-
挥发性有机物(volatile organic compounds, VOCs)是一类备受关注的气态污染物,严重危害着环境和人体健康[1]. 催化燃烧法是目前最常用的VOCs治理技术之一,具有去除效率高、运行费用低、二次污染少等优点. 贵金属具有优异的催化氧化VOCs的活性[2],但价格昂贵、稳定性较差,因此研究者们将目光转向非贵金属. 其中,过渡金属锰价态丰富,氧传递性好,在VOCs催化燃烧领域具有良好的应用前景[3-5]. Jung等[6]发现,煅烧温度会影响MnOx/γ-Al2O3表面吸附氧的比例,相比于500 ℃和700 ℃,900 ℃下煅烧制备的Mn/Al(900)的表面吸附氧比例最高,催化氧化甲苯的活性也最强(T90≈325 ℃, WHSV= 30000 mL·g−1·h−1);Huang等[7]探究了负载量对MnOx/HZSM-5催化氧化甲苯活性的影响,发现锰负载量为10%的MnOx/HZSM-5活性最佳(T90=267 ℃, WHSV = 15000 mL·g−1·h−1);本课题组[8]发现,增大载体孔径可提升MnOx/MCM-41催化氧化甲苯的活性,以孔径4.64 nm的MCM-41制备的MnOx/M3活性最高(T90=335 ℃, WHSV= 50000 mL·g−1·h−1).
相比于传统的水溶液浸渍法,合适地改变浸渍液溶剂可以改善催化剂性能. Tian等[9-10]和Xie等[11]分别用乙醇浸渍法和乙二醇辅助浸渍法将镍负载于介孔分子筛孔道内,大大提高了镍的分散度,从而改善了催化剂活性和稳定性. 但是,关于浸渍液溶剂对负载型锰基催化剂的结构及催化氧化VOCs性能的影响研究较少.
本文以MCM-41为载体,采用等体积浸渍法制备负载型催化剂MnOx/MCM-41,探究浸渍液溶剂(水、乙醇和乙二醇)对MnOx/MCM-41的结构及其催化氧化甲苯的性能的影响,并借助XRD、TEM、H2-TPR、O2-TPD和XPS等表征手段,探讨催化剂的构效关系.
-
将4.3735 g十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)溶于40 mL纯水中,再加入10 mL四甲基氢氧化铵溶液(TMAOH,25%),然后在剧烈搅拌下缓慢加入6 g二氧化硅(Aerosil 200). 室温下搅拌0.5 h后,将混合物倒入带有聚四氟乙烯内胆的反应釜中,150 ℃下水热反应166 h;之后取出产物,过滤、洗涤,80 ℃下干燥12 h,最后以2 ℃·min−1的速率升温至550 ℃,煅烧6 h.
-
水溶液或乙醇溶液浸渍法:将0.7232 g硝酸锰溶液(50%)溶于2.5 mL纯水或乙醇中,然后逐滴滴入1 g MCM-41中,MCM-41已事先在120 ℃下真空干燥了4 h;将混合物在室温下静置12 h后移入烘箱,100 ℃干燥12 h,最后以2 ℃·min−1升温至400 ℃,煅烧6 h. 催化剂记作MnOx/M-W或MnOx/M-ET.
乙二醇共浸渍法:将0.7232 g硝酸锰溶液溶(50%)和0.1254 g乙二醇(Mn2+与乙二醇的物质的量比为1:1)溶于2.5 mL纯水中,然后逐滴滴入1 g MCM-41中,MCM-41已事先在120 ℃下真空干燥了4 h,将混合物在室温下静置12 h后,移入烘箱,100 ℃干燥12 h,最后以2 ℃·min−1升温至400 ℃,煅烧6 h. 此催化剂记作MnOx/M-EG.
-
X射线衍射(XRD):在德国Bruker公司的D8 Advance X射线衍射仪上进行. 射线源为Cu Kα (λ=0.15406 nm,工作电压40 kV,电流40 mV. 小角度XRD扫描范围为2θ=1°—6°,步长0.01°,步速0.3 s·step−1. 广角XRD扫描范围为2θ=10°—80°,步长0.02°,步速0.1 s·step−1.
氮气吸附-脱附:在美国Micromeritics公司的TriStar Ⅱ物理吸附仪上进行. 测试前样品先在200 ℃下真空脱气4 h,在77 K恒温下进行测试. 分别采用BET法和BJH法计算样品的比表面积和孔径.
透射电子显微镜(TEM):在日本JEOL公司的JEM 2100plus型透射电子显微镜上进行. 取少量样品置于乙醇中,超声分散后滴加在铜网上,烘干后放入仪器进行观测.
氢气程序升温还原(H2-TPR):在标准型化学吸附仪Vdsorb-91i上进行:首先称取80 mg催化剂置于U型石英管内,通入氦气(30 mL·min−1),以10 ℃·min−1的速率升温至300 ℃,持续吹扫1 h;待温度降至室温后,将气氛切换为H2/Ar(5%,30 mL·min−1)的,然后以10 ℃·min−1的速率从室温升至700 ℃. 信号值由热导池(TCD)检测器记录.
氧气程序升温脱附(O2-TPD):在标准型化学吸附仪Vdsorb-91i上进行:首先称取80 mg催化剂置于U型石英管内,通入氦气(30 mL·min−1),以10 ℃·min−1的速率升温至300 ℃持续吹扫1 h;待温度降至室温后,将气氛切换为的O2/He(5%,30 mL·min−1),并持续通入2 h;然后再将气氛改为氦气(30 mL·min−1),继续吹扫0.5 h;最后以10 ℃·min−1的速率从室温升至800 ℃. 信号值由热导池(TCD)检测器记录.
X射线光电子能谱(XPS):测试机型为PHI 5000,用Al Kα(hv=1486.8 eV)作为激发光源,所得能谱经C 1s=284.6 eV进行校准,谱图使用MultiPak软件进行分峰拟合.
傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR):测试机型为美国Perkin-Elmer公司的Frontier红外光谱仪,测试参数为:扫描范围为650—4000 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描次数为32次.
原位红外(in situ DRIFTS):用来检测催化剂表面吸附物质的变化,原位反应池型号为美国Harrick Scientific公司的DRK-4. 测试步骤为:将粉末状催化剂填入原位反应池后,通入氮气(50 mL·min−1),以10 ℃·min−1的速率升至300 ℃持续吹扫1 h;待温度降至室温后,采集背景值,然后升至反应温度,气氛切换为甲苯反应气(3700 mg·m−3,79%N2+21%O2,50 mL·min−1),持续反应1 h,每10 min采1次样,测试参数与FTIR一致.
原子吸收光谱(AAS):测试机型为Thermo Fisher公司的iCE 3500型原子吸收光谱仪. 催化剂经消解、稀释、定容后,进入仪器进行检测.
-
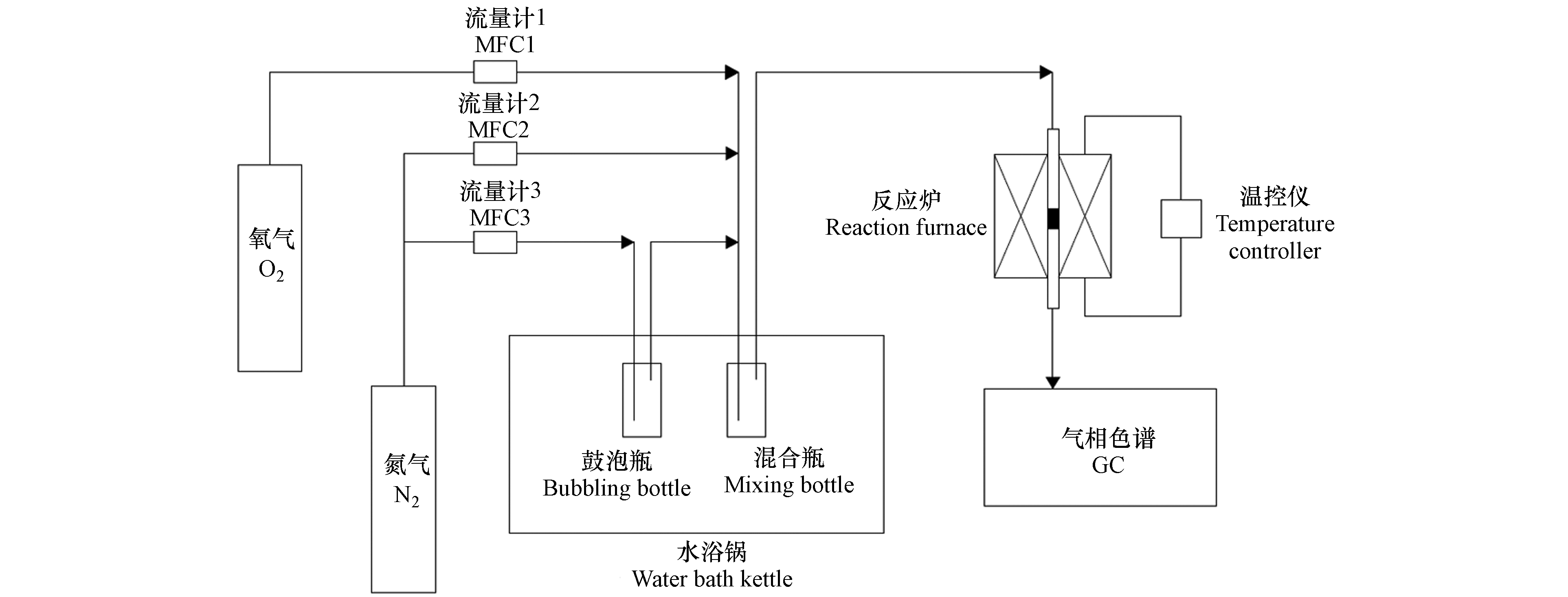
催化剂活性评价在固定床石英反应器(内径6 mm)中进行,活性评价装置流程如图1所示. 测试条件为:总气量100 mL·min−1 (79%N2+21%O2),30 ℃恒温条件下,氮气鼓泡法制得甲苯浓度为3700 mg·m−3,催化剂用量为0.12 g(40—60目),质量空速为50000 mL·g−1·h−1,体积空速为21200 h−1.
反应器出口气体由自动进样器注入气相色谱(GC9890,俊齐仪器设备(上海)有限公司)分析其成分及浓度,气相色谱分析条件为:毛细管柱型号:SE-54;填充柱型号:TDX-01;柱箱温度:120 ℃;进样器温度:120 ℃;甲烷转化炉温度:350 ℃;FID检测器温度:250 ℃.
甲苯转化率X由式(1)计算.
式中,Tin为进口甲苯浓度(mg·L−1),Tout为出口甲苯浓度(mg·L−1).
-
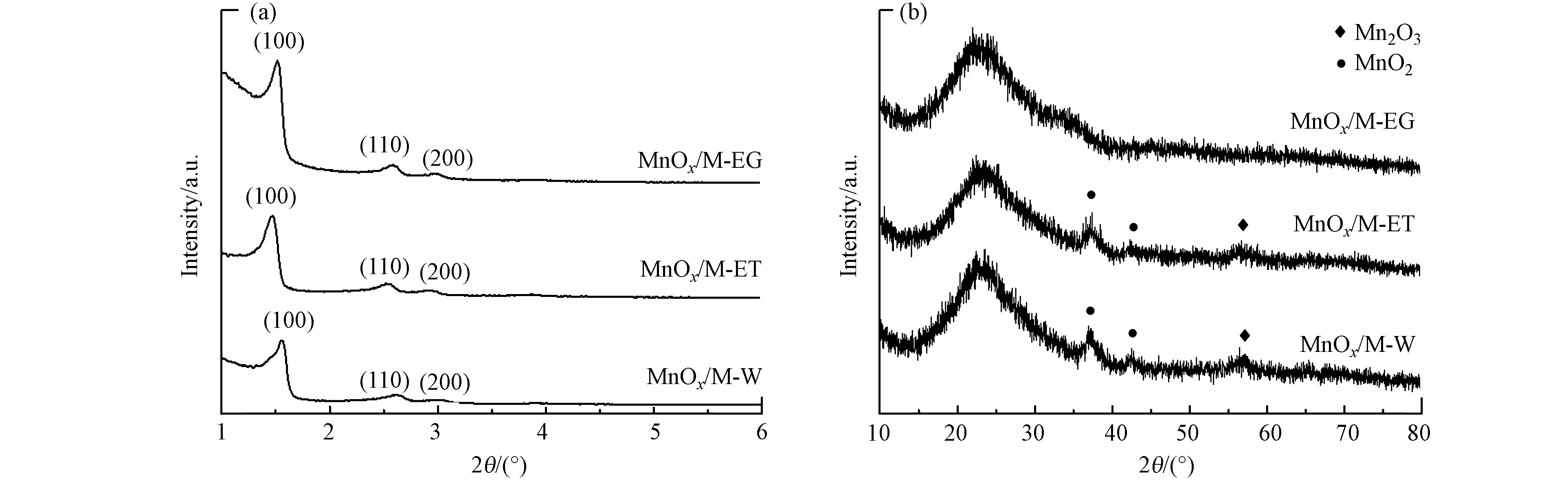
图2为3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的XRD谱图. 如图2(a)所示,3种催化剂中,载体MCM-41的(100)、(110)和(200)晶面衍射峰在小角度XRD谱图上清晰可见,表明催化剂具有良好的有序介孔结构;3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的广角XRD谱图如图2(b)所示,MnOx/M-W和MnOx/M-ET在2θ=57°处出现了Mn2O3的衍射峰,在2θ=36°和43°处出现了MnO2的衍射峰[12],而MnOx/M-EG上没有出现明显的锰氧化物特征衍射峰,表明MnOx/M-EG上的锰氧化物粒径较小,高度分散[13].
-
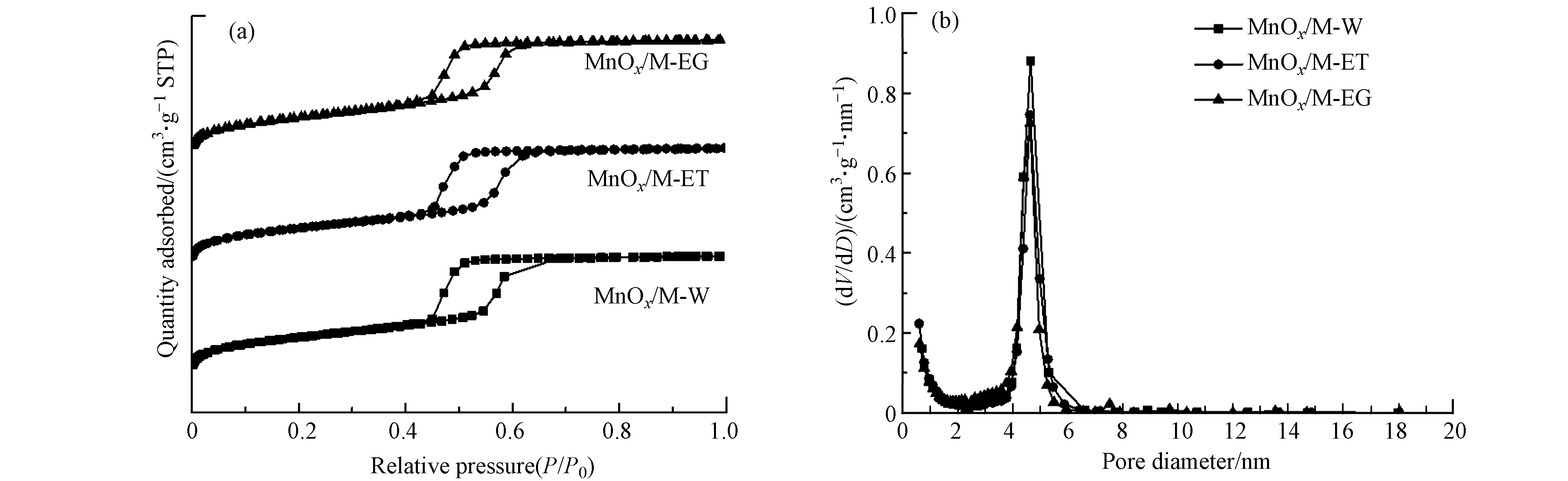
图3(a)为3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的氮气吸附-脱附等温线,3种催化剂的等温线都为Ⅳ型,具有H1型迟滞环,表明催化剂具有介孔结构;如图3(b)所示,3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的孔径分布窄,表明负载锰氧化物后,载体结构依然高度有序,这与小角XRD结果一致. 3种催化剂的孔结构参数如表1所示,相比于载体MCM-41,负载锰氧化物后,3种催化剂的比表面积、孔容和平均孔径皆有所减少;其中,MnOx/M-EG的孔容和平均孔径分别为0.71 cm3·g−1和4.35 nm,均为3种催化剂中最低,可能是由于更多的小粒径锰氧化物颗粒进入载体孔道. MnOx/M-W和MnOx/M-ET中的锰组分则主要负载于MCM-41外表面,并在制备过程中逐渐聚集,最终形成较大的锰氧化物颗粒,广角XRD结果可以印证这一点.
-
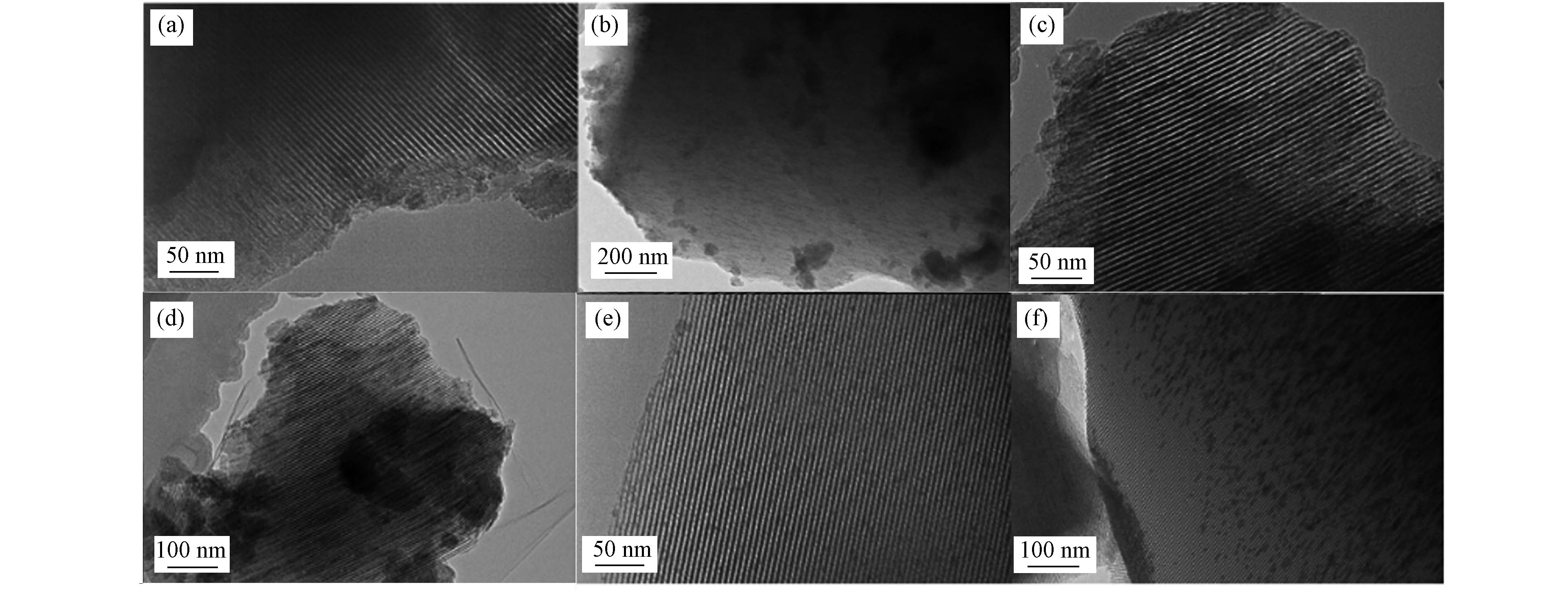
图4为3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的TEM图. 3种催化剂中,载体MCM-41的有序介孔结构清晰可见,这与小角XRD结果一致. MnOx/M-W和MnOx/M-ET上可见不少较大粒径的锰氧化物颗粒,而MnOx/M-EG中的锰氧化物颗粒较小,粒度均一,分散度高. 此结果与广角XRD结果一致,表明乙二醇共浸渍法可改善锰氧化物在MCM-41上的分散性.
MCM-41表面含有丰富的硅羟基,硅羟基主要有孤立的硅羟基、偕羟基和氢键相连的硅羟基3种[14],金属前体物与由氢键连接的硅羟基作用往往会形成较大的金属颗粒,而与孤立的硅羟基作用可形成较小的金属颗粒[15]. Lv等[16]利用傅里叶变换红外吸收光谱对比了经过乙二醇预处理和不经过乙二醇预处理的SiO2的表面性质,发现经过预处理的SiO2表面上由氢键连接的硅羟基含量下降,因此制备的Ni/SiO2中金属分散度更高. 与水溶液和乙醇溶液浸渍法相比,乙二醇共浸渍法干燥过程中浓缩液的较低表面张力和较高黏度,可有效避免锰前体的重新分布和附聚,使得煅烧后的锰氧化物高度分散,并呈窄粒度分布[17].
-
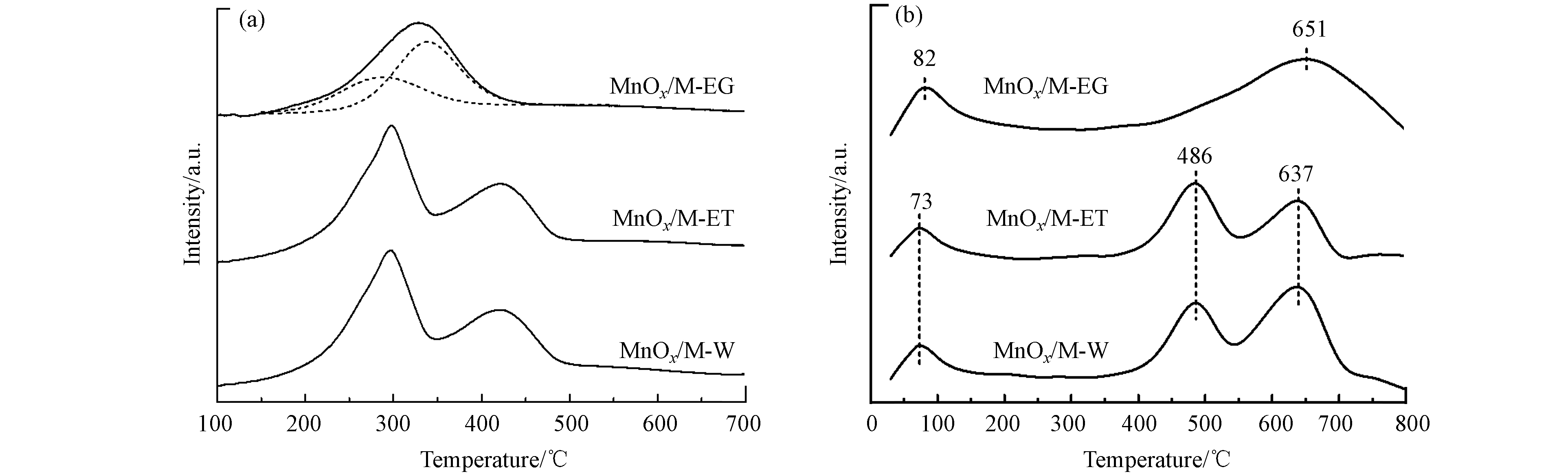
3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的H2-TPR和O2-TPD结果如图5所示. MnOx/M-W和MnOx/M-ET的H2-TPR和O2-TPD谱图极为相似,MnOx/M-EG的则明显不同,说明乙二醇显著改变了锰氧化物的还原性质和表面氧物种性质.
MnOx/M-W和MnOx/M-ET在297 ℃处出现了归属Mn4+→Mn3+的还原峰,在421 ℃处出现了归属Mn3+→Mn2+的还原峰[18-19]. MnOx/M-EG的谱图中只出现了一个还原峰,但通过分峰拟合发现,此峰是由分别位于286 ℃处和339 ℃处的还原峰叠加形成,前者代表Mn4+→Mn3+还原过程,后者代表Mn3+→Mn2+还原过程. 如表2所示,MnOx/M-EG的还原峰温度低于MnOx/M-W和MnOx/M-ET,表明具有最强的氧化还原性. MnOx/M-W、MnOx/M-ET和MnOx/M-EG的总耗H2量分别为1.14、1.11 、0.76 mmol·g−1,表明MnOx/M-W、MnOx/M-ET和MnOx/M-EG中锰元素平均氧化态依次下降.
MnOx/M-W和MnOx/M-ET在73 ℃处出现吸附氧的脱附峰,在486 ℃处和637 ℃处出现晶格氧的脱附峰. Mn/M3-EG的谱图中只出现了两个脱附峰,分别为82 ℃处的吸附氧脱附峰和651 ℃处晶格氧的脱附峰[20]. 如表2所示,MnOx/M-W、MnOx/M-ET和MnOx/M-EG的吸附氧与晶格氧比例(Oads/Olat)分别为0.18、0.21和0.25,表明MnOx/M-EG中吸附氧比例最高.
-
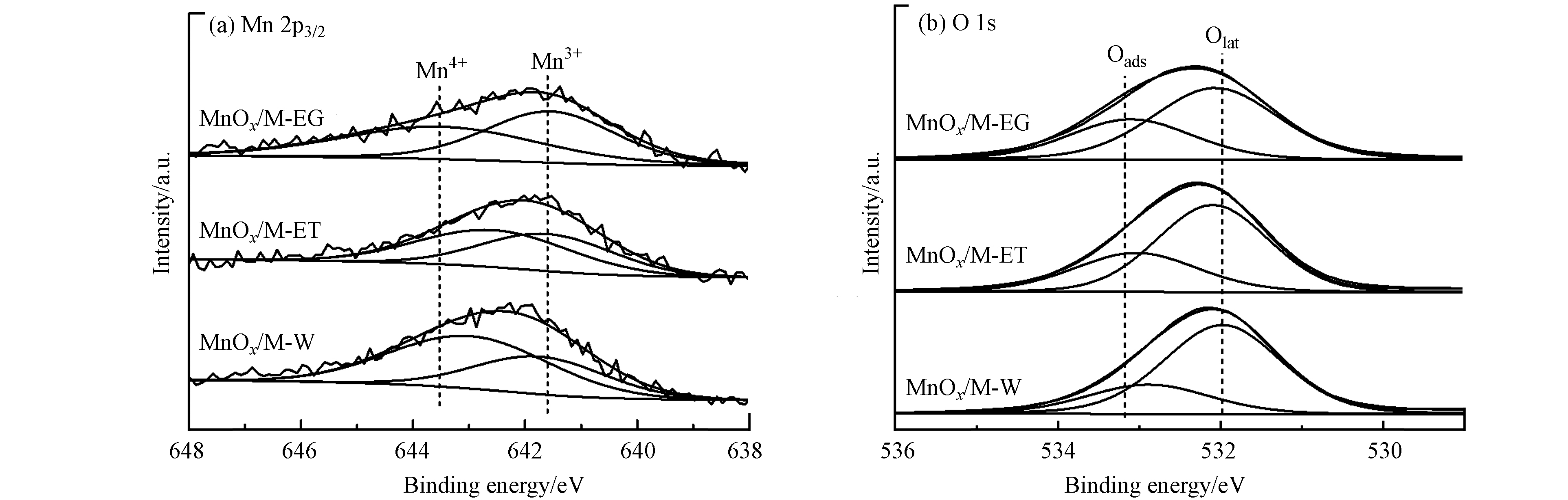
3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的Mn 2p3/2谱图如图6(a)所示,结合能在641.6 eV附近和643.5 eV附近的分峰分别归属Mn3+和Mn4+[21]. 如表3所示,MnOx/M-W、MnOx/M-ET和MnOx/M-EG中Mn3+含量分别为39.7%、46.2%和50.8%,MnOx/M-EG中的Mn3+含量最高. 浸渍液中加入的乙二醇改变了MCM-41的表面性质,增加了孤立硅羟基的含量,进而增强了金属-载体相互作用,锰组分与MCM-41间的电子转移使得MnOx/M-EG表面生成了更多的Mn3+,这与H2-TPR分析结果一致.
图6(b)为MnOx/M-W、MnOx/M-ET和MnOx/M-EG的O 1s谱图,结合能在532 eV和533.2 eV附近的分峰分别归属晶格氧(Olat)和吸附氧(Oads)[22]. 如表3所示,MnOx/M-W、MnOx/M-ET和MnOx/M-EG的吸附氧含量分别为25.9%、34.1%和35.8%,依次上升,此结果与O2-TPD分析结果一致.
根据电中性原则,Mn3+可作为氧空位(VO)存在的依据,原理如下[20]:
吸附氧通常易于吸附在氧空位处,因此锰氧化物中的Mn3+含量与吸附氧含量存在对应关系,MnOx/M-EG的Mn3+含量与吸附氧含量均为3种催化剂中最高,这与文献报道一致[23].
-
图7为甲苯在3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂上的降解特性曲线. 采用不同浸渍液溶剂制备的催化剂的活性存在明显差异. 如表4所示,MnOx/M-EG的T10、T50和T90分别为233 ℃、255 ℃和268 ℃,皆为3种MnOx/M催化剂中最低,表明MnOx/M-EG催化氧化甲苯的活性最强.
3种催化剂活性顺序为:MnOx/M-EG>MnOx/M-ET>MnOx/M-W,这与上述催化剂表征结果相一致. XRD和TEM结果表明,乙二醇共浸渍法大大提高了锰氧化物的分散度,这能为反应提供更多活性位点. H2-TPR结果表明乙二醇共浸渍法能提升MnOx/M-EG的氧化还原性. O2-TPD和XPS结果表明,乙二醇使得Mn3+含量和吸附氧含量增加. 综上,乙二醇共浸渍法能改变MCM-41的表面性质,提高锰前体物与载体的相互作用,改善锰氧化物的分散性和氧化还原性,提升Mn3+含量和吸附氧含量,因此,增强了MnOx/M-EG催化氧化甲苯的活性.
-
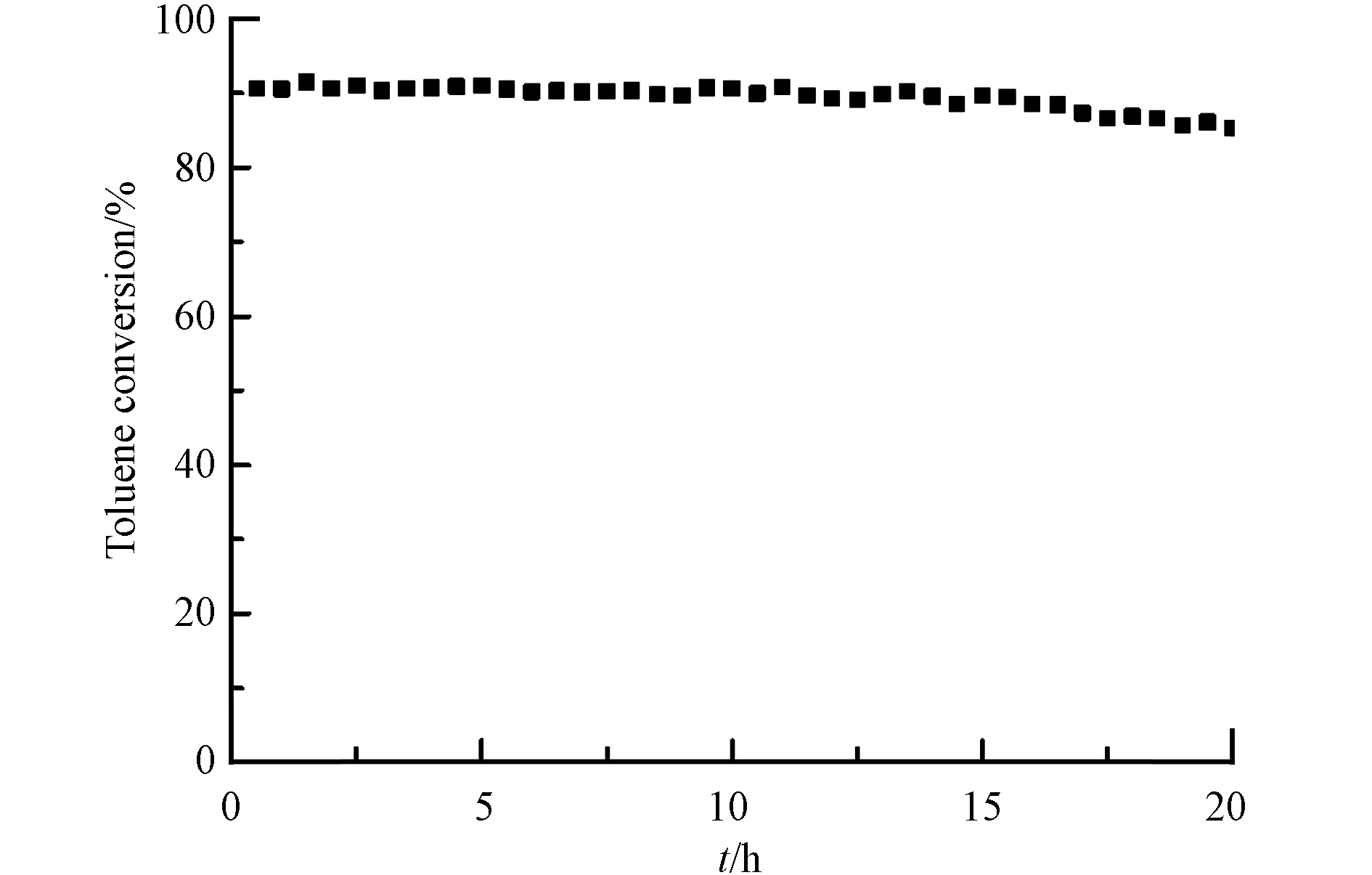
在甲苯浓度3700 mg·m−3、质量空速为50000 mL·g−1·h−1、体积空速为21200 h−1和反应温度270 ℃条件下,测试了MnOx/M-EG的催化活性. 结果如图8所示,MnOx/M-EG在20 h内的催化活性总体保持平稳.
-
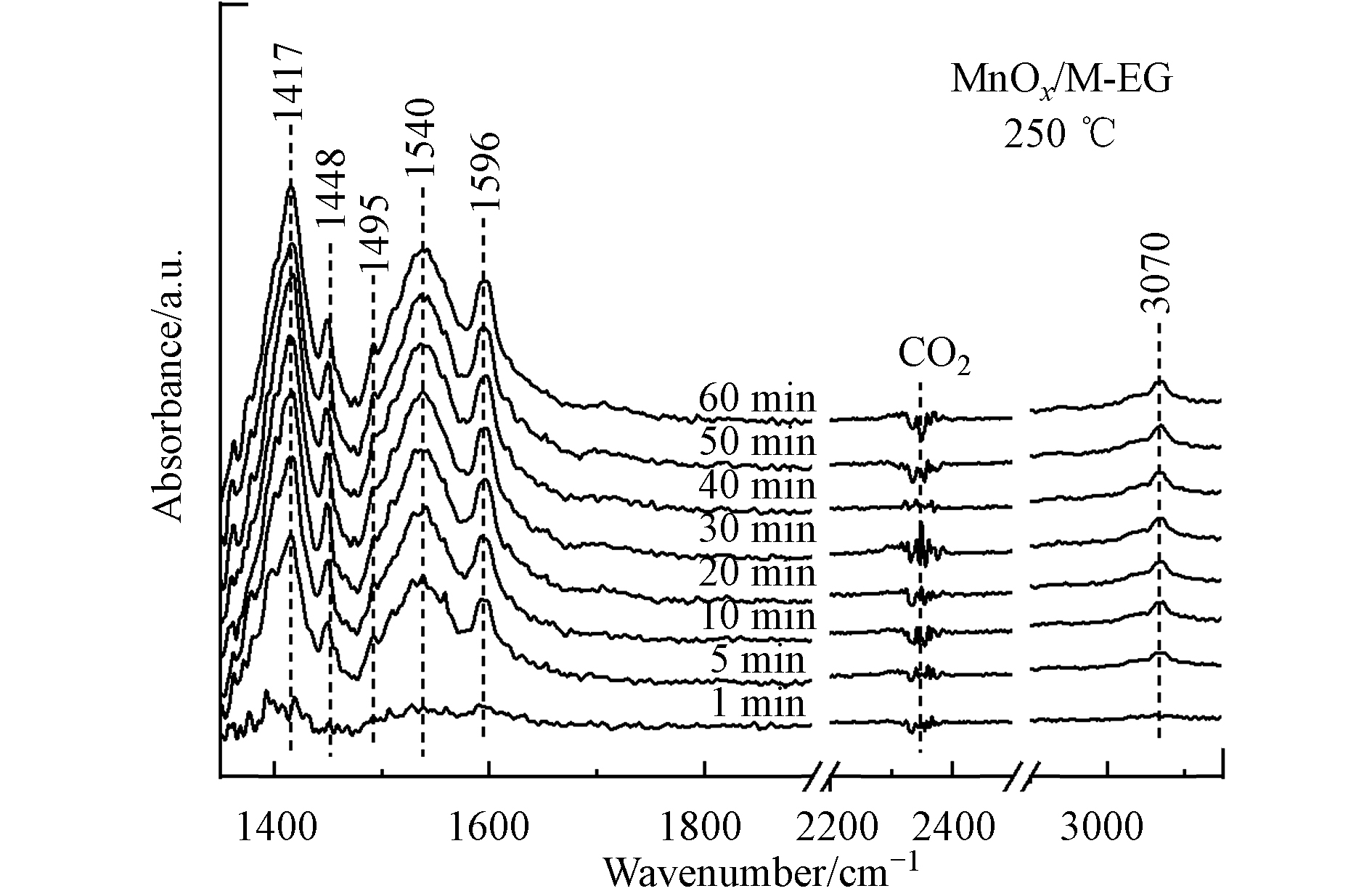
为探究甲苯在MnOx/M-EG上的降解反应过程,进行了MnOx/M-EG在250 ℃下催化氧化甲苯反应的原位红外实验,结果如图9所示. 1448 cm−1、1495 cm−1和1596 cm−1处为苯环骨架振动峰;3070 cm−1处为苯甲基ν(CH)的振动峰[24],表明甲苯在催化剂表面的被吸附活化;1417 cm−1和1540 cm−1处分别为羧酸盐ν(COOH)的非对称和对称振动峰,是苯甲酸的特征峰[25]. 随着反应时间的延长,各振动峰逐渐增强并最终达到平衡,表明MnOx/M-EG具有稳定的催化氧化甲苯的活性,与稳定性实验结果一致.
-
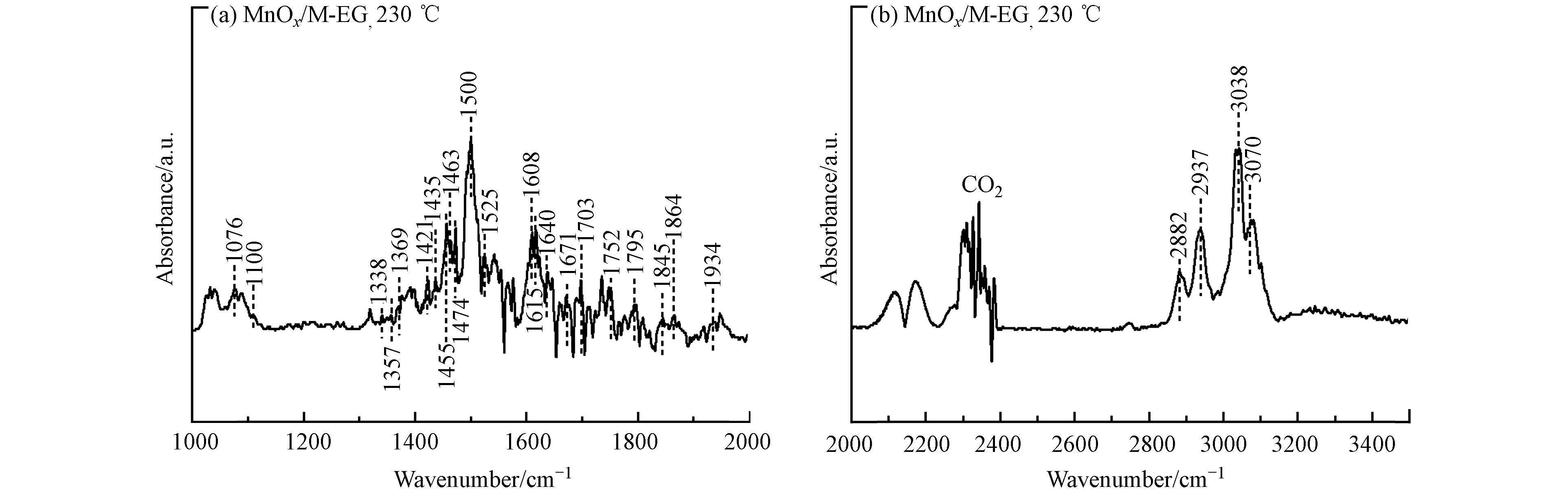
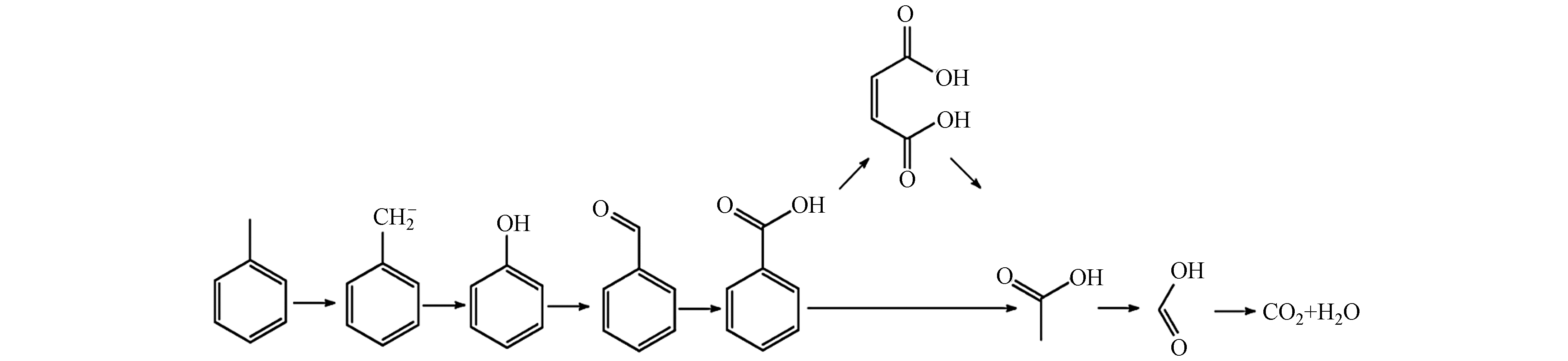
图10为MnOx/M-EG在230 ℃下催化氧化甲苯时反应尾气的红外谱图. 除了CO2的振动峰外,2882 cm−1和2937 cm−1处为亚甲基中对称ν(CH)的振动峰;3038 cm−1和3070 cm−1处为苯甲基的振动峰,表明甲苯被催化剂活化. 1076 cm−1和1110 cm−1处的振动峰属于苯甲醇,这是甲苯被初步氧化的产物. 1640 cm−1和1703 cm−1处的振动峰属于苯甲醛[26],这是苯甲醇被氧化的产物. 1357、1369、1421、1455 cm−1处为ν(COO)的振动峰[27],1500 cm−1和1608 cm−1处的振动峰可鉴定出苯甲酸,苯甲酸是苯甲醛被氧化的产物. 1435、1525、1752 、1795 cm−1处的振动峰属于马来酸,马来酸为一种长链有机物,可能是苯环的开环产物.
-
原位红外和气相红外检测到的苯甲基、苯甲醇、苯甲醛和苯甲酸等苯系物,为甲苯降解的中间产物;反应尾气中存在的马来酸极有可能是苯环断裂产生的,甲酸盐可能是甲基与苯环脱离的产物或者苯环被破坏的产物. 据此,推测甲苯在MnOx/M-EG上可能的降解途径如图11所示,甲苯先被活化脱氢,形成苯甲基,被吸附于催化剂表面. 然后苯甲基被氧化为苯甲醇、苯甲醛和苯甲酸. 随后苯环被破坏,苯甲酸裂解为马来酸、羧酸和甲酸等物质,最后被完全氧化为水和二氧化碳.
-
相比于水溶液和乙醇溶液浸渍法,采用乙二醇共浸渍法可改善MCM-41的表面性质,增强锰组分与载体之间的相互作用,从而提高锰氧化物的分散度、氧化还原性、Mn3+含量和吸附氧含量. 因此,MnOx/M-EG催化氧化甲苯的活性最强(T90=268 ℃,WHSV=50000 mL·g−1·h−1). 此外,采用乙二醇共浸渍法制备的MnOx/M-EG还具有较好的稳定性,20 h内的催化活性保持稳定.
红外结果表明,MnOx/M-EG催化氧化甲苯的反应途径为:甲苯先被活化脱氢,形成苯甲基,被吸附于催化剂表面. 然后苯甲基被氧化为苯甲醇、苯甲醛和苯甲酸. 随后苯环被破坏,苯甲酸裂解为马来酸、羧酸和甲酸等物质,最后被完全氧化为水和二氧化碳.
浸渍液溶剂对负载型MnOx/MCM-41结构及其催化氧化甲苯性能的影响
Influence of impregnation solvent on structure and catalytic oxidation of toluene over MnOx/MCM-41
-
摘要: 以MCM-41为载体,用水、乙醇和乙二醇作为浸渍液溶剂制备了3种负载型催化剂MnOx/MCM-41,采用XRD、TEM、H2-TPR、O2-TPD和XPS等对催化剂进行了表征,探究了浸渍液溶剂(水、乙醇、乙二醇)对MnOx/MCM-41的结构及催化氧化甲苯性能的影响. 结果表明,乙二醇作浸渍液溶剂可提高锰氧化物的分散度、氧化还原性和表面吸附氧的含量. 因而,在相同的质量空速下(WHSV = 50000 mL·g−1·h−1),相比于水溶液浸渍法制备的MnOx/M-W(T90=289 ℃)和乙醇溶液浸渍法制备的MnOx/M-ET(T90=277 ℃),乙二醇共浸渍法制备的MnOx/M-EG具有最强的催化活性(T90=268 ℃);20 h的稳定性评价实验结果表明,MnOx/M-EG具有较好的稳定性.Abstract: Three MnOx/MCM-41 catalysts were prepared by incipient wetness impregnation method using water, ethanol and ethylene glycol as solvents, and were marked as MnOx/M-W, MnOx/M-ET, and MnOx/M-EG, respectively. The influence of the impregnation solvents on the properties of MnOx/MCM-41 was studied by XRD, TEM, H2-TPR, O2-TPD and XPS. Moreover, the catalytic oxidation of toluene on three MnOx/MCM-41catalysts was investigated. The results showed that the ethylene glycol as impregnation solvent could improve the dispersion and redox properties of manganese oxides as well as the amount of surface adsorbed oxygen species on MCM-41. Under the same WHSV (50000 mL·g−1·h−1), the MnOx/M-EG exhibited the best catalytic activity (T90=268 ℃) compared to MnOx/M-W (T90=289 ℃) and MnOx/M-ET (T90=277 ℃). In addition, a 20 h stability test showed that MnOx/M-EG had good catalytic stability.
-
Key words:
- VOCs /
- MCM-41 /
- solvents of impregnation solution /
- catalytic oxidation.
-
砷作为一种剧毒的类金属,其毒性与砷的价态有很强的相关性:As(Ⅲ) > As(Ⅴ). 研究报告表明,天然水体中的砷浓度范围很广,从小于0.5 μg·L−1到大于5000 μg·L−1,地热水中的砷浓度甚至可达50 mg·L−1,在地下水缺氧环境中,As(Ⅲ)是主要形态[1]. 全球约有9400万人至2.2亿人可能接触到高砷浓度的地下水,其中绝大多数(94%)在亚洲[2]. 美国和中国都参照世界卫生组织规定要求饮用水中砷的浓度不得高于10 μg·L−1. As(Ⅲ)对混凝剂和吸附剂的亲和力较弱,As(Ⅲ)相较于As(Ⅴ)更难去除,将As(Ⅲ)氧化为As(Ⅴ)是提高总砷去除的关键步骤[3]. 通过氯和臭氧等化学氧化手段可以将As(Ⅲ)氧化为As(Ⅴ),但很可能产生有毒副产物;通过UV/Fe[4]、UV/TiO2[5]、UV/碘化物[6]、UV/氢氧化铁[7]等方法可以将As(Ⅲ)氧化为As(Ⅴ),但引入了金属离子,不利于环境安全. H2O2在pH > 9.0时可以氧化As(Ⅲ)[8],且H2O2作为一种温和无害的氧化剂,具有绿色氧化过程,不会产生有害的副产物,但由于H2O2运输困难、不易保存,因此H2O2的原位产生技术受到了广泛关注.
MB+[9]是一种知名的噻嗪光敏剂,被大量用作染色剂、光催化剂、抗氧化剂、防腐剂和单态氧敏剂等使用,能够在光照下产生单线态氧(1O2). 除MB+外,核黄素[10]、血卟啉衍生物[11]、联吡啶钌[12]和亚甲基紫[13]等光敏剂在光照下也能够产生和MB+类似的效应. 由于MB+等噻嗪染料价格低廉,光照下对水体中污染物具有较好的氧化效果[14],受到国内外学者的广泛研究. 乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)[15]、H2A[16]、亚硫酸盐[17]等还原剂存在下的MB+的光化学现象已有诸多报道. 当不存在还原剂时,MB+通过光敏化过程(反应1 −3)产生1O2[15]. 但还原形式的无色亚甲基蓝(LMB)只有在还原剂存在时通过反应(4)和(5)才产生,其中Rred和Rox分别表示还原剂的还原形式和氧化形式,反应(6)为反应(4)和反应(5)的总式. 此外,还原性的染料自由基(半还原性MB+·)在没有O2存在时是稳定的,在O2存在时,MB+·会失去其未成对电子,产生过氧化氢自由基(HO2·)(反应(7))[18]. 抗坏血酸(H2A)是常见的抗氧化剂,具有较强的还原性,被广泛应用于有机污染物的降解[19-20]. 已有研究表明H2A/MB+在可见光激发下能够产生抗坏血酸自由基(A·−),进而还原分子氧产生H2O2(反应(8)和反应(9))[21]. 因此,在某些还原剂存在时,MB+的光解可能会诱导分子氧的活化. MB+在许多行业和化学实验室中得到了广泛的应用(如著名的“蓝瓶子”实验). MB+排放前需要对其进行处理,将废弃MB+用来处理其它污染物不失为更好的应用.
MB++hv→1MB+∗ (1) 1MB+∗→3MB+∗ (2) 3MB+∗+O2→MB++1O2 (3) 3MB+∗+Rred→MB+⋅+R⋅ox (4) 2MB+⋅→LMB+MB+ (5) 23MB+∗+2Rred→LMB+MB++2R⋅ox (6) MB+⋅+O2→MB++O⋅−2(HO⋅2) (7) 3MB+∗+HA−→MB+⋅+A⋅− (8) A⋅−+O⋅−2(HO⋅2)→DHA+H2O2 (9) 本研究拟探索可见光/MB+/H2A体系氧化水中As(Ⅲ)的可行性与内在机理,考察了光照、pH、H2A浓度、MB+浓度、As(Ⅲ)初始浓度及水中常见阴离子(Cl−、HCO3−、NO3−)和有机质富里酸(FA)对As(Ⅲ)氧化的影响. 通过活性物种识别(自由基清除实验)和溶液光谱变化确定了可见光/MB+/H2A体系氧化As(Ⅲ)的主要活性物种及其生成机理.
1. 实验部分 (Experimental section)
1.1 实验材料
实验中所用的盐酸、硼氢化钾、氢氧化钾、十水硼酸钠、氢氧化钠、叔丁醇(TBA)、碳酸氢钠、抗坏血酸、硝酸钠、氯化钾、磷酸等均购于国药集团化学试剂公司,亚砷酸钠购于西亚试剂有限公司,砷酸氢二钠七水化合物购于阿法埃莎化学有限公司,富里酸购于阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司,过氧化氢酶(CAT),超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)购于源叶生物科技有限公司,实验中用水均为去离子水,所用药品均为分析纯.
1.2 仪器
ALB−124电子天平秤(赛多利斯仪器公司),R6200氢化物发生−原子荧光光度计(北京博晖创新光电技术股份有限公司),LC−10 ADVP液相泵(日本岛津公司),超纯水机(四川优普科技有限公司),pH 320−S精密数字酸度计(梅特勒−托利多公司),Bante 980溶解氧仪(上海班特仪器公司),801磁力搅拌装置(上海三信公司),UV-1600紫外可见分光光度计(日本岛津公司).
1.3 实验方法与分析方法
在圆柱形开放式夹套反应器(内直径100 mm)中配制500 mL含有5 μmol·L−1 As(Ⅲ)、0.1 mg·L−1 MB+、100 μmol·L−1 H2A、10 mmol·L−1不同类型缓冲液的反应液(醋酸盐缓冲液是pH=4.0、磷酸盐缓冲液是pH=6.0—8.0、硼酸盐缓冲液是pH=9.0—9.5),通过连接外部水循环恒温系统将反应温度控制在(25±1)℃,将LED灯源放置于反应器四周,通过磁力搅拌装置混匀溶液. 打开LED灯并开始计时,分别于0、10、20、30、45、60、90、120 min取4.5 mL反应液,加入0.5 mL 1:1的盐酸以猝灭反应,再进行分析.
采用液相−氢化物发生−原子荧光光度法(LC−HG−AFS)测定As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)形态的量[22],流动相为磷酸盐(45 mmol·L−1, pH=5.6)和超纯水,流速为1.3 mL·min−1,色谱柱为离子色谱柱(PRP−X100,hamilton,Switzerland),进样体积为100 μL.
本实验所用LED灯是从网上采购. 其最大发射波长为630 nm (图1). 通过紫外分光光度计在200−800 nm范围内分别扫描MB+、劳氏紫(Thionine)、天青B(Azure B)的光谱. MB+、劳氏紫和天青B的可见光区域最大吸收峰分别为660、600、600 nm(图1).
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
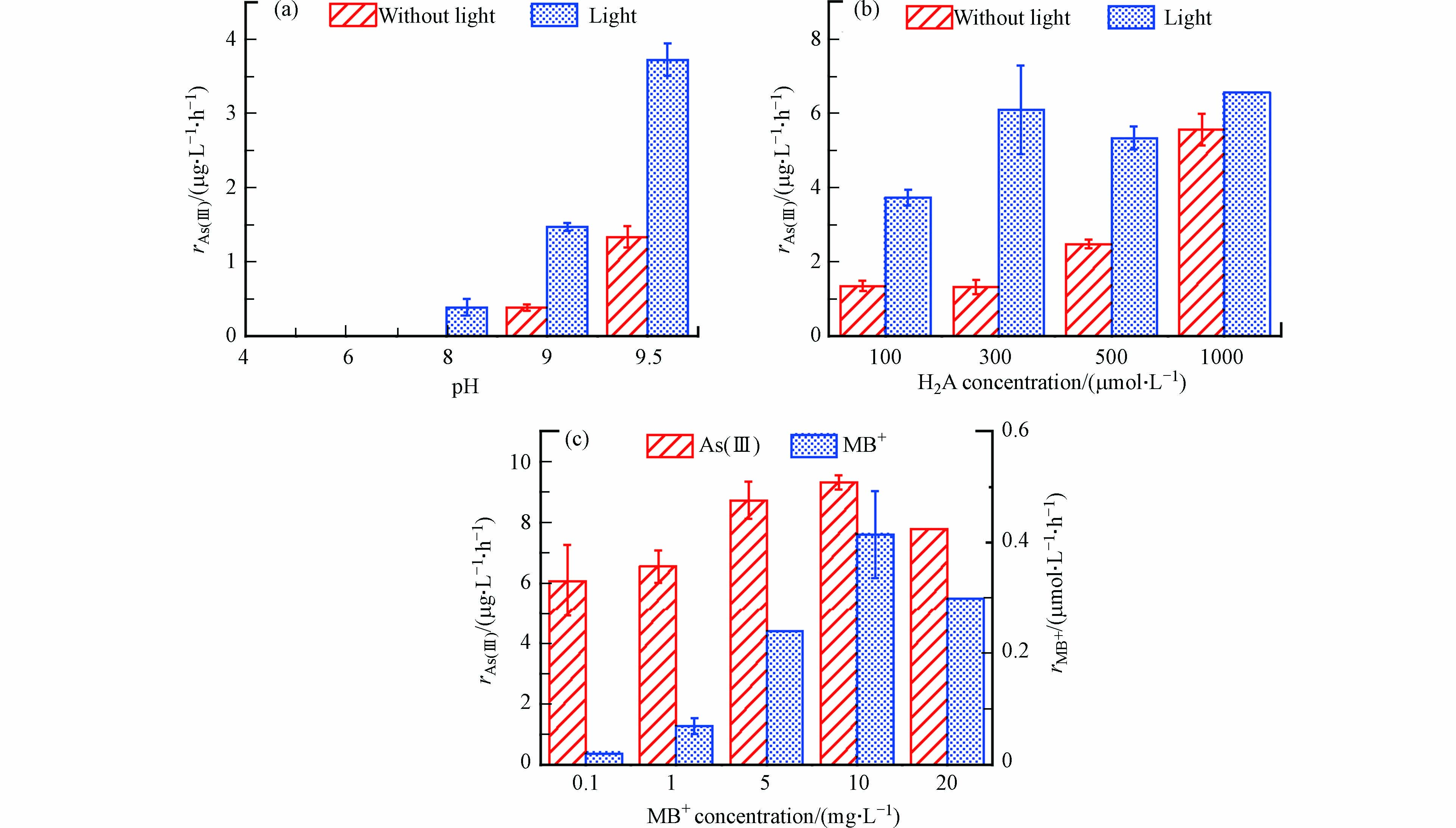
2.1 pH、H2A浓度、MB+和砷浓度的影响
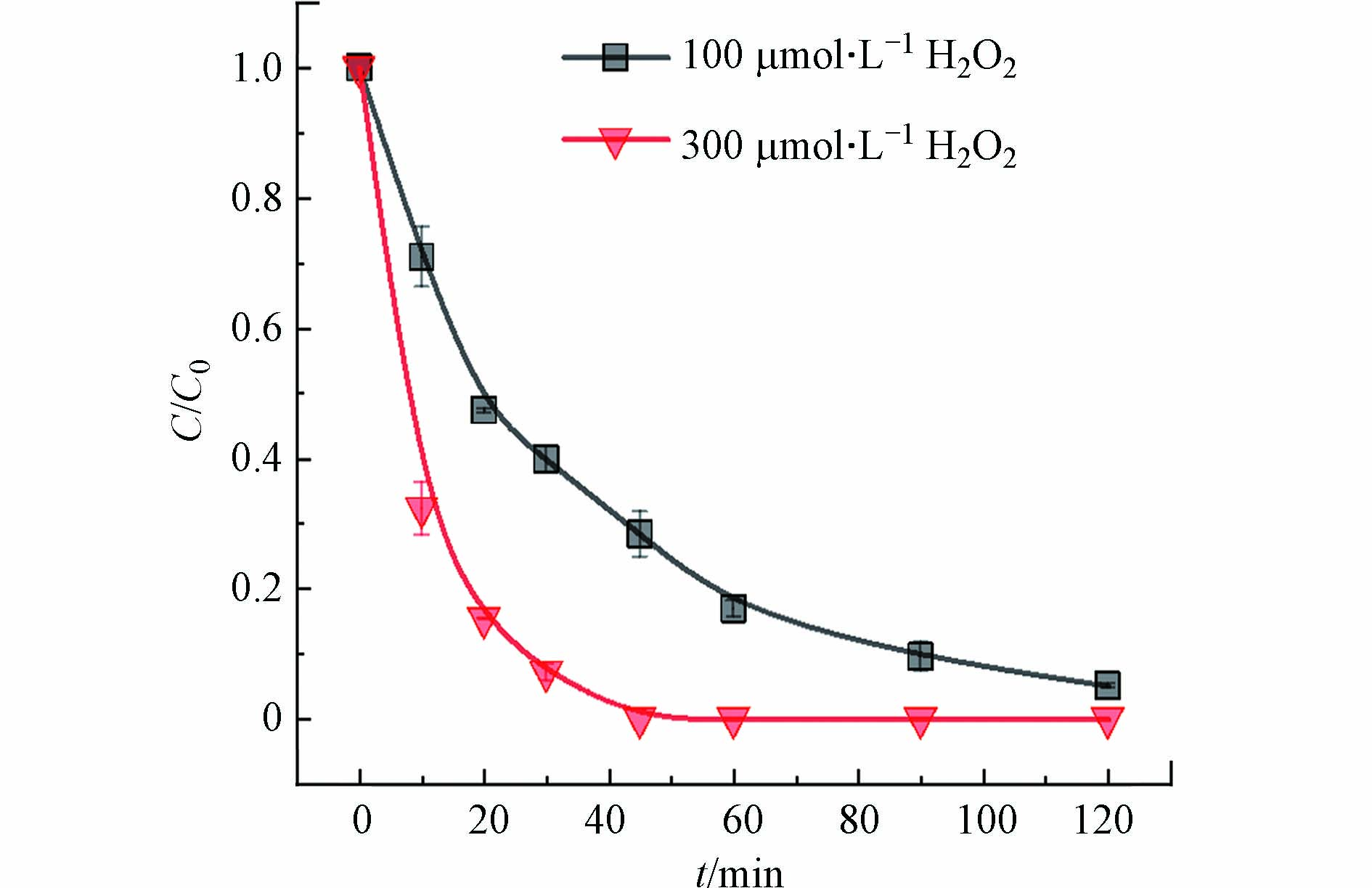
图2a为As(Ⅲ)在MB+/H2A体系和可见光/MB+/H2A体系中不同pH条件下的氧化. 当pH < 6.0时,As(Ⅲ)在MB+/H2A体系和可见光/MB+/H2A体系中均未发生氧化;随着pH从8.0增加至9.5,MB+/H2A体系和可见光/MB+/H2A体系中As(Ⅲ)的氧化速率分别从0、0.39 μmol·L−1·h−1增加至1.34、3.73 μmol·L−1·h−1. 由此可见,在MB+/H2A体系中加入可见光后,As(Ⅲ)的氧化速率和氧化率均明显提高.
pH会影响抗坏血酸和As(Ⅲ)的形态分布与氧化还原电位. 抗坏血酸的两个酸式解离常数分别为4.17、11.57. pH=6—10时,抗坏血酸主要以HA−形态存在,随着pH增加,A2−形态的量会进一步增加,A2−相较于HA−更容易与分子氧反应产生H2O2[8]. As(Ⅲ)的3个酸式解离常数分别为9.22、12.1、13.4,pH > 9.0时As(Ⅲ)主要以解离态存在,解离态的As(Ⅲ)在碱性条件下更容易被H2O2氧化为As(Ⅴ). LMB的3个酸式解离常数分别为1.7、4.5、5.9,因此LMB在溶液中存在四种形态(H3LMB2+、H2LMB+、HLMB、LMB−)[23]. LMB被溶解氧(DO)氧化产生MB+在中性和碱性条件下更快. 考虑到As(Ⅲ)的氧化速率和氧化率,后续反应在pH=9.5下进行.
图2b为H2A浓度对MB+/H2A体系和可见光/MB+/H2A体系中的As(Ⅲ)氧化的影响. As(Ⅲ)在MB+/H2A体系中的氧化速率随着H2A浓度增加而增加,而As(Ⅲ)在可见光/MB+/H2A体系中的氧化速率则随着H2A浓度增加先增加后趋于稳定. H2A投加量的增加一方面会促进活性物种H2O2的产生,另外一方面H2A作为还原剂,过量的H2A则会竞争消耗产生的活性物种. 在Fe(Ⅲ)/H2O2/H2A[24]和Fe(Ⅲ)/PS/H2A[25]体系中,也存在过量的抗坏血酸抑制底物降解的现象. 综上,H2A最佳投加量为300 μmol·L−1.
图2c为MB+浓度对可见光/MB+/H2A体系中的As(Ⅲ)和MB+氧化的影响. 随着MB+浓度从0.1 mg·L−1增加至5 mg·L−1,As(Ⅲ)的氧化速率提高,继续增加MB+浓度至20 mg·L−1,As(Ⅲ)的氧化速率变化不明显. 随着MB+浓度从0.1 mg·L−1增加至10 mg·L−1,MB+的氧化速率从0.02 μmol·L−1·h−1增加至0.42 μmol·L−1·h−1,继续增加MB+浓度至20 mg·L−1,MB+的氧化速率降至0.3 μmol·L−1·h−1. 这是因为随着MB+浓度的增加,MB+吸收光能增多,使得1O2浓度增加,从而有利于反应进行;但MB+达到一定浓度,足以充分使体系中氧分子转变为1O2[26],继续提高MB+浓度并不会对As(Ⅲ)和MB+的氧化产生影响. 综上,MB+最佳投加量为5 mg·L−1.
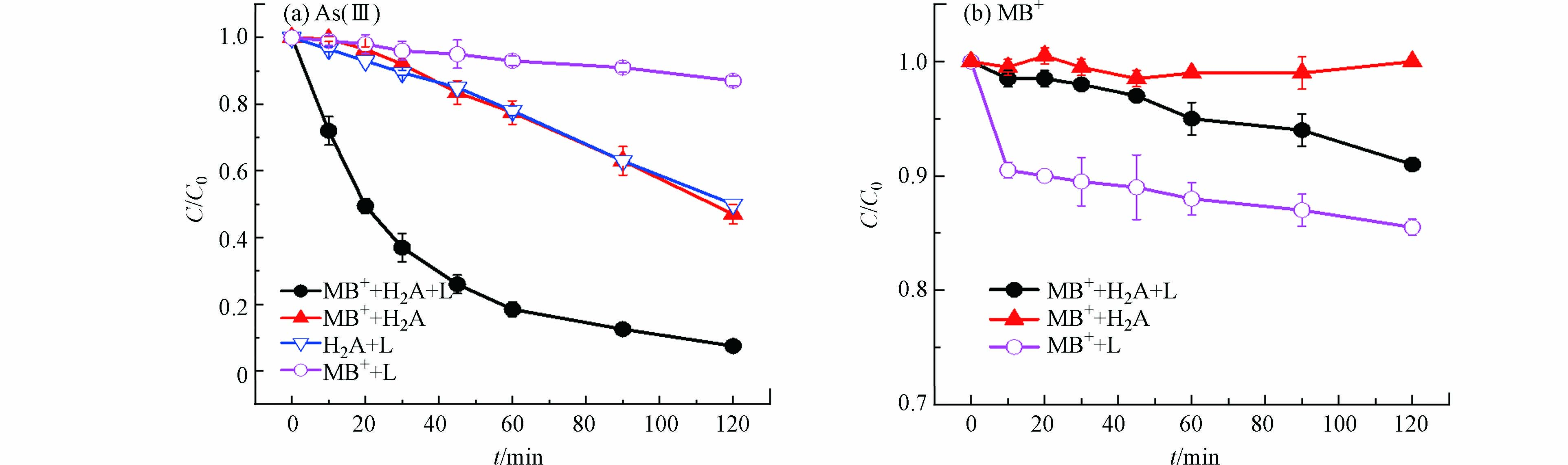
图3a和图3b分别给出了不同体系中As(Ⅲ)和MB+随时间变化结果. 在可见光/MB+/H2A体系中As(Ⅲ)和MB+的氧化率分别为90%、10%. 图3a显示As(Ⅲ)的氧化率在MB+/H2A体系和可见光/H2A体系中相同,为50%,说明pH 9.5时H2A可以活化分子氧产生H2O2氧化As(Ⅲ). 图3b显示,MB+在MB+/H2A体系中并未发生氧化,说明H2O2并不能氧化MB+. 可见光/MB+体系可以产生1O2,As(Ⅲ)和MB+在可见光/MB+体中氧化率分别为10%和15%,说明1O2对As(Ⅲ)的氧化能力很弱. 而在可见光/MB+/H2A体系中,由于溶液中的H2A会竞争消耗1O2,导致此条件下MB+氧化率低于可见光/MB+体系.
图4a为As(Ⅲ)初始浓度对可见光/MB+/H2A体系氧化As(Ⅲ)的影响. 当As(Ⅲ)浓度从5 μmol·L−1上升到50 μmol·L−1时,As(Ⅲ)的氧化率从90%降低至80%(相应的As(Ⅲ)氧化量分别为2.25 μmol和20 μmol),As(Ⅲ)的氧化率没有显著的改变,但As(Ⅲ)的氧化量显著增加. As(Ⅲ)的初始氧化速率和As(Ⅲ)的浓度成正比(图4b). 这说明可见光/MB+/H2A体系可以用来处理高浓度含砷废水.
2.2 机理探究与氧气浓度的影响
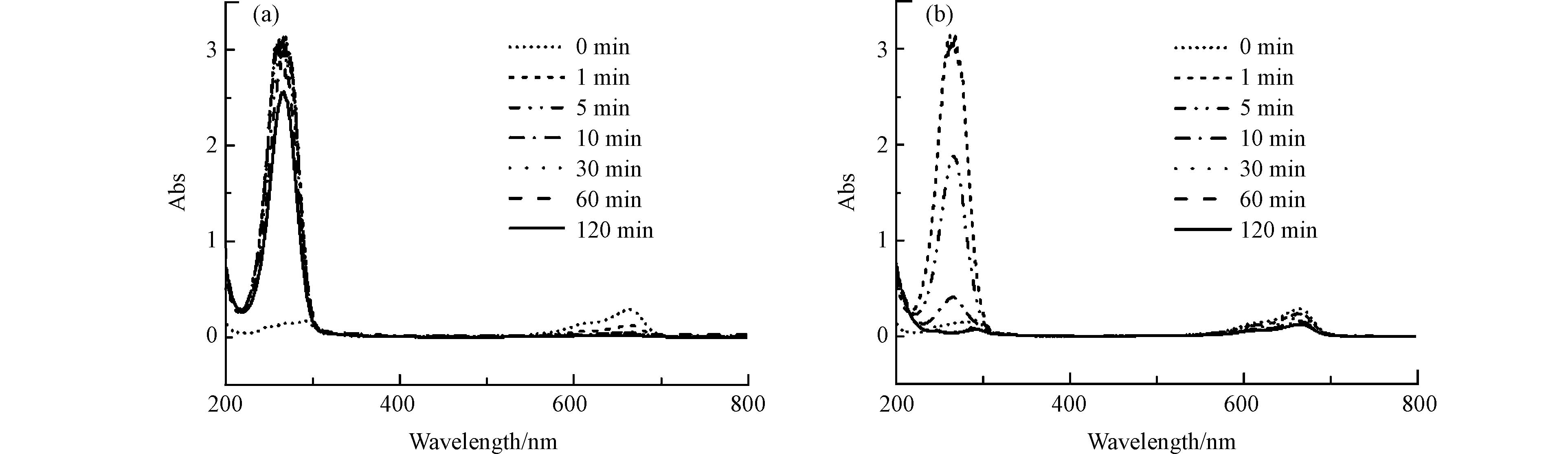
As(Ⅲ)在可见光/MB+/H2A体系中的氧化可以从MB+的激发、激活的MB+(MB+*)与H2A相互作用以及反应活性物种的产生三个角度来进行说明. MB+是一种最大吸收峰为660 nm的蓝色染料,而LMB为无色且在265 nm处具有最大吸收峰[16]. 当预先用氮气曝气半小时以去除溶液中的DO,可见光照射,可以观察到MB+在660 nm处的最大吸收峰迅速消失(0—5 min),而在265 nm处出现LMB的最大吸收峰(0—120 min)(图5a). 在有氧搅拌条件下可见光照射后,反应液中DO迅速减少,溶液中部分LMB无法氧化,出现LMB的吸收峰(0—10 min),此后溶液复氧(10—120 min), LMB最大吸收峰消失(图5b). 由于实际反应是在空气氛围下进行,与N2氛围相比,MB+下降的速率较慢. 这是因为在O2存在时,MB+首先被H2A还原成LMB,然后LMB被O2氧化成MB+,这个过程非常迅速,所以在O2存在下无法观察到MB+的循环过程. 此外,当可见光照射脱氧的MB+/H2A反应溶液重新暴露于空气中,观察到无色溶液迅速变为蓝色(图6). 这也可以解释上述现象,即LMB很容易被O2氧化[17].
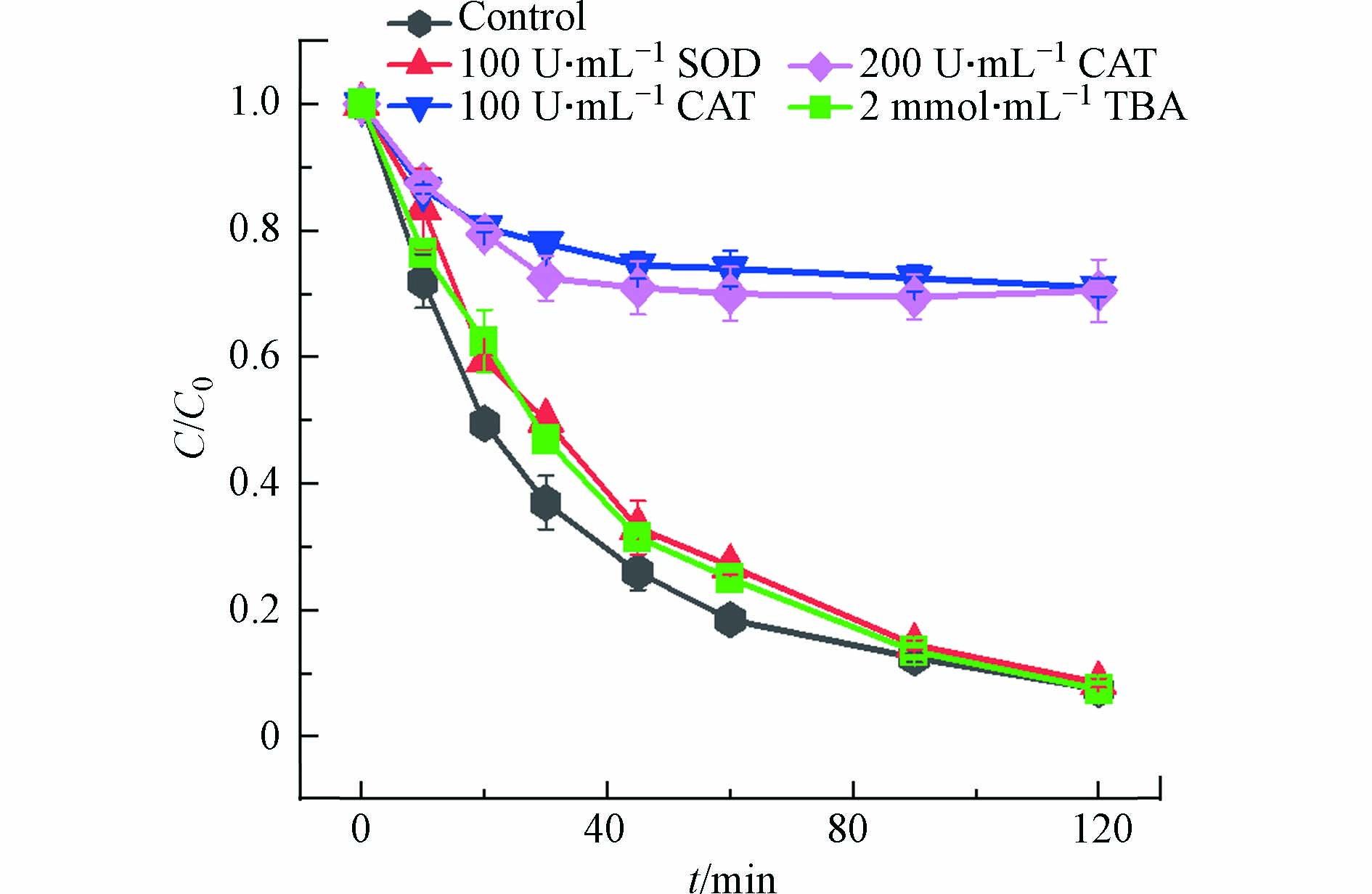
为了进一步理解可见光/MB+/H2A体系中的As(Ⅲ)的氧化机理,利用自由基抑制实验来捕获产生的活性物种. SOD和TBA分别作为HO2·和HO·猝灭剂,SOD与HO2·的反应速率常数为1.6×109 L·mol−1·s−1,TBA与HO·的反应速率常数为7.6×108 L·mol−1·s−1. 分别投加100 U·mL−1 SOD和2 mmol·L−1 TBA(图7),均未对As(Ⅲ)的氧化产生明显影响,表明O2·−(HO2·)或HO·不是氧化As(Ⅲ)的主要活性物种. CAT可以快速分解H2O2,因而被用于清除反应中产生的H2O2. 分别投加100 U·mL−1和250 U·mL−1的CAT,反应前30 min,As(Ⅲ)的氧化率由65%下降到25%,此后并未观察到As(Ⅲ)进一步氧化,说明反应30 min后As(Ⅲ)的氧化被完全抑制. 上述结果说明H2O2是氧化As(Ⅲ)的主要活性物种. 如图8所示,pH=9.5时,单独的H2O2能够快速氧化As(Ⅲ).
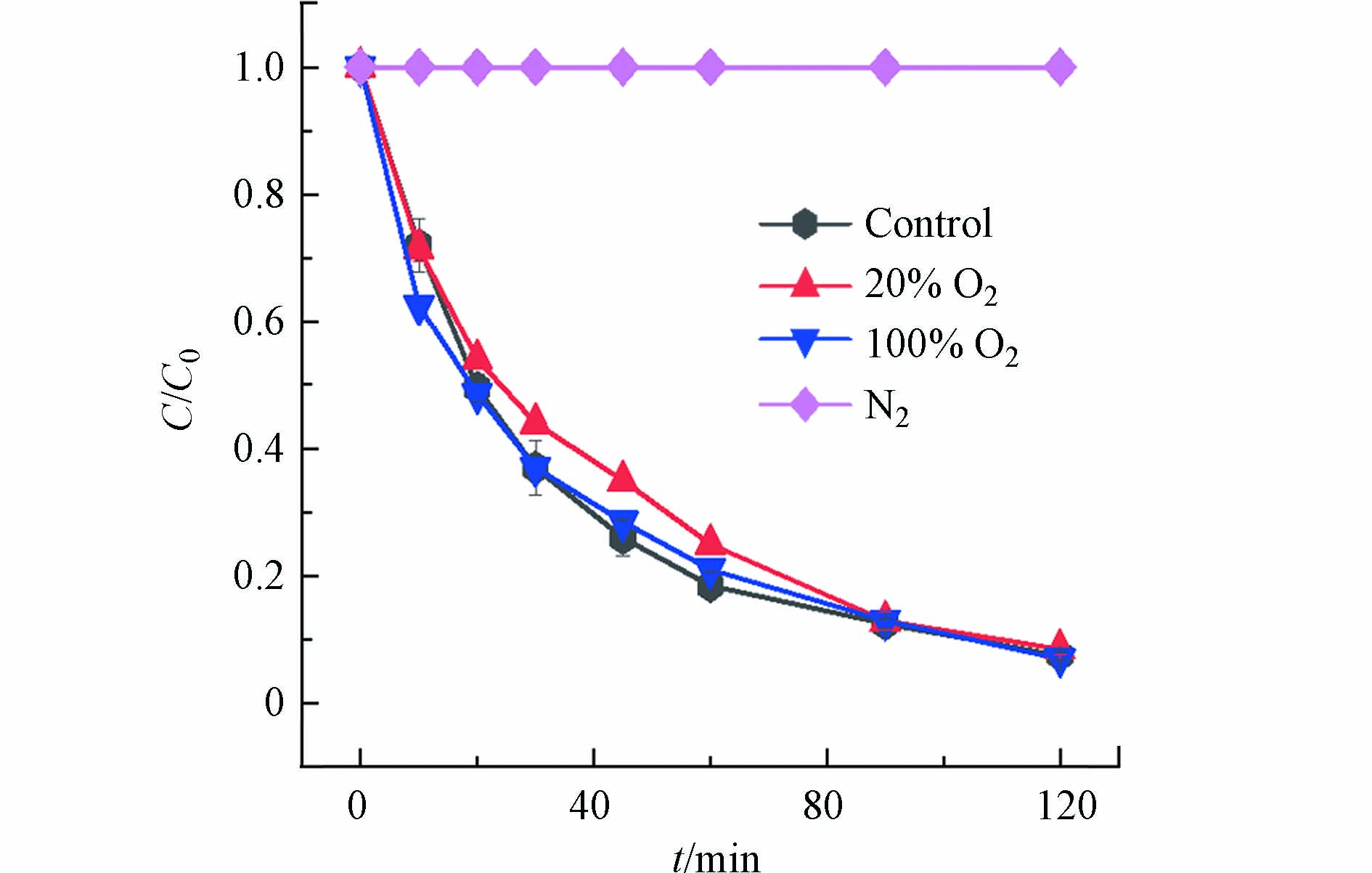
在N2氛围下,As(Ⅲ)在可见光/MB+/H2A体系中不会发生氧化(图9). 说明即便MB+和HA−之间能够电子转移,但是体系中没有分子氧,产生MB+·和A·−也不能进行后续产生H2O2的反应. 这与无氧条件下碱/H2A体系无法产生H2O2的实验结果一致[8]. 而分别通入20% 或100% O2,As(Ⅲ)的氧化效率与搅拌条件下一致,表明过多O2也没有促进体系中As(Ⅲ)的氧化.
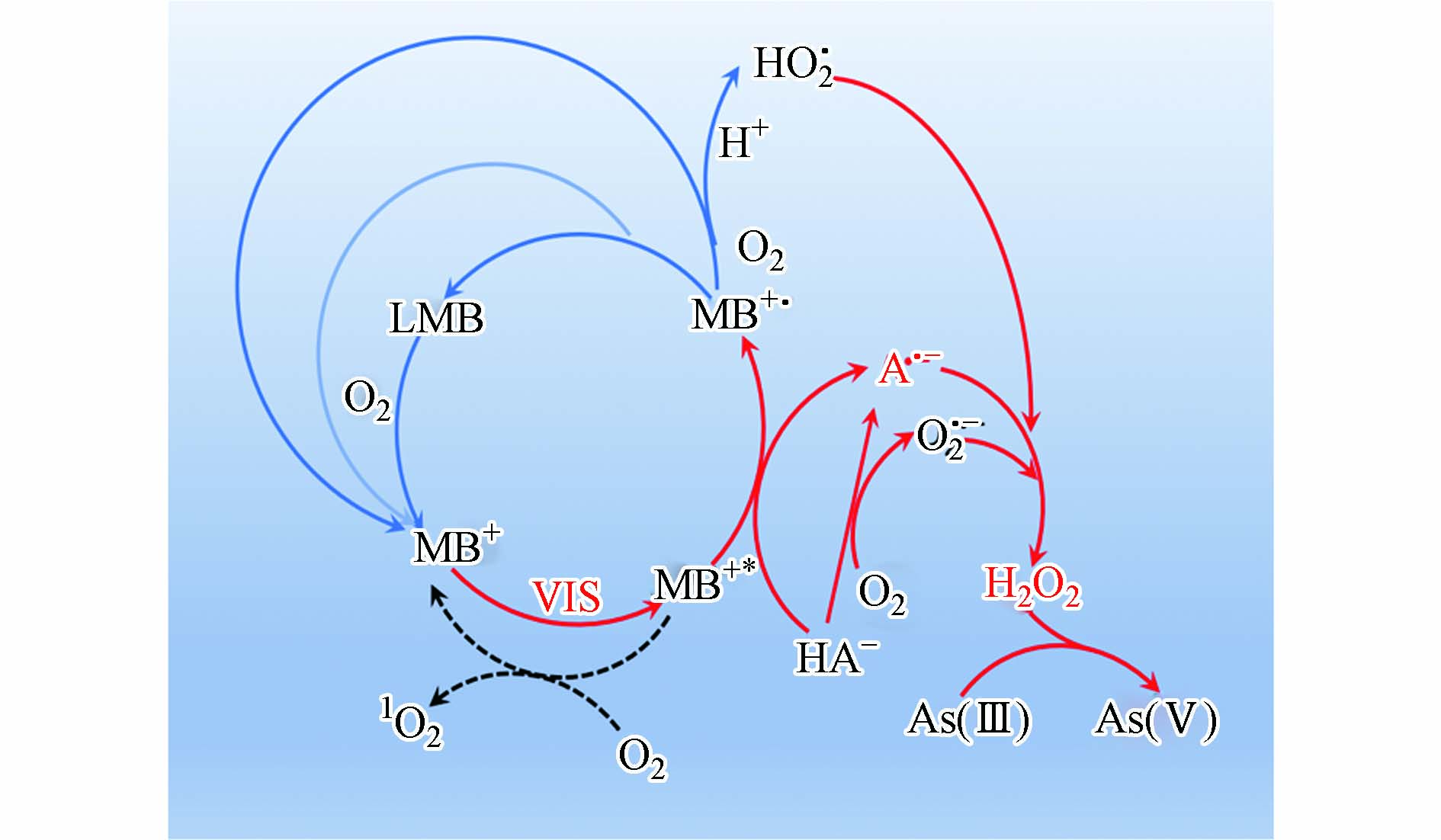
在可见光/MB+/H2A体系中,活性物种通过以下途径产生(图10):首先,MB+通过可见光激发产生单线态1MB+(公式1),随后1MB+快速转变为三重态(3MB+)(公式2),3MB+和分子氧(3O2)反应产生1O2(公式3);其次,3MB+可以从HA−处得到一个电子生成MB+·和A·−(公式8),MB+·也可以通过歧化反应产生LMB和MB+(公式5),LMB再与O2反应产生MB+;最后,A·−与O2·−(HO2·)反应产生H2O2(公式9). HA−也可以直接与分子氧通过双电子转移产生H2O2,MB+和可见光的引入加速HA−的氧化,从而产生更多的H2O2. 在可见光/MB+/H2A体系中存在H2A可清除产生的1O2, 1O2对As(Ⅲ)的氧化贡献微乎其微,H2O2对As(Ⅲ)的氧化起主要作用.
2.3 常见阴离子与有机质的影响
HCO3−、Cl−、NO3−、FA在土壤间隙水和地下水中普遍存在,HCO3−、Cl−、NO3−、FA对As(Ⅲ)氧化的影响如图11所示,HCO3−、Cl−、NO3−对As(Ⅲ)氧化基本无影响,这是因为HCO3−、Cl−、NO3−加入反应液后并不会使MB+的吸收光谱发生变化,因此不会影响可见光/MB+/H2A体系中As(Ⅲ)的氧化,这和碱/H2A体系中环境基质对As(Ⅲ)氧化的影响一致[8]. 但FA对As(Ⅲ)氧化有一定的影响,这是因为FA加入反应液后使得MB+的吸收光谱发生了显著变化,使得MB+在660 nm处的吸收变弱,从而抑制了MB+和HA−之间的电子转移.
2.4 其他两种噻嗪染料的效果
探讨了将其他噻嗪染料用于可见光/H2A体系活化分子氧氧化As(Ⅲ)的可能性. 劳氏紫和天青B也是常见的噻嗪染料,在可见光/H2A/劳氏紫体系和可见光/H2A/天青B体系中分别对测定了As(Ⅲ)和染料的浓度的变化,结果如图12所示. 实验结果表明,劳氏紫和天青B均能促进H2A活化分子氧产生H2O2氧化As(Ⅲ),但促进效果均不如MB+,这是因为相同浓度下MB+有最大的吸光度值,能更好地吸收能量. 噻嗪染料的相似行为可能是由于它们具有相同的官能团和激发状态. 推测其他光敏剂如核黄素[9]和茜素[27]都具有接受电子的能力,同样可以促进H2A活化分子氧产生H2O2氧化水中的As(Ⅲ).
3. 结论(Conclusion)
本文从可见光/MB+/H2A活化分子氧体系出发,研究了可见光/MB+/H2A体系氧化水中As(Ⅲ)的可行性与内在机理. 其中,可见光光照、pH值、H2A与MB+的投加量对于As(Ⅲ)的氧化过程有着不同影响. 实验结果表明:
(1)可见光光照可以促进MB+/H2A体系氧化As(Ⅲ); pH越高,As(Ⅲ)氧化越快;pH=9.5下,H2A浓度的增加对As(Ⅲ)氧化呈现先促进后稳定的趋势,且O2浓度对于该体系对As(Ⅲ) 的氧化过程的影响较小. 最终得出该体系下As(Ⅲ)氧化的最佳条件:最佳H2A投加量为300 μmol·L−1;最佳MB+投加量为5 mg·L−1.
(2)通过自由基抑制剂分析验证了可见光/MB+/H2A活化分子氧体系氧化As(Ⅲ)的主要活性物种为H2O2, 1O2对As(Ⅲ)的氧化贡献微乎其微.
(3)同MB+一样,在可见光/MB+体系中添加劳氏紫和天青B这两种噻嗪染料也能促进As(Ⅲ)的氧化.
-
表 1 3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的孔结构参数
Table 1. Pore structure properties of three kinds of MnOx/MCM-41
样品 Sample 负载量 Mn content BET比表面积/(m2·g−1) BET surface area 孔容/(cm3·g−1) Pore volume 平均孔径/nm Average pore diameter MCM-41 — 745.9 0.92 4.64 MnOx/M-W 9.63% 609.6 0.73 4.57 MnOx/M-ET 9.16% 606.4 0.72 4.61 MnOx/M-EG 9.29% 624.5 0.71 4.35 表 2 3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的H2-TPR表征结果
Table 2. H2-TPR results of three kinds of MnOx/MCM-41
样品 Sample 还原温度/℃ Reduction temperature 耗H2量/(mmol·g−1) H2 consumption Oads/Olat 峰Ⅰ Peak Ⅰ 峰Ⅱ Peak II 峰Ⅰ Peak I 峰Ⅱ Peak II 总量 Total MnOx/M-W 297 421 0.80 0.34 1.14 0.18 MnOx/M-ET 297 421 0.69 0.36 1.05 0.21 MnOx/M-EG 286 339 0.26 0.50 0.76 0.25 表 3 3种MnOx/MCM-41催化剂的XPS结果
Table 3. XPS results of three kinds of MnOx/MCM-41
样品Sample Mn3+/% Mn4+/% Mn3+/Mn4+ Oads/% Olat/% Oads/Olat MnOx/M-W 39.7 60.3 0.66 25.9 74.1 0.35 MnOx/M-ET 46.2 53.8 0.86 34.1 65.9 0.52 MnOx/M-EG 50.8 49.2 1.03 35.8 64.2 0.56 表 4 3种MnOx/M CM-41催化剂催化氧化甲苯的活性
Table 4. The catalytic activity for toluene combustion over three kinds of MnOx/MCM-41
样品Sample T10/℃ T50/℃ T90/℃ MnOx/M-W 253 275 289 MnOx/M-ET 240 264 277 MnOx/M-EG 233 255 268 -
[1] 冯爱虎, 于洋, 于云, 等. 沸石分子筛及其负载型催化剂去除VOCs研究进展 [J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(10): 757-773. doi: 10.6023/A18060250 FENG A H, YU Y, YU Y, et al. Recent progress in the removal of volatile organic compounds by zeolite and its supported catalysts [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2018, 76(10): 757-773(in Chinese). doi: 10.6023/A18060250
[2] 陈丹, 田树梅, 石静, 等. 多孔氧化硅负载银催化剂催化消除VOCs的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(11): 3145-3152. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019082701 CHEN D, TIAN S M, SHI J, et al. Research progress in catalytic elimination of VOCs by porous SiO2 supported silver catalysts [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(11): 3145-3152(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019082701
[3] HUANG N, QU Z P, DONG C, et al. Superior performance of α@β-MnO2 for the toluene oxidation: Active interface and oxygen vacancy [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2018, 560: 195-205. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2018.05.001 [4] 黄海凤, 徐琴琪, 陈晓, 等. 整体式Mn基复合金属氧化物催化燃烧VOCs性能研究 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(7): 1583-1590. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017101307 HUANG H F, XU Q Q, CHEN X, et al. Catalytic combustion of VOCs by integral Mn-based mixed metal oxide [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(7): 1583-1590(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017101307
[5] PENG Y X, ZHANG L, CHEN L, et al. Catalytic performance for toluene abatement over Al-rich Beta zeolite supported manganese oxides [J]. Catalysis Today, 2017, 297: 182-187. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.04.058 [6] JUNG S C, PARK Y K, JUNG H Y, et al. Effects of calcination and support on supported manganese catalysts for the catalytic oxidation of toluene as a model of VOCs [J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2016, 42(1): 185-199. doi: 10.1007/s11164-015-2333-6 [7] HUANG H, ZHANG C H, WANG L, et al. Promotional effect of HZSM-5 on the catalytic oxidation of toluene over MnOx/HZSM-5 catalysts [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(12): 4260-4270. [8] 吴宇昊, 张健, 龙超. MCM-41孔径对负载MnOx催化氧化甲苯性能的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2022, 42(4): 373-382. WU Y H, ZHANG J, LONG C, Influence of pore size of MCM-41 on catalytic oxidation of toluene over MnOx/MCM-41[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2022, 42(4): 373-382 (in Chinese)
[9] TIAN J Q, LI H C, ZENG X, et al. Facile immobilization of Ni nanoparticles into mesoporous MCM-41 channels for efficient methane dry reforming [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 40(9): 1395-1404. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63403-0 [10] 田井清. 甲烷干重整催化剂的设计及其在工业尾气转化中的应用研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2020. TIAN J Q. Design of methane dry reforming catalysts and its application in industrial tail gas conversion[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2020(in Chinese).
[11] XIE T, SHI L Y, ZHANG J P, et al. Immobilizing Ni nanoparticles to mesoporous silica with size and location control via a polyol-assisted route for coking- and sintering-resistant dry reforming of methane [J]. Chem Commun, 2014, 50(55): 7250-7253. doi: 10.1039/C4CC01441C [12] WANG L, ZHANG C H, HUANG H, et al. Catalytic oxidation of toluene over active MnOx catalyst prepared via an alkali-promoted redox precipitation method [J]. Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis, 2016, 118(2): 605-619. doi: 10.1007/s11144-016-1011-z [13] ZHANG C H, HUANG H, LI G Q, et al. Zeolitic acidity as a promoter for the catalytic oxidation of toluene over MnOx/HZSM-5 catalysts [J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, 327: 374-381. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.03.019 [14] van der MEER J, BARDEZ-GIBOIRE I, MERCIER C, et al. Mechanism of metal oxide nanoparticle loading in SBA-15 by the double solvent technique [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(8): 3507-3515. doi: 10.1021/jp907002y [15] QU Z P, HUANG W X, ZHOU S T, et al. Enhancement of the catalytic performance of supported-metal catalysts by pretreatment of the support [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2005, 234(1): 33-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2005.05.021 [16] LV X Y, CHEN J F, TAN Y S, et al. A highly dispersed nickel supported catalyst for dry reforming of methane [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2012, 20: 6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2012.01.002 [17] QIU S B, ZHANG Q, LV W, et al. Simply packaging Ni nanoparticles inside SBA-15 channels by co-impregnation for dry reforming of methane [J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(39): 24551-24560. doi: 10.1039/C7RA00149E [18] XU H M, QU Z, ZHAO S J, et al. Different crystal-forms of one-dimensional MnO2 nanomaterials for the catalytic oxidation and adsorption of elemental mercury [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 299: 86-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.012 [19] 乔彤, 刘长红, 柳志刚, 等. 载体平衡离子对MnOx/ZSM-5催化NH3-SCR性能影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(7): 3176-3183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.07.020 QIAO T, LIU C H, LIU Z G, et al. The effect of equilibrium ion on the NH3-SCR performance of MnOx/ZSM-5 catalysts [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(7): 3176-3183(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.07.020
[20] JIA J B, ZHANG P Y, CHEN L. Catalytic decomposition of gaseous ozone over manganese dioxides with different crystal structures [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 189: 210-218. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.055 [21] CHENG G, YU L, HE B B, et al. Catalytic combustion of dimethyl ether over α-MnO2 nanostructures with different morphologies [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 409: 223-231. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.218 [22] SHAO Q, DONG H, ZHANG J, et al. Manganese supported on controlled dealumination Y-zeolite for ozone catalytic oxidation of low concentration toluene at low temperature [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 271: 129604. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129604 [23] ZHANG X J, ZHAO H, SONG Z X, et al. Insight into the effect of oxygen species and Mn chemical valence over MnOx on the catalytic oxidation of toluene [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 493: 9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.06.255 [24] MO S P, ZHANG Q, LI J Q, et al. Highly efficient mesoporous MnO2 catalysts for the total toluene oxidation: Oxygen-Vacancy defect engineering and involved intermediates using in situ DRIFTS [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 264: 118464. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118464 [25] WANG F, DENG J, IMPENG S, et al. Unraveling the effects of the coordination number of Mn over α-MnO2 catalysts for toluene oxidation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 396: 125192. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125192 [26] YANG W H, SU Z A, XU Z H, et al. Comparative study of α-, β-, γ- and δ-MnO2 on toluene oxidation: Oxygen vacancies and reaction intermediates [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 260: 118150. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118150 [27] ZHANG Q, MO S P, LI J Q, et al. In situ DRIFT spectroscopy insights into the reaction mechanism of CO and toluene co-oxidation over Pt-based catalysts [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9(17): 4538-4551. -





 下载:
下载: