-
大气中的氮氧化物是产生雾霾和酸雨的主要原因之一[1]。NH3-SCR作为最有效的NOx还原方法,广泛应用于燃煤发电厂烟气净化等领域。低温等离子体 (NTP) 能够在O2存在时产生非常高浓度的活性氧,NO被活性氧O或O3氧化为NO2[2]。然而,由于等离子体中存在大量高活性物质,在转化过程中还会产生副产物N2O[3]或发生逆反应抑制NO的去除[4],反应如式(1)~(2)所示。
等离子体-催化剂协同催化已被证明是一种有效提高催化效果的手段,并且多种热催化领域的催化剂都已被证实会在与NTP结合时表现出协同作用[5]。LI等[6]研究等离子体并提高了用烃类作为还原剂的SCR性能,亦证明了等离子体通过产生醛提高了对NOx的还原能力。ZHU等[7]的研究表明NTP和Mn-Cu/ZSM5催化剂的组合显著提高了NO的去除效率。等离子体-催化剂的协同效应还体现在等离子体的应用能使催化剂的形态发生变化[8]、改变催化的反应途径[9]。进一步研究发现,催化剂的纳米特征能导致电场增强、多孔催化剂中微放电的形成及放电类型的改变[10]。近年来,由于过渡金属Mn具有多种氧化态,能在NH3-SCR过程中提供自由电子而广泛应用于快速SCR的研究[11]。CeO2具有特殊的氧化还原能力和高储氧性能,也常被作为催化剂助剂用于各种催化反应[12]。然而,目前低温等离子体作用下Ce掺杂对强化MnOx基催化剂性能机制尚未清楚。
本研究合成纳米Mn基催化剂,通过其催化氧化性、SCR活性、XRD、XPS等表征与分析等手段以探讨Ce掺杂对MnO2在等离子体中NH3-SCR的作用,以及等离子体对该型催化剂产生结构变化的影响,同时对等离子体条件下催化剂硫水耐受性进行分析,以期为NTP协同NH3-SCR去除NO的实际应用提供参考。
-
本实验催化剂采用水热沉积法制备,将KMnO4和Ce(NO3)3·6H2O按照一定物质的量比例溶解于去离子水中,将混合后的溶液密封放置在干燥箱中90 ℃反应24 h。过滤洗涤后的样品在105 ℃干燥12 h,并过筛得到40~60目催化剂。Mn和Ce的摩尔比为1/1,记作Mn-Ce,同时以相同方法制备α-MnO2。上述样品在含SO2气氛中反应后表示为MnO2-PS、Mn-Ce-PS。
XRD表征采用德国Bruker公司的D8 Advance型X射线衍射仪,Cu Kα辐射源,扫描范围为2θ=3°~80°,管电流40 mA,管电压40 kV。XPS表征采用美国Thermo ESCALAB 250Xi对催化剂表面的元素组成、含量进行测定,光源为Al Kα(1 486.6 eV)射线,能谱采用C1s的标准结合能284.5 eV进行校正,采用Avantage软件对谱图进行分峰拟合。样品形貌使用日立SU8020型扫描电子显微镜分析,扫描工作电压为15 kV。
-
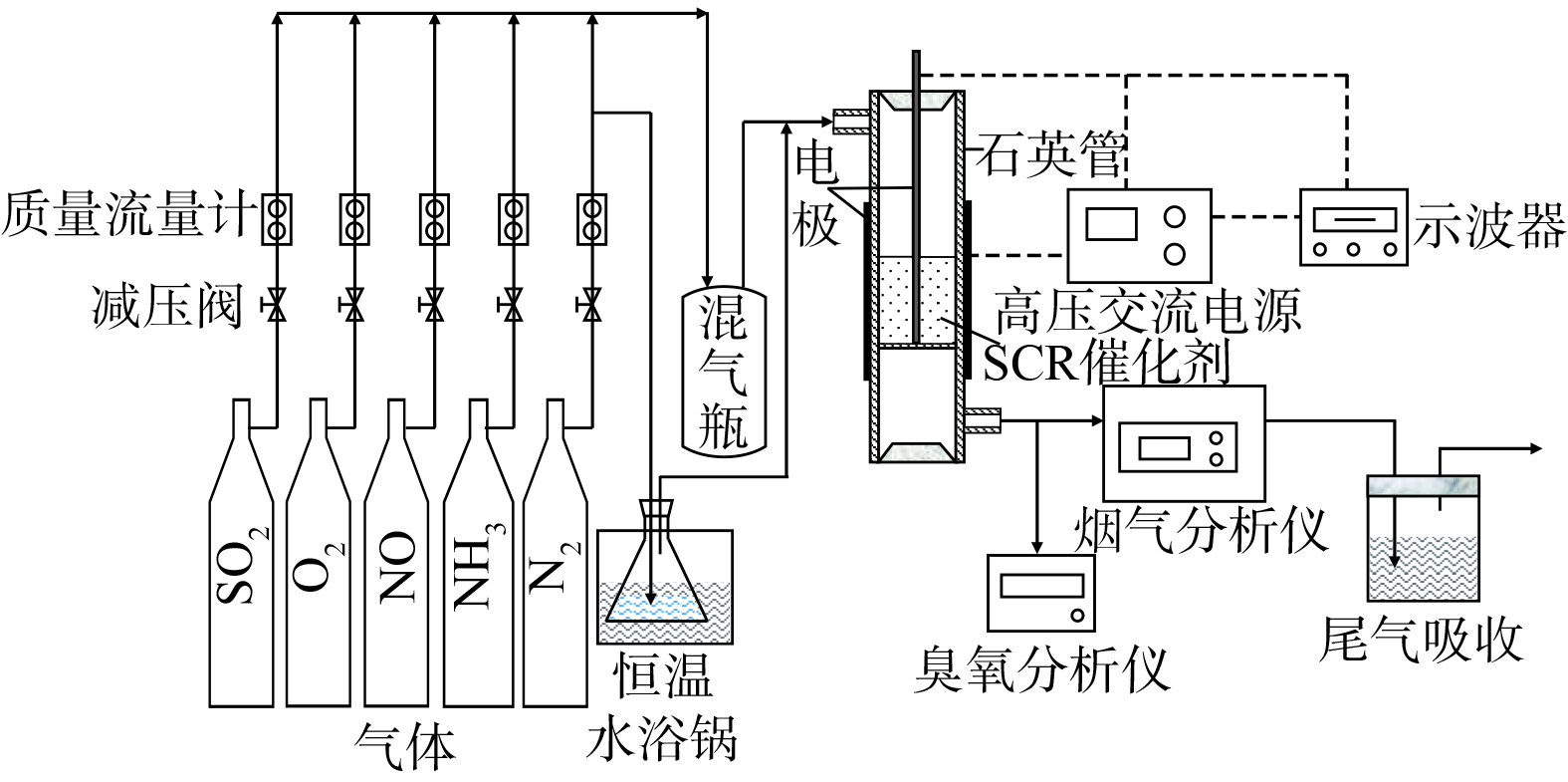
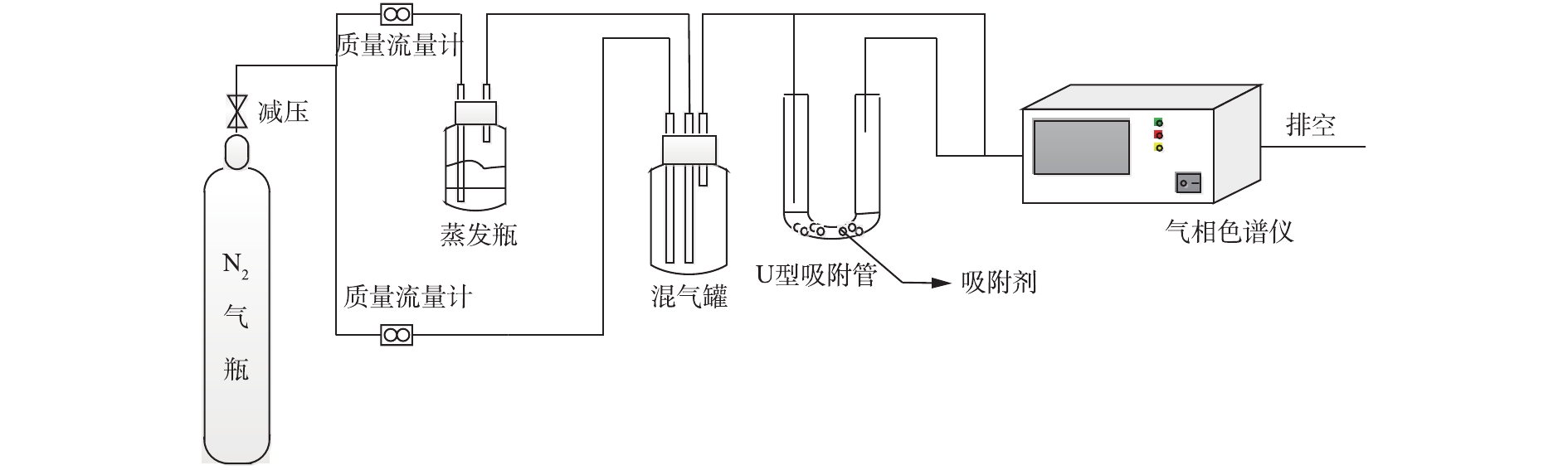
催化剂活性测试装置由配气系统、等离子体反应装置和气体分析系统组成,“一段式”介质阻挡放电协同催化还原脱硝实验流程如图1所示。NH3、NO、O2、SO2、H2O及N2平衡气模拟反应气体由质量控制器控制进入反应器。将装有去离子水的锥形瓶放在水浴锅中加热以产生水蒸气,通过氮气流与进料气体混合后通入反应器。反应在室温条件下进行,气体流量1 300 mL·min−1,其中NO进口质量浓度为535.7 mg·m−3,NH3进口质量浓度为265.6~607.1 mg·m−3,[NH3]/[NO]为1,O2为8%,SO2进口质量浓度为1 142.9 mg·m−3,N2为平衡气。进出口处气体浓度由Testo Pro.350烟气分析仪测量,O3 质量浓度由UV-1000V臭氧检测仪测得。
介质阻挡放电 (dielectric barrier discharge,DBD) 等离子体反应器由2个电极和1个石英管组成。石英管长200 mm,内径8 mm。高压电极是直径为2 mm的不锈钢棒,同轴安装在石英管内。石英管外紧密缠绕200目铜网作为负极,在等离子体反应器的放电区填充催化剂。
-
催化活性实验中,根据式 (3) 计算NOx的转化率。放电能量密度 (SIE) 是低温等离子体降解NO效果评价的重要参数之一[13],根据式 (4) 进行计算。NO、NH3氧化率分别通过式 (5) 和 (6) 计算。
式中:
ηNOx 为NOx去除率;P为反应器放电功率,W;Q为模拟废气的流速,L·min−1。 -
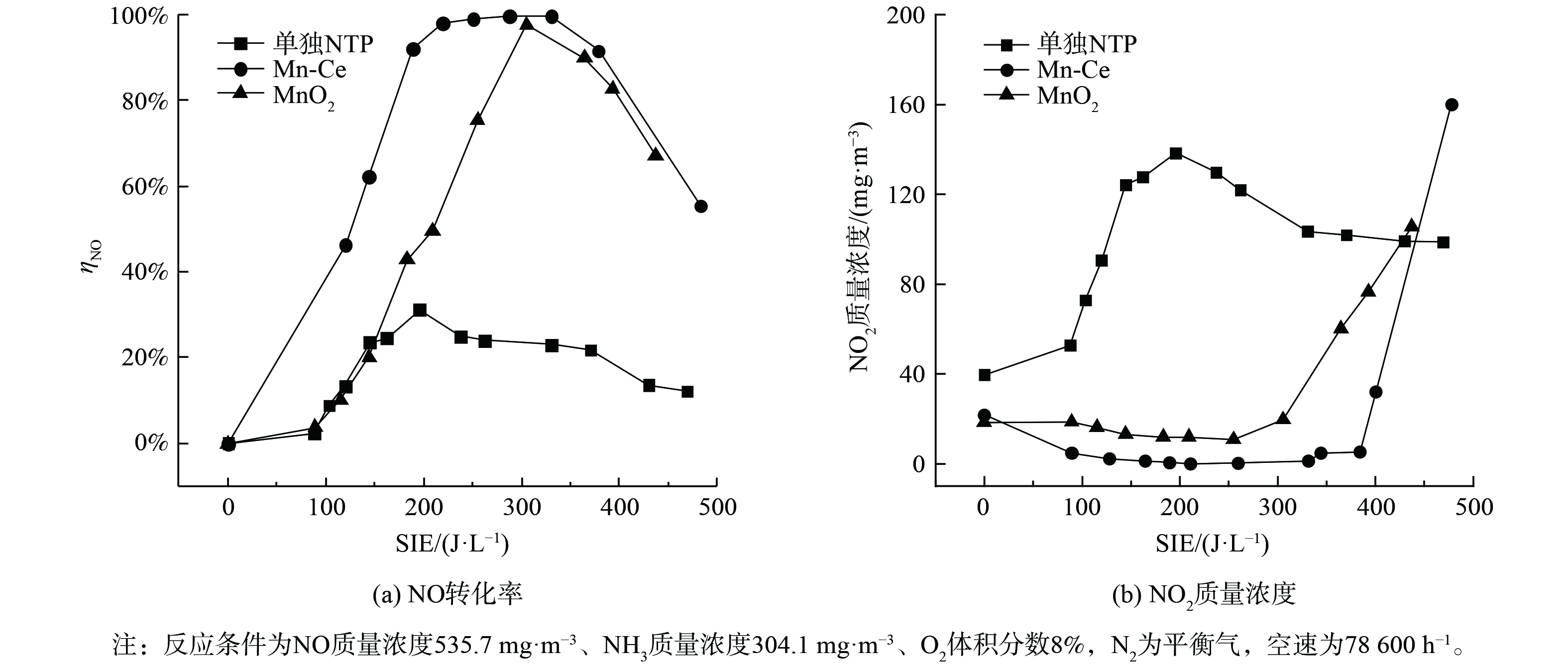
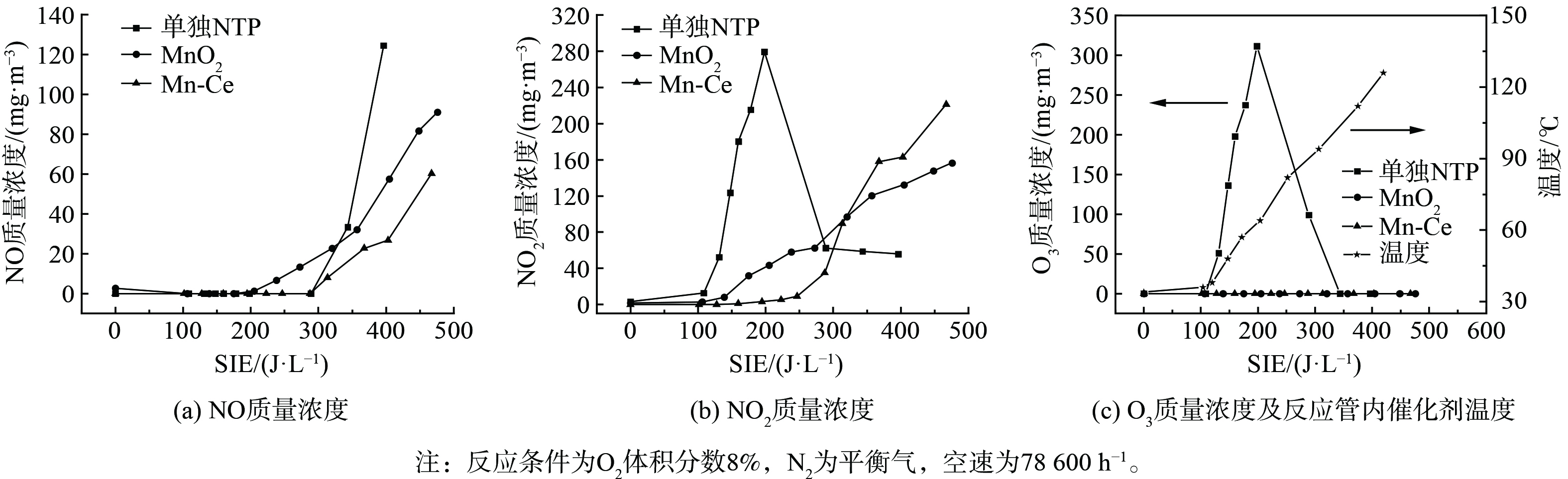
图2比较了在低温等离子条件下无催化剂、α-MnO2及Mn-Ce催化剂在NO转化率和NO2质量浓度的变化。当没有催化剂参与反应时,图2(a)显示出NO的转化率最高只有25%,仅依靠高能电子与气体组分碰撞产生的活性粒子与NO反应[13],NO转化率低。由于O2的解离能为4.81 eV,小于N2的解离能9.79 eV[14],在能量密度较小时,O2比N2更容易解离,NO主要通过O和O3生成NO2。因此,从图2(b)可发现,在SIE达到200 J·L−1之前,NO2质量浓度一直升高。其反应机理可如式(7)~(10)所示[15]。
当在反应器中加入催化剂后, NO的去除率均得到了较大幅度的提升。图2(a)表明MnO2催化剂在300 J·L−1时达到最高NO转化率97%。同时,图2(b)表明,在SIE达到280 J·L−1之前,NO2质量浓度维持在约16 mg·m−3,保持不变。这说明NO没有被大量氧化。但MnO2催化剂能量密度反应窗口较窄,SIE仅为约300 J·L−1。而图2(a)显示Mn-Ce催化剂在200~380 J·L−1下保持了90%以上的NO转化率,并且在380 J·L−1前NO2质量浓度均小于5 mg·m−3。与单纯等离子体放电相比,能量密度相对较低时,Mn-Ce催化剂使得NO2质量浓度大幅降低。这表明由NO氧化产生的NO2通过快速SCR反应参与了NO的去除。
比较图3中填充催化剂前后反应器伏安特性曲线发现,随着电压的升高,放电通道的数量和强度均增加,故放电电流也随之增加。催化剂的加入引起催化剂表面附近电场的增强,这是由于催化剂颗粒表面的局部高曲率,以及在介电材料存在引起的电荷累积和极化效应[16]。这也表明催化剂存在时放电起始电压更低,并且前期在相同电压下产生的电流更大。
-
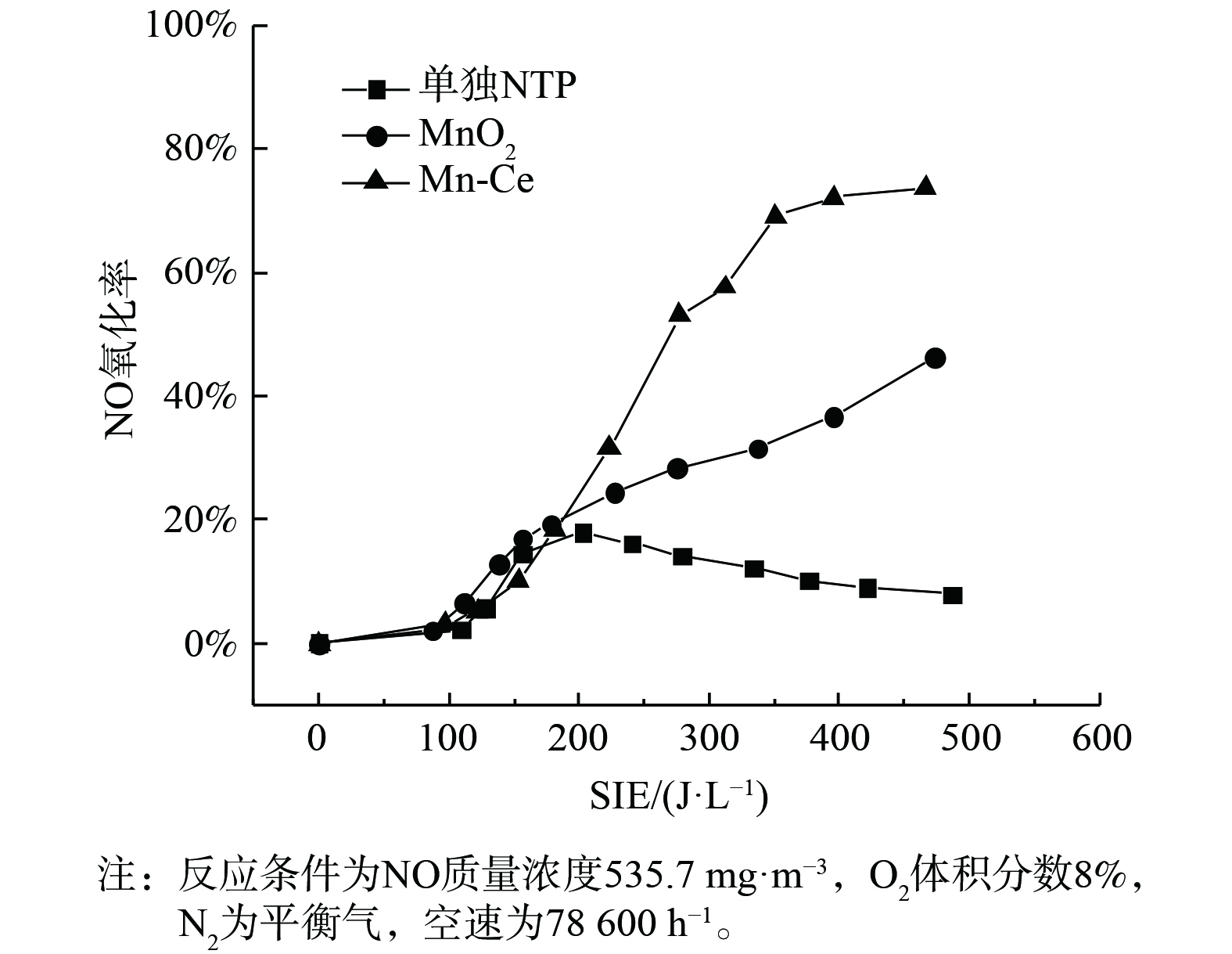
JANSSENS等[17]发现,当反应温度为200 ℃时,NH3-SCR反应可被认为是NO氧化和快速SCR反应的耦合,即发生反应2NH3+NO+NO2 → 2N2+3H2O。因此,催化剂对NO的催化氧化活性可决定其NH3-SCR反应的活性。为此,进行了等离子协同下NO氧化活性测试,结果如图4所示。
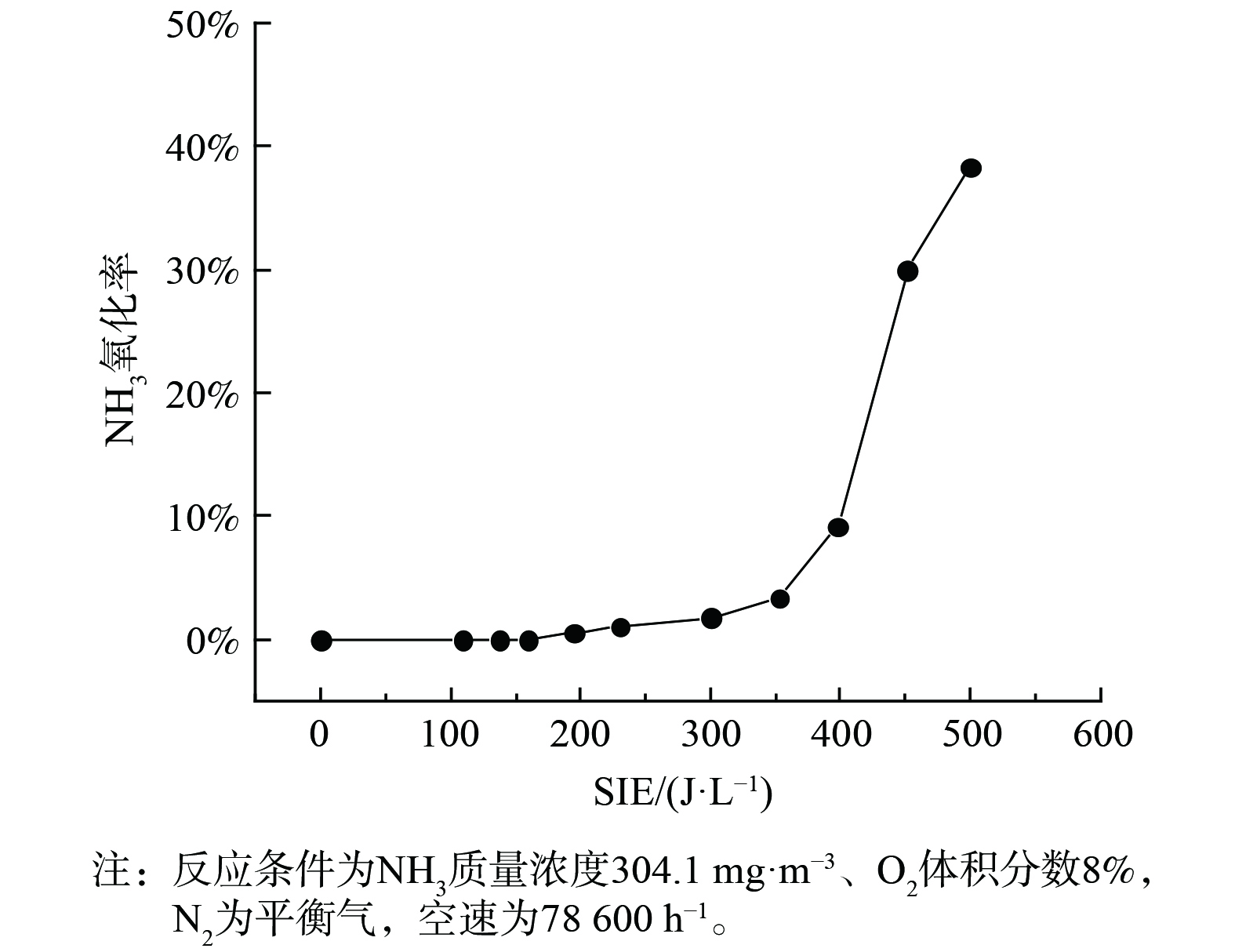
在无催化剂存在时,NO氧化率随能量密度变化关系与图2曲线变化一致。这也说明了空管反应器中NO的浓度变化主要由等离子体产生的活性粒子对NO的氧化而引起。3种条件下NO氧化活性的顺序为:Mn-Ce>MnO2>无催化剂,这与其NTP-SCR活性基本一致。2种催化剂对NO的氧化率均随能量密度的增加而上升,且Mn-Ce的NO氧化率要明显高于MnO2。这表明Ce的引入提高了Mn基催化剂的NO氧化活性,从而使其在低温下具有较高的NH3-SCR活性。同时,图2表明,能量密度大于300 J·L−1时MnO2和Mn-Ce的NO转化率开始下降,这是由于能量密度的增加使得Mn基催化剂氧化NH3生成NO,如图5所示。
-
在NTP协同催化去除NO过程中,影响催化剂性质及NO去除反应路径的主要是等离子体放电产生的O活性物种[18]。以N2/O2为气体组分,分析比较NTP放电过程中不同催化剂体系中物质变化及反应前后Mn-Ce性质的变化,进而研究NTP对催化剂的影响,结果如图6所示。在没有催化剂的条件下,随着能量密度的增加,NO2在能量密度为100~200 J·L−1时发生急剧上升,此段NO始终没有产生,并且O3含量变化趋势基本上与NO2吻合。这说明在臭氧存在时更容易形成NO2而不是NO。随能量输入的增加,反应管内温度上升臭氧开始分解,体系中NO含量开始上升。
在Mn-Ce催化体系中,NO2在能量密度159 J·L−1开始生成,此初始值高于无催化时生成NO2的初始能量密度。JIA等[19]发现,臭氧在不同晶型的Mn基催化剂表面均会发生分解,在Mn-Ce催化剂测试过程中一直没有检测到臭氧存在,这也证明了能量密度低时NO2的生成与臭氧相关。在Mn-Ce体系中,能量密度为287 J·L−1时检测到NO的存在,与无催化剂存在时NO产生的初始能量密度相近,因此臭氧对NO的产生影响较小。在能量密度为300~400 J·L−1时,3种体系中NO生成量关系为无催化剂>MnO2催化剂>Mn-Ce催化剂。Mn原子通过氧化过程将增加了电子转移到臭氧中的能力,这导致臭氧更快被分解为原子[20],促进了NO向NO2的氧化。
-
DBD放电产生等离子体会对催化剂产生影响,改变催化剂的表面性质[21]。化学吸附氧在催化还原过程中发挥了重要的作用。图7(a)显示了在N2/O2气氛中经等离子体处理前后Mn-Ce催化剂O1s区域的XPS光谱。DANIELLE等[22]发现,结合能在531 eV的O1s峰属于化学吸附氧 (Oad) ,结合能在529.5 eV的峰归属于晶格氧 (Oβ) 。与新鲜催化剂相比,等离子体处理后的Oad/Oβ从0.61下降到0.54,由于Mn-Ce催化剂的加入导致臭氧浓度减少,因此催化剂化学吸附氧含量的变化可能由催化剂分解臭氧而产生。臭氧在Mn基催化剂上的分解会使部分Mn3+可转化为Mn4+,发生反应式见式(13)和(14)。此过程导致晶格氧Oβ的增加[23]。因此,可初步得出引起Mn价态的变化是臭氧分解对催化剂的主要影响,这也与Mn的价态变化结果相对应。
催化剂上Mn2p3/2和Mn2p1/2光谱如图7(b)所示,Mn2p3/2峰经过分峰拟合后,分成Mn4+ (644.7 eV) 和Mn3+ (642.5 eV) 。比较等离子体反应前后Mn4+和Mn3+的比例发现,Mn4+的比例增加。有研究表明,Mn4+组分对NO的氧化有明显的作用[24],并且Mn4+含量的增加相应的晶格氧含量也会增加,对应XPS结果中Oβ/Oad比例的增大。
YANG等[20]发现,Ce3+ (3d104f1初始电子态) 对应位于903.7 eV和885.3 eV结合能的能带,而结合能位于907.4 eV、901.1 eV、898 eV、888 eV和882.1 eV的峰对应于Ce4+离子。Ce3+取代Ce4+时会造成晶格缺陷,有利于表面氧空位的形成,可加快活性氧的流动性。图7(c)显示等离子处理后催化剂Ce3+/(Ce4++Ce3+)比例增加了1.23%,这表明其更容易吸附氧物质和活化还原剂。
-
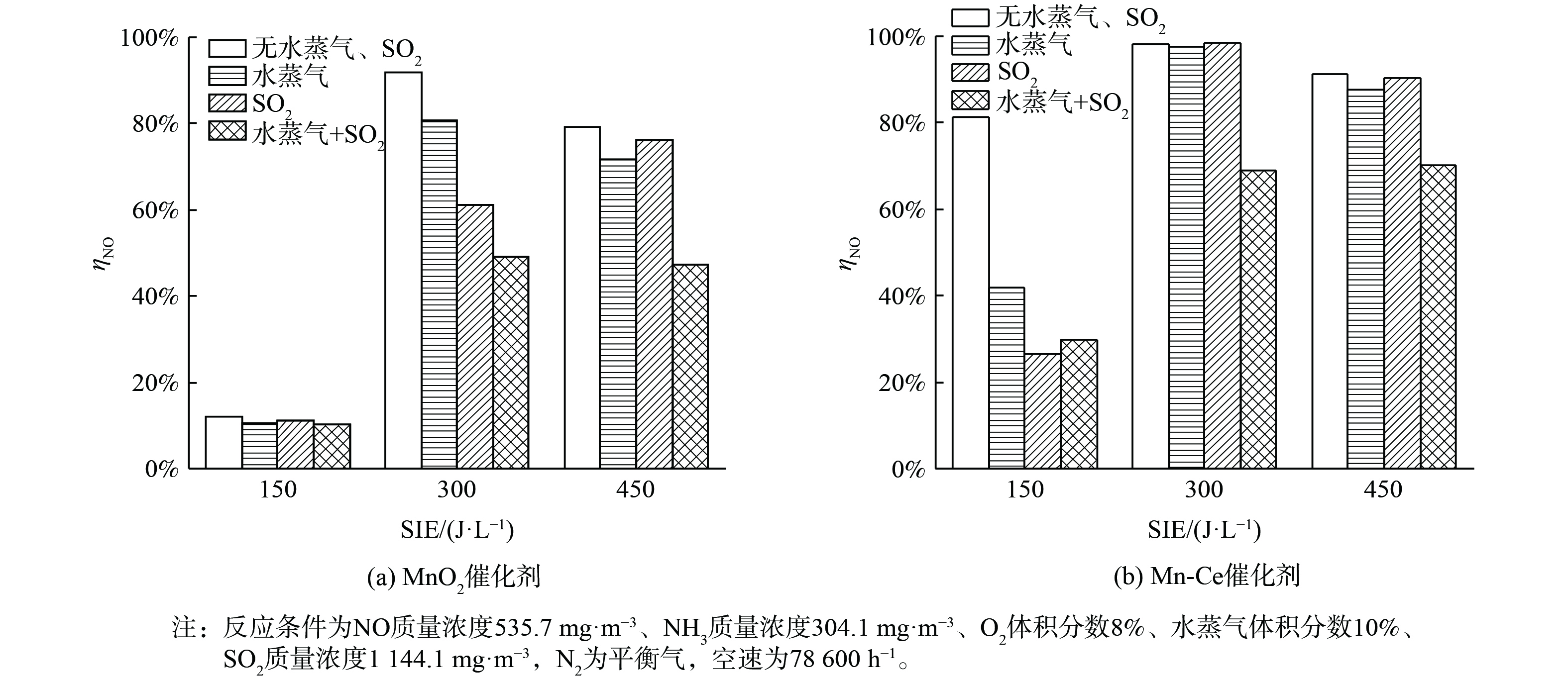
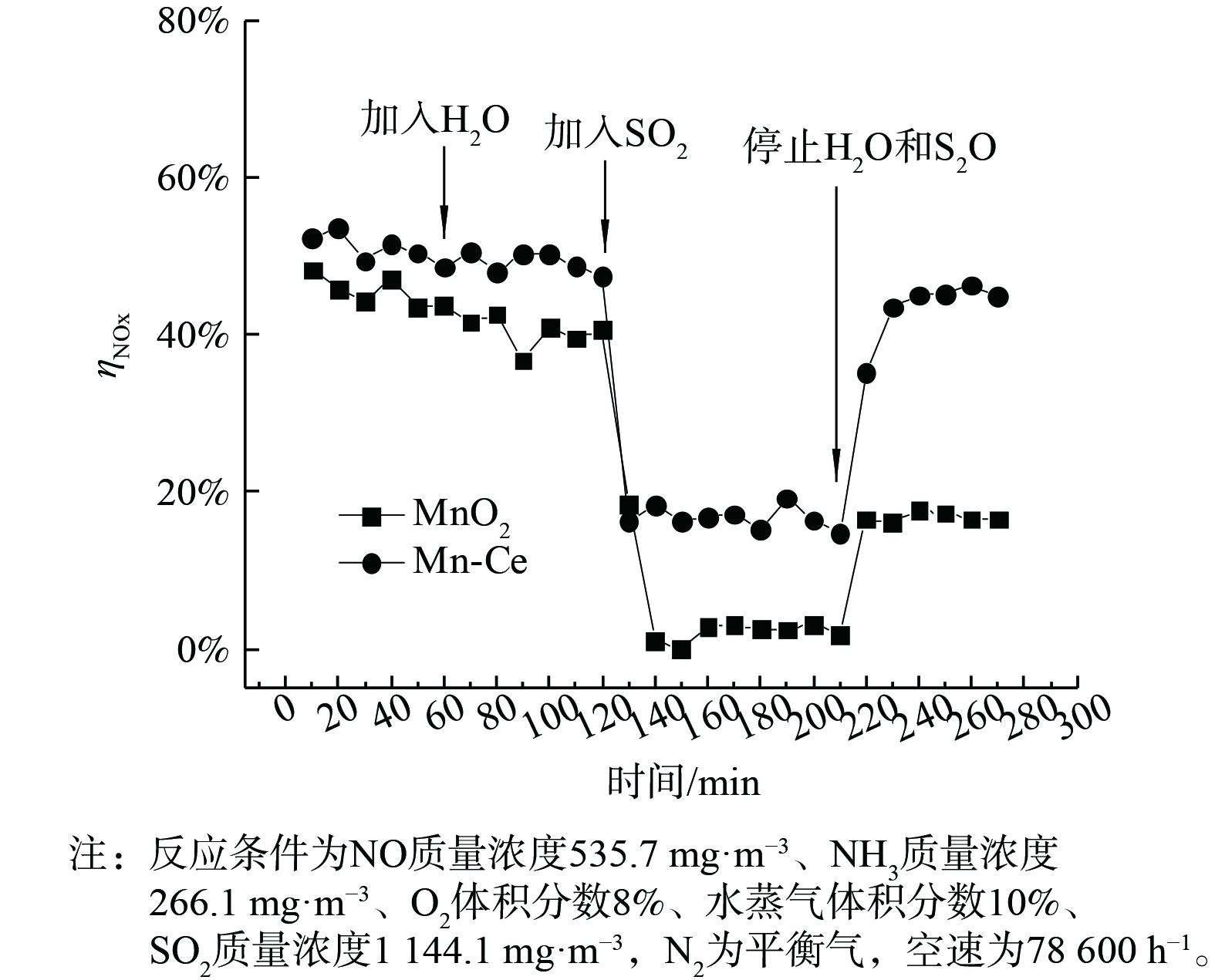
图8说明了H2O和SO2在不同能量密度下对2种催化剂的SCR活性的影响。结果表明,与单独存在H2O或SO2的情况相比,初始气体中H2O和SO2的共存更明显地导致了SCR活性的降低。当系统中存在H2O时,SO2能被O·和·OH自由基氧化,发生反应式为式 (15) 和 (16) 。氧化产物能与水反应生成H2SO4[25]。
造成催化剂失活的原因可能是还原剂NH3与SO2氧化生成的硫酸根离子在催化剂表面生成硫酸盐,覆盖催化剂活性位点并减少了参与还原NO反应的氨量。另外,催化剂的活性组分可能在SO2和H2O存在的条件下流失并硫酸化,从而导致催化剂造成不可逆失活。
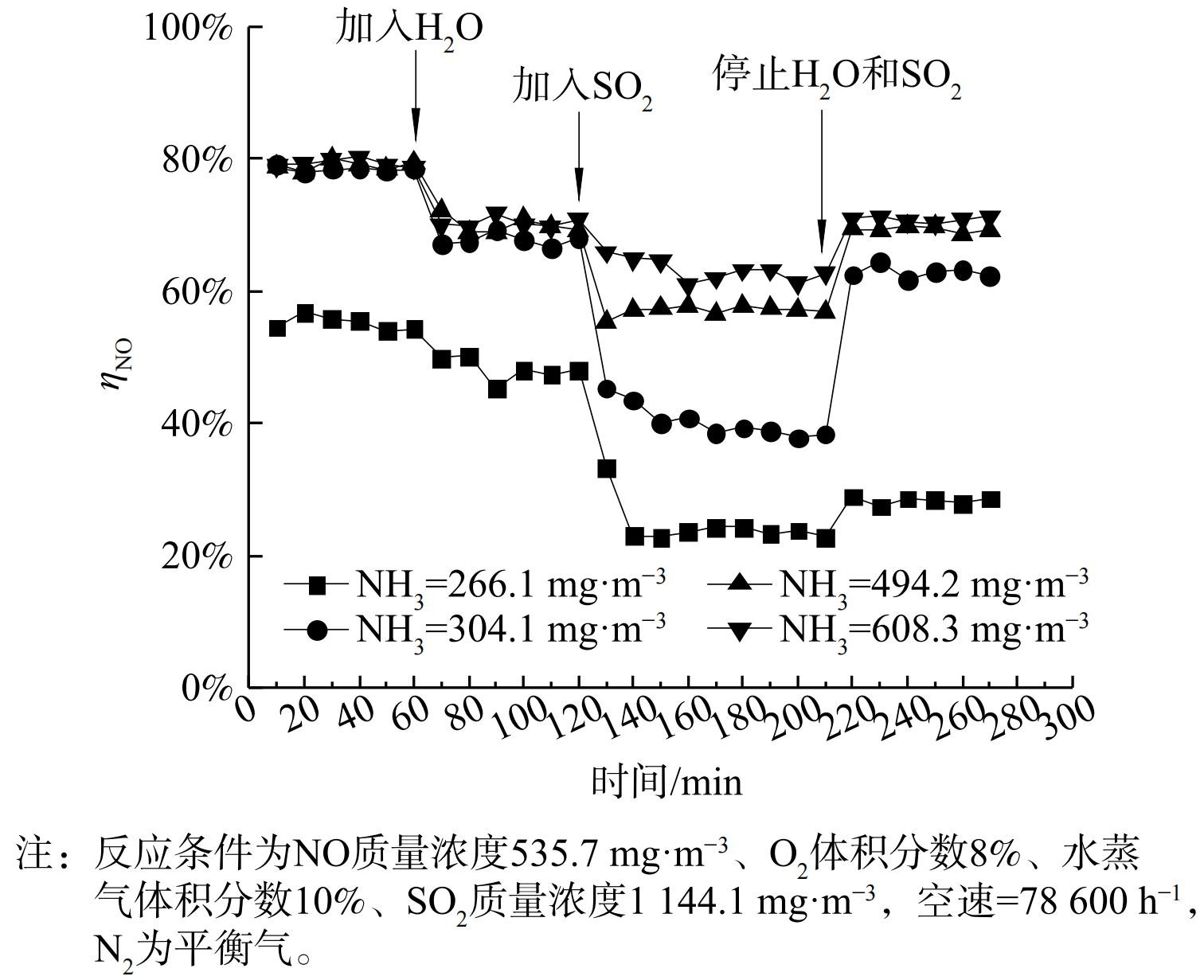
为分析等离子体条件下H2O和SO2造成催化剂失活的原因,在不同的氨气初始含量下进行SO2瞬态响应实验,能量密度为300 J·L−1,结果如图9所示。当使用MnO2催化剂时,NH3初始质量浓度的改变对催化剂脱硝活性及对H2O和SO2的耐受性显示出一定的差别。NH3量小于初始NO量时表现出最低的NO转化率,并且加入H2O和SO2后,根据NOx含量变化看出反应器中不再发生SCR反应,NO的转化全部归于等离子体对NO的氧化。当NH3/NO>1时,水蒸气对等离子催化脱硝的影响与氨含量无关。这表明通入的氨首先被SO2消耗,过剩的氨参与NO的还原。中断SO2和H2O的通入后,MnO2不能恢复到初始活性,造成了不可逆失活。ZOU等[26]发现,当烟气中同时存在NO和SO2时,SO2的吸附能力远高于NO,故SO2占据Mn的活性位点,催化剂被硫酸化。
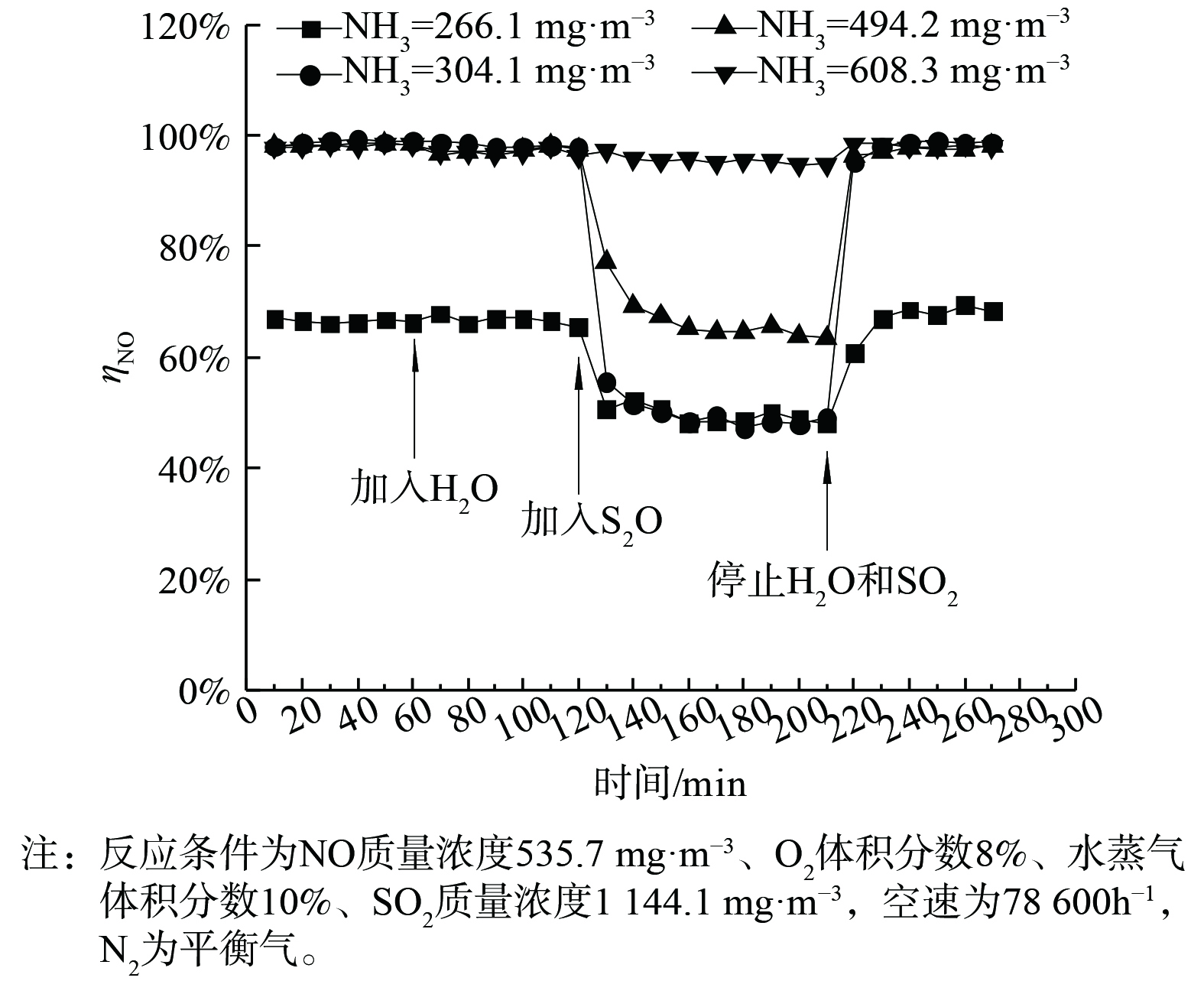
使用Mn-Ce催化剂时,与MnO2相比,在不同氨浓度下均能得到最高的NO转化率 (图10) 。水蒸气的加入对Mn-Ce催化剂转化NO只有非常微弱的影响。当NH3质量浓度为227 mg·m−3时,水蒸气和SO2的加入造成NO去除率下降,但与MnO2反应结果不同。如图11所示,Mn-Ce体系中NOx转化率并未降至0,而是维持在约18%,氨并未完全被SO2消耗。在停止通入水蒸气和SO2后,Mn-Ce催化剂的NO转化率能够恢复至初始水平。Mn-Ce催化剂与MnO2相比显示出更高的脱硝活性及耐水耐硫性。这可能是由于Ce的掺杂提高了MnOx的分散性及活性位点数量[27],并且Ce与SO2反应更敏感,因此在催化剂表面上减少了NH4HSO4和(NH4)2SO4的形成[28]。
-
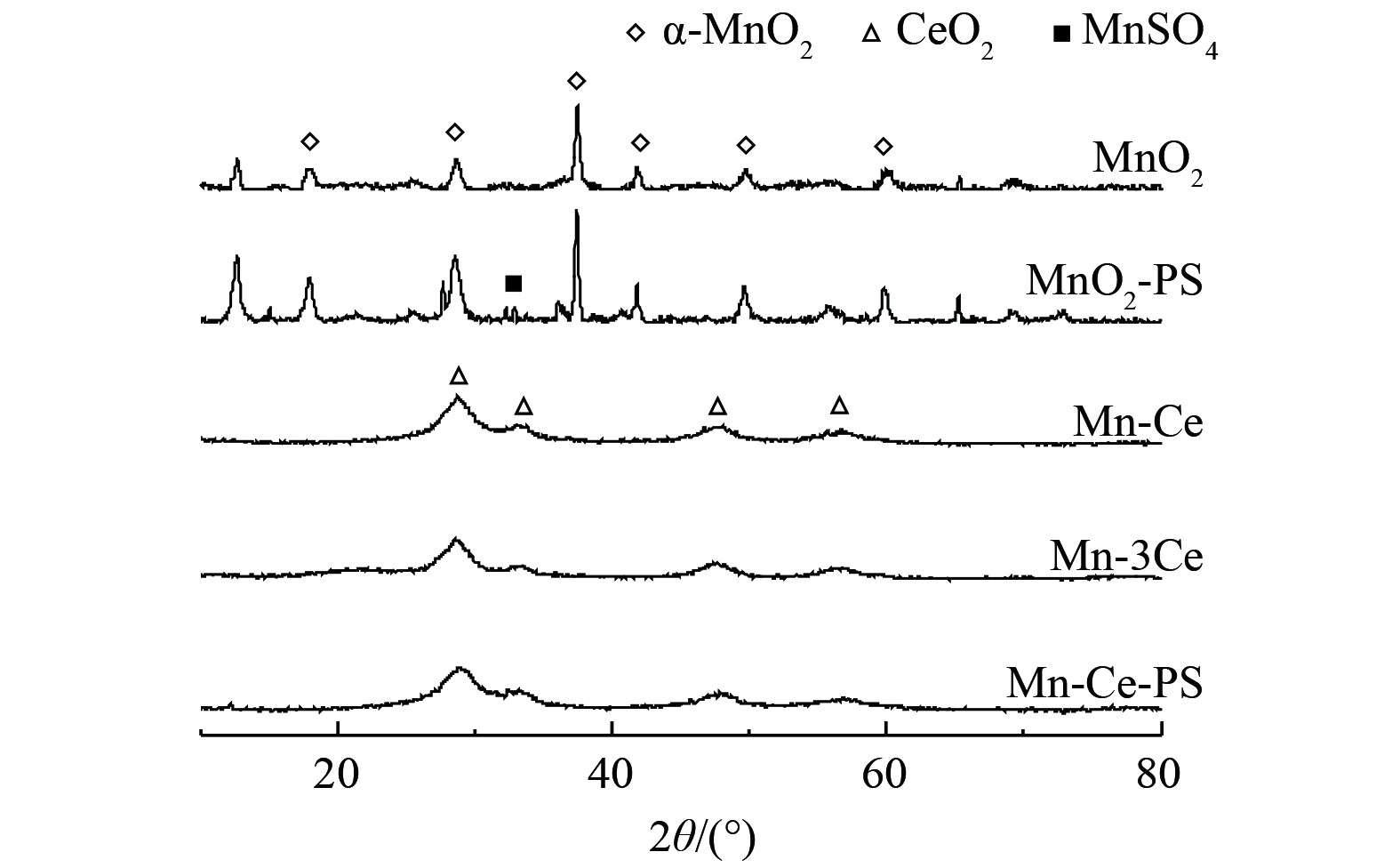
等离子体反应前后的催化剂XRD光谱如图12所示。反应前MnO2的XRD衍射峰尖锐且较窄,这说明MnO2有非常明显的结晶,对照α-MnO2的标准特征峰,所得MnO2的XRD图谱与其标准图谱完全一致,结合图13 (a) 和 (c) ,制备的MnO2为α-MnO2纳米棒。当气体组分中存在SO2放电反应后,MnO2的XRD图谱出现了新的衍射峰,已证明为MnSO4。该物质的生成引起了催化剂表面形貌的改变,并且减少了催化剂中活性组分Mn的位点数量造成催化剂活性降低。同时,对比放电前后MnO2的XRD图谱发现,经过放电使得对应的峰更加尖锐和宽泛。等离子作用后杂峰的出现表明放电对催化剂产生了负面影响。
Mn-Ce和Mn-3Ce催化剂XRD图谱表明,掺杂Ce后催化剂的衍射峰较宽。这说明2种催化剂的结晶度都不高,并且Mn-Ce催化剂中未出现MnO2特征峰。28.4°、47.4°和56.3°代表了CeO2的典型特征峰。其中,28.4°以结晶形式出现 (111) 晶面的立方体二氧化铈。对比反应前后Mn-Ce、Mn-3Ce可知,锰氧化物和铈氧化物未出现明显的新衍射峰。这表明晶格未发生变化,加入硫后附着在表面的硫酸盐以无定型态分散分布。
与MnO2相比,Mn-Ce催化剂的锰衍射峰消失。这说明MnOx以无定型形式存在,这可能是由于锰氧化物高度分散在催化剂表面、锰氧化物已进入氧化铈的晶格中所导致。结合图13 (b) 和 (d),Mn-Ce催化剂为纳米花形貌,并且拥有更丰富的孔结构。Ce掺杂后对催化剂的结晶度和结晶粒度产生了影响,削弱了等离子体和SO2对催化剂晶型结构的负面影响,从而提高了催化活性。
-
与普通的SCR反应不同,等离子体协同条件下会改变气体组分和催化剂性能。等离子体在空管部分能产生多种活性粒子,直接与NO发生碰撞[18]。在此过程中,NO大部分被转化为NO2。除了NO在高能粒子作用下被氧化为NO2之外,部分NO也能在Mn-Ce催化剂的晶格氧上氧化为NO2,并且Mn基催化剂中的Mn4+有利于NO氧化为NO2。在SCR反应中,Mn4+被还原为Mn3+,在O3和O自由基等活性物质作用下Mn3+可快速氧化为Mn4+,从而加速了NO催化氧化和快速SCR反应。快速SCR反应方程式如式 (17) 、 (18) 所示[29]。
-
1) 相比与单独等离子体放电和MnO2 ,Mn-Ce催化剂协同低温等离子体脱硝过程中拥有更高的脱硝效率和更宽的SCR反应活性区间。在室温、200~380 J·L−1条件下,Mn-Ce催化剂的NO去除率保持在90%以上。2) 在低温等离子体条件下,Mn-Ce催化剂氧化NO能力更强,会促进“快速SCR”反应发生。3) Mn-Ce催化剂能分解等离子体产生的O3,并使Mn-Ce上的Mn4+和晶格氧含量更高,更有利于NO的催化还原。4) SO2的加入会被等离子体氧化并首先消耗NH3,从而阻碍SCR反应的发生。Ce的掺杂能减少硫酸盐的生成,改变催化剂的晶型和微观形貌,增加活性位点的数量,使得耐水耐硫性得到提升。
Ce掺杂对MnOx在低温等离子体协同下的脱硝性能影响
Effect of Ce doping on the denitrification performance of MnOx in the presence of low temperature plasma
-
摘要: 低温等离子体活化反应气组分、改变催化反应历程,甚至对催化剂本身产生影响,从而使催化剂展现出一些优异特性。其中,低温等离子协同下的NH3选择性催化还原NOx的高活性备受关注。采用水热沉积法合成纳米Mn-Ce催化剂,在等离子体协同下对NH3-SCR、N2氧化、和NO氧化催化活性进行了考察与分析。结果表明,纳米Mn-Ce催化剂比纳米MnO2具有更宽的SCR活性区间、较好的水与硫耐受性。这是由于,一方面Ce的引入促进了MnO2分散;另一方面,等离子体产生的O活性物种能够增加Mn-Ce中Mn4+和晶格氧含量,从而触发更强快速SCR反应、促进NOx消除。SO2会消耗等离子体产生的活性物种,并与NH3反应,从而阻碍NO转化,但Ce掺杂会改变Mn基催化剂的晶型结构并提升抗硫性。本研究可为低温等离子体去除NO的实际应用提供参考。Abstract: Non-thermal plasma activates the reaction gas components, changes the catalytic reaction process, and even affects the catalyst itself, thus reflecting some excellent characteristics. Among them, the high activity of NH3 selective catalytic reduction of NOx under the cooperation of non-thermal plasma has attracted much attention. In this study, nano-Mn-Ce catalysts were synthesized by hydrothermal deposition to investigate the catalytic activities of NH3-SCR, oxidation activities of N2 and NO under the cooperation of plasma. The results showed that nano-Mn-Ce had wider SCR activity interval and better water and sulfur tolerance than nano-MnO2. The reason was that, on the one hand, the introduction of Ce could promote the dispersion of MnO2, and on the other hand, the O-active species produced by plasma could increase the content of Mn4+ and lattice oxygen in Mn-Ce, thereby triggering a stronger fast SCR reaction and promoting NOx elimination. SO2 consumed the active species generated by plasma and react with NH3, thus hindering NO conversion. However, Ce doping changed the crystal structure of Mn-based catalyst and improved sulfur resistance. This study can provide reference for the practical application of non-thermal plasma removal of NO.
-
Key words:
- non-thermal plasma /
- NH3-SCR /
- Mn-Ce catalyst /
- synergistic catalysis
-
随着我国经济的快速发展和人民生活水平的提高,汽油的使用量日益增长。由于汽油等轻质油品挥发性强[1],在储运销过程中会产生挥发性有机化合物(volatile organic compounds,VOCs,行业俗称其为“油气”),对环境及人类健康造成一定的危害[2],同时也造成油品损失和浪费[3-5]。2018年,国内汽油使用量超过1.3亿t[6],排入空气中油气达到6亿m3。因此,油气回收治理已成为我国重要的环保工作之一。
目前,油气回收与净化技术主要包括吸收法、吸附法、冷凝法和膜分离法等。吸附法由于回收率高、净化后尾气排放浓度低及一次性投资成本低等优点,单独或与其他技术集成的处理工艺已成为当前国内外油气回收的主要技术,其中,作为吸附法油气回收技术的核心,吸附剂的选择至关重要[7-9]。油气回收工艺中使用的吸附剂几乎都采用活性炭(activated carbon,AC)[10],能有效地吸附不同的有机烃类物质。但是普通的活性炭吸附油气时存在吸附容量较小、穿透时间较短等缺点[11-14],因此,活性炭表面改性一直是人们关注的焦点[15],可以采用合适的方法对活性炭进行改性处理以制备高效的炭基VOCs吸附剂。
活性炭的改性方法主要包括酸碱改性法、负载杂原子和化合物改性法、低温等离子体改性法、微波改性法等[16],在活性炭改性的诸多方法中,酸碱改性方法由于操作简单且效果较好而被广泛应用[17-19]。常用的酸碱改性剂包括硫酸溶液、硝酸溶液和氢氧化钠溶液等[20-22],其他研究中的改性方法多为碱改性和酸碱改性,对常见的酸碱盐改性并未进行系统的对比。因此,本研究采用酸碱盐分别对活性炭进行改性实验,通过表征方法分析改性对活性炭微观结构的调变,结合性能评价实验和动力学模拟参数计算,探讨改性与吸附性能的内在联系;通过原位红外简要分析吸附过程机理,为材料改性的研究和活性炭吸附油气的工业应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 样品制备
将活性炭装入锥形瓶中,加入的改性液体浓度均为1%,室温下,在摇床中振荡2 h后,抽滤,用去离子水清洗至中性后放入烘箱,150 ℃烘干6 h。
将未改性活性炭命名为0#样品,按浸渍液将改性活性炭分别命名为1#样品(盐酸改性)、2#样品(醋酸改性)、3#样品(氨水改性)、4#样品(氢氧化钠改性)、5#样品(氢氧化钾改性)、6#样品(硝酸铜改性)、7#样品(磷酸二氢钾改性)、8#样品(磷酸氢二钾改性)。
1.2 样品表征
XRD分析采用日本岛津公司的XRD-7000型X光衍射光谱仪。测试条件:Cu靶,Kα射线,Ni 滤光片,光源波长λ=0.154 18 nm,管压40 kV,管电流30 mA。扫描角度为10˚~80˚,扫描速度10(˚)min−1,扫描步长0.018˚。
比表面积和孔结构分析采用美国康塔仪器公司Autosorb-iQ全自动比表面积和孔径分布分析仪。测试条件:样品测定前在150 ℃下真空脱气3 h以上。
SEM采用美国FEI公司的Quanta 200F场发射扫描电子显微镜,对材料进行微观形貌分析。测试条件:加速电压为200 V ~ 30 kV,分辨率<1.2 nm,放大2 000~20 000倍。
Situ-IR采用德国布鲁克公司的Tensor27红外光谱仪(配有高真空系统)。测试条件:LN-MCT检测器,测量范围为600~4 000 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1。在50 mL·min−1纯氮气气氛下,吹扫30 min,通入C4H10-N2反应气,每隔3 min扫描一次;脱附实验也在50 mL·min−1纯氮气气氛下进行吹扫,每隔3 min扫描一次,直到谱图基本不变为止。
1.3 实验装备
本研究在固定床吸附装置(如图1所示)上进行对油气动态吸附性能评价。汽油在一定条件下气化后通过氮气吹扫产生,通过调节氮气平衡气的流量,控制油气体积浓度为1.5%,气体总流量为60 mL·min−1。将吸附剂样品装入内径为6 mm的U型石英管,氮气保护,加热到110 ℃,去除表面吸附的水分子和其他有机小分子杂质,待冷却到室温后,再进行吸脱附实验。从固定床出来的气流通过六通阀与北分BF-3420气相色谱仪相连,在线检测吸附前后尾气中油气的浓度,直至峰面积不再变化为止。在吸附后尾气中油气浓度CA为0.1C0时,对应的时间为穿透时间。
气相色谱检测的条件:总烃柱宽×高为3 mm×1 m,FID检测器,进样口温度为100 ℃,柱箱温度为80 ℃,检测器温度为150 ℃;氢气流量为40 mL·min−1,空气流量为300 mL·min−1,载气(氮气)流量为30 mL·min−1;定量管的体积为0.1 mL。
样品的吸附容量计算方法如式(1)所示。
q=m2−m1m2−m0 (1) 式中:q为吸附容量;m0为U型管质量,g;m1、m2为吸附前、后样品和U管的质量,g。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 改性对活性炭表面及孔径结构的影响
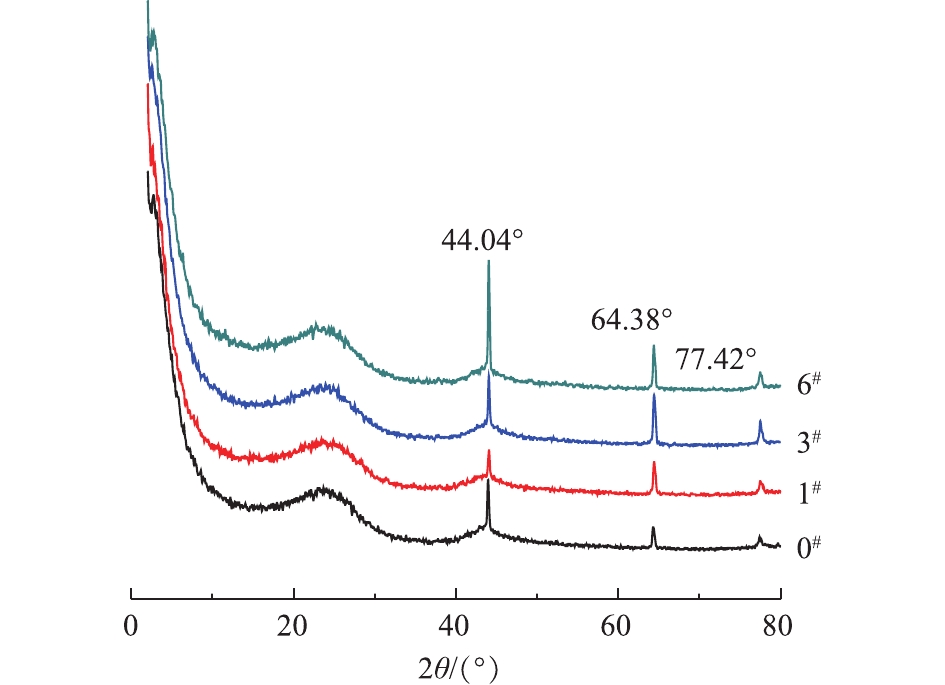
1)活性炭的XRD表征。改性前后样品均在2θ=44.04°、64.38°和77.42°有特征峰,说明不同溶液改性基本不会影响活性炭的结构,这可能与活性炭材料的无定型结构有关,但是碱改性和盐改性之后的峰强略有变宽,表明经过改性处理后,活性炭材料的完整性和对称性可能会受影响。
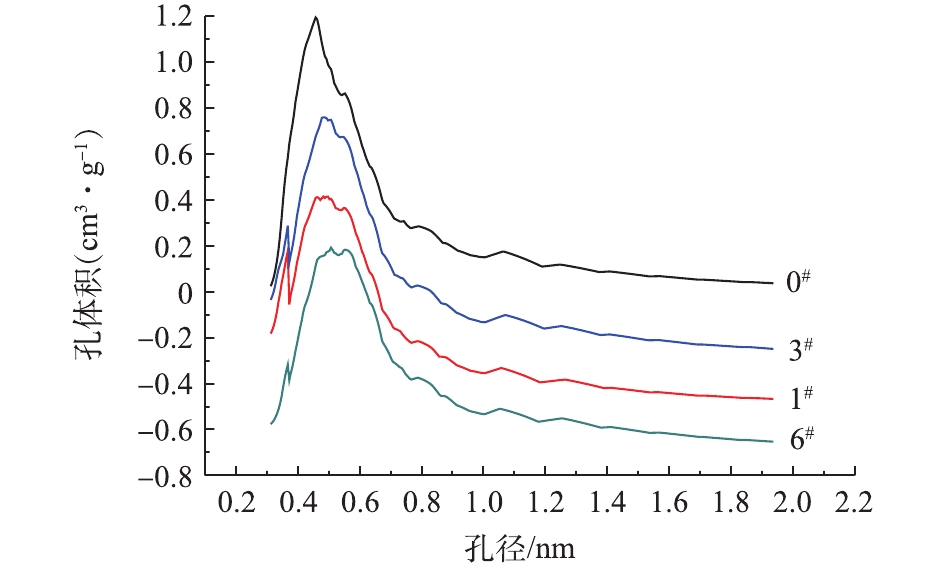
2)活性炭的孔结构性质。样品的比表面积和微观结构测试结果见表1。
表 1 样品的表面及孔道结构数据Table 1. Surface property and pore structure data of the samples编号 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 总孔容/(cm3·g−1) 微孔孔容/(cm3·g−1) 平均孔径/nm 0# 1 072.57 0.50 0.44 1.87 1# 1 080.23 0.49 0.44 1.82 2# 1 264.33 0.65 0.56 1.83 3# 1 189.56 0.60 0.49 2.07 4# 1 131.84 0.62 0.54 1.94 5# 1 088.55 0.59 0.51 1.85 6# 1 062.31 0.52 0.44 1.94 7# 1 090.17 0.55 0.48 1.90 8# 1 103.42 0.56 0.50 1.87 未改性活性炭的比表面积为1 072.57 m2·g−1,平均孔径为1.87 nm,微孔孔容占总孔容的88%,改性后样品(除6#外)的比表面积均有所增加,其中以2#(醋酸改性)比表面积的增加最为明显,增加到1 264.33 m2·g−1。对于酸改性而言,醋酸改性样品的微观结构数据都优于盐酸改性的样品;在碱改性样品中,3#样品的比表面积1 189.56 m2·g−1和平均孔径2.07 nm最大,4#样品的总孔容0.62 cm3·g−1和微孔孔容0.54 cm3·g−1最大;对于盐改性样品而言,总孔容均不断增加,相比未改性样品,6#样品的比表面积减小到1 062.31 m2·g−1,8#样品的比表面积增加到1 103.42 m2·g−1。
由图3和表1可知,1#样品总孔容和平均孔径减少,这是由于盐酸的强酸性对于活性炭具有强烈的蚀刻作用,一方面导致活性炭内部某些孔道被腐蚀,同时活性炭内部分微孔被盐酸氧化侵蚀交联,导致活性炭孔容和平均孔径均有减少[23-24]。另一方面,活性炭经过碱改性后,原来附着在活性炭表面或者堵塞在孔道里的杂质得以清除或者溶解在改性溶剂里,从而“腾出”了新的孔道空间[25-26],使得改性后样品微孔表面积及微孔容积有所增加;活性炭经过盐溶液浸渍后,可能会改变活性炭内部的孔道结构,拓宽孔道,使得改性后的平均孔径和总孔容增加。
活性炭孔道结构的改变会影响油气蒸气的吸附性能,内部空间增大能容纳更多的油气分子,也相应增加了油气的吸附容量。
3)活性炭SEM表征和EDS能谱。图4和图5分别为样品的扫描电镜SEM图和典型样品的EDS能谱图。
由图4可知,经过酸浸渍液浸渍之后的活性炭样品(1#和2#)较未处理的样品表面均出现了不同程度的凹凸不平、烧蚀现象[27],使活性炭表面孔结构有不同程度的破坏,其平均孔径从1.87 nm减少到1.83 nm左右;碱改性的3#和4#样品堵塞的孔道较少,活性炭微孔体积有所增加,从而增加了活性炭的比表面积及孔容,活性炭的炭层经过碱改性处理后,出现了新的断层,这也在一定程度上扩大了活性炭的孔道,其中3#、4#和5#样品微孔孔容均有增加,从0.44 cm3·g−1分别增加至0.49、0.54和0.51 cm3·g−1;盐改性后,6#、7#和8#样品的孔道结构均出现堵塞,其中8#样品堵塞最为严重,孔径内壁增厚,使孔径变得最小,为1.87 nm。
EDS分析可以提供活性炭改性前后表面的元素分布信息,因为活性炭表面吸附活性位点与含氧官能团有关,含氧官能团作为表面官能团可以决定活性炭表面一些物化性质,如极性、亲/疏水性等,所以会对吸附物质产生一定的影响[28]。未改性活性炭及典型的酸碱盐改性后的EDS能谱图见图5,由图5以及表2可知,在未改性活性炭表面和孔内部主要是C、O元素,其他样品中出现Cl、N、Na、K、Cu、P等新元素。所有的样品中均含有氧元素,这表明在样品表面都含有含氧官能团,含氧基团是影响有机蒸气吸附的一个重要因素,说明改性后的样品会对蒸气吸附有影响[28]。
表 2 0#~8#活性炭样品的EDS能谱元素含量Table 2. Elements content determined by EDS spectra of AC samples 0#~8#元素 0# 1# 2# 3# 4# 5# 6# 7# 8# 质量分数 原子占比 质量分数 原子占比 质量分数 原子占比 质量分数 原子占比 质量分数 原子占比 质量分数 原子占比 质量分数 原子占比 质量分数 原子占比 质量分数 原子占比 C 84.8 88.1 87.6 92.7 91.8 95.1 83.0 88.3 83.4 89.4 86.7 92.1 90.4 94.1 88.7 93.1 93.7 95.8 O 15.1 11.8 6.7 5.3 4.9 3.8 7.1 5.7 8.7 7.0 7.3 5.9 5.6 4.4 7.0 5.5 4.7 3.6 N − − − − − − 4.4 4.0 − − − − − − − − − − Si − − − − − − 0.4 0.2 0.9 0.4 − − − − − − − − P − − − − − − 0.5 0.2 0.5 0.2 − − − − 0.2 0.1 0.2 0.1 Cl − − 2.9 1.0 1.4 0.5 0.4 0.1 0.4 0.1 0.7 0.2 0.3 0.1 0.6 0.2 − − K − − 2.5 0.8 1.8 0.5 2.7 0.8 2.6 0.8 5.0 1.6 2.5 0.8 2.3 0.7 1.2 0.3 Ca − − − − − − 1.1 0.3 − − − − − − − − − − Al − − − − − − − − − − − − − − − − − − Na − − − − − − − − 3.0 1.7 − − 0.9 0.5 − − − − Mg − − − − − − − − 0.2 0.1 − − − − − − − − Cu − − − − − − − − − − − − − − 1.0 0.2 − − 2.2 活性炭吸附性能评价
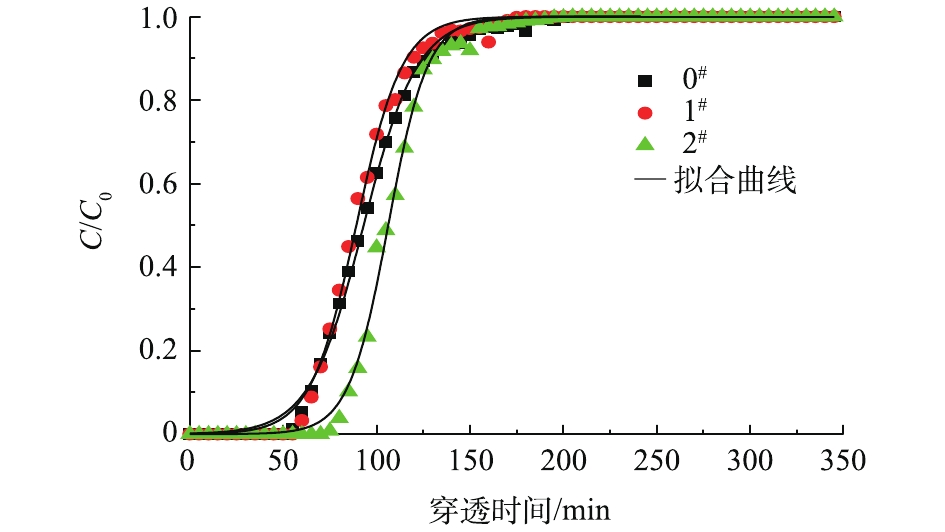
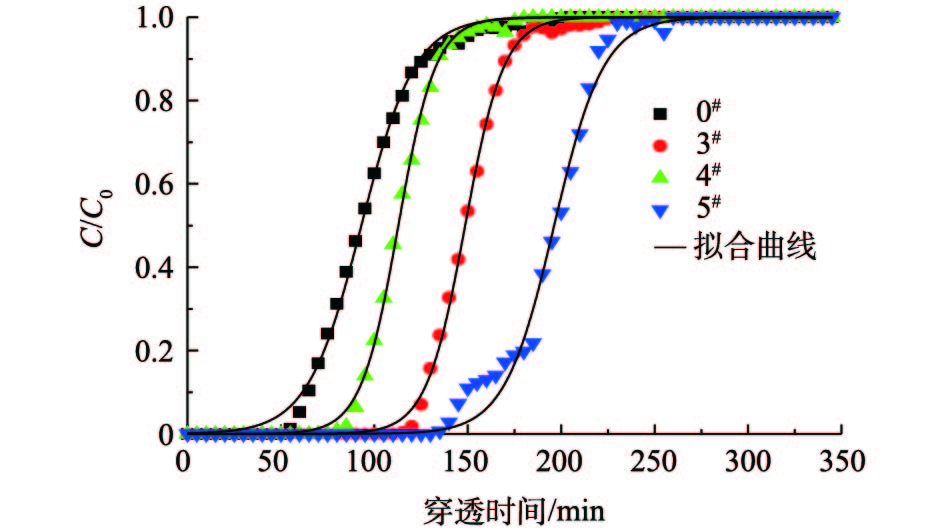
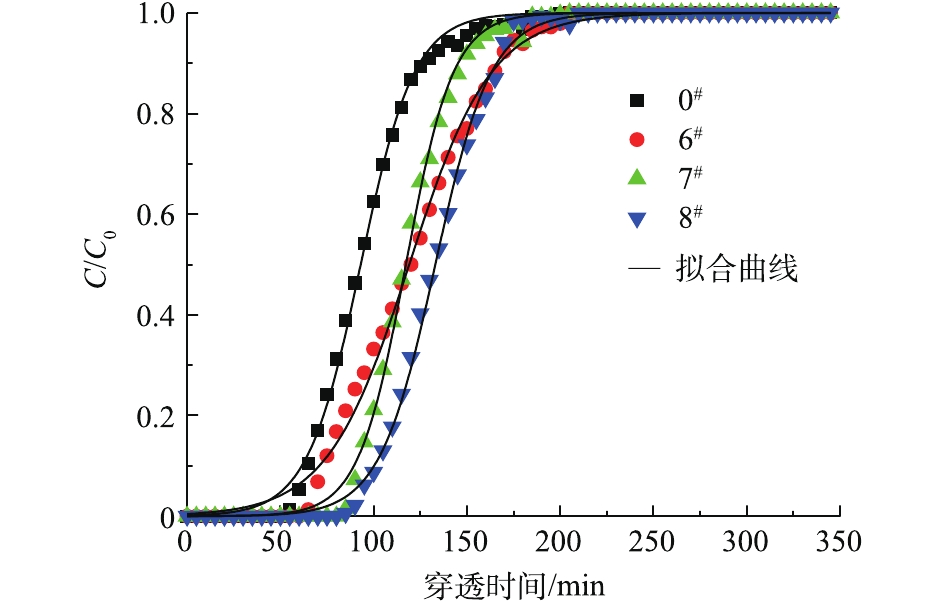
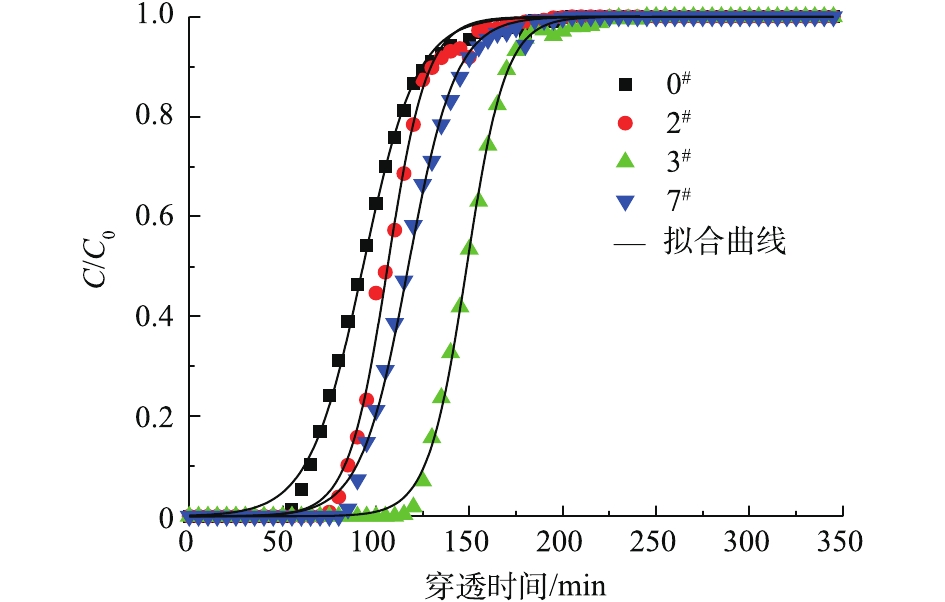
1)不同改性方法对吸附性能的影响。改性活性炭对油气的吸附性能见表3。改性后活性炭对油气的吸附容量和穿透时间都有所增加,其中碱改性3#样品吸附容量最大,从0.179 g·g−1增加到0.279 g·g−1,5#样品穿透时间从50 min延长到130 min,酸改性2#样品穿透时间仅增加了20 min,盐改性7#和8#样品仅增加了30 min,说明碱性溶液处理活性炭得到的吸附效果较好。
表 3 活性炭样品对油气的吸附性能Table 3. Adsorption performance of AC samples towards oil vapour编号 实验数据 拟合数据 吸附容量/(g·g−1) 穿透时间/(min) τ0/min K’ /min−1 R2 0# 0.179 50 93.043 0 0.069 6 0.998 4 1# 0.268 55 89.143 2 0.081 6 0.997 8 2# 0.270 70 106.219 4 0.094 8 0.998 2 3# 0.279 110 148.597 3 0.096 3 0.999 4 4# 0.271 75 112.848 1 0.100 1 0.999 4 5# 0.269 130 196.225 7 0.075 4 0.996 6 6# 0.272 60 119.053 3 0.045 5 0.997 7 7# 0.272 80 117.298 8 0.078 8 0.998 7 8# 0.271 80 133.056 3 0.066 9 0.999 1 2)吸附过程动力学。为更好地分析出口气体浓度与时间的关系,本研究运用吸附理论经典模型对穿透曲线进行预测,计算方法[29]如式(2)所示。
CAC0=11+exp[k′(τ0−t)] (2) 式中:CA、C0分别为吸附床层出口和进口气流中VOCs的浓度;τ0为化学计量时间(即在CA=0.5C0的时间点),min;k’为吸附速率常数,min−1。
①不同酸溶液对AC改性后的分析。图6为未改性活性炭与酸改性活性炭的拟合曲线。酸改性能改善活性炭对油气的吸附性能,其中醋酸改性2#样品性能提升尤为明显,饱和吸附量为0.270 g·g−1,比0#样品增加了50.8%;吸附穿透时间为70 min,比盐酸改性的1#样品穿透时间延长15 min,说明醋酸改性样品吸附效果强于盐酸改性,这可能是因为强酸浸渍后活性炭的孔道结构坍塌,1#样品孔容和平均孔径均有减少[23-24]。根据动力学拟合计算结果,1#样品吸附速率常数为0.081 6 min−1,2#样品吸附速率常数为0.094 8 min−1,盐酸改性样品的吸附速率低于醋酸改性样品的吸附速率。
②不同碱溶液对AC改性后的分析。图7为未改性活性炭与碱改性活性炭吸附油气的拟合曲线。碱改性活性炭对油气吸附性能均有所提升。氨水改性3#样品对油气吸附量在110 min达到饱和,相比0#样品,饱和吸附量提高了约56%;氢氧化钾改性5#样品的穿透时间最长达到130 min,相比未改性活性炭延长了80 min;4#和5#样品中均含氢氧根,由于在5#样品中K+是活化的主要组分,也是活性炭形成发达微孔的主要途径,游离K+的存在可形成负载金属,使活性炭吸附性能提高[30],因此,5#样品吸附性能强于4#样品,结合表3,3#样品吸附速率常数为0.096 3 min−1,5#样品吸附速率常数为0.075 4 min−1,可见氨水改性活性炭对其吸附能力提高较大。碱改性对吸附性能有着较好的改善主要是因为碱改性能提高活性炭表面含氧碱性基团的数量,导致表面零电势点的pHpze升高,从而增强活性炭表面非极性[24,28],提高对油气的吸附量。
③不同盐溶液对AC改性后的分析。图8为未改性活性炭与盐改性活性炭的拟合曲线。硝酸铜改性6#样品和磷酸二氢钾改性7#样品饱和吸附量为0.272 g·g−1,相比0#样品提高了52.0%;7#样品和8#样品吸附穿透时间为80 min,比6#样品穿透时间延长20 min,这主要是因为KH2PO4中K+是活化的主要组分,也是活性炭形成发达微孔的主要途径,游离K+可在活性炭表面富集,使活性炭吸附性能提高[30]。6#、7#和8#样品吸附速率常数分别为0.045 5、0.078 8和0.066 9 min−1,7#样品吸附效果较好。
④酸碱盐溶液对AC改性后的分析。图9为未改性活性炭与较好酸碱盐改性活性炭的拟合曲线。氨水改性活性炭对油气饱和吸附量最高,比0#样品提高了55.9%;吸附穿透时间为110 min,比2#和7#样品的穿透时间分别延长40 min和30 min,因此,氨水改性活性炭的吸附性能最好。对比表3中2#、3#和7#样品的吸附速率常数值,也表明碱改性效果强于酸和盐改性。
在样品的改性浸渍过程中,随着样品表面和样品缝隙中的杂质被清理掉或者掉落溶液中与溶质进行反应,使得活性炭样品发生了2个方面的变化:一是活性炭内部的孔道结构发生变化,比表面积的增加和孔径的增大都会使吸附速率变快,活性炭中微孔孔径越小,油气在其中的传质阻力越大,吸附速率也越慢,活性炭增大的内部空间能容纳更多的油气,也增加了活性炭对油气的吸附量;二是样品表面元素含量发生了数量变化,元素含量的变化使得活性炭对油气的组分吸附有了选择性,造成了吸附量和穿透时间的不同[23-24]。
2.3 吸附过程中的原位红外分析
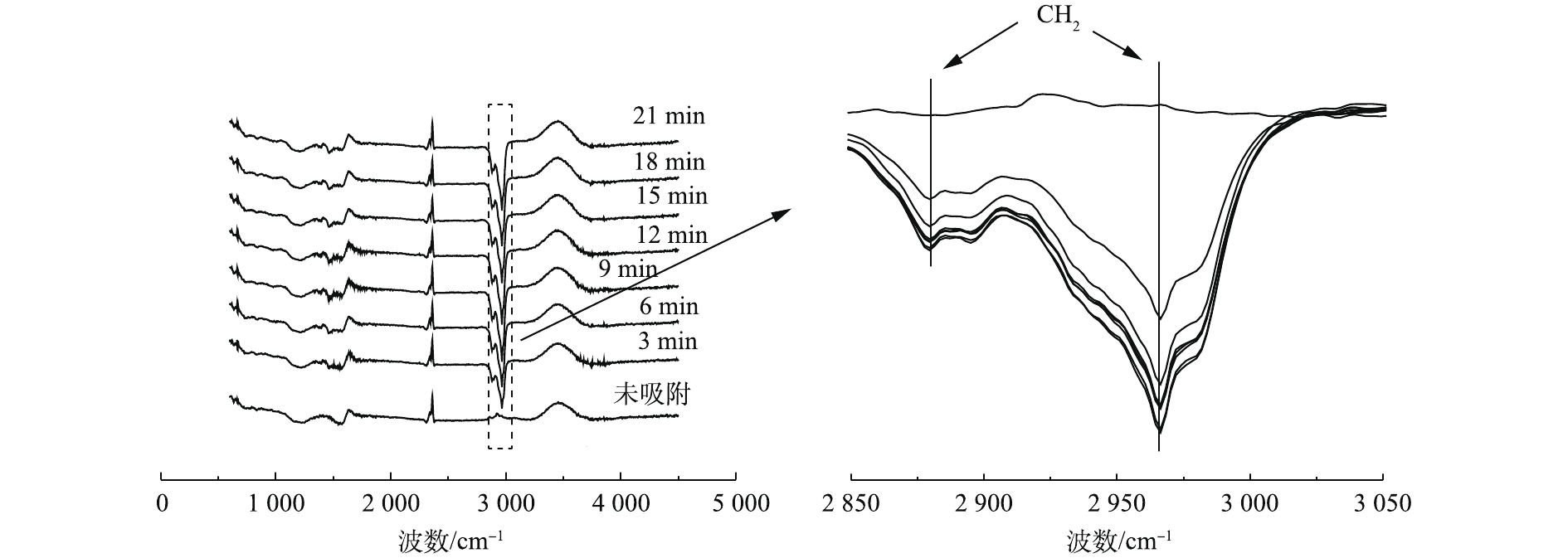
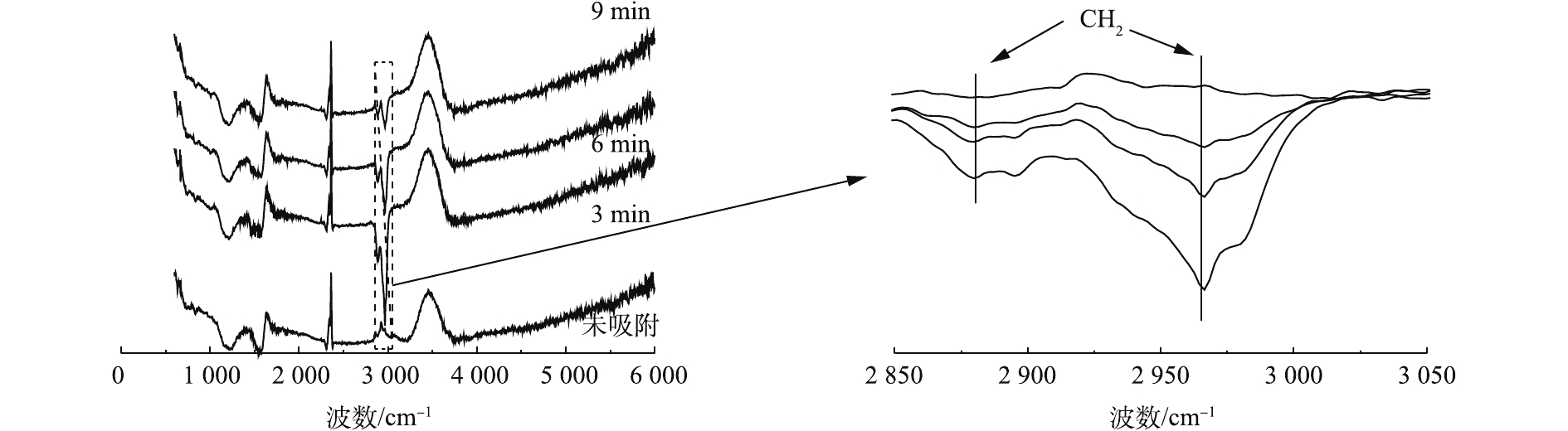
本研究选用吸附性能最好的3#样品,以正丁烷为探针,研究原位红外测试改性活性炭在1.98%C4H10-N2吸脱附过程中吸附剂表面基团的变化情况,结果见图10和图11。
由图10可知,3 440 cm−1和1 630 cm−1处的峰强度有所增加,这表明改性处理后增加了活性炭表面的—OH 与C=C含量;在样品吸脱附正丁烷过程中,波数为2 960 cm−1和2 880 cm−1处新出现2个吸收峰;2 800~3 000 cm−1为—CH2伸缩振动υ峰,可推测在活性炭吸附正丁烷的过程中,主要是由正丁烷中—CH2基团吸附在吸附剂表面,在脱附过程的原位红外谱图中,经N2吹扫脱附后,样品表面对应于—CH2基团的吸收峰峰强减弱了,这说明正丁烷在样品表面的脱附速率较快。
3. 结论
1)活性炭经过酸碱盐改性后的比表面积和微孔结构有了很大改变,并且对汽油油气的吸附性能产生了不同的影响。
2)在所有酸碱盐改性样品中,3#样品(氨水改性)得到了最大的吸附容量0.279 g·g−1,2#样品(醋酸改性)有最大的比表面积1 264.33 m2·g−1,5#样品(氢氧化钾改性)的穿透时间最长为130 min,结合吸附动力学参数,其中2#样品吸附速率常数为0.094 8 min−1,3#样品吸附速率常数为0.096 3 min−1,7#样品吸附速率常数为0.078 8 min−1,表明碱改性活性炭的吸附效果强于酸和盐改性活性炭的吸附效果,吸附穿透曲线可用吸附理论经典模型拟合。
3)以正丁烷为探针,根据原位红外光谱分析结果,改性处理后增加了活性炭表面的—OH与C=C含量,正丁烷主要是以—CH2基团吸附在吸附剂表面,且脱附速率较快。
-
-
[1] LIU Z S, YU F, MA C H, et al. A Critical Review of Recent Progress and Perspective in Practical Denitration Application[J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9: 771-810. doi: 10.3390/catal9090771 [2] SCHIEFERSTEIN M, KOHSE-HÖINGHAUS K, STUHL F. Temperature Dependence of the Rate Constants of the Reaction O+NO+M→NO2+M (M = He, NO, N2, CH4)[J]. Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische Chemie, 1983, 87: 361-366. [3] TALEBIZADEH P, BABAIE M, BROWN R, et al. The role of non-thermal plasma technique in NOx treatment: A review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 40: 886-901. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.194 [4] JIANG B Q, ZHAO S, WANG Y L, et al. Plasma-enhanced low temperature NH3-SCR of NOx over a Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 catalyst under oxygen-rich conditions[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2021, 286: 119886. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119886 [5] WALLIS A E, WHITEHEAD J C, ZHANG K. Plasma-assisted catalysis for the destruction of CFC-12 in atmospheric pressure gas streams using TiO2[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2007, 113: 29-33. doi: 10.1007/s10562-006-9000-x [6] LEE B J, KANG H-C, JO J, et al. Consideration of the role of plasma in a plasma-coupled selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with a hydrocarbon reducing agent[J]. Catalysts, 2017, 7: 325-339. doi: 10.3390/catal7110325 [7] ZHU T, ZHANG X, NIU W F, et al. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by NH3 Using a Combination of Non-Thermal Plasma and Mn-Cu/ZSM5 Catalyst[J]. Catalysts, 2020, 10: 1044-1060. doi: 10.3390/catal10091044 [8] GUO Y F, YE D Q, CHEN K F, et al. Toluene decomposition using a wire-plate dielectric barrier discharge reactor with manganese oxide catalyst in situ[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2006, 245: 93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2005.09.013 [9] WANG L, ZHAO Y, LIU C Y, et al. Plasma driven ammonia decomposition on a Fe-catalyst: eliminating surface nitrogen poisoning[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49: 3787-3789. doi: 10.1039/c3cc41301b [10] TU X, WHITEHEAD J C. Plasma-catalytic dry reforming of methane in an atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge: Understanding the synergistic effect at low temperature[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 125: 439-448. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.06.006 [11] ZHOU C C, ZHANG Y P, WANG X L, et al. Influence of the addition of transition metals (Cr, Zr, Mo) on the properties of MnOx-FeOx catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by Ammonia[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 392: 319-324. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2012.10.002 [12] WANG K L, LIU X Z, TU S H, et al. Low temperature catalytic performance of manganese and cerium complex oxide catalyst towards toluene[C]// Shenzhen: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020: 431-438. [13] TALEBIZADEH P, RAHIMZADEH H, ANAGHIZI S J, et al. Experimental study on the optimization of dielectric barrier discharge reactor for NOx treatment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2016, 23: 3283-3293. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2016.005690 [14] LIN H, GAO X, LUO Z Y, et al. Removal of NOx with radical injection caused by corona discharge[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83: 1349-1355. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2004.01.004 [15] CAO X, ZHAO W X, ZHANG R X, et al. Conversion of NO with a catalytic packed-bed dielectric barrier discharge reactor[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2017, 19: 67-74. [16] LIANG W J, MA L, LIU H, et al. Toluene degradation by non-thermal plasma combined with a ferroelectric catalyst[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(10): 1390-1395. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.05.042 [17] JANSSENS T V W, FALSIG H, LUNDEGAARD L F, et al. A consistent reaction scheme for the selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5: 2832-2845. doi: 10.1021/cs501673g [18] WANG J G, YI H H, TANG X L, et al. Oxygen plasma-catalytic conversion of NO over MnOx: Formation and reactivity of adsorbed oxygen[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2017, 100: 227-231. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2017.07.007 [19] JIA J B, ZHANG P Y, CHEN L. Catalytic decomposition of gaseous ozone over manganese dioxides with different crystal structures[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 189: 210-218. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.055 [20] YANG C, YANG J, JIAO Q R, et al. Promotion effect and mechanism of MnOx doped CeO2 nano-catalyst for NH3-SCR[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46: 4394-4401. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.10.163 [21] WITVROUWEN T, PAULUSSEN S, SELS B. The use of non-equilibrium plasmas for the synthesis of heterogeneous catalysts[J]. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 2012, 9(8): 750-760. [22] DUPIN J C, GONBEAU D, VINATIER P, et al. Systematic XPS studies of metal oxides, hydroxides and peroxides[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2000, 2: 1319-1324. doi: 10.1039/a908800h [23] KONOVA P, STOYANOVA M, NAYDENOV A, et al. Catalytic oxidation of VOCs and CO by ozone over alumina supported cobalt oxide[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2006, 298: 109-114. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2005.09.027 [24] TANG X L, GAO F Y, XIANG Y, et al. Low temperature catalytic oxidation of nitric oxide over the Mn–CoOx catalyst modified by nonthermal plasma[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2015, 64: 12-17. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2015.01.027 [25] DING J, ZHONG Q, ZHANG S L. Simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification of flue gas by catalytic ozonation over Ce-Ti catalyst[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2014, 128: 449-455. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.08.003 [26] ZUO J L, CHEN Z H, WANG F R, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over novel Mn–Zr mixed oxide catalysts[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53: 2647-2655. [27] YANG X C, XIAO H P, LIU J, et al. Influence of Ce-doping on MnOx-ZSM-5 catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO/NO2 with NH3[J]. Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis, 2018, 125: 1071-1084. doi: 10.1007/s11144-018-1460-7 [28] FRANCE L J, YANG Q, LI W, et al. Ceria modified FeMnOx —Enhanced performance and sulphur resistance for low-temperature SCR of NOx[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 206: 203-215. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.01.019 [29] ZHU L, YANG H, ZHONG Z P, et al. NH3-SCR performance of Mn-Fe/TiO2 catalysts at low temperature in the absence and presence of water vapor[J]. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 2016, 227: 476. 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 马倩,王赫,屈嘉鑫,吉硕,王薇,黄宇,党小庆. Ni-Ce复合协同促进CO同步催化去除NO的性能和机理. 中国环境科学. 2025(02): 671-681 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李朝兵,杨泽勇,胡德浩,宋捷,赖金平,米高丽,于洁. 沿面介质阻挡放电协同催化剂脱除NO/SO_2/Hg~0实验研究. 动力工程学报. 2025(02): 292-299 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张敬东,杨娇羽,揭翠,李鸿鹄,彭喜燕,安淼. Mn-Fe改性碳基磁性吸附剂去除Hg~0性能及机制. 中国环境科学. 2024(12): 6628-6640 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 袁圆,孙冉,侯剑源,张新忠,刘新刚,张仁熙. 低温等离子体技术在VOCs治理中的应用及局限性. 中国环保产业. 2023(11): 75-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载: