-
分子印迹技术(MIT)是一种模拟了酶—底物或者抗原—抗体识别体系,使用特定的化学方法在载体的空间结构和结合位点上构建具有特异性结合特定分子聚合物的方法. 自1993年瑞典Lund大学的Mosbach等[1] 在Nature上研究报道以后,便成为国内外的研究热点. 分子印迹材料(MIPs)具有识别性强、物化性质稳定、制备简便、溶剂消耗量小、可重复使用等优点,在物质分离纯化、仿生传感、药物分析、环境治理等多个领域均具有广阔的应用前景. 分子印迹技术在小分子领域已经趋于成熟,而生物大分子(如蛋白质、多糖和核酸等)具有大分子量和复杂的表面结构等原因,导致其印迹具有很大的挑战性. 传统的MIPs由于具有固液分离复杂、难回收等问题,在发展和应用上受到了一定的限制,而磁性材料具有易回收分离、超顺磁性等特点,将磁性材料引入到MIPs的制备中不仅可以保留其对目标分子的高选择性与高识别性的特性,还可以赋予其超顺磁性,为材料的分离、回收和新性能的应用与拓展提供了可能,因此,磁性分子印迹材料(MMIPs)受到了广泛关注.
本文综述了生物大分子磁性分子印迹材料(BMMIPs)的制备原理及其方法、生物大分子分离领域取得的成就,并对其在生物大分子领域的发展现状及问题进行了阐述,最后讨论了该领域未来发展趋势和存在的挑战.
-
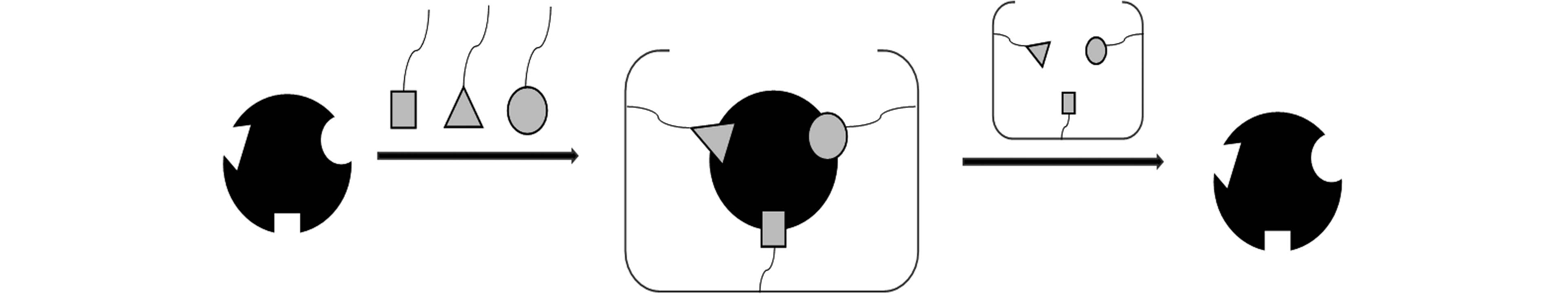
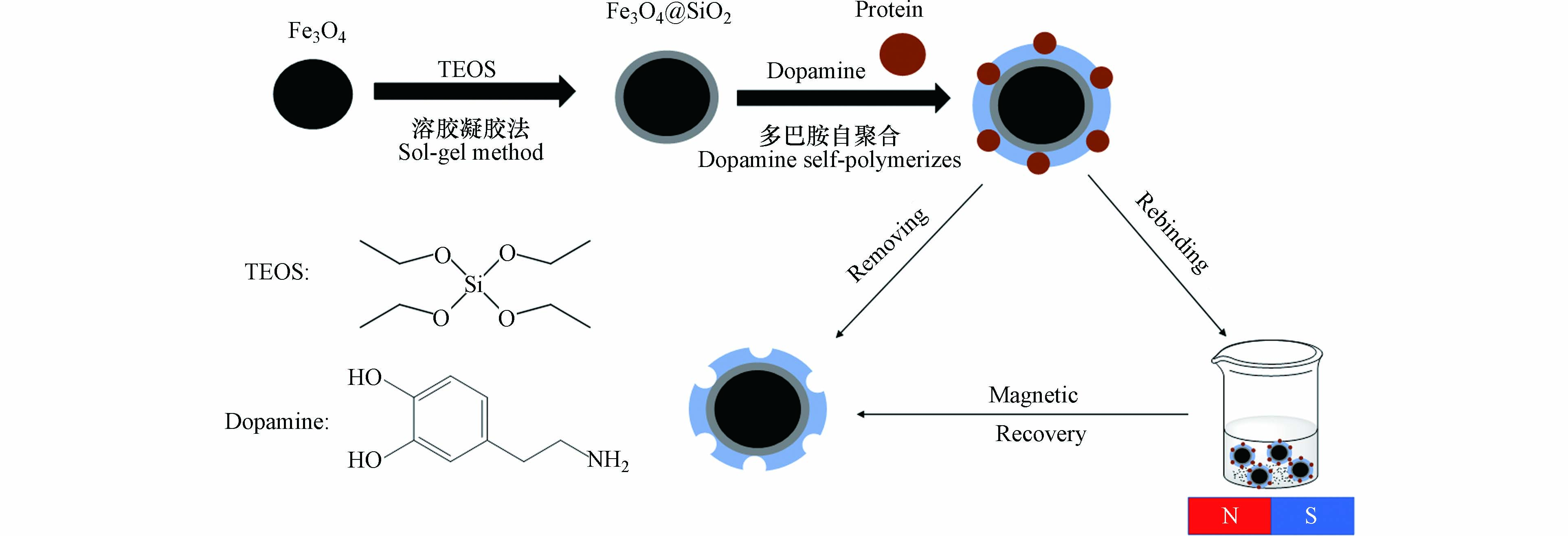
分子印迹技术即用目标分子作为模板分子制备具有印迹腔或结合位点的MIPs;在分子印迹材料上去除模板分子后,会存在与模板分子尺寸结构相匹配、位点互补的孔洞,从而达到对目标分子实现特异性识别的目的. 图1为分子印迹原理示意图.
功能单体与模板分子主要采用非共价结合、共价结合以及半共价结合的结合方式. 由于共价结合较为稳定,模板分子与功能单体之间的存在较强的作用力,不易设计合适的模板-单体复合物且洗脱条件要求较高[2];相反,由于非共价结合的相互作用力较弱,吸附和解离过程容易,大量单体和模板之间可以相互作用,目前多用这种方法制备MIPs;而半共价方法则是结合了以上两种方法的优点,在聚合物制备过程中功能单体与模板分子通过共价作用结合,而在实际应用中通过非共价作用结合 [3]. MIPs由于优良的选择性、稳定性和具有特异性结合等优点,被广泛的应用到复杂环境中的特定分子的分离和富集领域[4].
-
BMMIPs的制备步骤通常包括:(1)功能单体与模板分子通过非共价、共价或者半共价的结合方式形成复合物;(2)反应体系中的交联剂与功能单体发生聚合将模板分子包埋进聚合物内(3)用特定的方法去除包埋在聚合物内的模板分子,之后会留下与模板分子在大小、空间、形状上相匹配的孔穴,在应用的过程中这个孔穴可以与模板分子特异性结合(图2). 与小分子印迹相比,BMMIPs的制备在模板尺寸、合成路线方面要求均更高.
常见的制备MMIPs的方法:
(1)溶胶-凝胶法
这种方法通常选择的前驱体具有较高的化学活性组分,使其在液相中与原料混合均匀后发生水解缩合反应生成透明胶体,之后经过陈化的胶粒聚合形成凝胶,充满凝胶网络间的溶剂失去了流动性,经过干燥或者固化制备出分子印迹材料. 溶胶-凝胶法在磁性粒子表面包覆SiO2无机层是最常用的保护和修饰的方法,例如Jia等[5]利用溶胶-凝胶法在Fe3O4微粒表面包覆二氧化硅涂层,然后通过多巴胺自聚合在其表面印迹了牛血红蛋白用于分离与富集.
(2)自由基聚合法
①沉淀聚合:是反应生成的聚合物不溶于其单体或者反应介质,从而在反应体系中沉淀出来[6]. 蒸馏沉淀聚合是基于在沉淀聚合的方法加以改良[7],通常以乙腈作为溶剂,具有溶剂需求量少、回收率高的特点. ROSSETTI等[8]使用沉淀聚合法以Pro Gastrin特征肽为模板合成分子印迹聚合物用于临床快速检测和提取样本.
②悬浮聚合:悬浮聚合法有正相和反相悬浮聚合[9]. 正相悬浮聚合是以有机相为聚合相,水相为分散相,单体在搅拌和分散剂的作用下分散成小液滴悬浮在分散相,随后加入引发剂使聚合反应发生. 水溶性单体印迹主要采用反向悬浮聚合法,反相悬浮聚合法的聚合相和有分散相分别是水相和有机相. Yu等[10]以牛血清蛋白(BSA)为模板在甲苯中利用悬浮聚合法制备分子印迹聚合物,结合化学发光技术应用于BSA的检测.
③原子转移自由基聚合:氧化还原反应中夺取去引发剂烷基卤化物中的卤原子,使重金属离子被氧化成高价态的金属配合物和烷基自由基. 然后,烷基自由基与单体发生加成反应生成的中间体再从高价态的金属配合物中夺取卤素. 循环上述过程会生成分子量较大的聚合物 [11]. Gai等[12]在水媒介中用此方法合成溶菌酶蛋白(Lyz)磁性分子印迹聚合物可从标准蛋白和混合蛋清中快速分离样品.
④可逆加成断裂链转移聚合:常以二硫代酯及其衍生物用作链转移剂,链转移和链平衡的反应都朝着正方向进行,随着转移试剂对自由基浓度的抑制,极大地降低了终止反应的概率,使得聚合中活性/可控得以实现. Gai等[13]基于可逆加成断裂链转移聚合法在温和的反应条件下印迹BSA磁性分子印迹聚合物用于牛血清蛋白的快速分离.
(3)除上述方法之外还有本体聚合法、乳液聚合法等[14].
传统方法如本体聚合法和悬浮聚合制备MMIPs有诸多问题,如表面结合位点数量少、聚合物主体内的识别位点难以接近、形态不均匀以及会包藏少量单体不利于清除等,特别是生物大分子(如蛋白质,多糖和核酸等)在印迹材料制备上的问题更为突出. 除传统方法外,新近发展起来的有表面印迹、抗原决定基印迹、金属螯合物印迹法以及硼酸亲和法,将在2.2节详细介绍. 这些新方法在一定程度上解决了以生物大分子为模板所引起的洗脱困难、传质速率低等问题,使得分子印迹技术在生物大分子方面的应用取得了快速发展.
-
过去20年中,分子印迹技术作为一种新型的具有高效选择性吸附分离技术在小分子模板的 MMIPs 制备方面取得了巨大成功[15]. 从表1可以看出,以小分子为模板的磁性分子印迹材料印迹因子和选择因子明显高于以生物大分子为模板的分子印迹材料.
与小分子相比,MMIPs在生物大分子方面的发展相对滞后. 其原因可分为以下几个方面:(1)生物大分子难以到达识别位点及脱附再生存在困难;(2)与普通小分子相比生物大分子拥有巨大的分子量,在设计印迹聚合物的过程中要考虑到模板分子的传质能力;(3)其次是分子印迹材料的制备和特异性识别在水相中进行时会存在问题.
-
经过几十年的探索,尤其是新型纳米材料的出现,以及表面分子印迹技术、抗原决定基印迹技术、有机-无机杂化分子印迹技术等制备新方法的发展,使得BMMIPs 的制备和应用有了实质性的突破.
-
新型纳米材料可以提升MIPs的特异性识别. 新型纳米材料作为载体使用时可以减少识别位点包埋现象从而提高MIPs的特异性识别作用,同时又赋予一些传统材料所不具有的特性,例如SiO2纳米颗粒、磁性纳米粒子、石墨烯以及碳纳米管等(表2). 尤其磁性材料由于具有强顺磁性,在外界磁场的作用下很容易将其从复杂环境中分离出来,在提高MIPs分离或识别效果的同时大大简化了制备过程.
磁性纳米材料由于具有高稳定性、大比表面积、小毒性、低成本、易制备等优点,特别是在制备以生物大分子为模板分子的MIPs方面广泛受到研究者的青睐. 以磁性材料为MIPs的载体,结合特异性识别作用和磁性分离特性,便获得一种新型分子印迹材料—MMIPs. 这种新型分子印迹材料结合磁性材料和分子印迹材料的优点,具有高吸附效率、高选择性、操作方便、利于从复杂样品中快速分离等优点 [29]. 并且磁性纳米材料还可以通过表面功能化修饰表现出多重特性,例如Sun等[30]以使用多孔TiO2,合成新型磁性载体Fe3O4@pTiO2,以糖蛋白辣根过氧化物酶为模板分子,制备了适用于弱酸环境的新型的MIPs,以实现较为复杂的生物样本的对低丰度糖蛋白进行快速检测识别与分离. 这项研究证明了以多孔TiO2作为载体可以有效提高了吸附量,并将其适用范围拓宽至弱酸环境,这项研究为磁性分子印迹技术在弱酸环境下快速识别分析生物样品提供了新思路.
-
(1)表面分子印迹技术可以有效克服空间位阻的影响. 表面分子印迹技术使印迹材料与目标分子的识别点位设计在材料表面或近表面,借助这种方式提高传质效率,有效解决了传统方法的空间位阻大、识别效率低、反应速率慢等弊端[31]. 如Yang[18]等运用表面印迹法制备新型BSA表面印迹磁性碳纳米管,具有优良的再生性能,并且在应用于真实样品胎牛血清中时,可以从较复杂的实际样品中有效分离BSA(IF=1.43).
(2)抗原决定基克服物理化学性质不稳定的影响. 抗原决定基印迹法(又称表位印迹法和固定模板法)是模拟抗体会特异性结合抗原某一特征片段而建立起来的方法[32]. 抗原决定基肽段由于其构象与整蛋白质相比更为稳定,且可以通过人工合成获得,这种以抗原决定基肽段作为模板分子的印迹技术使生物大分子模板难获得、构象不稳定的问题得以解决[33]. 如Li等[34]原决定基印迹法以修饰了His-tag的HSA的 C端九肽为模板,利用His-tag与金属镍之间的特异性配位作用,采用多巴胺自聚合反应,制备了能对HAS特异性识别(IF=2.12)的MMIPs,并且由于锚定的His-tag具有良好的亲水性,这种策略可以应用于不同极性的表面位点的印迹.
(3)金属螯合印迹法加强模板分子固定. 金属螯合印迹法普遍以表面具有暴露的氨基酸残基的蛋白质为模板,因螯合作用的强度比非共价结合要强,有利于模板分子固定在载体上. 金属螯合印迹法通过金属螯合单体或目标蛋白暴露的氨基酸与金属离子的相互作用,在交联剂的存在下交联成聚合物,有效解决了模板分子容易脱落的问题. Li等[24]通过Cu2+和螯合敏感单体在37℃下以Lyz为模板分子合成温敏MIPs,这种有效的方法合成的MIPs具有极高的印迹因子(IF=22.7)和较大的比吸附容量.
(4)硼酸亲和法加强对糖类生物大分子的特异性. 硼酸亲和法是利用硼酸共价结合顺式二醇基团可逆的缩合反应生成功能单体和模板的加成物. 当所处条件的溶液pH值大于硼酸分子的pKa值的时候,硼酸基团与糖类或糖蛋白上的顺式二醇基团发生缩合反应,使模板分子固定在载体上. 当溶液的pH值小于硼酸分子的pKa值的时候,复合物发生解离,利于洗脱并富集吸附的模板生物大分子. 但普通的硼酸亲和法限制了BMMIPs对蛋白质类型的应用,Xing等[35]报道了一种可控定向表面印迹的硼酸盐亲和锚定表位印迹法,先将载体表位进行糖化,之后聚合形成印迹层. 这种新型方法克服了硼酸亲和法对蛋白质类型的应用限制,大大推进了生物大分子印迹技术的发展与创新.
新型分子印迹技术的发展可有效克服空间位阻大和物理化学性质不稳定的影响,同时具有强特异性识别能力和良好的机械强度和稳定性,在化学、医学、环境等许多领域都具有良好的应用前景.
-
有机-无机杂化 MMIPs既有无机组分溶胶-凝胶的稳定性、也有有机聚合物的机械强度以及分子印迹选择性的优点,从而赋予MMIPs良好的机械强度和稳定性,并且克服了分子印迹有机与无机聚合物合成复杂的问题,成为了分子印迹发展的新方向,为BMMIPs的制备提供方法学保障.
有机-无机杂化分子印迹技术制备的MMIPs具有许多新优点:①溶胶-凝胶过程操作条件温和;②杂化 MMIPs 主体多孔,一般具有交联度高、化学稳定和热稳定性高的特点;③材料形状可控度高;④通过控制溶胶-凝胶过程,可以控制MMIPs 的孔径和比表面积. 由于有机-无机杂化分子印迹技术制备的MMIPs同时具备有机与无机的机械强度高和耐溶剂性好的优点,现已经成为一种崭新的分子印迹技术.
表3列举了近年一些以生物大分子为模板的MMIPs的应用,可以看出随着新型纳米材料和新型分子印迹技术突破将大大拓宽其在不同范围内的研究与应用,为制备以大生物分子为模板的磁性分子印迹材料提供方法学保障.
-
MMIPs由于其对模板分子具有极高的特异性吸附效果,可用于高效分离纯化蛋白质、多糖、核酸等生物大分子. Fang等[41]以Fe3O4@TiO2作为载体,磷蛋白溶菌酶作为模板分子,聚多巴胺作为聚合物层制备磁性分子印迹纳米颗粒,这种BMMIPs在标准溶液中显示出极低的检测限,在人类血清和尿液中的分离表现出预期的优异性能,显示了其在分离与纯化磷蛋白生物标记物方面的巨大潜力的. Li等[42]以褐藻糖胶和褐藻酸为模板制备了一种双模板磁性分子印迹材料,并用7种类型的深共晶溶剂对材料进行了改性. 结果表明,一种改性后的磁性分子印迹材料对褐藻糖胶和褐藻酸的实际回收率为89.87%和92.0%,实际提取量为20.6 μg·g−1和18.7 μg·g−1,表现出了优异的分离与纯化效果.
-
MMIPs可作为一种临床免疫分析和医疗诊断的新型技术手段还可以作为靶向药物输送的载体等[43]. 如刘振课题组提出的硼亲和可控定向表面印迹技术[44],具有印迹效率高、通透性好、抗干扰和亲和能力强、适用pH范围广等特点,在生物医药、药物识别与检测等方面有良好的应用前景[45]. Zhou等[46]结合表面和表位印迹技术以及抗原决定基技术,以二氧化硅包覆的磁性氧化铁纳米粒子为载体,3-氨基苯硼酸(APBA)为功能单体,在加入引发剂过硫酸铵后,以人免疫球蛋白G为模板,在其表面聚合制备出一种BMMIPs作为探针,构建了一种快速、经济的电化学发光免疫传感器,用于超灵敏检测人类免疫缺陷病毒1型抗体(抗HIV-1). 该方法简单快捷、成本低、灵敏度高,为临床免疫分析提供了一种新方法.
-
MMIPs作为一种性能良好的固相萃取材料可用于复杂环境中痕量物质的监测. 如Tian等[47]在水溶剂中以Fe3O4纳米颗粒为载体,多巴胺为功能单体,β-雌二醇(E2)为模板分子合成了磁性分子印迹纳米球,结果显示,合成的材料对E2具有较强的特异性结合能力,其中吸附量为41.48 mg·g−1,印迹因子高达9.07,可用于环境中痕量物质的灵敏监测. Ming等[48]结合荧光检测技术制备了一种磁性分子印迹材料,结果显示这种BMMIPs可以对水样中的17β-E2达到快速、灵敏检测的目的,检出限为0.03 μmol·L−1,湖泊和河流水样中17β-E2的回收率 范围为98.2%—103.8%,相对标准偏差在1.1%—3.8%之间. 由于方法简单、可靠、可循环使用,为从复杂水体样本中对17β-E2实施监测提供了一个有效的方法.
-
MMIPs可用于复杂环境中特殊污染物的吸附去除. MMIPs已经广泛应用到了复杂环境中抗生素、农药等小分子物质的吸附去除,如Tan等[49]将多巴胺包覆的氧化石墨烯印迹磁性纳米颗粒,应用于海水中氟喹诺酮类抗生素的吸附,去除率可以达到95%以上,用此种方法制备的磁性分子印迹材料可以有效去除水环境中的抗生素. 近年来随着材料和制备技术方面的突破,在复杂环境中生物大分子的吸附去除也表现出了良好的应用潜力. 作者所在课题组利用MMIPs选择性吸附MBR系统中引起膜污染的多糖、蛋白质等生物大分子,有效降低了膜过滤阻力,从而减缓了膜污染进程. 有趣的是,MBR系统中膜污染物质主要为几类特殊的同源性物质,对MMIPs的精确识别性能不如产品分离纯化要求高,只需能选择性吸附这几类同源性物质即可达到延缓膜污染的目的,更为其在膜污染调控方面的应用提供了可能. 并且,磁性材料的引入还可以显著改善环境微生物的生产和代谢活动,同时实现减缓膜污染和提高生物反应运行效能的目的. 如作者所在课题组将磁性材料引入MBR反应器,发现微纳米磁性粒子的磁致效应引起了污泥混合液特性的变化继而减缓膜污染速率[50];同时发现充分的磁化活性污泥预驯化对于提高MBR的临界通量是非常必要的[51-53].
-
MMIPs还可以作为传感器的敏感材料,如Zhang等[54]提出一种新的分子印迹磁性荧光纳米复合传感器的设计和构建策略可用于人尿和蛋清样品中溶菌酶的检测,Liang等[55]用纳米分子印迹聚合物修饰玻碳电极提出了一种选择性、灵敏的溶菌酶电化学检测传感器,可用于生物样品中微量蛋白质的检测. MMIPs还可用于食品安全风险评估[56]、色谱分析[57]等领域.
-
现阶段,MMIPs在生物大分子分离领域的研究和应用中在材料和制备技术方面均取得了诸多突破,但距离商品化应用仍有很长的路要走,面临着诸多困难和挑战:
(1)吸附容量低、功能单体单一:由于MMIPs的一些识别位点常被埋在聚合物的三维结构中使有效印迹位点减少,从而导致吸附容量较低.
(2)对生物大分子(如蛋白质、糖类、病毒等)精确识别困难:生物大分子的尺寸使得交联度和聚合物网络内的转移得以限制,且对pH、离子浓度以及温度和溶剂种类都较敏感,洗脱过程中容易造成损害(特别是蛋白质的变性).
(3)克服现有的水相识别过程中造成的印迹效率降低的问题,如寻找亲水单体、更合适的交联剂等.
磁性分子印迹材料在生物大分子分离方面的研究及应用
Study and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers in the separation of biomacromolecules
-
摘要: 磁性分子印迹材料(MMIPs)具有识别性强、化学和物理稳定性高、生物兼容性好、回收简单、可重复使用等优点,已发展成为高亲和性、高选择性分离小分子物质的重要手段. 生物大分子,如糖类、蛋白质和核酸等,因其传质阻力大、结构复杂,MMIPs在生物大分子分离方面的研究和应用相对滞后. 本文简要介绍了MMIPs技术的原理、制备方法及其在生物医药、环境监测、环境治理等领域的应用现状,并重点综述了MMIPs分离生物大分子方面的最新进展和有待解决的问题,以期为MMIPs在生物大分子分离领域的发展和应用提供参考.Abstract: Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (MMIPs) have been developed as an important method to separate small molecules with high affinity and good selectivity due to their specific recognition, high physical-chemical stability, good biological compatibility, easy recovery and perfect reusability. However, the study and application of MMIPs in the separation of biological macromolecules is behind that of small molecular substances. As the biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides, proteins and nucleic acids, have the high mass transfer resistance and complex structure. In this paper, the principle, the preparation methods and applications of MMIPs are briefly introduced. Following, the latest developments and present problems in the field of biomacromolecule separation by MMIPs are critically reviewed. It is expected to provide references for the development and application of MMIPs in the separation of biological macromolecules.
-
Key words:
- magnetic molecular imprinting polymers /
- biomacromolecules /
- separation /
- protein /
- polysaccharide /
- nanomaterials.
-
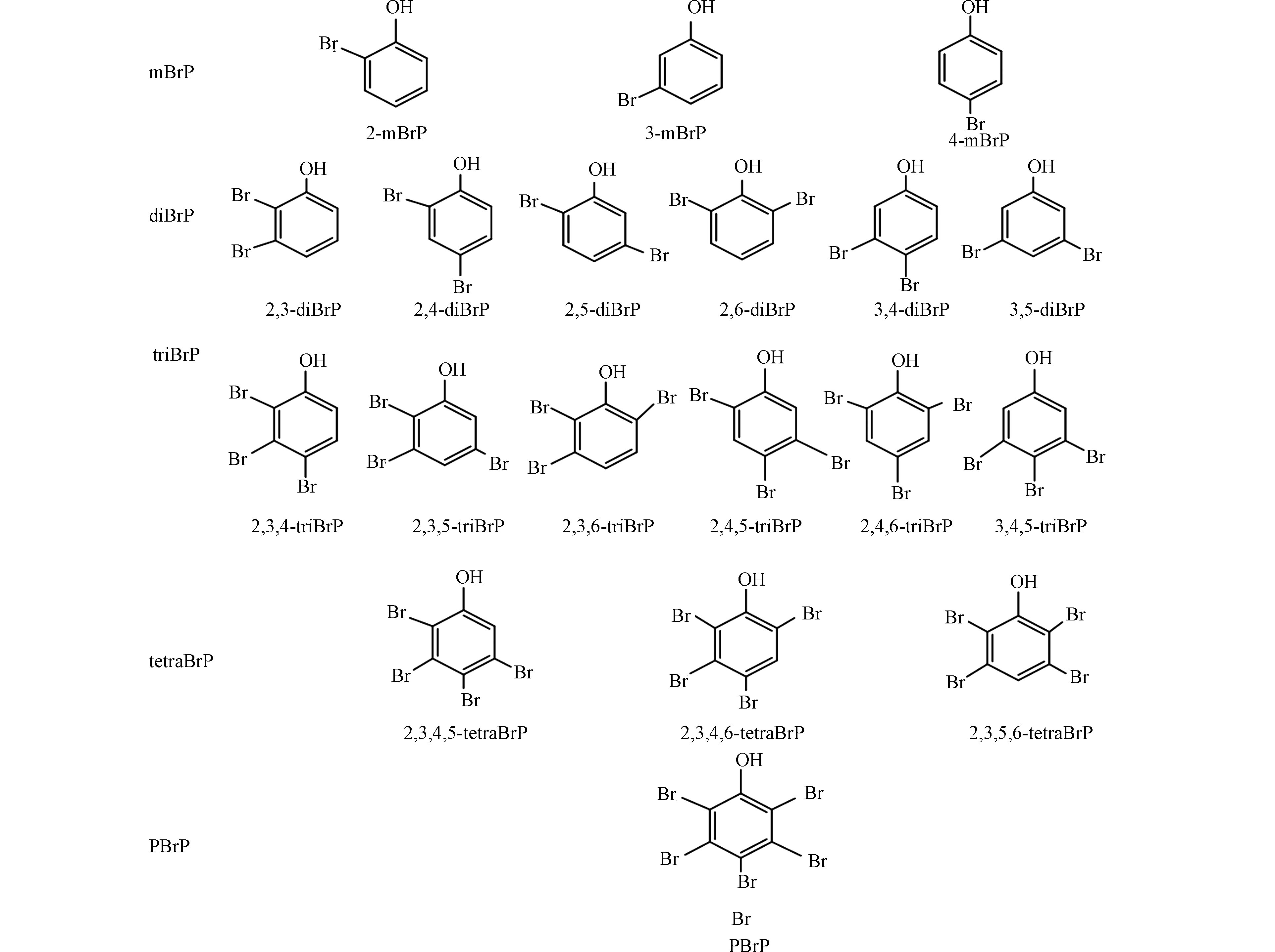
溴酚类化合物(bromophenols,BrPs)不仅具有人为来源,被用作阻燃剂、木材防腐剂等,也具有海洋藻类合成等天然来源,是重要的海洋风味物质[1-2]. 根据苯环上溴原子的取代数目和位置不同,BrPs有19种化合物(图1),在大气、水、土壤、油松树皮及海洋生物等环境样本中均有检出[3-6],甚至在血液和脐带血等人体样本中也有检出[7],电子厂工人血清中检出的BrPs浓度为360 pg·g−1 ww (湿重) [8]. 2,4,6-三溴酚 (2,4,6-bromophenol,2,4,6-triBrP)和五溴酚(pentabromophenol,pBrP)不仅能破坏生物体内甲状腺激素的平衡,也具有显著的抗雌激素效应[9-10]. 因此,BrPs逐渐引起学者们的广泛关注.
海洋中的螺类、贝类和鱼类等动物经摄食藻类可以累积BrPs,经转化等途径也可以将一些人为污染物(如多溴代二苯并二噁英及多溴代二苯并呋喃等)转化为BrPs[11]. 海产品在居民(特别是沿海居民)的膳食结构中占有重要地位,随着人们对健康生活的需求,海产品在膳食中所占的比重呈现显著增加趋势,因此关注海产品质量安全极为必要. 已有研究发现,中国香港市售不同种类海产品中BrPs的含量和分布存在差异[12],但我国其他城市市售海产品中BrPs的赋存情况,特别是海产品中常食用的部位(如贝肉、鱼肉)中BrPs的赋存尚不清晰. 因此,本研究选取9种居民喜食且消费量大的海产品,开展江苏省连云港市海产品中19种BrPs的组织分布及种间差异的研究,为BrPs的生态健康风险和食品安全提供数据支撑.
1. 材料与方法 (Material and methods)
1.1 样品采集和制备
于2021年7月在江苏省连云港市某海鲜市场采集了人们广泛食用、销售量较大的一些海产品,包括双壳类软体动物(牡蛎、紫贻贝和扇贝)、螺类(脉红螺、扁玉螺和花螺)、和鱼类(海鲈鱼、小黄花鱼和金鲳鱼)共9种捕捞的野生海产品. 每种海产品均采集个体大小相近的新鲜样品,在冷藏条件下运回实验室. 贝类和螺类用去离子水清洗后分离去壳,用解剖刀和镊子将每个双壳贝类个体的鳃、外套膜和肉(包含闭壳肌)部分分离,用吸水纸吸干组织表面水分. 由于贝类除鳃和外套膜以外的其他组织以大量贝肉和少量内脏为主,无法将内脏清晰分离,且人们食用这几种贝类通常是净化处理后将贝肉(包括闭壳肌)和内脏团一起食用,因此将内脏合并到贝肉中进行分析和讨论. 螺类样品则分离为螺肉和内脏部分. 为保证足够的样品量并避免个体差异的影响,每种贝与螺的每种组织都由20—35只个体的样品混合而成. 鱼类样品则被分离为鳃、肉和内脏(所有内脏混合在一起)部分,每种组织的样品均由3—4条鱼体的组织混合制备. 每种生物组织的混合样品均进行了准确的质量称量,精确到0.01 g. 随后将所有样品冷冻干燥后用小型粉碎机将其研磨为粉末状固体,密封在棕色玻璃瓶中,置于-20 ℃冰箱中. 海产品个体的干重、湿重等信息详见表1.
表 1 9种海产品的样本数量、组织重量以及含水率.Table 1. Numbers, weights, and the moisture content for the 9 tested seafood samples.种类Species 拉丁名Latin name 数量Quantities 部位Tissues 湿重/gWet weight 干重/gDry weight 含水率/%Moisture content 牡蛎 Crassostrea gigas n=20 鳃 17.0 3.09 81.8 外套膜 20.6 4.49 78.2 肉 91.0 21.0 76.9 扇贝 Patinopecten yessoensis n=30 鳃 23.9 5.96 75.1 外套膜 25.3 6.72 73.4 肉 157 37.7 75.9 紫贻贝 Mytilus edulis n=35 鳃 17.4 3.42 80.3 外套膜 43.8 12.0 72.6 肉 105 22.1 79.0 脉红螺 Rapana venosa n=20 内脏 46.5 14.5 68.9 肉 113 27.4 75.7 花螺 Babylonia areolata n=35 内脏 55.7 18.2 67.2 肉 113 27.4 75.7 扁玉螺 Glossaulax didyma n=35 内脏 99.5 32.4 67.4 肉 200 55.0 72.5 小黄花鱼 Larimichthys crocea n=4 鳃 18.5 6.42 65.3 内脏 67.1 29.2 56.6 鱼肉 553 210 61.9 金鲳鱼 Trachinotus ovatus n=3 鳃 17.8 6.08 65.8 内脏 57.3 35.6 37.8 鱼肉 487 210 57.0 海鲈鱼 Lateolabrax japonicus n=3 鳃 38.4 13.1 66.0 内脏 88.8 58.7 33.9 鱼肉 621 180 70.9 注:湿重、干重、含水率均基于n个个体的混合样品计量. Note:The wet weight, dry weight, and the moisture content were based on the mixed samples of individualities. 1.2 试剂材料
19种BrPs标准物质,包括2-一溴酚(2-monobromophenol, 2-mBrP)、3-一溴酚(3-bromophenol, 3-mBrP)、4-一溴酚(4-bromophenol, 4-mBrP)、2,3-二溴酚(2,3-dibromophenol, 2,3-diBrP)、2,4-二溴酚(2,4-dibromophenol, 2,4-diBrP)、2,5-二溴酚(2,5-dibromophenol, 2,5-diBrP)、2,6-二溴酚(2,6-dibromophenol, 2,6-diBrP)、3,4-二溴酚(3,4-dibromophenol, 3,4-diBrP)、3,5-二溴酚(3,5-dibromophenol, 3,5-diBrP)、2,3,4-三溴酚(2,3,4-tribromophenol, 2,3,4-triBrP)、2,3,5-三溴酚(2,3,5-tribromophenol, 2,3,5- triBrP)、2,3,6-三溴酚(2,3,6-tribromophenol, 2,3,6-triBrP)、2,4,5-三溴酚(2,4,5-tribromophenol, 2,4,5-triBrP)、2,4,6-triBrP、3,4,5-三溴酚(3,4,5-tribromophenol, 3,4,5-triBrP)、2,3,4,5-四溴酚(2,3,4,5-tetrabromophenol, 2,3,4,5-tetraBrP)、2,3,4,6-四溴酚(2,3,4,6-tetrabromophenol, 2,3,4,6-tetraBrP)、2,4,5,6-四溴酚(2,4,5,6-tetrabromophenol, 2,4,5,6-tetraBrP)、pBrP,均购自加拿大Wellington Laboratories. 同位素内标物质13C6-4-mBrP、13C6-2,4-diBrP、13C6-2,4,6-triBrP、13C6-2,3,4,6-tetraBrP 和13C6-pBrP购自美国Cambridge Isotope Laboratories. 以上标准物质纯度均大于95%. 所有标准溶液均保存于棕色毛细管瓶,并放于4℃冰箱中保存. 色谱级甲醇、乙腈、二氯甲烷等有机溶剂均购自J.T. Baker公司. Poly-Sery WAX(500 mg/6 mL, CNW Technologies GmbH) 和醋酸铵购自中国上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司,盐酸购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司.
1.3 样品前处理
前处理方法参照已有文献[13],并依据样品性质进行了微调. 准确称量2.00 g样品置于50 mL离心管中,加入20 mL乙腈:二氯甲烷溶液(1:1, 体积比)和20 μL同位素混合内标(13C6-4-mBrP、13C6-2,4-diBrP、13C6-2,4,6-triBrP,浓度分别为(500 ng·mL−1). 分别经超声(53 kHz,20 min)和振荡 (275 次·min−1,20 min)顺序萃取,以3500 r·min−1速度离心10 min取其上清液. 重复萃取3次,合并的萃取液氮吹至近干,用甲醇复溶后过0.22 μm聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)滤膜,随后用盐酸调节样品pH值至2.0±0.01. 随后用Poly-Sery WAX固相萃取柱(500 mg/6 mL)进行浓缩和净化,萃取柱先用6 mL甲醇和6 mL超纯水预处理,上样后用3 mL超纯水洗去杂质. 再用15 mL甲醇进行洗脱,收集洗脱液置于棕色小瓶中,经氮吹定容至500 μL.
1.4 色谱与质谱条件
本研究采用高效液相色谱-三重四极杆串联质谱仪(HPLC-MS/MS)(Ultimate 3000, Thermo Fisher Science, U.S.;Triple-Quad 5500, AB SCIEX, U.S.)检测19种BrPs.
液相色谱条件:色谱分离柱为 Inertsil ODS-4(150 mm×3.0 mm×2 μm, GL Science, Japan),进样量为 5 μL,柱温控制在40 ℃,流动相为含1 mmol·L−1 醋酸铵的水(A)和含0.1%乙酸的乙腈(B)的混合溶剂,流速为0.3 mL·min−1. 流动相梯度为:0 min,45%B/55%A;15 min,70%B/30%A;20—23 min,80%B/20%A;27 min,60%B/40%A;27.5—30 min,45%B/55%A. 质谱条件:在负离子多反应监测模式下对BrPs进行检测,离子源为电喷雾离子源,温度为500℃,离子化电压为-4500 V,气帘气和喷雾气的流速分别设定为38 psi和50 psi. 不同种BrPs检测的母离子、定量离子、碰撞能和去簇电压见表2.
表 2 不同BrPs的母离子、定量离子、碰撞能和去簇电压Table 2. The precursor and quantitative ion, collision energy, and declustering potential for different BrP congeners.化合物Compounds 母离子(m/z)Precursor ion 定量离子(m/z)Quantitative ion 碰撞能/eVCollision energy 去簇电压/eVDeclustering potential mBrPs 170.8 78.8 −22 −85 172.8 80.8 −22 −85 diBrPs 250.8 78.8 −30 −110 80.8 −30 −110 triBrPs 328.8 78.8 −70 −120 80.8 −70 −120 tetraBrPs 408.6 78.8 −85 −130 80.8 −85 −130 pBrP 488.6 78.8 −82 −130 80.8 −82 −130 13C6−4-mBrP 176.8 78.8 −22 −85 178.8 80.8 −22 −85 13C6−2,4-diBrP 256.8 78.8 −30 −110 80.8 −30 −110 13C6−2,4,6-triBrP 334.9 78.8 −70 −120 80.8 −70 −120 13C6−2,3,4,6-tetraBrP 414.6 78.8 −85 −130 80.8 −85 −130 13C6−PBrP 494.6 78.8 −82 −130 80.8 −82 −130 1.5 海产品个体中BrPs平均含量的计算方法
基于海产品不同组织混合样品的质量与对应组织中BrPs浓度,计算得到每个海产品中不同种类BrPs及∑4BrPs的个体平均含量,公式如下:
海产品个体平均含量=m1×C1+m2×C2+m3×C3+…m1+m2+m3… 其中,m1、m2、m3、…分别代表不同组织混合样品的质量(g),C1、C2、C3、…分别代表对应的不同组织混合样品中BrPs含量(ng·g−1 dw).
1.6 质量控制和质量保证
每10个样品分析一组9点标准曲线(0.1、 0.2、0.5、1.0、2.0、5.0、10.0、20.0、50.0 ng·mL−1,R2>0.995). 用2.00 g色谱纯硅藻土作为空白样品进行相同的全流程提取分析,在程序空白和仪器空白实验中均未检出BrPs. 每个样品均加入10.0 ng 同位素内标物质(20 μL, 500 ng·mL−1),以校正和消除样品前处理及仪器波动的影响. 除2,3,4,5-tetraBrPs回收率为58.8%外,海产品中其他18种BrPs回收率范围为77.1%—105%. BrPs的浓度值以干重计量,方法检出限(3倍噪声)范围为0.0248—32.1 ng·g−1 dw. 为了便于与文献数据进行对比,文献中BrPs含量如果以湿重或脂重计,则通过文献中给出的含水率(若文献中无含水率数据则按照贝、螺、鱼的含水率(80%)计算)或脂肪含量推算为以干重计的BrPs含量.
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 不同海产品中的BrPs
在采集的螺、贝和海鱼样品中,共检出了4种BrPs,分别为4-mBrP、2,4-diBrP、2,6-diBrP和2,4,6-triBrP,在所有海产品各部位样品中的检出率分别为87.5%、54.2%、50.0%和100%,其他15种BrPs在海产品中均未检出. 有研究表明[12, 14],4-mBrP、2,6-diBrP、2,4-diBrP和2,4,6-triBrP是藻类、鱼类、软体动物、甲壳类动物等海洋生物中广泛检出的BrPs,其中以2,4,6-triBrP占比最高,与本研究结果一致. 在多个海产品相关的研究中还检出了2-mBrP、2,3,4-triBrP、2,3,5-triBrP、2,3,6-triBrP、2,4,5-triBrP、2,4,6-triBrP、3,4,5-triBrP、2,3,4,5-tetraBrP、2,3,4,6-tetraBrP、2,3,5,6-tetraBrP、pBrP等其他多种BrPs[15-17],但这些BrPs在本研究中均未检出,这可能与不同种BrPs的来源、环境暴露浓度、累积特性以及海产品种类有关.
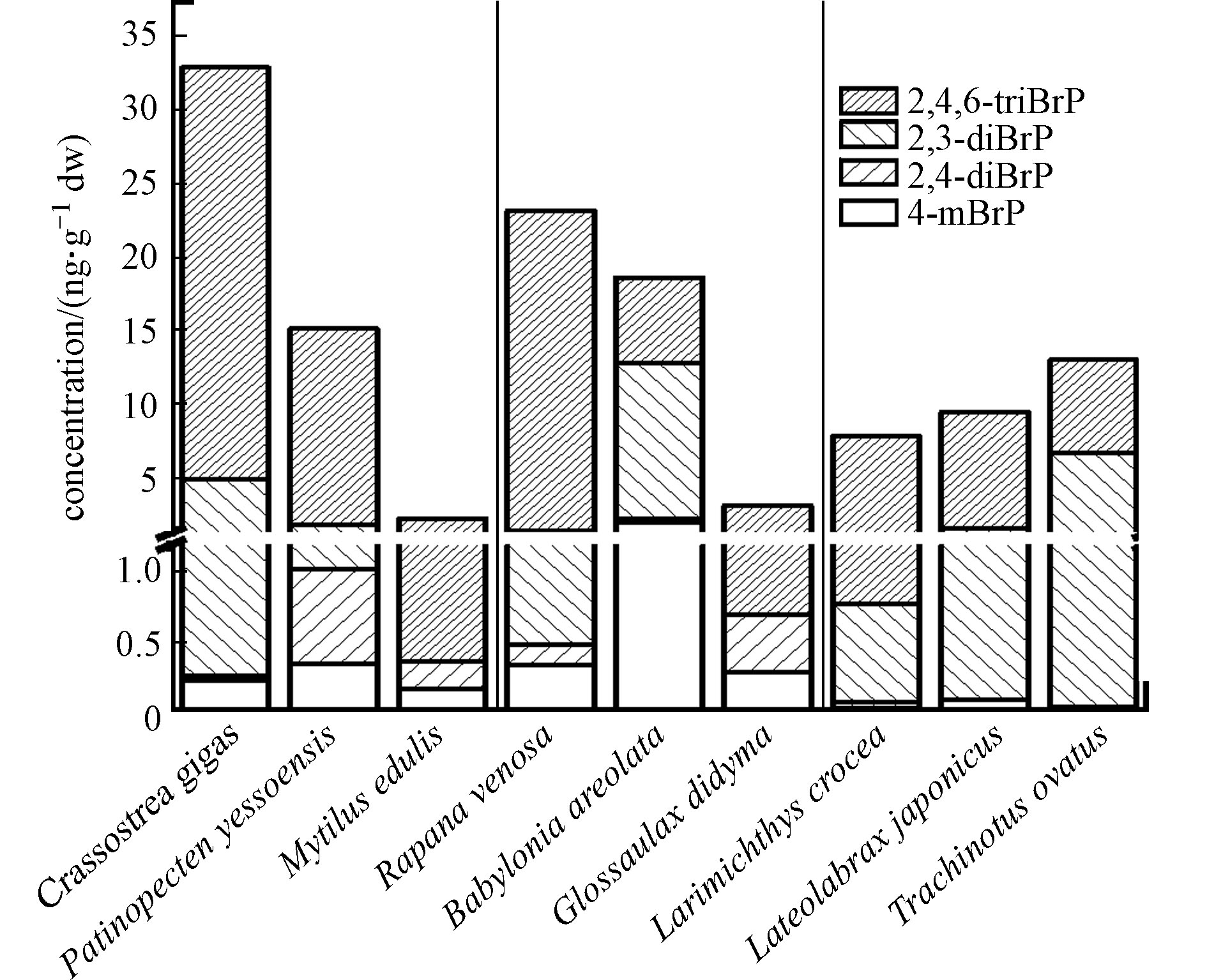
经海产品个体中BrPs含量推算,牡蛎、扇贝、紫贻贝、脉红螺、花螺、扁玉螺、小黄花鱼、海鲈鱼、金鲳鱼中∑4BrPs个体平均含量分别为33.0、15.2、2.25、23.2、18.7、3.11、7.85、9.52、13.0 ng·g−1 dw(图2). 比较不同海产品的含量发现,3种贝类中∑4BrPs、2,4-diBrP、2,4,6-triBrP个体平均含量((16.8±12.6)、(0.304±0.272)、(14.4±10.7) ng·g−1 dw)高于3种螺类((15.0±8.60)、(0.284±0.112)、(10.0±8.43) ng·g−1 dw)和鱼类((10.1±2.17)、(0.0136±0.0193)、(7.10±0.654) ng·g−1 dw),4-mBrP和2,6-diBrP则在螺类((0.863±0.785) ng·g−1 dw和(3.82±4.76) ng·g−1 dw)中高于贝类和鱼类. BrPs在物种间的差异,与生物的习性和生活环境有关,在韩国东南沿海、中国北江等区域的研究显示,BrPs在海洋沉积物中的浓度高于海水[5, 18],因此,贝类样品,特别是牡蛎和扇贝中某些BrPs单体的含量远高于螺类和鱼类,可能与其长期在沉积物中的底栖生活习性相关.
在3种贝类中,牡蛎的∑4BrPs、2,6-diBrP、2,4,6-triBrP个体平均含量最高(33.0、4.70、28.0 ng·g−1 dw),接下来是扇贝(15.2、0.774、13.4 ng·g−1 dw),二者均远高于紫贻贝(2.24、<MDL、1.88 ng·g−1 dw). 扇贝的4-mBrP和2,4-diBrP含量(0.343、0.677 ng·g−1 dw)高于牡蛎(0.221、0.0352 ng·g−1 dw)和紫贻贝(0.161、0.200 ng·g−1 dw). 本研究牡蛎中的溴酚单体4-mBrP、2,4,6-triBrP的个体平均含量高于中国香港地区牡蛎中对应BrPs的含量(<MDL、平均值(8.98±6.82) ng·g−1 dw,范围1.37–18.1 ng·g−1 dw)[12]和美国俄勒冈州州立大学海洋研究站获取的两种牡蛎样品中对应BrPs含量(<MDL、10.0、6.00 ng·g−1 dw)[19];2,6-diBrP处在中等水平,高于中国香港地区牡蛎(平均值(0.858±0.616) ng·g−1 dw,范围0.345—2.18 ng·g−1 dw)[12]低于美国俄勒冈州州立大学海洋研究站的两种牡蛎(含量5.00 ng·g−1 dw和6.00 ng·g−1 dw)[19];但溴酚单体2,4-diBrP的含量远低于中国香港牡蛎(平均值(30.6±18.5) ng·g−1 dw,范围9.8—52.9 ng·g−1 dw)[12]和在美国俄勒冈州的牡蛎(6.00 ng·g−1 dw和6.00 ng·g−1 dw)[19]. 本研究3种贝类中2,4,6-triBrP的个体含量的平均值((14.4±10.7) ng·g−1 dw)远高于在欧洲意大利、丹麦、法国、爱尔兰、西班牙等国家市场上采集的软体动物/甲壳类动物中2,4,6-triBrP的含量(范围0.316—3.73 ng·g−1 dw,数据经文献中脂肪含量换算)[20].
在3种螺类中,∑4BrPs和2,4,6-triBrP的含量按照脉红螺(23.2 ng·g−1 dw和21.8 ng·g−1 dw)、花螺(18.7 ng·g−1 dw和5.85 ng·g−1 dw)、扁玉螺(3.11 ng·g−1 dw和2.41 ng·g−1 dw)依次递减. 花螺中4-mBrP和2,6-diBrP含量(1.97 ng·g−1 dw和10.5 ng·g−1 dw)高于脉红螺(0.337 ng·g−1 dw和0.935 ng·g−1 dw)、扁玉螺(0.278 ng·g−1 dw和<MDL). 与另外3种BrPs不同,2,4-diBrP在扁玉螺中最高为0.419 ng·g−1 dw,接下来依次为花螺(0.288 ng·g−1 dw)和脉红螺(0.144 ng·g−1 dw).
对于3种鱼类,在金鲳鱼中∑4BrPs、2,6-diBrP含量(13.0、6.70 ng·g−1 dw)最高,接下来依次为海鲈鱼(9.52、1.51 ng·g−1 dw)和小黄花鱼(7.85、0.713 ng·g−1 dw). 海鲈鱼中2,4,6-triBrP和4-mBrP含量(7.91 ng·g−1 dw和0.0854 ng·g−1 dw)高于小黄花鱼(7.07 ng·g−1 dw和0.0244 ng·g−1 dw)和金鲳鱼(6.31 ng·g−1 dw和0.0332 ng·g−1 dw). 金鲳鱼和小黄花鱼均为咸水鱼,只能在海洋中生活,而海鲈鱼在海水与淡水中均能生活,因此海鲈鱼还有可能受到淡水生活环境的影响,而2,4,6-triBrP作为人为生产的溴代阻燃剂,往往对流经城市和人类生活区的淡水水体影响更大,这也可能是海鲈鱼体内2,4,6-triBrP含量高的原因.
2.2 三种贝类中BrPs的组织分布
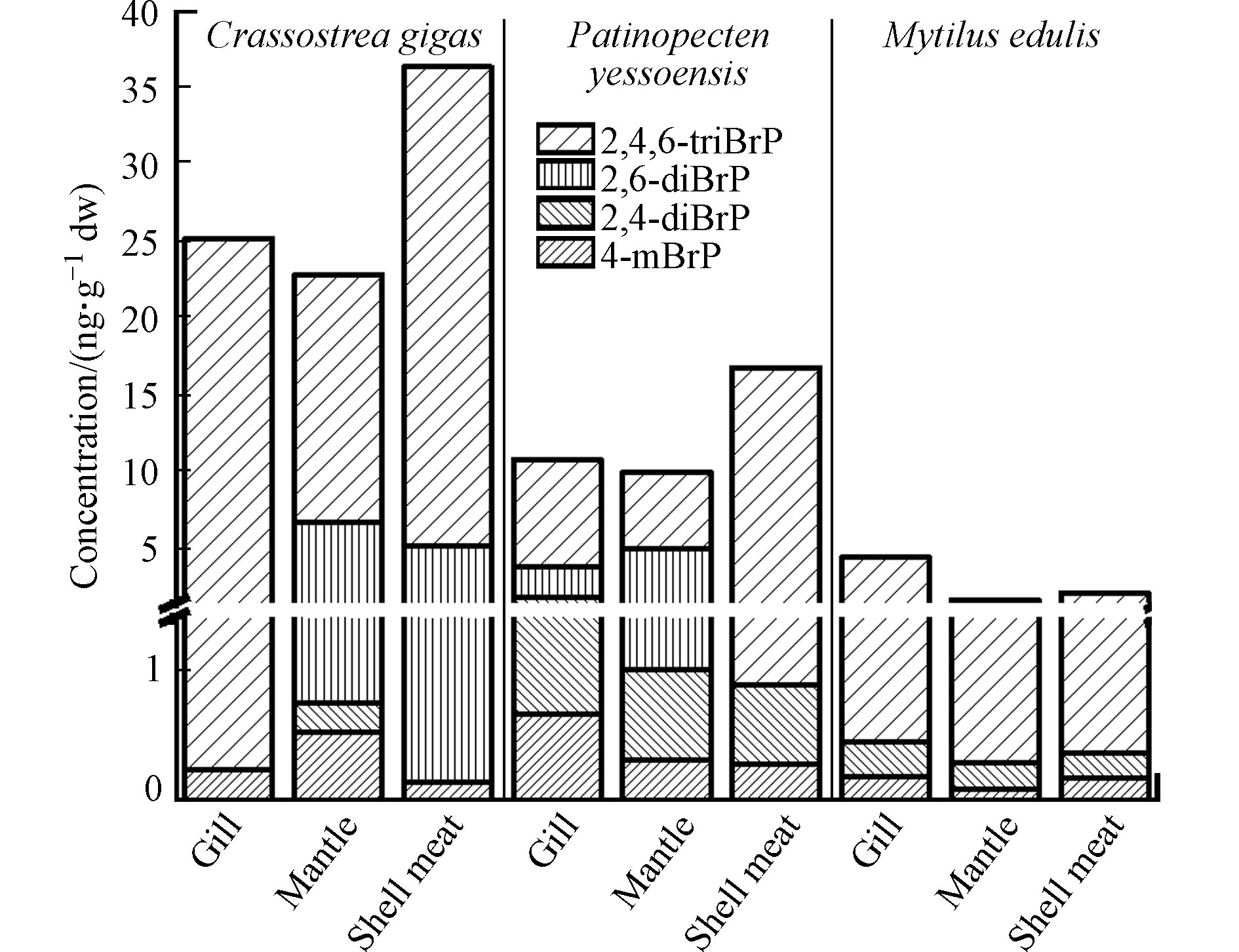
对于紫贻贝,除2,6-diBrP未检出外,检出的BrPs(4-mBrP、2,4-diBrP、2,4,6-triBrP)及∑4BrPs(0.197、0.262、4.00、4.46 ng·g−1 dw)均主要累积在鳃内(图3),高于贝肉(0.187、0.188、1.81、2.19 ng·g−1 dw)和外套膜(0.102、0.204、1.42、1.73 ng·g−1 dw)中对应BrPs的含量. 扇贝鳃中4-mBrP(0.663 ng·g−1 dw)和2,4-diBrP(1.20 ng·g−1 dw)也高于外套膜(0.326 ng·g−1 dw和0.681 ng·g−1 dw)和贝肉(0.295 ng·g−1 dw和0.594 ng·g−1 dw). 这说明鳃也是贝类BrPs暴露及分布的重要组织. 牡蛎和扇贝的贝肉中2,4,6-triBrP(31.0 ng·g−1 dw和15.9 ng·g−1 dw)、∑4BrPs的含量(36.3 ng·g−1 dw 和16.8 ng·g−1 dw)高于鳃和外套膜. 另外,牡蛎与扇贝中2,6-diBrP在外套膜中(6.04 ng·g−1 dw与4.00 ng·g−1 dw)高于鳃和贝肉中含量. 对3种贝类中BrPs的组织分布进行比较,发现紫贻贝各组织中的∑4BrPs均远低于牡蛎和扇贝,BrPs在3种贝类中的组织分布差异与3种贝类不同的生活方式和生长特性有关,牡蛎、扇贝多生活在潮间带、潮下带、低潮带底泥中,而紫贻贝多生活于浅海区附着在岩礁上,从BrPs浓度相对较低的海水中滤食,使其体内BrPs含量相较牡蛎和扇贝要低. 而紫贻贝的外套膜占个体干重的32.0%,远高于牡蛎(15.7%)和扇贝(13.3%). 紫贻贝、牡蛎、扇贝外套膜中∑4BrPs含量分别占对应贝类个体BrPs含量的24.6%、10.9%、8.79%. 由此可见,不同种贝类间相同生物组织在其体重中的占比也影响了BrPs的浓度分布. 整体上,贝类肉中∑4BrPs((18.4±14.0) ng·g−1 dw)高于鳃中((13.5±8.68) ng·g−1 dw)和外套膜((11.5±8.71) ng·g−1 dw).
2.3 三种螺类中BrPs的组织分布
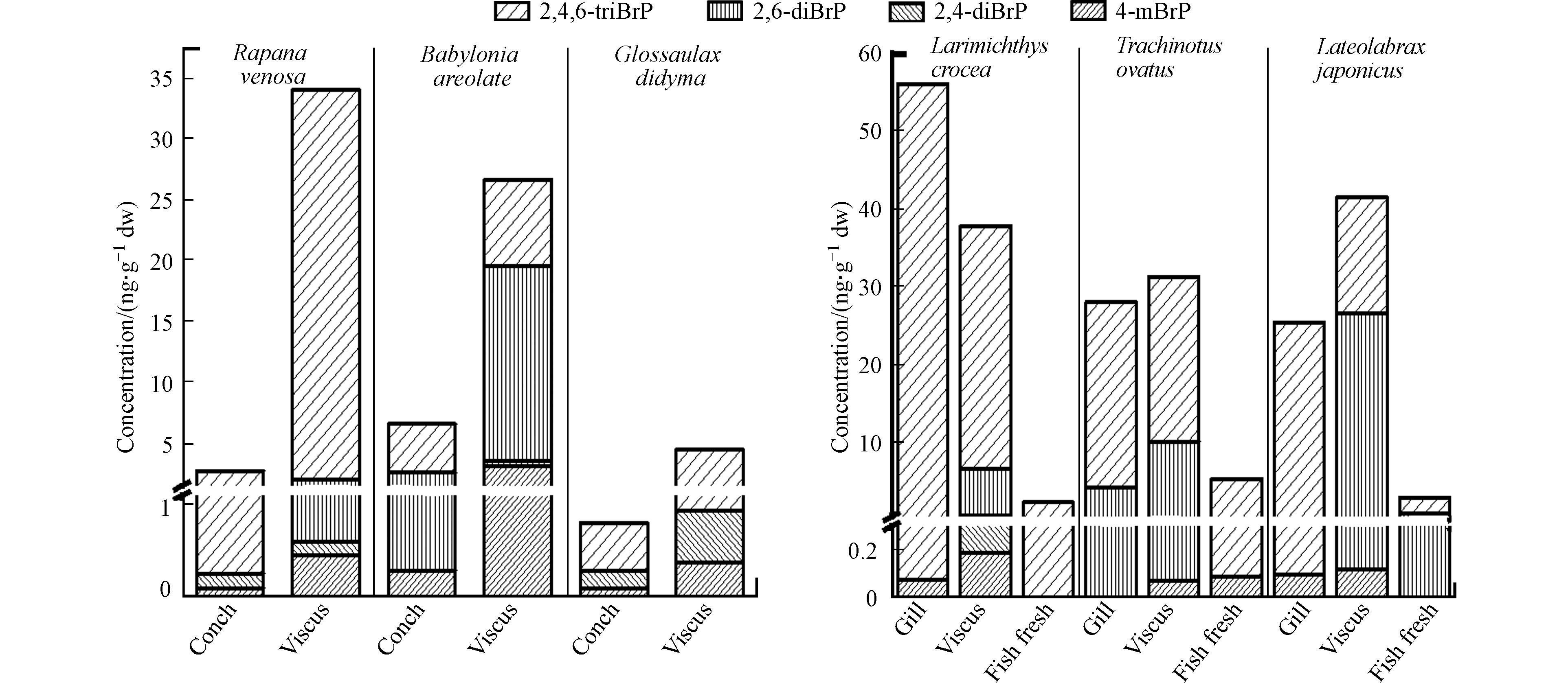
3种螺中各种BrPs及∑4BrPs在内脏中的含量均远高于螺肉中的含量(图4). 3种螺内脏中∑4BrPs平均含量((21.7±12.6) ng·g−1 dw)远高于螺肉((3.37±2.41) ng·g−1 dw). 对于螺肉样品,花螺螺肉中∑4BrPs最高(6.59 ng·g−1 dw)(图4),分别是脉红螺(2.71 ng·g−1 dw)和扁玉螺 (0.806 ng·g−1 dw)的2.43倍和8.18倍. 花螺的螺肉和内脏中4-mBrP、2,6-diBrP、2,4,6-triBrP的含量均高于脉红螺、扁玉螺的对应部位. 2,4-diBrP的最高浓度出现在扁玉螺的螺肉和内脏团中(图4). 3种螺螺肉中∑4BrPs的平均含量((3.37±2.41) ng·g−1 dw,范围0.806—6.59 ng·g−1 dw)远低于3种贝肉的平均含量((18.4±14.0) ng·g−1 dw,范围2.19—36.3 ng·g−1 dw),但花螺和脉红螺螺肉中∑4BrPs的含量则高于紫贻贝贝肉.
2.4 三种鱼体中BrPs的组织分布
如图4所示,小黄花鱼、海鲈鱼和金鲳鱼肉中的∑4BrPs含量(2.21、5.29、2.87 ng·g−1 dw)均远低于内脏(37.8、31.3、41.5 ng·g−1 dw)和鳃中的含量(56.1、28.0、25.4 ng·g−1 dw). 检出率最高的2,4,6-triBrP在鱼体中的最高浓度均出现在3种鱼的鱼鳃(56.0、28.0、25.3 ng·g−1 dw)中. 这说明鳃也是鱼类2,4,6-triBrP暴露与分布的重要组织. 4-mBrP和2,6-diBrP在内脏团中的含量均高于鱼肉和鱼鳃中(图4). 其中金鲳鱼内脏中的2,6-diBrP(26.4 ng·g−1 dw)占∑4BrPs(41.5 ng·g−1 dw)的63.6%,超过了检出率最高的2,4,6-triBrP(15.0 ng·g−1 dw,占比36.1%),这一比例也远高于小黄花鱼和海鲈鱼中2,6-diBrP所占比例(15.9%和31.9%)以及文献中报道的鱼类肠胃中2,6-diBrP所占的比例(0—16.9%)[1, 12]. 2,4-diBrP除在小黄花鱼的内脏团中检出(0.344 ng·g−1 dw)外,在小黄花鱼其他组织、海鲈鱼和金鲳鱼的所有组织中均未发现. 3种鱼中检测到的BrPs的∑4BrPs平均含量在内脏中含量最高为(36.9±4.22) ng·g−1 dw,高于鳃((36.5±13.9) ng·g−1 dw)和鱼肉((3.46±1.32) ng·g−1 dw),与其他研究中发现的内脏含量高于肉中含量的现象是一致的.
本研究的海鲈鱼鱼肉中以2,4,6-triBrP为主要BrPs单体,与文献中同种鱼的检测结果一致,但2,4,6-triBrP的含量(5.20 ng·g−1 dw)高于澳大利亚市场上采集的野生与养殖尖吻鲈鱼鱼肉中的含量(平均值(0.0857±0.0481) ng·g−1 dw,范围<MDL—0.800 ng·g−1 dw,经含水率80%计算)[21],低于在瑞典斯德哥尔摩群岛的Nämdö岛周围采集的鲈鱼鱼肉的含量(平均值(6.59±3.15) ng·g−1 dw,范围:(1.45—10.0) ng·g−1 dw,经含水率80%换算)[22];4-mBrP含量((0.0900) ng·g−1 dw)低于澳大利亚尖吻养殖鲈鱼鱼肉中的含量((0.250) ng·g−1 dw,以鱼肉含水率80%计干重)[21]. 本研究海鲈鱼鱼肉中2,4-diBrP和2,6-diBrP均未检出,但在澳大利亚尖吻野生鲈鱼中均有检出.
与其他种类的鱼相比,本研究3种鱼鱼肉中2,4,6-triBrP含量平均值((3.17±1.44) ng·g−1 dw)低于在中国香港市场上采集的不同季节的河豚与褐斑石斑鱼的鱼肉(平均值(15.6±9.91) ng·g−1 dw,范围(2.43–39.2) ng·g−1 dw)[12]和从美国阿拉斯加、密歇根湖、威斯康星州等地采集的鲑鱼、鲱鱼等鱼肉中2,4,6-triBrP的含量((18.5—166) ng·g−1 dw)[19]. 本研究3种鱼内脏中2,4,6-triBrP含量平均值((22.5±6.72) ng·g−1 dw)也均低于在中国香港的河豚与褐斑石斑鱼(平均值(49.1±50.2) ng·g−1 dw,范围(2.18—155) ng·g−1 dw)[12]和澳大利亚新南威尔士州采集的多种底栖食肉性与杂食性鱼类(平均值(203±264) ng·g−1 dw,范围<MDL—850 ng·g−1 dw,按照含水率80%计算)[23] 内脏中2,4,6-triBrP的含量. 本研究3种鱼类的鱼肉及内脏中BrPs含量低于其他研究1—2个数量级,整体上处在较低水平.
3. 结论(Conclusion)
在贝类、螺类和鱼类的鳃、外套膜、内脏、肉等不同组织中共检出4种BrPs,4-mBrP、2,4-diBrP、2,6-diBrP、2,4,6-triBrP,其中2,4,6-triBrP含量水平和检出率均相对较高,在9种海产品所有组织中的浓度范围为0.512—56.0(平均值:(14.1±13.8) ng·g−1 dw),∑4BrPs的范围为0.806—56.1(平均值:(18.2±15.5) ng·g−1 dw). 3种贝类中∑4BrPs个体平均含量高于3种螺类和鱼类. 3种贝类鳃中∑4BrPs高于外套膜和贝肉. 3种螺的内脏和鳃中∑4BrPs含量平均值远高于螺肉中的含量. 3种鱼内脏中的∑4BrPs含量平均值远高于鳃和鱼肉. 研究证实了BrPs在不同海产品内脏中的高累积,另外鳃也是海产品BrPs暴露及分布的重要组织.
-
表 1 MMIPs研究现状
Table 1. Research status of MMIPs
表 2 新型载体在生物大分子分子印迹上的应用
Table 2. Application of novel carriers in molecular imprinting of biomacromolecules
表 3 以生物大分子为模板的MMIPs应用
Table 3. Application of MMIPs targeting biomacromolecules
-
[1] VLATAKIS G, ANDERSSON L I, MÜLLER R, et al. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting [J]. Nature, 1993, 361(6413): 645-647. doi: 10.1038/361645a0 [2] HU T L, CHEN R, WANG Q, et al. Recent advances and applications of molecularly imprinted polymers in solid-phase extraction for real sample analysis [J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2021, 44(1): 274-309. doi: 10.1002/jssc.202000832 [3] FUCHS Y, SOPPERA O, HAUPT K. Photopolymerization and photostructuring of molecularly imprinted polymers for sensor applications—A review [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2012, 717: 7-20. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.12.026 [4] HUANG C, WANG H W, MA S J, et al. Recent application of molecular imprinting technique in food safety [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2021, 1657: 462579. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462579 [5] JIA X P, XU M L, WANG Y Z, et al. Polydopamine-based molecular imprinting on silica-modified magnetic nanoparticles for recognition and separation of bovine hemoglobin [J]. The Analyst, 2013, 138(2): 651-658. doi: 10.1039/C2AN36313E [6] NGUYEN H T, VUONG BUI N T, KANHOUNNON W G, et al. Co-precipitation polymerization of dual functional monomers and polystyrene-co-divinylbenzene for ciprofloxacin imprinted polymer preparation [J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(54): 34281-34290. doi: 10.1039/D1RA05505D [7] 鹿现永, 黄达, 杨新林, 等. 蒸馏沉淀聚合法制备窄分散聚二乙烯基苯-co-丙烯腈功能聚合物微球 [J]. 高分子学报, 2007(2): 103-107. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3304.2007.02.002 LU X Y, HUANG D, YANG X L, et al. Preparation of monodisperse poly(divinylbenzene-co-acrylonitrile) microspheres by distillation precipitation polymerization [J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2007(2): 103-107(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3304.2007.02.002
[8] ROSSETTI C, ŚWITNICKA-PLAK M A, GRØNHAUG HALVORSEN T, et al. Automated protein biomarker analysis: On-line extraction of clinical samples by molecularly imprinted polymers [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 44298. doi: 10.1038/srep44298 [9] 赖家平, 孙慧, 陈芳, 等. 分子印迹微米微球的合成方法及在固相萃取中的应用研究进展 [J]. 分析测试学报, 2012, 31(9): 1161-1169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2012.09.024 LAI J P, SUN H, CHEN F, et al. Progresses on synthesis methods of molecularly imprinted microspheres and their applications in solid-phase extraction [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2012, 31(9): 1161-1169(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2012.09.024
[10] YU J H, WAN F W, ZHANG C C, et al. Molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres for determination of bovine serum albumin based on flow injection chemiluminescence sensor [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2010, 26(2): 632-637. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.07.009 [11] DADASHI-SILAB S, LORANDI F, FANTIN M, et al. Redox-switchable atom transfer radical polymerization [J]. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(5): 612-615. doi: 10.1039/C8CC09209E [12] GAI Q Q, QU F, LIU Z J, et al. Superparamagnetic lysozyme surface-imprinted polymer prepared by atom transfer radical polymerization and its application for protein separation [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2010, 1217(31): 5035-5042. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2010.06.001 [13] GAI Q Q, QU F, ZHANG T, et al. The preparation of bovine serum albumin surface-imprinted superparamagnetic polymer with the assistance of basic functional monomer and its application for protein separation [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218(22): 3489-3495. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.03.069 [14] FENG Y G, LIU Q, YE L F, et al. Ordered macroporous quercetin molecularly imprinted polymers: Preparation, characterization, and separation performance [J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2017, 40(4): 971-978. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201601011 [15] MOEIN M M. Advancements of chiral molecularly imprinted polymers in separation and sensor fields: A review of the last decade [J]. Talanta, 2021, 224: 121794. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121794 [16] QIN Y P, JIA C, HE X W, et al. Thermosensitive metal chelation dual-template epitope imprinting polymer using distillation-precipitation polymerization for simultaneous recognition of human serum albumin and transferrin [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(10): 9060-9068. [17] QU X, WANG F F, SUN Y, et al. Selective extraction of bioactive glycoprotein in neutral environment through Concanavalin A mediated template immobilization and dopamine surface imprinting [J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(89): 86455-86463. doi: 10.1039/C6RA11040A [18] YANG Z T, WANG J Q, SHAH T, et al. Development of surface imprinted heterogeneous nitrogen-doped magnetic carbon nanotubes as promising materials for protein separation and purification [J]. Talanta, 2021, 224: 121760. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121760 [19] FAN J P, YU J X, YANG X M, et al. Preparation, characterization, and application of multiple stimuli-responsive rattle-type magnetic hollow molecular imprinted poly (ionic liquids) nanospheres (Fe3O4@void@PILMIP) for specific recognition of protein [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 337: 722-732. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.159 [20] KUHN J, AYLAZ G, SARI E, et al. Selective binding of antibiotics using magnetic molecular imprint polymer (MMIP) networks prepared from vinyl-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 387: 121709. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121709 [21] 焦琳娟, 徐先燕, 吴晓莹, 等. 基于SI-ATRP技术制备磁性甲基对硫磷分子印迹聚合物及其吸附性能 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(1): 89-100. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019070503 JIAO L J, XU X Y, WU X Y, et al. Synthesis of methyl-parathion molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-ATRP) and its adsorption properties [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(1): 89-100(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019070503
[22] 张鑫, 李彦松, 汤波, 等. 磁性分子印迹微球的制备及其对熊果酸的选择性分离 [J]. 分析化学, 2021, 49(4): 628-635. doi: 10.19756/j.issn.0253-3820.201603 ZHANG X, LI Y S, TANG B, et al. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted microspheres for selective separation of ursolic acid [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 49(4): 628-635(in Chinese). doi: 10.19756/j.issn.0253-3820.201603
[23] KONG D L, QIAO N, WANG N, et al. Facile preparation of a nano-imprinted polymer on magnetite nanoparticles for the rapid separation of lead ions from aqueous solution [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics:PCCP, 2018, 20(18): 12870-12878. doi: 10.1039/C8CP01163J [24] LI W, SUN Y, YANG C C, et al. Fabrication of surface protein-imprinted nanoparticles using a metal chelating monomer via aqueous precipitation polymerization [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(49): 27188-27196. [25] YANG Z T, YANG K, CUI Y H, et al. Synthesis of surface imprinted polymers based on wrinkled flower-like magnetic graphene microspheres with favorable recognition ability for BSA [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 74: 203-215. [26] WU X, CHEN X M, ZHONG G Q, et al. A novel Wulff-type boronate acid-functionalized magnetic metal-organic framework imprinted polymer for specific recognition of glycoproteins under physiological pH [J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2020, 43(19): 3785-3792. doi: 10.1002/jssc.202000437 [27] ZHAO Y J, CHEN Y J, FANG M Y, et al. Silanized carbon dot-based thermo-sensitive molecularly imprinted fluorescent sensor for bovine hemoglobin detection [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2020, 412(23): 5811-5817. doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-02803-5 [28] HASHEMI M, NAZARI Z. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer based on the magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for selective separation and spectrophotometric determination of melamine in milk samples [J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2018, 69: 98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2018.02.010 [29] LI J Y, WANG Y R, YU X X. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers: Synthesis and applications in the selective extraction of antibiotics [J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 9: 706311. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.706311 [30] SUN X Y, MA R T, SHI Y P. Preparation and analysis of glycoprotein magnetic imprinted particles in weak acid environment [C]. Proceedings of the 22nd National Chromatography Academic Report and Instrument Exhibition of Chinese Chemical Society (Volume 1), 2012: 202-203. [31] DONG C Y, SHI H X, HAN Y R, et al. Molecularly imprinted polymers by the surface imprinting technique [J]. European Polymer Journal, 2021, 145: 110231. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.110231 [32] WANG X D, CHEN G, ZHANG P, et al. Advances in epitope molecularly imprinted polymers for protein detection: A review [J]. Analytical Methods:Advancing Methods and Applications, 2021, 13(14): 1660-1671. [33] 杨开广, 李森武, 刘路宽, 等. 抗原决定基印迹材料及其应用 [J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(13): 1368-1379. doi: 10.1360/N972018-01033 YANG K G, LI S W, LIU L K, et al. Recent advances and application of epitope imprinted materials [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(13): 1368-1379(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N972018-01033
[34] LI S W, YANG K G, LIU J X, et al. Surface-imprinted nanoparticles prepared with a His-tag-anchored epitope as the template [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(9): 4617-4620. doi: 10.1021/ac5047246 [35] XING R R, MA Y Y, WANG Y J, et al. Specific recognition of proteins and peptides via controllable oriented surface imprinting of boronate affinity-anchored epitopes [J]. Chemical Science, 2018, 10(6): 1831-1835. [36] HUANG W, HOU X Y, TONG Y K, et al. Determination of sialic acid in serum samples by dispersive solid-phase extraction based on boronate-affinity magnetic hollow molecularly imprinted polymer sorbent [J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(10): 5394-5401. doi: 10.1039/C9RA00511K [37] LEE M H, LIN C C, THOMAS J L, et al. Epitope recognition of magnetic peptide-imprinted chitosan composite nanoparticles for the extraction of CRISPR/dCas9a proteins from transfected cells [J]. Nanotechnology, 2021, 32(18): 18LT02. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/abde00 [38] BIE Z J, CHEN Y, YE J, et al. Boronate-affinity glycan-oriented surface imprinting: A new strategy to mimic lectins for the recognition of an intact glycoprotein and its characteristic fragments [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(35): 10211-10215. doi: 10.1002/anie.201503066 [39] CHEN G N, SHU H, LU W, et al. A surfactant-mediated Sol-gel method for the preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers and its application in a biomimetic immunoassay for the detection of protein [J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2020, 190: 113511. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113511 [40] CHEN F F, MAO M, WANG J Y, et al. A dual-step immobilization/imprinting approach to prepare magnetic molecular imprinted polymers for selective removal of human serum albumin [J]. Talanta, 2020, 209: 120509. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120509 [41] FANG X W, WANG Z D, SUN N R, et al. Magnetic metal oxide affinity chromatography-based molecularly imprinted approach for effective separation of serous and urinary phosphoprotein biomarker [J]. Talanta, 2021, 226: 122143. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122143 [42] LI G Z, ROW K H. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for recognition and enrichment of polysaccharides from seaweed [J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2017, 40(24): 4765-4772. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201700947 [43] DINC M, ESEN C, MIZAIKOFF B. Recent advances on core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for biomacromolecules [J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 114: 202-217. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.03.008 [44] WANG S S, YE J, BIE Z J, et al. Affinity-tunable specific recognition of glycoproteins via boronate affinity-based controllable oriented surface imprinting [J]. Chemical Science, 2014, 5(3): 1135. doi: 10.1039/c3sc52986j [45] DAR K K, SHAO S N, TAN T W, et al. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective recognition of microorganisms [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 45: 107640. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107640 [46] ZHOU J, GAN N, LI T H, et al. A cost-effective sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of HIV-1 antibody using magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers as capture probes [J]. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2014, 54: 199-206. [47] TIAN X, SONG H J, WANG Y, et al. Hydrophilic magnetic molecularly imprinted nanobeads for efficient enrichment and high performance liquid chromatographic detection of 17beta-estradiol in environmental water samples [J]. Talanta, 2020, 220: 121367. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121367 [48] MING W N, WANG X Y, LU W H, et al. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the fluorescent detection of trace 17β-estradiol in environmental water [J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2017, 238: 1309-1315. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.111 [49] TAN F, LIU M, REN S. Preparation of polydopamine-coated graphene oxide/Fe3O4 imprinted nanoparticles for selective removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in water [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 5735. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06303-y [50] 张王超, 郭洪成, 郭冀峰, 等. 微纳米磁性粒子对膜生物反应器运行效能的影响 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(10): 2719-2727. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201910144 ZHANG W C, GUO H C, GUO J F, et al. Effect of magnetic microparticles and nanoparticles on the performance of membrane bioreactor [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(10): 2719-2727(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201910144
[51] GUO H C, HU J J, LI J X, et al. Systematic insight into the short-term and long-term effects of magnetic microparticles and nanoparticles on critical flux in membrane bioreactors [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 582: 284-288. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2019.04.015 [52] LIU Y, LIU Q, LI J X, et al. Effect of magnetic powder on membrane fouling mitigation and microbial community/composition in membrane bioreactors (MBRs) for municipal wastewater treatment [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 249: 377-385. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.027 [53] LIU Y, LI J X, GUO W S, et al. Use of magnetic powder to effectively improve the performance of sequencing batch reactors (SBRs) in municipal wastewater treatment [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 248: 135-139. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.069 [54] ZHANG X, TANG B, LI Y S, et al. Molecularly imprinted magnetic fluorescent nanocomposite-based sensor for selective detection of lysozyme [J]. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 11(6): 1575. doi: 10.3390/nano11061575 [55] LIANG A X, TANG B, HOU H P, et al. A novel CuFe2O4 nanospheres molecularly imprinted polymers modified electrochemical sensor for lysozyme determination [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 853: 113465. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113465 [56] LI H H, AHMAD W, RONG Y W, et al. Designing an aptamer based magnetic and upconversion nanoparticles conjugated fluorescence sensor for screening Escherichia coli in food [J]. Food Control, 2020, 107: 106761. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.106761 [57] ARABI M, OSTOVAN A, BAGHERI A R, et al. Strategies of molecular imprinting-based solid-phase extraction prior to chromatographic analysis [J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 128: 115923. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.115923 -






 下载:
下载: