-
矿产的开采和冶炼是重金属进入农田土壤的重要途径[1],农产品中重金属的积累,对直接或间接食用该产品的动物以及人类构成了风险[2-3]. 研究表明,重金属可以经呼吸、皮肤接触和饮食等方式进入人体,相对于皮肤接触、呼吸,饮食由于种类复杂、摄取量大、食物中重金属含量差别明显等原因,成为重金属进入人体最重要的途径[4]. 针对作物重金属污染问题,国内外专家、学者进行了大量研究[5-10],有学者研究了玉米籽粒的重金属含量水平及人体摄入的健康风险,结果发现重金属含量均值很少高于标准,但长期摄入会对儿童造成健康风险[5-7];另有学者研究不同作物的含量水平及对人体产生的健康风险,发现玉米籽粒中部分重金属含量均值超过标准且存在单一健康风险,成人和儿童通过食用玉米会对健康造成危害[8-10].
目前安徽省关于矿区周边农田作物重金属污染研究主要集中在铜陵、淮南、淮北等地[10-12]. 亳州市玉米、小麦、豆类等产量丰富,2018年,亳州市主要农产品单位面积产量在安徽省处于前三,玉米产量156.309万吨,占安徽省玉米总产量的26.24%[13]。
为探究煤矿开采等相关活动对矿区周边作物的影响,本文以涡北煤矿外围农田玉米为研究对象,对重金属(Ni、As、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd、Pb)含量进行测试,通过污染指数法评估了籽粒重金属污染程度,并评价了儿童和成人摄入煤矿周边玉米造成的健康风险,为当地农产品质量安全和居民健康提供依据.
-
涡北煤矿位于安徽省亳州市涡阳县境内,距涡阳县城仅4 km. 主要开采国家稀缺的焦煤,年产煤约180万吨,矿区内地势平坦,地面标高29.49—31.80 m,地势西北高东南低. 该区属暖温带半湿润季风气候,年平均降水量为811.8 mm,降雨多集中在七、八月份. 主要土壤类型为潮土、砂姜黑土等. 秋季煤矿周围农田以种植玉米为主.
-
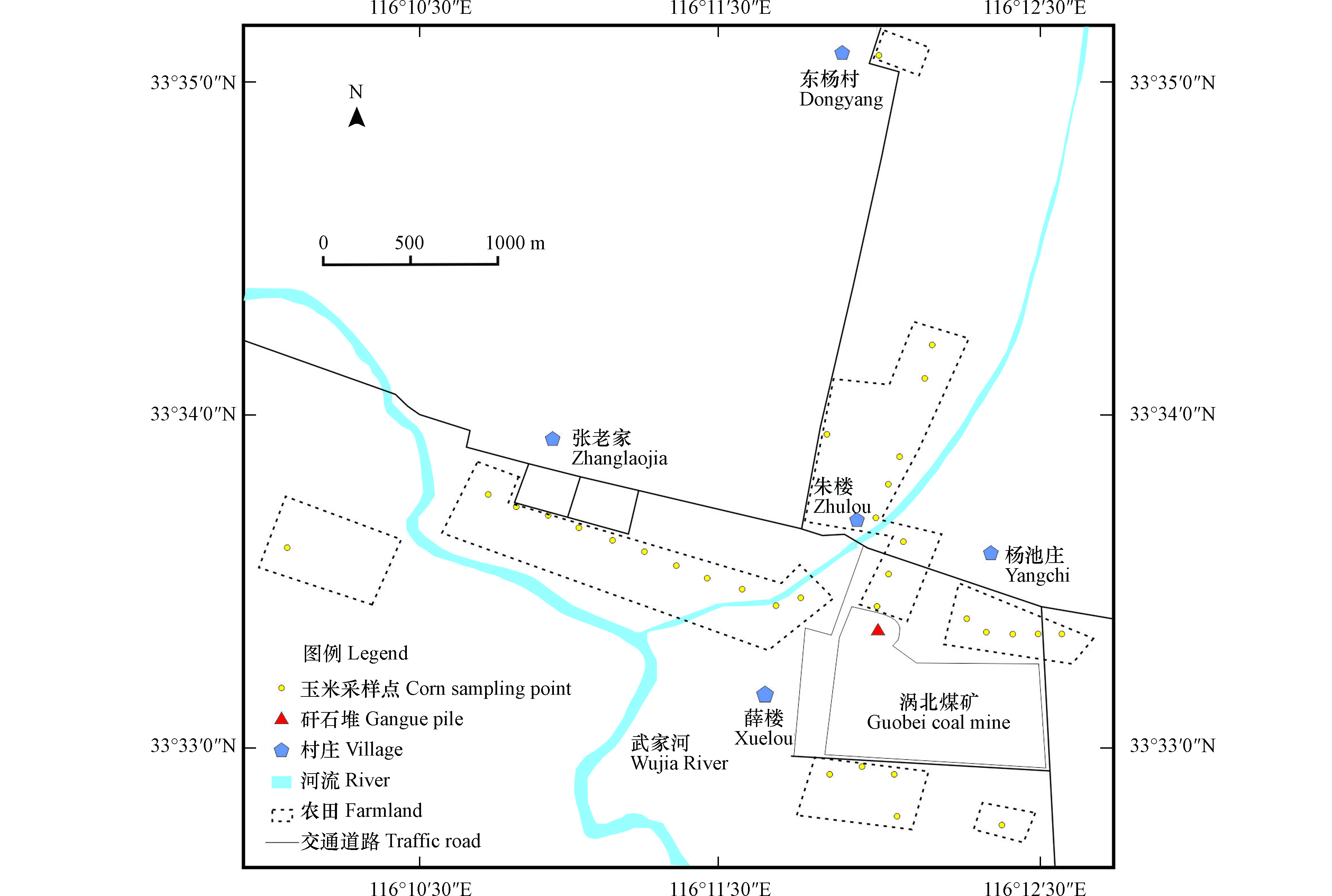
根据农作物收获季节,在研究区内采集玉米样品32个,同步采集土壤样品32个. 在每个调查区内,采取网格法布点,以200 m×200 m农田为1个调查网格,每个调查网格内原则上布设1个采样点,每个采样点采集1个农作物样品,同步采集1个表层(0—20 cm)土壤样品. 分别在研究区西北部、北部、南部和东部采集农作物及土壤样品各12、9、5、6个,研究区及采样采样位置如图1.
将采回的玉米用蒸馏水洗净表面的灰尘和土壤颗粒,放于烘箱中烘至恒重(60℃),将干燥好的玉米剥下籽粒,经研磨机(德国Retsch)研磨过筛后保存备用. 将带回的土壤样品除去植物根系、石砾等杂物后风干,采用四分法将土壤取出,用玛瑙研钵研磨过200目(74 μm)筛,装入样品袋中备用.
玉米籽粒和土壤重金属测试分析参照国家相关标准(GB5009.268—2016,HJ803—2016). 玉米和土壤样品分别采用HNO3微波消解和湿法消解,重金属(Ni、As、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd和Pb)含量测试采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS,NexION 2000B,美国铂金埃尔默). 分析测试过程中按国家相关标准进行质量控制,样品回收率在95%—105%之间,试剂均为优级纯. 样品测试由安徽省煤田地质测试中心完成. 数据分析统计采用Excel 2018 和 SPSS 25.0软件,在ArcGIS 10.7上运用克里金插值法绘制玉米籽粒中重金属含量的空间分布图.
-
玉米籽粒重金属污染程度采用单因子污染指数法[14]和内梅罗污染指数法[15](Nemero)开展评价.
式中,Pi为矿区外围农田玉米籽粒中重金属i的单因子污染指数;Ci为矿区外围农田玉米籽粒中重金属i的测试值(mg·kg−1);Si为玉米籽粒中重金属i的标准限值.
式中,P综合为煤矿外围农田玉米籽粒中重金属的综合污染指数;Pimax为煤矿外围农田玉米籽粒中重金属i的最大污染指数;Piave为煤矿外围农田玉米籽粒中重金属i的单因子污染指数的均值. 单因子污染指数法和综合污染指数法分级标准见表1.
-
为了评价当地居民摄食涡北煤矿外围农田玉米的健康风险,通过玉米摄入的重金属日平均摄入量采用美国EPAMMSOILS模型中水、食物摄入和大气吸入的暴露评价方程. 具体评价参数见表2.
式中,ADD为重金属经玉米的日平均摄入量(mg·kg−1·d−1);Ci为玉米中重金属的含量均值(mg·kg−1);IR为研究区人体每日对玉米的食用量(kg·d−1);ED为暴露时间;BA为生物可利用分数;EF为暴露频率;BW为研究区的平均体重(kg);AT为生命期望值.
人体摄入玉米的单一重金属健康风险指数(HQ)计算公式如下:
式中,HQ指健康风险指数,RfD为口服参考剂量(mg·kg−1·d−1). HQ≤1表明不会对人体健康造成风险;HQ>1表明容易对人体健康造成风险,且HQ的值越大表明越容易对人体健康造成风险.
人体摄入玉米的重金属高危指数(HI)计算公式如下:
如果HI≤1.0,表明没有明显的健康影响;HI>1.0,表明对人体健康造成影响的可能性大;当HI>10时,表明存在慢性毒性.
-
研究区玉米籽粒中重金属Ni、As、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd和Pb含量见表3,其含量均值分别为0.73、0.11、0.81、23.76、2.09、0.01、0.23 mg·kg−1,其中Zn的含量最高,Cu次之,Ni、As、Cr和Pb的含量最低. 玉米籽粒中重金属Ni和Pb的平均含量均超过国家相关食品卫生标准,超标率分别为75%和34.4%,玉米籽粒中Cr、As和Zn含量在部分点位出现超标情况,超标率分别为21.9%、6.3%和3.1%,其中Ni污染最严重,超标1.83倍. 从变异系数来看,玉米籽粒中Ni、As、Cr、Cu、Cd和Pb的变异系数均大于50%,属于强变异;Zn的变异系数为38.3%,属于中等变异,表明玉米籽粒中这7种重金属受人类活动影响较大.玉米籽粒中Ni、Cr、Pb存在超标现象,与滕州矿区[25]、铜陵矿区[10]、西南山地某铅锌矿区[9]以及平度市金矿区[26]玉米相比,Ni含量偏高,可能与涡北煤矿外围农田土壤中Ni含量偏高有关[7];Pb含量高于滕州矿区和铜陵矿区,低于西南山地铅锌矿区和平度市金矿区;Cr元素含量明显偏低,可能是因为玉米籽粒对Cr的富集能力较差[12]. 与其它研究区对比,玉米籽粒中各重金属元素处于不同的污染程度,这可能与不同的工矿业活动、玉米种植方式以及参照标准有关[27].
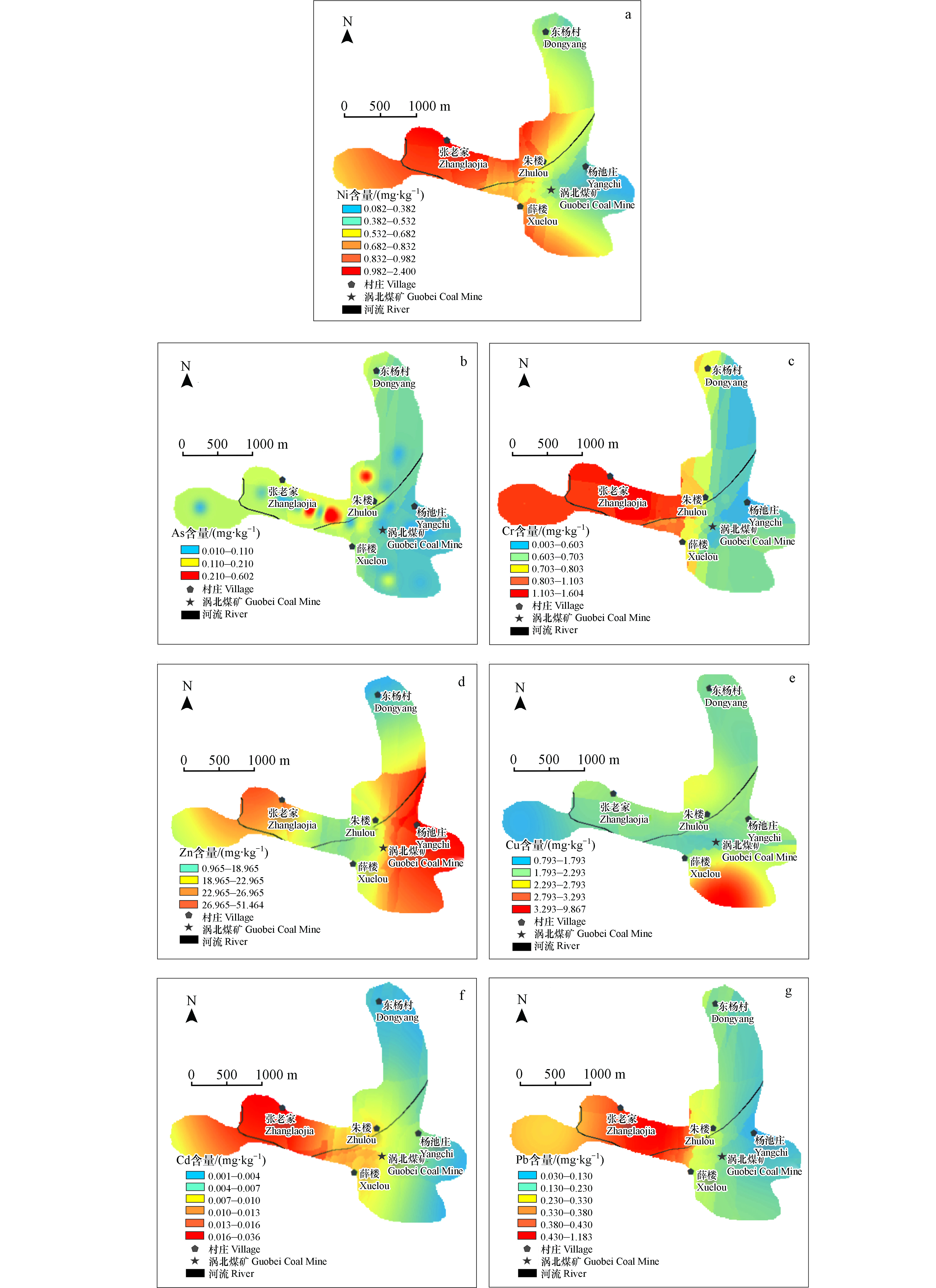
根据玉米籽粒重金属的含量空间分布图(图2),并结合表3,重金属Ni、Pb和Cr出现了局部超标的现象,研究区北部和西北部重金属含量较高,东部和南部重金属含量较低,Cr超标点位出现在北部、西北部以及南部,最大值在西北部;Pb超标点位分布在北部以及西北部,最大值在西北部;Ni超标点位出现在西北部以及南部,最大值在西北部. 煤矿西北方向交通路线较为复杂且有煤矸石堆积点,Ni、Cr、Cd和Pb含量的空间分布特征具有相似性,整体呈现西北高东南低的趋势,且在玉米籽粒中累积量最大的区域均在研究区西北方向,这可能与矿西北方向煤矸石的堆积且紧邻交通道路有关.
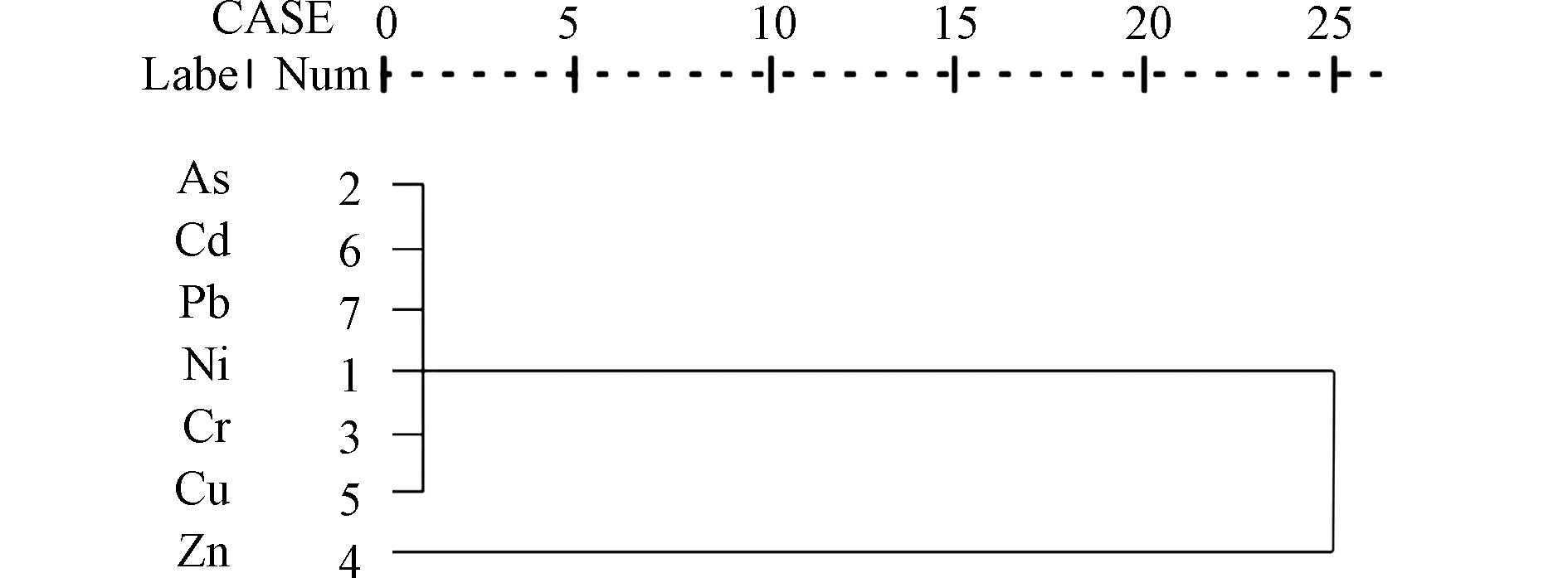
为进一步分析玉米籽粒各重金属间的相关性,对研究区玉米籽粒重金属进行聚类分析. 聚类分析将7种重金属分为2类(见图3),其中Ni、As、Cr、Cu、Cd和Pb为 Ⅰ 类,Zn为 Ⅱ 类. 因此,Ni、As、Cr、Cu、Cd和Pb之间相关性较强,具有一定的同源性,结合玉米籽粒中重金属含量的空间分布图可知,Ni、As、Cr、Cu、Cd和Pb主要受煤矿堆积及交通道路的影响[30-31];Zn为一类,可能来源于有机肥的施用[32].
-
研究区土壤中Ni、As、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd和Pb的含量见表4,其均值分别为46.62、15.03、80.53、95.20、35.19、0.30、29.02 mg·kg−1,其中Ni、Cr、Zn、Cu和Pb的含量均值均超出安徽省土壤元素背景值,其中Cu污染最严重,超标1.73倍. 研究区土壤Ni、Cr、Zn、Cu和Pb超标较为严重.
利用Pearson相关系数分析土壤对玉米籽粒的影响,玉米籽粒与土壤重金属含量间的相关系数如表4所示.玉米籽粒与土壤重金属含量间没有明显的相关性,这可能是由于作物中重金属含量与土壤中重金属总量并无明显线性关系,但是与土壤中重金属的化学形态、有效态含量以及生物有效性直接相关[33]. 因此,今后开展农作物的健康风险评估时,除了要考虑土壤中重金属的总量,还要将土壤重金属有效态含量纳入评价指标内.
-
研究区玉米籽粒中重金属污染评价结果见表5. 玉米籽粒中重金属含量的单因子污染指数呈Ni>Pb>Cr>Zn>As>Cu>Cd的污染特征. Ni和Pb的单因子污染指数均大于1,As、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd的单因子污染指数均小于1,表明研究区玉米受到了Pb和Ni的污染,尚未明显受到As、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd的污染. 从综合污染指数来看,Cd的综合污染指数小于0.7,处于安全水平;Cu、As、Zn的综合污染指数处于0.7—1之间,处于警戒线水平;玉米籽粒中Ni、Pb的综合污染指数分别为4.437和4.258,均属于重度污染. 相比于重金属Ni和Pb,玉米籽粒中As、Zn和Cu的含量没有超过标准限量,这可能是由于As、Zn和Cu在玉米植株体内的移动性较大,玉米籽粒中浓度比玉米根系中浓度小[34]. 从单因子指数来看,在32个采样点中,玉米籽粒中Ni超标(Pi>1)点位占24个,单因子污染指数较大的点位分布在研究区西北部、北部以及南部,西北部玉米籽粒的单因子污染指数更是达到了最大(6.00);玉米籽粒中Pb超标点位占11个,单因子污染指数较大的点位分布在西北部以及北部,西北部玉米籽粒的单因子污染指数达到了最大值(5.92). 就绝大多数点位来看,相对于其它元素,玉米籽粒中Ni和Pb的污染情况可能更为严重. 从综合污染指数来看,Ni和Pb达到了重度污染水平,这与单因子污染指数评价结果一致.
-
农作物中的重金属元素绝大部分通过根系吸收进入作物体内,并在不同器官及组织内富集,如果玉米籽粒中重金属含量过高,人体摄入玉米就会产生健康风险[18].由研究区玉米籽粒的重金属摄入量及健康风险结果可知(表6),成人对玉米籽粒中Ni、As、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd、Pb的日平均摄入量(ADD)均小于参考暴露剂量(RfD),说明这7种重金属几乎不会对成人造成影响. 儿童对玉米籽粒中As的平均日摄入量大于参考暴露剂量,对Ni、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd、Pb的日平均摄入量均小于参考暴露剂量,说明As会对儿童造成健康风险. 对比7种重金属对成人和儿童造成的健康风险,单一健康风险指数(HQ)排序均为As>Zn>Pb>Cu>Ni>Cd>Cr,As和Zn对成人和儿童造成的健康风险较大,其中As对人体造成的健康风险最显著,占总HQ值的贡献比例为62.6%,可能是因为As允许参考摄入剂量为0.0003 mg·kg−1,处于较低水平,因此产生的健康风险较大. 此外,儿童的单一健康风险指数均高于成人,表明重金属经玉米摄入对儿童造成的健康风险明显高于成人,虽然各个研究区的健康风险指数可能有所差异,但是儿童的健康风险指数往往大于成人[7,35]. 这是因为身体各组织器官功能尚未发育健全,尤其是肝肾等代谢器官的解毒、排毒能力较差,受各种有毒有害物质的危害更为强烈[36].
就高危指数而言,成人的高危指数(HI)小于1,表明食用玉米对成人的健康没有明显影响;儿童的高危指数大于1,且儿童的高危指数是成人2.1倍,表明食用玉米对儿童产生影响的可能性大.
-
(1) 研究区玉米籽粒中Ni含量超过了我国食品卫生标准限量,其它6种重金属均未超过.玉米籽粒中Pb、Ni的单因子污染指数均大于1,其它5种重金属均小于1;综合污染指数表明,玉米籽粒中Cd处于安全水平,As、Zn、Cu处于警戒线水平,Ni和Pb达到重度污染水平. 根据聚类分析结果,推断玉米籽粒中Ni、As、Cr、Cu、Cd和Pb可能受煤矿堆积以及选煤活动的影响,Zn可能受有机肥施用的影响.
(2) 玉米籽粒中Ni、Cr和Pb含量的空间分布具有一定的相似性,整体呈现东南向西北递增的趋势,累积量最大的区域均在涡北煤矿西北方向,可能与矿西北方向煤矸石的堆积且紧邻交通道路有关. 结合涡北煤矿外围农田土壤重金属的平均含量,玉米籽粒与土壤重金属含量间相关性不明显.
(3) 涡北煤矿外围农田玉米籽粒重金属(Ni、As、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd和Pb)对成人造成的健康风险较小,As对儿童的健康风险指数大于1,其它6种重金属对儿童的健康风险指数小于1,重金属通过玉米籽粒摄入对儿童存在健康风险,所以居民通过摄食玉米产生的健康风险应该引起关注.
涡北煤矿外围农田玉米重金属污染特征及健康风险评价
Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals from maize in the surrounding farmland of Guobei Coal Mine
-
摘要: 为全面了解涡北煤矿外围农田玉米重金属污染现状,本文测定了玉米籽粒及对应土壤样品的重金属含量,运用单因子及综合污染指数分析重金属在玉米籽粒中的污染状况,并采用美国EPAMMSOILS风险评价模型评价了摄食玉米对人体造成的重金属健康风险. 结果表明,研究区玉米籽粒中Ni、As、Cr、Zn、Cu、Cd和Pb的平均含量分别为0.73、0.11、0.81、23.76、2.09、0.01、0.23 mg·kg−1,除Ni和Pb外,其它重金属含量均值均未超过我国食品卫生标准. 综合污染指数显示Ni和Pb为4.26和4.44,属于重度污染,Cr则介于1—2之间,属于轻度污染,Cd、Cu、As、Zn都小于1,表明无污染. Ni、Cr、Cd和Pb的含量空间分布均呈现东南向西北递增的趋势. As对儿童的健康风险指数大于1,其它6种重金属对儿童的健康风险指数小于1,各重金属对成人的健康风险较小,另外,重金属复合污染对儿童存在健康风险,所以居民通过摄食玉米产生的健康风险应该引起关注.Abstract: In order to fully understand the heavy metal pollution of maize grains in the surrounding farmland of Guobei Coal Mine, the contents of heavy metals in maize and corresponding soil samples were measured by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry; the pollution of heavy metals in maize were analyzed using a single factor pollution index and a comprehensive pollution index; the health risk of heavy metals for maize ingestion in human were estimated with EPAMMSOILS risk assessment model. Results show that the average contents of Ni, As, Cr, Zn, Cu, Cd and Pb were 0.73, 0.11, 0.81, 23.76, 2.09, 0.01, 0.23 mg·kg−1 in maize grains, respectively. Except Ni and Pb, the average concentrations of other heavy metals were lower than national food hygiene standards. The Nemero index of Ni and Pb were 4.26 and 4.44 belonging to heavy pollution level and that of Cr were between 1 and 2 belonging to light pollution level, as well as the Nemero index of Cd, Cu, As and Pb contents all suggests a decreasing trend from northwest to southeast. The health risk index of As for children is greater than 1 while that of other six heavy metals are lower than 1, and the low health risk exists in adults. In addition, combined heavy metal is harmful to children. Therefore, the health risks of residents through ingestion of maize should be taken seriously.
-
Key words:
- heavy metal /
- health risk /
- maize grains /
- Guobei Coal Mine
-
磷(P)是自然生态系统中生物生长的关键营养素,其过量存在会使水体出现富营养化,从而引发藻类过度生长、水质恶化、鱼类和植物死亡等严重的环境问题[1-3]。近年来,国家实施了严格的磷排放限值管理,并结合“五水共治”、“水十条”等相关政策法规的制定,目的是降低进入接收水体中的磷含量以减少其环境危害性[4-7]。
工业废水的排放和农业径流是水生生态系统中磷含量增加的主要原因,因而针对它们的脱磷技术和工艺研究对磷污染控制具有关键作用。目前已被广泛采纳的磷去除方法包括生物法、化学法和物理法等。其中生物除磷方法[8-10],即常规的活性污泥法,成本低廉、磷去除效果好。但由于微生物的磷酸盐代谢能力会随着水中磷浓度降低而显著下降,因而对低磷水体的处理能力变弱,无法实现达标排放;化学法脱磷时[11-12],伴随着水中磷酸根的有效降解,常会有大量污泥产生,且目标排放浓度越低需要加入的药剂量就越大,二次污染严重;而以反渗透和电渗析为代表的物理方法[13-14],在实际应用中则存在着对进水水质要求高、处理费用昂贵和磷去除效率低等缺点。吸附法[15-17]与上述各类除磷方法相比,具有操作简单、去除磷效率高、吸附速度快和环境污染小等特征,因而在低磷废水处理中有重要作用。
对比常用的磷吸附剂如天然矿物、工业废渣、金属氧化物、生物质等,镧基吸附剂是化学稳定性较高的稀土金属吸附剂[18]。镧基吸附剂不但除磷效率高、磷重新释放程度小,而且还有磷亲和力强和饱和吸附量大的独特性质,因此,近年来在针对水和废水的磷去除材料研发中备受关注。典型的镧吸附剂包括镧化合物以及各种镧负载复合物等,如氢氧化镧、氧化镧纳米棒、氢氧化镧改性水凝胶、镧改性介孔二氧化硅等[19-22],其在应用中保持了良好的磷脱除能力和稳定性。然而研究人员在研究中也发现,上述这些镧基吸附剂在碱性条件下使用时,磷去除率与酸性和近中性下的结果相比能力变差,表现出在碱性条件下脱磷效率偏低的缺陷,因而限制了其在中性和碱性水体处理领域中的广泛应用[23-24]。
基于上述研究结果,本研究以碳酸镧作为吸附剂主体,采用在合成反应中加入晶型导向剂和控制反应温度的方法,获得了具有脱磷溶液pH适用范围宽、对水中磷组分平衡吸附量大、能被再生和重复进行脱磷的无定型纳米碳酸镧吸附剂,并初步探讨了该吸附剂在脱磷过程中的热力学和动力学特征。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
六水氯化镧(LaCl3·6H2O)购自阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)、七水合硫酸镁(MgSO4·7H2O)、乙醇(EtOH)、钼酸铵((NH4)2MoO4)、酒石酸锑钾、抗坏血酸、磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)、盐酸(HCl)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)等均为分析纯,购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 分析方法
X射线衍射仪(XRD,X`Pert PRO,荷兰帕纳科公司)分析得到样品的晶体衍射谱图;透射电镜(TEM,JEM-2100,日本电子株式会社)和冷场发射扫描电镜(SEM, SU8010,日本日立公司)表征分析样品的形貌;动态光散射仪(DLS,Zen-3600,英国Malvem公司)测定纳米复合物的Zeta电位;电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS,iCAP6300,美国赛默飞世尔公司)分析金属离子含量。
1.3 碳酸镧的制备
将160 mL的0.05 mol·L−1氯化镧溶液在25 ℃或85 ℃下磁力搅拌5 min,加入镁盐使c(Mg2+)∶c(La3+)=1∶1,继续搅拌10 min,按照1滴·s−1的速度将40 mL的 0.8 mol·L−1的碳酸氢钠溶液滴加到上述溶液中,继续搅拌30 min后,陈化30 min。待冷却后,抽滤并用蒸馏水清洗3次,45 ℃干燥12 h。将25 ℃和85 ℃下制备的碳酸镧分别标记为LC(25)和LC(85)。
在相同合成条件下,没有镁盐存在时制备的碳酸镧分别标记为LC0(25)和LC0(85)。
1.4 水中磷的吸附实验
称取一定质量的碳酸镧吸附剂置于250 mL锥形瓶中,加入100 mL不同质量浓度的磷溶液,在25 ℃恒温振荡器中振荡24 h后,取上清液经0.45 μm滤膜过滤,用钼酸铵比色法直接测定滤液中磷酸盐的质量浓度。吸附剂的平衡吸附量(qe)和磷去除率(η)按照式(1)和式(2)进行计算。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) 式中:C0为磷溶液初始质量浓度,mg·L−1(以P计);qe为平衡时的磷吸附量,mg·g−1(以P计);Ce为平衡时磷溶液质量浓度,mg·L−1(以P计);V为溶液体积,L;m为吸附剂质量,g。
1) pH的影响。将0.02 g的吸附剂加入到100 mL、磷溶液质量浓度为 20 mg·L−1溶液中,用0.5、1 mol·L−1氢氧化钠和盐酸调节溶液pH分别为3.0、4.0、5.0、7.0、9.0、11.0。在25 ℃下,250 r·min−1的摇床中反应24 h,用0.45 μm滤膜过滤,测定溶液吸光度,计算去除率。
2)反应动力学。将0.04 g的LC(85)和LC(25)吸附剂分别加入到体积200 mL、质量浓度为20 mg·L−1的磷溶液中,在25 ℃、250 r·min−1的摇床中反应,间隔指定的时间后取样,用0.45 μm滤膜过滤。分别用准一级动力学方程(式(3))、准二级动力学方程(式(4))拟合实验结果。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (3) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (4) 式中:qt 为t时间的吸附量,mg·g−1;qe为平衡时的磷吸附量,mg·g−1;t为吸附时间,h;k1为拟一级动力学吸附速率常数,h−1;k2为拟二级动力学吸附速率常数,g·(mg·h)−1。
3)等温吸附。将0.15 g吸附剂,加入到100 mL、质量浓度分别为 15、18、20、25和30 mg·L−1的磷溶液中,在25 ℃下,250 r·min−1的摇床中反应24 h,用0.45 μm滤膜过滤。分别用Langmuir (式(5))和Freundlich(式(6))模型拟合实验数据。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (5) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (6) 式中:qe为平衡时吸附量,mg·g−1;qm为理论最大吸附量,mg·g−1;Ce是反应平衡时的磷溶液质量浓度,mg·L−1;KL为Langmuir常数,L·mg−1;KF 为Freundlich常数,mg·g−1;n是Freundlich模型中评价吸附强度的常数。
4)吸附剂加入量。在100 mL质量浓度为2 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1磷溶液中分别加入一定量的吸附剂,使吸附剂的质量浓度分别为0.05、0.10、0.15、0.20、0.25、0.30和0.40 g·L−1,在25 ℃,250 r·min−1的摇床中反应24 h。
5)再生和循环吸附。称取0.1 g吸附饱和的LC(85),加入到浓度3 mol·L−1的50 mL氢氧化钠溶液中,在100 ℃油浴中回流反应5 h。反应结束后,抽滤、用蒸馏水清洗至中性,45 ℃干燥12 h。取再生后的LC(85)吸附剂0.02 g,置于体积100 mL、质量浓度为20 mg·L−1的磷溶液中,25 ℃下反应24 h。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 碳酸镧的结构和形貌表征
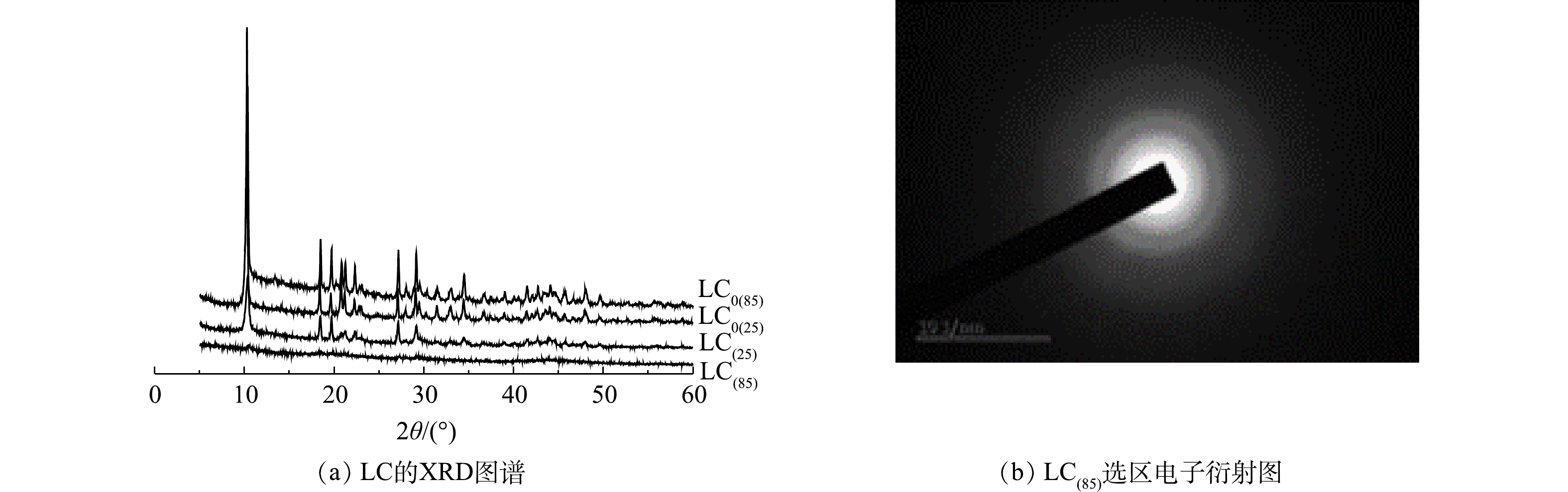
1) XRD和选区电子衍射分析。在晶型诱导剂Mg2+存在条件下,25 ℃和85 ℃下制备的碳酸镧LC(25)和LC(85)的XRD图谱如图1(a)所示。已知10.27°处的尖锐强衍射峰是La2(CO3)3·8H2O (PDF #25-1400) (002)晶面的特征衍射峰,18.51°、20.79°、21.24°、27.08°和29.06°处的衍射峰则分别对应La2(CO3)3·8H2O的(020)、(004)、(022)、(220)和(222) 晶面。比较晶型诱导剂Mg2+存在条件下制备的LC(85)和LC(25)图谱,发现合成温度的改变会影响产物的特征结晶峰大小,当制备温度由25 ℃升高到85 ℃时,碳酸镧(002)特征结晶峰明显变小到近乎消失,表明二者结晶状态发生了变化,即由晶体态的LC(25)转变到无定型的LC(85)。对比图1中同时给出的不使用晶型诱导剂Mg2+时,碳酸镧产物LC0(25)和LC0(85)的XRD图谱,发现他们也存在着(002)特征结晶衍射峰,由此可知,仅LC(85)具有独特的非晶态特征。另一方面,从LC(85)的选区电子衍射图(图1(b))中可知,其衍射图是多个弥散的衍射环,因而得出的结论也是LC(85)具有非结晶状态的特征。已知吸附剂的非晶态相比晶态相更有利于脱磷[25],因此,LC(85)的制备为获得高效脱磷剂提供了可能。
2) SEM和TEM分析。加入晶型诱导剂Mg2+前后,不同温度下制备的碳酸镧SEM和TEM表征结果如图2所示。可以看出,随着合成温度的升高,碳酸镧颗粒变小且形貌发生显著变化。如碳酸镧在25 ℃合成时,无晶型诱导剂Mg2+存在下制备的LC0(25) (图2(a))为规则的六边形片状结构,大小介于几百纳米至几个微米之间;升高温度到85 ℃时,LC0(85) (图2(b))转变成不规整的片状结构,粒径变小。而在晶型诱导剂Mg2+存在时,25 ℃合成的LC (25) (图2(d))尽管保持了不规则片状多边形结构,但粒径与LC0(25)相比显著变小,多介于300到500 nm之间;而当制备温度升高至85 ℃时,LC(85) (图2(e))突变为粒径小于50 nm的均匀球形纳米颗粒,微观形貌与LC0(85)、LC0(25)和LC(25)的片状结构均不相同。
另一方面,从LC(85)和LC(25)的TEM分析结果可以看出,LC(85) (图2(f))为球型,粒径约为50 nm;而LC(25) (图2(c))的TEM图谱则为多边形的片状形貌,径向尺寸大于100 nm。显然,LC(85)和LC(25)的TEM表征结果与上述的SEM结论相吻合,即LC(85)与其他LC样品相比具有更小的粒径和特征的球形微观结构。
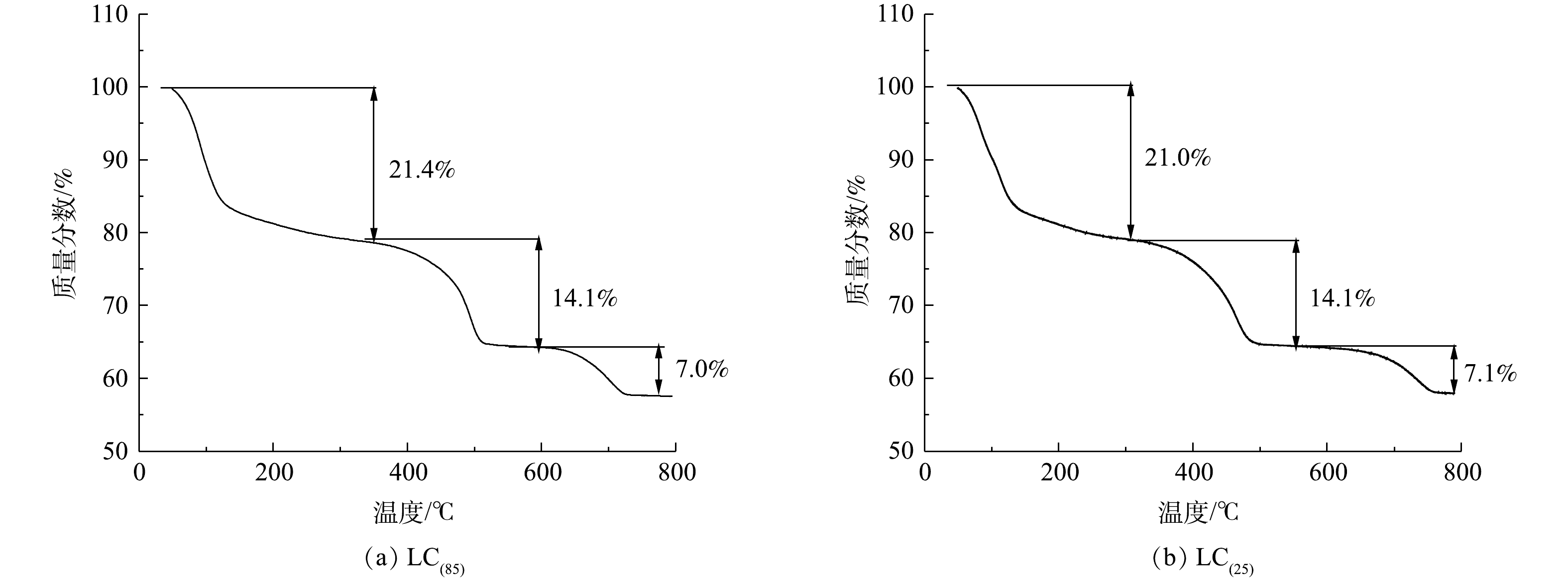
3) TGA和ICP分析。图3是不同温度下制备的LC(85) (图3(a))和LC(25) (图3(b))的TG图谱。可以看出,二者的热重曲线均可分为3个阶段:第1阶段在350 ℃之前(质量损失21.0%~21.4%);第2阶段在350~600 ℃(质量损失14.1%);第3阶段在600~800 ℃(质量损失7.0%~7.1%),总质量损失为42.1%~42.5%。由于LC(85)和LC(25)在每个阶段失重百分比差别较小,因而可以认为,制备温度的改变对碳酸镧所含结晶水的数量影响小,LC(85)和LC(25)均是含有8个结晶水的碳酸镧。
取LC(85)和LC(25)样品用16 mol·L−1的浓硝酸溶解,然后定容稀释至指定浓度,经滤膜过滤后,用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪进行检测。得到的ICP分析结果是,纳米吸附剂LC(85)和LC(25)中镧含量分别为45.82%和45.28%,镁含量分别为0.09%和0.02%。已知La2(CO3)3·8H2O的理论镧含量是46.16%,2个样品的ICP的表征结果与其相差很小,同时考虑到Mg2+在LC(85)和LC(25)中含量很低,因此,有理由认为Mg2+在碳酸镧的合成过程中,没有随着反应的进行以碳酸镁或氢氧化镁的形式转变为产物而共存于LC(85)中,而仅作为晶型控制剂存在于反应液中,且本身质量在反应中几乎无损耗。本研究中Mg2+在晶体制备中的这种作用,与马俊等[26]得出的Mg2+能作为晶型控制剂对碳酸钙进行晶型调控的结论相符。
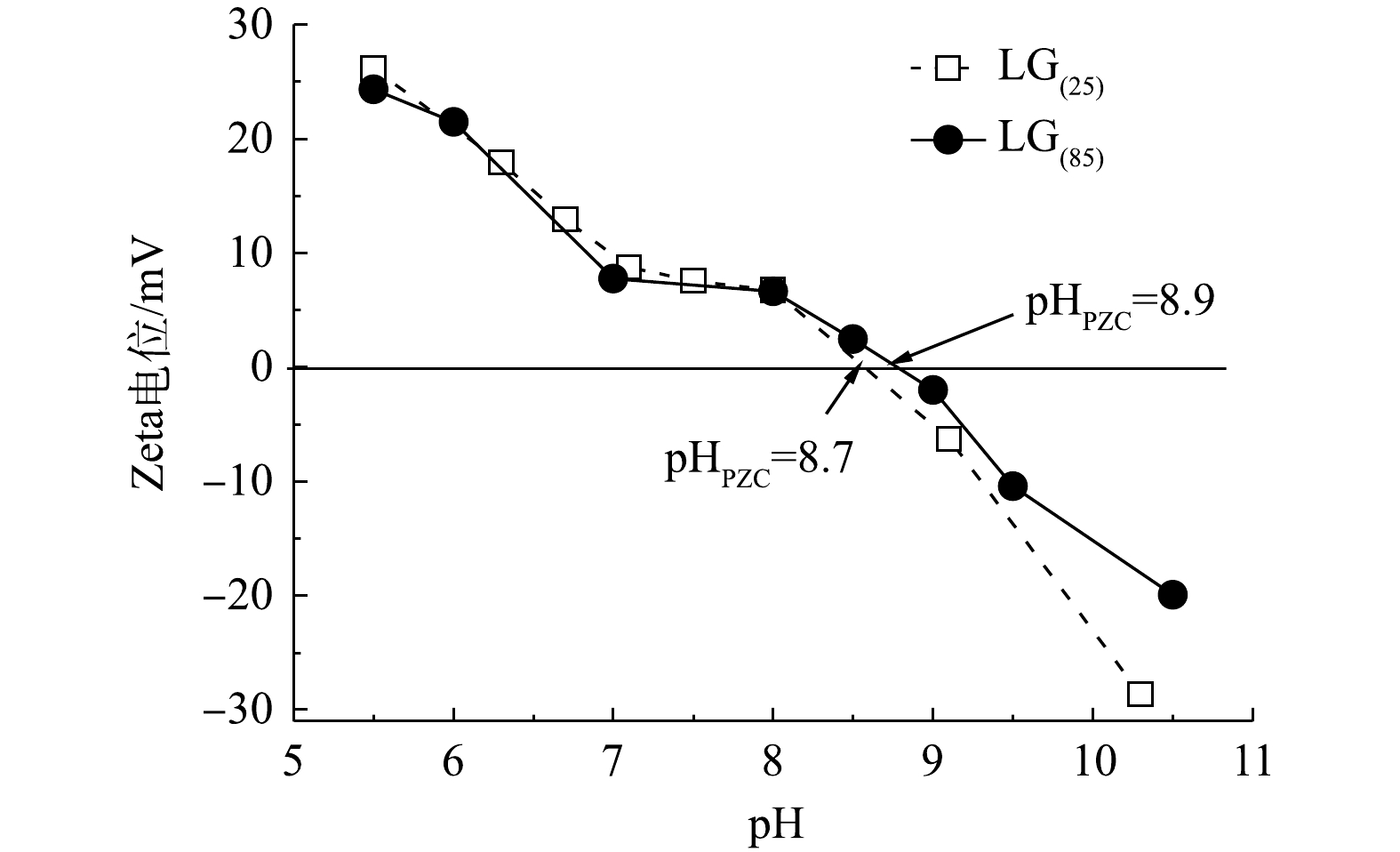
4) Zeta(ζ)电位的变化。由LC(85)和LC(25)的Zeta电位图(图4)可知,LC(85)和LC(25)的等电点pHpzc分别为8.9和8.7,与不加入诱导剂Mg2+制备的LC0(25)的Zeta电位相比(pHpzc=7.4),不但在任一特定pH条件下LC(85)的Zeta电位高于LC(25),且其对应的pHpzc也均大于LC0(25)。由于当溶液的pH低于pHpzc,碳酸镧纳米吸附剂会发生质子化和正电荷化,因而能强化同带负电荷磷酸根离子间的静电相互作用,导致碳酸镧吸附磷酸根的能力增强;而当溶液的pH高于pHpzc时,碳酸镧表面脱质子化而显示出负电性,造成纳米吸附剂与磷酸根之间的静电斥力,不利于磷酸根在碳酸镧表面的吸附。晶型诱导剂Mg2+加入后,LC(85)和LC(25)的pHpzc均变大,因而为增强碳酸镧吸附磷酸根的效果提供了较好的界面性质。
2.2 吸附性能分析
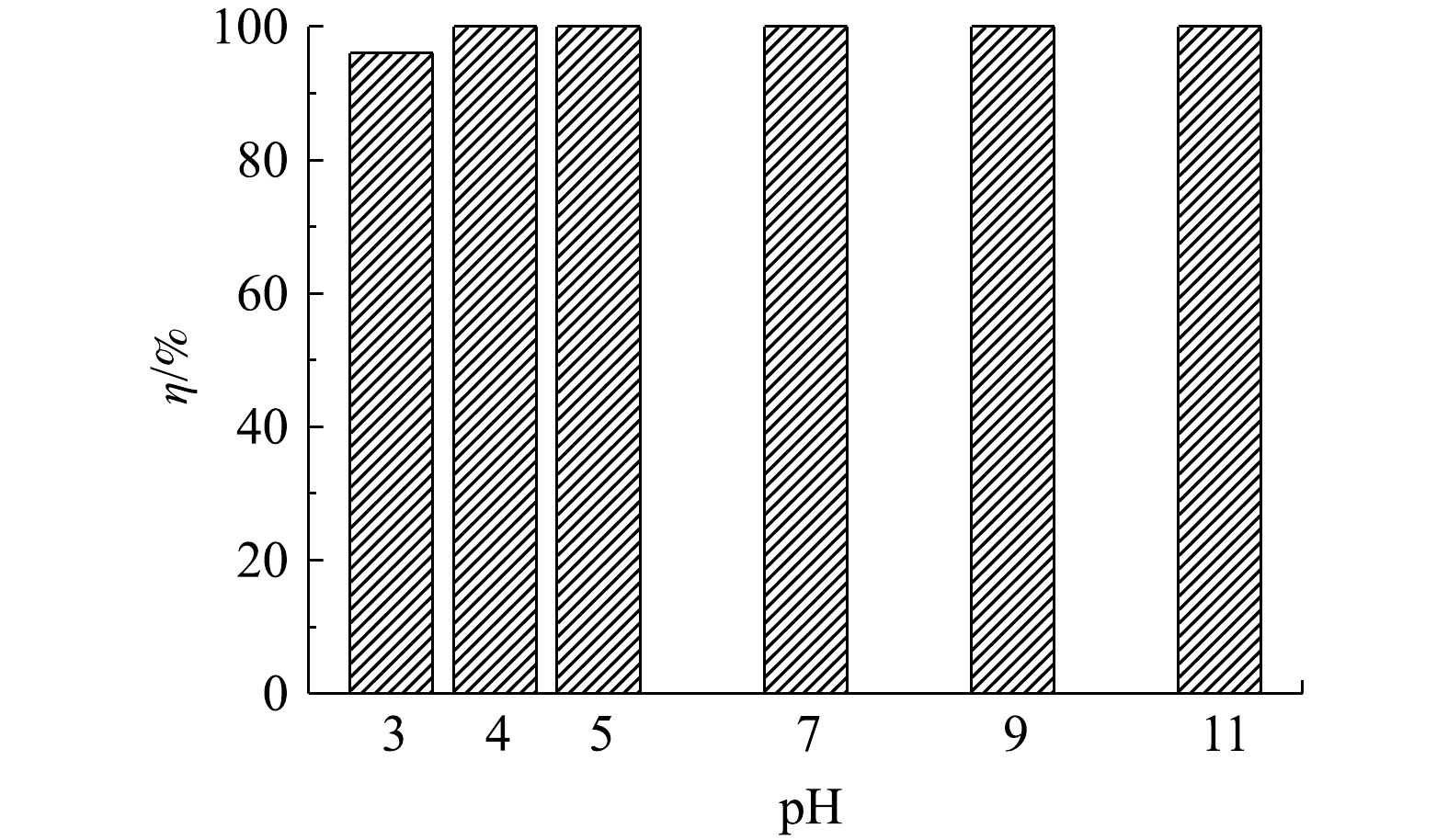
1) pH对吸附效果的影响。溶液pH会影响吸附剂的表面电位以及磷酸根在溶液中的价态和电离度,因而是评价脱磷剂性能的重要因素之一。为了考察pH对LC(85)吸附磷能力的影响,将溶液的pH调节在3.0~11.0,研究其对初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1磷溶液的脱磷效果。由图5可以看出,LC(85)不但脱磷能力强而且在宽pH条件内保持了高脱磷稳定性,即随着溶液pH由3.0增大到11.0,磷去除率一直保持在95%以上。已知在酸性条件下,由于溶液中磷酸根主要以
H2PO−4 HPO2−4 H2PO−4 HPO2−4 2)吸附动力学。在脱磷过程中LC(85)的吸附量随时间变化曲线如图6(a)所示。可以看出,该吸附剂对磷酸根的去除过程可分为2个阶段:第1阶段为快速吸附过程,LC(85)的磷吸附量在1 h内迅速达到97.6 mg·g−1;第2阶段为缓慢增加直至达到平衡值,即继续延长吸附时间到12 h,LC(85)对磷的吸附量仅增大为100.5 mg·g−1。在相同条件下,对比LC(25)吸附磷酸根的动力学曲线,发现LC(85)和LC(25)的磷平衡吸附量尽管近似相等,但由于LC(85)的快速吸附过程仅需1 h,而LC(25)的快速吸附过程则延长到4 h,因此,LC(85)在第1阶段的吸附过程中具备了更快的脱磷能力。
对LC(85)和LC(25)吸附数据进行拟一级和拟二级动力学模型的拟合(图6(b)和图6(c))。由表1所示的拟合结果可知,LC(85)和LC(25)吸附曲线经动力学拟合后得到的磷平衡吸附量均接近实测值。但由于LC(85)和LC(25)的拟二级动力学(R2分别为0.999 9 和0.999 9)比拟一级动力学(R2分别为0.364 1 和 0.985 2)更好地模拟了磷酸根在LC上的吸附过程,所以溶液中磷的去除过程主要应是通过碳酸镧进行化学吸附或化学键合来实现的。此外,对比表1中给出的二级动力学常数k2,发现当制备纳米碳酸镧的反应温度从25 ℃升高到85 ℃时,对应的k2也从LC(25)的0.078 8增大到了LC(85)的0.345 6,因而证明了LC(85)相比于LC(25)具有更快脱磷反应速度。显然,LC(85)所特有的球状微观结构和较小的颗粒尺度,使其在脱磷过程中能表现出较佳的动力学特征。
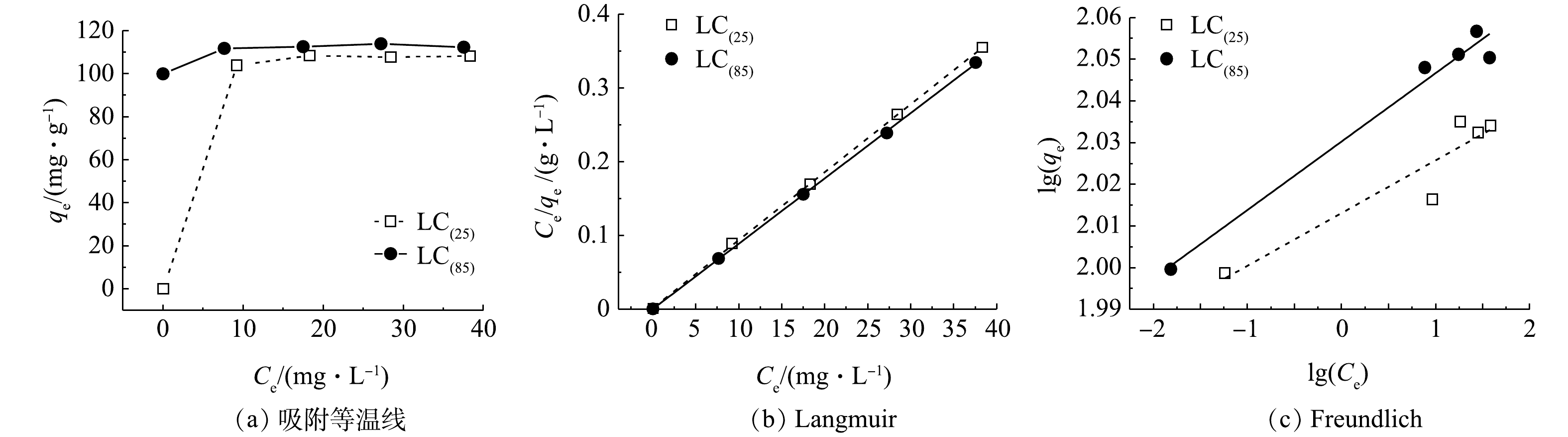
表 1 拟一级和拟二级动力学参数Table 1. Adsorption kinetic parameters of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order equations吸附剂 qe, exp/(mg·g−1) 准一级动力学方程 准二级动力学方程 k1/h−1 qe/(mg·g−1) R2 k2/(g·(mg·h)−1) qe/(mg·g−1) R2 LC(25) 100.2 0.917 2 43.64 0.985 2 0.078 8 100.7 0.999 9 LC(85) 100.5 0.470 8 6.60 0.364 1 0.345 6 100.1 0.999 9 3)吸附等温线。吸附等温线体现了材料吸附能力的强弱,是反应体系中平衡浓度与表面吸附量之间的关系。Langmuir吸附等温式基于吸附剂表面是均质的以及吸附质分子间无相互作用两个基本假设,其主要用于单分子层吸附的拟合;Freundlich吸附等温式则适用于非均质或多层吸附的拟合。将LC(85)和LC(25)在室温下的吸附等温线数据(图7(a))分别用Langmuir和 Freundlich 模型进行拟合(图7(b)和图7(c)),拟合结果见表2。由于LC(85)和LC(25) 的Langmuir吸附等温式R2分别为0.999 8和0.999 8,均高于Freundlich吸附等温式R2的0.967 9和0.840 4,表明其吸附过程更符合Langmuir模型,因而可以认为溶液中的磷酸根是以单分子层方式分别吸附在LC(85)和LC(25)上。再根据Langmuir模型计算出LC(85)和LC(25)最大饱和吸附量,可知分别为112.8 mg·g−1和108.5 mg·g−1。
表 2 LC(25)和LC(85)吸附磷酸根的等温方程参数Table 2. Isotherm parameters of phosphate adsorption by LC(25) and LC(85)吸附剂 Langmuir模型 Freundlich模型 qm/(mg·g−1) KL/(L·mg−1) R2 1/n KF/(mg·g−1) R2 LC(25) 108.5 6.73 0.999 8 79.11 103.07 0.840 4 LC(85) 112.8 195.53 0.999 8 60.94 107.22 0.967 9 4)吸附剂加入量的影响。图8是在磷溶液质量浓度分别为2 mg·L−1或20 mg·L−1时,水样的磷去除率随LC(85)投加量改变的情况。可以看出,随着LC(85)投加量的增加,水样中的磷去除率上升。如当LC(85)的投加量由0.05 g·L−1增加到0.2 g·L−1时,2 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1水样的磷去除率分别由71.9%和27.4%增大到接近100%。再继续增加LC(85)到0.4 g·L−1时,两模拟水样的磷去除率接近饱和,所以选择0.2 g·L−1的LC(85)投加量作为磷溶液质量浓度为2~20 mg·L−1水样的最佳加入量。
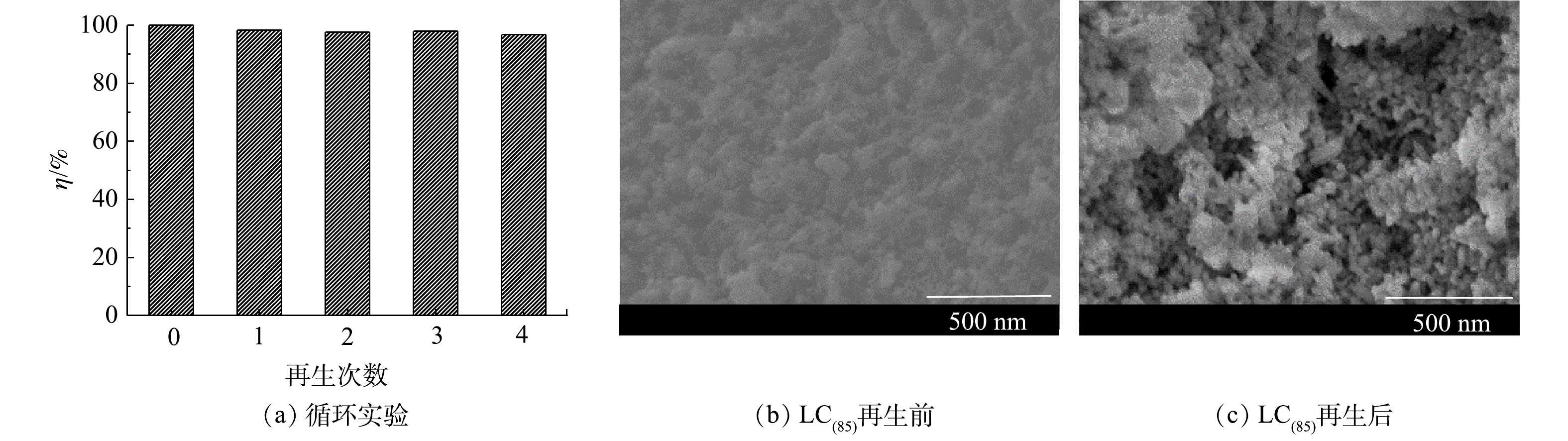
5)循环吸附性能。将吸附脱磷后的LC(85)样品进行再生,考察LC(85)作为脱磷剂使用时的稳定性和可重复性。经4次再生/吸附后的脱磷效果如图9所示。由此可知,LC(85)在连续5个脱磷周期内均保持了良好的磷酸根去除能力,对于磷溶液质量浓度为20 mg·L−1的水样,脱磷率由99.8%下降到96.8%,表明LC(85)经多次吸附再生后仍能保持良好的脱磷性能,因而在工业化方面具备较好的应用前景。
比较LC(85)经碱再生前后的SEM图谱(图9(b)和图9(c)),可以看出LC(85)吸附水中的磷酸根之后,其颗粒表面变粗糙且有黏连;而经碱再生的LC(85),虽然粒子间出现了少量团聚,但大部分颗粒能独立存在且表面光滑,基本保持了吸附前LC(85)的纳米尺度和微观形貌,因而为LC(85)在多次循环脱磷过程中保持高脱磷性提供了结构上的保证。
3. 结论
1)在晶型诱导剂Mg2+存在条件下,85 ℃时制备的碳酸镧LC(85)具有无定型球状纳米结构。烧瓶实验结果表明,该吸附剂在pH为3.0~11.0范围内均表现出良好的除磷性能。
2) Langmuir吸附比Freundlich吸附更好地模拟了脱磷过程,表明溶液中磷酸根的吸附过程主要通过单分子层吸附方式进行,其最大饱和吸附量可达112.8 mg·g−1;另一方面,LC(85)的拟二级模型的系数(R2=0.999 9)比拟一级模型的系数(R2=0.364 1)高,说明LC的脱磷主要是通过化学吸附或化学键合来实现的。
3)当模拟水样的磷质量浓度为20 mg·g−1时,脱磷后产生的LC(85)经碱再生后可继续保持高脱磷能力,4次再生操作后磷去除能力仍可达96.8%。
-
表 1 重金属污染分级标准
Table 1. Classification standard of heavy metal pollution index
单因子污染指数Single factor pollution index 污染等级Pollution level 综合污染指数Comprehensive pollution index 污染等级Pollution level Pi≤1 清洁 P综合≤0.7 安全 1<Pi≤2 轻污染 0.7<P综合≤1 警戒线 2<Pi≤3 中污染 1<P综合≤2 轻污染 Pi>3 重污染 2<P综合≤3 中污染 P综合>3 重污染 表 2 评价模型参数
Table 2. Evaluates model parameters
评价参数Evaluation parameters 儿童参考值Children reference value 成人参考值Adult reference value 文献References IR/(kg·d−1) 0.05 0.1 [6] ED/a 10 30 [16] EF/(d·a−1) 365 365 [17] BW/kg 32.7 60 [17] BA 1 1 [17] AT/d 3650 10950 [17] RfD(Ni)=2.00×10−2 [18] RfD(As)=3.00×10−4 [19] RfD(Cr)=1.5 [20] RfD/(mg·kg−1·d−1) RfD(Zn)=3.00×10−1 [21] RfD(Cu)=4.00×10−2 [22] RfD(Cd)=1.00×10−3 [23] RfD(Pb)=36.00×10−4 [24] 表 3 涡北煤矿外围农田中玉米籽粒和土壤重金属含量水平
Table 3. Maize grains and soil heavy metal content levels in the surrounding farmland of Guobei Coal Mine
重金属Heavy metals 范围/ (mg·kg−1)Range 平均值±标准差/ (mg·kg−1)value±SD 变异系数/%CV 超标率/%Over standardRate 标准限值/ (mg·kg−1)Standard limit 玉米Maize Ni 0.08—2.4 0.73±0.52 71.2 75.0 0.4 As 0.01—0.60 0.11±0.15 136.4 6.3 0.5 Cr 0.003—1.60 0.81±0.48 59.3 21.9 1.0 Zn 10.97—51.46 23.76±9.11 38.3 3.1 50 Cu 0.79—9.87 2.09±1.61 77.0 0 10 Cd 0.001—0.036 0.01±0.008 80.0 0 0.1 Pb 0.03—1.18 0.23±0.25 108.7 34.4 0.2 土壤Soil Ni 34.00—50.21 43.62±3.74 8.6 100 29.8 As 10.34—23.63 15.03±2.32 15.4 0 30.0 Cr 65.48—91.25 80.53±6.61 8.2 96.9 66.5 Zn 15.33—119.25 95.20±18.59 19.5 93.8 62 Cu 22.68—63.52 35.19±6.41 18.2 100 20.4 Cd 0.23—0.43 0.30±0.06 20.0 43.8 0.3 Pb 19.93—33.19 29.02±3.02 10.4 87.5 26.6 注:玉米籽粒中As、Cr、Cd、Pb及Zn、Cu含量评价标准分别参照GB2762—2017和NY861—2004中的最大限量值;Ni含量评价标准参照参考文献[28] .土壤中As、Cr、Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni含量评价标准参照安徽省土壤重金属背景值[29]. Note: The As, Cr, Cd and Pb concentration evaluation standards in maize grains refer to the GB2762-2017; The Zn and Cu concentration evaluation standards refer to the NY861-2004; the evaluation standard of Ni concentration is derived from literature [28].The As, Cr, Cd, Pb, Zn, Cu and Ni concentration evalution standards in soils refer to background values of heavy metals in soils of Anhui Province[29]. 表 4 玉米籽粒与土壤重金属含量相关性
Table 4. Correlation of maize grains and soil heavy metal content
土壤重金属Soil heavy metals 玉米籽粒重金属Heavy metals in maize grains Ni As Cr Zn Cu Cd Pb Ni −0.216 −0.244 −0.222 0.366 0.153 −0.227 −0.115 As 0.217 0.216 −0.015 0.195 0.266 −0.060 0.157 Cr −0.349 −0.287 −0.251 0.324 0.066 −0.287 −0.149 Zn 0.094 −0.022 0.142 0.151 0.097 0.284 0.137 Cu −0.260 −0.233 −0.124 0.365 0.068 −0.111 −0.087 Cd 0.202 −0.096 0.028 0.164 0.217 −0.012 0.023 Pb 0.093 −0.049 0.070 0.257 0.173 0.112 0.121 表 5 涡北煤矿外围农田玉米籽粒中重金属污染指数
Table 5. Heavy metal pollution index in maize grains in the surrounding farmland of Guobei Coal Mine
元素Element 单因子污染指数(Pi) 综合污染指数(P综合) 最小值Minimum 最大值Maximum 平均值Average Ni 0.205 6.000 1.835 4.437 As 0.018 1.204 0.220 0.865 Cr 0.003 2.163 0.811 1.633 Zn 0.219 1.029 0.475 0.801 Cu 0.079 0.453 0.209 0.713 Cd 0.010 0.360 0.100 0.117 Pb 0.035 5.915 1.130 4.258 表 6 涡北煤矿外围农田玉米籽粒的重金属摄入量及健康风险
Table 6. Heavy metal intake and health risks of maize grains in the surrounding farmland of Guobei Coal Mine
元素 Element ADD/(mg·kg−1·d−1) HQ HI 儿童Children 成人Adult 儿童Children 成人Adult 儿童Children 成人Adult Ni 2.29×10−3 1.22×10−3 1.14×10−1 6.12×10−2 1.90 0.91 As 3.44×10−4 1.83×10−4 1.15 6.10×10−1 Cr 2.53×10−3 1.35×10−3 1.69×10-3 9.01×10−4 Zn 7.43×10−2 3.96×10−2 2.48×10−1 1.32×10−1 Cu 6.53×10−3 3.48×10−3 1.62×10−1 8.70×10−2 Cd 3.13×10−5 1.67×10−5 3.13×10−2 1.67×10−2 Pb 7.19×10−4 3.77×10−4 2.00×10−1 1.05×10−1 -
[1] YU L, WANG Y B, GOU X, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables around non-ferrous metals mining and smelting sites, Baiyin, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 18(6): 1124-1134. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(06)60050-8 [2] LIU C, CUI J, JIANG G F, et al. Soil heavy metal pollution assessment near the largest landfill of China [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:An International Journal, 2013, 22(4): 390-403. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2013.733447 [3] CHEN H Y, TENG Y G, LU S J, et al. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 512/513: 143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025 [4] GRASMUCK D, SCHOLZ R W. Risk perception of heavy metal soil contamination by high-exposed and low-exposed inhabitants: the role of knowledge and emotional concerns [J]. Risk Analysis, 2015, 7(6): 611-622. [5] GU Q B, YU T, YANG Z F, et al. Prediction and risk assessment of five heavy metals in maize and peanut: A case study of Guangxi, China [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2019, 70: 1-8. [6] 盛蒂, 朱兰保, 陈健. 蚌埠地区主要谷物重金属含量及健康风险评价 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2014, 14(4): 263-266. SHENG D, ZHU L B, CHEN J. Heavy metals content and health risk assessment of cereals in Bengbu area, Anhui [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2014, 14(4): 263-266(in Chinese).
[7] 胡青青, 聂超甲, 沈强, 等. 矿业废弃复垦地主导作物重金属健康风险评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(3): 534-543. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0630 HU Q Q, NIE C J, SHEN Q, et al. Assessment of health risk of heavy metals in major crops in mining abandoned reclamation land [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(3): 534-543(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0630
[8] ULLAH Z, NAZ A, SADDIQUE U, et al. Potentially toxic elements concentrations and human health risk assessment of food crops in Bajaur Agency, Pakistan [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(14): 1-8. [9] 杨刚, 沈飞, 钟贵江, 等. 西南山地铅锌矿区耕地土壤和谷类产品重金属含量及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(9): 2014-2021. YANG G, SHEN F, ZHONG G J, et al. Concentration and health risk of heavy metals in crops and soils in a zinc-lead mining area in southwest mountainous regions [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(9): 2014-2021(in Chinese).
[10] 王娟, 李玉成, 黄欣欣, 等. 铜陵矿区植物重金属富集行为及健康风险评估 [J]. 生物学杂志, 2020, 37(3): 76-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2020.03.076 WANG J, LI Y C, HUANG X X, et al. Enrichment of heavy metals and health risk assessment of plants in Tongling mining area [J]. Journal of Biology, 2020, 37(3): 76-80(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2020.03.076
[11] 刘旭, 郑刘根, 陈欣悦, 等. 淮南潘集矿区农田土壤重金属污染特征及在小麦中累积特征研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(8): 959-964,978. LIU X, ZHENG L G, CHEN X Y, et al. Study on the heavy metals pollution characteristics of agricultural soil and their accumulation characteristics in wheat in Panji mining area, Huainan [J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 2019, 41(8): 959-964,978(in Chinese).
[12] 熊霜, 桂和荣, 彭位华. 矿区土壤-玉米重金属富集及健康风险 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(8): 80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.08.013 XIONG S, GUI H R, PENG W H. Accumulation and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-maize system from coal mining area [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(8): 80-86(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.08.013
[13] 安徽省统计局, 安徽统计年鉴[J]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018. Anhui Provincial Bureau of Statistics, Anhui Statistical Yearbook[J]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2018 (in Chinese).
[14] 陆金, 赵兴青. 铜陵狮子山矿区土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(9): 1958-1967. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017010304 LU J, ZHAO X Q. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of polluted soil by heavy metals in Shizishan, Tongling [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(9): 1958-1967(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017010304
[15] 刘丹, 赵永红, 周丹, 等. 赣南某钨矿区土壤重金属污染生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(7): 1556-1567. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.07.2016112701 LIU D, ZHAO Y H, ZHOU D, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in a tungsten mine soil in south of Jiangxi Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(7): 1556-1567(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.07.2016112701
[16] US EPA. Risk assessment guidance for superfund volume I: human health evaluation manual (part A)[R]. EPA/540 /1-89 /002. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, 1989. 35-52. [17] US EPA. Superfund public health evaluation manual[R]. EPA/540 /1-86 /060. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, 1986. 1-52. [18] 吴迪, 杨秀珍, 李存雄, 等. 贵州典型铅锌矿区水稻土壤和水稻中重金属含量及健康风险评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(10): 1992-1998. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2013.10.013 WU D, YANG X Z, LI C X, et al. Concentrations and health risk assessments of heavy metals in soil and rice in zinc-lead mining area in Guizhou Province, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(10): 1992-1998(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2013.10.013
[19] US EPA. CASRN 7440- 38- 2 Arsenic, inorganic [S]. Washington, DC: Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Risk Information System, 1993. [20] US EPA. CASRN 18540-29-9, Chromium(VI) [S]. Washington, DC: Environmental Protection Agency, 1998. [21] US EPA. CASRN 7440-66-6, Zinc and compounds [S]. Washington, DC: Environmental Protection Agency, 2005. [22] US EPA. CASRN 7440-50-8 Copper [S]. Washington, DC: Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Risk Information System, 1991. [23] US EPA. CASRN 7440-43-9, Cadmium [S]. Washington, DC: Environmental Protection Agency, 1994. [24] US EPA. CASRN 7439-92-1: Lead and compounds (inorganic)[S]. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, 2004. [25] 刘书江, 王敏, 高宗军, 等. 滕州矿区土壤与玉米籽粒重金属富集特征 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2018, 46(17): 137-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.17.040 LIU S J, WANG M, GAO Z J, et al. Enrichment characteristics of soil and maize heavy metals in Tengzhou Mining Area [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(17): 137-140(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.17.040
[26] 陈璐, 王凯荣, 王芳丽, 等. 平度市金矿区农田土壤-玉米系统重金属污染风险评价 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2018, 35(2): 161-166. CHEN L, WANG K R, WANG F L, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in the agricultural soil-maize system of a gold mining area in Pingdu City, China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2018, 35(2): 161-166(in Chinese).
[27] 陆素芬, 张云霞, 余元元, 等. 广西南丹土壤-玉米重金属积累特征及其健康风险 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2017, 33(8): 706-714. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2017.08.005 LU S F, ZHANG Y X, YU Y Y, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal accumulation in soil-corn system contents and their health risks in Nandan, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2017, 33(8): 706-714(in Chinese). doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2017.08.005
[28] 傅逸根, 胡欣, 俞苏霞. 食品中镍限量卫生标准的研究 [J]. 浙江省医学科学院学报, 1999, 37: 9-11. FU Y G, HU X, YU S X. Study on the tolerence limit of nickel in foods [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Academy of Medical Sciences, 1999, 37: 9-11(in Chinese).
[29] 中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990. China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Background values of Soil elements in China[M]. Beijing : China Environmental Press, 1990 (in Chinese).
[30] 罗飞, 巴俊杰, 苏春田, 等. 武水河上游区域土壤重金属污染风险及来源分析 [J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(2): 195-203. LUO F, BA J J, SU C T, et al. Contaminant assessment and sources analysis of heavy metals in soils from the upper reaches of the Wushui River [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(2): 195-203(in Chinese).
[31] 蒋璇, 熊晶, 吴亦潇, 等. 湖北省农田土壤重金属来源解析与质量评价 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(12): 211-217. JIANG X, XIONG J, WU Y X, et al. Source Apportionment and pollution characteristics of heavy metal in agricultural soil in Hubei Province [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 42(12): 211-217(in Chinese).
[32] 黄华斌, 林承奇, 胡恭任, 等. 基于PMF模型的九龙江流域农田土壤重金属来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 430-437. HUANG H B, LIN C Q, HU G R, et al. Source appointment of heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Jiulong River Basin Based on Positive Matrix Factorization [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 430-437(in Chinese).
[33] FAIRBROTHER A, WENSTEL R, SAPPINGTON K, et al. Framework for metals risk assessment [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2007, 68(2): 145-227. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.03.015 [34] 纪玉琨, 李广贺. 作物对重金属吸收能力的研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2006, 25(S1): 104-108. JI Y K, LI G H. Adsorption of wheat and maize on heavy metals in soils [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2006, 25(S1): 104-108(in Chinese).
[35] 王北洪, 马智宏, 冯晓元, 等. 北京市蔬菜重金属含量及健康风险评价 [J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2015, 6(7): 2736-2745. WANG B H, MA Z H, FENG X Y, et al. Concentrations and health risk evaluation of heavy metals in vegetables in Beijing [J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2015, 6(7): 2736-2745(in Chinese).
[36] 杨胜香, 袁志忠, 李朝阳, 等. 湘西花垣矿区土壤重金属污染及其生物有效性 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(5): 1718-1724. YANG S X, YUAN Z Z, LI Z Y, et al. Heavy metal contamination and bioavailability in huayuan manganese and Lead/Zinc Mineland, Xiangxi [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(5): 1718-1724(in Chinese).
-






 下载:
下载: