-
油基钻井液与水基钻井液相比,具有抗高温、利于井壁稳定、润滑性好和对油气层损害程度较小等多种优点[1]。我国主要将其应用在海上的大位移水平井、塔里木油田山前构造的深井复杂井以及重庆、四川页岩气、克拉玛依致密油藏强水敏性地层等[2-5]。近2年,新疆油田在南缘钻井现场的多口井中应用了油基钻井液,平均机械钻速提高6倍以上[6],显著减少了复杂事故,突破了南缘钻井中多个技术局限。然而,在油基钻井液使用过程中产生的油基岩屑被列入《国家危险废物名录》,故其存在一定的环境风险[7-10]。根据《陆上石油天然气开采含油污泥资源化综合利用及污染控制技术要求》(SY/T 7301-2016)及新疆、陕西、黑龙江等地区的地方标准,要求无害化处理后残渣的含油率≤2%。
热脱附法是采用热源对装有油基岩屑的腔体加热,控制物料温度不超过600 ℃[11],使油和岩屑分离的一种无害化处理方法。热脱附法具有处理后残渣达标,基础油可回收等优点[12-15],已在重庆、四川、新疆等油田应用。但针对不同来源的物料,如何设计合理工艺参数,控制处理能耗(成本)是工业化应用的重点和难点。
在油基岩屑热脱附处理工艺参数中,影响单位处理能耗的因素较多。郭文辉等[16]利用自制的热脱附模拟装置研究了四川威远白油基岩屑,结果表明,加热温度和停留时间对热脱附处理后残渣的含油率影响较大,在550 ℃下加热30 min后,含油率可低于1%。孙静文等[17]采用电磁加热热脱附装置研究了白油基岩屑热脱附过程中加热温度、进料速度和加热时间3个影响因素,结果表明,在375 ℃、45 min、进料速度为15 L·h−1和350 ℃、50 min、进料速度为20 L·h−1的条件下,热脱附后含油率均<1%。FALCIGLIA等[18]以柴油为对象,研究了加热温度、加热时间和粒径对热脱附残渣的影响,4~840 μm的黏土和粗砂在250 ℃、30 min条件下,能实现柴油的热脱附分离。HOU等[19]在研究微波处理油基岩屑热脱附过程中发现,在300、400、500 ℃下分别得到碳原子数<C12、C12~C20、C21~C24的组分。但关于在各单因素之间的交互作用影响的研究还鲜有报道。
本研究以新疆某井经离心机分离后的油基岩屑为研究对象,以残渣的含油率≤2%为评价指标,通过单因素实验筛选了加热温度、停留时间、油基岩屑固相含量的适宜条件;在此优化条件下,以能耗为评价指标,加热温度、停留时间、油基岩屑固相含量作为主要的影响因素,进行3因素6水平的中心组合实验设计(CCD);并采用响应面法进行分析,回归拟合全局范围内的因素与结果之间的函数关系,以此来反映热脱附处理过程中各因素间的交互作用,建立数学模型并通过实验进行验证[20-21],以便于准确快捷地选择最佳处理工艺参数,探索辅助热脱附工业化装置运行参数的设计方法,为油基岩屑热脱附装置运行参数优化与节能降耗提供参考。
全文HTML
-
材料:四氯化碳(光谱级)、对照品油混合物原料(光谱级)、正十六烷、异辛烷、氯苯、硅胶固相提取小柱(40 μm粒度,6 nm,0.5 g),硅胶(60~200目,用蒸馏水和硅胶按质量比112∶ 100混合并充分振荡,去除硅胶活化能力)、硫酸镁、盐酸,以上试剂均为分析纯,购自于成都科龙化工有限公司。油基岩屑样品取自新疆油田某井场,固相含量为70.52%、含水率为9.85%、含油率为19.63%。
仪器:红外光谱仪(WQF520型,北京瑞利);玻璃比色皿(IR-级,成都安恒达);磁力搅拌器(HX-6057型,山东菏泽华兴);马弗炉(5x-12-10型,北京中兴伟业);电子天平(FA2004B型,上海精密);智能电能表(DDZY666C型,浙江正泰)。
-
在进行含油率和油基岩屑固相含量的测定时,按GB 5085.6-2007中的要求,测量油基岩屑和油基岩屑热脱附处理后残渣中的可回收石油烃总量,含油率根据式(1)进行计算。油基岩屑固相含量根据式(2)进行计算。
式中:R1为含油率;C表示可回收石油烃总量的浓度,mg·kg−1。R2为油基岩屑固相含量;m1、m2 依次为油基岩屑样品于105 ℃下恒温烘干至恒重前、后的质量,g。
在进行不同比例固相含量配制实验时,选取现场油基岩屑样品和配制油基钻井液使用的油,进行不同比例固相含量配置实验。在降低油基岩屑固相含量时,按比例加入配制油基钻井液使用的基础油;在提高油基岩屑固相含量时,将样品与烘干至恒重的油基岩屑按比例混拌均匀。
在进行能耗测量实验时,以马弗炉加热油基岩屑模拟热脱附装置电加热处理油基岩屑,采用智能电表单独连接马弗炉。将样品放入250 mL空坩埚内,通入氮气,马弗炉从0 ℃升温开始时的电能表数记为Q1,待马弗炉升温至设计温度,至设计停留时间,关闭马弗炉后的电能表数记为Q2;放入样品,通入氮气,马弗炉由0 ℃开始升温时的电能表数记为Q3,待马弗炉升温至设计温度,至设计停留时间,关闭马弗炉后的电能表数记为Q4,能耗按照式(3)进行计算。
式中:Q为以马弗炉加热油基岩屑所需能耗,kWh·kg−1;m为样品质量,g。
在进行油基岩屑热脱附实验时,取250.00 g油基岩屑,置于坩埚内铺平,放置在已达到设定温度的马弗炉内,启动升温开始计时,达到设计停留时间,取出样品,室温下冷却后,混拌均匀,测量其含油率,记录能耗。
1.1. 材料与仪器
1.2. 实验方法
-
含油岩屑热脱附处理的主要影响因素有加热温度、停留时间和油基岩屑固相含量,对以上3个影响因素分别进行了单因素实验研究[16],具体实验方案如表1所示。
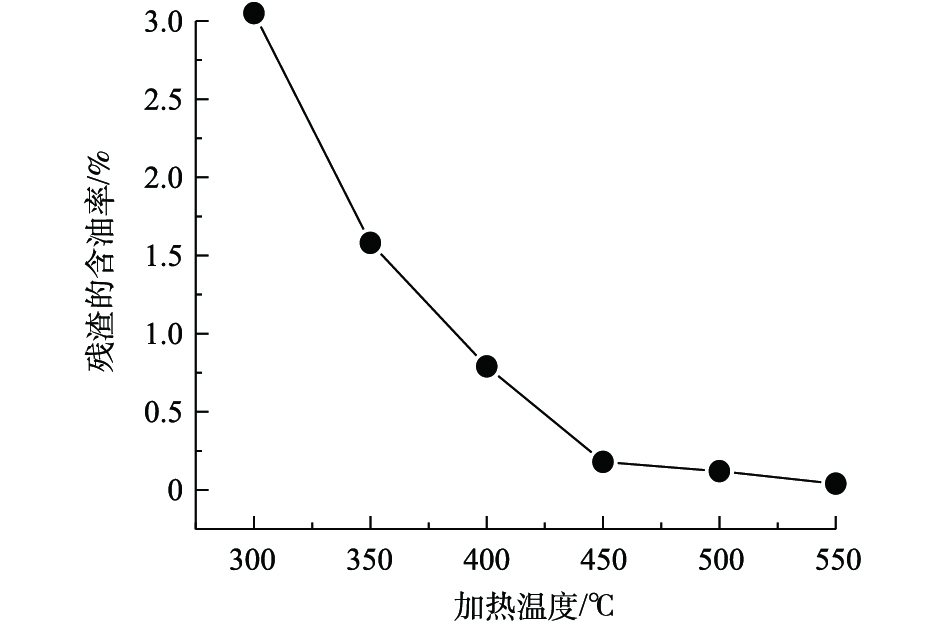
在考察加热温度对残渣含油率的影响时,本研究所使用的油基岩屑是以0#柴油配制的油基钻井液在钻井过程中产生的,0#柴油的沸点为180~370 ℃。根据油基岩屑中油受热达到其沸点后从岩屑上脱吸附的特点,研究了在停留时间45 min,油基岩屑固相含量70%的条件下,加热温度300~550 ℃对油基岩屑加热处理后残渣的含油率的影响,结果如图1所示。在300 ℃时,油基岩屑处理后残渣的含油率已降低至3.02%。随着加热温度的升高,残渣的含油率明显有所下降,在350 ℃时已接近1.58%,满足指标2%的要求;在550 ℃时含油率降低到0.04%。随着温度的升高,油基岩屑中的油升温速度加快。有研究[22]表明,油相从岩屑中脱吸附更彻底,残渣中可测出的含油量就越低。油基岩屑进入热脱附装置腔体后,须经过水分蒸发、轻质油蒸发、油相蒸发等过程。实验结果表明,当停留时间为45 min,油基岩屑固相含量为70%时,适宜加热温度为350~550 ℃。
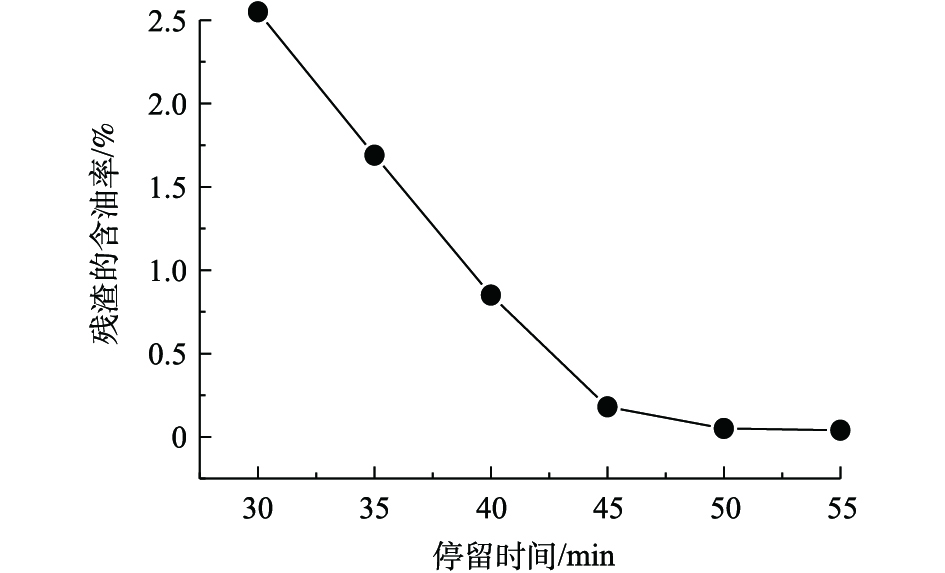
在考察停留时间对残渣含油率的影响时,当油基岩屑在热脱附装置反应腔体里停留时,热量从油基岩屑表面向内部传递,黏附和浸入油基岩屑的液相逐步受热并从岩屑中迁移出来,停留时间会影响热脱附装置反应腔体的热量向油基岩屑及其内部传递的速度,从而影响油基岩屑中油相受热脱吸附的效果。本研究考察了在450 ℃、油基岩屑固相含量为70%的条件下,不同停留时间对油基岩屑加热处理后残渣的含油率的影响,结果如图2所示。随着停留时间的增加,残渣的含油率明显降低,但是停留时间越长,热脱附装置的处置能力越低,且能耗也增加。当停留时间大于35 min时,残渣的含油率就可以降低至2%以下;而在停留时间超过50 min后,由于油基岩屑中残留的油相(其沸点低于设定温度(450 ℃))含量很低,导致油相脱附量少,残渣的含油率降低并不明显。因此,在加热温度为450 ℃、油基岩屑固相含量70%的条件下,适宜停留时间为35~55 min。
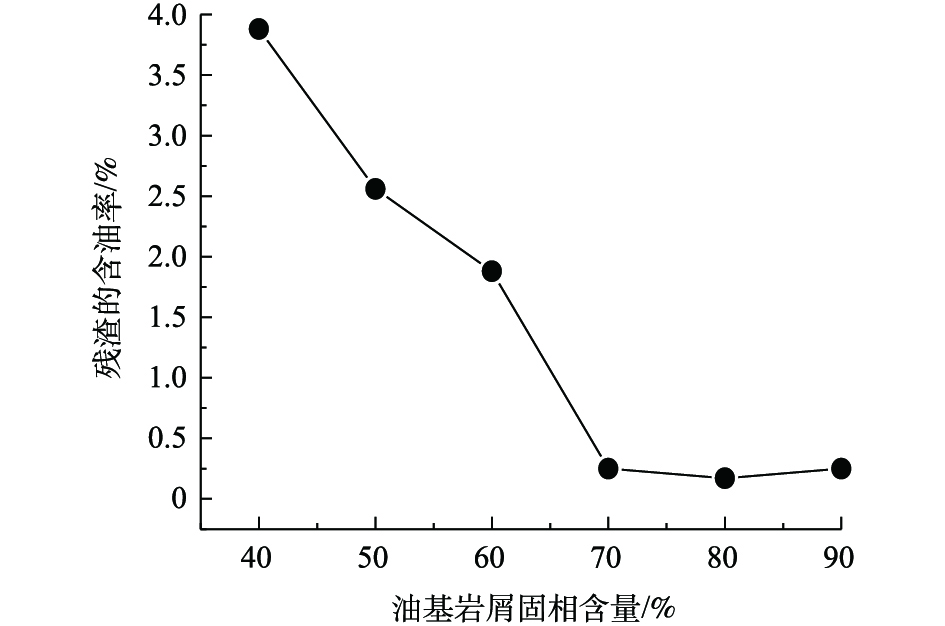
实验考察了油基岩屑固相含量对残渣含油率的影响。油基岩屑中含有油、水、固三相,液相(油、水)含量越高,汽化过程中吸热量越大,油基岩屑受热面积、传热速度、耗热量等因素影响越大。本研究探讨了温度为450 ℃、停留时间45 min的条件下,不同油基岩屑固相含量对残渣的含油率的影响,结果如图3所示。随着油基岩屑固相含量的增大,残渣的含油率呈现明显下降的趋势。当油基岩屑固相含量为80%时,残渣的含油率为0.17%;油基岩屑固相含量90%时,残渣的含油率为0.25%。随着油基岩屑固相含量的增加,油基岩屑需要的热量越多,油基岩屑中油脱吸附的难度越大,导致残渣的含油率上升。当加热温度为450 ℃,停留时间为45 min时,油基岩屑固相的适宜含量为60%~90%。在工业化生产过程中,经离心机处理后的油基岩屑固相含量约为70%[23]。为提高其固相含量,只能通过预处理蒸发水分或掺混固相含量更高的粉状吸水物料,但预处理和掺混均会增加综合处理成本。
-
针对3个单因素选择适宜范围的参数,可以使油基岩屑加热处理后残渣的含油率达到≤ 2%的标准。热脱附装置的单位处理能耗是热脱附处理工艺实用性的关键评价指标。本研究在加热温度、停留时间和油基岩屑固相含量3个单因素实验结果的基础上,确定了各因素的中心值,并以单位处理能耗为响应因子,对油基岩屑热脱附处理工艺参数进行了研究。采用软件Design-Expert 8.0中的Box-Behnken模型进行模拟,选择的实验因素及水平见表2。
实验设计方案和结果见表3。当加热温度为350 ℃,停留时间为45 min,油基岩屑固相含量90%时,热脱附装置的单位处理能耗达到最低,为1.88 kWh·kg−1。
根据实验结果,选择Design-Expert 8.0模拟分析模块中二阶回归模型,得到油基岩屑加热过程中能耗与影响因子的二次多项回归方程,如式(4)所示。
根据式(4)中交互项系数,可知X1X2之间为拮抗作用,X1X3、X2X3之间为协同作用。表4为回归模型方差分析和显著性检验的结果。模型中的F=158.99、P(Prob>F)<0.000 1,这说明该模型可信度较高。失拟项P=0.144 7(P>0.05),响应效果不显著,模型合理。理论计算的
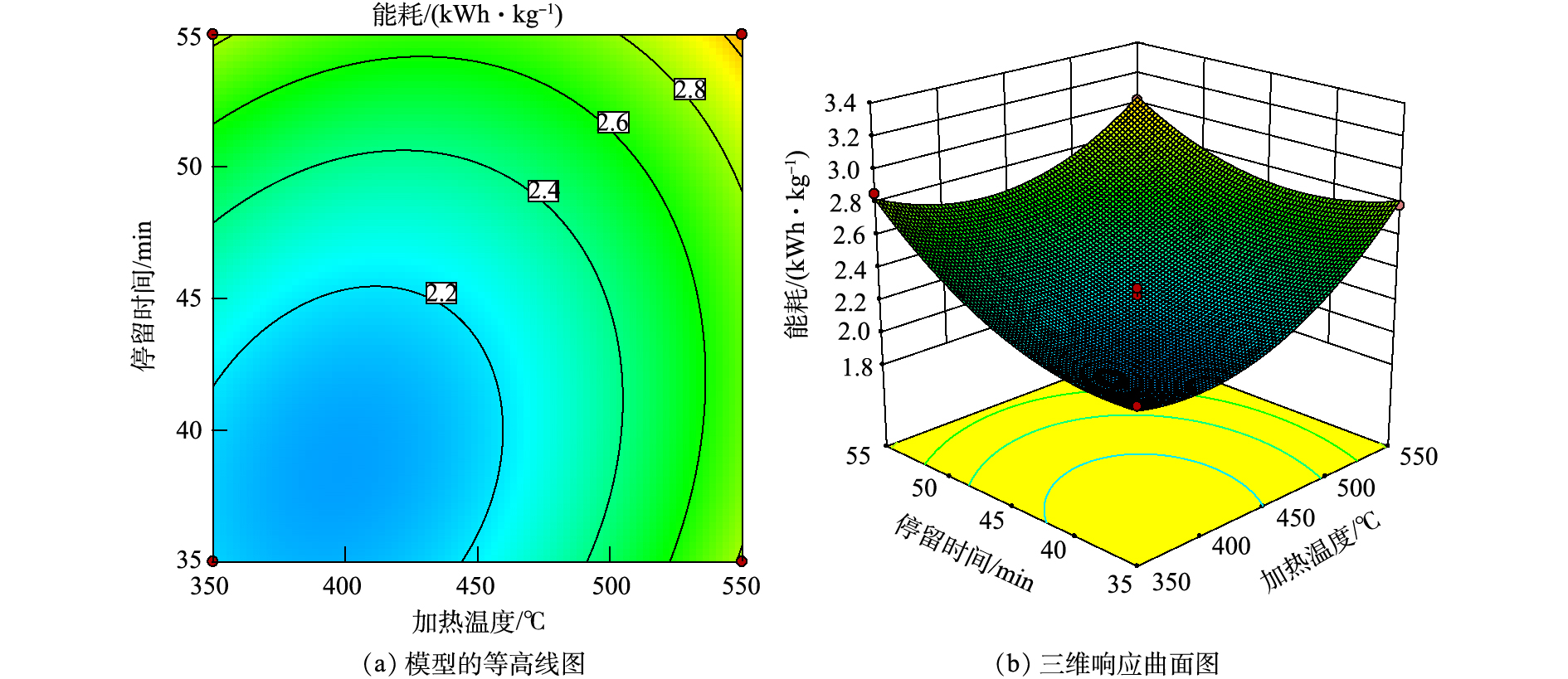
R2Adj =0.988 9,表明仅有1.11%的数据不能由该模型解释;实际所得的R2=0.995 1,表明模型预测与实际值之间的具有较好的一致性,故可用该模型对热脱附处理油基岩屑能耗进行分析和预测。通过显著性检验发现,加热温度(X1)、停留时间(X2)、油基岩屑固相含量(X3)、加热温度与停留时间(X1X2)、停留时间与油基岩屑固相含量(X1X3)、停留时间与油基岩屑固相含量(X2X3)均为显著影响因子。F值越大,说明该因子与实验结果的相关性越强,影响越大。对比自变量的F值可得出,不同因素的影响次序是固相含量>停留时间>加热温度,但停留时间与加热温度的F值相近。响应曲面法得到模型的等高线和三维响应曲面图(图4~图6)。图4反映了当油基岩屑固相含量为75%时,加热温度和停留时间的交互作用对能耗的影响。由图4可看出,随着加热温度和停留时间的增加,能耗均呈现增大的趋势,曲面整体呈右后角较高,其他位置较低的现象。当加热温度为350~440 ℃,停留时间为35~42 min时,能耗最低,经济效益最佳。加热温度为350 ℃时,随着停留时间的增加,能耗缓慢增加;加热温度为550 ℃时,随着停留时间的增加,能耗呈上升趋势,但是上升并不明显。当加热温度不变时,增加油基岩屑在热脱附装置内的停留时间,热量从岩屑表面传递进入内部,油基岩屑内部受热更充分、油从岩屑中脱吸附更充分彻底[24-26]。随着停留时间的进一步延长,岩屑中剩余水、油的含量少,脱吸附反应趋于停止,能耗增加趋势变缓。通过曲面的倾斜程度可看出停留时间为35 min时,加热温度对能耗影响较大;停留时间55 min时,加热温度和停留时间相互作用对能耗影响较大,停留时间足够热量从油基岩屑表面传导至内部,内部受热逐渐趋于平衡,因此,加热温度和停留时间协同作用明显,与模型分析所得的结果一致。
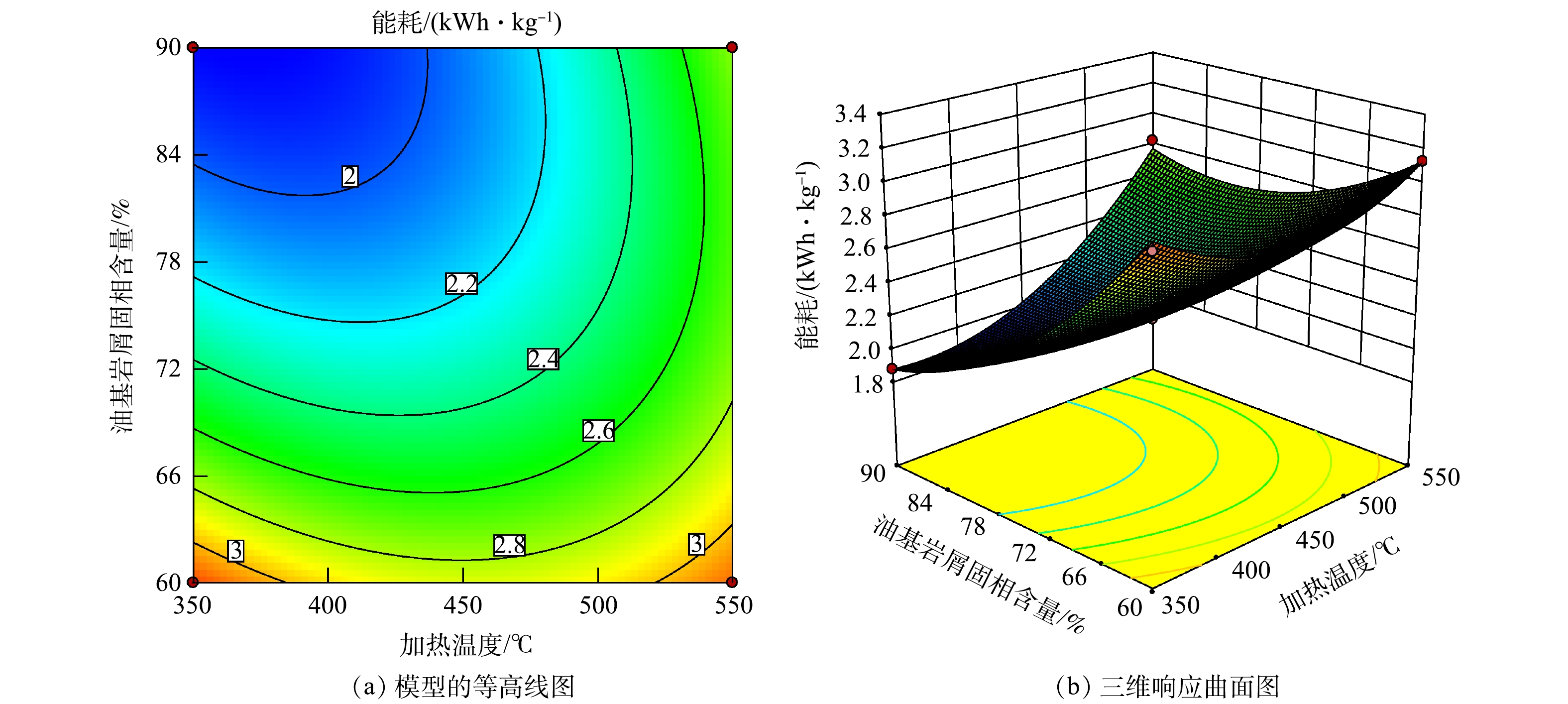
图5为停留时间45 min时,加热温度和油基岩屑固相含量的交互作用对能耗的影响。由图5可看出,随着加热温度和油基岩屑固相含量的增加,曲面整体呈现右上角较高,左后角较低的现象。在加热温度为350~440 ℃,油基岩屑固相含量为83%~90%时,能耗最低,经济效益最佳。油基岩屑中的油主要是配制油基钻井液的基础油,烃类分布范围相对集中。当加热温度为350 ℃时,油基岩屑中大量的油已被分离出来,固相含量越低,需要分离的液相越多,所需要的能量越大。当加热温度为550 ℃时,吸附在岩屑颗粒表面的沥青、脂肪族化合物等部分开始裂解[27-29],颗粒内部热量传递速度加快,固相含量对能耗的影响相对减弱,能耗增加趋势减缓。当油基岩屑固相含量较低时,热量主要损耗在游离态油和水、吸附态油和水的脱附过程中。在一定时间内,加热温度越高,传热速度越快,残渣的含油率越低,加热温度对能耗影响较大;当固相含量较高时,游离态、吸附态的油和水含量也较少,热量损耗主要在对岩屑及其内部油和水的脱附过程中,加热温度和固相含量之间的交互作用对能耗影响较大,与模型分析结果一致。
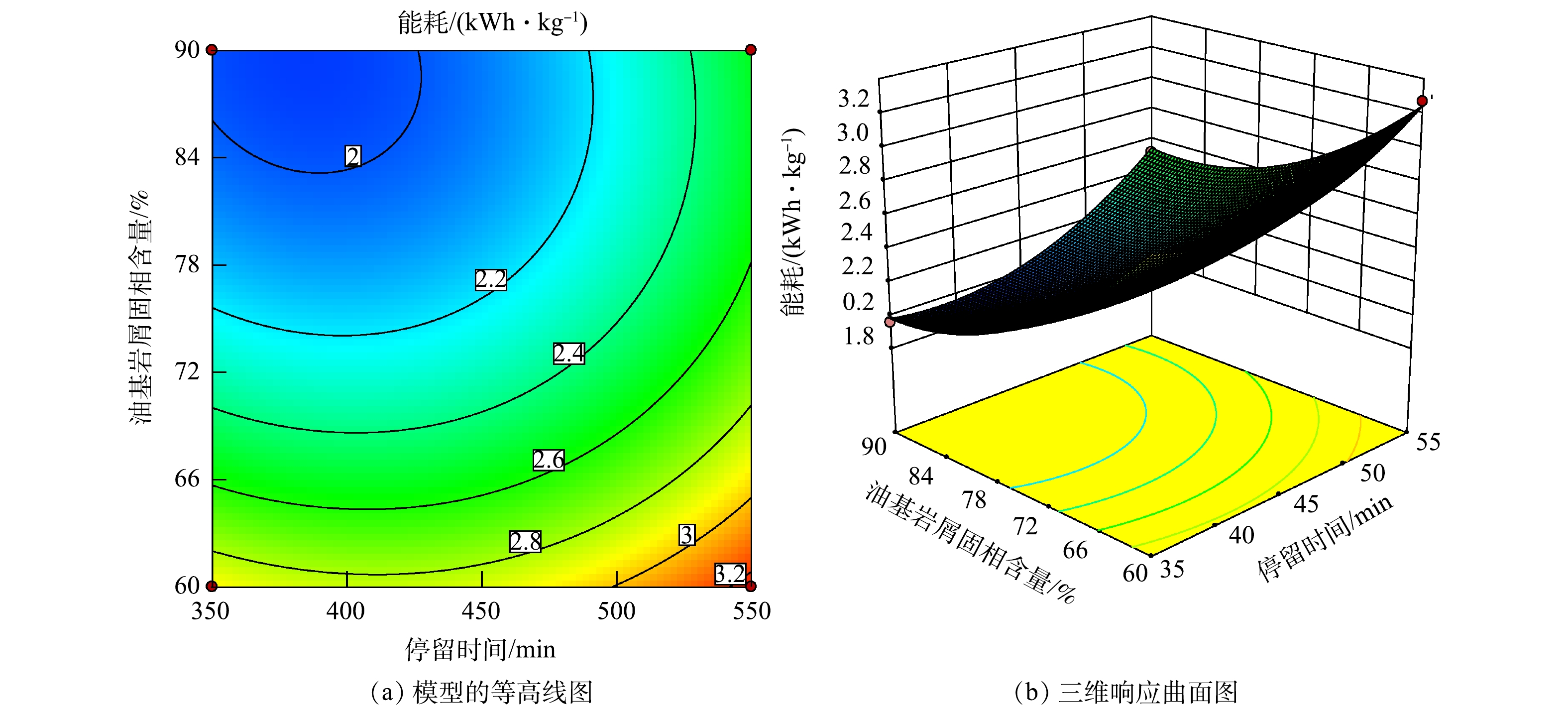
图6反映了加热温度为450 ℃时,停留时间和固相含量的交互作用对能耗的影响。由图6可知,随着停留时间和固相含量的增加,曲面整体呈现左后角较低,右上角较高的现象。当停留时间为35~43 min、固相含量为85%~90%时,能耗最低,经济效益最佳。随着停留时间的增加,固相含量在增加或是减小的条件下,能耗均增加,相比固相含量为60%,在固相含量为90%时的停留时间增加趋势更明显。停留时间越长,油基岩屑中水、油脱附越彻底[30-31],固相含量越高,油基岩屑中水、油含量较低,需要增加的能耗主要是油基岩屑中岩屑升温需要的能耗,相对于水、油分离需要的能耗减少。通过曲面的倾斜程度可知,停留时间与固相含量之间的交互作用对能耗的影响较大,与模型的分析结果一致。
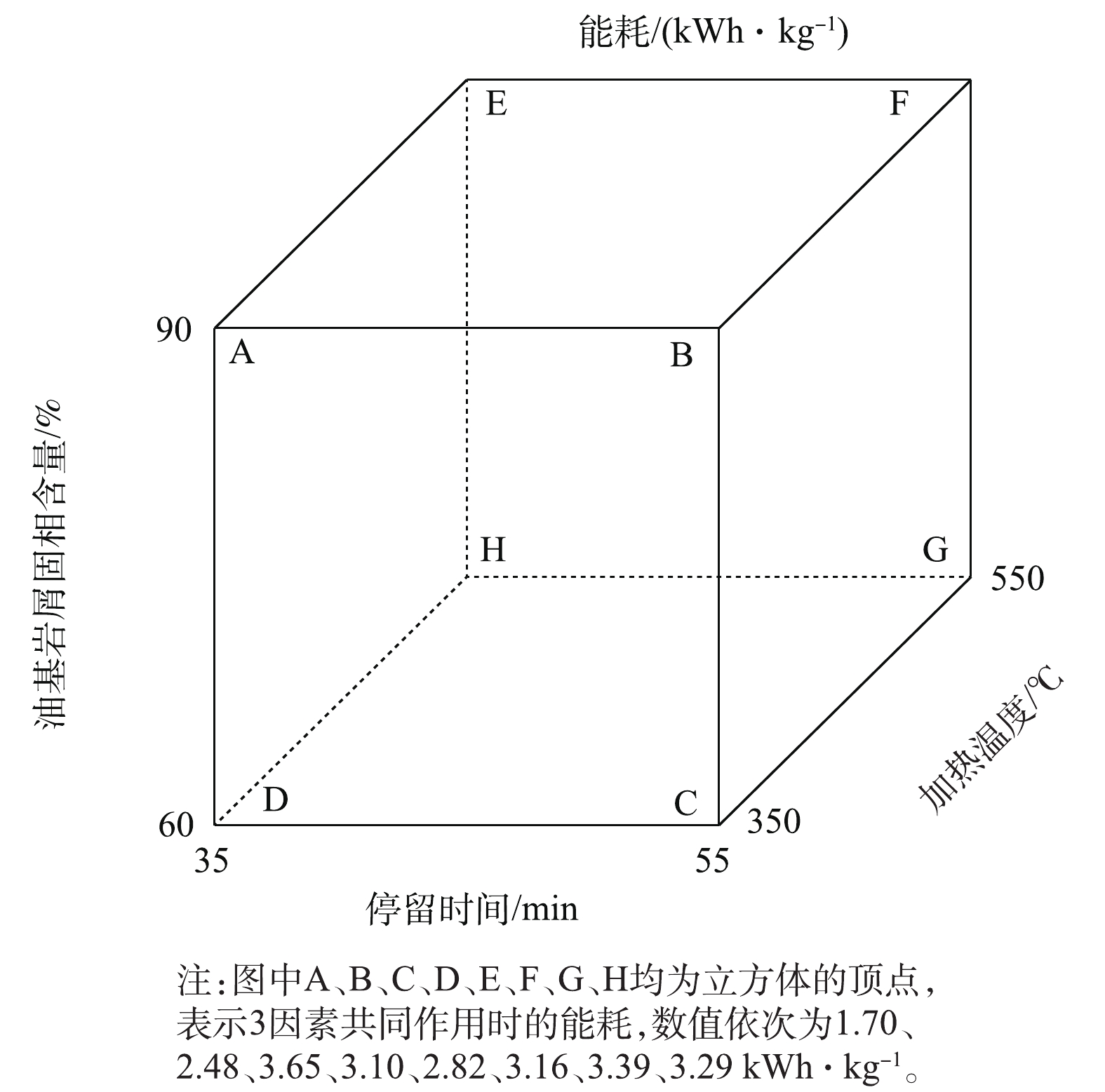
在加热温度、停留时间和油基岩屑固相含量3个变量同时变化的情况下,其对能耗的影响结果如图7所示。当加热温度为350 ℃、停留为55 min、油基岩屑固相含量为60%时,能耗最高为3.65 kWh·kg−1;当加热温度为350 ℃、停留为35 min、油基岩屑固相含量为90%时,能耗最低为1.70 kWh·kg−1,此时热脱附装置能耗优于其他条件下的能耗。
利用Design Expert软件的优化功能设定各影响因素的约束条件,求解出约束条件下的最小能耗。钻井现场一般会经过离心机对油基岩屑进行固液分离,分离后油基岩屑固相含量约为70%,若需进一步提高固相含量以减少热脱附能耗,需要额外增加预处理费用。综合考虑加热温度、停留时间、油基岩屑固相含量等因素,离心机处理后的油基岩屑(实验样品)固相含量为70.52%。在能耗最小的条件下,优化计算得到的加热温度为430.52 ℃,停留时间为40.01 min。但在工业化热脱附装置实际运行中,考虑到加热温度和停留时间设置值均为整数,确定最佳条件为加热温度430 ℃、停留时间40 min、固相含量70%。在对最优条件进行回归方程和模型验证过程中,为减少实验的偶然误差,进行了3组平行实验,能耗分别为2.31、2.43、2.37 kWh·kg−1,实验平均值2.37 kWh·kg−1,模型预测值为2.29 kWh·kg−1。实验结果略高于预测值,但两者相对误差仅为3.3%,进一步证明了该模型可以用来预测和分析油基岩屑热脱附处理工艺参数的可靠性。
在进行工艺参数优化效果实验分析时,取现场离心机处理后油基岩屑固相含量为70.52%的样品进行实验。工艺参数优化前和优化后,对不同的加热温度和停留时间条件下,能耗和残渣的含油率进行对比,实验结果见表5。由模型显著性系数可知,加热温度和停留时间相互作用显著,适当降低加热温度和减少停留时间,可降低热脱附处理的能耗,优化后热脱附装置的单位处理能耗较优化前降低了17.47%(表5)。但温度降低和停留时间减少会导致热脱附效率的相对降低,残渣的含油率升高到0.26%,也满足《农用污泥中污染物控制标准》(GB 4284-2018)B级污泥产物污染物限值<0.3%要求,明显低于《陆上石油天然气开采含油污泥资源化综合利用及污染控制技术要求》(SY/T 7301-2016)中要求低于2%的标准要求。
2.1. 单因素实验
2.2. 响应曲面分析实验
-
1)当残渣的含油率≤2%时,各参数经过单因素实验优化后,所得的适宜条件分别为加热温度350~550 ℃、停留时间35~55 min、油基岩屑固相含量60%~90%。
2)当油基岩屑固相含量为70%时,在能耗最小的条件下,最优热脱附处理工艺参数为加热温度430 ℃、停留时间40 min。验证实验的能耗平均值为2.37 kWh·kg−1,预测值与实验值的相对误差仅为3.3%,故可有效证明该二次多项模型的准确性和可行性。
3)采用最优油基岩屑热脱附处理工艺条件后,可节约能耗17.47%,残渣的含油率<0.3%。实验结果表明,在热脱附装置现有的设计范围内,通过工艺参数优化,可在实现残渣的含油率达标的前提下节能降耗,从而克服了油基岩屑热脱附处理工业化应用的经济效益差的难题。






 下载:
下载: