-
近年来,有机污染土壤对生态环境和人体健康的潜在危害已成为全球关注问题[1]。二次污染相对可控的原位修复技术是有机污染地块修复的较佳选择,修复效率高、周期短、见效快和修复成本低的原位化学氧化技术 [2]和地质环境适应性强、加热均匀的原位电阻加热技术(electrical resistance heating,ERH)[3-4]均得到广泛应用。ERH是现阶段发展较快的一种能耗低、效率高、施工相对简单的原位热脱附技术[5],该技术利用焦耳定律将土壤均匀加热至水沸点,达到热脱附条件 [6]。相较于燃气、电加热棒等土壤加热技术,ERH不仅对土壤施加低温热场,且有电场(<9.8 V·cm−1)存在 [7- 8],可活化氧化剂、提高污染物的蒸气压及溶解度促进其挥发和溶解 [9],从而提升氧化效率并增强与污染物的接触能力,缩短修复周期,降低修复成本。
多技术协同发挥各自优势,提高效率、降低成本实现可持续修复已成为业界共识。关于ERH协同化学氧化修复有机污染土壤,文献报道并不多见。本文将结合实践,探讨、分析ERH修复原理及ERH耦合化学氧化技术修复有机污染物的研究现状,以期为有机污染土壤原位高效低碳修复提供借鉴。
-
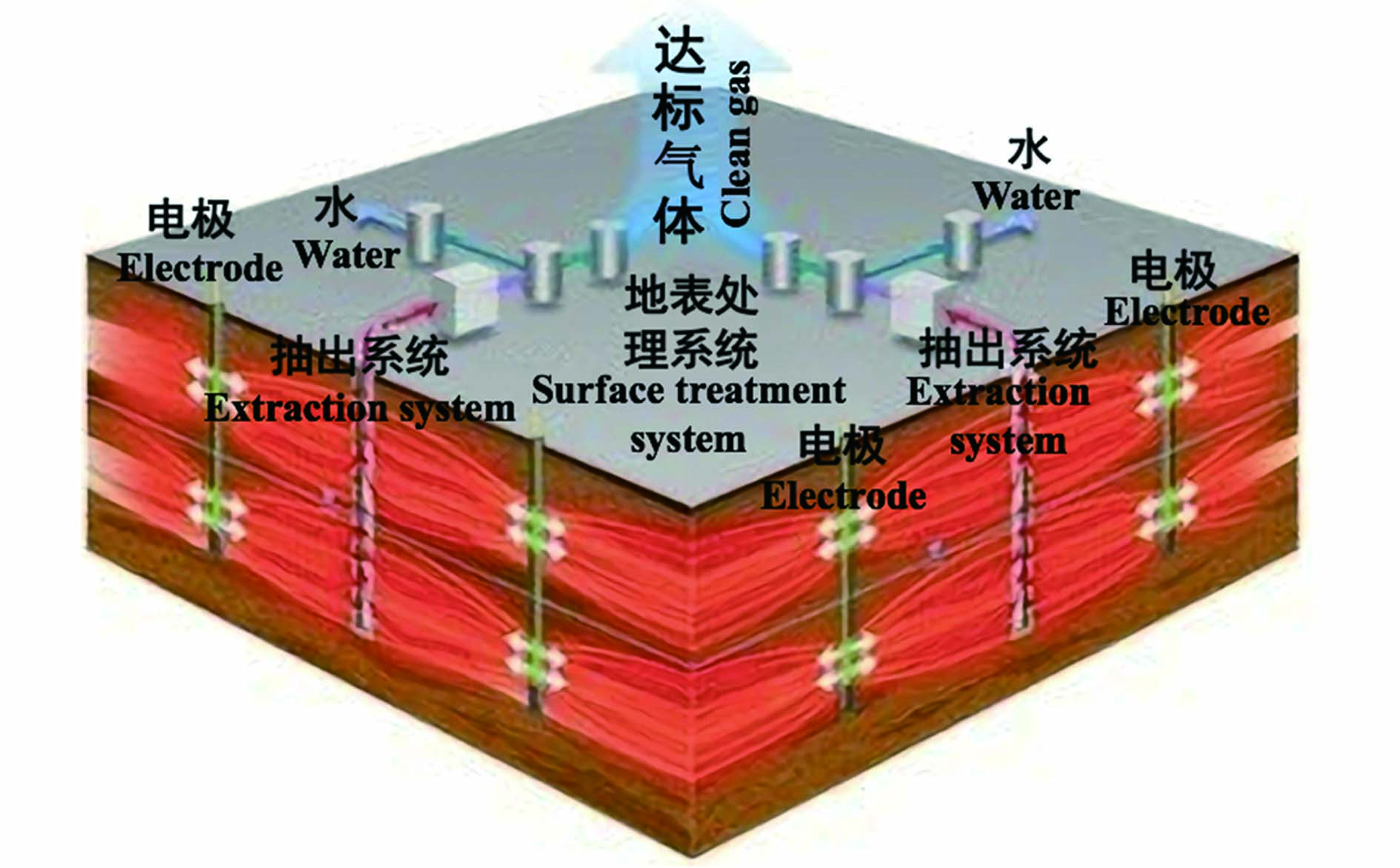
20世纪90年代初,美国能源部科技办公室资助太平洋西北国家实验室,首次进行了ERH在土壤修复领域的应用研究 [3]。ERH修复示意图见图1。ERH是将电极直接安装在污染地块区域,电极形成回路对土壤放电,利用土壤溶液的导电性将电能转换成热能,以此提高地下温度,土壤中水分转化成热蒸汽作为载气,驱使易挥发性有机污染物从土壤中脱附进入更易渗透的蒸汽流动区域,汽水混合有机污染物经气相抽提装置收集于地面处理系统进行净化处理,实现土壤修复的目标 [10-12]。理论上,ERH修复技术电极间距为4.27—6.71 m[3],实际实施时,根据实际情况调整电极间距,最高可将土壤的温度加热至120 ℃ [13],温度越高越有利于污染物脱附,在室温至120 ℃的温度范围内,土壤对有机污染物的吸附能力随温度升高而降低 [14]。该技术通过2种主要机制加快污染物的去除:强化挥发和原位蒸汽汽提,随着土壤温度上升,污染物蒸汽压和相应的污染物提取率通常会增加约30倍 [3]。
ERH对污染物去除具有广适性,尤其适用于挥发性污染物和石油烃的原位热修复[3],不受地质条件限制,在低渗透的淤泥和粘土中表现优良,在高渗透的沙子和砾石也有较好的处置效果 [4]。该技术相较于其他原位加热修复技术,具有加热更均匀、对土壤损害更小等优点而被更多地应用于有机污染土壤修复 [15-16]。美国污染地块普遍较小且能源价格较国内低很多,致使该技术在我国的基础研究滞后 [17]。我国于2016年引进该技术,但受制于土壤电阻加热效率影响因素、污染物去除机制等科学问题不明的限制,目前能耗和修复效率提升仍无法达到预期效果 [5, 18]。
-
ERH属于加热温度在120 ℃以内的低温加热,致使修复时间较长。因此,缩短修复时间成为提升ERH能耗及成本的有效途径。近10 年来,化学氧化技术已成为修复有机物污染土壤的主要技术之一 [19],具有高效去除土壤有机污染物的优点,可协同突破ERH加热温度偏低导致高沸点污染物的去除效率不高的限制 [11]。氧化剂和传输方式是ERH与化学氧化协同修复有机污染物的两大核心要素,因此,本文重点介绍其研究进展。
-
原位化学氧化修复通过向污染土壤注入氧化药剂以实现污染物氧化分解的目的,具有修复效率高、成本低等优势,已被大量应用于有机污染土壤的修复 [20]。在常用的过硫酸钠、臭氧、芬顿等氧化剂中,过硫酸钠因具有更高的氧化还原电位(E0=2.01 V),可产生氧化性更强的硫酸根自由基(SO4-·,E0=2.60 V)与羟基自由基(·OH−,E0=2.80 V),且稳定性强、活化方式多,目前已成为有机污染土壤修复领域应用最多的氧化剂 [21-22]。
-
热活化是提升过硫酸钠氧化效果的有效途径 [9]。热活化可将过硫酸钠对污染物的降解率从40 ℃的79.2%提高至60 ℃的92.4% [23]。ERH提供的室温至120 ℃的温度场,可加速过硫酸盐产生自由基,提高土壤PAHs的降解速率 [24],但因过量自由基在传递过程中发生淬灭而被消耗,其速率需要调节 [25]。
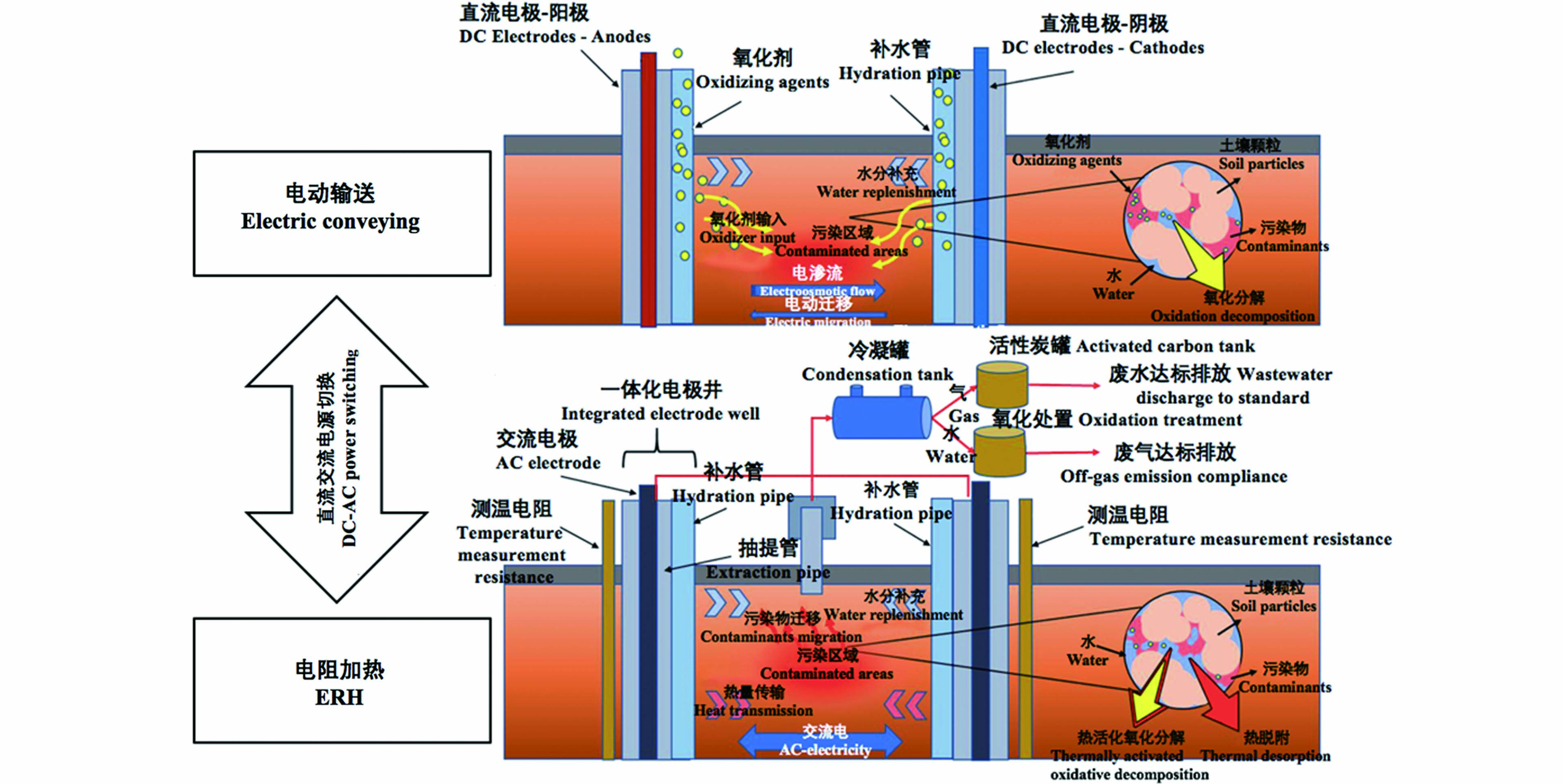
ERH提供的热场、电场可通过促进土壤有机污染物的可及性而提升过硫酸钠氧化修复的效率[26-27]。过硫酸钠的引入也会将ERH修复污染土壤的机制由物理分离为主变为物理分离、化学分解相结合,且抽提尾气成分随之改变、排放量大幅减少[28]。主要的协同去除机制如下:(1)在氧化条件下,有机物分解成短链结构而被去除 [29];(2)随着ERH温度的升高,土壤中有机污染物被脱附,过硫酸钠对其可及性逐步升高 [30-31];(3)电场所产生的电渗流可促进土壤毛细孔中物质流动,增强氧化剂与土壤污染物的有效接触,可提高有机污染物去除率 [32];(4)电场提供的电迁移能力,导致土壤颗粒内部污染物随电迁移至颗粒表层,对污染物的去除也有促进作用[33]。
结合上述去除机制分析,仅有少量文献报道了ERH协同过硫酸钠修复有机污染土壤的相关理论基础研究,见表1。Costanza等 [6]研究表明,单用ERH,30 d时四氯乙烯的去除率仅52%,与过硫酸钠结合在19 d时即可去除93%的四氯乙烯,效率大幅提升。ERH协同过硫酸钠修复多环芳烃污染土壤的去除率与沸点密切相关,Han等 [34]研究表明,相比于单一ERH修复,菲(沸点:340 ℃)的去除率增加了43.52%,苯并芘(沸点:475 ℃)的去除率增加了61.97%。ERH协同过硫酸钠的修复方式除了对有机污染土壤有较优的修复效果外,对含有四氯乙烯的低渗透性淤泥的修复效果也较为突出 [35]。
综上所述,ERH协同过硫酸钠修复有机污染土壤的理论研究较少,并且主要涉及污染物的去除效果研究,其深入研究十分薄弱,而ERH产生的热场、电场综合作用下活化过硫酸钠机制、污染物可及性增强及耦合修复产物变化规律等机理性研究,是阐明电阻加热协同化学氧化耦合机制的基本途径,需进一步明晰。
-
将氧化剂输送至目标区域与污染物充分接触是原位ERH技术与化学氧化耦合的前提条件 [36]。电动输送是指在污染土壤中施加直流电场时,土壤中的离子或有机胶体会通过电迁移、电渗析、电泳作用发生定向移动,从而被精准送达目标区域 [37]。土壤电动输送对异质性高、渗透性弱的土壤适应性强、传输效果好,是很有潜力的药剂输送技术 [38]。
土壤水分含量、酸碱度、电极平面分布等均对土壤中离子及胶体传输产生影响。较低水分含量时(<30%)电迁移与电渗流的作用较小,能耗高,当含水率达到饱和时,电动输送达到较好的效果 [39]。酸碱度调整可增加土壤中多种类型离子迁移能力,阳极附近土壤呈酸性对电动输送有利,但阴极区域的碱性会造成盐分溶解度降低,沉淀堵塞毛细孔减少离子移动路径,造成过碱现象 [40]。正负极交替可有效缓解电动输送过碱现象,污染物平均去除效率由未交替的37.5%提高到43.1% [32,41]。但对ERH提供的高频交流电场是否也能对过碱现象有效缓解这一关键机制尚无明确认识。
-
ERH协同电动输送氧化剂作用机理及影响因素的研究属创新尝试。电动输送可将氧化剂精准传输至目标污染区域,ERH可活化氧化剂和提升污染物的可及性,理论上两者耦合效率将协同提升。土壤ERH修复的关键设备与电动输送相似性很高,如电极井、抽提井、水分补充系统、盐分补充系统等,增强了协同技术的可行性,ERH协同电动输送氧化剂修复有机污染土壤原理见图2。通过在土壤中施加直流电场,将氧化剂由补水管注入土壤,在电渗流、电迁移动力作用下,氧化剂输送至目标污染区域与污染物发生初步的氧化分解反应;氧化剂输送完毕后,切换交流电源,通过电阻效应产生热量,在热活化氧化剂与热脱附综合作用下,挥发性或半挥发性污染物在土壤中迁移转化、挥发或发生共沸,再通过抽提系统和处理系统收集和处理废水、废气,从而达到有机污染土壤的修复效果。
电动输送氧化剂至低渗透区的应用研究已有文献报道 [42]。电动输送过硫酸钠在低渗透土壤中的迁移速度约为2.0 cm·d−1,结合ERH所提供的对氧化剂低温热活化及对污染物的热脱附作用,促使其在18 d内将模拟污染土壤中的四氯乙烯几乎全部去除,修复效率大幅提升 [35]。该研究将ERH协同电动输送氧化剂修复有机污染土壤从理论可行提高到了实验验证阶段。
-
目前, ERH协同化学氧化修复有机污染土壤的研究尚处发展阶段,还需进行以下深入研究。
(1)ERH与化学氧化耦合可大幅提高处置效率,然而化学氧化技术的关键在于氧化剂与土壤污染物难以接触,ERH提供的温度虽适宜于氧化剂发生反应,但并未证明ERH能提高氧化剂与污染物的接触率。因此,还需开展提高氧化剂与污染物接触率的理论研究,为ERH耦合化学氧化技术的广泛应用奠定科学基础。
(2)由于ERH协同化学氧化修复机制不明。因此,开展ERH产生的热场-电场综合作用下活化氧化剂的机制、污染物可及性变化及修复产物变化规律等机理性研究,可为阐明ERH协同化学氧化耦合机制提供理论支撑。
(3)结合ERH活化和增强脱附、电动输送精准传输、氧化剂高效降解污染物的优势,理论上将有效提升修复效率、节约修复成本,但实际成效如何?如何影响污染物去除?上述关键科学问题的研究可为实际工程应用提供理论支撑。
(4)电动输送可将氧化剂精准传输至目标污染区域,从而可强化其协同修复作用,明晰电动输送氧化剂的规律及其协同电阻加热去除有机污染土壤的耦合机制,可避免资源浪费、实现精准高效修复,需进行深入研究。
(5)目前,主要开展了室内ERH协同化学氧化修复研究,仍未实现协同修复技术的工程放大与示范验证。今后,应选取典型污染地块开展技术装备的工程实践,验证协同修复技术的处置效能,为有机污染地块原位高效修复提供科学依据和修复技术选择。
电阻加热协同化学氧化修复有机污染土壤
Remediation of organic contaminated soil by electrical resistance heating coupled chemical oxidation
-
摘要: 近年来,由于我国涉污染企业搬迁,造成了严重的有机污染土壤环境污染问题,多技术协同治理是修复有机污染地块的必然选择。电阻加热(electrical resistance heating,ERH)和化学氧化均是主流的污染土壤修复技术,且互补性强,二者耦合技术具有较好的工程化应用前景。本研究分析了ERH的修复原理及其适用性,讨论了ERH协同化学氧化的研究现状,创新性地提出了ERH协同电动输送氧化剂的设想,并对后期发展进行了总结和展望,以期为我国有机污染土壤高效、快速、绿色的原位修复技术的应用提供借鉴。Abstract: In recent years, due to the relocation of pollution-related enterprises in China has caused serious soil environmental pollution problems, and multi-technology synergistic treatment is an inevitable choice for remediation of organic contaminated soil. Both electrical resistance heating (ERH) and chemical oxidation are mainstream remediation technologies for contaminated soils and complementary, and the coupling technology of both has good prospects for engineering applications. The remediation principle of ERH and its applicability was analyzed, the current research progress of ERH synergistic chemical oxidation was discussed, the innovative idea of ERH synergiatic electric delivery of oxidant was proposed, and the later development was summarized and prospected. It is expected that the results will provide reference for the application of efficient, rapid and green in-situ remediation technologies in organics-contaminated soil.
-
表 1 ERH与过硫酸钠协同修复中的重要参数
Table 1. Key factors of ERH and sodium persulfate coupled remediation
目标污染物Target pollutant 处置浓度/(mg·kg−1)Disposal concentration 加热温度/℃ Heating temperature 加热时间/dHeating time 电场强度/(V·cm-1)Electric field strength 去除率/% Removal rate 文献来源References 前Front 后Back 四氯乙烯 — 74—100 19—30 — 52 93 [6] 菲 101.61 70—9070—90 0.330.33 88 35.90 23.50 [34][34] 苯并芘 2.17 79.42 85.47 四氯乙烯 — <50 >60 — — * [35] 注:“—”为无准确信息;“*”表示低于检测限。 -
[1] ZHAO C, DONG Y, FENG Y P, et al. Thermal desorption for remediation of contaminated soil: A review [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 221: 841-855. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.079 [2] 苗竹, 魏丽, 吕正勇, 等. 原位化学氧化技术在有机污染场地的应用[C]// 中国环境科学学会. 2015 年中国环境科学学会学术年会论文集, 2015: 470-478. ZHU M, LI W, ZHENGYONG L, et al. Application of in situ chemical oxidation technology to organic contaminated sites[C]//Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences . Proceedings of the 2015 Annual Academic Conference of the Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences, 2015: 470-478.
[3] WOLF J W, BARTON T, GOMES T, et al. Electrical resistance heating: Rapid treatment for soil and groundwater remediation[EB/OL]. Águas Subterrâneas, 2009.https://aguassubterraneas.abas.org/asubterraneas/article/view/21953. [4] BEYKE G, FLEMING D. In situ thermal remediation of DNAPL and LNAPL using electrical resistance heating [J]. Remediation Journal, 2005, 15(3): 5-22. doi: 10.1002/rem.20047 [5] HAN Z Y, JIAO W T, TIAN Y, et al. Lab-scale removal of PAHs in contaminated soil using electrical resistance heating: Removal efficiency and alteration of soil properties [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 239: 124496. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124496 [6] COSTANZA J, MARCET T, CÁPIRO N L, et al. Tetrachloroethene release and degradation during combined ERH and sodium persulfate oxidation [J]. Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation, 2017, 37(4): 43-50. [7] 焦文涛, 韩自玉, 吕正勇, 等. 土壤电阻加热技术原位修复有机污染土壤的关键问题与展望[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(9): 2027-2036. JIAO W T, HAN Z Y, LYU Z Y, et al. Key issue and expectation of soil electrical resistance heating remediation technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2019, 13(9): 2027-2036(in Chinese).
[8] TRUEX M J, MACBETH T W, VERMEUL V R, et al. Demonstration of combined zero-valent iron and electrical resistance heating for in situ trichloroethene remediation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(12): 5346-5351. [9] GREISH S, RINNAN Å, MARCUSSEN H, et al. Interaction mechanisms between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and organic soil washing agents [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(1): 299-311. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0374-7 [10] TRIPLETT KINGSTON J L, DAHLEN P R, JOHNSON P C. State-of-the-practice review of in situ thermal technologies [J]. Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation, 2010, 30(4): 64-72. [11] OBERLE D, CROWNOVER E, KLUGER M. In situ remediation of 1, 4-dioxane using electrical resistance heating [J]. Remediation Journal, 2015, 25(2): 35-42. doi: 10.1002/rem.21422 [12] 康绍果, 李书鹏, 范云. 污染地块原位加热处理技术研究现状与发展趋势 [J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(7): 2621-2631. KANG S G, LI S P, FAN Y. Research status and development trend of in situ thermal treatment technologies for contaminated site [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(7): 2621-2631(in Chinese).
[13] HERON G, CARROLL S, NIELSEN S G. Full-scale removal of DNAPL constituents using steam-enhanced extraction and electrical resistance heating [J]. Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation, 2005, 25(4): 92-107. [14] SAEEDI M, LI L, GRACE J. Effect of co-existing heavy metals and natural organic matter on sorption/desorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil: A review [J]. Pollution, 2020, 6(1): 1-24. [15] KINGSTON J L T, JOHNSON P C, KUEPER B H, et al. In situ thermal treatment of chlorinated solvent source Zones[M]. Chlorinated Solvent Source Zone Remediation, 2014: 509-557. [16] MARTIN E J, MUMFORD K G, KUEPER B H. Electrical resistance heating of clay layers in water-saturated sand [J]. Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation, 2016, 36(1): 54-61. [17] LI J J, WANG L, PENG L B, et al. A combo system consisting of simultaneous persulfate recirculation and alternating current electrical resistance heating for the implementation of heat activated persulfate ISCO [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 385: 123803. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123803 [18] SONG T S, ZHANG J G, HOU S, et al. In situ electrokinetic remediation of toxic metal-contaminated soil driven by solid phase microbial fuel cells with a wheat straw addition [J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2018, 93(10): 2860-2867. [19] BOUZID I, MAIRE J, FATIN-ROUGE N. Comparative assessment of a foam-based method for ISCO of coal tar contaminated unsaturated soils [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7(5): 103346. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103346 [20] ZHOU Z, LIU X T, SUN K, et al. Persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for organic-contaminated soil remediation: A review [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 372: 836-851. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.213 [21] DENG R R, XIE Z M, LIU Z H, et al. Enhancement of vanadium extraction at low temperature sodium roasting by electric field and sodium persulfate [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 189: 105110. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.105110 [22] WATTS R J, AHMAD M, HOHNER A K, et al. Persulfate activation by glucose for in situ chemical oxidation [J]. Water Research, 2018, 133: 247-254. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.050 [23] 曾晓岚, 汤红亮, 张玉, 等. 热活化过硫酸钠氧化甲基紫的研究 [J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(5): 54-57. ZENG X L, TANG H L, ZHANG Y, et al. Study on oxidizing methyl violet by heat activated sodium persulfate [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(5): 54-57(in Chinese).
[24] 李轶涵, 姜恬, 周旭, 等. 热活化过硫酸盐氧化降解水溶液中的抗生素卡巴多司和奥喹多司 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(11): 3821-3831. LI Y H, JIANG T, ZHOU X, et al. Thermally activated persulfate oxidation of antibiotics carbadox and olaquindox in aqueous solution [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(11): 3821-3831(in Chinese).
[25] ZOU X, LI X M, CHEN C, et al. Degradation performance of carbamazepine by ferrous-activated sodium hypochlorite: Mechanism and impacts on the soil system [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 389: 123451. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123451 [26] XU H T, SONG Y, CANG L, et al. Ion exchange membranes enhance the electrokinetic in situ chemical oxidation of PAH-contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 382: 121042. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121042 [27] SHI Y, LUO Z H, WANG Y X, et al. New advances in in situ thermal desorption technology for contaminated soil [J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2019, 62(11): 2075-2076. doi: 10.1007/s11431-019-9619-3 [28] 贾存珍, 柳修楚, 柴超, 等. 化学氧化修复对农田土壤和菠菜中多环芳烃含量和组成的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(7): 1518-1527. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018092803 JIA C Z, LIU X C, CHAI C, et al. Effects of chemical oxidation remediation on concentration and composition of PAHs in agricultural soils and spinach [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(7): 1518-1527(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018092803
[29] ABD MANAN T S B, BEDDU S, KHAN T, et al. Step by step procedures: Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in potable water using photo-Fenton oxidation process [J]. MethodsX, 2019, 6: 1701-1705. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2019.07.011 [30] LIU H, MA S T, ZHANG X L, et al. Application of thermal desorption methods for airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon measurement: A critical review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254: 113018. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113018 [31] ZHAO T, YU Z, ZHANG J F, et al. Low-thermal remediation of mercury-contaminated soil and cultivation of treated soil [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(24): 24135-24142. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2387-2 [32] 师帅, 李芸邑, 刘阳生. 化学氧化耦合电动力技术修复有机污染土壤 [J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(9): 160-165. SHI S, LI Y Y, LIU Y S. Remediation of organic polluted soil by electrokinetic combined with chemical oxidation [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(9): 160-165(in Chinese).
[33] da SILVA MENDONÇA de PAIVA S, da SILVA I B, de MOURA SANTOS E C M, et al. Coupled electrochemical processes for removing dye from soil and water [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165(9): 318-324. doi: 10.1149/2.0391809jes [34] HAN Z Y, LI S H, YUE Y, et al. Enhancing remediation of PAH-contaminated soil through coupling electrical resistance heating using Na2S2O8 [J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 198: 110457. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110457 [35] CHOWDHURY A I A, GERHARD J I, REYNOLDS D, et al. Low permeability zone remediation via oxidant delivered by electrokinetics and activated by electrical resistance heating: Proof of concept [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(22): 13295-13303. [36] PAC T J, BALDOCK J, BRODIE B, et al. In situ chemical oxidation: Lessons learned at multiple sites [J]. Remediation Journal, 2019, 29(2): 75-91. doi: 10.1002/rem.21591 [37] SONG Y, CANG L, ZUO Y L, et al. EDTA-enhanced electrokinetic remediation of aged electroplating contaminated soil assisted by combining dual cation-exchange membranes and circulation methods [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 243: 125439. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125439 [38] RAMADAN B S, SARI G L, ROSMALINA R T, et al. An overview of electrokinetic soil Flushing and its effect on bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 218: 309-321. [39] 孟凡生, 王业耀. 含水量对电动修复铬污染高岭土的影响 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2009, 32(B06): 23-26. FANSHENG M, YEYAO W. Effect of Water Content on the Electrokinetic Remediation of Cr(VI) from Kaolin [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2009, 32(B06): 23-26(in Chinese).
[40] ZANG J C,. Field test on electro-osmosis in a heavy metal contaminated soil: Electrokinetic remediation and reinforcement of the soil [J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2020: 1230-1241. doi: 10.20964/2020.02.07 [41] 刘广容, 叶春松, 钱勤, 等. 电动生物修复湖泊底泥中直链烷基苯磺酸钠 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2011, 34(9): 59-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2011.09.015 LIU G R, YE C S, QIAN Q, et al. Bioremediation of lake sediment contaminated by linear alkylbenzene sulphonates using electrokinetic technology [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 34(9): 59-62(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2011.09.015
[42] SHI S, LI Y Y, LI Y S. Remediation of organic polluted soil by electrokinetic combined with chemical oxidation [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(9): 160-165. [43] HODGES D, FOURIE A, THOMAS D, et al. Overcoming permanganate stalling during electromigration [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 139(5): 677-684. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000660 -




 下载:
下载: