-
膜生物反应器(membrane bioreactor,MBR)是将微生物和膜分离有机结合的一种污水处理技术,具有容积负荷高、剩余污泥少、出水效果好等优点,所结合的膜组件类型包括平板膜、管式膜、中空纤维膜等。管式膜MBR是将生物处理单元与管式膜结合的一种外置式MBR技术,它具有通量大、耐污性强、易于维护等特点,近些年被广泛应用于垃圾渗滤液、油田水处理等领域[1]。但管式膜MBR为维持高通量和较强的耐污染性,一般膜面错流速度需维持在2.0~4.0 m·s−1,运行能耗较大,并且膜污染问题仍然存在[2]。目前,关于膜污染控制的研究较多,内容涉及膜材料改性、膜组件和生物反应器设计及运行参数优化、微生物和电化学调控膜分离等[3-4]。通过向膜组件导入气体,使膜表面形成气液两相流,可增强膜表面气液扰动,抑制膜表面浓差极化和滤饼层形成,从而显著提高膜的抗污染水平,减少维护频次[5-7];并且有研究表明,气体的导入可在较低膜面流速下使膜污染控制在较低水平,这有利于节省运行能耗[5]。但曝气的引入也可能引发一些不利影响,如污泥粒径变小[8]、污泥破碎引发的胞外聚合物释放[8-9]等,进而加重膜污染,这些问题对膜长周期运行产生不利影响。目前,在管式膜MBR体系下,采用生物曝气尾气导入管式膜组件用以减轻膜污染的研究较少,且此种方式下曝气量对于生化系统影响及膜污染过程机制仍需进一步开展研究。
本研究将移动床生物膜反应器(moving bed biofilm reactor, MBBR)与管式膜串联构建气提式管式膜MBR处理生活污水,采用MBBR曝气尾气对管式膜组件进行气泡持续强化清洗,研究了气提式管式膜MBR污染物去除效果,并对不同曝气量下膜污染状况、污泥特性及膜污染形成机制进行了探讨。本研究结果将为气提式管式膜MBR膜污染控制提供数据支持。
-
本研究所采用实验装置如图1所示。污水由进水泵泵入MBBR反应柱,反应柱内装填亲水性悬浮填料,填料密度为0.98 g·cm−3,比表面积为650 m2·m−3,填料填充率为40%。MBBR曝气通过曝气头由空压机提供,进水量和曝气量分别通过液体流量计1和气体流量计控制,MBBR出水和曝气尾气经气液分流装置共同进入膜组件促使管式膜腔内形成气液两相流以减轻膜污染。实验过程中采用相同尺寸和结构的有机玻璃管代替膜组件用高速相机观察不同曝气量下膜组件内气液流态。管式膜组件采用恒通量运行模式,抽吸泵与膜组件之间装有负压表P0,管式膜组件两端装有数显压力表P1和P2,P1和P2压力平均值为膜组件内部平均压力P3,膜组件跨膜压力ΔP=P3-P0;管式膜浓缩液进入缓冲池,并通过循环泵将液体循环至MBBR,循环泵流量通过液体流量计2调节控制;MBBR顶部和管式膜组件设有取样池,以定期对出水分析检测。
-
本实验采用人工模拟海上钻井平台生活污水。其中,污水COD为546~812 mg·L−1,氨氮为52~61 mg·L−1,TP约为5~8 mg·L−1。实验所采用MBBR反应器高度1.5 m,直径200 mm,反应器有效容积约为40 L,进水流量控制在5 L·h−1,水力停留时间约为8 h。MBBR曝气量通过气体流量计调节,以考察不同曝气量下管式膜MBR体系下污染物降解与膜污染状况。本实验通过驯化培养完成MBBR挂膜,运行稳定后开始实验,实验共持续2个月左右,分3个阶段运行:第1阶段(0~20 d)、第2阶段(21~40 d)和第3阶段(41~60 d),3个阶段的曝气量分别为50、100和150 L·h−1。
本研究使用的管式膜组件来自天津工业大学膜技术中心,膜材质为PVDF,孔径为0.03 µm,膜组件长度约1 m,膜组件由4根膜管通过环氧树脂密封制成,单个膜管流道内径为8 mm,总有效过滤面积约0.1 m2。膜组件采用恒通量运行,膜通量控制在50 L·(m2·h)−1左右,液体流量计2控制在100 L·h−1。当跨膜压力上升至55 kPa左右时,采用0.5% NaClO溶液对膜组件进行化学清洗,清洗时间约1~2 h,以保证膜通量恢复至初始水平。
-
本实验常规水质指标包括COD、NH4+-N、MLSS、VSS和浊度采用《水和废水检测分析方法》中的标准方法进行测定[10],溶解氧(DO)采用哈希HQ30d 测定,污泥粒径采用马尔文激光粒度测定仪进行测定。
胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances, EPS)主要成分包括多糖(polysaccharide, PS)和蛋白质(protein, PN)。其中,溶解态EPS提取方法:取悬浊液10 mL,在4 ℃,9 000 r·min−1件下,离心20 min,所得上清液在4℃冰箱保存4 h,然后分析测定其组分。结合态EPS提取采用甲醛-NaOH法[11]:将上述离心后剩余固体污泥用去离子水稀释至10 mL,摇匀,加入37.5%HClO的溶液60 μL,充分摇匀,在4℃下放置1 h,取出,加入1 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液4 mL,再次摇匀,在4℃下放置3 h,取出,在4 ℃,13 500 r·min−1条件下,离心20 min,所得上清液测定结合态EPS。EPS中PS采用苯酚—硫酸法[12],在485 nm下比色测定;PN采用Lowry法[13],在750 nm下比色测定。气提式管式膜MBR混合液中EPS为溶解态和结合态之和,膜表面EPS通过高速物理冲洗方式将污染物清洗下来,而后进行分类测定。
管式膜内气、液表观流速通过公式(1)进行计算。
式中:Qi为管式膜进气或进液流量,m³·s−1;D为单个膜管流道内径,取0.008 m。因小试试验氧的利用效率较低,管式膜内进气流量按近似等于MBBR曝气量处理。
本实验膜污染阻力测定包括膜总过滤阻力Rt、膜本身过滤阻力Rm、滤饼阻力Rc及不可逆污染阻力Rf,他们之间的关系如式(2)[14]所示。
式中:膜本身过滤阻力Rm采用新膜或膜化学清洗后过滤去离子水测定;膜总过滤阻力Rt采用膜污染后过滤去离子水测定;单次膜过滤周期后,采用海绵球配合高速水流刮擦膜表面,用于去除滤饼层污染,从而得出Rm+Rf;根据上述公式可分别计算出Rf和Rc。
-
在气提式管式膜MBR体系下,不同曝气量下MBBR及膜出水状况如表1所示。随着曝气量由50 L·h−1增至150 L·h−1,MBBR出水COD平均值由96.24 mg·L−1降至41.54 mg·L−1,膜出水COD平均值由63.73 mg·L−1降至24.28 mg·L−1。由图2可以看出,MBBR生物填料上平均生物量由22.2 g·m−2增至31.7 g·m−2,混合液中悬浮态污泥质量浓度由672 mg·L−1降至150 mg·L−1左右。这主要由于:曝气量的增加促进了MBBR反应器内污染物与生物膜表面的传质作用,提高了微生物活性和污染物降解能力;同时,体系中较高的溶解氧浓度促使生物膜维持较高的生物活性,使微生物与填料结合更加牢固,而填料表面生物量的增加势必提高污水处理效率。此外,由于膜对颗粒物及大分子污染物的截留作用,在相同曝气量下膜出水水质均好于MBBR出水。另外,在第1阶段(0~20 d),MBBR出水氨氮平均质量浓度维持在16.82 mg·L−1;而在第2、3阶段,氨氮出水平均质量浓度在1.84 mg·L−1以下。这主要因硝化菌生长周期较长,在第1阶段有机污染物浓度较高,不利于硝化菌的生长;随着第2、3阶段曝气量的增加和运行周期的延长,污染物浓度进一步降低,并在管式膜截留作用下,此时反应器内硝化菌已成为优势菌种。
值得注意的是,当曝气量增至150 L·h−1时(第3阶段),MBBR中悬浮污泥质量浓度为131~519 mg·L−1,波动较大。一方面,可能由于过高的曝气量容易使MBBR内形成强烈气液扰动,促使生物膜更新加快;另一方面,由于该阶段MBBR出水COD平均质量浓度在41.54 mg·L−1左右(见表1),反应器内底物已消耗殆尽,MBBR内填料上生物膜因底物不足无法维持结构而脱落,最终导致此阶段悬浮污泥浓度波动较大[15]。此外,由表1可看出,在气提式管式膜MBR体系下,相同曝气量下膜出水DO浓度高于MBBR上清液。这主要因为MBBR出水和曝气尾气在管式膜腔内形成强烈的气液扰动和传质作用,提高了膜出水溶解氧水平和氧的利用率。不仅如此,管式膜内强烈的气液扰动对膜污染也将产生较大影响。
-
1)曝气量对管式膜内流态和膜污染周期影响。一般情况下,管式膜内气含率不同,膜内会形成不同流态的气液两相流,具体流态随气含率ε而变化。当ε≤0.2时,管式膜内为气泡流;当0.2<ε<0.9时,管式膜内为活塞流,即此时气泡横向尺寸与单个膜管内径相同,流向上不存在混合现象;当ε≥0.9时,为环形流[16]。其中,气含率根据式(3)进行计算。
式中:ε为气含率;vg为管式膜内气体表观流速,m·s−1;vl为管式膜内液体表观流速,m·s−1。
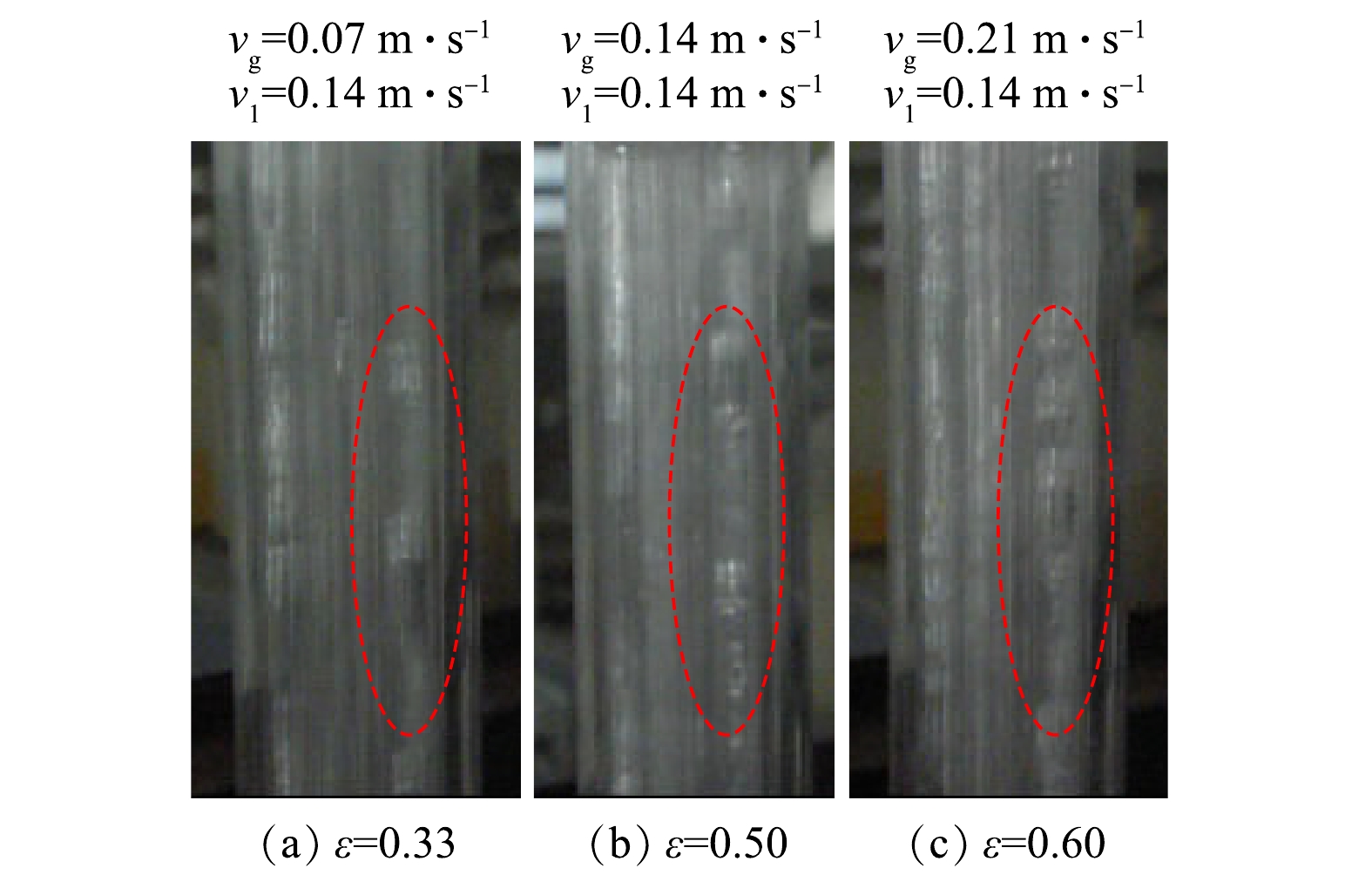
由图3可看出,本实验3个阶段管式膜内气含率ε分别为0.33、0.50和0.60,即管式膜腔内均形成“活塞流”流态,它使膜腔内形成强烈的气液扰动并在膜表面形成较强的错流剪切作用,抑制膜表面浓差极化层和滤饼层形成,从而减缓膜污染。另外,随着曝气量增加,管式膜内产生“活塞流”频率增加,这主要因为 “活塞流”气泡大小取决于管式膜腔内径,因此,同一膜组件内气泡清洗频率与进气流量之间关系如式(4)[17]所示。
式中:Qg为管式膜内进气流量,L·h−1;V为单个气泡体积,mL;f为气泡频率,s−1。
由于管式膜内径不变,则单个活塞流气泡体积基本变化不大,又因本实验中管式膜进气量与曝气量基本相等,因此,随着曝气量的增加,产生活塞流气泡频率将呈线性增加,即膜表面气泡清洗频次增大。由图4可看出,随着曝气量由50 L·h−1增至150 L·h−1,膜操作周期由6~7 d延长至17 d左右,不同曝气阶段内化学清洗频次由3次降至1次。这主要由于气泡频率的增加,强化了膜表面清洗效果,减缓了膜污染速率,从而延长了膜操作运行时间。值得注意的是,在整个膜操作周期内,气提式管式膜MBR膜面液体表观流速维持在0.14 m·s−1左右,显著低于传统管式膜错流速度2.0~4.0 m·s−1,即通过向管式膜引入MBBR曝气尾气,可实现在较低膜面流速下控制膜污染。这有助于节约能耗,对工程化应用具有重要意义。
2)曝气量对临界通量影响。图5为不同曝气量下跨膜压力增长速率随膜通量变化状况。当膜通量维持在50 L·(m2·h)−1时,曝气量分别为50、100和150 L·h−1时,膜污染速率分别为1.54、0.45、0.21 kPa·h−1,即随着曝气量的增加,跨膜压力增长速率显著下降,膜污染速率得到有效抑制。不仅如此,根据临界通量定义,当膜操作通量低于临界通量时,跨膜压力增速缓慢,膜污染速率处于较低水平;但当膜操作通量大于临界通量时,跨膜压力出现快速增长,膜污染速率会出现陡增现象。因此,当曝气量分别为50、100和150 L·h−1时,膜临界通量分别为20~30、40~50和70~80 L·(m2·h)−1,即随着曝气量的增加,膜操作临界通量也出现增加。这可能由于曝气量增加了膜表面气液混合流速,增大了膜表面剪切作用,而膜面流速与临界通量成正比关系[18]。由于本实验采用恒通量运行,膜通量维持在50 L·(m2·h)−1左右,即通过将MBBR曝气尾气导入管式膜,使第1阶段膜实际操作通量处于超临界通量区,第2阶段和第3阶段膜实际操作通量分别处于临界通量区和次临界通量区。因此,第1阶段膜污染最为严重,第2阶段次之,第3阶段最轻。这与膜操作周期相符(图4)。
-
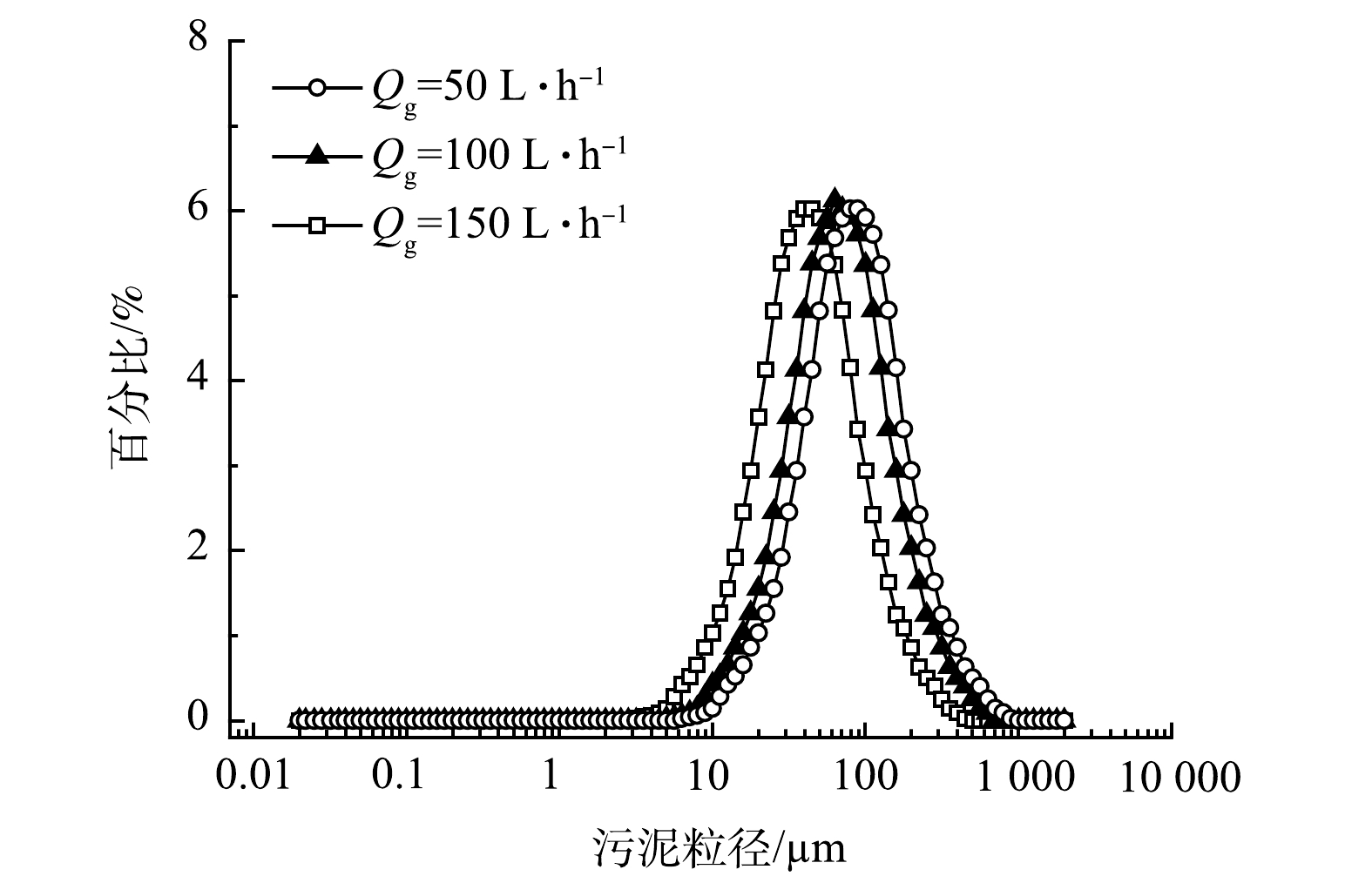
1)曝气量对悬浮污泥浓度及粒径影响。曝气量直接影响气提式管式膜MBR中溶解氧水平和水力状况,进而对悬浮污泥浓度和粒径产生影响,而这些都将对膜污染产生影响。由图2可看出,在整个操作阶段,MBBR混合液中悬浮态污泥质量浓度均小于700 mg·L−1,并且随着曝气量增加,尽管反应器内气液扰动加剧,但混合液中悬浮态污泥浓度有减小趋势。这主要由于曝气量的增加提高了反应器溶解氧水平,填料上生物膜活性较高,结合较为牢固,但强烈的气液扰动所产生的剪切力可能使污泥破碎,从而影响膜污染过程[8]。
由图6可看出,当曝气量为50、100和150 L·h−1时,MBBR反应器中悬浮污泥平均粒径分别为84.48、75.29和42.34 μm,即随着曝气量的增加,悬浮污泥平均粒径有减小趋势,特别是当曝气量增至150 L·h−1时,污泥粒径明显减小。一方面,MBBR反应器内和管式膜内气液扰动所产生的剪切力促使悬浮态污泥破碎,导致粒径变小;另一方面,随着曝气量的增加,出水中有机物浓度较低,微生物长期处于内源代谢期,所形成的微生物碎片促使悬浮颗粒粒径变小,这容易使膜表面形成致密滤饼层或引发膜孔堵塞等,致使膜发生不可逆性污染。
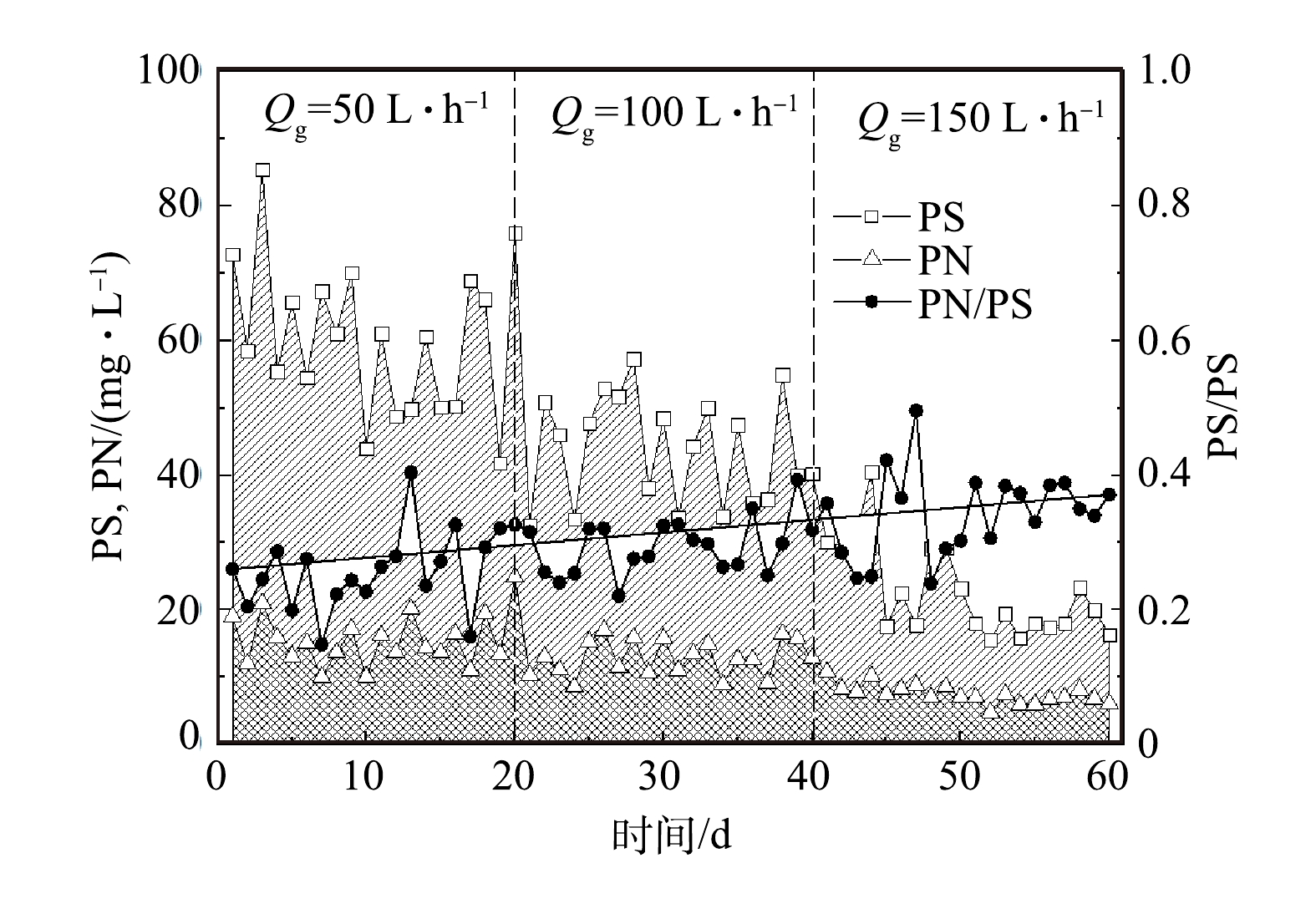
2)曝气量对混合液中EPS的影响。在微生物生长代谢过程中,细胞表面会吸附有机物并产生EPS,而EPS在膜污染过程中有重要作用。由图7可看出,随着曝气量由50 L·h−1增至150 L·h−1,MBBR混合液EPS中PS质量浓度由42~85 mg·L−1降低至16~41 mg·L−1,PN质量浓度由10~25 mg·L−1降至4~11 mg·L−1,即两者浓度均随曝气量增加呈现减小趋势。这与膜污染速率和运行周期的变化趋势相符(图4和图5),即膜污染与混合液中EPS有较大关系[19]。一方面,悬浮物污泥浓度随曝气量减小,降低了混合液中结合态EPS浓度;另一方面,由于曝气量会改变了反应器内污染物浓度和DO水平,MBBR体系中微生物活性和代谢方式也会因此发生显著变化。有研究表明,相对稳定的生物膜结构所分泌EPS的量明显减少[15,20]。在第1、2阶段,反应器内维持相对较高污染物浓度,DO维持在2.56~3.76 mg·L−1,此阶段微生物活性较高,代谢活性较强,胞外聚合物分泌量较多;在第3阶段,反应器内COD平均值维持在41.54 mg·L−1,污染物浓度较低,此时MBBR反应器内DO达到4.65 mg·L−1左右,微生物内源代谢增强,生物膜处于相对稳定状态,微生物所分泌EPS相对较少,这有利于膜污染控制。值得注意的是,通过对EPS组成分析发现,PN/PS随着曝气量的增大由0.24增至0.38左右(图7),即EPS中PN分泌比例增加。LU等[14,20]的研究表明,当生物膜处于稳定阶段后,所分泌的EPS中PN和PS比率呈逐渐升高趋势。
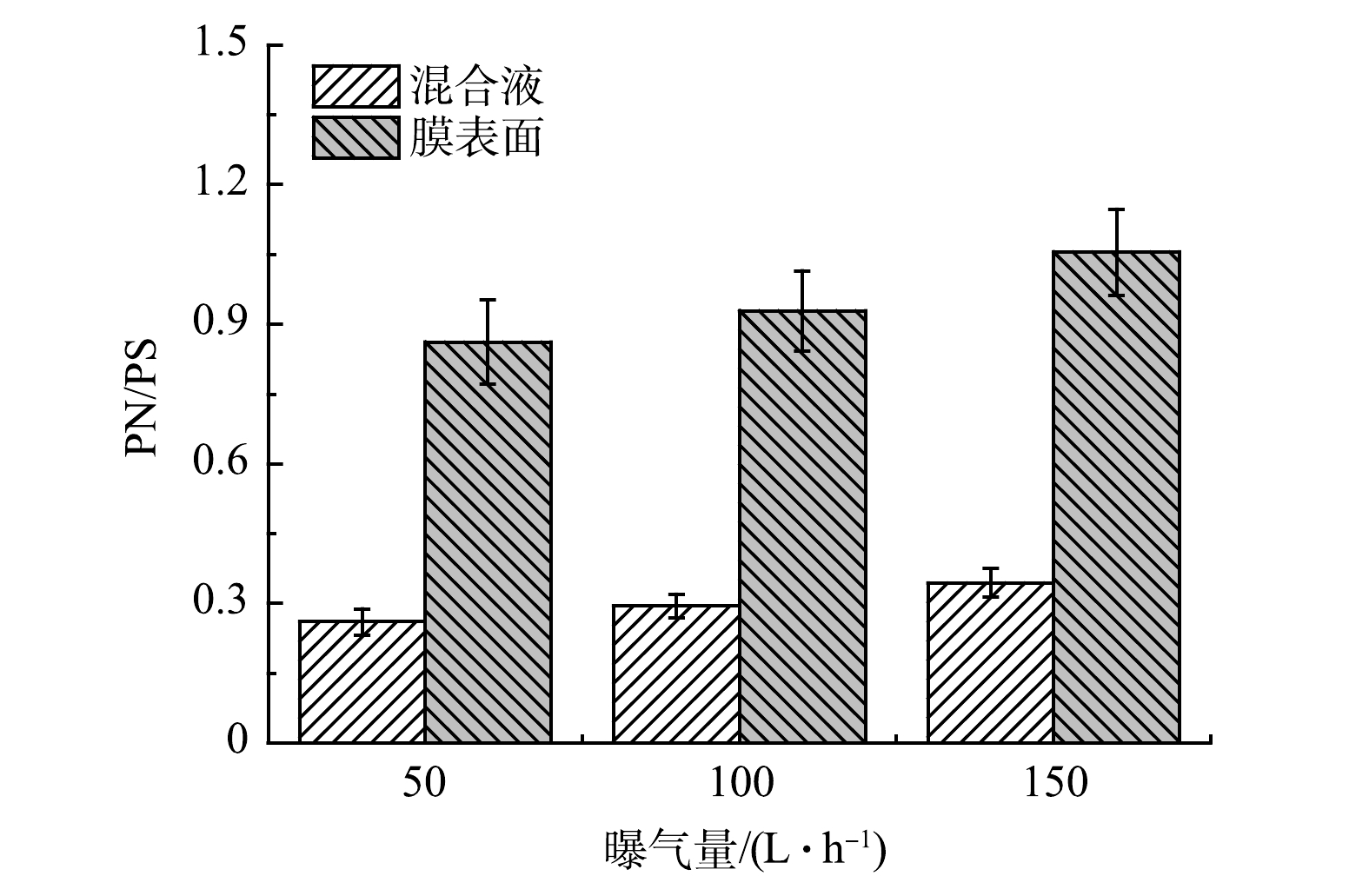
为进一步探讨MBBR体系中EPS对膜污染的影响,对不同曝气量下MBBR混合液和膜表面EPS组分进行了分析。如图8所示,不同曝气量下膜表面PN/PS均显著高于混合液。这表明膜对蛋白质等大分子物质具有截留作用,致使其在膜表面发生累积现象,并且随着曝气量的增加,蛋白质累积作用加强。此外,随着曝气量的增加,出水COD逐渐降低,微生物内源呼吸作用加强,导致部分微生物细胞裂解释放蛋白质,而膜的截留作用势必进一步增加体系内胞外聚合物中蛋白质的比例。尽管如此,随着曝气量的增加,膜操作周期仍然大幅提高。这说明将MBBR曝气尾气导入管式膜所产生的气泡清洗作用对于膜污染控制至关重要,但膜表面强烈气液扰动也可能引发膜孔堵塞,进而发生不可逆污染。
-
一般情况下,膜表面气液湍流程度和传质情况对膜污染形成过程和机理均有较大影响,最终所形成的污染阻力构成也不尽相同。为进一步探讨气提式管式膜MBR下膜污染形成状况,对不同曝气量下每次运行结束时进行化学清洗前,即当跨膜压差增至55 kPa左右时的膜污染阻力构成进行了分析。由图9可以看出,当曝气量由50 L·h−1增至150 L·h−1时,膜表面滤饼阻力由40.1%降到25.1%,不可逆污染阻力由54.6%增至 69.6%,即在气提式管式膜MBR体系下,膜表面污染阻力主要为不可逆污染。这与传统膜过滤阻力构成有较大区别。另外,由图10可以看出,管式膜运行结束经物理清洗后,不同曝气量下膜表面均出现不同程度的膜孔堵塞,且随曝气量增加堵塞更为严重。这与不可逆污染阻力增加相符。一方面,由于气提式管式膜MBR下膜表面形成气液两相流,增大了膜表面错流剪切作用,促使滤饼脱落从而减轻了滤饼污染,但滤饼层的剥落增加了膜孔堵塞和吸附污染概率[9];另一方面,随着曝气量的增加和运行时间的延长,MBBR体系内污泥内源代谢作用加强,大分子蛋白质和细胞碎片也增加了膜孔吸附和堵塞风险[20],并且由于膜孔堵塞和吸附污染均为不可逆污染,因此,一旦膜通量下降,必须进行化学清洗方可恢复膜通量。值得注意的是,在气提式管式膜MBR体系下,由图4和图9可看出,每次化学清洗后,管式膜初始过滤跨膜压差和膜自身过滤阻力并未增加,相同曝气量下膜过滤操作周期重复性较好且随曝气量增加而延长。总之,通过将MBBR曝气尾气引入管式膜构建气提式管式膜MBR仍然可显著提高膜污染操作周期,最大程度上延长膜化学清洗周期,减少清洗频率,因而在一定程度上节省了运行能耗和药剂成本。
-
1)通过MBBR与管式膜构建了气提式管式膜MBR,膜出水水质优于MBBR,出水DO质量浓度高于MBBR;膜组件内呈“活塞流”流态,气泡清洗频率随曝气量增加而增加,膜污染速率由1.54 kPa·h−1降至0.21 kPa·h−1,膜的临界操作通量变大,膜操作周期由6~7 d延长至17 d左右。
2) MBBR中悬浮污泥平均粒径随曝气量增加由84.48 μm降至42.34 μm,混合液EPS中PN和PS均呈减小趋势,但PN/PS比例由0.24增至0.38,而膜表面PN/PS比例均在0.85以上,蛋白质在膜表面发生了累积现象。
3)膜表面污染阻力以不可逆污染阻力为主,曝气量的增加使膜表面滤饼阻力由40.1%降到25.1%,不可逆污染阻力由54.6%增至 69.6%。
曝气对MBBR联合管式膜MBR处理生活污水的影响及膜污染分析
The membrane fouling analysis and effect of aeration on the performance of MBBR combined tubular membrane MBR system treating domestic wastewater
-
摘要: 采用移动床生物膜反应器(MBBR)联合管式膜构建气提式管式膜MBR体系用以处理生活污水,考察了曝气对污水处理效果、膜内气液流态及膜过程的影响,探讨了污泥特性的变化及其对膜污染过程的影响机制。结果表明,气提式管式膜MBR体系下膜出水DO浓度高于混合液,且随着曝气量由50 L·h−1提高至150 L·h−1,管式膜内气含率由0.33增至0.60并呈“活塞流”流态,操作周期由6~7 d延长至17 d,膜污染速率由1.54 kPa·h−1降至0.21 kPa·h−1,临界通量显著增大;同时,MBBR混合液中EPS总量呈减小趋势,但MBBR内悬浮污泥粒径变小,且膜表面EPS中PN/PS比例显著高于MBBR混合液。膜表面污染阻力构成分析表明,气提式管式膜MBR体系下容易发生膜孔堵塞,膜污染以不可逆污染阻力为主。Abstract: The air-lifting tubular MBR system was constructed by a moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) combined with tubular membranes for domestic wastewater treatment. The effects of aeration on the wastewater treatment effect, gas-liquid flow pattern in membrane module and membrane process were investigated, and the changes of sludge characteristics and its influence mechanism on membrane fouling process were also discussed. The results indicated that the DO level of the membrane effluent was higher than the mixed solution in air-lifting tubular MBR systems. Moreover, with the increase of the aeration rate from 50 L·h−1 to 150 L·h−1, the void fraction in the tubular membrane increased from 0.33 to 0.60 and "slug flow" state occurred in the tubular membrane, and the membrane operation time was extended from 6~7 d to 17 d, the membrane fouling rate decreased from 1.54 kPa·h−1 to 0.21 kPa·h−1 and the critical flux increased significantly. In addition, the total EPS in MBBR mixture showed a decreasing trend, but the particle size of the suspended sludge in MBBR decreased, and the ratio of PN/PS on the membrane surface was significantly higher than the mixture in MBBR system. The composition of the resistance to fouling on the membrane surface showed that the tubular membrane was prone to clogging of the membrane pores, and the membrane fouling was dominated by irreversible fouling resistance.
-
国内外主流烟气脱硫技术为石灰石-石膏湿法脱硫[1],同时,湿式氨法脱硫工艺存在吸收塔出口气溶胶颗粒物排放浓度大的缺陷[2-3],导致烟囱出口形成“蓝色烟尾”的现象[4-5]。根据统计,在2015年签订合同的烟气脱硫新建工程机组中,氨法烟气脱硫机组占4%,与《火电厂烟气脱硫工程技术规范 氨法》(HJ 2001—2010)颁布时国内氨法脱硫机组占所有烟气脱硫工程机组不到1%相比,氨法脱硫的应用取得了长足发展,并开发了多段分区吸收塔技术代替原有空塔技术[6]。《燃煤电厂超低排放烟气治理工程技术规范》[7]中规定:氨法脱硫塔的结构须分区设置烟气洗涤降温区、SO2吸收区、颗粒物及氨逃逸控制区等,不同功能区间用托盘分隔。其中,烟气洗涤降温区设置1~2层喷淋,SO2吸收区设置不应少于3层喷淋,颗粒物和氨逃逸控制区设置1~2层喷淋,以及不少于3级的高效除雾器,使出口雾滴浓度不大于20 mg·m−3(其中硫酸铵的浓度约为9 mg·m−3)。
针对氨法脱硫工艺在实践中气溶胶颗粒物排放浓度大的问题,国内学者进行了实验室与实践中的研究[8-9]。张文武等[10]研究了氨法脱硫工艺气溶胶生成机理与物理特性,并得出气相NH3与SO2反应在硫酸铵气溶胶生成中占主导地位的结论;彭学江等[11]总结了氨法脱硫在硫酸生产工业中的实际应用问题,并研究了通过改造除雾器与加装冲洗水喷雾的方式,使脱硫塔出口硫酸铵颗粒平均物浓度从40 mg·m−3降到25 mg·m−3。同时,不同工业中的氨法脱硫工艺,在入口烟气温度不同的情况下,出口硫酸铵浓度表现出不同特性,如硫酸生产工业中,使用先干法脱硫再氨法脱硫的工艺,在氨法脱硫入口温度为60 ℃的条件下,出口颗粒物浓度仅为2.8~4.2 mg·m−3[12];烧结烟气的氨法脱硫塔入口温度分别为140 ℃左右,在结构更优的氨法脱硫塔情况下,其出口硫酸铵颗粒物浓度却高达280 mg·m−3[13];燃煤电厂氨法脱硫塔入口烟气温度在130 ℃左右,须在脱硫塔出口增设湿式电除尘器[3, 14]或采用声波凝并等技术[15],才能使出口硫酸铵颗粒物浓度满足超洁净排放的要求。但目前缺乏对电厂多段分区吸收塔在不同工况条件下出口硫酸铵排放浓度变化规律的研究,缺乏对结构改造案例效果的对比分析[16]。
本研究针对氨法脱硫出口硫酸铵颗粒物浓度高且不易控制的现象,通过连续跟踪与控制锅炉负荷、吸收塔浆液密度、入口烟气温度、3级循环区域淋洗水量等,对比分析吸收塔中烟气处理量、烟气降温区域浆液中硫酸铵浓度、烟气温度、工艺水淋洗等因素对吸收塔出口硫酸铵浓度的影响,并对改造后吸收塔结构性能进行测定与评价,针对降低出口硫酸铵颗粒物浓度与节能的要求,提出了氨法脱硫优化运行的建议与氨法脱硫工艺改造的新思路。
1. 实验对象
被选择的、优化后的多段分区脱硫塔系统如图1所示。烟气洗涤降温区的循环浆液为吸收塔浆液,其利用进口烟气的热量,使硫酸铵溶液达到饱和并析出晶体——塔内结晶;SO2吸收区的循环浆液来自设置在吸收塔外的2级循环槽;颗粒物及氨逃逸控制区的循环液为工艺水,来自设置在吸收塔外的3级循环槽。针对原脱硫出口硫酸铵颗粒物浓度高的情况,电厂对控制颗粒物及氨逃逸的3级循环区域结构进行了改造,改造内容包括:扩大了该区域结构的直径;工艺水淋洗喷淋层由1层变为2层,并加大了原有工艺水淋洗水量;在原有的2层V型除雾器的基础上,增加了1层高效除雾器;多孔填料用塑料丝替换原有的斜板通道。
2. 实验方法
2.1 常规采样方法
悬浮于排放烟气中的可过滤颗粒物(FPM)采样方法依据规范1——《固定污染源排气中颗粒物和气态污染物采样方法》[17]与规范2——《固定污染源废气 低浓度颗粒物测定 重量法》[18]中的烟道内过滤法进行,规范1采用的玻璃纤维与刚玉滤筒对于直径为0.5 μm粒子的捕集效率不低于99%,规范2采用的滤膜对于直径为0.3 μm标准粒子的捕集效率应大于99.5%。
2.2 优化采样方法
前期在锅炉75% BRL负荷、SO2排放浓度小于10 mg·m−3的条件下,跟踪、测试吸收塔进、出口颗粒物浓度结果如表1所示。可以看出,在吸收塔入口烟尘浓度很低的情况下,吸收塔出口颗粒物浓度是进口烟尘浓度的4~5倍,且冷凝液中离子态硫酸铵浓度约为颗粒物浓度的60%,即运用常规采样方法不能准确反映氨法脱硫塔出口硫酸铵颗粒物浓度。同时,不管是哪种运行条件,出口颗粒物浓度在线CEMS监测仪均无法准确反映烟气中实际的颗粒物浓度。有研究表明,氨法脱硫吸收塔出口硫酸铵粒径分布集中在0.07~0.70 μm[19],即存在硫酸铵穿透滤膜或滤筒的可能,且目前缺乏高湿度条件下,滤膜与滤筒对硫酸铵颗粒捕集效率的研究结果(规范2检测滤膜在实际使用中是否会发生穿透情况是在水泥厂与电厂除尘器上做的测试)。因此,分析中采用滤筒或滤膜上可过滤颗粒物(FPM)与可凝结颗粒物(CPM)[20]之和作为出口硫酸铵浓度。
表 1 前期测试与跟踪的进、出口颗粒物浓度Table 1. Particle concentrations of the inlet and outlet through initial tracking and testing运行条件 测试编号 入口FPM浓度/(mg·m−3) 出口FPM浓度/(mg·m−3) 出口CEMS监测颗粒物平均浓度/(mg·m−3) CPM浓度/(mg·m−3) CPM/FPM/% 吸收塔不向硫酸铵生产线供浆液 1 4.57 17.35 5.32 10.25 59.08 2 4.33 21.16 5.18 12.62 59.64 吸收塔向硫酸铵生产线供浆液 1 4.21 101.42 7.83 68.59 61.51 2 5.56 127.73 6.27 41.25 48.93 依据美国EPA颁布的可凝结颗粒物采样方法——Method 202[21],采样与分析包括6个步骤。
1)采样前,用去离子水对采样枪、采样连接管、气水分离器进行清洗。
2)启动采样仪,对清洗后的采样枪、采样连接管、气水分离器进行抽空气风干。
3)在采样过程中,采样枪的把手端向下倾斜5°~10°,采样连接管以向下倾斜的方式连接采样枪与气水分离器。
4)采样后,保存滤膜或滤筒的同时,收集从采样枪、采样连接管、气水分离器中被采烟气中冷凝出的冷凝液。
5)采样后,用去离子水对采样枪、采样连接管、气水分离器进行清洗,并收集清洗液。
6)用去离子水溶解滤筒或滤膜上的可过滤态硫酸铵,再利用阳离子色谱仪测定溶液中
NH+4 量,计算脱硫塔出口可过滤颗粒态(FPM)硫酸铵浓度;同时,利用阳离子色谱仪测定冷凝液与清洗液中NH+4 量,计算脱硫塔出口可凝结颗粒态硫酸铵(CPM)浓度(以硫酸铵与亚硫酸铵形式存在的可凝结颗粒,均计算成硫酸铵颗粒),各个条件下平行采样2次,取平均值。3. 结果分析与讨论
3.1 烟气处理量
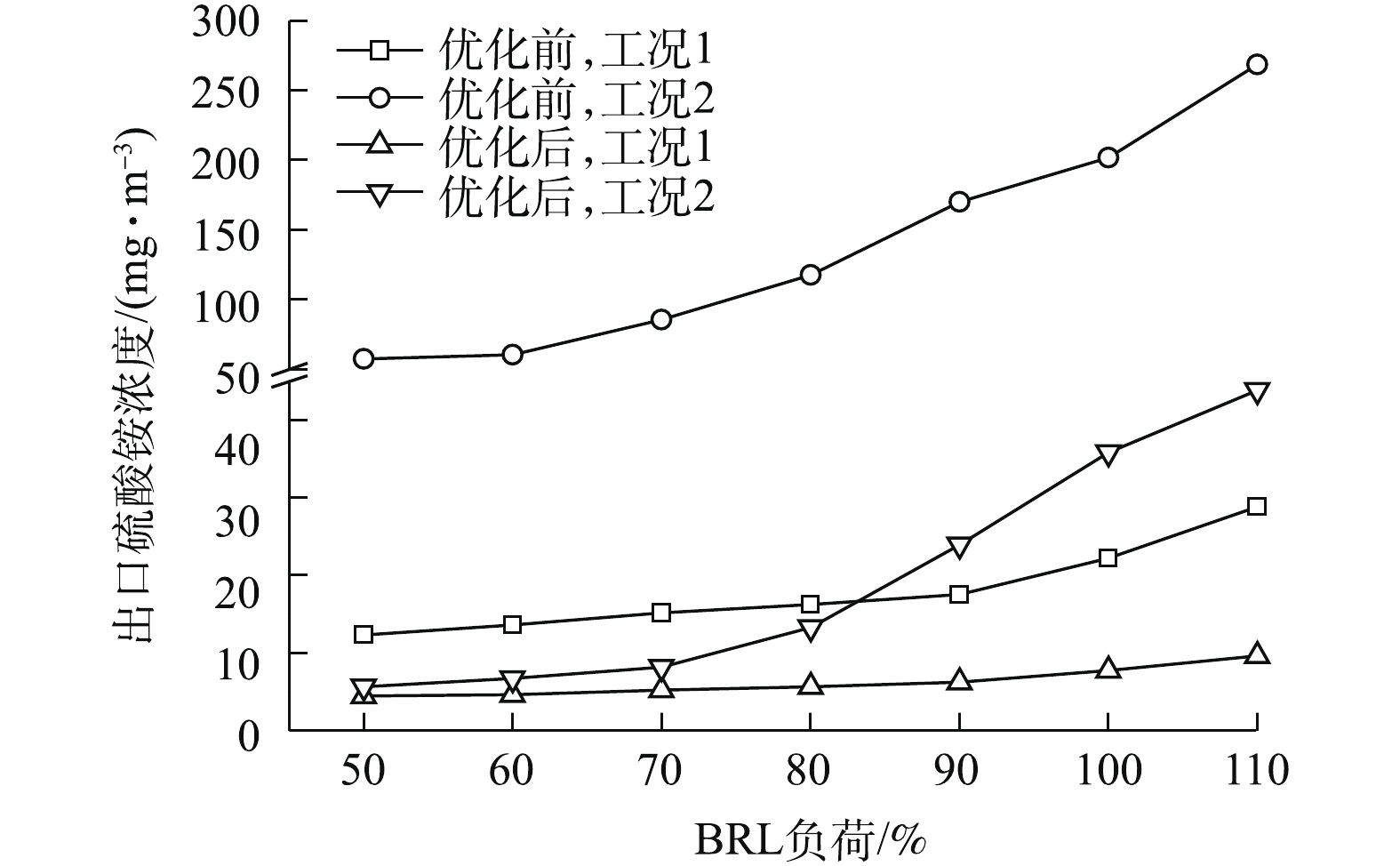
在不同负荷下,脱硫塔结构优化前、后出口硫酸铵浓度如图2所示。可以看出,在结构优化前的工况1(吸收塔浆液含固量为25%)条件下,随锅炉负荷50%~90% BRL,出口硫酸铵浓度缓慢由12.35 mg·m−3缓慢增长至17.56 mg·m−3,但随锅炉负荷再往上增加时,出口硫酸铵浓度增长速度变大,锅炉负荷110% BRL时,其出口为28.84 mg·m−3。为进一步分析两者间的变化关系,设计了工况2(吸收塔浆液含固量为55%)实验。在结构优化前的工况2条件下,随锅炉负荷的增长,出口硫酸铵浓度增长速度逐渐变大,其浓度由57.53 mg·m−3增长为268.54 mg·m−3,增长到4.67倍。即吸收塔内空塔气速的增长,导致出口硫酸铵浓度在复杂的吸收塔因素影响下,表现为增长的趋势,且增长趋势随吸收塔浆液含固量的增加而增大。
在结构优化后的工况1条件下,出口硫酸铵浓度随负荷变化很小,但依然呈逐渐上升的趋势,由4.45 mg·m−3增长至9.61 mg·m−3,增长到2.16倍。在结构优化后的工况2条件下,出口硫酸铵浓度随负荷的变化趋势与结构优化前的工况2条件下类似(锅炉110% BRL负荷下的点除外),为递增2次函数关系,出口硫酸铵浓度由5.65 mg·m−3增长为43.85 mg·m−3,增长到7.76倍,再次证明了优化前得出的出口硫酸铵浓度随负荷与吸收塔浆液含固量变化而变化的趋势。
在锅炉110% BRL负荷下,结构优化前、后,工况2出口硫酸铵浓度由原来的268.54 mg·m−3降为43.85 mg·m−3;工况1出口硫酸铵浓度由原来的28.85 mg·m−3降为9.61 mg·m−3。这表明:结构优化后性能改善效果明显;但在工况2条件下,锅炉90%~110% BRL负荷时出口硫酸铵浓度仍然无法达到≤20 mg·m−3的要求(规范中要求的颗粒物排放浓度不包括冷凝液中离子态的硫酸铵浓度)。
3.2 吸收塔浆液含固量
吸收塔浆液含固量测定见式(1)。
φ=m0m2−m1×100% (1) 式中:
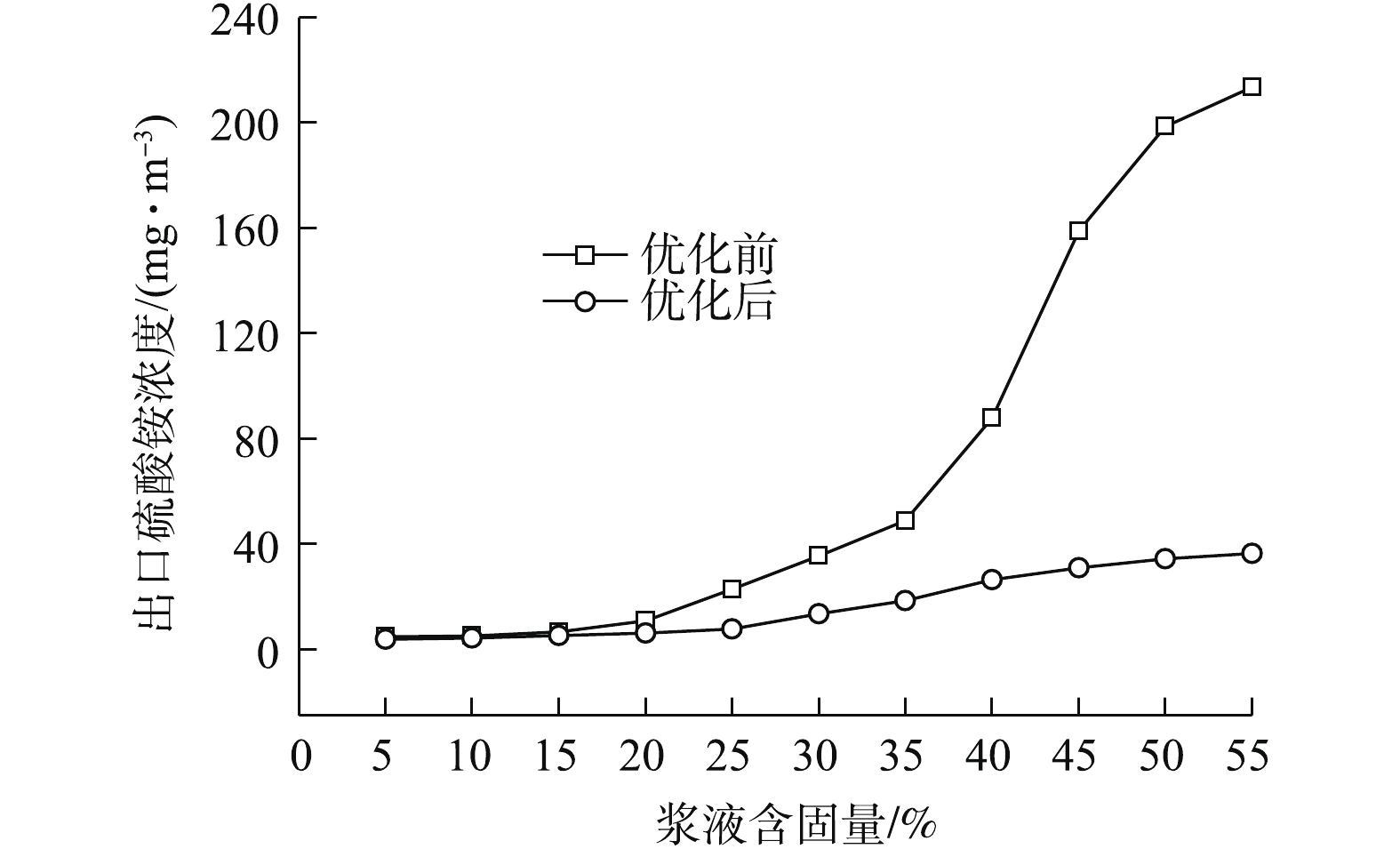
φ 为浆液含固量,%;m1 为取样前容器质量,g;m2 为取样后容器与浆液总质量,g;m0 为浆液烘干后析出的硫酸铵质量,g。在锅炉100% BRL负荷下,结构优化前、后,吸收塔浆液含固量对出口硫酸铵浓度的影响如图3所示。可以看出,随着浆液含固量的增加,出口硫酸铵浓度呈递增趋势,增长速度由小变大,再变小;结构优化前,出口硫酸铵浓度由5%含固量下的4.74 mg·m−3增长至55%含固量下的213.57 mg·m−3;结构优化后,其浓度由5%含固量下的3.85 mg·m−3增长至55%含固量下的36.64 mg·m−3。同时,5%~20%是出口硫酸铵浓度缓慢增长的含固量区间;25%~40%是其快速增长的含固量区间;45%~55%是其增长速度下降的含固量区间。
根据烟气与浆液间热量传递守恒定律,吸收塔浆液水的理论蒸发量计算方法见式(2)~式(4)。
M=(Q1+Q2)(T3−T4)β+δ (2) Q1=V(1−ε)ρ(T1−T2)α (3) Q2=18×Vε22.4(T3−T4)β (4) 式中:
Q1 为干烟气放热量,kJ·h−1;Q2 为烟气水蒸汽放热量,kJ·h−1;V 为吸收塔入口烟气量,m3·h−1;ε 为入口烟气湿度;ρ 为烟气密度,kg·m−3;T1 为入口烟气温度,℃;T2 为烟气洗涤降温区后的烟气温度,℃;α 为烟气比热容;T3 为吸收塔浆液温度,℃;T4 为工艺水温度,℃;β 为水的比热容,kJ·(kg·K)−1;δ 为水的汽化潜热,kJ·kg−1。在负荷100% BRL时,
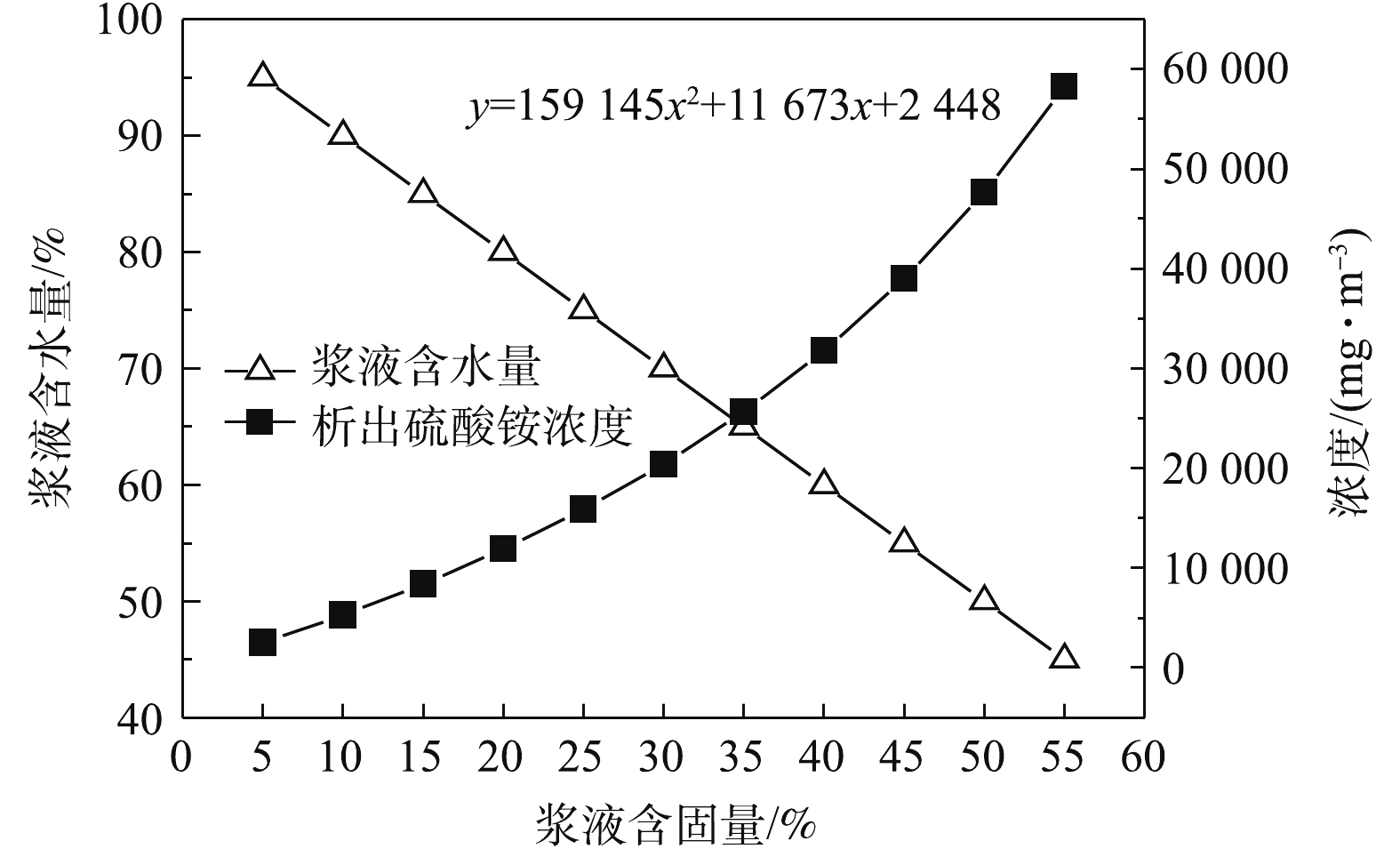
V =595 894 m3·h−1(标况、湿态、实际氧),ε =8.2%,ρ =1.29 kg·m−3(标况、湿态、实际氧),T1 =131 ℃,T2 =60 ℃,α =1.0 kJ·(kg·K)−1,T3 =51 ℃,T4 =20 ℃,β =4.2 kJ·(kg·K)−1,δ =2 258.77 kJ·kg−1。在上述条件下,吸收塔浆液水的理论蒸发量为26 069.6 kg·h−1。在不同浆液含固量下,理论析出硫酸铵的浓度如图4所示,理论析出硫酸铵浓度与浆液含固量为二次函数
y=159145x2+11673x+ 2448 关系。理论析出硫酸铵浓度由5%含固量下的2 508 mg·m−3增长至55%含固量下的58 248 mg·m−3,而这个过程中吸收塔浆液中析出的NH3浓度变化不大。结合图3推论出:在工业实践的实验工况条件下,吸收塔浆液蒸发导致硫酸铵析出是氨法脱硫工艺出口硫酸铵浓度的主导因素,而通过浆液中析出气态NH3反应生成的硫酸铵对出口硫酸铵浓度影响不大。依据硫酸铵的溶解特性,当含固量小于45%时,浆液中的硫酸铵均以离子态存在,在热交换过程中,小粒径浆液滴水分蒸发后析出硫酸铵晶体,被烟气带走或部分水分的蒸发,导致粒径变更小后直接被烟气带走;大粒径液滴则被蒸发部分水分后,掉入循环浆液池。随着含固量的增加,浆液滴含水量逐渐降低,即水能被完全蒸发的浆液滴临界粒径逐渐增大,使更多硫酸铵晶体颗粒或小粒径浆液滴随烟气带走,这是图3中5%~45%含固量区域,出口硫酸铵浓度增长速度越来越快的原因;当含固量大于45%时,多余硫酸铵会自然结晶出来(60 ℃下饱和硫酸铵浆液的含固量为46.64%),浆液滴中的硫酸铵晶体有利于浆液滴水分蒸发过程中,以其为晶核生成大粒径的硫酸铵颗粒。在晶体粒径大的情况下,更易被工艺水淋洗与除雾器捕捉而不被烟气带走,这是图3中45%~55%含固量区域出口硫酸铵浓度增长速度下降的原因。
3.3 入口烟气温度
由式(2)可以推导出:喷淋浆液水分蒸发量与进、出口烟气温度密切相关。为对比论证浆液蒸发量对吸收塔出口硫酸铵浓度的影响,在锅炉冷态(锅炉燃烧器改造后,进行冷态风量标定实验期间)、热态以及热态+事故喷淋3个运行条件下进行对比实验,出口硫酸铵浓度如表2所示。在冷态工况下,锅炉50%与80% BRL负荷,出口硫酸铵颗粒浓度均很小。浆液含固量为25%时,冷态工况约为热态工况下出口硫酸铵浓度的20%;浆液含固量为45%时,冷态工况约为热态工况下出口硫酸铵浓度的5%。浆液含固量上升,占比下降的主要原因:1)热态工况下出口硫酸铵浓度增长较大;2)优化结构可对随烟气带走的硫酸铵进行有效地去除。同时,在冷态、浆液含固量为45%工况下,80% BRL负荷出口硫酸铵浓度显著大于50% BRL负荷,这是因为少数小粒径浆液被烟气流速携带所导致。
表 2 出口硫酸铵浓度与入口烟气温度的关系Table 2. Relationship between the ammonium sulfate concentration of outlet and the flue gas temperature of inletBRL负荷/% 锅炉运行状态 入口烟气温度/℃ 出口硫酸铵浓度/(mg·m−3) 25%含固量 45%含固量 50 冷态 31 2.61 2.68 50 热态 105 13.58 48.82 50 热态+事故喷淋 68 5.86 12.74 80 冷态 31 3.39 5.35 80 热态 125 17.13 98.46 80 热态+事故喷淋 75 6.32 21.53 在锅炉50%与80% BRL负荷、浆液含固量25%条件下,热态+事故喷淋实验工况下,出口硫酸铵浓度分别为热态工况下的43.15%与36.89%;在锅炉50%与80% BRL负荷、浆液含固量45%条件下,热态+事故喷淋实验工况下,出口硫酸铵浓度分别为热态工况下的26.10%与21.87%,即随着浆液含固量的增加,事故喷淋对减少脱硫出口硫酸铵浓度的效果呈快速上升趋势。同时,随着锅炉负荷的增加,事故喷淋对减少脱硫出口硫酸铵浓度的效果呈缓慢上升趋势。
3.4 工艺水淋洗水量
工艺水淋洗水量对出口硫酸铵浓度的影响如表3所示。可以看出,优化前,在浆液含固量为25%与55%的情况下,停止工艺水淋洗,出口硫酸铵浓度较运行工艺水淋洗分别增加至1.67倍与1.96倍。这是因为运行工艺水淋洗不仅可以对脱硫后的烟气进行洗涤,通过颗粒间的碰撞来脱除烟气携带的硫酸铵颗粒,而且能对多孔填料区域的斜板通道进行冲洗并在表面形成液膜,增强对硫酸铵颗粒的附着与去除。优化后,在浆液含固量为25%与55%情况下,停止1层工艺水淋洗,出口硫酸铵浓度较运行2层工艺水淋洗分别增加至1.67倍与1.84倍;停止2层工艺水淋洗,出口硫酸铵浓度分别较运行2层工艺水淋洗增加至4.47倍与6.24倍。增长倍数间的差异主要与喷淋水量与多孔填料区域材料的变化有关。同时,从增长倍数可以得出:浆液含固量越高,停止工艺水淋洗对出口硫酸铵浓度增长越大,这种趋势在结构优化前、后均存在。
表 3 出口硫酸铵浓度与工艺水淋洗水量的关系Table 3. Relationship between the ammonium sulfate concentration of outlet and the leaching amount of fresh water实验装置 淋洗水量/(t·h−1) 出口硫酸铵浓度/(mg·m−3) 含固量25% 含固量55% 优化前 0 40.54 425.78 优化前 450 24.34 216.95 优化后 0 32.48 223.42 优化后 670 12.15 65.94 优化后 670(2层) 7.26 35.79 基于上述分析,为降低结构优化后吸收塔向硫酸铵生产线供浆液时(吸收塔浆液含固量为50%~55%)出口硫酸颗粒的浓度,提出如下建议:在锅炉负荷低于80% BRL时,进行往硫酸铵生产线供浆液,同时,必须运行2层工艺水淋洗;在锅炉100%~110% BRL负荷时,维持吸收塔浆液低含固量运行。为节约能耗,提出如下建议:在锅炉负荷低于80% BRL、吸收塔浆液含固量低于35%时,可以只运行1层工艺水淋洗喷淋。采取上述运行建议后,出口硫酸铵浓度均小于15 mg·m−3,其中的颗粒物浓度均小于10 mg·m−3。
依据浆液蒸发量对出口硫酸铵浓度的影响,提出系统优化的2种新思路。
1)通过改造入口烟道内的事故喷淋系统,减小液滴雾化粒径,并增加液滴分散度,实现对烟气进行预降温的目的,进而减少吸收塔浆液的蒸发量,减少硫酸铵的析出量。
2)通过增大吸收塔浆液输出泵的出力,在吸收塔浆液含固量高的情况下,快速将浆液排入事故浆液箱,再通过事故浆液箱以正常速度向硫酸铵生产线供浆液,从而缩短在吸收塔浆液含固量高情况下的运行时间,减少污染物的排放。
4. 结论
1)常规烟尘采样方法不能完全捕集氨法脱硫塔出口颗粒态与气溶胶态的硫酸铵,采样管与气液分离器冷凝水中硫酸铵浓度约占滤筒或滤膜颗粒物浓度的50%~60%。
2)随锅炉负荷的增长,出口硫酸铵浓度表现为增长速度逐渐加快的趋势,且吸收塔浆液含固量越大,其增长速度越快;工艺水喷淋能有效降低出口硫酸铵浓度,吸收塔浆液含固量越大,其净化效果越好。
3)吸收塔浆液含固量由5%增至55%,结构优化前出口硫酸铵浓度由4.74 mg·m−3增至213.57 mg·m−3;结构优化后由3.85 mg·m−3增长至36.64 mg·m−3,浆液蒸发导致硫酸铵析出是氨法脱硫工艺出口硫酸铵生成的主要原因,浆液含固量与入口烟气温度是影响硫酸铵析出量的关键因素。
4)浆液含固量为25%与45%条件下,冷态工况出口硫酸铵浓度分别约为热态工况下的20%与5%;热态工况下,随浆液含固量的增加,事故喷淋对减少出口硫酸铵浓度的效果呈快速上升趋势;随锅炉负荷的增加,事故喷淋对减少脱硫出口硫酸铵浓度的效果呈缓慢上升趋势。
-
表 1 不同曝气量下MBBR和膜出水状况
Table 1. Average characteristics of the MBBR and MBR effluent water at different aeration rates
曝气量/(L·h−1) MBBR出水 膜出水 COD/(mg·L−1) NH+4 浊度/NTU DO/(mg·L−1) COD/(mg·L−1) NH+4 浊度/NTU DO/(mg·L−1) 50(0~20 d) 96.24±19.61 16.82±4.21 10.11±2.55 2.56±0.25 63.73±10.11 13.21±2.15 0.51±0.29 3.12±0.51 100(21~40 d) 55.67±10.36 2.21±0.98 5.46±1.35 3.76±0.47 42.55±7.32 1.84±0.54 0.36±0.17 4.83±0.76 150(41~60 d) 41.54±9.61 1.21±0.32 7.13±2.55 4.65±0.65 24.28±3.16 1.02±0.21 0.42±0.25 5.81±1.02 -
[1] 薛怡亭, 党岩, 郭慧雯, 等. 外置管式MBR处理垃圾焚烧渗沥液中的膜污染[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(3): 1269-1275. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150346 [2] 李春杰, 何义亮, 欧阳铭. 错流膜生物反应器水力清洗特性研究[J]. 环境科学, 1999, 20(2): 57-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.1999.02.014 [3] MENG F G, ZHANG S Q, OH Y, et al. Fouling in membrane bioreactors: An updated review[J]. Water Research, 2017, 114: 151-180. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.02.006 [4] 于伯洋, 苏帆, 孙境求, 等. 电控膜生物反应器技术回顾与展望[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(12): 4215-4224. [5] MONSALVO V M, LOPEZ J, SOMER M M, et al. Short-term fouling control by cyclic aeration in membrane bioreactors for cosmetic wastewater treatment[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2015, 56: 3599-3606. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2014.974217 [6] BUETEHORN S, VOLMERING D, VOSSENKAUL K, et al. CFD simulation of single- and multi-phase flows through submerged membrane units with irregular fiber arrangement[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 384: 184-197. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2011.09.022 [7] FRAPPART M, MASSE A, JAFFRIN M Y, et al. Influence of hydrodynamics in tangential and dynamic ultrafiltration systems for microalgae separation[J]. Desalination, 2011, 265: 279-283. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.061 [8] DING A, LIANG H, LI G B, et al. Impact of aeration shear stress on permeate flux and fouling layer properties in a low pressure membrane bioreactor for the treatment of grey water[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 510: 382-390. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2016.03.025 [9] BRAAK E, ALBASI C, ANNE-ARCHARD D, et al. Impact of aeration on mixed liquor in submerged membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment: From macro to local scale[J]. Chemical Engineering and Technology, 2017, 40(8): 1453-1465. doi: 10.1002/ceat.201600470 [10] 国家环境保护局. 水和废水监测分析方法(第四版)[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [11] LIU H, FANG H H P. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2002, 95: 249-256. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(02)00025-1 [12] DUBOIS M, GILLES K A, HAMILTON J K, et al. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1956, 28: 350-356. doi: 10.1021/ac60111a017 [13] FRØLUND B, PALMGREN R, KEIDING K, et al. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin[J]. Water Research, 1996, 30: 1749-1758. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(95)00323-1 [14] LU H, XUE Z, SAIKALY P, et al. Membrane biofouling in a wastewater nitrification reactor: Microbial succession from autotrophic colonization to heterotrophic domination[J]. Water Research, 2016, 88: 337-345. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.013 [15] 王俊杰, 张姚, 刘清华, 等. 连续/间歇曝气下MBBR-亚硝化生物膜特性[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(1): 261-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.01.029 [16] VERA L, DELGADO S, ELMALEH S. Dimensionless numbers for the steady-state flux of cross-flow microfiltration and ultrafiltration with gas sparging[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2000, 55: 3419-3428. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2509(00)00016-6 [17] BRAAK E, MARION A, SYLVIE S, et al. Aeration and hydrodynamics in submerged membrane bioreactors[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 379: 1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2011.06.004 [18] ZHANG K S, CUI Z F, FIELD R W. Effect of bubble size and frequency on mass transfer in flat sheet MBR[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2009, 332: 30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2009.01.033 [19] NEEMANN F, ROSENBERGER S, JEFFERSON B, et al. Non-covalent protein-polysaccharide interactions and their influence on membrane fouling[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 446: 310-317. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2013.06.054 [20] 李珊, 段亮, 周北海, 等. 不同泥龄MBR中溶解性微生物代谢产物对膜污染的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(6): 2731-2738. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150631 -





 下载:
下载: