-
燃煤电厂已全面实施烟气的超低排放,且取得了显著的环保效益[1]。钢铁行业执行2012年环境保护部颁布的《钢铁烧结、球团工业大气污染物排放标准》(GB 28662-2012)。2013年2月27日,环境保护部印发《关于执行大气污染物特别排放限值的公告》,规定烧结机球团焙烧设备、烧结机机尾带式焙烧机机尾其他生产设备的烟尘特别排放限值分别为40、20 mg·m−3。2017年6月,环境保护部发布的GB 28662-2012修改单(征求意见稿)中提出,根据重点地区环境空气质量管理需求,应进一步深化钢铁烧结、球团工业烟气治理,加严特别排放限值要求[2],将烟尘特别排放限值再提升至20 mg·m−3。目前,部分地区的工业锅炉、钢铁、水泥等行业也陆续效仿燃煤电厂,实施烟气超低排放政策,即规定烟尘限值为10 mg·m−3。目前,烧结机头除尘部分均安装电除尘器,机尾除尘部分也基本安装除尘设备,早期大多数以电除尘器为主,现逐步改为袋式除尘器[3-6]。
随着对电除尘性能要求的提高,气流分布对电除尘器的重要程度越来越显著,尤其是在有限增容的前提下,充分利用气流分布技术进行提效,已成为实现烧结烟气超低排放改造的关键之一。宋孝红等[7]用计算流体力学商用软件CFX模拟了某190 m2烧结机“电改袋”流场分布;孟思明[8]研究了烧结粉尘特性,并采用CFD方法对实验用电除尘器的流场特性进行了计算分析,设计了合理的气流分布方案;王锦[9]针对某265 m2烧结机烟气除尘器,利用ICEM-CFD软件进行了网格划分,采用FLUENT进行了模拟计算,研究了“电改袋”流场分布特性;常玉锋[10]采用数值模拟方法研究了横向双极静电除尘器极配参数对伏安特性和流场分布的影响规律,并成功应用于烧结机头烟尘净化系统的提效改造,但数值模拟结果未进行现场实测验证;王宏波[11]采用FLUENT软件,对上海某烧结机头电除尘器流场进行了模拟分析,为工程设计提供参考,但未涉及颗粒相的分配情况及电场计算。本研究基于商业CFD软件,对某600 m2烧结机头电除尘器流场及烟尘分配情况进行模拟计算,基于电场及颗粒相分析模拟计算了电除尘器的除尘效率,为电除尘器的设计提供参考,并在后续的性能测试中得到了有效验证。
全文HTML
-
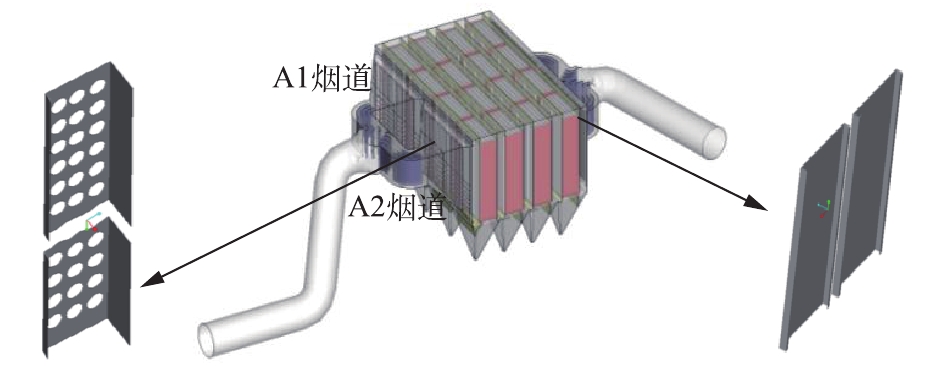
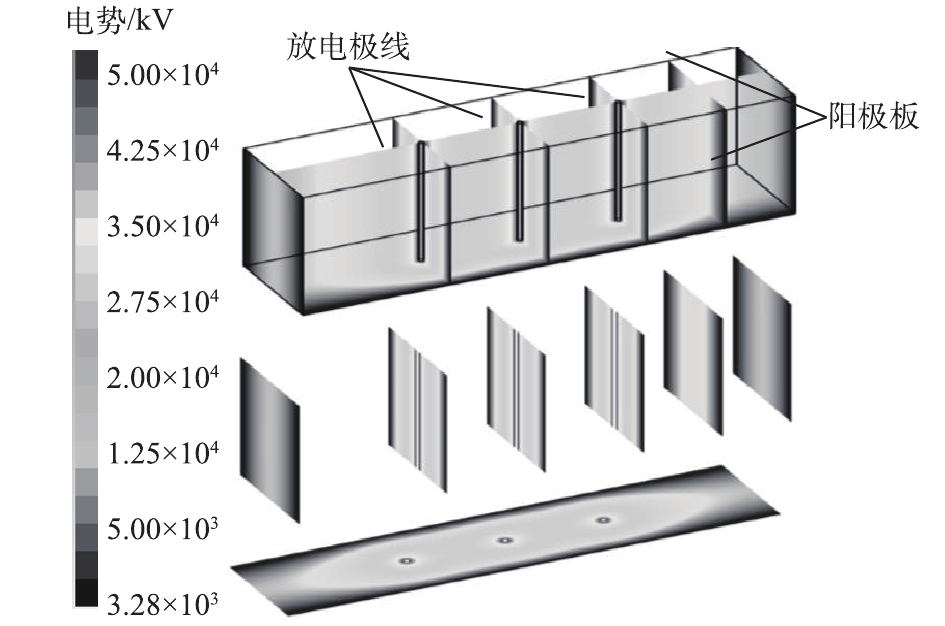
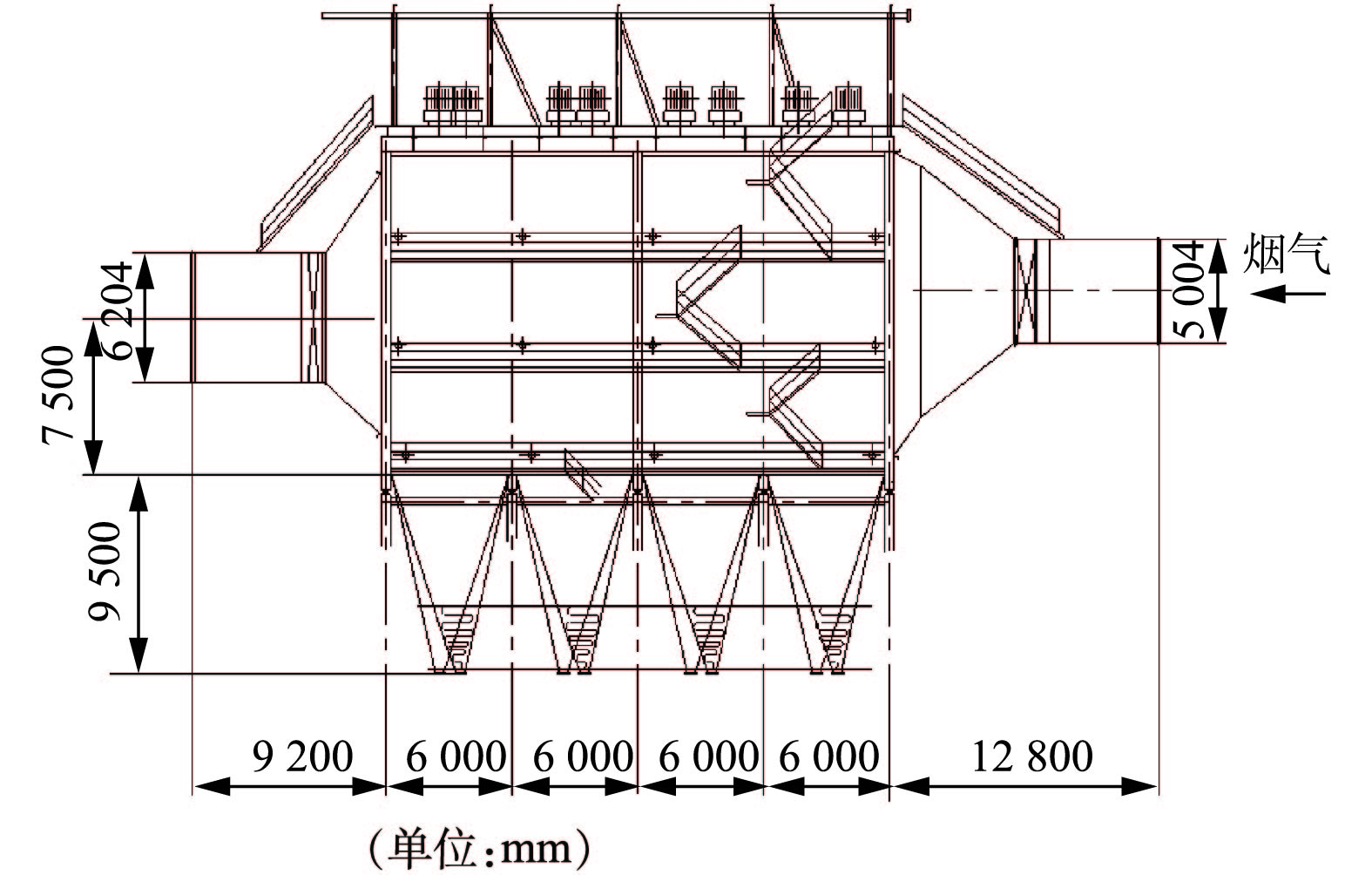
600 m2烧结机头电除尘器基本结构如图1所示,为2室4电场电除尘器,处理烟气量约3.6×106 m3·h−1,电除尘器内设计烟气流速为0.8 m·s−1,有效比集尘面积约110 m2·(m3·s)−1,同极间距为450 mm,阳极板为480C型,前3个电场阴极线为RS芒刺线,第4电场采用螺旋线,振打方式为侧部振打,电源规格为0.2 A/72 kV,入口烟尘浓度为3 g·m−3,入口烟气温度为120 ℃,设计出口烟尘浓度≤30 mg·m−3。
-
商业CFD软件内自带了一些基于基本假设的经典计算模型,如假设流体为定常(软件中的一种计算方式,即不随时间变化,算的是一个平均值)运动的不可压缩流体,且在整个流动过程中不发生温度变化,机头电除尘器前烟道进口处烟气流速为恒定值,且截面上分布均匀,烟尘颗粒假设为实心球体。连续相流场计算采用k-ε模型,静电场计算采用电磁流体模型(MHD),颗粒相计算采用离散相模型(DPM)。连续方程、动量方程、湍动能k方程、耗散率ε方程及电磁感应方程的计算[12-13]如式(1)和表1所示,颗粒相运动轨迹方程[14-15]如式(2)所示。
式中:Fs为Saffman力;Fd为连续相的黏性阻力;Fg为颗粒自身重力。
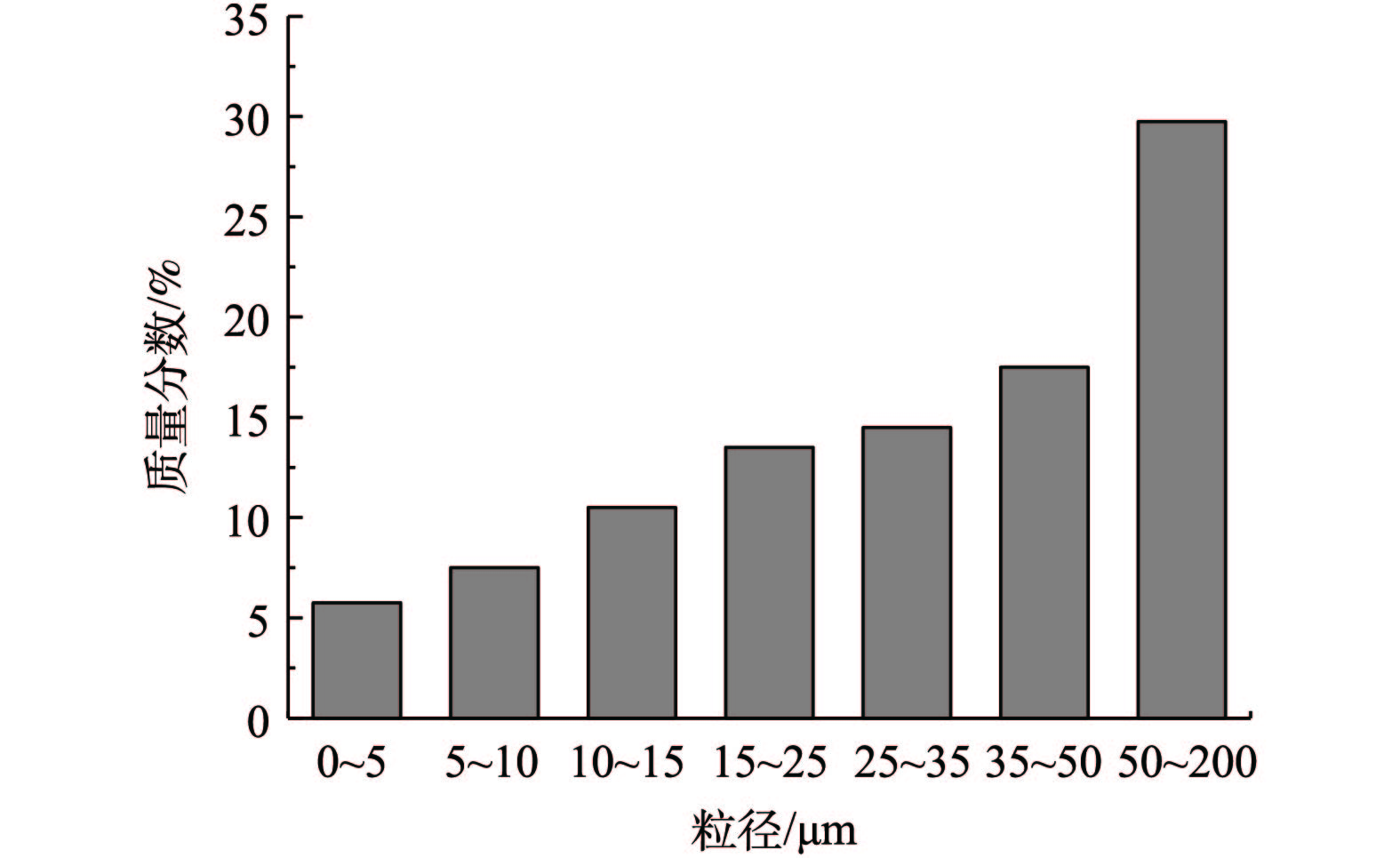
模型计算的主要边界条件如表2所示,现场采用滤筒采集飞灰样品,并用激光粒度分析仪(LT3600 Plus)对样品进行分析,得到烟尘颗粒的粒径初始分布如图3所示。
-
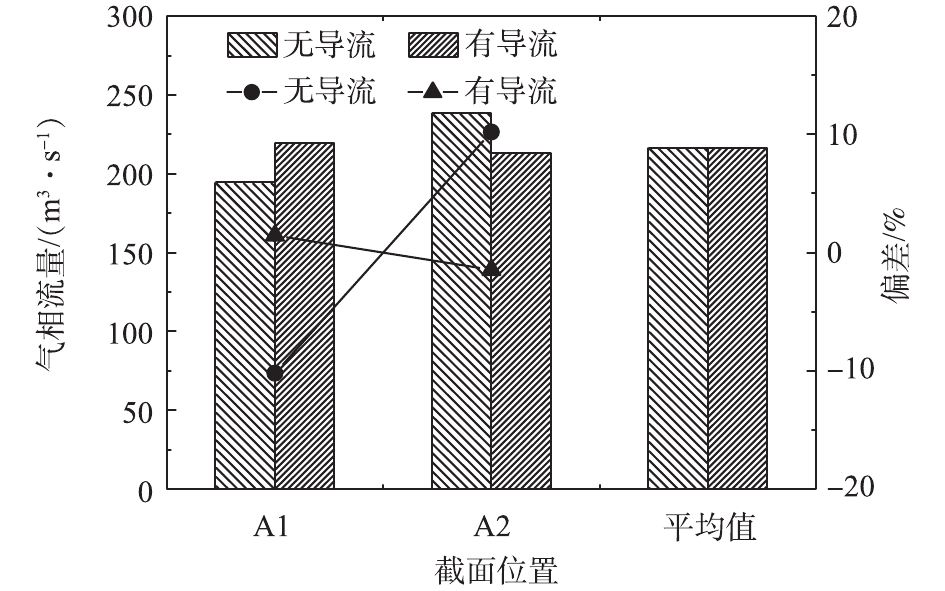
1) 烟气流量及偏差。电除尘器各室进口的烟气流量是否均匀直接影响各室的除尘效率及除尘器的稳定运行。一旦流量分配不均,高流速通道的除尘效率将大打折扣,极容易造成电除尘器排放超标,且前端的部件磨损加剧;低流速通道的前端烟道如存在弯头等回流区,则会增加积灰风险,影响设备的安全稳定运行。
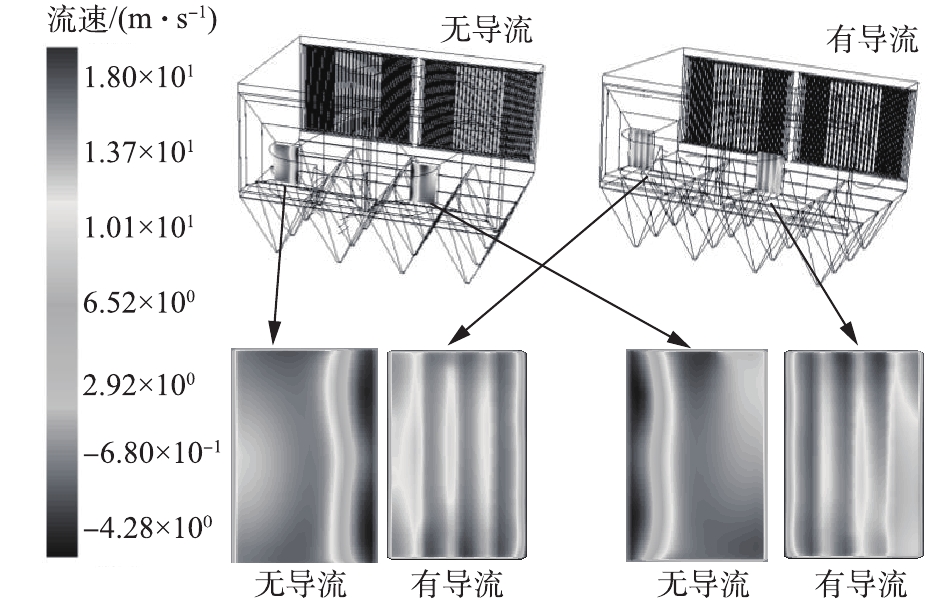
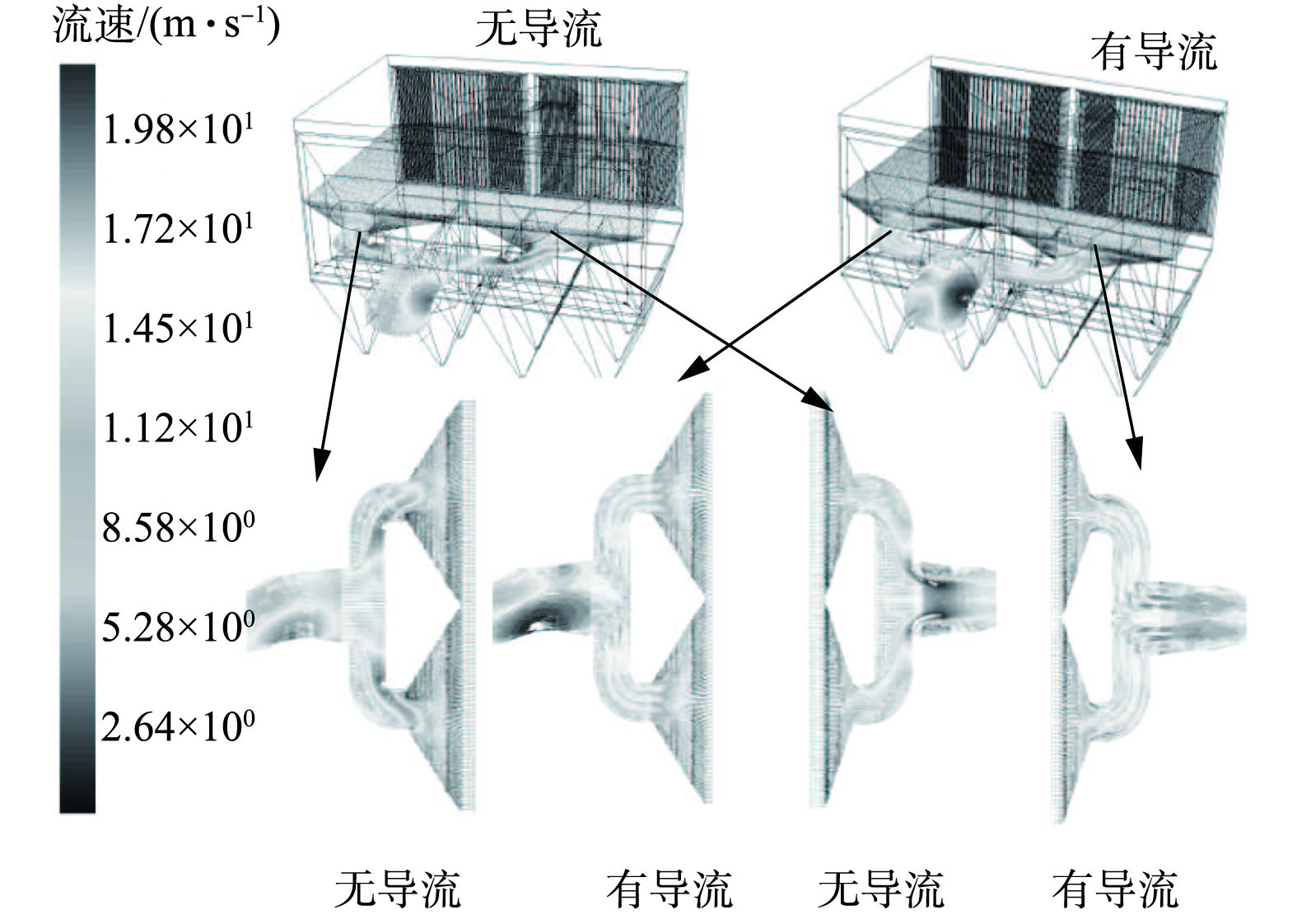
电除尘器进、出口烟道内导流板布置前、后,电除尘器进口截面的速度分布云图计算结果如图4所示,电除尘器进、出口烟道截面的速度分布云图计算结果如图5所示。在未布置导流板之前,电除尘器两侧烟道的进口截面的速度分布很不均匀,在烟道内侧流速高,烟道外侧流速低,这不但会影响电除尘器的收尘性能,还会加剧烟道的局部磨损、积灰风险,布置导流板后,该现象得到明显改善。
定量计算各截面的流量分布及其偏差,如图6所示。无导流板时,电除尘器两侧烟道的进口烟气流量分别为194.5 m3·s−1和238.6 m3·s−1,各烟道的烟气流量偏差分别为−10.2%和+10.2%,不能满足JB/T 7671-2017规定的±5%的标准要求;有导流板时,电除尘器两侧烟道的进口烟气流量分别为219.8 m3·s−1和213.4 m3·s−1,各烟道的烟气流量偏差分别为+1.5%和−1.5%,流量偏差得到显著改善。
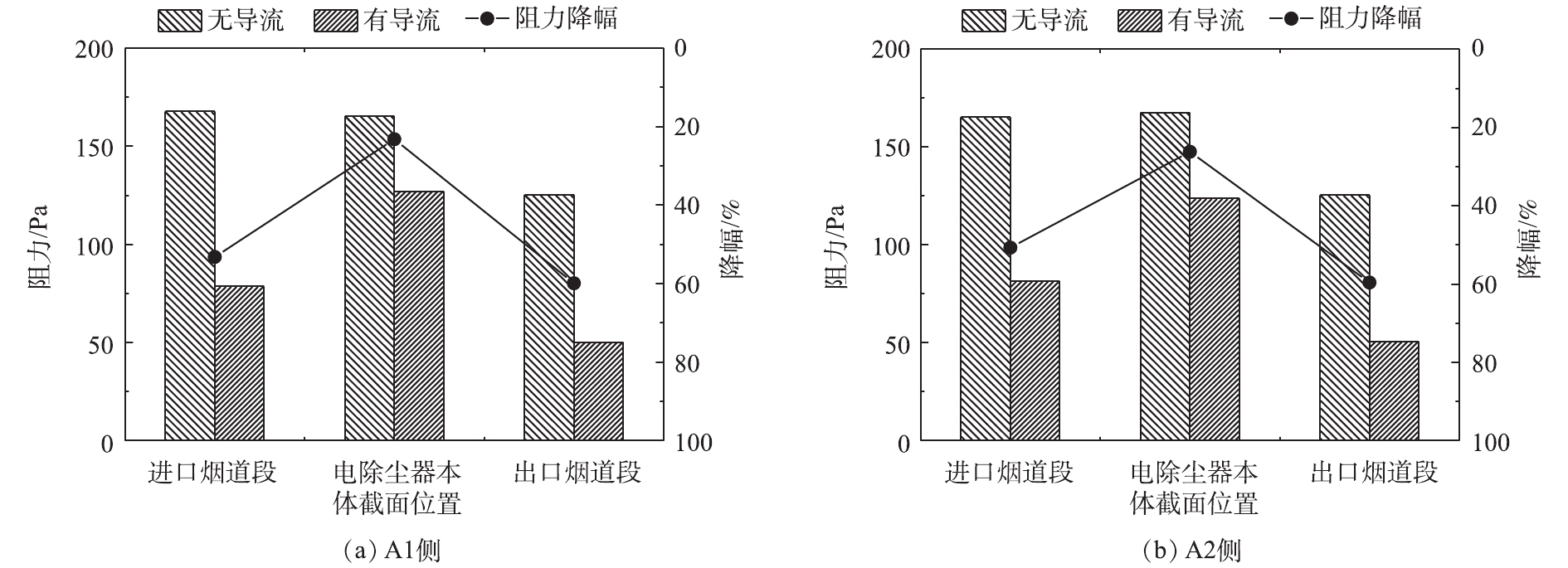
2) 阻力。设备阻力是电除尘器的重要性能参数,影响风机电耗及电除尘器的运行费用。布置导流板后,电除尘器进口烟道的烟气流量偏差得到了有效控制,进口烟道段、电除尘器本体、出口烟道段的阻力也得到了有效控制,导流板布置前后各段的阻力计算结果及阻力降幅如图7所示。导流板布置前,A1侧进口烟道段、电除尘器本体、出口烟道段的阻力分别为167.8、165.4、125.3 Pa,布置导流板后,阻力明显减低,分别为78.5、127.1、50.2 Pa,阻力降幅分别为53.2%、23.2%、59.9%;导流板布置前,A2侧进口烟道段、电除尘器本体、出口烟道段的阻力分别为165.3、167.7、125.5 Pa,布置导流板后,阻力分别降为81.5、123.7、50.7 Pa,阻力降幅分别为50.7%、26.2%、59.6%。
-
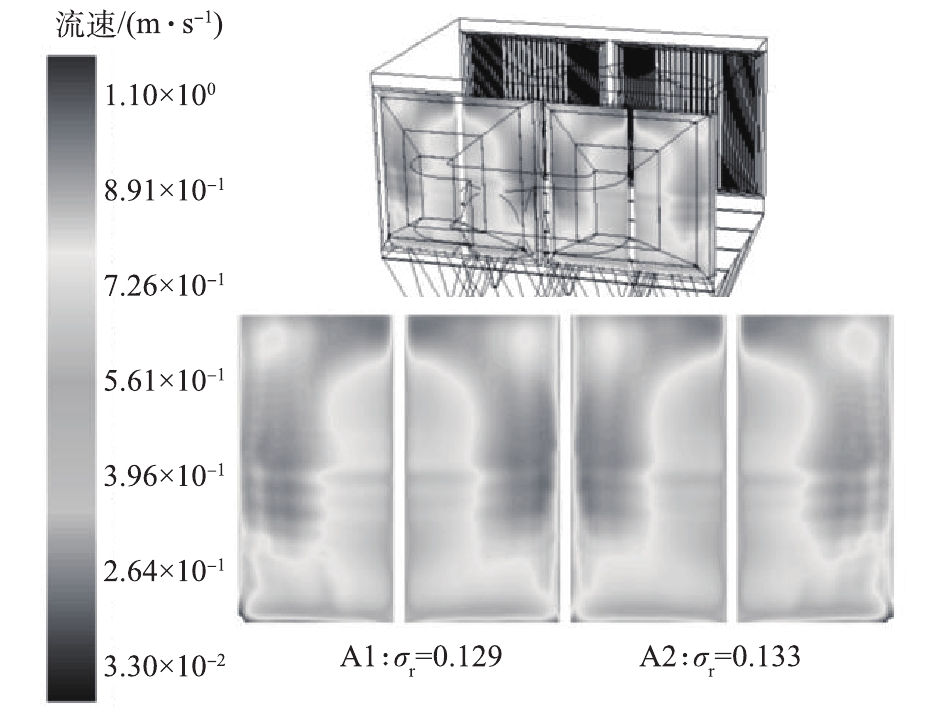
第1电场进口截面的气流分布均匀,有利于充分发挥整个电场断面的收尘作用。电除尘器进口封头内布置开孔率分别为40%、35%、35%的3层气流分布板,且在第2层、第3层多孔板后布置合适的导流叶片,经计算,2室第1电场进口截面的气流分布情况如图8所示,电场截面气流分布均匀性相对均方根差(σr)分别为0.129、0.133,符合JB/T 7671-2017规定的小于0.25的标准要求。
-
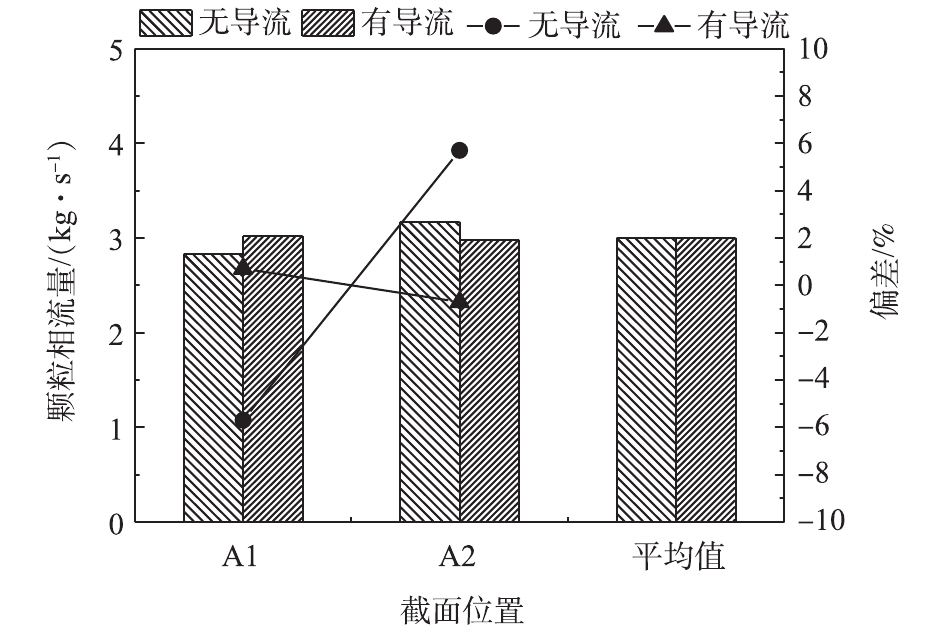
JB/T 7671-2017中未对颗粒相参数给出规定,但实际上,颗粒相的相关参数是电除尘器性能的最直接影响因素,烟气量及烟气流速的均匀性对电除尘器性能的影响也是通过颗粒相的参数来发挥作用的。有/无导流板时电除尘器进口烟道颗粒相质量流量及偏差如图9所示。在未布置导流板之前,电除尘器两侧烟道的进口颗粒相质量流量分别为2.83 kg·s−1和3.17 kg·s−1,经换算,流量偏差分别为−5.7%和+5.7%,颗粒相的偏差较连续相要小一些;布置导流板后,颗粒相的质量流量的偏差得到显著改善,颗粒相质量流量分别为3.02 kg·s−1和2.98 kg·s−1,经换算,其流量偏差分别改善了0.7%和−0.7%。
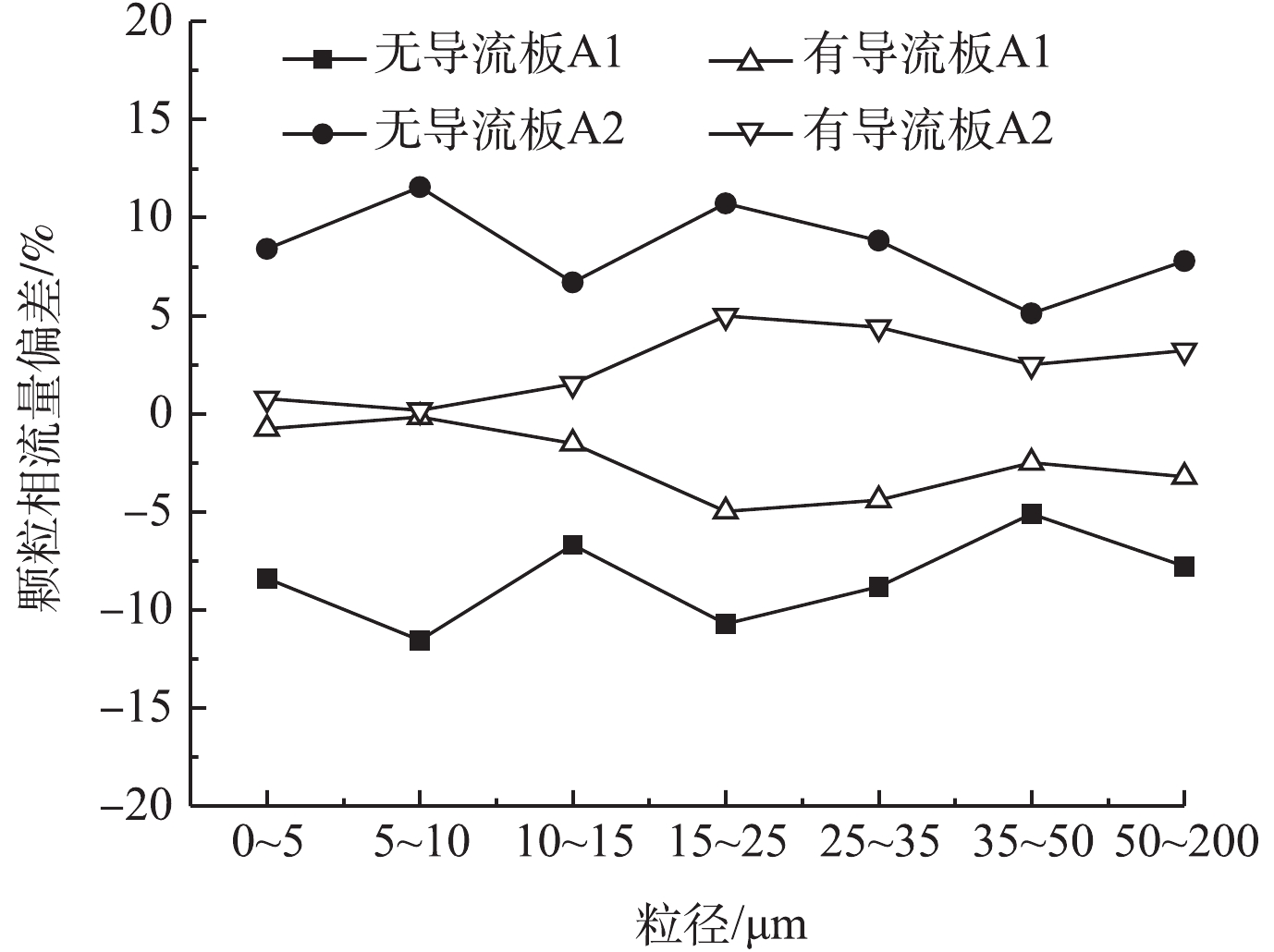
烟尘颗粒在运动过程中主要受连续相拽力及自身重力作用,但运动方向发生偏转时,颗粒相因受自身运动惯性影响,其偏移会较连续相滞后,且不同粒径的烟尘颗粒惯性不同,因此,其分布特征也不尽相同。有/无导流板时电除尘器进口烟道内颗粒相各级粒径段分布偏差计算结果如图10所示。烟道内导流板布置之前,颗粒相各个粒径段均有较大偏差,偏差为±5.1%~±11.5%,布置导流板后,颗粒相分配不均的偏差幅度得到明显的改善,偏差降至±0.2%~±4.9%。
-
1) 电场分布。电除尘器通过电场力进行收尘,放电极与收尘极间形成电晕电场,烟尘颗粒在电场中荷电,然后再在电场力作用下被收集到阳极板,因此,电除尘器的电场分布是影响电除尘器性能的主要因素。为简化计算,选电除尘器局部区域为研究对象,仅计算3根圆杆线放电时的电场分布特性。供电电压50 kV,采用电磁流体模型(MHD)[16-17]进行计算,经计算,电场内电势分布规律如图11所示,各个截面的电势分布都是不均匀的,在电极周围最低,越靠近阳极板,电势越接近零,且电极间有互相干涉的区域。
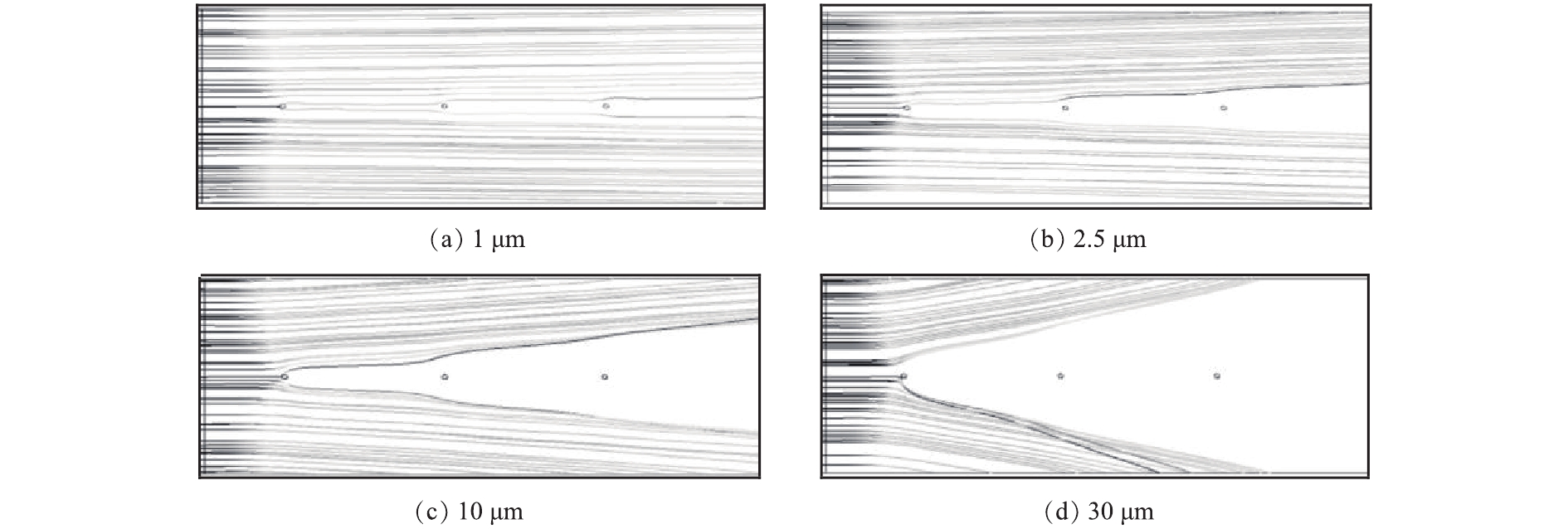
2) 颗粒运动轨迹。通过将颗粒的离散相模型(DPM)与电磁流体模型(MHD)进行耦合,可以计算分析荷电颗粒在电场中的运动规律。进一步简化计算步骤,在二维模型中分别计算1、2.5、10、30 μm单分散粒径颗粒在电场内的运动轨迹,忽略颗粒间库仑力作用,入口流速为1 m·s−1,计算结果如图12所示。在电场内电场力的作用下,荷电颗粒向阳极板方向偏转,且粒径越大,偏转的幅度也越明显,大粒径颗粒(30 μm)在第1根阴极线处就发生了较大幅度的偏转,而小粒径颗粒(1 μm)更容易发生逃逸。
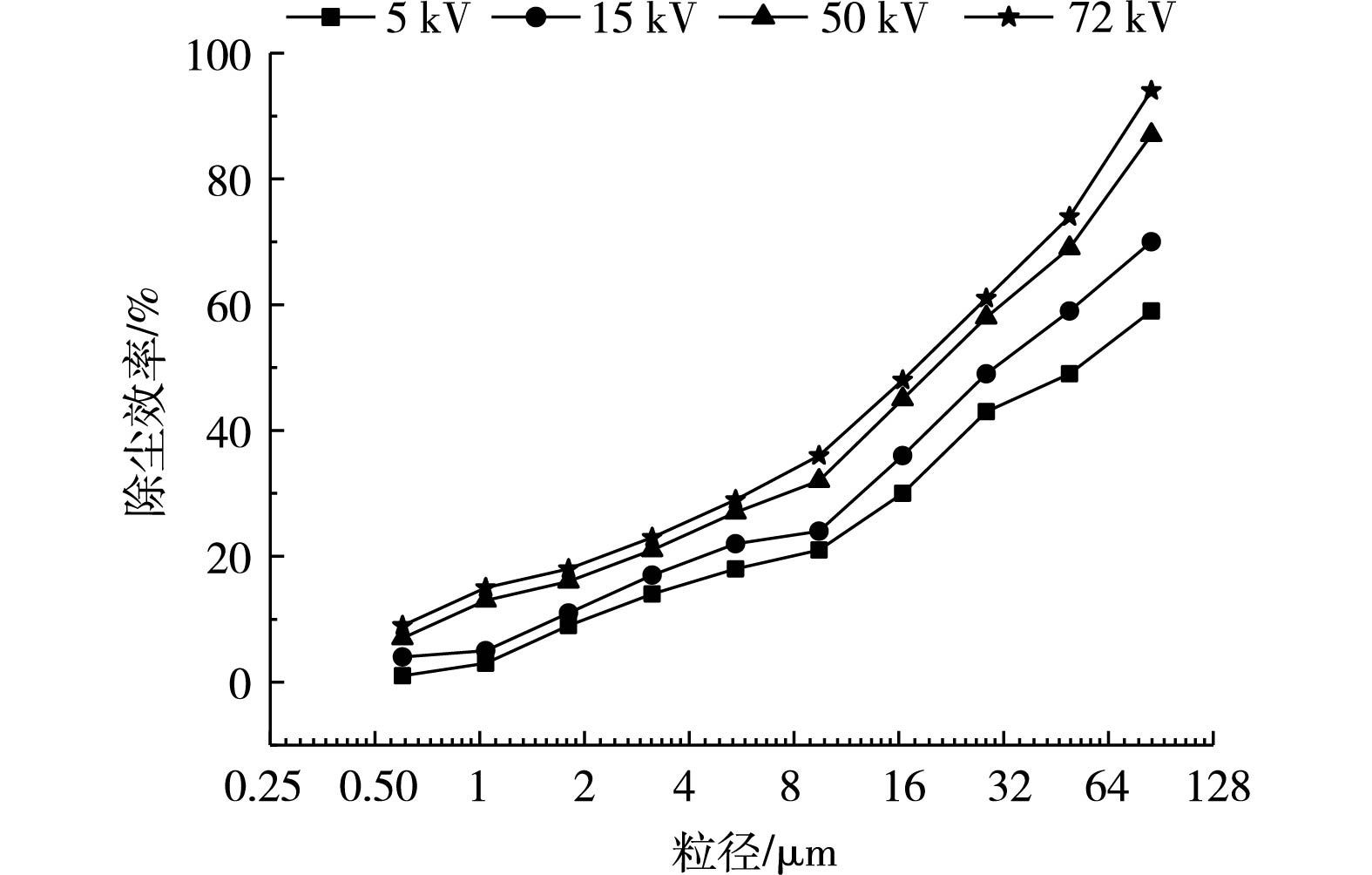
3) 除尘效率。除尘效率与颗粒的运动轨迹直接相关,颗粒运动到收尘极,表明颗粒被有效捕集。为进一步分析除尘效率,采用上述二维模型进行计算,颗粒相粒径分布按图3所示进行设置,荷电颗粒碰到阳极板即认为是被捕集,不考虑二次扬尘的影响。分别在供电电压为5、15、50和72 kV时,计算模型的除尘效率,计算结果如图13所示。除尘效率与电场供电电压具有相关性,与颗粒粒径也具有相关性,该规律与龙正伟等[18]的研究计算结果相符。
4.1. 烟气流量偏差及阻力
4.2. 第1电场进口截面
4.3. 颗粒相的流量偏差及均匀性
4.4. 除尘效率计算
-
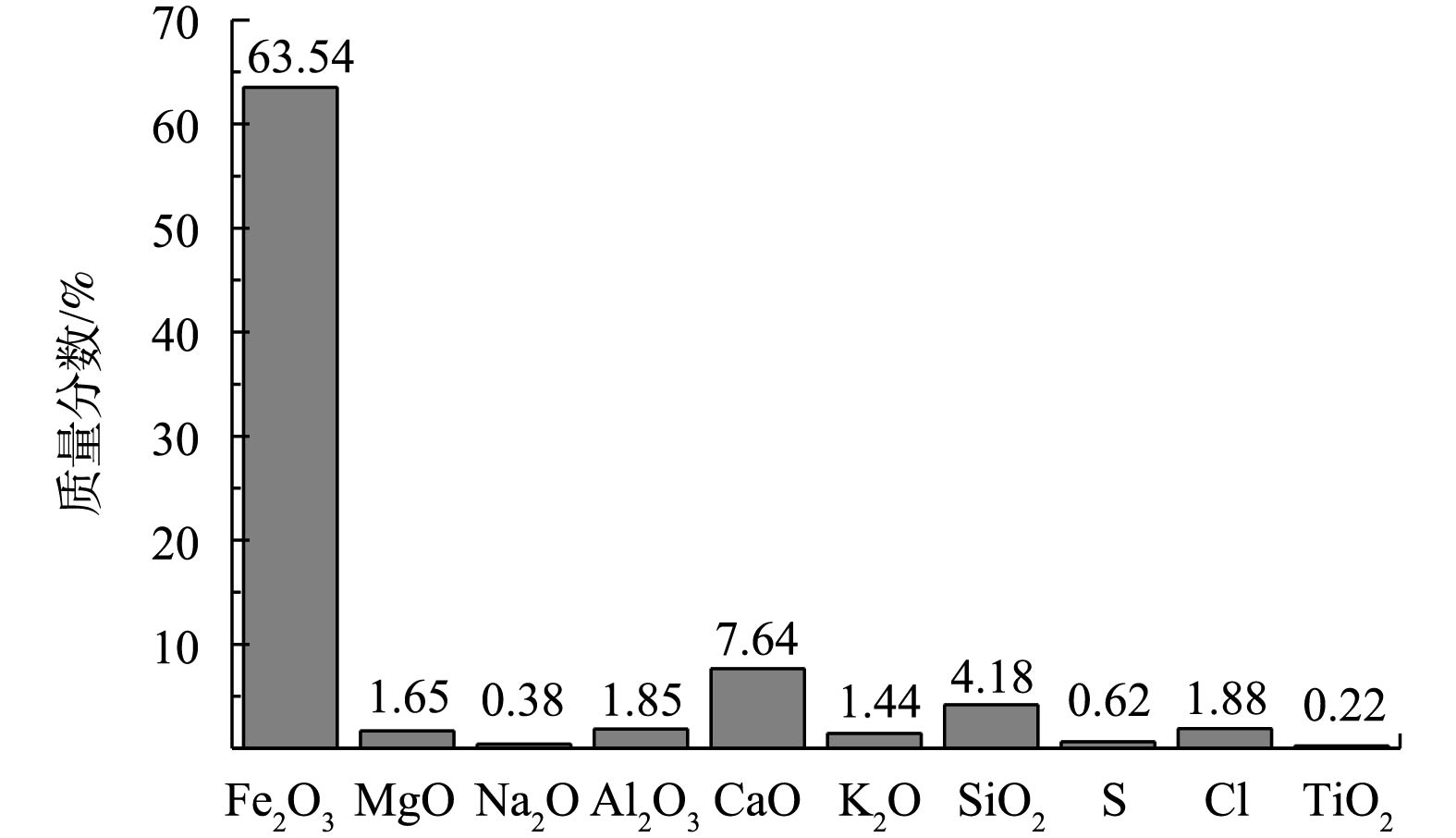
在该项目实施后,2019年3月,对该烧结机组开展了现场实测验证。调整电除尘器入口烟气参数在设计工况条件下,经性能测试,气流分布参数、本体阻力、除尘效率、出口烟尘浓度等性能参数均达到设计要求。采用JCY-80E(S)型自动烟尘烟气测试仪(配套滤筒采样枪)测定电除尘器进口烟气流量及电除尘器进出口烟尘浓度值,测试方法符合《电除尘器性能测试方法》(GB/T 13931-2017)的相关规定。采用便携式风速仪测定电除尘器第1电场入口截面处各采样点的风速,测试方法符合JB/T 7671-2017的相关规定。粉尘的化学成分对电除尘器性能影响较大,采用赛默飞ICAP 7200电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱仪,对电除尘器前收集的飞灰样品进行成分分析,分析结果如图14所示。飞灰中氧化铁含量较高。氧化铁属于磁性物质,相关研究表明,外加电压可使烟尘颗粒带电,产生磁性,吸引周围带电磁粒,产生所谓“导电通径”,降低比电阻,有利于电除尘器收尘[19-20]。另外,飞灰中钠含量高,也有利于降低比电阻;钙、镁含量高,则会引起比电阻升高。经BDL型工况飞灰在线工况比电阻测试仪测试,其飞灰工况比电阻为1.92×1011 Ω·cm,属于中比电阻粉尘,适合电除尘器脱除。
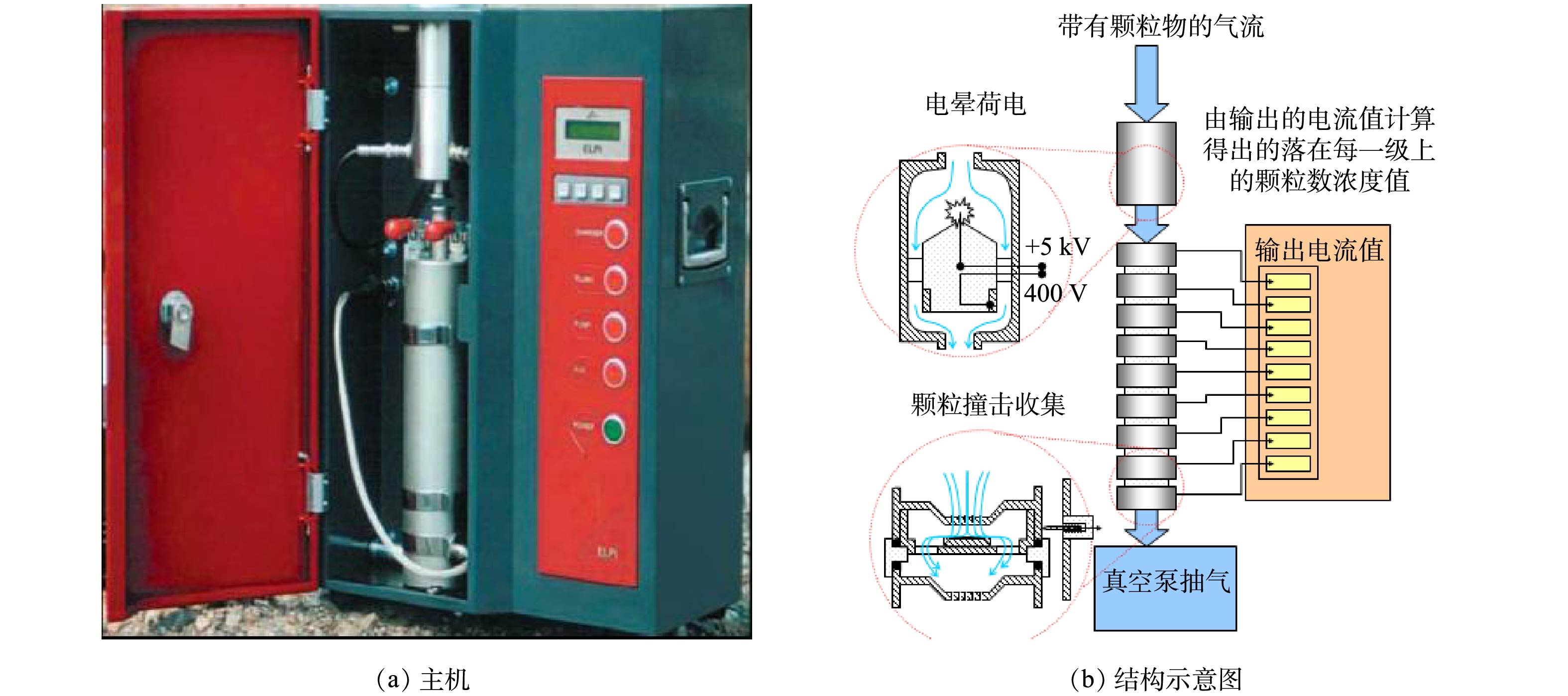
电除尘器进、出口烟尘颗粒的空气动力学粒径分布采用静电低压撞击器(ELPI)进行测定,该仪器可实时获得数据读数。烟尘进入该仪器前,先经过一级旋风切割器,将10 μm以上的颗粒拦截下来;10 μm及以下的颗粒进入该仪器,并先经过荷电器将烟尘颗粒荷电,然后通过12级的撞击器将烟尘颗粒在粒径为0.03~10 μm进行分级,荷电颗粒撞击每级撞击器的铝膜产生的微电流,通过布置在各级撞击器上电流探针获取该电流信号,从而间接换算烟尘颗粒的数量及质量浓度[21-22],ELPI的主机及结构示意图如图15所示。
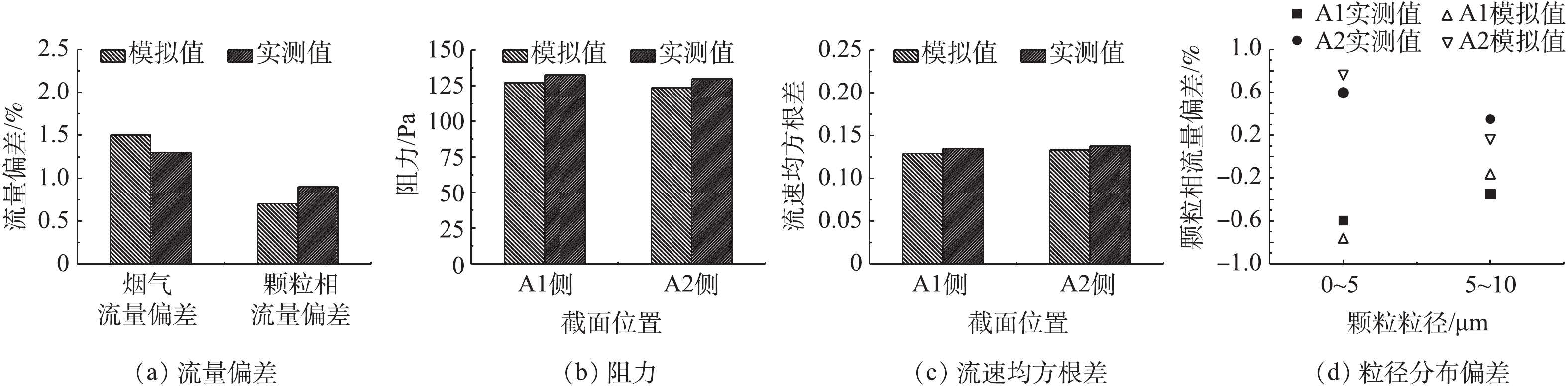
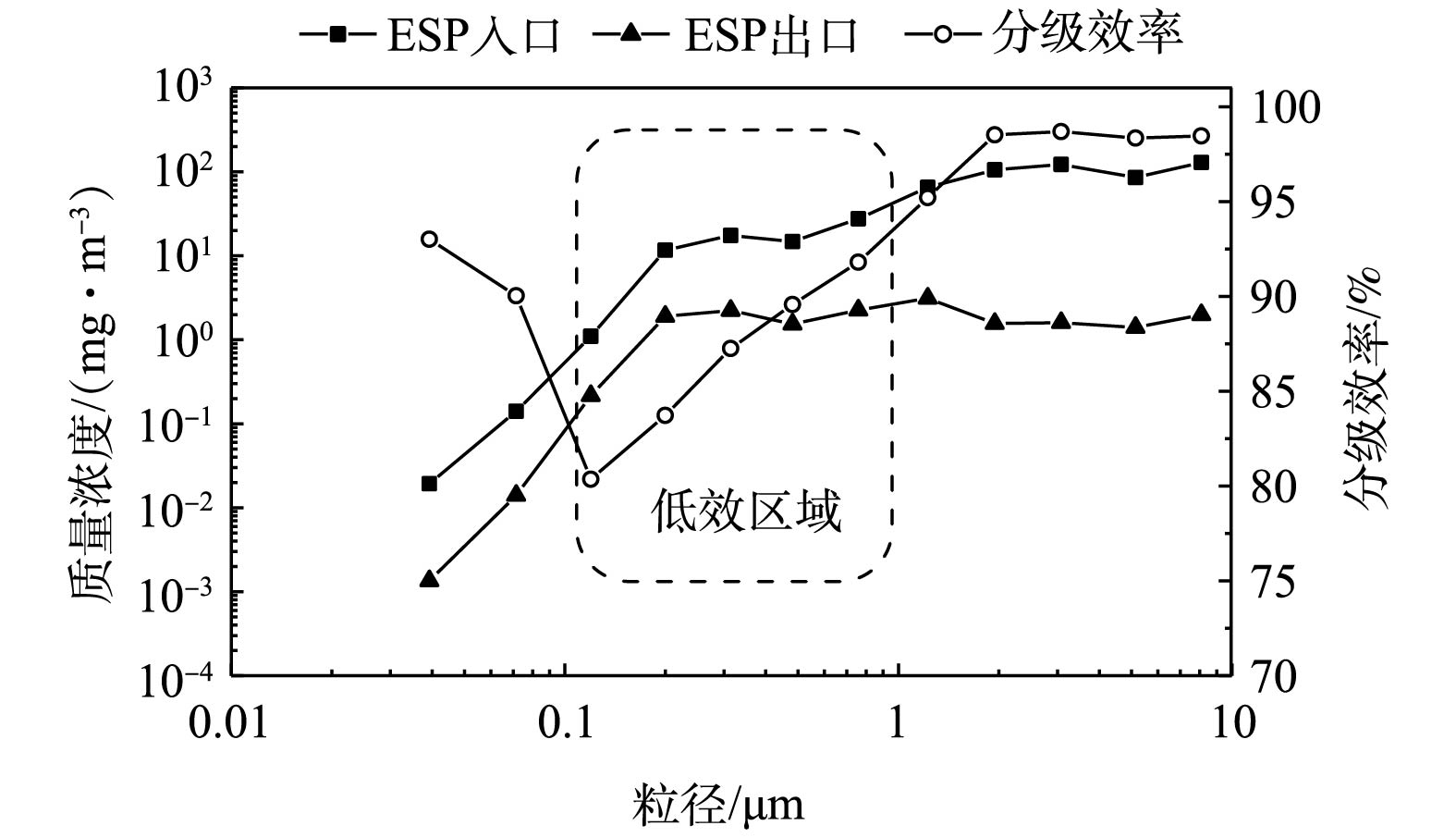
经换算,各参数的实测值与模拟值对比结果如图16所示。可以看出,模拟值与实测值一致性较好,均满足相关标准及工程要求,有效验证了前文所述的数值模拟方法的准确性、可靠性。经测定,电除尘器进、出口烟尘浓度分别为3 209.5 mg·m−3和25.8 mg·m−3,除尘效率达99.20%,优于设计值。电除尘器进、出口粒径分布及分级除尘效率的实测结果如图17所示,颗粒粒径为0.03~10 μm,分级除尘效率为80.35%~98.69%。其中0.1~1 μm粒径段的分级除尘效率为80.35%~91.81%,除尘效率较低。这是因为该粒径段的颗粒电场荷电、扩散荷电的电迁移速率均较低,因此,难以有效荷电,造成电除尘器对该粒径段颗粒的除尘效果不佳,该粒径段也被称为烟尘颗粒的穿透窗口[23-24]。
-
1)布置合适的烟道导流布置后,电除尘器进口烟气流量偏差得到了有效改善,流量偏差均不超过±5%,各段的阻力也得到了有效控制。
2)布置合适的烟道导流布置及进口封头气流均布板之后,电除尘器第1电场截面气流均匀性均得到了改善,烟气流速的相对均方根差值均小于0.25。
3)布置合适的烟道导流板后,电除尘器进口颗粒相总质量流量偏差及粒径分布均匀性均得到明显改善。
4)电除尘器的除尘效率与供电电压、颗粒粒径具有相关性。
5)现场实测值与模拟值较吻合,且实测值电除尘器出口烟尘浓度为25.8 mg·m−3,除尘效率达99.20%,优于设计值;粒径为0.03~10 μm的颗粒物分级除尘效率为80.35%~98.69%,其中,0.1~1 μm的颗粒段存在穿透窗口,其分级除尘效率为80.35%~91.81%。





 下载:
下载: