-
据世界卫生组织(WHO)调查,全球80%的疾病,约30%的死亡率都与饮用水被污染相关[1],因此饮用水质安全一直是环境领域的研究热点. 我国2022年3月15日发布了《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB5749-2022). 根据已有文献报道,饮用水中的污染物主要包括金属及其氧化物、营养盐、持久性有机物以及微生物. 这些污染物往往以胶体状态存在,其比表面积大,吸附位点丰富,易与其他污染物吸附、团聚,形成稳定的团聚体[2]. 污染物的这种环境行为被称为“胶体泵”效应[3]. 该效应的发生会影响胶体态污染物的迁移和富集,从而对饮用水质和人体健康产生严重污染和危害.
然而,目前专家学者们对“污染物可能以胶体态形式存在”这一观点,关注度并不高. 在Web of Science中检索“colloidal pollutant”和“drinking water”关键词,仅有30篇相关综述. 大多数研究集中在污染物的去除,Lu等[4]综述了电化学氧化灭活病原微生物的研究进展;Song等[5]和Chellam等[6]总结了电絮凝去除水中结垢、金属、消毒副产物以及病毒的研究现状;许多研究者们讨论了臭氧氧化[7]、光催化[8]等高级氧化工艺的去除效果. 此外,利用金属氧化物和聚合物材料辅助去除胶体态污染物也是研究热度较高的方向[9 − 11]. 截至目前,中国知网尚未有关于胶体态污染物的相关综述发表. 这表明目前国内外对饮用水中胶体态污染物的综述相对匮乏. 然而,污染物在饮用水中的长期赋存,必然发生吸附、团聚等环境行为,从而形成易迁移的胶体,加剧其对饮用水质的污染,对人类健康构成潜在威胁.
因此,有必要对饮用水中胶体态污染物的研究进展进行综述. 本文聚焦于饮用水中的胶体态污染物,从胶体态污染物的概念、种类、迁移行为及去除效果四个方面综述饮用水中胶体态污染物的研究现状,以期提高研究者们对胶体态污染物的关注,为保障饮用水质安全和人类健康提供参考和帮助.
-
19世纪60年代,英国科学家格雷哈姆首次提出“胶体”的概念. 胶体又称胶状分散系,是一种均匀混合物,包含分散和连续2种不同相态的物质. 其中,分散部分由微小颗粒或液滴组成,分布在连续相态中. 在胶体化学领域,胶体是分散质粒子直径在1 nm—1 μm之间的分散系. 在水环境领域中,胶体通常指能经过0.45 μm过滤膜而被1 kDa超滤膜截留的物质[12]. 胶体是介于溶液和颗粒之间的一种物质,既不下沉,也不溶解,但添加电解质后,可发生不可逆的聚沉现象. 胶体具有丁达尔效应,可产生电泳现象,并不停地做布朗运动. 此外,胶体粒径小,比表面积大,吸附能力强,往往能与周围环境中的物质相互作用[13].
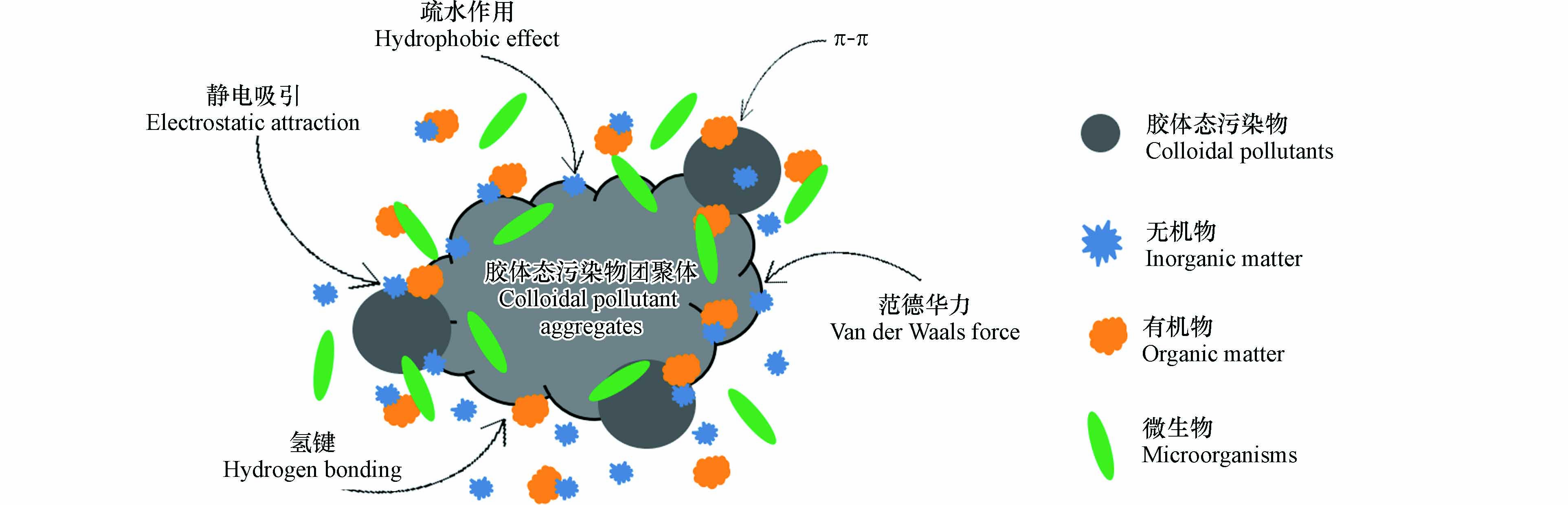
胶体是介于溶解态和颗粒态之间的一种特殊状态,而不是一种物质. 与溶解态物质相比,胶体态物质比表面积更大,吸附位点更多,更容易与环境中其他物质吸附、团聚;与颗粒态物质相比,胶体态物质不易受重力沉降,迁移能力更强[14]. 饮用水包括水源水、出厂水、管网水和龙头水,当饮用水环境条件发生变化,水中污染物可能由非胶体态转化为胶体态. 当饮用水中的污染物以胶体状态存在时,污染物往往悬浮于饮用水中,与其他污染物发生吸附、团聚[15],呈现易迁移、吸附能力强等胶体性质. 本文把饮用水中这种状态下的污染物定义为胶体态污染物. 在氢键、静电吸引、范德华力等的作用下,饮用水中的胶体态污染物可能发生胶体泵效应[3],导致饮用水质的复合污染.
-
饮用水中许多污染物是溶解态和胶体态共存的,饮用水环境的不断变化也将影响污染物的赋存状态. 本文主要关注饮用水中呈胶体态的污染物. 经迁移、吸附和团聚后,有些污染物自身转化为胶体态,如金属、腐殖酸、微生物等;有些污染物虽以非胶体态存在,但易被胶体吸附,形成复合胶体态污染物,这些污染物以有机物居多,如消毒副产物、抗生素等. 本文把饮用水中的胶体态污染物分为了无机胶体、有机胶体和生物胶体3类,具体如表1所示.
-
饮用水中主要的无机胶体是黏土,主要存在于饮用水源中. 黏土胶体作为饮用水中污染物的理想载体,能够将周围污染物吸附到自身的团聚体中,促进污染物的迁移和富集. 当水环境条件发生变化时,金属和氮、磷营养盐的存在形态会发生变化,部分以胶体态赋存于饮用水中. Locsin等[17]证实了饮用水中铅以胶体形式存在,Trueman等[18]观察到饮用水中50—200 nm的铅、铜、锰等金属呈相对致密胶体态. 与颗粒态金属相比,胶体态金属具有毒性更强、更难降解、更易积累以及持久性更强的特点,更易与水中污染物相互作用,产生金属协同效应,影响其在水中的赋存和去除. 有机氮、有机磷[19]往往以胶体态存在于饮用水中,导致其迁移和富集加剧,形成越来越大的团聚体. 氮、磷虽为营养物质,但其高浓度的赋存,将引起饮用水质污染和对人体健康的危害. 根据已有文献报道,我国江苏、安徽[34]以及湖北[35]等华东地区的饮用水均受到了有机氮的污染,而松花江、海河以及黄河等饮用水源受胶体磷的污染最严重. 饮用水中高度聚集的胶体态氮、磷将对饮用水质造成严重污染,被人体摄入后,可能引起人体内消化道疾病和神经系统中毒[36]等.
-
研究表明,腐殖质、全氟化合物和微纳塑料有部分以胶体态存在于饮用水中. 腐殖质胶体主要存在于饮用水源中[20],出厂水和龙头水中含量较低. 而胶体态全氟化合物广泛存在于我国长江三角洲、珠江三角洲、中北部等氟化产业发达地区的河流、湖泊及水库中[37],其疏水疏油,难降解,具有生物积累性,进入人体后将引起人体呼吸系统疾病和神经毒性[21]等. 类似地,胶体态微纳塑料存在于饮用水流经的各个环节[22],具有耐腐蚀,寿命长,不易降解等特性,持久存在于饮用水中,因此被人体摄入的可能性更大. 微纳塑料进入人体后,将释放出有毒物质,这可能对人体胃肠道功能[38]、肝肾功能[39]和免疫系统造成严重损伤.
此外,腐殖质表面含有大量苯环、羟基和羧基等官能团[40],可通过化学键与重金属、有机物以及微生物等污染物相互作用,而全氟化合物和微纳塑料由于粒径小、比表面积大、吸附能力强,也极易与污染物结合[41]. 因此,这些胶体态污染物将作为载体,吸附饮用水中其他污染物,形成胶体态复合污染物团聚体,对饮用水质产生不利影响,并对人体健康产生潜在威胁.
除上述自身呈胶体态的物质外,还有许多有机物能够被胶体态污染物吸附,形成复合有机胶体态污染物,例如,消毒副产物、抗生素和有机磷酸酯等. 消毒副产物目前已被检出700余种[42],作为饮用水中广泛存在的具有健康风险的污染物,其对人类遗传性疾病和癌症发病率有一定影响[43]. 抗生素和有机磷酸酯已被证实存在于饮用水源[28 − 30]、出厂水[44]以及龙头水[45]中. 抗生素的过度赋存将导致细菌产生耐药性,耐药性细菌可通过各种途径感染人体,增加对人体健康的风险危害[46];有机磷酸酯在人体内的赋存则会引起肝脏、胃肠道损伤和代谢紊乱[47]等. 这些污染物原本呈溶解态,然而,它们在迁移过程中,往往与胶体态污染物相互作用,被胶体态污染物吸附,成为复合有机胶体态污染物. 这促进了消毒副产物、抗生素和有机磷酸酯的富集,污染物之间的相互作用可能对饮用水质和人体健康造成更严重的污染和危害.
-
饮用水中的微生物包括细菌、病毒、藻类等,新发布的《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB5749-2022)中涉及的大肠杆菌、贾第鞭毛虫[33],隐孢子虫,大肠埃希氏菌,铜绿假单胞菌[48]等微生物经过吸附、团聚行为后,往往以生物胶体形式存在. 此外,微生物也可能附着在胶体态污染物表面,形成稳定的生物膜[49]. 随着时间的推移,生物膜厚度的增加使污染物的体积增大,胶体态污染物发生团聚,从而促进其他污染物的富集,加剧对饮用水质的污染,并威胁人体健康.
-
胶体态污染物普遍具有体积小、比表面积大、吸附位点多等特点,能与饮用水中污染物相互作用,吸附机理可能有静电引力、范德华力、π-π键以及氢键[50 − 51]等. 团聚是胶体态物质独有的动态特征. 胶体态污染物经吸附、团聚后,体积会增大,并逐步形成大团聚体,发生胶体泵效应,胶体态污染物的吸附、团聚行为及作用机理如图1所示. DLVO理论基于胶体间双电层的静电排斥力以及范德华作用的吸引力,建立了能够预测胶体稳定性的模型[14],目前广泛应用于胶体态污染物迁移的理论研究. 当胶体相互靠近时,会产生范德华引力,且胶体间距越小,范德华引力越大. 胶体颗粒具有双电层结构,当颗粒足够接近时,扩散双电层则会重叠,从而破坏电层的静电平衡,导致胶体间产生静电排斥力,其大小由胶体颗粒的间距和形状决定[52]. 静电排斥力和范德华引力的相对大小决定胶体呈稳定分散状态还是发生团聚. 当胶体间静电排斥力占主导时,其作用大于胶体布朗运动产生的影响,胶体不能发生团聚,而是在水中稳定分散;反之,当范德华引力占主导时,胶体间排斥能垒下降,胶体颗粒开始发生团聚,当排斥能垒降至零时,胶体团聚速率达到最大.
污染物结构、水质条件等因素会对胶体态污染物的吸附、团聚行为产生影响. 首先,由于有机胶体态污染物自身碳含量较高,促进了其他污染物在其表面的附着[51, 53]. 其次,胶体态污染物的疏水性也是影响吸附、团聚的主要因素之一,以全氟化合物为例[54],全氟化合物分子通常含有稳定的疏水骨架结构[F(CF2)n],其中的极性C—F键,使其具有极强的抗水解能力,从而可以吸附在胶体表面. 此外,溶液pH值的变化会影响无机胶体态污染物的表面电势. 随着pH的降低,无机物表面由负电荷转为正电荷. 当无机物呈电中性时胶体态污染物间的静电排斥力最小,此时最容易团聚. 对于有机胶体态污染物,碱性条件下有助于物质的分解,抑制了污染物的团聚. 溶液离子强度的提高将使胶体态污染物的平均分子量升高,从而使污染物体积增大,促进了团聚行为.
-
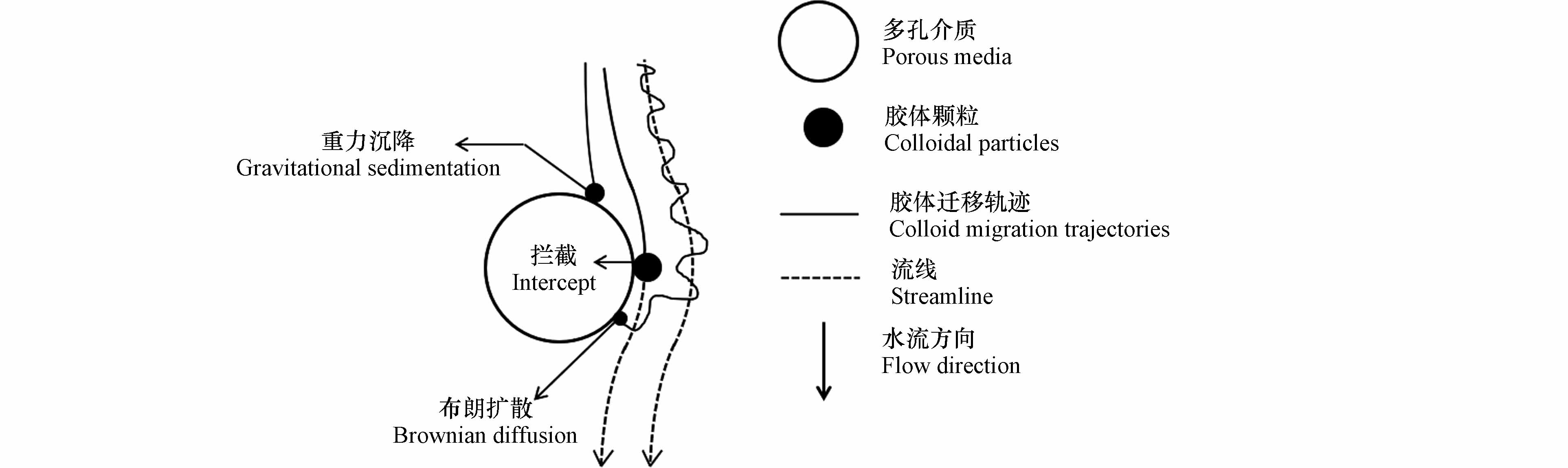
关于胶体态污染物迁移的理论研究除上述DLVO理论外,胶体过滤理论也对研究胶体态污染物的迁移行为提供了理论支撑. 胶体过滤理论用于研究胶体在多孔介质中的迁移和沉积过程,该理论认为胶体沉积到土壤和石英砂等多孔介质表面的过程包括胶体向多孔介质迁移以及胶体在多孔介质表面吸附沉积2个过程[55]. 如图2所示,在迁移过程中,胶体受拦截、重力沉降、布朗扩散3种作用. 其中,拦截是指当胶体粒径较大时,随水流流线迁移的胶体与多孔介质接触的过程;重力沉降是指若胶体密度大于水,在重力沉降作用下,胶体不再随流线轨迹迁移而与多孔介质接触的过程;布朗扩散是指在布朗运动作用占优势的情况下,小粒径胶体颗粒做不规则运动与多孔介质接触的过程[56]. 胶体吸附沉积过程的作用机制是胶体颗粒与多孔介质的相互作用[57],该机制与上节中提到的吸附机理类似,涉及的相互作用有范德华力、静电力、疏水作用等.
有专家学者们对胶体态污染物在饮用水中的迁移进行了研究. 巩霏等[59]模拟了水源土壤沉积物中胶体态多环芳烃的纵向迁移行为,发现其浓度随土柱加深而减少,而迁移行为在低浓度有机质中更为明显,这说明多种污染物共存时可能影响胶体态污染物的迁移. Zhao等[60]研究了胶体态微纳塑料和四环素在饱和多孔介质中的共迁移行为,发现在K+溶液中,四环素抑制微纳塑料的迁移,而在Ca2+溶液中起促进作用,这可能是因为疏水作用、静电斥力、对介质表面沉积位点的竞争以及污染物性质等因素的综合影响,说明胶体态污染物的共迁移行为会根据水体环境条件的变化而变化. Zhao等[61]研究了多孔介质中铜绿微囊藻的迁移行为,研究表明无论离子强度、介质大小、流速以及水中是否有溶解性有机物存在,都不能抑制铜绿微囊藻在多孔介质中的迁移,迁移率始终高于0.85,这说明污染物种类及其自身性质是影响其迁移的关键因素.
除胶体态污染物在多孔介质中迁移的相关研究外,研究者还对供水管网中胶体态污染物的迁移进行了研究. 出厂水在供水管网中将与管壁发生反应,并继续水厂内未完成的反应,形成胶体态金属腐蚀物质,这将成为导致水质下降的“二次污染源”. 何楠等[62]研究发现,经过长时间的积累、富集,供水管网内金属污染物含量可能远高于《生活饮用水卫生标准》中的限值,从而引起饮用水质污染问题. pH值[63]、温度[64]、溶解氧[65]以及离子强度是影响胶体态污染物迁移和富集的重要水质因素. 此外,水锤、管道冲刷等水力条件的变化[66]可能使胶体态污染物之间的团聚力降低,促进污染物的释放和迁移.
胶体态污染物的迁移受多种污染物共存、污染物种类及性质、水质和水力条件等多种因素的影响. 深入研究胶体态污染物的迁移理论(DLVO理论和胶体过滤理论),可为探明胶体态污染物在饮用水中的迁移规律提供理论基础,这也有助于后续高效去除胶体态污染物,稳定饮用水水质.
-
目前对饮用水中胶体态污染物的去除研究主要集中于有机污染物,对无机物和微生物的研究相对较少. 本文总结分析了常规和典型深度处理工艺对胶体态污染物的去除效果,包括混凝沉淀、过滤、消毒、臭氧氧化-活性炭过滤和膜分离,具体去除效果对比如表2所示.
-
混凝沉淀能有效去除粒径>10 μm的胶体态污染物,这是因为混凝是胶体态污染物吸附、团聚的主要作用阶段,也是胶体泵效应的主要作用阶段,粒径较大的污染物更容易附着在絮凝体上,因此具有良好的沉降性能[73]. Prokopova等[67]研究了硫酸铁和硫酸铝两种混凝剂对<50 μm PVC的去除效果,结果表明,铝基盐混凝剂的去除效率优于铁基盐,可将PVC的去除率提高至80%,其中>10 μm的污染物去除率为99%. 然而,张静等[68]研究发现,铁基盐混凝剂对四环素和磺胺类抗生素的吸附效率更高. 这可能是因为胶体态污染物性质不同,导致不同种类混凝剂对其去除效率存在差异. 此外,Yu等[69]以羧甲基壳聚糖和磁性氧化铁为原料,制备了用于去除重金属的磁性混凝剂,发现该混凝剂对Cu的去除率为92%. 这也与Liu等[76]的研究结果一致,说明磁性混凝剂可能是去除重金属的针对性混凝剂.
混凝沉淀对>10 μm胶体态污染物的去除效果良好,但对<10 μm的去除效果较差. 胶体态污染物的性质对混凝剂的作用效果产生影响. 在未来的研究中,进一步探索不同种类混凝剂对胶体态污染物的作用机制,研发针对性混凝剂、助凝剂,可有效提高胶体态污染物在混凝阶段的去除率.
-
传统过滤对胶体态污染物的去除率很低. Zhao等[61]和张静等[68]分别以玻璃珠和石英砂为滤料去除铜绿微囊藻和磺胺类、喹诺酮类等抗生素,发现无论离子强度、滤料尺寸以及流速大小,铜绿微囊藻和抗生素均无显著去除效果,说明过滤不是去除藻类微生物和抗生素的主要工艺. 同样地,传统过滤对全氟化合物的去除效率低于5%[70]. 然而,也有研究认为过滤可高效去除胶体态污染物. Tong等[71]研究了Fe3O4-生物炭改性石英砂对不同尺寸(0.02、0.2、2 μm)微纳塑料的去除效果,发现改性石英砂可使微纳塑料的去除率提高到97%. Zhang等[77]研究以无烟煤为滤料去除饮用水中的180 nm—125 μm微纳塑料,发现除10—20 μm的胶体态污染物,其余尺寸污染物几乎被全部去除. 这是因为10—20 μm是过滤效率最低的一个临界粒径范围. 当污染物尺寸>20 μm,滤料孔隙小于粒径,因此能够被截留;当微纳塑料尺寸<10 μm时,可能引发胶体泵效应,附着在滤料表面. 强化过滤可有效提高胶体态污染物的去除率,未来需继续探索针对不同种类胶体态污染物的具体强化过滤方式.
传统过滤不是去除胶体态污染物的主要工艺,但强化过滤可有效提高其去除率. 过滤作为典型的物化方法,几乎不会对水的天然属性产生影响,被专家学者认为是绿色工艺[78]. 2022年11月发布的《“十四五”生态环境领域科技创新专项规划》中明确指出“饮用水绿色净化与韧性系统构建技术”是“十四五”的重点研究内容,要研发少药剂、短流程、自动化、智能化工艺与装备及特殊水源的可持续净化技术. 过滤工艺符合饮用水绿色可持续净化技术的要求,是饮用水绿色净化领域的发展方向. 在未来的研究中,可深入研究不同性质的滤料,或将滤料与其他物质(磁性生物炭等)结合,以提高胶体态污染物的去除率.
-
消毒是常规饮用水处理流程的最终环节,用来杀灭水中的病原微生物. 目前饮用水厂主要采用氯消毒,其作用原理是在次氯酸根的作用下,通过抑制酶活性而使微生物死亡,从而消灭饮用水中有害病原体. 然而,消毒过程中胶体态消毒副产物会与氯相互作用,从而抑制了消毒剂对病原微生物的作用,导致消毒效果的降低[79]. 有研究表明,对于饮用水中的胶体态消毒副产物,可通过改变消毒条件[80]、消毒剂的投加位置和方式[81]等优化措施来控制.
-
深度饮用水处理工艺主要包括臭氧氧化-活性炭过滤、膜分离技术以及高锰酸钾氧化、UV/H2O2、UV/Cl等高级氧化工艺. 然而,目前应用最广泛、去除污染物效果最好的是臭氧氧化-活性炭过滤和膜分离技术. 因此,本文对这两种工艺进行综述. 王赛等[73]研究发现,臭氧氧化-活性炭过滤是去除<5 μm胶体态污染物的有效工艺. 这与许龙[24]、Wang等[82]的研究结果一致. 经臭氧氧化处理后,胶体态污染物被分解成许多小部分,从而提高了其生物降解能力[83],随后通过后续活性炭过滤过程中的物理吸附和生化降解协同作用去除胶体态污染物. 膜分离可根据污染物的粒径大小选择合适的膜孔径,实现胶体态污染物的高效去除,且出水水质远高于国家标准[74]. 然而,其局限性在于不能在较高膜通量的情况下高效去除胶体态污染物,因此,秦源等[75]提出在膜中加入金属有机框架复合物,以提高膜通量及污染物去除率.
深度处理是去除<10 μm胶体态污染物的高效处理工艺,在一定程度上弥补了常规饮用水处理工艺的不足.
-
(1)胶体是物质存在的一种特殊状态,饮用水中胶体态无机物、有机物和微生物呈现吸附能力强、易迁移等胶体性质,往往与其他污染物发生吸附、团聚,可能引发“胶体泵”效应,对饮用水质和人体健康造成复合污染和严重危害. 在未来的研究中,应提高对胶体态污染物和胶体泵效应的关注,探明胶体泵效应作用机制和引发条件,为胶体态污染物的迁移和去除提供理论基础. 探索饮用水中胶体态污染物的有效控制方法,从源头降低其对饮用水质的污染. 此外,胶体态污染物在饮用水中的迁移受污染物种类及性质、水质条件和水力条件等多种因素的影响,探明胶体态污染物的迁移规律,是提高胶体态污染物去除率的基础. 深入研究DLVO理论和胶体过滤理论,可为探明胶体态污染物在饮用水中的迁移规律提供理论支撑.
(2)目前,常规饮用水处理工艺中,混凝可有效去除>10 μm的胶体态污染物,传统过滤不是去除胶体态污染物的主要工艺. 深度处理作为常规处理工艺的补充,是去除<10 μm胶体态污染物的高效工艺. 然而,有众多研究表明,通过改进常规工艺,也可高效去除胶体态污染物. 过滤作为典型的传统绿色工艺,不会对水质产生二次污染,是目前最经济有效的去除胶体态污染物的工艺,符合《“十四五”生态环境领域科技创新专项规划》中提出的饮用水绿色可持续净化技术的要求,是饮用水绿色净化领域的发展方向. 发展过滤工艺,对于“十四五”规划中提到的“构建饮用水绿色净化与韧性系统技术体系”具有重要的支撑作用. 未来可通过强化过滤的方式提高胶体态污染物的去除率,例如,滤料改性、将滤料与微生物或生物炭相结合等.
饮用水中胶体态污染物的研究进展
Research progress on colloidal pollutants in drinking water
-
摘要: 饮用水中的污染物经过迁移、吸附、团聚等行为,往往以胶体态形式存在,并作为载体吸附水中其他污染物,对饮用水质造成严重污染. 聚焦于饮用水中的胶体态污染物,从胶体态污染物的概念、主要分类、迁移行为和去除效果4个方面,总结和阐述了近年来饮用水中胶体态污染物的研究进展. 总结得出,饮用水中呈胶体态的无机物、有机物和微生物往往会与其他污染物吸附、团聚,可能引发胶体泵效应,影响污染物的迁移、富集和去除. 在常规饮用水处理工艺中,混凝可有效去除>10 μm的胶体态污染物,传统过滤不是去除胶体态污染物的主要工艺. 臭氧氧化-活性炭吸附和膜分离等深度处理是去除<10 μm胶体态污染物的高效工艺. 最后,基于研究现状对胶体态污染物的控制进行了展望,以期为保障饮用水质提供借鉴和帮助.Abstract: After pollutants in drinking water have undergone migration, adsorption, agglomeration and other processes, they often exist in colloidal form, serving as carriers that adsorb other pollutants and seriously affecting drinking water quality. This review summarized the research progress on colloidal pollutants in drinking water in recent years, with a focus on their main classification, migration behavior and removal effect in drinking water treatment processes. It is concluded that colloidal inorganic matter, organic matter and microorganisms in drinking water are often adsorbed and aggregated with other pollutants, which may cause the colloid pump effect and affect the migration, enrichment and removal of pollutants. In conventional drinking water treatment processes, coagulation can effectively remove colloidal pollutants with particle sizes >10 μm, while traditional filtration is not the main process for the removal of colloidal pollutants. Ozone oxidation-activated carbon adsorption and membrane separation are efficient processes for the removal of colloidal pollutants with particle sizes <10 μm. Finally, based on the available research in this field, prospects were discussed for the effective control of colloidal pollutants, with the aim of providing guidance for the protection of drinking water quality.
-
Key words:
- colloidal pollutants /
- drinking water /
- migration /
- removal effect.
-
抗生素被广泛的应用于医疗、畜牧业、农作物养殖等方面。抗生素的大量使用会导致其在环境中积累,并在城市污水处理厂中被检测到[1-2]。由于抗生素具有生物毒性,故其对生物降解具有很高的抗性[3]。这导致含有抗生素的医疗废水、生活废水等排放至污水处理厂却无法得到高效的去除,危害着生态以及人类健康[4-6]。
光催化技术可用于抗生素的强化去除,但也存在降解不彻底、反应不易控制、能耗较高等缺点[7]。因此,在难降解废水处理中,常将光催化作为前处理,提高废水可生化性,并与生物法耦合,提高污染物的生化降解效率。LI等[8]将TiO2负载在改进的多孔载体上,以提高三氯苯酚的降解,三氯苯酚通过吸附、光降解、光催化和生物降解4个途径得到去除。ZHOU等[9]通过将Er3+:YAlO3/TiO2负载到多孔载体上,将光催化与生物降解耦合,提高了含酚废水的降解效率。DING等[10]选择紫外光催化对含有抗生素的废水进行预处理,发现光催化有助于分解抗生素中的主要官能团以消除其抗菌活性,有利于后续生物处理。FU等[11]成功将TiO2附着在载体表面并通过光催化协同去除水体中的异味物质2-甲基异冰片和土臭素,发现该系统能保持较好的去除效率和稳定性。然而,目前该领域仍然存在一些待解决的问题。例如,光催化剂在载体表面的高效附着、光催化对生物的毒性作用、光催化与生物降解耦合后对污染物的去除途径和机理等。
好氧颗粒污泥(aerobic granular sludge, AGS)是由微生物、胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances, EPS)、无机盐等聚集而成的生物聚集体。其内部环境相对稳定、菌落丰富,在处理难降解废水时具有一定的优势。HUANG等[12]利用AGS与光催化相结合处理染料废水,染料通过AGS吸附、脱附后在自净洗脱液中光解。鉴于AGS较强的吸附能力,且其紧凑的颗粒结构能为内部微生物提供很高的保护,将纳米二氧化钛(TiO2 P25)负载到AGS表面制备生物纳米材料,通过表面光催化与内部生物降解耦合,有望强化抗生素的降解。本研究综合考虑吸附动力学和负载TiO2对AGS内生物活性等方面的影响,确定了最佳TiO2负载量;考察了该生物纳米材料对磺胺类抗生素磺胺嘧啶(sulfadiazine, SDZ)的降解性能,并通过检测磺胺嘧啶及中间产物,确定了降解途径。
1. 实验材料与方法
1.1 AGS的培养
实验的接种污泥取自污水处理厂二沉池,在序批式反应器(sequencing batch reactor, SBR)中以模拟废水培养AGS。SBR主体为内径8 cm、高100 cm的有机玻璃,工作体积为4 L。反应周期为4 h,包括进水12 min、曝气210 min、沉淀加出水18 min,体积交换率为50%。曝气阶段空气通过曝气泵从底部微孔曝气头通入,并用气体转子流量计维持气体流速在0.25~0.30 m3·h−1。
SBR中初始混合液污泥质量浓度(mixed liquor suspended solid, MLSS)约为5 g·L−1。模拟废水的具体组分如下:641 mg·L−1 CH3COONa、469 mg·L−1 C6H12O6、191.1 mg·L−1 NH4Cl、23 mg·L−1 KH2PO4、60 mg·L−1 CaCl2、300 mg·L−1 NaHCO3、24 mg·L−1 MgSO4·7H2O、21 mg·L−1 FeSO4·7H2O、20 mg·L−1 EDTA、1.6 mg·L−1 FeCl3·6H2O以及0.5 mL·L−1微量元素。其中微量元素包括240 mg·L−1 MnCl3·4H2O、300 mg·L−1 Na2MoO4·2H2O、60 mg·L−1 CuSO4·5H2O、300 mg·L−1 H3BO3、60 mg·L−1 KI、240 mg·L−1 ZnCl2和116 mg·L−1 CoCl2·6H2O。模拟废水中碳氮比为100:5,NaHCO3将进水pH控制在7.1~7.9。反应器在室温下(约为25 ℃)运行长达160 d,以使污泥达到性能稳定。培养后的AGS粒径在1~5 mm,MLSS约为10 g·L−1,混合液挥发性悬浮固体质量浓度(mixed liquor volatile suspended solids, MLVSS)与MLSS的比值在0.8右,污泥体积指数(sludge volume index, SVI)为37 mL·g−1,COD以及
NH+4 1.2 吸附实验及脱附实验
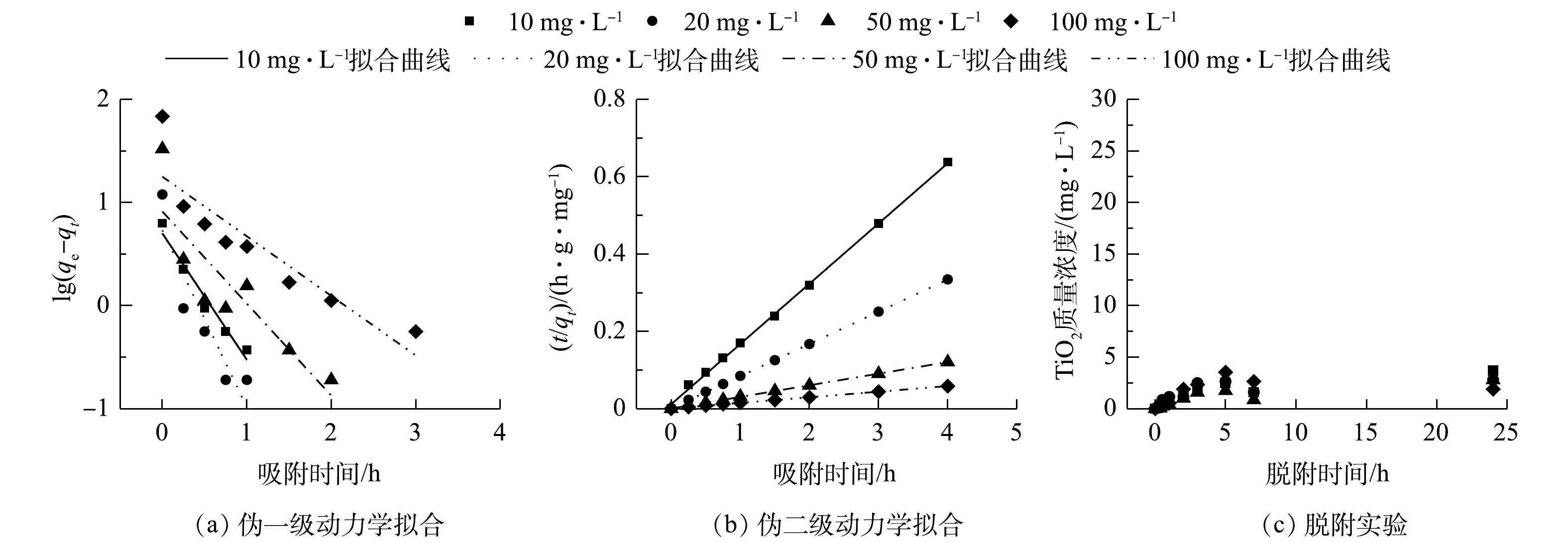
选择TiO2 P25为光催化剂,在4个锥形瓶中分别加入MLSS约为1.42 g·L−1的AGS。初始TiO2质量浓度分别为10、20、50、100 mg·L−1。以150 r·min−1在30 ℃进行AGS上TiO2的吸附动力学实验。吸附动力学实验完成后,将污泥用去离子水清洗后恢复至原体积,在30 ℃下以150 r·min−1振荡进行24 h的脱附实验并检测水相中的TiO2。
通过吸附动力学分析吸附机理,采用伪一级动力学方程(式(1))、伪二级动力学方程(式(2))分别对不同质量浓度TiO2的吸附实验数据进行拟合[13]。
lg(qe−qt)=lgqe−k12.303t (1) tqt=1k2qe2+1qet (2) 式中:t为时间,h;k1为伪一级动力学吸附速率常数,g·(mg·h)−1;k2为伪二级动力学吸附速率常数,g·(mg·h)−1;qe和qt分别为平衡状态和t时的吸附容量,mg·g−1。
1.3 反应装置的运行
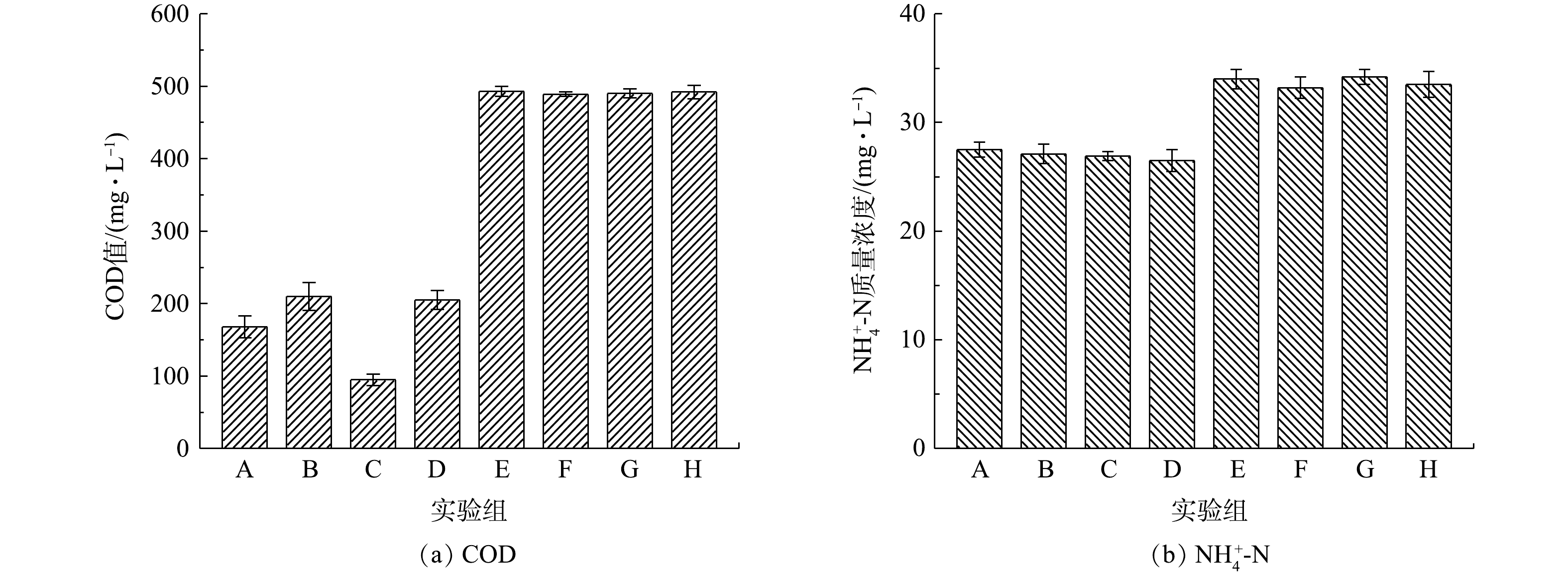
为了探究光照条件对附着TiO2后的生物纳米材料性能的影响,并考察其对SDZ的降解性能和途径,进行了一系列批实验。实验所用废水初始COD值为500 mg·L−1,
NH+4 在100 mL的烧杯中,研究不同光照条件对生物纳米材料微生物活性的影响。设置不同光照模式:(I)紫外光照射0 h+可见光照射4 h;(II)紫外光照射1 h+可见光照射3 h;(III)紫外光照射2 h+可见光照射2 h。设置不同紫外光光照时间:分别设置0、1、2 h 的紫外光光照时间进行实验。通过调节紫外光光源距离调整光照强度,分别为0、0.3、0.45 mW·cm−2。
在工作体积为1 L的有机玻璃反应器内探究SDZ的降解途径以及降解产物。选用没有被TiO2负载的原始AGS和以20 mg·L−1 TiO2负载的AGS (T-AGS),进行8组10 h的批实验,分别为:AGS在紫外光下运行为A组;AGS在可见光下运行为B组;T-AGS在紫外光下运行为C组;T-AGS在可见光下运行为D组;不添加AGS和T-AGS在紫外光下运行为E组;不添加AGS和T-AGS在可见光下运行为F组;AGS加NaN3可见光下运行为G组;T-AGS加NaN3可见光下运行为H组。
1.4 分析方法
COD、
NH+4 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 TiO2的吸附与脱附
对AGS吸附负载TiO2的过程进行了动力学拟合。伪一级动力学拟合结果分别以t和lg(qe−qt)为横、纵坐标作图,计算30 ℃下不同TiO2初始浓度下的k1和qe。结果如图1(a)和表1所示。伪一级动力学方程的拟合情况较差,可决系数低;伪二级动力学拟合中不同浓度TiO2吸附实验对应的R2均大于0.99,远高于伪一级模型的拟合结果。考虑到模型拟合和实验观察到的吸附能力之间的良好一致性以及较高的可决系数,说明TiO2在AGS上的吸附反应较符合伪二级动力学模型。该动力学模型包括表面吸附、颗粒内扩散和液膜扩散等吸附过程,能够全面地反映AGS吸附TiO2的动力学过程机制。在最初的0.5 h内,TiO2的吸附速率很快,随着反应的进行,吸附位点也越来越少,随后达到吸附平衡。投加量为20 mg·L−1的TiO2拥有最快的伪二级动力学吸附速率。
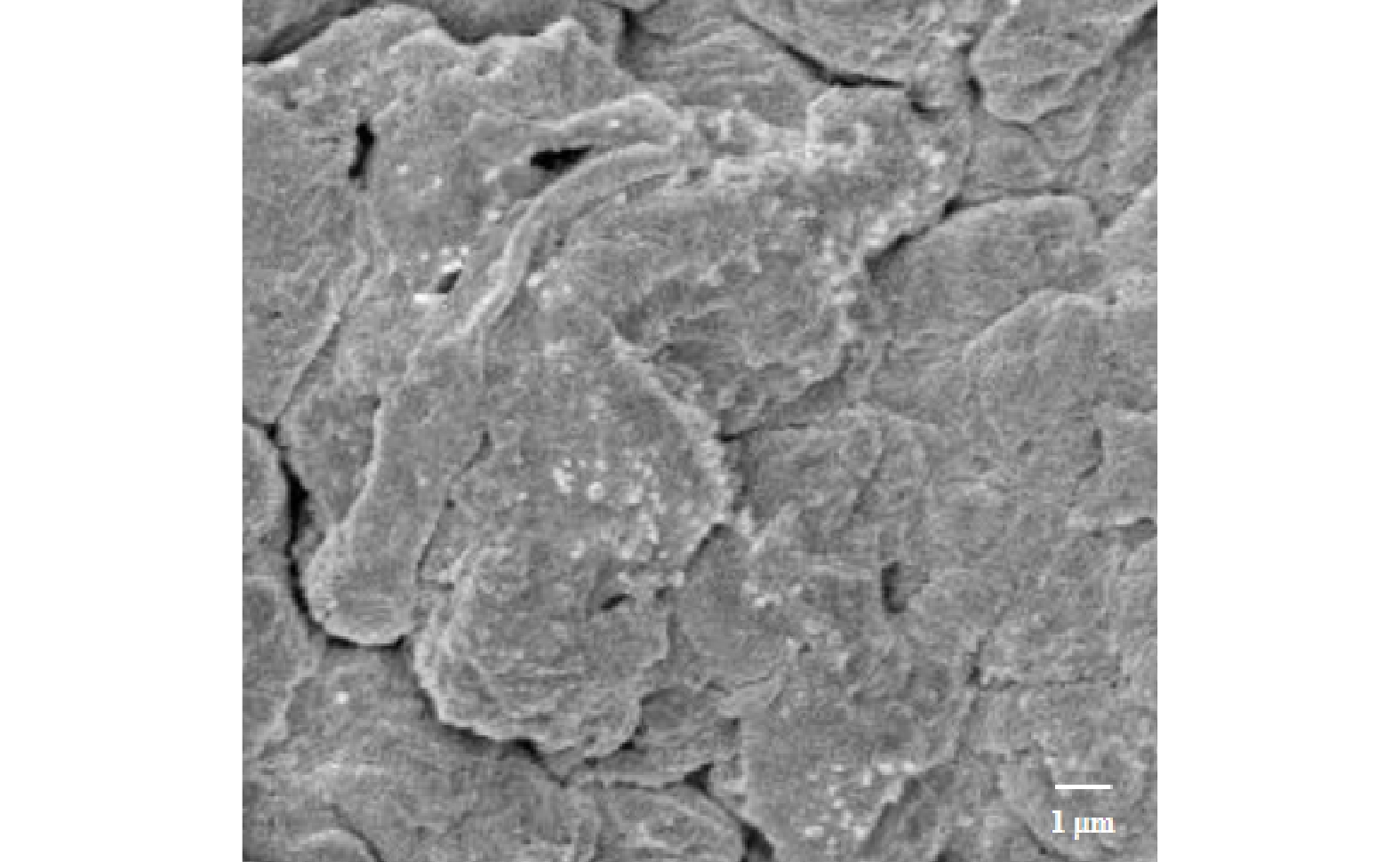
表 1 AGS上纳米TiO2的附动力学方程拟合参数Table 1. Adsorption kinetic fitting parameters for TiO2 on AGSTiO2/(mg·L−1) qe,exp/(mg·g−1) 伪一级动力学 伪二级动力学 k1/(g·(mg·h)−1) qe,cal/(mg·g−1) R2 k2/(g·(mg·h)−1) qe,cal/(mg·g−1) R2 10 6.27 2.82 5.01 0.95 2.07 6.42 1.00 20 11.96 3.95 5.37 0.79 5.63 12.01 1.00 50 33.10 2.06 8.18 0.72 1.30 33.27 1.00 100 68.38 1.33 17.80 0.79 0.35 68.82 1.00 为了研究负载后的TiO2是否会随着反应的运行而从AGS上脱附,从而影响后续实验,故开展了24 h的脱附实验。由图1(c)可知,负载10、20、50、100 mg·L−1 TiO2的AGS在24 h振荡后几乎没有发生TiO2脱附,脱附反应可以忽略不计。这说明本实验制备的生物纳米材料可以在反应器中长期运行。对负载20 mg·L−1 TiO2后的AGS进行SEM分析。由图2可以看出,TiO2在AGS的表面比较清晰,大部分呈球形颗粒。有些模糊的部分可能是因为被颗粒表面EPS所包裹所致。
2.2 负载TiO2对生物的影响
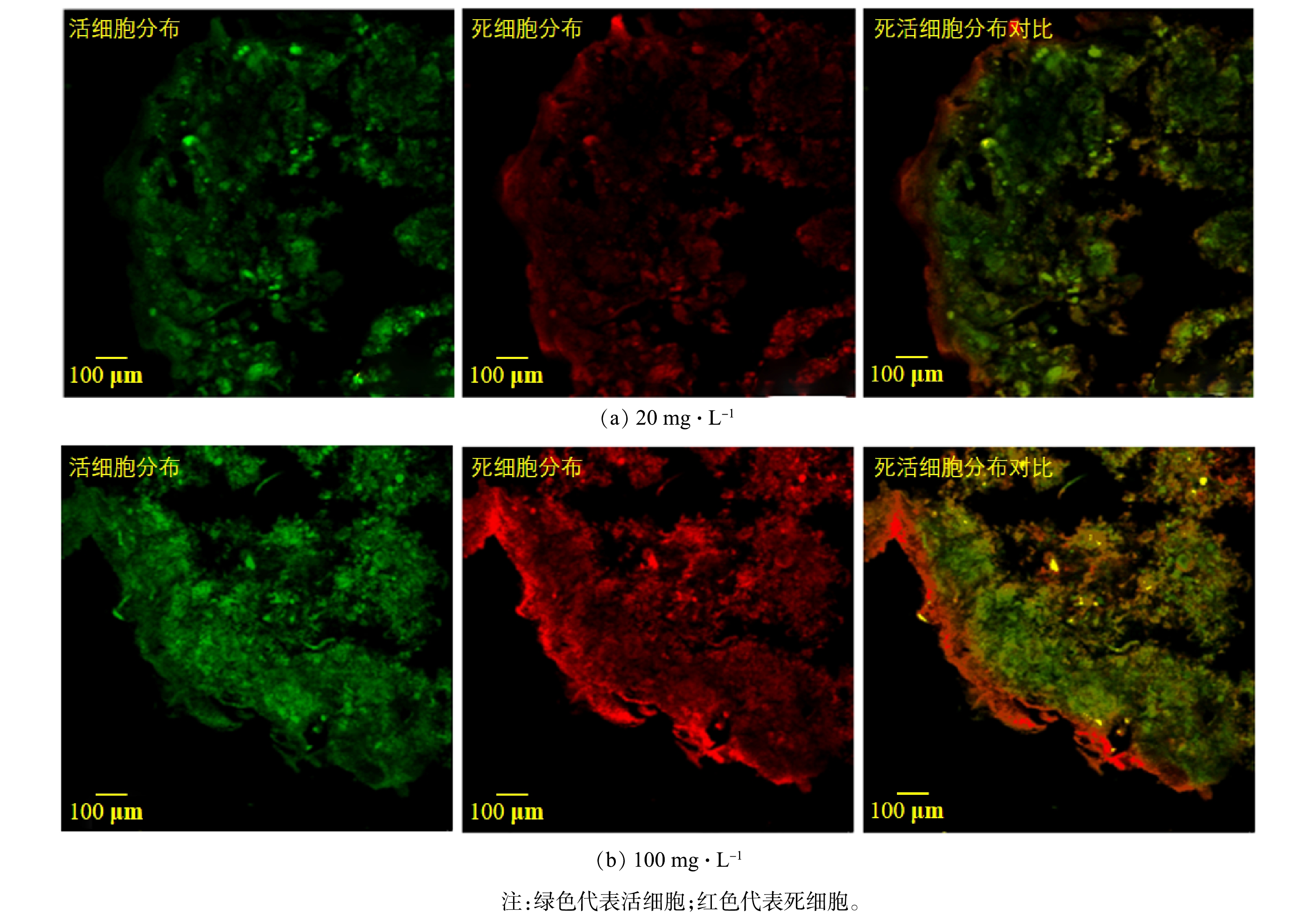
为了观察负载的TiO2对AGS内细胞生物的影响,对AGS吸附TiO2 12 h后切片观察死活细胞分布。图3(a)和图3(b)分别是在20 mg·L−1和100 mg·L−1 TiO2条件下制备的生物纳米材料,其中绿色代表活细胞,红色代表死细胞。结果表明,AGS最外侧的细菌受到严重影响,这可能是由于纳米颗粒引起微生物的氧化损伤,从而导致细胞膜失去完整性[22]。前述吸附动力学研究结果表明,TiO2在AGS上的吸附包括颗粒内部扩散,所以AGS内部的微生物也会受到影响[20]。与20 mg·L−1相比,在负载100 mg·L−1 TiO2的AGS内部微生物受到的伤害成都明显增加,颗粒内外大量细胞已经死亡。
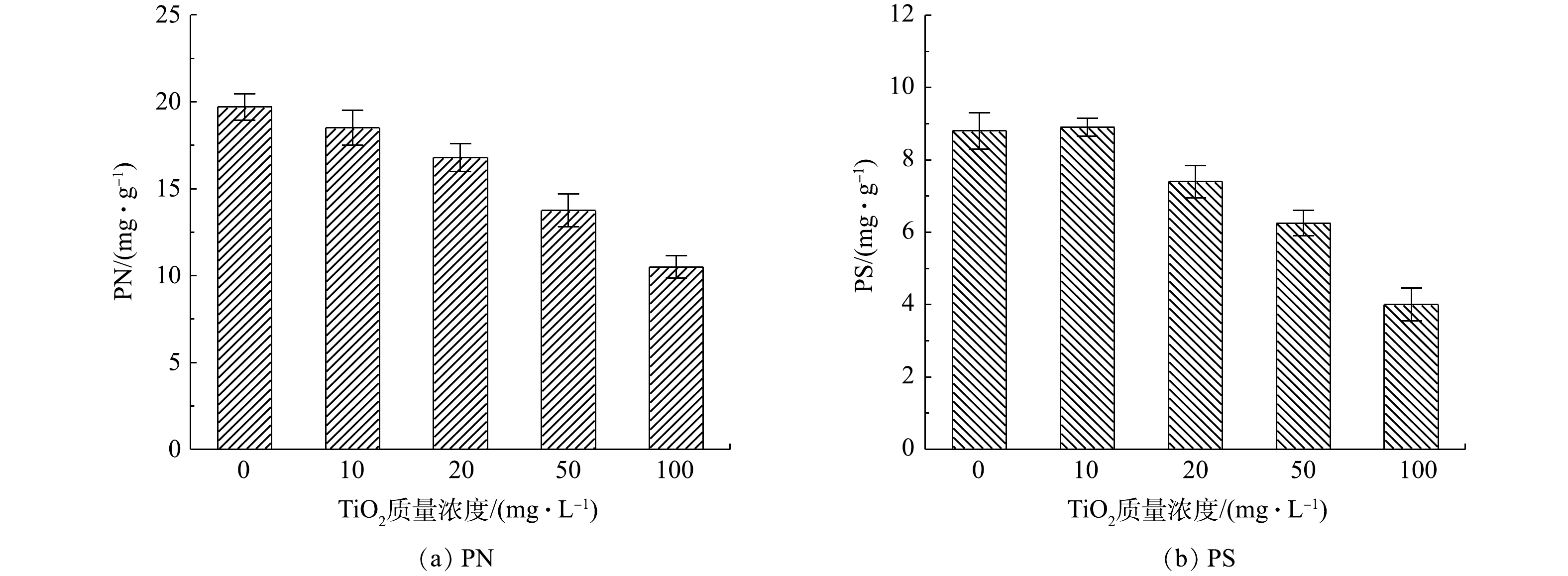
EPS是AGS的重要组成部分,对AGS的结构稳定起着重要的作用[23]。如图4所示,原始AGS中蛋白质(protein, PN)和多糖(polysaccharide, PS)含量分别为19.7 mg·g−1和8.8 mg·g−1。随着TiO2质量浓度的增加,污泥内PN和PS逐渐减少。当初始TiO2投加量为50 mg·L−1时,PN和PS含量已经显著下降到13.8 mg·g−1和6.3 mg·g−1。EPS能够保护细胞,减少外界有毒有害物质的影响,在较低的EPS含量下,其保护作用逐渐减弱。这可能是图3中100 mg·L−1 TiO2投加量下制备的生物纳米材料内部死细胞明显增加的原因所在。同时EPS的减少对AGS的结构稳定性造成影响,同样会增加微生物与TiO2的接触,对微生物活性产生抑制[24]。综合AGS对TiO2的吸附动力学结果和TiO2对AGS细胞和EPS的影响,本实验选择20 mg·L−1 TiO2条件下制备的生物纳米材料进行后续研究。
2.3 光照条件对AGS的影响
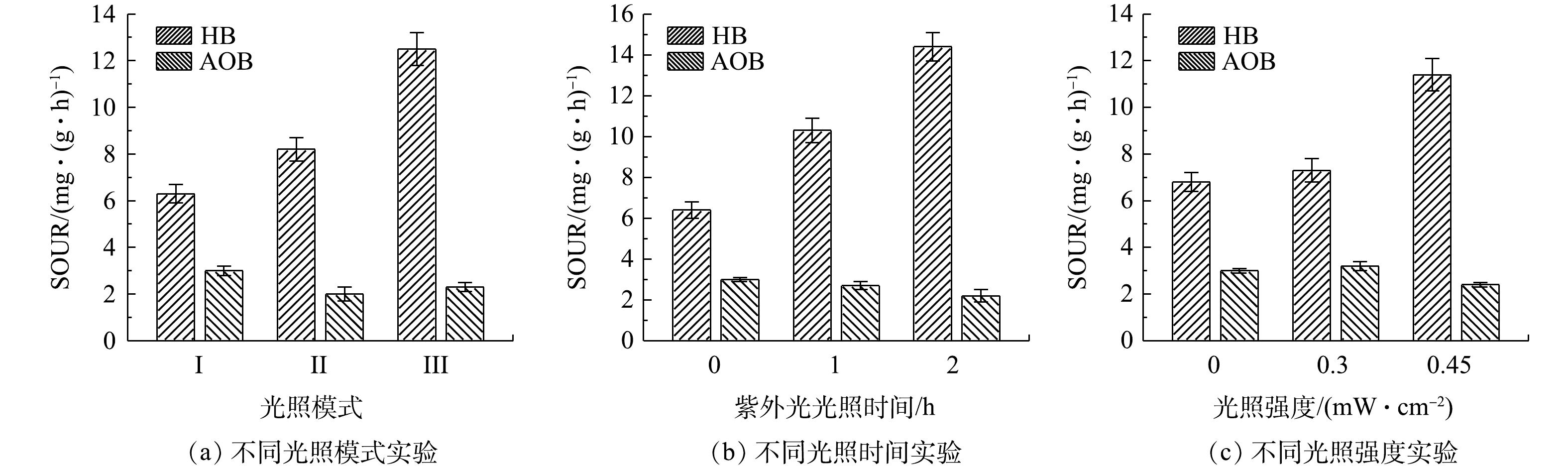
图5所示为不同光照条件对负载20 mg·L−1 TiO2的AGS (T-AGS)活性的影响。分别对异养菌(heterotrophic bacteria, HB)及氨氧化菌(ammonia oxidizing bacteria, AOB)的SOUR进行了测定。由图5(a)可知,从不同光照模式下SOUR的变化情况来看,模式I(紫外光照射0 h+可见光照射4 h)中HB的SOUR最低、AOB的活性最高;在模式II(紫外光照射1 h+可见光照射3 h)和模式III(紫外光照射2 h+可见光照射2 h)中,引入紫外光照射提高了HB活性,但对AOB活性有一定的抑制作用。图5(b)中仅有紫外光照射时的实验结果也验证了紫外光对HB活性的促进和对AOB活性的抑制作用。另外,与图5(a)中模式III(紫外光照射2 h+可见光照射2 h)相比,图5(b)中仅有紫外光照射2 h后AOB的SOUR略有提高。这可能是由于经紫外光照射后的AOB在可见光光照下发生了光复活性,例如酶促DNA修复使紫外光下造成的阻碍基因正常复制的二聚体裂开,损伤的细胞自我恢复活性使SOUR回升[25]。进一步研究了不同紫外光光强对T-AGS中SOUR的影响。如图5(c)所示,在0.3 mW·cm−2光强下,T-AGS中HB和AOB的活性均有小幅上升;而将紫外光光强提升至0.45 mW·cm−2时,虽然HB活性有所提高,但AOB活性受到抑制。因此,后续实验中选择0.3 mW·cm−2的光照强度。
2.4 SDZ降解途径及产物
在探究SDZ降解途径以及降解产物的批实验中,首先对10 h后反应器中剩余的耗氧有机物(以COD计)和
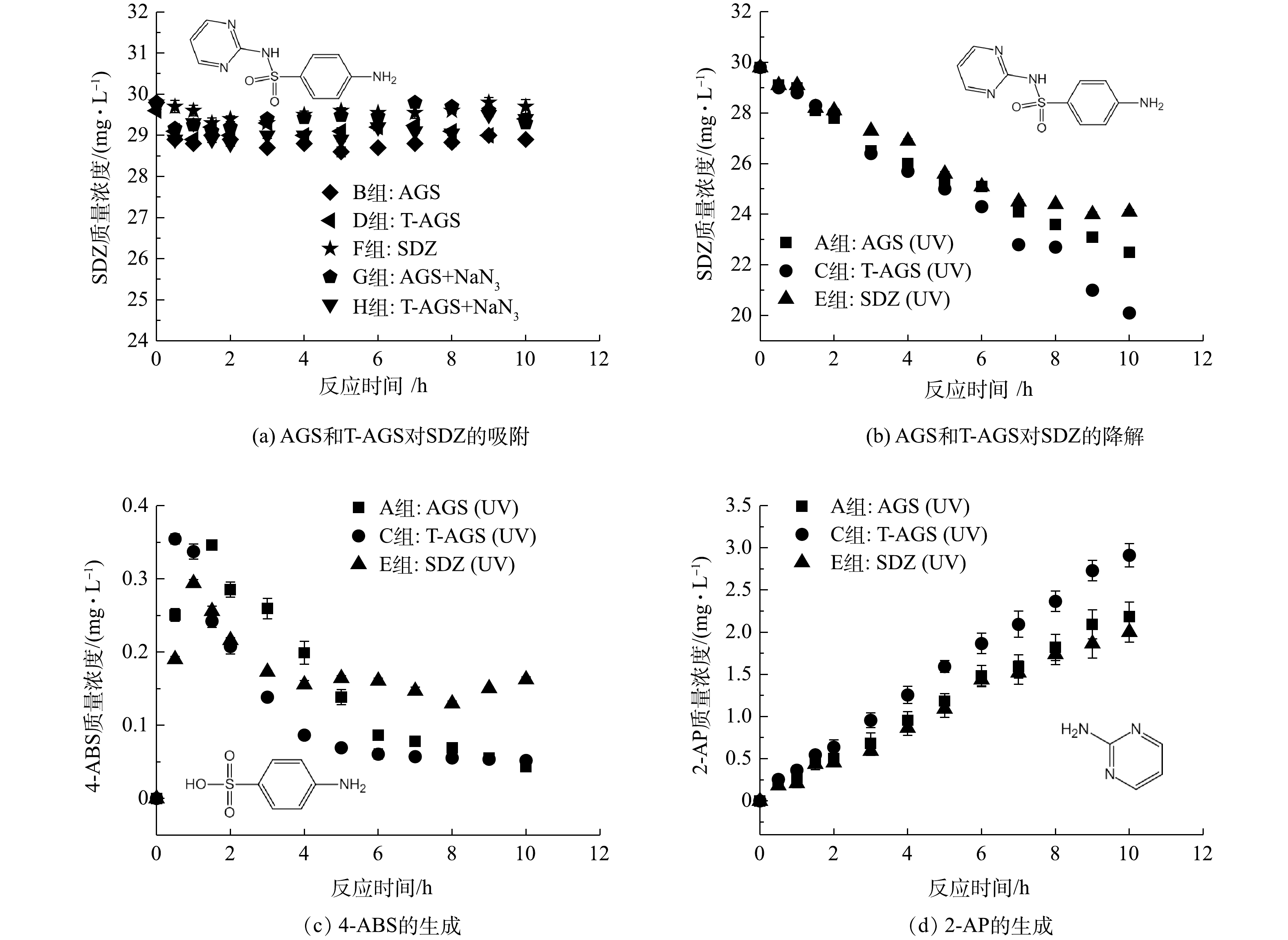
NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 图7显示了各实验组中SDZ及其中间产物的质量浓度随时间的变化情况。B组在可见光下运行的普通AGS和D组T-AGS几乎无法降解SDZ(图7(a)),这是由于SDZ具有生物毒性,其无法诱导生物体内的相应酶或辅因子对SDZ进行生物降解[26]。F组是不添加AGS和T-AGS在可见光下运行的反应,表明SDZ几乎不被可见光光解。G组和 H组由于加入NaN3进行生物失活,AGS与T-AGS在前0.5 h内通过物理吸附去除了1 mg左右的SDZ,随后达到吸附平衡,SDZ不再减少。由图7(b)可见,在紫外光照射下,A、C和E组内SDZ质量浓度随时间逐渐降低,在10 h内SDZ的平均降解速率分别为0.73、0.97、0.57 mg·(L·h)−1。不添加生物质的E组内SDZ可以在紫外光照射下得到少量降解,而在A组中由于紫外光刺激提高了普通AGS中HB的生物活性,使得SDZ去除率稍有提升。T-AGS在紫外光光照下具有最好的SDZ降解效果,这是由于负载在颗粒表面的TiO2在紫外光下生成了羟基自由基,因而加速了SDZ的降解。
图7(c)和图7(d)是对SDZ降解过程中可能的中间产物(氨基苯磺酸(4-ABS)和2-氨基嘧啶(2-AP))进行了检测。在SDZ降解过程中,由于苯环和嘧啶环之间相连的磺酰胺基团中的S与N之间的化学键断裂而分离,分别形成4-ABS和2-AP。4-ABS在SDZ降解初期生成量较大,而后逐渐降低。这可能是由于4-ABS不稳定,被微生物或紫外光进一步降解,且其降解速率大于SDZ降解生成4-ABS的速率,导致其无法在体系内积累。添加生物质的A组及C组中4-ABS的积累明显少于E组。这说明生物降解对于4-ABS去除的重要性,也证明了生物与光催化相结合更有助于SDZ及中间产物的去除。相比之下,2-AP更不易被进一步降解,其质量浓度不断积累,表明2-AP无法被微生物利用且紫外照射下较稳定。2-AP具有较强的毒性,通过羟基化反应使其进一步转化[27],或可通过高锰酸钾氧化为2-硝基嘧啶,以降低其生物毒性[28]。
3. 结论
1)利用AGS吸附TiO2制备了稳定性较好的新型生物纳米材料,AGS对TiO2的吸附过程符合伪二级动力学。
2)综合考虑吸附动力学和负载TiO2对AGS内生物活性等方面的影响,确定了最佳TiO2负载量为20 mg·L−1。
3) 0.3 mW·cm−2强度的紫外光会促进T-AGS中HB的活性,提高对耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)的去除率,且不会对AOB及
NH+4 4)紫外光照射促进了T-AGS对SDZ的降解及其中间产物的去除,中间产物中4-ABS易被进一步降解,而2-AP较为稳定。
-
图 2 胶体过滤理论中的胶体迁移机制[58]
Figure 2. Colloid migration mechanism in colloid filtration theory
表 1 饮用水中胶体态污染物的种类
Table 1. Types of colloid pollutants in drinking water
表 2 饮用水处理工艺对胶体态污染物的去除效果比较
Table 2. Comparison of removal effect of colloidal pollutants by drinking water treatment processes
处理工艺Treatment processes 去除污染物Pollutants removed 尺寸范围/μmSize range 处理效果Removal effect 改进方向Improvement direction 参考文献References 混凝沉淀 微纳塑料 <50 高效去除>10 μm的胶体态污染物,对<10 μm的具有局限性;不同种类污染物对应的高效混凝剂不同 投加针对性混凝剂/助凝剂 [67] 抗生素 — [68] 重金属 — [69] 过滤 微生物(铜绿微囊藻) 4.5 传统过滤不是去除胶体态污染物的主要工艺,强化过滤可有效提高去除率 滤料改性/与其他物质(微生物、生物炭)结合 [61] 抗生素 — [68] 全氟化合物 <0.45 [70] 微纳塑料 <2 [71] 消毒 微生物(大肠杆菌) <0.22 消灭病原微生物,但胶体态消毒副产物的存在抑制了消毒效果 优化消毒条件、消毒剂的投加顺序和方式 [72] 臭氧氧化-活性炭过滤 微纳塑料 <5 去除<5 μm胶体态污染物的有效工艺 — [73] 膜分离 抗生素 由膜孔径决定 出厂水质高于国家标准限值 膜改性处理 [74 − 75] -
[1] 刘文君, 王小𠇔, 王占生. 饮用水水质标准的发展: 从卫生、安全到健康的理念[J]. 给水排水, 2017, 53(10): 1-3, 61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2017.10.001 LIU W J, WANG X T, WANG Z S. Development of drinking water quality standards: From hygiene, safety to health concept[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2017, 53(10): 1-3, 61 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2017.10.001
[2] LEAD J R, WILKINSON K J. Aquatic colloids and nanoparticles: Current knowledge and future trends[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2006, 3(3): 159. doi: 10.1071/EN06025 [3] HONEYMAN B D, SANTSCHI P H. Coupling adsorption and particle aggregation: Laboratory studies of “colloidal pumping” using iron-59-labeled hematite[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1991, 25(10): 1739-1747. [4] LU S, ZHANG G. Recent advances on inactivation of waterborne pathogenic microorganisms by (photo) electrochemical oxidation processes: Design and application strategies[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 431: 128619. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128619 [5] SONG P P, YANG Z H, ZENG G M, et al. Electrocoagulation treatment of arsenic in wastewaters: A comprehensive review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 317: 707-725. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.086 [6] CHELLAM S, SARI M A. Aluminum electrocoagulation as pretreatment during microfiltration of surface water containing NOM: A review of fouling, NOM, DBP, and virus control[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 304: 490-501. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.054 [7] IBHADON A, FITZPATRICK P. Heterogeneous photocatalysis: Recent advances and applications[J]. Catalysts, 2013, 3(1): 189-218. doi: 10.3390/catal3010189 [8] MANSAS C, MENDRET J, BROSILLON S, et al. Coupling catalytic ozonation and membrane separation: A review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 236: 116221. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116221 [9] YU J J, JIAO R Y, SUN H Y, et al. Removal of microorganic pollutants in aquatic environment: The utilization of Fe(VI)[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 316: 115328. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115328 [10] KRAKOWIAK R, MUSIAL J, BAKUN P, et al. Titanium dioxide-based photocatalysts for degradation of emerging contaminants including pharmaceutical pollutants[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(18): 8674. doi: 10.3390/app11188674 [11] ARQUEROS C, ZAMORA F, MONTORO C. A perspective on the application of covalent organic frameworks for detection and water treatment[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 11(7): 1651. doi: 10.3390/nano11071651 [12] 魏俊峰, 戴民汉, 洪华生, 等. 海洋中胶体的分布与微形貌特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2009, 33(3): 76-79. WEI J F, DAI M H, HONG H S, et al. The distribution of marine colloids and their morphological characteristics[J]. Marine Sciences, 2009, 33(3): 76-79 (in Chinese).
[13] KNAPPENBERGER T, ARAMRAK S, FLURY M. Transport of barrel and spherical shaped colloids in unsaturated porous media[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2015, 180: 69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2015.07.007 [14] 王沛芳, 包天力, 胡斌, 等. 天然胶体的水环境行为[J]. 湖泊科学, 2021, 33(1): 28-48. doi: 10.18307/2021.0100 WANG P F, BAO T L, HU B, et al. Environmental behaviors of natural colloids in water environment[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2021, 33(1): 28-48 (in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2021.0100
[15] ZHOU J L, LIU R, WILDING A, et al. Sorption of selected endocrine disrupting chemicals to different aquatic colloids[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(1): 206-213. [16] 赵伟高. 饮用水处理中胶体在过滤过程的迁移行为和沉积机理研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2020. ZHAO W G. Transport behavior and deposition mechanism of colloids in drinking water treatment during filtration[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[17] LOCSIN J A, HOOD K M, DORÉ E, et al. Colloidal lead in drinking water: Formation, occurrence, and characterization[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2023, 53(1): 110-136. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2022.2039549 [18] TRUEMAN B F, ANAVIAPIK-SOUCIE T, L'HéRAULT V, et al. Characterizing colloidal metals in drinking water by field flow fractionation[J]. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 2019, 5(12): 2202-2209. [19] JUDY J D, KIRBY J K, FARRELL M, et al. Colloidal nitrogen is an important and highly-mobile form of nitrogen discharging into the Great Barrier Reef lagoon[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1-11. [20] 周蕾, 周永强, 张运林, 等. 重要饮用水源地天目湖水库有色可溶性有机物来源与组成特征[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(8): 3709-3718. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202012280 ZHOU L, ZHOU Y Q, ZHANG Y L, et al. Characterizing sources and composition of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in a key drinking water reservoir lake tianmu[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(8): 3709-3718 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202012280
[21] 张美, 楼巧婷, 邵倩文, 等. 全氟化合物污染现状及风险评估的研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(3): 30-53. ZHANG M, LOU Q T, SHAO Q W, et al. Research progress of perfluorinated compounds pollution status and risk assessment[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(3): 30-53 (in Chinese).
[22] LI Y, LI W Y, JARVIS P, et al. Occurrence, removal and potential threats associated with microplastics in drinking water sources[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(6): 104527. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104527 [23] DALMAU-SOLER J, BALLESTEROS-CANO R, FERRER N, et al. Microplastics throughout a tap water supply network[J]. Water and Environment Journal, 2022, 36(2): 292-298. doi: 10.1111/wej.12766 [24] 许龙, 王志峰. 某水厂中微塑料的赋存及去除特性[J]. 净水技术, 2020, 39(7): 109-113, 120. doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2020.07.018 XU L, WANG Z F. Occurrence and removal of microplastics in a water treatment plant[J]. Water Purification Technology, 2020, 39(7): 109-113, 120 (in Chinese). doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2020.07.018
[25] TONG H Y, JIANG Q Y, HU X S, et al. Occurrence and identification of microplastics in tap water from China[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 252: 126493. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126493 [26] HU S Y, GONG T T, ZHU H T, et al. Formation and decomposition of new iodinated halobenzoquinones during chloramination in drinking water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(8): 5237-5248. [27] ZHANG Z X, ZHU Q Y, HUANG C, et al. Comparative cytotoxicity of halogenated aromatic DBPs and implications of the corresponding developed QSAR model to toxicity mechanisms of those DBPs: Binding interactions between aromatic DBPs and catalase play an important role[J]. Water Research, 2020, 170: 115283. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115283 [28] STANGE C, YIN D, XU T, et al. Distribution of clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Lake Tai, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 655: 337-346. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.211 [29] STOLL C, SIDHU J P S, TIEHM A, et al. Prevalence of clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in surface water samples collected from Germany and Australia[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(17): 9716-9726. [30] DEVARAJAN N, LAFFITE A, GRAHAM N D, et al. Accumulation of clinically relevant antibiotic-resistance genes, bacterial load, and metals in freshwater lake sediments in Central Europe[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6528-6537. [31] WU D H, ZHOU Y, LU G H, et al. The occurrence and risks of selected emerging pollutants in drinking water source areas in Henan, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(21): 4109. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16214109 [32] 曹美苑, 兰青, 许凭厘, 等. 城市生活饮用水中有机磷酸酯阻燃剂分布特征研究[J]. 广州化工, 2019, 47(5): 119-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2019.05.044 CAO M Y, LAN Q, XU P L, et al. Study on distribution characteristics of organic phosphate flame retardant in drinking water in Guangzhou[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2019, 47(5): 119-122 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2019.05.044
[33] 冯雨欣, 马雪婷, 杨坤澎, 等. 饮用水中微生物检测技术的研究现状与发展方向[J]. 广东化工, 2022, 49(2): 62-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.02.024 FENG Y X, MA X T, YANG K P, et al. Research status and development direction of microbial detection technology in drinking water[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2022, 49(2): 62-63 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.02.024
[34] 丁润楠, 姚晓龙, 傅大放, 等. 中国东部湖泊有机氮浓度时空特征及影响因素[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(6): 35-42. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2021.06.005 DING R N, YAO X L, FU D F, et al. Spatial and seasonal characteristics of organic nitrogen concentrations in lakes of Eastern China and its influencing factors[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(6): 35-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2021.06.005
[35] BRONK D A, SEE J H, BRADLEY P, et al. DON as a source of bioavailable nitrogen for phytoplankton[J]. Biogeosciences, 2007, 4(3): 283-296. doi: 10.5194/bg-4-283-2007 [36] 丁浩东, 万红友, 秦攀, 等. 环境中有机磷农药污染状况、来源及风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(3): 463-479. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051405 DING H D, WAN H Y, QIN P, et al. Occurrence, sources and risk assessment of organophosphorus pesticides in the environment, China[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(3): 463-479 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051405
[37] 刘建超, 郑超亚, 任静华, 等. 平原河湖系统中典型全氟化合物的胶体吸附特征及生态风险评估[J]. 湖泊科学, 2021, 33(6): 1714-1726. doi: 10.18307/2021.0609 LIU J C, ZHENG C Y, REN J H, et al. Adsorption characteristics of perfluorinated compounds from colloids in the river-lake system of the plain and their ecological risk[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2021, 33(6): 1714-1726 (in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2021.0609
[38] YUAN Z H, NAG R, CUMMINS E. Human health concerns regarding microplastics in the aquatic environment - From marine to food systems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 823: 153730. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153730 [39] RAMIREZ ARENAS L, RAMSEIER GENTILE S, ZIMMERMANN S, et al. Fate and removal efficiency of polystyrene nanoplastics in a pilot drinking water treatment plant[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 813: 152623. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152623 [40] ANIRUDHAN T S, BRINGLE C D, RIJITH S. Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions and nuclear industry effluents using humic acid-immobilized zirconium-pillared clay[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2010, 101(3): 267-276. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2009.12.001 [41] ANDERSON J C, PARK B J, PALACE V P. Microplastics in aquatic environments: Implications for Canadian ecosystems[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 218: 269-280. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.06.074 [42] 魏文哲, 罗家怡, 赵佳焱, 等. 饮用水中新型环状消毒副产物的毒性研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2021, 16(6): 87-103. WEI W Z, LUO J Y, ZHAO J Y, et al. Research progress on toxicity of new cyclic disinfection byproducts in drinking water[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2021, 16(6): 87-103 (in Chinese).
[43] WAGNER E D, PLEWA M J. CHO cell cytotoxicity and genotoxicity analyses of disinfection by-products: An updated review[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 58: 64-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.04.021 [44] 杨露敏, 宋晓翠, 张颖, 等. 自来水给水系统中有机磷酸酯的污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(8): 3268-3278. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0040 YANG L M, SONG X C, ZHANG Y, et al. Pollution profile and risk assessment of organophosphate esters in a drinking water supply system of Tianjin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(8): 3268-3278 (in Chinese) doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0040
[45] LI J F, HE J H, LI Y N, et al. Assessing the threats of organophosphate esters (flame retardants and plasticizers) to drinking water safety based on USEPA oral reference dose (RfD) and oral cancer slope factor (SFO)[J]. Water Research, 2019, 154: 84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.01.035 [46] 陈玲, 杨潇, 张琳钰, 等. 食品中环境新污染物危害管控研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24(6): 99-106. CHEN L, YANG X, ZHANG L Y, et al. Hazard and management of emerging environmental pollutants in food of China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022, 24(6): 99-106 (in Chinese).
[47] 叶长春, 李颖, 陈子璐, 等. 饮食中有机磷酸酯暴露现状及其对消化系统影响的研究进展[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2022, 29(5): 677-682. YE C C, LI Y, CHEN Z L, et al. Research progress on dietary organophosphate esters exposure and its effect on digestive system[J]. Chinese Journal of Bases and Clinics in General Surgery, 2022, 29(5): 677-682 (in Chinese).
[48] 慕妮, 何薛纯, 樊青青, 等. 包装饮用水中铜绿假单胞菌检测方法的比较分析[J]. 生物化工, 2021, 7(6): 151-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0387.2021.06.038 MU N, HE X C, FAN Q Q, et al. Comparative analysis of detection methods of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in packaged drinking water[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering, 2021, 7(6): 151-155 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0387.2021.06.038
[49] HE S Y, JIA M Y, XIANG Y P, et al. Biofilm on microplastics in aqueous environment: Physicochemical properties and environmental implications[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 424: 127286. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127286 [50] 汤鸿霄. 环境水质学的进展: 颗粒物与表面络合(上)[J]. 环境科学进展, 1993(1): 25-41. TANG H X. Advances in environmental aquatic quality science: Particulates and surface complexation, Ⅰ[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 1993(1): 25-41 (in Chinese).
[51] PAN B, QIU M Y, WU M, et al. The opposite impacts of Cu and Mg cations on dissolved organic matter-ofloxacin interaction[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2012, 161: 76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.09.040 [52] 马骁腾. 饱和多孔介质中微塑料和大肠杆菌迁移沉积影响因素研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2019. MA X T. Influencing factors on transport and deposition of microplastics and Escherichia coli in saturated porous media[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2019 (in Chinese).
[53] LI X Q, HUA Z L. Multiphase distribution and spatial patterns of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) associated with catchment characteristics in a plain river network[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 263: 128284. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128284 [54] GIESY J P, KANNAN K. Perfluorochemical surfactants in the environment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(7): 146A-152A. [55] 张文静, 周晶晶, 刘丹, 等. 胶体在地下水中的环境行为特征及其研究方法探讨[J]. 水科学进展, 2016, 27(4): 629-638. doi: 10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2016.04.018 ZHANG W J, ZHOU J J, LIU D, et al. A review: Research methods that describe the environmental behavior of colloids in groundwater[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2016, 27(4): 629-638 (in Chinese). doi: 10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2016.04.018
[56] 姚舜译. 大肠杆菌在饱和多孔介质中的迁移过程研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2016. YAO S Y. Transport of Escherichia coli in saturated porous media[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016 (in Chinese).
[57] 崔丽敏. 大肠杆菌在不同表面粗糙度多孔介质中的迁移行为研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2020. CUI L M. The transport behaviors of Escherichia coli in porous media under different surface roughness[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[58] YAO K, HABIBIAN M T, O’MELIA C R. Water and waste water filtration: Concepts and applications[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 1971, 5(11): 1105-1112. doi: 10.1021/es60058a005 [59] 巩霏, 李华, 孙艺嘉, 等. 有机质对土壤中多环芳烃纵向迁移的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(7): 1681-1689. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.03.13 GONG F, LI H, SUN Y J, et al. Effect of organic matter on longitudinal migration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(7): 1681-1689 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.03.13
[60] ZHAO P, CUI L M, ZHAO W G, et al. Cotransport and deposition of colloidal polystyrene microplastic particles and tetracycline in porous media: The impact of ionic strength and cationic types[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 753: 142064. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142064 [61] ZHAO W G, ZHAO P, TIAN Y M, et al. Transport and retention of Microcystis aeruginosa in porous media: Impacts of ionic strength, flow rate, media size and pre-oxidization[J]. Water Research, 2019, 162: 277-287. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.07.001 [62] 何楠, 郭浩, 刘菁, 等. 供水管道中金属污染物富集与释放研究进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(2): 21-29. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2022.02.004 HE N, GUO H, LIU J, et al. Research progress on enrichment and release of metal pollutants in water supply pipelines[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2022, 38(2): 21-29 (in Chinese). doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2022.02.004
[63] LIU Q L, HAN W Q, HAN B J, et al. Assessment of heavy metals in loose deposits in drinking water distribution system[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2018, 190(7): 388. doi: 10.1007/s10661-018-6761-9 [64] LI M J, LIU Z W, CHEN Y C, et al. Effects of varying temperatures and alkalinities on the corrosion and heavy metal release from low-lead galvanized steel[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(2): 2412-2422. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06893-2 [65] MANNING B A, HUNT M L, AMRHEIN C, et al. Arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) reactions with zerovalent iron corrosion products[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(24): 5455-5461. [66] LIU J Q, CHEN H Y, YAO L D, et al. The spatial distribution of pollutants in pipe-scale of large-diameter pipelines in a drinking water distribution system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 317: 27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.048 [67] PROKOPOVA M, NOVOTNA K, PIVOKONSKA L, et al. Coagulation of polyvinyl chloride microplastics by ferric and aluminium sulphate: Optimisation of reaction conditions and removal mechanisms[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(6): 106465. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106465 [68] 张静, 张晓岚, 蔡佳男, 等. 抗生素在给水厂中的去除及其对水质的影响研究综述[J]. 净水技术, 2022, 41(1): 23-30. doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2022.01.004 ZHANG J, ZHANG X L, CAI J N, et al. Review of research on antibiotics removal and effects on water quality in waterworks[J]. Water Purification Technology, 2022, 41(1): 23-30 (in Chinese). doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2022.01.004
[69] YU Y Y, SUN Y J, ZHOU J, et al. Preparation and characterization of high-efficiency magnetic heavy metal capture flocculants[J]. Water, 2021, 13(13): 1732. doi: 10.3390/w13131732 [70] 钟婷婷, 林涛, 刘威. 饮用水处理过程中全氟化合物的分布、转化及去向[J]. 环境科学, 2022: 1-18. ZHONG T T, LIN T, LIU W. Distribution, tansformation, and fate of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in drinking water treatment[J]. Environmental Science, 2022: 1-18 (in Chinese).
[71] TONG M P, HE L, RONG H F, et al. Transport behaviors of plastic particles in saturated quartz sand without and with biochar/Fe3O4-biochar amendment[J]. Water Research, 2020, 169: 115284. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115284 [72] 徐丽梅, 张崇淼, 王晓昌, 等. 紫外线和次氯酸钠对Escherichia coli和Poliovirus的消毒作用[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(5): 1928-1935. XU L M, ZHANG C M, WANG X C, et al. Disinfection action of ultraviolet radiation and chlorination on Escherichia coli and poliovirus[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(5): 1928-1935 (in Chinese).
[73] 王赛, 张岚, 陈永艳, 等. 饮用水处理技术去除微塑料的效果及进展[J]. 净水技术, 2021, 40(10): 20-25, 61. doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2021.10.003 WANG S, ZHANG L, CHEN Y Y, et al. Effect and progress of microplastics removal in drinking water treatment process[J]. Water Purification Technology, 2021, 40(10): 20-25, 61 (in Chinese). doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2021.10.003
[74] 王少华, 施卫娟, 贺鑫, 等. 纳滤深度处理在饮用水厂的应用与实践[J]. 给水排水, 2021, 57(10): 13-19. doi: 10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2021.10.003 WANG S H, SHI W J, HE X, et al. Application and practice of nanofiltration advanced treatment in water treatment plant[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2021, 57(10): 13-19 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2021.10.003
[75] 秦源, 于水利, 顾正阳, 等. MOFs改性纳滤膜去除饮用水中微量有机物进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(4): 44-48. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2022.04.008 QIN Y, YU S L, GU Z Y, et al. Research progress of the trace organic pollutants removal from drinking water by modified nanofiltration membranes with metal organic frameworks[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2022, 38(4): 44-48 (in Chinese). doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2022.04.008
[76] LIU B Z, CHEN X, ZHENG H L, et al. Rapid and efficient removal of heavy metal and cationic dye by carboxylate-rich magnetic chitosan flocculants: Role of ionic groups[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 181: 327-336. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.089 [77] ZHANG Y L, DIEHL A, LEWANDOWSKI A, et al. Removal efficiency of micro- and nanoplastics (180nm–125μm) during drinking water treatment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 720: 137383. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137383 [78] 李圭白, 梁恒, 白朗明, 等. 绿色工艺: 第三代饮用水净化工艺的发展方向[J]. 给水排水, 2021, 57(9): 1-5. LI G B, LIANG H, BAI L M, et al. Green process: Development direction of the third generation drinking water purification process[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2021, 57(9): 1-5 (in Chinese).
[79] 孙晓晨, 易琳雅, 汪楠, 等. 微塑料在饮用水中的去除研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(6): 211-218. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2021.06.026 SUN X C, YI L Y, WANG N, et al. Research progress on the removal of microplastics in drinking water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(6): 211-218 (in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2021.06.026
[80] JIANG J Y, ZHANG X R. A smart strategy for controlling disinfection byproducts by reversing the sequence of activated carbon adsorption and chlorine disinfection[J]. Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(18): 1167-1169. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.07.022 [81] 陈超, 张晓健, 朱玲侠, 等. 控制消毒副产物及前体物的优化工艺组合[J]. 环境科学, 2005, 26(4): 87-94. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2005.04.017 CHEN C, ZHANG X J, ZHU L X, et al. Optimal process combination for control of disinfection by-products and precursors[J]. Environmental Science, 2005, 26(4): 87-94 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2005.04.017
[82] WANG Z F, LIN T, CHEN W. Occurrence and removal of microplastics in an advanced drinking water treatment plant (ADWTP)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 700: 134520. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134520 [83] ROSS P S, van der AA L T J, van DIJK T, et al. Effects of water quality changes on performance of biological activated carbon (BAC) filtration[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 212: 676-683. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.11.072 -







 下载:
下载: