-
燃煤发电脱硫系统的污染排放治理与系统能效的协同耦合机理对实现节能优先的目标具有决定性作用,也是集中治理燃煤污染、解决环境问题的关键。石灰石-石膏湿法烟气脱硫技术是国内外大型燃煤电厂应用范围最广的脱硫技术[1-4],而脱硫过程是涉及三传一反等多因素相互关联的复杂工艺流程,因此,湿法脱硫系统的污染物治理与能耗协同评价仍是一项技术挑战。目前,国内外脱硫系统的能效评价指标体系主要以统计方法构建数学模型,单一地从脱硫系统能耗或者脱硫效率的角度进行分析和评价。在对脱硫效率的评价及分析中,GUO等[5]将数学模型与人工神经网络(ANN)[6-7]联合,建立了一种预测二氧化硫排放的新型WFGD模型;王俊[8]通过SPSS利用多元统计学的方法[9]对某机组脱硫系统的运行数据进行了多元回归建模,确定了影响脱硫效率的关键因子。在对脱硫系统能耗评价方面,杨勇平等[10]以我国典型火电机组湿法脱硫系统实际运行数据[11]为基础,对主要参数进行多元回归分析,建立了脱硫能耗的数学模型;王岳宸[12]设计了基于电耗的能耗计算方法,将石灰石消耗和工艺水耗折算为电耗[13],构建了基于单位SO2脱除量的系统综合能效指标。尽管张健华[14]在建立火电能效综合评价指标体系的基础上,借助灰色关联度分析[15-17]、模糊综合分析[18]、矢量投影理论分析对电厂的能效利用水平进行全面综合的评价分析[19],但只是单纯围绕能效评价而未涉及污染物治理层次。可以看出,现有的评价指标主要存在的不足是不能综合反映脱硫系统污染物治理和系统能耗的协同影响问题。
本研究以某盐化公司220 t·h−1锅炉脱硫塔为例,利用脱硫控制系统在线运行数据,基于支持向量机的深度自学习方法[20],构建了SO2污染排放与系统能效的智能自适应预测模型,系统研究了脱硫系统的污染排放治理与系统能效的协同耦合作用机理,提出了综合考虑污染与能耗协同的评价方法,为实际工业锅炉的能效评价提供参考。
全文HTML
-
支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)是建立在统计学理论基础上的一种数据挖掘方法,可广泛地应用于统计分类以及回归分析。支持向量机的原理是将向量映射到一个更高维的空间里,在这个空间里建立一个最优超平面,在分开数据的超平面的两边建有2个互相平行的超平面,分隔超平面使2个平行超平面的距离最大化。假定平行超平面间的距离越大,分类或回归的总误差越小[21-22]。
-
假设有一样本集:(y1,x1),……,(yi,xi),y∈R,其回归函数线性方程[23]见式(1)。
式中:f(x)为回归函数;w为变量x的函数系数;b为常数。考虑到允许拟合误差的情况,引入松弛因子
ξi ≥0和ξ∗i ≥0,通过函数的最小值找到最佳的回归函数(式(2))。式中:
ξi 和ξ∗i 为松弛变量,ξi 为上限,ξ∗i 为下限;C为平衡因子。在对方程式(2)求解时,一般采用对偶理论,把它转化成二次规划问题。不敏感耗损函数的定义见式(3)。式中:
Ly 为不敏感耗损函数;ε为不敏感系数,用于控制耦合精度。建立Lagrange方程,并对参数求偏导,可得到对偶优化模型[24],模型见式(4)。在约束条件下,方程如式(5)所示。
用SMO算法[25]求出式(5)最小时对应的αi向量的值αi*向量,得到w值(式(6))。
最后得到的回归函数见式(7)。
1.1. 支持向量机回归基本理论
1.2. 支持向量机回归预测的简单算法
-
模型训练样本来自盐化公司220 t·h−1锅炉脱硫塔的817组历史运行数据,主要依据石灰石-石膏湿法脱硫系统反应机理分析和历史运行数据分析结果,明晰支持向量机模型的关键输入变量:脱硫反应塔的入口烟气温度、入口烟气流量、入口SO2浓度、氧气含量、浆液pH、浆液密度和浆液循环泵台数,并综合考虑这7个输入变量对出口SO2浓度的影响。选取的参数如下:入口烟气温度为85.42~136.77 ℃;入口烟气流量为80.925 1~331.779 53 km3·h−1;入口SO2浓度为1 002.33~3 683.48 mg·m−3;氧气含量为3.43~10.75%;浆液pH为3.3~6.6;浆液密度为1 001~1 716 kg·m−3;浆液循环泵1~4台;出口SO2浓度为0.02~173.16 mg·m−3。
-
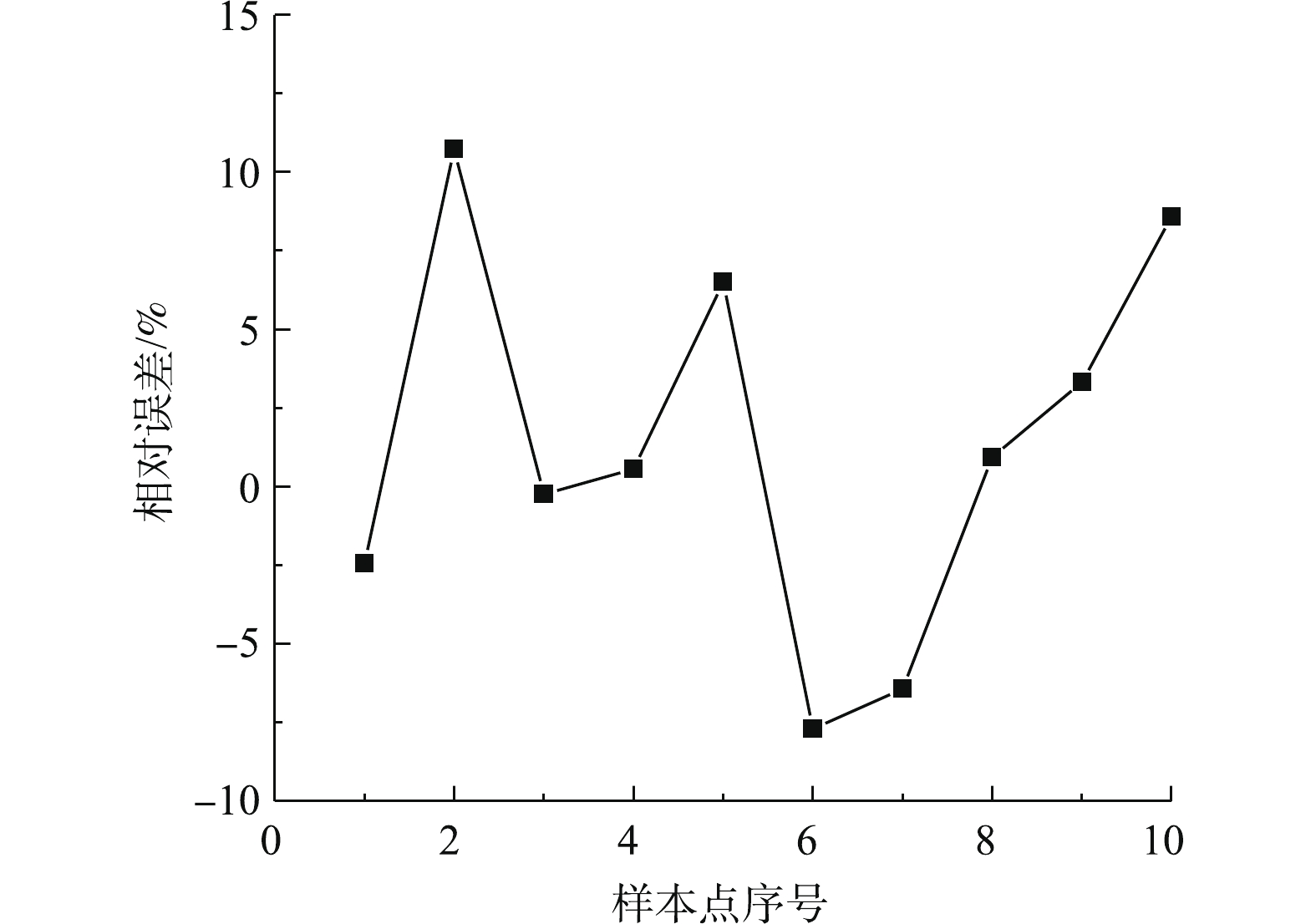
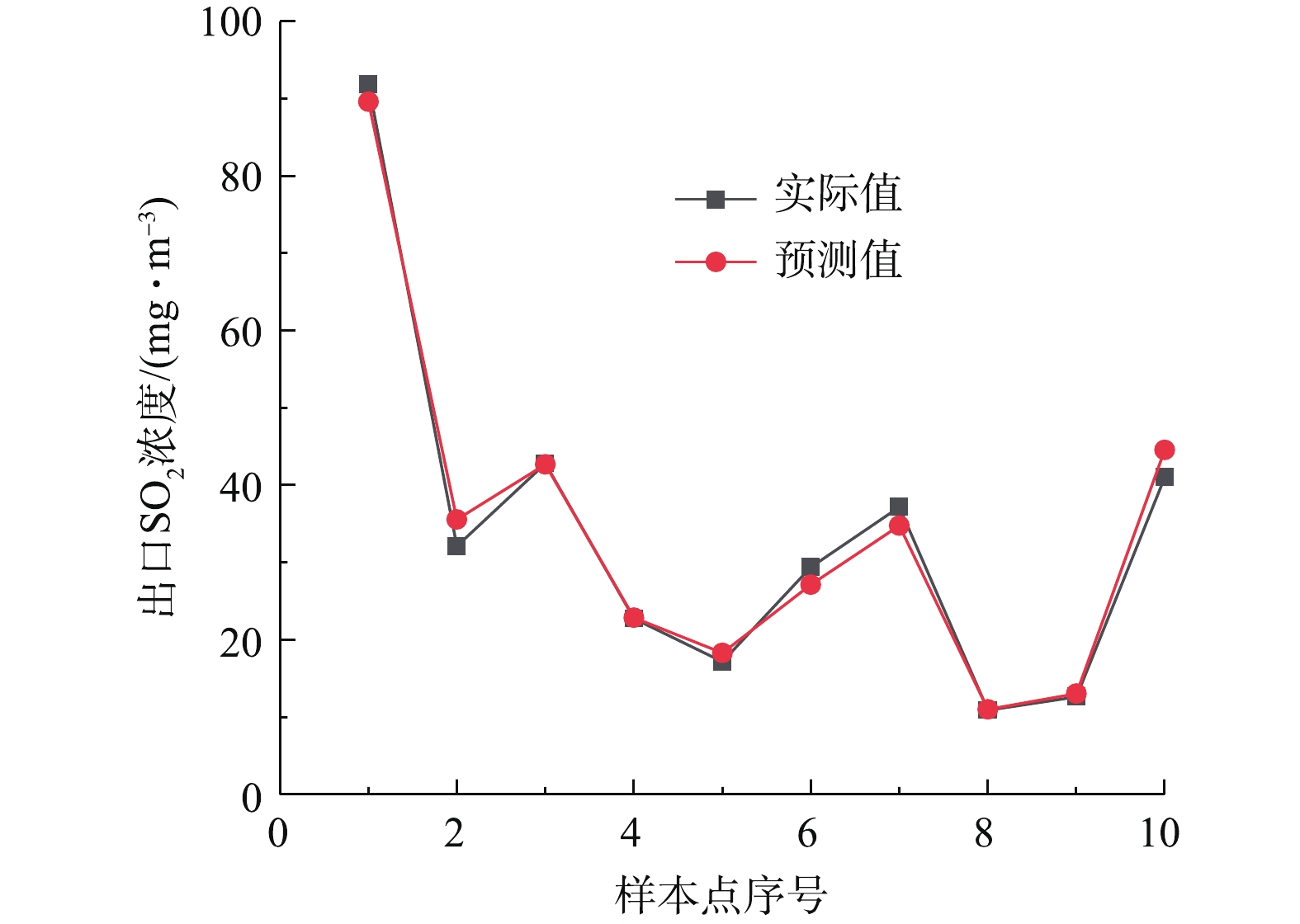
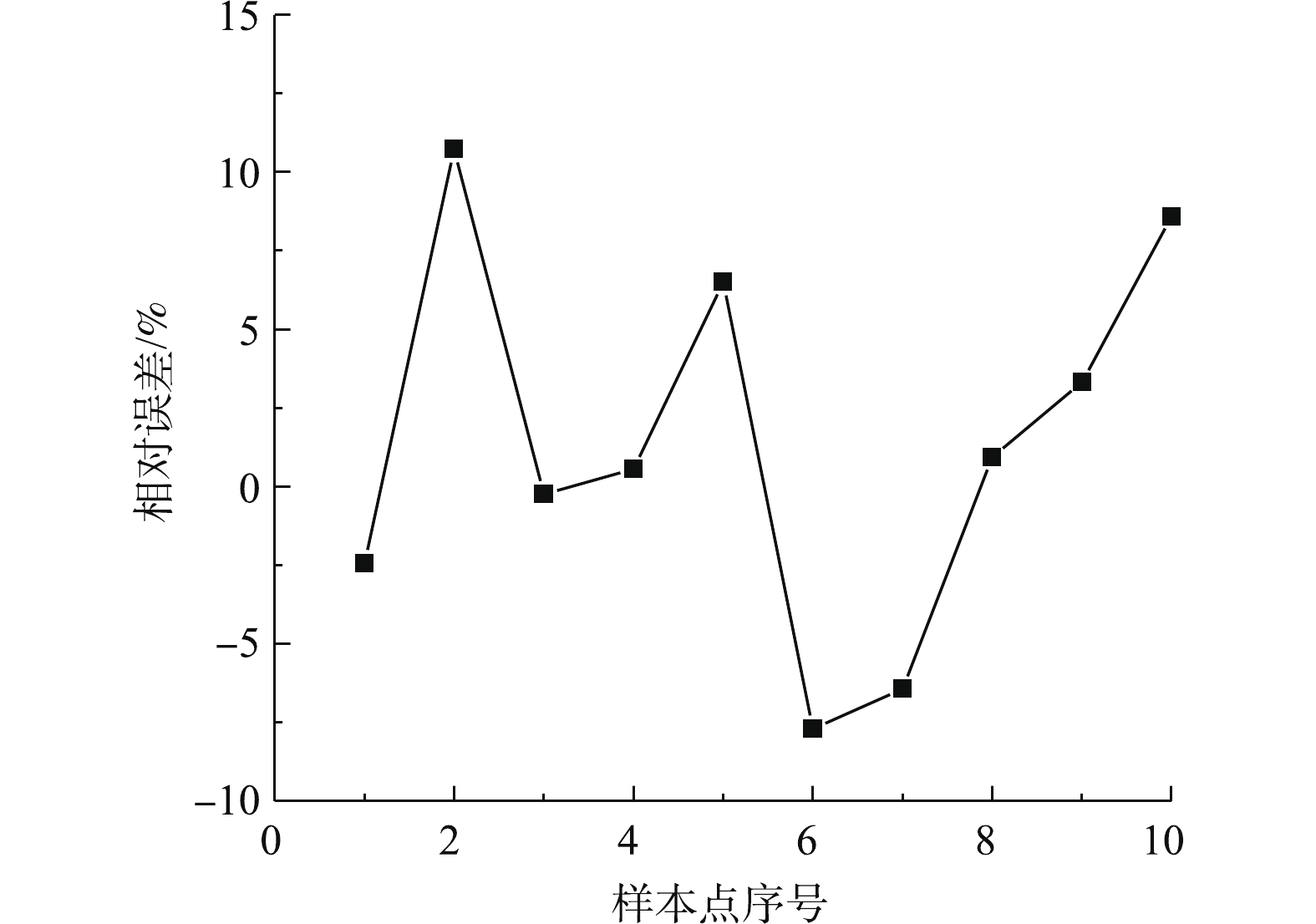
在Matlab的支持向量机工具中,将全部样本数据集分成10个分区进行交叉验证,选择所有类型回归模型进行训练,选取拟合精度最高的二次SVM作为回归模型。随机选取实际运行工况下的10组数据(表1)进行SVM模型预测值和控制系统在线测量值的对比分析。图1和图2分别为预测模型预测值与实际值对比曲线和预测模型相对误差分布曲线,其最大误差不超过10%。可以看出,基于支持向量机回归构建的出口二氧化硫排放浓度预测模型能准确预测脱硫反应塔出口二氧化硫排放浓度。
-
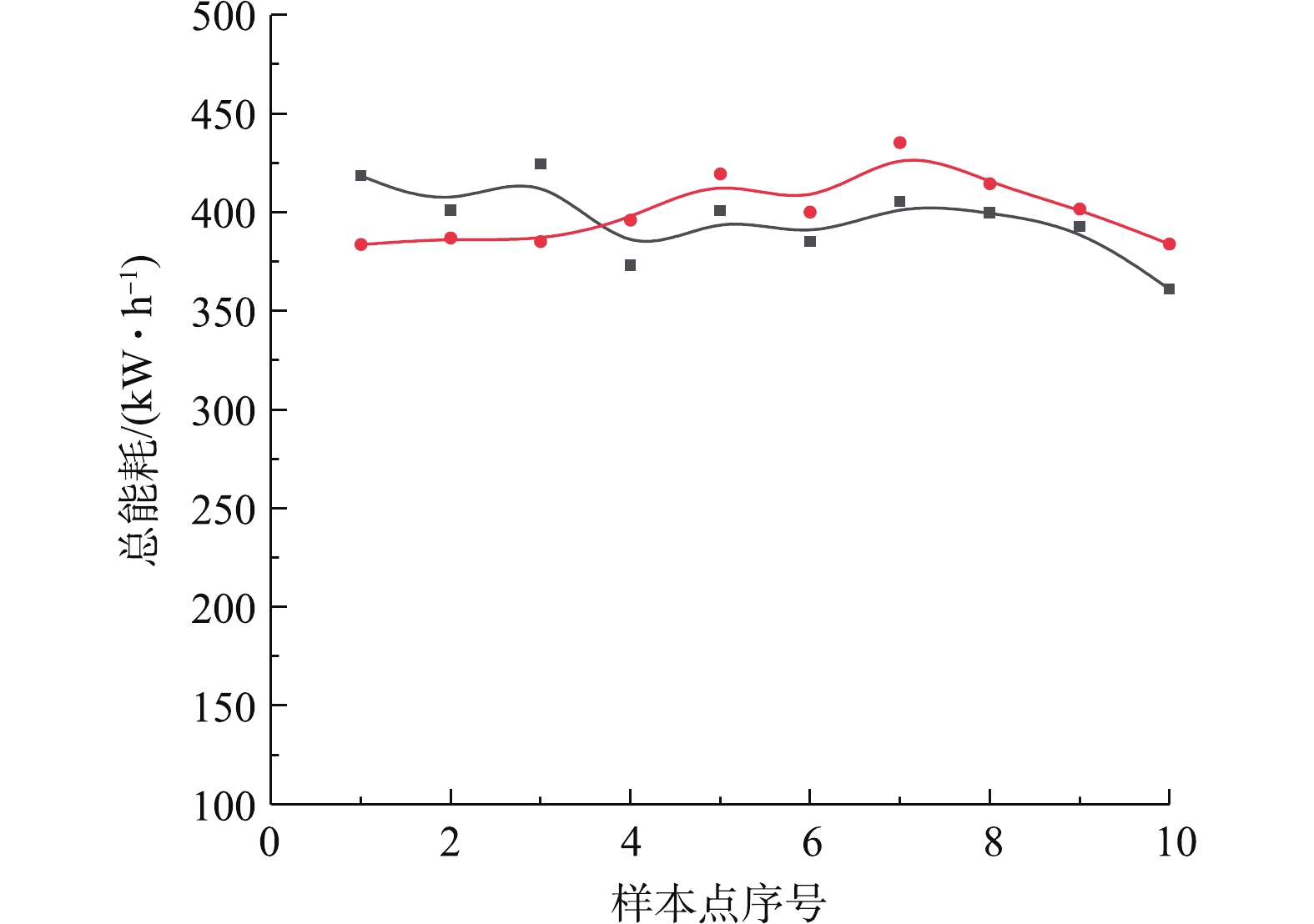
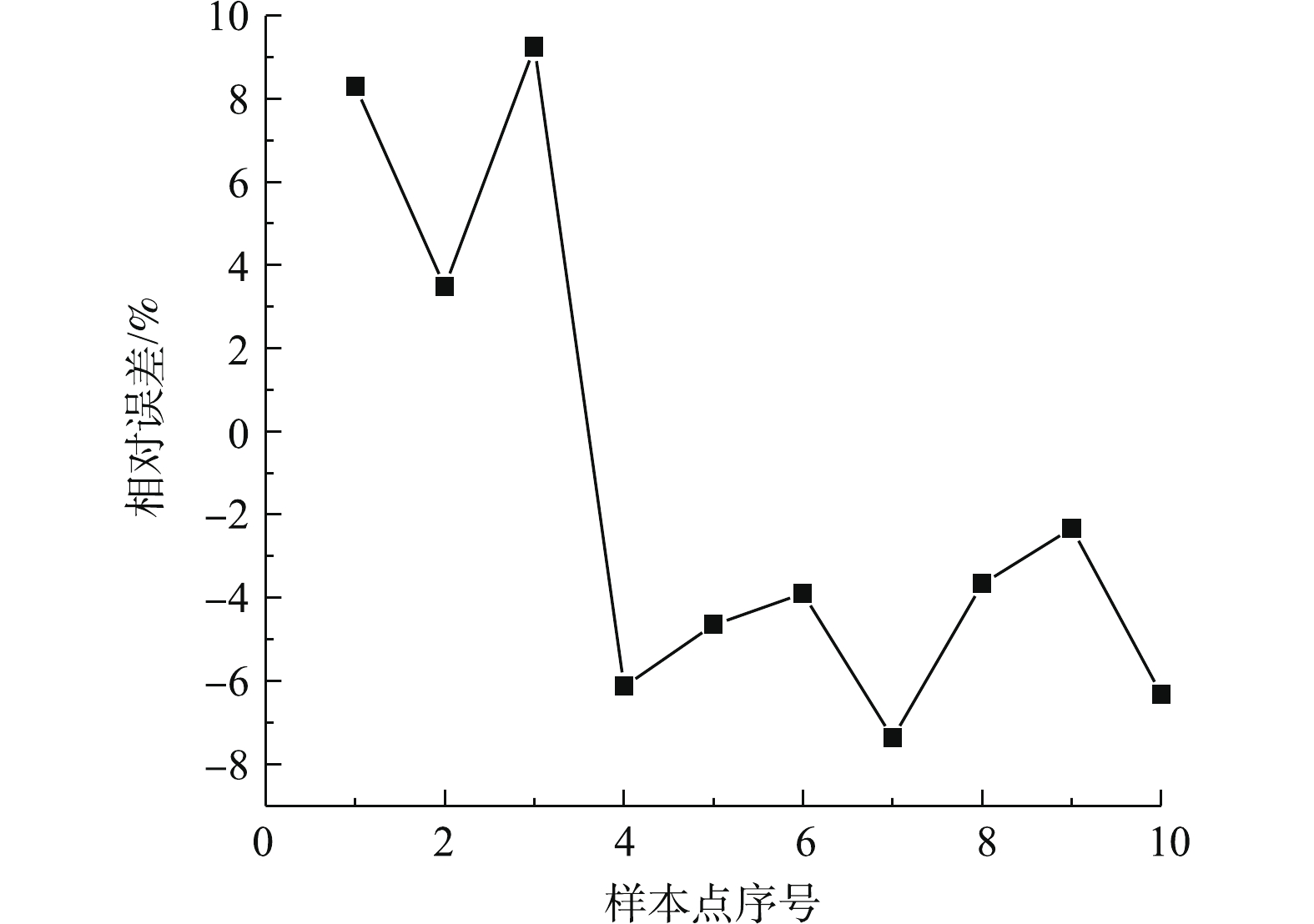
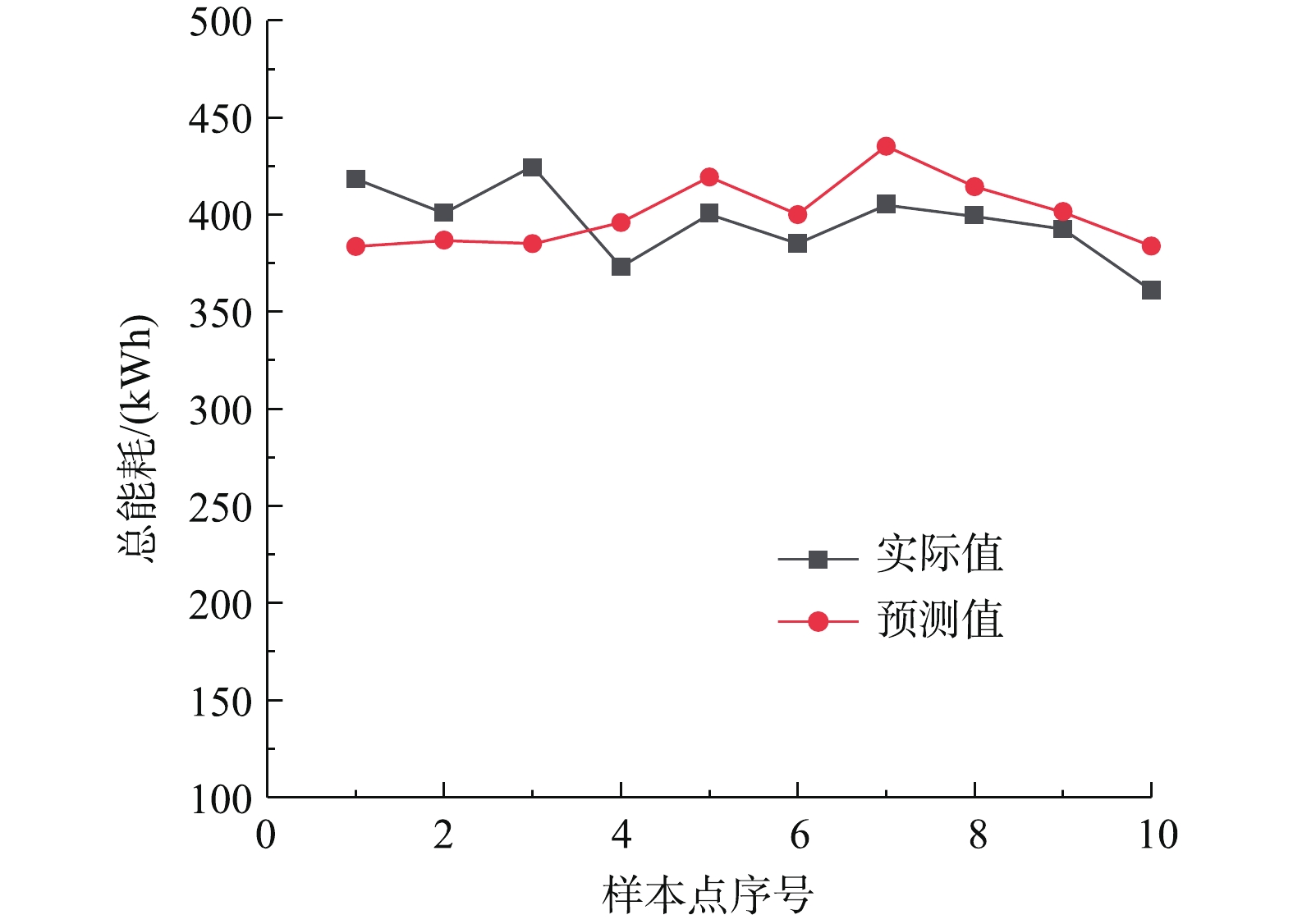
为研究脱硫系统污染与能效的协同关系,基于脱硫系统历史运行数据中的各设备的监测电流及相应参数,计算总能耗,以关键输入变量为基础选取参数组合,以支持向量机的智能学习方法训练,构建系统能耗的预测模型。图3和图4分别为能耗预测模型的预测值与控制系统在线测量值的对比分析曲线,其误差不超过10%。可以看出:基于支持向量机深度自学习回归构建的脱硫系统能耗预测模型能准确预测脱硫塔运行总能耗。
2.1. 模型参数的选取
2.2. 出口二氧化硫排放浓度预测模型的建立与误差分析
2.3. 脱硫系统能耗预测模型的建立与误差分析
-
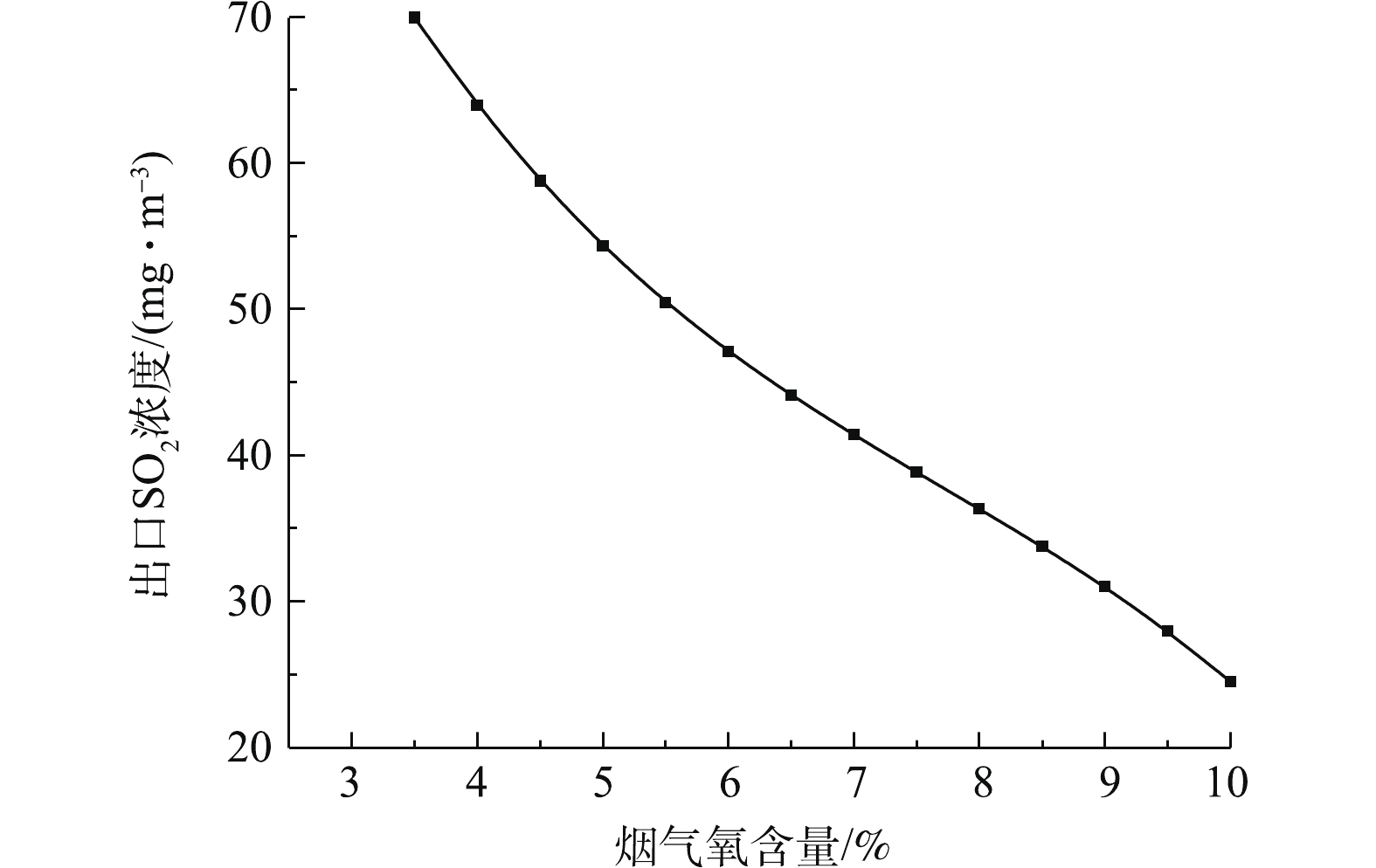
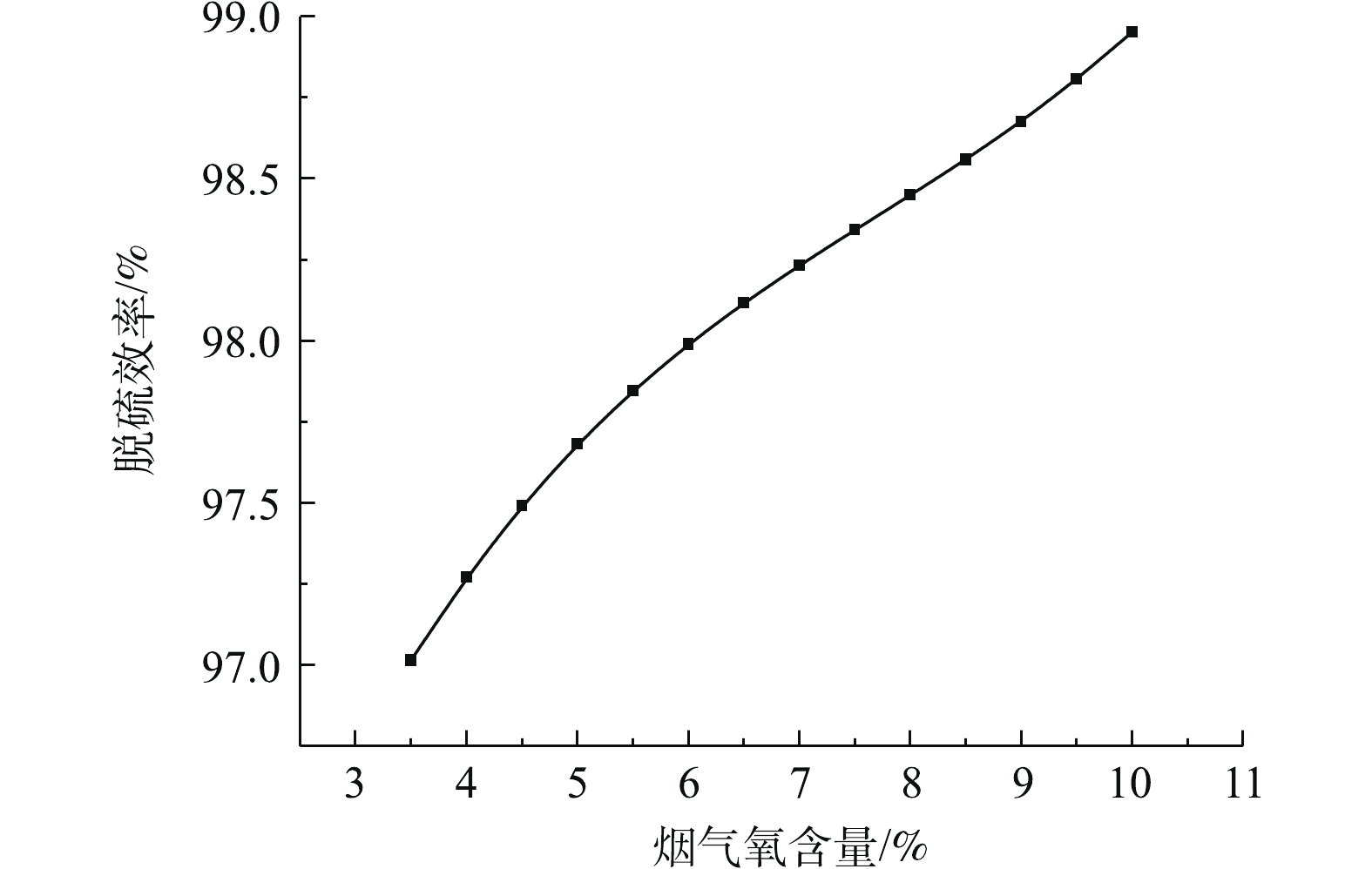
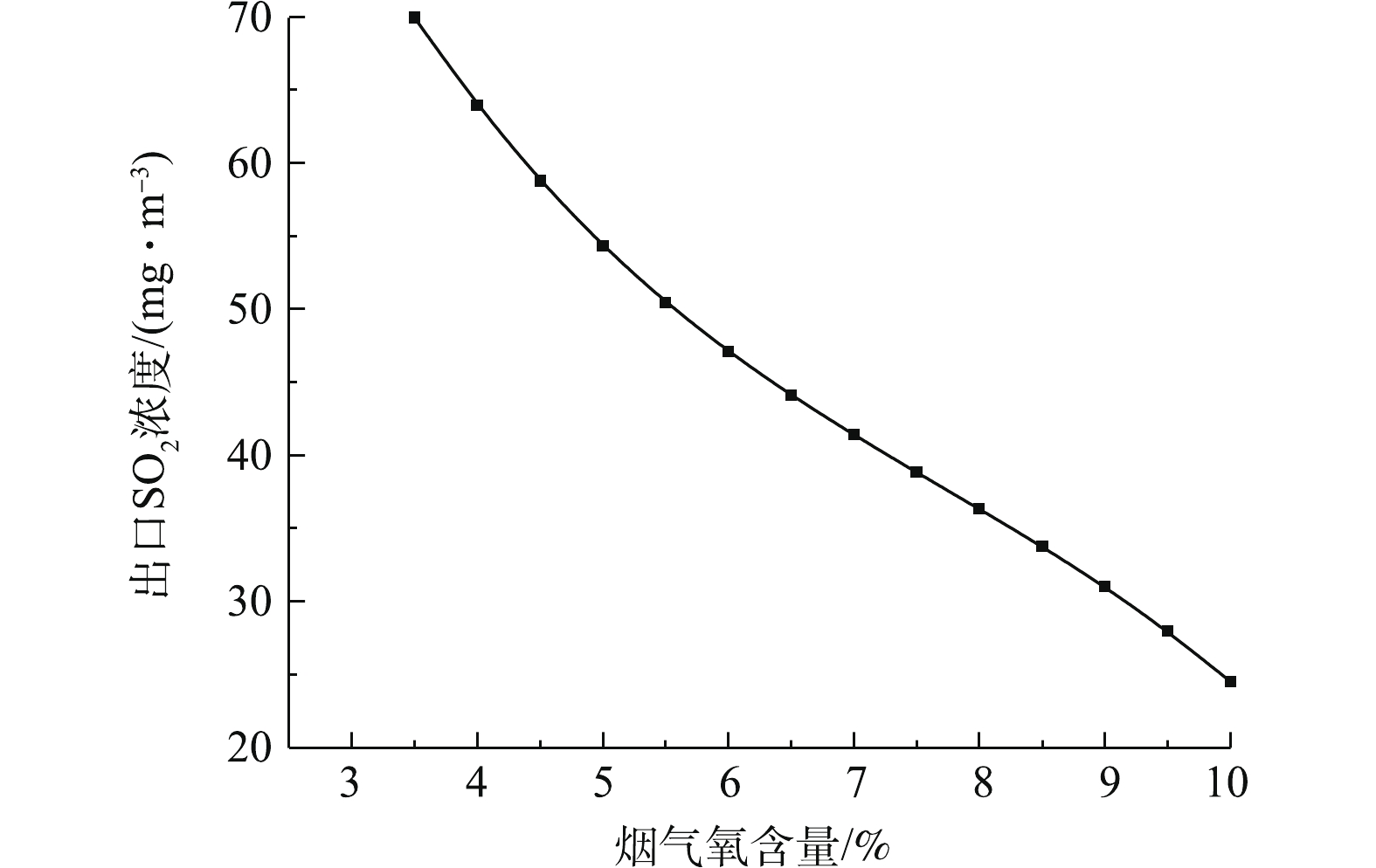
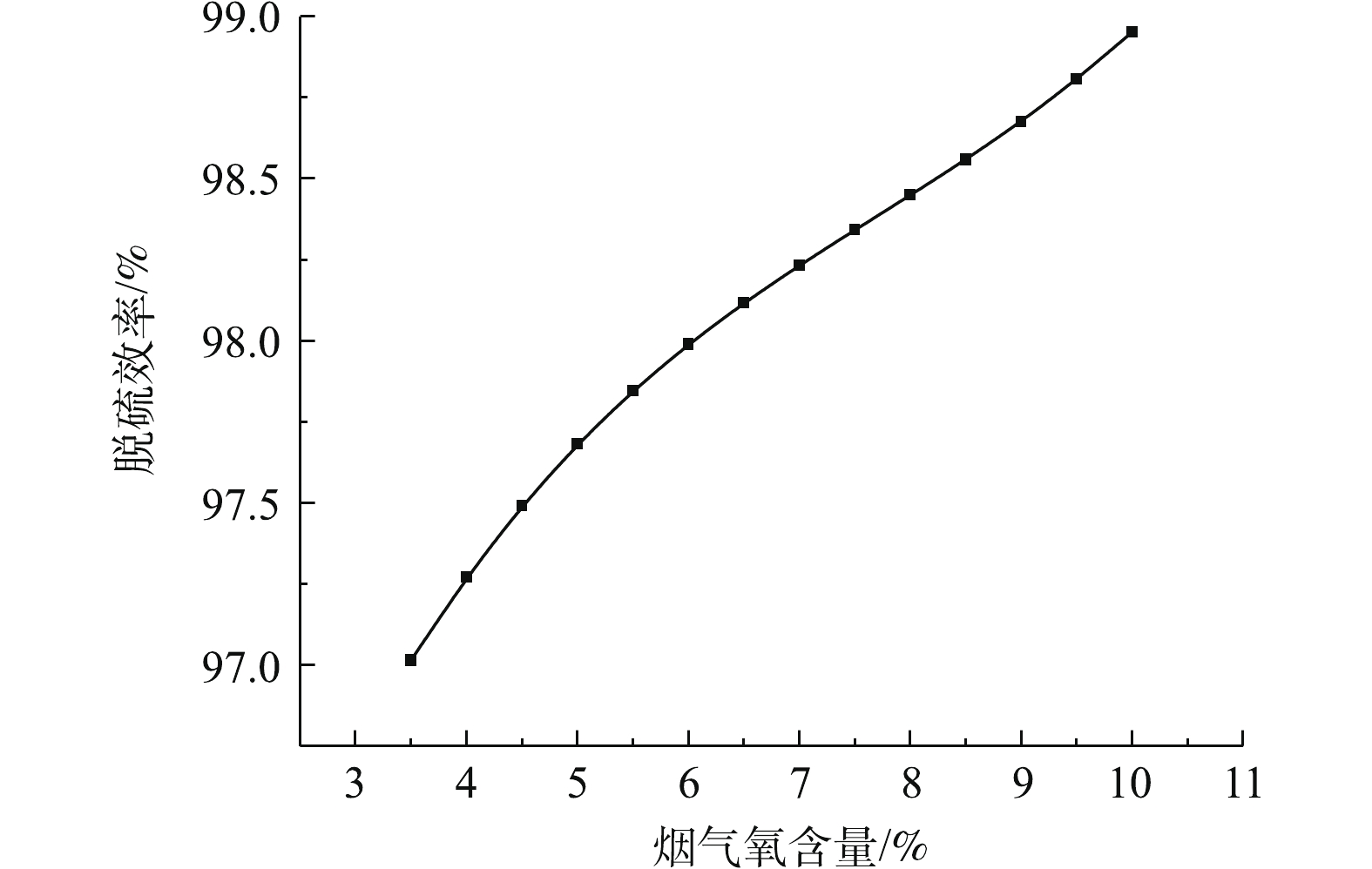
图5反映了烟气氧含量对脱硫反应塔出口SO2浓度的影响。图6反映了烟气氧气含量对脱硫系统的脱硫效率的影响。研究结果表明:脱硫塔的出口SO2排放浓度与烟气氧含量近似呈线性负相关关系,而脱硫效率与烟气氧含量近似呈线性正相关关系。这是由于烟气含氧量升高,反应过程中的氧化作用增强,有利于亚硫酸根的氧化,CaSO4·2H2O的形成也加快,从而促进二氧化硫的吸收[26-27]。因此,在生产过程中,应适当保证充分的氧化风机鼓风量,提高脱硫系统的脱硫效率。
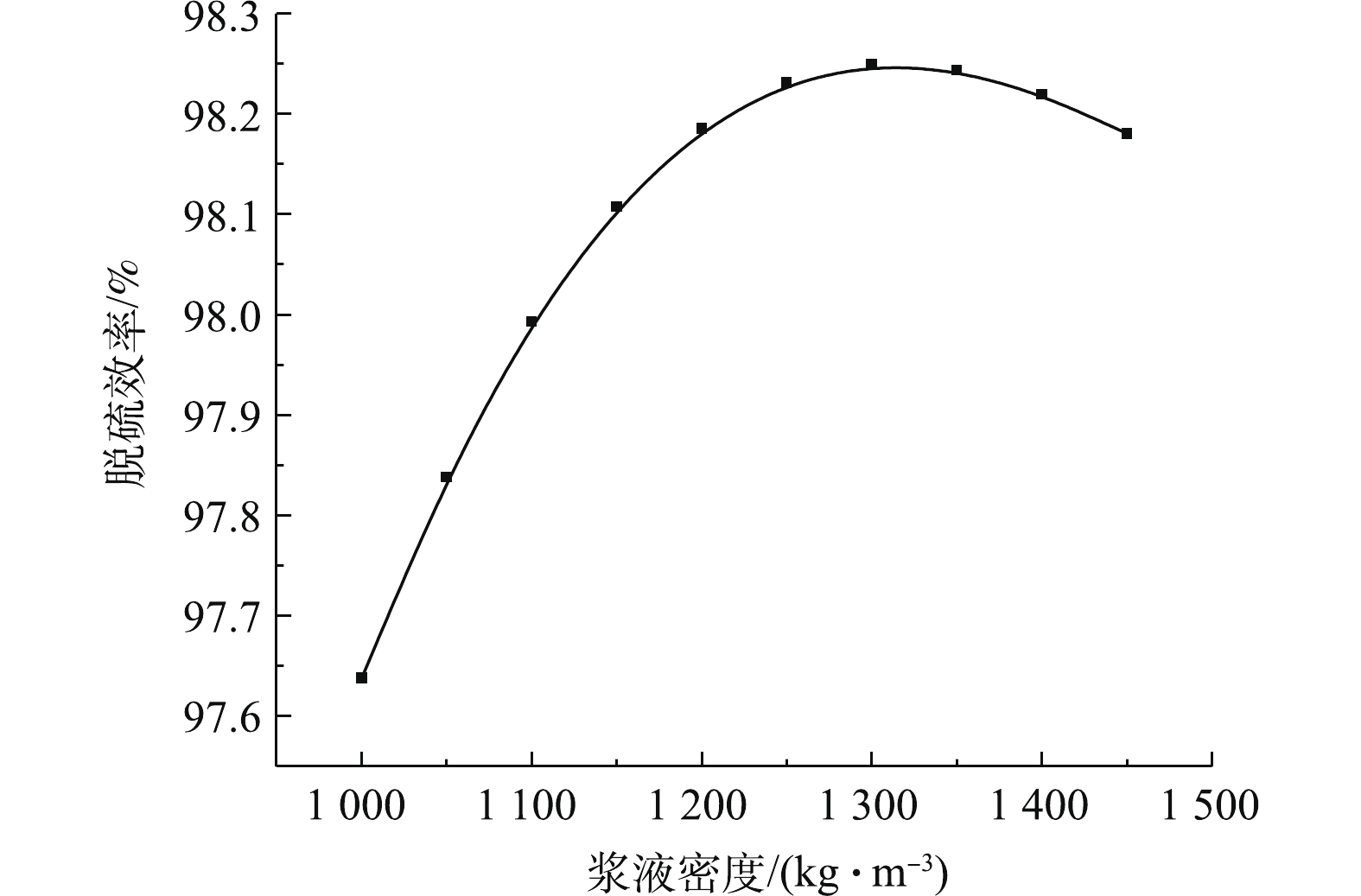
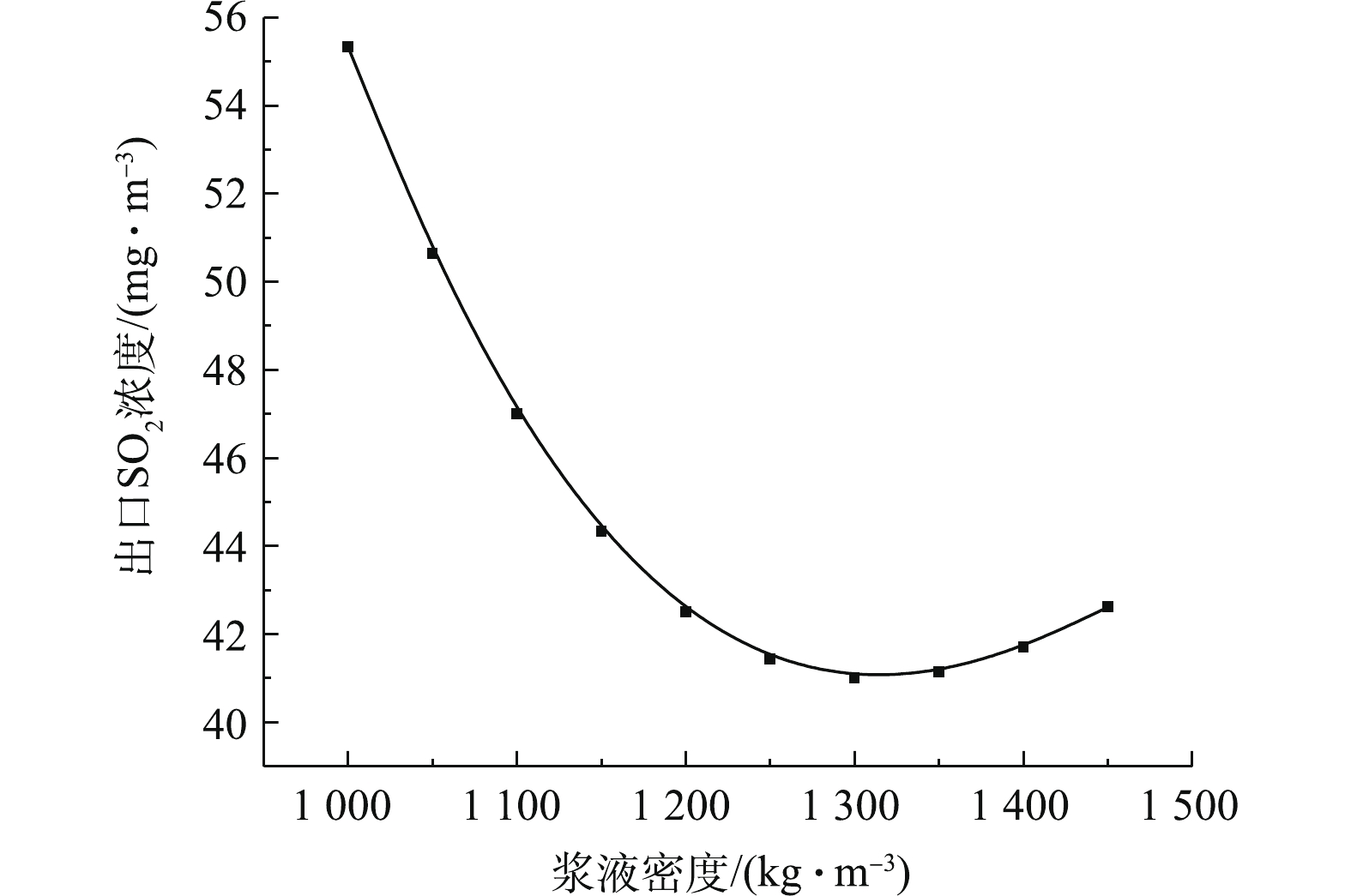
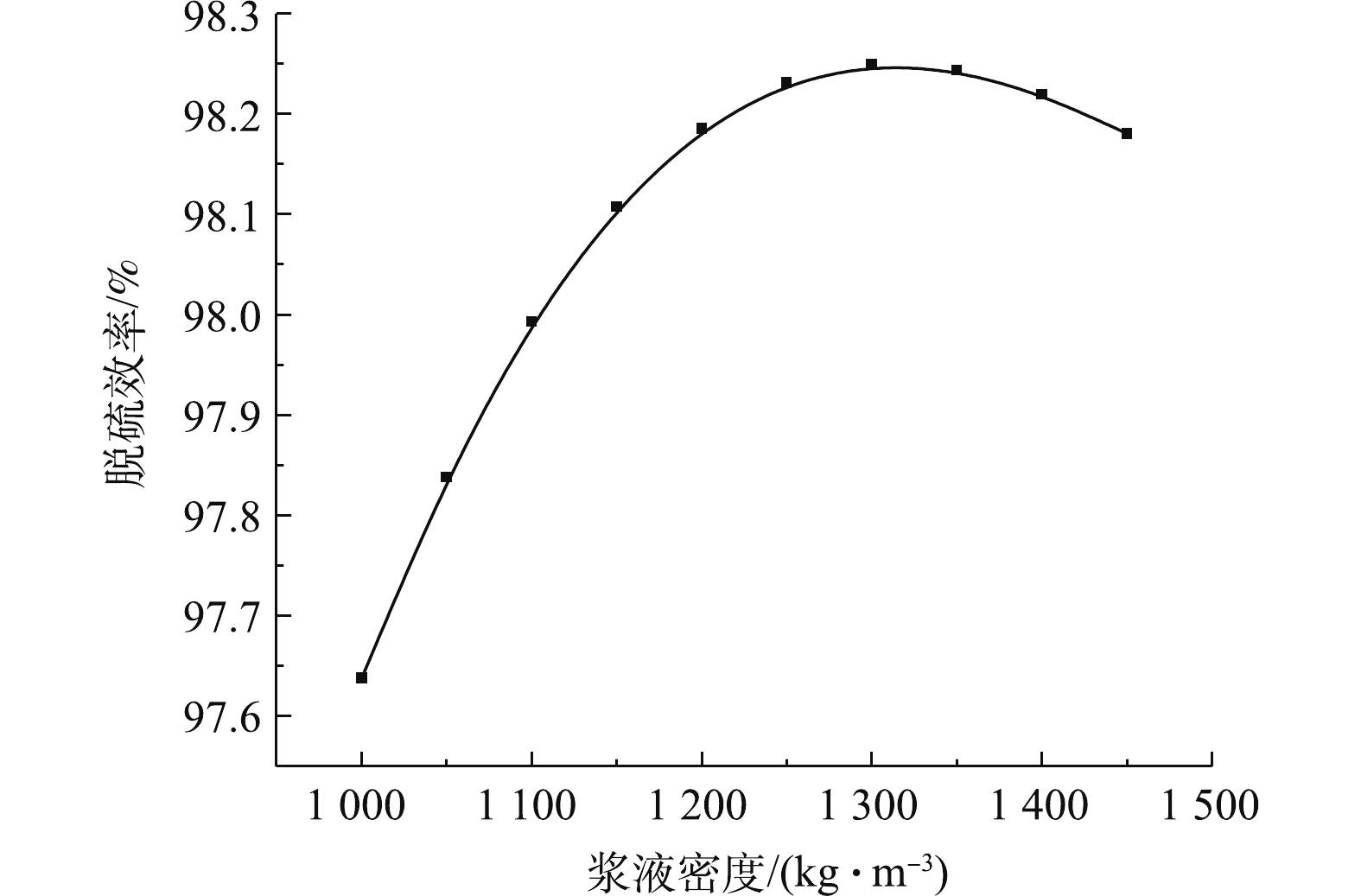
图7反映了浆液密度对脱硫反应塔出口SO2浓度的影响规律。图8反映了浆液密度对脱硫效率的影响规律。研究结果表明,脱硫塔的出口SO2排放浓度与浆液密度呈先降后增的抛物线关联关系,相反,脱硫效率与浆液密度呈先增后降的抛物线关联关系。研究表明,浆液密度在1 250 kg·m−3左右,脱硫系统的脱硫特性处于最佳状态。这是因为在浆液密度较低时,浆液中CaSO4·H2O含量较低,而CaCO3含量较高,石灰石溶解不够,反应正向进行不充分,SO2吸收不完全。随着循环浆液密度的增加,脱硫效率增加,但当CaSO4·H2O和CaCO3浓度都趋于饱和状态下,脱硫效率开始下降[28-29]。
-
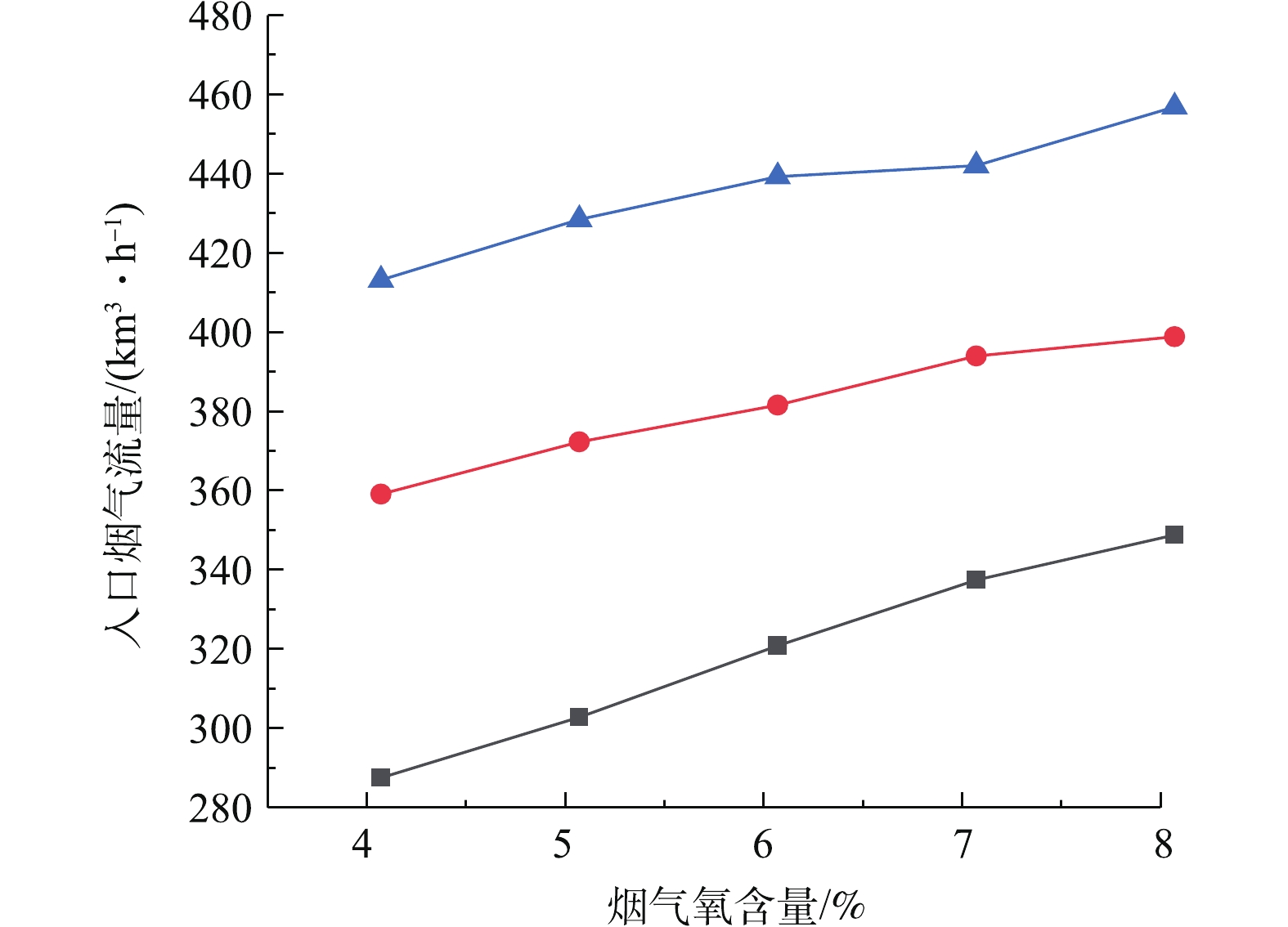
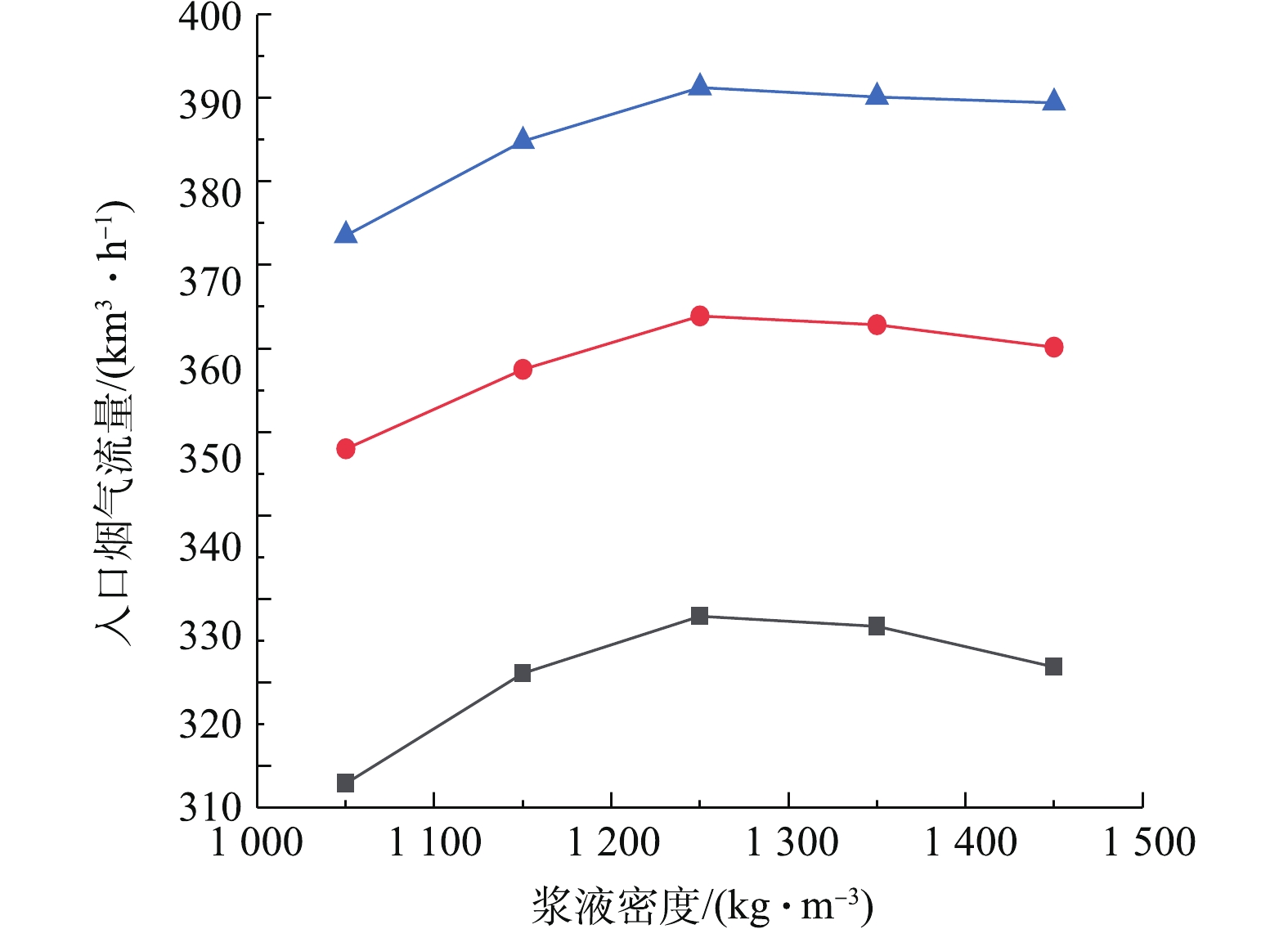
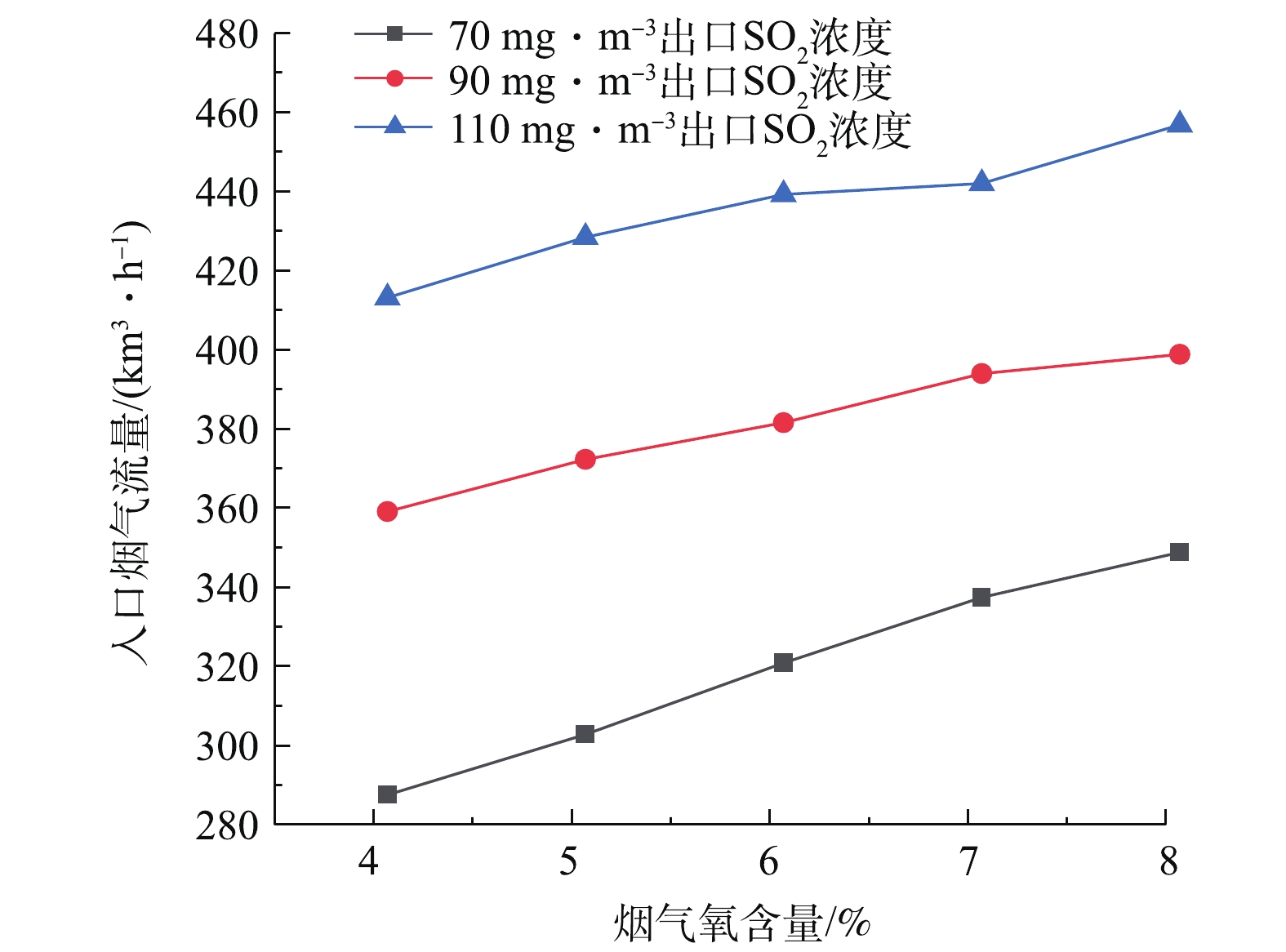
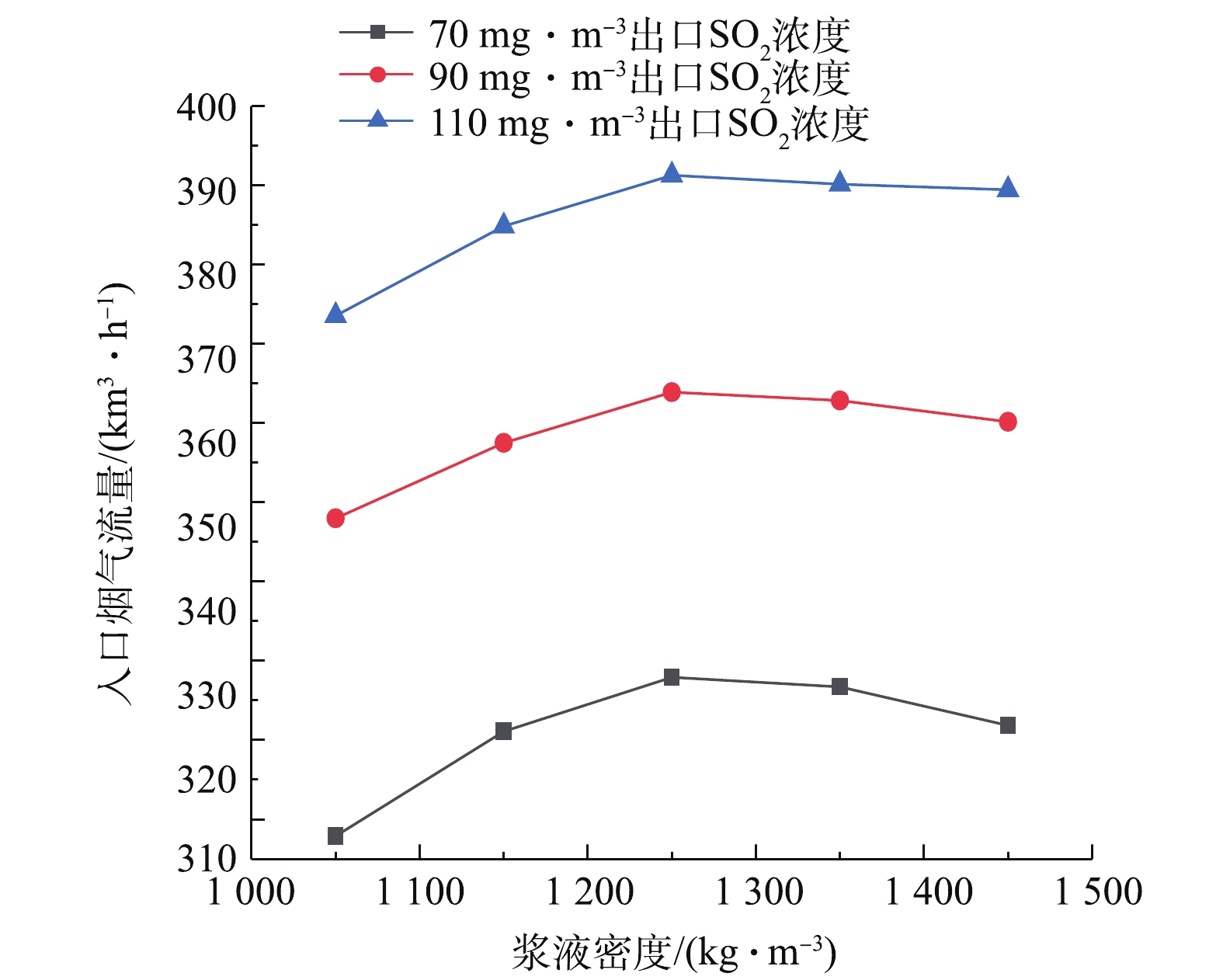
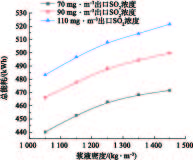
为了研究脱硫系统污染排放治理与系统能耗的协同机理,需要研究建立脱硫塔在等值SO2出口排放浓度约束控制条件下,关键调控参数之间的协同耦合关联曲线。图9反映了出口SO2浓度分别为70、90、110 mg·m−3的等值约束控制条件下,烟气氧含量对可处理最大入口烟气流量的影响。研究表明,在SO2排放浓度等值约束条件下,可处理最大入口烟气流量与氧含量近似呈线性正相关关系,随氧含量的增加而增大。这是由于烟气氧含量的增加会促进烟气中SO2吸收化学反应中的亚硝酸根的氧化,使得脱硫塔的脱硫特性增强,导致脱硫塔入口烟气流量增加。图10反映了出口SO2浓度分别为70、90、110 mg·m−3等值约束条件下,浆液密度对可处理最大入口烟气流量的影响。研究表明,可处理最大入口烟气流量与浆液密度呈先增后减的抛物线关联关系。在浆液密度低于1 250 kg·m−3时,SO2吸收反应随着浆液密度的增加而增强,导致脱硫塔的脱硫特性随着浆液密度的增加而增强,最大可处理入口烟气流量增加。在浆液密度超过1 250 kg·m−3时,SO2吸收反应随着浆液密度的增加而减弱,导致脱硫塔的脱硫特性随着浆液密度的增加而减弱,最大可处理入口烟气流量减小。脱硫特性在浆液密度约为1 250 kg·m−3时处于最佳状态。
-
为了综合考虑负荷变化和煤种变化的影响,本研究提出脱硫系统综合能耗指标体系的计算方法见式(8)。
式中:I为综合能效指标;N为石灰石-石膏湿法脱硫塔系统总能耗,kWh;
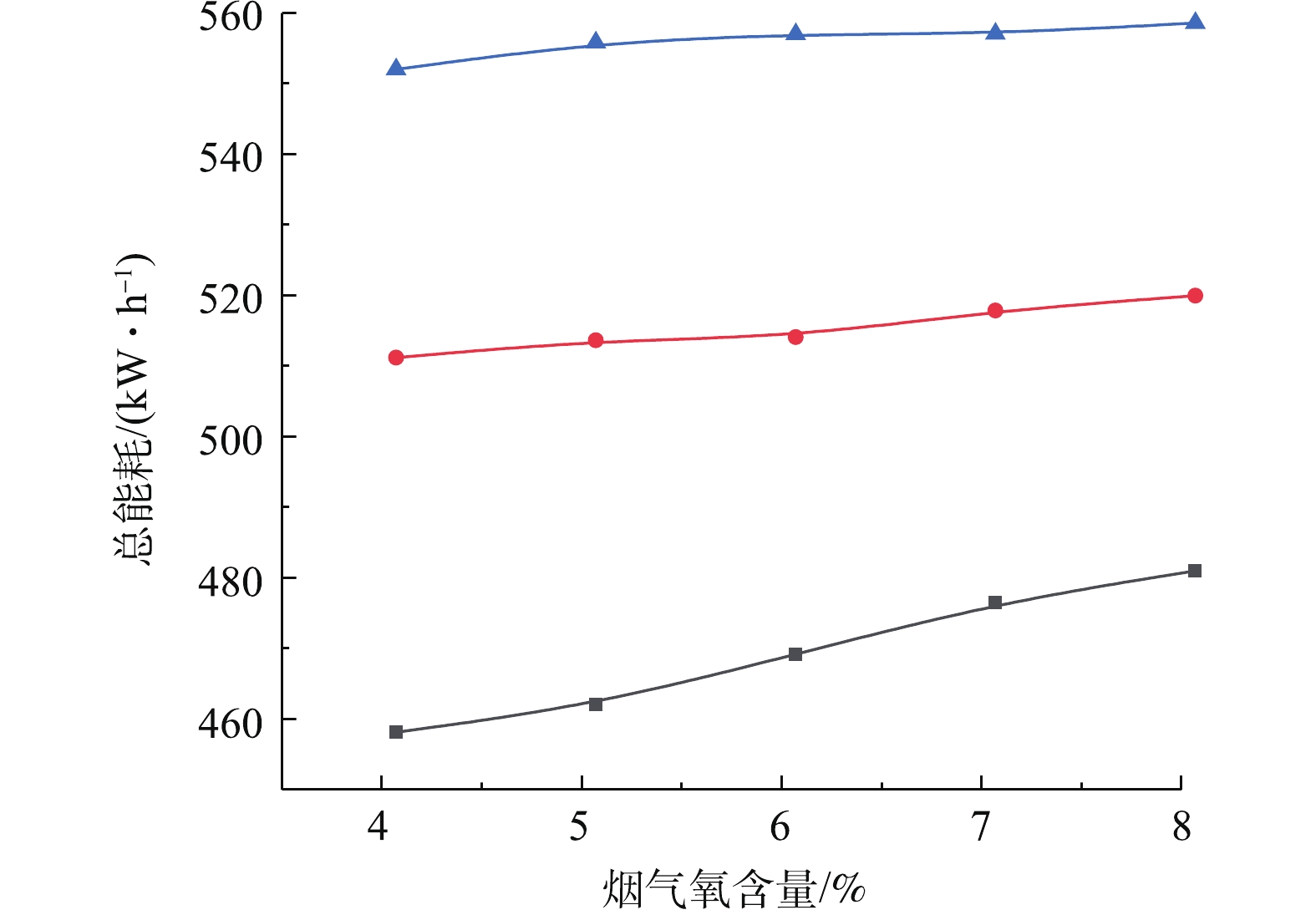
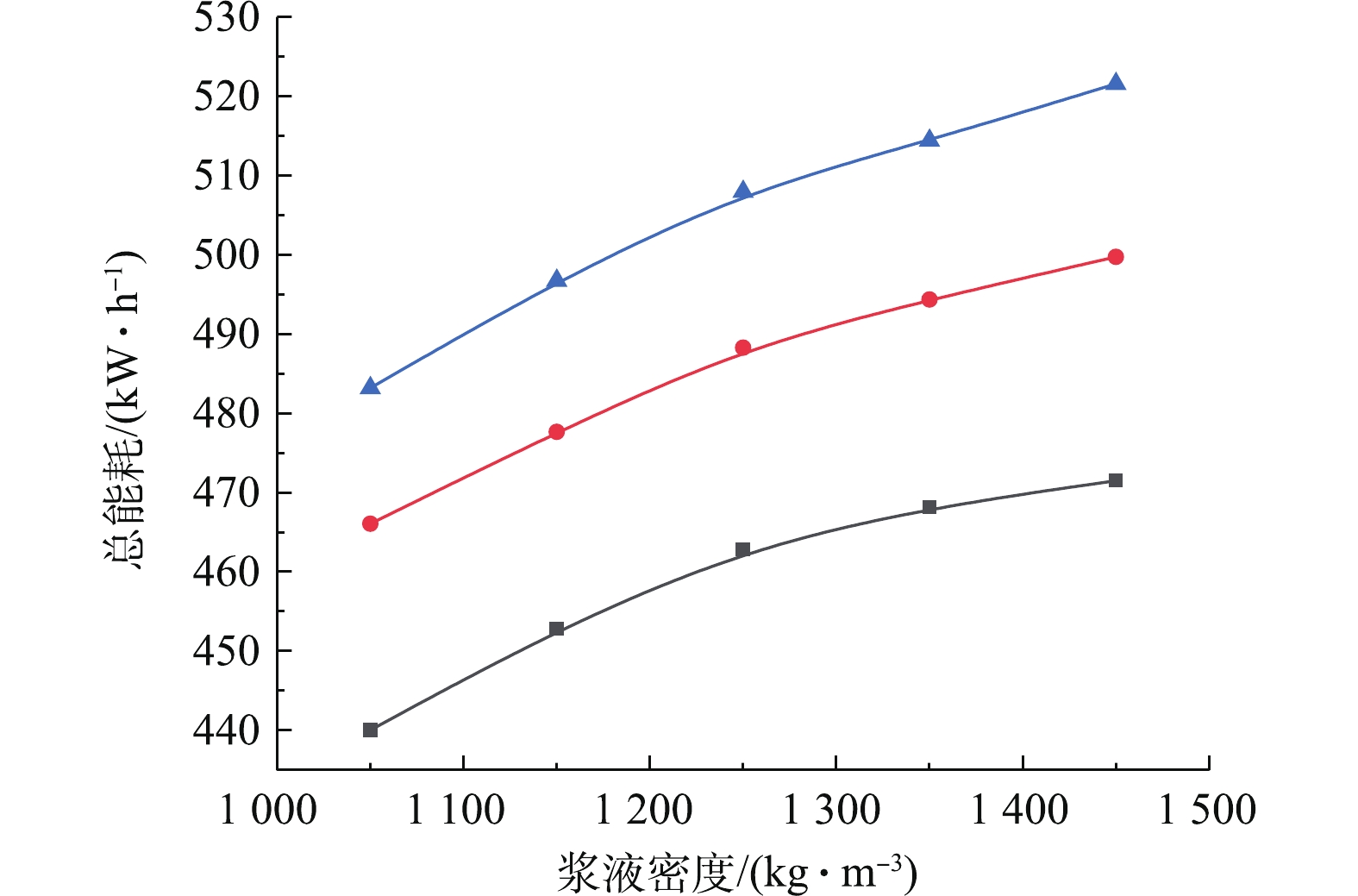
Qg 为烟气进口标准体积流量,km3·h−1;Φ 为烟气进出口二氧化硫体积分数。能耗除以烟气进口标准体积流量可真实反映负荷变化的影响,而除以烟气进口二氧化硫体积浓度可真实反映煤种变化诱发的烟气进口二氧化硫体积浓度的变化影响。综合能耗指标越小,说明脱硫系统污染物治理和能耗协同效果越好。为探究烟气氧含量-污染排放-系统能耗的协同耦合规律,依据图9的出口SO2排放浓度等值约束下烟气氧含量与入口烟气流量的耦合曲线,可得到指定氧含量下的最大可处理入口烟气流量,再根据能耗预测模型得出总能耗,从而考察烟气氧含量-污染排放-系统能耗的协同耦合规律。现指定SO2排放标准分别为70、90、110 mg·m−3(标准状况下),考察不同排放标准下烟气氧含量与污染排放及系统总能耗三者间的耦合影响关系。图11是烟气氧含量-污染排放-系统总能耗协同耦合关联曲线。研究结果表明,在给定出口SO2排放浓度等值约束下,系统总能耗与烟气氧含量近似呈线性正相关的协同耦合规律。产生这一协同耦合规律的机理是,随着氧含量的增加,在给定的出口SO2排放浓度等值约束下,系统最大可处理入口烟气流量也会增加,这必然会导致氧化风机和增压风机运行能耗增加,最终导致系统总能耗的增加。另外,随着出口SO2排放浓度由110 mg·m−3降低到70 mg·m−3(标准状况下),曲线下移,系统总能耗降低,系统总能耗与出口SO2排放浓度呈正相关协同耦合规律。产生这一协同耦合规律的机理是,在给定氧含量条件下,出口SO2排放浓度降低,意味着污染排放治理要求的提高,系统可处理最大入口烟气流量减小,导致总能耗降低。
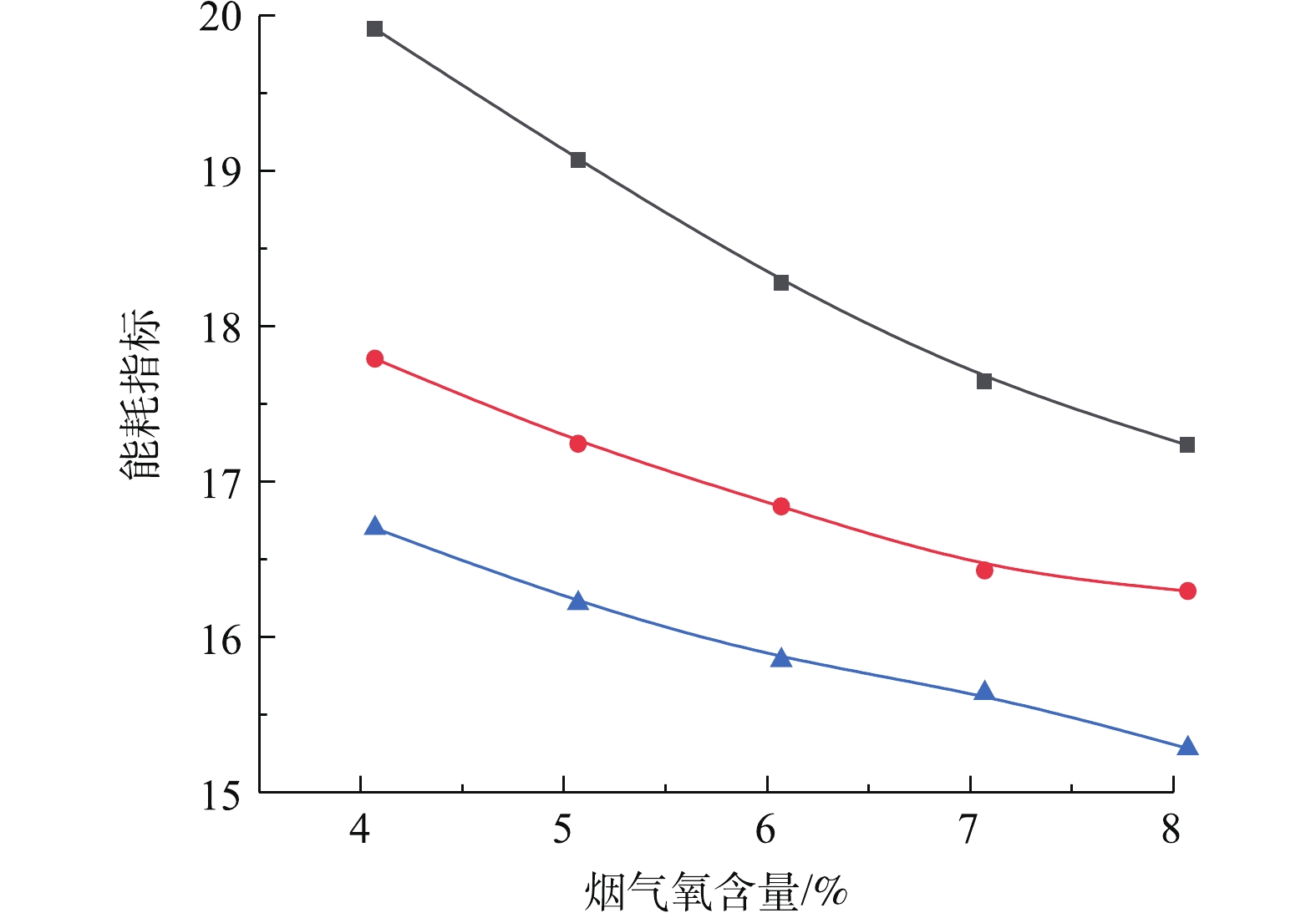
图12是等值排放约束控制条件下,烟气氧含量-污染排放-系统能耗指标的协同耦合关联曲线。研究结果表明,在给定出口SO2排放浓度等值约束条件下,系统综合能耗指标与烟气氧含量近似呈非线性负相关的协同耦合规律。产生这一协同耦合规律的机理是,随着氧含量的增加,在给定出口SO2排放浓度等值约束下,系统最大可处理入口烟气流量也会增加;尽管会导致氧化风机和增压风机运行能耗增加,使系统总能耗增加,但此时系统最大可处理入口烟气流量增加速度超过系统总能耗增加速度。由于系统能耗指标与总能耗呈正比,而与入口烟气流量呈反比,因而导致系统综合能耗指标与烟气氧含量近似呈非线性负相关的协同耦合规律。由此可见,增加氧含量,可以提高系统最大可处理烟气流量,使单位入口烟气流量的系统能耗降低,导致能效的利用效率增加。另一方面,在给定出口SO2排放浓度等值约束条件下,出口SO2排放浓度与系统能耗指标呈负相关的协同耦合规律,即提高系统污染排放治理要求,会降低系统综合能耗指标。
综合以上结果可知,在给定出口SO2排放浓度等值约束条件下,增加烟气氧含量,可以有效降低脱硫系统综合能耗指标。当烟气氧含量由4%增至8%时,在出口SO2排放浓度为110 mg·m−3,脱硫系统综合能耗指标由16.7降为15.3,系统综合能耗指标降低8.3%,取得明显的节能效果。当烟气氧含量固定为5%时,出口SO2污染排放浓度由110 mg·m−3降至70 mg·m−3,脱硫系统综合能耗指标由16.2升为19.1,系统综合能耗指标升高17.9%,说明实现超低排放,要以牺牲系统能效为代价。
在探究浆液密度-污染排放-系统能耗的协同耦合规律时,依据图10的等值约束下浆液密度与入口烟气流量的耦合曲线,可得到指定浆液密度下的最大可处理入口烟气流量,再根据能耗预测模型得出总能耗,从而考察浆液密度-污染排放-系统能耗的协同耦合规律。指定环保排放指标的二氧化硫排放浓度为70、90、110 mg·m−3,图13为浆液密度-污染排放-系统能耗的协同耦合关联曲线。研究结果表明,在给定SO2排放浓度等值约束下,系统总能耗与浆液密度近似呈正相关的协同耦合规律。产生这一协同耦合规律的机理是:在浆液密度从1 000 kg·m−3增加至1 250 kg·m−3左右时,由于浆液密度的增加,促进了SO2的吸收,在等值排放约束下可处理的最大烟气流量增加,导致总能耗增加;在浆液密度超过1 250 kg·m−3时,由于此时浆液密度的增加反而会抑制SO2的吸收反应,导致最大可处理的烟气量减少,但密度的增加会导致增压引风机运行能耗升高,导致脱硫塔的总能耗随着浆液密度的增加而增加。随着出口SO2排放浓度从110 mg·m−3降低至70 mg·m−3,曲线下移,最大系统总能耗由520 kWh降低到460 kWh,系统总能耗与出口SO2排放浓度呈正相关协同耦合规律。产生这一协同耦合规律的机理是:在给定浆液密度一定条件下,出口SO2排放浓度降低,意味着出口SO2污染排放治理要求提高,满足系统最大可处理入口烟气流量减小,必然导致系统总能耗降低。
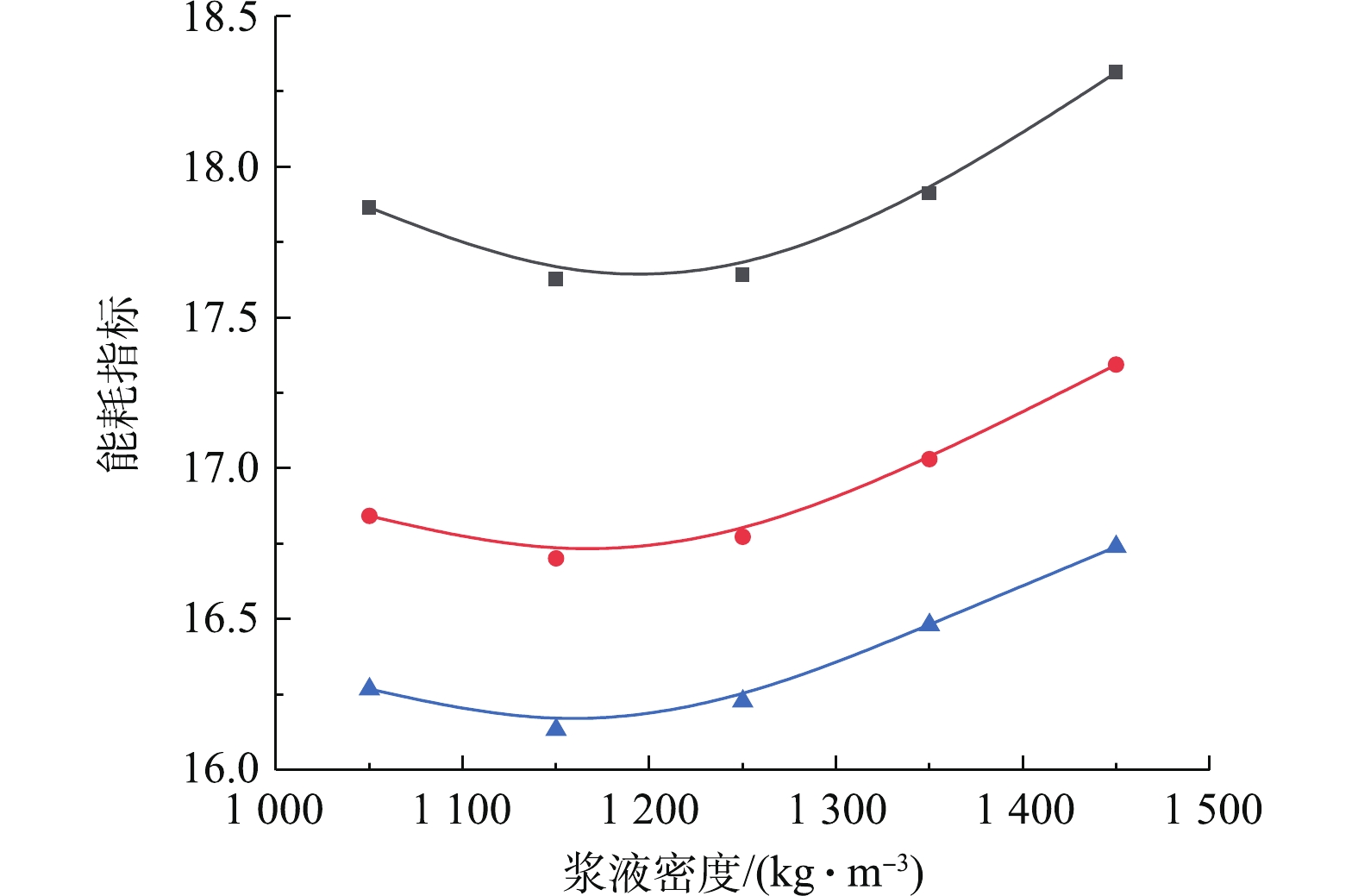
图14反映了等值排放约束控制条件下,浆液密度-污染排放-系统能耗指标的协同耦合规律。研究结果表明:在等值SO2浓度排放约束下,浆液密度与综合能耗指标呈先减后增的抛物线耦合规律。产生这一协同耦合规律的机理是,在浆液密度从1 000 kg·m−3增加至1 250 kg·m−3左右时,虽然可处理的最大烟气流量和能耗都在增加,但可处理的最大烟气流量增加速度大于系统总能耗增加速度。由于系统能耗指标与总能耗成正比,而与入口烟气流量成反比,因而导致系统综合能耗指标减少。在浆液密度超过1 250 kg·m−3时,SO2吸收反应的减弱导致最大可处理的烟气量减少,同时总能耗却再进一步增加,两者必然导致能耗指标的增加。另一方面,在给定浆液密度条件下,出口SO2排放浓度与系统综合能耗指标呈负相关的协同耦合规律,即提高系统污染排放治理要求,会增加系统综合能耗指标。
综合以上结果可知,在给定出口SO2排放浓度等值约束条件下,将浆液密度控制在1 250 kg·m−3左右时,脱硫系统综合能耗指标最小,处于最佳节能状态。当出口SO2污染排放浓度为70 mg·m−3时,浆液密度由1 450 kg·m−3降至1 250 kg·m−3,系统综合能耗指标由18.31降至17.63,降幅为3.7%,可取得较好节能效果。当浆液密度固定为1 450 kg·m−3时,出口SO2污染排放浓度由110 mg·m−3降至70 mg·m−3,脱硫系统综合能耗指标由16.7升为18.3,系统综合能耗指标升高9.5%,说明实现超低排放要以牺牲系统能效为代价。
3.1. 关键调控参数对出口二氧化硫排放的影响
3.2. 等值SO2排放浓度下关键调控参数的协同耦合关系
3.3. 脱硫系统能耗指标建立及协同分析
-
1)基于脱硫塔控制系统历史运行数据和在线监测数据,应用支持向量机回归方法构建的脱硫系统二氧化硫排放预测模型及总能耗预测模型,其两者模型验证最大相对误差都小于10%,均可进行准确结果预测。
2)脱硫塔的出口二氧化硫排放浓度与烟气含氧量呈负相关关系,而脱硫效率与烟气含氧量呈正相关关系;脱硫塔的出口二氧化硫排放浓度与浆液密度呈先降后增的抛物线型相关关系,脱硫效率与浆液密度呈先增后降的抛物线型相关关系。
3)研究提出了能同时反映系统负荷及煤种品质的综合能耗评价指标,其物理意义表示为单位体积流量进口烟气和单位体积浓度进口二氧化硫下的系统能耗值。
4)在出口二氧化硫排放浓度等值约束控制下,脱硫塔的总能耗与烟气氧含量及浆液密度呈非线性的正相关关系的协同耦合关系,而脱硫塔的综合能耗指标与烟气氧含量呈非线性负相关的协同耦合关系,与浆液密度呈先减后增的抛物线协同耦合关系。





 DownLoad:
DownLoad:




 百度学术
百度学术


