-
联合国政府间气候变化专门委员会(IPCC)在2021年第6次气候变化评估报告(AR6)中首次从区域角度对气候变化进行了更详细的评估[1],指出全球整个气候系统的变化前所未有,全球变暖造成的海平面持续上升在长期内并不可逆转,同时更迅速的变暖会加剧全范围内的水循环,影响降水特征,中国将是受气候变化影响最大国家之一,强降水事件发生已趋于常态化。区域气候的显著性很大程度会受到降水变化的影响[2]。江苏省盐城市是中国东部沿海地区,全境为平原地貌,属气候过渡地带,季风气候明显,适宜的气候条件非常有利于稻的种植与生长。极端降水对于农作物的影响最为普遍和频繁[3],作为全省水稻的主产区,应对极端气候变化积极采取措施,否则将会对地区经济的发展产生影响[4]。王充等[5]在对固原市原州区60年的降水分析时发现其年降水和汛期、秋季突变情况类似,不同季节发生降水突变的情况也不尽相同;祝莹等[6]通过分析沱江流域极端降水的时空演变,发现其极端降水主要出现在流域中下游,并极端降水量呈逐年降低趋势;陈红卫[7]对盐城市降水的地区分布、年际变化和年内分配特性进行了具体论述,由于欠缺对于降水突变趋势及降水变化周期的研究,对降水集中期(PCP)和集中度(PCD)也未做进一步探讨,农业生产过程的指导性不强,故盐城市降水特性分析还有待完善。本研究以盐城市4个气象站点近60年的逐日降水数据为数据基础,在年际、年内降水特征分析的基础上,对降水PCP、PCD,全年和夏季降雨的突变、周期变化情况进行深度分析,以期把握极端降水的出现规律,为区域水资源管理及防洪防灾提供科学依据,为农业生产实践及生态环境保护提供参考。
-
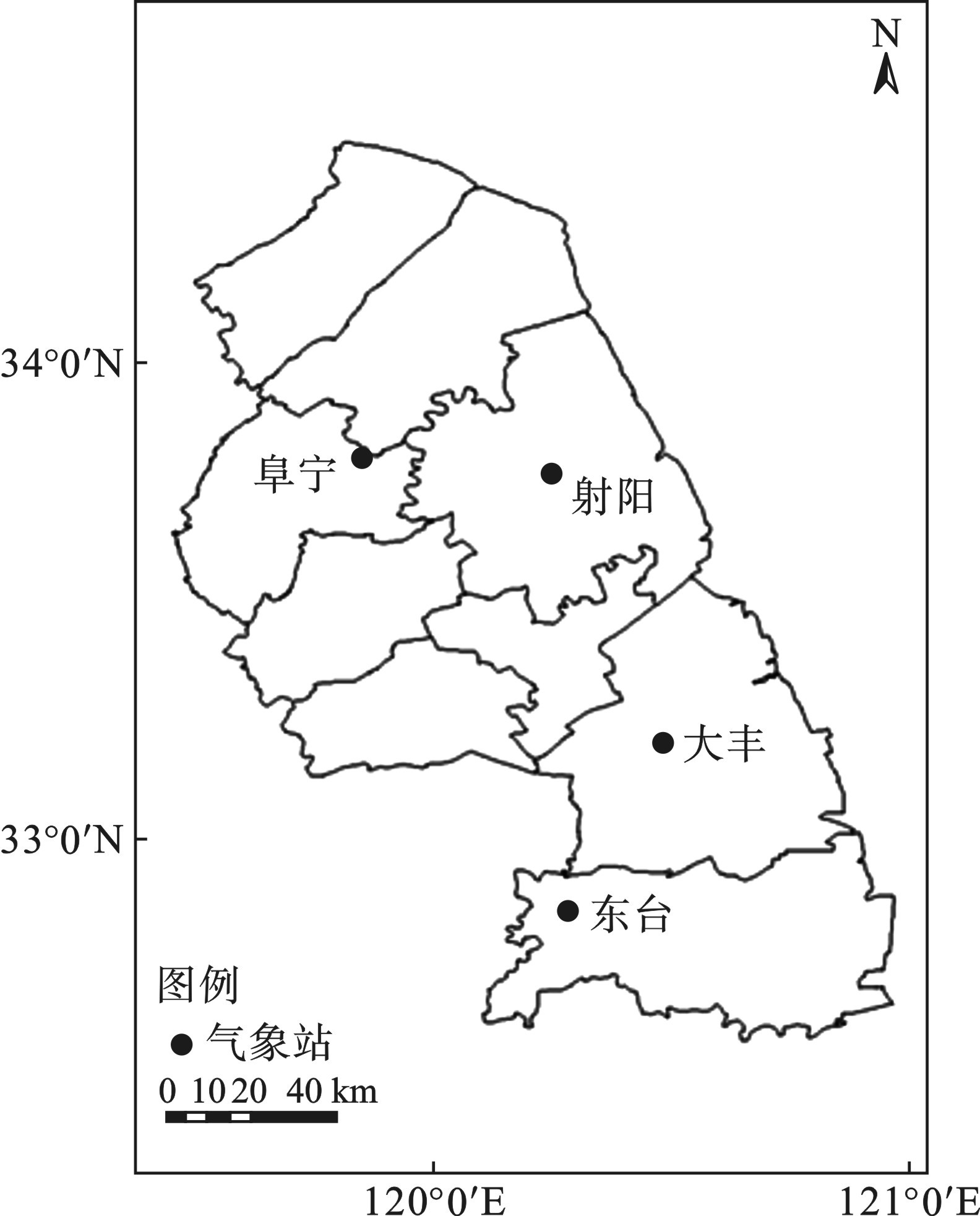
1960—2020年盐城市气象站点的逐日降水数据由国家气象中心提供,对于极异常的降水数据进行剔除从而保证数据的质量及可靠性;为使气象站所测的降水数据代表所在区域的平均降水更具科学性和真实性,运用泰森多边形法[8]计算各年年均降水,气象站点在盐城市内均匀分布,见图1。
-
Mann-Kendall 检验方法[9-10]无需数据服从何种分布,且少数异常值的存在不会对检验结果产生影响,可用于分析各阶段序列变化的显著性,大致确定突变发生时间及次数[11-12],在检验降水历年变化趋势及发生突变时间上具有极高适用性。
对于时间序列x构造一秩序列
$ {S}_{k} $ ,秩序列Sk表示第i时刻数值大于j时刻数值个数的累计数,见式(1~2):计算Sk的方差和均值,见式(3~4):
将Sk标准化,见式(5):
对于时间序列逆序列,同样可按以上步骤计算,使UBk = −UFk,得UB曲线。在给定U0.05 = ± 1.96区间内,两曲线交点即确定为突变点。
-
降水PCD和PCP利用向量原理对时间序列进行定义,来对区域降水的不均匀性做出评价[13],见式(6~7):
式中:
${R}_{xi}=\displaystyle \sum\limits_{j=1}^{n}{R}_{ij}\times \mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}{\theta }_{j};{R}_{yi}=\displaystyle \sum\limits_{j=1}^{n}{R}_{ij}\times \mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}{\theta }_{j};{R}_{ij}$ 为某天降水量;$ {R}_{xi} $ 为i年的降水量垂直分量之和;$ {R}_{yi} $ 为i年的降水量水平分量之和;$ {R}_{i} $ 为i年的降水总量;$ {\theta }_{j} $ 为对应的方位角。 -
小波分析是将某一信号用一簇小波函数系来进行表示,来揭示某时间序列中存在的多种变化趋势及周期。对于时间序列函数f(t),小波函数定义见式(8):
式中,ψ(t)为基小波函数,
$\text{ψ} *\left( {\dfrac{{t - b}}{a}} \right) $ 是$\text{ψ}\left( {\dfrac{{t - b}}{a}} \right) $ 的复共轭函数。小波方差解析式见式(9):
式中:
$ {W}_{f}\left(a,b\right) $ 为小波变换系数;a为伸缩因子,b为平移因子。本研究采用Morlet小波为小波母函数,对盐城降水资料进行连续小波变换,得到小波系数实部,通过Surfer 13软件进行等值线图绘制,直观展现其降水周期变化情况。小波方差图反映时间尺度影响下的能量波动情况,能量表现强的地方为该序列内的主周期。
-
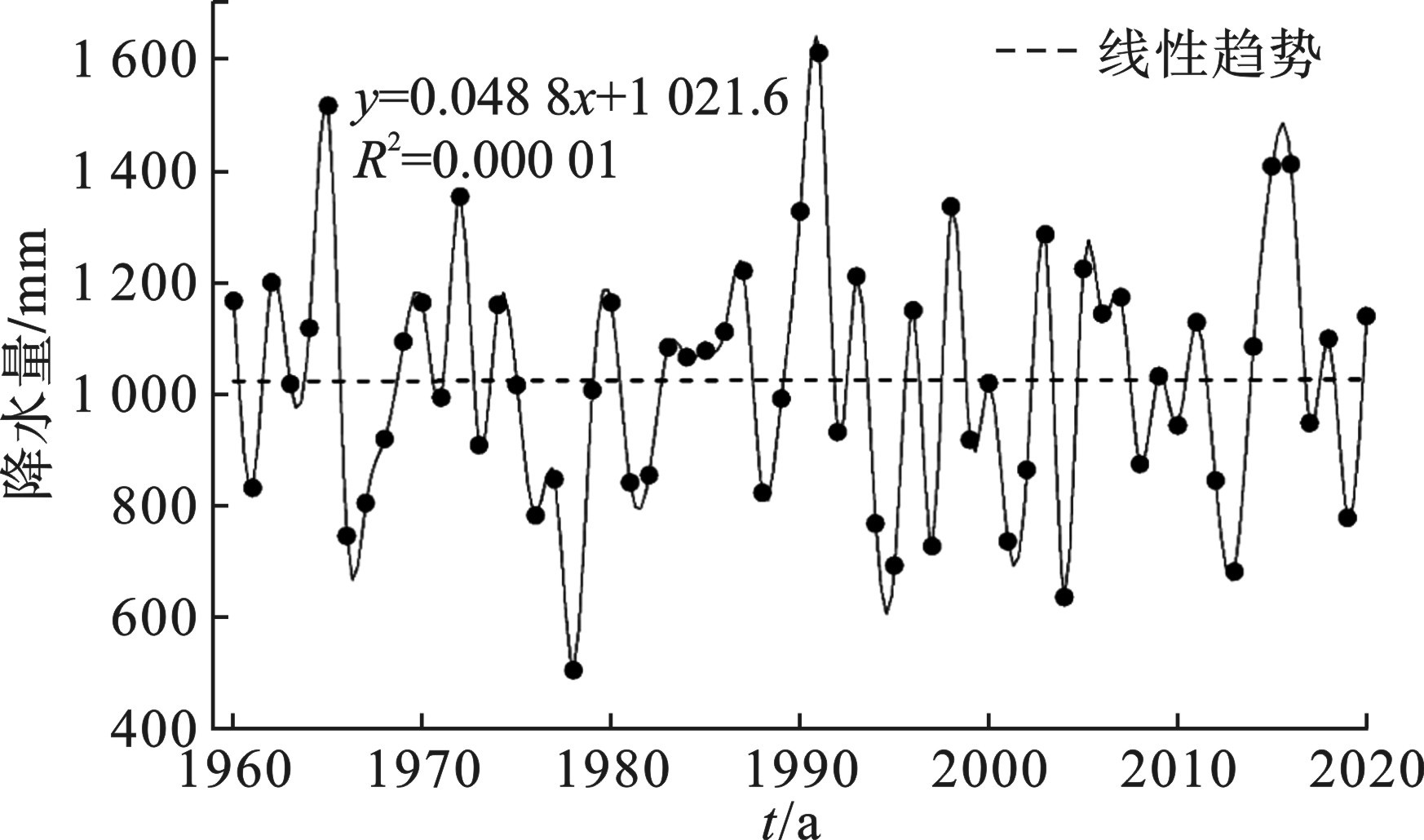
对盐城市1960 — 2020年的降水数据进行分析统计,利用泰森多边形法计算该地区内的年均降水量变化情况,见图2。
图2可知,年降水量变化区间在503~1 609 mm,多年平均降水量为1 023.16 mm。降水丰枯年差异大,1991年降水量为1609.58 mm,为多年最强降水年;1978年降水量为503.33 mm,为降水极枯年;每10年线性递增率为0.48 mm,呈小幅上升趋势,但趋势不明显。
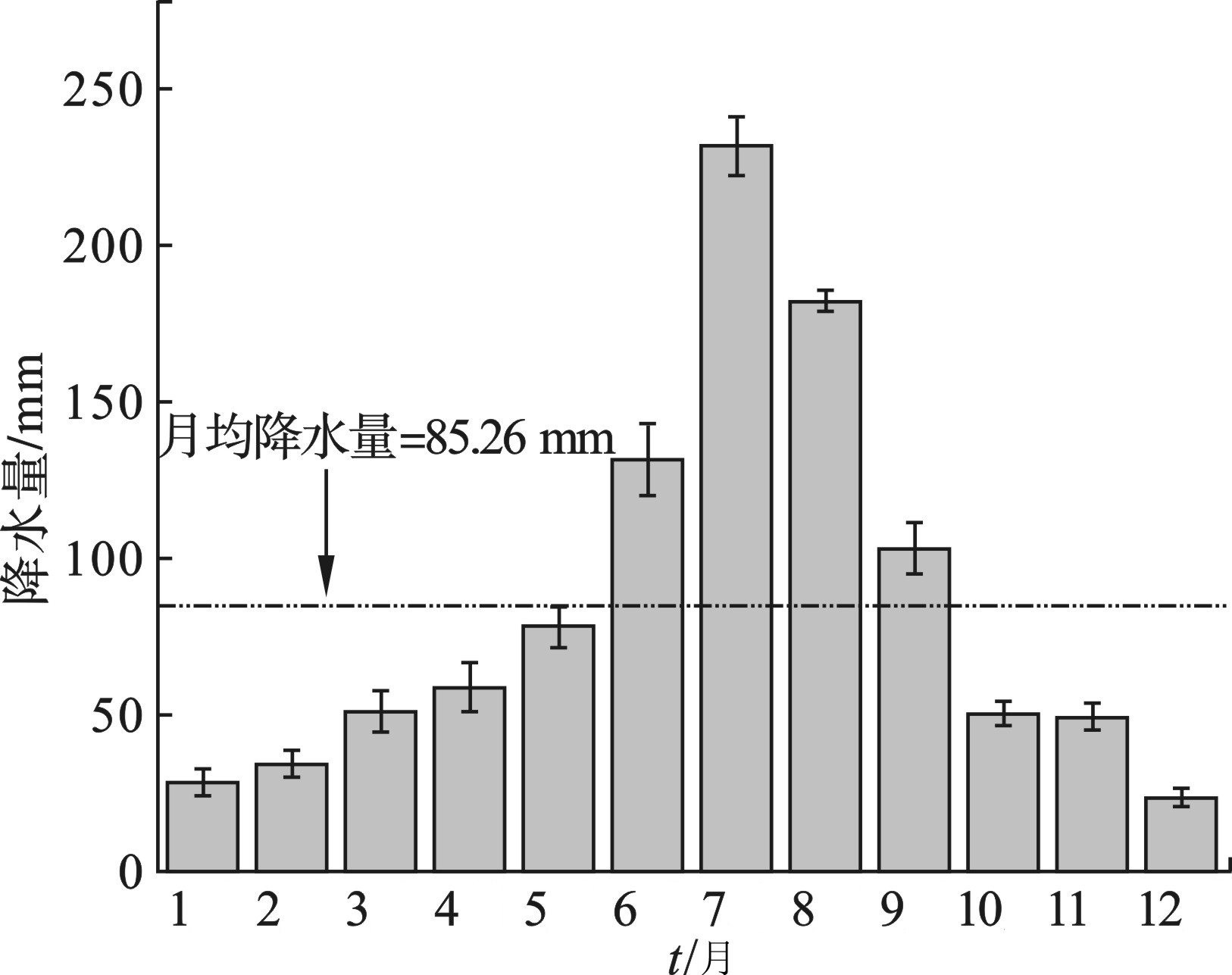
年内各月降水量差异明显,见图3。降雨主要集中于6—9月,均超过了多年月均降水量85.26 mm,多年平均降水中7月降水量明显高于其他月份,12月降水量处于全年最低水平。四季降水量分别为188.15、545.56、203.03和86.34 mm,年内夏季降水比重占全年总降水54%,冬季占8%,年内降水分配总体不平衡,季节降水差异明显。
-
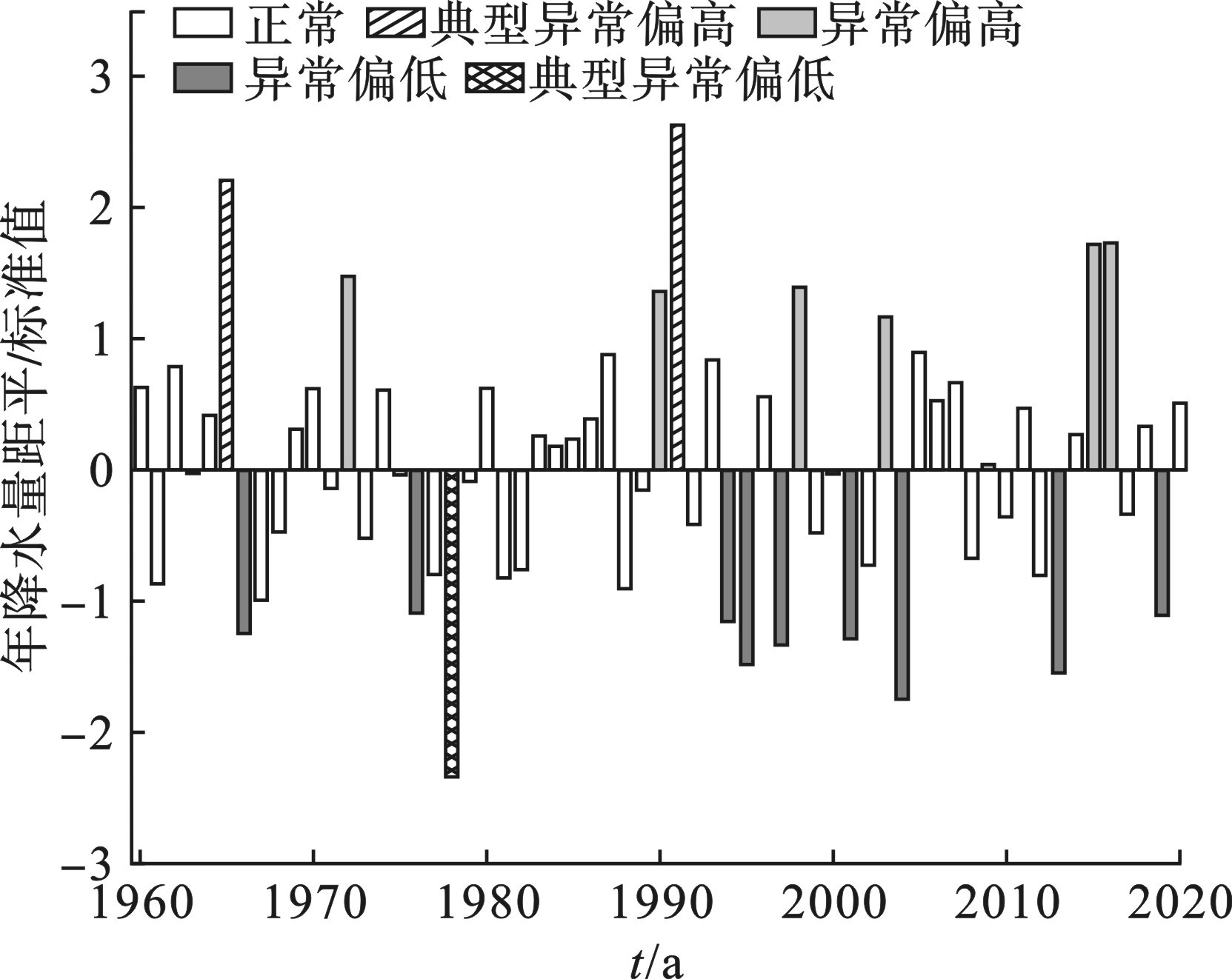
将年降水距平值与标准值作比,来确定盐城市极端降水出现的年份,见图4。
图4可知,降水量典型异常偏高年份在1965和1991年;异常偏高年份在1972、1990、1998、2003、2015和2016年;异常偏低年份在1966、1976、1994、1995、1997、2001、2004、2013和2019年;典型异常偏低年份在1978年。前31年(1960—1990年)年降水异常值出现的次数为6次,近30年(1991—2020年)年降水异常值出现的次数为12次,可见近年的降水异常出现的概率呈增长趋势。
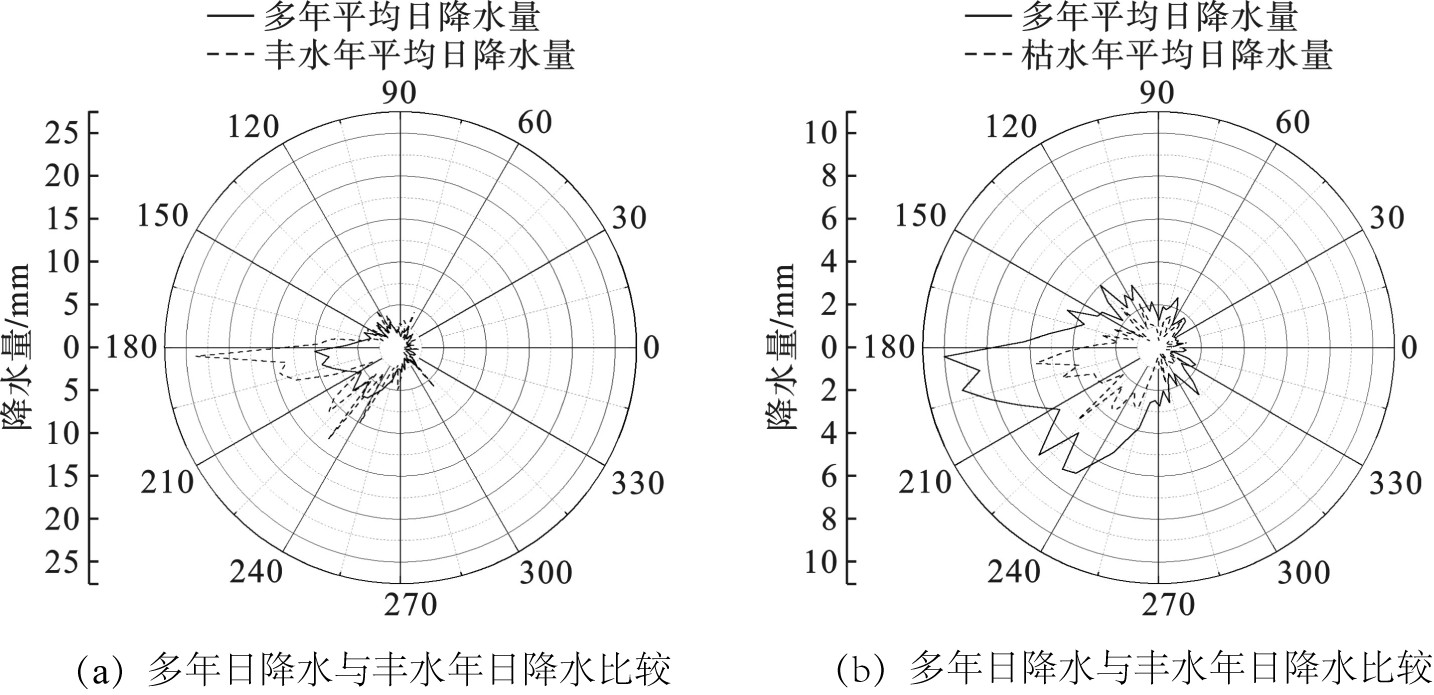
根据1960—2020年逐日气象数据,对历史降水量进行日平均,得出多年平均日降水量,由年均日降水分布极坐标图更直观地反映导致年内降水异常的集中时段,见图5。
图5可知,分别将历年降水量、丰水年降水量和枯水年降水量按天作均值,然后将365 d在0°~360°进行分配,近似的0°~30°代表0~30 d,方向向量的长度即表示日降水量的大小。图5可知,年内存在明显降水倾向,且多年平均和枯丰年内的表现具有一致性,降水高值均向180°~270°倾斜,对应于年内的7—9月,丰水年日均降水曲线、多年日平均降水曲线和枯水年日均降水曲线主要差异均在7—9月体现,其他月份降水量差距不明显,故夏季降水多少直接影响年降水枯丰变化。
采用降水PCP和PCD来分析盐城降水的时间分布情况,PCP分布在7月初到9月初,平均降水PCP在8月上旬,倾向率为每10年0.018 mm,PCP呈小幅上升趋势,照此发展,盐城市的主汛期发生时间将可能推迟。降水PCD分布在0.10~0.77之间,多年平均值为0.43。当PCD值处于均值线之上时,表明该年降水较为集中,PCD最大值出现在1962年,为0.76,表明该年降水最为集中;最小值出现在1988年,为0.11,该年内降水均匀,从历年变化趋势来看,整体呈下降趋势,倾向率为每10年−0.023 mm ,见图6。
-
利用Mann-Kendall 检验,在给定U0.05 = ± 1.96条件下,对盐城市年降水突变情况进行分析。
1960—1970年和2010—2020年内,UF和UB存在交点,但考虑到这些时段处在整个时间序列的始末端,分析可靠性不强,故选取中间段交点进行突变分析。1987年两曲线相交,交点处于0之下,降水呈下降趋势;1990—1992年之间交点值>0,降水量突变呈上升趋势,上升趋势较小;2005年为第3个降水量突变点,降水量呈下降趋势,见图7。
图3可知,年内降水多集中于夏季,因此对夏季降水突变与全年突变特征进行相关性分析。图7所示的全年降雨MK统计量曲线与夏季降雨MK统计量曲线变化趋势均为“W”型,1973年突变开始,之后夏季降水呈上升趋势,1987年,交点值小于0,呈下降趋势;1991年之后UF>0,呈上升趋势,到1998年,两曲线在0处浮动,说明此时段内降雨趋势处于平稳状态,突变不显著;2004年时,降水量突变呈下降趋势,趋势较小。由上述分析,夏季降水突变年份与全年降水突变大致相同,年内降水突变的形成与夏季降水的增多或减少密切相关。
-
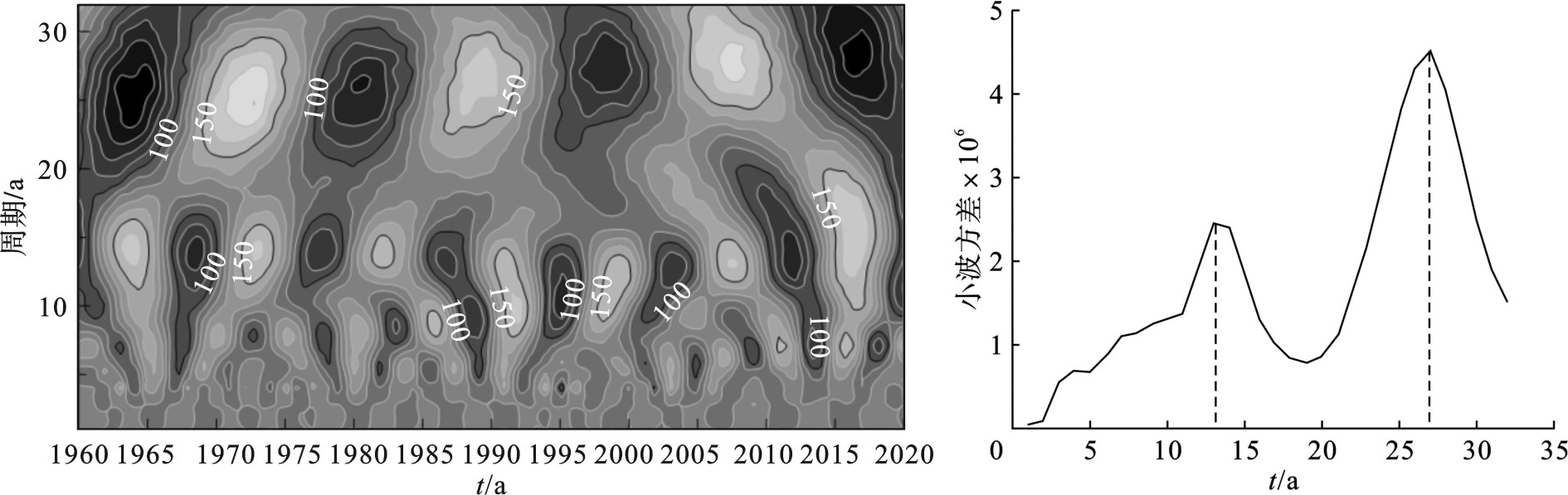
利用Matlab软件的Morlet小波分析工具包对盐城市的降水序列进行计算和处理,进一步探讨该地区降水量的整体周期变化情况。
该地区年降水量存在着3个不同尺度的变化周期,分别是20~32年、10~20年和3~10年尺度。在20—32年时间尺度上降水量“枯—丰”交替出现,呈准3次震荡;在10~20年时间尺度上降水量“丰—枯”交替出现,呈准6次震荡;3~10年时间尺度上周期变化趋势较稳定。小波方差图上在13年和27年存在2个明显峰值,周期震荡强烈,27年对应最大峰值,即为该降水序列的第一主周期,13年为第二主周期,见图8。
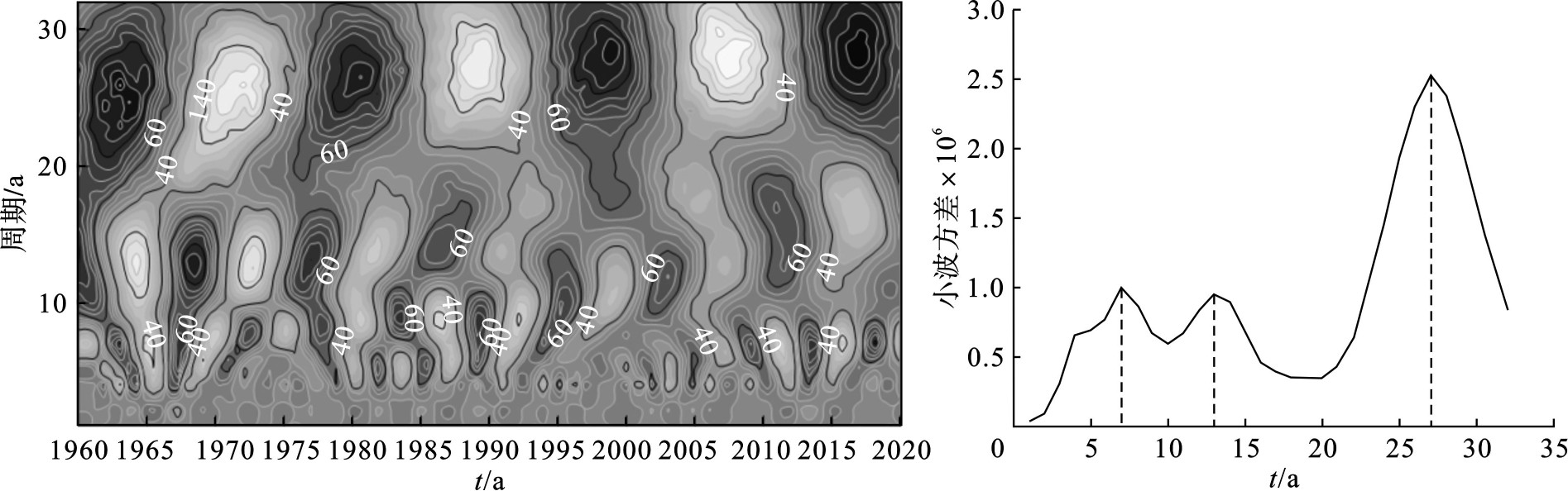
夏季降水量在四季内所占比重最大,且易发生强降雨天气,直接影响年降水量,加剧其枯丰变化情况,对夏季降水进行周期变化分析,掌握夏季与全年降水周期的相关性,见图9。
图9可知,盐城市夏季降水的枯丰交替变化同样存在3个周期尺度,分别为20~32年、10~18年和5~10年。夏季降水周期变化与全年相比较,现有时间尺度内枯丰交替现象相同,周期尺度相吻合。夏季降水共有3个主周期,第一主周期在27年,第二主周期在13年,第三主周期在7年。
-
(1)分析盐城市1960—2020年降水量在时间序列上的变化趋势,在以每10年0.48 mm的速率逐年小幅上升,年内降水不均匀,逐日降水量曲线直观反映了年内降水的集中月份(7—9月),PCP变化范围在7月上旬到9月上旬,在8月中旬时降水集中现象显著;PCD变化范围在0.10~0.77,变化幅度相对较大,有微弱下降趋势。
(2)在极端降水及降水突变分析中发现,降水异常现象由年内夏季降水主导。1991年降水突变呈上升趋势,降水突变特征明显;2004年降水突变呈下降趋势,但趋势较小。故应加强对夏季强降水的管理,科学规划,在预防洪涝灾害发生的同时提高降水资源的利用率。
(3)从降水量周期分析可知,盐城市历史降水在各个时间尺度内均存在显著的降水枯丰交替变化,年尺度降水小波周期变化与夏季小波周期变化均在27年震荡最强,是降水时间序列的第一主周期,13年为第二主周期。综合分析可较为科学地预测盐城市未来降水将呈上升趋势,研究结果以期能够为当地生产活动提供指导,科学应对极端天气,更好地实现社会经济的发展可持续。
盐城市1960—2020年降水变化规律研究
Variation law of precipitation in Yancheng from 1960 to 2020
-
摘要: 盐城市是江苏省产粮第一大市,研究其降水变化特征对于防旱防涝、保障农业生产可持续具有积极意义。根据1960—2020年的逐日降水数据,采用Mann - Kendall检验和Morlet小波分析对盐城市60年降水突变及周期变化规律进行分析,引用降水集中期 PCP和集中度 PCD 讨论年内降水在时间上的分布。结果表明:盐城市近60年多年平均降水量为1 023.16 mm,年降水量有小幅增长趋势,线性递增率为每10年0.48 mm,月降雨序列不稳定,夏季降水比重占全年54%; PCD处于0.10~0.77之间,倾向率为每10年-0.023 mm; PCP主要表现在8月中旬,历年变化呈微弱上升,汛期有逐渐提前趋势;极端降水由夏季降水主导,全年和夏季降水均在1991年发生由少变多突变,且降水周期第一主周期为27年,第二主周期为13年。研究结果可为盐城市粮食生产中极端降水防治及水资源管理提供科学指导。
-
关键词:
- 降水变化 /
- Mann - Kendall检验 /
- 集中度 /
- 集中期 /
- Morlet小波分析 /
- 盐城市
Abstract: Yancheng is the largest grain-producing city in Jiangsu Province. Studying the characteristics of precipitation changes is of positive significance for preventing droughts and floods and ensuring sustainable agricultural production. Using the daily precipitation data from 1960 to 2020, the Mann-Kendall mutation test and Morlet wavelet analysis were used to analyze the sudden change of precipitation in the study area and the regularity of periodic changes. The PCP and PCD of the precipitation concentration period were used to discuss the annual precipitation temporal distribution. The results showed that the average precipitation in Yancheng in the past 60 years was 1 023.16 mm. The annual precipitation had a slight growth trend, and the linear increase rate was 0.48mm/10a. The monthly rainfall sequence was unstable, and the proportion of summer precipitation accounted for 54% of the whole year. PCD was between 0.10 and 0.77, and the trend rate was -0.023 mm/10a. PCP was mainly manifested in mid-August, with a slight increase over the years, and the flood season had a gradual advance trend. The extreme precipitation was dominated by the summer precipitation. And both annual and summer precipitation was with a sudden change in 1991 when the annual occurrence changed from less to more. The first main period of the precipitation cycle was 27 a, and the second main period was 13 a. The results could provide a scientific guidance for extreme precipitation prevention and water resource management in a grain production in Yancheng.-
Key words:
- precipitation change /
- Mann-Kendall test /
- PCD /
- PCP /
- Morlet wavelet analysis /
- Yancheng
-

-
-
[1] IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis[R]. 2021. [2] 凌敏华, 韩洪宝. 1960—2018年河南省降水时空变化特征及重心[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(17): 7008 − 7016. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.17.006 [3] 俞书傲. 气候变化对农作物生产的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. [4] 魏永富, 崔英杰, 吴英杰. 基于Mann-Kendall法与草地分类的气候变化特征[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(24): 1 − 8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.24.001 [5] 王充, 燕宁娜, 李超超, 等. 固原市原州区近60a降水变化特征分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(20): 8043 − 8049. [6] 祝莹, 敖天其, 陈婷, 等. 沱江流域汛期极端降水事件时空演变特征[J]. 水电能源科学, 2021, 39(7): 1 − 4. [7] 陈红卫. 盐城市降水特性分析[J]. 水文, 2000(S1): 62 − 65. [8] 张涛, 王祥, 杨欣玥, 等. 面雨量计算方法对水文模拟的影响[J]. 人民长江, 2017, 48(19): 42 − 47. [9] 姜瑶, 徐宗学, 王静. 基于年径流序列的五种趋势检测方法性能对比[J]. 水利学报, 2020, 51(7): 845 − 857. doi: 10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.20200066 [10] MANN H B. Nonparametric tests against trend[J]. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 1945: 245 − 259. [11] 曹鸿兴. 评新书《现代气候统计诊断与预测技术》[J]. 应用气象学报, 2000(1): 128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2000.01.016 [12] 邱临静, 郑粉莉, 尹润生. 1952—2008年延河流域降水与径流的变化趋势分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(3): 49 − 53. [13] ZHANG L, QIAN Y F. Annual distribution features of the yearly precipitation in China and their interannual variations[J]. Acta Mereorologica Sinica, 2003, 17(2): 146 − 163. -



 下载:
下载: