-
作为典型的非点源污染,城市地表灰尘可通过重力等自身因素以及各种人为活动累积到地面或建筑物表面中,目前已经成为城市地表分布最为广泛的污染物载体之一[1].大气积尘作为地表灰尘的一种,其累积来源十分复杂,例如地表土壤扬尘可通过风力的水平迁移和自身重力导致的二次沉降使得积尘在水平与垂直方向上出现空间累积差异,交通排放的尾气颗粒物也可以在风力等作用下造成积尘的累积,王萧等[2]对北京市大气灰尘研究发现其来源也受到周围沙地的影响.
随着中国城市化进程加快,经济快速发展,各种能源消耗的增加所带来的大气污染会对城市和人类健康产生一系列不利影响.近年来,对于大气积尘重金属的研究主要为分析其污染特征、健康风险评价,来源解析等,主要的研究方法有地累积指数法[3]、富集因子法[4]、潜在生态健康评价法[5]、主成分分析法[6]、PMF[7]等方法.Wang等[8]通过富集因子法和因子分析法对2008—2009年北京市地面降尘来源研究发现,通过风蚀作用而使农田产生的土壤粉尘是其主要来源,建筑扬尘是第二贡献者,汽车尾气次之;刘玥等[9]用PMF法对地表灰尘的来源进行分析发现土壤、燃煤和交通是其主要污染源.稀土元素(REE)的化学性质较为稳定,在风化、搬运等作用中不易受到影响,可以作为示踪元素来研究大气降尘来源[10],目前对于稀土元素的研究多为其浓度、地球化学特征[11]和来源解析[12]等,Wang等[13]对厦门市PM2.5中稀土元素的分布及来源研究发现,稀土元素并非以当地天然土壤为主,并且城市PM2.5中的稀土元素主要来自汽油车和柴油车尾气,郊区PM2.5中的稀土元素主要来自汽油车尾气.
近年来,对于大气积尘中微量元素的研究大多数以近地面水平方向为主,在其垂直高度上的研究较少.马志强[14]对大气垂直污染物的分布研究中发现,人类日常的生活生产活动早已达到了100 m以上,导致在垂直高度上污染物进行累积.本文研究了北京市近地面不同高度上积尘的微量金属元素包括11种重金属和14种稀土元素污染水平和来源解析,揭示其在垂直高度微量金属变化特征,为研究积尘在垂直高度上的污染防治提供科学依据.
-
如图1所示,在北京市海淀区西三环首都师范大学校本部内(39°57′N,116°17′E)共设置了十四个点位,且点位主要位于西三环主路附近,基本可以代表北京城区基本状况.为避免降雨影响,选择具有窗沿的平台作为采样区域,最大程度模拟积尘的自然累积状态,于2021年9—11月进行采样,每个采样点采样时间为(30±3)d,共采集3次,并将采样点分为低、中、高的3个范围层次进行采集,采样点个数分别为5、4、5个,其平均高度分别6、17、41 m.在采样点布设1 m
× 1 m木框,并用PO膜进行木框底部覆盖,PO膜防静电、不粘尘,使积尘自然降落于采样框内,并可以自然迁移,木框用混凝土砖压实,防止大风及恶劣天气对采样收集框的破坏,利用塑料刷将PO膜区域内所有积尘进行采集到信封中,最后共采集到42份有效积尘样品. -
积尘样品采集完成后,将收集到的样品使用塑料镊子将其中的植物组织、石头碎屑、虫子尸体等杂物取出,将较大颗粒杂质于过滤筛中过滤,过筛后的样品放置在烘箱(105 °C)内烘干2 h,烘干结束后放入干燥器内储存.本实验采用ICP-MS(8800)对样品进行分析,分析前样品加入6 mL HNO3、2 mL H2O2、0.25 mL HF的酸体系进行微波消解预处理,将预处理的样品定容至100 mL容量瓶中,静置24 h后进行上机分析.在前处理过程中,每一批消解做试剂空白和质控样品(GSS-3),并保证各个无机元素的回收率在80%—120%之间以及测试金属元素浓度低于仪器检出限.
-
目前,重金属的污染评价方法有内梅罗综合污染指数法、地积累指数法、基于GIS的地统计学评价法、单因子质量指数法等[15],其中内梅罗综合污染指数法没有考虑土壤中各种污染物对作物毒害的差别,只能反映污染的程度而难于反映污染的质变特征;单因子质量指数法只能对单元素进行污染评价,不能综合地反映污染程度;而地积累指数法不仅考虑了环境地球化学背景值,人为污染因素,还可以反应出重金属的自然分布特征,给出很直观的重金属污染级别,近年来被广泛的应用于大气及土壤重金属污染评价,本文选用地累积指数法对其进行重金属污染评价,其计算公式如下[16]:
其中,Cn是元素在积尘中的浓度;Bn是该元素的地球化学背景值;k为考虑各地岩石差异可能会引起背景值的变动而取的系数(一般取值为1.5),用来表征沉积特征、岩石地质及其他影响.
跟据Igeo分级从而确定重金属污染程度:Igeo<0,0级,无污染;0≤Igeo<1,1级,轻度污染;1≤Igeo<2,2级,中度污染;2≤Igeo<3,3级,中度-严重污染;3≤Igeo<4,4级,严重污染;4≤Igeo<5,5级,严重-极度污染;Igeo≥5,6级,极度污染.
-
富集因子法于1974年Zoller首次提出,是评价重金属污染程度和来源的重要指标,该方法选择具有一定条件的元素作为参考标准,对测试样品中元素进行标准化处理[17].参比元素的选择要求其性质较稳定,具有较强的抗风化能力和较小的分布离散性,李丽娟等[18]将Ti,Al,Fe元素作为参考元素对比发现,三者均可以用作参比元素来计算其富集程度,本文选用Fe元素作为参比元素对其进行计算,计算公式如下[17]:
其中,Cn、Cr分别为测定金属元素和参比元素Fe的浓度;CN、CR分别为该元素和参比元素Fe的地球化学背景值.若EF<1,认为元素相对于地壳未富集,主要来源为自然源,由土壤岩石风化造成;若EF在1—10范围内,认为元素被轻微富集,受到自然源和人为共同作用;若EF>10,则认为元素被富集,主要由人为活动所影响,来源为人为源.
-
对积尘重金属数据用Excle 2019和Spss 26版本进行处理和统计分析,采用GraphPad Prism 9.0版本进行绘图.
-
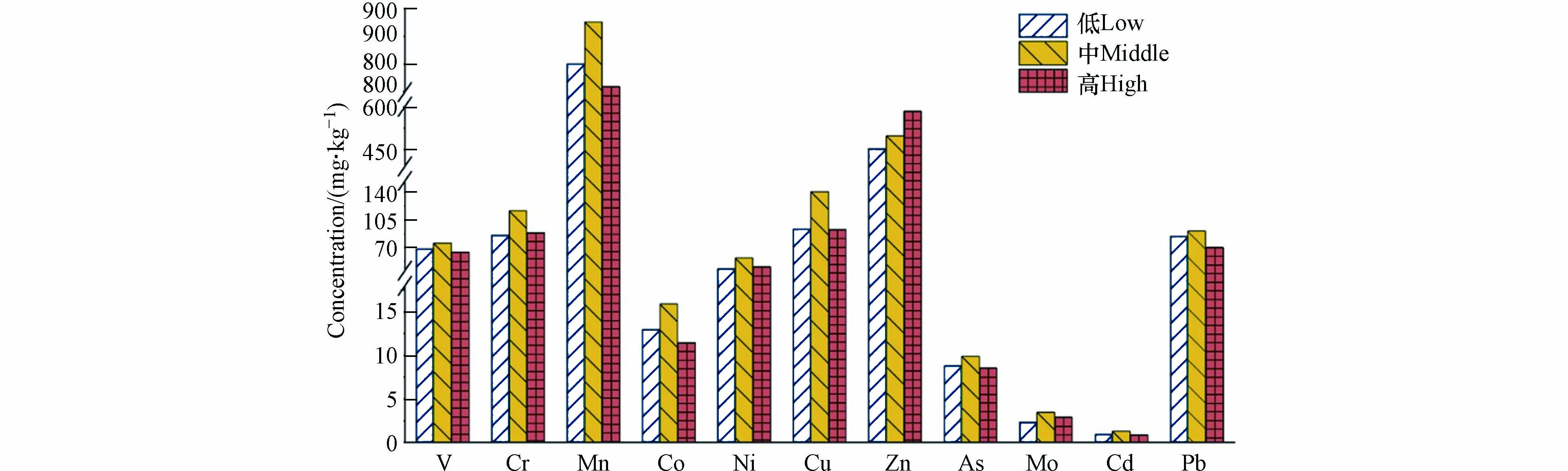
图2显示,在所有高度中积尘11种重金属平均浓度由高到低顺序为Mn>Zn>Cu>Cr>Pb>V>Ni>As>Co>Mo>Cd,其浓度分别为808.5、496.05、105.18、93.95、82.19、68.74、46.43、13.29、8.97、2.87、0.98 mg·kg−1,与中国土壤元素背景值(不受人为活动影响土壤元素浓度)Mn>V>Cr>Zn>Ni>Pb>Cu>Co>As>Mo>Cd相比,积尘中Zn、V、Cd、As元素受人为影响较大.
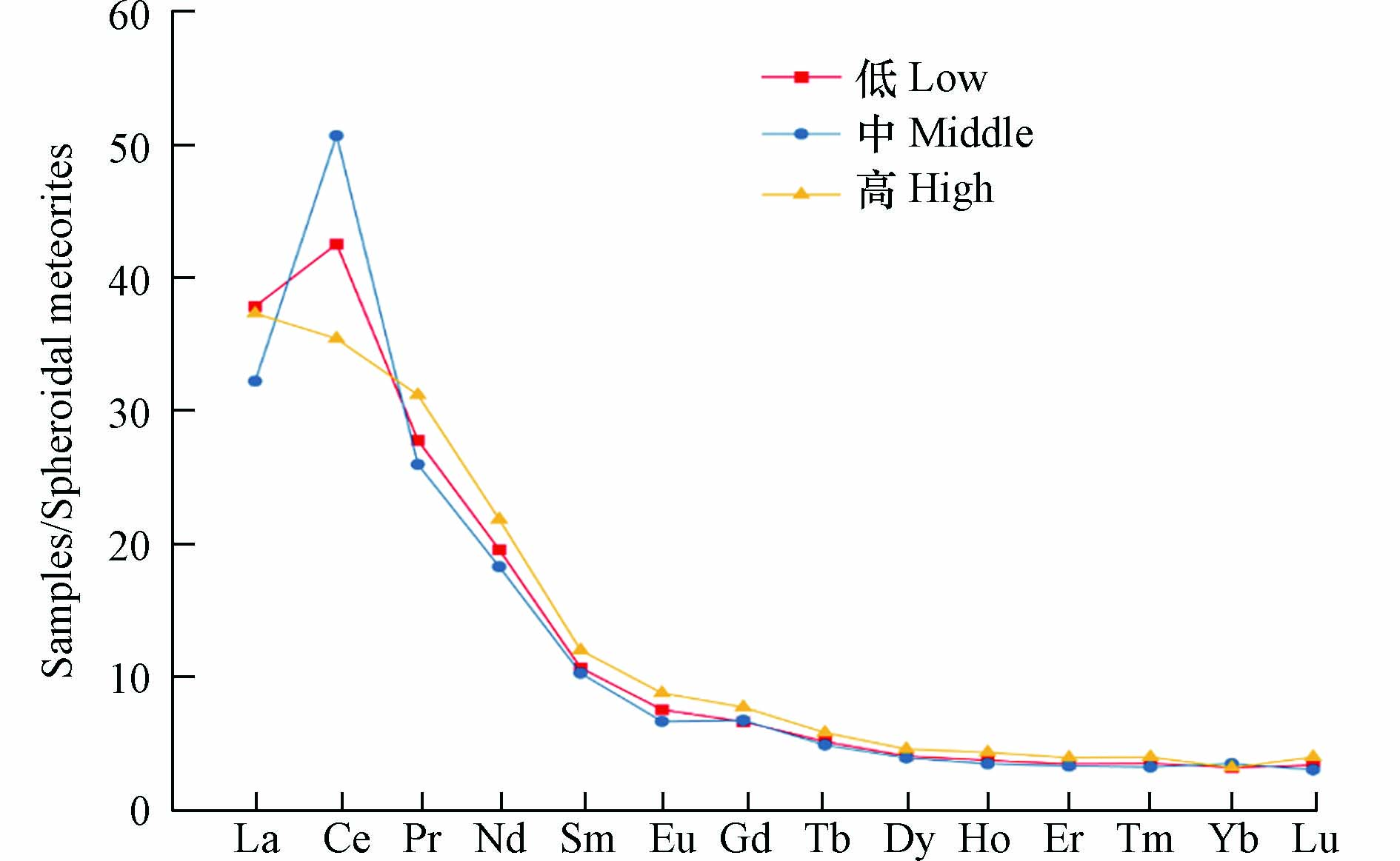
在垂直高度中,积尘中11种重金属从低层至中层均呈现随高度升高浓度增加的趋势,V、Mn、Zn、As、Pb、Co元素变化比例较小,增长范围在7.40%—22.53%之间,其余元素变化比例较大,增长范围在32.81%—52.21%之间,一方面,秋季气旋活动频繁,地面尘埃等磁性矿物易在大风天被扬起,一部分颗粒物被带入至低空中,产生近地面吹扬模式[19],本研究积尘量从低层至高层分别为0.25 t·(km2·30 d)−1、0.39 t·(km2·30 d)−1、0.16 t·(km2·30 d)−1表现为从低层至高层先升高后减少的趋势,这与11种重金属浓度从低层至中层趋势一致;另一方面,研究发现受高空气流的影响,大气颗粒物会随大气环流的输送进行扩散沉降[20],进而使得中层元素重金属浓度受到高层气流影响而升高;对比中层和高层元素重金属浓度发现,Zn元素呈现出随高度增加而浓度增加的趋势,张舒婷等[21]对贵阳市不同高度重金属浓度进行研究发现,Zn元素浓度整体随高度增加浓度减少,但仍在中层区域出现高值,与本研究Zn元素浓度趋势相似.V、Mn、Ni、Cu、Pb等重金属元素从中层至高层浓度呈递减趋势,分析其原因为,当风受到建筑物的阻尼作用时,会在动力学上产生衰减反应,有研究表明发现,在建筑物的低层高度上,风速衰减明显[22],当土壤尘埃等磁性矿物通过近地面吹扬模式使得颗粒物聚集后,处于高层的颗粒物易受到风的影响,高度越高,所受到的风速越快,一些细粒级颗粒物易受到风的影响而进行扩散,谢华林等[23]对重金属元素在不同粒径上的形态分布发现,V、Cu、Pb等元素主要富集在<2 μm的细颗粒中,属于亲气元素,并且积尘采集方式通常情况下有两种,一种为降尘缸干湿采集法,另一种为将积尘收集在露天采集框中进行采集,本研究采用第二种收集方式进行样品采集,受到风力条件影响较大,从而易造成在细颗粒物中富集的重金属元素浓度降低的现象;对比低层和高层二者重金属浓度发现,Cr、Ni、Zn、Mo高层浓度较低层浓度有所升高,V、Co、Cu、As、Mn、Pb元素高层浓度较低层浓度有所下降,但11种元素整体变化范围不大.
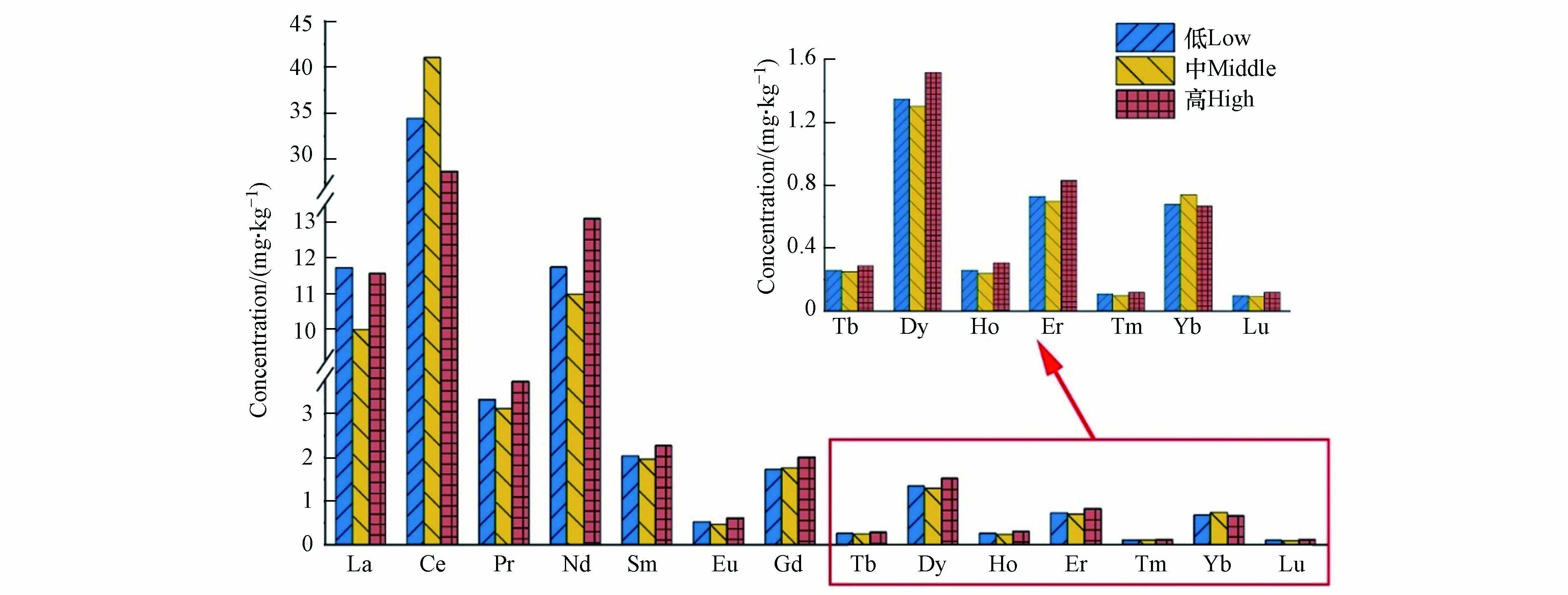
图3显示为不同高度稀土元素浓度分布,14种元素平均含量从高到低为Ce>Dy>Er>Eu>Gd>Ho>La>Lu>Nd>Pr>Sm>Tb>Tm>Yb,均未超出土壤环境背景值,表明降尘中稀土元素相对于土壤未被污染,且14种元素其原子序数为偶数的元素明显高于两侧原子序数为奇数的元素,符合奥多-哈尔金斯定律,与土壤稀土元素分布特征一致[24],表明积尘中稀土元素的来源可能为土壤源.除Ce、Gd、Yb外,其余元素都在中层出现低值,与重金属在中层浓度高的现象呈现相反规律,分析可能原因为中层采样平均高度与北京市西三环主路高度接近,交通活动所产生的重金属会导致中层浓度升高,而稀土元素受交通源影响较小所致.从低层至高层,14种元素整体呈现出随高度升高浓度先减小后增加的趋势,这可以用“爬墙效应”[25]来解释,即地表污染物会在气流的作用下,使得污染物浓度随着高度增加而下降,但超过其一半高度时浓度上升,进一步表明其主要受地表土壤的影响.
-
表1和表2分别为不同高度积尘重金属地累积指数及其分级,从整体看,积尘中11种重金属污染程度次序为Cd>Zn>Cu>Pb>Ni>Cr>Ni>Mn>V>Co>Mo;其中Cd在低层与中层污染最为严重,污染程度为严重污染,在高层污染程度略有降低为中度-严重污染;Cu、Zn、Pb污染等级为2级,为中度污染,虽然3种元素在不同高度上展示出相同的污染等级,但从地累积指数数值来看,Cu、Cd在中层污染数值最大分别为1.93、3.46,Zn元素在高层污染数值最大为4.59,表明Zn元素除受到地表交通等影响外,可能也与空中灰尘带的沉降和扩散有关[20];Ni、Cr在低层中污染等级为均为0级,为无污染状态,但在中层污染等级达到最高为轻度污染;As、Mn、Mo、Co、V污染程度均为无污染,但对于低层与高层地累积指数来看,中层污染指数相对较高.
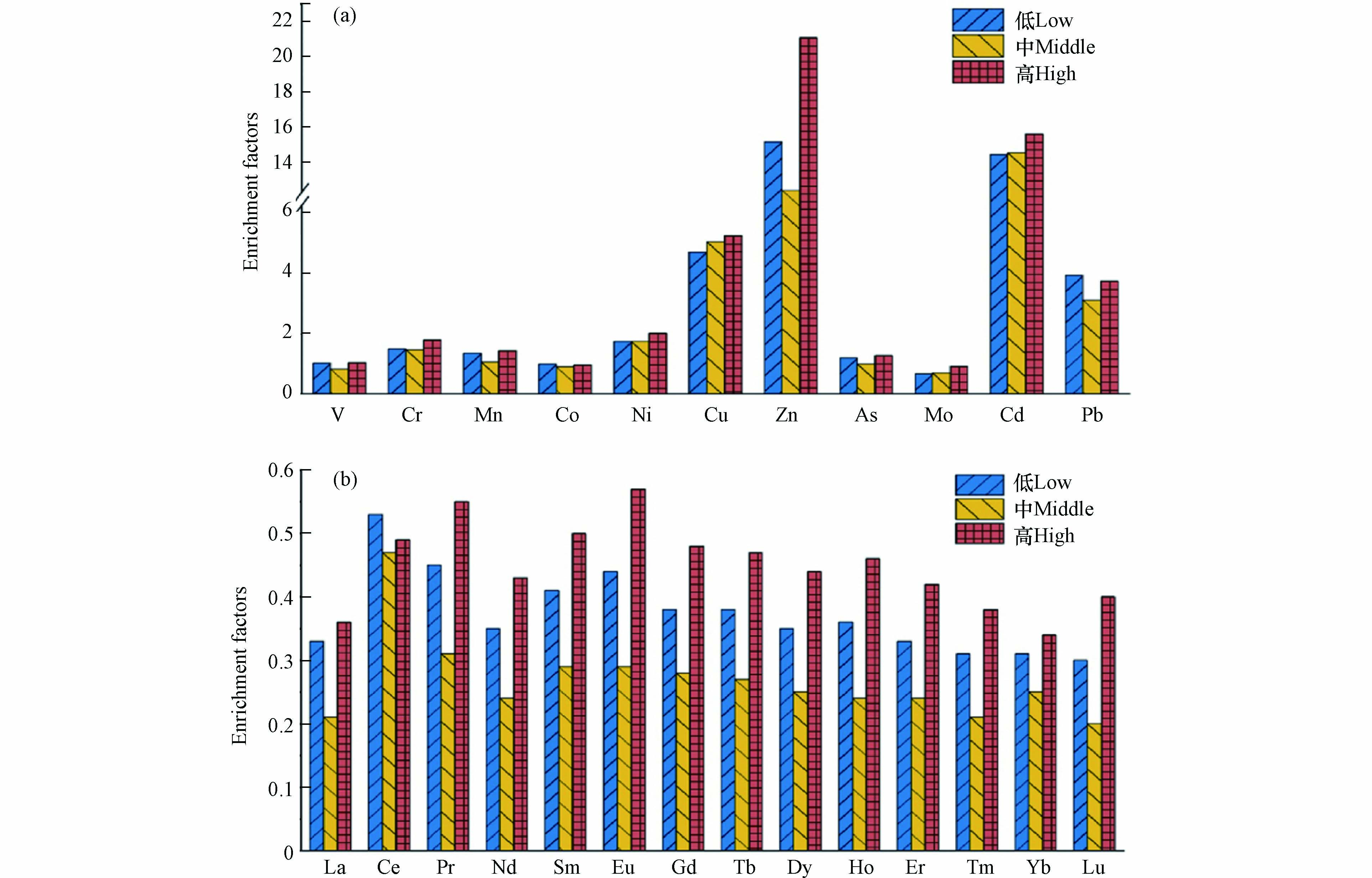
图4a为重金属富集因子显示结果,不同高度下11种元素整体富集程度在中层出现低值;其中富集因子接近于1的元素为V、Cr、Mn、Co、As、Mo、Ni、As、Mo,说明其来源主要为自然源,受其周边土壤影响;富集因子为1-10的元素为Pb、Cu,受到轻微富集,说明其除去受到周边土壤影响外,还受到人为因素的影响;富集因子均大于10的元素为Zn、Cd,表明二者均被富集,受到明显的人为因素影响. 图4b为稀土元素富集因子结果,从图中可以看出14种稀土元素富集因子都小于1,表明其未受到人为因素的影响,主要来源为自然源,但在不同高度下,其高层富集因子明显高于中层,这可能与周边区域传输影响有关.由富集因子结果可知,稀土元素主要来源为自然源,部分重金属元素主要受人为因素影响.
-
稀土元素按地球化学理论可分为15种镧系元素以及Y和Sc两种元素,其中La-Eu元素为轻稀土(LREE),Gd-Lu为重稀土(HREE),表3和图5分别为不同高度积尘稀土元素特征参数和配分模式结果,其中特征参数结果显示从低层至高层LREE/HREE值分别为4.39、4.47、3.89,均低于北京市土壤稀土元素LREE/HREE背景值9.91,表明北京市积尘中轻稀土元素相对土壤富集程度低,且在不同高度下高层轻稀土富集程度低于中层与低层;不同高度下(La/Yb)N值变化范围为9.17—11.75之间,表明稀土元素内部分馏明显,轻稀土元素较为富集,中层相比于高层与低层分馏程度较低;(La/Sm)N与(Gd/Yb)N在不同高度下变化范围分别为3.10—3.54,1.92—2.42,表明其轻稀土内部分馏程度较重稀土分馏明显.分布模式结果显示,不同高度下其配分模式基本相似,具有一致性,整体表现为右倾,LREE与HREE分馏明显,表现为Eu负异常,并且其配分模式图与北方黄土和黄河沉积物配分图相似,表明北京市积尘来源受到其影响.
-
为进一步了解其来源,对重金属元素进行主成分分析,表4为经过最大公差旋转的主成分分析结果,三个主成分因子共解释了原始变量的78.2%,第一主成分解释了原始变量的34.3%,主要由V、Co、Ni、Zn、As、Pb构成,各元素因子负荷分别为0.566、0.804、0.871、0.761、0.832、0.606.结合富集因子结果可知,V、Co、Ni、As未被富集,主要来源为自然源;Xiong等[26]对北京城区冬季降尘来源进行了分析,表明北京市微量元素主要来源为地壳来源,包括道路的再悬浮粉尘等,本研究与其研究结果一致;Pb、Zn主要来源于轮胎、汽车刹车、润滑油中[27],这些活动可以将重金属重新释放到空气中从而造成道路灰尘的二次吸附,王利军[28]对宝鸡市街尘重金属研究发现,Zn元素浓度远远超出当地环境背景值,尤其出现在重交通区中;除此以外,北京市从1997年开始禁止使用含铅汽油,2000年起全国禁止生产含铅汽油,但Pb作为一种持久性的元素,难以在短时间内消失,Gioia等[29]研究显示,虽然巴西早已禁止含铅汽油的使用,但在环境中检测到的Pb元素浓度依然较高,Pan等[30]对西安的一项研究中发现尽管含铅汽油已经停止使用,但道路灰尘中的Pb元素仍为125.0 mg·kg−1.
因此本研究认为第一主成分为以V、Co、Ni组成的地壳源和以Zn、Pb元素组成的交通源混合来源.第二主成分解释了原始变量的31.3%,主要由Mn、Cu、Mo组成,各元素因子负荷为0.842、0.863、0.924,其中Cu常在油泵材料中使用,Amato等[31]指出井盖的腐蚀、发动机排放和刹车片的使用是Cu产生的来源之一.另外Cu、Mn作为工业活动的代表元素,建筑材料、电线等也是其产生来源之一[27],本研究采样点位于首都师范大学内,临近西三环主要交通道路,附近无明显的工业活动,因此本研究认为第二主成分为交通源;第三主成分解释了原始变量的12.6%,主要元素为Cd,因子负荷为0.783,Cd作为燃料燃烧的产物,存在于汽车尾气,煤炭燃烧和工业活动中,息朝庄等[32]对贵州省大气降尘中Cd研究发现,其污染来自于地壳源、工业三废、燃煤的综合影响,刘进等[33]研究表明,2015—2019年大气降尘已经成为华北农田土壤Cd的主要输入源,贡献占总输入源的1/2,是未来需要关注的重点途径,因此本研究认为第三主成分为燃烧源.
-
1)从低层至中层,北京城区积尘中11种重金属元素浓度呈现出随高度增加浓度增大的现象;高层中Zn元素浓度高于中层,其余元素呈现相反趋势;Cr、Ni、Zn、Mo高层浓度较低层浓度有所升高,V、Mn、Co、Cu、As、Mn、Pb元素高层浓度较低层浓度有所下降,但11种元素整体变化范围差距不大. 14种稀土元素整体上在中层出现低值,在低层与高层浓度相差不大.
2)不同高度下北京城区积尘中14种稀土元素浓度均未超出环境背景值,11种重金属在不同高度中整体处于同一等级污染水平,其中Cd为中度-严重污染,Cu、Zn、Pb为中度污染, As、Mn、Mo、Co、V为无污染,11中重金属除Zn外,其余元素均在中层表现出最高的污染累积指数.
3)北京城区积尘中轻稀土元素相对土壤富集程度较低,不同高度下配分模式基本一致,表现为轻稀土富集的Eu负异常地球化学元素特征,与北方黄土和黄河沉积物配分图相似,表明北京市积尘来源受到其影响.
4)通过富集因子显示V、Cr、Mn等重金属和14种稀土元素主要来源为自然源,Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd主要受人为因素的影响;通过主成分分析结果显示,北京城区秋季积尘中重金属共有3个主要贡献源,分别为地壳源、交通源和燃烧源.
北京城区秋季不同高度积尘中微量元素污染特征及源解析
Characteristics and source analysis of trace element pollution in dust accumulated at different heights in Beijing
-
摘要: 为研究北京市城区大气积尘中微量元素在不同高度下的污染特征及来源,于2021年9—11月采集了积尘样品,用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪ICP-MS(8800)分析了11种重金属元素(Mn、Zn、Cu、Cr、Pb、V、Ni、As、Co、Mo、Cd)和14种稀土元素,采用地累积指数法、富集因子法、配分模式图和主成分分析法对其进行污染特征和来源分析.结果表明,11种重金属元素的浓度从低层至中层逐渐升高,低层与高层浓度相差不大,Zn元素浓度从中层至高层呈上升趋势,在高层出现最大值584.3 mg·kg−1,而V、Mn、Ni、Cu等元素浓度从中层至高层降低,14种稀土元素浓度均在中层最低,其浓度在所有高度下均未超出环境背景值.地累积指数结果表明, Cd元素在中层污染最为严重,污染等级为4级,Zn元素在高层污染最为严重,污染等级为2级,而As、Mn、Mo、Co、V污染程度均为无污染,但相对于低层与高层,中层污染指数较高.通过富集因子、配分模式图和主成分分析结果显示,14种稀土元素来源为自然源,11种重金属元素来源为地壳源、交通源和燃烧源.Abstract: To study the pollution characteristics and sources of trace elements in Beijing's atmospheric dust at different heights, dust samples were collected from November to December, 2021, and the contents of 11 heavy metals (Mn, Zn, Cu, Cr, Pb, V, Ni, As, Co, Mo, Cd) and 14 rare earth elements were analyzed by ICP-MS(8800). The results show that the contents of 11 heavy metal elements gradually increase from the lower layer to the middle layer, and the contents of the lower layer and the upper layer are not much different, while the maximum value of Zn element is 584.3 mg·kg−1 in the upper layer, and the concentrations of 14 rare earth elements are all in the middle layer and the bottom region, and their contents do not exceed the environmental background values at all heights. The results of the ground accumulation index show that Cd elements are the most polluted in the middle layer with pollution level 4, Zn elements are the most polluted in the upper layer with pollution level 2, while As, Mn, Mo, Co, V pollution levels are non-polluted, but the pollution index is higher in the middle layer compared to the lower and upper layers. The results of enrichment factors and principal component analysis show that 14 rare earth elements are from crustal sources and 11 heavy metals are from crustal, traffic and combustion sources.
-
Key words:
- dust accumulation /
- different heights /
- heavy metals /
- rare earth elements /
- pollution characteristics /
- sources
-
邻苯二甲酸酯(phthalate esters,PAEs)是邻苯二甲酸形成的酯的统称,近年来因其在塑料、建筑材料、个人护理品、食品包装和医疗产品中的广泛使用而受到越来越多的关注[1]. 由于PAEs与聚合物之间没有化学键合,因此很容易从产品中释放出来. 目前PAEs已经在多种环境基质中检测到,包括空气[2]、水[3]、土壤[4]和生物群体[5]. 作为典型的内分泌干扰物,PAEs具有致畸、致癌和致突变“三致”效应[6],长期接触会带来许多不良后果. 由于PAEs的广泛应用、大规模生产和对人类健康的不利影响,美国环境保护署(USEPA)已将邻苯二甲酸二甲酯(DMP)、邻苯二甲酸二乙酯(DEP)、邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBP)、邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯(BBP)、邻苯二甲酸(2-乙基己基)(DEHP)和邻苯二甲酸二辛酯(DnOP)列为6种“优先控制的有毒污染物”,随后我国环境保护局也将DMP、DBP和DnOP列入重点控制污染物黑名单[7].
土壤是重要的环境介质,也是污染物的主要储存库[8]. 近年来,PAEs在土壤中的污染越来越突出,在我国个别地区甚至达到mg·kg−1级别[9],通过食物链对人类健康构成风险,这使它们成为土壤中最受关注的有机污染物之一. 农用薄膜(棚膜和地膜)是我国农业土壤中PAEs污染的重要来源,随着设施农业规模的不断扩大,我国己成为世界上最大的农膜覆盖区[10]. 土壤中的PAEs还与农业实践活动有关,通过各种方式进入土壤环境,例如有机肥料,地表径流,废水灌溉和大气沉降等[11].
目前,国内外很多学者已经开始关注PAEs在土壤中的污染,这些研究涵盖了不同的耕地,包括塑料温室[8, 12]、菜地[13 − 14]、果园[13]、和农田作物[15]等等,然而大多数只分析了一种类型的土地. 农业实践类型受人类活动的影响,并决定了区域环境的植被覆盖和耕作方式,因此PAEs的含量可能与不同的农业类型有关. 事实上,农药、有机肥以及农膜的施用,土壤深度,土壤理化性质及周边污染源的影响均有可能导致不同类型土壤中PAEs的差异[13]. 目前少有关于农业土壤与PAEs污染综合分析的研究.
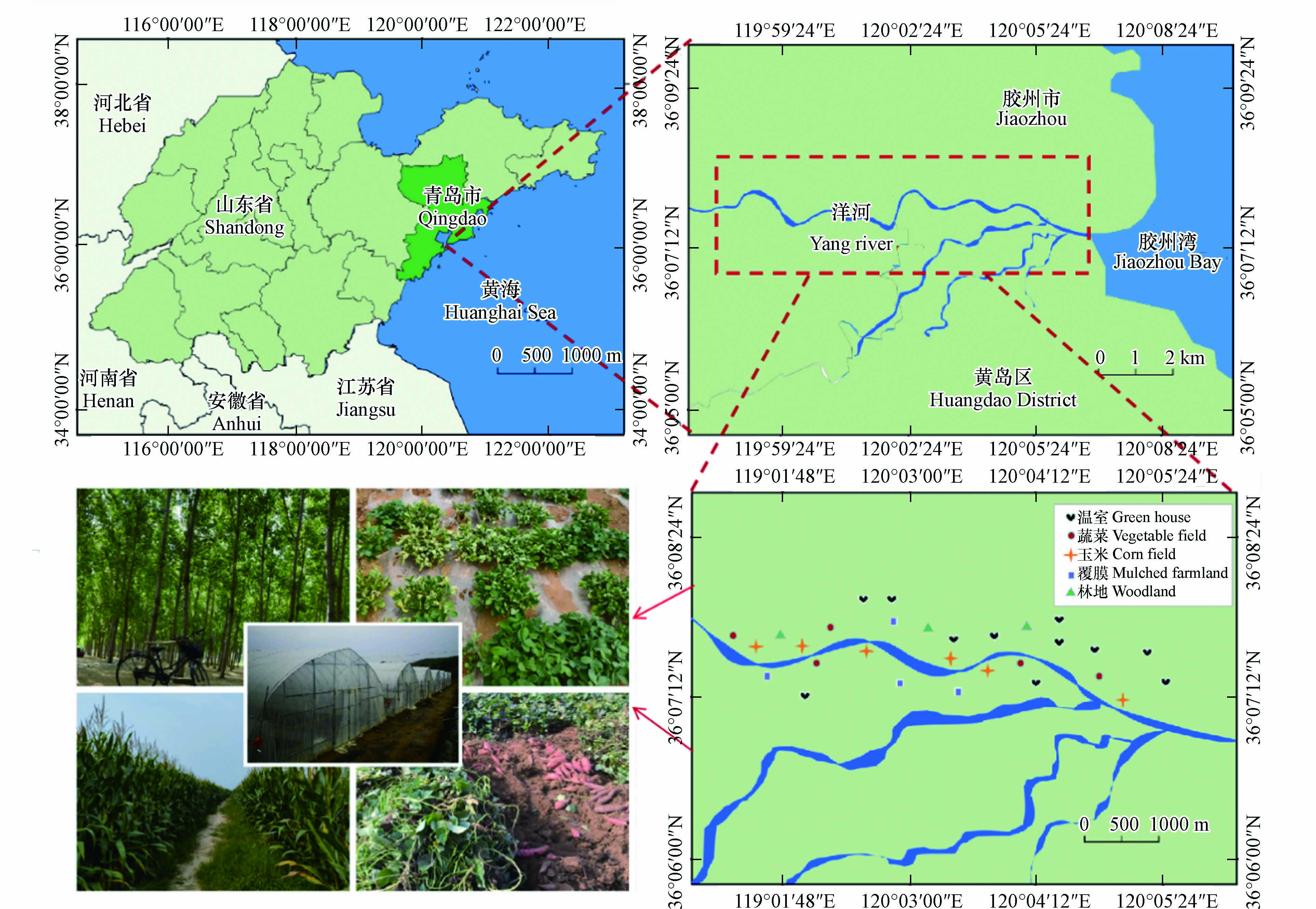
洋河位于中国北方的胶东半岛,发源于青岛市黄岛区北部,于胶州湾入海. 地处北温带季风区域,降雨主要发生在夏季. 河流两岸主要是村庄、农业区和产业园,农业基础雄厚,粮食生产和经济作物的种植占据主要地位. 同时也有其自身的特点,例如不同的作物种植和不同的覆盖类型. 农田土壤附近多有农药瓶、化肥包装袋、垃圾堆放和农膜残留等现象,“白色污染”不容小觑. 所有这些因素都可能对土壤中PAEs的残留产生影响,目前尚未有关于该地区土壤中PAEs污染的相关报道. 因此,本论文研究了洋河农业区不同实践类型的农业土壤中PAEs的分布模式以及土壤理化性质与PAEs的关系,进一步分析潜在的污染源,为建立农业生态系统中PAEs控制措施提供支持.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 样品采集
2021年9月,根据洋河周边的农业生产布局和种植类型(图1),共收集56份具有代表性的土壤样本,包括温室土地(n=22)、覆膜耕地(n=8)、玉米地(n=12)、蔬菜地(n=8)和林地(n=6).遵循五点采样法,每3份子样品形成1个复合样品,钢尺精确测量距离和深度,使用不锈钢铲采集土壤样品(0—10 cm、10—20 cm). 取样时去除枯枝落叶、大块石子以及破碎的塑料薄膜,远离植物根部和刚刚施肥的区域. 样品储存在预先清洗的棕色玻璃瓶中,于−50 ℃冷冻干燥,研磨过100目筛,储存在−4 ℃冰箱中待分析.
1.2 仪器与试剂
仪器:气质联用仪(日本岛津,GC-MS 2010Plus);冷冻干燥机(北京亚星,LGJ-10N);超声振荡仪(上海科号,SK5200H);台式离心机(奥豪斯,FC576);涡旋振荡器(上海精业,XW-80A);旋转蒸发仪(BUCHI,R-10);氮吹仪(Organomation Associates,N-EVAP111).
试剂:6种PAEs混合标准溶液(DMP、DEP、DBP、BBP、DEHP和DnOP)和内标物(磷酸三丁酯-d27、苯甲酸苄酯)浓度均为1000 µg·mL−1,购自美国AccuStandard公司;正己烷、丙酮和二氯甲烷均为色谱级,购自天津科密欧公司. 柱层析硅胶(100—200 目,青岛海洋化工厂)和氧化铝(100—200目,上海国药试剂)使用前分别在180 ℃和400 ℃活化4 h,冷却后加入5%去离子水;无水硫酸钠(分析纯,上海国药试剂)使用前在马弗炉450 ℃灼烧4 h.
1.3 样品处理
参考之前的文献方法[16],准确称取10.0 g样品置于玻璃离心管中,添加已知量的磷酸三丁酯-d27,加入20 mL正己烷-丙酮(1:1, V/V)涡旋混合,经两次超声(35 ℃,15 min)和离心(3000 r·min−1,10 min),合并上清液. 上清液经旋蒸浓缩后,转移至从下到上填充有中性氧化铝-硅胶-无水硫酸钠(高度分别为6 cm、12 cm和1 cm)的玻璃层析柱中,依次用20 mL正己烷、20 mL二氯甲烷-丙酮混合液(1:1, V/V)和20 mL乙酸乙酯洗脱. 氮气条件下吹干,加入已知量的苯甲酸苄酯,正己烷定容到200 µL.
同时分析了土壤样品的理化性质:土壤pH通过多参数水质检测仪(美国HACH)在土壤-水(1:2.5, W/V)提取中测量;元素分析仪(德国Elementar)用来测定土壤中的总有机碳(TOC)和总氮(TN).
1.4 GC-MS测定条件
色谱条件:使用GC-MS 2010Plus(日本岛津)和DB-5MS石英毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 µm)进行色谱分离. 载气:高纯氮气;柱流量:1 mL·min−1;进样体积:1 µL,不分流进样;进样口和柱箱温度分别为250 ℃和50 ℃. 升温程序:初温50 °C,保持1 min,以15 °C·min−1的速率升温至200 °C,保持2 min;以8 ℃·min−1的速率升温至300 °C,保持8 min.
质谱条件:选择性离子监测为SCAN模式,离子源和传输线温度分别为230 ℃和280 ℃.
1.5 质量保证与控制
实验过程中不使用任何塑料制品,所有非计量玻璃器皿经纯水洗涤和有机溶剂淋洗后经马弗炉450 ℃灼烧4 h. 分析过程中,每12个样品进行一组程序空白、基质加标和样品平行样. 在程序空白中检测到少量DBP、DEHP,实际检测样品均经过空白校正. 将回收内标添加到所有样品中,回收率为81.21%±5.38%. 6种目标单体的回收率范围为78.32%—118.63%,相对标准偏差<10%. 仪器检出限定义为信噪比的3倍,范围为0.61—2.36 ng·L−1. 采用0.05、0.1、0.2、0.5、1、5、10、20 ng·L−1的6种PAEs绘制标曲,各物质标曲R2=0.995—0.999,满足要求.
1.6 健康风险评价
洋河农业区内居民的非致癌和致癌风险根据USPEA推荐的模型进行评估. DMP、DEP、DBP、和DnOP被认为是与人体健康相关的非致癌物质,DEHP和BBP是致癌物质. 当地居民主要通过饮食途径(食物摄入)和非饮食途径(土壤摄入、皮肤接触、呼吸)摄入PAEs. 公式如下:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (3) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (4) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (5) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (6) 其中,Csoil是土壤中目标单体的浓度(mg·kg−1);ADDi是饮食或非饮食途径的日平均摄入量(mg·kg−1·d−1);HQ为非致癌风险;CR为致癌风险,其它参数见详见表1. 对于非致癌物质,若HQ>1,则该物质表现出非致癌风险;对于致癌物质,若CR>10−6,则该物质表现出致癌风险,通常认为CR>10−4是不可接受的.
表 1 健康风险评估模型的参数Table 1. Parameter factors of the health risk assessment model参数Parameter 参数含义Meaning 单位Units 取值 Value 参考文献Reference 成人 Adults 儿童 Children IRS 土壤日均摄入量 mg·d−1 100 200 [17] IRF 居民日均摄取食物量 mg·d−1 710000 1/3×710000 [17] EF 暴露土壤频率 d·a−1 350 [17] ED 暴露持续时间 a 24 6 [17] BW 体重 kg 70 15 [17] AT 平均暴露时间 a 致癌风险:25550非致癌风险:365×ED [17] CF 转换系数 — 10−6 [17] SA 暴露皮肤的表面积 cm2 d−1 57000 28000 [17] AF 土壤-皮肤黏附系数 mg·cm−2 0.07 0.2 [17] ABS 从土壤中吸收的污染物的比例 — 0.1 [17] Ij 呼吸速率 m3·d−1 13.5 [17] PEF 微粒排放因子 m3·kg−1 1.36×109 [17] CFS 致癌率 (mg·kg−1·d−1)−1 BBP:0.0019 DEHP:0.014 [18] RfDi 非致癌物经某种途径摄入的日均推荐剂量 mg·kg−1·d−1 DMP:10 DEP:0.8DBP:0.1 BBP:0.2DEHP:0.02 DnOP:0.04 [18] BAF PAEs从土壤到食物的富集系数 — DMP:0.108 DEP:0.108DBP:0.108 BBP:0.166DEHP:0.166 DnOP:0.166 [18] 2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 洋河农业区PAEs总含量与单体污染特征
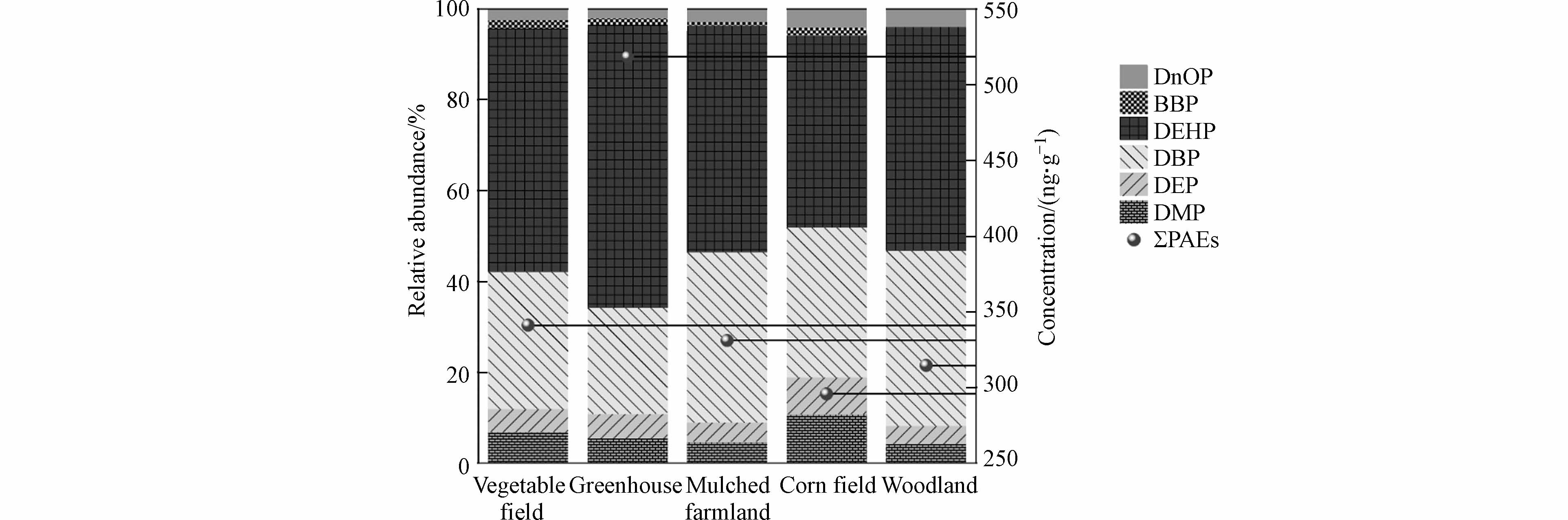
洋河流域农业土壤中PAEs各单体含量以及检出情况见表2. 6种PAEs单体在土壤中的平均含量顺序依次为DEHP>DBP>DMP>DEP>BBP>DnOP. 除DnOP外,其余单体检出率在80%以上,意味着这些物质在该地区被广泛使用. Σ6PAEs含量范围在183.63—780.50 ng·g−1,平均值和中位数分别为396.75 ng·g−1和365.87 ng·g−1. DEHP是土壤中最丰富的单体,含量范围在70.77—473.15 ng·g−1,平均值为219.98 ng·g−1,占Σ6PAEs的平均百分比为55.45%. 其次是DBP,占比为28.74%. DMP和DEP含量相当,占比分别为6.21%和5.60%. BBP和DnOP的占比相对较低,二者总占比仅为4.00%. 其中,DMP和DBP均超过了美国纽约州制定的土壤PAEs控制标准,超标率为32%和48%,最高超标分别达到3.1倍和3.5倍,值得关注和重视.
表 2 洋河流域土壤中PAEs含量、检出率与超标率Table 2. Concentration, detected ratio and excess ratio of soil PAEs in Yanghe River Basin化合物Compound DMP DEP DBP BBP DEHP DnOP Σ6PAEs 最小值/(ng·g−1) nd 7.30 46.87 nd 70.77 nd 183.63 最大值/(ng·g−1) 61.65 45.24 284.24 36.53 473.15 23.40 780.50 中值/(ng·g−1) 23.33 19.82 107.06 11.40 176.04 nd 365.87 平均值/(ng·g−1) 24.65 22.21 114.04 10.57 219.98 5.30 396.75 检出率/% 91.07 100 100 80.36 100 39.29 100 USEPA控制标准/(ng·g−1) 20 71 81 1215 4350 1200 — 超标率/% 32.00 0 48.00 0 0 0 — 注:“nd”表示未检出. Note: “nd” means no detect. 洋河农业区土壤中PAEs组成以DEHP和DBP为主,与西安城市[19]、雷州半岛[20]报道的情况类似. PAEs各单体含量差异,可能与单体性质、环境来源以及土壤的理化性质和环境条件有关[14]. DEHP和DBP由于分子量相对较大,水溶性较低,辛醇-水分配系数(lgKow)较大,在土壤中易于吸附富集,流动性较差,导致质量百分比偏高;而DMP、DEP等短链PAEs的水溶性相对较高,lgKow相对较小,相比于较长的烷基碳链的PAEs,更易被生物降解或通过挥发、淋溶和植物吸收等途径消失[21]. 另外,DEHP、DBP是农膜中使用最广泛的增塑剂,在各种有机肥料中也被大量检测到,因此在农业土壤中的应用范围更广.
如表3所示,洋河农业区PAEs污染程度与北京温室和泰安温室土壤基本相似,高于东北三江平原和黄河三角洲,但低于银川和天津菜地土壤. 不难看出土壤中PAEs污染水平有一定的区域差异性,分析这种差异可能归因于地区间不同的灌溉方式、土地利用方式和种植结构等[13]. 洋河流域是青岛市典型的灌溉农业区,利用洋河水源沿流域两岸农田自流灌溉. 关于灌溉水中的PAEs污染已有报道,特别是在地表河流和湖泊中[22]. 尽管地表水环境的PAEs含量低得多,但随着时间的推移,河水从灌溉源到农田的运输过程可能会导致PAEs在土壤中的积累. 与印度和英格兰相比,洋河农业区土壤中PAEs各单体污染水平明显偏高,这与我国的人口基数与塑料制品的需求量大密切相关.
表 3 不同地区不同土地利用类型中PAEs含量 (ng·g−1)Table 3. Comparison of concentration of PAEs in different land use types soils from different regions (ng·g−1)地点Location 土地类型Land type DMP DEP DBP BBP DEHP DnOP Σ6PAEs 参考文献Reference 北京 温室 8.0 20.0 440.0 4.0 380.0 2.0 850.0 [8] 杭州西湖 景区 432.8 41.0 519.9 2.1 1964.2 3.3 2963.3 [23] 天津 农田 3—88 3—81 7—189 nd—1790 39—2370 nd—647 91—2740 [13] 果园 3—32 3—30 20—138 nd—125 26—358 nd—728 53—1080 菜地 2—101 2—114 13—285 nd—385 28—4170 nd—9780 50—10400 黄河三角洲 乡村 1—5 nd—1 136—1039 nd 431—2449 nd—68 716—3251 [24] 公园 6—16 1—6 15—141 nd—1 43—801 0—16 70—923 咸阳 蔬菜基地 53.3 19.5 316.6 42.3 166.2 39.5 639.3 [14] 三江平原 蔬菜 12—34 20—46 22—209 nd—5317 34—218 nd—54 163—469 [25] 水稻 13—49 33—97 15—354 nd—72 77—583 nd—163 268—947 银川 蔬菜 89—3293 210—1381 139—2653 nd—1055 330—6017 nd—1713 1997—11659 [26] 泰安 温室 nd nd 110—166 19—22 199—564 20—27 350—767 [12] 印度 城市土壤 nd—8 9—12 8—36 20—35 16—30 nd—33 53—154 [27] 英格兰 城市黏土 0.1 0.9 8 0.6 76 14 92.6 [28] 青岛洋河 农业土壤 nd—61.7 7.3—45.2 46.9—284.2 nd—36.5 70.8—473.2 nd—23.4 183.6—780.5 本研究 注:“nd”表示未检出. Note: “nd” means no detect. 2.2 洋河农业区不同类型土壤中PAEs污染水平与组成特征
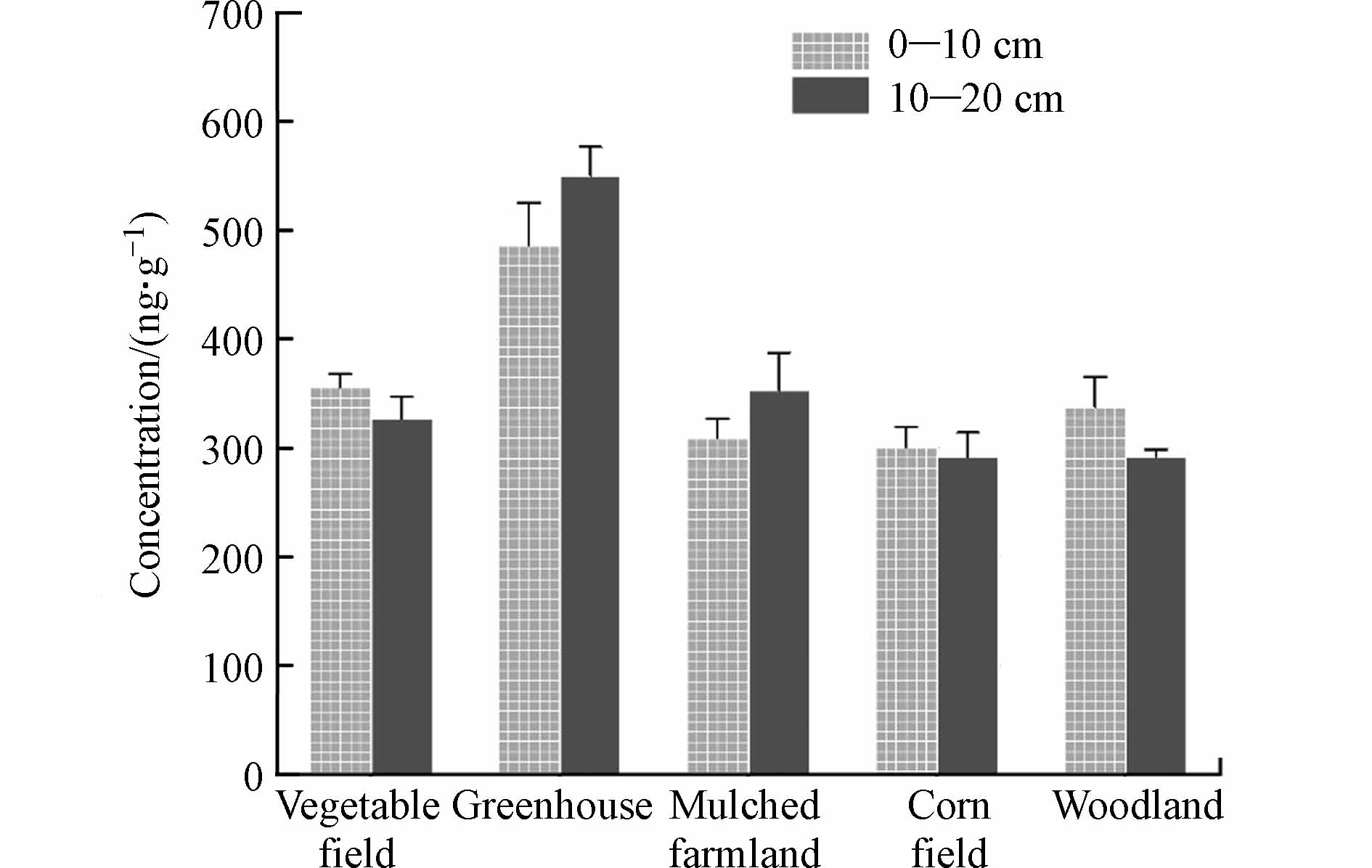
洋河农业区不同类型土壤中Σ6PAEs的含量情况见表4. Σ6PAEs的平均含量由高到低依次为:温室土壤(518.38 ng·g−1)>蔬菜地(341.13 ng·g−1)>覆膜耕地(331.02 ng·g−1)>林地(314.56 ng·g−1)>玉米地(295.74 ng·g−1). 整体上,不同类型土壤的Σ6PAEs含量差异不显著,不存在严重的局部偏差. 可能是该地区以农业生产为主,远离城市和工厂,工业活动和城市垃圾产生的PAEs有限.
表 4 洋河农业区不同土地类型土壤中PAEs的含量 (ng·g−1)Table 4. The PAEs concentration in soil of different types of land in Yanghe River Basin (ng·g−1)土地类型Land type Σ6PAEs 范围Range 平均值±标准差Mean±SD 中值Median 总数(n=56) 183.63—780.50 396.75±146.35 365.87 温室土壤(n=22) 191.51—780.50 518.38±155.71 467.12 覆膜耕地(n=8) 241.47—482.69 331.02±75.69 330.63 玉米地(n=12) 183.63—377.91 295.74±69.48 299.29 蔬菜地(n=8) 277.62—404.34 341.13±46.28 348.17 林地(n=6) 278.38—415.48 314.56±50.93 298.34 温室土壤中PAEs来源较为复杂. 一方面与棚膜的使用有关,另一方面,温室频繁地进行人为干预,如大水漫灌、化肥与农药杀虫剂大量施用等[29],这种集约化管理方式导致温室土壤中PAEs浓度显著高于其它农业土壤;地膜只在作物生长季节铺设,覆盖时间短,释放出的PAEs较少,且通过淋溶、下渗等途径迁移[18],因此覆膜耕地中残留的PAEs低于温室土壤;相比之下,蔬菜地由于不受地膜的阻挡或庇护,来自有机肥料、生活垃圾和道路交通灰尘的外部输入都可能是土壤中PAEs的重要来源;大气沉降或许是造成林地中PAE累积的原因:PAEs在土壤大气环境中的交换主要通过两个途径:一是大气中黏附有PAEs的气溶胶颗粒通过干沉降和湿沉降的方式进入土壤,二是土壤赋存态PAEs向大气环境中挥发[30],其中沉降为主要途径. 相对于普通露天农田而言,林地具有一定的阻挡作用,大气中的PAEs更容易在此处沉降[18];本研究中玉米种植土壤中PAEs含量最低,可能是因为采样时间为9月,临近玉米收获期,土壤耕作以及化肥和农药的施用频率降低.
评估土壤中PAEs污染情况,仅考虑其总浓度是不够的,还应考虑污染物单体的组成和浓度范围(图2). 尽管不同农业土壤中PAEs单体平均含量不尽相同,但贡献率较高的单体(DEHP、DBP)与研究区主要污染组成情况相一致. 其中,DEHP占Σ6PAEs百分比范围分别是42.42%—62.26%,顺序依次为温室土壤(62.26%)、蔬菜土壤(53.52%)、覆膜耕地(49.90%)、林地土壤(49.31%)、玉米土壤(42.42%);而DBP在不同土壤类型中的占比相差不大,占比范围在23.36%—38.63%.
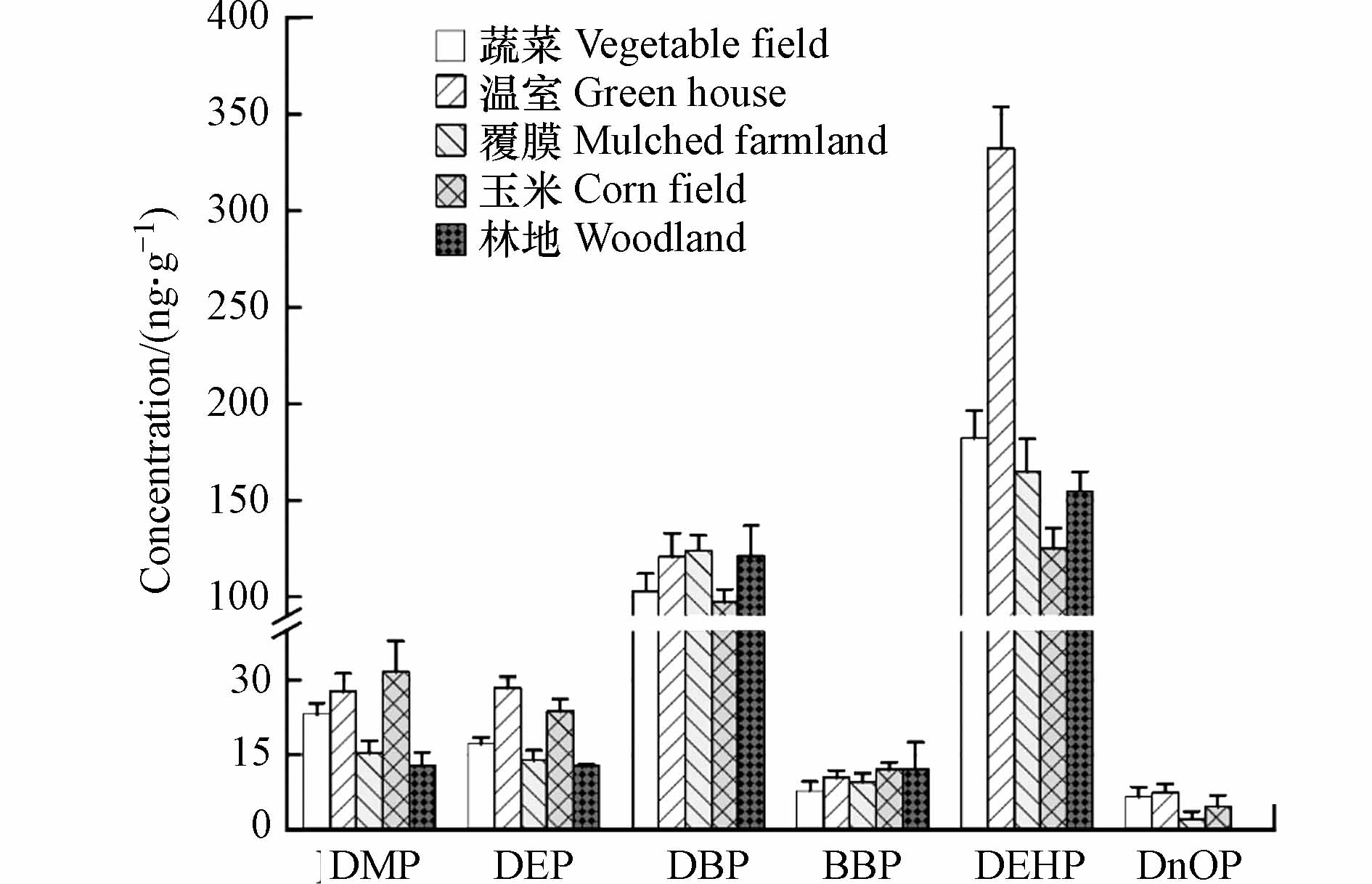
就单体检出含量来看(图3),DBP和DEHP在温室土壤中的平均浓度均高于蔬菜地、玉米地和林地,其余几种单体未见显著增高. 相反,玉米土壤中DMP和DEP的平均浓度较温室土壤还略高.
对于覆膜土壤而言,DBP的平均含量和占比高于3种露天土壤,这与DBP常作为增塑剂这一事实一致,但只对玉米土壤来说差异显著(P=0.019,<0.05). 这可以解释为,采样时间为9月,覆膜土壤经过了整个夏季的太阳辐射和雨季降水. 尽管DBP较高的溶解度和蒸汽压使其容易从塑料薄膜中渗出,但覆膜环境下适宜的温度和湿度条件可能会促进DBP的降解,从而打破土壤中PAEs输入和减少之间的平衡. Wu等[31]的研究支持了这一结果:随着温度从25 °C升高到30°C,土壤中DBP的降解速率迅速增加. Wang等[32]将聚乙烯农膜埋在土壤中4年,农膜中的PAEs浓度降低了79.2%—98.0%,然而农膜覆盖下的土壤与附近土壤背景之间几乎没有发现PAEs浓度的差异. Xie等[33]报道,DBP在28 °C时的半衰期为8.53 d,意味着农膜中释放的DBP在土壤中的保留时间较短. 事实上,覆膜土壤中其余单体含量(DEHP除外)均处于较低水平,说明PAEs确实容易在该环境下降解. 同样作为塑料制品中使用最广泛的增塑剂,覆膜土壤中的DEHP呈现出与DBP类似的规律,但平均浓度要高于DBP. DEHP的半衰期在18.5—41.4 d[32],是DBP的8—10倍,相比之下较难被微生物降解. 另外,DEHP是有机肥料中最常被检测到的物质,地膜的覆盖一定程度上阻碍其输入,因此DEHP浓度小于蔬菜土壤也就不足为奇了. 由此可见,地膜覆盖对土壤中PAEs的残留影响较小.
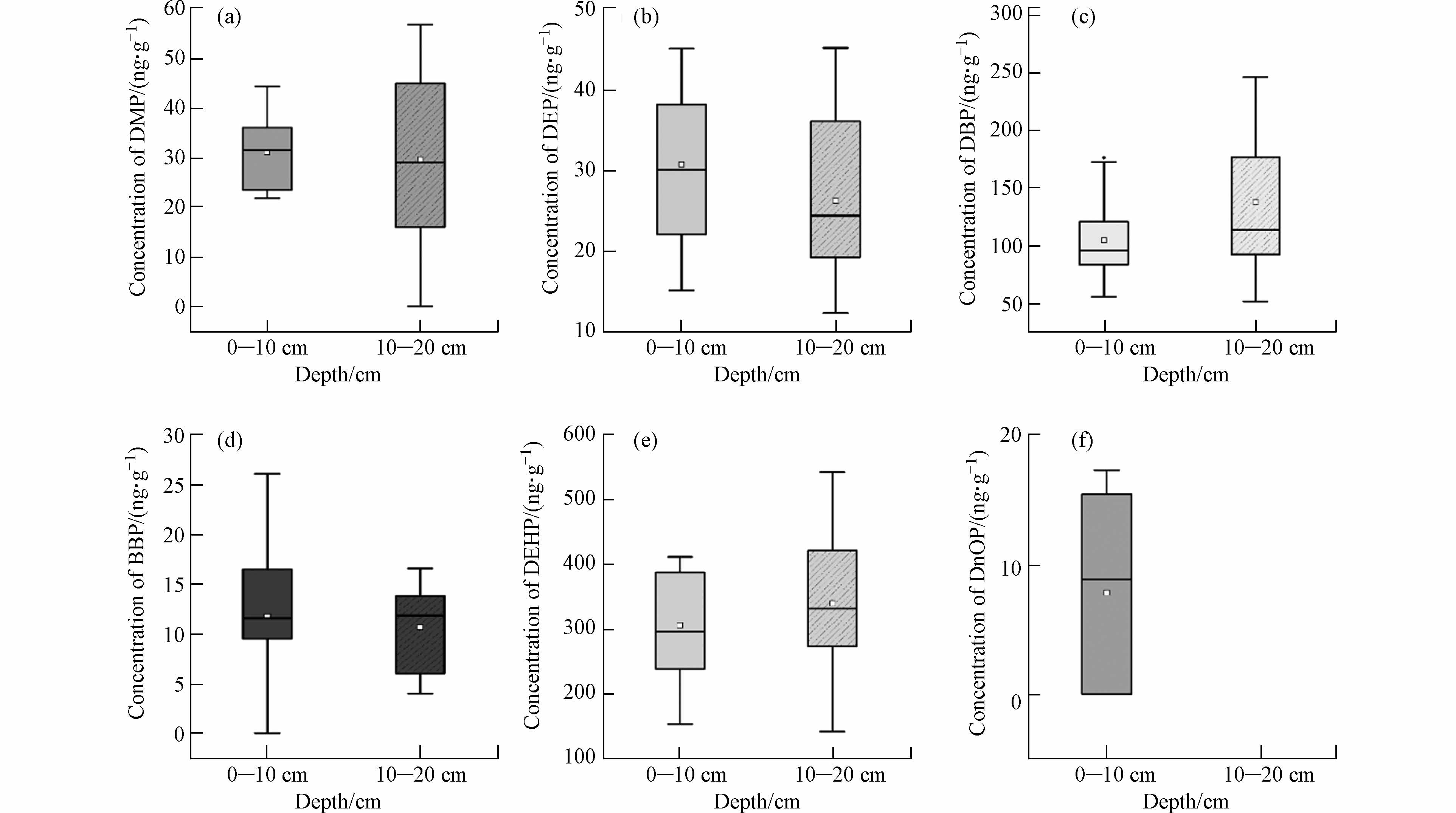
2.3 洋河流域农业区不同类型土壤中PAEs的垂直分布
一些研究表明,随着土壤深度的增加,土壤中PAEs浓度逐渐降低[34]. 然而该规律仅在蔬菜地、玉米地和林地中得以体现(图4),原因可能是林地土壤质地紧实、偏砂质,PAEs更倾向于在地表积累而难以渗透到深层当中. 已经证实,植物根部的PAEs的含量显著高于土壤中,意味着植物可以通过根部从土壤中吸收和积累PAEs[35]. 因此对于玉米和蔬菜地而言,体现在10—20 cm土壤中PAEs的含量的低于0—10 cm. 这种趋势与温室和覆膜耕地明显不同,土壤的频繁翻转可以部分解释这种差异,特别是对于温室来说,频繁翻转可能会增加土壤中PAEs的挥发并促进好氧生物降解,从而降低PAEs在表层土壤中的浓度.
本研究土壤中(蔬菜地、玉米地和林地)呈现的变化趋势与江汉农田土壤不一致[36],这种差异可能归因于降雨对PAEs浸出的影响. 江汉平原处于水循环非常活跃的气候潮湿地区,通过土壤浸出的水会将PAEs沿土壤剖面输送到深处. 由于此处相对缺乏氧气和微生物质,PAEs的降解速率受限,因此土壤深层的PAEs含量较高. 在洋河流域,农业耕地通常每半年一犁,温室则更为频繁,这有助于PAEs在浅层和深层之间的垂直转移,可能是导致不同层间PAEs含量差异不够显著的原因. 总体而言,不同研究中PAEs垂直分布可能与许多因素有关,包括土壤耕作、采样深度、降水以及生物和机械干扰[10].
另一个值得关注的问题是PAEs单体随深度的变化情况. 以温室为例,DnOP在深层土壤中均没有被检出,其余5种单体均存在下渗的情况,但分布规律不尽相同(图5). DMP在各层间含量相当,由于水溶性和易于降解,因此在土壤各层中污染程度不高;DBP有与相似的物理性质和化学结构,其分布规律与DMP类似. DBP溶解度大、易于下渗,温室土壤灌溉频率较高,因此更容易向土壤深处迁移. DEHP作为最主要污染物,分布情况与Σ6PAEs相同,主要集中在深层,但各层的残留也较高. BBP土壤中污染程度小,在深层土壤中很少检出.
2.4 PAEs含量与土壤理化性质的相关性
为了进一步了解洋河农业区PAEs的各种潜在来源以及典型理化性质对土壤中PAEs积累之间的关系,本研究计算了PAEs单体残留水平与土壤理化性质之间的Spearman相关系数,如图6所示. 结果表明,土壤中发现的主要单体(DEP、DBP和DEHP)的浓度彼此之间有明显的相关性(P<0.05),并且这3种单体与Σ6PAEs密切相关(r=0.67、0.62和0.93;P<0.01). 这些相关性可能表明各种单体在土壤中可能有类似的输入途径和命运.
TOC、TN和pH是影响包括PAEs在内的疏水性有机污染物(HOCs)行为的重要因素. 本研究区域土壤中TOC、TP和pH值范围为0.130%—1.348%、0.001‰—0.086%和4.92—7.74,平均值为0.423%、0.031%和6.47. 其中,TOC值远低于北京(0.97%)[37]、寿光(1.14%)[38]等地区. 与其它HOCs一样,PAEs亲油性强、易与有机物结合,这一物理化学特性使得PAEs很大程度上会被土壤有机质吸附[39],因此研究区土壤中较低的TOC含量可能是导致土壤捕获PAEs较低的原因. 然而PAEs和TOC之间没有相关性,可能是环境中存在连续的HOCs来源,导致HOCs与TOC之间不相关[40]. 在洋河农业区,农药、化肥与农用塑料被频繁使用或更换,这些含有丰富PAEs的新鲜材料被连续引入土壤中,可能会打破PAEs和TOC之间的平衡. 在山东半岛的温室土壤中也发现了类似的现象[41]. 另外,本研究中也没有发现PAEs与土壤pH和TN值之间的相关性.
2.5 洋河农业区土壤中PAEs的来源解析
污染物的环境来源诊断对于风险管理和环境修复具有重要意义. 本研究中,主成分分析和聚类分析被用于识别PAEs的环境来源. 考虑到本研究区域可用于林地、覆膜和蔬菜的样本量相对有限,因此将所有土壤样本组合在一起进行分析. 土壤中PAEs主成分分析(KMO值为0.756,Bartlett's球形检验显著)结果见表5,使用kaiser进行标准化正交旋转,提取了4个主成分。
表 5 洋河农业区土壤PAEs主成分分析结果Table 5. Results of principal component analysis of PAEs in soils of Yanghe agricultural area化合物PAEs 主成分因子Principal component factors PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 DMP 0.13 0.93 0.12 0.09 DEP 0.34 0.55 0.57 0.13 DBP 0.14 0.12 0.95 0.08 BBP 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.99 DEHP 0.68 0.33 0.23 -0.03 DnOP 0.90 0.03 0.08 0.09 方差贡献率/% 43.75 15.82 12.96 11.19 方差累计贡献率/% 43.75 59.57 72.52 83.71 第一主成分(PC1)方差贡献率为43.75%,DEHP和DnOP载荷较高,单体之间呈显著正相关(r=0.43,P<0.05),说明它们可能有相似的来源. 研究表明,DEHP和DnOP主要用作增塑剂[1]. 其中,DEHP是应用最为广泛的PAEs类增塑剂,能添加到于大多数塑料中,如PVC. DnOP也应用于乙烯地板的生成,油墨、皮革等橡胶制品中[42].
第二主成分(PC2)方差贡献率为15.82%,DMP的载荷最高. 主要作为农药和杀虫剂中的溶剂,化妆品和个人护理品中也有所检出[43].
第三主成分(PC3)方差贡献率为12.96%,由DBP与部分DEP构成,呈现显著相关性(r=0.54,P<0.05). 有报道称化肥中含有DBP和DEP[43]. 其次DBP也是常用的PAEs类增塑剂之一.
第四主成分(PC4)方差贡献率为11.19%,BBP载荷最高. BBP多来源于增塑剂,建筑和装饰材料的挥发,以及含有PAEs颗粒的大气沉积[42].
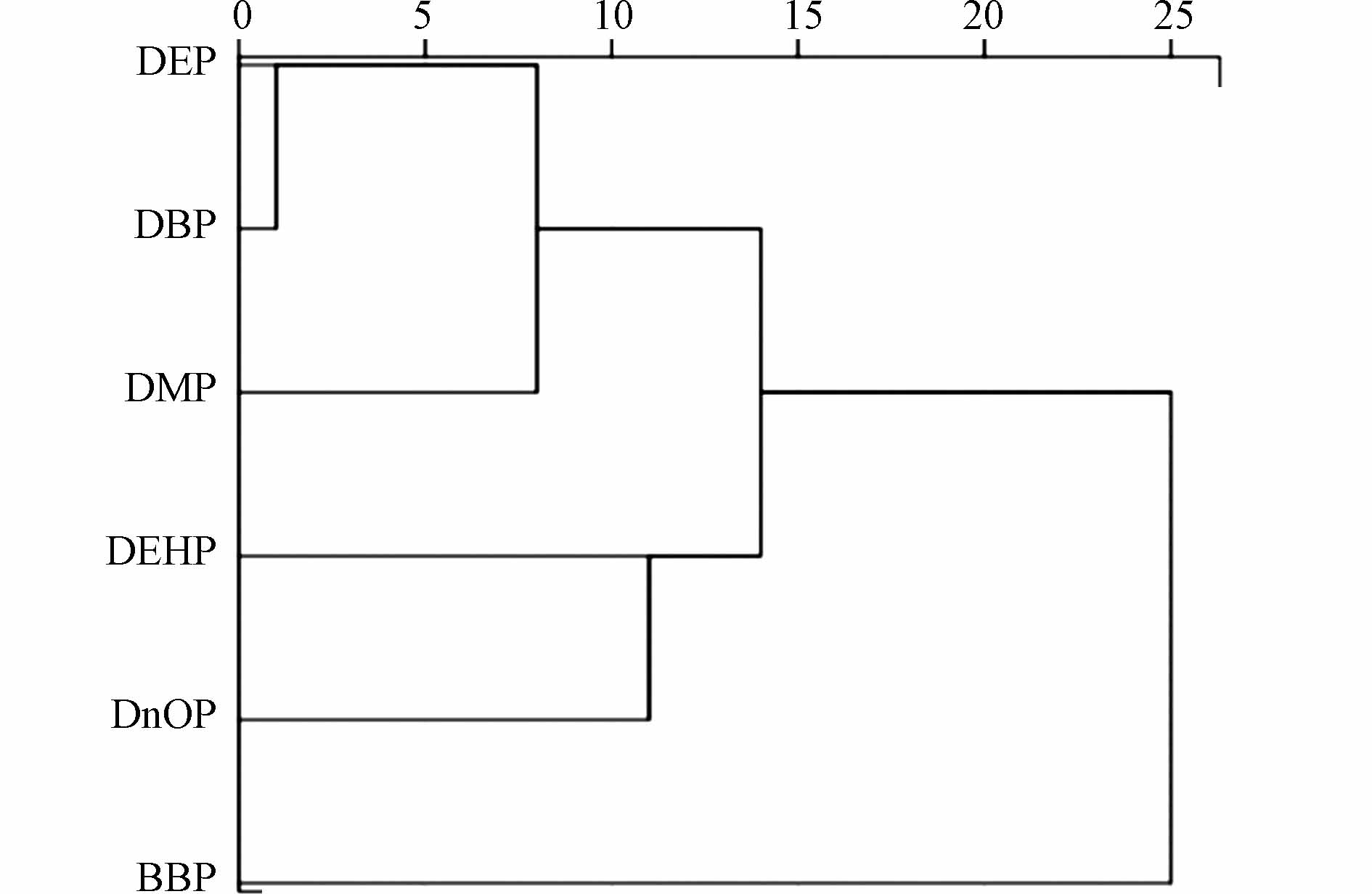
聚类分析(图7)将土壤中的PAEs分为4类:DEP和DBP为类1,DEHP和DnOP为类2,DMP、BBP分别为类3和类4,与主成分分析结果一致. 同时,类1、类2和类3在高更层次又形成了的一个新的集群,这反映出它们可能还有另一个共同的环境来源.
通常认为,PAEs的支链长度与来源相关[44]. 农业生态系统中,短链PAEs,如DMP和DEP,通常来源于农药、污灌和有机肥;而长链PAEs,如DBP、DEHP、BBP和DnOP,在聚合物工业中被广泛用作增塑剂,约80%的PAEs用于此目的,在聚体中的含量从10%—60%不等[1]. 本研究区的PAEs主要以DBP和DEHP为主,这与我国主要使用它们为增塑剂的事实一致,但主成分分析和聚类分析结果表明这两种单体并不属于一类,说明它们可能具有复合来源. 实地考察发现,洋河农业区土壤中PAEs的来源具有一定的复杂性和广泛性. 一方面,这两种单体广泛存在于各个环境介质(水、土壤和大气)和农业投入品(塑料增塑剂、有机肥和污灌)中[45]. 另一方面,覆膜下适宜的湿度和温度促使农膜中释放的PAEs迅速减少,特别是对DBP来说. 相比之下BBP和DnOP来源较为单一,主要作为增塑剂随塑料制品进入土壤,这也就解释了为什么BBP和DnOP在洋河农业区不同类型土壤中显示出较强的特异性,体现在3种露天农田土壤中的检出率和含量都很低.
2.6 洋河农业区土壤中PAEs的健康风险评估
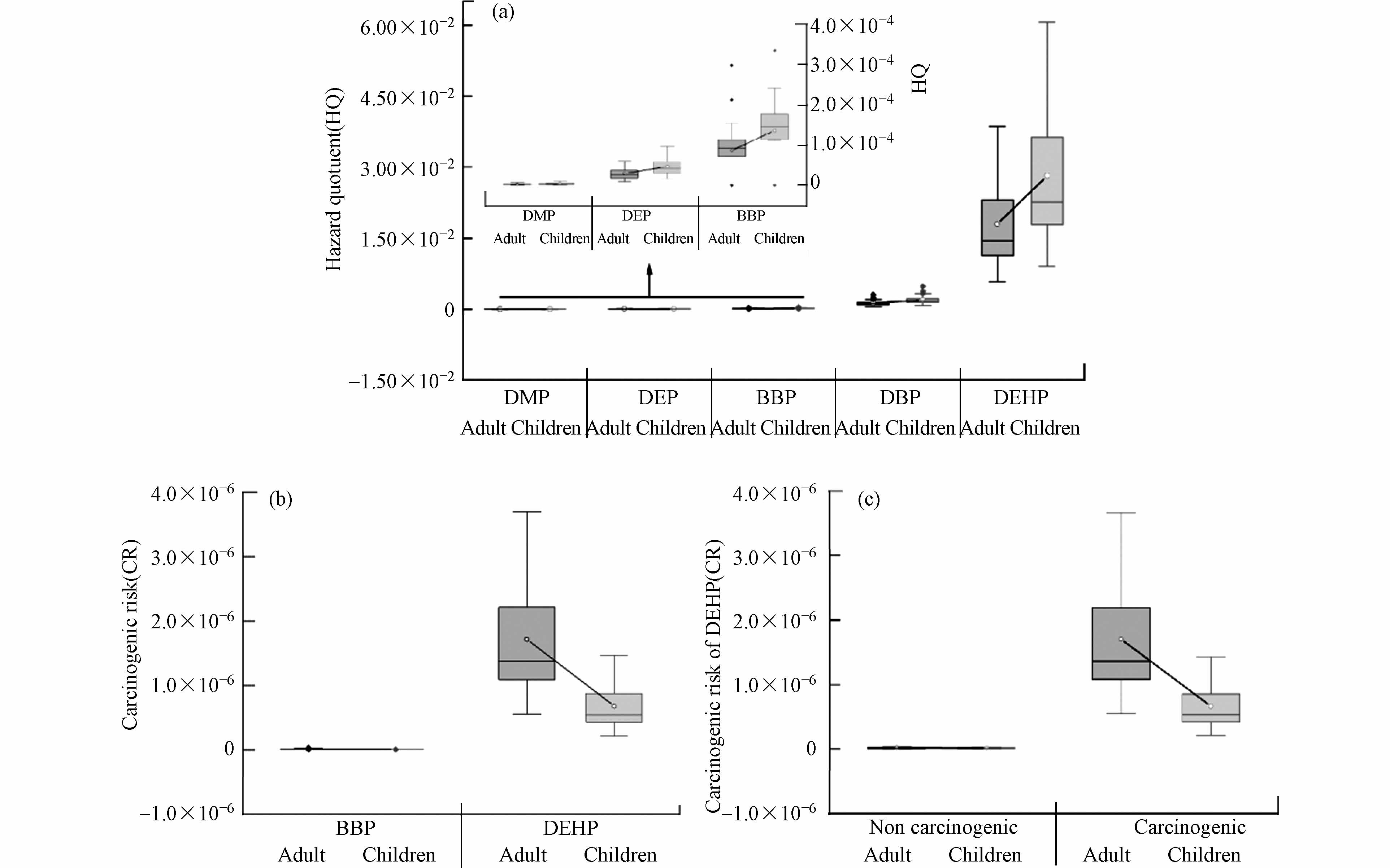
根据1.6中的健康风险模型,计算出不同暴露途径下成人和儿童对PAEs的日均摄入量(表6). 由于DnOP检出率较低,因此不进行计算. 从各单体对日均摄入量的贡献来看,无论是对于成人还是儿童,DEHP所占比例最大,约为65.0%. 从各种暴露途径来看,饮食途径的日均摄入量均显著高于非饮食途径,其对日均摄入量的贡献率分别为成人的98.5%和儿童的86.8%. 非饮食途径中,成人的PAEs的日均摄入量顺序为呼吸摄入>皮肤接触>土壤摄入,儿童则为皮肤接触>土壤摄入>呼吸摄入. 值得注意的是,尽管从事农业生产的主要是成年人,但成年人对PAEs的总日均摄入量明显低于儿童,这表明儿童可能更容易从土壤环境中摄入PAEs.
表 6 不同暴露途径下成人和儿童对PAEs的日均摄入量(mg·kg−1·d−1)Table 6. The ADD values of PAEs for adults and children via different exposure pathway(mg·kg−1·d−1)化合物PAEs 类别Type 饮食途径Dietary routes 非饮食途径Non-Dietary routes 饮食摄入Intake 土壤摄入Ingest 皮肤接触Dermal 呼吸摄入Inhale DMP 成人 2.59×10−5 3.37×10−8 1.35×10−7 2.35×10−7 儿童 4.02×10−5 3.16×10−7 8.83×10−7 2.35×10−7 DEP 成人 2.33×10−5 3.04×10−8 1.21×10−7 2.11×10−7 儿童 3.62×10−5 2.84×10−7 7.95×10−7 2.11×10−7 DBP 成人 1.20×10−4 1.56×10−7 6.23×10−7 1.09×10−6 儿童 1.86×10−4 1.46×10−6 4.08×10−6 1.09×10−6 BBP 成人 1.71×10−5 1.45×10−8 5.78×10−8 1.00×10−7 儿童 2.65×10−5 1.35×10−7 3.78×10−7 1.00×10-7 DEHP 成人 3.55×10−4 3.01×10−7 1.20×10−6 2.09×10−6 儿童 5.51×10−4 2.81×10−6 7.88×10−5 2.09×10−6 图8a显示,各单体的非致癌风险值从大到小依次为DEHP(1.79×10−2和2.82×10−2)、DBP(1.22×10−3和1.93×10−3)、BBP(8.62×10−5和1.36×10−4)、DEP(2.96×10−5和4.69×10−5)和DMP(2.60×10−6和4.11×10−6),不同PAEs均未对人体健康产生非致癌风险(HQ<1). 尽管如此,DEHP和DBP的危害熵值显著高于DMP、DEP和BBP,表明这两种污染物的非致癌风险相对较高. 儿童表现出比成人更高的非致癌风险,这可以归因于由于身体不成熟和新陈代谢弱而对毒性的易感性[46]. 图8b可以看出,BBP的致癌风险非常低,但DEHP对成人和儿童致癌风险范围在5.53×10−7—3.70×10−6和2.19×10−7—1.46×10−6,分别有83.93%和17.86%的采样点超过USEPA推荐值,呈现出一定的致癌风险,但仍在可接受的范围内(10−6<CR<10−4). 与非致癌风险不同,成年人表现出更高的致癌风险,可能因为成人对污染物的摄入是持续且长期的,导致更高的致癌性[46]. 考虑到儿童本身抵抗力低,因此对于儿童的潜在致癌风险不容忽视.
由于BBP的风险可忽略不计,因此选择DEHP进一步评估分别在非饮食和饮食途径下的致癌风险. 图8c可以看出,无论是成人还是儿童,致癌风险都是由饮食途径引发的,致癌风险范围在6.65×10−7—3.66×10−6,平均值为(1.18±0.82)×10−6. 有研究表明,土壤中的DEHP能够通过食物链的富集作用对人体健康构成严重的威胁,一方面因为DEHP在土壤中的浓度较大,还受其生物积累因子(BAF)及每日摄入受污染食物的最大参考剂量(RfDo)的影响[45],因此有必要对其进行进一步研究,以充分了解土壤环境中PAEs的健康风险和机制.
3. 结论(Conclusion)
通过对青岛洋河流域典型农业土壤中6种PAEs的浓度和分布的研究,发现各单体均有不同程度检出,土壤受到一定程度的污染.
(1)土壤中Σ6PAEs含量范围在183.63—780.50 ng·g−1之间,平均值为432.4 ng·g−1. DBP与DEHP是研究区土壤中PAEs的主要组成部分. DMP和DBP含量超过美国纽约州土壤PAEs控制标准.
(2)不同农业土壤中Σ6PAEs平均值大小顺序依次为:温室土壤>蔬菜地>覆膜土壤>玉米地>林地. 蔬菜地、玉米地和林地表层中6种PAEs高于深层,温室和覆膜耕地则相反. PAEs分布多与农业活动有关,并受土壤微生物降解的影响.
(3)土壤中主要单体(DEP、DBP和DEHP)的浓度间有明显的相关性(P<0.05). 统计分析表明,农用塑料、施肥和农药杀虫剂是洋河农业区土壤中PAEs的主要来源.
(4)各单体对成人和儿童产生的非致癌风险均未超过美国EPA推荐的非致癌水平(HQ<1),但DEHP在饮食暴露途径下对居民致癌风险超过了阈值水平(CR>10−6). 今后应采取相应措施,更加关注PAEs在土壤中的污染状况以及对当地居民健康的潜在影响.
-
表 1 不同高度积尘重金属地累积指数
Table 1. Geoaccumulation index of heavy metals in dust at different heights
元素Elements 地累积指数Ground Accumulation Index 低层(6 m)Low Level 中层(17 m)Middle Level 高层(41 m)High Level V −0.80 −0.67 −0.91 Cr −0.26 0.16 −0.13 Mn −0.40 −0.31 −0.46 Co −0.85 −0.55 −1.02 Ni −0.04 0.40 0.03 Cu 1.40 1.93 1.41 Zn 1.55 1.70 1.88 As −0.58 −0.42 −0.63 Mo −1.42 −0.91 −1.10 Cd 3.02 3.46 2.99 Pb 1.14 1.24 0.93 表 2 不同高度积尘重金属地累积指数分级
Table 2. Grading of the geoaccumulation index of heavy metals in dust at different heights
元素Elements 地累积指数级别Ground Cumulative Index Level 低层(6 m)Low Level 中层(17 m)Middle Level 高层(41 m)High Level V 0 0 0 Cr 0 1 0 Mn 0 0 0 Co 0 0 0 Ni 0 1 1 Cu 2 2 2 Zn 2 2 2 As 0 0 0 Mo 0 0 0 Cd 4 4 3 Pb 2 2 2 表 3 不同高度积尘稀土元素特征参数
Table 3. Characteristic parameters of rare earth elements in dust at different heights
特征参数Characteristic parameters 低层(6 m)Low Level 中层(17 m)Middle Level 高层(41 m)High Level ΣREE 179.24 176.36 184.32 ΣLREE 145.99 144.13 146.60 ΣHREE 33.26 32.23 37.72 ΣLREE/HREE 4.39 4.47 3.89 δEu 0.90 0.80 0.91 δCe 1.31 1.75 1.04 (La/Yb)N 11.75 9.17 11.65 (La/Sm)N 3.54 3.13 3.10 (Gd/Yb)N 2.07 1.92 2.42 表 4 不同高度积尘重金属主成分分析
Table 4. Principal component analysis of heavy metals in dust at different heights
变量元素Variable elements 因子负荷Factor load 1 2 3 V 0.57 0.48 0.51 Cr 0.47 0.68 −0.15 Mn −0.01 0.84 0.42 Co 0.80 0.39 0.11 Ni 0.87 0.26 −0.03 Cu 0.33 0.86 0.03 Zn 0.76 −0.12 0.27 As 0.83 0.31 0.26 Mo 0.25 0.92 0.17 Cd 0.17 0.11 0.87 Pb 0.61 0.29 0.06 特征值 3.8 3.4 1.4 方差贡献率% 34.3 31.3 12.6 累计贡献率% 34.3 65.6 78.2 -
[1] CHANG J, LIU M, HOU L J, et al. Concept, pollution character and environmental effect of urban surface dust[J]. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = the Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(5): 1153-1158. [2] 王萧. 北京市街道灰尘地球化学特征及物源分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021. WANG X. Geochemical characteristics and source analysis of street dust in Beijing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2021 (in Chinese).
[3] LOSKA K, WIECHUŁA D, KORUS I. Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry[J]. Environment International, 2004, 30(2): 159-165. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00157-0 [4] WANG X H, BI X H, SHENG G Y, et al. Chemical composition and sources of PM10 and PM2.5 aerosols in Guangzhou, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2006, 119(1): 425-439. [5] NKANSAH M A, OPOKU F, ACKUMEY A A. Risk assessment of mineral and heavy metal content of selected tea products from the Ghanaian market[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2016, 188(6): 332. doi: 10.1007/s10661-016-5343-y [6] XIA D S, WANG B, YU Y, et al. Combination of magnetic parameters and heavy metals to discriminate soil-contamination sources in Yinchuan—a typical oasis city of Northwestern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 485/486: 83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.070 [7] TAN J H, DUAN J C, CHAI F H, et al. Source apportionment of size segregated fine/ultrafine particle by PMF in Beijing[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2014, 139: 90-100. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.01.007 [8] WANG R D, ZOU X Y, CHENG H, et al. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of atmospheric dust fall at Beijing during spring of 2008-2009[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(5): 3547-3557. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3583-3 [9] 刘玥, 郭文强, 武晔秋. 基于PMF模型的大同市城区公园地表灰尘中重金属污染评价及来源解析[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(5): 1616-1628. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021091103 LIU Y, GUO W Q, WU Y Q. Pollution assessment and source analysis of surface dust heavy metals in parks of Datong city based on Positive matrix factorization model[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(5): 1616-1628 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021091103
[10] TANG Y, HAN G L, WU Q X, et al. Use of rare earth element patterns to trace the provenance of the atmospheric dust near Beijing, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 68(3): 871-879. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1791-z [11] 张棕巍, 于瑞莲, 胡恭任, 等. 泉州市大气降尘中稀土元素地球化学特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(12): 4504-4513. ZHANG Z W, YU R L, HU G R, et al. Geochemical characteristics and source apportionment of rare earth elements in the dustfall of Quanzhou city[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(12): 4504-4513 (in Chinese).
[12] GWENZI W, MANGORI L, DANHA C, et al. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 636: 299-313. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.235 [13] WANG S S, YU R L, HU G R, et al. Distribution and source of rare earth elements in PM2.5 in Xiamen, China[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2017, 36(12): 3217-3222. doi: 10.1002/etc.3902 [14] 马志强, 王跃思, 孙扬, 等. 北京大气中常规污染物的垂直分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 2007, 20(5): 1-6. MA Z Q, WANG Y S, SUN Y, et al. Characteristics of vertical air pollutants in Beijing[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2007, 20(5): 1-6 (in Chinese).
[15] 胡永兴, 宿虎, 张斌, 等. 土壤重金属污染及其评价方法概述[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(17): 33-39. HU Y X, SU H, ZHANG B, et al. Soil heavy metal pollution and its evaluation methods: A review[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(17): 33-39 (in Chinese).
[16] 李友平, 刘慧芳, 周洪, 等. 成都市PM2.5中有毒重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(7): 2225-2232. LI Y P, LIU H F, ZHOU H, et al. Contamination characteristics and health risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in PM2.5 in Chengdu[J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(7): 2225-2232 (in Chinese).
[17] ZOLLER W H, GLADNEY E S, DUCE R A. Atmospheric concentrations and sources of trace metals at the South pole[J]. Science, 1974, 183(4121): 198-200. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4121.198 [18] 李丽娟, 温彦平, 彭林, 等. 太原市采暖季PM2.5中元素特征及重金属健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(12): 4431-4438. LI L J, WEN Y P, PENG L, et al. Characteristic of elements in PM2.5 and health risk assessment of heavy metals during heating season in Taiyuan[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(12): 4431-4438 (in Chinese).
[19] 孔春霞, 郭胜利, 汤莉莉. 南京市生活区夏秋季节大气颗粒物垂直分布特征[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2009, 34(11): 35-38. KONG C X, GUO S L, TANG L L. Vertical distribution characteristics of atmospheric particles in summer and autumn in Nanjing[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2009, 34(11): 35-38 (in Chinese).
[20] 倪刘建, 张甘霖, 阮心玲, 等. 南京市不同功能区大气降尘的沉降通量及污染特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2007, 27(1): 2-6. NI L J, ZHANG G L, RUAN X L, et al. The flux and pollution character of dust-fall in different functional zones of Nanjing[J]. China Environmental Science, 2007, 27(1): 2-6 (in Chinese).
[21] 张舒婷, 李晓燕, 陈思民. 贵阳市不同空间高度灰尘和重金属沉降通量[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(6): 1630-1637. ZHANG S T, LI X Y, CHEN S M. Vertical characteristics of deposition fluxes of dust and heavy metals of Guiyang City[J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(6): 1630-1637 (in Chinese).
[22] 刘红年, 苗世光, 蒋维楣, 等. 城市建筑动力学效应对对流边界层影响的敏感性试验[J]. 气象科学, 2008, 28(6): 599-605. LIU H N, MIAO S G, JIANG W M, et al. The sensitivity study on the effect of city buildings’ dynamics on turbulence characteristic of convective boundary layer[J]. Scientia Meteorologica Sinica, 2008, 28(6): 599-605 (in Chinese).
[23] 谢华林, 张萍, 贺惠, 等. 大气颗粒物中重金属元素在不同粒径上的形态分布[J]. 环境工程, 2002, 20(6): 55-57, 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8942.2002.06.018 XIE H L, ZHANG P, HE H, et al. Distribution of heavy metal elements in the different diametral atmospheric particulate matters[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2002, 20(6): 55-57, 5 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8942.2002.06.018
[24] 王章玮. 大气中的稀土元素及稀土农用对温室气体排放的影响[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2003. WANG Z W. Rare earth elements of atmosphere and effects of rare earth elements on emissions of greenhouse gases[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2003 (in Chinese).
[25] 吴铎, 魏海涛, 赵瑞瑞, 等. 兰州市室内大气降尘环境磁学特征及其随高度变化研究[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(1): 79-84. WU D, WEI H T, ZHAO R R, et al. Magnetic properties of indoor dustfall at different heights in Lanzhou[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(1): 79-84 (in Chinese).
[26] XIONG Q L, ZHAO W J, GUO X Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of dustfall trace elements during winter in Beijing[J]. Huan Jing Ke Xue= Huanjing Kexue, 2015, 36(8): 2735-2742. [27] NARGIS A, HABIB A, ISLAM M N, et al. Source identification, contamination status and health risk assessment of heavy metals from road dusts in Dhaka, Bangladesh[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2022, 121: 159-174. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2021.09.011 [28] 王利军, 卢新卫, 雷凯, 等. 宝鸡市街尘重金属元素含量、来源及形态特征[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(8): 2470-2476. WANG L J, LU X W, LEI K, et al. Content, source and speciation of heavy metal elements of street dusts in Baoji city[J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(8): 2470-2476 (in Chinese).
[29] GIOIA S M C L, BABINSKI M, WEISS D J, et al. An isotopic study of atmospheric lead in a megacity after phasing out of leaded gasoline[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2017, 149: 70-83. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.10.049 [30] PAN H Y, LU X W, LEI K. A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi'an, China: Contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 1361-1369. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.004 [31] AMATO F, PANDOLFI M, VIANA M, et al. Spatial and chemical patterns of PM10 in road dust deposited in urban environment[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2009, 43(9): 1650-1659. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.12.009 [32] 息朝庄, 吴林锋, 张鹏飞, 等. 贵州省惠水土壤-灌溉水-雨水-大气降尘中Cd、As等微量元素特征及来源讨论[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(1): 192-205. XI C Z, WU L F, ZHANG P F, et al. Characteristics and sources of Cd and As trace elements in soil-irrigation-rainwater-atmospheric dust-fall in Huishui County, Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(1): 192-205 (in Chinese).
[33] 刘进, 潘月鹏, 师华定. 华北地区农田土壤镉来源及大气沉降的贡献[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(8): 1698-1708. LIU J, PAN Y P, SHI H D. Atmospheric deposition as a dominant source of cadmium in agricultural soils of North China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2022, 41(8): 1698-1708 (in Chinese).
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 刘福志,赵妍妍,肖默,邓锂峰,陈扬佳,王晓森,涂卓特. 丰泽区室内灰尘常见重金属污染特征及其生态风险评价. 医学动物防制. 2025(06): 556-561 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李睿. 气溶胶及其潜在有毒元素(PTEs)污染评估研究方法综述. 山东化工. 2024(19): 127-131 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载: