-
2016—2018年,我国平均工业用水量为3 005.5亿m3,占总用水量的20%以上,且用水效率偏低。其中,食品加工、制革、纺织印染、石油化工、煤化工和制药等行业均产生大量高盐废水,约占总废水量的5%,且产生量还在持续增加[1]。高盐废水中盐类物质主要为Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、
SO2−4 等,且含有机物和至少1%的总含盐量(通常以NaCl含量计)[1]。高盐废水若未经处理直接排放,会污染环境、破坏生态系统,还会造成资源的浪费[2]。2015年,国务院印发《水污染防治行动计划》(水十条),对十大重点行业提出了专项整治要求(造纸、焦化、氮肥、有色金属、印染、农副食品加工、原料药制造、制革、农药、电镀),要求制定行业专项治理方案并实施清洁化改造,实现“趋零排放”以最大限度地降低环境污染、减少危险废物,并回收可再生资源[3]。同时,愈发严格的环境监管政策、不断增加的淡水价值和持续上升的废水处理成本,促使“趋零排放”成为可持续废水管理的必要策略[4]。目前,高盐废水“趋零排放”是指采用封闭水循环系统,废水经过适当处理后实现重复使用,系统中无任何废水排放。这种体系可消除废水排放造成的污染,并极大地提高用水效率[5]。实现“趋零排放”的处理流程中,核心技术为高盐废水盐浓缩与连续结晶技术。高盐废水的浓缩常采用热法蒸发进行。浓缩产生的蒸馏水被收集起来重新利用,而产生的母液则通过后续蒸发结晶成固体,而作为有价值的盐副产品进行回收[6]。然而,热法脱盐为能源密集型产业,投资运行成本高,不适合处理大流量废水,是限制其广泛工业应用的最主要障碍之一[7]。因此,在蒸发结晶前,通常会利用其他技术预先浓缩废水,以提高废水含盐量并减少废水体积,进而降低工艺能耗及成本[8]。
在膜分离技术中,利用压力驱动脱盐的反渗透(reverse osmosis,RO)技术不需要进行相变实现盐水分离,消除了与蒸发和冷凝相关的不可逆损失,其模块化特性也为其应用于废水处理提供了通用性。因此,RO技术被广泛应用于“趋零排放”系统中。然而,RO浓缩液的盐度一般为5%~7%,若要达到更高浓度还需使用超高压反渗透或碟管式反渗透,技术的稳定性较差,且无法大规模的工程应用。近年来,新型膜浓缩技术,如正向渗透(forward osmosis,FO)、膜蒸馏(membrane distillation,MD)和电渗析(electrodialysis,ED)等,已成为研究热点。这些膜技术可将RO浓缩液的盐度从5%~7%提高至15%~20%,大幅降低投资与运行成本[9-13]。其中,ED技术可实现海水制盐,将海水含盐量浓缩至20%,再利用热法蒸发结晶。该技术已成为日本海水制盐的主流工艺。但高盐废水的浓缩不同于海水制盐,废水中的杂盐及有机污染是制约废盐资源化的核心问题。目前,常用纳滤和冷冻结晶等技术进行分质结晶,以提高“趋零排放”系统中结晶盐的纯度。但其中的膜污染、无机盐溶解度对温度不敏感等导致分盐效率降低的问题仍不可忽视[14]。这些有机污染问题常用高级氧化、热解、絮凝和电解等技术处理,但相关技术的成本较高,且会引入新的化学药剂[15-17]。ED技术因其选择性分离溶解性离子的优势,可在电场力作用下低成本、高效率地实现分质浓缩,将杂盐纯化并与有机物分离。
ED技术是指在膜两侧电势差的推动下,带正、负电荷的电解质离子分别通过阳膜和阴膜进行从淡室向浓室的定向迁移,从而对料液进行浓缩、脱盐和提纯等过程[18]。在“趋零排放”系统中,ED因具有良好的料液浓缩性能和较低的能量消耗,常用于浓缩蒸发结晶前的高盐废水。提高废水的含盐量并对水中有机物的迁移进行调控,最终提高整个废水处理系统与稳定性,同时降低投资运行的成本投入[19]。已有研究表明,ED技术可低成本地将高盐废水含盐量浓缩至20%左右。处理相同浓度的高盐废水,热法浓缩能耗为20~25 kWh·m−3,而ED技术仅需7~15 kWh·m−3[6]。此外,ED技术对进料液的水质要求较低,预处理程序较少,结垢程度较轻,也减少了对化学药剂的使用和依赖[20]。传统ED技术主要应用于脱盐。近年来,因高盐废水“趋零排放”的技术需求,以溶解性离子选择性分离为核心的新型选择性ED技术成为研究热点。本文综述该技术在高盐废水处理中的应用现状,从高盐废水浓缩、杂盐纯化、有机物分离3方面总结研究进展,并梳理出新型ED技术的发展方向,以期为利用ED技术实现高盐废水“趋零排放”提供参考,亦为相关工业废水的处理及达标排放提供技术借鉴。
全文HTML
-
在浓缩高盐废水处理中,ED具有明显技术优势:水回收率高、操作简单、膜寿命长、成本较低、浓缩上限较高等。同时,由于离子交换膜的性能和有机物分子的电迁移惰性,ED在一二价离子分离、离子与有机物分离,以及有机物的去除等方面也有不可替代的优势,在以“趋零排放”为目标的高盐废水处理系统中广泛应用。
在该系统中,ED技术常用于进一步浓缩RO出水以提高废水含盐量。ZHANG等[21]在污水处理厂采用了实验性ED工艺处理的RO浓缩液,综合处理系统可使污水处理厂的总水回收率达到95%。在实际应用中,ZHANG等[22]利用ED技术处理RO浓缩液,废水电导率从3.9 mS·cm−1提升至25.0 mS·cm−1,且系统运行成本低至0.19欧元·m−3;通过调节ED浓室溶液的pH至6.0,进行酸化脱碳处理以防止膜结垢。
同时,利用膜中离子迁移速度和膜对不同价态离子亲和性的差异,一、二价选择性离子交换膜可有效分离不同价态的离子,为杂盐纯化提供技术支持。SELVARAJ等[23]通过在ED膜堆中耦合单价选择性阴离子交换膜和2种不同类型的阳离子交换膜构建了四室单价离子选择性电渗析系统,从工业废水中回收甲酸钠和硫代硫酸钠。低电流密度可以增加甲酸盐离子在单价选择性阴离子交换膜中的扩散,并避免了膜表面边界层的形成和过程中的能量损失。在最佳电流密度30 mA·cm−2下,甲酸钠纯度为87%,电流效率约为70%,整个过程的能耗约为96 kWh·m−3。
此外,针对高盐废水中的有机物污染问题,利用有机物分子在电渗析中的迁移惰性可实现盐与有机物的分离。如LI等[24]对ED进料液采用酸化预处理(将溶液pH从9.8调节至2),可将浓水有机物截留率从85%提升至93%。
-
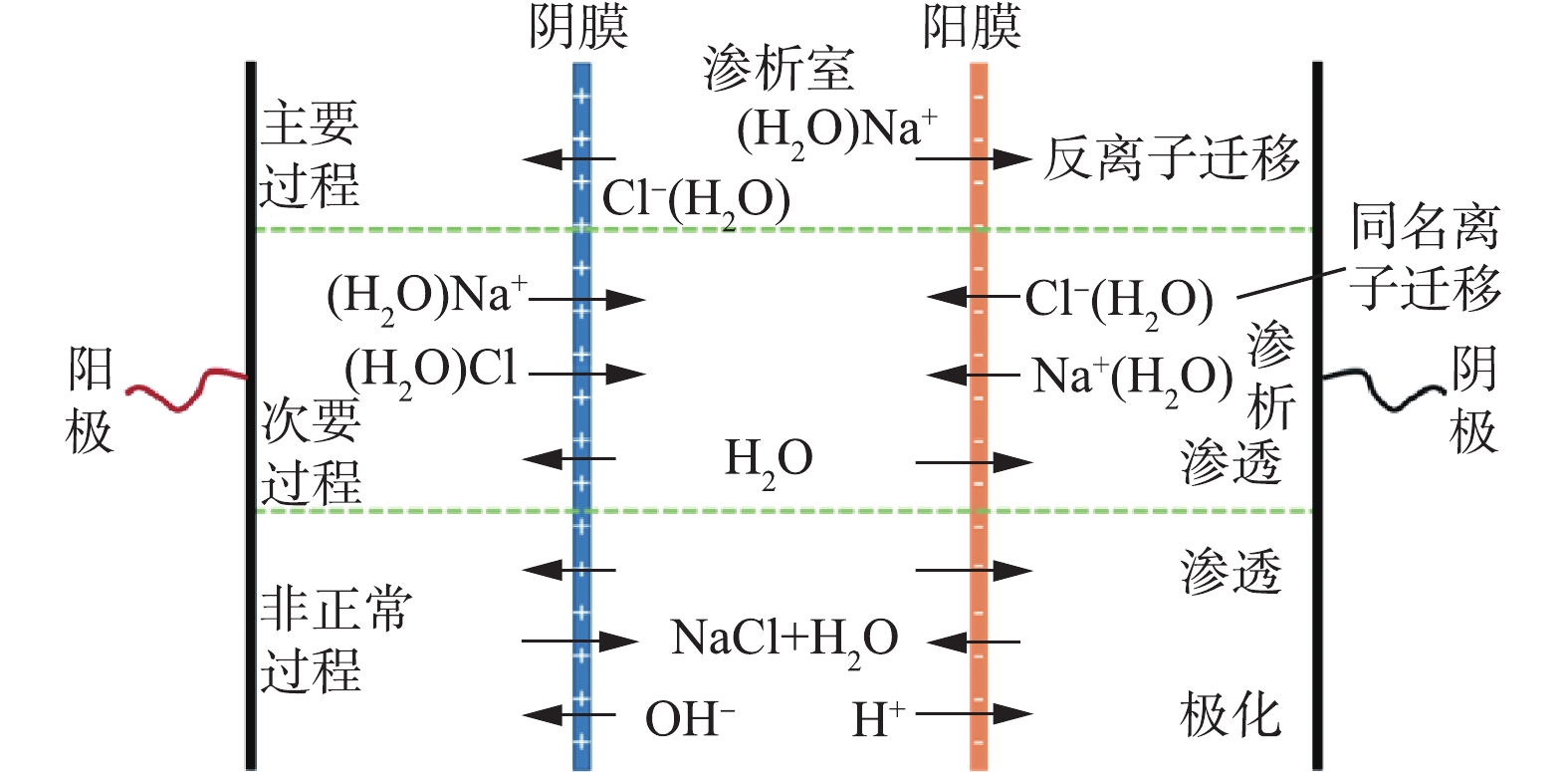
在ED技术的反应过程中,除离子因电势差进行迁移这一基本过程之外,还会有其他伴随过程发生,可分为主要过程(反离子迁移)、次要过程(同名离子迁移、渗析、渗透)和非正常过程(电渗失水、渗漏、电解、极化)[25](图1)。
离子在ED过程中的迁移主要为电场力作用下的电迁移和浓差驱动下的扩散。水在ED过程中的迁移主要包括:以结合水形式随离子迁移而发生的电渗透,浓差驱动下的渗透。对ED过程中离子、水迁移进行分析的总传质方程[26]见式(1)和式(2)。
式中:J为离子通量,mol·(m2·s)−1;λ为离子电迁移系数,mol·(A·s)−1;i为电流密度,A·m−2;μ为离子浓差扩散系数,m·s−1;q为水通量,m3·(m2·s)−1;φ为水的电渗透系数,m3·(A·s)−1;ΔC为浓、淡室浓度差,mol·m−3;ρ为水的浓差渗透系数,m4·(mol·s)−1。
根据总传质方程,提高离子通量可以从增大离子电迁移系数λ和降低离子浓差扩散系数μ两方面入手。为提高离子电迁移系数λ,需要尽量使溶液在膜表面以湍流状态运动以减小边界层的厚度,从而提高离子迁移速率。同时,为减少ED过程中离子在膜内部的停留时间,以及膜对同名离子的泄漏,应通过提高膜的自身性能来提高离子通量[27]。反离子从浓室向淡室的反向扩散也会降低离子通量。为降低离子浓差扩散系数μ以减少反离子反向扩散和同名离子迁移,应尽量减小浓缩液和淡化液的浓差。
ED技术低成本浓缩的核心控制因素为电流效率。在ED过程中,电解质离子的迁移是装置用电量的主要消耗途径,且在过程中不发生相变,使得ED技术能耗较低[28]。高盐废水浓缩过程中,电流效率主要由膜电阻及淡水侧的盐浓度决定,ED技术可通过调节运行参数来控制浓缩倍数及电流效率,并在50 000~200 000 mg·L−1高盐度范围内高电流效率浓缩。该技术可适应不同类型的高盐废水处理工程的要求,经济效益显著。然而,在高盐废水盐度较低的情况下,ED技术的脱盐成本较高。因此,一个独立的、单级的ED系统在大多数情况下都不适合用于实现“趋零排放”[29]。在“趋零排放”系统中,RO浓缩液常用ED进一步浓缩,以提高废水含盐量并减小体积,从而降低系统能耗、提高水回收率。MCGOVERN等[30]对ED和RO-ED集成技术的成本进行了研究和比较发现:当RO处理水的成本为ED装置处理水成本的60%~70%时,独立ED和RO-ED集成技术处理水的成本几乎一致;当RO装置处理水的成本较低时,可利用RO将废水浓缩至较高含盐量,解决了ED处理低盐度废水时高成本的问题;当RO装置处理水的成本过高时,则使用单独ED技术更具经济效益。因此,在实际应用中应综合考虑进水水质、装置能耗和产水要求,选择ED和RO-ED集成中的最优技术,充分发挥ED与RO各自的优势。
水的迁移是ED浓缩过程中不可忽略的因素,主要受水的电迁移和浓、淡室浓差的影响。水的电渗透与浓度梯度无关,但与电流密度成正比,而浓差渗透只取决于浓度梯度。当浓、淡室的浓度梯度低于1 mol·L−1时,水的浓差渗透通量至少是电渗透通量的8倍[31]。然而,随着ED装置中盐浓缩过程的进行,浓、淡室的浓度梯度势必越来越大,这时水的浓差渗透逐渐占据主导地位。JIANG等[28]研究了ED过程中水的迁移速率与离子种类之间的关系。对于单价离子Li+、Na+、K+和
NH+4 ,Li+水化半径大、原子半径小、迁移率高,所以流速最高。对于不同价态的离子而言,一方面,水的电渗透会随离子价态的升高而减弱;另一方面,低价态的阳离子在ED浓缩过程中浓、淡室浓差较高,即水的浓差扩散较强。这两个相反的因素相互作用,导致水迁移速率的顺序为VE (Cu2+)>VE (K+)>VE (Al3+)。对于相同的离子种类,水的迁移速度随着膜的离子交换容量和基质材料的亲水性而增加。为了减弱这种影响,应对膜基质材料进行改性,选择合适的离子交换容量、官能团或引入配体,以减少水在ED中从淡室向浓室的迁移,以获得高脱盐能力和低水迁移速率的双赢耦合。另外,在高盐废水浓缩过程中,ED的浓缩极限很大程度上受浓淡室浓差的影响。因此,在实际应用中,多采用多级ED,降低浓淡室浓差,最大程度减少浓差渗透水,并提高ED浓缩的极限。多级ED会进一步降低能耗。这是由于每个阶段都可以在其各自的最佳状态下运行,而不需要根据整个系统的最佳状态来选择应用条件[32]。YAN等[33]利用模拟高盐水进行了二级ED和三级ED实验,其浓缩液的含盐量分别从3.5%提升至17.9%和20.6%,总能耗分别为0.31 kWh·kg−1和0.45 kWh·kg−1。 -
高盐废水经浓缩后产生的高盐度废水通常经过热法蒸发、分质结晶后形成固体盐,可作为工业盐出售或者其他方式资源化利用。由于高盐废水中离子种类繁多,产生的工业盐纯度较低,故在市场上难以找到销售出路。因此,提升这些工业盐的纯度,进而提升其价值,成为近年来研究的热点。
反离子(与选择透过性离子交换膜固定集团所带电荷相反的离子)在电位梯度推动下逆离子浓度梯度方向发生迁移,是电渗析的主要传质过程,具有两大特性:1)方向性,即阴离子向阳极迁移而阳离子向阴极迁移;2)可调控性,即选择性分离溶解性离子的特性可使浓缩过程实现杂盐纯化。在ED过程中,因为阴离子和阳离子所带电荷的电性不同,可通过离子交换膜进行分离。除此以外,由于不同离子的淌度存在差异,导致其迁移速率不同,从而实现阴离子或阳离子中不同价态离子的分离,如Nernst-Planck[34]方程(式(3))所示。
式中:Ji为离子i的传质速率,mol·(cm2·s)−1;Di为离子i的扩散系数,cm·s−1;Ci为溶液中离子i的浓度,mol·cm−3;x为x方向(垂直于膜方向)上的距离,cm;zi为离子i的核电荷数,个;F为法拉第常数,取F=96 485 C;R为气体常数,取R=8.314 J·(mol·C)−1;T为溶液的热力学温度,K;Ψ为电位,V;vx为流体在x方向上的平均流速(取流体重心的运动速率),cm·s−1。
ED技术中离子通量主要包含上述3项。其中第1项、第3项的意义为由扩散、对流造成的离子通量,离子交换膜结构致密,在研究离子的竞争性时通常可忽略,即离子通量主要由电迁移造成[25]。除此之外,ED技术中离子的选择透过性还受其他因素影响。奚凤翔[35]认为,离子的选择透过性主要由膜的性质决定,即膜对离子的选择透过性主要由树脂决定,受膜孔径影响甚微;通常阳膜的选择透过性顺序为Ca2+>Mg2+>K+>Na+,阴膜的选择透过性顺序是
SO2−4 >Cl−>F−>HCO−3 。SATA[36]则认为阴离子吉布斯水合能的差异决定了其在ED技术中的选择透过性,即电渗析中阴离子相对于氯离子的转运数不是由阴离子的水合离子尺寸的差异决定,而是由阴离子的吉布斯水合能的差异决定。各阴离子的水合能大小为SO2−4 >F−>Cl−>Br−>NO−3 >I−。双极膜ED(bipolar membrane electrodialysis,BMED)中使用的离子交换膜是由阴离子交换层、阳离子交换层和界面亲水层复合而成的双极膜。BMED在电场作用下可将水解离,在膜两侧分别得到H+和OH−,将溶液中的盐转化为对应的酸和碱,在无机盐资源化利用方面具有较好的应用前景[37]。YE等[38]采用BMED从草甘膦溶液中回收NaOH,并将NaOH作为CO2的捕集剂进一步反应,同时回收废水中的草甘膦。通过BMED可以获得浓度为1.45 mol·L−1、纯度为96.5%的NaOH溶液,且草甘膦的回收率可达98.2%。JIANG等[39]采用BMED从蛋氨酸盐中同时捕获二氧化碳和提取蛋氨酸。首先,用蛋氨酸盐捕集CO2;然后通过BMED工艺将混合物转化为蛋氨酸和CO2,蛋氨酸提取率可达99.57%,捕获CO2的能耗则低至7.0 kWh·kg−1。该技术既避免了大量使用酸和碱,又充分利用了燃料气体中的CO2。TRAN等[40]利BMED工艺再生重金属废水制得H2SO4和NaOH,当电流密度为60 mA·cm−2时,制酸和制碱的能耗分别为5.5 kWh·kg−1和4.8 kWh·kg−1,产物可应用于工业生产中。在长期实验中可产生高浓度的酸和碱,分别达到1.76 mol·L−1和2.41 mol·L−1,此时的阳膜表面仅有轻微结垢。
在混盐分离方面,CHEN等[41]提出利用选择性BMED对RO浓缩液进行处理,即将一价选择性离子交换膜和双极膜集成在选择性BMED中,实现了NaCl与Na2SO4的选择性分离并同时将NaCl转化为HCl与NaOH,产品纯度均可达99%。由此可见,双极膜ED在无机盐资源化和混盐分离方面均有良好的应用价值和潜力,适用于以“趋零排放”为目标的高盐废水处理系统。
-
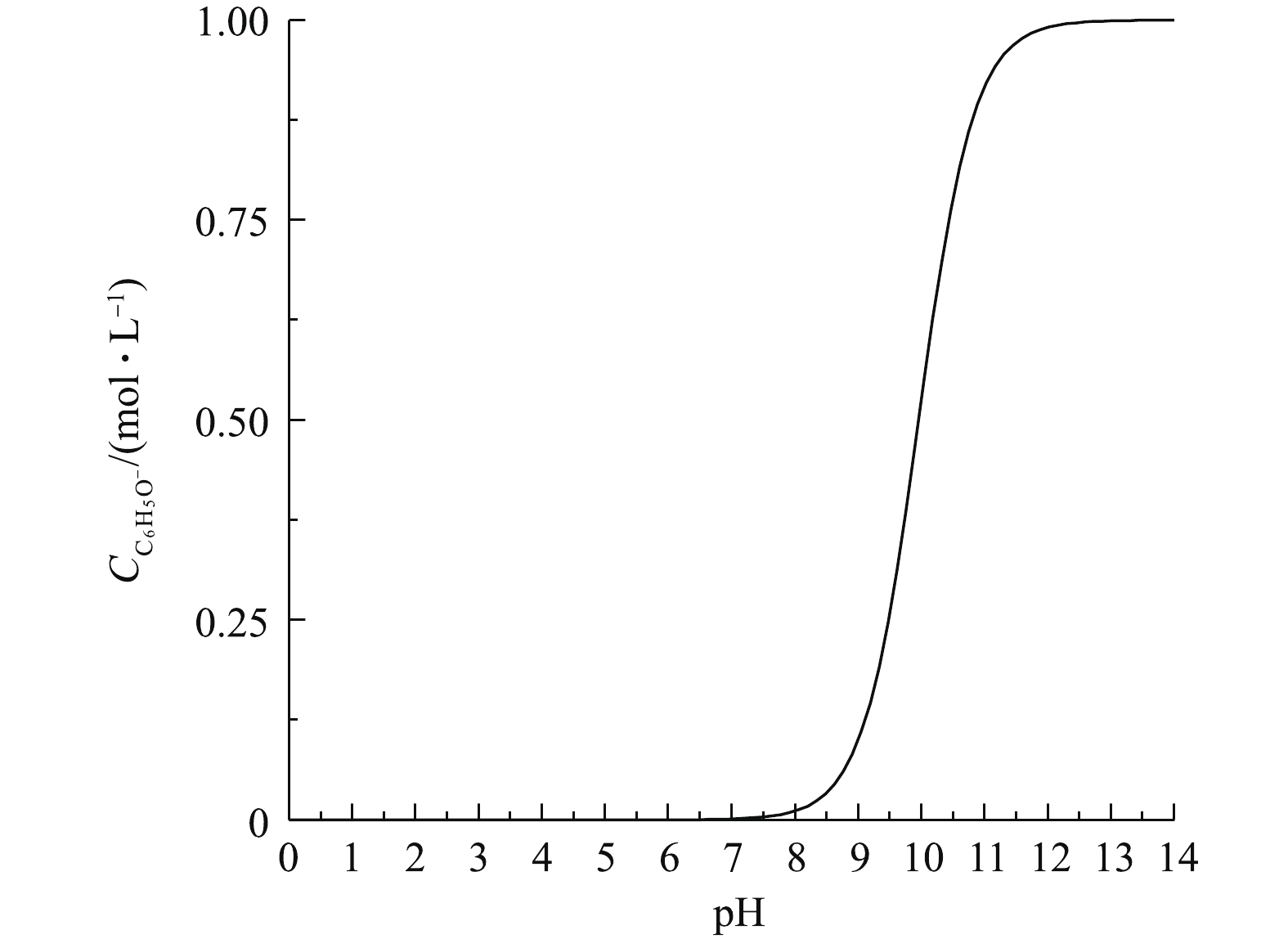
经生化处理后,高盐废水COD通常为0~100 mg·L−1。在“趋零排放”系统中经UF、RO等工艺浓缩之后,COD可达到300~1 200 mg·L−1[3]。浓缩液在“趋零排放”系统中作为后续热法蒸发的进料液,会导致结晶盐被有机物污染[4]。因此,有机物的分离与去除是废盐资源化利用的核心技术。ED技术以电场力为驱动力,离子交换膜仅允许溶解性离子通过。在理想状态下,ED中仅有极少部分有机物分子会因为对流传质而进行迁移。但是,弱电解质有机物会在水中发生微弱电离。以苯酚为例,在标准条件下,苯酚在水溶液中的电离平衡曲线如图2所示。通过调节溶液pH,苯酚在溶液中的形态可分为分子态、混合态(分子态和离子态的混合物)和离子态[42]。分子态苯酚会因对流传质进行少量迁移。处于离子状态的苯酚迁移遵循电渗析中电解质迁移的规律。混合态时,由于离子态有机物会电迁移到浓室中,导致淡室中离子态有机物不断减少,电离平衡不断向右(离子态)偏移产生更多的离子态有机物,会导致弱电解质有机物的迁移增加,从而有机物总迁移率增大[42]。
对于弱电解质有机物,可通过酸化处理抑制其电离,使电离平衡向左偏移保持其在分子态。HAN等[43]通过调节pH,使CH3CO−转化为CH3COOH (中性形式)从而减少了迁移,并增强了系统中离子(
SO2−4 )的迁移。在实际高盐废水的处理中,LUIZ等[44]采用ED对生物精炼厂的高盐废水进行了处理。其中,木质纤维素废水(电导率23.4 mS·cm−1,COD 38 000 mg·L−1)的浓缩率高达96%,有机物迁移率仅为0.3%;糖蜜废水(A)(电导率为48.5 mS·cm−1,COD为380 000 mg·L−1)的浓缩率为61%,有机物迁移率为6.3%;糖蜜废水(B)(电导率为72.4 mS·cm−1,COD为200 000 mg·L−1)的浓缩率为61%,有机物迁移率为2.5%。有机物的迁移率均随进料液中COD增加而增加。这可能是由于浓度梯度增加所引起的扩散通量增加,导致有机物迁移率增强,但与离子迁移量相比仍较少。此外,无机盐离子与有机物离子或分子间存在竞争效应,也会使得盐与有机物分离。离子半径越小、极化率越大的离子在溶液中更容易受到溶剂分子的阻碍,故而迁移速率更小,即离子的淌度越小。ZHANG等[45]研究了小型有机离子通过离子交换膜的传输机制。结果表明,有机溶质的摩尔质量越高,分离效果越好。相较于尺寸较小的离子,尺寸较大的离子能更多地保留在淡室中,与尺寸排斥效应一致。而总电荷为0的两性离子则几乎全部留在淡水侧。此外,使用ED对高盐废水的RO浓缩液进行处理,其中85%以上的有机组分都保持在淡水侧,说明利用ED从盐中分离有机物是可行的。之后,ZHANG等[46]还研究了ED技术中小型有机离子迁移的影响因素。根据离子迁移模型,可以观察到膜的选择性取决于有机离子的大小、电荷和官能团。同时,通过比较甲酸盐离子、乙酸盐离子、丙酸盐离子、丁酸盐离子、天冬氨酸盐离子和酒石酸盐离子在阴膜中的迁移速度可以发现,酒石酸盐离子的迁移速度最快,渗透性接近无机阴离子,说明亲水性较高的有机离子更容易通过离子交换膜进行迁移。
除分离盐和有机物之外,ED还可以将目标有机污染物从有机杂质中分离出来。生物发酵液中苯乙酸(phenylacetic acid,PAA)的浓度较低,所以当ED分离时,会有相当数量的PAA停留在阴离子交换膜中。FEHÉR等[47]对含有磷酸缓冲液、PAA和有机杂质的模拟发酵液进行了ED处理。处理工艺采用两级ED:在第1阶段,因为以苯基乙胺为代表的中性有机杂质不能通过ED装置中的离子交换膜进行迁移,故可以将PAA从有机杂质中分离出来;在第2阶段,结合在阴离子交换膜的活性位点上的PAA被无机阴离子取代进而回收,最高回收率可达95%。
2.1. 高盐废水浓缩
2.2. 杂盐纯化
2.3. 有机物分离
-
虽然ED技术已在盐浓缩、物质分离和盐资源化等方面得到了广泛的应用,但传统ED技术研究以脱盐为主,无法满足更高的技术需求,急需开展以溶解性离子选择性分离为核心的新型ED机制与过程以及应用研究。热点研究方向包括:单价选择性离子交换膜、新型选择性ED膜堆和膜污染控制等。
-
ED技术中使用的离子交换膜为分离膜的一种,即膜内固定基团带有特定电荷,从而使膜具有选择透过性,是ED选择性分离溶解性离子的基础。但在实际应用过程中,离子交换膜仍存在低渗透选择性和一价离子选择性相对较低等缺陷。因此,通过有效的膜改性,以提高其综合性能是当今研究的重要方向之一。其中,单价选择性离子交换膜因其选择性分离单价离子性能,在高盐废水杂盐纯化领域受到广泛关注[48]。离子交换膜的表面改性主要有:有机溶液涂覆改性、等离子体表面改性、电沉积表面改性、射线辐射表面改性、化学结合表面改性、无机纳米粒子掺杂改性和石墨烯掺杂改性等方法。改性技术简单易操作,可明显提高膜的单价选择性[49]。
IRFAN等[50]将烷基垫片直接接枝于与亲水羧基和磺酸基相连的以氮为中心的阳离子,设计并制备了具有可调侧链疏水性和亲水季铵盐、磺酸和羧酸基团单价选择性阳离子交换膜。悬链调节膜的疏水性以促进微相分离,可以获得更高的阳离子通量、更高的膜选择性和更好的空间稳定性,其中疏水链最长的单价选择性阳离子交换膜选择性最高可达25.26。
PAN等[51]采用季铵化法制备了溴化聚(2,6-二甲基- 1,4 -苯基氧化物)阴离子膜,然后通过电沉积对该膜进行改性,将聚乙烯亚胺共价固定在阴离子交换膜表面,从而制备了单价选择性阴离子交换膜。与未改性的离子交换膜相比,渗透选择性从0.79提高到4.27,
SO2−4 泄漏率从39.6%降低到19.4%。 -
ED装置中,阴、阳膜通常交替排列形成浓缩室和淡化室,达到浓缩或淡化的目的。然而,通过改变膜堆中离子交换膜的类型、数量和排列方式等,可以形成不同功能的隔室以满足处理不同废水的需求。
YE等[52]将一价选择性阴离子交换膜和一价选择性阳离子交换膜集成到传统的ED装置中,开发了一种新型的ED工艺。该工艺可同时从饲料废水中分离出阴离子产物流(
PO3−4 、SO2−4 )、阳离子产物流(Mg2+、Ca2+)和盐水流(K+、NH+4 ),用于废水的脱盐和养分回收。回收的产物流可以搭配在一起生产高价值产品。在恒压模式下,各离子迁移的能耗分别为28.380 kWh·kg−1(PO3−4 )、17.995 kWh·kg−1(SO2−4 )、6.103 kWh·kg−1(Mg2+)、6.638 kWh·kg−1(Ca2+)、5.220 kWh·kg−1(K+)和0.783 kWh·kg−1(NH+4 )。CHEN等[53]针对N-甲基二乙醇胺(methyldiethanolamine,MDEA)吸附液中热稳定盐(heat stable salt,HSS)含量过高的问题,设计了三室电渗析耦合离子交换树脂(RTED)装置。即在双室电渗析装置中增加NaOH室构建三室电渗析(TED)装置,并进一步在淡化室中填充阴离子交换树脂。对3种装置在HSS脱除率、MDEA损耗率以及经济成本做了对比分析。结果表明,双室电渗析中HSS去除率为50.48%,MDEA损耗率为18.23%,装置去除1 kg HSS的成本为1.04 美元;TED装置中HSS去除率为82.66%,MDEA损耗率为5.78%,1 kg HSS处理成本为0.92 美元;RTED装置中HSS脱除率为89.61%,MDEA损耗率为5.78%,处理成本最低,1 kg HSS处理成本为0.88 美元。TED与TEDR装置中均增加了NaOH室,利用NaOH溶液中OH−再生MDEA以降低其损耗。研究表明,NaOH溶液不超过3%时,既有利于提高HSS的去除率,又有利于降低MDEA在TED和RTED中的损失。
-
膜污染是各种膜分离过程中普遍存在的现象,也是限制膜分离技术大规模工业应用的瓶颈问题之一。由于高盐废水中的大多数有机化合物都带负电荷,故当施加电场时,有机物会迁移到阴离子交换膜(anion exchange membrane,AEM)的表面,然后在膜表面沉积并形成污垢层。AEM的有机污染主要由带负电荷的有机质引起,如腐殖酸、牛血清白蛋白、表面活性剂等,其膜污染程度主要受有机物与AEM之间的静电相互作用与亲和作用的影响[54]。表面改性是抑制AEM有机污染的有效方法,可以提高AEM的负电荷密度、亲水性和表面粗糙度等理化性质,进而提高其防污性能。PAL等[55]采用低温直流氨等离子体处理聚丙烯腈共聚合物膜,通过氧和氮官能团的结合,改善了膜的表面亲水性,进而显著改善膜的防污性能。膜经过等离子体改性(450 V脉冲电压、70%占空比和8 min暴露时间)后,处理含油量为500 mg·L−1的废水时,膜通量提高了32%。ZHAO等[56]通过聚(4-苯乙烯磺酸钠)(PSS)和聚二烯丙基二甲基氯化铵(PDADMAC)叠层修饰膜表面对AEM进行了改性。顶层的PSS使得膜表面呈负电性,并提高了其亲水性,有助于提高AEM对溶液中有机物的排斥能力。同时,膜表面负电荷密度和膜表面亲水性均随PSS/PDADMAC双分子层数的增加而增加。LI等[57]分别采用氧化石墨烯(graphene oxide,GO)电沉积、聚多巴胺(polydopamine,PDA)涂层以及GO-PDA集成3种技术对AEM进行了改性处理。GO-PDA技术即首先用GO电沉积法对AEM进行修饰,然后将其浸入PDA溶液中形成一层薄薄的PDA涂层。改性后其脱盐率较原始膜提高了39.3%,且GO与PDA组成的复合修饰层更加光滑致密,从而降低了膜表面的粗糙度。这些特性使得改性后的AEM在长时间运行中具有良好的防污性能。
此外,高盐废水中通常含有大量Ca2+和Mg2+。当料液中的
CO2−3 或OH达到一定浓度,极易与其反应生成不溶性的碳酸盐或氢氧化物,并堆积在膜表面或堵塞膜孔,造成可逆或不可逆的膜污染。膜污染使得膜电阻增加,电流效率降低,能耗升高。目前,对于可逆膜污染常采用化学试剂清洗或倒极清洗等方式处理。但是,长期清洗会对离子交换膜造成损伤,如破坏膜表面形成凹状孔等[58]。然而,对于由污染物渗透入膜内部引起膜结构破坏而造成的不可逆膜污染,运用上述方式难以清洗彻底,而需从源头解决。因此,可以通过加强预处理来降低进料液中Ca2+、Mg2+和CO2−3 等离子的浓度,从而对这类污染进行预防和控制。常用朗格利尔饱和指数(Langelier saturation index,LSI)来评估废水结垢的潜力,当LSI大于2时,废水中碳酸钙的结垢潜力非常高[59]。ZHANG等[60]对典型ED进料液(RO浓缩液)的各离子含量进行了研究发现,当ED进料液的LSI为2.21时,引起结垢电位的离子是Ca2+、Mg2+和CO2−3 。因此,可对ED浓、淡室进料液或仅对浓室进料液进行酸化脱碳处理,即将料液的pH调整至5.5~6.5,以确保大部分无机碳以重碳酸盐(HCO−3 )的形式存在,以预防ED结垢。同时,该研究者建立了临界结垢浓度因子(critical scaling concentration,CSC)来预测ED结垢情况。在特定条件下,溶液达到临界标度点(LSI=1.00)的碳酸氢盐浓度即CSC。当溶液中碳酸氢盐浓度低于CSC时,不会引起结垢。实验表明,通过对ED进料液或浓缩液进行酸化脱碳处理,可使得ED装置在稳定状态下进行长时间的工作(42 h),并且RO-ED的综合处理系统可使废水处理厂系统的总水回收率达到95%。
3.1. 单价选择性离子交换膜
3.2. 选择性ED膜堆
3.3. 膜污染控制
-
为实现高盐废水“趋零排放”,ED技术已在高盐废水浓缩、杂盐纯化、有机物分离等方面取得了一定的进展,进行了一定规模的工程应用。此外,ED在传统脱盐模型的基础上,根据各类型高盐废水的处理需求,发展出了一些新的研究方向,如单价选择性离子交换膜、新型选择性ED膜堆和膜污染控制等。这些研究进一步提高了ED技术在高盐废水处理中的应用潜力。尽管ED技术在高盐废水浓缩方面已取得一定进展,但是其浓缩性能和水迁移控制性能等仍需进一步提升。膜污染是ED浓缩高盐废水时中不可忽视的问题,提高离子交换膜的耐污性是亟需解决的问题。在许多情况下,独立或单级系统并不适合于“趋零排放”系统,故常用多级ED工艺来处理高盐废水。但这样会增加投资成本,亟需开发新的产品及工艺来降低ED的投资成本。





 下载:
下载: