-
臭氧(O3)常温下呈淡蓝色,具有强氧化性. 平流层的臭氧可通过吸收紫外线,降低紫外线对植物的伤害;对流层的臭氧增加则会污染空气[1],是近地面重要的大气污染物. 近地面O3主要由人为源和天然源排放的挥发性有机物(VOCs)和氮氧化物(NOX)等污染物通过光化学反应生成[2]. 近地面臭氧会影响生态系统及危害人类健康,进而影响全球气候变化[3]. 因此,对近地面臭氧的分析与研究具有重要的意义.
近几年,我国环境空气中以O3为首要污染物的天数逐年递增[4],已成为我国大气污染治理存在的主要问题之一,其变化特征和形成机理是近年来研究环境空气污染状况的方向和重点,是污染防控措施的前提和基础[4]. 我国大气污染过程是一个复合型污染,在不同地区,不同影响因素,表现出不同的变化特征. 例如京津冀、成渝各季节O3浓度值均呈现相似规律夏季>春季>秋季>冬季的变化特征[5-6];长三角地区呈现春夏高,秋冬低的季节变化特征[7];珠三角地区则呈现出秋季高,春季次之,夏、冬低的特点[8]. 林文鹏等[9]研究分析我国2019 年243 个城市共计1215 个站点的臭氧浓度数据,表明中我国大部分城市臭氧高发期主要集中在夏季6、7 月份,春末秋初次之,冬季基本不发生污染的变化特征,与海南省现有研究呈相反的特征[10-11]. 目前海南省大气臭氧污染研究,主要集中在海口市和三亚市等重点城市,对非重点城市研究较少.
文昌市位于海南省东北角,紧邻海口市,与雷州半岛隔海相望,是海南省受珠三角地区污染传输影响最先到达的区域. 本文以2017—2021 年文昌市O3浓度变化趋势与前体物氮氧化物浓度及风速、风向、温度、相对湿度等气象因子进行关联性分析,同时对2019 年9 月底和2021 年1 月上旬两次典型O3污染过程的输送路径及潜在源区进行分析,为了解我国南部区域臭氧传输机理以及为文昌市大气污染防治工作提供科学帮助.
-
文昌市以市国土环境资源局办公大楼站点和文城镇镇政府站点2 个省控城市环境空气质量自动监测站作为文昌市评价站点,均开展6项常规污染物O3、PM2.5、PM10、NO2、SO2和CO自动监测,数据来自海南省空气质量发布系统(http://hnsthb.hainan.gov.cn:8009/EQGIS/).
气象资料为文昌市观象台每小时的地面风速、风向、相对湿度、降水和温度观测数据,采用统计分析等方法,综合研究O3浓度与气象要素之间的关系.
-
后向轨迹聚类分析采用HYSPLIT模式[12],将文昌市空气质量监测站点作为模拟受点,挑选文昌市2019 年9 月20—29 日和2021 年1 月4—6 日两次典型的O3污染过程,基于每个气流轨迹的传输和方向,通过反向轨迹聚类分析空间相似度最接近的轨迹进行分类. 以每个时刻到达受点的48 h后向气流轨迹进行聚类,每个轨迹起始高度选择500 m,聚类分析的气象数据采用FNL全球分析数据(http://www.arl.noaa.gov/).
-
潜在源贡献分析法(PSCF)是一种基于气流轨迹识别区域内潜在污染源的方法[13]. 在本研究中,将研究区域以0.25°×0.25°划分网格来计算PSCF值,计算方法见公式(1).
式中,Mij为研究区域内途径网格ij的污染轨迹数,Nij为途径网格ij所有轨迹数.
污染轨迹是受体点浓度超过某浓度阈值时所对应的轨迹,浓度阈值一般为所有轨迹对应浓度的平均值,本文取所有轨迹对应的O3平均浓度作为阈值. 高PSCF值的网格单元表明,该区域对文昌市O3浓度的贡献更大. 然而,具有较小Nij值(很少轨迹通过)的网格单元将在PSCF结果中产生很大的不确定性,为减少其不确定性,本文参照前人研究[14-15],通过乘以权重函数Wij来计算相应潜在源贡献因子法(WPSCF),减少这些单元中的不确定性WPSCF,见公式(2).
本文使用权重函数Wij见公式(3).
-
PSCF只能反应网格中污染轨迹贡献,不能反应轨迹浓度水平,本文采用浓度权重轨迹分析法(CWT)定量计算各网格对文昌市的O3浓度贡献[16-17]. CWTij计算方法见公式(4).
式中,CWTij为网格ij上的平均权重浓度,ι代表气团的轨迹τijι表示轨迹l在网格ij内的停留时间,M为轨迹的总数;Cι表示轨迹ι经过网格ij时对应的O3质量浓度. CWT采用与PSCF相同的权重函数,见公式(5). 浓度权重轨迹分析(WCWT)反应污染贡献大小,WCWTij越高表示其网格对文昌市O3污染贡献越大.
-
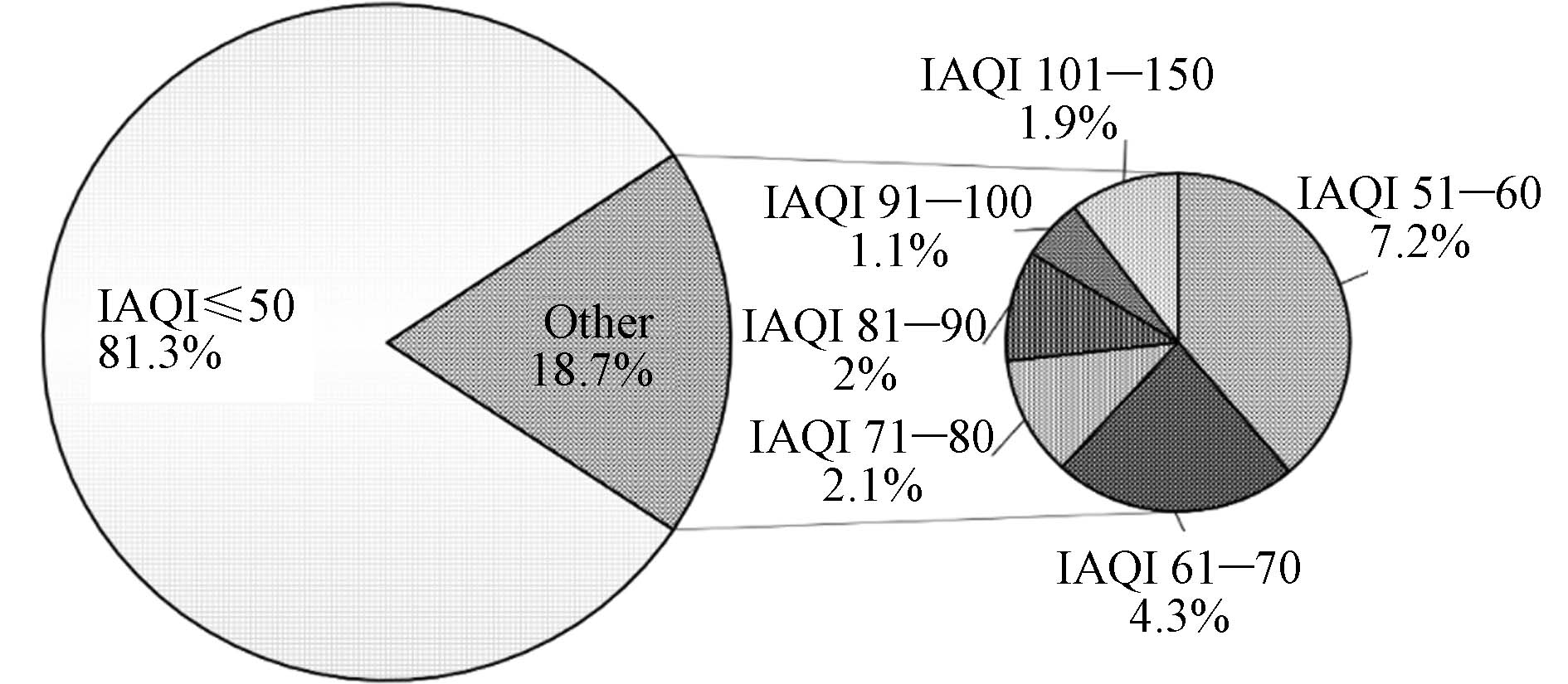
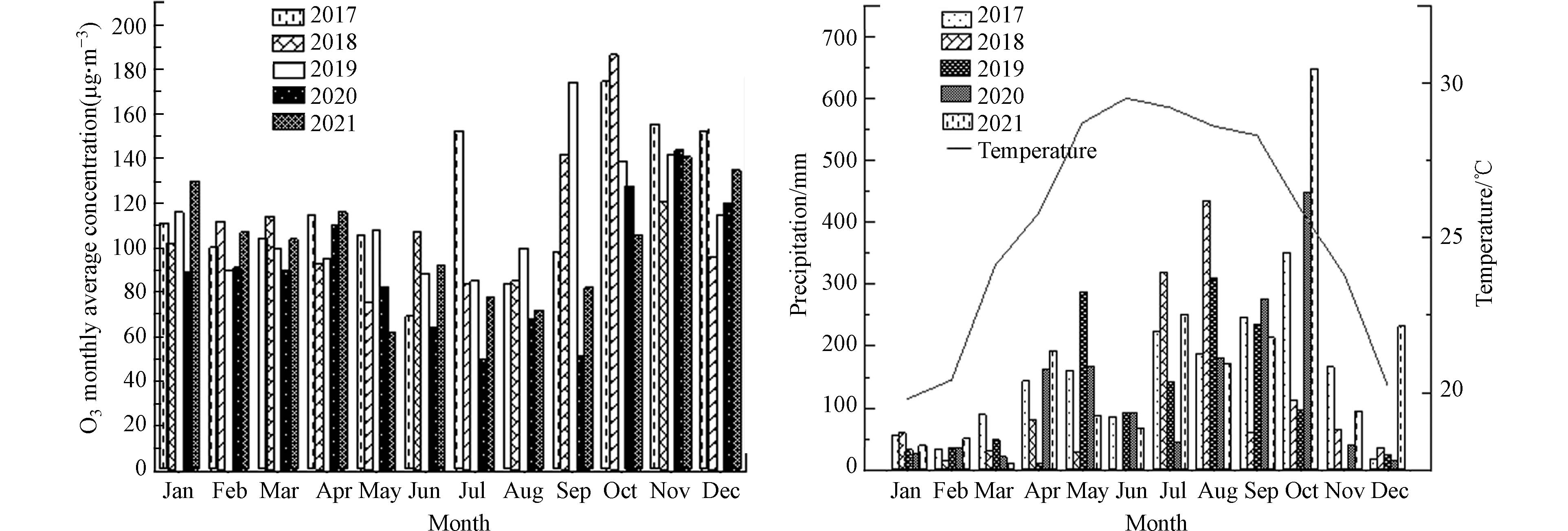
2017—2021 年,文昌市O3日最大8 h滑动平均质量浓度(O3-8h)在18—212 μg·m−3之间,按照《环境空气质量指数(AQI) 技术规定(试行)》,对应的空气质量分指数(IAQI)为9—148. O3以优良为主,其中O3处于优级(IAQI≤50)天数比例为81.3%,良级(50<IAQI≤100)天数比例为16.7%,轻度污染(150≥IAQI>100)天数比例为1.9%,总超标天数为36 d,没有中度污染、重度污染和严重污染. O3优级以下IAQI处于51—60和61—70区间的占比较大,分别为7.2%和4.3%(图1).
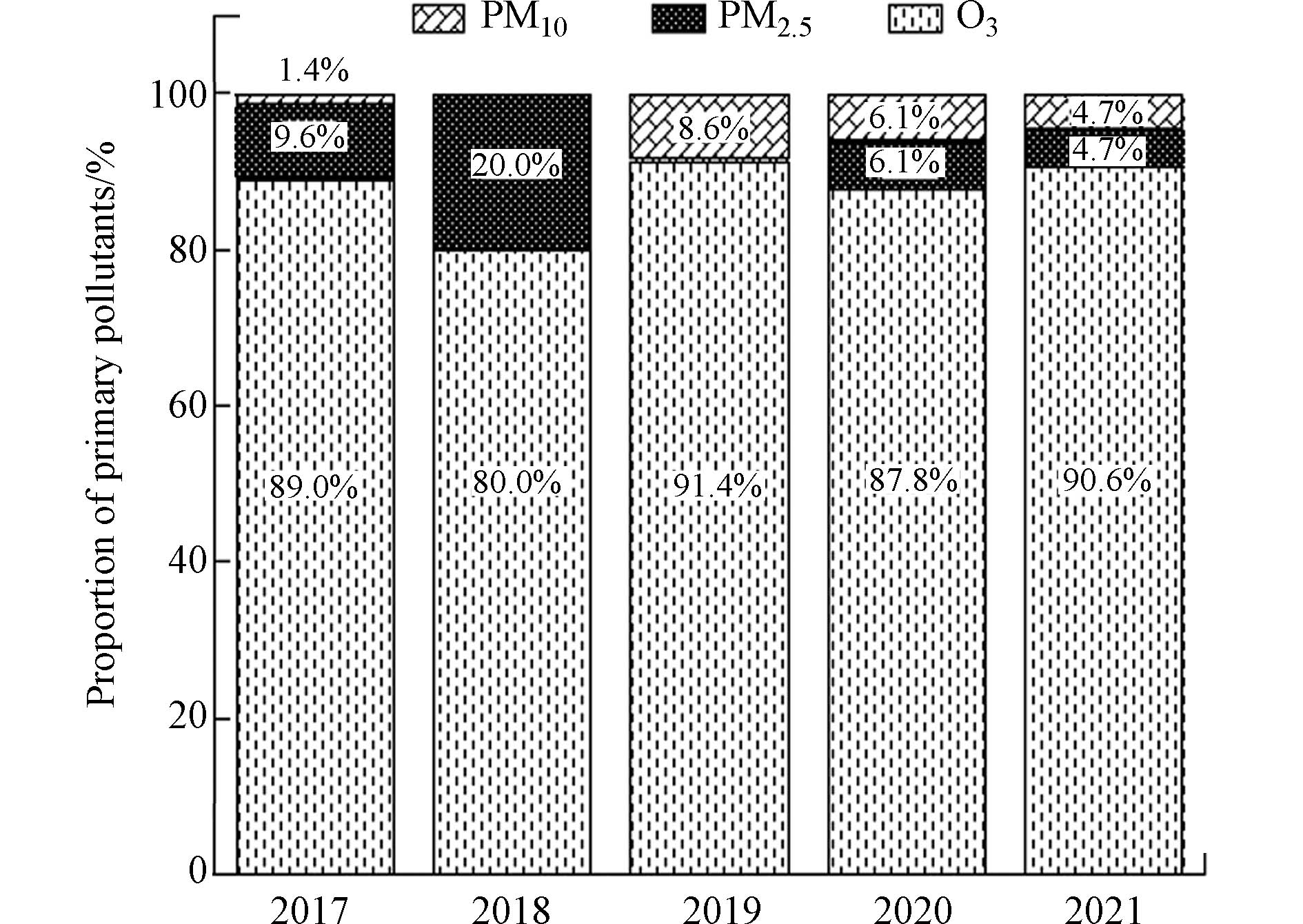
2017—2021 年,文昌市首要污染物为O3、PM2.5和PM10,占比分别为87.7%、8.1%和4.2%,其中PM2.5和PM10占比呈波动下降趋势,O3呈现波动上升趋势. 2017—2021 年,文昌市污染天的超标污染物均为O3,其中2019 年O3超标天数最多,有12 d出现轻度污染,O3已成为影响文昌市空气质量达标的最主要污染物(图2).
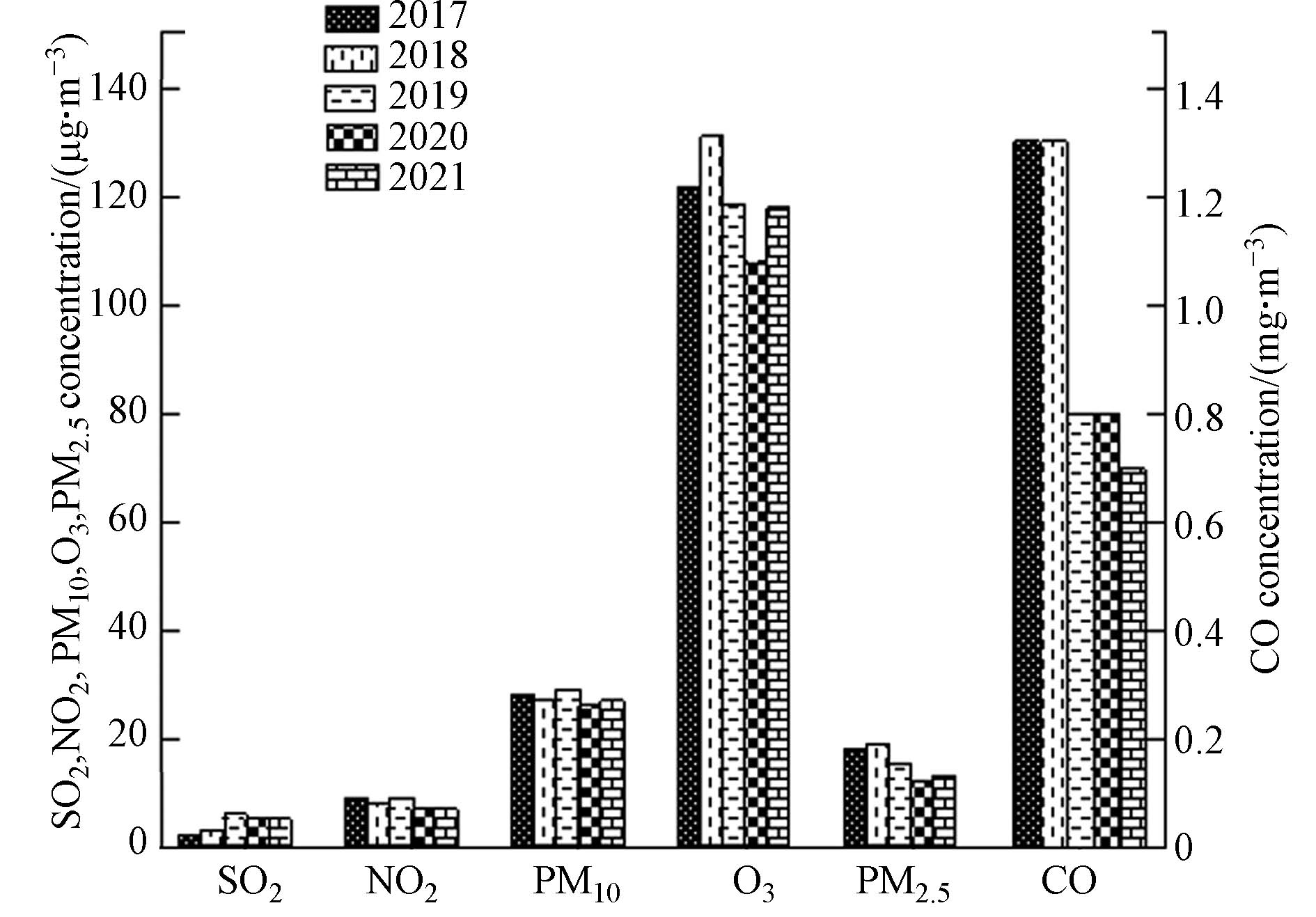
六项污染物从年度变化趋势上看,SO2在极低浓度水平下略有上升,由2 μg·m−3上升至5 μg·m−3;CO第95百分位数浓度在极低浓度水平下,呈下降趋势,由1.3 mg·m−3下降至0.7 mg·m−3;PM2.5年均浓度整体呈波动下降趋势,由18 μg·m−3下降至13 μg·m−3;PM10、NO2和O3下降不明显,PM10年均浓度在27 μg·m−3左右波动;NO2年均浓度在8 μg·m−3左右波动,总体处于极低浓度水平;O3-8h的第90百分位数浓度总体在120 μg·m−3左右波动,O3浓度与海口市相当,而机动车、工业企业等人为活动均明显低于海口市(图3).
-
我国大气污染通常由污染物排放、光化学反应、气象条件和区域输送等因素影响[18]. 在全国范围近地臭氧浓度的季节大小关系为夏季、秋季、春季、冬季依次递减[19]. 文昌市季节变化与国内大部分城市有较大差异.
文昌市O3-8 h月均浓度与温度呈相反特征(图4),2017—2021 年,O3-8h月均浓度最高值出现在9 月至次年1 月之间,范围在109—147 μg·m−3之间. 3—8 月温度较高,O3-8 h浓度却相对较低,月份均值在92 μg·m−3左右,最低值在8 月和6 月份,分别为82 μg·m−3和84 μg·m−3;9 月—次年2 月则反之,最高值在10—11 月份,分别为147 μg·m−3和141 μg·m−3. O3超标天集中在9 月至11 月,其中9 月和10 月超标天数最多,分别最高达8 d,11 月出现3 d;12 月、1 月和3 月偶尔出现1—2 d;4—8 月无O3超标天(图5). 综上分析,10 月前后超标天较12 月和1 月明显增多,可能与温度相对较高有关,10 月前后文昌市月均浓度在26 ℃左右,具有较好的光化学反应条件,有利于O3生成并达到高浓度.
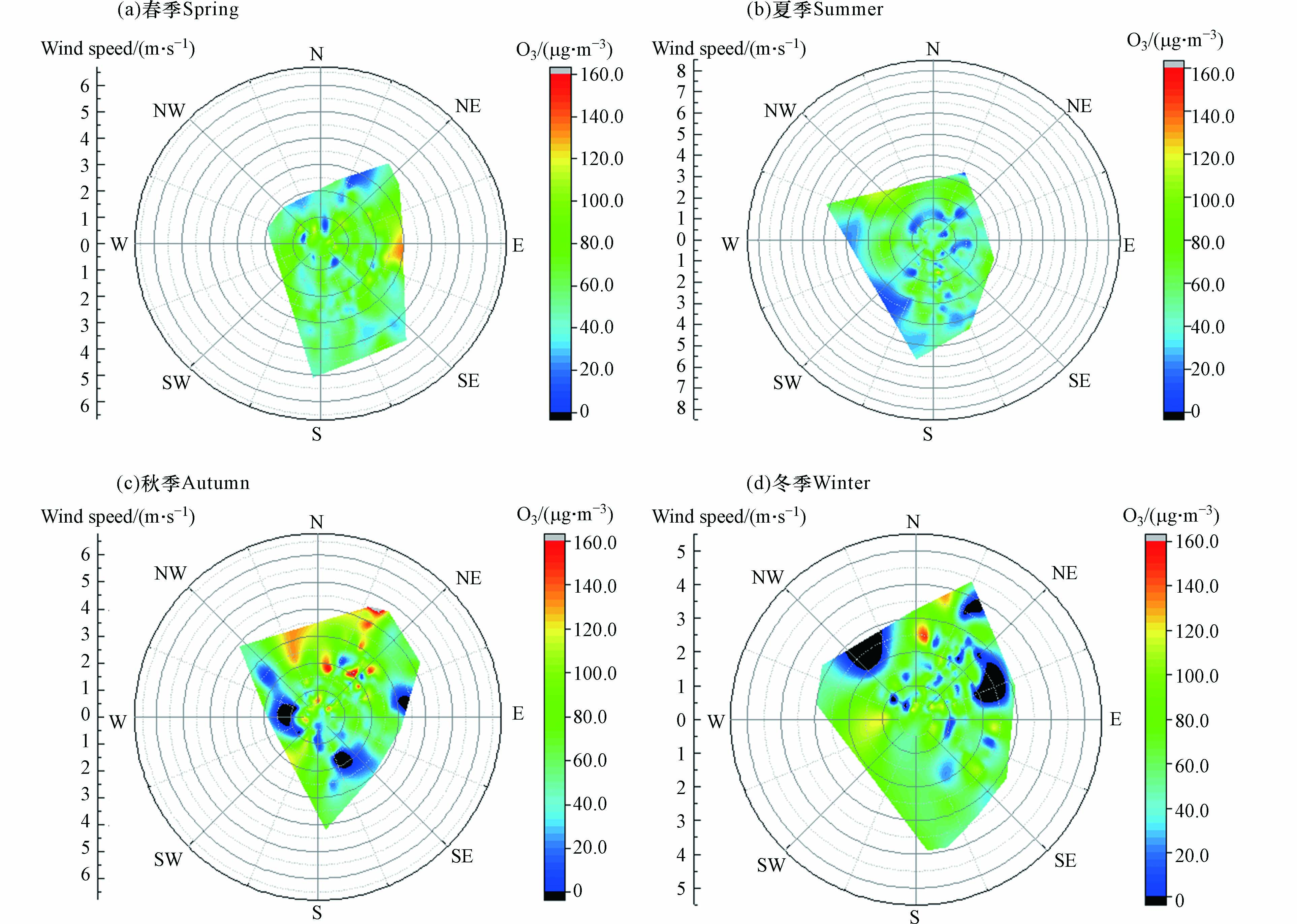
文昌市O3浓度与风向密切相关,夏季以偏南风为主,来自清洁的海洋气团,可稀释和清除臭氧及其前体物的作用[20];加上文昌市夏季降水较多,对O3浓度起到降低的作用,因此夏季O3浓度较低. 9 月后转为东北风为主,风力也明显加大,易受内陆区域污染气团输送影响,且文昌市秋冬季的月均气温均在20 ℃左右,叠加本地污染源,仍有利于O3生成,因此O3浓度在秋冬季处于高值.
-
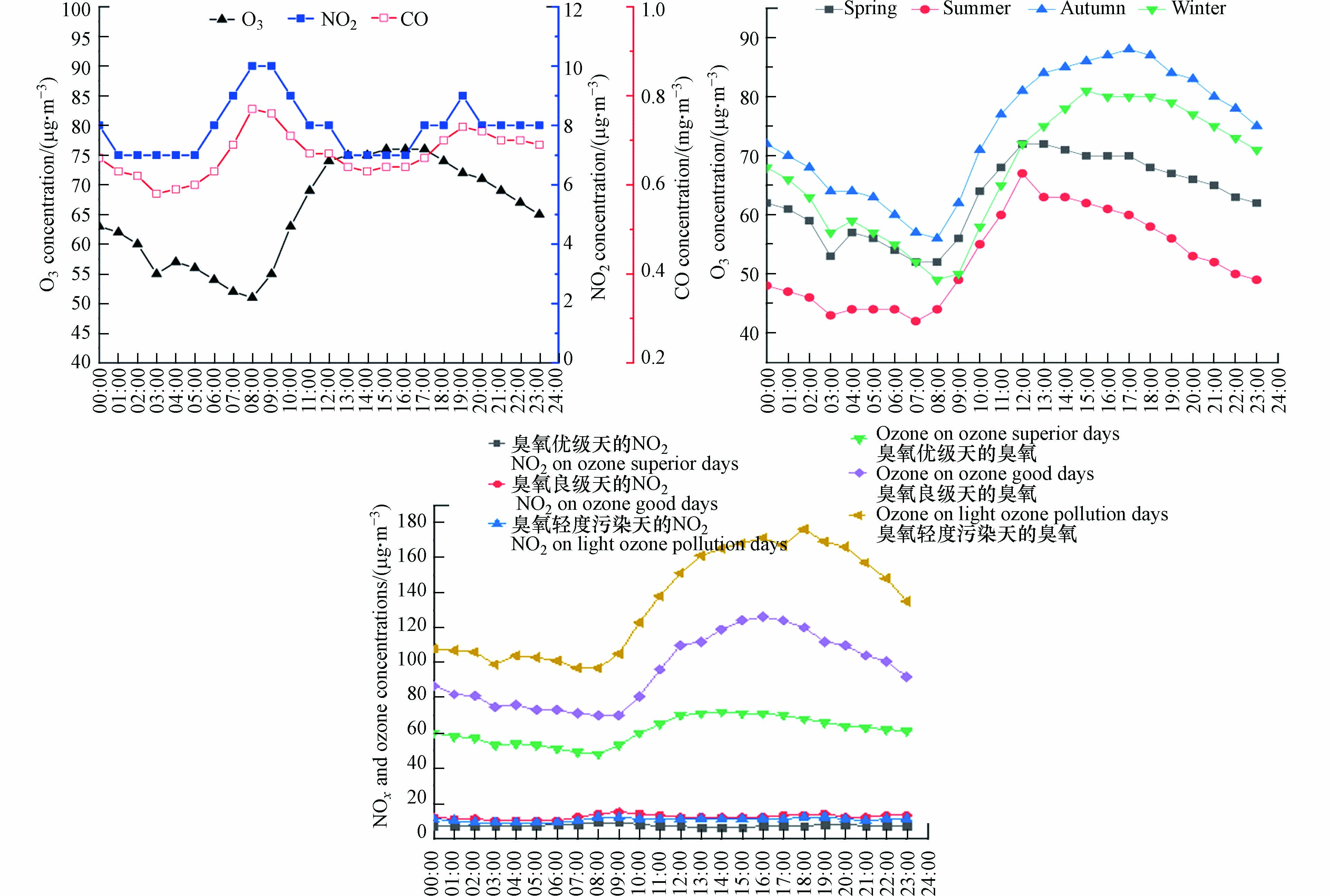
臭氧为二次污染物,在空气中臭氧浓度与其前体物浓度密切相关[21]. 从2017—2021 年文昌市O3小时浓度值变化情况看,文昌市O3浓度日变化呈现出单峰型特征,08 时出现谷值,12 时至17 时出现峰值,具有明显的日变化特征. NOx具有明显早高峰特点. NO2和CO与O3相反,夜间至早晨时段边界层高度降低,扩散条件不利,同时凌晨时段机动车明显减少,NO2变化不大,早上随着上班早高峰机动车的不断增加,机动车尾气排放的NOx增多,导致8至9 时出现峰值;同时NOx中的NO,会与O3发生光化学反应消耗臭氧,产生“滴定作用”[2]. 8 时后边界层高度升高,扩散条件有利,同时太阳辐射逐渐增强,光化学反应加强,O3逐渐被NO2光解生成,NO2质量浓度逐渐下降,O3质量浓度则逐渐升高[22]. 午后太阳辐射强度达到最大值,光化学速率最大,加上文昌市日照时间较长,且化学反应的平衡存在一定的滞后性,导致地面的O3浓度在12 时至17 时为峰值期,峰值持续时间较长. 17 时后随着太阳辐射和气温逐渐降低,O3浓度呈逐渐下降趋势,但文昌市O3浓度下降幅度不是很大,可能跟白天日照长和温度高有关,日照时数和O3浓度变化呈现明显的正相关. 另一方面,文昌市O3小时浓度峰值与谷值比为1.5,低于海口市峰谷值(2.4),且显著低于国内其他重点城市[10],这可能与文昌市O3前体物NOx浓度较低有关,文昌市机动车保有量仅占海口市的5.5%左右,NOx浓度排放较低.
文昌O3浓度在不同季节各时刻的小时质量浓度表现出秋季>冬季>春季>夏季的特征,春季和夏季O3峰值出现在12 时,秋季和冬季O3峰值分别出现在17 时和15 时(图6). 从文昌市优级天、良级天和轻度污染天3种不同级别天O3日变化情况看,均呈现单峰型变化特点,分别在14 时、16 时和18 时出现峰值,8 时出现谷值,峰谷值比分别为1.5、1.8和1.8(图6). 文昌市超标天峰谷值比明显低于海口市[11],且NO2变化较为平缓,可能与受传输影响更显著有关.
-
近地面臭氧浓度变化易受气象条件影响,温度、相对湿度、太阳辐射等影响光化学反应条件,风向和风速等影响O3的区域输送累积作用[22]. 从2017—2021 年来看(表1),文昌市O3-8 h浓度与平均气温、降水量、相对湿度和平均风速为负相关关系. 气温高,一方面有利于光化学反应,另一方面增强大气垂直输送能力[23]. 文昌市O3-8 h浓度与气温相关性为−0.235(P<0.01),表明大气垂直扩散能力对O3浓度有显著影响. 文昌市O3-8 h浓度与降水量相关系数为−0.021(P<0.01),大量研究表明,降水时,云层被遮挡,太阳辐射降低,臭氧不易生成,加上降水本身对臭氧及其前体物有冲刷作用[24],臭氧浓度有所降低. 文昌市O3-8h浓度与相对湿度的相关系数为−0.092(P<0.01),湿度较高时大气中的水蒸气含量较大,导致云层较厚,会减少太阳辐射,进而降低臭氧通过光化学反应生成的速率[25],同时会形成湿沉降,可湿清除臭氧及其前体物[26]. 风速大小可作为天气静稳状态的一个指标条件,静稳天气下大气污染物浓度会扩散减弱,从而导致近地层容易浓度积聚上升[27],风力较大,可以达到稀释和清除臭氧及其前体物的作用[28]. 文昌市O3-8h浓度与平均风速的相关系数为−0.047(P<0.01),表明风速扩散力对O3浓度有显著影响.
O3浓度与风向相关性密切(图7). 整体上看,当风向偏北风时,O3小时平均浓度相对较高;当偏南风时,O3小时平均浓度相对于其他方位明显偏低. 季节上看,在夏季各风向方位的O3小时平均浓度明显低于其它三个季节,这与前面的分析较吻合. 在秋冬季,偏南风O3浓度处于较低浓度水平,而东北风向时O3浓度相对较高.
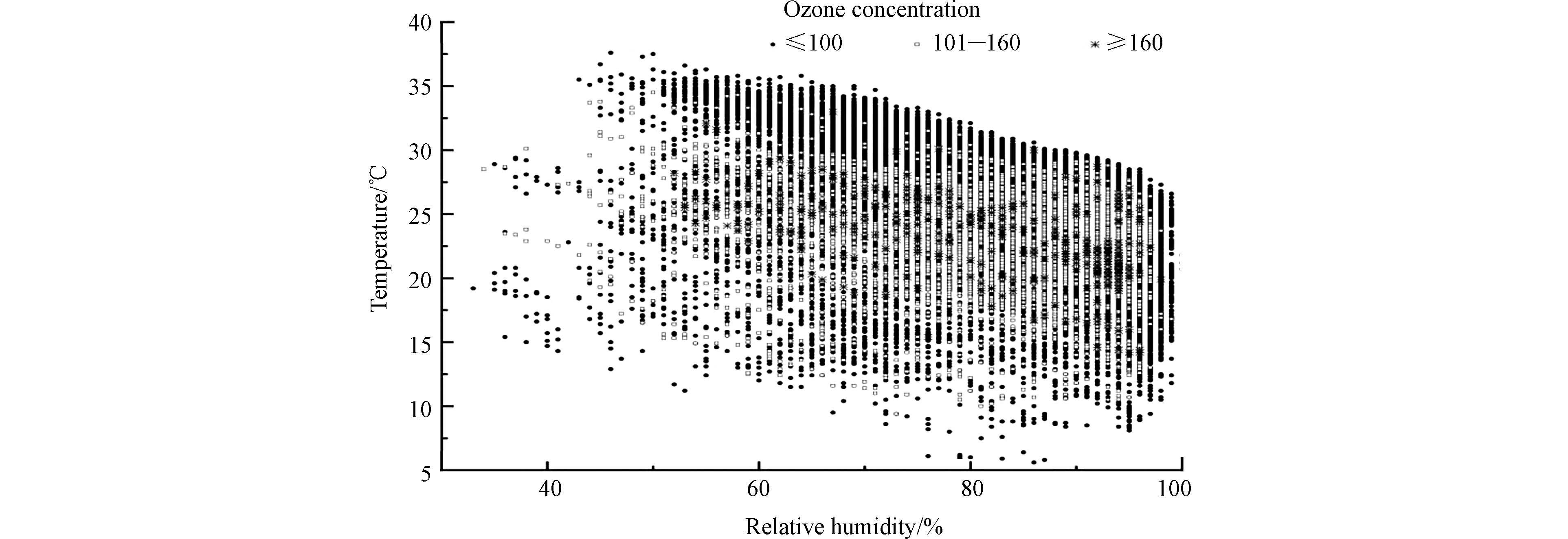
O3浓度与温度、湿度具有一定相关性(图8). 当温度在20—30 ℃,相对湿度在58—70%时,文昌市易发生O3污染. 当在相同温度情况下,O3-8h浓度会随着相对湿度的增加而降低.
-
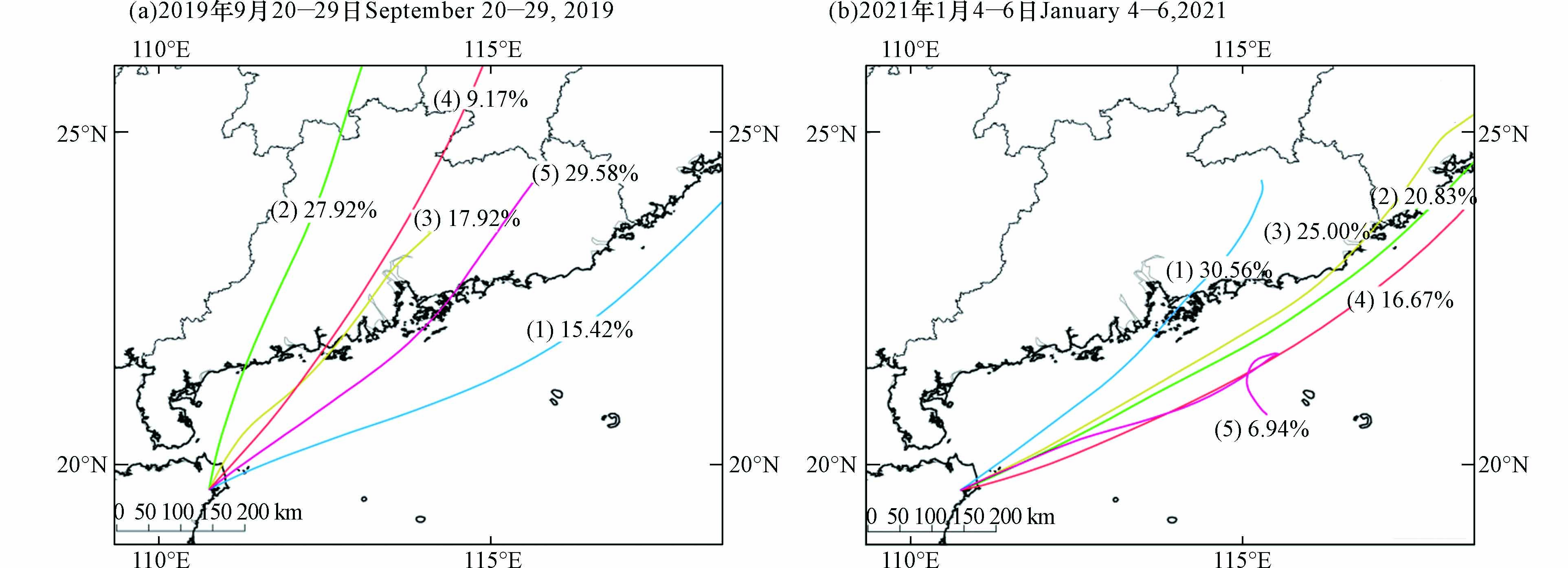
利用Meteoinfo软件,选取2019 年、2021 年逐小时臭氧浓度数据,对到达文昌市的后向气流轨迹进行聚类分析(图9),研究文昌市气流输送路径. 气流到达文昌市所经过的地区用气流输送路径和方向表示,轨迹长短表示气流移动速度,短的轨迹表示气流移动缓慢,长的轨迹表示气流移动速度较快.
高浓度时段的选取如下:2019 年9 月20—29 日、2021 年1 月4—6 日. 从图9可以看到,2019年9 月影响文昌市的气流可分为五大类,出现概率从大到小依次为:第五类(29.58%)>第二类(27.92%)>第三类(17.92%)>第一类(15.42%)>第四类(9.17%). 由此可知,大部分气流轨迹主要是源自广东省中、短距离的气流,其余少数源自华东中部及沿海. 结合表2可知,第三类、第四类气流臭氧小时平均浓度较高,分别为(154±46)μg·m−3、(150±22)μg·m−3,两类气流来向相同,发源地及流速存在差异,第四类气流源自安徽省中部,途径江西省,随后与第三类气流路径重合,由珠三角地区,到达文昌.
2021 年1 月4—6 日影响文昌市的气流可分为五大类,来源于广东省的内陆短气流以及浙江、福建及广东省沿海一带的气流,结合表2可知,聚类(1)到达文昌市对应O3小时平均浓度最高,且污染轨迹在总超标轨迹占比达84.6,说明此次外来输送主要来自广东省东北部的梅州,途径惠州、深圳等到达文昌.
-
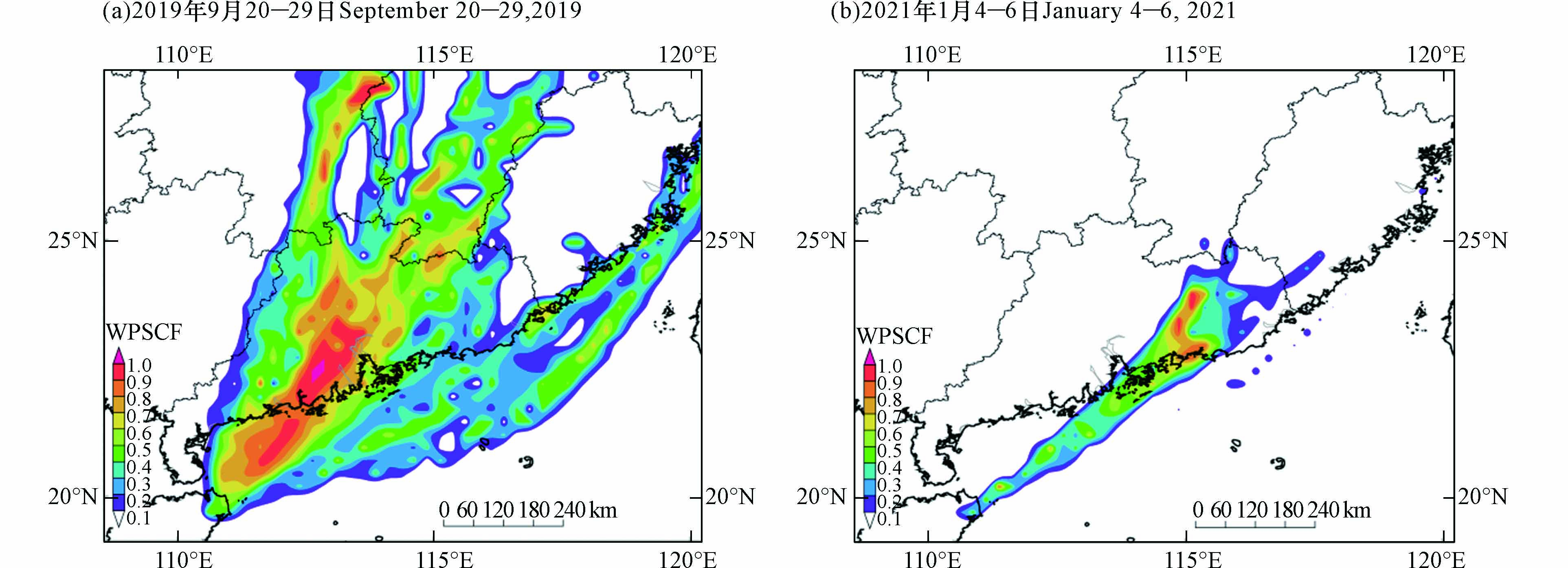
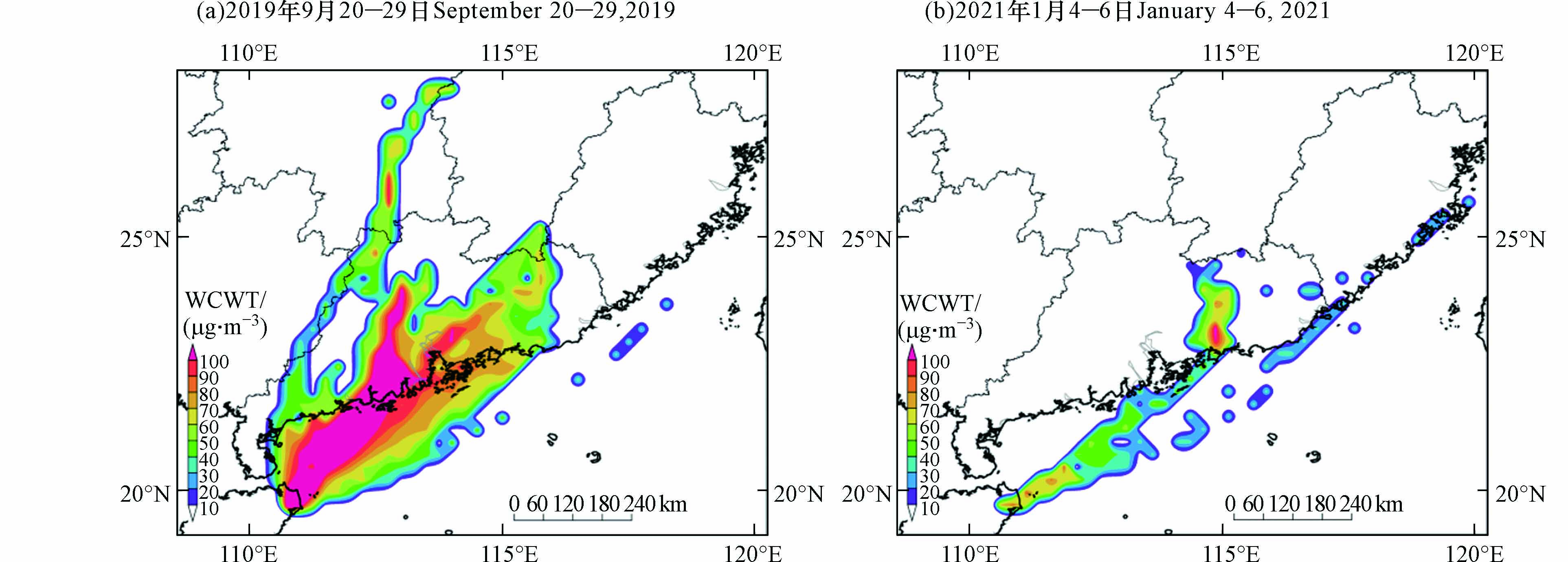
为进一步研究文昌市大气臭氧输送源,可用WPSCF和WCWT进行计算,气流轨迹所覆盖的区域利用网格化为0.25°×0.25°表示,考虑到文昌市臭氧整体浓度水平及污染情况较国内多数城市低、少,因此按照文昌市年均值定义臭氧标准值与污染轨迹阈值分别为119 μg·m−3 (2019 年)、118 μg·m−3 (2021 年). WPSCF值越大说明该区域污染轨迹占比越大,即对文昌市臭氧浓度的贡献越大,定义为臭氧污染的主要潜在源区.
计算结果见图10,WPSCF高值区主要集中在广东省中部及东部,其值在0.8以上. 另外,湖南及江西交界处也存在部分区域WPSCF值超过了0.7. 说明以上区域的污染传输对文昌市臭氧浓度有较大的影响,文昌市臭氧污染发生时,外来输送主要以近距离的跨省输送为主.
由于WPSCF法仅反映潜在源区贡献率的大小,对数值的大小无法模拟,为此本文使用WCWT法进一步反映潜在源区的污染程度. 由图11可知,两次污染过程的潜在源区较为相似,较高WCWT的区域主要位于珠三角地区,其WCWT>80 μg·m−3,另外广东省东部也存在高值点,如2021 年的高值区域位于梅州、揭阳、潮州和汕头,说明临近广东省是文昌臭氧外来输送的主要源区.
-
(1)2017—2021 年文昌市空气质量以优良级(优级81.3%、良级16.7%)为主,其中良级首要污染物O3占87.7%,污染天超标污染物均为O3,O3已成为影响文昌市空气质量达标的最主要污染物.
(2)2017—2021 年文昌市O3-8h浓度与平均气温、相对湿度、平均风速和降水量呈负相关关系,与风向关系密切. 整体上看,当风向偏北风时,O3小时平均浓度相对较高,当偏南风时,O3小时平均浓度相对于其他方位明显偏低.
(3)文昌市O3日变化为明显的单峰型特征,NOX. 具有明显早高峰特点. 早间上班高峰,NOx在8 时至9 时出现峰值,而O3在8 时出现谷值,12 时至17 时出现峰值,峰谷比为1.5,略低于海口市峰谷值(2.4),且显著低于国内重点城市,可能与受污染传输更明显有关. O3浓度在不同季节各时刻的小时质量浓度表现为秋季>冬季>春季>夏季的特征.
(4)2019 年和2021 年两个污染过程到达文昌市的气团输送路径均全部来自东北方向,同时潜在源区分析WPSCF与WCWT高值区域较为一致,表明O3污染潜在源区主要来自珠三角地区. 因此,文昌市不仅要加强本地污染防控,还应加强与上风向区域特别是珠三角地区的联防联控,对有效控制O3污染具有重要意义.
文昌市臭氧污染特征、输送路径及潜在源区分析
Characteristics, transport routes and potential sources of ozone pollution in Wenchang
-
摘要: 通过对2017—2021 年文昌市O3和气象观测数据的分析,利用后向轨迹聚类和潜在源区等分析方法,研究了该文昌市O3污染特征. 研究结果发现,2017—2021 年文昌市O3总体优良,O3日最大8 h滑动平均值在18—212 μg·m−3之间,超过160 μg·m−3的超标天多发生在9 月—次年1 月. 与国内多数城市不同,文昌市O3浓度与平均气温、相对湿度、平均风速、降水量为负相关关系;O3浓度与风向变化关系密切;夏季以偏南风为主,受外来污染传输影响较小,O3浓度较低;秋冬季主导风向为东北风,O3浓度较高,受内陆区域的污染传输影响明显增多. 文昌市O3超标的天气形势主要表现为台风外围和冷高压南下两种. 经聚类分析表明文昌市O3污染主要潜在源区为珠三角地区.Abstract: Based on the analysis of O3 and meteorological observation data in Wenchang City from 2017 to 2021, the characteristics of O3 pollution in Wenchang City were studied by using the methods of potential source areas and backward trajectory clustering models. The results showed that: (1) O3 in Wenchang City is generally excellent from 2017 to 2021 and the daily maximum 8-hour average O3 concentrations between 18 μg·m-3 and 212 μg·m−3; and the days exceeding the standard of 160 μg·m−3 mostly occurred from September to January of the following year. (2) Unlike most cities in China, the O3 concentration in Wenchang was negatively correlated with negative correlation with mean temperature,relative humidity, mean wind speed and precipitation, and was closely related to wind direction; in summer, it was mainly southerly wind, which was less affected by external pollution transmission, and the O3 concentration was low.in autumn and winter, the dominant wind direction was the northeast wind, and the concentration of O3 was higher, whichwas obviously affected by the pollution transmission in inland areas. (3) The weather situation of O3 over-standard in Wenchang was mainly manifested in the periphery of the typhoon and the southward movement of the cold high. Cluster analysis showed that the main potential source of O3 pollution in Wenchang was Pearl River Delta.
-
Key words:
- Wenchang /
- ozone /
- pollution /
- weather patterns /
- potential sources
-
活性焦是煤炭经炭化、活化等过程制成的多孔碳材料[1-4],主要用于烟气脱硫脱硝[5-7],可以通过低温再生循环利用,但在再生过程中会有一部分活性焦形成粉末状筛下物,达不到再利用要求而成为废料,即废弃活性焦[8-9]。废弃活性焦具有丰富的孔隙和表面官能团[10],能有效吸附营养物质、改善土壤结构,且含碳量高[11],同时含有氢、氧、氮、硫等元素[1,12],有潜力应用于土壤改良。
利用废弃活性焦进行土壤改良已有一定研究。秦文芳等[13]发现在土壤里直接施用少量废弃活性焦可以有效提高土壤团聚体含量,降低土壤pH,但过量施用会因其较高的硫和盐含量[8]对植物生长产生影响;利用酸化改性使废弃活性焦S含量降低57.1%,电导率降低约15倍,应用于土壤中有效促进植物的光合作用和养分吸收[8]。酸改性改善了废弃活性焦的性质,但提高了利用成本。
堆肥是一种常见的利用废弃物制备土壤改良剂的方法[14-15]。生物炭是近年来常见的堆肥添加材料。WANG等[16]以生物炭与猪粪和稻草进行堆肥,发现二者均能提升氮含量并且优化细菌群落结构,有效加快腐熟进程;李宇航等[17]和夏璇[18]的研究均发现生物炭的加入可以有效固氮,同时提升全磷、全钾的含量,使堆肥产品养分含量增加。利用废弃活性焦作为辅料堆肥的研究尚未见报道,但活性焦与生物炭性质类似,均具有丰富孔隙和表面官能团,生物炭作为调理剂可有效促进堆肥腐熟[19-20],如果将废弃活性焦作为掺料与其他物质进行堆肥利用达到土壤改良效果,则更具经济性,因而有必要探究废弃活性焦作为辅料制堆肥产品的可行性。
因此,本研究将废弃活性焦与鸡粪按比例混合进行堆肥,以秸秆、再生焦粉和新焦粉作为对比,探究废弃活性焦制堆肥产品的可行性,分析不同配比下堆肥产品性质以及对植物生长的影响,确定废弃活性焦的最佳配比,旨在充分探究废弃活性焦在土壤改良方向的应用潜力,为废弃活性焦的资源化利用提供理论和技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料
实验所用废弃活性焦、再生焦粉、新焦粉均产出于山西清环能创环境科技有限公司;玉米秸秆来源于长治屯留县;鸡粪从运城高村镇宏运养殖场获得;菌剂选购于广东立得生物科技有限公司生产的EM真菌原液。原料的主要特性如表1。
表 1 原料理化性质Table 1. Properties of materials原料 总养分/% N/% P2O5/% K2O/% pH 有机碳/% C/N As/(mg·kg−1) Cd/(mg·kg−1) Cr/(mg·kg−1) Pb/(mg·kg−1) 废弃活性焦 2.81 2.3 0.41 0.1 7 24.04 10.45 2.26 ND 2.58 2.87 再生焦粉 1.23 0.35 0.79 0.09 7.98 13.78 39.36 13.3 ND 0.64 5.15 新焦粉 0.89 0.36 0.44 0.09 8.23 13.71 38.07 1.28 ND 0.07 0.52 鸡粪 8.36 1.94 3.68 2.74 9.04 17.35 8.95 8.24 ND ND 2.89 秸秆 3.4 0.9 0.33 2.17 7.31 29.9 33.22 1.28 ND 0.07 0.52 注:ND表示未检出。 1.2 堆肥过程
堆肥初始阶段的物料合适C/N比一般要求为25~35[17-20];活性焦含碳物质生物可利用性较低;实验所用废弃活性焦的C/N比为10.45,鸡粪C/N比为8.95,按照合理的C/N比区间与鸡粪混配无法完成,再生焦粉和新焦粉的C/N比为39.36和38.07,按合理区间配置的焦粉配比在90%以上。其他煤基固废如风化煤、粉煤灰和煤矸石添加量在0~60%的区间内均有探究[21-23],但其C/N比较高(如煤矸石C/N比57.44),应用于堆肥可以调节堆肥C/N比在25~35之间。结合废弃活性焦的性质,其配比过高无法完成堆肥。
为使堆肥顺利进行,本研究初步设定活性焦配比为35%~55%,并添加了EM菌液以进一步促进发酵过程。利用搅拌机将鸡粪和EM菌液按表2的质量配比混合,分别添加35%的废弃活性焦、新焦粉、再生焦粉以及秸秆以分析其可行性,分别编号为BH、XJ、ZS、JG,向堆体添加纯水将含水率控制到60%左右。4组堆肥产品的初始C/N比分别为9.53、11.64、11.59、13.79,初始含水率依次为56.98%、53.27%、51.49%、57.04%。对废弃活性焦的最佳配比进行探究,按表3的质量配比混合,在30%~55%之间设置6个废弃活性焦的配比梯度,分别编号为BH-30、BH-35、BH-40、BH-45、BH-50、BH-55,C/N比在9~10之间,初始含水率在55%~57%之间。
表 2 不同材料堆肥产品配比Table 2. Composting product ratios of different materials材料 秸秆 废弃活性焦 再生焦粉 新焦粉 鸡粪 65% 65% 65% 65% 秸秆 35% — — — 废弃活性焦 — 35% — — 再生焦粉 — — 35% 新焦粉 — — — 35% EM菌液 0.10% 0.10% 0.10% 0.10% 表 3 废弃活性焦不同配比的堆肥产品的原料配比Table 3. Raw material ratios of composting products with different ratios of waste activated coke编号 废弃活性焦 鸡粪 EM菌液 BH-30 30% 70% 0.10% BH-35 35% 65% 0.10% BH-40 40% 60% 0.10% BH-45 45% 55% 0.10% BH-50 50% 50% 0.10% BH-55 55% 45% 0.10% 每个处理有3个平行,共27个堆体,每个堆体重300 kg,堆肥时间为26 d,堆体在第0、6、11、16、26 d进行翻堆并适当补水。所有处理堆体的温度和含水率均使用16路温湿测定器(16UC,JK3008,辉达隆电子科技有限公司,中国)进行记录,将探针插入堆体,探针位置距离堆体表面5~10 cm左右,先稳定10 min,然后快速读取并记录堆体的温度和含水率,每个堆体取3个点位进行随机测定并取均值;在此基础上,利用烘干法(GB/T 8576—2010)[24]对16路温湿测定器的含水率结果进行校正,校正后的含水率作为最终的堆体含水率。在堆肥过程中,通过随机混合堆体五个位置的样品以获取均匀样品,将一部分样品储存在−4 ℃的冰箱中,剩余部分干燥并研磨过0.4 mm筛。
1.3 性质测定
堆肥样本的性质测定均根据《有机肥料》(NY/T 525—2021)标准[25],酸碱度测定利用pH计(FE38,梅特勒-托利多公司,美国)记录;有机质含量利用重铬酸钾容量法进行测定;总养分(氮、磷、钾)测定分别利用凯氏定氮法、分光光度计法以及等离子体发射光谱法;种子发芽指数(GI)测定利用10粒大小一致的胡萝卜种子于放置定性滤纸上的培养皿中,加入10 mL试样浸取液培养48 h来确定;As、Cr、Cd、Pb等重金属检测依据NY/T 1978—2010标准中等离子体发射光谱法[26]进行测定。
1.4 植物种植
花盆的规格为7 cm×5 cm×7.8 cm,每个花盆装200 g土,分别加2 g的不同配比的废弃活性焦堆肥产品的样品与土壤混合进行盆栽实验,对照为纯土壤(CK)、加0.2 g化肥(HF)以及2 g秸秆堆肥产品样品(JG),种植狗牙根,设置3个平行,在30 d进行收获,对狗牙根的鲜重、株高进行记录。
1.5 数据分析
使用SPSS 27.0对各组进行单因素方差分析(One-Way ANOVA),多重比较采用LSD法,显著水平为P<0.05。使用Origin 2021进行作图。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 不同原料的堆肥产品在堆肥过程中的指标比较
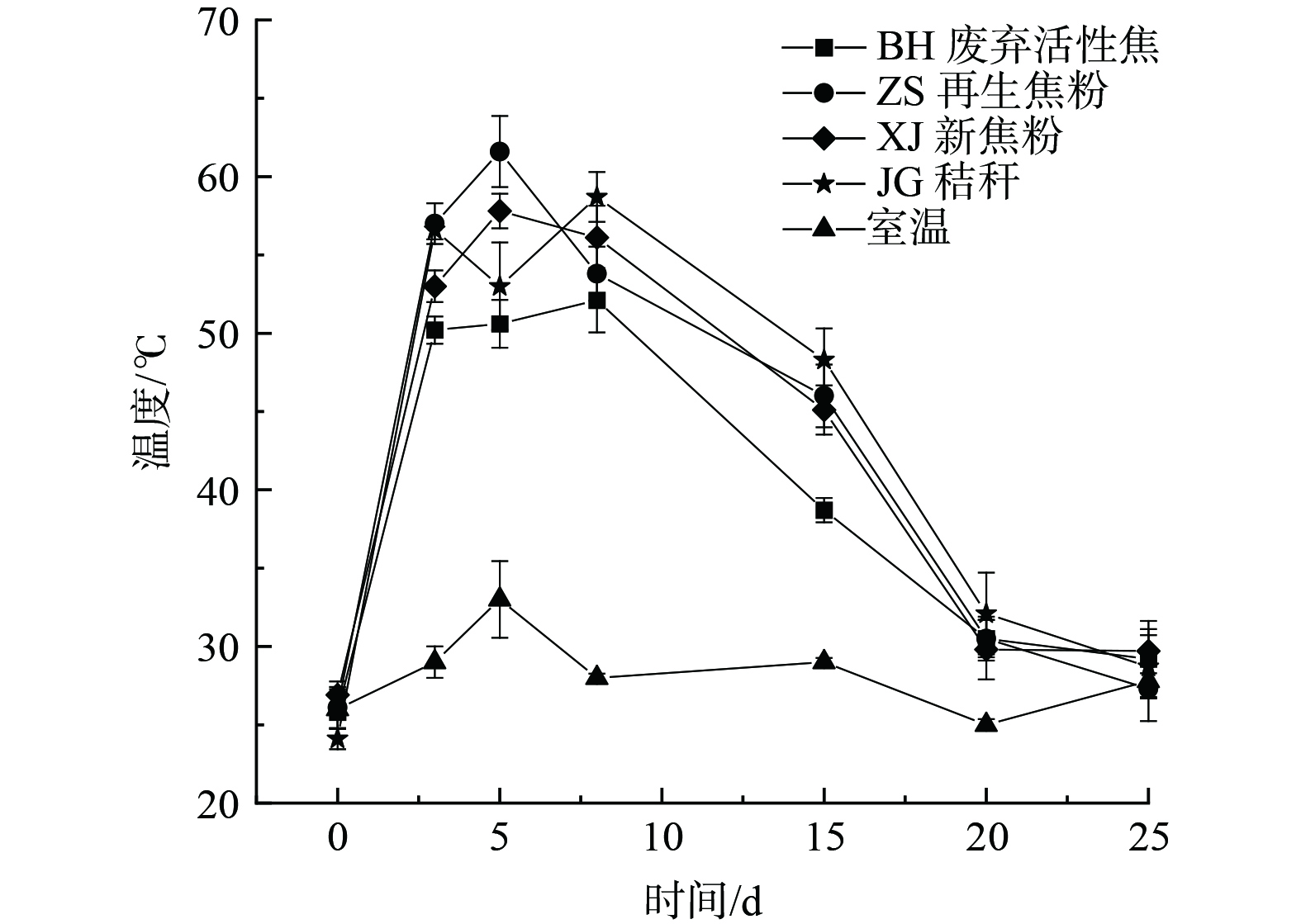
图1是同配比不同原料的堆肥产品的温度随时间的变化情况。由图可知BH、ZS、XJ、JG的堆体温度在26 d内均呈现出上升-稳定-下降的规律,最高发酵温度均超过了50 ℃。BH、ZS、XJ、JG组在3 d内迅速升温并达到50 ℃以上,说明堆体的养分和初始含水率满足微生物活动的需求[27-28],因而升温阶段迅速。ZS组在升温阶段变化最快,在高温持续阶段堆体温度维持在53~62 ℃;BH组在第0、3、5、8、15、20、25 d的温度分别为25.8、50.2、50.6、52.1、38.7、30.5、29.2 ℃,测定最高温度为52.1 ℃,在高温阶段持续达5 d,BH组高温阶段温度低于3个对照,高温阶段变化较小更有利于微生物的代谢活力[29];从21 d开始各堆体的平均温度逐渐接近室温,4组堆肥产品在第25 d的平均温度均降低,与室温基本一致。温度是堆肥过程中最重要的测量指标,影响着堆肥的腐熟程度[30],4组堆肥产品在堆肥过程中均经历了升温、持续高温、降温腐熟阶段,在高温阶段持续超过5 d[31]。
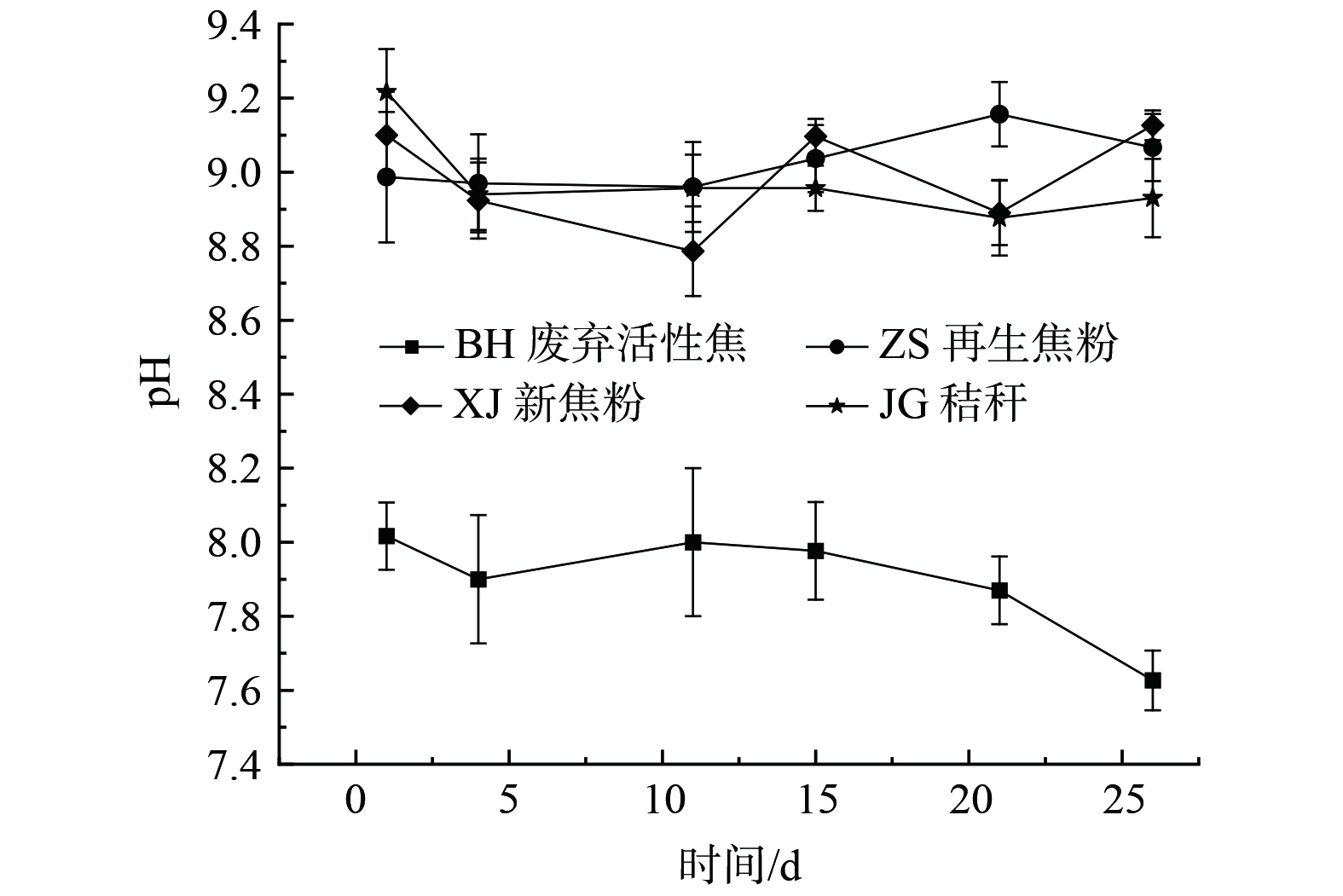
图2是不同原料堆肥产品在堆肥过程中pH值的变化情况。在堆肥的整个过程中,BH组的pH值有明显下降的趋势,pH值8.02降到7.63,ZS组的pH值有上升的趋势,最终pH稳定在9.07,XJ组pH值变化趋势较大,在堆肥前10 d之内下降明显,最后保持在与初始值相近的水平为9.13,JG组pH呈下降趋势,最后稳定在8.93,可见不同材料的堆肥pH值的变化趋势不尽相同[32],与秸秆、再生焦粉和新焦粉相比,废弃活性焦堆肥后的pH值远低于三者,符合NY/T 525—2021的标准,这是由于活性焦在烟气脱硫脱硝过程中吸持了一些硫酸、硝酸等酸性物质[33],对于降低pH值起到明显作用,微碱性环境更有利于微生物的生长繁殖以及代谢活动[34]。
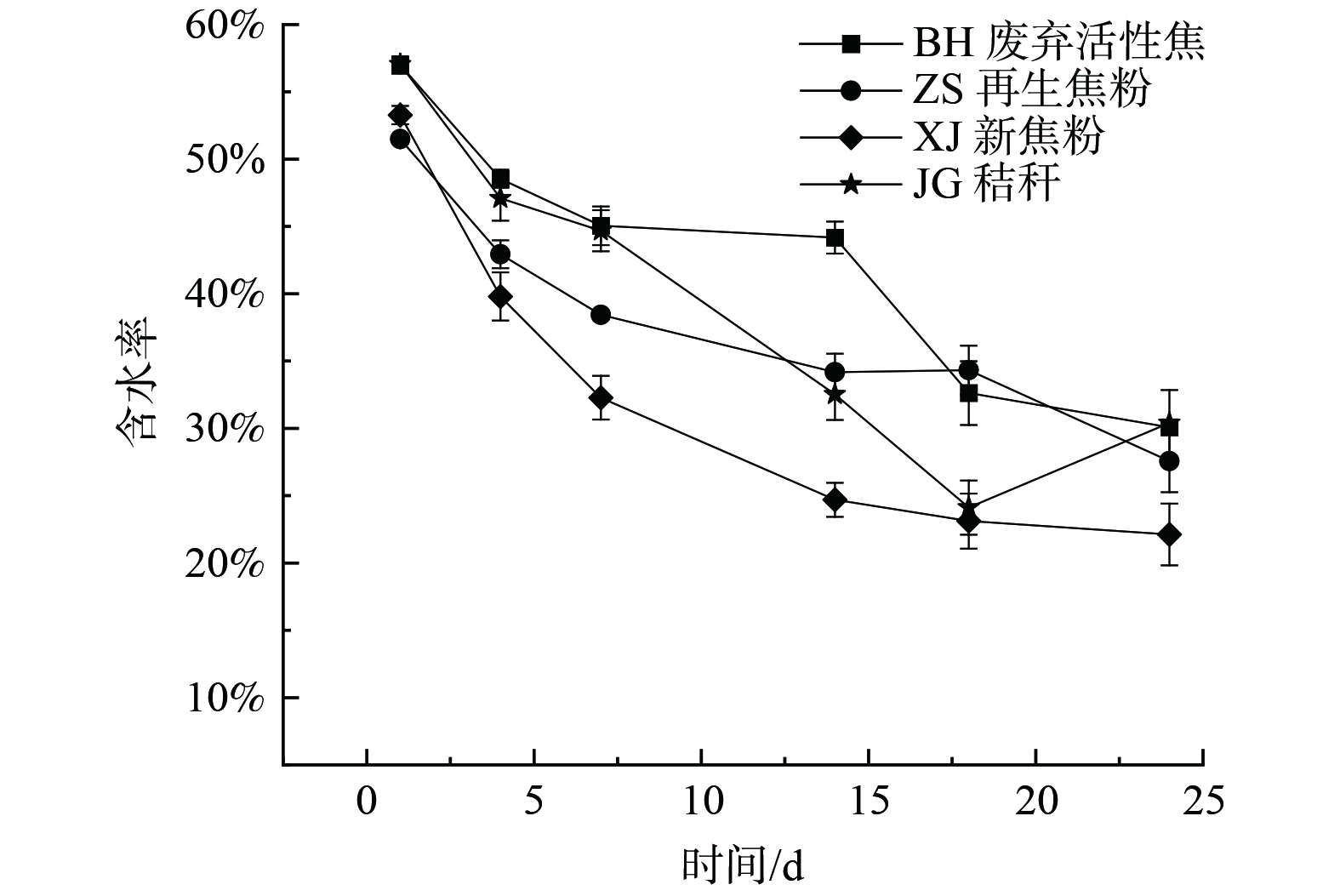
图3是不同原料堆肥产品堆肥含水率的变化情况。堆体堆肥过程中水分含量呈下降趋势,4组产品的含水率在升温期和高温期损失最快,在14 d以后含水率变化较缓慢,BH组初始的含水率高于JG组、ZS组和XJ组,在第7 d含水率损失了20.95%,最终含水率稳定在30.08%,高于ZS组和XJ组,废弃活性焦的初始含水率高对于微生物的分解代谢活动有利,不同原料堆肥产品的含水率损失不同,XJ组含水率损失最多,在第14 d含水率已降到24.69%,可能会造成微生物分解活动微弱[35]。不同原料堆肥产品含水率变化与李宇航等[17]对堆肥含水率的变化规律基本一致,含水率的变化与温度的变化相一致。
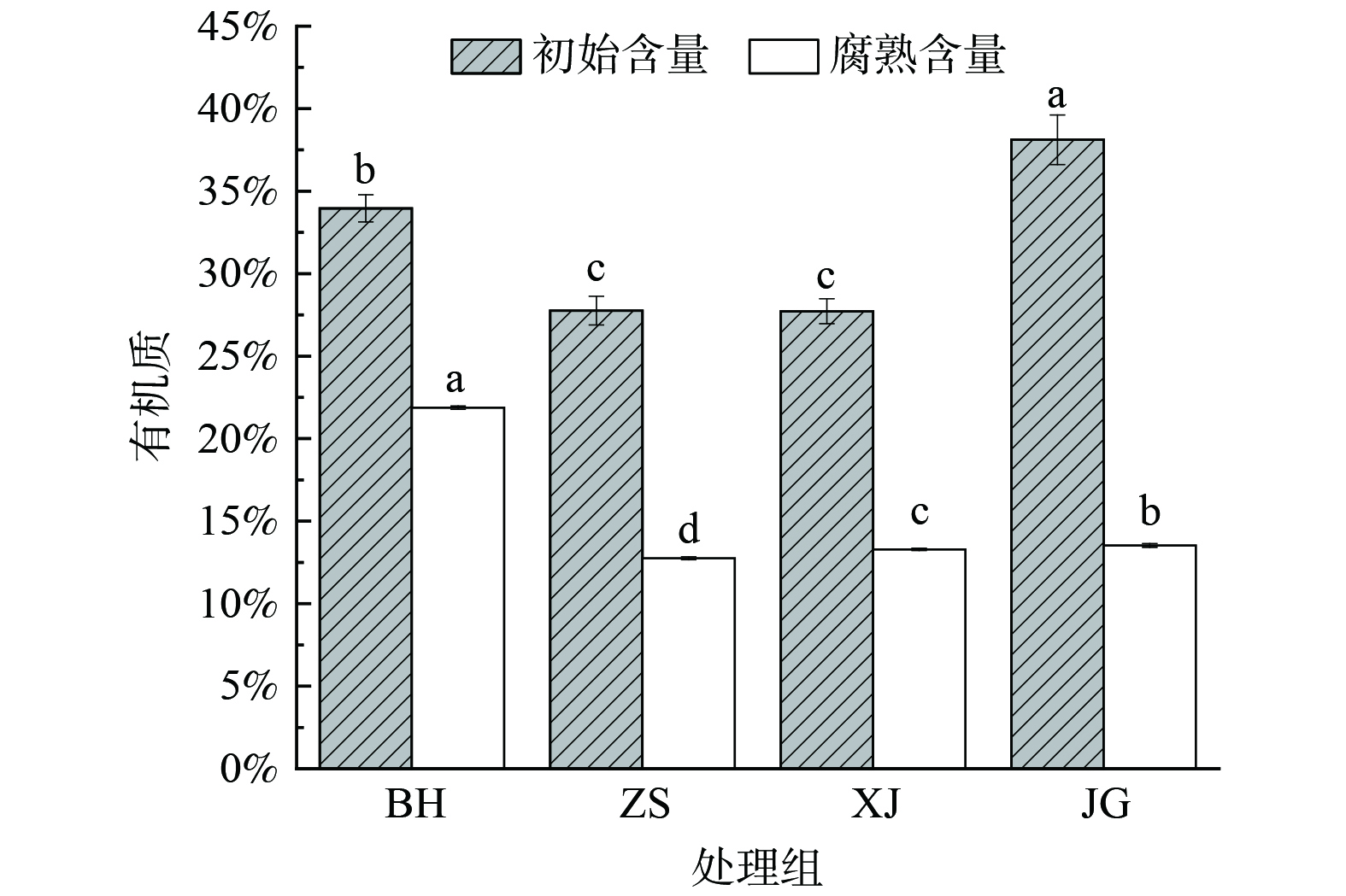
图4是不同堆肥产品的有机质含量变化。堆肥有机质含量在一定的时间范围内呈现下降的趋势是因为堆肥中微生物分解有机质导致的[36]。图中将BH、ZS、XJ、JG的结果对比发现,JG组起始的有机质含量最高,显著高于其余处理组(P<0.001),因原料有机质的差异,BH组的初始有机质含量也显著高于ZS和XJ组(P<0.001);在堆肥结束时BH组高于其他组,有极显著性差异(P<0.001),且BH组的腐熟有机质含量为21.88%。废弃活性焦的堆肥产品在腐熟之后的有机质含量远高于再生焦粉和新焦粉,再生焦粉和新焦粉的堆肥产品的初始有机质含量接近,这是由于活性焦的原料为煤,废弃活性焦吸附了烟气中一些挥发性有机污染物[4],因而初始有机物含量高于新焦粉和再生焦粉,腐熟之后有机质含量也高于再生焦粉和新焦粉组。但废弃活性焦堆肥产品的有机质含量仍达不到NY/T 525—2021的标准,小于30%,是因为在堆肥产品好氧发酵过程中有机物被好氧微生物利用,微生物的生长繁殖将物料中大量的有机质消耗并转化成气体以二氧化碳的形式释放到空气中[37],所以有机质不断损失,试验所用废弃活性焦有机质含量约为41.45%,腐熟以后由于损耗多,有机质并不能保留到30%以上。此外,废弃活性焦的堆肥产品在高温持续阶段温度变化小,稳定在50~53 ℃之间,有利于好氧微生物的持续活动,加快了有机质的分解。
表4所含不同原料组堆肥后的总养分(N+P2O5+K2O)以及重金属含量的变化情况,发现4个原料组堆肥腐熟后的总养分含量均高于4%,BH-35与JG-35的总养分含量接近均达到5.4%,ZS-35组总养分为4.9%,XJ-35组总养分最低为4.11%;4个组的N有显著性差异(P<0.05),BH-35组的氮含量极显著高于3个对照(P<0.001),JG-35组的K2O含量最高,XJ-35组所含养分最低,这是由于废弃活性焦的总氮含量为2.3%,而再生焦粉和新焦粉的总氮含量为0.35%和0.36%,秸秆的总氮含量为0.9%,废弃活性焦自身在氮含量上的优势促使废弃活性焦堆肥产品的总养分与秸秆堆肥产品的总养分接近,而再生焦粉和新焦粉堆肥产品的总养分主要依靠鸡粪的配比;4个不同原料组的重金属含量接近,As的含量最高,废弃活性焦Pb和As含量低于JG组,Cr含量接近,但都符合NY/T 525—2021的要求。
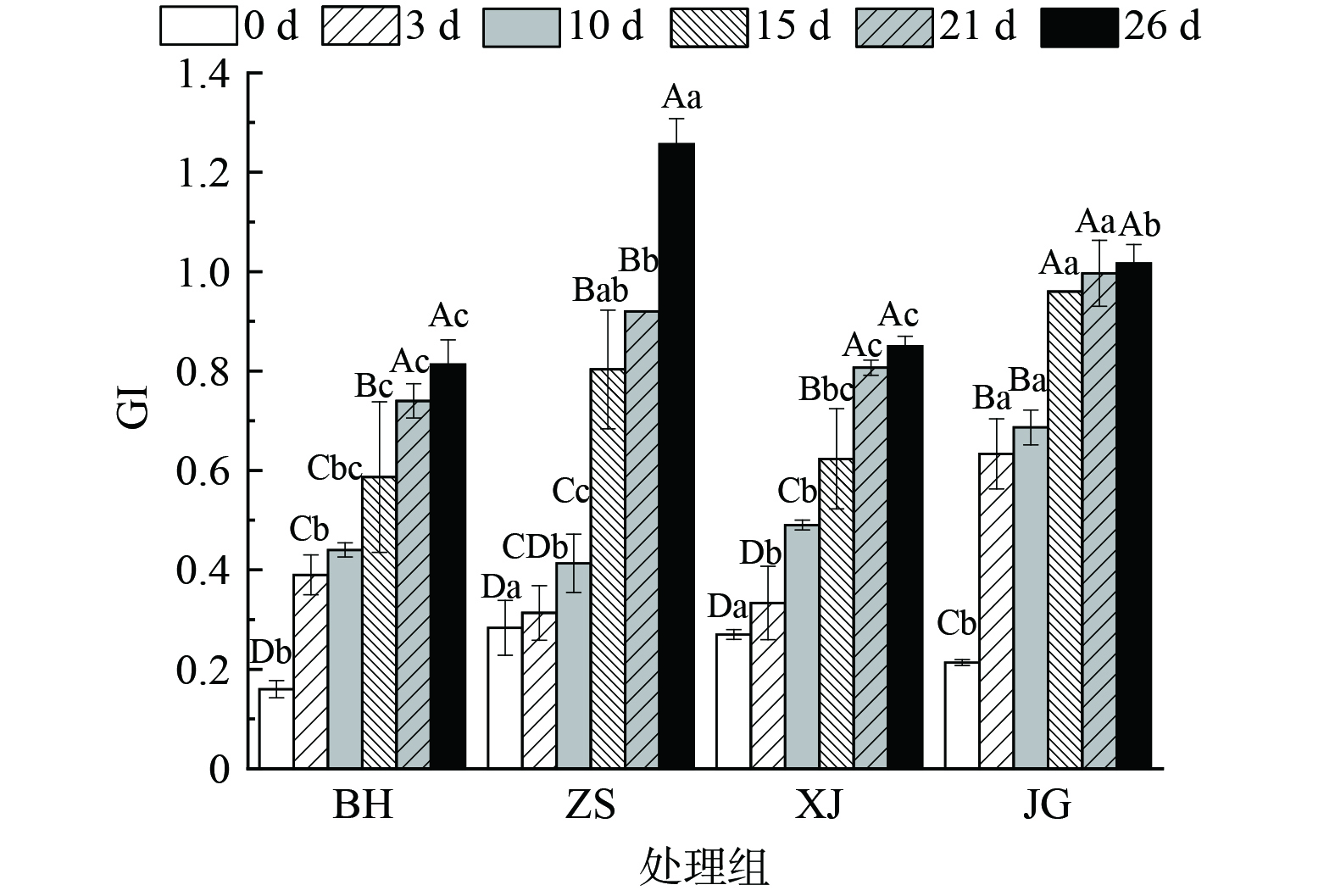
表 4 不同堆肥产品的总养分及重金属含量变化Table 4. Changes of total nutrient and heavy metal contents of different composting products检测指标 总养分/% N/% P2O5/% K2O/% As/(mg.kg−1) Cr/(mg.kg−1) Cd/(mg.kg−1) Pb/(mg.kg−1) BH-30 5.59±0.17a 1.57±0.04ab 2.06±0.00ab 1.96±0.25b 1.57±0.06bcd 0.08±0.01d ND 0.08±0.02e BH-35 5.41±0.14a 1.44±0.05cd 2.11±0.06a 1.86±0.07bc 1.54±0.09cd 0.08d ND 0.15±0.03cd BH-40 5.34±0.20a 1.50±0.05bc 2.01±0.02bc 1.83±0.17bc 1.45±0.04de 0.06e ND 0.13d BH-45 4.66±0.09b 1.29±0.03e 1.55±0.02e 1.82±0.15bc 1.67±0.10abc 0.13b ND 0.17±0.01c BH-50 4.91±0.13b 1.68±0.05a 1.68±0.01d 1.55±0.12c 1.61±0.15abcd 0.11±0.02c ND 0.12±0.01d BH-55 3.73±0.14d 1.33±0.08de 1.26±0.02f 1.14±0.26d 1.62±0.16abcd 0.16±0.01a ND 0.24±0.03a ZS-35 4.9±0.14b 0.83±0.09g 1.68±0.04e 2.39±0.14a 1.53±0.14ce 0.07de ND 0.16±0.04cd XJ-35 4.11±0.15c 0.60±0.11h 1.56±0.09e 1.95±0.19b 1.77±0.20ab 0.07±0.01de ND 0.18±0.02bc JG-35 5.43±0.05a 1.06±0.11f 1.96±0.02c 2.41±0.18a 1.81±0.08a 0.07±0.01de ND 0.22±0.02ab NY525— 2021 总养分(N+P2O5+K2O)百分比≥4% ≤15 ≤150 ≤3 ≤50 注:不同小写字母表示不同处理组间总养分及重金属含量存在显著性差异(P<0.05);ND表示未检出。 图5是不同堆肥产品对堆肥过程GI变化的影响,由图可知,4组原料的堆肥产品的GI值随着堆肥时间变化呈上升趋势,四个处理组GI值均在26 d达到最大,且除ZS组外其余组在21 d和26 d的GI变化没有显著性差异,可见堆肥产品在26 d的腐熟是较为完全的,BH组在第26 d的GI值为0.79,符合有机肥料标准。本试验中的4组堆肥产品在堆肥结束时发芽指数都在0.7以上,说明废弃活性焦、再生焦粉、新焦粉添加到堆肥产品中堆肥品质是合格的[38],但是BH组最低,这可能是由于废弃活性焦含有较多的盐,在堆肥腐熟过程中逐渐溶出,升高了浸出液的盐度[39-40],影响种子萌发。
通过分析废弃活性焦混配鸡粪的堆肥产品在堆肥过程中温度变化符合腐熟过程,其pH、总养分、GI等均符合有机肥料标准,废弃活性焦的添加有助于降低pH,可能是由于活性焦对堆肥过程中产生的挥发NH3进行了吸附,因为废弃活性焦BET表面积可达97.54 m2·g−1[13],这一结果与石建新等[19]对生物炭堆肥降低了堆体的pH的结果一致,废弃活性焦虽表现出良好吸附性,但其浸出液的所含盐分抑制了种子的萌发,这一结果与生物炭表现出的效果并不相同,可见二者虽有相似的性质,应用于堆肥的效果却不同,夏璇[18]在对生物炭堆肥的研究中发现其添加增加了全钾和全磷的含量,而废弃活性焦的添加增加了鸡粪堆肥产品的全钾含量,减少了全磷含量,可能是因为废弃活性焦自身磷贡献少且对磷素活化无促进作用。综上,废弃活性焦作为辅料堆肥是具备可行性的,但是由于添加废弃活性焦的鸡粪堆肥产品的初始C/N比低于15,可能造成氮素的损失[27],在后续的研究中应该考虑添加C/N比更高的辅料调节产品的C/N比至合理的区间。
2.2 不同配比的废弃活性焦堆肥产品的性质对比
图6为不同配比的废弃活性焦堆肥产品有机质含量,废弃活性焦配比在30%~55%之间的堆肥产品腐熟后的有机质含量在10.23%~22.92%之间,当废弃活性焦的添加量在35%、40%、45%时腐熟有机质含量分别为21.88%、22.92%、22.9%;随着废弃活性焦含量增加有机质的初始含量基本呈增加趋势,BH-50组有机质含量前后变化最大,堆肥产品腐熟完成后有机质含量减少了23.5%,其次为BH-30组和BH-55组减少较多,分别为23.15%、22.97%;BH-35和BH-40的腐熟含量有极显著性差异(P<0.001),BH-40与BH-45腐熟有机质含量无差异,废弃活性焦添加比例在40%~45%之间更加接近NY/T 525—2021标准的要求。
由表1可知不同配比废弃活性焦的6组堆肥产品的总养分含量在5.31%~6.7%之间,由表4可知6组处理的堆肥产品腐熟后总养分含量在3.73%~5.59%之间,除BH-55外其余组均符合有机肥料标准,堆肥产品不同配比影响总养分的变化[35, 41],总养分含量随废弃活性焦的配比增加而减少,其中BH-30的总养分含量最高为5.59%,配比在30%~40%的堆肥产品总养分在5.30%以上,且BH-30、BH-35、BH-40的总养分之间没有显著差异,但与其余处理有极显著性差异(P<0.001)。6组堆肥产品的总氮含量与配比变化不呈比例,BH-50的N最高为1.68%,其次为BH-30与BH-40的N含量接近在1.5%以上,BH-45与BH-55的N含量接近在1.3%左右。总磷含量从废弃活性焦配比为45%的堆肥产品开始显现差异,废弃活性焦配比为30%、35%、40%时堆肥产品P2O5含量在2%以上废弃活性焦配比为45%、50%、55%时P2O5含量均在1.70%以下。由于鸡粪的总钾含量是饱和焦粉的27.4倍,堆肥产品的总钾含量变化主要受鸡粪的影响,因而不同配比废弃活性焦堆肥产品随鸡粪配比的增加而增加。鸡粪的总磷含量是废弃活性焦的8.98倍,堆肥产品的总磷含量也主要受鸡粪配比的影响,堆肥产品的总磷含量随着鸡粪的配比增加而增加反而减少,表4不同配比堆肥产品的总磷和总钾变化也符合这一规律。
6组堆肥产品的重金属含量见表4,各处理的重金属均符合NY/T 525—2021标准的要求。随着废弃活性焦比例的增加,Cr含量基本呈现增加趋势,除BH-30与BH-35含量接近,其他各组均有显著性差异(P<0.05),BH-55的Cr含量最高;Pb含量基本呈现增加趋势,废弃活性焦配比在30%~50%之间的堆肥产品Pb含量接近,BH-55的Pb含量最高;As含量变化接近。
2.3 狗牙根盆栽试验
用狗牙根作为受试植物评估不同配比废弃活性焦堆肥产品对植物生长的影响。由图7(a)可知,不同配比废弃活性焦堆肥产品组的株高均高于CK组,其中BH-45组的株高最高为32.5 cm左右,BH-50组株高最低为22.3 cm左右,与加化肥的处理HF组相比,BH-35、BH-40、BH-45组的株高均显现优势,增长了6.22%~21.86%;与JG组相比,只有BH-45组株高与其接近,其余组株高均极显著低于JG组(P<0.001)。由图7 (b)可知废弃活性焦组的鲜重均高于CK,BH-35组的鲜重最大为18.14 g,其次为BH-40组,除了BH-50与BH-55组以外其余处理组的鲜重均高于HF组,增加了6.40%~26.19%;与JG组相比,废弃活性焦配比在30%~40%的组鲜重均显著高于JG组鲜重(P<0.05),BH-45和BH-50鲜重接近于JG,BH-55组鲜重低于JG。由此可知,不同配比的废弃活性焦堆肥产品没有对植物生长产生负面影响,部分配比可以促进植物的生长效果优于化肥,初步说明添加适量废弃活性焦堆肥产品是可行的。狗牙根的株高和鲜重与不同配比废弃活性焦堆肥产品的总养分含量有一定相关性但不显著,BH-35和BH-40的总养分均在5.3%以上,2个组的鲜重均达到最大,株高虽低于JG组却高于其他对照,虽然BH-30的总养分在5.59%,狗牙根的株高却无优势,但鲜重高于对照处理,BH-45的总养分含量在4.66%,植物的株高优势却最明显,可见总养分含量与植物生长指标之间关联不显著,结合有机质含量变化确定当废弃活性焦配比在40%时产品性质及应用效果较为理想。
3. 结论
1)与秸秆相比,同配比废弃活性焦的添加使鸡粪堆肥产品的pH降低了14.55%,N含量增加了35.85%,腐熟有机质增加了61.76%;与再生焦粉和新焦粉相比,同配比废弃活性焦的添加显著增加了产品的总养分(P<0.05),分别增加了10.41%和31.63%,有机质分别增加了71.63%和64.64%。
2)添加废弃活性焦的鸡粪堆肥产品含水率达到20.21%,pH为7.63,种子发芽指数在81.33%,As、Cr、Pb等重金属的含量属极低,总养分含量为5.41%,均符合有机肥料的标准,有机质含量达到21.88%,废弃活性焦作为掺料与鸡粪制堆肥产品具备可行性。综合废弃活性焦不同配比堆肥产品的养分及有机质指标以及对植物生长指标的影响确定废弃活性焦配比为40%时产品性质和效果更理想。
-
表 1 气象因子与O3-8 h浓度的相关系数
Table 1. The correlation coefficient between meteorological factors and O3-8h concentration
季节Season 平均气温/℃Mean temperature 相对湿度/%Relative humidity 平均风速/(m·s−1)Mean wind speed 降水量/mmPrecipitation 春季 −0.308** 0.102** −0.228** 0.004 夏季 −0.014 0.045** 0.020* −0.001 秋季 −0.269** −0.203** 0.118** −0.050** 冬季 −0.067** −0.241** −0.012 −0.01 全年 −0.235** −0.092** −0.047** −0.021** ** 在0.01级别(双尾),相关性显著. ** At 0.01 level (two-tailed) , the correlation was significant. * 在0.05级别(双尾),相关性显著. * At 0.05 level (two-tailed) , the correlation was significant. 表 2 文昌市后向轨迹聚类统计结果
Table 2. Clustering statistical results of backward trajectory of Wenchang City
聚类Clustering 聚类轨迹占所有轨迹/%Cluster trajectories accounted for all trajectories 到达受体点对应O3小时平均浓度/(μg·m−3)Reaching the receptor site corresponds to the hourly average concentration of O3 超标轨迹占总超标轨迹/%Out-of-standard track accounted for the total out-of-standard track 超标轨迹对应O3小时平均浓度/(μg·m−3) The over-standard trajectory corresponds to the hourly average concentration of O3 2019 年9 月20—29 日 1 15.42 106±35 11.9 137±19 2 27.92 120±34 27 149±17 3 17.92 154±46 22.2 174±26 4 9.17 150±22 14.3 159±12 5 29.58 111±41 24.6 154±18 2021 年1 月4—6 日 1 30.56 126±41 84.6 161±23 2 20.83 98±13 7.7 118±0 3 25 89±16 7.7 119±0 4 16.67 74±12 0 0 5 6.94 90±1 0 0 -
[1] 杨洋, 秦本念. 环境空气中臭氧的污染防治对策研究 [J]. 皮革制作与环保科技, 2021, 2(16): 70-71. YANG Y, QIN B N. Study on prevention and control countermeasures of ozone pollution in ambient air [J]. Leather Manufacture and Environmental Technology, 2021, 2(16): 70-71(in Chinese).
[2] 陈金媛, 郑凯允, 朱俊, 等. 湖州市近地面臭氧污染特征及一次污染过程分析 [J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2021, 49(6): 683-690. CHEN J Y, ZHENG K Y, ZHU J, et al. Analysis on the characteristics of near-surface ozone pollution and a pollution process in Huzhou [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 2021, 49(6): 683-690(in Chinese).
[3] 张秀丽, 陶士康, 董韶妮, 等. 臭氧污染特征及影响因素研究 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2022, 47(2): 47-50,66. ZHANG X L, TAO S K, DONG S N, et al. Study on characteristics and influencing factors of ozone in Yantai [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2022, 47(2): 47-50,66(in Chinese).
[4] 王琰, 杨倩倩. 2019—2020年泰安城区臭氧污染特征分析[J]. 黑龙江环境通报, 2022, 35(1): 12-14, 21. WANG Y, YANG Q Q. Analysis of O3 pollution characteristics in Tai'an urban area from 2019 to 2020[J]. Heilongjiang Environmental Journal, 2022, 35(1): 12-14, 21(in Chinese). (6): 683-690.
[5] 崔梦瑞. 京津冀地区臭氧时空分布特征与影响因素分析[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2020. CUI M R. Analysis of the characteristics and influencing factors of ozone temporal and spatial distribution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2020(in Chinese).
[6] 张青, 宫正宇, 孟晓艳, 等. 成渝地区臭氧污染特征分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(增刊1): 9-11. ZHANG Q, GONG Z Y, MENG X Y, et al. Analysis of ozone pollution in Chengdu-Chongqing region[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(Sup 1): 9-11 (in Chinese).
[7] 孙睿, 张红, 汪水兵, 等. 长三角区域典型城市臭氧时空分布及其与气象因素相关性研究 [J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2021, 16(6): 483-494. SUN R, ZHANG H, WANG S B, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of ozone in typical cities of Yangtze River Delta region and its correlation with meteorological factors [J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2021, 16(6): 483-494(in Chinese).
[8] 赵伟, 高博, 卢清, 等. 2006—2019年珠三角地区臭氧污染趋势 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(1): 97-105. ZHAO W, GAO B, LU Q, et al. Ozone pollution trend in the Pearl River Delta region during 2006-2019 [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(1): 97-105(in Chinese).
[9] 林文鹏, 郭欣瞳. 中国城市群臭氧时空分布特征分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(6): 2481-2494. LIN W P, GUO X T. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of ozone in Urban agglomerations in China [J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(6): 2481-2494(in Chinese).
[10] 徐文帅, 邢巧, 孟鑫鑫, 等. 海口市臭氧污染特征 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2017, 33(4): 186-193. XU W S, XING Q, MENG X X, et al. Characteristics of ozone pollution in Haikou [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2017, 33(4): 186-193(in Chinese).
[11] 谢文晶, 邢巧, 徐文帅, 等. 三亚市臭氧污染特征、输送路径及潜在源区分析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2022, 38(3): 83-95. XIE W J, XING Q, XU W S, et al. Characteristics, transport routes and potential sources of ozone pollution in Sanya [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2022, 38(3): 83-95(in Chinese).
[12] DRAXLER R. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modelling system for trajectories, dispersion, and deposition [J]. Australian Meteorological Magazine, 1998, 47(4): 295-308. [13] ARA BEGUM B, KIM E, JEONG C H, et al. Evaluation of the potential source contribution function using the 2002 Quebec forest fire episode [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(20): 3719-3724. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.03.008 [14] POLISSAR A V, HOPKE P K, HARRIS J M. Source regions for atmospheric aerosol measured at Barrow, Alaska [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(21): 4214-4226. [15] WANG Y Q, ZHANG X Y, ARIMOTO R. The contribution from distant dust sources to the atmospheric particulate matter loadings at XiAn, China during spring [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 368(2/3): 875-883. [16] SHARMA A, MANDAL T K, SHARMA S K, et al. Relationships of surface ozone with its precursors, particulate matter and meteorology over Delhi [J]. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 2017, 74(4): 451-474. doi: 10.1007/s10874-016-9351-7 [17] HSU Y K, HOLSEN T M, HOPKE P K. Comparison of hybrid receptor models to locate PCB sources in Chicago [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2003, 37(4): 545-562. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00886-5 [18] 李刚, 王海林, 伯鑫, 等. 2017年冬季沧州市一次重污染过程PM2.5污染特征及成因 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(8): 2551-2560. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021042204 LI G, WANG H L, BO X, et al. PM2.5 pollution characterization and cause analysis of a heavy pollution event in winter 2017, Cangzhou City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(8): 2551-2560(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021042204
[19] 刘玉红. 中国臭氧污染时空分布特征及影响因素研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2021. LIU Y H. Research on the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of ozone pollution in China[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2021 (in Chinese).
[20] 沈瑞珊, 王琼, 熊险平. 沧州近地面臭氧浓度与气象条件关系 [J]. 环境科学导刊, 2020, 39(5): 50-59. doi: 10.13623/j.cnki.hkdk.2020.05.019 SHEN R S, WANG Q, XIONG X P. Correlation between near-surface ozone concentration and meteorological conditions in Cangzhou [J]. Environmental Science Survey, 2020, 39(5): 50-59(in Chinese). doi: 10.13623/j.cnki.hkdk.2020.05.019
[21] 王文婧, 吴婷, 严云志, 等. 芜湖市臭氧污染现状及其影响因素分析 [J]. 青岛理工大学学报, 2022, 43(1): 85-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4602.2022.01.013 WANG W J, WU T, YAN Y Z, et al. Analysis of ozone pollution and its influencing factors in Wuhu City [J]. Journal of Qingdao University of Technology, 2022, 43(1): 85-92(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4602.2022.01.013
[22] 杨允凌, 郝巨飞, 杨丽娜, 等. 一次连续臭氧污染过程的气象条件分析 [J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(3): 448-456. YANG Y L, HAO J F, YANG L N, et al. Analysis of meteorological conditions of a continuous ozone pollution process in Xingtai of Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(3): 448-456(in Chinese).
[23] 符传博, 徐文帅, 丹利, 等. 前体物与气象因子对海南省臭氧污染的影响 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(7): 45-50. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.07.007 FU C B, XU W S, DAN L, et al. Impacts of precursors and meteorological factors on ozone pollution in Hainan Province [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(7): 45-50(in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.07.007
[24] 郭燕燕. 河北省臭氧污染特征及影响因素分析[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2021. GUO Y Y. Analysis of characteristics and influencing factors of ozone pollution in Hebei Province[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[25] 兰梦迪. 宜春市臭氧污染特征及其影响因素分析 [J]. 河南科技, 2022, 41(9): 114-118. doi: 10.19968/j.cnki.hnkj.1003-5168.2022.09.025 LAN M D. Analysis of ozone pollution characteristics and influencing factors in Yichun city [J]. Henan Science and Technology, 2022, 41(9): 114-118(in Chinese). doi: 10.19968/j.cnki.hnkj.1003-5168.2022.09.025
[26] 赵玉敏. 盐城市大丰区臭氧污染特征及影响因素分析[J]. 绿色科技, 2021, 23(12): 117-119. ZHAO Y M. Analysis of ozone pollution characteristics and influencing factors in Dafeng District of Yancheng City[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2021, 23(12): 117-119 (in Chinese). Science and Technology, 2021, 23(12): 117-119(in Chinese).
[27] 杨云芸, 胡燕, 肖童觉, 等. 湖南省长株潭城市群臭氧分布特征研究及分析 [J]. 灾害学, 2021, 36(2): 97-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.02.017 YANG Y Y, HU Y, XIAO T J, et al. Distribution characteristics of ozone in Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration of Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2021, 36(2): 97-103(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.02.017
[28] 刘怡卉. 我国臭氧污染现状及管控措施建议 [J]. 山东化工, 2021, 50(1): 253-254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2021.01.112 LIU Y H. Present situation of ozone pollution in China and suggestions on control measures [J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(1): 253-254(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2021.01.112
-




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: