-
随着太湖周边城市规模的不断扩大和经济的高速发展,污染日趋严重,蓝藻水华已经成为太湖区域最突出的环境问题之一。每年夏秋的蓝藻暴发时期,太湖蓝藻浆的每日打捞量可达上万吨[1]。打捞上岸后的蓝藻浆经破气囊、絮凝和初步脱水后得到蓝藻泥,其含水率仍高达85%~95%[2],这给运输、储存和进一步处理带来很大的困难。由于蓝藻泥易腐、恶臭且含有藻毒素[3],加上其生长量和品质受季节因素影响较大[4],目前仍未找到适宜的资源化途径。主要原因在于:1)蓝藻泥中有机质含量高,细胞外存在不溶于水的荚膜多糖[5],将蓝藻细胞周围吸附水、间隙水都包裹在一起[6],导致脱水和干化成本很高;2)当前比较经济的蓝藻脱水技术需添加大量的氧化钙、聚合氯化铝[7]和稀释水,导致滤饼中无机组分含量高达总干质量的40%~60%,使后续资源化处理途径受到限制。目前,打捞上岸后的蓝藻泥末端出路受阻,当地政府联合热电企业,推进干化-焚烧工艺,但处理费用高,同时亦影响到太湖蓝藻的打捞规模和治理效果。因此,蓝藻泥的深度脱水和资源化处理方法已成为非常迫切的技术需求。
高有机物原料是制备优质生物炭的前提条件,但脱水过程中加入大量无机助滤剂将使蓝藻泥的高有机质优势丧失殆尽。为解决滤饼中无机组分含量较高的问题,需要从pH、温度、絮凝剂种类[8]等方面改变压滤条件。其中,热压滤技术由于不引入无机物、显著降低料液黏度和过滤比阻,是较为经济、简洁的方式之一[9]。以氯化铁为高效助滤剂,在脱水过程中迁移进蓝藻饼,在后续的热解碳化过程中,发挥FeCl3的催化效果[10]和赋磁性能,生成磁性生物炭[11]。近年来,磁性生物炭的制备和在环境领域的应用得到了快速发展,在重金属和有机污染物吸附领域中得到了广泛应用[12]。磁性生物炭的制备方法主要有浸渍法、液相沉淀法和液相还原法[13]。一般是将制备完成的生物炭与铁盐混合,再调节pH,使铁盐转化为磁性的铁氧化物[14]。JUANG等[11]将活性炭与Fe3O4纳米颗粒通过化学键结合,制备出具有去除废水中有毒污染物能力的材料。ZHANG等[15]利用浸渍和微波加热的方法得到改性竹炭材料(Fe-MBC),并将其应用于水溶液中Pb2+的去除。
本研究将热压滤深度脱水技术和磁性生物炭制备技术通过铁盐进行耦合,建立蓝藻泥资源化利用中试工艺;通过研究不同的压滤组合条件,提出最优参数组合,并成功地利用热压滤之后的含铁盐蓝藻饼,制备出品质优良的蓝藻磁性生物炭;探讨了铁盐的蓝藻泥热絮凝和生物炭催化赋磁作用,并对整个工艺进行经济性分析。该中试工艺可为蓝藻泥进行无害化、减量化和资源化处理提供参考。
全文HTML
-
实验所使用的蓝藻泥取自无锡市某藻水分离站,其含水率为92.56%±1.27%、VS/TS为85.36%±2.78%、pH为6.42±0.37。
-
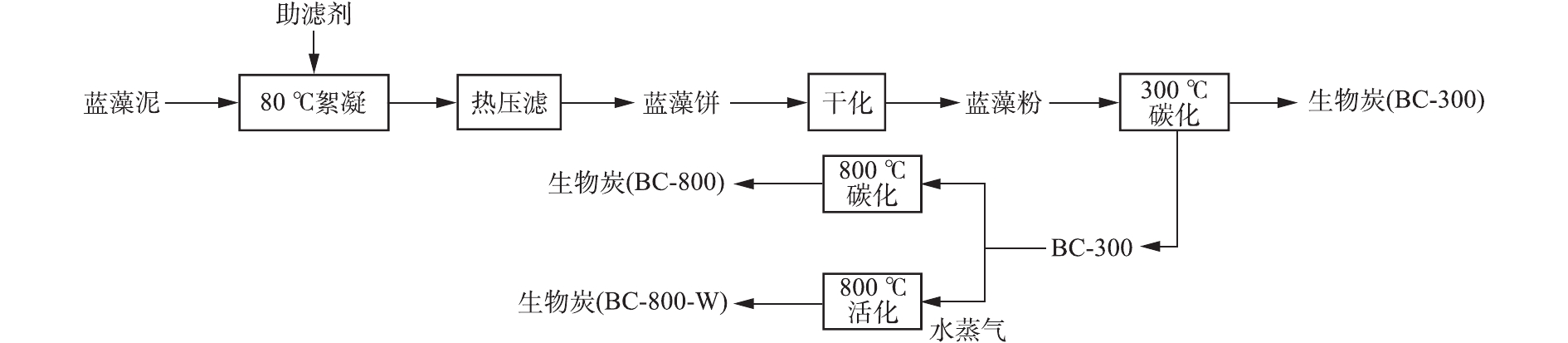
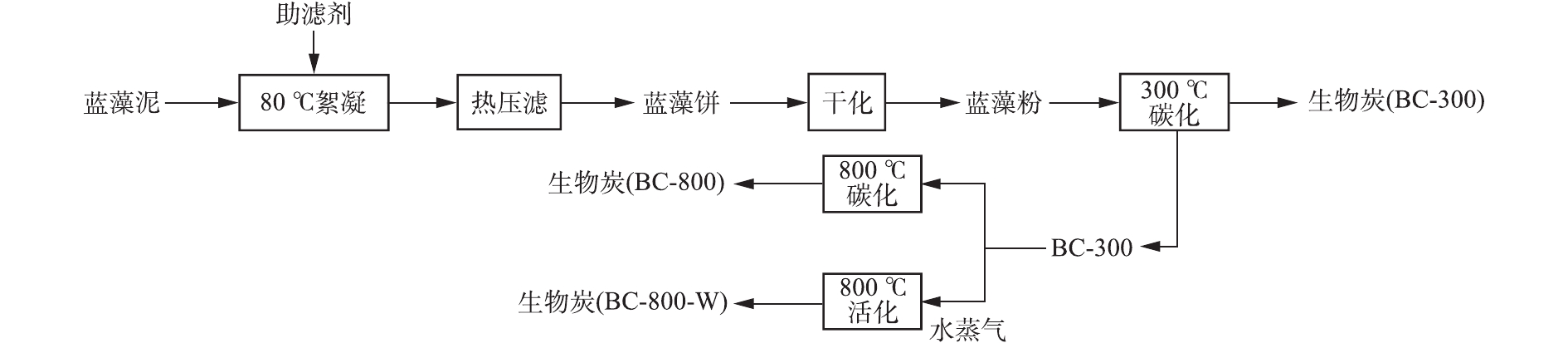
蓝藻泥热压滤深度脱水耦合制备磁性生物炭的工艺流程如图1所示。向蓝藻泥中加入干基10%的助滤剂,搅拌并用水蒸气加热至80 ℃,泵入增强聚丙烯压滤机。压滤机过滤面积为20 m2、滤室总容积为290 L、进料压力为0.8 MPa、进料时间为2 h、压榨压力为0.9 MPa。实验组1添加10%氯化铁,在80 ℃条件下压滤;实验组2添加10%聚合硫酸铁,在80 ℃条件下压滤;实验组3添加10%氯化铁和40% CaO,由于添加CaO后物料的流动性较差,需要添加2倍体积的水进行稀释后再进行压滤操作,常温下压滤。各组的其他压滤操作条件相同。
将压滤后的蓝藻饼运输至圆盘干化机,以水蒸气为热源进行干化,得到蓝藻泥干颗粒。以天然气为燃料加热回转炉,设置升温速率为5 ℃·min−1,使炉温升高至300 ℃,同时向回转炉内通入氮气(120 L·min−1)。将蓝藻泥干颗粒运输至回转炉中,停留60 min,获得生物炭BC-300;再将生物炭BC-300在800 ℃下停留120 min,获得生物炭BC-800。另取生物炭BC-300在800 ℃下停留120 min,同时向炉内通入流量为100 kg·h−1的水蒸气,获得生物炭BC-800-W。
-
增强聚丙烯压滤机(X16AGZFDR20/800-UK型,杭州兴源环保设备有限公司);圆盘干化机(wg-10型,浙江清风源环保科技有限公司);回转炉(ROJ-95-9型,无锡奥普瑞炉业公司);水分测定仪(HE53/02型,上海梅特勒-托利多国际贸易有限公司);马弗炉(KSY-12-16型,上海跃进医疗器械有限公司);高性能比表面积分析仪(JW-BK200型,北京精微高博科学技术有限公司);扫描电子显微镜(SU1510型,日立高新技术公司);振动样品磁强计(VersaLab型,深圳市蓝星宇电子科技有限公司)。
-
采用水分测定仪测定含水率;采用国家标准方法测定VS/TS[16]和磁性生物炭碘吸附值[17];采用比表面积分析仪测定磁性生物炭比表面积;采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察磁性生物炭表面结构;采用能谱仪(EDS)测定样品元素含量;采用振动样品磁强计测定磁性生物炭磁滞回线。
1.1. 实验原料
1.2. 蓝藻泥的处理工艺
1.3. 实验仪器
1.4. 分析方法
-
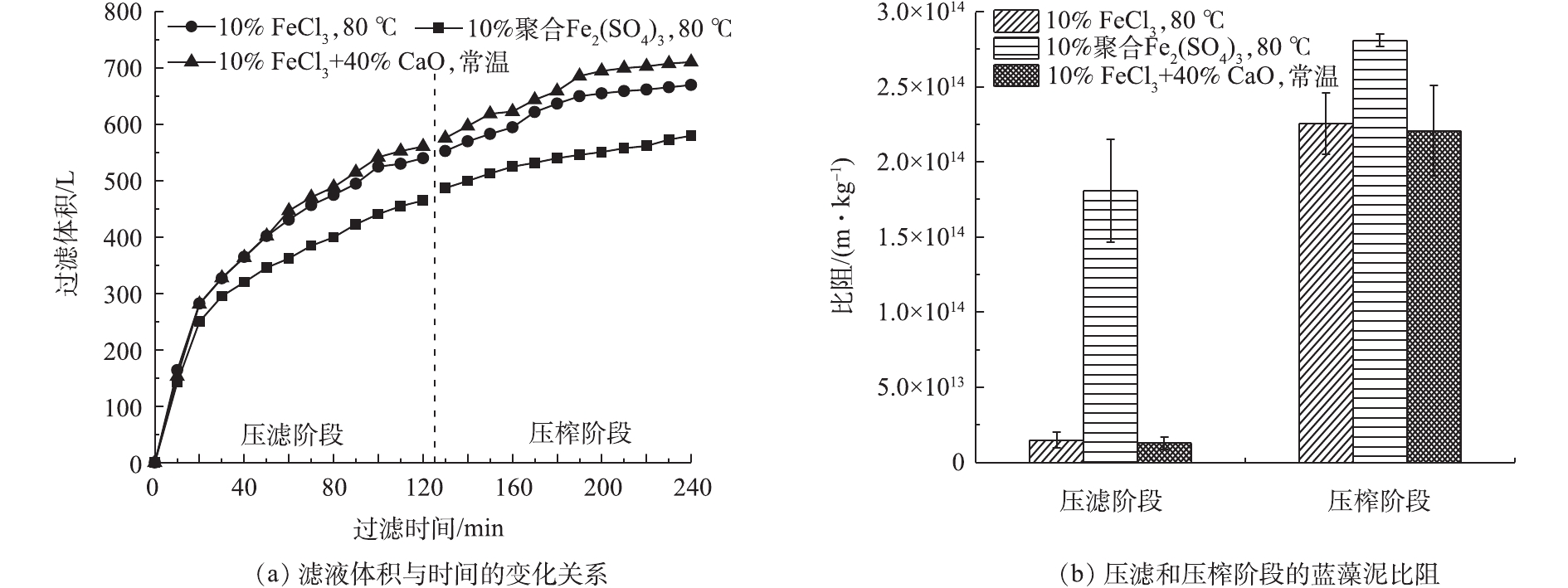
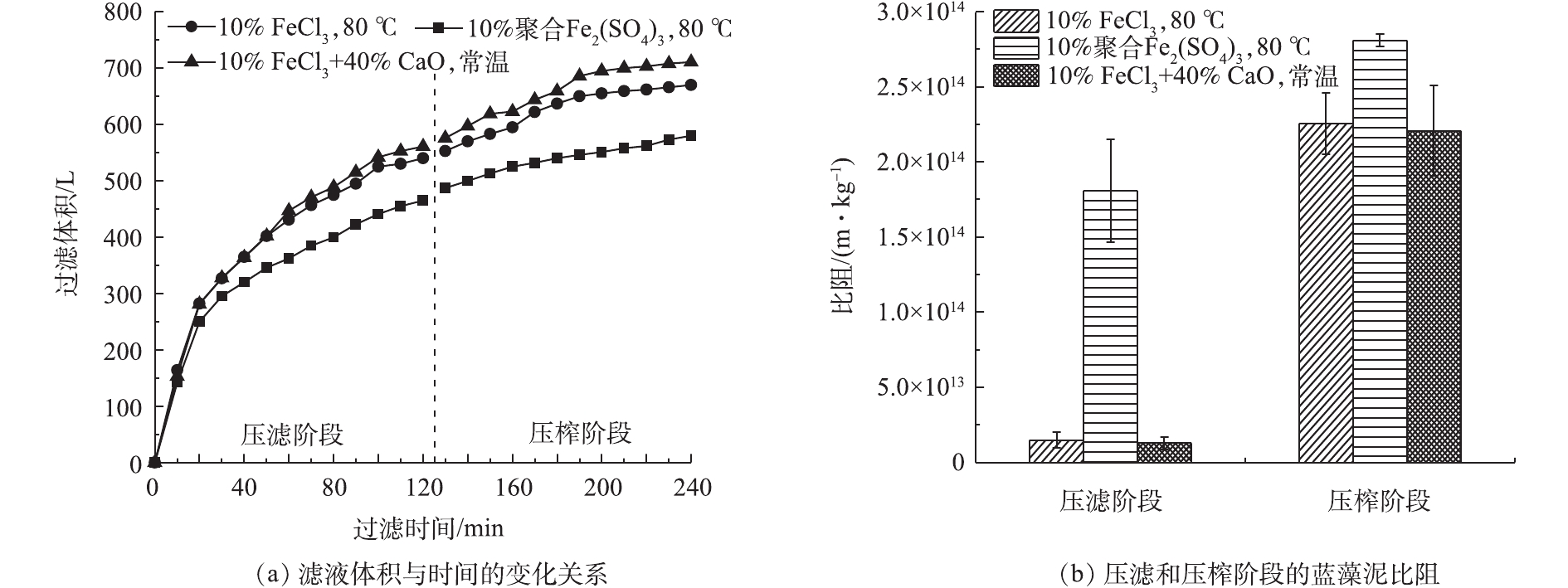
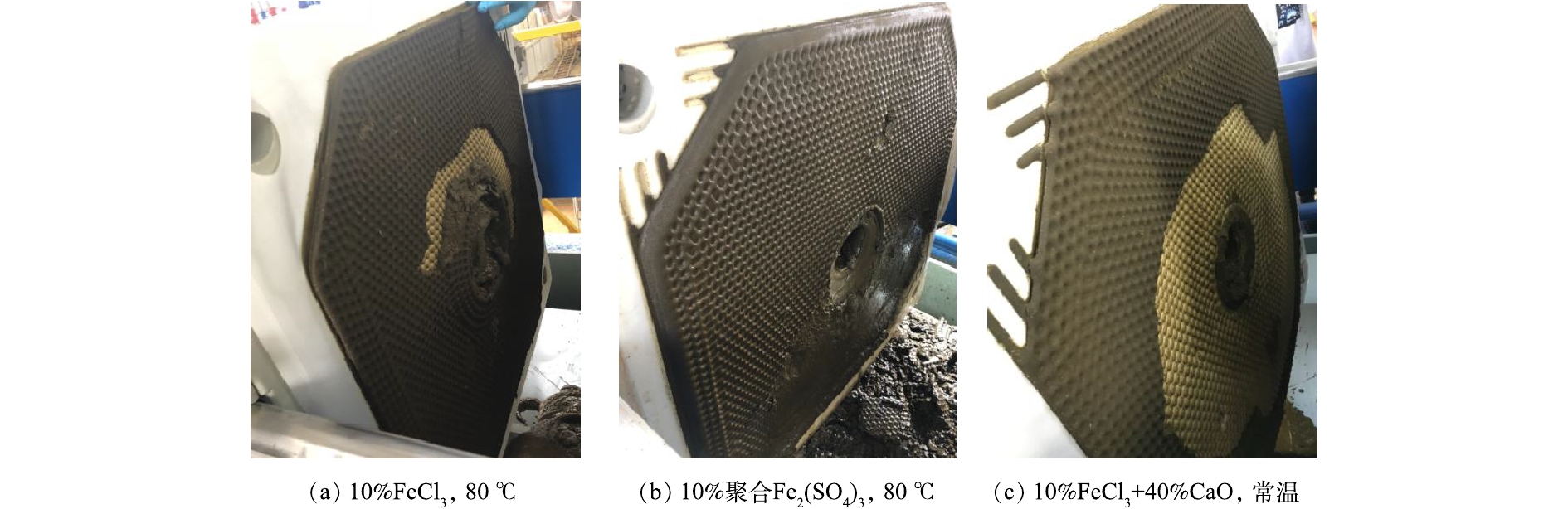
通过研究絮凝剂、温度等基础工艺条件对蓝藻泥热压滤脱水性能的影响,最终得出最佳的热压滤条件:添加蓝藻泥干质量10%的FeCl3,热滤温度为80 ℃ [18]。图2反映了中试条件下热压滤脱水时滤液体积随时间的变化关系以及蓝藻饼的比阻。
由图2(a)可知,在压滤最初的20 min内,3组实验的压滤速度相似。随着压滤的进行,实验组1(10% FeCl3,80 ºC)和实验组3(10%FeCl3+40%CaO,常温)的滤液体积逐渐大于实验组2(10%聚合Fe2(SO4)3,80 ℃)。结合图2(b)的比阻数据可知,压滤阶段实验组1、3的比阻分别为1.48×1013 m·kg−1、1.28×1013 m·kg−1,小于实验组2的比阻。因此,在压滤阶段呈现出更优越的压滤性能。随着进料泵的持续工作,滤腔中的料液不断被填充、压紧,过滤速度逐渐变慢。当压滤阶段完成后,仅靠进料泵的压力无法对不断压紧的滤料进一步压滤,此时关闭进料阀,向隔膜腔内通入压榨水,挤压腔内滤料,使滤饼得到进一步压实。在压榨阶段,3组实验仍旧呈现不同的压滤性能,实验组1比阻为2.25×1014 m·kg−1,实验组2比阻为2.81×1014 m·kg−1,实验组3比阻为2.21×1014 m·kg−1。最终,3组实验的滤液总体积分别为670、560和 700 L。
图3为3组压滤脱水之后的蓝藻饼。实验组1滤腔内具有成形的蓝藻饼,平均厚度为15 mm,易与滤布分开和脱落;实验组2滤腔内的蓝藻饼基本成形,但与滤布的粘连情况较为明显,含水率较高;实验组3滤腔内也具有成形的蓝藻饼,但由于加入了大量的CaO,物料充满滤腔时的最大有效进料量受到限制(0.29 t),导致体积减容率较低。
由表1可知,实验组1采用的脱水方式效果较好,蓝藻饼含水率可以降低至65.3%。这是由于热压滤和FeCl3的絮凝效果共同起作用的结果。根据Kozeny-Carman方程[19]可知,压滤的比阻主要取决于体系中颗粒的大小、颗粒的形状(比表面积)、颗粒的可压缩性。当加热蓝藻泥时,铜绿微囊藻(蓝藻泥的主要微生物组成)细胞外的荚膜多糖被融化,导致藻细胞团离散而使颗粒变小,这是加热对压滤不利的一面;但有利的一面是,由于加热导致细胞壁的直接裸露而使颗粒的刚性增强(可压缩性变小),而且FeCl3使离散的细胞重新絮凝聚合,对颗粒进行了重新“组装”而使絮凝后的颗粒变大。在后者的作用下,调理后的蓝藻泥脱水性能得到改善。另外,由于本工艺引入了热压滤工艺,使得无机调理剂的添加量从蓝藻干质量的50%(蓝藻泥处理企业的当前工艺参数)下降至10%,体积减容率也从57.2%提高到71.3%,藻饼的有机质含量从45.6%提高到78.5%。
对比中试实验的结果,选取FeCl3作为助滤剂进行热压滤脱水。在后续的蓝藻饼干化阶段,以水蒸气为热源,采用圆盘干化机将含水率为65.3%的蓝藻饼干化为含水率为30%的蓝藻泥干颗粒,以进行磁性生物炭的制备。而干化阶段蒸发1 t水需要大约1.3 t水蒸气。
FeCl3是耦合蓝藻泥深度脱水和生物炭赋磁的桥联物质。在蓝藻脱水过程中,FeCl3的添加能够中和蓝藻颗粒所带的电荷,减小蓝藻颗粒与水分子的亲和力,使蓝藻颗粒得以絮凝,改善其脱水效率。在制备磁性生物炭过程中,铁元素的存在能够催化蓝藻干颗粒的热解碳化并且使生物炭赋磁[20]。
分析滤液和蓝藻饼中铁元素可知,经过热压滤脱水后的蓝藻饼中约有70%的铁元素得以保留,用于后续的生物炭制备。目前成熟的磁性生物炭制备工艺是在原有的生物炭基础上,利用三价铁离子在碱性条件下陈化形成磁性物质Fe3O4,从而使生物炭赋磁。在本研究中,将生物炭赋磁工艺与碳化热解工艺相结合,在不添加碱性物质的前提下制备磁性生物炭。
-
蓝藻磁性生物炭制备的实验条件:碳化温度300 ℃、碳化时间60 min、活化温度800 ℃、活化时间120 min。由表2可知,经过300 ℃初步碳化后,生物炭BC-300具有一定的碘值和比表面积。当反应温度达到800 ℃时,生物炭BC-800的碘值达到340 mg·g−1,比表面积达到105 m2·g−1,并且总孔容和平均孔径也有相应的提高。由于生物炭BC-800-W采用水蒸气作为活化剂,相较于前2种生物炭具有更好的性能,其碘值相较于生物炭BC-300提高了接近47%,达到391 mg·g−1,比表面积提高了近2倍,达到165 m2·g−1。史宸菲等[21]利用磷酸浸泡蓝藻泥的方式,在500 ℃热解温度下制备蓝藻生物炭,其比表面积为109.55 m2·g−1,低于生物炭BC-800-W的比表面积。其原因是,生物炭BC-800-W制备时热解温度(800 ℃)更高,同时FeCl3和水蒸气在热解过程中发挥催化和活化作用。
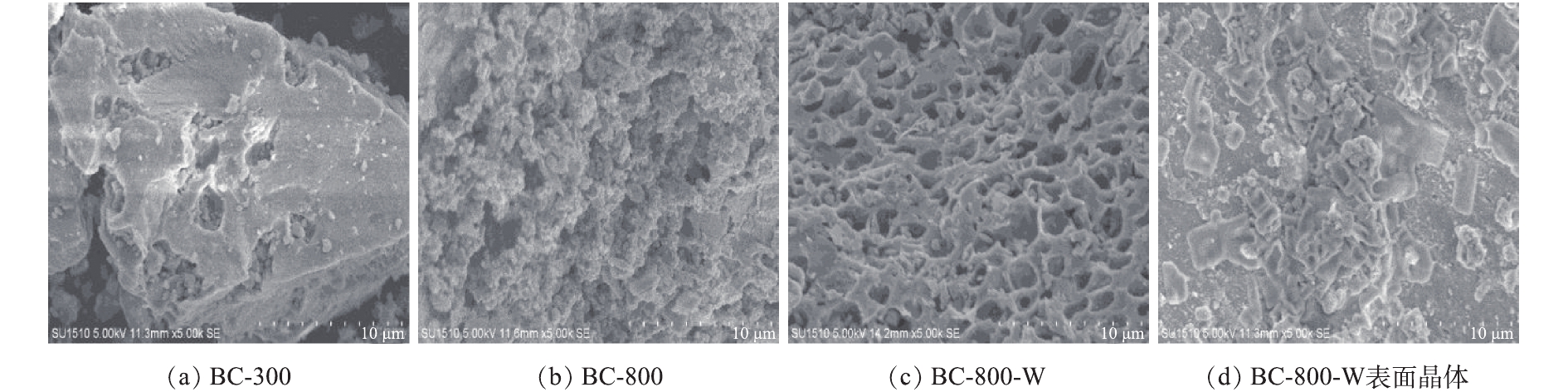
通过SEM表征3种生物炭的形貌和微观结构。图4(a)显示了生物炭BC-300的表观形态。可以看出少量直径约为3 μm的细孔,经过300 ℃碳化后,生物炭表面已经发生少量的还原反应[22]而产生细孔。图4(b)显示了生物炭BC-800拥有相对粗糙的表面。由于反应温度升高,使其发生进一步的还原反应,形成更加细小的孔,增大比表面积。图4(c)显示了生物炭BC-800-W在原有的细孔基础之上又重新蚀刻出新的孔,其表面已经形成整齐排布的致密孔层结构,孔状为圆形,直径约为1.5 μm。由图4(d)可知,生物炭BC-800-W表面已经有明显的晶体生成,推测这些晶体可能为一种铁磁性物质[23]。程伟凤等[24]利用脱水污泥和发酵污泥制备的生物炭,但其表面并未形成整齐排布的致密孔层结构,原因在于制备生物炭的原料有差异。脱水污泥和发酵污泥的VS/TS分别为66.35%和41.10%[24],远低于蓝藻的VS/TS(85.36%)(见1.1节)。正是由于蓝藻泥中有机组分含量较高,在热解过程中更有利于碳还原反应的发生,从而蚀刻出更多致密排列的细孔。
通过EDS对干化之后的蓝藻干颗粒和3种生物炭进行元素分析。由表3可知,在碳化的过程中,碳元素的相对含量升高,氢元素的相对含量较低,证明在该过程中已经发生脱氢固碳的还原反应[21];随着反应温度的升高和水蒸气[25]的引入,脱氢固碳反应发生更加明显,碳元素的相对含量在整个过程中逐渐升高,氢元素的相对含量逐渐降低。同时,虽然氧元素和氮元素有一定程度的降低,但依然会存在于生物炭中,有利于在其表面形成含氧、氮的官能团[26];铁元素经过碳化、活化反应之后会有一定程度的损失,大部分铁元素仍旧以FeCl3的形式附着在生物炭表面,经过酸洗、水洗后被除去,但仍会有1.50%左右的铁元素存在。后续将会对制备出的生物炭进行磁滞回线分析,以探究生物炭是否具有磁性。
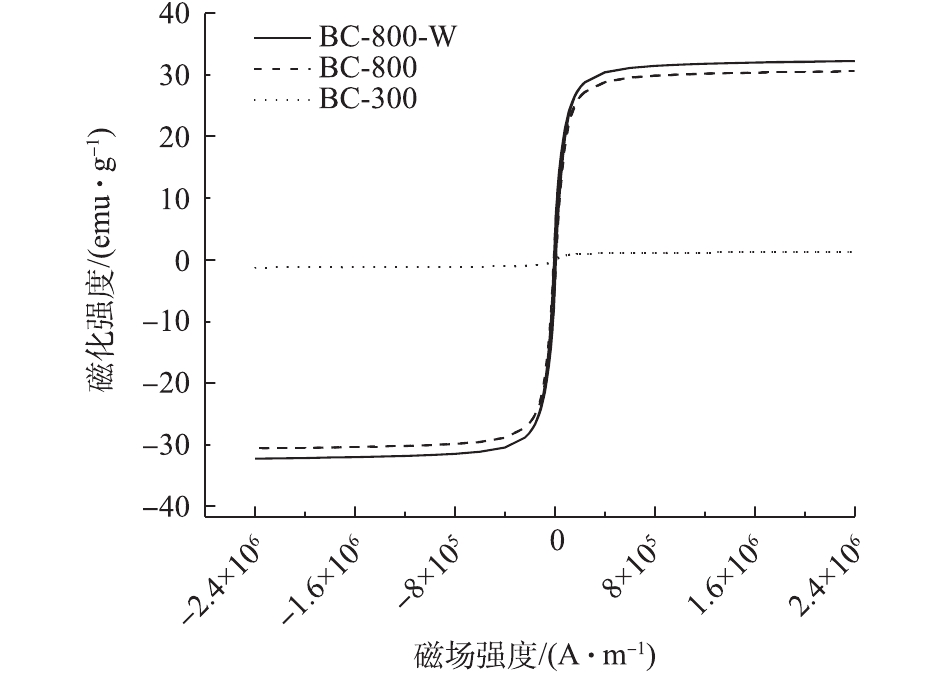
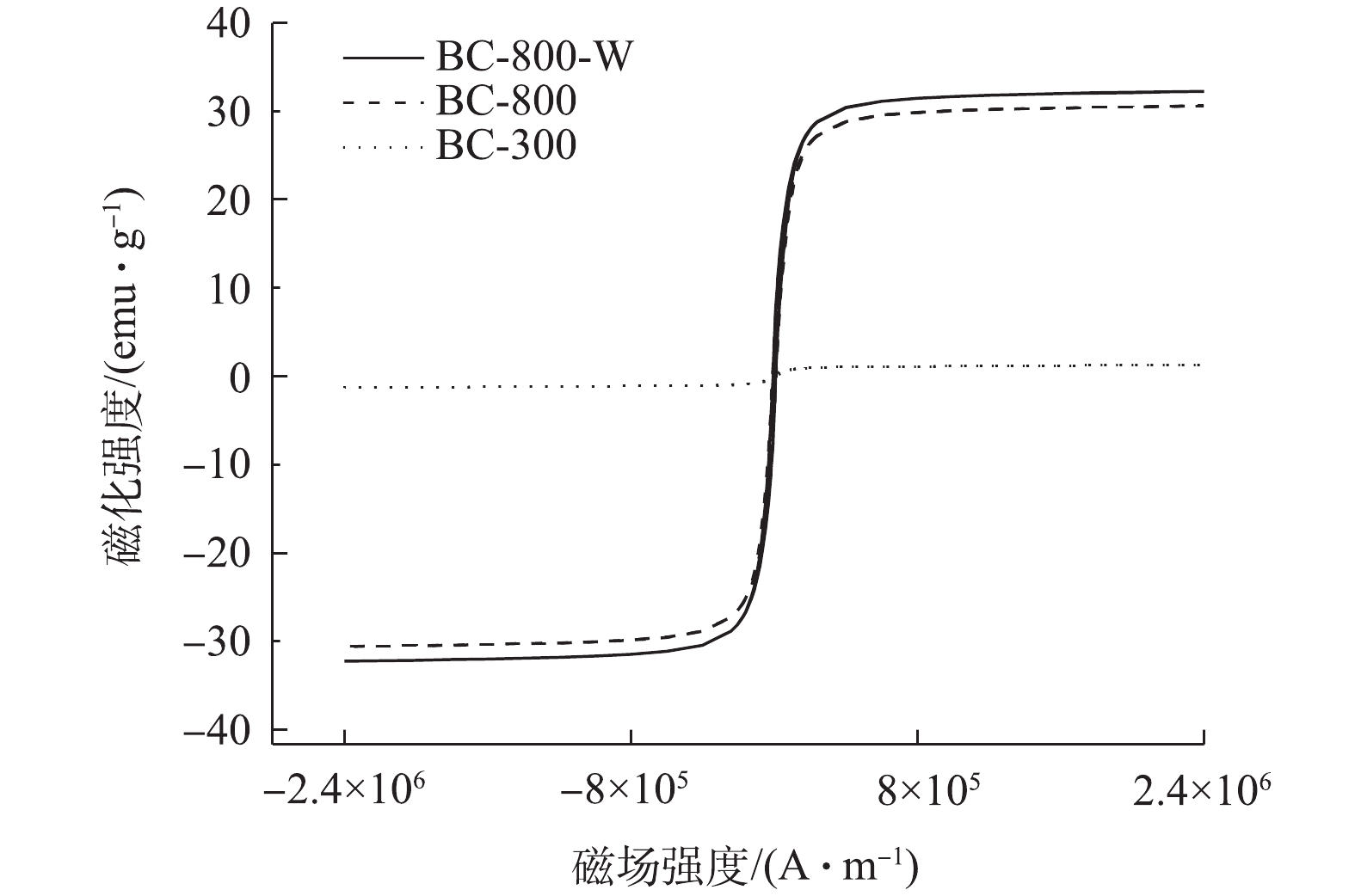
采用磁滞回线检测并判断生物炭的饱和磁化强度。由图5可知,由于3种生物炭的磁滞回线皆表现为重合状态,说明3种生物炭皆表现为可忽略不计的矫顽力和磁化滞后[27]。具体表现为生物炭BC-300饱和磁化强度约为2 emu·g−1,生物炭BC-800饱和磁化强度约为30 emu·g−1,生物炭BC-800-W饱和磁化强度约为32 emu·g−1。由图4(d)看出,在生物炭BC-800-W表面可能已经形成铁磁性物质。而饱和磁化强度的差异,可能是由于铁元素的存在形式存在差异[28]而导致的。与利用油茶树果壳制备的磁性生物炭[29]相比,该研究制备的生物炭BC-800-W饱和磁化强度较高,高于其制备磁性生物炭的饱和磁化强度21.57 emu·g−1。原因在于,生物炭BC-800-W在制备过程中,活化温度更高且有水蒸气的参与,利用的是FeCl3作为赋磁原料。与利用油茶树果壳制备的磁性生物炭[29]相比,生物炭BC-800和BC-800-W所具有的磁化强度,可以使用永久性磁体将其从水溶液中分离出来。
2.1. 蓝藻泥的热压滤脱水
2.2. 蓝藻磁性生物炭的理化性质
-
1)中试规模的蓝藻热压滤深度脱水耦合制备磁性生物炭工艺实验表明,以蓝藻泥干质量10% 的FeCl3作为助滤剂, 在80 ºC时进行热压滤;热压滤阶段会产生670 L的压滤水,压滤阶段蓝藻泥比阻约为1.48×1013 m·kg−1,压榨阶段蓝藻泥比阻约为2.25×1014 m·kg−1,形成蓝藻饼含水率约为65.3%,厚度约为15 mm,体积减容率达到71.3%,VS/TS约为78.5%。
3)经过水蒸气活化后制备的磁性生物炭碘吸附值为391 mg·g−1,比表面积为165 m2·g−1,饱和磁化强度为32 emu·g−1,在其表面可能有铁磁性物质晶体生成。
4) FeCl3作为耦合热压滤深度脱水工艺和制备磁性生物炭工艺的桥联物质,既在前段工艺起到热絮凝的作用,又在后段工艺起到催化反应和生物炭赋磁的作用。



 下载:
下载: