-
目前,低浓度废水的处理工艺主要包括A2O、氧化沟、SBR等,其技术核心为活性污泥法[1]。传统活性污泥法普遍存在着能耗高、污泥产量大的问题。相比而言,厌氧生物处理技术因其能耗低、污泥产量少且能产生甲烷而受到了越来越多的关注,但厌氧生物处理技术存在污泥流失和处理效果不佳的问题,故需进一步改进[2-3]。
厌氧膜生物反应器(anaerobic membrane bioreactor,AnMBR)是一种将膜分离技术与厌氧生物处理技术有效结合的新型废水处理工艺[4]。该工艺能通过膜的过滤截留作用,实现水力停留时间(HRT)和污泥龄(SRT)的完全分离[5]。荆延龙等[6]采用AnMBR处理低浓度生活废水,结果表明,经过117 d的稳定运行,COD去除率高达90.6%;许美兰等[7]研究了不同HRT对AnMBR处理低浓度废水运行效果的影响,经过35 d的稳定运行,发现HRT的缩短未对COD的去除产生显著差异。这说明AnMBR在处理低浓度废水方面稳定性良好,拥有广阔的发展前景[8]。但一直以来,膜成本和膜污染是困扰该技术走向实际工程应用的限制性条件[9]。而动态膜技术的出现,有望解决MBR中存在的膜成本过高及膜污染严重的问题[10]。程刚等[11]利用不锈钢丝网为基材构建AnMBR处理低浓度生活废水,结果表明,选用300目的不锈钢丝网,在污泥浓度(MLSS)为2 mg·L−1的条件下,可稳定运行240 h。赵立健等[12]在常温下利用无纺布为基材构建AnMBR处理人工合成低浓废水,结果表明,COD平均去除率为89.5%。尽管现有的研究已证实AnMBR对低浓度废水有较好的处理效果,但对其运行过程中膜污染的评估研究较少。
本研究利用廉价不锈钢丝网作为膜材料,构建新型AnMBR,在HRT为10 h的条件下,考察了反应器运行效果、产甲烷能力、膜污染程度以及对温度的适应性,旨在为AnMBR在实际低浓度废水中的应用提供技术支撑。
-
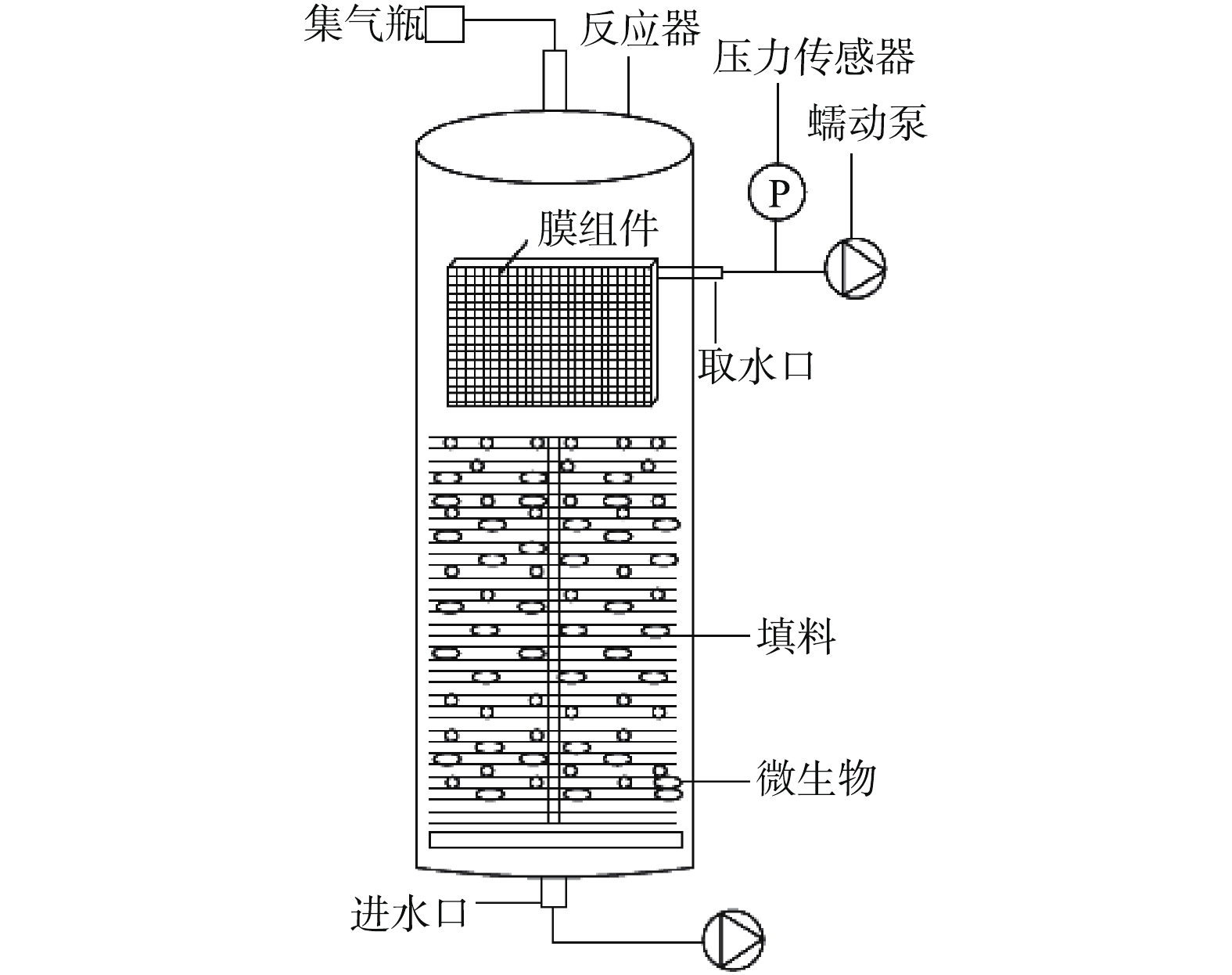
实验采用升流式厌氧反应器,实验装置如图1所示,其总容积为3 L,有效容积为2.4 L。反应器底部装有生物膜填料,中上部装有1 000目不锈钢丝网制成的膜组件,膜组件的尺寸为13 cm×8 cm×3.5 cm,总过滤面积为0.011 m2。反应器外层装有一层保温层和循环水管,使反应器内的水温控制在35 ℃。
-
本实验所采用的低浓度废水为人工合成废水,含有主要元素和微量元素[13-14]。其成分包括蔗糖(C12H22O11 500 mg·L−1)、碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3 350 mg·L−1)、三水合磷酸氢二钾(K2HPO4·3H2O 21 mg·L−1)、碳酸氢铵(NH4HCO3 41 mg·L−1)、氯化钙(CaCl2 50 mg·L−1)、四水合氯化锰(MnCl2·4H2O 5 mg·L−1)、六水合氯化钴(CoCl2·6H2O 5 mg·L−1)、六水合氯化铝(AlCl3·6H2O 5 mg·L−1)、硼酸(H3BO3 5 mg·L−1)、四水合钼酸铵((NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O 5 mg·L−1)、六水合氯化镍(NiCl2·6H2O 5 mg·L−1)、氯化锌(ZnCl2 5 mg·L−1)、五水合硫酸铜(CuSO4·5H2O 5 mg·L−1)。反应器接种的污泥取自合肥市某污水处理厂,接种时的污泥浓度(MLSS)为4 g·L−1,实验期间没有剩余污泥排出。
-
实验采用连续进出水的方式,总共连续运行66 d,反应器进水速度为240 mL·h−1,整个运行期间HRT控制在10 h。在33~39 d,由于加热系统出现故障导致温度降低到25 ℃,维持7 d后,恢复至35 ℃。低浓度废水在蠕动泵的作用下经反应器底部进入反应器内,并利用蠕动泵从膜组件抽取出水。实验内容分为2个阶段:第1阶段是反应器启动运行阶段(0~15 d);第2阶段是反应器稳定运行阶段(16~66 d)。
-
出水溶解性COD采用重铬酸钾法[15]测定;VFAs和气体采用气相色谱法测定;跨膜压差(TMP)采用压力传感器(MIK-P300,杭州米科传感技术有限公司)测定;膜面污染物采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)(XL-30 ESEM,美国FEI)分析;膜阻及膜阻增长速率[16-17]分别根据式(1)和式(2)进行计算。
式中:R为膜阻,m−1;ΔP为跨膜压差,Pa;μ为渗滤液动力黏度系数,Pa·s;Ri为膜阻增长速率,m−1·h−1;J为瞬时膜通量,m3·(m2·h)−1;T为运行时间,d。
-
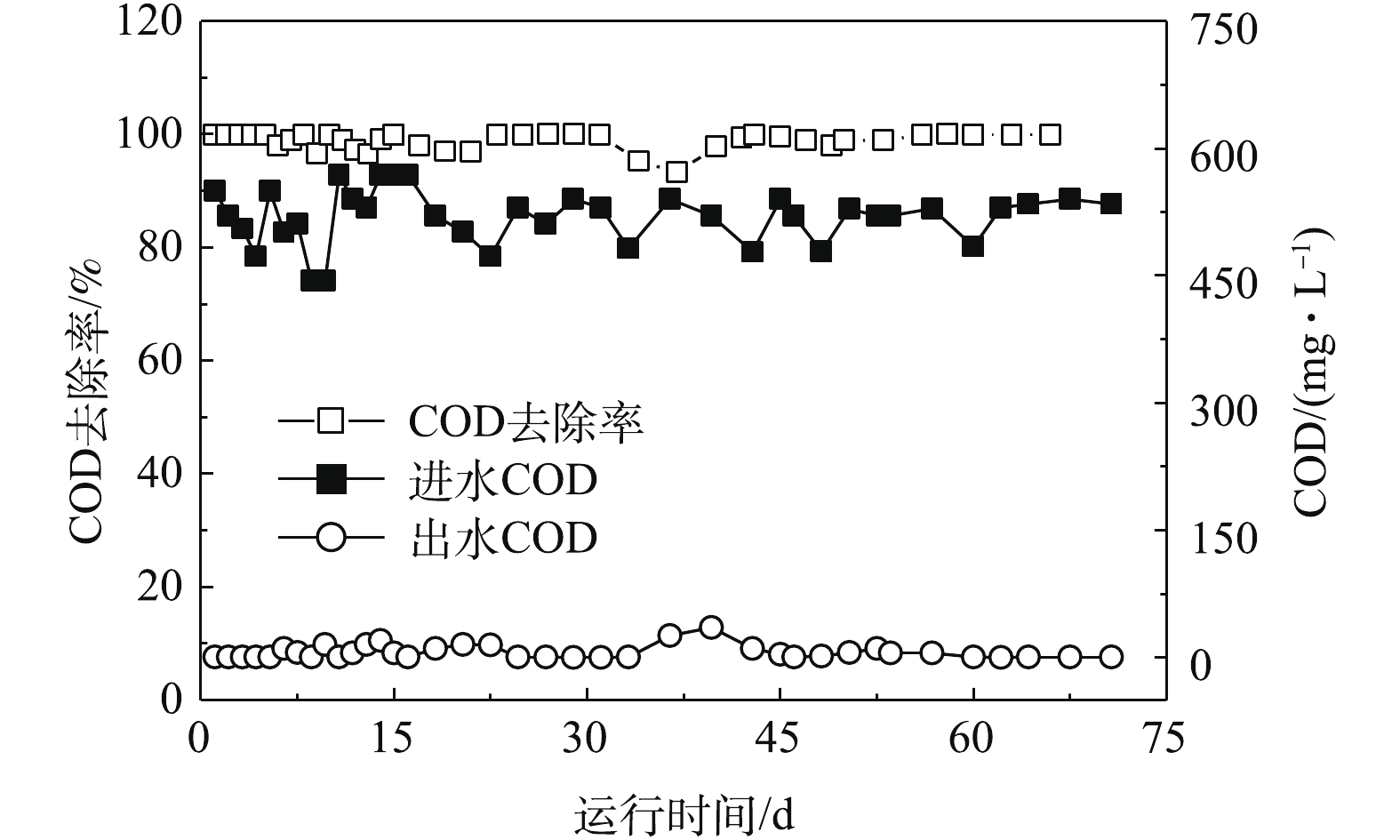
1)反应器运行过程COD去除效果。在HRT为10 h、进水COD在500 mg·L−1的条件下,AnMBR共运行66 d,进出水COD及去除率的变化如图2所示。在0~33 d内,COD的平均去除率为95%,出水COD始终低于30 mg·L−1;从第33天开始,反应器运行温度由35 ℃变为25 ℃,经过7 d的运行后,COD的去除率仍维持在93%以上。从第40天开始,温度恢复至35 ℃后,COD的去除率又维持在95%。这说明本系统在HRT为10 h的条件下,获得了稳定的运行效果,且对温度波动有较强的适应能力,能始终保持较高的COD去除率,保证出水COD的达标排放。
2)反应器运行过程VFA累积情况。VFAs浓度是判断产酸菌和产甲烷菌活性的重要指标[18]。在整个实验阶段,出水中的VFAs仅可检测到乙酸,其浓度的变化如图3所示。由图3可知,运行期间乙酸的平均浓度低于10 mg·L−1。在前33 d内,出水中的乙酸浓度维持在4 mg·L−1以下,未出现积累。这是因为反应器内的产甲烷菌的活性较高,能有效地将乙酸转化成甲烷[19]。在33~39 d内,当温度下降至25 °C时,乙酸浓度从4 mg·L−1逐渐升高至24 mg·L−1。这表明在该温度下,产甲烷菌的活性受到了抑制,影响了乙酸的消耗和甲烷的稳定产出[20]。随着反应器温度的回升,出水中的乙酸浓度又在较短的时间内降低至原先水平,这说明产甲烷菌活性也随着温度的升高而恢复。这一结果和COD去除率的变化趋势相似,表明了该系统对温度波动具有较强的适应能力。
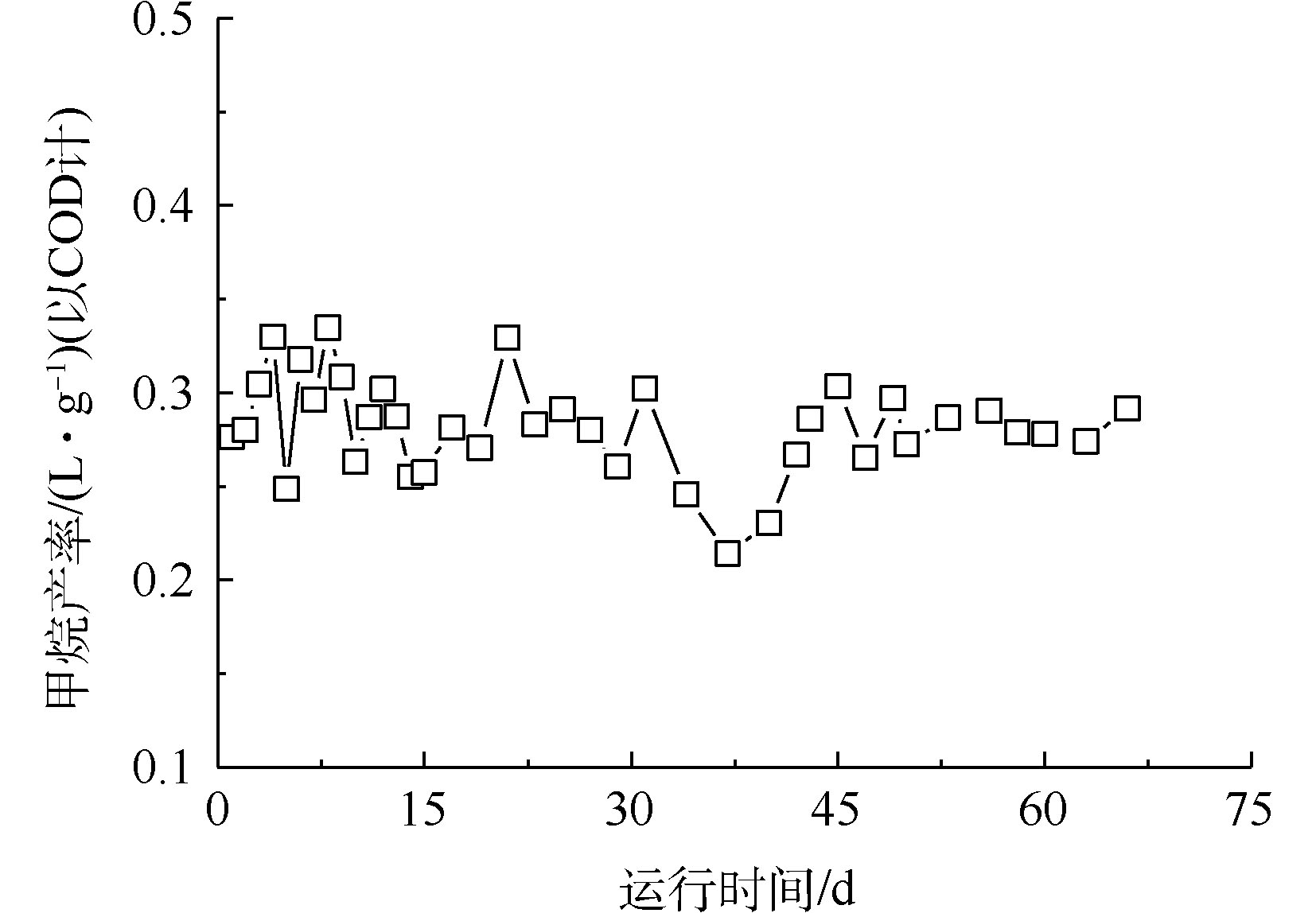
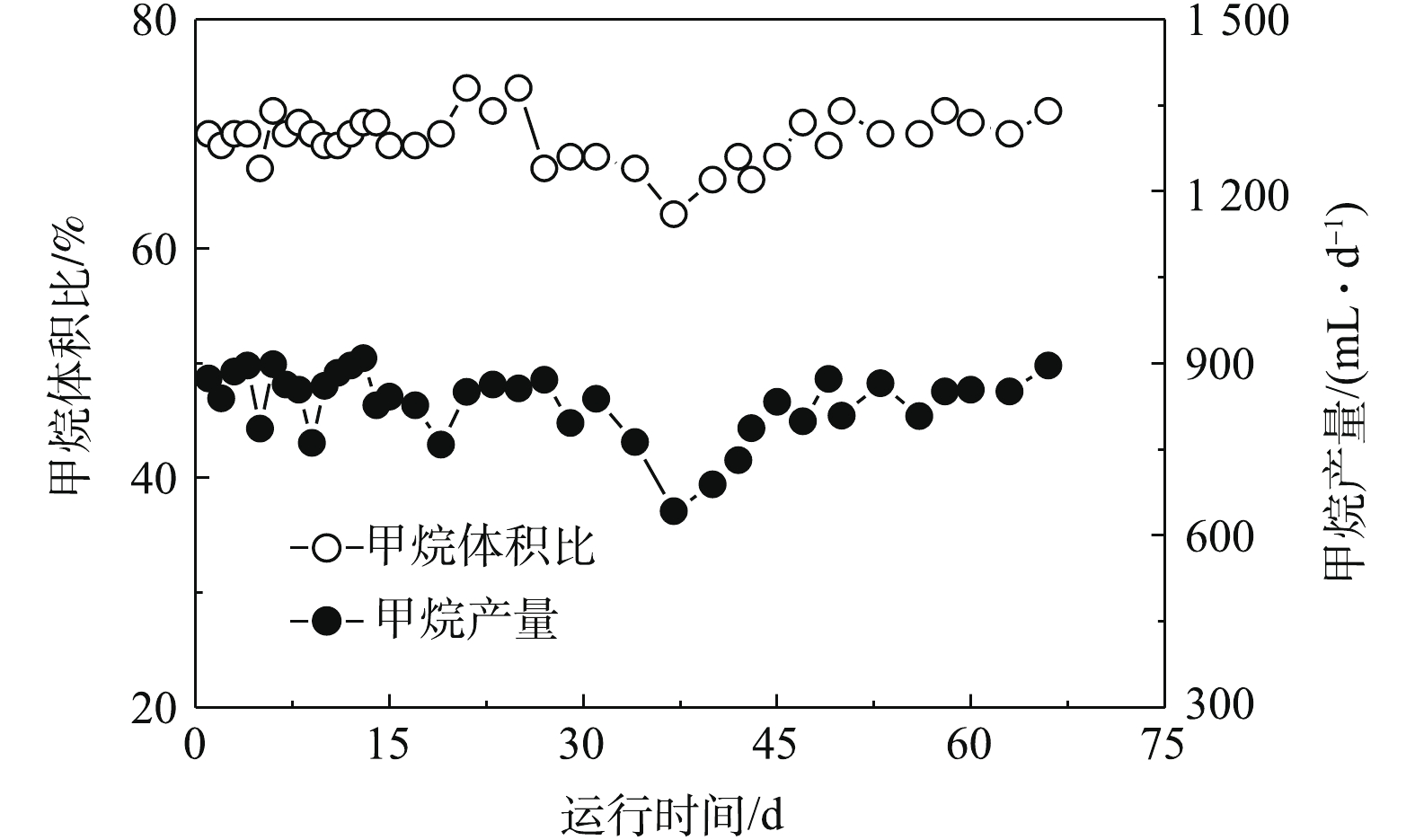
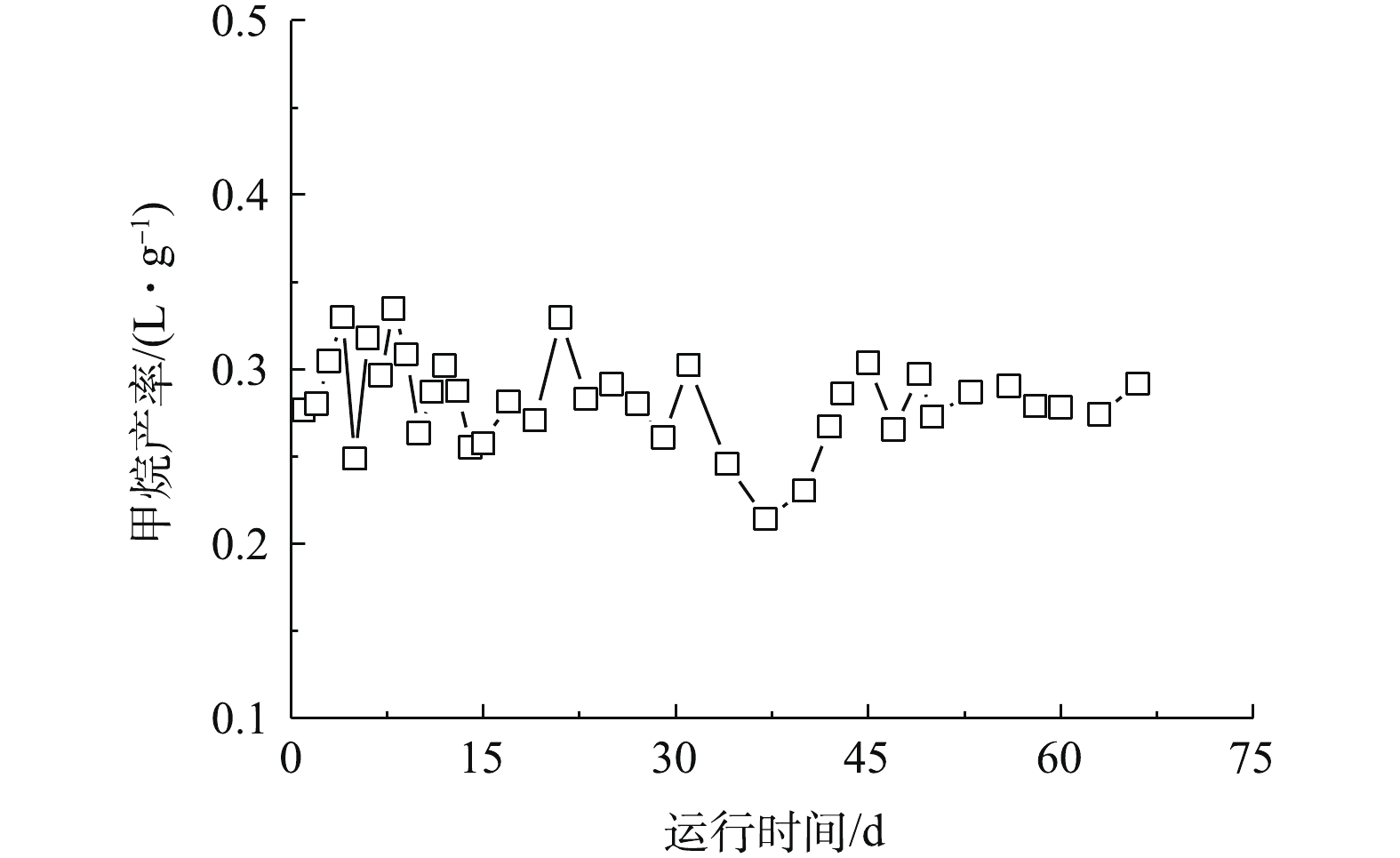
3)反应器运行过程中甲烷产量及产率的变化。在厌氧处理过程中,大部分的COD被转化成沼气,而甲烷作为沼气的主要成分,其产量就成为衡量AnMBR运行效果的一个重要指标[21]。本反应器运行期间甲烷体积比和甲烷产量的变化如图4所示。在前33 d运行过程中,反应器展现了良好的产甲烷性能,甲烷所占体积比一直稳定在70%左右,甲烷的平均产量为830 mL·d−1;在33~39 d温度降低后,甲烷产量明显降低(温度降低,对产甲烷菌的活性起到了一定的抑制作用[22]),但随着温度的回升,甲烷产量又逐渐升高并趋向于稳定,这一结果和COD的去除结果相一致。图5显示的是运行期间甲烷产率的变化,反应器甲烷的平均产率为0.28 L·g−1 (以COD)计。
-
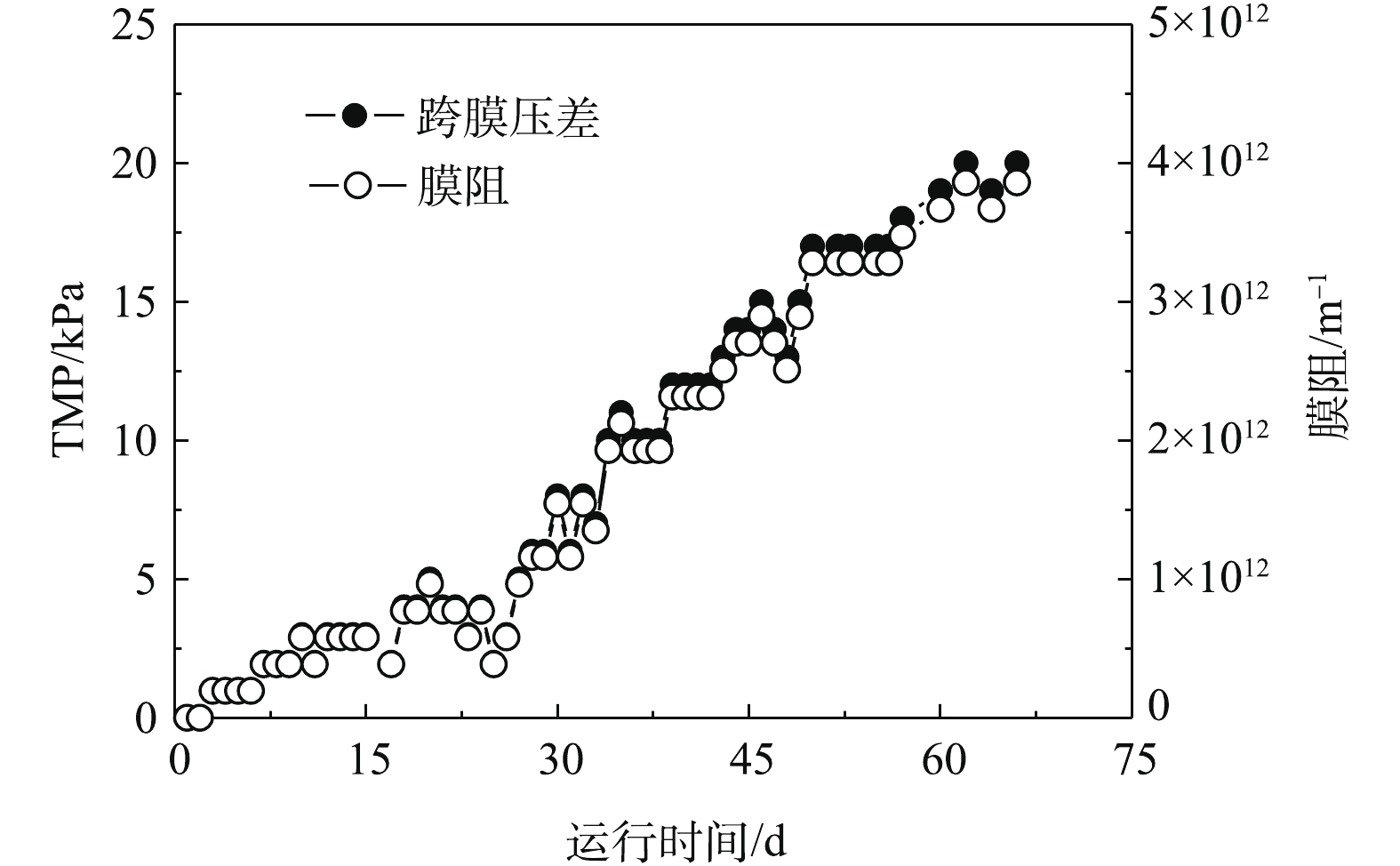
1)膜污染程度表征。膜通量衰减和TMP的升高是反映膜污染程度的重要指标[23]。在整个运行期间,没有进行膜清洗操作,AnMBR中TMP和膜阻的变化如图6所示。由图6可知,TMP呈缓慢增长的趋势。在66 d的运行期间内,TMP和膜阻分别上升至20 kPa和4×1012 m−1。相关研究[24]表明,在以陶瓷膜或中空纤维超滤膜为膜组件构建的AnMBR处理低浓度废水的过程中,仅运行15 d,TMP分别可增长至27 kPa和20 kPa。相比而言,本研究在生物膜填料和不锈钢丝网膜组件的共同作用下,能够显著地减缓TMP增长。通过对膜阻增长速率的计算发现,本反应器在温度为35 ℃ (0~33 d)时,膜阻增长速率为1.7×109 m−1·h−1,在温度降低阶段(33~39 d),膜阻增长速率提高至5.7×109 m−1·h−1,而当温度回升时,膜阻增长速率又下降至2.3×109 m−1·h−1。因此,温度的波动会加剧膜污染。
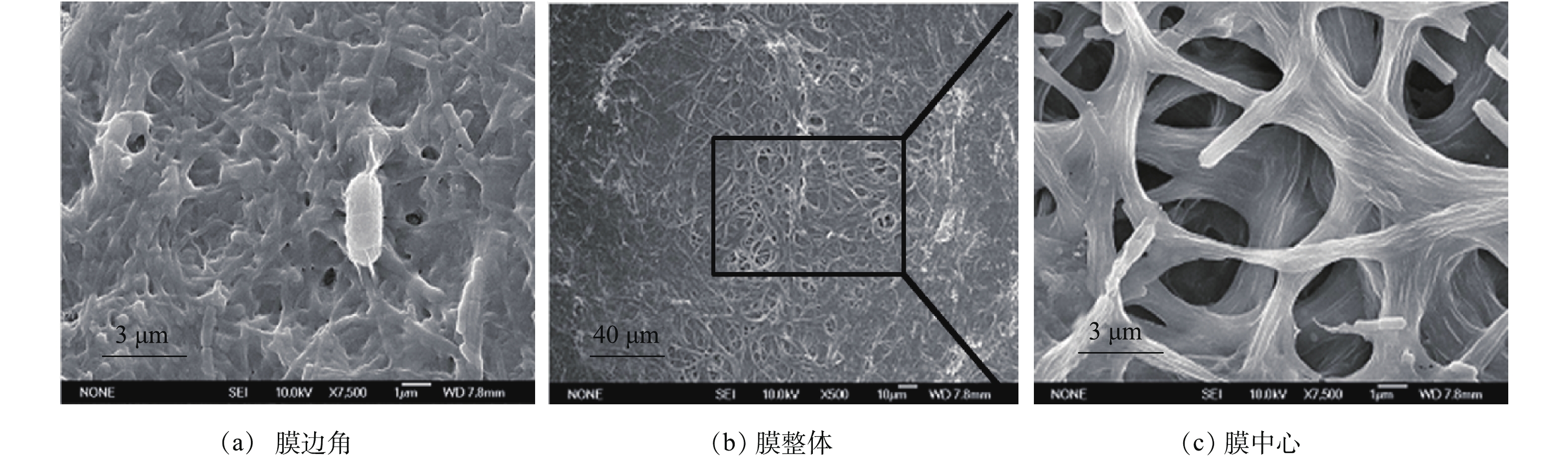
2) SEM表征结果。为了观察钢丝网膜组件生物膜上膜污染分布情况,在反应器运行66 d后,将钢丝网膜组件从反应器中取出,截取膜边角和膜中心部分,通过SEM对膜污染进行表征(图7)。结果发现,当运行周期结束后,不锈钢丝网膜表面形成了一层泥饼层(图7 (a)和图7 (b)),但对比膜中心和膜边角位置的污染情况,膜中心的污染层含有一定的孔状结构,这对于保持膜的高出水通量,减缓系统的膜污染起到了促进作用[25]。
-
1) 以廉价不锈钢丝网为膜组件构建AnMBR并将其用于处理低浓度废水,在整个实验过程中,HRT维持在10 h,温度为35 ℃和25 ℃,其COD去除率均能保持在93%以上。
2) 系统的产气率较高,甲烷体积比稳定在70%左右,甲烷平均产率为0.28 L·g−1 (以COD计)。
3) 不锈钢丝网的添加缓解了反应器的膜污染,整个运行期间(66 d),TMP增长为0~20 kPa,膜阻最高为4×1012 m−1。
厌氧膜生物反应器处理低浓度废水的运行效能及膜污染特性
Performance and membrane fouling properties of anaerobic biofilm membrane bioreactor for low-concentration wastewater treatment
-
摘要: 针对厌氧膜生物反应器(AnMBR)成本高、膜污染严重的问题,构建了以不锈钢丝网作为膜材料的新型厌氧膜生物器并将其用于处理低浓度废水,探究了其稳定运行以及耐温度波动的能力。同时,对甲烷产量、跨膜压差(TMP)以及反应器出水中的COD和挥发性有机酸(VFAs)进行了监测和分析,并利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对膜污染进行了表征。结果表明:反应器的COD去除率稳定在93%以上;出水中的VFAs仅可检测到乙酸,且平均浓度低于10 mg·L−1;甲烷平均产率为0.28 L·g−1 (以COD计);当温度由35 ℃降到25 ℃时,反应器有较强的耐受能力;在66 d的运行期间内,TMP从0 kPa增长到20 kPa,膜阻最高为4×1012 m−1。以不锈钢丝网为膜材料构成的新型AnMBR,出水效果良好、产能高、运行稳定。Abstract: To deal with the high cost and serious membrane fouling of anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR), a novel AnMBR with stainless steel wire mesh as membrane material was constructed to treat the low-concentration municipal wastewater. Its operation stability and resistance to temperature shock were investigated. During the period of AnMBR running, methane production, transmembrane pressure (TMP), effluent COD and effluent volatile fatty acids (VFAs) were monitored and analyzed. The membrane fouling was also characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Results show that the COD removal efficiency was above 93%. Only acetate could be detected in the effluent with average concentration less than 10 mg·L−1. The average methane yield was as high as 0.28 L·g−1 (calculated based on COD). When the temperature was reduced from 35 ℃ to 25 ℃, the AnMBR had a strong tolerance. In addition, during 66 d operation, the TMP slowly increased from 0 kPa to 20 kPa and the highest membrane resistance was 4×1012 m−1. The novel AnMBR with stainless steel wire mesh as membrane material achieved good effluent quality, high energy productivity and operation stability.
-
目前,低浓度废水的处理工艺主要有A2O、氧化沟、SBR等,其技术核心为活性污泥法[1]。传统活性污泥法普遍存在着能耗高、污泥产量大的问题。相比而言,厌氧生物处理技术因其能耗低、污泥产量少且能产生甲烷而受到了越来越多的关注,但厌氧生物处理技术存在污泥流失和处理效果不佳的问题,故需进一步改进[2-3]。
厌氧膜生物反应器(anaerobic membrane bioreactor,AnMBR)是一种将膜分离技术与厌氧生物处理技术有效结合的新型废水处理工艺[4]。该工艺能通过膜的过滤截留作用,实现水力停留时间(HRT)和污泥龄(SRT)的完全分离[5]。荆延龙等[6]采用AnMBR处理低浓度生活废水,结果表明,经过117 d的稳定运行,COD去除率高达90.6%;许美兰等[7]研究了不同HRT对AnMBR处理低浓度废水运行效果的影响,经过35 d的稳定运行,发现HRT的缩短未对COD的去除产生显著差异。这说明AnMBR在处理低浓度废水方面稳定性良好,拥有广阔的发展前景[8]。但一直以来,膜成本和膜污染是困扰该技术走向实际工程应用的限制性条件[9]。而动态膜技术的出现,有望解决MBR中存在的膜成本过高及膜污染严重的问题[10]。程刚等[11]利用不锈钢丝网为基材构建AnMBR处理低浓度生活废水,结果表明,选用300目的不锈钢丝网,在污泥浓度(MLSS)为2 mg·L−1的条件下,可稳定运行240 h。赵立健等[12]在常温下利用无纺布为基材构建AnMBR处理人工合成低浓废水,结果表明,COD平均去除率为89.5%。尽管现有的研究已证实AnMBR对低浓度废水有较好的处理效果,但对其运行过程中膜污染的评估研究较少。
本研究利用廉价不锈钢丝网作为膜材料,构建新型AnMBR,在HRT为10 h的条件下,考察了反应器运行效果、产甲烷能力、膜污染程度以及对温度的适应性,旨在为AnMBR在实际低浓度废水中的应用提供技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置
实验采用升流式厌氧反应器,实验装置如图1所示,其总容积为3 L,有效容积为2.4 L。反应器底部装有生物膜填料,中上部装有1 000目不锈钢丝网制成的膜组件,膜组件的尺寸为13 cm×8 cm×3.5 cm,总过滤面积为0.011 m2。反应器外层装有一层保温层和循环水管,使反应器内的水温控制在35 ℃。
1.2 实验用水及接种污泥
本实验所采用的低浓度废水为人工合成废水,含有主要元素和微量元素[13-14]。其成分包括蔗糖(C12H22O11 500 mg·L−1)、碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3 350 mg·L−1)、三水合磷酸氢二钾(K2HPO4·3H2O 21 mg·L−1)、碳酸氢铵(NH4HCO3 41 mg·L−1)、氯化钙(CaCl2 50 mg·L−1)、四水合氯化锰(MnCl2·4H2O 5 mg·L−1)、六水合氯化钴(CoCl2·6H2O 5 mg·L−1)、六水合氯化铝(AlCl3·6H2O 5 mg·L−1)、硼酸(H3BO3 5 mg·L−1)、四水合钼酸铵((NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O 5 mg·L−1)、六水合氯化镍(NiCl2·6H2O 5 mg·L−1)、氯化锌(ZnCl2 5 mg·L−1)、五水合硫酸铜(CuSO4·5H2O 5 mg·L−1)。反应器接种的污泥取自合肥市某污水处理厂,接种时的污泥浓度(MLSS)为4 g·L−1,实验期间没有剩余污泥排出。
1.3 实验方法
实验采用连续进出水的方式,总共连续运行66 d,反应器进水速度为240 mL·h−1,整个运行期间HRT控制在10 h。在33~39 d,由于加热系统出现故障导致温度降低到25 ℃,维持7 d,后恢复至35 ℃。低浓度废水在蠕动泵的作用下经反应器底部进入反应器内,并利用蠕动泵从膜组件抽取出水。实验内容分为2个阶段:第1阶段是反应器启动运行阶段(0~15 d);第2阶段是反应器稳定运行阶段(16~66 d)。
1.4 分析方法
出水溶解性COD采用重铬酸钾法[15]测定;VFAs和气体采用气相色谱法测定;跨膜压差(TMP)采用压力传感器(MIK-P300,杭州米科传感技术有限公司)测定;膜面污染物采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)(XL-30 ESEM,美国FEI)分析;膜阻及膜阻增长速率[16-17]分别根据式(1)和式(2)进行计算。
R=ΔPμJ×3600 (1) Ri=ΔP24μJT×3600 (2) 式中:R为膜阻,m−1;ΔP为跨膜压差,Pa;μ为渗滤液动力黏度系数,Pa·s;Ri为膜阻增长速率,m·h−1;J为瞬时膜通量,m3·(m2·h)−1;T为运行时间,d。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 AnMBR运行特征
2.1.1 反应器运行过程COD去除效果
在HRT为10 h、进水COD在500 mg·L−1的条件下,AnMBR共运行66 d,进出水COD及去除率的变化如图2所示。在0~33 d内,COD的平均去除率为95%,出水COD始终低于30 mg·L−1;从第33天开始,反应器运行温度由35 ℃变为25 ℃,经过7 d的运行后,COD的去除率仍维持在93%以上。从第40天开始,温度恢复至35 ℃后,COD的去除率又维持在95%。这说明本系统在HRT为10 h的条件下,获得了稳定的运行效果,且对温度波动有较强的适应能力,能始终保持较高的COD去除率,保证出水COD的达标排放。
2.1.2 反应器运行过程VFA累积情况
VFAs浓度是判断产酸菌和产甲烷菌活性的重要指标[18]。在整个实验阶段,出水中的VFAs仅可检测到乙酸,其浓度的变化如图3所示。由图3可知,运行期间乙酸的平均浓度低于10 mg·L−1。在前33 d内,出水中的乙酸浓度维持在4 mg·L−1以下,未出现积累。这是因为反应器内的产甲烷菌的活性较高,能有效地将乙酸转化成甲烷[19]。在33~39 d内,当温度下降至25 °C时,乙酸浓度从4 mg·L−1逐渐升高至24 mg·L−1。这表明在该温度下,产甲烷菌的活性受到了抑制,影响了乙酸的消耗和甲烷的稳定产出[20]。随着反应器温度的回升,出水中的乙酸浓度又在较短的时间内降低至原先水平,这说明产甲烷菌活性也随着温度的升高而恢复。这一结果和COD去除率的变化趋势相似,表明了该系统对温度波动具有较强的适应能力。
2.1.3 反应器运行过程中甲烷产量及产率的变化
在厌氧处理过程中,大部分的COD被转化成沼气,而甲烷作为沼气的主要成分,其产量就成为衡量AnMBR运行效果的一个重要指标[21]。本反应器运行期间甲烷体积比和甲烷产量的变化如图4所示。在前33 d运行过程中,反应器展现了良好的产甲烷性能,甲烷所占体积比一直稳定在70%左右,甲烷的平均产量为830 mL·d−1;在33~39 d温度降低后,甲烷产量明显降低(温度降低,对产甲烷菌的活性起到了一定的抑制作用[22]),但随着温度的回升,甲烷产量又逐渐升高并趋向于稳定,这一结果和COD的去除结果相一致。图5显示的是运行期间甲烷产率的变化,反应器甲烷的平均产率为0.28 L·g−1 (以COD)计。
2.2 AnMBR膜污染特性
膜污染程度和SEM表征结果见图6和图7。
2.2.1 膜污染程度表征
膜通量衰减和TMP的升高是反映膜污染程度的重要指标[23]。在整个运行期间,没有进行膜清洗操作,AnMBR中TMP和膜阻的变化如图6所示。由图6可知,TMP呈缓慢增长的趋势。在66 d的运行期间内,TMP和膜阻分别上升至20 kPa和4×1012 m−1。相关研究[24]表明,在以陶瓷膜或中空纤维超滤膜为膜组件构建的AnMBR处理低浓度废水的过程中,仅运行15 d,TMP分别可增长至27 kPa和20 kPa。相比而言,本研究在生物膜填料和不锈钢丝网膜组件的共同作用下,能够显著地减缓TMP增长。通过对膜阻增长速率的计算发现,本反应器在温度为35 ℃ (0~33 d)时,膜阻增长速率为1.7×109 m−1·h−1,在温度降低阶段(33~39 d),膜阻增长速率提高至5.7×109 m−1·h−1,而当温度回升时,膜阻增长速率又下降至2.3×109 (m·h)−1。因此,温度的波动会加剧膜污染的程度。
2.2.2 SEM表征结果
为了观察钢丝网膜组件生物膜上膜污染分布情况,在反应器运行66 d后,将钢丝网膜组件从反应器中取出,截取膜边角和膜中心部分,通过SEM对膜污染进行表征(图7)。结果发现,当运行周期结束后,不锈钢丝网膜表面形成了一层泥饼层(图7 (a)和图7 (b)),但对比膜中心和膜边角位置的污染情况,膜中心的污染层含有一定的孔状结构,这对于保持膜的高出水通量,减缓系统的膜污染起到了促进作用[25]。
3. 结论
1) 以廉价不锈钢丝网为膜组件构建AnMBR并将其用于处理低浓度废水,在整个实验过程中,HRT维持在10 h,温度为35 ℃和25 ℃,其COD去除率均能保持在93%以上。
2) 系统的产气率较高,甲烷体积比稳定在70%左右,甲烷平均产率为0.28 L·g−1 (以COD计)。
3) 不锈钢丝网的添加缓解了反应器的膜污染,整个运行期间(66 d),TMP增长范围为0~20 kPa,膜阻最高为4×1012 m−1。
-
-
[1] 欧阳勇, 罗建中, 陈宝才, 等. 低浓度废水处理的研究进展[J]. 轻工科技, 2009, 25(1): 85-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2673.2009.01.044 [2] 杨积德, 陈晓娟. 厌氧工艺在低浓度废水处理中的应用[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2012, 32(3): 51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2012.03.021 [3] 许颖, 夏俊林, 黄霞. 厌氧膜生物反应器污水处理技术的研究现状与发展前景[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2016, 36(4): 139-149. [4] 林红军, 陆晓峰, 梁国明, 等. 厌氧膜生物反应器的研究和应用进展[J]. 净水技术, 2007, 26(6): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0177.2007.06.001 [5] HO J, SUNG S. Methanogenic activities in anaerobic membrane bioreactors (AnMBR) treating synthetic municipal wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 101(7): 2191-2196. [6] 荆延龙, 李菲菲, 朱佳迪, 等. 室温下厌氧膜生物反应器处理生活污水的运行特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(10): 5393-5399. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201612202 [7] 许美兰, 李元高, 叶茜, 等. 常温下厌氧膜生物反应器处理生活污水研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(13): 23-26. [8] VISVANATHAN C, ABEYNAYAKA A. Developments and future potentials of anaerobic membrane bioreactors (AnMBRs)[J]. Membrane Water Treatment, 2012, 3(1): 1-23. doi: 10.12989/mwt.2012.3.1.001 [9] 何丽玲, 陈辉, 刘安娜, 等. 厌氧膜生物反应器在污水处理中的应用[J]. 杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 15(6): 606-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-232X.2016.06.009 [10] 赵立健. 厌氧自生动态膜生物反应器处理低浓度废水的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2010. [11] 程刚, 朱雷, 许颖, 等. 厌氧动态膜生物反应器中动态膜形成及其运行周期的影响因素分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(5): 1408-1415. [12] 赵立健, 赵婷婷, 王曙光. 厌氧自生动态膜生物反应器处理生活污水的研究[J]. 山东大学学报(理学版), 2010, 45(3): 10-14. [13] LI L L, TONG Z H, FANG C Y, et al. Response of anaerobic granular sludge to single-wall carbon nanotube exposure[J]. Water Research, 2015, 70: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.11.042 [14] LI N, HU Y, LU Y Z, et al. In-situ biogas sparging enhances the performance of an anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) with mesh filter in low-strength wastewater treatment[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(13): 6081-6089. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7455-2 [15] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [16] LEE J, AHN W Y, LEE C H. Comparison of the filtration characteristics between attached and suspended growth microorganisms in submerged membrane bioreactor[J]. Water Research, 2001, 35(10): 2435-2445. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00524-8 [17] LI N, HE L, LU Y Z, et al. Robust performance of a novel anaerobic biofilm membrane bioreactor with mesh filter and carbon fiber (ABMBR) for low to high strength wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 313: 56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.073 [18] WIJEKOON K C, VISVANATHAN C, ABEYNAYAKA A. Effect of organic loading rate on VFA production, organic matter removal and microbial activity of a two-stage thermophilic anaerobic membrane bioreactor[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(9): 5353-5360. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.081 [19] 张玉鹏, 李建政, 刘凤琴, 等. 碳酸氢盐对嗜氢和嗜乙酸产甲烷菌的影响机制[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(5): 1937-1944. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.042 [20] 金仁村, 郑平, 黄可谈, 等. 环境和水质条件冲击下厌氧生物反应器的稳定性研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2006(5): 13-17. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4320.2006.05.003 [21] 闫林涛, 黄振兴, 肖小兰, 等. 厌氧膜生物反应器处理高浓度有机废水的中试研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2015, 34(12): 1248-1255. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2015.12.003 [22] 张立国, 班巧英, 李建政. UASB反应器中产甲烷菌对温度胁迫的响应[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(4): 1082-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.04.018 [23] 郑云丽, 李慧强, 刘璐. 厌氧膜生物反应器膜污染影响因素及控制技术研究进展[J]. 环境科技, 2015, 28(4): 71-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2015.04.016 [24] 刘莉莉, 高大文, 张明慧. 分置式厌氧陶瓷膜生物反应器处理模拟生活污水试验研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(11): 4259-4265. [25] 王敬斌. 浸没式双轴旋转厌氧膜生物反应器处理啤酒废水的研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2008. 期刊类型引用(9)
1. 邵文歆,刘杰,伏小勇,郭一令. HRT对EGSB反应器处理低浓度有机废水的影响. 青岛理工大学学报. 2023(03): 9-14+41 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张靖雨,汪邦稳,龙昶宇,张卫,张世杰,赵黎明. 不同处理措施对农村生活污水净化效果研究. 安徽农业科学. 2022(02): 211-216 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 田帅,朱易春,黄书昌,连军锋,秦欣欣,任黎晔,李鑫. 厌氧生物处理低浓度污水研究进展. 化工进展. 2021(04): 2338-2346 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张蕾. 膜生物反应器在高浓度有机废水处理中的应用. 中国资源综合利用. 2021(06): 199-201 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 覃宁波. 膜生物反应器污水处理技术的研究进展. 大众科技. 2021(06): 13-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 邹小玲,余江涛,张本凯. 厌氧生物法处理高盐废水研究进展. 现代化工. 2020(03): 44-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 淡玄玄,陈占江,杨海霞,张朝鹏,原晓丽. 高含盐废水处理技术研究现状及应用. 氯碱工业. 2020(06): 1-5 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 赵以国,张靖雨,汪邦稳,龙昶宇,张卫,张世杰,赵黎明. 农村生活污水生态综合治理技术现状与研究进展. 环境科技. 2020(04): 74-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 宋建超,尚斌,陶秀萍,董红敏,王俊,郭江鹏. 絮凝预处理对奶牛场膜生物反应器膜污染影响的中试试验. 农业工程学报. 2020(20): 34-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(16)
-







 下载:
下载: