-
随着工农业的发展,水环境的污染状况依然严峻,而人类对环境水体及饮用水水质要求又日益提高,由紫外与氯联合组成的紫外/氯高级氧化技术能产生HO·、Cl·和O−·等强氧化性自由基[1] (式(1)),能有效降解水中药物和个人护理产品等有机污染物[2-7]及氨氮等无机污染物[8-9],已迅速发展为一种高效水处理技术,日益受到研究者的关注,具有广阔的应用前景。
在紫外/氯高级氧化过程中,氯浓度对处理效果影响很大,氯浓度越高,处理效果越好[2-8]。但氯的浓度在处理过程中可能会由于光解作用而不断降低,直接影响处理效率。已有研究发现,在采用紫外消毒的水处理工艺中,经过预氯化的水进入紫外消毒单元时,残余的氯会吸收紫外光,并在紫外处理单元发生光解,导致氯浓度明显降低[10-11],而且降低程度随水质变化较大,并对紫外剂量、消毒效果、出水水质均产生了一定的影响[11]。根据这些研究结果可推断紫外/氯高级氧化过程中氯的浓度也将随紫外剂量增加而降低,并且在不同工艺及水质条件下氯的分解程度可能具有较大差异,从而影响紫外/氯工艺的处理效果。
目前,紫外处理系统中应用最广泛的是低压汞灯(LP)和中压汞灯(MP)。前者主要发射254 nm 的单色光,而后者的发射光谱为一段连续光谱(200~600 nm)。与LPUV相比,MPUV具有波谱范围广,功率更高,在处理相同水量达到同等效果时,所需的反应器体积小,灯管数量少,占地面积省等优点。因此,在实际中使用量较LPUV 更多(约38%采用LPUV,62%采用MPUV)。本研究通过测定不同中压紫外剂量下氯浓度的变化,考察了中压紫外/氯高级氧化过程中氯的分解规律,并探讨不同水处理工艺参数及水质条件对氯分解的影响,根据所获得的数据可以估算不同条件下余氯浓度,为中压紫外/氯高级氧化技术及预氯化-中压紫外消毒过程提供基础数据和技术支持,获得最佳水处理效果。
全文HTML
-
中压紫外/氯高级氧化光照实验采用紫外平行光束仪进行,光源为贺利氏中压紫外灯(DQ3024,3.5 kW,功率可调节),反应器为6 cm培养皿,放置于平行光束正下方的磁力搅拌器上,搅拌器下设升降台,用于调节高度。实验开始前对紫外平行光束仪进行预热,待发射光强稳定后开始实验。取配制好的反应液20 mL于培养皿中,打开紫外光路的同时按照所需浓度投加次氯酸钠溶液开始反应,照射一定时间后,移出一定量水样立即测量其吸光度值,计算氯的浓度。整个实验过程用磁力搅拌使反应液呈完全混合状态,但又不至于引起明显的液面变化。
-
反应液用2 mmol·L−1磷酸二氢钠配制(无机离子的影响实验中为10 mmol·L−1),并用氢氧化钠调节pH至预定值。实验中所用氯、磷酸二氢钠、氢氧化钠、腐殖酸、氯化钠、硝酸钠、碳酸氢钠及硫酸钠等药品均为分析纯及以上。
紫外光剂量采用International Light ILT1700辐照计测定光强后,根据国际紫外线协会提供的计算表格进行计算。pH用FE28-S型 pH计(梅特勒托利多公司)测定,使用前用标准缓冲液标定。氯的浓度使用北京普析通用公司的T6新世纪紫外可见分光光度计参照中华人民共和国国家环境保护标准HJ 586-2010 DPD分光光度法测定。
-
用一级反应动力学方程(式(2))拟合氯的分解速率。
式中:C0、Ct分别为初始及反应t时间的氯浓度,mg·L−1;kobs为一级表观速率常数,cm2·mJ−1;F为中压紫外剂量,mJ·cm−2。
1.1. 光照实验
1.2. 试剂、仪器和测试方法
1.3. 计算方法
-
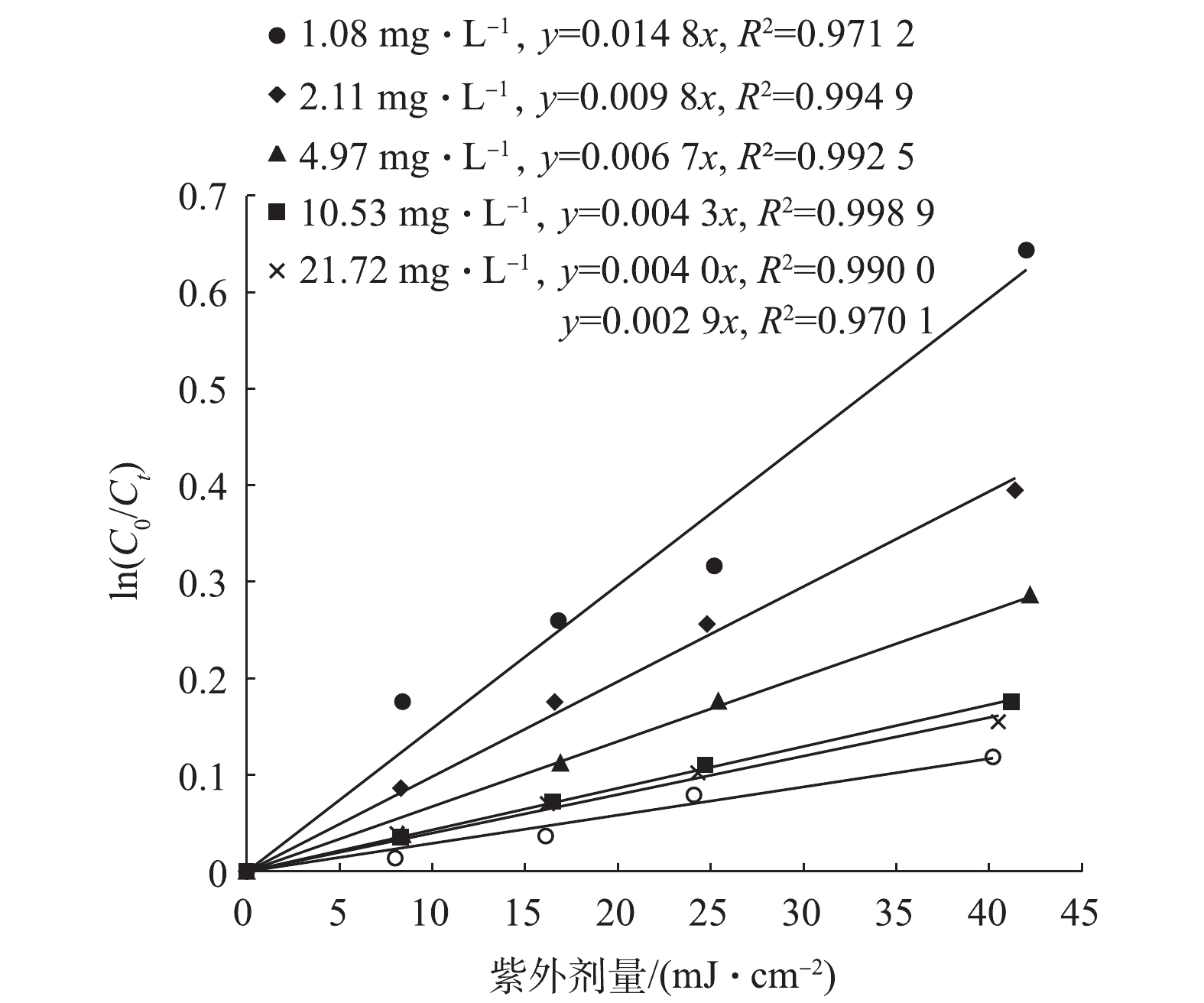
在紫外/氯高级氧化技术使用中,投氯量都是影响消毒效果的重要因素之一。因此,在pH = 7.25、温度为14 ℃条件下,考察了不同浓度自由氯在中压紫外下的分解规律,结果如图1所示。由图1可以看出,自由氯在不同浓度条件下的分解均遵循一级动力学,随着氯浓度的升高,自由氯的分解速率常数kobs降低。当氯初始浓度为1.08 mg·L−1时,kobs为0.014 8 cm2·mJ−1;氯浓度升高到10.53 mg·L−1时,kobs下降到0.004 3 cm2·mJ−1,分解速率常数降低了71%,之后氯浓度的增加导致kobs降低的程度有所减缓。其他类物质,如磷酰基乙酸、哒嗪硫磷、普萘洛尔、四环素及2, 4-D 丁酯等[12-16]在紫外光下的降解也具有相同的规律。这可能是由于在光降解过程中,单位时间单位光照面积内,光强一定时,进入反应体系的光子数相同,氯浓度越大,吸收了光子能量的氯占氯总浓度比例越小,导致光解速率常数降低。通过测定不同浓度的氯在中压紫外波长范围内的吸光度发现,吸收了光子能量的氯(以吸光度表征,吸光度越大吸收了光子能量的氯分子越多)占氯总浓度比例确实随氯总浓度增大而减小,以反应液在293 nm (OCl−的最大吸收波长) 处的吸光度为代表,当氯浓度从1.08 mg·L−1升高到51.31 mg·L−1,该比例从0.002 778降低为0.001 325。该结果与上述推测一致。
-
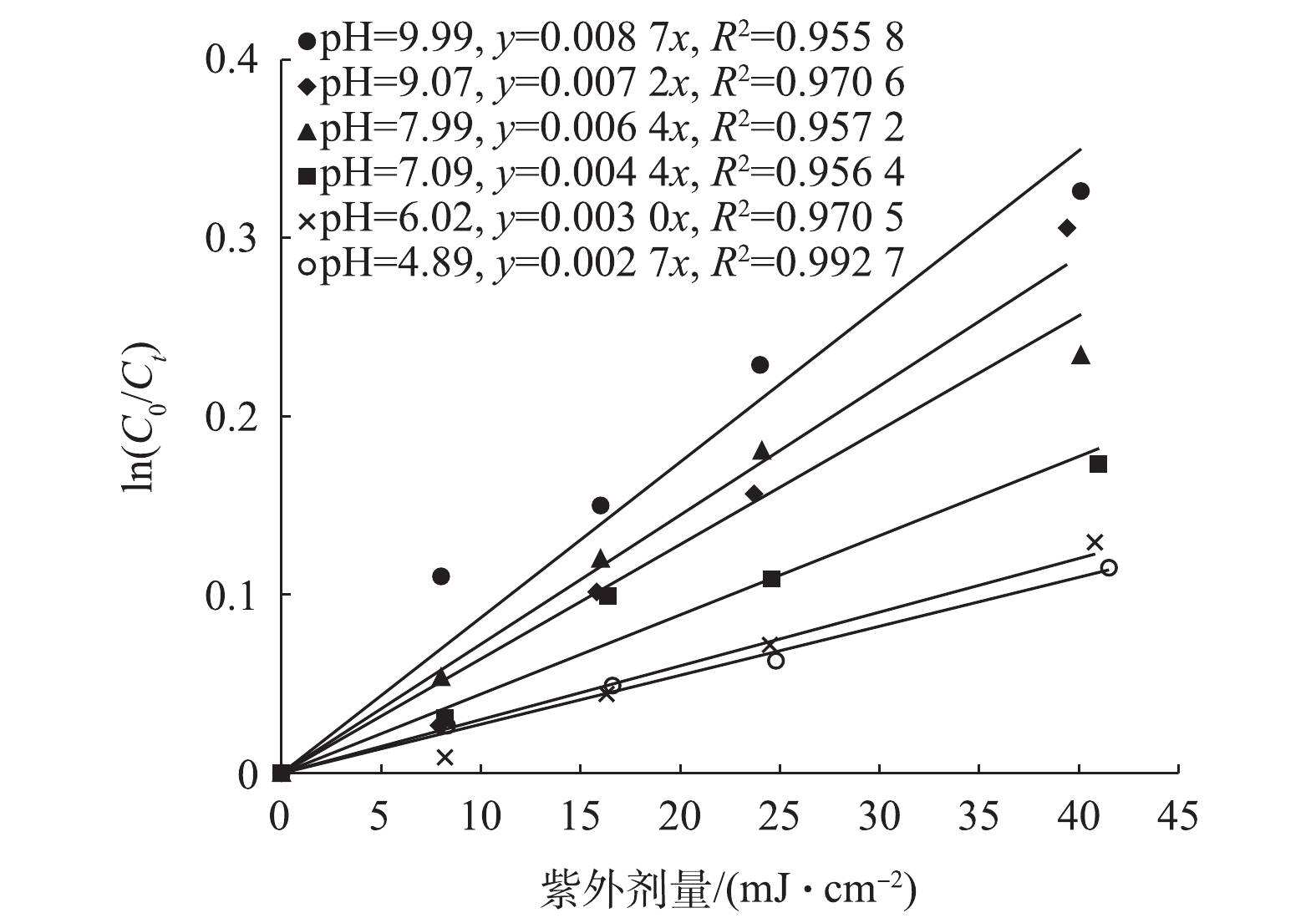
pH一直被认为是水处理中最重要的指标之一,一般水体pH为6~9。在常规水处理条件下,自由氯的存在形态以HOCl和OCl−为主,其相对浓度强烈依赖于pH。由于不同种类的自由氯的吸收光谱和摩尔吸收系数不同,可能导致不同pH条件下,氯的中压紫外光解速率不同。已有研究[17]发现,在低压紫外下pH对氯的光解几乎没有影响,但在太阳光下氯的光解速率受pH影响较大,说明不同光源对氯的光解规律不同。因此,在氯初始浓度为20 mg·L−1,温度为16 ℃条件下,考察了不同pH条件下自由氯在中压紫外线下的分解规律,结果如图2所示。
由图2可以看出,当pH低于6时,分解速率变化较小,之后随着pH升高,自由氯的分解速率明显升高。当pH=6时,氯分解的一级动力学速率常数kobs为0.003 cm2·mJ−1,氯分解一半的紫外剂量为231 mJ·cm−2;pH升高到9时,kobs升高为0.007 2 cm2·mJ−1,分解一半所需的剂量降低为96 mJ·cm−2,分解速率提高了1.4倍。自由氯在pH较低时,主要以HOCl的形式存在;而高pH条件下则主要以OCl−的形式存在,说明OCl−更容易被中压紫外光解。该结果与氯在太阳光下的光解规律[17]相同。
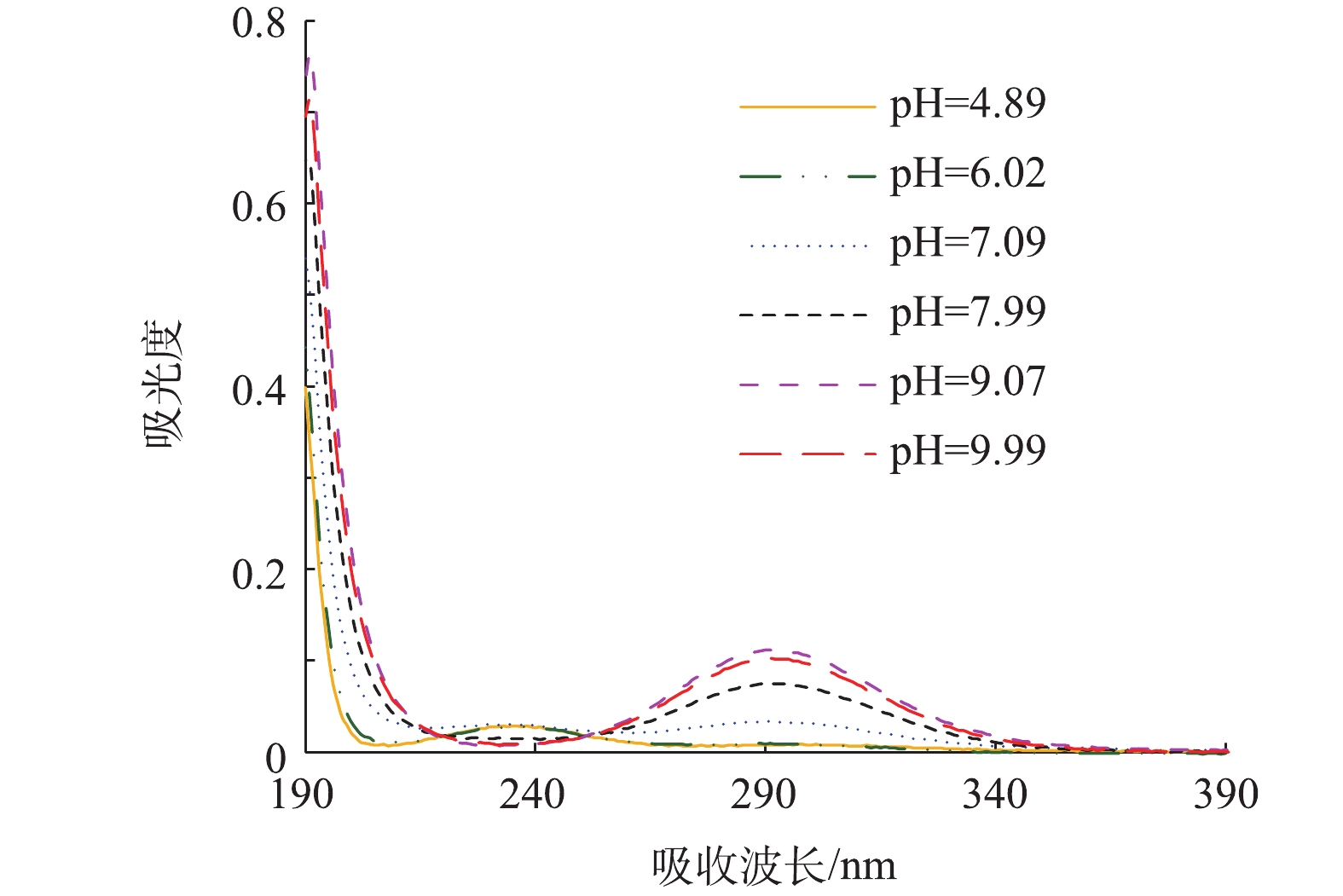
为进一步分析其机理,本研究测定了不同pH条件下相同浓度自由氯溶液的光谱扫描图(图3),可以看出OCl−的吸收峰为292 nm,且吸收峰较宽,峰值随pH的增大而升高;而HClO的吸收峰为236 nm,其峰值随pH降低而升高,并且OCl−的摩尔吸光系数(365±8) L·(mol·cm)−1,要远大于HOCl (101±2) L·(mol·cm)−1[10]。而中压紫外灯在292 nm附近的辐照强度要明显大于236 nm附近的辐照强度。水中物质通常对其最大吸收波长的光吸收最强,也就是说OCl−可吸收的紫外剂量也相应更大。因此,pH越大,OCl−的浓度比例越大,能够吸收和可供吸收的光能量都要大于HOCl,导致其光解速率明显快于HOCl。
此外,有研究结果[1]表明,氯在紫外照射下产生的HO·和Cl·会与HOCl和ClO−发生反应,且与ClO−反应的速率常数更大,反应如式(3)~式(6)所示。另有研究[18-19]发现,HOCl的紫外光解过程是可逆自由基反应,而ClO−的紫外光解过程不可逆,不会生成HClO或者ClO−,这些因素都会导致HOCl比ClO−的总体降解速率低。
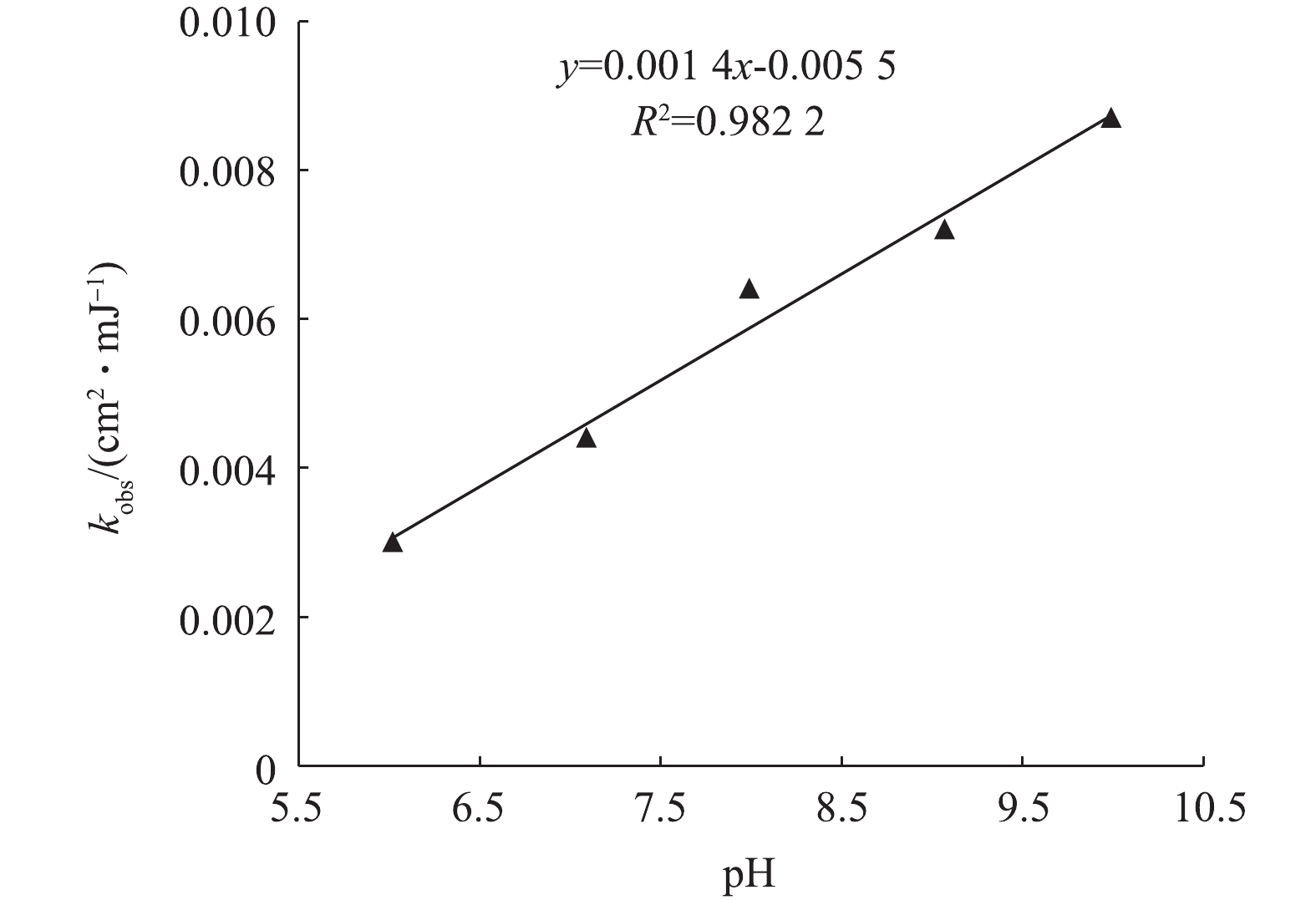
中压紫外/氯高级氧化技术在降解水中有机物时,通常在低pH条件下处理效果较好[3-7],一般认为是产生的自由基种类不同导致的,根据本实验结果表明氯浓度的大小可能也是影响因素之一,即:低pH条件下氯的分解量少,能保持较高的自由基浓度,从而保持对有机物的高效降解。为保证中压紫外/氯高级氧化技术的高效率,需保持一定的氯浓度,根据氯分解速率常数kobs可以估算各紫外剂量下(或反应时间)的氯浓度。将pH在6~10内的kobs与pH作图(图4),发现该范围内pH与kobs成线性关系,根据此线性方程可以推算在此范围内任意pH对应的氯分解速率,进而计算水中余氯,从而为氯投加量提供数据支持。
-
腐殖酸物质在自然界中广泛存在,腐殖质是天然水体中有机物的主要组成部分,约占水中总有机物的50%~80%[20]。已有研究发现在低压紫外下腐殖酸会作为一种内部过滤器抑制氯的分解[1],而在没有紫外光条件下腐殖酸的存在又会加快氯的衰减[21-22]。另外腐殖酸也是一种光敏化剂,并且在很宽的波谱范围内具有较强的吸收能力,而中压紫外发射的光谱更广,腐殖酸能吸收到更多的光能量,因此,腐殖酸的存在也可能会对氯在中压紫外下的分解具有较大影响。在pH为7.25,温度为25.9 ℃,氯浓度为4.6 mg·L−1条件下,给水样中投加不同浓度的腐殖酸,分别测定氯在不同中压紫外剂量下的余量,以明确具体影响规律。
由于腐殖酸在测定氯浓度采用的515 nm波长处有吸收,而且会被紫外光分解[23],因此,腐殖酸的存在可能对氯浓度的测定产生影响,为排除该影响。测定了不同照射时间时,水样(即其中的腐殖酸)在515 nm处的吸光度值,结果如表1所示。
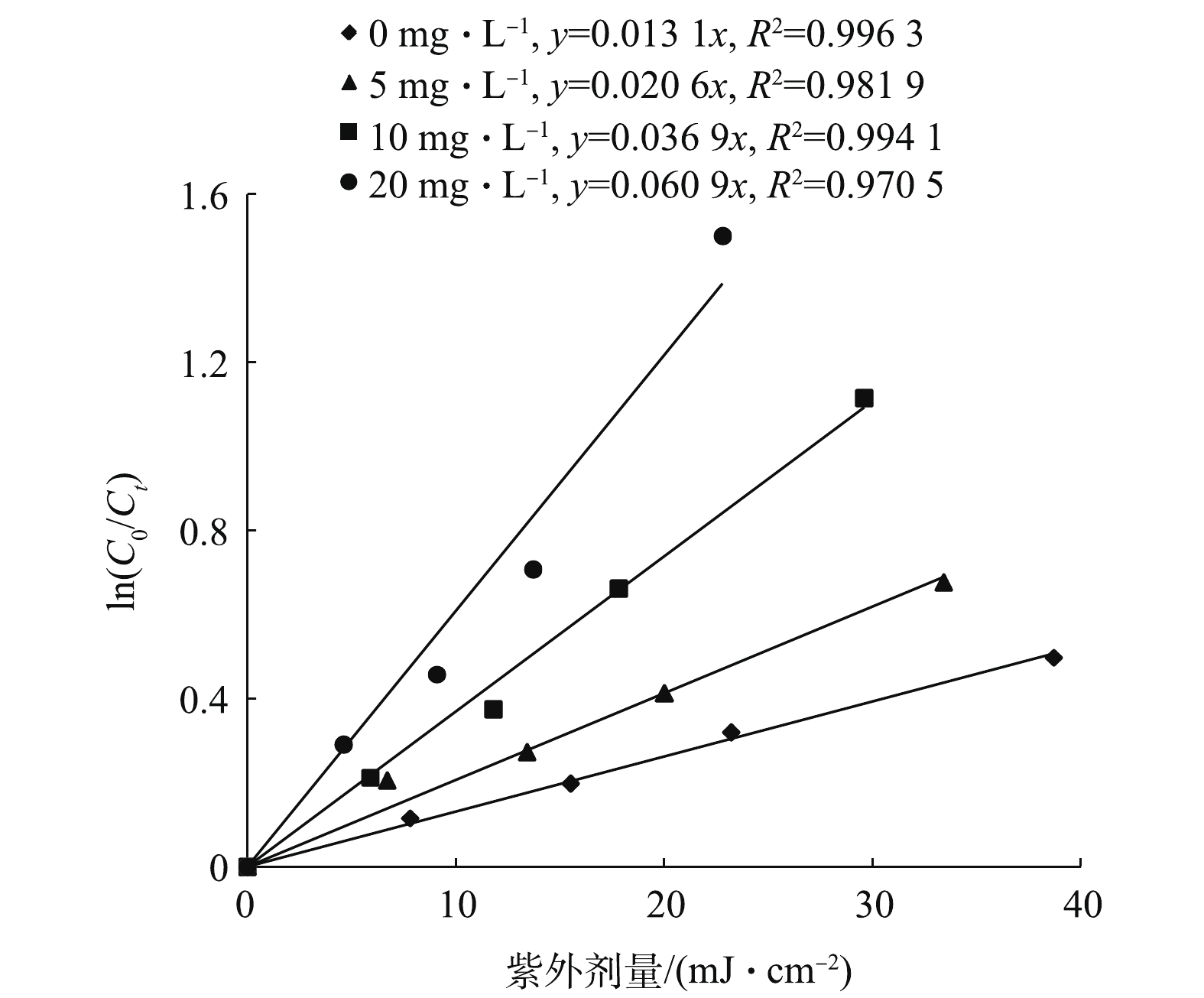
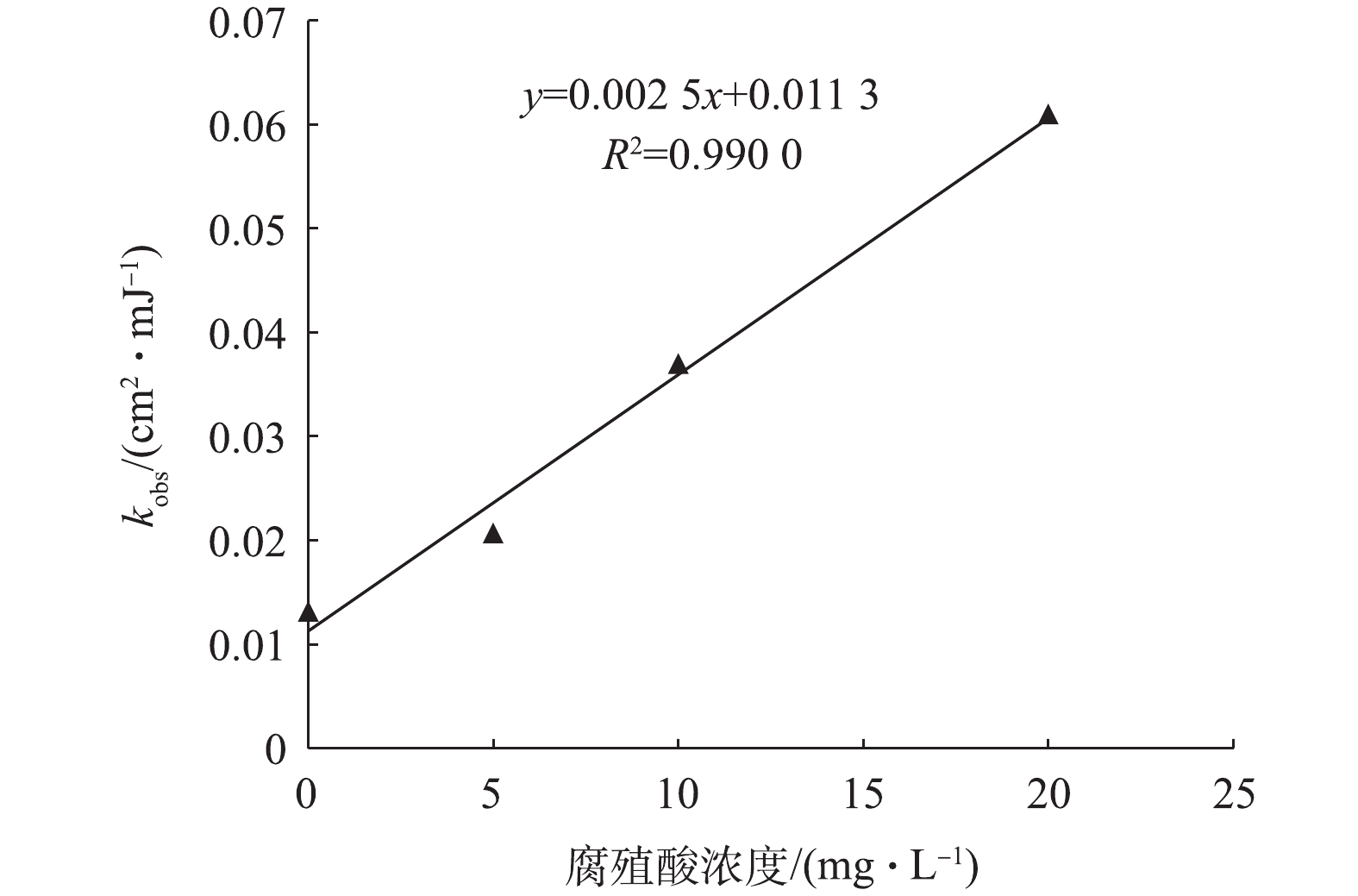
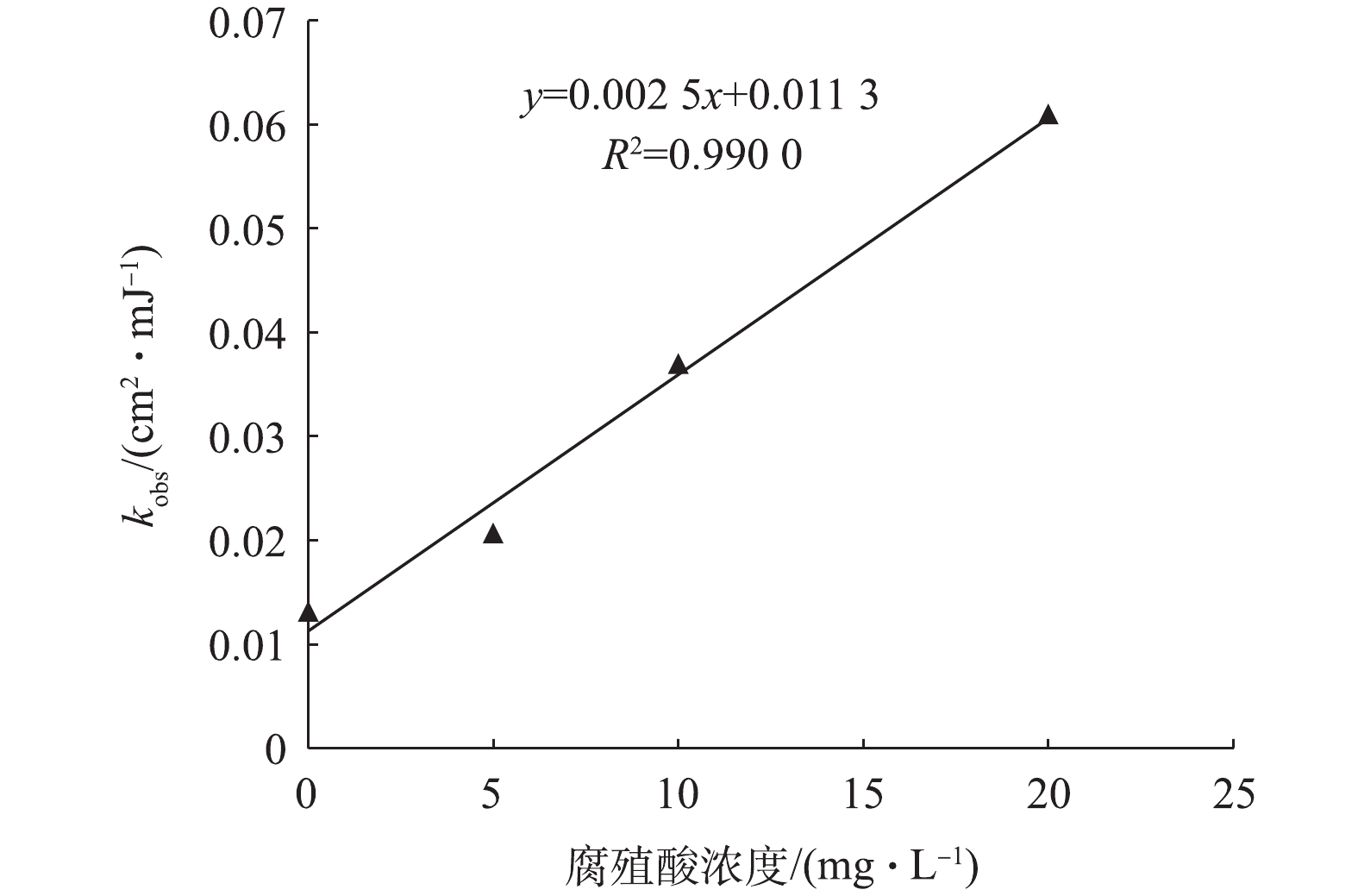
由表1可知,在本实验条件下,腐殖酸在515 nm处的吸光度随照射时间增加而降低,说明腐殖酸在中压紫外下发生明显降解,直接测定的氯浓度获得的氯分解速率包含了腐殖酸的降解,因此,在氯浓度计算中将腐殖酸在此处的吸光度值扣除,获得氯的真实浓度及分解速率,结果如图5所示。由图5可看出,腐殖酸浓度越高,自由氯的分解速率越大,腐殖酸的存在明显促进了氯的分解。当溶液中不含腐殖酸时,自由氯的分解速率常数kobs为0.013 1 cm2·mJ−1。当腐殖酸浓度升高至20 mg·L−1时,kobs升高至0.060 9 cm2·mJ−1,分解速率提高了3.6倍。该结果与在低压紫外下腐殖酸作为一种内部过滤器抑制氯的分解不同[1],说明物质在中压紫外光下的降解规律并不会与低压紫外光完全一致。腐殖酸能促进氯在中压紫外下的分解可能有2方面因素:一方面腐殖酸本身与氯会发生反应[21-22],导致氯的衰减,并且腐殖酸浓度越大氯的衰减越快;另一方面腐殖酸的吸收光谱范围更广,中压紫外灯的发射光谱也更宽,因此腐殖酸能够为反应体系吸收更多的光能量,从而促进氯的光解。腐殖酸浓度为5 mg·L−1时,紫外剂量仅为34 mJ·cm−2时,50%的氯就会被分解,因此当水中腐殖酸浓度较高时要保持一定的氯浓度,需要提高氯投加量。
将氯在不同浓度腐殖酸条件下的分解速率常数kobs与腐殖酸浓度作图(图6)发现,kobs与腐殖酸浓度呈线性关系,可决系数达0.990 0,根据该线性关系可近似计算其他腐殖酸浓度条件下氯的分解速率常数。
-
实际水体中最主要的几种阴离子包括
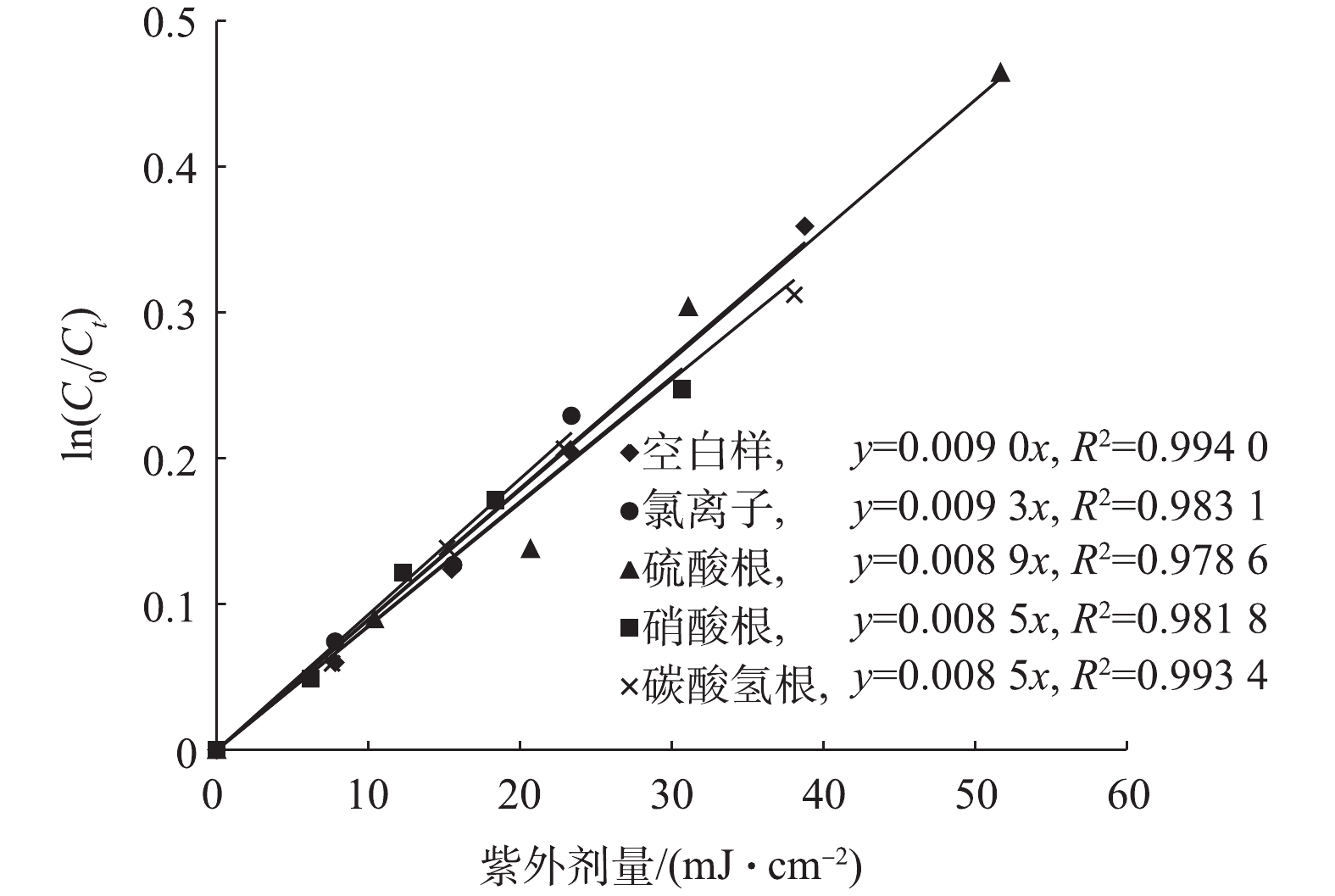
HCO−3 、Cl−、SO2−4 及NO−3 ,其中HCO−3 是一种常见的自由基淬灭剂,NO−3 是一种光敏物质,它们的存在可能对氯的光解产生影响,Cl−和SO2−4 也被发现会对紫外光降解系统产生影响[24]。为研究清楚这些离子对氯在中压紫外下分解的影响,在pH为7,温度为18 ℃,氯浓度为4.5 mg·L−1,硫酸根离子、氯离子和碳酸氢根离子为10 mmol·L−1,硝酸根离子为10 mg·L−1条件下,考察了这些离子以较高浓度分别存在时氯的分解规律,结果如图7所示。由图7可知,水中不存在任何离子时,氯的分解速率常数kobs为0.009 cm2·mJ−1,当氯离子存在时,kobs上升为0.009 3 cm2·mJ−1,升高仅为3.3%。当碳酸氢盐或硝酸根存在时,kobs下降为0.008 5 cm2·mJ−1,下降了5.6%,当硫酸根存在时,kobs为0.008 9 cm2·mJ−1,下降仅为1.1 %。以上结果表明,水体中的这几种主要阴离子对氯的分解速率几乎没有影响。由于这些离子本身在中压紫外/氯下可能产生活性大小不同的自由基,因此,虽然这些离子的存在对氯浓度变化的影响较小,但是对不同污染物质在中压紫外/氯下的降解规律可能不同[6,9]。 -
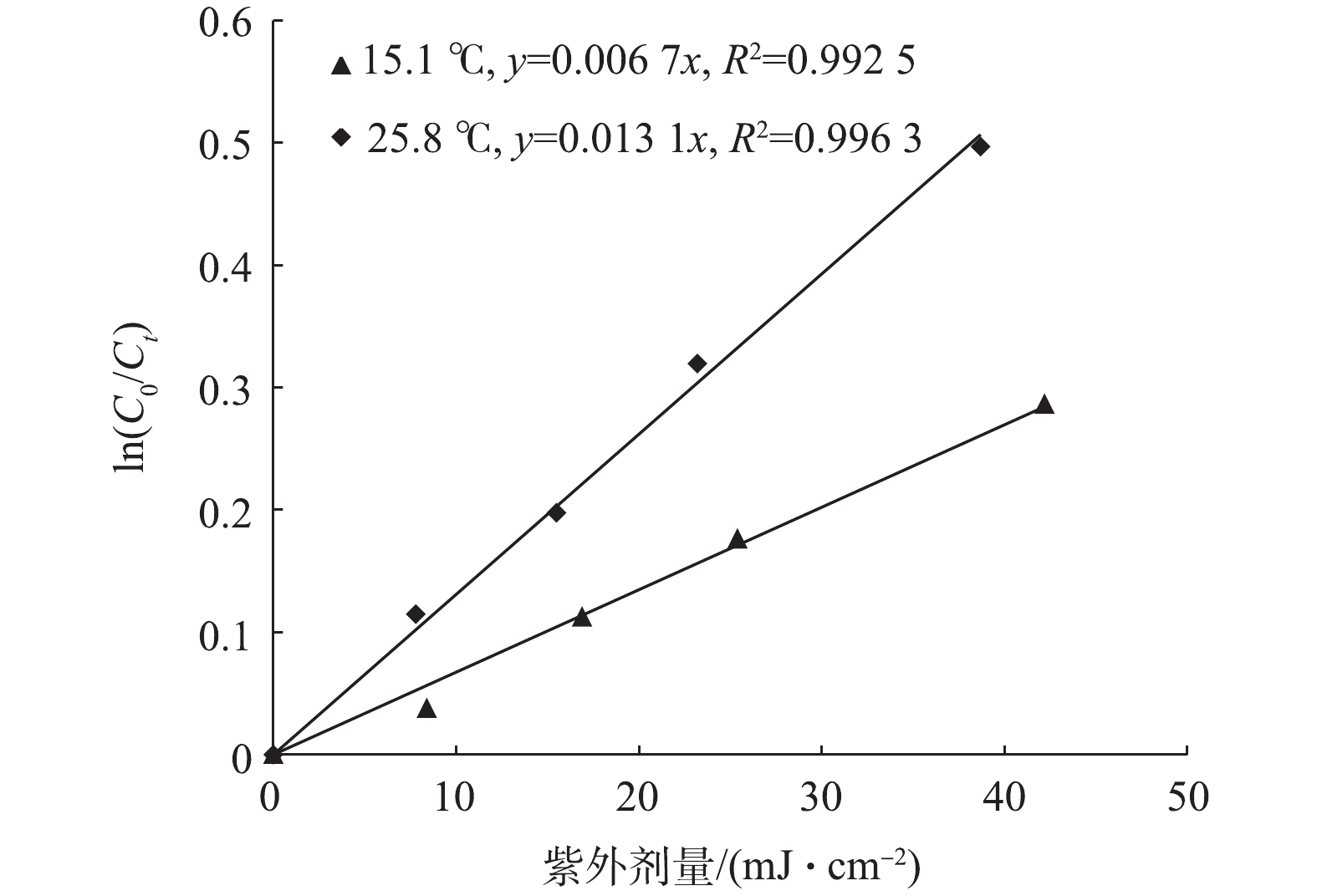
在实际水处理过程中,不同季节水温会发生较大变化,一般温度对紫外光降解效率影响较小,但是也有研究[25]发现,土霉素在紫外光下的降解会受到温度的影响。因此,在pH为7.25,氯浓度为4.94 mg·L−1条件下,研究了不同温度下自由氯的分解作用,结果如图8所示。由图8可以看出,温度越高,自由氯的分解速率越快。当水温为15.1 ℃时,分解速率常数kobs为0.006 7 cm2·mJ−1;温度升高到25.8 ℃,kobs升高到0.013 1 cm2·mJ−1,分解速率提高了1倍。根据万巧玲等[26]的研究结果,当温度从15 ℃升高到24 ℃时,氯本身的衰减速率常数提高了1.3倍,该变化规律与本实验结果近似,由此可推断,温度升高引起氯在中压紫外下的分解速率加快,这主要是由于氯本身的衰减速率随温度升高加快导致,而中压紫外光对氯的光解速率可能受温度的影响较小。由此可推测,当中压紫外/氯工艺用于处理水中污染物时,温度对处理效果的影响可能主要是由于氯浓度发生了变化,进而引起产生的自由基浓度变化导致,而不是紫外光降解效率受温度影响。由于温度引起氯的分解速率变快,在夏季水温较高时,要保持相同的余氯量需适当提高氯的投加量。
2.1. 不同浓度自由氯的分解规律
2.2. 不同pH条件下自由氯的分解规律
2.3. 腐殖酸对自由氯分解的影响
2.4. 水中无机离子对自由氯分解的影响
2.5. 温度对自由氯分解的影响
-
1)氯在中压紫外/氯工艺过程中的分解遵循一级动力学,且分解速率常数随其浓度升高而降低,浓度超过10 mg·L−1以后,分解速率常数降低的趋势变缓。
2)氯的分解速率常数随pH升高而增大,且在pH 6~10内与pH成线性关系,ClO−的分解速率要明显快于HOCl。
3)腐殖酸的存在会大大加快自由氯的分解,且氯的分解速率常数与腐殖酸的浓度成正相关关系,当原水中腐殖酸浓度较高时,要适当提高氯投加量。
4)实际水体中存在的主要离子(
HCO−3 、SO2−4 、NO−3 和Cl−)对氯的分解速率影响非常小。5) 氯的分解速率常数随其温度升高而增大,夏季温度较高时保持相同余氯量需适当提高氯投加量。











 下载:
下载: