-
铁炭微电解具有操作简单、条件温和的特点而被广泛用于废水净化领域。王宇峰等[1]等利用铁碳微电解预处理高盐废水,其COD去除率约为61.2%。SUN等[2]和赖波等[3]分别利用铁碳微电解净化工业废水,废水TOC的去除率分别约为55.3%和52.6%。由于铁、炭材料处于混合状态,曝气条件下铁材料容易发生钝化、板结,而且氢氧化物会包覆在活性炭的表面,影响活性炭的导电性能,并降低活性炭比表面积,最终致使传统铁炭微电解的污水净化能力下降,同时电偶腐蚀生成的Fe2+容易被氧化为Fe3+,而Fe3+则会进一步消化Fe0,导致废水处理的铁泥量大和成本增加等问题[4-7]。
利用铁、炭之间的电势差,通过形成化学原电池来实现废水污染物的净化与资源回收的研究目前较为稀少。YING等[8]在2个极室内分别放置铁电极和炭电极,以Na2SO4为电解质,采用盐桥方式形成化学原电池,考察了铁电极和炭电极在去除2,4-二氯苯酚的作用机制,但该研究的出发点仍在于探究传统铁炭微电解中的铁电极和炭电极在污染物净化中的作用。LAI等[9]以高纯度铁板作为阳极,炭材料作为阴极,并通过质子膜将两室隔开,获得了98%的废水磷回收率。针对模拟烟气的同步脱硫、脱硝、脱碳,本课题组前期采用铁炭双池原电池反应器进行了实验研究,结果表明,铁炭原电池反应器的脱硫、脱硝、脱碳率分别高达99%、85%和约50%[10]。
相对于传统的铁碳微电解,铁炭原电池反应器的铁、炭相对独立地在各自的反应极室中,铁室中不曝气,而碳室曝气。这样不仅可以避免传统铁碳微电解的铁材料消耗量大、铁泥多的问题,同时避免了铁材料的钝化、板结以及净化效率较低等问题,而且铁室和炭室各自相对独立地净化污染物,该原电池反应器具有更多的污染物净化工艺路线选择。为此,本研究考察了铁炭原电池反应器在高盐废水有机物的净化效果,并进一步探究了操作模式(间隙、半连续和连续)以及影响因素对高盐废水有机物去除的影响规律。
-
本研究中所用废水为国内某煤化工生产企业的反渗透浓缩后的高盐废水。高盐废水的pH为1.70,硫酸根离子的质量浓度为13 100 mg·L−1,氯离子的质量浓度为79 500 mg·L−1,总溶解性固体(TDS)含量为16 8000 mg·L−1,总有机碳(TOC)含量为990 mg·L−1,耗氧有机污染物的浓度(以COD计)为5 500 mg·L−1。实验中所使用的铁粉、活性炭粉末和盐酸均为分析纯。该高盐废水中的主要无机盐分别为NaCl和Na2SO4。
-
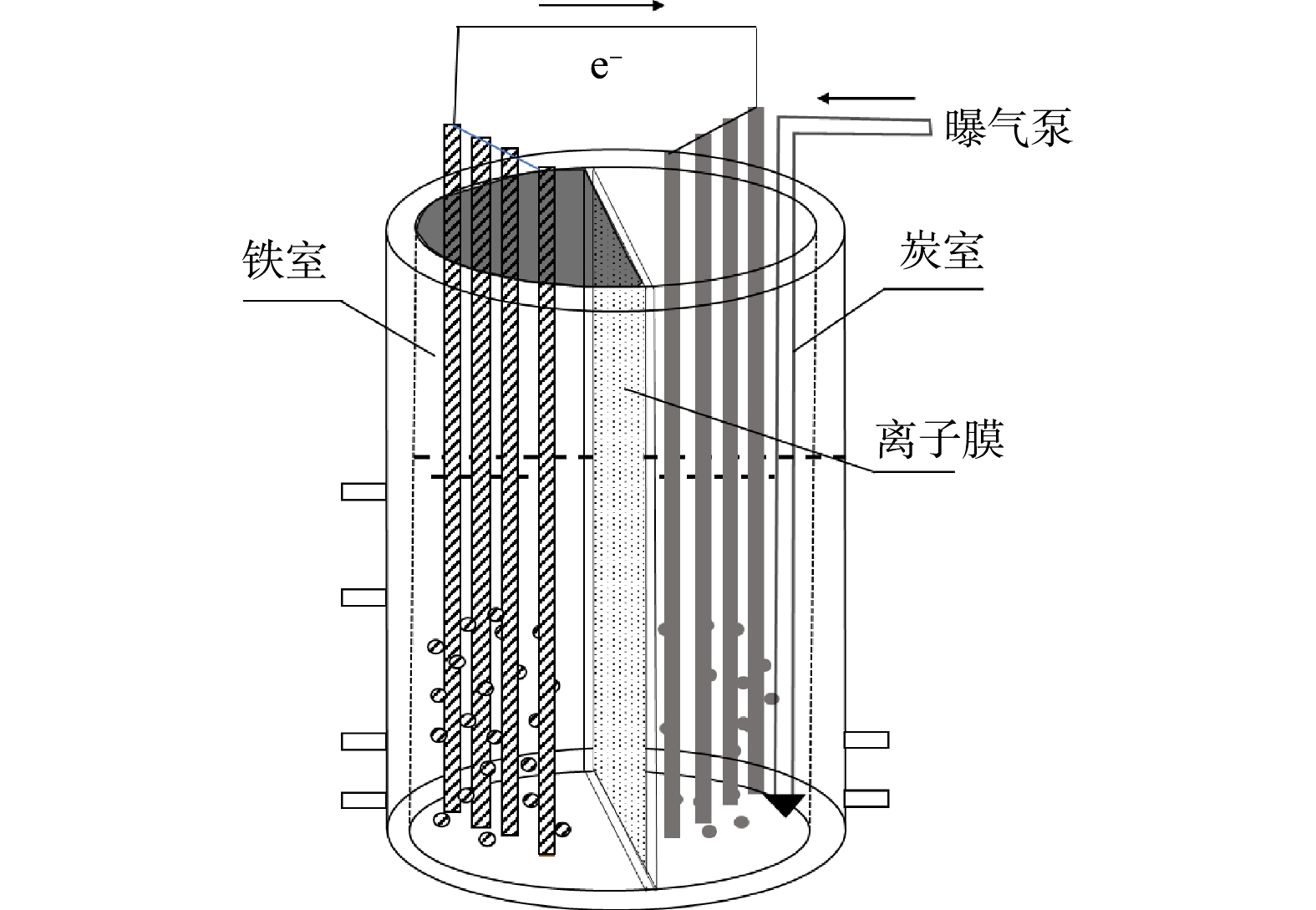
图1为铁炭原电池反应器示意图。铁室与炭室通过阴离子膜(FAA-3-20,Fumasep)分隔。铁室内放置有铁粉和铁电极(φ=4 mm×13 mm)。铁室外侧从上至下设有循环进水口、循环出水口、废水进水口和废水出水口。循环泵型号为HD-602。铁室顶部密封。炭室内放置有活性炭粉末和石墨电极(φ=6 mm×6 mm),外侧从上至下设有废水进水口和废水出水口。炭室曝气,曝气泵为DP-160S。铁电极和石墨电极均先各自采用导线连接后,再通过一根导线把铁电极和石墨电极进行连接。
-
反应器净化性能评价设计了4组实验。实验A断开导线,实验B和实验C均连接导线。实验D为传统铁炭微电解。实验A、B、C和D的铁粉均为新鲜铁粉,实验A、B、D的活性炭为新鲜原料,实验C的活性炭为实验B用过的活性炭。4组实验中的铁粉、活性炭质量比均为1:1,铁粉和活性炭质量均为54 g。实验A、B、C、D均为半连续操作模式。实验A、B、C的铁室和碳室各自的进料流量均为1.0 mL·min−1,实验D的进水流量2.0 mL·min−1。实验A、B、C的铁室和炭室的初始废水体积均为300 mL,而实验D的初始废水体积为600 mL。4组实验处理的总废水体积和净化时间均相同。
操作模式的影响实验。间歇模式,铁室和炭室内分别加入600 mL废水,关闭所有进水口和出水口。半连续模式,前0.5 h内分别向铁室和炭室加入300 mL废水,随后以1.0 mL·min−1的速度向铁室和炭室内各自加入废水。间隙以及半连续模式下,铁室和碳室被离子隔膜完全隔离。连续模式,铁室和炭室的初始废水体积分别为600 mL和300 mL,调节阴离子膜的安装高度以实现铁室废水自动流入炭室。连续操作模式下,废水由铁室进水口进入,随后越过离子膜顶部流入炭室,随后从碳室下部的出水口流出。铁室进水流量与碳室出水流量均为1.0 mL·min−1。本研究中的铁粉和活性炭用量均按照初始废水质量的15%投加。
操作因素的影响实验。在半连续操作模式下分别考察固液比(铁粉或活性炭粉末与初始废水的质量百分比)、废水pH以及废水流量对有机物净化的影响。固液比影响实验:在初始pH为1.70、进水流量为1.0 mL·min−1的条件下,设置固液比分别为5%、10%和15%。废水pH的影响实验:在固液比为15%、进水流量为1.0 mL·min−1的条件下,pH分别设为1.00、1.30和1.70。进水流量的影响:在固液比为15%、pH为1.70的条件下,设置流量分别为0.3、0.6和1.0 mL·min−1。以上实验中铁粉与活性碳质量比均为1:1。本研究中实验时间均为5 h,铁室的循环泵和炭室的曝气泵均常开,曝气流量和废水循环流量固定为3.0 L·min−1。
-
实验过程中每15 min记录1次铁室和炭室的氧化还原电位(oxidation-reduction potential, ORP)、pH和电流(I)。每1 h取水样进行有机物含量分析。ORP(ORP分析仪,型号SX630,Labsen)和pH(pH计,Phb-4,雷磁)均测定溶液中部位置。水样从溶液中部位置采取。万用表(DEM11,DELIXI ELECTRIC)测定电流。
废水有机物含量用TOC表示。TOC采用总有机碳分析仪(TOC-VCPH,岛津,日本)测定。TOC去除率根据式(1)进行计算。
式中:η为TOC去除率,%;Ct和C0分别为TOC采样质量浓度和初始质量浓度,mg·L−1。
-
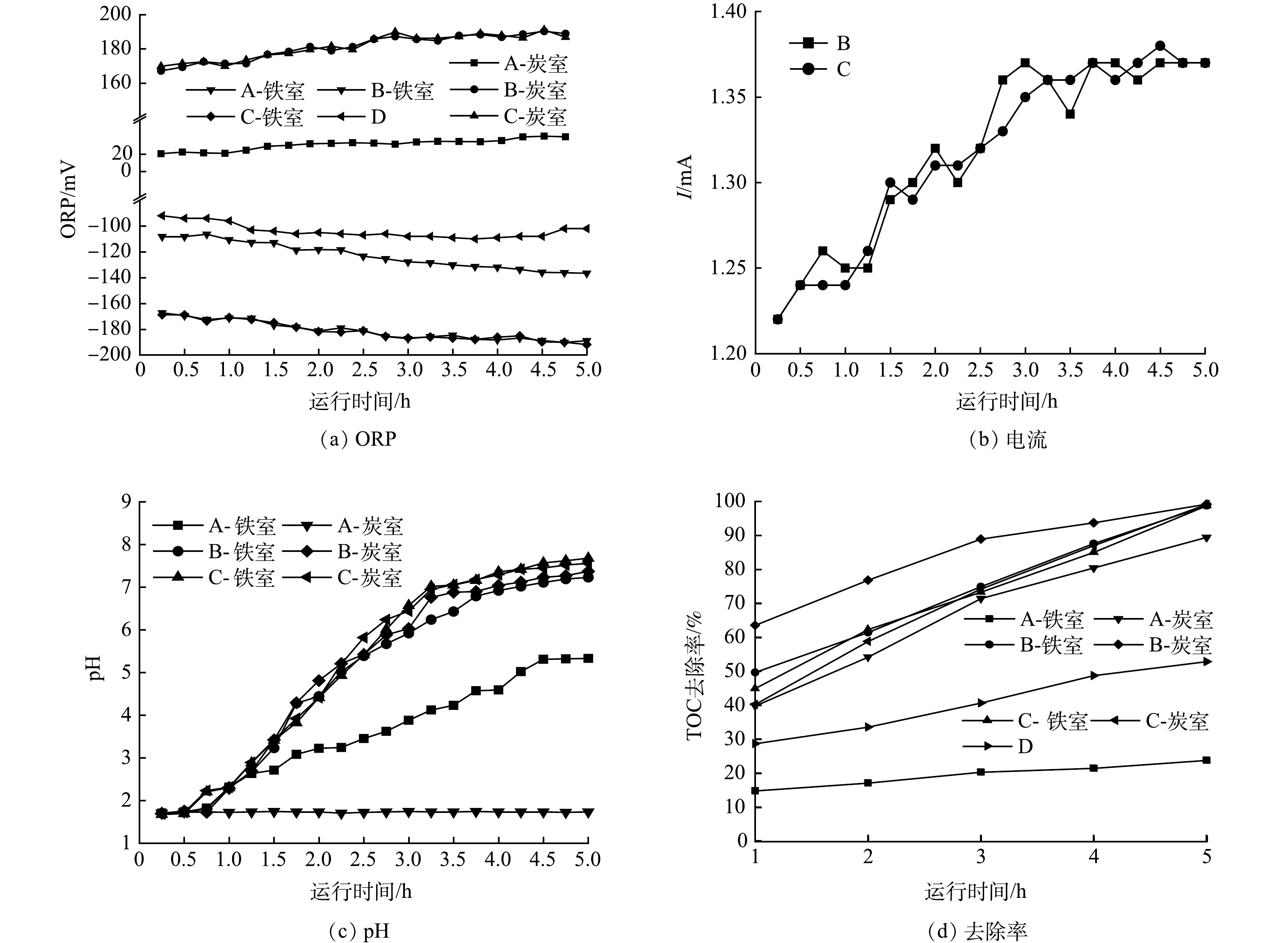
1)反应器净化性能分析。由图2(a)可见,在5 h内,实验A的炭室ORP由20.3 mV逐步升至30.2 mV,铁室ORP则由−108.2 mV下降至−136.6 mV;实验B的炭室ORP则由167.2 mV上升至188.9 mV,铁室ORP由−167.3 mV降至−188.9 mV;实验C的铁室ORP和炭室ORP与实验B的结果基本一致;实验D的ORP则基本在−100 mV附近。ORP检测结果表明,单纯铁粉环境下的ORP要比微电解下的ORP更负,而原电池反应器的铁室ORP则明显更负,说明原电池铁室的还原性比单纯的铁粉以及微电解的还原性更强;导线断开时的炭室ORP比原电池的炭室的ORP小,说明原电池的炭室的氧化性更强。由ORP可见,原电池的铁室具有更为显著的还原性,而炭室具有明显的氧化性。显然,该现象有利用铁炭原电池反应器对高盐废水中有机物的净化。图2(b)为电流变化情况。可见,实验A和D无电流,实验B和C有电流。实验B和实验C的电流数值及其变化趋势相似,初期电流约为1.26 mA,5 h后升至1.37 mA,电流在前3 h上升较为明显,随后电流趋于稳定。
图2(c)为pH的变化趋势。可见,在5 h内,实验A的铁室废水pH由1.70升至5.33,炭室废水pH基本稳定在1.70附近;实验B中铁室和炭室的pH由初期的1.70分别升高至结束时的7.23和7.74;实验C铁室和炭室的pH由初始的1.70分别升高至结束时的7.68和7.56;实验D的pH由初期的1.70升高至4.70,且其pH在前135 min变化较为明显,随后pH变化缓慢。废水净化过程中pH变化幅度从大到小的顺序为原电池反应器的铁室和炭室>单纯铁粉处理>铁炭微电解以及活性炭吸附过程。废水中pH的变化表明这4组实验在有机物净化之间的差异性。铁炭微电解过程中废水pH在前135 min升高明显,但随后变化缓慢,其原因可能与铁粉的表面钝化有关。单纯铁粉处理过程中的铁粉仅发生酸腐蚀作用,但由于没有曝气,因此,铁粉表面的钝化现象比铁炭微电解的要弱,因此,pH呈现不断上升的趋势。铁炭原电池反应器不仅避免了铁粉的钝化现象,同时也保留了酸腐蚀与间接电偶腐蚀,因此,其废水的pH最高,其最终的pH环境也有利于避免传统铁炭微电解的返色现象。
图2(d)为废水TOC去除率的5 h变化趋势。铁室和炭室中废水TOC去除率均随时间而增加。实验A的铁室的净化效果较差,最终的TOC去除率仅为23.8%;而炭室对TOC的去除效果相对较好,TOC去除率可达89.4%。实验B中的铁室对TOC去除率约为98.8%,而炭室TOC去除率约为99.2%。实验C中的铁室废水TOC去除率约为98.7%,而炭室废水TOC去除率约为99.1%。实验D中TOC去除率约为52.80%。比较4组实验中的TOC去除率可知,铁炭原电池反应器对高盐废水中有机物净化效果较好,远远优于单纯的铁粉处理效果,也明显优于传统铁炭微电解(实验D)效果,也比单纯活性炭的吸附效果要好。由此可见,铁炭原电池反应器对高盐废水有机物净化具有显著优势。比较实验B和C的炭室净化效果发现,活性炭是否更换对TOC的净化效率影响较小。该现象表明活性炭在该原电池反应器中无需更换,可以重复使用。
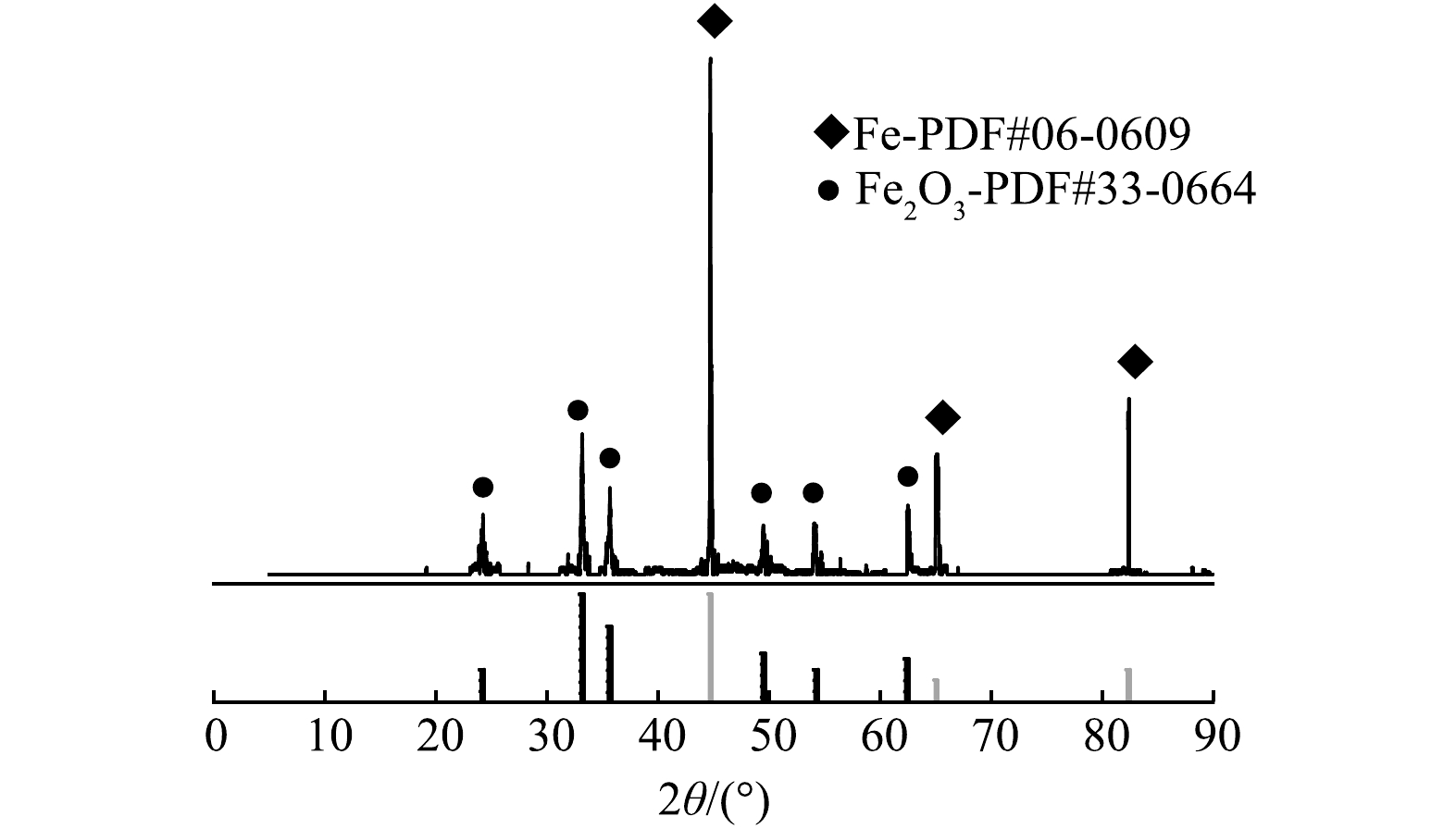
2)反应器净化原理分析。依据铁水体系的pH-电位相图[11]以及本课题组测定的铁电极电势[10],本研究中铁室不会出现Fe3+,只有Fe2+。本研究在实验结束后对铁室粉末固体进行分离、干燥、煅烧与称重。同时对煅烧粉末进行了X射线衍射(XRD)分析,发现粉末中只有铁粉和氧化铁(图3)。依据质量衡算,铁室对单位体积高盐废水5 h处理所消耗的铁粉质量为6.4~6.9 kg·m−3。依据废水pH以及氢氧化亚铁溶度积,理论分析铁室应该会生成氢氧化亚铁。根据文献[10],炭室电极电势可达0.80 V以上,而氧气与氢离子生成双氧水的标准电极电势约为0.68 V[12],显然,炭室会产生双氧水。
综上所述,本铁炭原电池反应器对高盐废水有机物的去除途径为:铁室主要通过电化学氧化还原、铁单质的化学氧化还原[13]以及氢氧化亚铁吸附;炭室主要通过电化学氧化还原、活性炭吸附以及双氧水化学氧化还原。
-
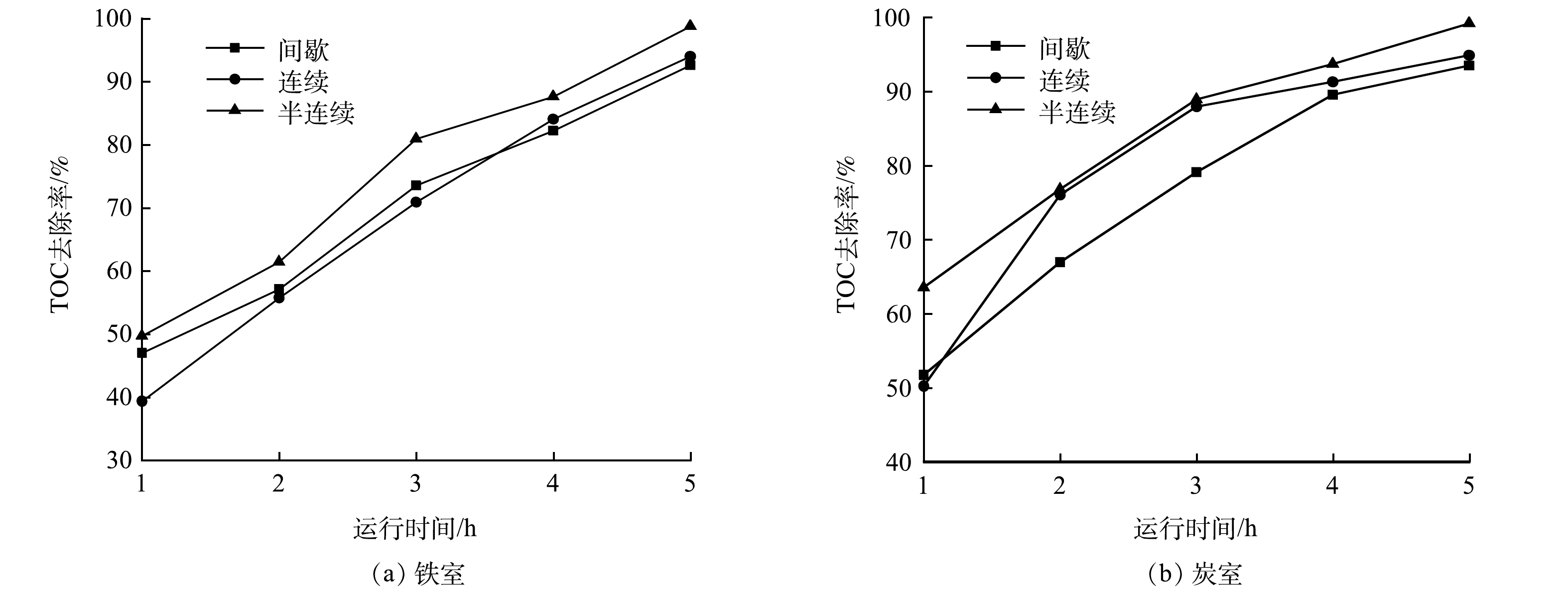
图4(a)和图4(b)为不同操作模式下铁室和炭室对废水TOC的去除率变化趋势。在3种模式下,铁室和炭室中废水TOC去除率均逐渐上升。总体上,无论是铁室还是炭室,半连续操作模式下高盐废水TOC去除效率最高,间歇模式的净化效果相对要差一些。间歇模式、连续模式以及半连续模式下,5 h后铁室废水TOC去除率分别为92.6%、94.0%和98.8%,炭室废水TOC去除率分别为93.5%、94.9%和99.2%。由此可见,铁炭原电池反应器的半连续操作模式为最佳模式。因此,后续实验中选择半连续操作模式,在此基础上考察固液比、废水pH以及废水流量对废水有机物净化的影响规律。
-
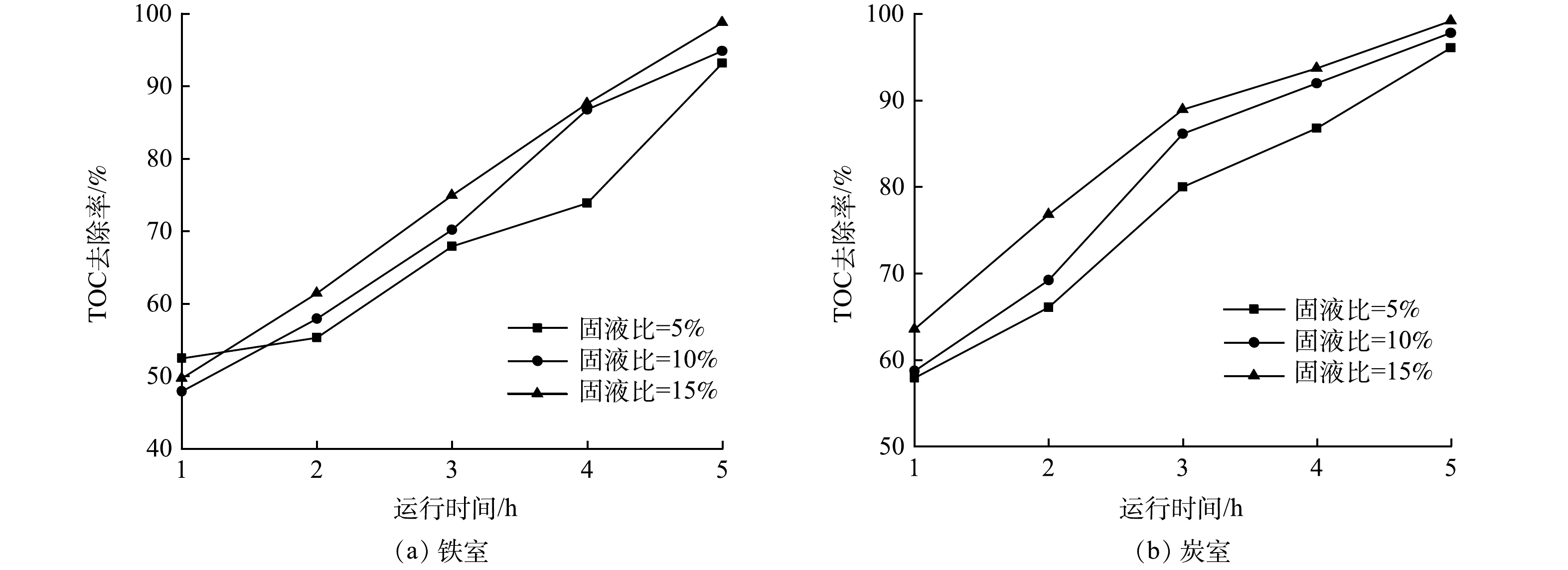
1)固液比的影响。图5(a)和图5(b)为不同固液比时铁室和炭室对废水TOC去除率的变化趋势。可见,铁室和炭室对废水TOC的去除率均随时间的增加而上升。铁室以及炭室对高盐废水中有机物的去除效率随固液比增加而升高。在固液比分别为5%、10%和15%时,5 h后铁室对废水TOC去除率分别为93.2%、94.9%和98.8%,而炭室对废水TOC去除率分别为96.1%、97.8%和99.2%。显然,高固液比有利于铁室和炭室对废水中TOC的去除。其原因是固液比的增加使得相同体积的废水中的单质铁和活性炭浓度上升,与铁电极和石墨电极的接触和碰撞概率更高,电化学反应场所扩大,电子转移数量增加,废水有机物的去除速率增加。因此,增加铁炭原电池反应器的固液比有利于提升对高盐废水中TOC的去除率。
2)初始pH的影响。图6(a)和图6(b)分别为pH对铁室和炭室废水TOC的去除率的影响趋势。3种不同pH情况下,铁室和炭室中废水TOC的去除率均随时间延长而上升。总体上,前4 h时pH较低时的去除率曲线位于最上面,而pH较高时TOC去除率曲线位于下面。但5 h后,pH对废水TOC的去除率影响不大。废水pH为1.0、1.3和1.7时,5 h后铁室对废水TOC去除率分别为98.7%、98.8%和98.8%,而炭室对废水TOC的去除率分别为99.2%、99.0%和99.2%。废水pH会影响铁室和炭室的氧化还原性能和电极电位[10],最终影响废水中有机物的去除。依据废水TOC的去除效果,选择原始废水pH为佳。
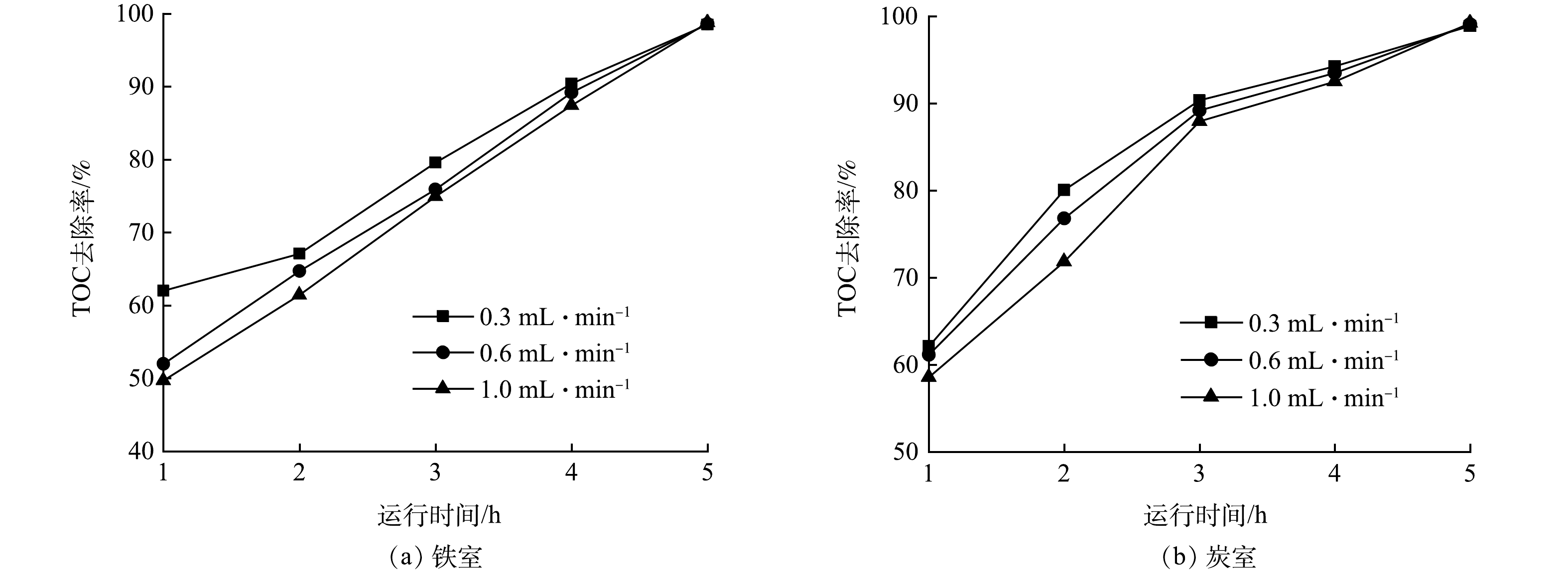
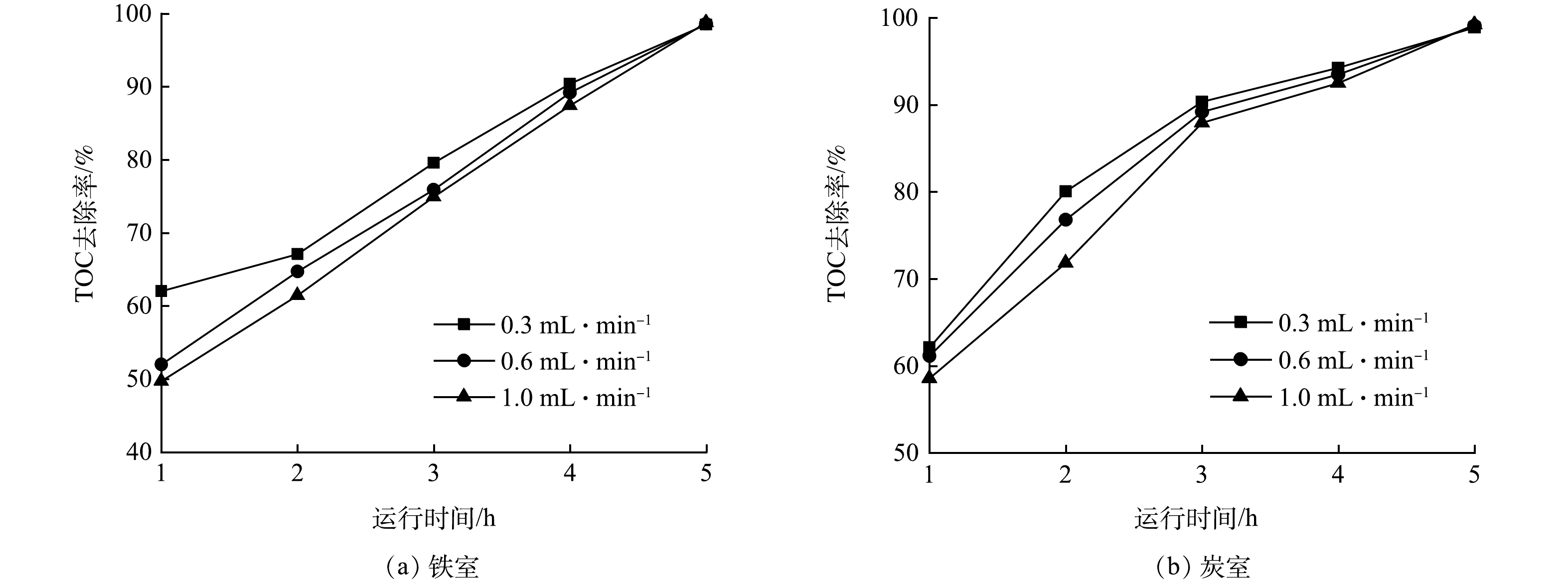
3)进水流量的影响。图7(a)和图7(b)为进水流量对废水TOC的去除率的影响情况。总体上,处理的前4 h无论是铁室还是炭室,当废水流量较低时,对应的TOC去除率要高一些。然而在5 h后则是废水流量较高时废水TOC去除率要稍高一些,但差异性并不大。当流量为0.3、0.6和1.0 mL·min−1时,5 h后铁室废水TOC去除率分别为98.5%、98.6%和98.8%,炭室废水TOC去除率分别为98.9%和99.1%和99.2%。TOC去除率随流量变化的原因应该与物料流动状态、有机物负荷以及氢离子含量有关。依据废水有机物去除效率以及废水处理体积,选择1.0 mL·min−1的为最佳流量。
-
1)铁炭原电池反应器对于高盐废水有机物具有显著的净化效果,其净化效率远高于单纯的铁粉处理,明显优于传统铁炭微电解,也优于活性炭吸附方法。
2)铁室和炭室主要通过电化学氧化还原、吸附与化学氧化还原作用对高盐废水有机物进行去除。该反应器主要消耗铁粉,而活性炭可重复使用。
3)在固液比为15%、pH为1.7、流量1.0 mL·mim−1的较佳操作条件下,铁炭原电池反应器的铁室和炭室的最佳操作方式为半连续模式。
4)在固液比为15%、pH为1.7、流量1.0 mL·mim−1操作条件下,铁炭原电池反应器的铁室对高盐废水TOC的去除率可达98.7%以上,而炭室对高盐废水TOC的去除率可达99.1%以上。
铁炭原电池反应器净化高盐废水初探
First exploration on the purification of high salinity wastewater by iron-carbon primary battery reactor
-
摘要: 利用铁、炭间接电偶腐蚀原理,设计了铁炭原电池反应器。围绕该反应器对高盐废水总有机碳(TOC)的净化性能、操作模式(间歇、连续与半连续)以及影响因素等方面进行了研究。结果表明:铁炭原电池反应器的铁室具有良好的还原性,炭室具有良好的氧化性,高盐废水有机物的去除效果显著;反应器的半连续操作模式对高盐废水有机物去除效果最佳;半连续模式下的较佳操作条件为:固液比为15%,pH=1.7,流量为1.0 mL·min−1。在较佳操作条件下,铁室对废水TOC的去除率可达98.7%以上,而炭室对废水TOC的去除率可达99.1%以上。Abstract: An iron-carbon primary battery reactor has been designed in this study using the principle of indirect galvanic corrosion of iron and carbon. The purification performance, operation mode (batch mode, continuous mode and semi continuous mode) and influencing factors of the reactor removing total organic carbon (TOC) from high salinity wastewater were experimentally explored. The results show that for the iron-carbon primary battery reactor, its iron chamber had a good reducibility, its carbon chamber had a good oxidability, and the removal effect of organic matter in high salinity wastewater was significant; The semi continuous operation mode of the reactor had the best removal effect on organic matter in high salinity wastewater; Under the semi continuous operation mode, the optimal operating conditions were following: the solid-liquid ratio of 15%, pH=1.7, and the flow rate of 1.0 mL·min−1. Under optimal operating conditions, TOC removal rate from wastewater by the iron chamber could reach over 98.7%, while TOC removal rate from wastewater by the carbon chamber could reach over 99.1%.
-
Key words:
- wastewater /
- iron-carbon primary battery /
- reactor /
- purification /
- organic carbon
-
铁炭微电解具有操作简单、条件温和的特点而被广泛用于废水净化领域。王宇峰等[1]等利用铁碳微电解预处理高盐废水,其COD去除率约为61.2%。SUN等[2]和赖波等[3]分别利用铁碳微电解净化工业废水,废水TOC的去除率分别约为55.3%和52.6%。由于铁、炭材料处于混合状态,曝气条件下铁材料容易发生钝化、板结,而且氢氧化物会包覆在活性炭的表面,影响活性炭的导电性能,并降低活性炭比表面积,最终致使传统铁炭微电解的污水净化能力下降,同时电偶腐蚀生成的Fe2+容易被氧化为Fe3+,而Fe3+则会进一步消化Fe0,导致废水处理的铁泥量大和成本增加等问题[4-7]。
利用铁、炭之间的电势差,通过形成化学原电池来实现废水污染物的净化与资源回收的研究目前较为稀少。YING等[8]在2个极室内分别放置铁电极和炭电极,以Na2SO4为电解质,采用盐桥方式形成化学原电池,考察了铁电极和炭电极在去除2,4-二氯苯酚的作用机制,但该研究的出发点仍在于探究传统铁炭微电解中的铁电极和炭电极在污染物净化中的作用。LAI等[9]以高纯度铁板作为阳极,炭材料作为阴极,并通过质子膜将两室隔开,获得了98%的废水磷回收率。针对模拟烟气的同步脱硫、脱硝、脱碳,本课题组前期采用铁炭双池原电池反应器进行了实验研究,结果表明,铁炭原电池反应器的脱硫、脱硝、脱碳率分别高达99%、85%和约50%[10]。
相对于传统的铁碳微电解,铁炭原电池反应器的铁、炭相对独立地在各自的反应极室中,铁室中不曝气,而碳室曝气。这样不仅可以避免传统铁碳微电解的铁材料消耗量大、铁泥多的问题,同时避免了铁材料的钝化、板结以及净化效率较低等问题,而且铁室和炭室各自相对独立地净化污染物,该原电池反应器具有更多的污染物净化工艺路线选择。为此,本研究考察了铁炭原电池反应器在高盐废水有机物的净化效果,并进一步探究了操作模式(间隙、半连续和连续)以及影响因素对高盐废水有机物去除的影响规律。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料
本研究中所用废水为国内某煤化工生产企业的反渗透浓缩后的高盐废水。高盐废水的pH为1.70,硫酸根离子的质量浓度为13 100 mg·L−1,氯离子的质量浓度为79 500 mg·L−1,总溶解性固体(TDS)含量为16 8000 mg·L−1,总有机碳(TOC)含量为990 mg·L−1,耗氧有机污染物的浓度(以COD计)为5 500 mg·L−1。实验中所使用的铁粉、活性炭粉末和盐酸均为分析纯。该高盐废水中的主要无机盐分别为NaCl和Na2SO4。
1.2 实验装置
图1为铁炭原电池反应器示意图。铁室与炭室通过阴离子膜(FAA-3-20,Fumasep)分隔。铁室内放置有铁粉和铁电极(φ=4 mm×13 mm)。铁室外侧从上至下设有循环进水口、循环出水口、废水进水口和废水出水口。循环泵型号为HD-602。铁室顶部密封。炭室内放置有活性炭粉末和石墨电极(φ=6 mm×6 mm),外侧从上至下设有废水进水口和废水出水口。炭室曝气,曝气泵为DP-160S。铁电极和石墨电极均先各自采用导线连接后,再通过一根导线把铁电极和石墨电极进行连接。
1.3 实验方法
反应器净化性能评价设计了4组实验。实验A断开导线,实验B和实验C均连接导线。实验D为传统铁炭微电解。实验A、B、C和D的铁粉均为新鲜铁粉,实验A、B、D的活性炭为新鲜原料,实验C的活性炭为实验B用过的活性炭。4组实验中的铁粉、活性炭质量比均为1:1,铁粉和活性炭质量均为54 g。实验A、B、C、D均为半连续操作模式。实验A、B、C的铁室和碳室各自的进料流量均为1.0 mL·min−1,实验D的进水流量2.0 mL·min−1。实验A、B、C的铁室和炭室的初始废水体积均为300 mL,而实验D的初始废水体积为600 mL。4组实验处理的总废水体积和净化时间均相同。
操作模式的影响实验。间歇模式,铁室和炭室内分别加入600 mL废水,关闭所有进水口和出水口。半连续模式,前0.5 h内分别向铁室和炭室加入300 mL废水,随后以1.0 mL·min−1的速度向铁室和炭室内各自加入废水。间隙以及半连续模式下,铁室和碳室被离子隔膜完全隔离。连续模式,铁室和炭室的初始废水体积分别为600 mL和300 mL,调节阴离子膜的安装高度以实现铁室废水自动流入炭室。连续操作模式下,废水由铁室进水口进入,随后越过离子膜顶部流入炭室,随后从碳室下部的出水口流出。铁室进水流量与碳室出水流量均为1.0 mL·min−1。本研究中的铁粉和活性炭用量均按照初始废水质量的15%投加。
操作因素的影响实验。在半连续操作模式下分别考察固液比(铁粉或活性炭粉末与初始废水的质量百分比)、废水pH以及废水流量对有机物净化的影响。固液比影响实验:在初始pH为1.70、进水流量为1.0 mL·min−1的条件下,设置固液比分别为5%、10%和15%。废水pH的影响实验:在固液比为15%、进水流量为1.0 mL·min−1的条件下,pH分别设为1.00、1.30和1.70。进水流量的影响:在固液比为15%、pH为1.70的条件下,设置流量分别为0.3、0.6和1.0 mL·min−1。以上实验中铁粉与活性碳质量比均为1:1。本研究中实验时间均为5 h,铁室的循环泵和炭室的曝气泵均常开,曝气流量和废水循环流量固定为3.0 L·min−1。
1.4 分析方法
实验过程中每15 min记录1次铁室和炭室的氧化还原电位(oxidation-reduction potential, ORP)、pH和电流(I)。每1 h取水样进行有机物含量分析。ORP(ORP分析仪,型号SX630,Labsen)和pH(pH计,Phb-4,雷磁)均测定溶液中部位置。水样从溶液中部位置采取。万用表(DEM11,DELIXI ELECTRIC)测定电流。
废水有机物含量用TOC表示。TOC采用总有机碳分析仪(TOC-VCPH,岛津,日本)测定。TOC去除率根据式(1)进行计算。
η=(1−CtC0)×100% (1) 式中:η为TOC去除率,%;Ct和C0分别为TOC采样质量浓度和初始质量浓度,mg·L−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 反应器净化性能及原理分析
1)反应器净化性能分析。由图2(a)可见,在5 h内,实验A的炭室ORP由20.3 mV逐步升至30.2 mV,铁室ORP则由−108.2 mV下降至−136.6 mV;实验B的炭室ORP则由167.2 mV上升至188.9 mV,铁室ORP由−167.3 mV降至−188.9 mV;实验C的铁室ORP和炭室ORP与实验B的结果基本一致;实验D的ORP则基本在−100 mV附近。ORP检测结果表明,单纯铁粉环境下的ORP要比微电解下的ORP更负,而原电池反应器的铁室ORP则明显更负,说明原电池铁室的还原性比单纯的铁粉以及微电解的还原性更强;导线断开时的炭室ORP比原电池的炭室的ORP小,说明原电池的炭室的氧化性更强。由ORP可见,原电池的铁室具有更为显著的还原性,而炭室具有明显的氧化性。显然,该现象有利用铁炭原电池反应器对高盐废水中有机物的净化。图2(b)为电流变化情况。可见,实验A和D无电流,实验B和C有电流。实验B和实验C的电流数值及其变化趋势相似,初期电流约为1.26 mA,5 h后升至1.37 mA,电流在前3 h上升较为明显,随后电流趋于稳定。
图2(c)为pH的变化趋势。可见,在5 h内,实验A的铁室废水pH由1.70升至5.33,炭室废水pH基本稳定在1.70附近;实验B中铁室和炭室的pH由初期的1.70分别升高至结束时的7.23和7.74;实验C铁室和炭室的pH由初始的1.70分别升高至结束时的7.68和7.56;实验D的pH由初期的1.70升高至4.70,且其pH在前135 min变化较为明显,随后pH变化缓慢。废水净化过程中pH变化幅度从大到小的顺序为原电池反应器的铁室和炭室>单纯铁粉处理>铁炭微电解以及活性炭吸附过程。废水中pH的变化表明这4组实验在有机物净化之间的差异性。铁炭微电解过程中废水pH在前135 min升高明显,但随后变化缓慢,其原因可能与铁粉的表面钝化有关。单纯铁粉处理过程中的铁粉仅发生酸腐蚀作用,但由于没有曝气,因此,铁粉表面的钝化现象比铁炭微电解的要弱,因此,pH呈现不断上升的趋势。铁炭原电池反应器不仅避免了铁粉的钝化现象,同时也保留了酸腐蚀与间接电偶腐蚀,因此,其废水的pH最高,其最终的pH环境也有利于避免传统铁炭微电解的返色现象。
图2(d)为废水TOC去除率的5 h变化趋势。铁室和炭室中废水TOC去除率均随时间而增加。实验A的铁室的净化效果较差,最终的TOC去除率仅为23.8%;而炭室对TOC的去除效果相对较好,TOC去除率可达89.4%。实验B中的铁室对TOC去除率约为98.8%,而炭室TOC去除率约为99.2%。实验C中的铁室废水TOC去除率约为98.7%,而炭室废水TOC去除率约为99.1%。实验D中TOC去除率约为52.80%。比较4组实验中的TOC去除率可知,铁炭原电池反应器对高盐废水中有机物净化效果较好,远远优于单纯的铁粉处理效果,也明显优于传统铁炭微电解(实验D)效果,也比单纯活性炭的吸附效果要好。由此可见,铁炭原电池反应器对高盐废水有机物净化具有显著优势。比较实验B和C的炭室净化效果发现,活性炭是否更换对TOC的净化效率影响较小。该现象表明活性炭在该原电池反应器中无需更换,可以重复使用。
2)反应器净化原理分析。依据铁水体系的pH-电位相图[11]以及本课题组测定的铁电极电势[10],本研究中铁室不会出现Fe3+,只有Fe2+。本研究在实验结束后对铁室粉末固体进行分离、干燥、煅烧与称重。同时对煅烧粉末进行了X射线衍射(XRD)分析,发现粉末中只有铁粉和氧化铁(图3)。依据质量衡算,铁室对单位体积高盐废水5 h处理所消耗的铁粉质量为6.4~6.9 kg·m−3。依据废水pH以及氢氧化亚铁溶度积,理论分析铁室应该会生成氢氧化亚铁。根据文献[10],炭室电极电势可达0.80 V以上,而氧气与氢离子生成双氧水的标准电极电势约为0.68 V[12],显然,炭室会产生双氧水。
综上所述,本铁炭原电池反应器对高盐废水有机物的去除途径为:铁室主要通过电化学氧化还原、铁单质的化学氧化还原[13]以及氢氧化亚铁吸附;炭室主要通过电化学氧化还原、活性炭吸附以及双氧水化学氧化还原。
2.2 反应器操作模式对TOC去除率的影响
图4(a)和图4(b)为不同操作模式下铁室和炭室对废水TOC的去除率变化趋势。在3种模式下,铁室和炭室中废水TOC去除率均逐渐上升。总体上,无论是铁室还是炭室,半连续操作模式下高盐废水TOC去除效率最高,间歇模式的净化效果相对要差一些。间歇模式、连续模式以及半连续模式下,5 h后铁室废水TOC去除率分别为92.6%、94.0%和98.8%,炭室废水TOC去除率分别为93.5%、94.9%和99.2%。由此可见,铁炭原电池反应器的半连续操作模式为最佳模式。因此,后续实验中选择半连续操作模式,在此基础上考察固液比、废水pH以及废水流量对废水有机物净化的影响规律。
2.3 操作条件对TOC去除率的影响
1)固液比的影响。图5(a)和图5(b)为不同固液比时铁室和炭室对废水TOC去除率的变化趋势。可见,铁室和炭室对废水TOC的去除率均随时间的增加而上升。铁室以及炭室对高盐废水中有机物的去除效率随固液比增加而升高。在固液比分别为5%、10%和15%时,5 h后铁室对废水TOC去除率分别为93.2%、94.9%和98.8%,而炭室对废水TOC去除率分别为96.1%、97.8%和99.2%。显然,高固液比有利于铁室和炭室对废水中TOC的去除。其原因是固液比的增加使得相同体积的废水中的单质铁和活性炭浓度上升,与铁电极和石墨电极的接触和碰撞概率更高,电化学反应场所扩大,电子转移数量增加,废水有机物的去除速率增加。因此,增加铁炭原电池反应器的固液比有利于提升对高盐废水中TOC的去除率。
2)初始pH的影响。图6(a)和图6(b)分别为pH对铁室和炭室废水TOC的去除率的影响趋势。3种不同pH情况下,铁室和炭室中废水TOC的去除率均随时间延长而上升。总体上,前4 h时pH较低时的去除率曲线位于最上面,而pH较高时TOC去除率曲线位于下面。但5 h后,pH对废水TOC的去除率影响不大。废水pH为1.0、1.3和1.7时,5 h后铁室对废水TOC去除率分别为98.7%、98.8%和98.8%,而炭室对废水TOC的去除率分别为99.2%、99.0%和99.2%。废水pH会影响铁室和炭室的氧化还原性能和电极电位[10],最终影响废水中有机物的去除。依据废水TOC的去除效果,选择原始废水pH为佳。
3)进水流量的影响。图7(a)和图7(b)为进水流量对废水TOC的去除率的影响情况。总体上,处理的前4 h无论是铁室还是炭室,当废水流量较低时,对应的TOC去除率要高一些。然而在5 h后则是废水流量较高时废水TOC去除率要稍高一些,但差异性并不大。当流量为0.3、0.6和1.0 mL·min−1时,5 h后铁室废水TOC去除率分别为98.5%、98.6%和98.8%,炭室废水TOC去除率分别为98.9%和99.1%和99.2%。TOC去除率随流量变化的原因应该与物料流动状态、有机物负荷以及氢离子含量有关。依据废水有机物去除效率以及废水处理体积,选择1.0 mL·min−1的为最佳流量。
3. 结论
1)铁炭原电池反应器对于高盐废水有机物具有显著的净化效果,其净化效率远高于单纯的铁粉处理,明显优于传统铁炭微电解,也优于活性炭吸附方法。
2)铁室和炭室主要通过电化学氧化还原、吸附与化学氧化还原作用对高盐废水有机物进行去除。该反应器主要消耗铁粉,而活性炭可重复使用。
3)在固液比为15%、pH为1.7、流量1.0 mL·mim−1的较佳操作条件下,铁炭原电池反应器的铁室和炭室的最佳操作方式为半连续模式。
4)在固液比为15%、pH为1.7、流量1.0 mL·mim−1操作条件下,铁炭原电池反应器的铁室对高盐废水TOC的去除率可达98.7%以上,而炭室对高盐废水TOC的去除率可达99.1%以上。
-
-
[1] 王宇峰, 俞言文, 杨尚源, 等. 铁碳微电解耦合芬顿高级氧化技术对高盐废水COD去除性能的影响研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2017, 43(6): 65-67. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2017.06.015 [2] SUN Y, GUO A, GE R, et al. Pre-treatment of centrifugal mother liquid in polyvinyl chloride production by iron-carbon microelectrolysis technique[J]. Enuivonmental Science and Technology. 2014, 37(4): 139-144. [3] 赖波, 秦红科, 周岳溪 等. 铁碳微电解预处理ABS凝聚干燥工段废水[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(4): 1055-1059. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.04.031 [4] ZHU Q S, GUO S H, GUO C M, et al. Stability of Fe–C micro-electrolysis and biological process in treating ultra-high concentration organic wastewater[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2014, 255: 535-540. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.138 [5] WANG C W, LEI Z Y, LI J, et al. Operation mode of iron-carbon microelectrolysis pretreating high salinity pickle wastewater[J]. China Water & Wastewater. 2018, 34(15): 95-99. [6] ZHAO D M, SHI H X, XU G L, et al. Study on the pretreatment of p-fluoronitrobenzene wastewater by microelectrolysis[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry. 2002, 22(1): 15-18. [7] ZHANG W, CHEN L, CHEN H, et al. The effect of Fe0/Fe2+/Fe3+ on nitrobenzene degradation in the anaerobic sludge[J]. Journal of Hazard Materials. 2007, 143(1/2): 57-64. [8] YING D, PENG J, LI K, et al. Dual-cell reduction and group effect in an internal microelectrolysis reactor[J]. Electrochimica Acta. 2013, 89: 861-867. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.10.158 [9] LAI L L, LIU C, LIU M Y, et al. Condition optimization of iron-air fuel cell to treat phosphate-containing wastewater regarding sustainable development[J]. Chemosphere. 2023, 313: 137507. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137507 [10] 鲁浩. 铁碳双池法再生NO络合吸收液的规律研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2021. [11] 谢学军, 王浩, 邹品果, 等. 铁-水体系电位-pH图与氧化性水工况的腐蚀控制[J] 华北电力技术. 2011, 13 (5): 23-25. [12] 李子轩, 王继全. 铁碳微电解技术及其在处理工业废水中的研究进展[J] 建材世界. 2020, 41 (4): 100-102. [13] PRIYADARSHINI A, KUMAR S P, GHOSAL A, et al. Stabilization of zero-valent iron for wastewater treatment: Challenges and future prospective[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings. 2022, 67: 1073-1079. -






 下载:
下载: