-
城市固体废弃物 (MSW) 的时变性会影响填埋体的稳定 [1-3]。MSW组分复杂,随着填埋龄期增加,大量有机物和纤维状物质产生降解,其抗剪强度也会随之改变。而抗剪强度的降低是造成分层垃圾填埋体滑移的主要原因[4-6]。填埋体的滑移失稳破坏会导致大量填埋垃圾和渗滤液滑出场外,造成严重的环境污染及财产损失[7]。
抗剪强度是MSW重要的力学性能之一,其变化规律与填埋龄期密切相关。随着龄期的增加,MSW的内摩擦角会增大,而粘聚力逐渐降低直至为0[8-10],这会导致填埋体沿衬垫发生滑移破坏。因此,土-膜界面的剪切特性得到了学者们的广泛研究[11-15]。PUNETHA等[13]通过直剪实验研究了光面及糙面HDPE土工膜和各类土颗粒物界面抗剪强度。BACAS等[14]对8种土工合成材料和18种不同界面进行了直剪实验,分析了界面剪切强度特性。LI等[15]研究了冻融循环作用下,密实粘土衬垫与HDPE土工膜界面剪切特性。在稳定性分析方面,ZIENKIEWIEZ等[16]首次将强度折减法引入到有限元边坡分析中。UGAI等[17]、郑颖人等[18]和陈雪珍等[19]将有限元分析的安全系数应用在工程中,推动有限元强度折减法的发展。
学者们通常以实验确定各层垃圾土的抗剪强度,对分层填埋场进行稳定性分析[4,6]。但目前对分层填埋场的稳定性分析都集中在以粘土作为中间衬垫,HDPE土工膜因为其耐久性好、化学性质稳定、柔韧性佳等特性而被视为替代粘土的理想材料[20],同时又缺乏将土工膜作为中间衬垫的应用研究。因此,本研究以HDPE土工膜代替粘土作为中间衬垫,进行土-膜界面剪切实验,利用PLAXIS有限元软件模拟分层填埋体的滑移过程及其整体稳定性变化,并分析HDPE土工膜作为中间衬垫的可行性,以期为土工膜应用于填埋场作为中间衬垫提供参考。
-
直剪实验的材料取自某苏南平原型垃圾填埋场,总计填埋库容量为476.5×104 m3。实验土样分别取自该场地的改扩建工程、二期工程、续建工程、续建二期工程。其物理指标如表1所示。选用3种不同规格的HDPE土工膜,分别为喷着式、柱点式和光面式。其中,柱点式表面排布规则的小凸点;喷着式表面具有不规则纹理,粗糙程度比柱点式低;光面式表面则是光滑的平面。3种土工膜厚度均为1.5 mm,密度大于0.94 g·cm-3,炭黑含量在2%~3%。HDPE土工膜的物理参数如表2所示。
-
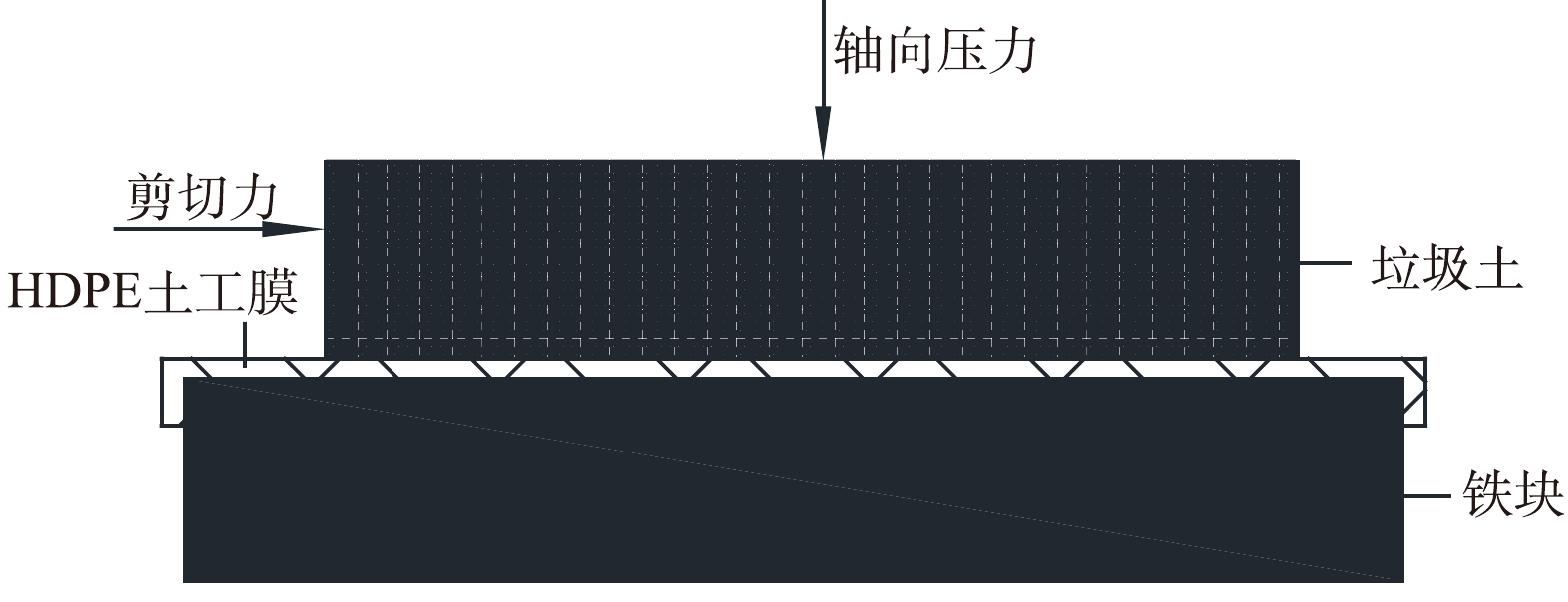
实验仪器与试样布置如图1所示,采用大尺寸直剪仪(THE-1000,天水红山实验机有限公司),上下剪切盒尺寸为500 mm×500 mm×410 mm,根据《土工合成材料测试规程》 (SL 235-2012) [21]进行实验 。
-
将试样按龄期分为4组,每组选择50、100、150、200 kPa竖向荷载进行压缩,压缩至少4 h,剪应变不小于20%,剪切位移设置为100 mm,剪切速率为2 mm·min-1。以土-膜界面峰值强度表征土-膜界面强度[21]。依据莫尔-库伦破坏准则,得到不同龄期MSW试样与HDPE土工膜的界面抗剪强度参数关系。
-
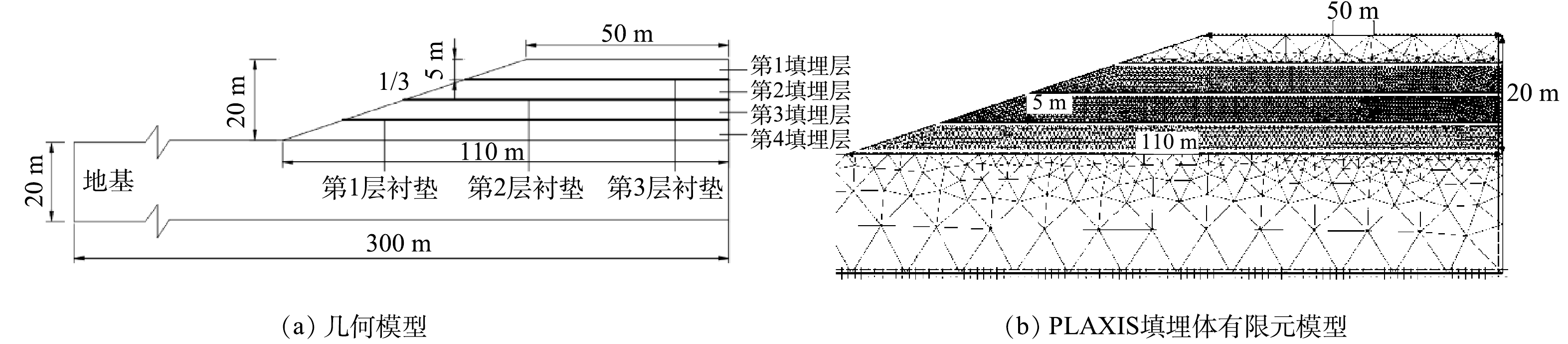
本研究参考某苏南平原型垃圾填埋场,建立的数值模型如图2所示。图2 (a) 从下至上为第1至第4填埋层;填埋体下底边长110 m、上底边长50 m、高20 m、斜坡度为1∶3,边界地基土深20 m、长300 m[22],分层处布设HDPE土工膜衬垫[23],有限元网格划分如图2 (b) 所示;不设HDPE土工膜的填埋体采用粘土封层,厚度为300 mm [22]。
-
基于Mohr-Coulomb准则,不考虑渗流影响,土-膜界面相互作用按照强度折减计算。土体物理参数取值见表3。土体抗剪强度参数按照表1赋予每一填埋层。 HDPE土工膜厚度和拉伸刚度按照表2分别赋予每层衬垫。由于垃圾土无剪胀性,不考虑剪胀效应,剪胀角取值为0[24]。
-
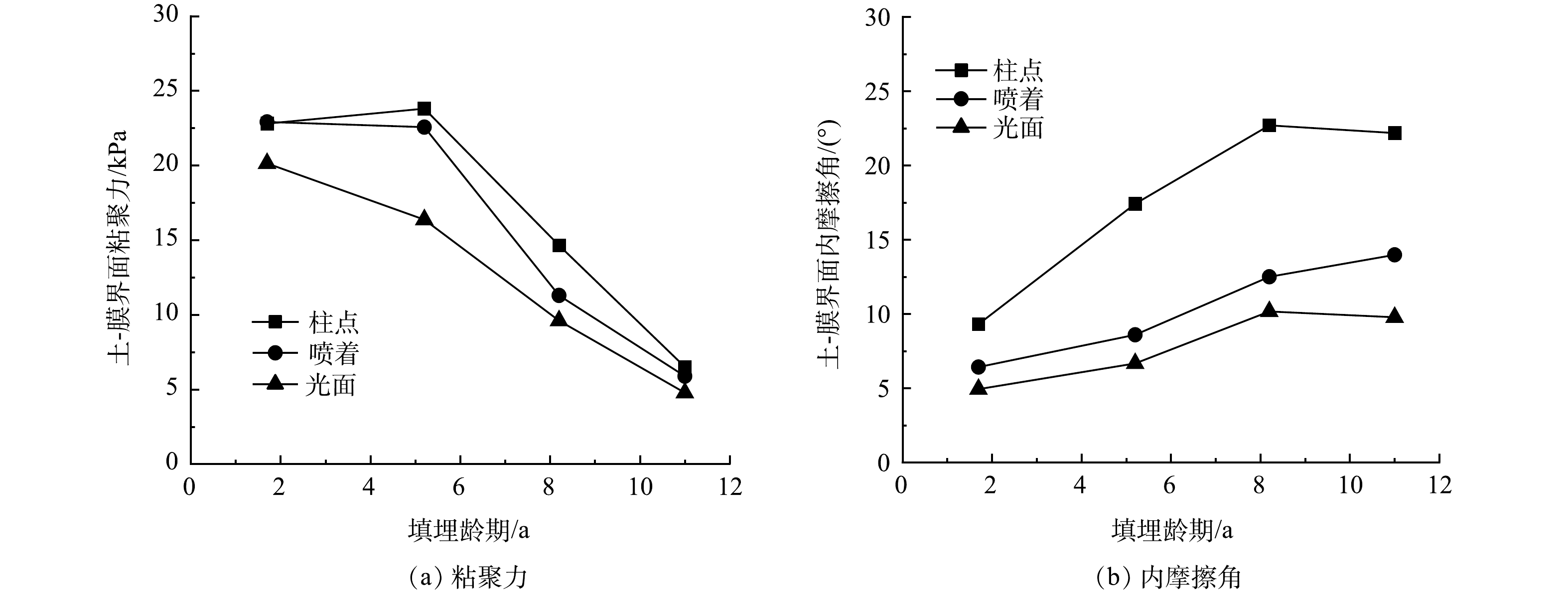
界面剪切实验结果如图3所示。由图3 (a) 可知,11 a内土-膜界面粘聚力呈现下降趋势,但在小于6 a时,土-膜界面粘聚力降低不明显。其原因可能是,在龄期较短时,MSW中有机质组分迅速降解,纤维物质降解缓慢导致其质量占比增加,因此,在剪切过程中能持续提供粘聚效果[9]。随着龄期增长,生物降解充分导致纤维物质含量降低,废渣等组分中颗粒含量增高[9],增大了土-膜界面的摩擦,因而,MSW失去粘聚力,土-膜界面内摩擦角呈现上升趋势,如图3 (b) 所示。垃圾土与HDPE土工膜界面剪切实验表明,相同的竖向荷载作用下,由于土工膜表面粗糙程度不同,随着法向应力的增大,表面越粗糙的的土工膜与MSW之间的摩擦越大,界面抗剪能力越好。3种不同土工膜按照剪切试验结果,抗剪强度表现为:柱点>喷着>光面。本实验研究了龄期影响下MSW与HDPE土工膜之间的界面抗剪强度变化特性,但未考虑土工膜本身随龄期变化产生的劣化影响。尽管HDPE土工膜相较于MSW受到龄期影响要小,但其水力性能会随时间下降并且产生而外的拉伸应变[25],此种影响仍不可忽略。因此,本次实验得到的数据结果较保守,龄期对HDPE土工膜材质的影响还有待研究。
-
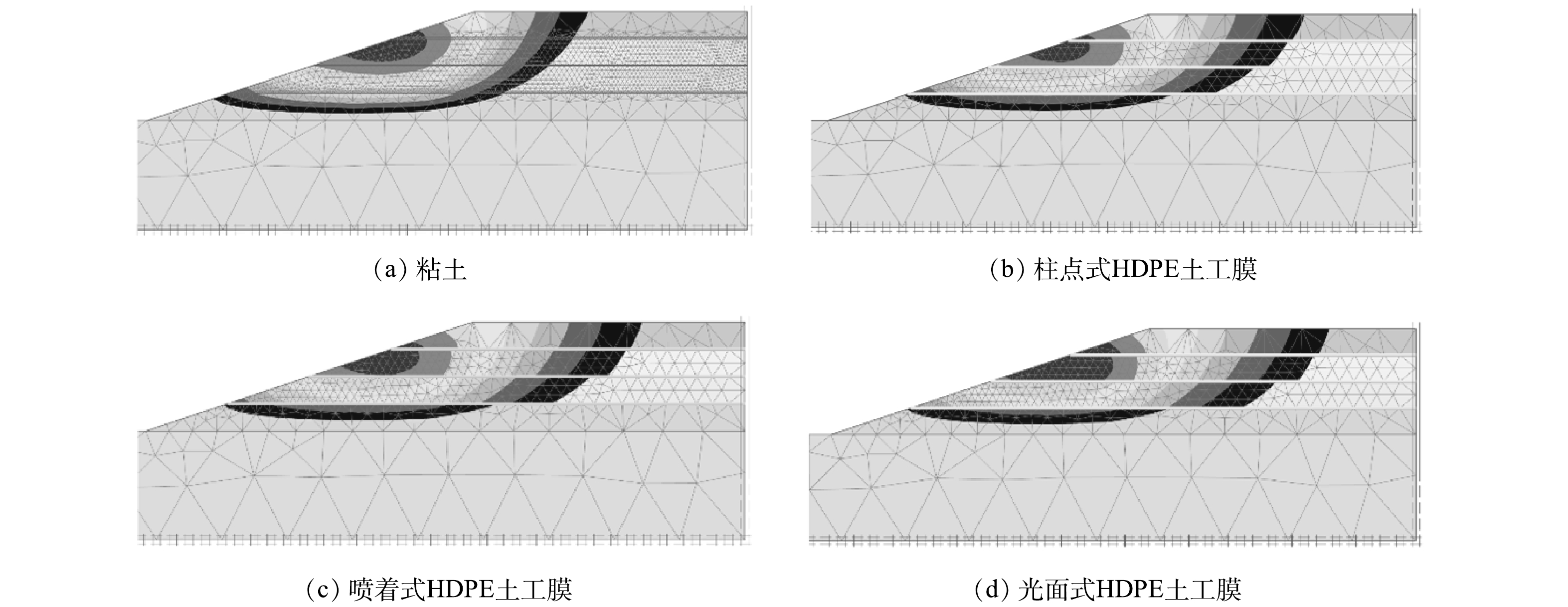
图4为不同材料作为中间衬垫的填埋体滑移情况,结果表明,分层填埋体在坡面中部产生应变集中。随着填埋龄期和高度的增加,MSW填埋体位移集中愈发明显,滑移区域不断扩展。结合实验结果可发现,可能是由于填埋体下层MSW的粘聚力较小,第4填埋层产生局部蠕变,随着龄期增长粘聚力进一步减小,坡体中部块体受重力影响沿坡面向坡脚推进,在坡面上部形成应变集中区,最终坡顶开始出现张拉裂缝,导致整个坡面滑移由表向里发展。图4 (a) 中临界滑动面连贯的穿透粘土衬垫,滑移面从坡顶向坡脚发展,直至贯通整个坡面。而HDPE土工膜替代粘土作为中间衬垫时,临界滑动面沿每层土-膜界面处均有一定滑移,在填埋体不同分层中错综发展,如图4 (b)~4 (d) 所示。图4滑移面分布情况表明,3种土工膜相较于粘土覆盖均延缓了上层滑移面的贯通,阻断了下方填埋体滑裂带的形成。根据实验结果可发现,首先,HDPE土工膜抗拉强度高于MSW,抵抗了上层填埋体对下层的剪应力;其次,由于每层MSW的参数不同,坡体下层填埋龄期较长,MSW的粘聚力很小,几乎接近于0,抗滑能力差,而上层填埋龄期较短,MSW的粘聚力跟内摩擦角能很好抵抗滑移。这解释了土-膜界面滑移由下至上越来越小的原因,但同时也会造成填埋体分层处的位移剧增。
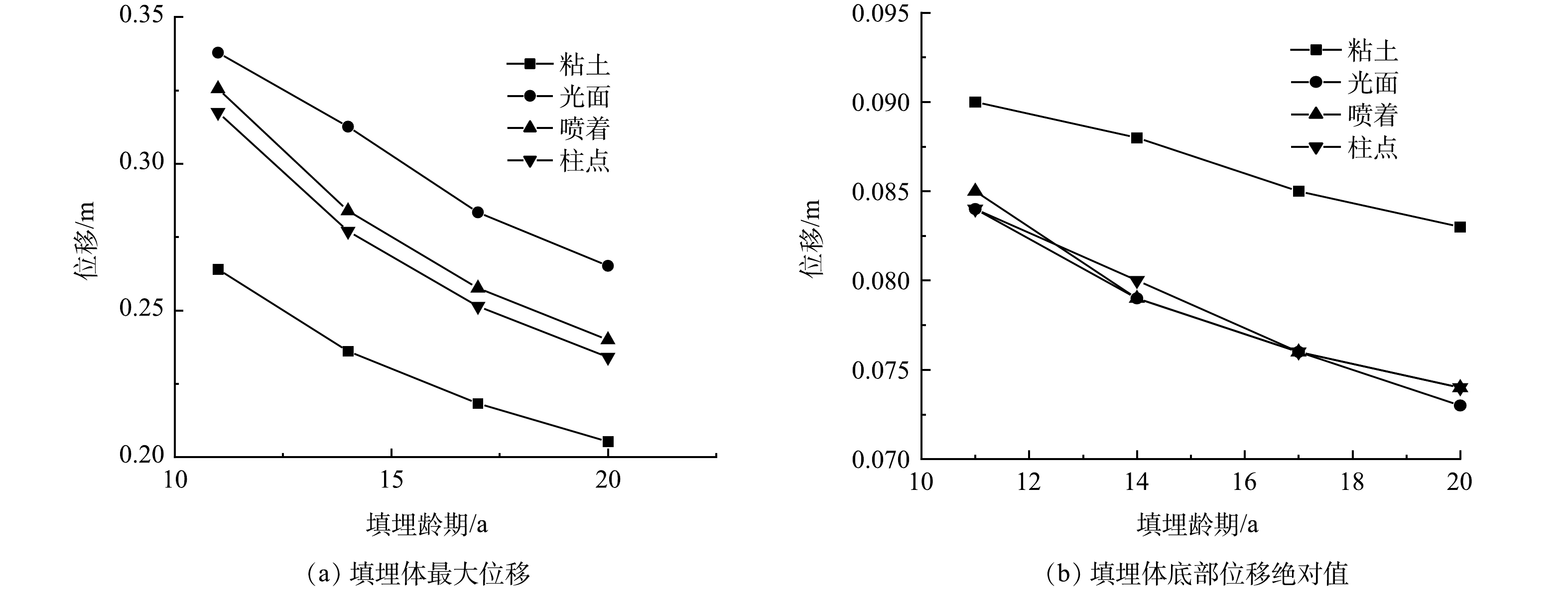
图5为11~20 a填埋体的位移数值变化。由图5 (a) 可知,临界滑动面在土-膜界面处产生水平滑移,故导致坡体最大位移明显高于粘土,分别比粘土覆盖的填埋体最大位移增加了29% (光面)、18% (喷着) 、17% (柱点) 。可以看出,具有一定表面粗糙度的柱点、喷着类型HDPE土工膜抗滑移能力稍好。由图5 (b) 可看出,底部位移绝对值由粘土覆盖的0.084 m减小到土工膜覆盖的0.073 m,降低了10%,3种类型HDPE土工膜均能很好抑制填埋体底部位移的发展。HDPE土工膜阻断了临界滑动面的形成,大大减小了底部位移。综合效果为:柱点>喷着>光面。
-
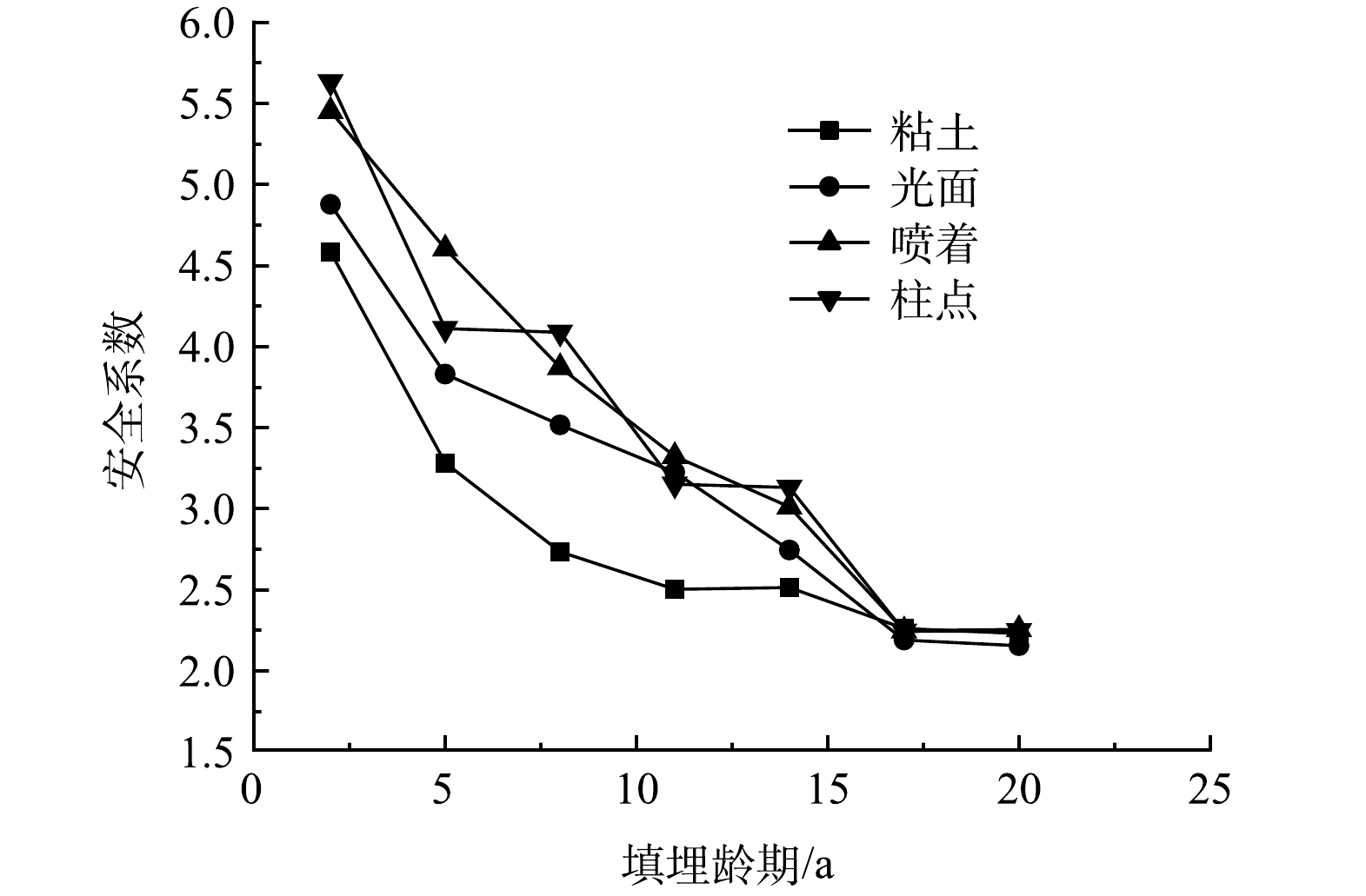
图6为20 a内填埋体整体稳定安全系数的变化。根据《生活垃圾卫生填埋场岩土工程技术规范》 (CJJ176-2012) [23]规定,填埋体整体稳定安全系数需高于1.25才能保证其稳定,数值模拟结果均达到要求。在17 a内,HDPE土工膜作为中间衬垫的填埋体整体稳定安全系数均高于粘土覆盖的填埋体。17 a之后的整体稳定安全系数则与粘土衬垫接近。这可能是因为,土工膜材料自身劣化导致其力学性能降低至与粘土接近引起的[25]。在20 a的模拟过程中,柱点类型的整体稳定安全系数从5.632减小到2.246;喷着类型与柱点类型降幅相近,从5.456减小到2.256;光面类型的整体稳定安全系数从4.877减小到2.154,与粘土作为中间衬垫相比分别增大了 28% (柱点) 、30% (喷着) 和18.5% (光面) 。可见,当MSW进行分层填埋时,HDPE土工膜能够代替粘土作为中间衬垫,将起到很好的安全稳定作用。
-
1) 随着龄期增长,土-膜界面粘聚力总体呈现下降趋势,内摩擦角先上升而后趋于平稳。表面越粗糙的HDPE土工膜与MSW的摩擦越大,柱点类型HDPE土工膜有更好的界面抗剪效果。
2) HDPE土工膜比粘土衬垫更能减小MSW填埋体底部位移绝对值,但会增加最大位移。
3) HDPE土工膜能延缓上层滑移面的贯通、阻断下方填埋体滑裂带的形成,提升坡体稳定性。其中柱点式与喷着式土工膜较粘土衬垫能提高30%左右安全性,起到很好的安全稳定作用。
土工膜衬垫对不同龄期垃圾填埋体稳定性的影响
The influence of geomembrane liner on the stability of landfill at different ages
-
摘要: 城市垃圾填埋场在填埋和运营过程中,垃圾土的抗剪强度会随着龄期的增长而变化,作为中间衬垫的土工膜规格和参数也将直接影响垃圾填埋场的稳定性。针对柱点、喷着和光面3种不同规格的HDPE土工膜衬垫,结合室内土-膜界面剪切实验和数值模拟手段,分析HDPE土工膜作为中间衬垫对垃圾填埋体稳定性的影响。结果表明,随着填埋龄期的增加,生物降解持续,垃圾土纤维物含量降低,废渣颗粒含量增加,导致土-膜界面粘聚力呈下降趋势,内摩擦角呈现上升趋势;相较于粘土覆盖,HDPE土工膜能有效抑制填埋体底部位移。结合工程实例,垃圾填埋体底部位移绝对值由粘土覆盖的0.084 m减小到土工膜覆盖的0.073 m;整体稳定安全系数较粘土覆盖分别增大 28% (柱点) 、30% (喷着) 和18.5% (光面) 。HDPE土工膜能明显延缓垃圾填埋体滑移面向填埋体中部和深部的发展,阻断滑裂带的形成。本研究结果可为垃圾填埋场设计和现场工程的安全性评价提供参考。Abstract: During the landfilling and operation of MSW landfills, the shear strength of waste soil will change with age. The specifications and parameters of geomembrane as the intermediate liner will also directly affect landfill stability. Aiming at three different specifications of HDPE geomembrane liners, such as salient point, textured and smooth, combined with indoor soil-geomembrane interface shear test and numerical simulation, the influence of HDPE geomembrane as an intermediate liner on the stability of landfill was analyzed. The results showed that with the increase in landfill age, the biodegradation continued, the fiber content of waste soil decreased, and the particle content of waste residue increased, resulting in the decrease of soil-film interface cohesion and the increase of internal friction angle. Compared with clay cover, HDPE geomembrane can effectively restrain the bottom displacement of landfill. Combining with the engineering example, the absolute value of the bottom displacement of the waste landfill decreases from 0.084 m of the clay coating cover to 0.073 m of the geomembrane coating cover. Compared with clay cover, the overall stability safety factor increases by 28% (salient point), 30% (textured) and 18.5% (smooth), respectively. HDPE geomembrane can delay the penetration of landfill slip towards the middle and deep of landfill and block the formation of slip zone. The results of this study provide a reference for landfill design and site engineering safety evaluation.
-
Key words:
- MSW landfill /
- stability /
- age /
- HDPE geomembrane /
- soil-geomembrane interface shear
-
城市固体废弃物 (MSW) 的时变性会影响填埋体的稳定 [1-3]。MSW组分复杂,随着填埋龄期增加,大量有机物和纤维状物质产生降解,其抗剪强度也会随之改变。而抗剪强度的降低是造成分层垃圾填埋体滑移的主要原因[4-6]。填埋体的滑移失稳破坏会导致大量填埋垃圾和渗滤液滑出场外,造成严重的环境污染及财产损失[7]。
抗剪强度是MSW重要的力学性能之一,其变化规律与填埋龄期密切相关。随着龄期的增加,MSW的内摩擦角会增大,而粘聚力逐渐降低直至为0[8-10],这会导致填埋体沿衬垫发生滑移破坏。因此,土-膜界面的剪切特性得到了学者们的广泛研究[11-15]。PUNETHA等[13]通过直剪实验研究了光面及糙面HDPE土工膜和各类土颗粒物界面抗剪强度。BACAS等[14]对8种土工合成材料和18种不同界面进行了直剪实验,分析了界面剪切强度特性。LI等[15]研究了冻融循环作用下,密实粘土衬垫与HDPE土工膜界面剪切特性。在稳定性分析方面,ZIENKIEWIEZ等[16]首次将强度折减法引入到有限元边坡分析中。UGAI等[17]、郑颖人等[18]和陈雪珍等[19]将有限元分析的安全系数应用在工程中,推动有限元强度折减法的发展。
学者们通常以实验确定各层垃圾土的抗剪强度,对分层填埋场进行稳定性分析[4,6]。但目前对分层填埋场的稳定性分析都集中在以粘土作为中间衬垫,HDPE土工膜因为其耐久性好、化学性质稳定、柔韧性佳等特性而被视为替代粘土的理想材料[20],同时又缺乏将土工膜作为中间衬垫的应用研究。因此,本研究以HDPE土工膜代替粘土作为中间衬垫,进行土-膜界面剪切实验,利用PLAXIS有限元软件模拟分层填埋体的滑移过程及其整体稳定性变化,并分析HDPE土工膜作为中间衬垫的可行性,以期为土工膜应用于填埋场作为中间衬垫提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
直剪实验的材料取自某苏南平原型垃圾填埋场,总计填埋库容量为476.5×104 m3。实验土样分别取自该场地的改扩建工程、二期工程、续建工程、续建二期工程。其物理指标如表1所示。选用3种不同规格的HDPE土工膜,分别为喷着式、柱点式和光面式。其中,柱点式表面排布规则的小凸点;喷着式表面具有不规则纹理,粗糙程度比柱点式低;光面式表面则是光滑的平面。3种土工膜厚度均为1.5 mm,密度大于0.94 g·cm-3,炭黑含量在2%~3%。HDPE土工膜的物理参数如表2所示。
表 1 MSW试样物理力学指标Table 1. Physical and mechanical indices of refuse MSW sample样品编号 填埋龄期/a 含水率 孔隙比 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/ (°) Z1 1.5~2.0 45%~76% 2.33 23.3 9.8 Z2 4.5~5.0 1.65 23.8 17.5 Z3 8.0~9.0 1.96 16.1 26.0 Z4 10.0~13.0 2.62 2.8 34.2 表 2 屈服应变下HDPE土工膜的物理参数Table 2. Physical parameter of HDPE geomembrane under yield strain类型 厚度/mm 拉伸强度/(kN·m−1) 屈服应变 拉伸刚度/(kN·m−1) 柱点式 1.50 17.80 16.00% 111.25 光面 1.50 20.51 14.00% 146.50 喷着式 1.50 17.51 14.00% 125.07 1.2 实验装置
实验仪器与试样布置如图1所示,采用大尺寸直剪仪(THE-1000,天水红山实验机有限公司),上下剪切盒尺寸为500 mm×500 mm×410 mm,根据《土工合成材料测试规程》 (SL 235-2012) [21]进行实验 。
1.3 实验方法
将试样按龄期分为4组,每组选择50、100、150、200 kPa竖向荷载进行压缩,压缩至少4 h,剪应变不小于20%,剪切位移设置为100 mm,剪切速率为2 mm·min-1。以土-膜界面峰值强度表征土-膜界面强度[21]。依据莫尔-库伦破坏准则,得到不同龄期MSW试样与HDPE土工膜的界面抗剪强度参数关系。
2. 分层填埋体数值模拟
2.1 几何模型建立
本研究参考某苏南平原型垃圾填埋场,建立的数值模型如图2所示。图2 (a) 从下至上为第1至第4填埋层;填埋体下底边长110 m、上底边长50 m、高20 m、斜坡度为1∶3,边界地基土深20 m、长300 m[22],分层处布设HDPE土工膜衬垫[23],有限元网格划分如图2 (b) 所示;不设HDPE土工膜的填埋体采用粘土封层,厚度为300 mm [22]。
2.2 计算参数确定
基于Mohr-Coulomb准则,不考虑渗流影响,土-膜界面相互作用按照强度折减计算。土体物理参数取值见表3。土体抗剪强度参数按照表1赋予每一填埋层。 HDPE土工膜厚度和拉伸刚度按照表2分别赋予每层衬垫。由于垃圾土无剪胀性,不考虑剪胀效应,剪胀角取值为0[24]。
表 3 各层土材料的参数Table 3. Table of material parameters of soil layers土层名称 压缩模量/MPa 泊松比 容重/(kN·m−3) 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/ (°) 地基土层砂土状强风化花岗岩 30 0.25 19.5 35.0 28.5 粘土覆盖层 23 0.25 21.0 12.0 25.0 MSW第1填埋层 2 0.40 10.5 23.3 9.8 MSW第2填埋层 23.8 17.5 MSW第3填埋层 16.1 26.0 MSW第4填埋层 2.8 34.2 3. 结果与讨论
3.1 龄期对土-膜界面强度的影响
界面剪切实验结果如图3所示。由图3 (a) 可知,11 a内土-膜界面粘聚力呈现下降趋势,但在小于6 a时,土-膜界面粘聚力降低不明显。其原因可能是,在龄期较短时,MSW中有机质组分迅速降解,纤维物质降解缓慢导致其质量占比增加,因此,在剪切过程中能持续提供粘聚效果[9]。随着龄期增长,生物降解充分导致纤维物质含量降低,废渣等组分中颗粒含量增高[9],增大了土-膜界面的摩擦,因而,MSW失去粘聚力,土-膜界面内摩擦角呈现上升趋势,如图3 (b) 所示。垃圾土与HDPE土工膜界面剪切实验表明,相同的竖向荷载作用下,由于土工膜表面粗糙程度不同,随着法向应力的增大,表面越粗糙的的土工膜与MSW之间的摩擦越大,界面抗剪能力越好。3种不同土工膜按照剪切试验结果,抗剪强度表现为:柱点>喷着>光面。本实验研究了龄期影响下MSW与HDPE土工膜之间的界面抗剪强度变化特性,但未考虑土工膜本身随龄期变化产生的劣化影响。尽管HDPE土工膜相较于MSW受到龄期影响要小,但其水力性能会随时间下降并且产生而外的拉伸应变[25],此种影响仍不可忽略。因此,本次实验得到的数据结果较保守,龄期对HDPE土工膜材质的影响还有待研究。
3.2 土工膜作为中间衬垫的填埋体滑移分析
图4为不同材料作为中间衬垫的填埋体滑移情况,结果表明,分层填埋体在坡面中部产生应变集中。随着填埋龄期和高度的增加,MSW填埋体位移集中愈发明显,滑移区域不断扩展。结合实验结果可发现,可能是由于填埋体下层MSW的粘聚力较小,第4填埋层产生局部蠕变,随着龄期增长粘聚力进一步减小,坡体中部块体受重力影响沿坡面向坡脚推进,在坡面上部形成应变集中区,最终坡顶开始出现张拉裂缝,导致整个坡面滑移由表向里发展。图4 (a) 中临界滑动面连贯的穿透粘土衬垫,滑移面从坡顶向坡脚发展,直至贯通整个坡面。而HDPE土工膜替代粘土作为中间衬垫时,临界滑动面沿每层土-膜界面处均有一定滑移,在填埋体不同分层中错综发展,如图4 (b)~4 (d) 所示。图4滑移面分布情况表明,3种土工膜相较于粘土覆盖均延缓了上层滑移面的贯通,阻断了下方填埋体滑裂带的形成。根据实验结果可发现,首先,HDPE土工膜抗拉强度高于MSW,抵抗了上层填埋体对下层的剪应力;其次,由于每层MSW的参数不同,坡体下层填埋龄期较长,MSW的粘聚力很小,几乎接近于0,抗滑能力差,而上层填埋龄期较短,MSW的粘聚力跟内摩擦角能很好抵抗滑移。这解释了土-膜界面滑移由下至上越来越小的原因,但同时也会造成填埋体分层处的位移剧增。
图5为11~20 a填埋体的位移数值变化。由图5 (a) 可知,临界滑动面在土-膜界面处产生水平滑移,故导致坡体最大位移明显高于粘土,分别比粘土覆盖的填埋体最大位移增加了29% (光面)、18% (喷着) 、17% (柱点) 。可以看出,具有一定表面粗糙度的柱点、喷着类型HDPE土工膜抗滑移能力稍好。由图5 (b) 可看出,底部位移绝对值由粘土覆盖的0.084 m减小到土工膜覆盖的0.073 m,降低了10%,3种类型HDPE土工膜均能很好抑制填埋体底部位移的发展。HDPE土工膜阻断了临界滑动面的形成,大大减小了底部位移。综合效果为:柱点>喷着>光面。
3.3 3种类型HDPE土工膜在龄期影响下填埋体稳定安全系数变化
图6为20 a内填埋体整体稳定安全系数的变化。根据《生活垃圾卫生填埋场岩土工程技术规范》 (CJJ176-2012) [23]规定,填埋体整体稳定安全系数需高于1.25才能保证其稳定,数值模拟结果均达到要求。在17 a内,HDPE土工膜作为中间衬垫的填埋体整体稳定安全系数均高于粘土覆盖的填埋体。17 a之后的整体稳定安全系数则与粘土衬垫接近。这可能是因为,土工膜材料自身劣化导致其力学性能降低至与粘土接近引起的[25]。在20 a的模拟过程中,柱点类型的整体稳定安全系数从5.632减小到2.246;喷着类型与柱点类型降幅相近,从5.456减小到2.256;光面类型的整体稳定安全系数从4.877减小到2.154,与粘土作为中间衬垫相比分别增大了 28% (柱点) 、30% (喷着) 和18.5% (光面) 。可见,当MSW进行分层填埋时,HDPE土工膜能够代替粘土作为中间衬垫,将起到很好的安全稳定作用。
4. 结论
1) 随着龄期增长,土-膜界面粘聚力总体呈现下降趋势,内摩擦角先上升而后趋于平稳。表面越粗糙的HDPE土工膜与MSW的摩擦越大,柱点类型HDPE土工膜有更好的界面抗剪效果。
2) HDPE土工膜比粘土衬垫更能减小MSW填埋体底部位移绝对值,但会增加最大位移。
3) HDPE土工膜能延缓上层滑移面的贯通、阻断下方填埋体滑裂带的形成,提升坡体稳定性。其中柱点式与喷着式土工膜较粘土衬垫能提高30%左右安全性,起到很好的安全稳定作用。
-
表 1 MSW试样物理力学指标
Table 1. Physical and mechanical indices of refuse MSW sample
样品编号 填埋龄期/a 含水率 孔隙比 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/ (°) Z1 1.5~2.0 45%~76% 2.33 23.3 9.8 Z2 4.5~5.0 1.65 23.8 17.5 Z3 8.0~9.0 1.96 16.1 26.0 Z4 10.0~13.0 2.62 2.8 34.2 表 2 屈服应变下HDPE土工膜的物理参数
Table 2. Physical parameter of HDPE geomembrane under yield strain
类型 厚度/mm 拉伸强度/(kN·m−1) 屈服应变 拉伸刚度/(kN·m−1) 柱点式 1.50 17.80 16.00% 111.25 光面 1.50 20.51 14.00% 146.50 喷着式 1.50 17.51 14.00% 125.07 表 3 各层土材料的参数
Table 3. Table of material parameters of soil layers
土层名称 压缩模量/MPa 泊松比 容重/(kN·m−3) 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/ (°) 地基土层砂土状强风化花岗岩 30 0.25 19.5 35.0 28.5 粘土覆盖层 23 0.25 21.0 12.0 25.0 MSW第1填埋层 2 0.40 10.5 23.3 9.8 MSW第2填埋层 23.8 17.5 MSW第3填埋层 16.1 26.0 MSW第4填埋层 2.8 34.2 -
[1] KOERNER R M, SOONG T Y. Leachate in landfills: the stability issues[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2000, 18(5): 293-309. doi: 10.1016/S0266-1144(99)00034-5 [2] BLIGHT G. Slope failures in municipal solid waste dumps and landfills: a review[J]. Waste Management & Research, 2008, 26(5): 448-463. [3] HUANG Y, FAN G B. Engineering geological analysis of municipal solid waste landfill stability[J]. Natural Hazards, 2016, 84(1): 93-107. doi: 10.1007/s11069-016-2408-8 [4] 范鑫萍, 黄茂松, 王浩然. 考虑龄期分层的固体废弃物填埋场边坡稳定分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(6): 1715-1720. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.06.023 [5] CHAVAN D, LAKSHMIKANTHAN P, MONDAL P, et al. Determination of ignition temperature of municipal solid waste for understanding surface and sub-surface landfill fire[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 97: 123-130. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.08.002 [6] HOSSAIN M S, HAQUE M A. Stability analyses of municipal solid waste landfills with decomposition[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2009, 27(6): 659-666. doi: 10.1007/s10706-009-9265-0 [7] 詹良通, 兰吉武, 邓林恒, 等. 浓缩液回灌对垃圾填埋体水位及稳定性的影响[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2012, 34(2): 126-131. [8] STARK T D, HUVAJ-SARIHAN N, LI G C. Shear strength of municipal solid waste for stability analyses[J]. Environmental Geology, 2009, 57(8): 1911-1923. doi: 10.1007/s00254-008-1480-0 [9] ABREU A E S, VILAR O M. Influence of composition and degradation on the shear strength of municipal solid waste[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 68: 263-274. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.05.038 [10] REDDY K R, HETTIARACHCHI H, GANGATHULASI J, et al. Geotechnical properties of municipal solid waste at different phases of biodegradation[J]. Waste Management, 2011, 31(11): 2275-2286. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2011.06.002 [11] FOX P J, ROSS J D. Relationship between NP GCL internal and HDPE GMX/NP GCL interface shear strengths[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2011, 137(8): 743-753. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000490 [12] BRACHMAN R W I, SABIR A. Long-term assessment of a layered-geotextile protection layer for geomembranes[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 2013, 139(5): 752-764. [13] PUNETHA P, MOHANTY P, SAMANTA M. Microstructural investigation on mechanical behavior of soil-geosynthetic interface in direct shear test[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes. 2017, 45(3): 197-210. [14] BACAS B M, CANIZAL J, KONIIETZKY H. Shear strength behavior of geotextile/geomembrane interfaces[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 7(6): 638-645. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.08.001 [15] LI L, FALL M, FANG K. Shear behavior at interface between compacted clay liner–geomembrane under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2020, 172: 103006. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2020.103006 [16] ZIENKIEWICZ O C, HUMPHESON C, LEWIS R W. Associated and non-associated visco-plasticity and plasticity in soil mechanics[J]. Géotechnique, 1975, 25(4): 671-689. [17] UGAI K, LESHCHINSKY D O V. Three-dimensional limit equilibrium and finite element analyses: a comparison of results[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1995, 35(4): 1-7. doi: 10.3208/sandf.35.4_1 [18] 郑颖人, 赵尚毅, 张鲁渝. 用有限元强度折减法进行边坡稳定分析[J]. 中国工程科学, 2002, 4(10): 57-61+78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2002.10.011 [19] 陈雪珍, 简文彬. 基于强度折减法的分步施工边坡稳定性分析[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报, 2018, 16(1): 207-210+223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2018.01.037 [20] 吴维兴, 周露明, 谢兴华, 等. 高密度聚乙烯土工膜与固体废物界面接触强度的试验研究[J]. 济南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 34(1): 30-34. doi: 10.13349/j.cnki.jdxbn.2020.01.005 [21] 中华人民共和国水利部. 土工合成材料测试规程: SL 235-2012[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2012. [22] 北京金土木软件技术有限公司. PLAXIS岩土工程软件使用指南[J]. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2010: 25-78. [23] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 生活垃圾卫生填埋场岩土工程技术规范: CJJ 176-2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. [24] Bolton M D. Discussion: The strength and dilatancy of sands[J]. Géotechnique, 1987, 37(2): 219-226. [25] SUN X C, XU Y, LIU Y Q, et al. Evolution of geomembrane degradation and defects in a landfill: impacts on long-term leachate leakage and groundwater quality[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 224: 335-345. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.200 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: