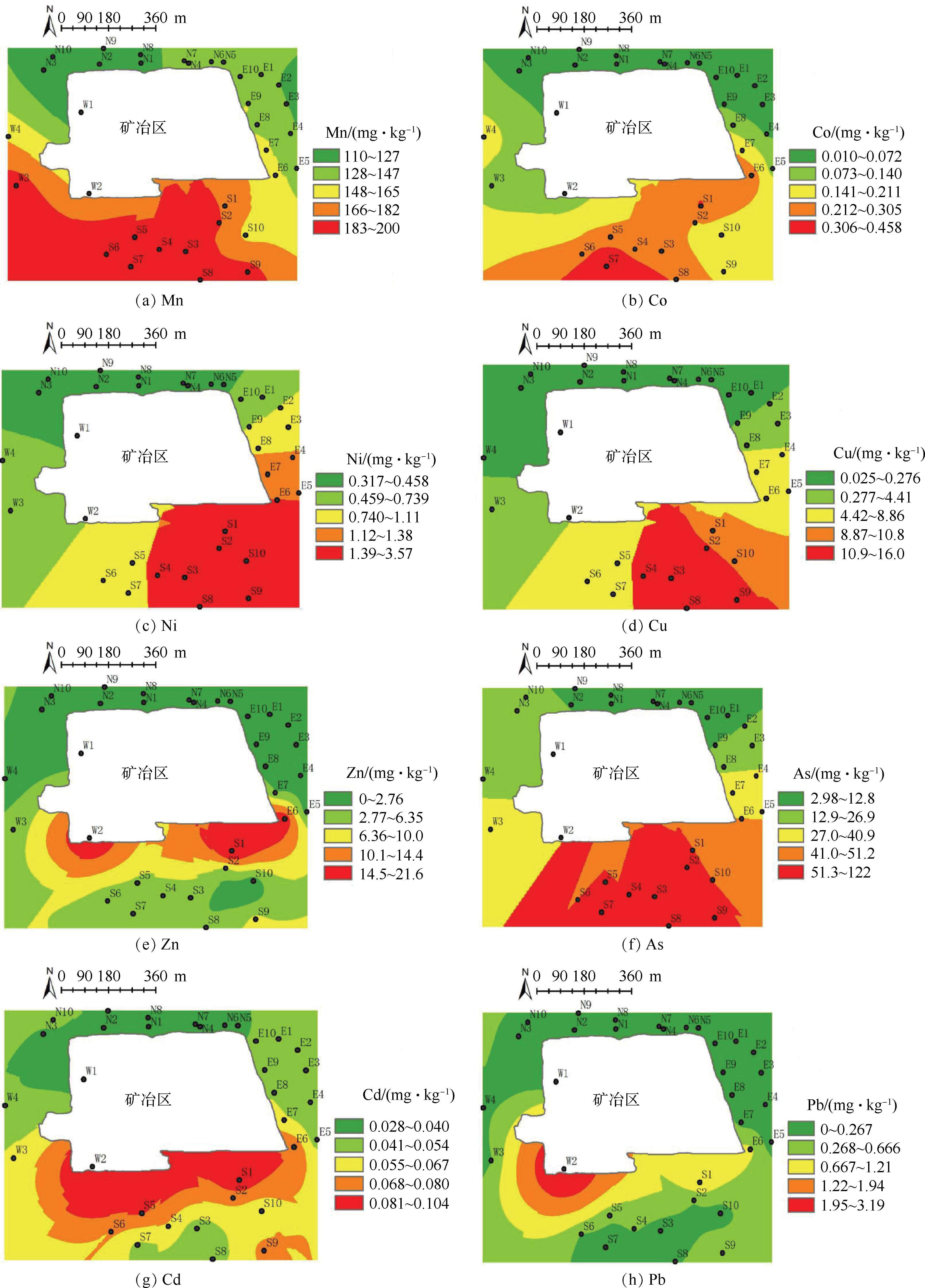
-
甲硫醇(CH3SH)是污水处理厂臭气中的主要特征污染物[1],具有强烈的刺激性气味[2]、嗅阈值低和高腐蚀等特性[3],是一种具有较高毒性的含硫挥发性有机化合物(VOCs)[4]。目前,对甲硫醇的去除技术主要包括氧化法、吸收法、吸附法和生物法等[5-6],其中的吸附法因具有简便高效的优势被广泛用于臭气处理[7-9]。活性炭作为常用的吸附材料,具有性能稳定、抗腐蚀等优点,但再生及更换频繁、除臭成本较高[10]。通过提高活性炭的吸附量,可延长其使用时间,减少再生及更换频次。
为提高活性炭的吸附量,通常采用碱溶液[11]、金属溶液[12]或氧化剂浸渍方法,修饰其表面的物理化学结构,以改善对甲硫醇的吸附性能[13]。相较碱溶液和金属溶液,氧化剂浸渍改性在使活性炭表面含氧官能团增加的同时,可以有效氧化扩大其内部微孔,进一步提升吸附性能而被普遍采用。目前,常用于活性炭改性的氧化剂有HNO3、H2O2和KMnO4等,而不同氧化剂改性对活性炭表面含氧官能团的修饰作用各异。其中HNO3[14]和H2O2[15]等改性后表面主要为羧酸、内酯和酚类等酸性基团,而KMnO4[16]改性则可以产生碳羰基、酮类和醚类等中性或碱性基团。由于甲硫醇呈偏酸性,碱性基团的存在更有利于活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附,因此,从理论上来讲,KMnO4改性可以较好地提高活性炭对于甲硫醇的吸附性能。但目前关于KMnO4改性活性炭的研究主要集中于对液相金属离子等污染物的去除,而用于甲硫醇吸附的研究鲜有报道。
本研究通过小试实验,采用KMnO4浸渍改性活性炭,在优化浸渍液浓度、浸渍时间、浸渍温度和浸渍比等条件的基础上,获得较优的改性活性碳;通过全自动比表面积和孔径分析仪、扫描电子显微镜和Boehm滴定法等表征其材料特性,揭示KMnO4改性活性炭对甲硫醇吸附量提高的原因;研究改性活性炭吸附甲硫醇的动力学和热力学特征,为甲硫醇吸附处理的实际应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
高锰酸钾(KMnO4,AR)、碳酸钠(Na2CO3,AR)和氯化铜(CuCl2,AR),均购自阿拉丁试剂(上海)有限公司;甲硫醇(1%),购自大连大特气体有限公司;椰壳活性炭(粒度8~20目,比表面积450~700 m2·g−1),购自广东冠森炭业科技有限公司。
Autosorb-iQ2-MP型全自动比表面积和孔径分析仪,购自美国康塔仪器公司;日立S-4700扫描电子显微镜,购自昆山伯莱恩光学有限公司;P300H超声仪,购自施锐(上海)贸易有限公司;岛津GC-2014C,购自岛津(广州)检测技术有限公司;DHG-9140A鼓风干燥箱,购自上海笃特科学仪器有限公司;LRH-150CA恒温培养箱,购自上海精密仪器仪表有限公司;惰性铝箔采样气袋,购自上海标卓科学仪器有限公司。
-
称取一定质量未改性椰壳活性炭,置于250 mL锥形瓶中;分别加入100 mL一定浓度KMnO4浸渍液并密封瓶口;在一定温度下,静置一定时间后,用300目不锈钢筛滤出活性炭,同时用蒸馏水多次清洗,以除去多余的浸渍溶质;在105 ℃下鼓风干燥3 h后,即可得到浸渍改性活性炭。
-
在25 ℃条件下,准确称取0.01 g活性炭加入N2清洗、抽真空后的惰性气袋;用注射器充入一定体积的甲硫醇标气,并补充空气至0.5 L,此时甲硫醇初始浓度为7 300 mg·m−3;分别于不同时刻测定气袋中残余的甲硫醇浓度,直至吸附平衡;通过计算(式(1)),得到改性活性炭对甲硫醇的静态吸附量。
式中,C0和Ct分别为初始时刻和t时刻的甲硫醇浓度,mg·m−3;ms为静态吸附量,mg·g−1;M为甲硫醇摩尔质量,取值48 g·mol−1;m为活性炭质量,取值0.01 g。
对改性活性炭制备过程中的条件进行优化,分别考察浸渍浓度(控制浸渍温度为25 ℃、浸渍时间为5 h和浸渍比为4∶100,浸渍浓度分别为0.5%、1%、3%和7%)、浸渍时间(控制浸渍温度为25 ℃、浸渍浓度为1%和浸渍比为4∶100,浸渍时间分别为0.5、1、2、4、6、8 h)、浸渍温度(控制浸渍时间为6 h、浸渍浓度为1%和浸渍比为4∶100,浸渍温度分别为10、25、40、60、80、100 ℃)和浸渍比(控制浸渍温度为25 ℃、浸渍时间为6 h和浸渍浓度为1%,浸渍比分别为1∶100、4∶100、8∶100、16∶100和30∶100)对改性活性炭吸附甲硫醇的性能影响,得到较优的制备条件。
在温度为20 ℃、甲硫醇初始浓度为5 000 mg·m−3条件下,进行改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附动力学实验。采用准一级动力学模型、准二级动力学模型及粒子内扩散模型对改性活性炭吸附甲硫醇的动力学过程进行描述,准一级动力学模型见式(2),准二级动力学模型见见式(3),粒子内扩散模型见式(4)。
式中:qt为t时刻的吸附量,mg·g−1;qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;t为吸附时间,min;k1为准一级吸附速率常数,min−1;k2为准二级吸附速率常数,g·(mg·min)−1;K为内扩散速率常数,mg·(g·min0.5)−1。
采用Langmuir方程和Freundlich方程对15、25、40和60 ℃条件下改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附等温线数据进行拟合分析,Langmuir方程见式(5),Freundlich方程见式(6)。
式中:qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;Ce为平衡浓度,mg·m−3;qc为饱和吸附量,mg·g−1;KL为Langmuir平衡参数;KF为Freundlich平衡参数;n为吸附强度。
引入Gibbs、van’t Hoff及Gibbs-Helmholtz方程,来计算温度为15、25、40和60 ℃条件下,吸附过程的吉布斯自由能变ΔG、焓变ΔH、熵变ΔS等热力学参数。
式中:ΔG为吉布斯自由能变,kJ·mol−1;ΔH为焓变,kJ·mol−1;ΔS为熵变,kJ·mol−1;K′为常数;Kd为热力学平衡常数;R为热力学常数,取值8.314 kJ·mol−1;T为热力学温度,K。
-
采用气相色谱仪测定甲硫醇的浓度,相关配置和参数为:3 m × 3 mm的硬质玻璃色谱柱,进样口温度为150 ℃。采用火焰光度检测器(PFPD),设定温度为200 ℃,载气为氮气,流量为70 mL·min−1,空气流量为50 mL·min−1,氢气流量为60 mL·min−1。程序升温设计初始温度为35 ℃,保持运行5 min后结束。
采用全自动比表面积和孔径分析仪对材料的比表面积和孔结构进行表征;采用扫描电子显微镜对表面形貌进行观察,耦合EDS分析表面的元素变化;采用Boehm滴定法测定表面酸碱性基团的数量。
1.1. 试剂与仪器
1.2. 改性活性炭制备
1.3. 实验方法
1.4. 分析与表征
-
不同浓度KMnO4浸渍液处理对改性活性炭吸附性能的影响如图1所示。由图1可知,KMnO4浸渍可以有效提高活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附量,吸附量高达231.98 mg·g−1,是未改性活性炭的1.93~2.78倍,且1% KMnO4浸渍液改性效果最佳。随着浸渍液浓度的增加,KMnO4与活性炭内外表面的接触概率增大,有效扩大活性炭的微孔容积并促进碱性基团的增多,有利于对甲硫醇的吸附。1% KMnO4浸渍液浓度时达到充分接触,继续增加浸渍液浓度,对微孔容积和碱性基团的改善效果不明显,反而堵塞了介孔通道,不利于对甲硫醇的吸附。因此,选择KMnO4浸渍改性活性炭的浓度为1%。
不同KMnO4浸渍时间对改性活性炭吸附性能的影响如图2所示。可以看出,随着浸渍时间的增加,改性活性炭对甲硫醇吸附量时增时减,在6 h时,达到335.56 mg·g−1的最高吸附量。KMnO4改性活性炭的过程是新孔隙生成和破坏同步进行的过程[17]。当浸渍时间小于1 h时,KMnO4对活性炭发生氧化作用,打开外部堵塞的孔隙,对甲硫醇的吸附量增加;浸渍时间为1~2 h时,孔隙结构受到破坏,不利于对甲硫醇的吸附;浸渍时间继续增加,KMnO4扩散至内部,氧化产生新的微孔,使甲硫醇的吸附量再次增加;浸渍时间大于6 h后,KMnO4对微孔的破坏起主导作用。因此,选择KMnO4浸渍改性活性炭的时间为6 h。
不同KMnO4浸渍温度对改性活性炭吸附性能的影响如图3所示。可以看出,随着浸渍温度的增加,改性活性炭对甲硫醇的平衡吸附量先增加后减小,在25 ℃浸渍时,吸附量最高,达到344.22 mg·g−1。分子热运动与温度有关,温度越高,则KMnO4分子活性越高,容易与活性炭内部接触[18]。过低的温度不利于KMnO4分子向活性炭内部扩散;温度增至25 ℃时,KMnO4分子与活性炭表面充分接触氧化;继续增加温度,进入活性炭内部的KMnO4分子过量,微孔破坏量大于产生量。因此,选择KMnO4浸渍改性活性炭的温度为25 ℃。
不同KMnO4浸渍比对改性活性炭吸附性能的影响如图4所示。可以看出,随着浸渍比的增加,改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附量呈现先增加后减小的规律。在浸渍比为8∶100时,甲硫醇吸附量最高,达到342.05 mg·g−1。当浸渍比过低时,单位活性炭被KMnO4氧化过度,使孔隙之间的壁面消融,导致微孔减少,不利于吸附甲硫醇;当浸渍比过高时,单位活性炭接触的KMnO4分子不充分,对其表面的氧化修饰效果较差。因此,选择KMnO4浸渍改性活性炭的浸渍比为8∶100。
-
为揭示浸渍改性后活性炭吸附量提高的原因,对KMnO4浓度为1%、温度为25 ℃、浸渍比为8∶100的条件下浸渍6 h获得的改性活性炭进行表征,并与未改性活性炭作对比分析。
图5是活性炭改性前、后的表面形貌和元素分布情况。由图5(a)和图5(b)可知:未改性活性炭的表面孔洞孔径较小,有堆叠现象;经KMnO4浸渍改性后,出现少量较大孔径的孔洞,且堆叠现象减少。由图5(c)和图5(d)可知:未改性活性炭的表面不含有K和Mn元素,主要为C和O元素,含量为83.65%和16.35%;经过KMnO4浸渍改性后,其表面的Mn元素显著增加,含锰量达到25.17%,C、O和K元素含量分别为59.58%、9.13%和5.72%。
KMnO4具有强氧化性,使得堵塞的孔洞得到清理,较薄的孔壁受到破坏,打开孔道,增加微孔数量,有利于改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附。
活性炭改性前、后的N2吸附-脱附等温曲线和微孔粒径分布如图6所示。由图6(a)可知,改性前、后活性炭对N2的吸附-脱附曲线表现为典型的Ⅰ型吸附等温线特征[10]。利用脱附曲线上不同相对压力时的脱附量,得到活性炭改性前、后的微孔粒径分布。由图6(b)可知,活性炭表面的微孔粒径为0.35~0.8 nm,经过KMnO4浸渍改性后,该部分粒径范围的微孔数量明显增加。将N2吸附-脱附过程的相对压力控制在0.05~0.25,采用BET方程计算其总孔比表面积,采用t-plot法计算材料的微孔比表面积和微孔容积。活性炭改性前后的孔结构参数计算结果见表1。
由表1可知,KMnO4浸渍改性活性炭的比表面积、微孔比表面积和微孔孔容显著增大,分别是未改性前的1.17、1.18和1.16倍;且可以发现,增加的微孔大部分为小孔径,集中在0.35~0.80 nm。
KMnO4浸渍改性可以有效增加活性炭上的微孔数量,与前面的表面形貌变化相符,微孔孔径主要分布在0.35~0.80 nm;而甲硫醇作为极性小分子物质,其分子动力学直径为0.38 nm,可以有效扩散到新增的微孔中被吸附。
活性炭表面的酸碱基团变化对其吸附碱性和酸性污染物的性能具有一定影响[19]。由表2可知,经过KMnO4浸渍改性后,活性炭表面的酸性基团数量变化不明显,由0.99 mmol·g−1降低至0.95 mmol·g−1;但碱性基团显著增加,由0.66 mmol·g−1增加至1.53 mmol·g−1,是原来的2.53倍。KMnO4浸渍改性后,在活性炭表面引入大量碱性基团;而甲硫醇作为一种酸性污染物,碱性基团的增加有利于活性炭对其进行吸附[20]。
-
改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附动力学拟合曲线如图7所示,拟合参数结果如下:准一级动力学模型的吸附速率常数k1为1.165 7,拟合系数为0.949 7;准二级动力学模型的吸附速率常数k2为5.154 4,拟合系数为0.998 3;粒子内扩散模型的内扩散速率常数第1阶段K1为9.280 5,第2阶段K2为3.121 5。由图7(a)、图7(b)和拟合参数结果可知,二级模型的拟合系数较优于准一级模型,拟合系数为0.998 3,说明准二级动力学模型可以更好地描述改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附行为。准一级动力学模型假定吸附受扩散步骤控制,适合于吸附初始阶段的吸附行为描述;而准二级动力学模型则描述了气相扩散、表面吸附和粒子内扩散等所有吸附过程,因此,可以更准确地反映甲硫醇在改性活性炭上的吸附机理。
另外,由图7(c)和拟合参数结果可知,改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附过程中,qt与t0.5不成直线关系,而是分阶段的线性关系。这说明吸附过程中可分为2个阶段:第1阶段为活性炭的表面吸附,该阶段吸附速率快,吸附常数大;第2阶段表面活性位被占据,甲硫醇需扩散至内部微孔中与活性位发生吸附,此时受到孔道阻力影响,吸附速率较慢,吸附常数小,是吸附过程的控速步骤。随着活性位的减少,吸附速率逐渐降低,直至吸附平衡。同时可以发现,2个吸附阶段的qt-t0.5拟合直线均不通过原点,说明粒子内扩散过程不是唯一控速步骤,吸附速率受到气相扩散和粒子内扩散的共同影响。改性活性炭对甲硫醇的等温吸附模型拟合图如图8所示,拟合结果见表3。由图8和表3的拟合结果可知,Freundlich模型的拟合度优于Langmuir模型,拟合系数在0.99以上,可以很好地描述改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附平衡,说明吸附过程具有多层吸附特征[21]。另外,Freundlich模型中的组分因数1/n反映了吸附的难易程度,改性活性炭对甲硫醇吸附过程的1/n拟合值为0.20~0.28,说明吸附过程容易进行,属于优惠吸附[22]。
由表4可知,吉布斯自由能ΔG为负值,说明吸附过程是自发过程,且吸附自由能随着温度的升高而升高,说明升温不利于反应的进行;焓变ΔH为负值,说明吸附过程为放热反应,升温不利于吸附正向进行;熵变ΔS为负值,说明吸附过程是一个熵减过程,与改性活性炭吸附甲硫醇使得吸附质自由度减少的事实相符。
2.1. KMnO4浸渍改性活性炭条件优化
2.2. 改性活性炭性能提升研究
2.3. 改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附机制
-
1)在KMnO4浓度为1%、浸渍温度为25 ℃、浸渍比为8∶100的条件下浸渍6 h,改性活性炭对甲硫醇的静态吸附量最高,达到344.22 mg·g−1,是未改性前的4.04倍。
2)改性活性炭对甲硫醇吸附量提高的原因主要是表面碱性基团的增加(是原来的2.53倍)以及微孔容积和比表面积的增加。
3)改性活性炭对甲硫醇的吸附符合准二级动力学模型,同时粒子内扩散模型表明吸附过程由气相扩散和粒子内扩散共同作用;符合Freundlich吸附等温方程,具有多层吸附特征,且吸附容易进行,属于优惠吸附,是一个自发、放热和熵减的过程,升温不利于对甲硫醇的吸附。



 下载:
下载: