-
胞外聚合物(Extracellular polymeric substance,EPS)是微生物分泌的具有黏性的高分子聚合物,其主要成分为蛋白质、多糖、腐殖酸等物质[1-2]。由于EPS的组成成分中含有大量的羟基、氨基、磷酸基等络合基团,能过通过点中和、络合、离子交换、静电吸引等作用吸附水中重金属[3-5],因此,是一种潜在的重金属吸附剂。近年来,研究人员已逐步开展关于胞外聚合物吸附重金属的研究,并且取得了不错的研究成果。MIAO等[6]提取紧密结合型EPS,对Cu2+进行了吸附实验,研究结果表明,紧密型结合型EPS含量的提高能够促进金属离子的吸附,同时紧密型结合型EPS中羟基、羧基和酰胺对重金属的去除具有重要的作用。SUN等[7]研究了好氧颗粒污泥中松散结合型EPS对Zn2+和Co2+的吸附机制,发现其不仅能起到吸附螯合作用,还能通过絮凝作用强化吸附过程。郑蕾等[8]采用不同组成的活性污泥EPS吸附Cd2+、Zn2+,发现EPS的吸附能力与蛋白质和糖的含量比具有相关性。从已有的研究[8-11]可以看出,关于EPS吸附重金属的研究主要集中在不同结构EPS吸附重金属的特征和机制及不同吸附条件下EPS吸附重金属的吸附效能及模型上,但有关EPS的提取方法对EPS吸附重金属的效能的影响研究较少。如何有效地提取EPS并且保留其有效吸附能力是EPS吸附重金属的研究及其工业化应用的一个重要前提。不同的EPS提取方法对EPS的提取效率和吸附重金属的能力存在一定的影响,从而影响EPS吸附重金属的效能。因此,有必要开展提取方法对EPS吸附重金属效能影响的研究。
目前,关于EPS的提取方法的研究有很多,主要通过破坏细胞与EPS之间的结合来实现分离提取EPS的目的[12-13]。常用的提取方法主要有NaOH法[13]、离心法[14]、超声法[15]、加热法[16]及其组合方法[15]等。SUN等[17]对EPS的提取方法进行了评价,结果表明化学法提取效率高于物理法。CAUDAN等[18]采用结合方法提取EPS,结果显示组合方法提取效率要高于单一方法。虽然关于EPS的提取方法的研究已有许多,但是主要集中在EPS提取效率方面,而提取过程中对于EPS吸附重金属的能力影响的相关研究较少。本研究通过考察pH、单一物理提取方法和组合方法对EPS的提取量及其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)能力的影响,确定了EPS吸附剂的最优提取方法,为EPS重金属吸附剂的有效提取及工业化应用提参考。
-
脱水污泥取自佛山禅城某生活污水处理厂的污泥脱水机房(污泥含水率为77%,有机质质量分数为36.78%),该污水处理厂处理工艺采用UNITANK工艺,污泥取回后,立即放置于−18 ℃冰箱,冷冻保存。
实验过程中使用的盐酸(HCl)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、氯化钠(NaCl)、碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)等化学药剂均为分析纯;硝酸(HNO3)、硝酸镉(Cd(NO3)2)为优级纯。
-
数显恒温水浴锅(HH-S2,常州万达升实验仪器有限公司);超声波清洗仪(GTSONIC-D20,广东固特超声股份有限公司);冷冻高速离心机(FC-18R,广州市方统生物科技有限公司);台式全温振荡器(ZQTY-70S,上海知楚仪器有限公司);原子吸收分光光度计(200AA,安捷伦科技有限公司);紫外-可见光分光光度计(UV-1800,日本岛津制作所);电子分析天平(AS 220.RS,RADWAG公司);pH计(ST-2100,美国OHAUS公司);恒温磁力搅拌器(HJ-6B,常州朗越仪器制造有限公司)。
-
在提取脱水污泥前,须对脱水污泥进行清洗,以去除脱水污泥表面的污染物质。按固液比为1∶7的比例加入纯水,充分混匀后,静置去除上清液,重复清洗污泥3遍,清洗后的脱水污泥待用。
首先确定不同的提取液pH对EPS提取量及吸附效能的影响。取适量污泥3份,按照固液比为1∶7的比例分别加入0.01 mol·L−1 HCl溶液、0.9% NaCl溶液和0.01 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液,在250 r·min−1转速下,搅拌2 h后,于12 000 r·min−1转速下离心20 min,取其上清液过45 µm滤膜,制备取得EPS。取0.01 g提取后EPS(投加量为100 mg·L−1),投加到100 mL 3.6 mmol·L−1 Cd(Ⅱ)模拟废水中,在165 r·min−1、25 ℃下振荡2 h后,取50 mL吸附溶液,转移进入透析袋(截留分子质量为8 000~12 000 Da)中;在350 r·min−1、25 ℃于500 mL纯水中透析6 h后,取透析袋外的纯水测定水中的Cd(Ⅱ)的浓度。
根据提取量和Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量确定提取液pH后,采用单一的物理处理方法和组合的物理处理方法提取EPS,以确定物理处理方法对EPS提取量及吸附效能的影响。
单一物理处理方法:取80 g预处理后污泥各3份,按照固液比为1∶7的比例加入相应的pH提取液,在250 r·min−1 转速搅拌2 h后,在离心(12 000 r·min−1)、超声(40 kHz)和加热(80 ℃)的条件下,处理20 min后,取其上清液过45 µm滤膜,制备取得EPS。
组合物理处理方法:取80 g预处理后污泥各3份,按照固液比为1∶7的比例加入相应的pH提取液,在250 r·min−1 转速搅拌2 h后,在超声(40 kHz,10 min)+离心(12 000 r·min−1,10 min)、超声(40 kHz,10 min)+加热(80 ℃,10 min)和加热(80 ℃,10 min)+离心(12 000 r·min−1,10 min)的组合条件下处理,取其上清液过45 µm滤膜,制备取得EPS。
取0.01 g提取后EPS,投加到100 mL 3.6 mmol·L−1 Cd(II)模拟废水中,在165 r·min−1、 25 ℃下振荡2 h后,取50 mL吸附溶液,转移进入透析袋(截留分子质量8 000~12 000 Da)中,在350 r·min−1、 25 ℃下于500 mL纯水中透析6 h后,取透析袋外的纯水测定水中的Cd(II)的浓度。
-
采用Folin-酚法测定提取的EPS中的蛋白质含量;采用蒽酮比色法测定提取的EPS中多糖的含量;采用蛋白质含量和多糖含量总和来表征EPS的总提取量;采用pH计测定pH;采用原子吸收分光光度计测定吸附前后的Cd(Ⅱ)浓度。各实验均进行3次平行实验,取平均值作为最终的实验结果。
-
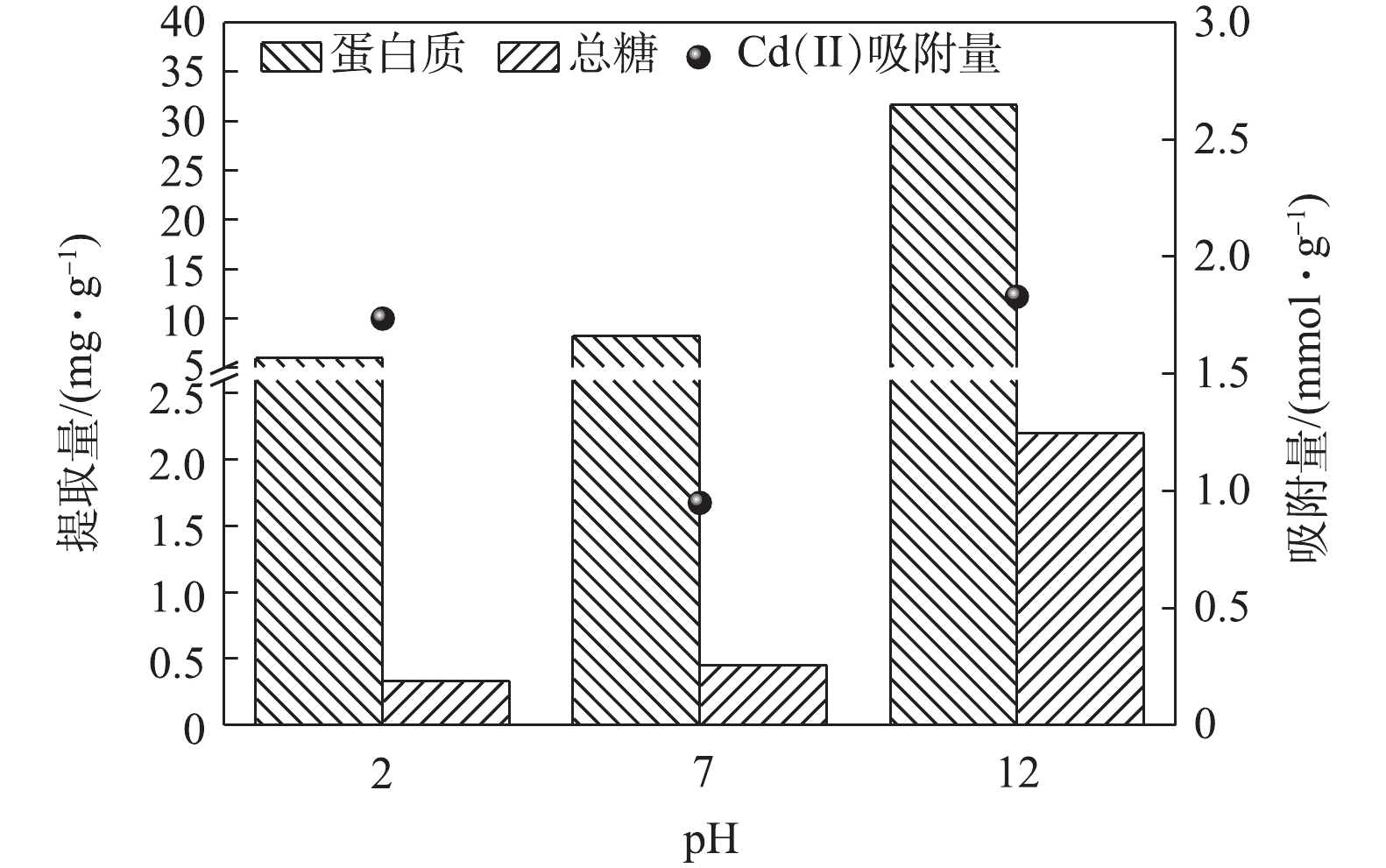
在离心条件下,不同pH对EPS的组分的提取量及其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量如图1所示。由图1可知,随着pH的升高,提取的EPS量呈现逐步增加的趋势,蛋白质的提取量影响最大。EPS提取量在酸性条件下和中性条件下较为接近,随着pH升高至碱性条件,EPS中的蛋白质有明显增加。LIAO等[19]研究表明,EPS表面带有大量的负电荷,可以影响其与其他物质之间的静电作用和氢键的形成,进而影响其提取量。由于pH与静电作用和氢键形成关系密切[20],因此,对EPS的提取以及性质影响也较为明显。强碱性条件能够破坏微生物的细胞壁,同时改变了EPS的水溶性,从而使大量的蛋白质和多糖得到释放[20-21],进而导致提取量剧增。
由图1可知,中性条件下提取的EPS对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量最小,而酸性或碱性条件下提取的EPS对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量较中性条件下的高。这说明酸碱的预处理有利于EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的有效成分的提取。在酸性条件下,虽然提取的EPS量较少,但其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力可达到1.73 mmol·g−1。这说明酸性条件下,提取EPS的有效成分或吸附位点较多。SU等[22]和宋小莉[23]的研究表明,蛋白质在强酸的条件下易发生水解,生成氨基酸类化合物,进而增加了EPS中的氨基和巯基等官能团,有利于EPS和重金属发生螯合反应;在碱性条件下,OH−促进了EPS的络合基团去质子化,从而活化EPS的络合基团,最终可增强EPS的络合吸附能力。
根据单位质量EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的量及单位污泥提取EPS的量,计算出酸性、中性和碱性条件下单位污泥提取的EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的总量分别为0.010 9、0.008 2和0.061 8 mmol·g−1。由不同pH的单位污泥提取EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的总量对比可以看出,碱性条件下单位污泥提取EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的总量约为酸性条件下的6倍左右。由此可见,虽然酸提和碱提都能够有效地提高EPS对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附效能,但是考虑到单位污泥提取EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)总量差异,确定碱性条件为提取EPS的最佳条件。
-
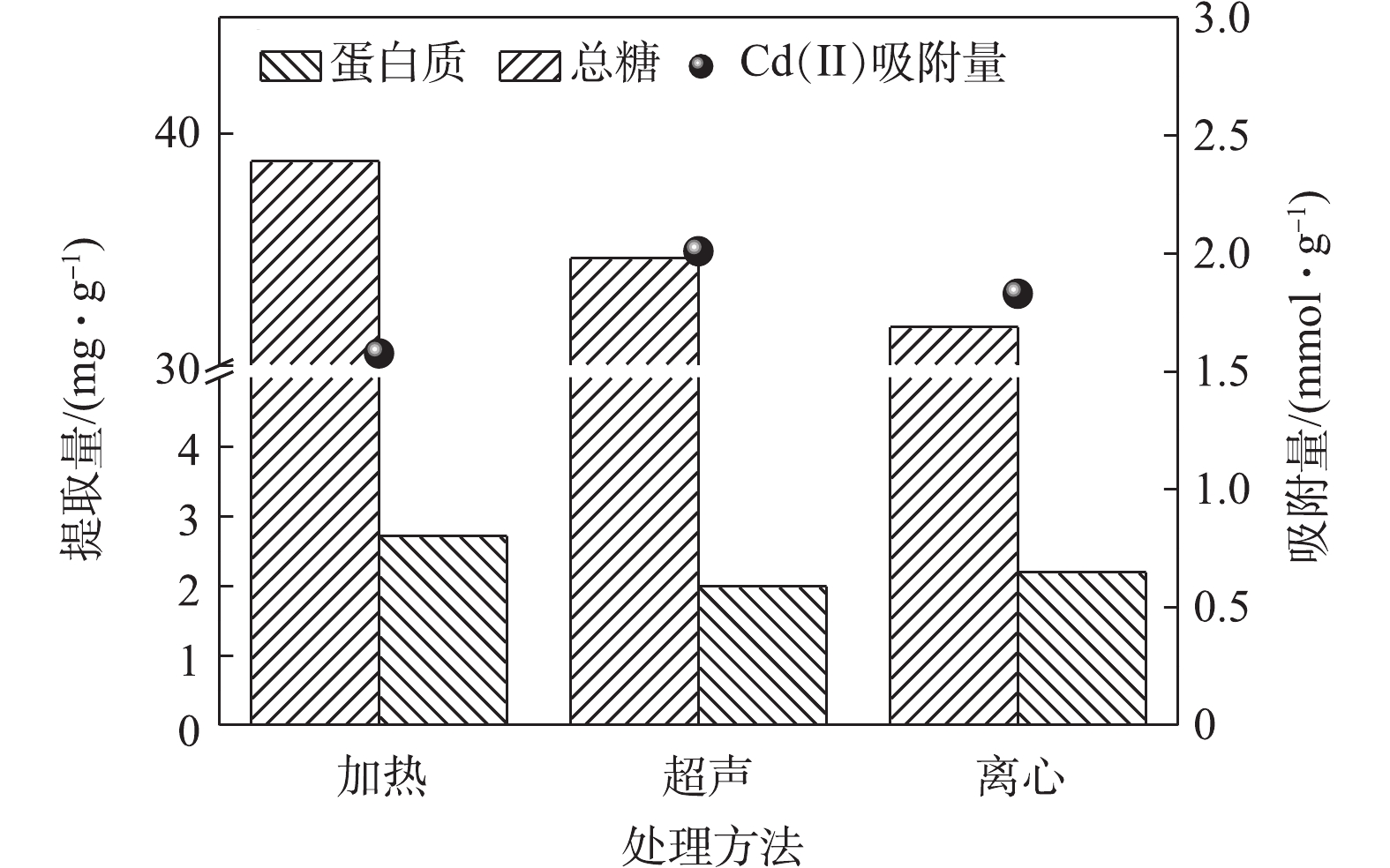
在碱性提取条件下,不同的物理处理方法对EPS的组分提取量及其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的效能影响如图2所示。不同的物理提取方法由于其作用的强度不同,因此,对EPS的提取量及其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的有效组分具有一定的影响。加热法主要通过加热使污泥结构松散,能够有效提高EPS的提取量[23];超声法利用剪切力和空穴形成的压力冲击来使EPS剥离[24];高速离心法主要利用离心力使得EPS脱离。对比3种方法的作用强度,可以看出,加热法最强,离心法最弱。由图2可知,不同的物理处理方法对EPS的提取量有较大的影响,其中加热法的提取量最大,其次为超声法,最低为离心法,这与以往的研究规律相符。虽然提取强度越大,越有利于提取量的增加,但过大的提取强度,容易对EPS中的有效组分造成影响,进而影响其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力。由图2亦可知,虽然加热法的提取量最高,但是其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力却为最低。这主要由于加热过程中,温度过高容易破坏EPS的有效组分[2],导致其吸附能力降低。而超声法通过剪切力等作用,相比加热法较为温和,在有效分离EPS有效组分的同时,又能够避免破坏EPS的有效组分, 其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力较加热法和离心法要高。因此,必须控制好提取作用强度,才能有效地提高EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的效能。
-
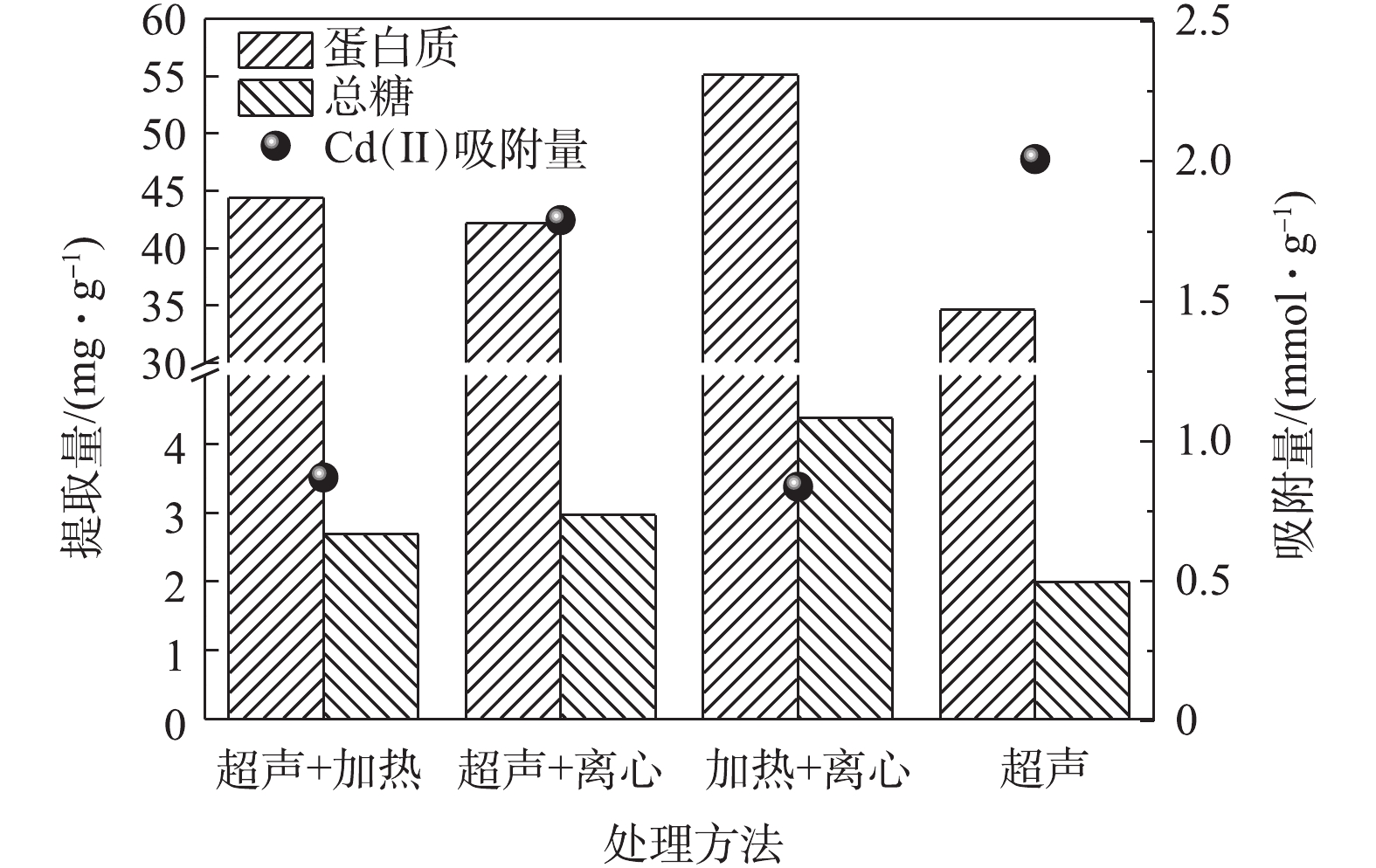
CAUDAN等[18]和MIAO等[25]研究表明,组合物理方法有利于提高EPS的提取量。由图3可知,组合物理处理方法提取的EPS总量均大于单一物理提取方法的EPS提取总量。其中,加热+离心组合预处理提取的EPS量最高,其次为超声+加热,而超声+离心组合处理提取EPS量最小。这主要是由于加热能让EPS大量释出,辅助高速离心,能够更大程度地将EPS分离出来,使得加热+离心的组合方法提取EPS效果最好。超声+离心提供的提取强度较其他的提取方法较弱,导致提取量最低。由不同组合方法吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量对比可以看出,虽然加热+离心的提取量最大,但是其吸附能力最差。原因可能是:由于提取强度的增加,虽然有利于EPS的提取,但是同时也可能破坏了EPS中的有效成分或官能基团,导致其吸附能力下降;同时,通过图3可以看出,单一处理方法提取的EPS的吸附能力均大于组合方法提取的EPS的吸附能力,综合考虑经济性和实用性,超声的预处理方法更有利于EPS吸附剂的提取。
-
1) pH对于EPS的提取有较大的影响,pH越高,EPS提取量越大。酸性或碱性条件有利于EPS的有效成分的释出,从而有利于Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附。同时考虑EPS提取量及吸附能力,碱性条件较佳。
2)提取强度与EPS的提取量具有正相关性,其排序为加热>超声>离心;EPS吸附Cd((Ⅱ)的能力与提取强度不具正相关性,提取强度过大,不利于EPS有效吸附组分的保留。在碱性条件下,利用超声处理方法提取的EPS对Cd(II)的吸附能力最强,吸附量达到2.01 mmol·g−1。
3)组合物理提取方法有利于EPS的提取,但其提取的EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力较单一物理提取方法提升不高,因此,EPS最佳提取方法为在碱性条件下进行超声提取。
不同提取方法对活性污泥胞外聚合物吸附废水中Cd(Ⅱ)效能的影响
Effect of different extracellular polymer extraction methods from activated sludge on its adsorption capacity of Cd(Ⅱ) in wastewater
-
摘要: 为了比较不同提取方法对胞外聚合物(EPS)的提取及其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的影响,考察了pH、单一物理提取方法和组合方法对脱水污泥中EPS的提取量及其对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附能力的影响。结果表明:碱性条件在能够提高EPS提取量的同时,也能够提高EPS对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附能力;不同物理处理方法对EPS的提取效率影响顺序为加热法>超声法>离心法,但其对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附能力影响顺序为超声法>离心法>加热法;组合物理方法虽然较单一方法的EPS提取效率要高,但其提取EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力较单一方法弱。以上结果可为EPS重金属吸附剂的有效提取和工业化应用提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 胞外聚合物(EPS) /
- Cd(Ⅱ) /
- 吸附能力 /
- 提取方法
Abstract: To compare the effects of extraction methods on Cd(Ⅱ) adsorption by extracellular polymers(EPS), the EPS extraction amount and its adsorption capacity of Cd(Ⅱ) corresponding to different pH and physical extraction methods were studied. The results showed that the alkaline condition was beneficial to increase the EPS extraction amount and its Cd(Ⅱ) adsorption capacity accordingly. The EPS extraction efficiency by different physical treatment methods followed the sequence of heating method>ultrasonic method>centrifugal method, while the adsorption capacity of Cd(Ⅱ) followed the sequence of ultrasonic method>centrifugal method>heating method. Although the combined physical method was more efficient than the single method in EPS extraction, its Cd(Ⅱ) adsorption capacity was lower than single method. The result of this study can provide some theoretical guidance for the extracted EPS as heavy metal adsorbent.-
Key words:
- extracelluar polymeric substances(EPS) /
- Cd(Ⅱ) /
- adsorption capacity /
- extraction method
-

-
-
[1] 吴桂荣, 储昭瑞, 荣宏伟, 等. 不同方法提取活性污泥胞外聚合物的特性分析[J]. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 16(6): 77-83. [2] 杨飘, 康得军, 谢丹瑜, 等. 不同方法组合对活性污泥胞外聚合物的提取[J]. 净水技术, 2016, 35(6): 88-92. [3] HA J G, LABERT A, SPORMANN A M, et al. Role of extracellular polymeric substances in metal ion complexation on shewanella oneidensis: Batch uptake, thermodynamic modeling, ATR-FTIR, and EXAFS study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.06.031 [4] LIU W, ZHANG J S, JIN Y J, et al. Adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) by extracellular polymeric substances extracted from aerobic granular sludge: Efficiency of protein[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 3(2): 1223-1232. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2015.04.009 [5] JIANG J Q, ZHAO Q L, WEI L L, et al. Extracellular biological organic matters in microbial fuel cell using sewage sludge as fuel[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(7): 2163-2170. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.12.033 [6] MIAO L Z, WANG C, HOU J, et al. Response of wastewater biofilm to CuO nanoparticle exposure in terms of extracellular polymeric substances and microbial community structure[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 579: 588-597. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.056 [7] SUN X F, WANG S G, ZHANG X M, et al. Spectroscopic study of Zn2+ and Co2+ binding to extracellular polymeric substances(EPS) from aerobic granules[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, 335(1): 11-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2009.03.088 [8] 郑蕾, 丁爱中, 王金生, 等. 不同组成活性污泥胞外聚合物吸附Cd2+、Zn2+特征[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(10): 2850-2855. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.10.029 [9] HU J L, HE X W, WANG C R, et al. Cadmium adsorption characteristic of alkali modified sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 121: 25-30. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.100 [10] SHENG G P, YU H Q, YU Z. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas acidophila[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2005, 67(1): 125-130. doi: 10.1007/s00253-004-1704-5 [11] 董明, 宋卫锋, 程亚杰. 苯胺黑药高效降解菌(Bacillus vallismortis)胞外聚合物去除重金属的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(12): 4367-4375. [12] D'ABZAC P, BORDAS F, VAN HULLEBUSCH E, et al. Effects of extraction procedures on metal binding properties of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from anaerobic granular sludges[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2010, 80(2): 161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.05.043 [13] LIANG Z W, LI W H, YANG S Y, et al. Extraction and structural characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), pellets in autotrophic nitrifying biofilm and activated sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 81(5): 626-632. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.03.043 [14] LU X Q, ZHEN G Y, ESTRADA A L, et al. Operation performance and granule characterization of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating wastewater with starch as the sole carbon source[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 180: 264-273. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.010 [15] D'ABZAC P, BORDAS F, VAN HULLEBUSCH E, et al. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from anaerobic granular sludges: comparison of chemical and physical extraction protocols[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 85(5): 1589-1599. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2288-x [16] LI N, WEI D, WANG S T, et al. Comparative study of the role of extracellular polymeric substances in biosorption of Ni(II) onto aerobic/anaerobic granular sludge[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 490: 754-761. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.12.006 [17] SUN M, LI W W, YU H Q, et al. A novel integrated approach to quantitatively evaluate the efficiency of extracellular polymeric substances(EPS) extraction process[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 96(6): 1577-1585. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4478-1 [18] CAUDAN C, FILALI A, LEFEBVRE D, et al. Extracellular polymeric substances(EPS) from aerobic granular sludges: Extraction, fractionation, and anionic properties[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2012, 166(7): 1685-1702. doi: 10.1007/s12010-012-9569-z [19] LIAO B Q, ALLEN D G, DROPPO I G, et al. Surface properties of sludge and their role in bioflocculation and settleability[J]. Water Research, 2001, 35(2): 339-350. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00277-3 [20] 邢奕, 王志强, 洪晨, 等. 不同pH值下胞外聚合物对污泥脱水性能及束缚水含量的影响[J]. 工程科学学报, 2015, 37(10): 1387-1395. [21] HWANG J, ZHANG L, SEO S, et al. Protein recovery from excess sludge for its use as animal feed[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(18): 8949-8954. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.05.001 [22] SU W, TANG B, FU F L, et al. A new insight into resource recovery of excess sewage sludge: Feasibility of extracting mixed amino acids as an environment-friendly corrosion inhibitor for industrial pickling[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 279: 38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.053 [23] 宋小莉. 基于蛋白质回收的剩余污泥热碱水解技术研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017. [24] 刘翔, 黄映恩, 刘燕, 等. 活性污泥和生物膜的胞外聚合物提取方法比较[J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2011, 50(5): 556-562. [25] MIAO L Z, WANG C, HOU J, et al. Contributions of different fractions of extracellular polymeric substances from waste-activated sludge to Cu(II) biosorption[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2015, 57(45): 21405-21416. -



 下载:
下载: