋白酶、α-淀粉酶、SDS、氯化钠、COD专用耗材、氢氧化钠、苯酚、氯化氢、无水乙醇、纳氏试剂等。其中,实验所用酶制剂基本性质及来源见表1,其他化学试剂均为分析纯,实验用水为去离子水。
实验主要仪器包括 YH-3BS远红外线恒温干燥箱(天津中环);SX-GO7103马弗炉(天津中环);MY3 000-6B混凝实验搅拌仪器(武汉梅宇仪器);721型可见分光光度计(上海佑科);VELOCITY 18R台式多功能离心机(Dynamica公司);FY-1C-N真空泵(浙江飞越);G9 800A三维荧光激发-发射光谱仪(美国安捷伦);PHS-3E型pH计(雷磁);HH-4电热恒温水浴锅(绍兴苏珀)。
-
取100 mL排水管网沉积物置于250 mL烧杯内,通过0.1 mol·L−1的盐酸或氢氧化钠溶液调节pH至 5~10;将烧杯放入水浴锅预热,使沉积物到目标温度(4~65 ℃)后;加入8%(质量百分比,酶质量与沉积物干质量比)污泥的复配酶(α-淀粉酶:中性蛋白酶=2:3),并加入0、1%、2%、5%、8%和10%(质量百分比)的SDS;在200 r·min−1下搅拌,连续反应 0~6 h。反应结束后,取部分污泥进行有机质含量的检测,将剩余部分污泥置于离心管中,在4 000 r·min−1下离心15 min,离心后取上清液经0.45 μm滤膜过滤;检测滤液中SCOD、氨氮、多糖,每个实验重复3次,取平均值分析4个因素对SDS促进复配酶水解排水管网沉积物的影响,确定其最佳反应条件,并分析最佳反应条件下的上清液EPS、三维荧光光谱、沉积物表面结构形态和粒径的变化。
-
氨氮采用纳氏分光光度法进行测定;溶解性化学需氧量(SCOD)采用快速消解分光光度法测定;多糖采用苯酚-硫酸法测定;蛋白质含量选用改良Lowry法测定;沉积物中有机质含量测定采用《中华人民共和国城镇建设行业标准》(CJ/T96-1999)中有机质灼烧法。EPS采用热提取法,EPS中各类物质变化采用三维荧光扫描光谱仪(安捷伦1260)检测;沉积物表面形态采用扫描电子显微镜 (7610F,日本电子株式会社) 分析。采用16s rRNA高通量测序方法表征微生物群落结构变化。
-
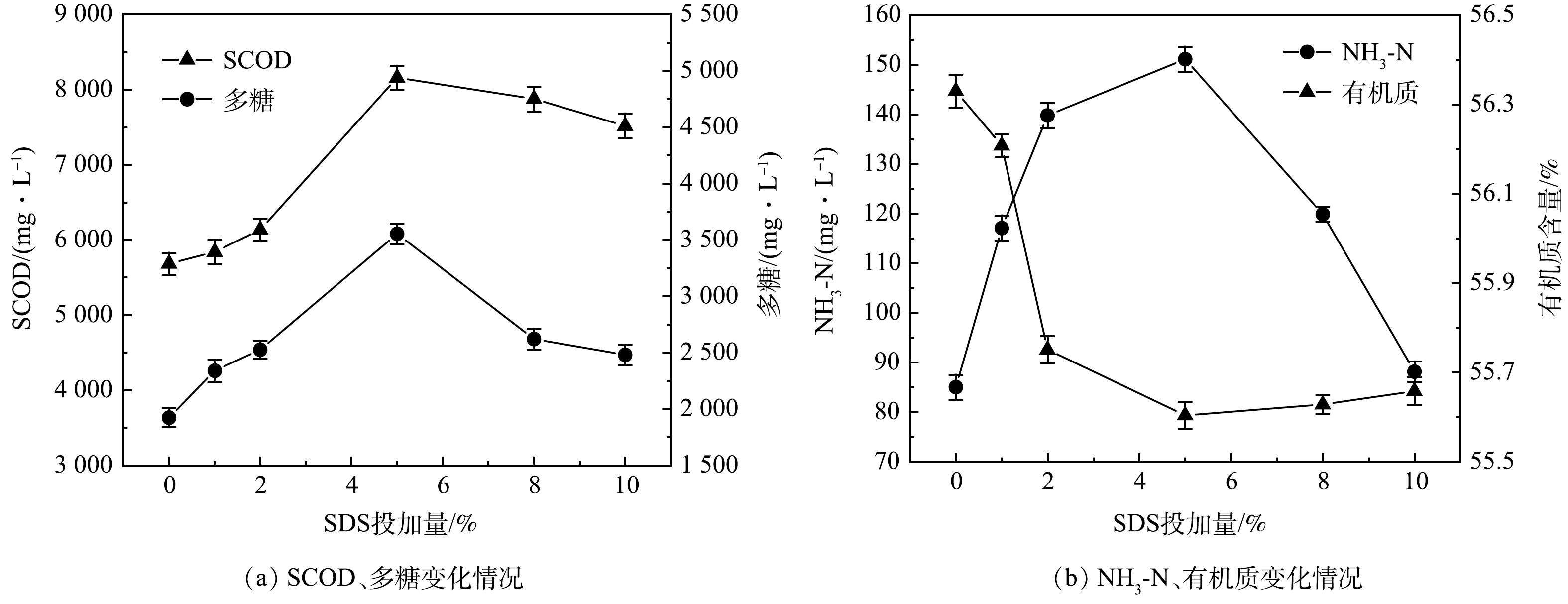
实验在原泥pH(7.28±0.3),8%(质量百分比)复配酶(α-淀粉酶:中性蛋白酶=2:3)、25 ℃反应2 h的条件下,SDS投加量对排水管网沉积物水解效果的影响结果见图1。由图1(a)可以看出,当SDS投加量在0%~5%时,SCOD与多糖浓度随SDS投加量增多而增长,在SDS投加量为5%时,SCOD和多糖达到峰值,分别由初始的5 686.9 mg·L−1和1 913.75 mg·L−1升至8 192.9 mg·L−1和3 561.29 mg·L−1;当投加量继续增加到10%,SCOD与多糖含量反而下降,在10%时,SCOD和多糖分别下降到7 545.9 mg·L−1和2 484.92 mg·L−1。由图1(b)可以观察到,氨氮与SCOD、多糖变化趋势相同,在SDS投加量为5%时,由原始的87.32 mg·L−1达到峰值的153.37 mg·L−1。有机质含量的变化与氨氮、SCOD、多糖变化趋势相反,在SDS投加量为5%时,有机质含量最低,为55.59%;当SDS投加量继续增大,有机质减量效果稍有提高,但与SDS投加量为5%时相差无几。有研究[16]表明,SDS作为酶调节分子,在较低剂量下可增强酶活性,在较高剂量下反而会抑制酶活性。这是由于SDS为阴离子表面活性剂,可以与带负电的沉积物发生静电排斥[14],在SDS含量为0%~5%,随投加量增加,沉积物更加分散,更利于复配酶与沉积物中有机质的接触,从而促进水解作用的发生;但当SDS投加过量时,SDS的烷基可与细胞壁结合,导致细胞破裂,从而部分影响微生物的活性,进而影响污泥水解效果[17]。因此,过低或过高的SDS均不利于生物酶对沉积物的水解。
-
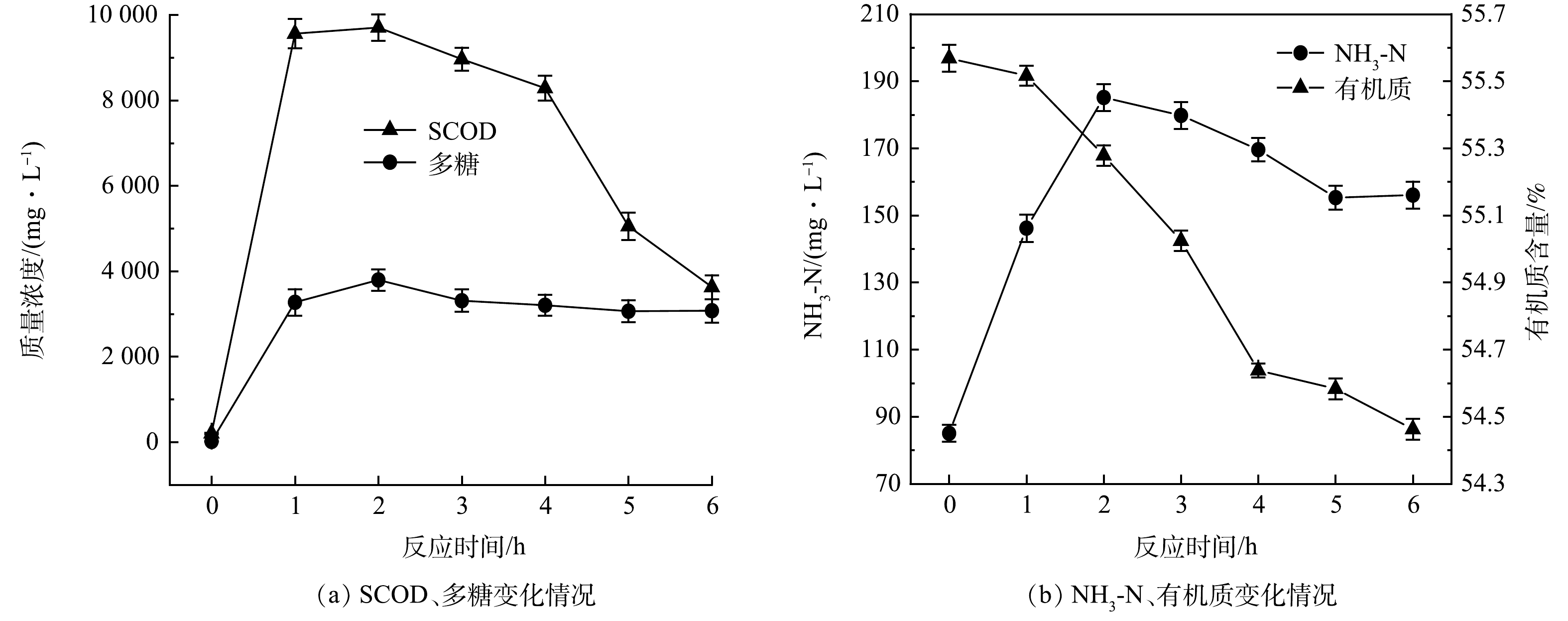
投加8%复配酶与5%SDS后,沉积物水解效果随反应时间的变化情况如图2所示。由图2可以看出,SCOD、多糖和氨氮随反应时间呈现先升高后下降的趋势。在反应2 h时,SCOD、多糖和氨氮含量分别由初始的211.3、18.38和87.32 mg·L−1升至9 726.5、3 868.84和185.12 mg·L−1。SDS的投加破坏了沉积物中微生物分泌出的EPS内部的非共价键,从而破坏沉积物结构,导致内部物质向外释放,促进了酶与沉积物之间的接触反应,从而使得SCOD、多糖和氨氮含量升高。随着反应时间继续延长,上清液中的SCOD、多糖与氨氮均开始了不同程度的下降,在6 h时,SCOD、多糖与氨氮质量浓度分别为3 581.5、3 056.05、156.09 mg·L−1。这可能是因为复配酶与SDS的协同作用随时间延长,沉积物的水解效果减弱,同时管网微生物对溶出物质进一步分解和利用[18],SCOD、多糖、氨氮的生成速率小于消耗速率,使得上清液中各物质浓度降低。有机质含量随反应时间呈现出一直下降的趋势,这说明水解反应在0~6 h内一直在进行,且在4 h后有机质分解速率变慢。综上所述,选择SDS协同复配酶水解排水管网沉积物的最佳反应时间为2 h。
-
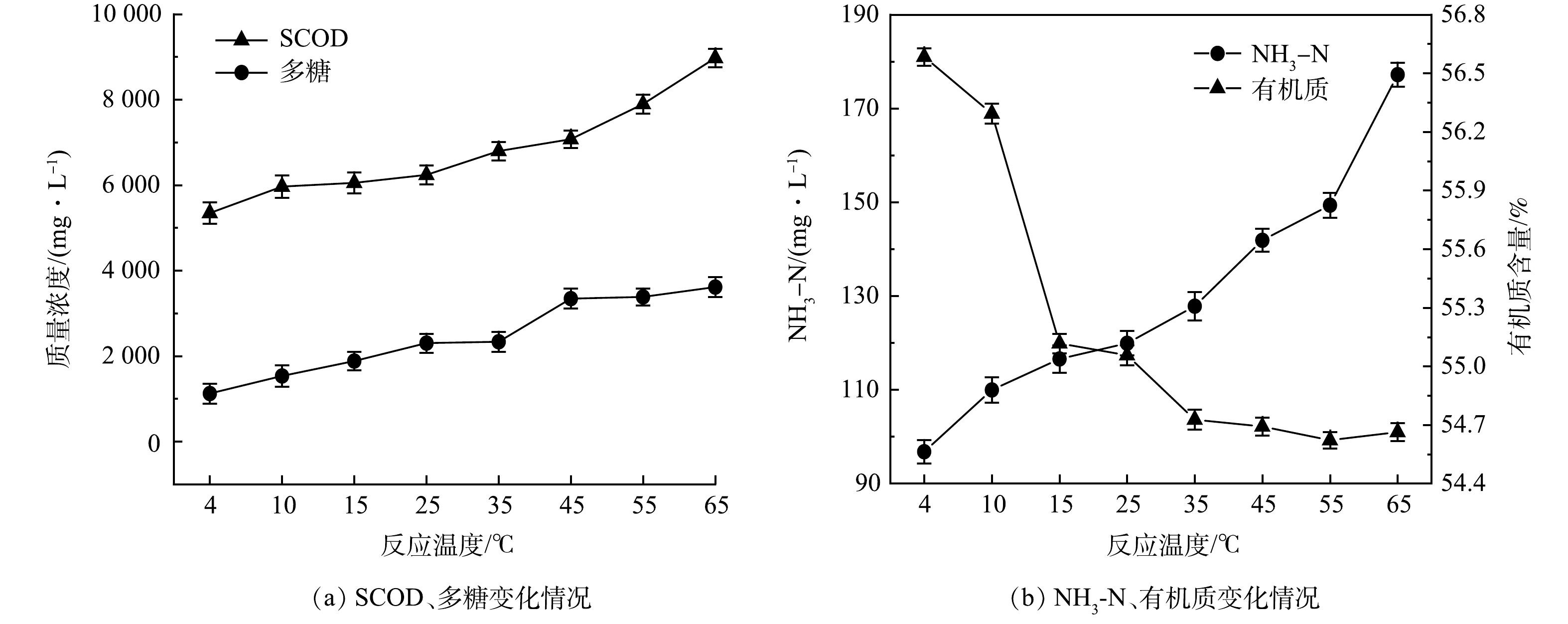
实验在原泥pH(7.28±0.3),反应2 h,5%SDS与8%复配酶协同作用下,考察了温度对沉积物水解效果的影响,结果如图3所示。从图3可以看出,在4~65 ℃内,SCOD和氨氮随温度的升高而升高,多糖先升高后趋于平缓,有机质含量随温度的升高逐渐下降,随后变得平缓。当温度由4 ℃升至65 ℃时,SCOD由5 341.0 mg·L−1逐步升至8 983.0 mg·L−1;多糖由1 100.96 mg·L−1升至3 649.16 mg·L−1;氨氮由96.44 mg·L−1升至176.84 mg·L−1。有机质含量在4~35 ℃内下降较快,由开始的56.58%下降到54.69%,降低了1.89%;在35 ℃后随温度的升高,有机质含量保持在54.65%左右。这可能是由于温度升高,中性蛋白酶和α-淀粉酶的活性基团逐渐被激活,酶制剂活性增强,并且在SDS的增溶作用下,酶制剂和沉积物的接触更加充分,水解效果更好。在上述SDS与复配酶的协同作用下,液相中的蛋白质被分解为多肽以及小分子氨基酸,碳水化合物被水解成多糖与单糖[19],水解效果增强,溶解性有机物浓度提高。
根据实验结果,在反应温度高于15 ℃时,SDS协同复配酶的水解效果较好,而市政污水管网常年在8~35 ℃,因此,综合考虑项目经济性和实用性,在实际应用过程中,生物酶水解排水管网沉积物可选择管网温度在15 ℃以上时进行。
-
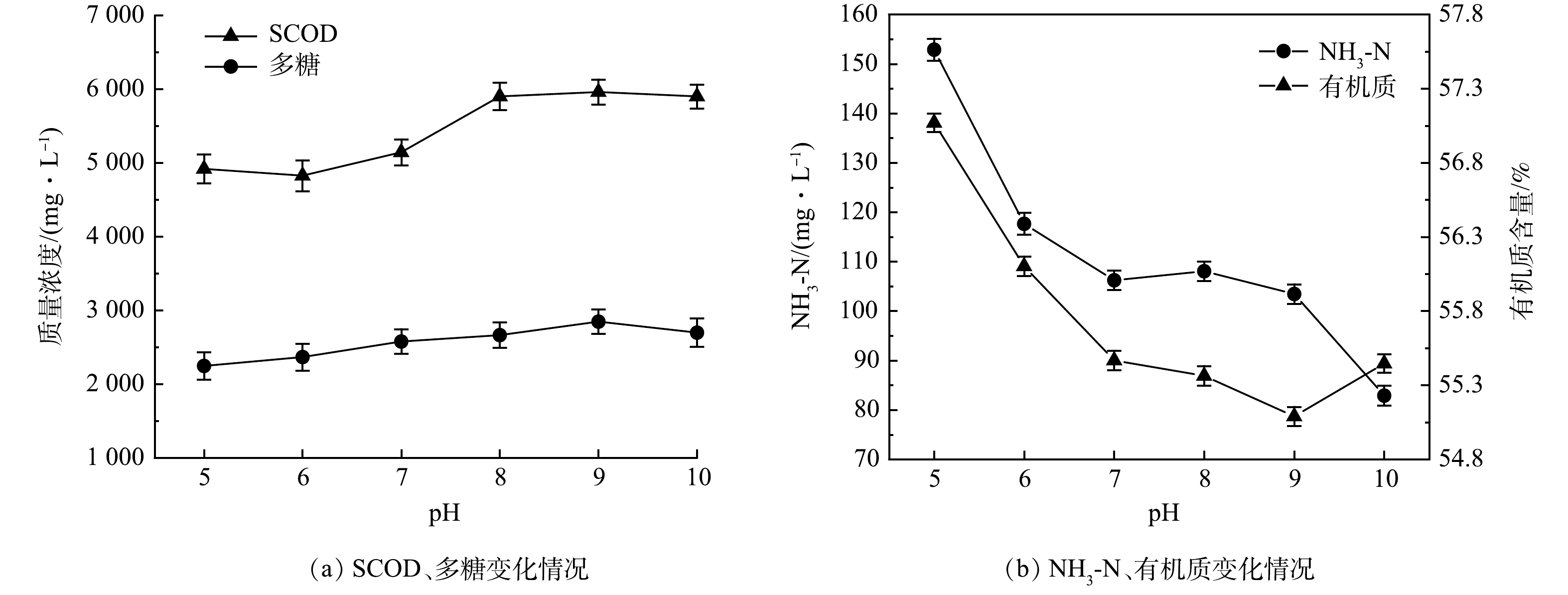
本实验考察了5%SDS与8%复配酶在25 ℃,反应2 h条件下,不同pH对沉积物水解效果的影响结果见图4。由图4(a)可以看出,SCOD与多糖在pH=5~6保持一个平稳的数值,当pH升高为8时,二者均有不同程度的提高,SCOD与多糖分别由pH=6的4 830.4 mg·L−1 和2 369.82 mg·L−1提高到pH=8的5 895.4 mg·L−1和2 660.64mg·L−1;当pH进一步升高为8~10时,SCOD与多糖含量几乎不变。由图4(b)可以看出,氨氮含量随pH增加而下降,氨氮由pH=5的152.87 mg·L−1降到pH=10的82.83 mg·L−1。这是由于碱性条件下氨氮容易从液相转移到气相中,从而使得氨氮含量出现大幅度下降[20]。在pH=5~9,有机质含量随着pH的增加逐渐下降,从57.08%下降到55.09%,当pH增加到10时,有机质含量出现回升。结合图4(a),在pH=10时SCOD、多糖含量变化不大,说明pH继续增大不能继续提升沉积物水解效果。在pH=7~9内,SDS+复配酶对排水管网沉积物的水解效果较好,而实际管网中沉积物pH大概在7~8,因此,在实际应用过程中不需要进行pH调节。
-
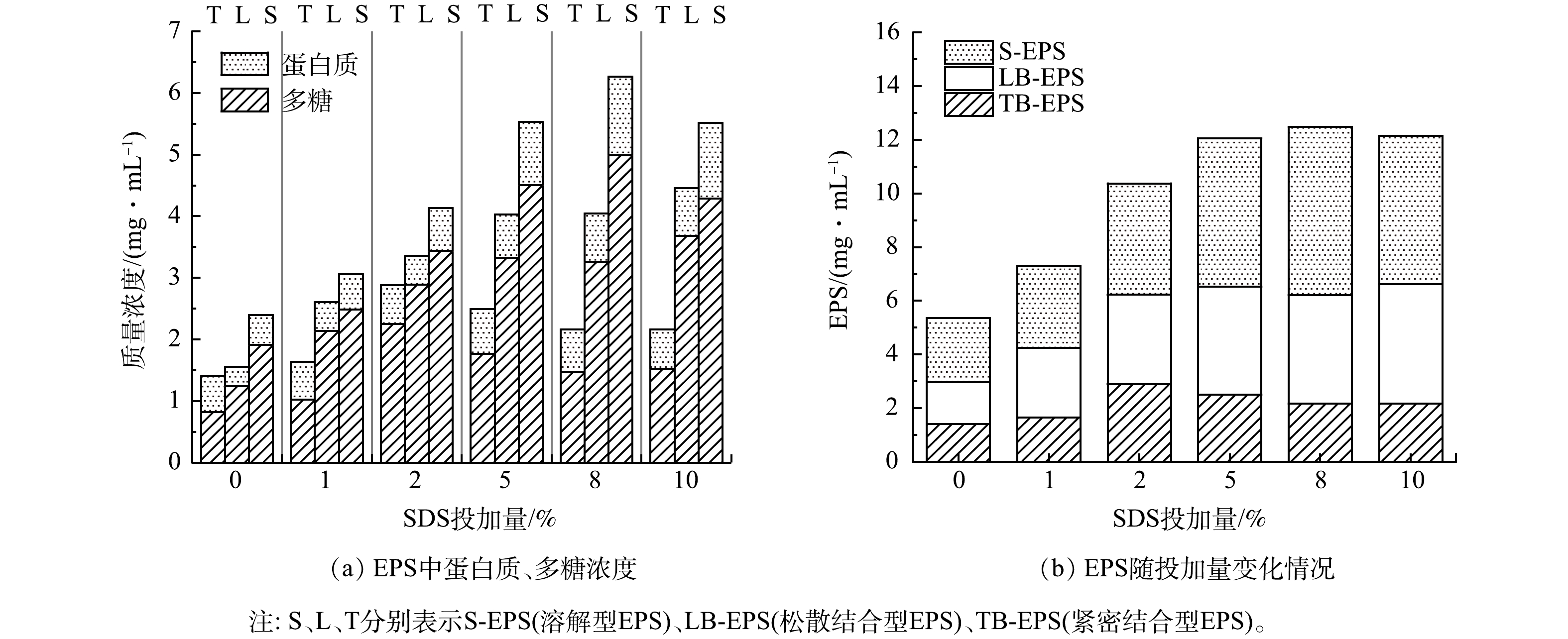
沉积物中存在微生物,微生物日常生长代谢会产生有粘性的EPS等物质,增加了沉积物的抗冲刷能力;同时,EPS还能吸附污水中的有机颗粒,增加排水管网沉积物厚度和管网淤堵的风险。复配酶可水解沉积物中蛋白类与糖类物质,SDS的两亲性可以改变界面处的能量关系,增加EPS的溶解[21]。研究了复配酶协同SDS水解管网沉积物对EPS及其蛋白质与多糖浓度变化的影响,结果见图5。从图5(a)可以看出,在复配酶投加量为8%,水解2 h条件下,沉积物上清液中TB-EPS(tightly bound EPS)、LB-EPS(loosely bound EPS)与S-EPS(soluble-EPS)的多糖与蛋白含量均随着SDS投加量的增加呈现先升高后下降的趋势,各层EPS总含量变化趋势为S-EPS>LB-EPS>TB-EPS,其中TB-EPS向S-EPS转移。有研究表明,表面活性剂的两亲性使得SDS有一定的的分散作用,可以通过其疏水性与细胞膜蛋白相互作用,这可能导致沉积物的侵蚀[22];当SDS与复配酶协同水解沉积物时,可以大大削弱LB-EPS与TB-EPS的结合[23],使得沉积物发生更严重的裂解和内部生物聚合物的释放,使不溶性的EPS剥离从而进入沉积物上清液中,同时内层TB-EPS向外部转移,TB-EPS含量下降,LB-EPS与S-EPS增多,EPS中可溶性蛋白质与多糖含量增加。
图5(b)为不同SDS投加量下EPS总量的变化情况。可以看出,随投加量增多,EPS含量先升高后基本不变。由于SDS具有增溶作用,大量大分子物质脱离沉积物固体溶解于液相[24],从而释放出更多的蛋白质、多糖等物质到EPS中,使其含量增多。但由于表面活性剂在较低剂量(0~5%)下增强酶活性,在较高剂量(5%~10%)下抑制酶活性[16],因此在SDS投加量高于5%后,随着SDS投加量进一步增加,复配酶失活,水解效果降低。
-
中性蛋白酶与α-淀粉酶能够破解复杂的高分子物质,例如蛋白质、碳水化合物等,将一部分难降解物质水解,并释放之液相。而SDS具有增溶的特性,能够加快非液相物质溶解到水中的速度,同时也会释放被沉积物捕获的酶制剂,暴露出更多的底物[25],从而促进沉积物中有机质的水解,增加进入液相中溶解性有机物的含量。而三维荧光光谱可以分析污泥中溶解性有机物的种类及分布,不同区域和不同荧光强度代表不同物质及相应的浓度。
由图6可以明显看出,经SDS+复配酶组处理后的沉积物上清液EPS中,I~III区域荧光强度较复配酶组大幅度下降。表明在投加SDS后,酪氨酸、色氨酸与富里酸类物质含量减小甚至消失。左锦静[26]研究表明,SDS与蛋白质之间可以通过疏水作用自发结合,SDS作为淬灭剂对蛋白质进行淬灭,使得三维荧光光谱中蛋白质类物质几近消失;IV区域内的荧光强度和范围略有缩减,这可能是因为SDS具有抑菌性,随着反应时间的延长,导致沉积物中部分微生物死亡,可溶性微生物代谢产物含量降低;V区域所代表的腐殖酸类为五类可溶性有机物中的主要物质,与经复配酶处理后的沉积物上清液的三维荧光光谱图进行对比可以看出,SDS+复配酶的投加使得沉积物上清液中腐殖酸含量急剧增加,且又出现了一种新的腐殖酸物质(Ex/Em为390~440 nm/440~500 nm),这2种腐殖酸浓度由内向外逐渐递增。一方面,SDS的两亲性使得复配酶更容易接触沉积物内部,释放出更多的物质,如腐殖酸;另一方面,微生物对腐殖酸利用率较低,容易在EPS中沉积,沉积物释放出的可溶性微生物副产物等物质更容易被微生物利用或被上清液中溶解的复配酶水解成小分子物质,导致腐殖酸含量高,溶性微生物副产物含量低。有研究[27]表明,腐殖酸浓度可以反映EPS溶解的程度,这也说明沉积物中腐殖酸类物质占比较高,腐殖酸浓度越大,溶解性EPS越多,沉积物水解减量效果越好。
-
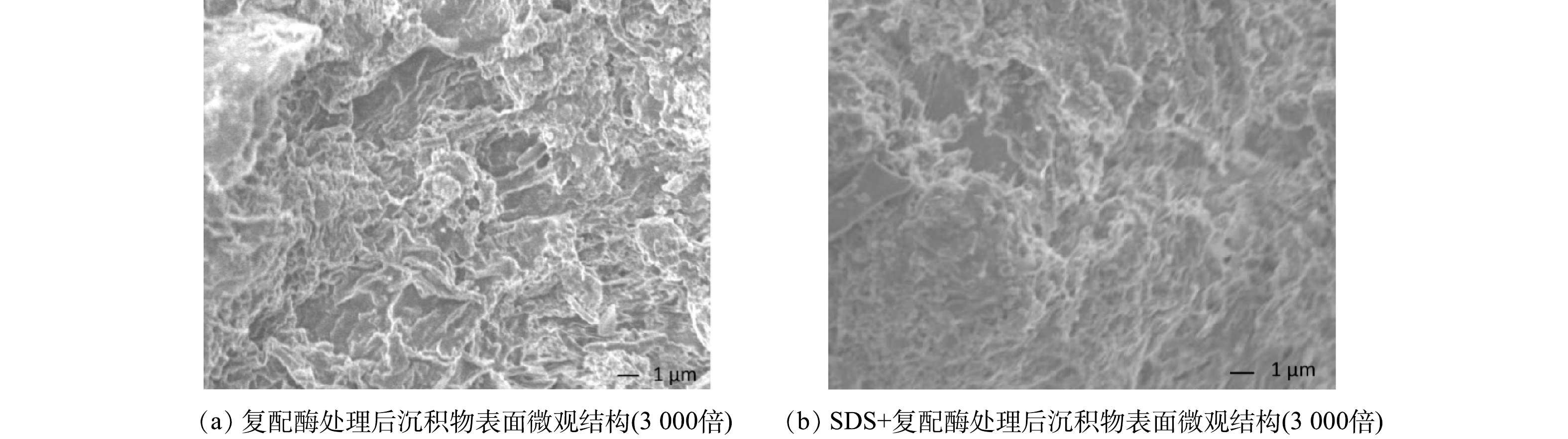
SEM可较直观的反映出沉积物水解前后表面微观结构的变化,经SDS+复配酶、复配酶水解后的沉积物表面结构变化如图7所示。沉积物在被SDS+复配酶、复配酶水解后均出现密集多孔的表面形态,说明SDS+复配酶与复配酶对沉积物均有明显的破坏效果。经SDS+复配酶处理后,沉积物表面层状更多,说明SDS的增溶作用会打破沉积物紧密连接的结构,使得复配酶能够与更深层的沉积物的接触反应,进而促进水解反应的发生。同时疏松多孔的表面形态使得沉积物更容易被水力冲刷,有利于达到延缓管网淤堵和沉积物减量化的目的。
-
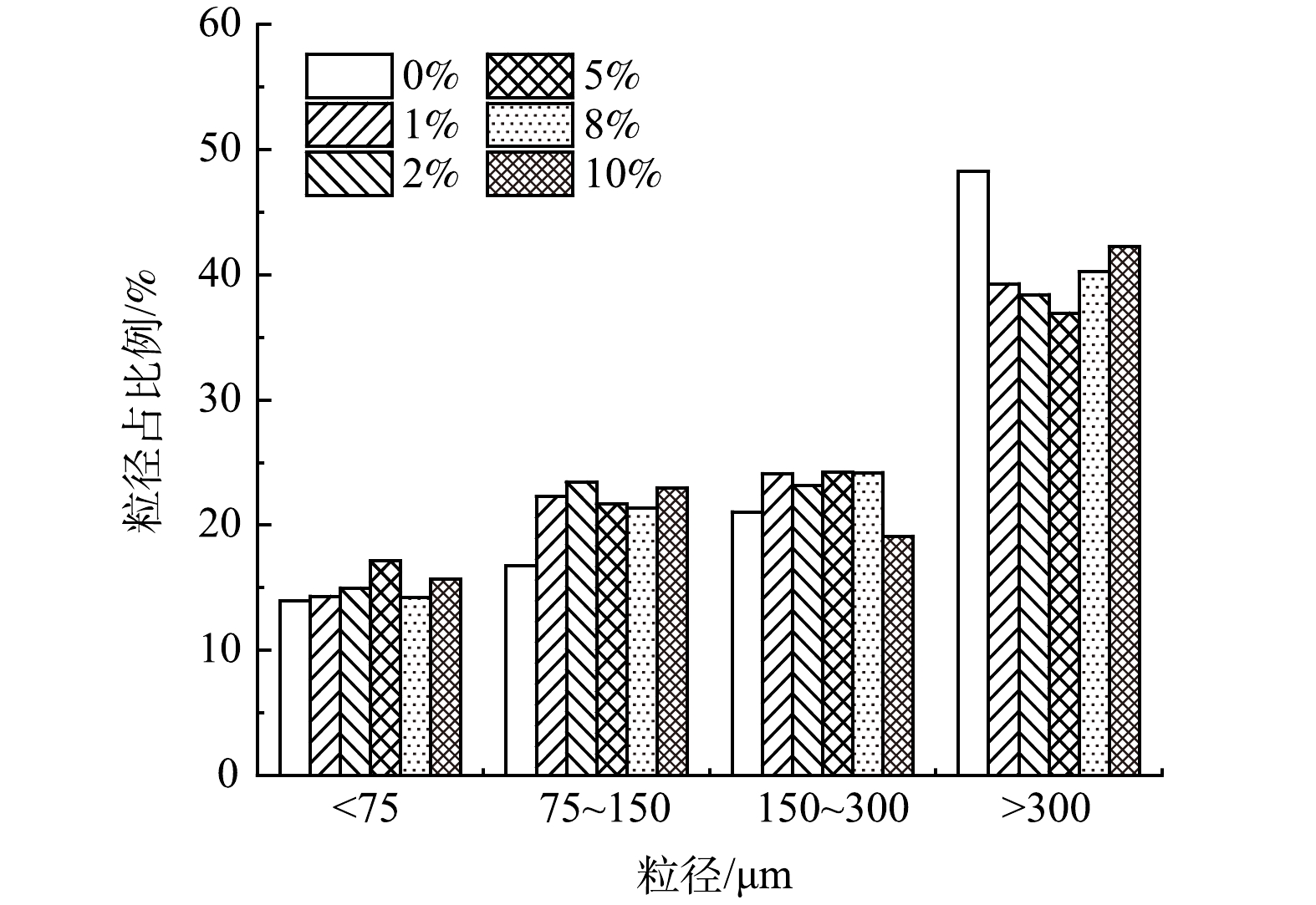
在复配酶投加量为8%的条件下,SDS投加量对沉积物粒径的影响结果见图8。可以看出,粒径>300 μm沉积物的质量占比由单独投加复配酶的48.25%下降到5% SDS投加量下的36.94%,随后SDS增加,此粒径沉积物的占比又增加;粒径在150~300 μm内的沉积物质量占比由独投加复配酶的21.05%升高到8%SDS的24.20%左右,随后其质量占比随SDS投加量增加而减小;粒径在75~150 μm内沉积物的质量分数由16.75%升至2%SDS下的23.5%,随后SDS投量增加,质量占比保持在22.0%左右;粒径<75 μm的沉积物质量分数占比由单独投加复配酶的13.95%升高到5%SDS的17.14%,随后SDS投量增加,其质量占比下降。
以上结果表明,在SDS+复配酶协同水解沉积物的过程中,随着SDS投加量的增加,在粒径>300 μm时,沉积物质量占比均有明显下降;小粒径占比增多。SDS的投加量在0%~5%内,投加量的增多会促进大颗粒物质向小颗粒转化。但当SDS投加量大于5%时,SDS对复配酶的水解起抑制作用,大颗粒向小颗粒转化效果变差。
-
1)排水管网沉积物Alpha多样性。利用16S rRNA基因测序技术对原沉积物和分别经复配酶、SDS+复配酶处理沉积物的菌群结构进行Alpha多样性指数分析,结果见表2。OTUs大小可反应样品中物种多样性[28]。由表2可知,原泥OTUs数量最多,投加复配酶后,OTUs数量显著降低,而采用SDS+复配酶处理后,OTUs又有大幅度回升。表明单独采用复配酶可降低管网菌种数量,但采用SDS与复配酶联用可减少对管网中微生物多样性的影响。Shannon和Simpson指数也表明,经过复配酶处理后的样品中,这2个指数均出现明显下降,而经SDS+复配酶处理后的样品Shannon和Simpson指数与原泥相比相差不大,说明微生物多样性和均匀性没有出现很大改变。本次实验中4组样品的覆盖率均大于0.98,表明本次微生物测序的有效性和可靠性。
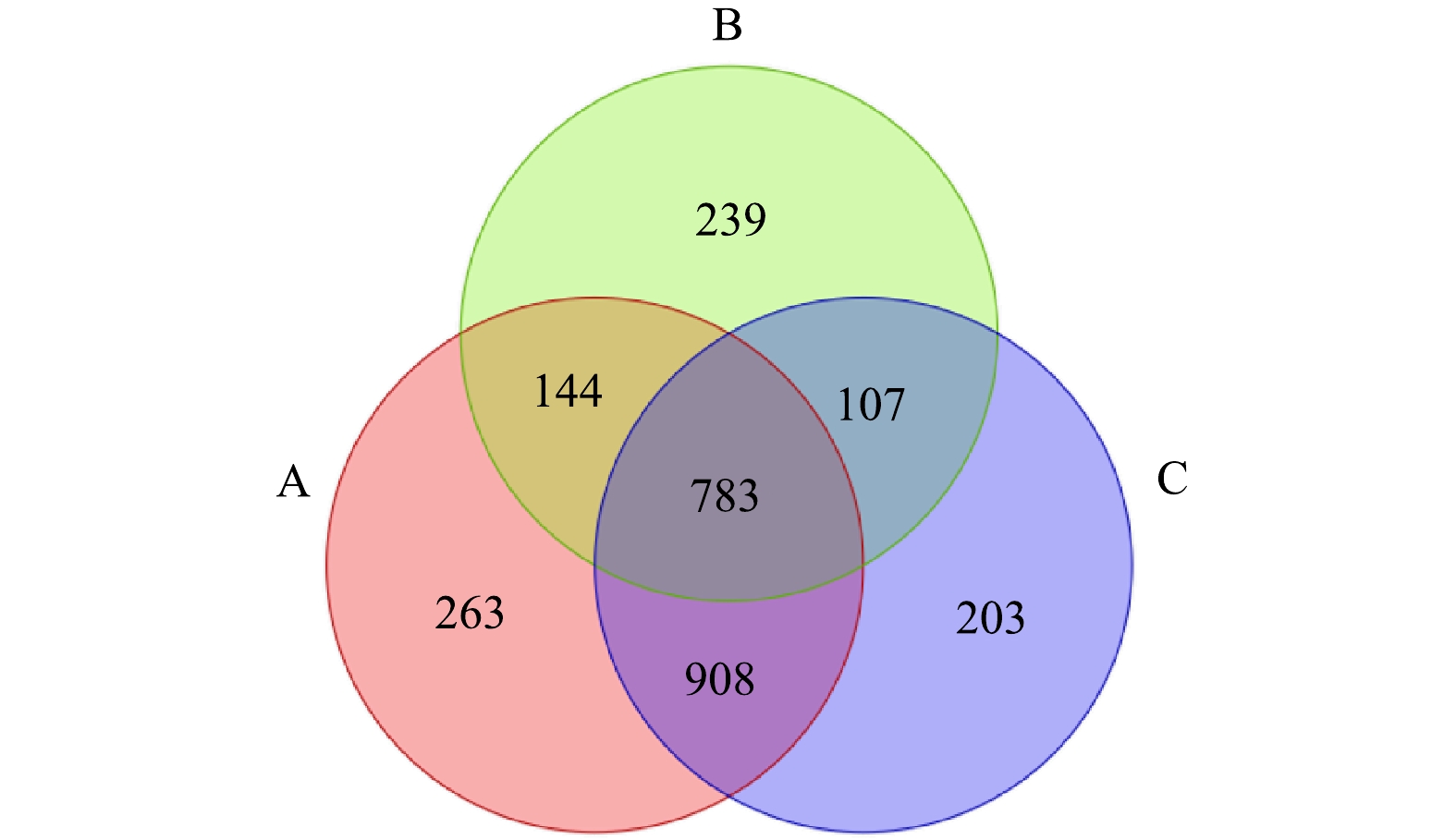
2)基于OTU的微生物群落Venn图分析。各组样品间的OTU彼此关联,根据3组沉积物样品测定的OTU数据,绘制了3组样品OTUs的Venn图,以反映不同处理条件下沉积物样品的物种多样性差异[29]。由图9可以看出,原泥组(A)、复配酶组(B)和SDS+复配酶组(C)样品的OTU数目分别为2 098、1 273和2 001,相较于原泥,各组OUT数均有不同程度的降低,表明在投加酶制剂后,物质多样性出现了不同程度的下降[30],其中复配酶下降最明显,而SDS+复配酶与原泥相差较小,这也与表2的结果一致。Venn图的重叠部分代表了不同样品的共有OTU,可知 3 组样品的共有OTU数为783,占总OTU数(2 647)的29.58%,说明酶制剂的投加会对排水管网沉积物中的微生物丰富度和多样性造成一定的影响[31]。
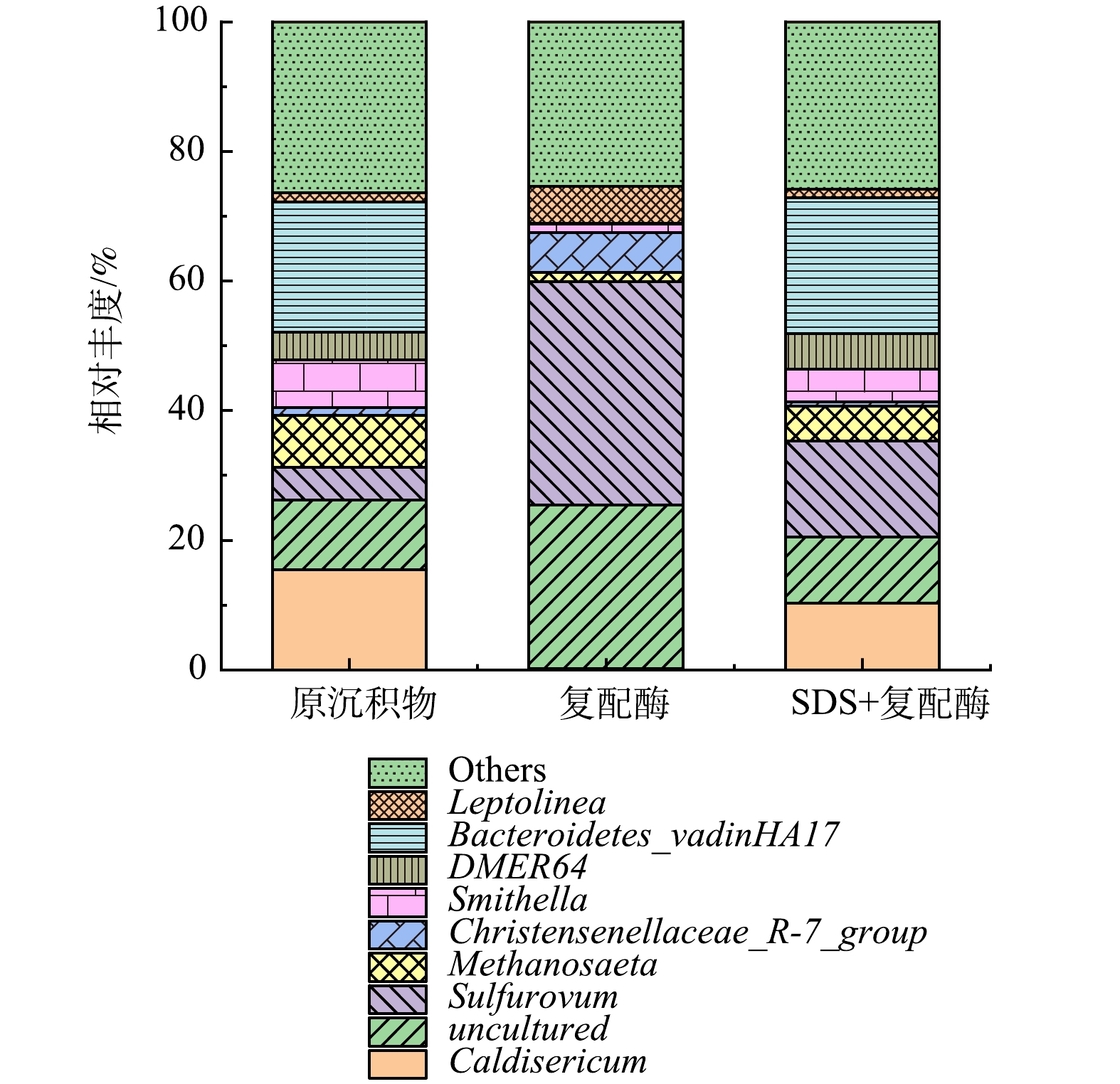
3)微生物属水平群落结构及功能菌群分析。观察了属水平上微生物群落结构演替(图10),沉积物经复配酶、SDS+复配酶处理后,Sulfurovum (反硝化硫菌)的相对丰度均有不同程度的增加,分别从原沉积物的5.02%增加为34.53%和14.85%,其中复配酶组增幅最大。这可能由于投加酶制剂后,沉积物中大分子物质溶出,氨氮升高,可能硝态氮也有所升高,有利于Sulfurovum的繁殖。Caldisericum(嗜热、硫代硫酸盐还原细菌)与Methanosaeta(甲烷丝菌属)在投加复配酶、SDS+复配酶后,相对丰度均出现下降的现象。Methanosaeta(甲烷丝菌属)在原沉积物、复配酶和SDS+复配酶中所占比例分别为8.09%、1.34%和5.33%。Methanosaeta属于产甲烷菌(MA)的一种,其新陈代谢会产生CH4和CO2,此菌种所占比例减少,一定程度上也会降低排水管道中CH4产量。Caldisericum的变化趋势与Methanosaeta相同,复配酶组、SDS+复配酶组相对丰度均小于原沉积物,表明经SDS+复配酶处理后会减少管网中H2S的产量,这有利于管网的后续维护。Uncultured表示未能在人工条件下获得纯培养的微生物。
-
1)采用SDS+复配酶可有效水解排水管网沉积物,在原泥pH(7.28±0.3)、25 ℃下反应2 h,沉积物上清液中SCOD、多糖和氨氮分别由初始的5 686.9、1 913.75和87.32 mg·L−1升至8 192.9、3 561.29和153.37 mg·L−1,有机质含量由56.32%降到55.59%,促进了有机质从固相向液相的转移。
2) SEM、EPS、粒径以及三维荧光光谱表征分析结果表明,SDS+复配酶处理管网沉积物后其内部紧实结构被破坏、粒径尺寸变小;在SDS投加量为0~5%内,随着投加量的增多,各层EPS总含量变化趋势为S-EPS>LB-EPS>TB-EPS,其中TB-EPS向S-EPS转移;与单独复配酶水解沉积物效果相比,SDS+复配酶水解沉积物过程中腐殖酸类物质由内向外转移,且荧光强度增强,溶解性EPS增多。这有利于破坏沉积物紧密连接的结构形态,降低沉积物黏性,增加被冲刷性能,延缓排水管网淤堵。
3) SDS+复配酶在一定程度上改变了沉积物中的功能菌群,使得沉积物中Sulfurovum相对丰度增加,而Caldisericum与Methanosaeta相对丰度下降,这对减少管网中CH4、H2S等的产生具有积极作用。SDS+复配酶对微生物的影响会降低管网内部的生化反应,有利于管网的后续维护。
SDS促进复配酶水解排水管网沉积物
SDS enhanced the hydrolysis effect of sediment in drainage pipe network by compound enzyme
-
摘要: 采用SDS协同复配酶水解排水管网沉积物,分别考察了SDS投加量、反应时间、pH、温度4个影响因素对沉积物水解效果的影响,并通过 SEM、EPS、三维荧光光谱以及粒径等表征方法进行机理分析。结果表明,投加5%(w:w)SDS与8%(w:w)复配酶,在原泥pH(7.28±0.3)、25 ℃、反应时间为2 h时,沉积物水解效果最好。此时SCOD、多糖和氨氮分别由初始的5 686.9、1 913.75和87.32 mg·L−1增加到8 192.9、3 561.29和153.37 mg·L−1,有机质含量由56.32%下降到55.59%。在SDS+复配酶处理管网沉积物后,其内部紧实结构被破坏,TB-EPS向S-EPS转移,腐殖酸类物质荧光强度增强,表明溶解性EPS增多,且沉积物粒径向<300 μm转变。高通量测序分析结果表明,SDS+复配酶对管网沉积物微生物种类的丰富度和多样性影响不大,但在一定程度上会改变微生物的功能菌群,减少CH4和H2S的产生。以上研究结果可为延缓排水管网淤堵问题提供数据支持。Abstract: SDS combined with the compound enzyme were used to hydrolyze the sediment of drainage pipe network. The effects of SDS dosage, reaction time, pH and temperature on the hydrolysis of the sediment were discussed. The mechanism was analyzed by SEM, EPS, 3D-EEM and particle size characterization methods. The results showed that the best hydrolysis effect of the sediment happened at 5% (w/w) SDS and 8% (w/w) compound enzyme, pH(7.28±0.3) of raw sediment, 25 ℃ and reaction for 2 h. Under these conditions, SCOD, polysaccharide and ammonia nitrogen increased from the initial values of 5 686.9mg·L−1, 1 913.75mg·L−1 and 87.32mg·L−1 to 8 192.9, 3 561.29 and 153.37mg·L−1, respectively. Organic matter content decreased from 56.32% to 55.59%. After treated by SDS+compound enzyme, the internal compact structure of sediment was destroyed, TB-EPS transferred to S-EPS, and the fluorescence intensity of humic acids increased, which indicated the increase of the dissolved EPS, and the particle size of sediment decreased to smaller than 300 μm. The results of high-throughput sequencing technology showed that SDS+compound enzyme had slight impact on the richness and diversity of microbial species in the sediments, but it could alter the functional microbial community of microorganisms to same extent, and reduced the production of CH4 and H2S. The results of this study provide a new method and data support for delaying the silting problem of the drainage pipe network.
-
Key words:
- SDS /
- compound enzyme /
- drainage pipe network /
- sediment /
- hydrolysis /
- microbial communities
-
随着时代不断发展,城市内涝频繁发生,排水管网淤堵问题备受人们关注。排水管道沉积物是污水中的可沉降颗粒物,在排水管网运行过程中,这些颗粒物在适当条件下发生沉降并逐渐积累,形成底层沉淀物沉积在排水管道中[1]。沉积堵塞排水管网的物质主要包括有机物、无机物以及固体垃圾[2]。管网沉积物中所含的有机质一般是复杂的高分子物质,如脂类、糖类、蛋白质、动植物腐殖质以及微生物等[3]。也有研究将管网沉积物分为3类:底层粗颗粒沉积物、有机层和生物膜[4]。其中,生物膜通常形成于水面附近的管壁,或受扰动作用较小的沉积物表面上,由覆盖在有机质上的微生物构成[5]。胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances, EPS)作为微生物的重要组成部分,其主要成分为多糖、蛋白质、核酸、脂肪、胞外 DNA 等[6],具有粘性和吸附性,对排水管道的淤积及冲刷具有重要影响。传统的管网机械清淤方法均存在人工消耗量大,施工过程中影响道路交通等问题。因此,探究生物或化学方法来减缓管网中沉积物的沉积速率,降低管网清淤与维护频率是解决排水管网淤堵问题新的研究方向。
相关研究表明,利用纤维素酶或蛋白酶可破坏污泥EPS,促使污泥颗粒变得细小分散,污泥颗粒比表面积增大,酶与细胞接触面积增加,并且EPS 的分解还降低了其对污泥细胞的保护作用,进而提高了酶对污泥的水解效率[7]。YANG等[8]研究发现经酶解后,污泥细胞破解,胞内物质流出,大大提高了污泥后续厌氧消化的效率并缩短了污泥消化时间。此外,LU等[9]报道了酸性处理过程中污泥内部酶(蛋白酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶)的释放也可以增强厌氧发酵污泥的破解。
同时,在污泥处理方面,表面活性剂也有其不可或缺的作用。表面活性剂的增溶作用和分散作用[10]使胞外聚合物脱离污泥溶于液相[11];而表面活性剂结构中自带的疏水烷基可与细胞壁相互作用,导致细胞溶解,破坏细胞结构和EPS[12]。王怡等[13]研究表明,添加SDS(十二烷基硫酸钠)可以促进剩余污泥水解,EPS中溶解性蛋白质和多聚糖含量大幅增加,污泥的粒径变小、比阻变大。WANG等[14]研究发现阴离子表面活性剂SDS可以增加体系中的负电荷,EPS与SDS之间的静电排斥和疏水相互作用使污泥中的EPS大量释放。LUO等[15]研究了SDS与酶制剂联合作用对剩余污泥水解酸化的影响,结果表明,组合体系比单一SDS和单一酶体系更能有效促进污泥水解,SDS和复配酶体系优于SDS和单一酶体系的水解性能。由于表面活性剂联合生物酶技术不仅反应条件温和,对管道无腐蚀和破坏性,并且两者联合对管网中有机沉积物具有较好的水解作用,有利于降低沉积物间的黏性,促进有机质从固相向液相转移,强化其冲刷性能,从而为解决排水管网淤堵问题提供新的解决方法,但目前尚未有关于该方面的报道。
基于对排水管网中沉积物的性质分析,根据课题组前期研究结果,本研究在确定复配酶(α-淀粉酶∶中性蛋白酶=2∶3)投加量的质量百分比为8%的条件下,探究不同SDS投加量、反应温度、初始pH(7.28±0.3)和反应时间对SDS+复配酶体系对沉积物水解效果的影响,根据反应前后沉积物EPS、三维荧光、粒径和SEM(scanning electron microscope)表征结果对其水解沉积物的机理进行了深入分析;采用高通量测序技术对经复配酶(α-淀粉酶∶中性蛋白酶=2∶3)、SDS+复配酶(α-淀粉酶∶中性蛋白酶=2∶3)水解后的排水管网沉积物中微生物群落结构与功能菌群的影响进行了分析,探讨了不同方法对微生物群落结构的影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 污泥样品
实验所用管网沉积物取自天津市某排水管道检查井,取回的污泥样品封装于样品袋中,存放在4 ℃冰箱内里冷藏待用。该沉积物样品的相关特性指标为:有机质含量为 (56.39±0.81)%,pH=7.28±0.3;沉积物上清液中SCOD(soluble chemical oxygen demand)值为 (206.9±16.9) mg·L−1、氨氮为 (85.03±2.53) mg·L−1、多糖为 (18.14±2.16) mg·L−1、蛋白质为 (0.08±0.01) mg·mL−1。
1.2 实验试剂和仪器
所用试剂主要包括中性蛋白酶、α-淀粉酶、SDS、氯化钠、COD专用耗材、氢氧化钠、苯酚、氯化氢、无水乙醇、纳氏试剂等。其中,实验所用酶制剂基本性质及来源见表1,其他化学试剂均为分析纯,实验用水为去离子水。
表 1 生物酶基本性质Table 1. Basic properties of biological enzymes生物酶种类 酶活性/(U·g−1) 适宜温度/ ℃ 适宜pH 来源 中性蛋白酶 2×105 50~55 6.0~7.0 合肥博美生物科技有限公司 α-淀粉酶 4 000 60~70 6.0~7.0 上海源叶生物科技有限公司 实验主要仪器包括 YH-3BS远红外线恒温干燥箱(天津中环);SX-GO7103马弗炉(天津中环);MY3 000-6B混凝实验搅拌仪器(武汉梅宇仪器);721型可见分光光度计(上海佑科);VELOCITY 18R台式多功能离心机(Dynamica公司);FY-1C-N真空泵(浙江飞越);G9 800A三维荧光激发-发射光谱仪(美国安捷伦);PHS-3E型pH计(雷磁);HH-4电热恒温水浴锅(绍兴苏珀)。
1.3 实验方案
取100 mL排水管网沉积物置于250 mL烧杯内,通过0.1 mol·L−1的盐酸或氢氧化钠溶液调节pH至 5~10;将烧杯放入水浴锅预热,使沉积物到目标温度(4~65 ℃)后;加入8%(质量百分比,酶质量与沉积物干质量比)污泥的复配酶(α-淀粉酶:中性蛋白酶=2:3),并加入0、1%、2%、5%、8%和10%(质量百分比)的SDS;在200 r·min−1下搅拌,连续反应 0~6 h。反应结束后,取部分污泥进行有机质含量的检测,将剩余部分污泥置于离心管中,在4 000 r·min−1下离心15 min,离心后取上清液经0.45 μm滤膜过滤;检测滤液中SCOD、氨氮、多糖,每个实验重复3次,取平均值分析4个因素对SDS促进复配酶水解排水管网沉积物的影响,确定其最佳反应条件,并分析最佳反应条件下的上清液EPS、三维荧光光谱、沉积物表面结构形态和粒径的变化。
1.4 测定方法
氨氮采用纳氏分光光度法进行测定;溶解性化学需氧量(SCOD)采用快速消解分光光度法测定;多糖采用苯酚-硫酸法测定;蛋白质含量选用改良Lowry法测定;沉积物中有机质含量测定采用《中华人民共和国城镇建设行业标准》(CJ/T96-1999)中有机质灼烧法。EPS采用热提取法,EPS中各类物质变化采用三维荧光扫描光谱仪(安捷伦1260)检测;沉积物表面形态采用扫描电子显微镜 (7610F,日本电子株式会社) 分析。采用16s rRNA高通量测序方法表征微生物群落结构变化。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 SDS投加量对沉积物水解效果的影响
实验在原泥pH(7.28±0.3),8%(质量百分比)复配酶(α-淀粉酶:中性蛋白酶=2:3)、25 ℃反应2 h的条件下,SDS投加量对排水管网沉积物水解效果的影响结果见图1。由图1(a)可以看出,当SDS投加量在0%~5%时,SCOD与多糖浓度随SDS投加量增多而增长,在SDS投加量为5%时,SCOD和多糖达到峰值,分别由初始的5 686.9 mg·L−1和1 913.75 mg·L−1升至8 192.9 mg·L−1和3 561.29 mg·L−1;当投加量继续增加到10%,SCOD与多糖含量反而下降,在10%时,SCOD和多糖分别下降到7 545.9 mg·L−1和2 484.92 mg·L−1。由图1(b)可以观察到,氨氮与SCOD、多糖变化趋势相同,在SDS投加量为5%时,由原始的87.32 mg·L−1达到峰值的153.37 mg·L−1。有机质含量的变化与氨氮、SCOD、多糖变化趋势相反,在SDS投加量为5%时,有机质含量最低,为55.59%;当SDS投加量继续增大,有机质减量效果稍有提高,但与SDS投加量为5%时相差无几。有研究[16]表明,SDS作为酶调节分子,在较低剂量下可增强酶活性,在较高剂量下反而会抑制酶活性。这是由于SDS为阴离子表面活性剂,可以与带负电的沉积物发生静电排斥[14],在SDS含量为0%~5%,随投加量增加,沉积物更加分散,更利于复配酶与沉积物中有机质的接触,从而促进水解作用的发生;但当SDS投加过量时,SDS的烷基可与细胞壁结合,导致细胞破裂,从而部分影响微生物的活性,进而影响污泥水解效果[17]。因此,过低或过高的SDS均不利于生物酶对沉积物的水解。
2.2 反应时间对沉积物水解效果的影响
投加8%复配酶与5%SDS后,沉积物水解效果随反应时间的变化情况如图2所示。由图2可以看出,SCOD、多糖和氨氮随反应时间呈现先升高后下降的趋势。在反应2 h时,SCOD、多糖和氨氮含量分别由初始的211.3、18.38和87.32 mg·L−1升至9 726.5、3 868.84和185.12 mg·L−1。SDS的投加破坏了沉积物中微生物分泌出的EPS内部的非共价键,从而破坏沉积物结构,导致内部物质向外释放,促进了酶与沉积物之间的接触反应,从而使得SCOD、多糖和氨氮含量升高。随着反应时间继续延长,上清液中的SCOD、多糖与氨氮均开始了不同程度的下降,在6 h时,SCOD、多糖与氨氮质量浓度分别为3 581.5、3 056.05、156.09 mg·L−1。这可能是因为复配酶与SDS的协同作用随时间延长,沉积物的水解效果减弱,同时管网微生物对溶出物质进一步分解和利用[18],SCOD、多糖、氨氮的生成速率小于消耗速率,使得上清液中各物质浓度降低。有机质含量随反应时间呈现出一直下降的趋势,这说明水解反应在0~6 h内一直在进行,且在4 h后有机质分解速率变慢。综上所述,选择SDS协同复配酶水解排水管网沉积物的最佳反应时间为2 h。
2.3 温度对沉积物水解效果的影响
实验在原泥pH(7.28±0.3),反应2 h,5%SDS与8%复配酶协同作用下,考察了温度对沉积物水解效果的影响,结果如图3所示。从图3可以看出,在4~65 ℃内,SCOD和氨氮随温度的升高而升高,多糖先升高后趋于平缓,有机质含量随温度的升高逐渐下降,随后变得平缓。当温度由4 ℃升至65 ℃时,SCOD由5 341.0 mg·L−1逐步升至8 983.0 mg·L−1;多糖由1 100.96 mg·L−1升至3 649.16 mg·L−1;氨氮由96.44 mg·L−1升至176.84 mg·L−1。有机质含量在4~35 ℃内下降较快,由开始的56.58%下降到54.69%,降低了1.89%;在35 ℃后随温度的升高,有机质含量保持在54.65%左右。这可能是由于温度升高,中性蛋白酶和α-淀粉酶的活性基团逐渐被激活,酶制剂活性增强,并且在SDS的增溶作用下,酶制剂和沉积物的接触更加充分,水解效果更好。在上述SDS与复配酶的协同作用下,液相中的蛋白质被分解为多肽以及小分子氨基酸,碳水化合物被水解成多糖与单糖[19],水解效果增强,溶解性有机物浓度提高。
根据实验结果,在反应温度高于15 ℃时,SDS协同复配酶的水解效果较好,而市政污水管网常年在8~35 ℃,因此,综合考虑项目经济性和实用性,在实际应用过程中,生物酶水解排水管网沉积物可选择管网温度在15 ℃以上时进行。
2.4 pH对沉积物水解效果的影响
本实验考察了5%SDS与8%复配酶在25 ℃,反应2 h条件下,不同pH对沉积物水解效果的影响结果见图4。由图4(a)可以看出,SCOD与多糖在pH=5~6保持一个平稳的数值,当pH升高为8时,二者均有不同程度的提高,SCOD与多糖分别由pH=6的4 830.4 mg·L−1 和2 369.82 mg·L−1提高到pH=8的5 895.4 mg·L−1和2 660.64mg·L−1;当pH进一步升高为8~10时,SCOD与多糖含量几乎不变。由图4(b)可以看出,氨氮含量随pH增加而下降,氨氮由pH=5的152.87 mg·L−1降到pH=10的82.83 mg·L−1。这是由于碱性条件下氨氮容易从液相转移到气相中,从而使得氨氮含量出现大幅度下降[20]。在pH=5~9,有机质含量随着pH的增加逐渐下降,从57.08%下降到55.09%,当pH增加到10时,有机质含量出现回升。结合图4(a),在pH=10时SCOD、多糖含量变化不大,说明pH继续增大不能继续提升沉积物水解效果。在pH=7~9内,SDS+复配酶对排水管网沉积物的水解效果较好,而实际管网中沉积物pH大概在7~8,因此,在实际应用过程中不需要进行pH调节。
2.5 SDS协同复配酶对沉积物EPS的影响
沉积物中存在微生物,微生物日常生长代谢会产生有粘性的EPS等物质,增加了沉积物的抗冲刷能力;同时,EPS还能吸附污水中的有机颗粒,增加排水管网沉积物厚度和管网淤堵的风险。复配酶可水解沉积物中蛋白类与糖类物质,SDS的两亲性可以改变界面处的能量关系,增加EPS的溶解[21]。研究了复配酶协同SDS水解管网沉积物对EPS及其蛋白质与多糖浓度变化的影响,结果见图5。从图5(a)可以看出,在复配酶投加量为8%,水解2 h条件下,沉积物上清液中TB-EPS(tightly bound EPS)、LB-EPS(loosely bound EPS)与S-EPS(soluble-EPS)的多糖与蛋白含量均随着SDS投加量的增加呈现先升高后下降的趋势,各层EPS总含量变化趋势为S-EPS>LB-EPS>TB-EPS,其中TB-EPS向S-EPS转移。有研究表明,表面活性剂的两亲性使得SDS有一定的的分散作用,可以通过其疏水性与细胞膜蛋白相互作用,这可能导致沉积物的侵蚀[22];当SDS与复配酶协同水解沉积物时,可以大大削弱LB-EPS与TB-EPS的结合[23],使得沉积物发生更严重的裂解和内部生物聚合物的释放,使不溶性的EPS剥离从而进入沉积物上清液中,同时内层TB-EPS向外部转移,TB-EPS含量下降,LB-EPS与S-EPS增多,EPS中可溶性蛋白质与多糖含量增加。
图5(b)为不同SDS投加量下EPS总量的变化情况。可以看出,随投加量增多,EPS含量先升高后基本不变。由于SDS具有增溶作用,大量大分子物质脱离沉积物固体溶解于液相[24],从而释放出更多的蛋白质、多糖等物质到EPS中,使其含量增多。但由于表面活性剂在较低剂量(0~5%)下增强酶活性,在较高剂量(5%~10%)下抑制酶活性[16],因此在SDS投加量高于5%后,随着SDS投加量进一步增加,复配酶失活,水解效果降低。
2.6 三维荧光光谱分析溶解性有机物的变化
中性蛋白酶与α-淀粉酶能够破解复杂的高分子物质,例如蛋白质、碳水化合物等,将一部分难降解物质水解,并释放之液相。而SDS具有增溶的特性,能够加快非液相物质溶解到水中的速度,同时也会释放被沉积物捕获的酶制剂,暴露出更多的底物[25],从而促进沉积物中有机质的水解,增加进入液相中溶解性有机物的含量。而三维荧光光谱可以分析污泥中溶解性有机物的种类及分布,不同区域和不同荧光强度代表不同物质及相应的浓度。
由图6可以明显看出,经SDS+复配酶组处理后的沉积物上清液EPS中,I~III区域荧光强度较复配酶组大幅度下降。表明在投加SDS后,酪氨酸、色氨酸与富里酸类物质含量减小甚至消失。左锦静[26]研究表明,SDS与蛋白质之间可以通过疏水作用自发结合,SDS作为淬灭剂对蛋白质进行淬灭,使得三维荧光光谱中蛋白质类物质几近消失;IV区域内的荧光强度和范围略有缩减,这可能是因为SDS具有抑菌性,随着反应时间的延长,导致沉积物中部分微生物死亡,可溶性微生物代谢产物含量降低;V区域所代表的腐殖酸类为五类可溶性有机物中的主要物质,与经复配酶处理后的沉积物上清液的三维荧光光谱图进行对比可以看出,SDS+复配酶的投加使得沉积物上清液中腐殖酸含量急剧增加,且又出现了一种新的腐殖酸物质(Ex/Em为390~440 nm/440~500 nm),这2种腐殖酸浓度由内向外逐渐递增。一方面,SDS的两亲性使得复配酶更容易接触沉积物内部,释放出更多的物质,如腐殖酸;另一方面,微生物对腐殖酸利用率较低,容易在EPS中沉积,沉积物释放出的可溶性微生物副产物等物质更容易被微生物利用或被上清液中溶解的复配酶水解成小分子物质,导致腐殖酸含量高,溶性微生物副产物含量低。有研究[27]表明,腐殖酸浓度可以反映EPS溶解的程度,这也说明沉积物中腐殖酸类物质占比较高,腐殖酸浓度越大,溶解性EPS越多,沉积物水解减量效果越好。
2.7 SEM表征
SEM可较直观的反映出沉积物水解前后表面微观结构的变化,经SDS+复配酶、复配酶水解后的沉积物表面结构变化如图7所示。沉积物在被SDS+复配酶、复配酶水解后均出现密集多孔的表面形态,说明SDS+复配酶与复配酶对沉积物均有明显的破坏效果。经SDS+复配酶处理后,沉积物表面层状更多,说明SDS的增溶作用会打破沉积物紧密连接的结构,使得复配酶能够与更深层的沉积物的接触反应,进而促进水解反应的发生。同时疏松多孔的表面形态使得沉积物更容易被水力冲刷,有利于达到延缓管网淤堵和沉积物减量化的目的。
2.8 SDS+复配酶对粒径变化的影响
在复配酶投加量为8%的条件下,SDS投加量对沉积物粒径的影响结果见图8。可以看出,粒径>300 μm沉积物的质量占比由单独投加复配酶的48.25%下降到5% SDS投加量下的36.94%,随后SDS增加,此粒径沉积物的占比又增加;粒径在150~300 μm内的沉积物质量占比由独投加复配酶的21.05%升高到8%SDS的24.20%左右,随后其质量占比随SDS投加量增加而减小;粒径在75~150 μm内沉积物的质量分数由16.75%升至2%SDS下的23.5%,随后SDS投量增加,质量占比保持在22.0%左右;粒径<75 μm的沉积物质量分数占比由单独投加复配酶的13.95%升高到5%SDS的17.14%,随后SDS投量增加,其质量占比下降。
以上结果表明,在SDS+复配酶协同水解沉积物的过程中,随着SDS投加量的增加,在粒径>300 μm时,沉积物质量占比均有明显下降;小粒径占比增多。SDS的投加量在0%~5%内,投加量的增多会促进大颗粒物质向小颗粒转化。但当SDS投加量大于5%时,SDS对复配酶的水解起抑制作用,大颗粒向小颗粒转化效果变差。
2.9 SDS协同复配酶水解排水管网沉积物微生物分析
1)排水管网沉积物Alpha多样性。利用16S rRNA基因测序技术对原沉积物和分别经复配酶、SDS+复配酶处理沉积物的菌群结构进行Alpha多样性指数分析,结果见表2。OTUs大小可反应样品中物种多样性[28]。由表2可知,原泥OTUs数量最多,投加复配酶后,OTUs数量显著降低,而采用SDS+复配酶处理后,OTUs又有大幅度回升。表明单独采用复配酶可降低管网菌种数量,但采用SDS与复配酶联用可减少对管网中微生物多样性的影响。Shannon和Simpson指数也表明,经过复配酶处理后的样品中,这2个指数均出现明显下降,而经SDS+复配酶处理后的样品Shannon和Simpson指数与原泥相比相差不大,说明微生物多样性和均匀性没有出现很大改变。本次实验中4组样品的覆盖率均大于0.98,表明本次微生物测序的有效性和可靠性。
表 2 微生物alpha多样性指数分析Table 2. Microbial alpha diversity index analysis样本 OTUs Chao1 Shannon Simpson 覆盖率 原泥 1 471 2 090 6.52 0.95 0.98 复配酶 (中性蛋白酶:α-淀粉酶=2:3) 791 1 086 4.84 0.88 0.99 SDS+复配酶 (中性蛋白酶:α-淀粉酶=2:3) 1 294 1 934 6.22 0.95 0.98 2)基于OTU的微生物群落Venn图分析。各组样品间的OTU彼此关联,根据3组沉积物样品测定的OTU数据,绘制了3组样品OTUs的Venn图,以反映不同处理条件下沉积物样品的物种多样性差异[29]。由图9可以看出,原泥组(A)、复配酶组(B)和SDS+复配酶组(C)样品的OTU数目分别为2 098、1 273和2 001,相较于原泥,各组OUT数均有不同程度的降低,表明在投加酶制剂后,物质多样性出现了不同程度的下降[30],其中复配酶下降最明显,而SDS+复配酶与原泥相差较小,这也与表2的结果一致。Venn图的重叠部分代表了不同样品的共有OTU,可知 3 组样品的共有OTU数为783,占总OTU数(2 647)的29.58%,说明酶制剂的投加会对排水管网沉积物中的微生物丰富度和多样性造成一定的影响[31]。
3)微生物属水平群落结构及功能菌群分析。观察了属水平上微生物群落结构演替(图10),沉积物经复配酶、SDS+复配酶处理后,Sulfurovum (反硝化硫菌)的相对丰度均有不同程度的增加,分别从原沉积物的5.02%增加为34.53%和14.85%,其中复配酶组增幅最大。这可能由于投加酶制剂后,沉积物中大分子物质溶出,氨氮升高,可能硝态氮也有所升高,有利于Sulfurovum的繁殖。Caldisericum(嗜热、硫代硫酸盐还原细菌)与Methanosaeta(甲烷丝菌属)在投加复配酶、SDS+复配酶后,相对丰度均出现下降的现象。Methanosaeta(甲烷丝菌属)在原沉积物、复配酶和SDS+复配酶中所占比例分别为8.09%、1.34%和5.33%。Methanosaeta属于产甲烷菌(MA)的一种,其新陈代谢会产生CH4和CO2,此菌种所占比例减少,一定程度上也会降低排水管道中CH4产量。Caldisericum的变化趋势与Methanosaeta相同,复配酶组、SDS+复配酶组相对丰度均小于原沉积物,表明经SDS+复配酶处理后会减少管网中H2S的产量,这有利于管网的后续维护。Uncultured表示未能在人工条件下获得纯培养的微生物。
3. 结论
1)采用SDS+复配酶可有效水解排水管网沉积物,在原泥pH(7.28±0.3)、25 ℃下反应2 h,沉积物上清液中SCOD、多糖和氨氮分别由初始的5 686.9、1 913.75和87.32 mg·L−1升至8 192.9、3 561.29和153.37 mg·L−1,有机质含量由56.32%降到55.59%,促进了有机质从固相向液相的转移。
2) SEM、EPS、粒径以及三维荧光光谱表征分析结果表明,SDS+复配酶处理管网沉积物后其内部紧实结构被破坏、粒径尺寸变小;在SDS投加量为0~5%内,随着投加量的增多,各层EPS总含量变化趋势为S-EPS>LB-EPS>TB-EPS,其中TB-EPS向S-EPS转移;与单独复配酶水解沉积物效果相比,SDS+复配酶水解沉积物过程中腐殖酸类物质由内向外转移,且荧光强度增强,溶解性EPS增多。这有利于破坏沉积物紧密连接的结构形态,降低沉积物黏性,增加被冲刷性能,延缓排水管网淤堵。
3) SDS+复配酶在一定程度上改变了沉积物中的功能菌群,使得沉积物中Sulfurovum相对丰度增加,而Caldisericum与Methanosaeta相对丰度下降,这对减少管网中CH4、H2S等的产生具有积极作用。SDS+复配酶对微生物的影响会降低管网内部的生化反应,有利于管网的后续维护。
-
表 1 生物酶基本性质
Table 1. Basic properties of biological enzymes
生物酶种类 酶活性/(U·g−1) 适宜温度/ ℃ 适宜pH 来源 中性蛋白酶 2×105 50~55 6.0~7.0 合肥博美生物科技有限公司 α-淀粉酶 4 000 60~70 6.0~7.0 上海源叶生物科技有限公司 表 2 微生物alpha多样性指数分析
Table 2. Microbial alpha diversity index analysis
样本 OTUs Chao1 Shannon Simpson 覆盖率 原泥 1 471 2 090 6.52 0.95 0.98 复配酶 (中性蛋白酶:α-淀粉酶=2:3) 791 1 086 4.84 0.88 0.99 SDS+复配酶 (中性蛋白酶:α-淀粉酶=2:3) 1 294 1 934 6.22 0.95 0.98 -
[1] 刘志长. 合流制排水管道沉积物的沉积状况及控制技术研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2011. [2] 黄乃先, 齐一凡, 金伟. 排水管道沉积物控制的研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2021, 11(3): 507-513. [3] 张宇, 李明智, 梅荣武, 等. 应用柠檬酸和酶制剂协同减量处理活性污泥[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(3): 1947-1952. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201511093 [4] AHYERRE M, CHEBBO G. Identification of in-sewer sources of organic solids contributing to combined sewer overflows[J]. Environmental Technology, 2002, 23(9): 1063-1073. doi: 10.1080/09593332308618353 [5] 陈珂莉, 李朋, 金伟, 等. 排水管道沉积物中胞外聚合物的提取及检测方法研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2018, 34(7): 32-36. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2018.07.007 [6] SHENG G P, YU H Q, LI X Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2010, 28(6): 882-894. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.08.001 [7] 钟为章, 丁雅婷, 秦学, 等. 城镇污水剩余污泥生物法水解研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2022, 42(10): 38-45. [8] YANG Q, LUO K, LI X M, et al. Enhanced efficiency of biological excess sludge hydrolysis under anaerobic digestion by additional enzymes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(9): 2924-2930. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.012 [9] LU Q, LIU Q, LIU X, et al. Enhanced dewaterability of anaerobically fermented sludge through acid-driven indigenous enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 323: 116212. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116212 [10] 周语桐, 杨英, 李卫华, 等. 表面活性剂增强超声法提取污泥胞外聚合物[J]. 湖北理工学院学报, 2023, 39(1): 55-59. [11] 陈东杰, 夏霆, 张旭, 等. 城市污泥脱水预处理技术研究进展[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 45(1): 12-23. [12] 石晶金, 方溢文, 官妍. 三种表面活性剂对表皮葡萄球菌生物膜渗透性及成膜关键基因agr表达的影响[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2023, 22(3): 267-274. doi: 10.12138/j.issn.1671-9638.20233382 [13] 王怡, 曲鹏程, 郑淑健, 等. SDS对污泥水解过程中胞外聚合物及性状的影响[J]. 中国给水排水, 2013, 29(15): 85-88. [14] WANG L F, WANG L L, LI W W, et al. Surfactant-mediated settleability and dewaterability of activated sludge[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 116: 228-234. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2014.05.014 [15] LUO K, YANG Q, YU J, et al. Combined effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate and enzyme on waste activated sludge hydrolysis and acidification[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(14): 7103-7110. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.023 [16] KAVITHA S, JAYASHREE C, KUMAR SA, et al. The enhancement of anaerobic biodegradability of waste activated sludge by surfactant mediated biological pretreatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 168: 159-166. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.118 [17] 陈子浩. 十二烷基苯磺酸钠对热水解污泥厌氧消化的影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2022. [18] 陈小粉, 李小明, 杨麒, 等. 淀粉酶促进剩余污泥热水解的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2011, 31(3): 396-401. [19] 李超, 高健磊, 闫怡新, 等. 中性蛋白酶催化水解污泥提取蛋白质的研究[J]. 能源环境保护, 2019, 33(6): 18-22. [20] 张琴, 何璐, 常少英, 等. 污泥干化冷凝废水电化学脱氮试验研究[J]. 绿色科技, 2022, 24(22): 104-108. doi: 10.16663/j.cnki.lskj.2022.22.016 [21] GUNG R, YUAN X, WU Z, et al. Functionality of surfactants in waste-activated sludge treatment: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 1433-1442. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.189 [22] WANG L F, HUANG B C, WANG L L, et al. Experimental and theoretical analyses on the impacts of ionic surfactants on sludge properties[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633: 198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.187 [23] HE X, HE L, LIN Z, et al. Deep dewatering of activated sludge using composite conditioners of surfactant, acid and flocculant: The mechanism and dosage model[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 150899. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150899 [24] 童震松, 洪晨, 邢奕, 等. 表面活性剂调理下污泥中胞外聚合物分布与束缚水含量的关系[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(8): 2913-2919. [25] KAVITHA S, KUMAR SA, YOGALAKSHMI KN, et al. Effect of enzyme secreting bacterial pretreatment on enhancement of aerobic digestion potential of waste activated sludge interceded through EDTA[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 150: 210-219. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.021 [26] 左锦静, 姚永志. 荧光法研究表面活性剂SDS与蛋白质的相互作用[J]. 轻工科技, 2018, 34(3): 16-17. [27] HUANG X, SHEN C, LIU J, et al. Improved volatile fatty acid production during waste activated sludge anaerobic fermentation by different bio-surfactants[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 264: 280-290. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.078 [28] 宋云龙, 张金松, 朱佳, 等. 基于高通量测序的微生物强化污泥减量工艺中微生物群落解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(7): 2099-2107. [29] 相延铮, 何成达, 朱腾义, 等. 碳源对除磷颗粒污泥去除效果和微生物特性的影响[J]. 工业水处理, 2023,DOI: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2022-1178. [30] 潘禹, 刘鲡, 智笑涵, 等. 纳米CaO_2促进污泥厌氧发酵产酸性能的微生物机制[J]. 环境科学研究, 2023, 36(7): 1426-1434. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2023.03.05 [31] 代梨梨, 彭亮, 陶玲, 等. 硫酸盐对淡水养殖池塘表层底泥微生物的影响[J]. 微生物学报, 2023, 63(10): 3811-3824. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20230075 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: