-
磷是自然水体的限制性营养元素之一[1],过剩的磷会导致水生生态系统初级生产力升高,进而导致水体富营养化,破坏水生生态系统平衡[2]。沉积物作为天然河道的组成部分,一方面,沉积物磷的赋存形态及含量、分布特征、迁移转化和吸附特性等影响着水体富营养化的进程[3];另一方面,在外源污染得到有效控制的同时,内源磷释放会成为主要的污染因子,导致水体富营养化[4]。影响磷在表层沉积物吸附释放的主要因素有沉积物组成粒径、各形态磷含量、腐殖质种类等沉积物本身的特性和pH、氧化还原电位、离子强度、温度等环境因素。目前,已经提出对沉积物不同形态磷的分析方法。朱广伟等[5]对沉积物不同形态磷进行了化学分级浸提,是目前比较系统的方法,该方法将沉积物中的磷分为7种形态,有效地分离了Fe/Al-P,减少后续投加富里酸对各形态磷影响研究的异议。
根据清远市人民政府网站公开数据,“十三五”期间漫水河黄坎桥断面水质为Ⅴ类-劣Ⅴ类,定类因子主要为总磷,而总磷质量浓度超标是造成水体富营养化的主要因素之一,从天地图可知,该流域污染源以畜禽养殖、农田及生活污水为主,其产生的废水富含有机物,排入河道会造成水体有机质含量上升[6]。
有机质作为大气二氧化碳和植物养分的来源以及连接土壤物理、化学和生物特性的主要因素,对其研究具有重要意义[7]。土壤有机质由生物化学组成、生物稳定性和碳周转率等各不相同的单元组成。腐殖化的有机质被称为腐殖质(腐殖酸HA、富里酸FA和胡敏素HA)[8],含有羧基、醇羟基、酚羟基等各种官能团。在腐殖质丰富的环境中,腐殖质与多种金属氧化物(Al2O3、Fe2O3、SiO2和TiO2等)通过络合、螯合和吸附等机理相互作用形成有机胶体,并随水体大量迁移,从而直接或间接影响土壤中磷酸盐的吸附和磷的有效性[9]。因此,本研究将通过模拟实验,向水环境中投加外源富里酸以探究腐殖质对沉积物中磷酸盐的吸附和磷有效性的影响。另外,有机质腐殖化是一个缓慢的过程,在实验过程中,添加外源富里酸可以在不等待有机质腐殖化的情况下增加有机质含量,是排除不同矿物组成和其他因素变化对实验结果造成影响的有效途径[10]。
目前,关于水体和沉积物营养盐污染的研究分析较多[11],对蓝藻、有机质等物质对沉积物磷形态迁移转化规律研究较为深入[12],也有研究者分析了FeO与腐殖质的结合机理[13]。但目前尚缺乏对腐殖质浓度影响沉积物总体磷形态迁移转化规律的研究。因此,本研究在已有研究的基础上,选取清远市清新区漫水河河段5条污染贡献比较高且污染来源不同的农灌渠作为研究对象,分析了其表层沉积物中磷的分布特征;通过投加外源富里酸探究了腐殖质浓度对沉积物各形态磷分布的影响,揭示了沉积物中各形态无机磷迁移转化的机制,以期为后续河道富营养化控制和内部养分负荷降解提供参考。
-
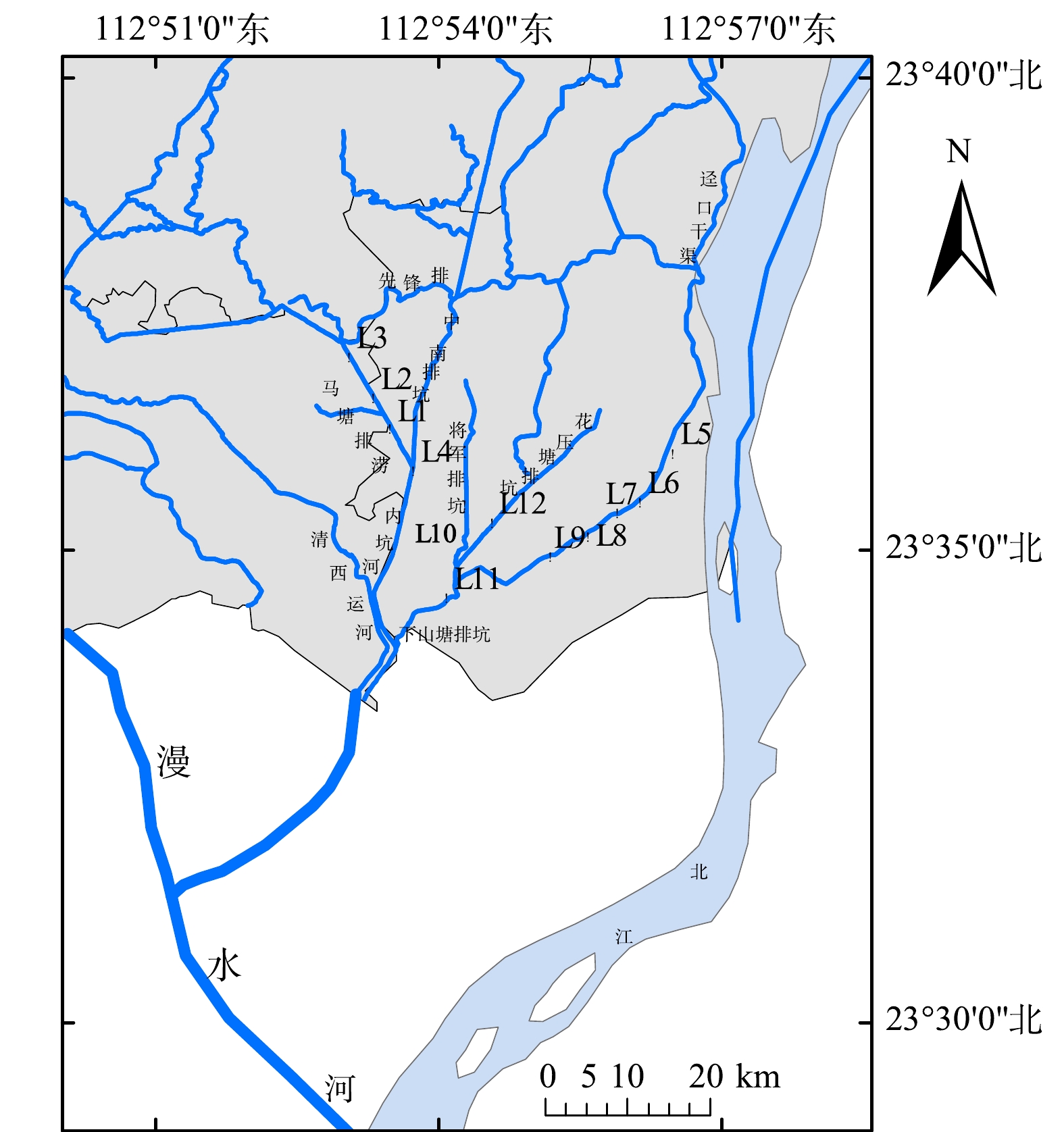
漫水河是珠江水系北江下游的一级支流,发源于广东省广宁县义和村湴仔顶,穿过广宁、四会、清新、三水,最后至佛山市三水区大塘圩澉鱼咀汇入北江,干流长75 km,集水面积791 km2。本研究选取境内5条污染贡献比较高的农灌渠,分别采取12个上覆水和沉积物样品,采样点的空间位置如图1所示。
-
1)样品采集与预处理。2021年3月对漫水河开展水样和沉积物样品采集,当采样点位水深小于2 m时,在水下20 cm处采集水样300 mL;若水深大于2 m时,则在水面下20 cm处和距水面1.5 m处分别采集水样后混合;水样采集后,取50%水样过0.45 μm滤膜后于4 ℃条件下避光保存。
沉积物采样点和水样采样点位保持一致,利用抓泥斗采集表层沉积物,每个样点平行采集3次后混合。运回实验室后,将沉积物自然风干,剔除石子及动植物残渣后,用玛瑙研钵研磨并过100目筛,用于氮、磷等相关指标分析。
2)相关指标分析。水样各指标分析均按《水和废水监测分析方法(第4版)》相应的标准方法进行测定;采集沉积物原样后,参考朱广伟等[5]对沉积物不同形态磷进行化学分级浸提,将沉积物总磷划分为交换态磷(Ex-P)、铝结合磷(Al-P)、铁结合磷(Fe-P)、闭蓄态磷(Oc-P)、自生磷(De-P)、碎屑磷(Ca-P)和有机磷(Or-P),提取液采用钼锑抗法测定,TP含量由7种磷组分的总和计算得出。测定过程中所用试剂均为优级纯,以上实验在相同条件下做3个平行实验,各样品重复测定3次取平均值,相对误差控制在5%以内。
-
利用采集的沉积物样品,以富里酸为代表,探讨腐殖质对沉积物磷形态的改变机制。取4只250 mL的烧杯,每只烧杯装10 g风干处理后的土样,分别加入0、13、35、87 mL质量浓度为0.5 mg·L−1 的富里酸溶液,所含总有机碳浓度用总有机碳分析仪测定。最后,在每个烧杯中加入同一采样点、同一时间采集且经过滤的上覆水并定容至200 mL,在室温和弱光条件下通风培养,使用磁力搅拌器在200 r·min−1下搅拌20 d后,所得样品于4 000 r·min−1条件下进行20 min离心处理,以此收集实验土样,测定各形态磷含量的变化。
-
采用Excel 2016和IBM SPSS Statistics 25软件统计分析实验数据,数据图形使用origin 2018软件绘制。
-
2021年3月共采集12个上覆水样品,各形态磷的分析结果如表1所示。由表1可见,水体TP质量浓度为0.87~2.83 mg·L−1,平均值为1.66 mg·L−1;XST干渠TP质量浓度为1.76 mg·L−1、JK干渠TP质量浓度为1.36~2.83 mg·L−1,JJ排坑TP质量浓度为1.07 mg·L−1,HYT排坑TP质量浓度为2.39 mg·L−1,JK干渠与JJ排坑、HYT排坑汇合后汇入XST排坑,故XST排坑TP浓度较JK干渠有所降低。另外,MT排涝TP质量浓度为0.87~1.43 mg·L−1,参考地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838-2002),上述干渠上覆水均为劣Ⅴ类水质,为了进一步分析该区域内源磷污染的可能性和风险,对上述采样点表层沉积物进行分析。
-
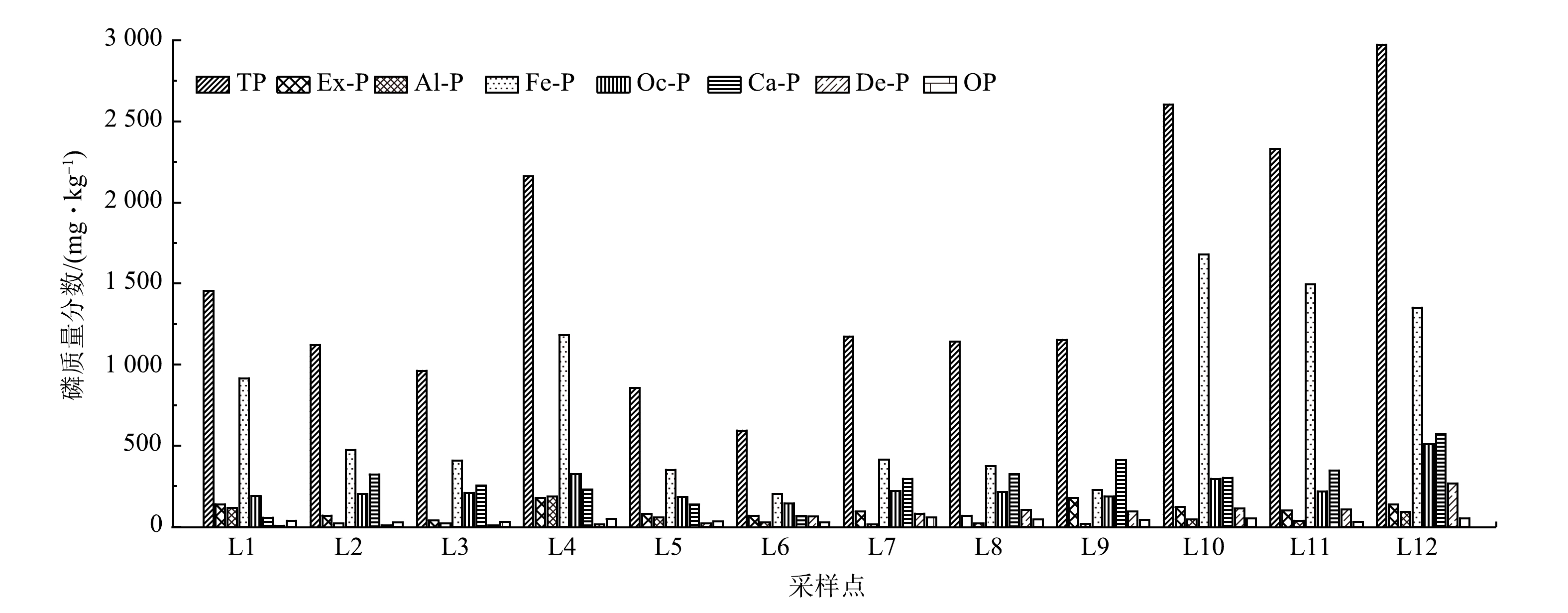
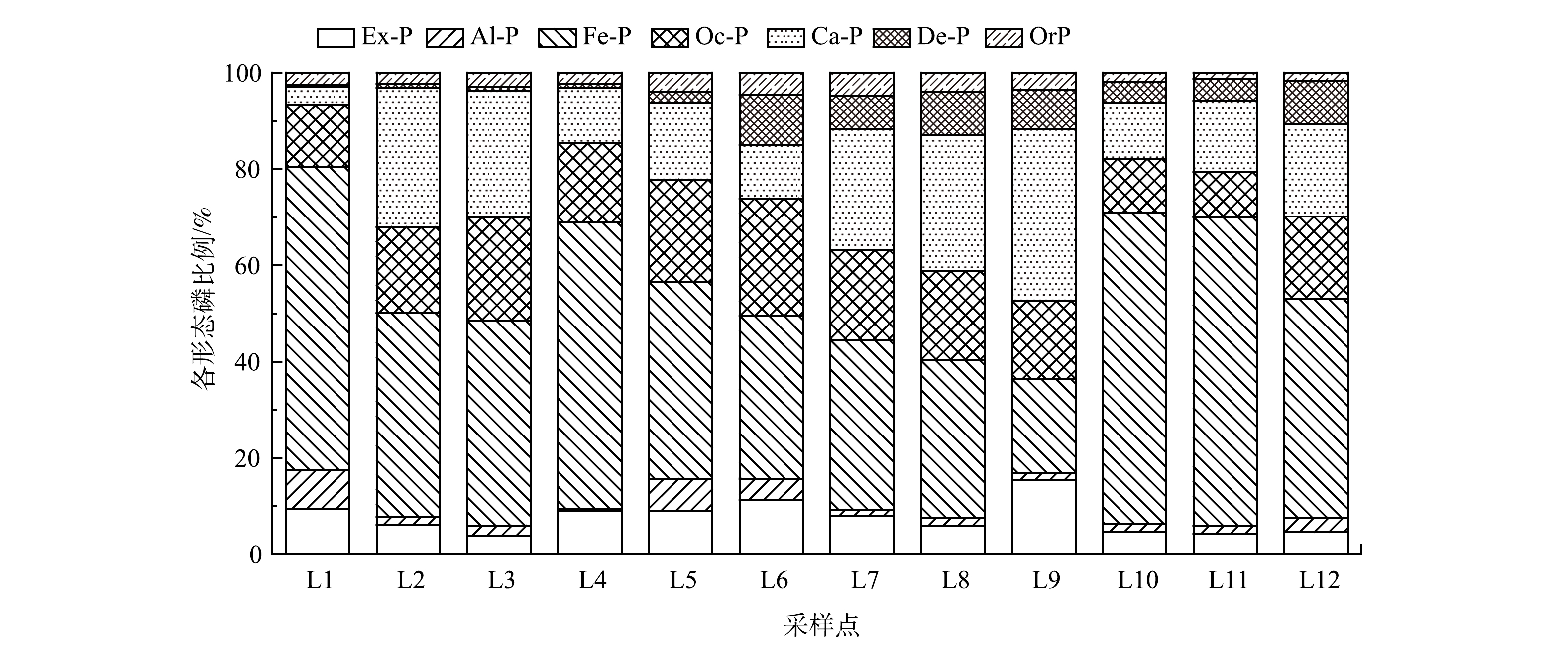
沉积物是河流的重要组成部分,沉积物中的磷以多种结合形态存在。关注沉积物中磷的赋存形态有助于揭示人为活动对水体富营养化的影响,并对河道水体富营养化控制提供指导。本研究选择漫水河清新区JK干渠、MT排涝、XST排坑、JJ排坑、HYT排坑5条农灌渠作为研究对象,共采集12个沉积物样品进行分析。如图2所示,漫水河清新区河段沉积物TP含量为593.35~2 973.00 mg·kg−1,平均含量为1 528.43 mg·kg−1;7种磷形态平均含量的排序为Fe-P>Ca-P>Oc-P>Ex-P>De-P>Or-P,无机磷为主要组分。变异系数排序为De-P>Al-P>Fe-P>Ca-P>Ex-P>Oc-P>Or-P。除Or-P外,其余磷形态变异系数均高于36%,达到高等变异水平,表明沉积物各形态磷分布波动程度相对较大[13]。
由图2可见,总磷含量的最大值出现在L12点位,最小值出现在L6点位。其主要原因可能是:HYT排坑周围遍布鱼塘,大量投饵养殖使得大部分未被生物完全利用的营养物质随鱼塘排水而进入HYT排坑,使得饵料残渣和鱼类排泄物直接或间接沉降到沉积物表面,不同赋存形态的磷酸盐与碳酸钙形成共沉淀或被氧化铁胶体吸附[14],导致该农灌渠整体总磷含量升高。
沉积物7种磷形态分级提取结果如图2和图3所示。可交换态磷(Ex-P)易通过解吸作用被水生植物直接吸收利用,一般代表沉积物无机磷中容易解吸的组分。该形态磷活性较强,对植物生长及控制上覆水体磷浓度具有重要影响,是造成水体富营养化的重要形态磷[15]。研究对象沉积物Ex-P含量为37.7~177.13 mg·kg−1,占TP比例为3.92%~15.38%,空间分布呈现一定的异质性。
铝结合磷(Al-P)和铁结合磷(Fe-P)通常被认为是生物可利用性磷,其含量与外源磷输入有关[16]。如图2和图3所示,沉积物Al-P含量为14.35~186.58 mg·kg−1,占TP含量比为1.22%~8.63%,表明研究对象沉积物Al-P含量整体水平较低;Fe-P占总磷的比例最大,含量为225.07~1 679.53 mg·kg−1,所占TP含量比为19.54%~64.47%。其中,JK干渠沉积物的Fe-P所占TP比例均低于40%,另外4条农灌渠的Fe-P所占TP比例为40%~60%,空间分布呈现出明显的区域特点。这一结果与YANG等[17]的研究结果相反。这可能与沉积物特性、环境条件等有关,反映了不同区域、水生生态系统沉积物中的Fe-P含量差异性较为明显。
闭蓄态磷(Oc-P)指被氧化铁胶膜包蔽的磷酸盐,在土壤体系中,Fe-P在还原条件下可被还原成可溶性磷酸亚铁,氧化还原电位升高后,亚铁离子又会迅速被氧化成氧化铁。由于铁和磷的化学亲和性,新形成的氧化铁易在磷酸盐(尤其是磷酸铁盐)周围形成胶膜,将磷酸盐包裹起来,故该形态的磷属于稳定态磷。研究对象沉积物中的Oc-P含量为144.44~507.99 mg·kg−1,平均含量为240.80 mg·kg−1,其含量高于Ex-P,仅次于Ca-P。这可能与水环境中氧化铁的形成及其与磷酸盐反应有关。有研究表明,人为排放的生活污水会导致上覆水水体较高浓度的Ca2+和溶解性磷酸盐形成难溶性的钙磷酸盐(Ca-P)沉淀,如羟基磷灰石和氟磷灰石,通常很难被生物体利用[18]。5条农灌渠沉积物中的Ca-P平均含量为275.57 mg·kg−1,仅次于Fe-P,表明排放生活污水可能是导致农灌渠水体富营养化的主要原因之一[19]。De-P和Oc-P、Ca-P一样较难分解,属稳定态磷,沉积物中De-P平均含量为73.37 mg·kg−1,占TP的0.37%~10.58%。
由图2和图3可见,5条农灌渠沉积物有机磷(Or-P)的含量最低,其质量浓度为26.47~56.82 mg·kg−1,平均含量仅为39.36 mg·kg−1,占TP比例小。这可能是由于浮游动植物、微生物在新陈代谢过程中产生的磷酸酶有生物作用,在其催化水解下,Or-P可以转化为其他可被生物所利用的形态磷[20]。
-
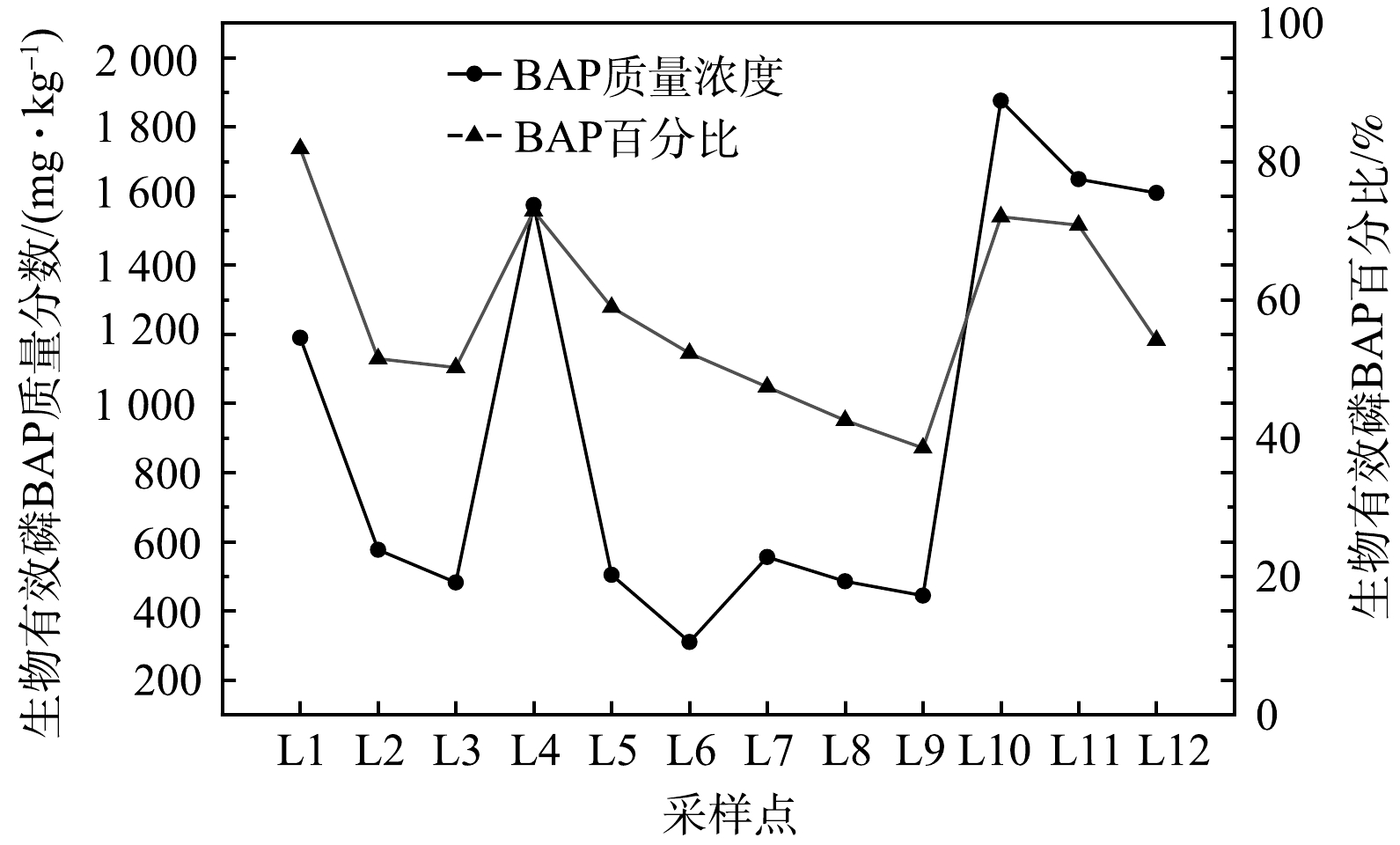
沉积物中的磷具有不同赋存形态,但并非所有形态的磷都易从沉积物释放并被生物所利用。因此,对沉积物中的生物有效磷(BAP)进行风险评估对预测河道富营养化生态问题有重要意义[21]。BAP可通过式(1)进行计算,计算结果如图4所示。
如图4所示,漫水河清新区5条农灌渠中沉积物各采样点生物有效磷分布差异较大,含量为309.94~1 875.12 mg·kg−1,平均含量为937.84 mg·kg−1,占TP的质量百分比为38.54%~81.84%,平均占比为57.73%,超过沉积物总磷的50%。因此,在一定条件下,沉积物会向上覆水释放磷,从而被水生生物所利用[22]。其中,采样点位L10的生物有效磷含量为1 875.12 mg·kg−1,占TP的质量百分比为71.98%。因此,选取该点位的沉积物进行模拟实验,探究富里酸对沉积物各形态磷含量变化的影响。
-
表层沉积物不同形态磷的含量及形态间的转化会影响沉积物的释磷能力,因此,探讨表层沉积物中各形态磷的相关性有利于掌握其分布规律。Pearson相关性分析结果见表2,沉积物中的TP含量和Fe-P(R=0.939,P<0.01)、Oc-P(R=0.833,P<0.01)、De-P (R=0.631,P<0.05)含量之间呈显著正相关,而TP含量与Ex-P、Al-P、Ca-P、Or-P含量间的相关性不大。由图3和图4可见,Oc-P和De-P含量及占比远低于Fe-P,这表明沉积物中TP的富集主要来自Fe-P含量的升高,Ex-P、Al-P、Ca-P及Or-P在迁移转化过程中对TP的影响不明显。此外,BAP与Al-P、Fe-P及Oc-P呈显著正相关,表明外源磷输入可能是沉积物释磷能力升高的主要原因之一。
-
土壤有机质(SOM)具有氧化还原活性,是营养物质迁移转化过程中的重要介质,对沉积物中氮、磷元素向上覆水扩散过程有重要影响,可以作为土壤中原生的电子穿梭体在污染物和微生物间传递电子[23]。有机质能与重金属和疏水性的有机污染物等结合,进而影响污染物在环境中的迁移、转化和分配等环境过程以及生物有效性。腐殖化的有机质主要包括腐殖酸HA、富里酸FA和胡敏素HA[12]。其中,富里酸可溶于酸碱,在实验过程中具有更好的可操控性,故本研究拟通过投加富里酸提高体系中的有机质含量。
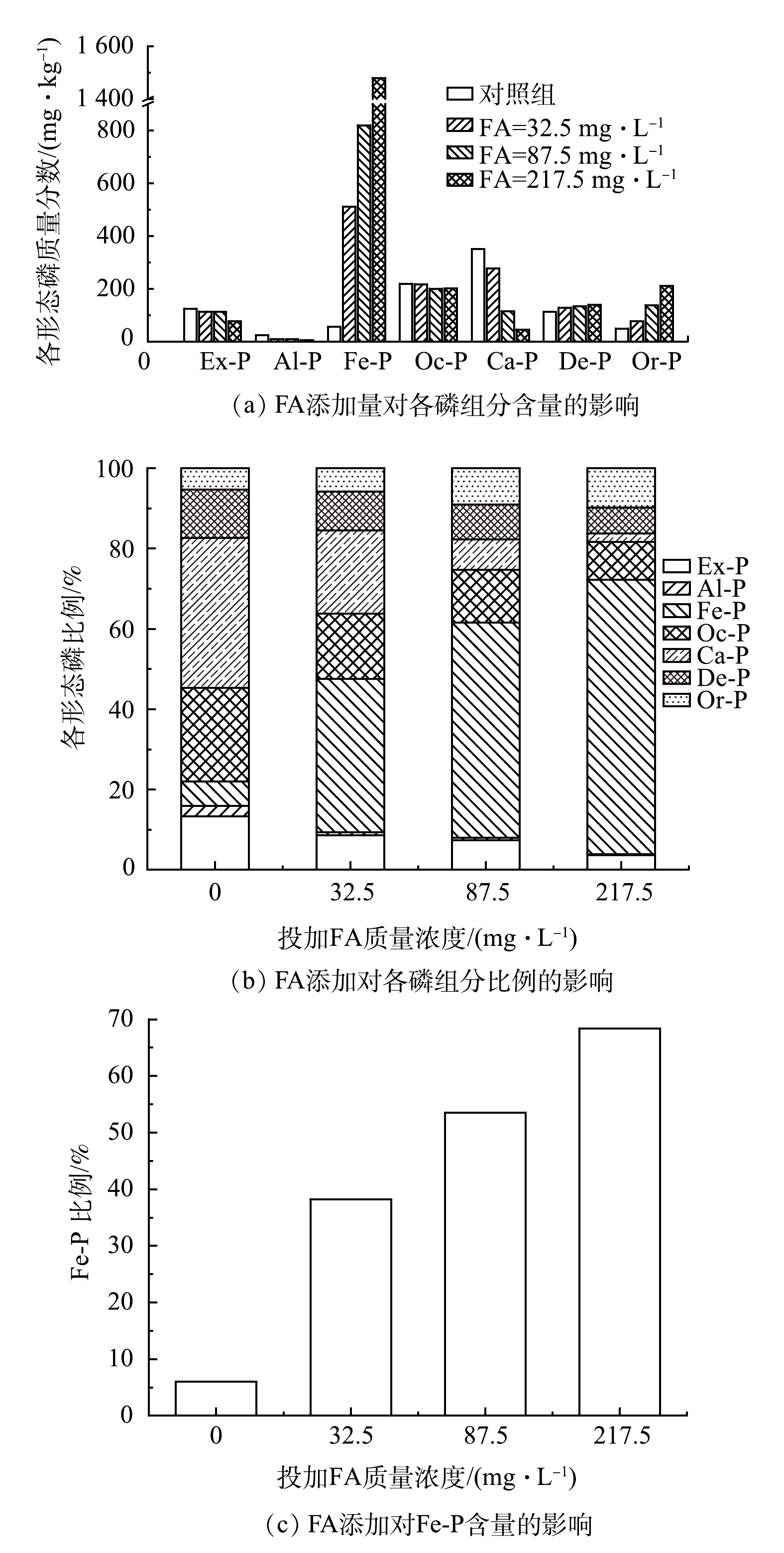
由图2和图3可见,L10点位的Fe-P浓度及占比最高,其中TP浓度仅次于L12点位。结合2.3的结论,选取L10点位的沉积物进行模拟实验,通过控制变量法将沉积物分为4组,加入不同质量的FA,实验条件如表3所示,FA对沉积物释磷影响的实验结果如图5所示。
L10点位沉积物原样的TP含量为2 604.97 mg·kg−1,Fe-P占TP含量的百分比为64.47%;而对照组的TP含量为940.67 mg·kg−1,Fe-P占TP含量的百分比为9.07%。这说明在不添加任何外源污染时,沉积物会因水动力扰动而释磷,主要释放的磷组分为Fe-P。
由图5可见,和对照组相比,组别3沉积物的TP含量升高至2 143.17 mg·kg−1。这说明以FA为代表的土壤有机质(SOM)有利于沉积物中的磷以束缚态形式存在,与DEBICKA等[24]的研究结果一致。Fe-P主要指通过物理或化学作用吸附在氢氧化铁胶体(FeOOH)表面的磷[26],其释放过程受颗粒大小、pH等多种因素影响。如图5(c)所示,随着FA浓度的增加,Fe-P的含量不断升高,Ca-P含量降低。
可见,投加外源富里酸会促进Ca3(PO4)2的还原,Fe2+被氧化为Fe3+,进一步导致FeOOH的溶解和Fe-P的形成[13],反应如式(2)所示。
-
1) 2021年3月,清远市清新区漫水河部分农灌渠水体TP质量浓度为0.87~2.83 mg·L−1,超过地表水环境质量标准Ⅴ类水浓度限值。
2)漫水河污染贡献比最高的5条农灌渠沉积物总磷含量为593.35~2 973.00 mg·kg−1,各形态磷在不同农灌渠的分布波动相对较大。其中,Fe-P占TP的质量比最高,为19.54%~64.47%;JK干渠沉积物的Fe-P占比低于40%;另外4条农灌渠的Fe-P占比为40%~60%。空间分布呈现明显的区域特征。
3)漫水河清新区河段沉积物各采样点生物有效磷分布差异较大,含量为309.94~1 875.12 mg·kg−1,平均值为937.84 mg·kg−1,占TP的质量比为38.54%~81.84%,平均值为57.73%,超过沉积物总磷的50%,说明沉积物有较大的释磷潜能,这可能是影响5条农灌渠水体富营养化的重要因素之一。
4)沉积物中的TP含量和Fe-P含量间呈显著正相关(R=0.939,P<0.01),与Oc-P、De-P含量间也呈显著正相关,而与Ex-P、Al-P、Ca-P、Or-P含量间的相关性不大,故沉积物中TP的富集可能主要来自于Fe-P、Oc-P含量的升高。BAP和Al-P、Fe-P与Oc-P呈显著正相关,表明外源磷输入可能是导致沉积物释磷能力升高的主要原因。
5)水动力扰动会促进沉积物大量释放磷,主要释放的形态为Fe-P;随着FA浓度的增加,沉积物的TP含量从对照组的620.80 mg·kg−1升至组别3的2 143.17 mg·kg−1,说明沉积物对磷的吸附能力随着FA浓度的升高而增强;同时,FA会促进Ca3(PO4)2的还原,Fe2+被氧化为Fe3+,导致FeOOH的溶解和Fe-P的形成。
漫水河清远流域磷污染特征及富里酸对沉积物释磷的影响
Characteristics of phosphorus pollution in Manshui River and the effects of fulvic acid on phosphorus release from sediments
-
摘要: 探讨了漫水河清新区境内流域上覆水和沉积物中磷的空间分布特征,以及富里酸含量对沉积物释磷的影响。结果表明:5条农灌渠水体总磷质量浓度为0.87~2.83 mg·L−1,超过地表水环境质量标准Ⅴ类水浓度限值;沉积物样本取自12个采样点,测得总磷含量为593.35~2 973.00 mg·kg−1,其中铁结合磷(Fe-P)占比最高,为19.54%~64.47%;沉积物各采样点生物有效磷分布差异较大,占总磷比例平均为57.73%,说明研究农灌渠的沉积物潜在释磷能力大。相关性分析结果表明,TP含量与Fe-P、闭蓄态磷(Oc-P)、自生磷(De-P)含量间呈显著正相关,表明外源磷输入是导致沉积物磷含量升高的主要原因。投加外源富里酸的模拟实验结果表明,富里酸浓度升高会提高沉积物对磷的吸附能力,进而促进Fe-P的形成。Abstract: In this study, the spatial distribution of phosphorus in the overlying water and sediments in the Qingxin District of the Manshui River was explored, and the effect of fulvic acid concentration on phosphorus release from sediments. The results showed that the total phosphorus concentrations at the 5 agricultural irrigation canals were 0.87~2.83 mg·L−1, which exceeded the surface water environmental quality standard V class water concentration limit; sediment samples were taken from 12 sampling points, the measured total phosphorus contents were 593.35~2 973.00 mg·kg−1, iron-bound phosphorus(Fe-P) accounted for the highest proportion of total phosphorus, which was 19.54%~64.47%; the distribution of biologically available phosphorus at each sampling point of the sediment was quite different, accounting for 57.73% of total phosphorus on average, which indicated that the potential release capacity of phosphorus from the sediments of the studied agricultural irrigation canals was large. The correlation analysis results showed that the significant positive correlations occurred between the content of TP and the content of Fe-P, closed storage state phosphorus(Oc-P), and authigenic phosphorus(De-P), indicating that the external source phosphorus input was the main reason for the increase of the phosphorus content of the sediment. The simulation experiment results of adding exogenous fulvic acid showed that the increase of the fulvic acid concentration could increase the adsorption capacity of the sediment for phosphorus, leading to Fe-P formation.
-
Key words:
- phosphorus /
- sediment /
- sequential extraction /
- iron-bound phosphorus /
- fulvic acid
-
城市化持续快速的推进,导致了不透水面积显著增加,从而引发城市水文的变化,严重的影响了水质和径流状况[1-2]。由于大量的污染物随着雨水径流排放到水体,城市雨水已成为城市河湖水质恶化的主要污染源[3]。水生生态系统中过量的氮输入将导致水体富营养化,最终会改变生态群落结构,降低生境质量,增加“藻华”事件的发生率和持续时间[4-5]。人工湿地(CWs)污水处理技术具有建造成本投入低、设施后期维护便捷、景观效果明显等优点,被广泛用于各类型污水的小型化和分散化处理。
国内外对CWs的研究已经很多,对CWs的除氮技术也在逐渐优化,单纯的处理工艺往往导致人工湿地的除氮效果不好,潮汐流(TF)和潜流(SF)CWs组合形成的好氧和厌氧环境[6-7],有利于氮进行硝化和反硝化反应,从而达到对氮的去除,可防止处理后的污水排入环境导致水体“富营养化”。CWs中的氮通过植物的吸收作用、基质的过滤和吸附、氨挥发、微生物的氨化、硝化反硝化和厌氧氨氧化等方式被去除[8]。研究表明,填料基质和植物作用所做的贡献仅占CWs脱N量的20%—30%[9]。ZHANG等[10]研究发现,微生物参与的硝化反硝化作用是CWs去除废水中TN的主要途径,可占66.9%—80.5%。DU等[11]研究发现,植物种植增加了微生物的丰富度和生物多样性;同时,相关的反硝化属假单胞菌、不动杆菌、根瘤菌、芽孢杆菌和红假单胞菌丰度的增加,增强了微生物对氮的去除作用。HE等[12]研究发现,γ–变形菌、α–变形菌和β–变形菌是人工湿地基质中的主要细菌,并在减少硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐的功能上发挥了重要作用。但是,现有的研究缺少潮汐流人工湿地污染物的去除途径和微生物群落相结合的分析,以及植物的种植对微生物群落以及微生物氮净化作用的影响分析。
本研究构建潮汐流和潜流人工湿地组合,采用工业废弃物—赤泥制成的颗粒作为基质,种植黄菖蒲作为净水植物,分析该潮汐流-潜流人工湿地组合对氮的去除效果以及微生物群落的变化,探讨水生植物和微生物群落对氮去除效果的影响,以期为人工湿地强化脱氮提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 基质填料
实验基质所用赤泥取自山西省吕梁市华兴铝业有限公司,取回后自然风干。将其研磨成粉,过100目筛,保存于干燥处。赤泥颗粒的具体实验方法:将过100目筛的赤泥和水泥粉末按照3∶7的比例混合,再加入2.5%的起泡剂,加入去离子水充分搅拌后放入模具中,放室温条件下养护24 h。自然晾干后取出赤泥块放于温度22℃、相对湿度≥ 90%的数控水泥砼标准养护箱中,28 d后取出,将其切割成粒径为10—20 mm的颗粒。
1.2 实验系统
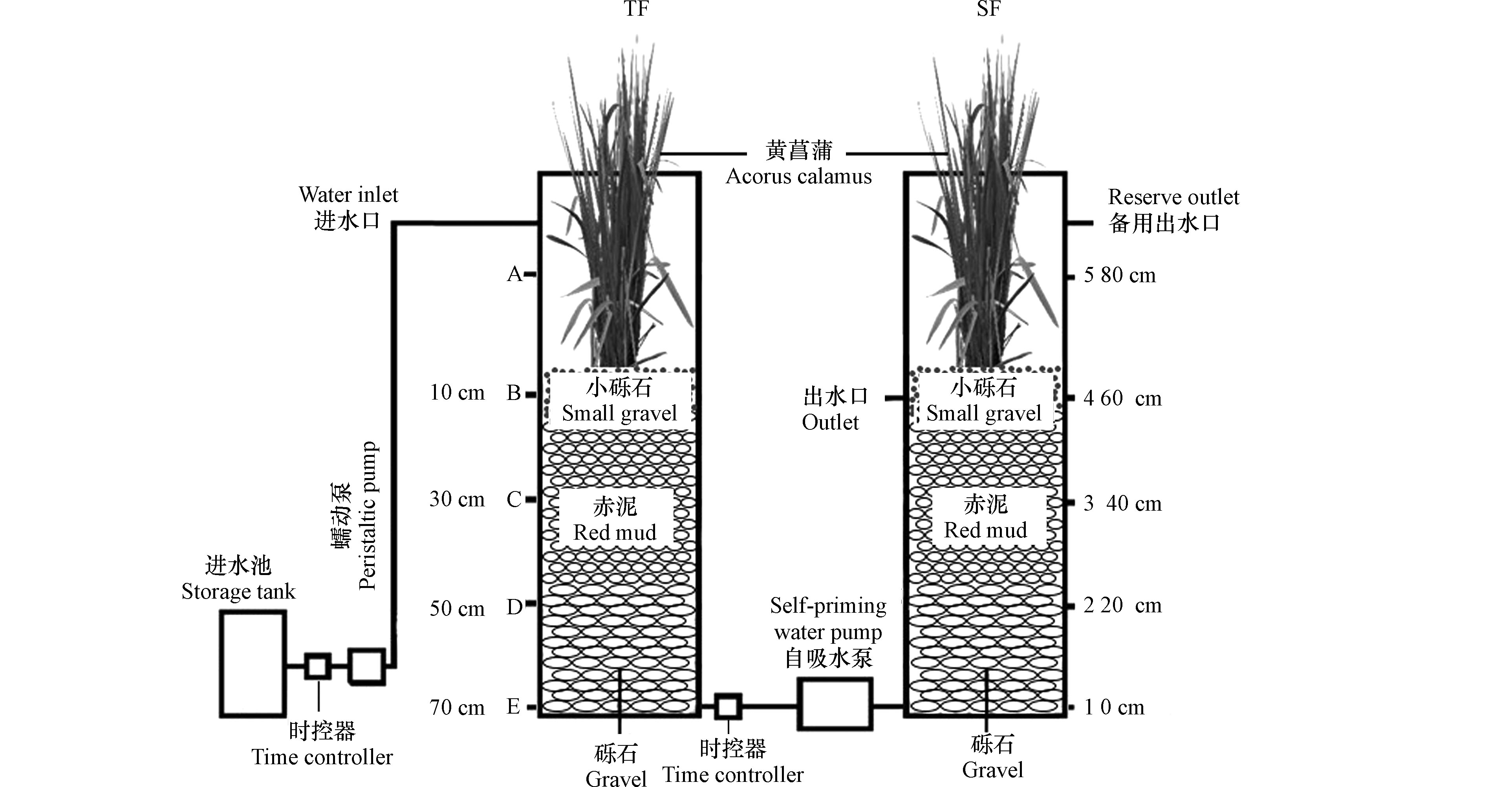
本实验中人工湿地模型工艺组合(TF–SF)由潮汐流湿地单元(TF)和潜流湿地单元(SF)组成(图1)。在装置运行上,TF采用间歇进水和瞬间排水,SF采用瞬间进水和缓慢排水,并且进水和排水同时进行,以保证基质始终处于淹没状态。用两台蠕动泵控制TF单元进水,进出水方式为下行流,PLC时控器负责定时调控装置的进出水;SF单元采用上行流方式进水,进水由自吸水泵控制。在TF单元,自上而下取样(10—70 cm),SF单元自下而上取样(0—40 cm)。TF-SF由两个亚克力圆柱体组成。圆柱体直径为30 cm,高度为100 cm,体积约为70 L。装置的填料高65 cm(底部为Ф25—50 mm砾石,厚度为25 cm;中部为Ф10—20 mm赤泥颗粒,厚度为30 cm;上部Ф2—5 mm砾石,厚度为10 cm),在潮汐流人工湿地单元和潜流人工湿地单元最上部砾石层种植黄菖蒲水生景观植物。为了植被的光合作用,在两个湿地单元上均设有30 W的节能灯作为补充光照,灯光由PLC时控器定时调控,光照时间为每天的6:30—18:30。
TF单元运行方式为:瞬时进水0.33 h—反应期4.82 h—瞬时排水0.05 h—闲置期5.80 h,每个周期12 h,每天2个周期,每个周期处理水量为10 L。SF单元运行方式为:瞬间进水和缓慢排水,且进水和排水同时进行,处理水量为10 L,水力停留时间为11.95 h。2019年7月启动反应器,实验室温度为18—25 ℃,实验用水为人工模拟污水,由葡萄糖、氯化铵、磷酸二氢钾配制,同时投加无水氯化钙、硫酸镁、FeSO4·7H2O等补充微量元素,污水pH为4.81—6.42。其他主要水质指标见表1。反应器进行为期2个月的微生物挂膜,直到出水稳定后,开始正式实验。
表 1 实验水质Table 1. Experimental water quality项目水质参数Project water quality parameters 初始浓度范围/(mg · L−1)Initial concentration range CODcr 304.72—902.62 NH+4 13.51—27.09 TN 15.12—26.54 NO−3 0.00—1.04 1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 水质指标测定
CODcr、TN、
NH+4 NO−3 1.3.2 植物生长监测分析
种植植物前,测定用于实验的植物生物量,供后续计算使用。植物高度在实验运行的全过程中进行长期测量,以观察植物长势,实验结束后,对湿地植物进行收割,分为地上、地下两部分,测定植物生物量、根长[14]。在实验的开始和结束时测定植物的湿重W1(g),挑选代表性的植株样品在105 ℃下干燥10 min,以灭活植物中酶的活性,然后在70 ℃下干燥12 h,测定干重W2(g),将植物粉碎成粉末(过40目筛),混合均匀并密封保存,采用H2SO4-H2O2溶液消解,采用半微量凯氏法测定植物全氮[14]。
植物氮积累量(PA),单位为mg·株−1,计算公式如下:
PA=PB×PC (1) 式中,PA为植物氮积累量(mg·株−1),PB为植物不同器官生物量(g·株−1),PC为植物不同器官全氮含量(mg·g−1)。
1.3.3 高通量测序分析方法
通过OMEGA Soil DNA试剂盒提取基质中微生物DNA。使用通用细菌引物16S rRNA的5′–ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG–3′和5′–GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT–3′(V3—V4区)对提取的DNA进行PCR扩增。PCR扩增条件:98 ℃(3 min)初始变性,然后进行25个循环,98 ℃变性30 s,50 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸30 s,最后5 min延伸至72 ℃。将所有序列读数聚类到操作分类单位(OTU)(相似性阈值为97%)。高通量测序服务由上海美吉生物平台提供(上海,中国)。
1.3.4 数据分析与处理
实验数据使用Microsoft Excel 2010统计分析,数据图使用Origin 2015软件进行绘制。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 潮汐流-潜流人工湿地系统对污水的净化效果
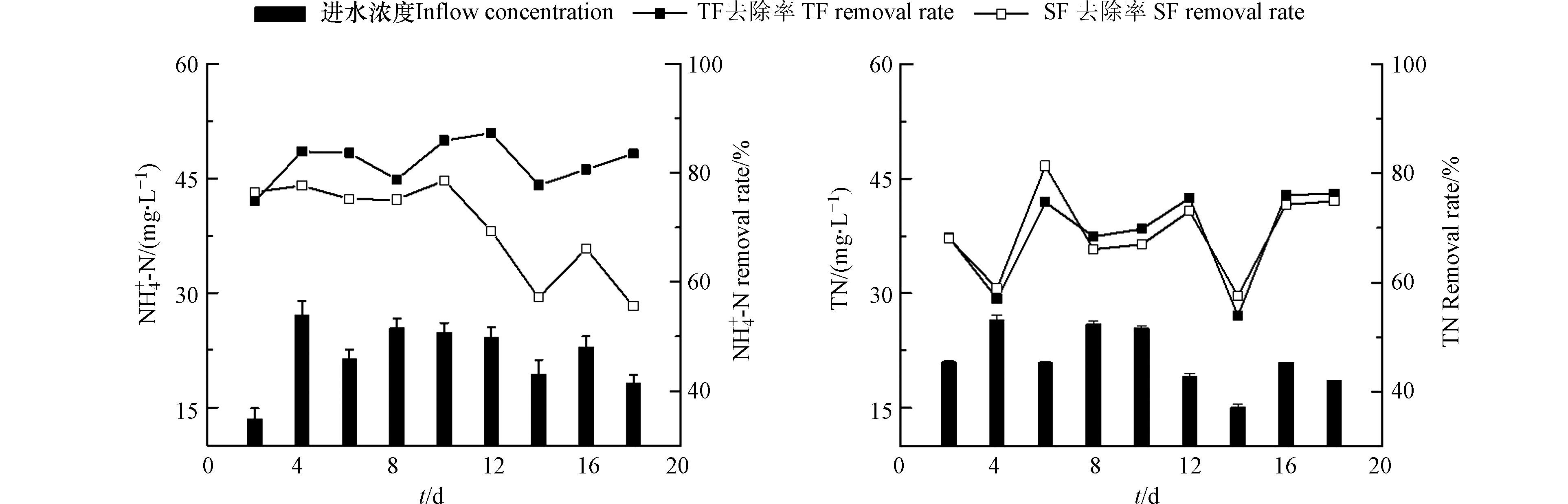
TF–SF的进水TN含量为15.12—26.54 mg·L−1,平均TN含量为21.52 mg·L−1(图2);潮汐流人工湿地单元(TF)出水的TN去除率为53.96%—76.22%,平均去除率为68.88%;TF–SF的出水TN去除率为57.52%—81.29%,平均去除率为68.99%。TF–SF进水的
NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 随着运行时间的增加,TF–SF的
NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 NH+4 NH+4 NO−3 与SF相比,TF单元表现出更好的
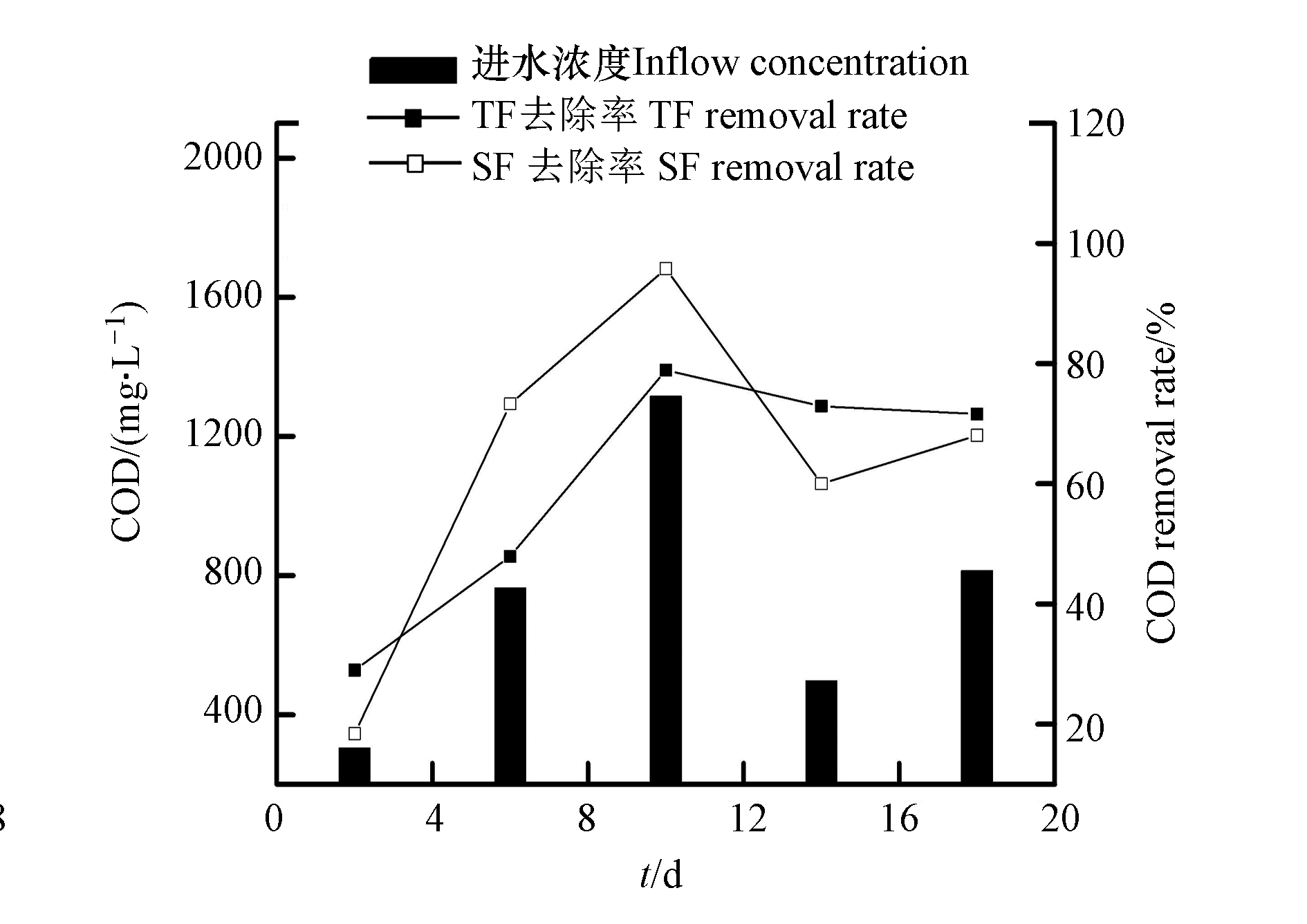
NO−3 NO−3 微生物吸收、基质过滤以及植物根系截留为人工湿地系统中有机物的主要去除途径,在对有机物的去除中,植物的贡献较小,可溶性有机物通过在淹水过程中与基质表面的微生物膜接触反应被消耗分解,不溶性有机物通过基质截留后在排空阶段、系统充氧时被微生物降解[17]。TF–SF进水的COD含量为304.72—1315.83 mg·L−1,平均含量为739.31 mg·L−1;TF出水的COD去除率为29.01%—78.91%,平均去除率为60.07%;TF–SF出水的COD去除率为38.43%—95.80%,平均去除率为67.12%(图4),说明TF–SF对有机物具有较好的去除效果。在TF–SF中,TF和SF都对有机物较好的去除。TF独特的间歇进水和瞬时排水的潮汐运行模式下,基质上附着的有机物在TF空置时被硝化作用利用,减少了COD含量。TF–SF进水的COD浓度变化较大,这是由于本实验进水配置采用葡萄糖作为碳源,4 d配置1次,葡萄糖在室温下易挥发[18],使得进水COD含量变化较大。
TF–SF中第2天的COD去除率较低,是因为TF–SF进水的COD含量较低,进水中可利用的碳源较低。然而,第2天的
NH+4 实验期间,进水和出水的pH、溶解氧(DO)的平均值如表2所示。与进水DO相比,在TF–SF中,TF和SF的出水DO浓度都下降了6.74—7.48 mg·L−1。这是因为微生物去除COD和氨氧化过程中消耗了水体中的DO。在TF中,好氧微生物利用进水中的溶解氧以及从大气携带进入的O2发生硝化反应,使得DO浓度降低;SF中的DO含量更低,说明SF单元为缺氧和厌氧环境,进行反硝化作用,可弥补TF由于氧含量高导致反硝化作用不好的缺点,可提高氮的去除率。
表 2 潮汐流-潜流人工湿地的进出水参数Table 2. Water inlet and outlet parameters of TF–SF组别Group pH DO / (mg·L−1) 进水 Inflow 5.74 8.62 TF出水 TF effluent 5.61 1.88 TF–SF出水 TF–SF effluent 5.82 1.14 在TF和SF中,硝化反应和反硝化反应的进行需要一定的碱性环境来维持系统内pH的缓冲性能。由于赤泥呈强碱性(pH=10—12),本实验设计时将进水配置呈弱酸性。在前期的培养实验中,基质的碱性被进水中和,装置内呈弱酸环境(表2)。因此,不适合的pH环境减弱了基质表面微生物的活性,导致对氮的去除效果降低。在今后的研究中,需注意进水的pH值。
2.2 潮汐流-潜流人工湿地系统微生物群落分析
2.2.1 潮汐流-潜流人工湿地系统微生物多样性分析
TF–SF的微生物多样性和丰富度见表3,采用Alpha多样性分析方法对TF–SF中细菌的多样性进行分析。在TF–SF中,TF和SF的微生物测序中样本文库覆盖率均大于0.99,说明测序结果能够代表湿地的真实情况[19]。TF–10(即TF中10 cm处理深度)、TF–30(即TF中30 cm处理深度)和SF–60(即SF中60 cm处理深度)的Ace指数分别为1587.47、1514.32、1550.49,Chao指数分别为1556.43、1499.46和1526.75,TF–10和SF–60的Ace指数和Chao指数均大于TF–30;TF–10、TF–30和SF–60的Shannon指数分别为5.54、5.23和5.59,Simpson指数分别为0.0110、0.0189和0.0109,TF–10和SF–60的Shannon指数均大于TF–30,且TF–30的Simpson指数最大,因为TF–10和SF–60这两个取样点都在植物根系周围,说明人工湿地中种植植物可拥有更高的微生物群落丰富度和多样性,进而提高了人工湿地对氮的去除作用。植物根系分泌氧气和有机物,可促进微生物富集生长,所以种植植物可以提高微生物群落多样性。
表 3 潮汐流-潜流人工湿地微生物多样性和丰富度Table 3. Microbial diversity and richness in samples of TF–SF组别Group 测序数量 Sequence number 丰富度指数 Richness index 多样性指数Diversity index 覆盖率Fraction of Coverage Sequences Sobs Ace Chao Shannon Simpson Coverage TFCW-10 45744 1381 1587.47 1556.43 5.54 0.0110 0.994 TFCW-30 41302 1279 1514.32 1499.46 5.23 0.0189 0.993 SFCW-60 49453 1428 1550.49 1526.75 5.59 0.0109 0.996 2.2.2 潮汐流-潜流人工湿地系统微生物门、纲分类水平组成差异分析
TF–SF中微生物独有和共有的OTU数目。从图5可知,在TF–SF中,TF–10、TF–30和SF–60检测到的细菌OTU数目分别为1381、1279和1428,说明相比于SF,TF的运行方式会使装置内细菌的种类减少,一些不能适应TF内部厌氧—好氧环境交替出现的菌群会逐渐消亡,最终留存下来的菌群成为优势菌群。TF–SF中共有的OTU有981个,分别占TF–10、TF–30和SF–60检测到的OTU数目的71.04%、76.70%和68.70%,说明TF–SF中,TF–10和TF–30微生物群落不同,这是因为TF中植物根系周围具有富集微生物的作用;TF–10和SF–60微生物群落不同,是因为TF和SF不同的运行方式致使其氧环境不同。
TF–SF微生物门(Phylum)水平组成见图6(a)。可将微生物检测频率>1%的菌门作为主要的菌门[20]。共发现有9个菌门,分别为Proteobacteria(变形菌门)、Actinobacteria(放线菌门)、Chloroflexi(绿弯菌门)、Bacteroidota(拟杆菌门)、Firmicutes(厚壁菌门)、Patescibacteria(髌骨细菌门)、Acidobacteriota(酸杆菌门)、Nitrospirota(硝化螺旋菌门)、Myxococcota(粘球菌门),这9种菌门在TF-SF中3个取样点的相对丰度比例之和为94.35%—96.27%。
本研究中的主要优势菌门为变形菌门,其在生物脱氮的过程中具有重要作用,这与ZHANG等[21]、LI等[22]的研究结果一致,说明人工湿地基质具有相似的优势菌门。MIAO等[23]研究表明,变形菌门和厚壁菌门对反硝化作用有重要作用,硝化螺旋菌门含有丰富的硝化功能的菌属。变形菌门在TF–10、TF–30和SF–60的相对丰度分别为28.04%、30.12%和21.90%,厚壁菌门的相对丰度分别为7.68%、9.01%和3.73%,硝化螺旋菌门的相对丰度分别为1.22%、0.79%和2.22%,变形菌门和厚壁菌门在3个取样点的相对丰度表现为TF–30 > TF–10 > SF–60,这种趋势与各取样点的氮去除率一致。TF–30处变形菌门的相对丰度高于TF–10,但TF–30硝化螺旋菌门的相对丰度却低于TF–10,这是因为植物的种植改善了微生物的多样性。
TF–SF微生物纲(Class)水平组成见图6(b)。将微生物检测频率>1%的菌纲作为主要的菌纲,共发现15个菌纲。变形菌门中的γ–变形菌纲(Gammaproteobacteria)、α–变形菌纲 (Alphaproteobacteria) 在TF–SF中3个取样点的相对丰度占比分别为14.89%—22.81%、7.01%—7.94%。γ–变形菌纲和α–变形菌纲均属于革兰氏阴性菌,说明TF–SF中的基质富集了革兰氏阴性菌,促进了系统中污染物的生物降解。LI等[24-25]发现γ–变形菌在去除
NO−3 NO−2 2.2.3 潮汐流-潜流人工湿地系统功能微生物差异性分析
有关研究表明,不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)、硫杆菌属 (Thiobacillus)和索氏菌属(Thauera)等具有反硝化作用,参与氮的转化[26-28]。硝化杆菌属(Nitrobacter)和硝化螺菌属(Nitrospira)具有硝化功能[29-30],亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)和亚硝化螺菌属(Nitrosospira)具有氨氧化功能[31]。另外,YAO等[32]研究表明,不动杆菌可通过异养来转化氮硝化和好氧反硝化。
TF–SF微生物属(Genus)水平组成见图6(c)。其中检测出相对丰度大于0.5%的菌属有71个,包括不动杆菌属、硝化螺菌属和亚硝化单胞菌属,以及其他未知属。TF–SF中硝化作用硝化螺菌属丰度(0.79%—2.22%)高于具有氨氧化细菌的亚硝化单胞菌属(0.12%—0.52%)。某些硝化螺菌属能将
NH+4 NO−3 不动杆菌属是丰度最高的异养反硝化菌属,在TN去除过程中具有重要作用。不动杆菌属在TF–10、TF–30和SF–60中的丰度分别为1.15%、1.38%和0.07%,TF–30处不动杆菌的丰度最高,且此处的氮去除效果最好,说明不动杆菌丰度的增加是微生物氮去除率较高的原因。
2.3 水生景观植物—黄菖蒲吸收对湿地系统除氮的贡献
黄菖蒲(学名:Iris pseudacorus L.)为鸢尾科、鸢尾属植物,为多年生湿生或挺水宿根草本植物,植株高大,根茎短粗,绿色长剑形叶,5—6月开黄色花[35]。实验所用黄菖蒲产自山东临沂,购买回幼苗后对其进行种植培养,使其适应生长环境。培养一段时间后,将植物移植到模型中。在移植到潮汐流-潜流人工湿地系统前,测量植物生物量,并选取相同高度的植物,测量其植物生物量和全氮含量。
在实验期间,实验室温度为15—22 ℃,是黄菖蒲的适生环境,植物地上部分颜色鲜亮,整个实验期间没有枯黄和枯萎的现象,植物均保持着良好的生长状态(表4)。TF内黄菖蒲的长势表现最好,株高、重量和根长也在整个系统中表现最大。TF在进水和排水空置床体时,氧气会进入到装置内,提高了植物根系周边环境的氧浓度,有利于根部细胞的有氧呼吸,促进根部生长,在生长过程中吸收水中的营养物质,从而表现出良好的长势。相比TF,SF内黄菖蒲的长势较差,其原因是潜流的运行方式使得植物周围氧浓度低,不利于植物根部的生长,也说明黄菖蒲能够在人工湿地中成活且长势良好。
黄菖蒲水生景观植物地上部分和地下部分的氮积累量均随着植物的生长而累积。人工湿地水生植物的氮积累量是评价水生植物对氮去除效果的重要指标[36]。TF–SF中黄菖蒲植物的氮积累量见表5。TF–SF中生长的黄菖蒲植物,对TN的累积作用以植株地上部分为主,黄菖蒲植物地上部分TN累积量占整株的42.74%—84.26%。研究表明,植物的收割方式由其体内营养物质的分配特点决定[37]。本研究结果表明,人工湿地植物内的氮可通过收割植物地上部分的方式来将氮移出人工湿地。其中,TF中黄菖蒲的地上部分TN累积量占整株比例为84.26%,SF中黄菖蒲的地上部分TN累积量占整株比例为77.64%。TF中种植的黄菖蒲植物氮积累量在相同生长时间内远大于SF,这与潮汐流人工湿地独特的运行方式密不可分。TF中充足的氧环境保障了植物根部细胞的有氧呼吸,使得植株生长健壮且生长迅速,表现出较高的植物生物量,从而具有较高的植物氮吸收量。
表 4 潮汐-潜流人工湿地黄菖蒲植物生长状况Table 4. The growth status of yellow calamus in TF–SF人工湿地Constructed wetland 地上部分Aboveground 地下部分Underground 株高/cm Plant height 鲜重/g Fresh weight 干重/gDry weight 根长/cm Root length 鲜重/g Fresh weight 干重/g Dry weight 种植前 36.3 8.53 0.92 14.5 5.22 2.15 潮汐流 128.2 56.48 8.08 23.8 19.40 3.00 潜流 74.2 32.03 5.11 20.1 16.06 2.51 表 5 潮汐流-潜流人工湿地黄菖蒲植物氮积累量Table 5. Nitrogen accumulation of acorus calamus in TF–SF人工湿地Constructed wetland 植物生物量/g Plant biomass 植物氮积累量/(mg·株−1)Plant nitrogen accumulation 地上部分Aboveground 地下部分Underground 总净重Total net weight 地上部分Aboveground 地下部分Underground 总净重Total net weight 种植前 0.92 2.15 3.07 18.17 24.34 42.51 潮汐流 8.08 3.00 11.08 195.05 36.44 231.49 潜流 5.11 2.51 7.62 111.18 32.01 143.20 3. 结论(Conclusion)
TF–SF的水力停留时间为11.95 h,运行周期为12 h时,对
NH+4 NH+4 黄菖蒲能够在人工湿地中成活且长势良好,能够在我国华北地区种植。植物生物量直接影响植物体内氮积累量,植物的除氮效果优劣可直接通过生物量得出结论。在今后的人工湿地建造过程中,多选择像黄菖蒲这样的具有高生物量的植物种类,有利于水体净化效果的提高。黄菖蒲植物表现出较高的去除率与其发达的根系、试验期间生长量大有关,根系的分泌物有利于微生物的生长,促进降解物质的分泌,从而对水体中的氮具有较高的去除率。
本研究采用TF和SF的组合形式,SF在除氮过程中未起到太大作用,是由于实验设置的水力停留时间太短,以及SF中的进水COD含量太低,不利于反硝化作用的进行。仍需继续研究来寻找TF、SF及多种组合方式的最优运行参数。在今后人工湿地的除氮实验中,应使进水的pH值控制在7.0—8.0,保证人工湿地系统的稳定除氮效果。
-
表 1 不同采样点各形态磷浓度Fig.1 Phosphorus concentration of each form at different sampling sites
采样点编号 所属农灌渠 各形态磷浓度/(mg·L−1) TP TDP TPP SRP DOP L1 MT排涝 1.05 0.21 0.84 0.19 0.02 L2 MT排涝 1.08 0.33 0.75 0.27 0.06 L3 MT排涝 0.87 0.15 0.72 0.10 0.05 L4 MT排涝 1.43 0.53 0.90 0.51 0.02 L5 JK干渠 2.08 0.54 1.54 0.13 0.41 L6 JK干渠 1.66 0.62 1.04 0.47 0.15 L7 JK干渠 2.83 1.78 1.05 1.51 0.27 L8 JK干渠 2.34 1.13 1.21 0.82 0.31 L9 JK干渠 1.36 0.48 0.88 0.33 0.15 L10 JJ排坑 1.07 0.44 0.63 0.05 0.39 L11 XST排坑 1.76 0.74 1.02 0.06 0.68 L12 HYT排坑 2.39 1.17 1.22 0.47 0.70 表 2 表层沉积物总磷及不同赋存形态磷之间的Pearson相关性(n=12)
Table 2. Pearson correlation between total phosphorus in surface sediments and phosphorus in different forms(n=12)
TP Ex-P Al-P Fe-P Oc-P Ca-P De-P Or-P BAP TP 1 — — — — — — — — Ex-P 0.520 1 — — — — — — — Al-P 0.468 0.625* 1 — — — — — — Fe-P 0.939** 0.415 0.482 1 — — — — — Oc-P 0.833** 0.413 0.472 0.637* 1 — — — — Ca-P 0.575 0.248 -0.154 0.312 0.673* 1 — — — De-P 0.641* 0.240 -0.074 0.419 0.736** 0.762** 1 — — Or-P 0.490 0.508 0.245 0.315 0.590* 0.448 0.530 1 — BAP 0.944** 0.517 0.580* 0.991** 0.662* 0.295 0.400 0.359 1 注: **表示在P<0.01级别相关性显著;*表示在P<0.05级别相关性显著。 表 3 模拟实验相关条件参数
Table 3. Relevant condition parameters of simulation experiment
组别 土样质量/g 添加FA体积/mL 定容后溶液体积/mL TOC质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 对照组 9.999 6 0 200 0 1 9.999 8 13 200 14.95 2 10.000 5 35 200 40.25 3 10.000 3 87 200 100.05 -
[1] AN M, HAN Y, XU L, et al. KINEROS2-based simulation of total nitrogen loss on slopes under rainfall events[J]. Catena, 2019, 177: 13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.01.039 [2] 房志达, 王淑萍, 苏静君, 等. 红壤丘陵区典型小流域不同下垫面非点源磷输出特征[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(5): 1724-1734. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202012057 [3] 万玲, 项颂, 牛勇, 等. 牛谷河表层沉积物氮、磷、有机质的分布及污染评价[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(1): 174-180. [4] 林灿阳, 田委民, 叶沛成, 等. 河流底泥活性覆盖板的制备及其对城市内河底泥氮磷释放的抑制效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(6): 1927-1936. [5] 朱广伟, 秦伯强. 沉积物中磷形态的化学连续提取法应用研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2003(3): 349-352. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2003.03.025 [6] YAN J, JIANG T, YAO Y, et al. Preliminary investigation of phosphorus adsorption onto two types of iron oxide-organic matter complexes[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 42: 152-162. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2015.08.008 [7] WANG L, AMELUNG W, PRIETZEL J, et al. Transformation of organic phosphorus compounds during 1500 years of organic soil formation in Bavarian Alpine forests - A P-31 NMR study[J]. Geoderma, 2019, 340: 192-205. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.01.029 [8] SUMMERHAYS J S, HOPKINS B G, JOLLEY V D, et al. Enhanced phosphorus fertilizer (CARBOND P (R)) supplied to maize in moderate and high organic matter soils[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2015, 38(9): 1359-1371. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2014.973039 [9] WANG H, ZHU J, FU Q L, et al. Adsorption of phosphate onto ferrihydrite and ferrihydrite-humic acid complexes[J]. Pedosphere, 2015, 25(3): 405-414. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(15)30008-4 [10] YANG X, CHEN X, YANG X. Effect of organic matter on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in a black soil from Northeast China[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 2019, 187: 85-91. [11] 张奇, 喻庆国, 王胜龙, 等. 滇西北剑湖沉积物磷形态、空间分布及释放贡献[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(10): 3792-3803. [12] CHEN M, SUN H-Q, JIANG H-L. The addition of FeOOH binds phosphate in organic matter-rich sediments[J]. Chemistry and Ecology, 2016, 32(5): 432-445. doi: 10.1080/02757540.2016.1150455 [13] JIN J, ZHOU W, SUN Y, et al. Reaction characteristics and existing form of phosphorus during coal-based reduction of oolitic iron ore[J]. Minerals, 2021, 11(3): 247. doi: 10.3390/min11030247 [14] 鲁群, 李秀, 李湘梅. 湖泊底泥中磷形态及分布特征研究[J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(4): 135-139. [15] MIN O J, KIM T-H, LEE J, et al. Behavioral characteristics of phosphorus in sediments according to the forms of phosphorus[J]. Journal of Ecology and Environment, 2015, 38(3): 319-326. doi: 10.5141/ecoenv.2015.032 [16] WANG Z, HUANG S, LI D. Decomposition of cyanobacterial bloom contributes to the formation and distribution of iron-bound phosphorus (Fe-P): Insight for cycling mechanism of internal phosphorus loading[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 652: 696-708. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.260 [17] JIAO Y, YANG C, HE W, et al. The spatial distribution of phosphorus and their correlations in surface sediments and pore water in Lake Chaohu, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(26): 25906-25915. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2606-x [18] 孙涛, 李发永, 刘晓, 等. 以农田高盐排水为替代镁源回收养殖废水中的磷素[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(12): 3883-3894. [19] 李慧, 雷沛, 李珣, 等. 天津市北大港湿地沉积物氮磷分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(10): 4086-4096. [20] 孙士权, 梁焱, 赵刚, 等. 粒径和底床地形对沉积物中有机磷释放的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(3): 1605-1614. [21] 刘永九, 黄素珍, 张璐, 等. 洪湖国际重要湿地沉积物磷空间分布特征及释放风险[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(7): 3198-3205. [22] NI Z, WANG S, WU Y, et al. Response of phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments to anthropogenic activities in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020: 699. [23] 姜杰, 杨浈, 任谦, 等. 土壤腐殖质氧化还原电位及其相应电子转移能力分布[J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(02): 219-224. [24] DEBICKA M, KOCOWICZ A, WEBER J, et al. Organic matter effects on phosphorus sorption in sandy soils[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2016, 62(6): 840-855. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2015.1083981 -






 下载:
下载: