-
含氧多环芳烃(oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons,OPAHs)是指在多环芳烃(PAHs)的苯环上含有一个或多个羰基氧,或是含有羟基基团的一类化合物;它主要由化石或生物质燃料不完全燃烧产生,也可由环境中的多环芳烃因光氧化反应、化学氧化反应或生物转换等多种方式产生。由于其较为稳定难以降解,具有比亲代PAHs更强的毒性[1 − 2]和致突变性[3],有一部分含氧多环芳烃单体还被认为是直接的诱变剂和致癌物[4].目前国内外对于含氧多环芳烃的研究,主要集中于该类化合物的总量分析、源解析或者毒性分析等相关领域[5],各种研究文献对OPAHs的检测数据相对较少[1],故为能快速补充数据库毒性数据,采用定量结构-毒性关系(quantitative structure-toxicity relationship,QSTR)相关研究为简便而又高效的理论研究方法. 金玲敏等[6]对此进行了富有成效的尝试,利用计算得到多种描述符,建构了预测OPAHs对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性的模型。但该法首先需要计算多种描述符,过程复杂,且创新稍有不足;其次预测的结果误差偏大,平均误差达到0.371. 为此本研究创新提出新的计算简单的结构参数,采用神经网络法建模,能提高预测准确度。该法对含氧多环芳烃急性毒性的QSTR研究未见有相关报道.
神经网络法是一种基于数据驱动的误差逆向传播算法,对复杂的非线性系统,具有很强的自适应和自学习能力[7],能模拟生命过程中的神经网络行为,对数据进行智能信息化处理,故该法在化学、环境、机械等众多学科中得到广泛应用[8 − 10]. 利用神经网络法进行QSTR研究[11],对环境污染物在环境中的危险性评价具有独特的作用. 在前期[12 − 13]研究工作的基础上,根据文献[6]所列32个含氧多环芳烃分子,分析这些OPAHs分子的结构与其对斑马鱼胚胎的毒性之间的相关关系,寻找毒性数据的大小与结构之间的内在规律,从而新定义了一种可表征原子电性结构与空间结构特性的原子特征值δi,并根据多环芳烃苯环上不同位置连接羟基时,毒性大小也不一样的变化特性,对基团原子特征值δi进行校正后,建构了一种新的定位键指数L. 利用建构的新指数,与利用软件计算并优化筛选的电性拓扑态指数、及电性距离矢量3类指数有机结合,建立了一种可用于预测含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性的神经网络模型,所得结果令人满意. 本研究工作成果对建立含氧多环芳烃的毒性数据库、对环境污染物的快速分析检测,具有重要的理论价值和实际意义.
-
32个含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性,相关数据来源于文献[6],这里毒性值采用半数效应浓度EC50的对数lgEC50表示,将分子及其生物毒性实验值lgEC50列于表1.
-
分子的结构决定分子的性质,分子中的原子不同、基团不同、连接位置不同、原子或基团受环境影响不同,均会影响分子的物理化学性质. 通过考察文献[6]中32个含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性与分子结构之间的关系,定义了一种新的可以应用于表征含氧多环芳烃OPAHs分子的原子特征值(δi)为:
式(1)中,mi、hi、χi分别为非氢原子i的价电子数、直接连接的氢原子个数、鲍林电负性值,χc为碳原子的鲍林电负性. 由于含氧多环芳烃中,连接在苯环上不同位置的基团,对含氧多环芳烃的毒性大小影响也不同,为此对含氧多环芳烃苯环上不同位置基团的特征值进行了校正:
式(2)中,Ji为基团连接在苯环上所在位置数. 如1,2-二羟基蒽醌分子,1位羟基氧原子的δi´值为34.274、2位羟基氧原子δi´值为37.701. 在分子拓扑理论基础上,建构一种新的指数L:
式(3)中的Σ表示每一个化学键对分子的贡献. 由于该指数是在校正了基团非氢原子在苯环上所连接的位置后,综合每个化学键对分子的贡献值,故将该指数命名为定位键指数. 根据公式(3)计算得到含氧多环芳烃的定位键指数值L列于表1中.
-
对于化合物对生物的毒性,很难只用一种指数反映其变化规律,故常需要2种甚至2种以上的指数进行有机结合,才能建立指数与化合物对生物毒性之间良好的相关关系。考察文献[6]中含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎毒性大小与分子结构的关系,用Chemoffice3D绘图软件勾画了OPAHs分子的分子结构。利用MATLAB应用软件自编的程序[14 − 15],计算了32个OPAHs分子的电性拓扑状态指数Em和电性距离矢量Mn。通过回归分析优化筛选了电性拓扑状态指数的E16、电性距离矢量的M14、M21、M32共4个结构参数,与定位键指数L结合,与含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性lgEC50的相关性最优. 描述符L表征的是对应于分子拓扑图中每一边(化学键)的本征值、电性拓扑状态指数E16表征的是非氢原子=O的本征值,电性距离矢量的M14表征的是第二类碳原子(—C—)之间的相互作用、M21表征的是第二类碳原子与羰基氧原子(=O)的相互作用、M32则表征的是第三类碳原子与第九类氧原子(—O)相互作用. 正是使用了3类不同的描述符结合,故本研究可对不同的类型化合物进行建立模型;由于毒性机制增加了系统的空间异质性和复杂性,而这里选择的几类参数蕴含了化合物的电性和空间结构信息,故参数与急性毒性之间能建立良好的相关关系;经过对定位键指数(主要是原子特征值)稍进行修正,发现将其应用于芳烃、农药分子的急性毒性研究,也能取得较好的结果. 将优化筛选的E16、M14、M21、M32等数据也列于表1.
-
将计算得到的32个含氧多环芳烃的定位键指数L、电性拓扑状态指数Em、电性距离矢量Mn等3类指数,与其对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性lgEC50(µmol·L−1),用MINITAB数据分析统计软件的最佳子集回归方法进行相关关系的分析,所得结果见表2.
式(4)中,n为总的分子样本数,b为所建模型的变量个数,R2为相应模型的决定系数,根据该式计算得到的各模型的FIT值列于表2。一般FIT值越大,所建模型稳定性越好,预测能力也越强.
从表2可以看出,综合考虑相关系数、标准误差和FIT值的大小,模型(5)最好,即当使用定位键指数L、电性拓扑状态指数的E16、电性距离矢量的M14、M21、M32共5个参数时,其与含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性有最佳的相关关系,建立的多元回归方程为:
根据该多元回归模型预测得到的急性毒性lgEC50,与文献列出实验值的平均绝对误差为0.395,误差相对较大,而且方程的相关系数为0.8273,对于预测毒性数据能基本达到要求,但预测结果并不理想.
-
为对含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性的预测进一步做神经网络研究,先对式(5)的稳定性、预测能力及是否有离域值进行检验. 采用公认的逐一剔除法进行检验,即每次剔除1个含氧多环芳烃分子,用剩余31个含氧多环芳烃分子回归,可建立32个方程,获得32个检验的相关系数(相关数据见表3),所有这些相关系数的平均值为r=0.8285,该值与式(5)的相关系数较为接近,说明预测生物毒性模型(5)的稳定性较好;再使用MINITAB数据预测分析统计软件,对多元线性回归预测毒性的模型(5),采用留一法进行交互检验,得到模型(5)交叉验证相关系数R2CV=0.5050,当R2CV大于0.5时,说明稳健性较好[17];再求R2adj(0.6238)与R2CV(0.5050)的差值,得到0.1188,两者差值小于0.3,一般认为当这两种相关系数的差值<0.3时,说明模型没有过拟合,不存在离域异常值,所以这里构建的多元回归预测模型有较好的稳定性,有一定的预测能力.
-
为了提高对含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性预测结果的准确度,在多元回归模型式(5)的基础上,进一步采用在众多领域得到广泛应用的神经网络方法进行研究[18]. 神经网络隐含层数,按照Andrea[19]和许禄[20]规则综合后计算得到,计算公式为:
式(6)中,n为样本总数,b为模型所取的变量数,H为神经网络三层结构中的隐含层数. 根据式(6)计算,H可取值2或3,经分别计算测试,发现H取3时,建立的神经网络预测模型相关系数最优. 故神经网络采用5-3-1的网络结构方式,并将32个含氧多环芳烃分子分为3个子集:训练集、测试集和验证集,以每5个分子作为一组,共分6组,具体分组分子见表4. 由于第六组只有1和2两个分子,故分别进入训练集和测试集. 神经网络模型的构成、总相关系数和各子集的相关系数见表4.
从表4可以看出,总相关系数RT的值达到0.9826,3个子集的相关系数与总相关系数之间,较为接近. 而且对于预测毒性的模型来说,相关系数能达到0.98以上,说明构建的模型比较理想,该模型的权重和偏置见表5.
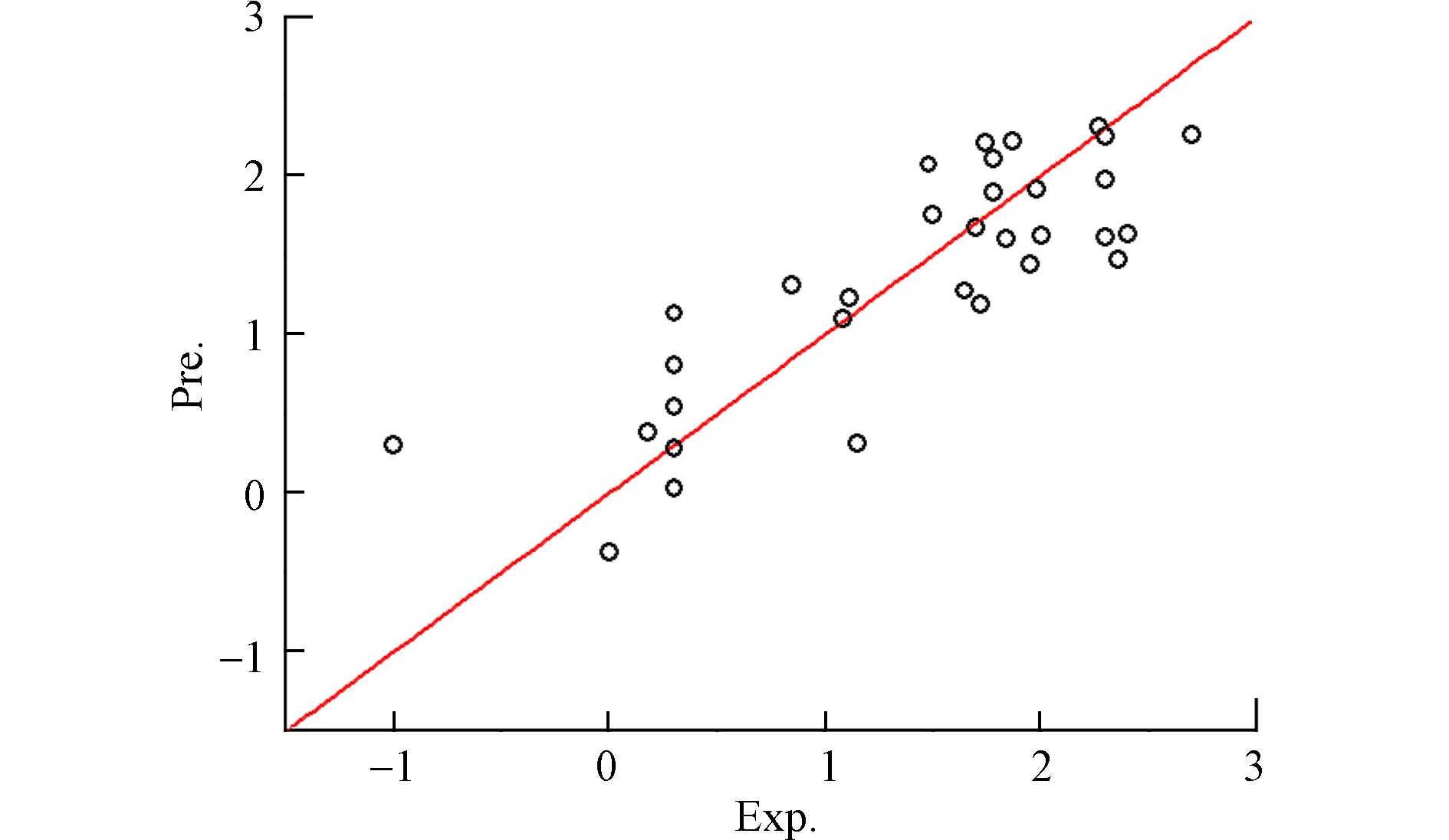
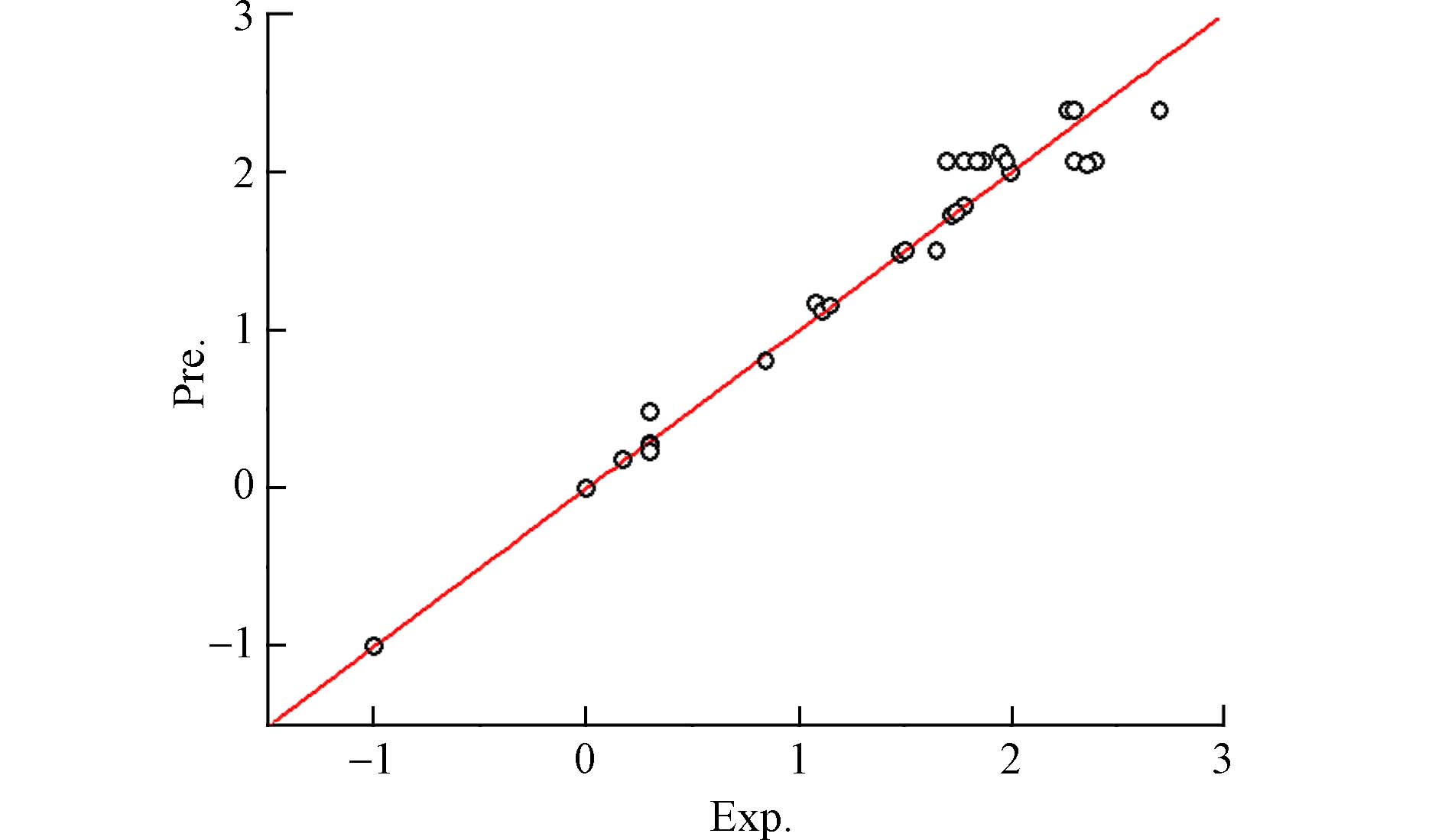
神经网络模型的相关性明显优于多元回归模型,说明含氧多环芳烃的分子结构参数与其对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性之间是一种非线性关系. 利用该建构的神经网络模型进行预测含氧多环芳烃的生物毒性lgEC50,预测值与实验值的平均误差为0.112;在两者之间进行相关,所得方程的R2adj=0.9644,该值明显高于多元回归方程的R2adj =0.6238,神经网络法所得预测误差的平均值明显小于多元回归法预测值的平均误差0.395,说明神经网络法模型比多元回归法的预测精度更高. 与文献[6]采用密度泛函理论中的B3LYP方法,优化了含氧多环芳烃(OPAHs)的分子结构,然后建立预测模型所得的结果进行比较,文献方法预测毒性值的平均误差为0.371,本法构建的神经网络预测毒性模型的预测精度更好. 将本文的多元回归法和神经网络法所得的预测值(Pre.)与实验值(Exp.),分别作关系图(图1和图2),从图1和图2可以看出,神经网络模型的毒性预测结果更为可靠,准确度更高. 将神经网络法对含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性lgEC50预测值也列入表1,将该值与实验值之间的误差,作雷达图(图3)可以看出,没有特别异常的误差值存在;将各化合物分子预测值的误差同时也作控制图(图4),同样可以看到各化合物急性毒性预测的最大误差和最小误差,均落在标准残差范围,正负残差基本对等,正负平均值就在零线,结果可控,说明预测化合物在应用域范围内,拟合效果也较好;也说明神经网络法预测lgEC50模型稳定可靠. 故建构的模型可应用于含氧多环芳烃毒性数据库的建立,是否适用于其它环境污染物毒性预测还需要实验验证.
-
含氧多环芳烃的毒性机制较为复杂,由于其含有羰基或羟基的极性氧原子,故化合物具有较好的水溶性,有更强的毒性[1];一般而言,多环芳烃的环数越多,毒性越强,即分子量越大的化合物,分子体积越大,疏水性越强,通常表现出更强的毒性[5];在含氧多环芳烃中,醌是一种高度氧化还原活性分子,更容易形成氧化的细胞大分子[1],从而表现出更强的毒性效应. 此外对含氧多环芳烃而言,羰基或羟基基团在苯环上连接的位置、连接的数量、相互之间的影响等等,均会影响含氧多环芳烃分子的生物毒性大小. 本文通过分析分子结构与毒性大小之间的关系,定义了原子特征值,并通过对连接在苯环上所在位置的基团,进行了原子特征值的校正,从而建构了新的定位键指数,分子体积越大,所得L值也越大,式(5)中定位键指数L前的系数也是正值,说明该指数与含氧多环芳烃的毒性变化规律一致;再将该指数与能反映基团电性的电性拓扑状态指数、能反映基团相互作用空间特性的电性距离矢量进行结合,从而建立良好的可以预测含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性的神经网络模型,从预测的毒性结果可看出,各个分子毒性预测值的误差较小;在32个含氧多环芳烃中,只有对31号分子芘-4,5-二酮的预测相对误差偏大,该分子的结构与其相邻的前3个分子的结构相近,但其毒性实验值lgEC50明显偏小,这可能与该分子处于相邻位置的两个羰基相互影响较大,导致lgEC50值异常有关. 总体而言,本文构建的含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性lgEC50的神经网络模型,预测结果的准确度较好,平均误差仅为0.112,优于文献方法预测误差的0.371.
预测模型中使用的定位键指数是一种新定义建构的分子结构指数,是一种创新性提出的新的分子结构指数,它充分考虑了原子的电子层级、电负性、价电子等信息,也考虑了氢原子及所处环境的拓扑空间结构信息,而且它对不同结构的分子有很好的区分能力,而且计算也较为简单. 虽然本研究的样本数偏少,但从结果看,预测效果较好,这对扩充相关类似物的急性毒性数据库的数据有一定的理论指导意义,当然这还需要进行适当的实验进行验证. 如果化合物的浓度等发生变化,相应毒性数据也会发生改变,但可以通过对训练集的数据调整,模型会有适当变化.
-
(1) 新定义了一个原子特征值,并对苯环上连接基团校正后,构建了一种新的定位键指数L,该指数对分子具有良好的区分性;同时计算并优化筛选了电性拓扑状态指数的E16、电性距离矢量的M14、M21、M32,将这5个参数有机结合,与含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性之间进行定量结构-毒性相关性分析,按照神经网络5-3-1的三层网络结构,建立了预测急性毒性的神经网络模型,其总相关系数RT的值达到0.9826,结构与毒性之间的相关性令人满意,lgEC50预测值的平均误差为0.112,既优于多元回归法毒性预测值的平均误差0.395,也优于文献方法预测值的平均误差0.371.
(2) 神经网络法比多元线性回归法的预测精度得到明显提高,说明分子结构与急性毒性之间是一种良好的非线性相关关系,呈现的不是线性关系.
(3)含氧多环芳烃的生物毒性,除与含环数目的多少有关外,还与羰基或羟基连接的数量、连接的位置有关,环数越多,毒性越大.
定位键指数用于含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性预测
Localization bond index was used for acute toxicity of oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to zebrafish embryos
-
摘要: 含氧多环芳烃化合物是一种在多环芳烃苯环上,含有一个或数个羰基氧原子的持久性污染物,它具有比亲代多环芳烃更强的毒性、致癌、致畸和致突变性,因此探究高效的研究方法来建立毒性数据库非常重要. 为研究含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性与其分子结构之间的定量结构-毒性关系,根据含氧多环芳烃分子中原子空间拓扑结构,提出了一种新的结构指数–定位键指数L,并分别计算了32个含氧多环芳烃化合物分子的电性拓扑态指数Em、电性距离矢量Mn,分析优化筛选了电性拓扑态指数其中的E16、电性距离矢量其中的M14、M21 和M32作为结构描述符,将它们与定位键指数L有机结合,与含氧多环芳烃化合物对斑马鱼胚胎的生物毒性进行回归分析,以5种结构参数为输入变量点价值,神经网络结构采用5-3-1,建构了一种预测含氧多环芳烃急性毒性lgEC50的神经网络模型,该预测模型的总相关系数RT值达到较高的0.9826,对毒性的预测值与实验值两者之间的平均误差仅为0.112;结果表明,含氧多环芳烃的急性毒性与定位键指数、电性拓扑态指数、电性距离矢量等结构参数有良好的非线性关系. 研究可为含氧多环芳烃的环境污染及生态风险评估提供理论指导.Abstract: Oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (OPAHs) were persistent organic pollutants, containing one or more base oxygens on the benzene ring of PAHs. OPAHs were more toxic, carcinogenic, teratogenic, and mutagenic than parental PAHs. Therefore, it was very important to explore efficient research methods to establish toxicity database. In order to investigate the quantitative structure-toxicity relationship (QSTR) between the acute toxicity of OPAHs to zebrafish embryos and their molecular structures, a novel structural index, the localization bond index L, was derived based on the spatial topology of atoms in OPAHs molecules. Moreover, the electrical topological state indices Em, electrical distance vectors Mn were calculated for 32 molecules of OPAHs compound, and the electrical topological state index E16, the electrical distance vectors M14, M21 and M32 were selected as structural descriptors. The electrical topological state index and electrical distance vectors were combined with localization bond index L, and they were introduced to the regression analysis of the acute toxicity of OPAHs to zebrafish embryos. Using the five molecular structural indices as enter the variable point value, and the neural network structure was performed using 5-3-1, a neural network model which predicted the acute toxicity lgEC50 of OPAHs was constructed. The total correlation coefficient RT was 0.9826, and the average error between the experimental and the predicted values of acute toxicity was only 0.112. The results showed that the acute toxicity of OPAHs had a good nonlinear relationship with the structural parameters of the localization bond index, the electrical topological state index, and the electrical distance vectors. The study provided theoretical guidance for environmental pollution and ecological risk assessment of OPAHs.
-
含氧多环芳烃(oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons,OPAHs)是指在多环芳烃(PAHs)的苯环上含有一个或多个羰基氧,或是含有羟基基团的一类化合物;它主要由化石或生物质燃料不完全燃烧产生,也可由环境中的多环芳烃因光氧化反应、化学氧化反应或生物转换等多种方式产生。由于其较为稳定难以降解,具有比亲代PAHs更强的毒性[1 − 2]和致突变性[3],有一部分含氧多环芳烃单体还被认为是直接的诱变剂和致癌物[4].目前国内外对于含氧多环芳烃的研究,主要集中于该类化合物的总量分析、源解析或者毒性分析等相关领域[5],各种研究文献对OPAHs的检测数据相对较少[1],故为能快速补充数据库毒性数据,采用定量结构-毒性关系(quantitative structure-toxicity relationship,QSTR)相关研究为简便而又高效的理论研究方法. 金玲敏等[6]对此进行了富有成效的尝试,利用计算得到多种描述符,建构了预测OPAHs对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性的模型。但该法首先需要计算多种描述符,过程复杂,且创新稍有不足;其次预测的结果误差偏大,平均误差达到0.371. 为此本研究创新提出新的计算简单的结构参数,采用神经网络法建模,能提高预测准确度。该法对含氧多环芳烃急性毒性的QSTR研究未见有相关报道.
神经网络法是一种基于数据驱动的误差逆向传播算法,对复杂的非线性系统,具有很强的自适应和自学习能力[7],能模拟生命过程中的神经网络行为,对数据进行智能信息化处理,故该法在化学、环境、机械等众多学科中得到广泛应用[8 − 10]. 利用神经网络法进行QSTR研究[11],对环境污染物在环境中的危险性评价具有独特的作用. 在前期[12 − 13]研究工作的基础上,根据文献[6]所列32个含氧多环芳烃分子,分析这些OPAHs分子的结构与其对斑马鱼胚胎的毒性之间的相关关系,寻找毒性数据的大小与结构之间的内在规律,从而新定义了一种可表征原子电性结构与空间结构特性的原子特征值δi,并根据多环芳烃苯环上不同位置连接羟基时,毒性大小也不一样的变化特性,对基团原子特征值δi进行校正后,建构了一种新的定位键指数L. 利用建构的新指数,与利用软件计算并优化筛选的电性拓扑态指数、及电性距离矢量3类指数有机结合,建立了一种可用于预测含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性的神经网络模型,所得结果令人满意. 本研究工作成果对建立含氧多环芳烃的毒性数据库、对环境污染物的快速分析检测,具有重要的理论价值和实际意义.
1. 定位键指数的建构及数据计算(Construction of localization bond index and data calculation)
1.1 生物毒性数据来源
32个含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性,相关数据来源于文献[6],这里毒性值采用半数效应浓度EC50的对数lgEC50表示,将分子及其生物毒性实验值lgEC50列于表1.
表 1 含氧多环芳烃的分子结构参数及其毒性Table 1. Molecular structural parameters and the toxicity of oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons序号No. 含氧多环芳烃Oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons L E16 M14 M21 M32 lgEC50 实验值Exp. 预测值Pre. 误差Err. 1 氧杂蒽酮Xanthone 71.637 12.028 37.064 7.201 7.730 2.000 1.996 −0.004 2 1,2-苯并苊醌Aceanthrenequinone 83.638 24.113 32.946 9.077 12.462 1.950 2.114 0.164 3 1,2-二羟基蒽醌1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone 97.699 24.375 21.206 16.522 17.428 2.270 2.381 0.111 4 4,5-亚菲基酮4,5-phenanthrylene ketone 71.712 12.192 33.992 6.508 9.100 1.480 1.480 0 5 9-芴酮9-fluorenone 59.783 11.888 35.483 6.792 7.631 2.400 2.060 −0.340 6 2,7-二羟基萘2,7-dihydroxynaphthalene 64.804 0 20.364 12.852 1.469 2.300 2.064 −0.236 7 1,6-二羟基萘1,6-dihydroxynaphthalene 63.834 0 22.492 12.015 2.858 1.780 2.065 0.285 8 2-羟基-9-芴酮2-hydroxy-9-fluorenone 72.992 11.929 26.253 12.353 8.584 1.500 1.499 −0.002 9 5,12-萘并萘醌5,12-naphthacenequinone 89.567 25.090 39.987 14.650 15.275 1.720 1.722 0.002 10 2,3-二羟基萘2,3-dihydroxynaphthalene 62.891 0 22.650 9.486 2.842 1.780 1.780 0 11 1,5-二羟基萘1,5-dihydroxynaphthalene 63.419 0 24.921 10.750 4.336 1.870 2.065 0.195 12 1,8-二羟基蒽醌1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone 100.685 24.406 21.315 17.793 17.634 2.300 2.381 0.081 13 萘嵌苯酮Perinaphthenone 59.712 11.585 33.513 8.071 5.133 1.080 1.163 0.083 14 11h-苯并[a]芴-11-酮11h-benzo[a]fluorene-11-one 77.712 12.502 45.710 7.142 9.537 1.700 2.063 0.363 15 2-羟基蒽醌2-hydroxyanthraquinone 84.919 24.273 23.761 18.391 13.913 1.110 1.115 0.005 16 1,4-二羟基蒽醌1,4-dihydroxyanthraquinone 98.769 24.406 21.216 17.632 17.682 2.700 2.381 −0.320 17 菲醌Phenanthrene-quinone 71.710 23.659 34.082 10.699 9.284 0.301 0.280 −0.021 18 1,2-萘醌1,2-naphthoquinone 53.710 22.136 22.278 10.674 4.491 0.301 0.281 −0.020 19 1,4-苯醌1,4-benzoquinone 35.710 20.566 9.066 13.534 1.213 0 −0.004 −0.004 20 1,4-蒽醌1,4-anthraquinone 71.567 23.271 27.685 14.982 8.531 0.301 0.267 −0.034 21 9-羟基苯并[a]芘9-hydroxybenzo[a]pyrene 100.278 0 60.746 7.923 1.593 0.301 0.229 −0.072 22 1,4-萘二醌1,4-naphthoquinone 53.710 22.384 20.406 13.670 6.891 −1.000 −0.997 0.003 23 12-羟基苯并[a]芘12-hydroxybenzo[a]pyrene 101.609 0 49.077 6.428 4.073 1.980 2.065 0.085 24 1,3-二羟基萘1,3-dihydroxynaphthalene 62.320 0 22.257 11.226 2.934 2.300 2.065 −0.235 25 2,6-二羟基萘2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene 64.333 0 20.318 13.012 1.480 1.840 2.065 0.225 26 苊醌Acenaphthenequinone 65.710 23.055 23.440 8.462 9.740 1.650 1.502 −0.148 27 1-羟基-9-芴酮 1-hydroxy-9-fluorenone 72.492 11.949 29.331 10.239 10.408 1.740 1.743 0.003 28 苯并[c]菲[1,4]醌Benzo[c]phenanthrene-1,4-dione 89.567 24.221 40.254 15.517 11.054 1.150 1.151 0.001 29 7,12-苯并蒽醌Benz[a]anthracene-7,12-dione 89.638 25.260 42.633 14.230 16.262 0.845 0.807 −0.038 30 苯并蒽酮1,9-benz-10-anthrone 77.712 12.494 45.859 7.733 8.894 2.360 2.046 −0.314 31 芘-4,5-二酮Pyrene-4,5-dione 83.638 24.186 32.708 10.279 11.516 0.301 0.483 0.182 32 1,4-菲醌Phenanthrene-1,4-dione 71.638 23.442 30.193 14.625 9.422 0.176 0.176 0 1.2 定位键指数L的建构
分子的结构决定分子的性质,分子中的原子不同、基团不同、连接位置不同、原子或基团受环境影响不同,均会影响分子的物理化学性质. 通过考察文献[6]中32个含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性与分子结构之间的关系,定义了一种新的可以应用于表征含氧多环芳烃OPAHs分子的原子特征值(δi)为:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) 式(1)中,mi、hi、χi分别为非氢原子i的价电子数、直接连接的氢原子个数、鲍林电负性值,χc为碳原子的鲍林电负性. 由于含氧多环芳烃中,连接在苯环上不同位置的基团,对含氧多环芳烃的毒性大小影响也不同,为此对含氧多环芳烃苯环上不同位置基团的特征值进行了校正:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) 式(2)中,Ji为基团连接在苯环上所在位置数. 如1,2-二羟基蒽醌分子,1位羟基氧原子的δi´值为34.274、2位羟基氧原子δi´值为37.701. 在分子拓扑理论基础上,建构一种新的指数L:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (3) 式(3)中的Σ表示每一个化学键对分子的贡献. 由于该指数是在校正了基团非氢原子在苯环上所连接的位置后,综合每个化学键对分子的贡献值,故将该指数命名为定位键指数. 根据公式(3)计算得到含氧多环芳烃的定位键指数值L列于表1中.
1.3 其它参数的计算
对于化合物对生物的毒性,很难只用一种指数反映其变化规律,故常需要2种甚至2种以上的指数进行有机结合,才能建立指数与化合物对生物毒性之间良好的相关关系。考察文献[6]中含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎毒性大小与分子结构的关系,用Chemoffice3D绘图软件勾画了OPAHs分子的分子结构。利用MATLAB应用软件自编的程序[14 − 15],计算了32个OPAHs分子的电性拓扑状态指数Em和电性距离矢量Mn。通过回归分析优化筛选了电性拓扑状态指数的E16、电性距离矢量的M14、M21、M32共4个结构参数,与定位键指数L结合,与含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性lgEC50的相关性最优. 描述符L表征的是对应于分子拓扑图中每一边(化学键)的本征值、电性拓扑状态指数E16表征的是非氢原子=O的本征值,电性距离矢量的M14表征的是第二类碳原子(—C—)之间的相互作用、M21表征的是第二类碳原子与羰基氧原子(=O)的相互作用、M32则表征的是第三类碳原子与第九类氧原子(—O)相互作用. 正是使用了3类不同的描述符结合,故本研究可对不同的类型化合物进行建立模型;由于毒性机制增加了系统的空间异质性和复杂性,而这里选择的几类参数蕴含了化合物的电性和空间结构信息,故参数与急性毒性之间能建立良好的相关关系;经过对定位键指数(主要是原子特征值)稍进行修正,发现将其应用于芳烃、农药分子的急性毒性研究,也能取得较好的结果. 将优化筛选的E16、M14、M21、M32等数据也列于表1.
2. 模型建构(model construction)
2.1 最优变量子集回归分析和多元回归模型
将计算得到的32个含氧多环芳烃的定位键指数L、电性拓扑状态指数Em、电性距离矢量Mn等3类指数,与其对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性lgEC50(µmol·L−1),用MINITAB数据分析统计软件的最佳子集回归方法进行相关关系的分析,所得结果见表2.
表 2 lgEC50与参数的最佳变量子集回归结果Table 2. Results of parameters and lgEC50 with best subsets regression序号No 变量子集Subset of variables b r Radj2 R2 F S FIT 1 E16 1 0.3502 0.0934 0.1226 4.192 0.8499 0.1270 2 L,E16 2 0.5244 0.2250 0.2750 5.500 0.7858 0.3056 3 L,E16,M32 3 0.7907 0.5850 0.6252 15.567 0.5750 1.1392 4 E16,M15,M21,M32 4 0.8050 0.5959 0.6480 12.427 0.5674 1.0355 5 L,E16,M14,M21,M32 5 0.8273 0.6238 0.6845 11.280 0.5475 0.9896 6 L,E16,M14,M15,M21,M32 6 0.8274 0.6089 0.6846 9.043 0.5582 0.7980 注:表2中b表示变量数;r表示相关系数;Radj2表示调整的判定系数;R2表示决定系数;F表示Fischer检验值;S表示估计标准误差;FIT表示Kubinyi函数. stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (4) 式(4)中,n为总的分子样本数,b为所建模型的变量个数,R2为相应模型的决定系数,根据该式计算得到的各模型的FIT值列于表2。一般FIT值越大,所建模型稳定性越好,预测能力也越强.
从表2可以看出,综合考虑相关系数、标准误差和FIT值的大小,模型(5)最好,即当使用定位键指数L、电性拓扑状态指数的E16、电性距离矢量的M14、M21、M32共5个参数时,其与含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性有最佳的相关关系,建立的多元回归方程为:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (5) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) 根据该多元回归模型预测得到的急性毒性lgEC50,与文献列出实验值的平均绝对误差为0.395,误差相对较大,而且方程的相关系数为0.8273,对于预测毒性数据能基本达到要求,但预测结果并不理想.
2.2 预测模型的稳定性、预测能力、离域性检验
为对含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性的预测进一步做神经网络研究,先对式(5)的稳定性、预测能力及是否有离域值进行检验. 采用公认的逐一剔除法进行检验,即每次剔除1个含氧多环芳烃分子,用剩余31个含氧多环芳烃分子回归,可建立32个方程,获得32个检验的相关系数(相关数据见表3),所有这些相关系数的平均值为r=0.8285,该值与式(5)的相关系数较为接近,说明预测生物毒性模型(5)的稳定性较好;再使用MINITAB数据预测分析统计软件,对多元线性回归预测毒性的模型(5),采用留一法进行交互检验,得到模型(5)交叉验证相关系数R2CV=0.5050,当R2CV大于0.5时,说明稳健性较好[17];再求R2adj(0.6238)与R2CV(0.5050)的差值,得到0.1188,两者差值小于0.3,一般认为当这两种相关系数的差值<0.3时,说明模型没有过拟合,不存在离域异常值,所以这里构建的多元回归预测模型有较好的稳定性,有一定的预测能力.
表 3 检验的相关系数Table 3. Inspection of correlation coefficient r剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数Correlation coefficient 剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数Correlation coefficient 剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数Correlation coefficient 剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数Correlation coefficient 剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数 Correlation coefficient 1 0.8276 8 0.8293 15 0.8273 22 0.8328 29 0.8335 2 0.8317 9 0.8338 16 0.8181 23 0.8245 30 0.8407 3 0.8211 10 0.8296 17 0.8195 24 0.8231 31 0.8401 4 0.8384 11 0.8296 18 0.8194 25 0.8271 32 0.8164 5 0.8362 12 0.8205 19 0.8162 26 0.8307 6 0.8339 13 0.8266 20 0.8173 27 0.8332 7 0.8266 14 0.8266 21 0.8338 28 0.8468 2.3 神经网络预测模型的构建
为了提高对含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性预测结果的准确度,在多元回归模型式(5)的基础上,进一步采用在众多领域得到广泛应用的神经网络方法进行研究[18]. 神经网络隐含层数,按照Andrea[19]和许禄[20]规则综合后计算得到,计算公式为:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (6) 式(6)中,n为样本总数,b为模型所取的变量数,H为神经网络三层结构中的隐含层数. 根据式(6)计算,H可取值2或3,经分别计算测试,发现H取3时,建立的神经网络预测模型相关系数最优. 故神经网络采用5-3-1的网络结构方式,并将32个含氧多环芳烃分子分为3个子集:训练集、测试集和验证集,以每5个分子作为一组,共分6组,具体分组分子见表4. 由于第六组只有1和2两个分子,故分别进入训练集和测试集. 神经网络模型的构成、总相关系数和各子集的相关系数见表4.
表 4 神经网络模型的构成及结果Table 4. Composition and Results of the neural network model神经网络模型Neural network model 总Total 训练集Training set 测试集Test set 验证集Validation set 网络结构Network structure 5-3-1 — — — — 每组分子Each group molecules — — 第2,4,5个 第1个 第3个 相关系数Correlation coefficient — 0.9826 0.9828 0.9812 0.9987 从表4可以看出,总相关系数RT的值达到0.9826,3个子集的相关系数与总相关系数之间,较为接近. 而且对于预测毒性的模型来说,相关系数能达到0.98以上,说明构建的模型比较理想,该模型的权重和偏置见表5.
表 5 神经网络模型的权重和偏置Table 5. Weights and bias of neural network model层间变化Inter layer variation 权重Weight 偏置Skewing 从输入层到隐蔽层Input to hidden 5.4333 1.8446 3.1702 7.1633 −18.8820 0.7736 −1.9282 −5.3205 −5.3938 −7.5461 16.0280 −0.1719 −0.6525 −0.9611 −3.7414 9.3688 5.4315 −1.6258 从隐蔽层到输出层Hidden to output −1.2688 −1.0919 −1.1762 −0.2436 神经网络模型的相关性明显优于多元回归模型,说明含氧多环芳烃的分子结构参数与其对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性之间是一种非线性关系. 利用该建构的神经网络模型进行预测含氧多环芳烃的生物毒性lgEC50,预测值与实验值的平均误差为0.112;在两者之间进行相关,所得方程的R2adj=0.9644,该值明显高于多元回归方程的R2adj =0.6238,神经网络法所得预测误差的平均值明显小于多元回归法预测值的平均误差0.395,说明神经网络法模型比多元回归法的预测精度更高. 与文献[6]采用密度泛函理论中的B3LYP方法,优化了含氧多环芳烃(OPAHs)的分子结构,然后建立预测模型所得的结果进行比较,文献方法预测毒性值的平均误差为0.371,本法构建的神经网络预测毒性模型的预测精度更好. 将本文的多元回归法和神经网络法所得的预测值(Pre.)与实验值(Exp.),分别作关系图(图1和图2),从图1和图2可以看出,神经网络模型的毒性预测结果更为可靠,准确度更高. 将神经网络法对含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性lgEC50预测值也列入表1,将该值与实验值之间的误差,作雷达图(图3)可以看出,没有特别异常的误差值存在;将各化合物分子预测值的误差同时也作控制图(图4),同样可以看到各化合物急性毒性预测的最大误差和最小误差,均落在标准残差范围,正负残差基本对等,正负平均值就在零线,结果可控,说明预测化合物在应用域范围内,拟合效果也较好;也说明神经网络法预测lgEC50模型稳定可靠. 故建构的模型可应用于含氧多环芳烃毒性数据库的建立,是否适用于其它环境污染物毒性预测还需要实验验证.
2.4 模型结果分析
含氧多环芳烃的毒性机制较为复杂,由于其含有羰基或羟基的极性氧原子,故化合物具有较好的水溶性,有更强的毒性[1];一般而言,多环芳烃的环数越多,毒性越强,即分子量越大的化合物,分子体积越大,疏水性越强,通常表现出更强的毒性[5];在含氧多环芳烃中,醌是一种高度氧化还原活性分子,更容易形成氧化的细胞大分子[1],从而表现出更强的毒性效应. 此外对含氧多环芳烃而言,羰基或羟基基团在苯环上连接的位置、连接的数量、相互之间的影响等等,均会影响含氧多环芳烃分子的生物毒性大小. 本文通过分析分子结构与毒性大小之间的关系,定义了原子特征值,并通过对连接在苯环上所在位置的基团,进行了原子特征值的校正,从而建构了新的定位键指数,分子体积越大,所得L值也越大,式(5)中定位键指数L前的系数也是正值,说明该指数与含氧多环芳烃的毒性变化规律一致;再将该指数与能反映基团电性的电性拓扑状态指数、能反映基团相互作用空间特性的电性距离矢量进行结合,从而建立良好的可以预测含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性的神经网络模型,从预测的毒性结果可看出,各个分子毒性预测值的误差较小;在32个含氧多环芳烃中,只有对31号分子芘-4,5-二酮的预测相对误差偏大,该分子的结构与其相邻的前3个分子的结构相近,但其毒性实验值lgEC50明显偏小,这可能与该分子处于相邻位置的两个羰基相互影响较大,导致lgEC50值异常有关. 总体而言,本文构建的含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性lgEC50的神经网络模型,预测结果的准确度较好,平均误差仅为0.112,优于文献方法预测误差的0.371.
预测模型中使用的定位键指数是一种新定义建构的分子结构指数,是一种创新性提出的新的分子结构指数,它充分考虑了原子的电子层级、电负性、价电子等信息,也考虑了氢原子及所处环境的拓扑空间结构信息,而且它对不同结构的分子有很好的区分能力,而且计算也较为简单. 虽然本研究的样本数偏少,但从结果看,预测效果较好,这对扩充相关类似物的急性毒性数据库的数据有一定的理论指导意义,当然这还需要进行适当的实验进行验证. 如果化合物的浓度等发生变化,相应毒性数据也会发生改变,但可以通过对训练集的数据调整,模型会有适当变化.
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1) 新定义了一个原子特征值,并对苯环上连接基团校正后,构建了一种新的定位键指数L,该指数对分子具有良好的区分性;同时计算并优化筛选了电性拓扑状态指数的E16、电性距离矢量的M14、M21、M32,将这5个参数有机结合,与含氧多环芳烃对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性之间进行定量结构-毒性相关性分析,按照神经网络5-3-1的三层网络结构,建立了预测急性毒性的神经网络模型,其总相关系数RT的值达到0.9826,结构与毒性之间的相关性令人满意,lgEC50预测值的平均误差为0.112,既优于多元回归法毒性预测值的平均误差0.395,也优于文献方法预测值的平均误差0.371.
(2) 神经网络法比多元线性回归法的预测精度得到明显提高,说明分子结构与急性毒性之间是一种良好的非线性相关关系,呈现的不是线性关系.
(3)含氧多环芳烃的生物毒性,除与含环数目的多少有关外,还与羰基或羟基连接的数量、连接的位置有关,环数越多,毒性越大.
-
表 1 含氧多环芳烃的分子结构参数及其毒性
Table 1. Molecular structural parameters and the toxicity of oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
序号No. 含氧多环芳烃Oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons L E16 M14 M21 M32 lgEC50 实验值Exp. 预测值Pre. 误差Err. 1 氧杂蒽酮Xanthone 71.637 12.028 37.064 7.201 7.730 2.000 1.996 −0.004 2 1,2-苯并苊醌Aceanthrenequinone 83.638 24.113 32.946 9.077 12.462 1.950 2.114 0.164 3 1,2-二羟基蒽醌1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone 97.699 24.375 21.206 16.522 17.428 2.270 2.381 0.111 4 4,5-亚菲基酮4,5-phenanthrylene ketone 71.712 12.192 33.992 6.508 9.100 1.480 1.480 0 5 9-芴酮9-fluorenone 59.783 11.888 35.483 6.792 7.631 2.400 2.060 −0.340 6 2,7-二羟基萘2,7-dihydroxynaphthalene 64.804 0 20.364 12.852 1.469 2.300 2.064 −0.236 7 1,6-二羟基萘1,6-dihydroxynaphthalene 63.834 0 22.492 12.015 2.858 1.780 2.065 0.285 8 2-羟基-9-芴酮2-hydroxy-9-fluorenone 72.992 11.929 26.253 12.353 8.584 1.500 1.499 −0.002 9 5,12-萘并萘醌5,12-naphthacenequinone 89.567 25.090 39.987 14.650 15.275 1.720 1.722 0.002 10 2,3-二羟基萘2,3-dihydroxynaphthalene 62.891 0 22.650 9.486 2.842 1.780 1.780 0 11 1,5-二羟基萘1,5-dihydroxynaphthalene 63.419 0 24.921 10.750 4.336 1.870 2.065 0.195 12 1,8-二羟基蒽醌1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone 100.685 24.406 21.315 17.793 17.634 2.300 2.381 0.081 13 萘嵌苯酮Perinaphthenone 59.712 11.585 33.513 8.071 5.133 1.080 1.163 0.083 14 11h-苯并[a]芴-11-酮11h-benzo[a]fluorene-11-one 77.712 12.502 45.710 7.142 9.537 1.700 2.063 0.363 15 2-羟基蒽醌2-hydroxyanthraquinone 84.919 24.273 23.761 18.391 13.913 1.110 1.115 0.005 16 1,4-二羟基蒽醌1,4-dihydroxyanthraquinone 98.769 24.406 21.216 17.632 17.682 2.700 2.381 −0.320 17 菲醌Phenanthrene-quinone 71.710 23.659 34.082 10.699 9.284 0.301 0.280 −0.021 18 1,2-萘醌1,2-naphthoquinone 53.710 22.136 22.278 10.674 4.491 0.301 0.281 −0.020 19 1,4-苯醌1,4-benzoquinone 35.710 20.566 9.066 13.534 1.213 0 −0.004 −0.004 20 1,4-蒽醌1,4-anthraquinone 71.567 23.271 27.685 14.982 8.531 0.301 0.267 −0.034 21 9-羟基苯并[a]芘9-hydroxybenzo[a]pyrene 100.278 0 60.746 7.923 1.593 0.301 0.229 −0.072 22 1,4-萘二醌1,4-naphthoquinone 53.710 22.384 20.406 13.670 6.891 −1.000 −0.997 0.003 23 12-羟基苯并[a]芘12-hydroxybenzo[a]pyrene 101.609 0 49.077 6.428 4.073 1.980 2.065 0.085 24 1,3-二羟基萘1,3-dihydroxynaphthalene 62.320 0 22.257 11.226 2.934 2.300 2.065 −0.235 25 2,6-二羟基萘2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene 64.333 0 20.318 13.012 1.480 1.840 2.065 0.225 26 苊醌Acenaphthenequinone 65.710 23.055 23.440 8.462 9.740 1.650 1.502 −0.148 27 1-羟基-9-芴酮 1-hydroxy-9-fluorenone 72.492 11.949 29.331 10.239 10.408 1.740 1.743 0.003 28 苯并[c]菲[1,4]醌Benzo[c]phenanthrene-1,4-dione 89.567 24.221 40.254 15.517 11.054 1.150 1.151 0.001 29 7,12-苯并蒽醌Benz[a]anthracene-7,12-dione 89.638 25.260 42.633 14.230 16.262 0.845 0.807 −0.038 30 苯并蒽酮1,9-benz-10-anthrone 77.712 12.494 45.859 7.733 8.894 2.360 2.046 −0.314 31 芘-4,5-二酮Pyrene-4,5-dione 83.638 24.186 32.708 10.279 11.516 0.301 0.483 0.182 32 1,4-菲醌Phenanthrene-1,4-dione 71.638 23.442 30.193 14.625 9.422 0.176 0.176 0 表 2 lgEC50与参数的最佳变量子集回归结果
Table 2. Results of parameters and lgEC50 with best subsets regression
序号No 变量子集Subset of variables b r Radj2 R2 F S FIT 1 E16 1 0.3502 0.0934 0.1226 4.192 0.8499 0.1270 2 L,E16 2 0.5244 0.2250 0.2750 5.500 0.7858 0.3056 3 L,E16,M32 3 0.7907 0.5850 0.6252 15.567 0.5750 1.1392 4 E16,M15,M21,M32 4 0.8050 0.5959 0.6480 12.427 0.5674 1.0355 5 L,E16,M14,M21,M32 5 0.8273 0.6238 0.6845 11.280 0.5475 0.9896 6 L,E16,M14,M15,M21,M32 6 0.8274 0.6089 0.6846 9.043 0.5582 0.7980 注:表2中b表示变量数;r表示相关系数;Radj2表示调整的判定系数;R2表示决定系数;F表示Fischer检验值;S表示估计标准误差;FIT表示Kubinyi函数. 表 3 检验的相关系数
Table 3. Inspection of correlation coefficient r
剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数Correlation coefficient 剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数Correlation coefficient 剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数Correlation coefficient 剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数Correlation coefficient 剔除分子Remove molecule 相关系数 Correlation coefficient 1 0.8276 8 0.8293 15 0.8273 22 0.8328 29 0.8335 2 0.8317 9 0.8338 16 0.8181 23 0.8245 30 0.8407 3 0.8211 10 0.8296 17 0.8195 24 0.8231 31 0.8401 4 0.8384 11 0.8296 18 0.8194 25 0.8271 32 0.8164 5 0.8362 12 0.8205 19 0.8162 26 0.8307 6 0.8339 13 0.8266 20 0.8173 27 0.8332 7 0.8266 14 0.8266 21 0.8338 28 0.8468 表 4 神经网络模型的构成及结果
Table 4. Composition and Results of the neural network model
神经网络模型Neural network model 总Total 训练集Training set 测试集Test set 验证集Validation set 网络结构Network structure 5-3-1 — — — — 每组分子Each group molecules — — 第2,4,5个 第1个 第3个 相关系数Correlation coefficient — 0.9826 0.9828 0.9812 0.9987 表 5 神经网络模型的权重和偏置
Table 5. Weights and bias of neural network model
层间变化Inter layer variation 权重Weight 偏置Skewing 从输入层到隐蔽层Input to hidden 5.4333 1.8446 3.1702 7.1633 −18.8820 0.7736 −1.9282 −5.3205 −5.3938 −7.5461 16.0280 −0.1719 −0.6525 −0.9611 −3.7414 9.3688 5.4315 −1.6258 从隐蔽层到输出层Hidden to output −1.2688 −1.0919 −1.1762 −0.2436 -
[1] 张玉洁, 云洋. 环境中的氧化多环芳烃综述[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(1): 150-163. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020022802 ZHANG Y J, YUN Y. Oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the environment: A review[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(1): 150-163 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020022802
[2] 高玉宗, 姬亚芹, 杨益, 等. 天津市大气中多环芳烃衍生物污染特征和来源[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(3): 1026-1034. GAO Y Z, JI Y Q, YANG Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon derivatives in the atmosphere of Tianjin[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(3): 1026-1034 (in Chinese).
[3] ACHTEN C, ANDERSSON J T. Overview of polycyclic aromatic compounds (PAC)[J]. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 2015, 35(2/3/4): 177-186. [4] 李宏宇, 李沛祺, 黄娟, 等. 兰州市大气OPAHs污染特征及潜在来源分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(8): 3561-3571. LI H Y, LI P Q, HUANG J, et al. Pollution characteristics and potential pollution source regions of atmospheric OPAHs in Lanzhou[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(8): 3561-3571 (in Chinese).
[5] 古鹏, 汤佳豪, 赵庆庆, 等. 土壤中9-芴酮和9, 10-蒽醌的分析方法及赋存形态[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2023, 42(5): 1091-1099. GU P, TANG J H, ZHAO Q Q, et al. Analytical method and speciation characteristics of 9-fluorenone and 9, 10-anthraquinone in soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2023, 42(5): 1091-1099 (in Chinese).
[6] 金玲敏, 徐童, 乔显亮. OPAHs对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性预测[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2021, 16(6): 53-59. JIN L M, XU T, QIAO X L. Prediction of acute toxicity by OPAHs to zebrafish embryos[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2021, 16(6): 53-59 (in Chinese).
[7] 张肖江, 周春桂, 王志军, 等. 基于BP神经网络PID的水下无人航行器舵机驱动智能控制系统[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2023, 45(2): 109-114. ZHANG X J, ZHOU C G, WANG Z J, et al. Underwater UAV steering gear driven intelligent control system based on BP neural network PID[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2023, 45(2): 109-114 (in Chinese).
[8] YANG J, XU Y Y, WANG B, et al. Group Lasso based redundancy-controlled feature selection for fuzzy neural network[J]. Optoelectronics Letters, 2023, 19(5): 284-289. doi: 10.1007/s11801-023-2053-x [9] DING Y, ZHANG Z L, ZHAO X F, et al. Deep hybrid: Multi-graph neural network collaboration for hyperspectral image classification[J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 23: 164-176. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.02.007 [10] 李晓晨, 白音包力皋, 李向东, 等. 基于IPSO-BP神经网络的高含沙水体对鱼类影响预测方法[J]. 水利学报, 2023, 54(3): 291-301. LI X C, BAIYINBAOLIGAO, LI X D, et al. Aprediction method for the impact of hyper-concentrated flow on fishes based on the IPSO-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2023, 54(3): 291-301 (in Chinese).
[11] 堵锡华, 陈艳, 宋明, 等. 神经网络用于卤代肉桂酸对羊角月牙藻毒性的预测研究[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2021, 16(3): 347-354. DU X H, CHEN Y, SONG M, et al. Predictive study on toxicity of halogenated cinnamic acid to selenastrum capricornutum by neural network method[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2021, 16(3): 347-354 (in Chinese).
[12] 堵锡华, 田林, 李靖, 等. 新的价键指数用于甲酰胺类似物活性的理论研究[J]. 分子科学学报, 2022, 38(3): 234-241. DU X H, TIAN L, LI J, et al. Theoretical study on activity of formamide analoguesby using new valence bond index[J]. Journal of Molecular Science, 2022, 38(3): 234-241 (in Chinese).
[13] 堵锡华, 吴琼, 李靖, 等. 有机污染物色度降解动力学常数的神经网络研究[J]. 徐州工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2022, 37(4): 30-35. DU X H, WU Q, LI J, et al. Neural network study on kinetic constants of chromatic degradation of organic pollutants[J]. Journal of Xuzhou Institute of Technology (Natural Sciences Edition), 2022, 37(4): 30-35 (in Chinese).
[14] 张婷, 梁逸曾, 赵晨曦, 等. 基于分子结构预测气相色谱程序升温保留指数[J]. 分析化学, 2006, 34(11): 1607-1610. ZHANG T, LIANG Y Z, ZHAO C X, et al. Prediction of temperature-programmed retention indices from molecule structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2006, 34(11): 1607-1610 (in Chinese).
[15] 胡黔楠, 梁逸曾, 王亚丽, 等. 直观队列命名法的基本原理及其在矩阵与拓扑指数计算中的应用[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2003, 20(4): 386-390. HU Q N, LIANG Y Z, WANG Y L, et al. The basic principles of heuristic queue notation and its applications in calculation of matrix and topological index for topological graphs[J]. Computers and Applied Chemistry, 2003, 20(4): 386-390 (in Chinese).
[16] SAÍZ-URRAL, PÉREZGONZÁLEZM, TEIJEIRAM. 2D-autocorrelation descriptors for predicting cytotoxicity of naphthoquinone ester derivatives against oral human epidermoid carcinoma[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2007, 15(10): 3565-3571. [17] 刘海春, 卢帅, 冉挺, 等. 基于分子对接和QSAR方法预测B-RafⅡ型抑制剂活性[J]. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31(11): 2191-2206. LIU H C, LU S, RAN T, et al. Accurate activity predictions of B-Raftype Ⅱ inhibitors via molecular docking and QSAR methods[J]. Acta Physico-ChimicaSinica, 2015, 31(11): 2191-2206 (in Chinese).
[18] WANG Y F, ZHOU M L, SHEN C L, et al. Time delay recursive neural network-based direct adaptive control for a piezo-actuated stage[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2023, 66(5): 1397-1407. doi: 10.1007/s11431-022-2081-7 [19] ANDREA T A, KALAYEH H. Applications of neural networks in quantitative structure-activity relationships of dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1991, 34(9): 2824-2836. doi: 10.1021/jm00113a022 [20] 许禄, 邵学广. 化学计量学方法[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 441. XU L, SHAO X G. Methods of chemometrics[M]. 2nded. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 441(in Chinese).
-




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: