-
汞具有较高的挥发性,其毒性具有持久性和生物累积性,可通过食物链传递,已经被世界卫生组织列为优先控制污染物[1-3]。煤炭燃烧是重要的大气汞排放污染源之一[4-5],我国最新修订的《火电厂大气污染物排放标准》,对燃煤电厂烟气中的汞及其化合物的排放进行了严格的限定,限值为30 μg·m−3。2017年8月6日,中国参与的全球首个汞限排国际公约《关于汞的水俣公约》正式生效[6]。燃煤汞污染问题的高效治理,已成为煤炭清洁利用的重要方面之一。
燃煤烟气中的汞主要以3种形态存在:气态单质汞(Hg0g)、气态二价汞(Hg2+g)和吸附态汞(Hgp)。Hg2+和Hgp可以通过电厂的空气污染控制装置(APCD)脱除[7-8]。由于Hg0易挥发且难溶于水的特性,电厂现有的APCD难以将烟气中的Hg0g有效地脱除。因此,燃煤烟气中Hg0g的高效脱除成为了烟气汞污染净化的重点和难点。
目前,燃煤电厂研究较多而且开始应用的汞排放控制方法是在烟道中喷射活性炭来吸附烟气中的汞[9-10]。然而,燃煤电厂现场的应用结果表明,活性炭用量较大,其对汞的脱除效果受烟气温度和组分影响很大,活性炭脱汞成本较高,使活性炭喷射技术在燃煤电厂脱汞的应用受到很大限制。近年来,经济高效的非碳基吸附剂特别是天然矿物吸附剂受到研究者的广泛重视[11-12]。
凹凸棒石(PG)是一种天然硅酸盐类黏土矿物,经处理后孔隙发达,比表面积大,具有良好的吸附性和热稳定性,而且成本低廉,来源广泛,是良好的催化剂载体。锰氧化物具有良好的低温催化氧化活性,可将Hg0氧化为容易脱除的Hg2+,负载MnOx的催化剂已被研究用于脱除燃煤烟气中的Hg0[13-18]。
本课题组前期研究结果表明,PG负载V2O5、CuO、MnOx等所形成的催化剂在排烟温度范围内对Hg0具有较高的氧化和吸附能力,其中凹凸棒石负载MnOx催化剂在低温展现了较高的脱除Hg0的能力[19-20]。为进一步研究MnOx/PG催化剂脱除烟气中Hg0的性能,本文研究了MnOx/PG催化剂制备条件、工况条件(反应温度、汞浓度、空速)等对MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的影响,并研究了脱除Hg0后MnOx/PG催化剂的再生及不同条件下再生后MnOx/PG催化剂的脱除Hg0活性。
-
将凹凸棒石黏土与蒸馏水按照一定比例混合后搅拌均匀、挤压,然后在烘箱中于110 ℃下干燥24 h,将充分干燥后的凹凸棒石样品研磨并筛选出30—60目的颗粒,在N2气氛中300 ℃下热处理2 h,即得凹凸棒石载体。采用等体积浸渍法制备MnOx/PG催化剂,根据所需制备催化剂的MnOx的负载量,将PG等体积浸渍于Mn(NO3)2溶液中,然后在室温静置2 h,50 ℃干燥5 h,110 ℃干燥5 h,最后依次在N2、N2+O2气氛中煅烧2 h,即可制得MnOx/PG催化剂[20]。
-
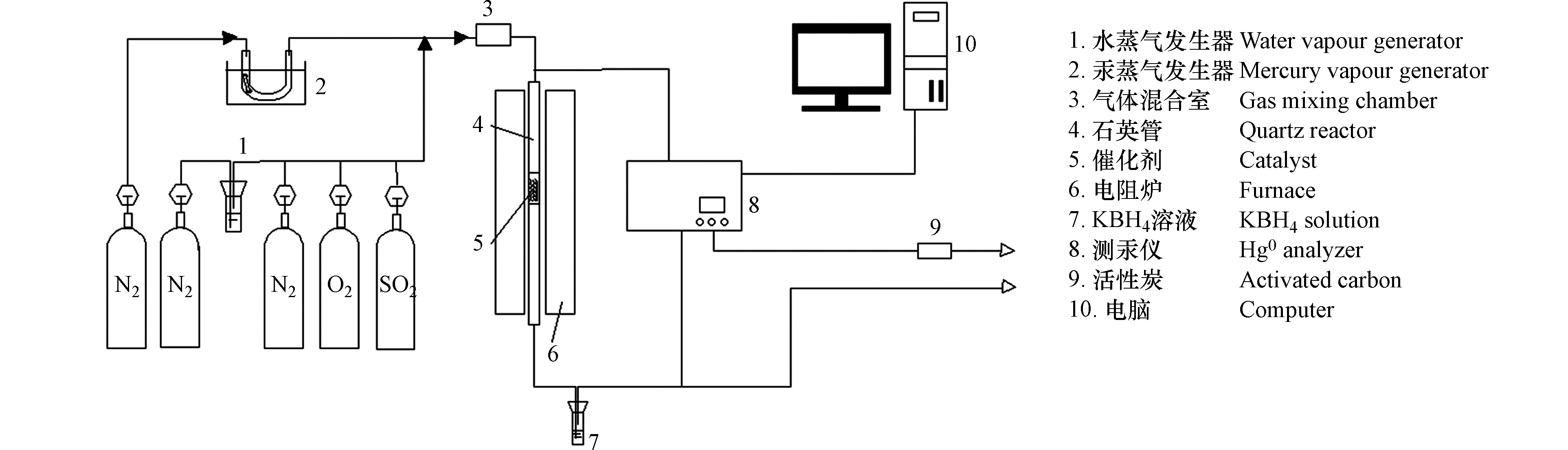
MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除实验装置如图1所示。
实验气氛为含有N2(平衡气)、O2、SO2和H2O的模拟烟气,Hg0蒸气由汞渗透管产生,Hg0 浓度为240 μg·m−3。催化剂装填量为0.5 g,反应温度为120—240 ℃,反应时间为400 min。利用测汞仪(俄罗斯Lumex公司,RA—915M型)在线连续检测催化剂前后气体中的Hg0浓度。实验管路采用加热带保温防止气态Hg0的冷凝,尾端利用装有疏松多孔活性炭的吸收塔处理尾气。MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的能力用脱除效率表示,本文中的实验数据均为3次测量的平均值[20]。
-
脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂进行热再生和水洗再生,再生后的催化剂再次进行脱除Hg0的实验。热再生在图1所示的固定床反应装置上进行。再生条件为:气体流量为100 mL·min−1的 N2气氛下,程序升温至再生温度(300—500 ℃)并保持恒温再生2 h,升温速率为10 ℃·min−1。
水洗再生的过程是将脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂在100 mL锥形瓶中与去离子水混合,将锥形瓶放入超声设备中振荡10 min后过滤,在真空干燥箱中110 ℃下干燥6 h,即得到再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂。
-
采用扫描电镜(SEM,JSM-6490LV,日本电子公司)表征载体PG和MnOx/PG催化剂的表面形貌。
-
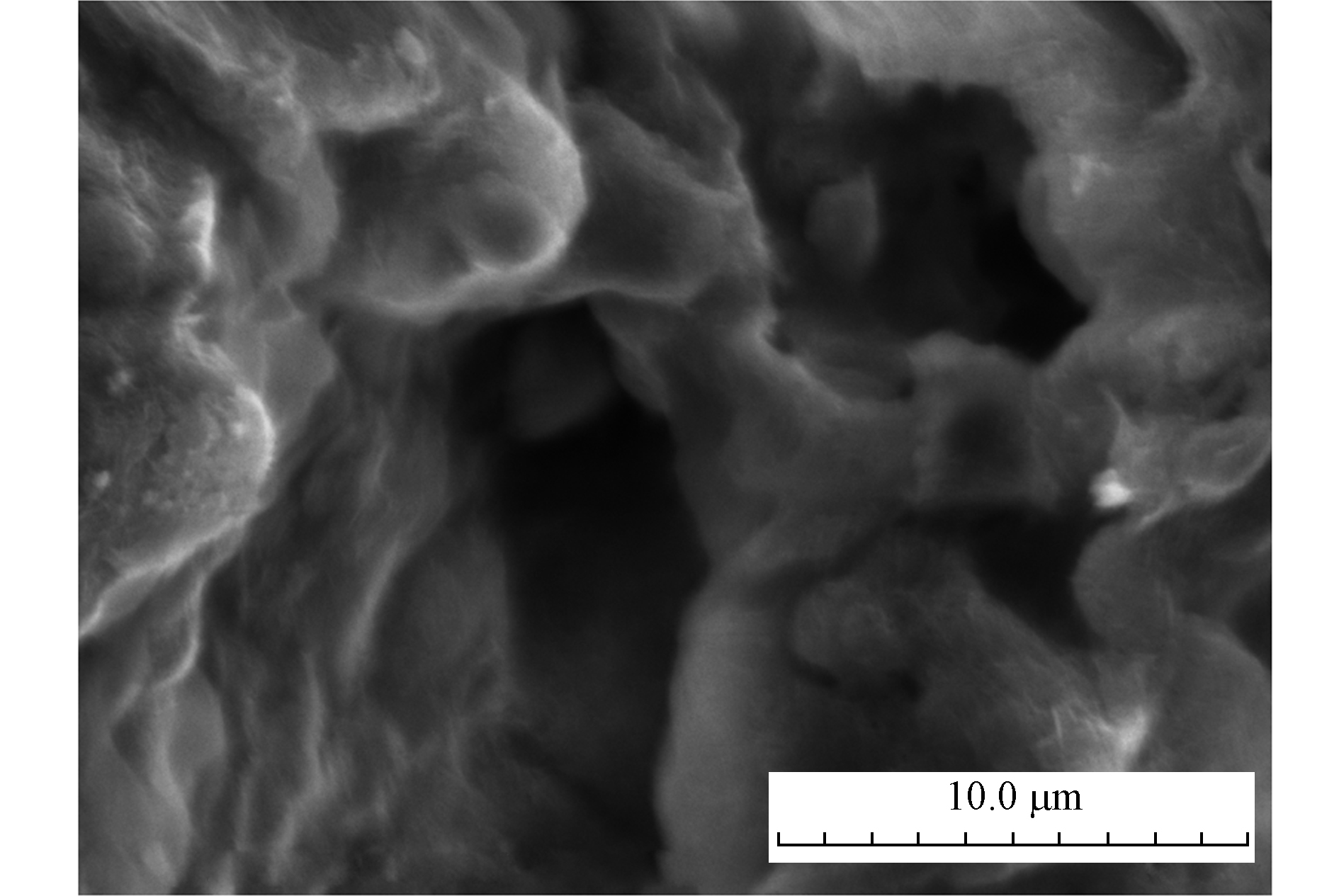
图2为MnOx负载量为8%的MnOx/PG催化剂的SEM图。可以看出,PG载体具有大量的孔道结构,使得MnOx/PG催化剂具有较高的比表面积,不仅有利于活性组分MnOx在PG载体上的分散负载,而且有利于含Hg0气体的扩散和Hg0在MnOx/PG催化剂上的吸附、氧化。
-
图3为不同MnOx负载量(0%、2%、4%、6%、8%、10%)的MnOx/PG催化剂在模拟烟气中400 min时对Hg0的脱除效率。可以看出,负载量0%的PG载体对Hg0的脱除效率较低,只有35%左右。随着MnOx负载量从2%增加到8%,Hg0的脱除效率明显升高,这表明MnOx的负载对Hg0的脱除起到了关键作用。MnOx负载量为8%的MnOx/PG脱除Hg0的效率最高,达到95.9%。随着MnOx负载量的继续增加,Hg0的脱除效率出现了下降。这是由于MnOx负载量较低时,MnOx能够较好的分散在载体PG表面,有利于Hg0的吸附、氧化,因此具有较高的Hg0的脱除效率。但MnOx负载量过高时,MnOx会发生团聚、阻塞载体的孔道,使得催化剂的比表面积下降,降低了对Hg0的吸附、氧化,从而导致催化剂脱除Hg0的能力有所降低[21-22]。
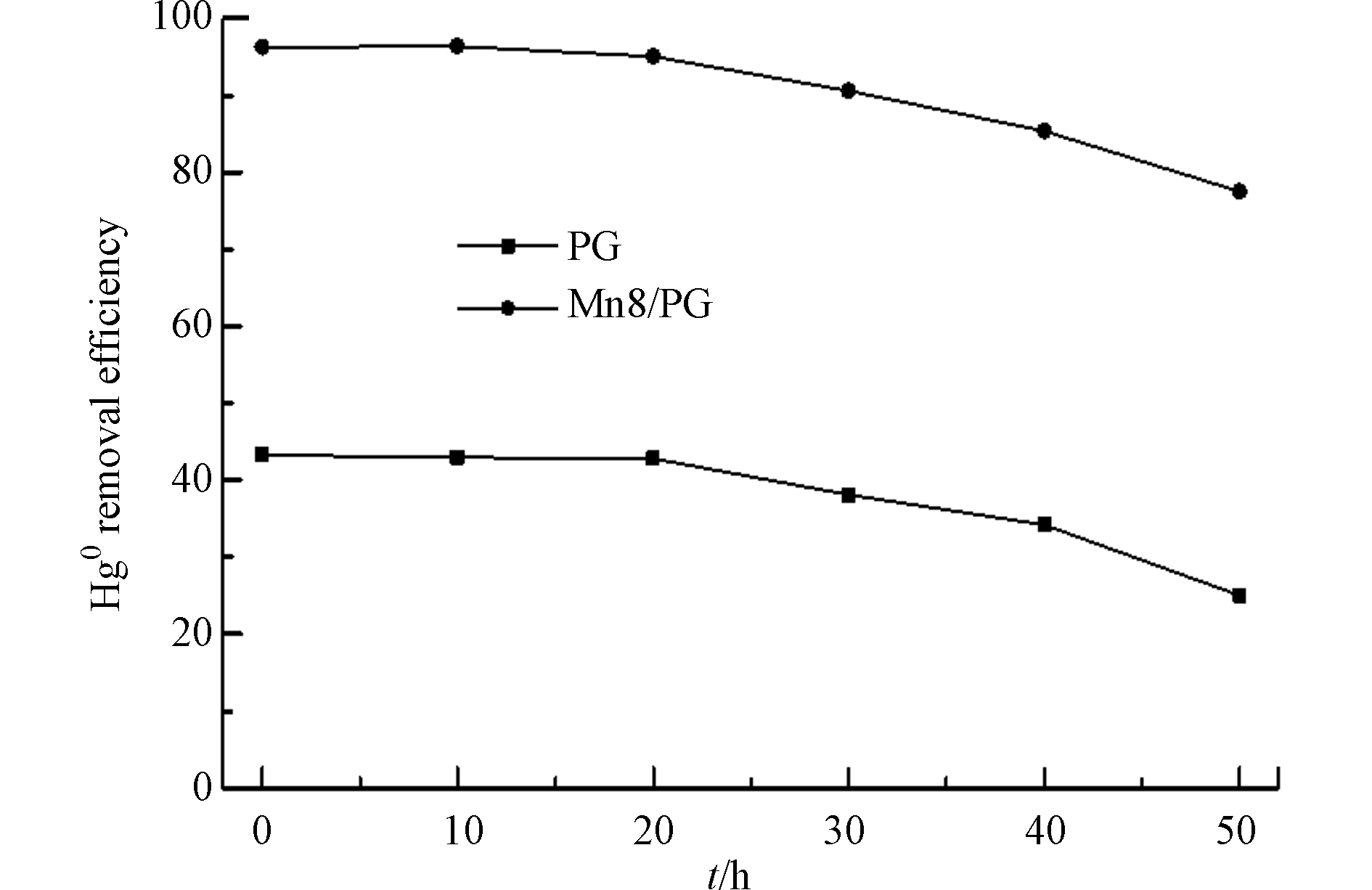
为考察MnOx/PG催化剂长时间使用的脱除Hg0的活性,在空速6000 h−1、温度210 ℃时,选用负载量8%的MnOx/PG催化剂进行了脱除Hg0 50 h的活性评价实验,结果如图4所示。可以看出,随着反应时间的延长,PG载体逐渐失活,50 h时的Hg0脱除效率已经降到了25%以下。而MnOx/PG催化剂一直保持了较高的脱除Hg0的活性,50 h时的Hg0脱除效率仍在80%左右,这表明MnOx/PG催化剂不仅具有优良的脱除Hg0的活性而且具有较长的使用寿命。
-
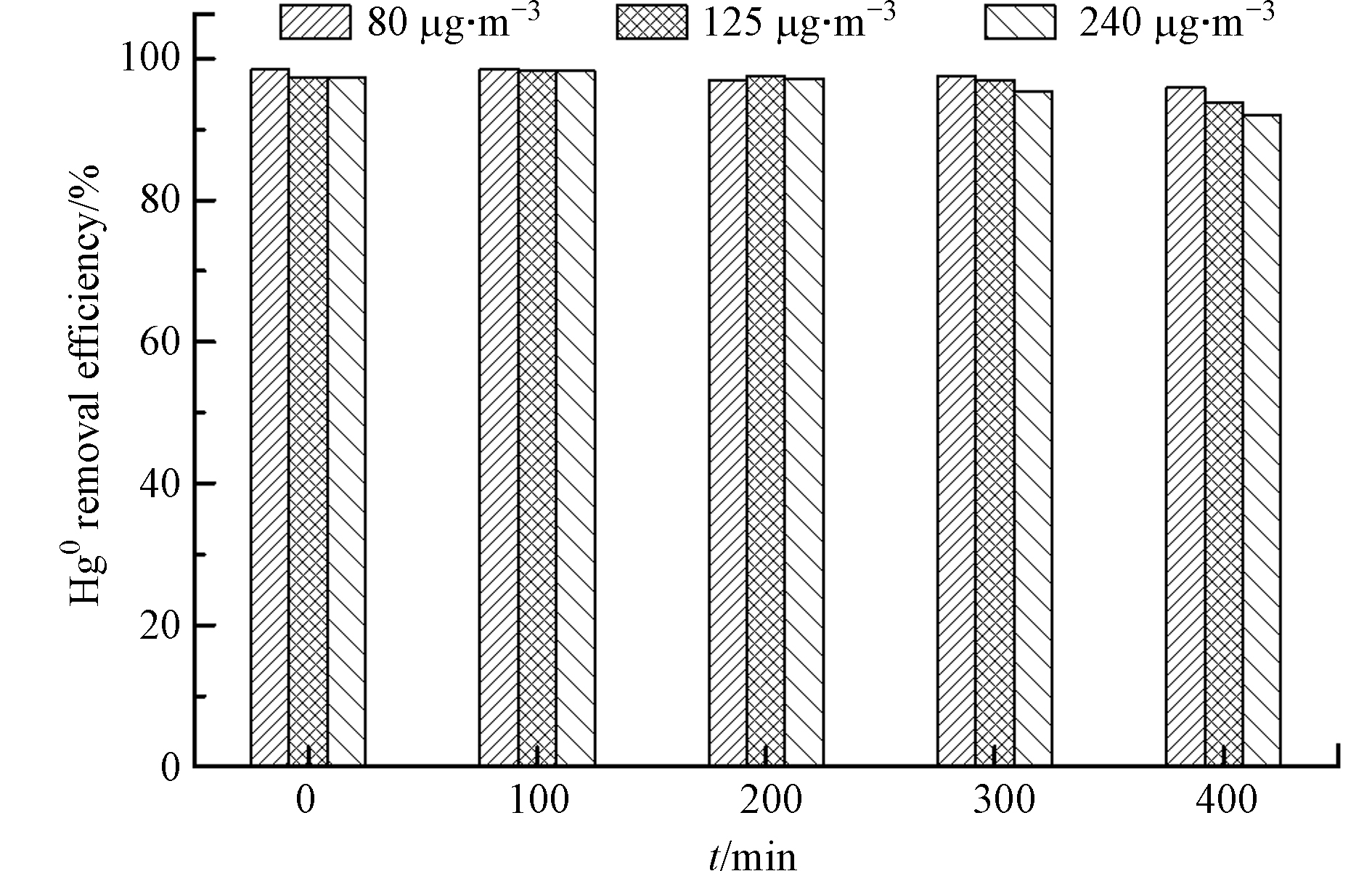
图5为MnOx/PG催化剂在80—240 μg·m−3的Hg0浓度范围内对Hg0脱除400 min的结果。可以看出,尽管Hg0的浓度变化较大,但对MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的能力影响很小。随着Hg0的浓度从80 μg·m−3升高到125 μg·m−3和240 μg·m−3,Hg0的脱除效率变化很小,均在95%以上。图5中的实验结果再次表明,MnOx/PG催化剂具有较高且稳定的脱除Hg0的能力,可用于在含有较高Hg0浓度的烟气中脱除Hg0。
-
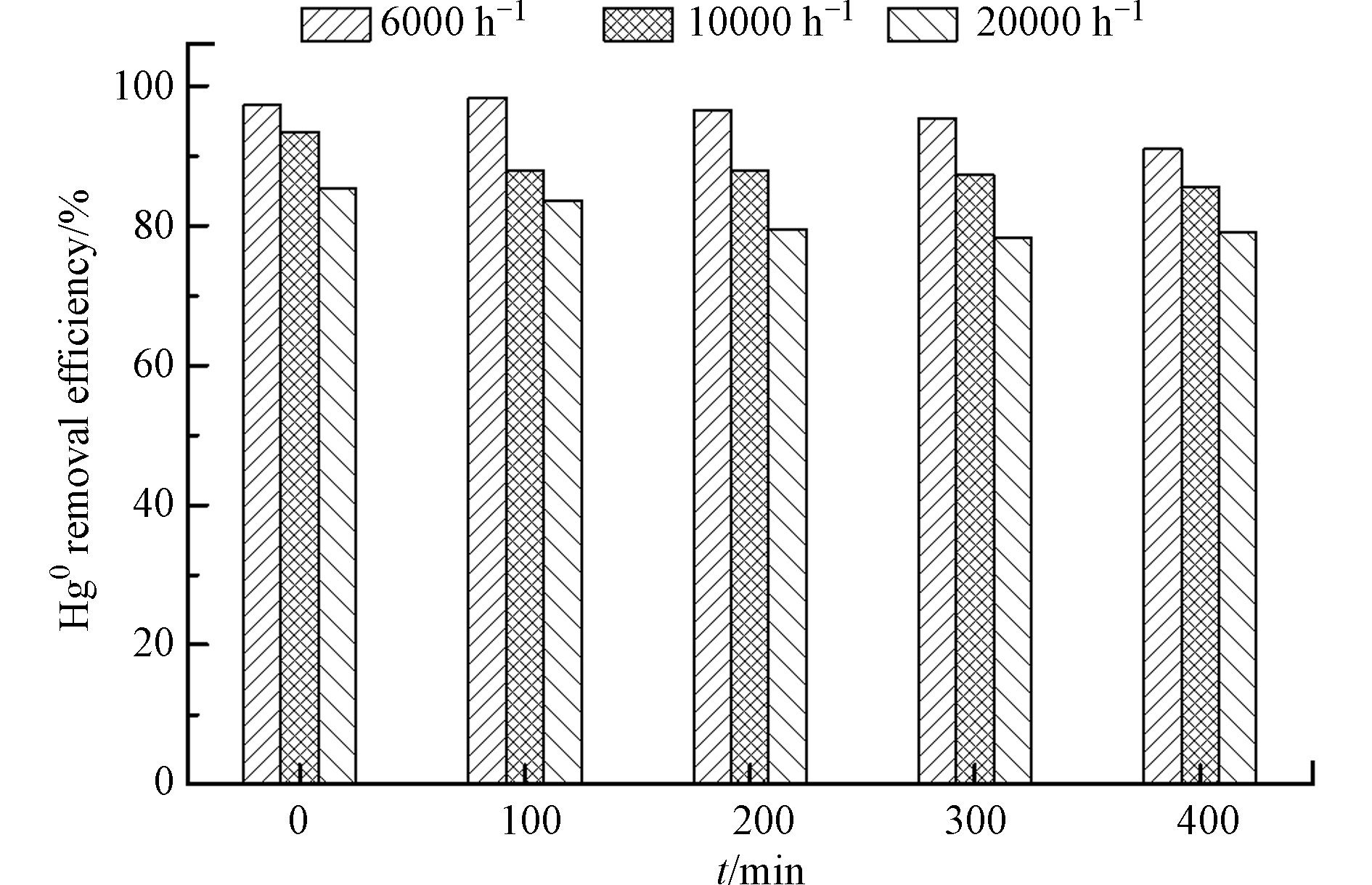
图6为MnOx/PG在6000—20000 h−1的空速范围内对Hg0 脱除400 min的结果。可以看出,在实验所用的空速范围内,空速由6000 h−1增大至20000 h−1,Hg0的脱除效率出现明显降低,400 min 时降低至80%。这主要是由于低空速下气体流速较慢,烟气与MnOx/PG催化剂的接触时间较长,有利于Hg0在MnOx/PG催化剂上吸附、氧化,从而提高了Hg0的脱除效率。而空速过大时,气体流速相应增大,烟气与MnOx/PG催化剂的接触时间变短,不利于Hg0在MnOx/PG催化剂上吸附、氧化,进而导致Hg0的脱除效率降低。
-
为考察MnOx/PG催化剂的再生及循环使用性能,对上述脱除Hg0 50 h后的MnOx/PG催化剂进行了热再生和水洗再生。图7(a)为在300 ℃、400 ℃和500 ℃的N2中热再生2 h的MnOx/PG催化剂再次脱除Hg0的效果。可以看出,热再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂仍保持了较高的脱除Hg0的能力,且400 ℃下的再生效果最好,400 min时Hg0的脱除效率仍保持在85%以上。而500 ℃下的再生效果不好,MnOx/PG脱除Hg0的能力明显下降,400 min时Hg0的脱除效率快速下降至25%左右。这主要是由于载体PG在500 ℃下的热稳定性较低,多孔结构发生坍塌堵塞部分孔道,导致MnOx/PG催化剂比表面积变小(新鲜MnOx/PG催化剂和500 ℃再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂的比表面积和孔结构数据见表1),影响了脱除Hg0的能力。
图7(b)为在水浴温度100 ℃下再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂再次脱除Hg0的性能。可以看出,水洗再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除能力较低,400 min时均降低至50%左右,这表明水洗再生的方法不能使脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂的活性有效恢复,这可能主要是由于水洗过程中会使得MnOx/PG催化剂的部分活性组分损失,导致MnOx/PG对Hg0的脱除能力下降。因此,选用热再生的方法对脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂进行再生。
-
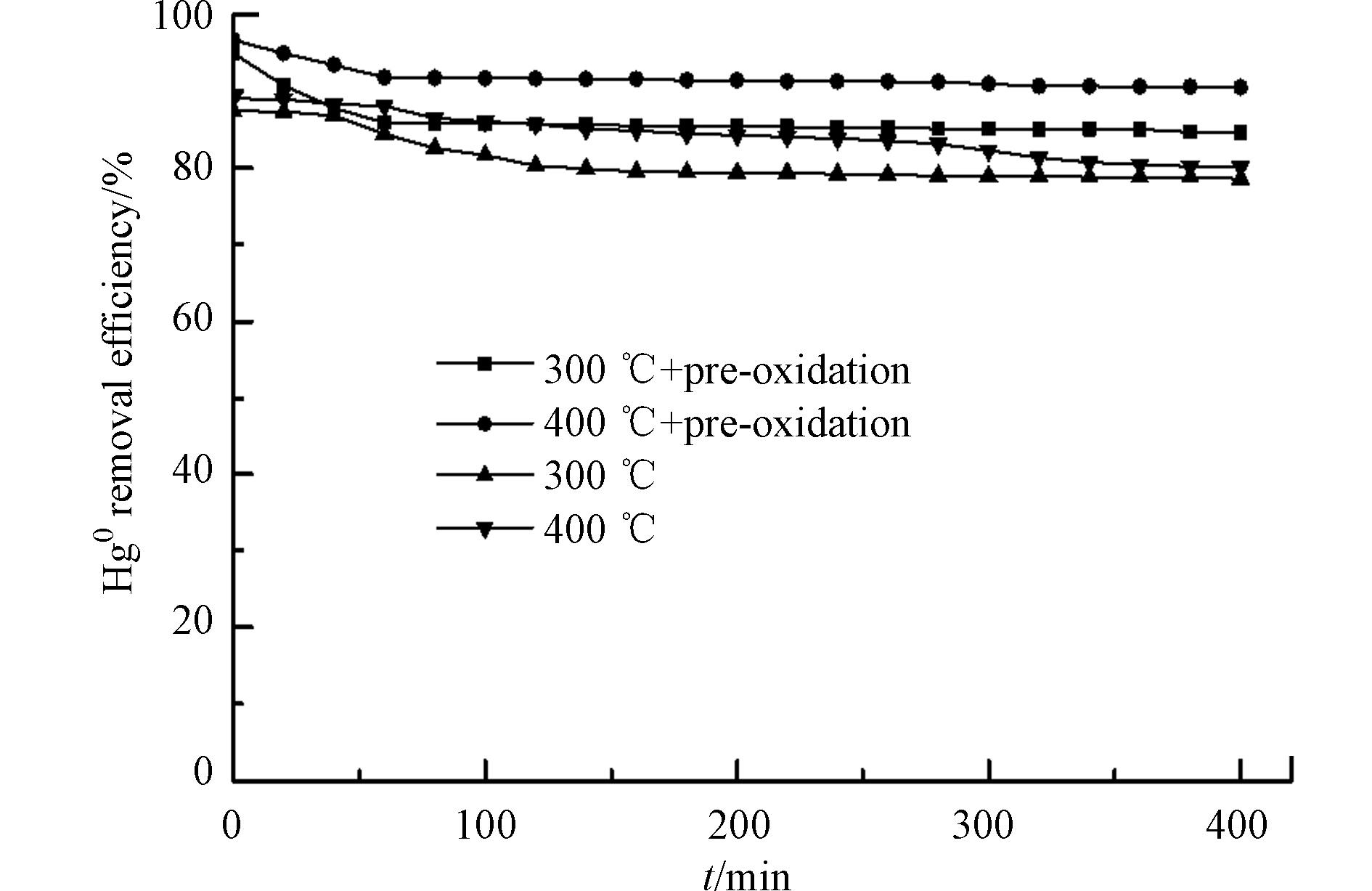
为进一步优化脱除Hg0后MnOx/PG催化剂的再生条件,对300 ℃和400 ℃再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂在空气气氛中250 ℃下预氧化处理2 h,并将其用于再次脱除Hg0,结果如图8所示。可以看出,在300 ℃和400 ℃两种温度下热再生后的催化剂经过预氧化处理有利于提高其脱除Hg0的能力,预氧化处理使得热再生后的催化剂对Hg0的脱除效率提高了10%左右。这表明,预氧化处理有利于提高再生后MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的能力,主要是由于预氧化过程中O2可将MnOx中低价态的Mn氧化成高价态,提高了MnOx对Hg0的氧化活性,使得MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的能力提高[23-25]。
-
图9为在400 ℃的再生温度下经过3次热再生-预氧化处理的MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除性能。可以看出,3次热再生-预氧化处理的MnOx/PG催化剂仍具有较高的脱除Hg0的能力。与新鲜的MnOx/PG催化剂相比,3次热再生-预氧化处理的MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除能力有所下降,但降低的幅度较小,第3次热再生-预氧化的MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除效率在400 min时仍高于75%,远高于PG载体对Hg0的脱除效率。这表明,MnOx/PG催化剂不仅具有较高的脱除Hg0的活性,而且具有良好的再生循环使用性能。
-
(1)MnOx/PG催化剂具有良好的脱除Hg0的活性和稳定性,载体PG的多孔结构有利于活性组分MnOx的分散和Hg0的吸附、氧化。
(2)低Hg0浓度和低空速条件下有利于MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除。
(3)热再生对脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂的再生效果好于水洗再生,最佳再生温度为400 ℃。热再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂仍具有良好的脱除Hg0的能力。
(4)脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂经400 ℃热再生和预氧化处理,可有效恢复其对Hg0的再次脱除能力。MnOx/PG催化剂不仅具有较高的脱除Hg0的活性,而且具有良好的再生循环使用性能。
MnOx/PG催化剂脱除气态Hg0及其再生性能
Study of MnOx/PG catalyst for Hg0 removal and regeneration
-
摘要: 本文研究了MnOx/PG催化剂脱除模拟烟气中Hg0的性能及脱除Hg0后MnOx/PG催化剂的再生。考察了Hg0浓度、空速等操作条件及再生方法对MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的影响。结果表明,MnOx/PG催化剂具有良好的脱除Hg0的能力和稳定性,在反应温度为210 ℃、空速为6000 h−1、Hg0浓度为80 μg·m−3的条件下400 min时的Hg0脱除效率保持在95%以上,50 h时仍能保持在80%左右。热再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂仍具有良好的脱除Hg0能力,最佳再生温度为400 ℃,水洗再生对MnOx/PG催化剂的再生效果不明显。热再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂经空气预氧化处理有利于提高其对Hg0的再次脱除能力。Abstract: Gas phase Hg0 removal by MnOx/PG catalyst was studied as well as the regeneration of the used MnOx/PG catalyst after Hg0 removal in this paper. The effects of Hg0 concentration, space velocity and regeneration method on Hg0 removal over MnOx/PG were investigated. The results showed that MnOx/PG catalyst had high and stable Hg0 removal capability. Hg0 removal efficiency was above 95% at 210 ℃ with the space velocity of 6000 h−1 and Hg0 concentration of 80 μg·m−3 for 400 mins, and could maintained about 80% for 50 h. MnOx/PG catalyst still had high Hg0 removal capability after thermal regeneration and the optimal regeneration temperature was 400 ℃, while the effect of water-washing regeneration was not obvious. The pre-oxidation treatment of MnOx/PG catalyst after thermal regeneration was beneficial to improve the Hg0 removal capability of MnOx/PG.
-
Key words:
- MnOx/PG /
- mercury /
- regeneration /
- flue gas
-
汞具有较高的挥发性,其毒性具有持久性和生物累积性,可通过食物链传递,已经被世界卫生组织列为优先控制污染物[1-3]。煤炭燃烧是重要的大气汞排放污染源之一[4-5],我国最新修订的《火电厂大气污染物排放标准》,对燃煤电厂烟气中的汞及其化合物的排放进行了严格的限定,限值为30 μg·m−3。2017年8月6日,中国参与的全球首个汞限排国际公约《关于汞的水俣公约》正式生效[6]。燃煤汞污染问题的高效治理,已成为煤炭清洁利用的重要方面之一。
燃煤烟气中的汞主要以3种形态存在:气态单质汞(Hg0g)、气态二价汞(Hg2+g)和吸附态汞(Hgp)。Hg2+和Hgp可以通过电厂的空气污染控制装置(APCD)脱除[7-8]。由于Hg0易挥发且难溶于水的特性,电厂现有的APCD难以将烟气中的Hg0g有效地脱除。因此,燃煤烟气中Hg0g的高效脱除成为了烟气汞污染净化的重点和难点。
目前,燃煤电厂研究较多而且开始应用的汞排放控制方法是在烟道中喷射活性炭来吸附烟气中的汞[9-10]。然而,燃煤电厂现场的应用结果表明,活性炭用量较大,其对汞的脱除效果受烟气温度和组分影响很大,活性炭脱汞成本较高,使活性炭喷射技术在燃煤电厂脱汞的应用受到很大限制。近年来,经济高效的非碳基吸附剂特别是天然矿物吸附剂受到研究者的广泛重视[11-12]。
凹凸棒石(PG)是一种天然硅酸盐类黏土矿物,经处理后孔隙发达,比表面积大,具有良好的吸附性和热稳定性,而且成本低廉,来源广泛,是良好的催化剂载体。锰氧化物具有良好的低温催化氧化活性,可将Hg0氧化为容易脱除的Hg2+,负载MnOx的催化剂已被研究用于脱除燃煤烟气中的Hg0[13-18]。
本课题组前期研究结果表明,PG负载V2O5、CuO、MnOx等所形成的催化剂在排烟温度范围内对Hg0具有较高的氧化和吸附能力,其中凹凸棒石负载MnOx催化剂在低温展现了较高的脱除Hg0的能力[19-20]。为进一步研究MnOx/PG催化剂脱除烟气中Hg0的性能,本文研究了MnOx/PG催化剂制备条件、工况条件(反应温度、汞浓度、空速)等对MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的影响,并研究了脱除Hg0后MnOx/PG催化剂的再生及不同条件下再生后MnOx/PG催化剂的脱除Hg0活性。
1. 实验部分(Experimental section)
1.1 催化剂制备
将凹凸棒石黏土与蒸馏水按照一定比例混合后搅拌均匀、挤压,然后在烘箱中于110 ℃下干燥24 h,将充分干燥后的凹凸棒石样品研磨并筛选出30—60目的颗粒,在N2气氛中300 ℃下热处理2 h,即得凹凸棒石载体。采用等体积浸渍法制备MnOx/PG催化剂,根据所需制备催化剂的MnOx的负载量,将PG等体积浸渍于Mn(NO3)2溶液中,然后在室温静置2 h,50 ℃干燥5 h,110 ℃干燥5 h,最后依次在N2、N2+O2气氛中煅烧2 h,即可制得MnOx/PG催化剂[20]。
1.2 Hg0的脱除实验
MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除实验装置如图1所示。
实验气氛为含有N2(平衡气)、O2、SO2和H2O的模拟烟气,Hg0蒸气由汞渗透管产生,Hg0 浓度为240 μg·m−3。催化剂装填量为0.5 g,反应温度为120—240 ℃,反应时间为400 min。利用测汞仪(俄罗斯Lumex公司,RA—915M型)在线连续检测催化剂前后气体中的Hg0浓度。实验管路采用加热带保温防止气态Hg0的冷凝,尾端利用装有疏松多孔活性炭的吸收塔处理尾气。MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的能力用脱除效率表示,本文中的实验数据均为3次测量的平均值[20]。
1.3 催化剂的再生实验
脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂进行热再生和水洗再生,再生后的催化剂再次进行脱除Hg0的实验。热再生在图1所示的固定床反应装置上进行。再生条件为:气体流量为100 mL·min−1的 N2气氛下,程序升温至再生温度(300—500 ℃)并保持恒温再生2 h,升温速率为10 ℃·min−1。
水洗再生的过程是将脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂在100 mL锥形瓶中与去离子水混合,将锥形瓶放入超声设备中振荡10 min后过滤,在真空干燥箱中110 ℃下干燥6 h,即得到再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂。
1.4 催化剂的表征
采用扫描电镜(SEM,JSM-6490LV,日本电子公司)表征载体PG和MnOx/PG催化剂的表面形貌。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 MnOx/PG催化剂的扫描电镜
图2为MnOx负载量为8%的MnOx/PG催化剂的SEM图。可以看出,PG载体具有大量的孔道结构,使得MnOx/PG催化剂具有较高的比表面积,不仅有利于活性组分MnOx在PG载体上的分散负载,而且有利于含Hg0气体的扩散和Hg0在MnOx/PG催化剂上的吸附、氧化。
2.2 MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的活性
图3为不同MnOx负载量(0%、2%、4%、6%、8%、10%)的MnOx/PG催化剂在模拟烟气中400 min时对Hg0的脱除效率。可以看出,负载量0%的PG载体对Hg0的脱除效率较低,只有35%左右。随着MnOx负载量从2%增加到8%,Hg0的脱除效率明显升高,这表明MnOx的负载对Hg0的脱除起到了关键作用。MnOx负载量为8%的MnOx/PG脱除Hg0的效率最高,达到95.9%。随着MnOx负载量的继续增加,Hg0的脱除效率出现了下降。这是由于MnOx负载量较低时,MnOx能够较好的分散在载体PG表面,有利于Hg0的吸附、氧化,因此具有较高的Hg0的脱除效率。但MnOx负载量过高时,MnOx会发生团聚、阻塞载体的孔道,使得催化剂的比表面积下降,降低了对Hg0的吸附、氧化,从而导致催化剂脱除Hg0的能力有所降低[21-22]。
为考察MnOx/PG催化剂长时间使用的脱除Hg0的活性,在空速6000 h−1、温度210 ℃时,选用负载量8%的MnOx/PG催化剂进行了脱除Hg0 50 h的活性评价实验,结果如图4所示。可以看出,随着反应时间的延长,PG载体逐渐失活,50 h时的Hg0脱除效率已经降到了25%以下。而MnOx/PG催化剂一直保持了较高的脱除Hg0的活性,50 h时的Hg0脱除效率仍在80%左右,这表明MnOx/PG催化剂不仅具有优良的脱除Hg0的活性而且具有较长的使用寿命。
2.3 Hg0浓度对MnOx/PG脱除Hg0的影响
图5为MnOx/PG催化剂在80—240 μg·m−3的Hg0浓度范围内对Hg0脱除400 min的结果。可以看出,尽管Hg0的浓度变化较大,但对MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的能力影响很小。随着Hg0的浓度从80 μg·m−3升高到125 μg·m−3和240 μg·m−3,Hg0的脱除效率变化很小,均在95%以上。图5中的实验结果再次表明,MnOx/PG催化剂具有较高且稳定的脱除Hg0的能力,可用于在含有较高Hg0浓度的烟气中脱除Hg0。
2.4 空速对MnOx/PG脱除Hg0的影响
图6为MnOx/PG在6000—20000 h−1的空速范围内对Hg0 脱除400 min的结果。可以看出,在实验所用的空速范围内,空速由6000 h−1增大至20000 h−1,Hg0的脱除效率出现明显降低,400 min 时降低至80%。这主要是由于低空速下气体流速较慢,烟气与MnOx/PG催化剂的接触时间较长,有利于Hg0在MnOx/PG催化剂上吸附、氧化,从而提高了Hg0的脱除效率。而空速过大时,气体流速相应增大,烟气与MnOx/PG催化剂的接触时间变短,不利于Hg0在MnOx/PG催化剂上吸附、氧化,进而导致Hg0的脱除效率降低。
2.5 脱除Hg0后MnOx/PG催化剂的再生
为考察MnOx/PG催化剂的再生及循环使用性能,对上述脱除Hg0 50 h后的MnOx/PG催化剂进行了热再生和水洗再生。图7(a)为在300 ℃、400 ℃和500 ℃的N2中热再生2 h的MnOx/PG催化剂再次脱除Hg0的效果。可以看出,热再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂仍保持了较高的脱除Hg0的能力,且400 ℃下的再生效果最好,400 min时Hg0的脱除效率仍保持在85%以上。而500 ℃下的再生效果不好,MnOx/PG脱除Hg0的能力明显下降,400 min时Hg0的脱除效率快速下降至25%左右。这主要是由于载体PG在500 ℃下的热稳定性较低,多孔结构发生坍塌堵塞部分孔道,导致MnOx/PG催化剂比表面积变小(新鲜MnOx/PG催化剂和500 ℃再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂的比表面积和孔结构数据见表1),影响了脱除Hg0的能力。
表 1 500 ℃热再生前后MnOx/PG的比表面积和孔结构Table 1. Properties of MnOx/PG and MnOx/PG after 500 ℃ regeneration样品Samples 比表面积/(m2·g−1)ABET 孔体积/(cm3·g−1)Vt 平均孔径/nmDave MnOx/PG 133.21 0.499 17.10 MnOx/PG-500 71.24 0.538 16.93 图7(b)为在水浴温度100 ℃下再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂再次脱除Hg0的性能。可以看出,水洗再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除能力较低,400 min时均降低至50%左右,这表明水洗再生的方法不能使脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂的活性有效恢复,这可能主要是由于水洗过程中会使得MnOx/PG催化剂的部分活性组分损失,导致MnOx/PG对Hg0的脱除能力下降。因此,选用热再生的方法对脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂进行再生。
2.6 预氧化对再生后MnOx/PG脱除Hg0的影响
为进一步优化脱除Hg0后MnOx/PG催化剂的再生条件,对300 ℃和400 ℃再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂在空气气氛中250 ℃下预氧化处理2 h,并将其用于再次脱除Hg0,结果如图8所示。可以看出,在300 ℃和400 ℃两种温度下热再生后的催化剂经过预氧化处理有利于提高其脱除Hg0的能力,预氧化处理使得热再生后的催化剂对Hg0的脱除效率提高了10%左右。这表明,预氧化处理有利于提高再生后MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的能力,主要是由于预氧化过程中O2可将MnOx中低价态的Mn氧化成高价态,提高了MnOx对Hg0的氧化活性,使得MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的能力提高[23-25]。
2.7 再生次数对MnOx/PG催化剂脱除Hg0的影响
图9为在400 ℃的再生温度下经过3次热再生-预氧化处理的MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除性能。可以看出,3次热再生-预氧化处理的MnOx/PG催化剂仍具有较高的脱除Hg0的能力。与新鲜的MnOx/PG催化剂相比,3次热再生-预氧化处理的MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除能力有所下降,但降低的幅度较小,第3次热再生-预氧化的MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除效率在400 min时仍高于75%,远高于PG载体对Hg0的脱除效率。这表明,MnOx/PG催化剂不仅具有较高的脱除Hg0的活性,而且具有良好的再生循环使用性能。
3. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)MnOx/PG催化剂具有良好的脱除Hg0的活性和稳定性,载体PG的多孔结构有利于活性组分MnOx的分散和Hg0的吸附、氧化。
(2)低Hg0浓度和低空速条件下有利于MnOx/PG催化剂对Hg0的脱除。
(3)热再生对脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂的再生效果好于水洗再生,最佳再生温度为400 ℃。热再生后的MnOx/PG催化剂仍具有良好的脱除Hg0的能力。
(4)脱除Hg0后的MnOx/PG催化剂经400 ℃热再生和预氧化处理,可有效恢复其对Hg0的再次脱除能力。MnOx/PG催化剂不仅具有较高的脱除Hg0的活性,而且具有良好的再生循环使用性能。
-
表 1 500 ℃热再生前后MnOx/PG的比表面积和孔结构
Table 1. Properties of MnOx/PG and MnOx/PG after 500 ℃ regeneration
样品Samples 比表面积/(m2·g−1)ABET 孔体积/(cm3·g−1)Vt 平均孔径/nmDave MnOx/PG 133.21 0.499 17.10 MnOx/PG-500 71.24 0.538 16.93 -
[1] OBRIST D, KIRK J L, ZHANG L, et al. A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use [J]. Ambio, 2018, 47(2): 116-140. doi: 10.1007/s13280-017-1004-9 [2] 王钧伟, 张庆平, 沈园园, 等. 凹凸棒石负载CuO催化剂脱除气态Hg0 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(5): 1097-1103. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.05.2016112602 WANG J W, ZHANG Q P, SHEN Y Y, et al. Removal of vapor-phase Hg0 over a CuO/PG catalyst [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(5): 1097-1103(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.05.2016112602
[3] NARAYANA S L, SUNG-OK B. Recent studies on the speciation and determination of mercury in different environmental matrices using various analytical techniques [J]. International Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 3: 1-28. [4] ZHAO Y, ZHONG H, ZHANG J, et al. Evaluating the effects of China's pollution controls on inter-annual trends and uncertainties of atmospheric mercury emissions [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 15(8): 4317-4337. doi: 10.5194/acp-15-4317-2015 [5] 孙阳昭, 陈扬, 蓝虹, 等. 中国汞污染的来源、成因及控制技术路径分析[J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32 (6): 937-942. SUN Y Z, CHEN Y, LAN H, et al. Study on pollution sources, cause of mercury pollution and its control technical roadmap in China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32 (6): 937-942 (in Chinese).
[6] REDDY B M, BHARGAVA S K. Abatement of gas-phase mercury-recent developments [J]. Catalysis Reviews, 2012, 54(3): 344-398. doi: 10.1080/01614940.2012.650966 [7] ZHENG C, XU L, LIU S, et al. Speciation and thermal stability of mercury in solid products from ultra-low emission air pollution control devices [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(12): 12655-12664. [8] 刘晶, 刘迎晖, 贾小红, 等. 燃煤烟气中汞形态分析的实验研究 [J]. 环境化学, 2003, 22(2): 172-176. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2003.02.013 LIU J, LIU Y H, JIA X H, et al. Mercury speciation in coal fired flue gas [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2003, 22(2): 172-176(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2003.02.013
[9] TAKAOKA M, CHENG Y, OSHITA K, et al. Mercury removal from the flue gases of crematoria via pre-injection of lime and activated carbon into a fabric filter [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 148: 323-332. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.10.027 [10] 白国梁, 蔡思敏, 毛德棋, 等. Fe2O3/AC脱除煤气中的Hg0 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 1145-1152. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019032703 BAI G L, CAI S M, MAO D Q, et al. Removal of Hg0 in coal-derived syngas by a Fe2O3/AC catalyst [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 1145-1152(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019032703
[11] 李晓航, 滕阳, 王鹏程, 等. 燃煤电站CFB锅炉飞灰热处理中汞释放特性 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(5): 1375-1383. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020010702 LI X H, TENG Y, WANG P C, et al. Release characteristics of mercury in fly ashes collected from coal-fired CFB power units during thermal treatment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(5): 1375-1383(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020010702
[12] 李扬, 刘冰, 杨赫, 等. MnOx-TiO2吸附剂对燃煤烟气中汞的脱除 [J]. 燃料化学学报, 2020, 048(5): 513-524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2020.05.001 LI Y, LIU B, YANG H, et al. Removal of mercury from coal-fired flue gas by MnOx-TiO2 adsorbent [J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry, 2020, 048(5): 513-524(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2020.05.001
[13] SHENG Z, HU Y, XUE J, et al. SO2 poisoning and regeneration of Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst for low temperature NOx reduction with NH3 [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2012, 30(7): 676-682. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60111-2 [14] 董璐, 黄亚继, 袁琦, 等. 锰负载钛锆和钛锡复合氧化物催化剂烟气脱汞实验研究 [J]. 燃料化学学报, 2020, 48(6): 741-751. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2020.06.014 DONG L, HUANG Y J, YUAN Q, et al. Experimental study on the mercury removal from flue gas using manganese modified titanium-zirconium and titanium-tin composite oxide catalysts composite oxide catalysts [J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry, 2020, 48(6): 741-751(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2020.06.014
[15] LIU M, LI C, ZENG Q, et al. Study on removal of elemental mercury over MoO3-CeO2/cylindrical activated coke in the presence of SO2 by Hg-temperature-programmed desorption [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 371: 666-678. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.088 [16] LIU Z, ADEWUYI Y G, SHI S, et al. Removal of gaseous hg0 using novel seaweed biomass-based activated carbon [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 366(15): 41-49. [17] 白国梁, 陶海兵, 蔡思敏, 等. 凹凸棒石(PG)负载V2O5催化剂脱除气态Hg0的研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(7): 2369-2376. BAI G L, TAO H B, CAI S M, et al. Study on the removal of gaseous Hg0 by V2O5 catalyst supported on Attapulgite [J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 2019, 39(7): 2369-2376(in Chinese).
[18] 谢亚婷. Mn、Ce改性γ-Al2O3催化剂脱除燃煤烟气汞及其抗硫特性实验研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2018. XIE Y T. Experimental study on mercury removal and sulfur resistance of Mn and Ce modified γ- Al2O3 catalysts[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[19] CAI S M, MAO D Q, WANG J W, et al. Removal of Vapor-phase Elemental Mercury over a CuO/PG Catalyst [J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 267: 032-030. [20] 王钧伟, 徐灿, 秦伟, 等. 凹凸棒石(PG)负载MnOx催化剂脱除气态Hg0的研究 [J]. 燃料化学学报, 2020, 48(12): 1442-1451. WANG J W, XU C, QIN W, et al. Hg0 removal by palygorskite (PG) supported MnOx catalyst [J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry, 2020, 48(12): 1442-1451(in Chinese).
[21] ZHOU Z J, LIU X W, XU J, et al. Elemental mercury removal over a novel starch-modified MnOx/bentonite composite [J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2019, 187: 16-20. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.01.006 [22] 郭会宾, 刘海刚, 唐宏学. WO3-MnOx/TiO2-ZrO2催化剂脱汞性能研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(6): 694-698. GUO H B, LIU H G, Tang H X. Study on mercury removal performance of WO3-MnOx/TiO2-ZrO2 catalyst [J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 2019, 41(6): 694-698(in Chinese).
[23] XIANG J, WANG P Y, SU S, et al. Control of NO and Hg0 emissions by SCR catalysts from coal-fired boiler [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2015, 135: 168-173. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.12.044 [24] YANG J, ZHAO Y, ZHANG J, et al. Regenerable cobalt oxide loaded magnetosphere catalyst from fly ash for mercury removal in coal combustion flue gas [J]. Environmental Science& Technology, 2014, 48(24): 14837-14843. [25] CHEN W, PEI Y, HUANG W, et al. Novel effective catalyst for elemental mercury removal from coal-fired flue gas and the mechanism investigation [J]. Environmental Science& Technology, 2016, 50(5): 2564-2572. -




 下载:
下载: